Abstract
Background
This meta-analysis based on prospective cohort studies aimed to evaluate the associations of lipid profiles with the risk of major adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD).
Methods
The PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library electronic databases were systematically searched for prospective cohort study published through December 2019, and the pooled results were calculated using the random-effects model.
Results
Twenty-one studies with a total of 76,221 patients with CHD met the inclusion criteria. The per standard deviation (SD) increase in triglyceride was associated with a reduced risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Furthermore, the per SD increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) was associated with a reduced risk of cardiac death, whereas patients with lower HDL-C were associated with an increased risk of MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death. Finally, the risk of MACE was significantly increased in patients with CHD with high lipoprotein(a) levels.
Conclusions
The results of this study suggested that lipid profile variables could predict major cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality in patients with CHD.
Keywords: Lipids, Prognosis, Coronary disease, Cardiovascular infections, Meta-analysis
Background
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, accounting for nearly 30% of the total deaths based on the World Health Organization (WHO) statistics. The WHO reported that about 17.3 million people have died of CVD in 2016 and that this number will reach up to 23.3 million by 2030 [1]. Currently, pharmacological therapies including antiplatelet agents, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers and lipid-lowering drugs play a crucial role in the secondary prevention of CVD [2–4]. However, a residual CVD risk remains, for which further management needs to be identified.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the role of the lipid profile in the progression of CVD. Increases in triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) levels could affect the constriction and abstraction of vessels in the heart, which are significantly correlated with the risk of CVD [5]. Moreover, increases in the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level could induce arteriosclerosis owing to accumulation of LDL-C in the intima-media of the artery, which could then promote thrombocytopoiesis [6]. However, the CVD risk might be reduced in persons with increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels. Therefore, individuals with high HDL-C and low non-HDL-C may be protected against the risk of CVD.
The ACC/AHA guideline used the intensity of statin therapy as the goal of treatment and recommend the maximum appropriate intensity of statin without adverse effects should be applied [7]. The ESC/EAS Guidelines suggested the treatment targets and goals for CVD prevention and the secondary targets of LDL-C were < 70 mg/dL, < 100 mg/dL, and < 115 mg/dL for very high-risk, high-risk, and low to moderate risk population, respectively [8]. The Japan Atherosclerosis Society Guidelines found the target for lipid profiles management in secondary preventing coronary artery diseases were < 100 mg/dL or < 70 mg/dL of LDL-C, < 130 mg/dL or < 100 mg/dL of non-HDL-C, < 150 mg/dL of TG, and > 40 mg/dL of HDL-C [9]. Although potential roles of lipid profile variables on the progression of CVD have been demonstrated; however, the impact of the lipid profile on the prognosis of patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) remains controversial. Clarifying the role of lipid profile variables in prognosis is particularly important in patients with CHD, as no systematic review and meta-analysis has provided definitive conclusions. Therefore, we attempted a large-scale examination of prospective cohort studies to determine the role of the lipid profile on the prognosis of patients with CHD.
Methods
Data sources, search strategy, and selection criteria
This review was conducted and reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis Statement issued in 2009 [10]. The eligible studies for inclusion in the review were those with a prospective cohort design and that investigated the role of lipid profile variables on prognosis in patients with CHD. There were no restrictions with respect to publication language and status. We systematically searched the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library electronic databases from their inception up to December 2019, using the following core search terms: (“Atherosclerosis” OR “Coronary Disease” OR “Coronary Artery Disease” OR “Coronary Occlusion” OR “Angina Pectoris”) AND (“total cholesterol” OR “triglyceride” OR “low-density lipoprotein” OR “high-density lipoprotein”) AND (“Death” OR “Recurrence” OR “Relapses” OR “Secondary Prevention” OR “risk” OR “prediction” OR “association” OR “correlation”) AND (“cohort” OR “prospective”). The detail of search strategy in PubMed are presented in Additional file 1. The reference lists of relevant review and original articles were also reviewed through manual searches to select any new eligible study.
Two authors independently performed the literature search and study selection following a standardized approach, and any inconsistencies between these 2 authors were resolved through a group discussion. The studies were judged for eligibility based on (1) study design (must be a prospective cohort study), (2) participants (all recruited patients must have a CHD diagnosis), (3) investigated variables (TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C, and lipoprotein(a)), (4) outcomes (major adverse cardiovascular events [MACE], all-cause mortality, and cardiac death), and (5) the investigated outcomes needed reported ≥ 2 cohorts. Studies with a retrospective observational design were excluded because of various confounding factors that could affect the results.
