Our paper focused on the identification of LC3-associated endocytosis and the role of this pathway in the clearance of beta-amyloid and mitigation of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease. Following publication, we have identified two errors in the original version of the article. First, the same FACS plot for TMEM119 expression was inadvertently presented for both 5xFAD/Rubicon+/− and 5xFAD/Rubicon−/− as shown in Figure S5C. A revised version of the figure is shown below with the correct TMEM119 FACS plot for the 5xFAD/Rubicon+/−, the original plot for the 5xFAD/Rubicon−/− was correct and is therefore unchanged. The second inadvertent error was the misplacement/mislabeling of the representative images for hippocampal Iba1 staining in FIP200fl/flMG-cre+ compared to FIP200fl/flMG-cre− mice found in Figure 4A. The original labels are reversed and therefore have been corrected in the revised version of Figure 4 below. These errors occurred during the preparation of the figures and do not affect the results in the paper or the interpretation of the data. The figures have been corrected online. We apologize for any confusion these errors may have caused.
Figure 4.
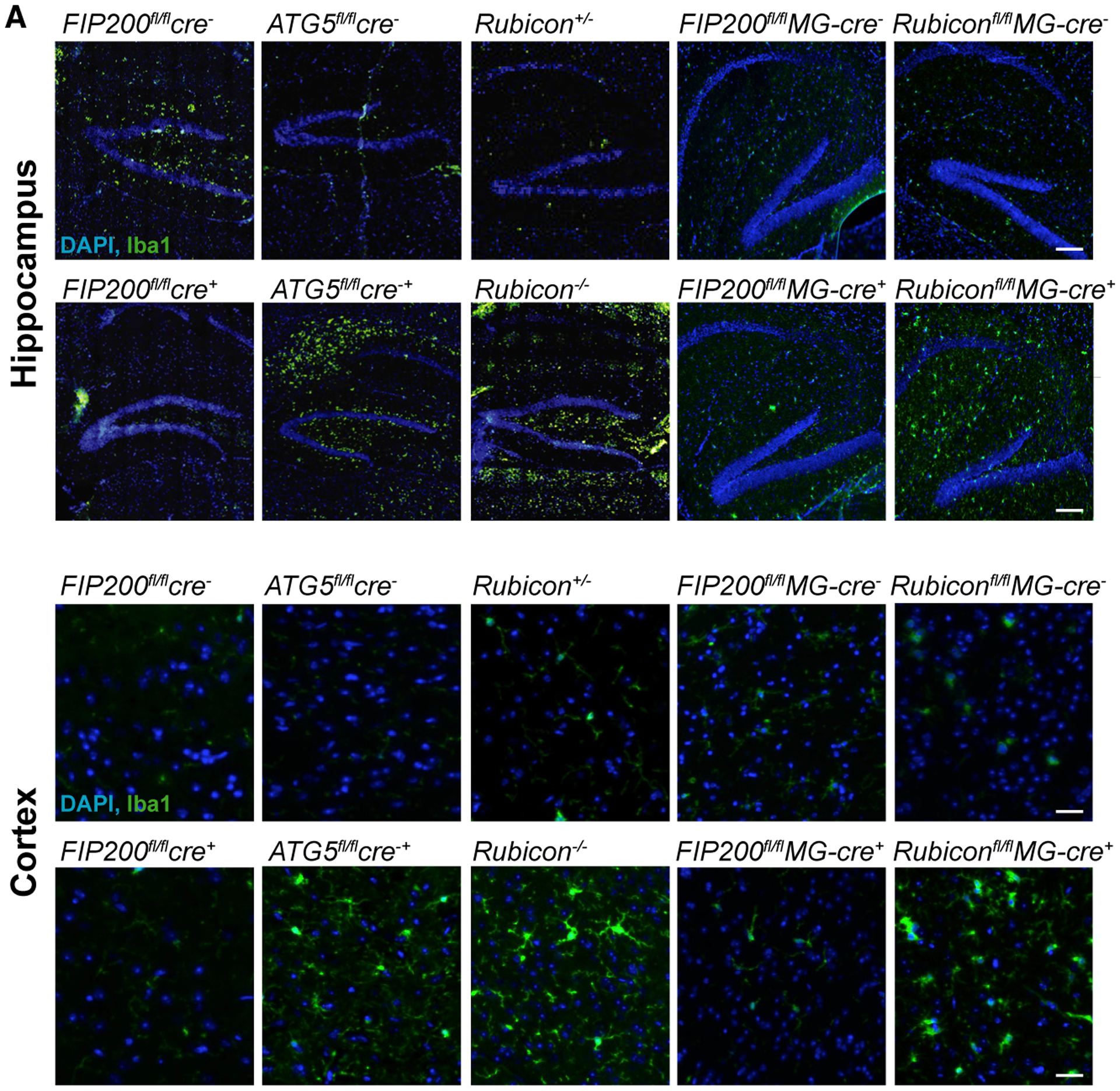
LANDO Decreases Ab-Induced Reactive Microgliosis (corrected)
Supplementary Material
Figure 4.