Data collection and quality assessment
Data collection and quality assessment were conducted by 2 authors, and any disagreement was resolved by a third author by referring to the original works. The collected information from the retrieved studies included the first authors’ surname, publication year, country, sample size, age at baseline, percentage of men, disease status, follow-up duration, exposure, adjusted factors, and investigated outcomes. We selected the effect estimate that was maximally adjusted for potential confounders if a study reported several multivariable-adjusted effect estimates. Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale, which was based on selection (4 items: 4 stars), comparability (1 item: 2 stars), and outcome (3 items: 3 stars). The “star system” for the assessment of each individual study ranged from 0 to 9 stars [11].
Statistical analysis
The role of the lipid profile on the prognosis of patients with CHD was assessed based on the effect estimates and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) in each individual study. The summary relative risks (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using the random-effects model [12, 13]. The heterogeneity of studies was assessed using the I2 and Q statistics, and P < 0.10 was considered to indicate a significant heterogeneity [14, 15]. Sensitivity analyses were conducted for factors reported in ≥ 5 cohorts to assess the impact of a single study on the overall analysis [16]. Publication bias was assessed using funnel plots from Egger and Begg test results for factors reported in ≥ 5 cohorts [17, 18]. All reported P values are 2-sided, and P < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance for all included studies. Statistical analyses were performed using STATA software (version 12.0; Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA).
Results
Literature search
The electronic searches of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library yielded 2318 records, of which 2231 were excluded for being duplicates and for having irrelevant topics. A total of 87 studies were selected for further evaluation, and 21 prospective cohort studies with a total of 76,221 patients with CHD were selected for the final meta-analysis (Fig. 1) [19–39]. No new eligible study was detected by manual search of the reference lists of retrieved studies.
Fig. 1.
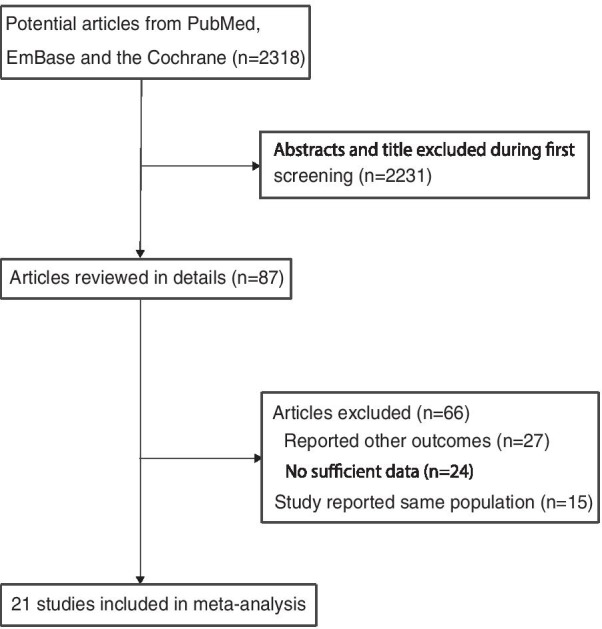
Flow diagram of the literature search and study selection
Study characteristics
Table 1 summarizes the baseline characteristics of the included studies. A total of 21 studies published between 1995 and 2018 were analyzed, and each study included from 102 to 11,563 patients. Two studies included male patients, 1 study included female patients, while the remaining 18 studies included both male and female patients. The follow-up duration ranged from 1.0 to 10.3 years, and the study quality ranged from 6 to 8 stars. Twelve studies were conducted in Western countries, and the remaining 9 studies were conducted in Eastern countries.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the studies included in the systematic review and meta-analysis
| Study | Publication year | Country | Sample size | Age at baseline | Percentage male (%) | Disease status | Follow-up (year) | Exposure | Adjusted factors | NOS score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigurdsson [19] | 1995 | Iceland | 9141 | 34–79 | 100.0 | CHD | 5–20 | Per SD increment | Age, smoking, glucose tolerance 90 min, heart volume | 7 |
| Tervahauta [20] | 1995 | Finland | 171 | 65–84 | 100.0 | CHD | 5.0 | Per SD increment | Age, area of residence, SBP, DBP, BMI, smoking habit and use of antihypertensive medication | 6 |
| Behar [21] | 1997 | Israel | 11,563 | 45–74 | 78.3 | CHD | 3.3 | Per SD increment; TC: < 160 mg/dL versus > 160 mg/dL | Age, gender, HDL; glucose, NYHA, previous MI, DM, COPD, hypertension, PVD, angina, current smoking | 8 |
| Mabuchi [22] | 2002 | Japan | 4599 | 60.1 | 42.2 | Hypercholesterolemia and CHD | 6.0 | Per 1 Log TG increment | Gender, age, hypertension, DM mellitus, smoking habit, and a history of MI | 7 |
| Vittinghoff [23] | 2003 | US | 2763 | 66.6 | 0.0 | CHD | 4.1 | Per SD increment | Age, ethnicity, smoking, alcohol, exercise, DM, previous MI, BMI, waist-to-hip ratio, hypertension, history of congestive heart failure | 8 |
| Leander [24] | 2007 | Sweden | 1635 | 45–70 | 67.3 | CHD | 6–9 | HDL (< 30.9/< 38.7 mg/dL versus > 30.9/ > 38.7 mg/dL) | Family history of CHD, current smoking, ex-smoking, job strain, PA, central obesity, DM, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, low socio-economic status, high peak cardiac enzyme, heart failure, beta-blocker therapy, and thrombolysis | 8 |
| Al-Mallah [25] | 2009 | US | 517 | 62.5 | 59.6 | Non ST segment elevation MI | 3.0 | LDL (> 105 versus < 105 mg/dL) | Crude | 6 |
| Ghazzal [26] | 2009 | US | 4088 | 64.8 | 70.9 | CHD after PCI | 1.0 | HDL (< 35 versus > 35 mg/dL) | Age, DM, PCI, EF | 7 |
| Seo [27] | 2011 | Korea | 2693 | 62.5 | 66.1 | CHD after PCI | 2.3 | HDL (< 40/50 versus > 40/50 mg/dL) | Age, sex, hypertension, DM, chronic renal disease, current smoker, ACS, ejection fraction, baseline HDL, baseline LDL, baseline TG, baseline hs-CRP, follow-up LDL, follow-up TG, follow-up hs-CRP, total stent length, mean stent diameter, number of stent, number of B2/C lesions | 7 |
| Bacquer [28] | 2013 | Europe | 5216 | ≤ 70.0 | 76.0 | CHD | 5.4 | TC (< 174 versus > 232 mg/dL); HDL (< 38.7/46.4 versus > 46.4/54.1 mg/dL); LDL (> 116 versus < 96.7 mg/dL) | Age and gender | 7 |
| Lin [29] | 2013 | China | 1114 | 65.5 | 74.9 | CHD | 5.3 | HDL (< 40/45 versus > 40/45 mg/dL) | Age, gender, smoking status, LDL, uric acid, creatinine, hypertension, DM, stroke, cancer, number of blocked coronary artery, MI, PCI, CABG, and medication status | 7 |
| van de Woestijne [30] | 2013 | The Netherlands | 5731 | 60.0 | 74.1 | clinically manifest vascular disease | 4.9 | TG (198.4 versus < 85.9 mg/dL) | Age, gender, smoking, lipid-lowering medication, BMI and LDL-C | 8 |
| Ding [31] | 2014 | China | 1916 | 63.7 | 65.2 | CHD | 3.1 | HDL (40–49 versus > 70 mg/dL); LDL (> 190 versus < 70 mg/dL) | Age, gender, education, marriage, leisure-time physical activity, smoking, alcohol drinking, type, severity, duration, and treatment of CHD, history of DM, history of heart failure, BMI, SBP, glomerular filtration rate, and use of antihypertensive drugs, antidiabetic drugs, antiplatelet drugs, use of cholesterol-lowering drugs | 7 |