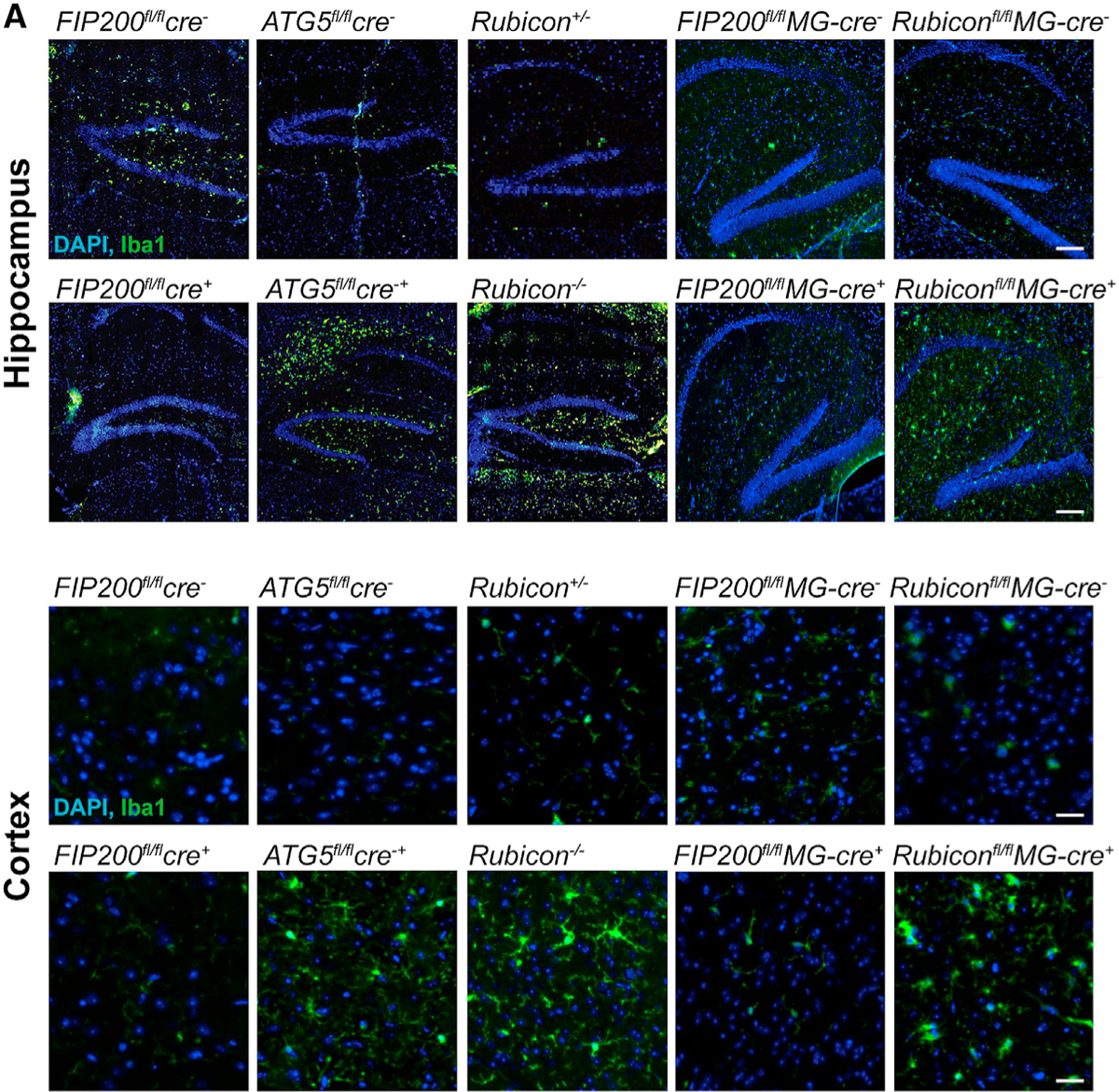
LANDO Decreases Ab-Induced Reactive Microgliosis (original)
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