| Martin [32] | 2014 | US | 4879 | 60.4 | 66.8 | Acute MI | 5.0 | HDL (< 40 versus > 40 mg/dL) | GRACE score, age, sex, race, insurance, education, tobacco use, DM, hypertension, AUDIT alcohol use scores, PA, BMI, non-HDL-C, log-transformed triglycerides, statins, and non-statin lipid-modifying medications, and site | 7 |
| Park [33] | 2015 | Korea | 595 | 63.5 | 65.2 | CHD after PCI | 3.0 | Lipoprotein(a) (> 50 versus < 50 mg/dL) | Gender, age, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking, multivessel disease, minimal luminal diameter after PCI, reference vessel diameter after PCI, LDLcholesterol, total lesion length | 6 |
| Li [34] | 2016 | China | 591 | 57.8 | 71.2 | CHD | 1.4 | HDL (< 41.6 versus > 41.6 mg/dL) | Age, male, BMI, smoke, family history of CHD, previous PCI/CABG, previous MI, SBP, LDL, TG, and glucose | 6 |
| Liu [35] | 2017 | China | 4205 | 57.7 | 71.4 | CHD | 2.3 | Not mentioned | Age, gender, BMI, hypertension, DM, smoking, family history of CHD, left ventricular ejection fraction | 7 |
| Tsai [36] | 2017 | China | 1520 | 69.0 | 72.8 | CHD | 2.7 | Per SD increment | Age, gender, education, marital status, malnourished, economic situation, smoking, alcohol, PA, DM, hypertension, medications | 7 |
| Nordenskjöld [37] | 2018 | Sweden | 9092 | 65.5 | 38.0 | MI with with non-obstructive coronary artery disease | 4.5 | Per SD increment | Gender, age, DM, hypertension, smoking status, previous MI, previous stroke, ECG changes at admission, creatinine, CRP, total cholesterol, LVEF measured during index stay and serious non-cardiac diseases | 8 |
| Dai [38] | 2018 | China | 4090 | 61.1 | 67.9 | CHD | 3.3 | Per SD increment | Other traditional cardiovascular risk factors | 7 |
| Winter [39] | 2018 | Austria | 102 | 37.3 | 79.4 | Premature MI | 10.3 | Per SD increment | Age and gender | 6 |
ACS acute coronary syndrome, BMI body mass index, CABG coronary artery bypass grafting, CHD coronary heart disease, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, DBP diastolic blood pressure, DM diabetes mellitus, HDL high density lipoprotein, hs-CRP high sensitivity C reactive protein, LDL low-density lipoprotein, MI myocardial infarction, PA physical inactivity, PCI percutaneous coronary intervention, PVD peripheral vascular disease, SBP systolic blood pressure, TG triglycerides
Total cholesterol
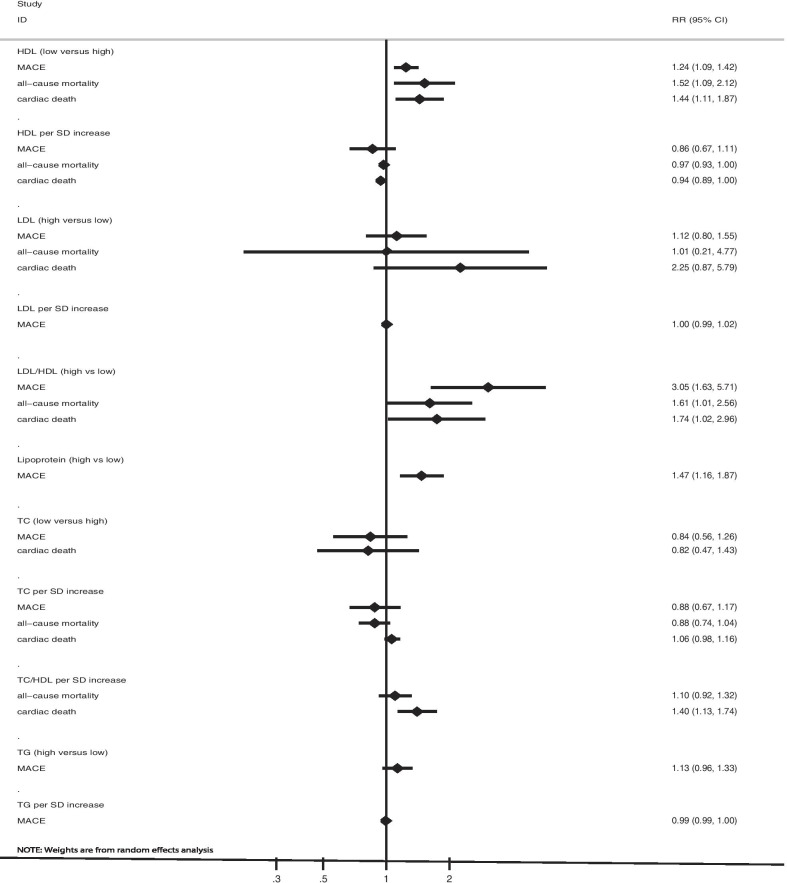
The number of studies (cohorts) available for the analysis of the association of each outcome with the per standard deviation (SD) increase in TC was 5, 2, and 3 for MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death, respectively (Fig. 2 and Table 2). Overall, we observed that the per SD increase in TC was not associated with the risk of MACE (RR: 0.88; 95% CI 0.67–1.17; P = 0.380; significant heterogeneity), all-cause mortality (RR: 0.88; 95% CI 0.74–1.04; P = 0.131; moderate heterogeneity), and cardiac death (RR: 1.06; 95% CI 0.98–1.16; P = 0.150; significant heterogeneity). The role of the per SD increase in TC on the risk of MACE in patients with CHD was altered when the study by Winter et al. [39], which had a longer follow-up duration, was excluded (Additional file 2). No significant publication bias was observed for MACE (Additional file 3).
Fig. 2.
Summarized results with respect to the role of lipid profile variables on the risk of major cardiovascular events, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death in patients with coronary heart disease
Table 2.
Summary results of lipid profile values and prognosis in patients with coronary heart disease
| Factors | Outcomes | References | RR and 95% CI | P value | Heterogeneity (%) | P value for heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC per SD increase | MACE | [36–39] | 0.88 (0.67–1.17) | 0.380 | 67.4 | 0.015 |
| All-cause mortality | [20, 37] | 0.88 (0.74–1.04) | 0.131 | 50.6 | 0.155 | |
| Cardiac death | [19–21] | 1.06 (0.98–1.16) | 0.150 | 79.7 | 0.007 | |
| TC (low versus high) | MACE | [21, 29] | 0.84 (0.56–1.26) | 0.389 | 56.6 | 0.129 |
| Cardiac death | [21, 28] | 0.82 (0.47–1.43) | 0.486 | 79.2 | 0.028 | |
| TG per SD increase | MACE | [36, 38, 39] | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.004 | 41.4 | 0.163 |
| TG (high versus low) | MACE | [21, 30, 35] | 1.13 (0.96–1.33) | 0.134 | 22.5 | 0.275 |
| LDL-C per SD increase | MACE | [23, 36, 38, 39] | 1.00 (0.99–1.02) | 0.640 | 81.4 | < 0.001 |
| LDL-C (high versus low) | MACE | [21, 25, 35] | 1.12 (0.80–1.55) | 0.512 | 69.7 | 0.037 |
| All-cause mortality | [25, 31] | 1.01 (0.21–4.77) | 0.994 | 84.1 | 0.012 | |
| Cardiac death | [28, 31] | 2.25 (0.87–5.79) | 0.093 | 59.6 | 0.116 | |
| HDL-C per SD increase | MACE | [23, 36, 38, 39] | 0.86 (0.67–1.11) | 0.252 | 76.5 | 0.002 |
| All-cause mortality | [20, 21, 29] | 0.97 (0.93–1.00) | 0.065 | 85.2 | < 0.001 | |
| Cardiac death | [20, 21, 29] | 0.94 (0.89–1.00) | 0.048 | 89.2 | < 0.001 | |
| HDL-C (low versus high) | MACE | [21, 24, 27, 32, 34, 35] | 1.24 (1.09–1.42) | 0.002 | 0.0 | 0.462 |
| All-cause mortality | [26, 27, 29, 31] | 1.52 (1.09–2.12) | 0.014 | 64.0 | 0.025 | |
| Cardiac death | [27–29, 31] | 1.44 (1.11–1.87) | 0.006 | 29.8 | 0.223 | |
| Lipoprotein(a) (high vs low) | MACE | [23, 33, 39] | 1.47 (1.16–1.87) | 0.001 | 0.0 | 0.386 |
The number of studies (cohorts) available for the analysis of the association of each outcome with low versus high TC was 2, and 2 for MACE, and cardiac death, respectively (Fig. 2 and Table 2). Overall, we noted no significant associations of TC with the risk of MACE (RR: 0.84; 95% CI 0.56–1.26; P = 0.389; moderate heterogeneity) and cardiac death (RR: 0.82; 95% CI 0.47–1.43; P = 0.486; significant heterogeneity).
Triglyceride
Data for the association of per SD increase in TG with the risk of MACE was available in 4 studies (cohorts) (Fig. 2 and Table 2). Overall, we noted that the per SD increase in TG was associated with a reduced risk of MACE (RR: 0.99; 95% CI 0.99–1.00; P = 0.004; moderate heterogeneity). Moreover, high TG was not associated with the risk of MACE (RR: 1.13; 95% CI 0.96–1.33; P = 0.134; unimportant heterogeneity).
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
Data for the association of per SD increase in LDL-C with the risk of MACE was available in 5 studies (cohorts) (Fig. 2 and Table 2). There was no significant association between the per SD increase in LDL-C and the risk of MACE (RR: 1.00; 95% CI 0.99–1.02; P = 0.640; significant heterogeneity). The sensitivity analysis indicated that the risk of MACE was stable and not altered by the sequential exclusion of individual studies (Additional file 2). Moreover, no significant publication bias was detected for MACE (Additional file 3).
The number of studies (cohorts) available for the analysis of the association of each outcome with high versus low LDL-C was 3, 2, and 2 for MACE, all-cause mortality and cardiac death, respectively (Fig. 2 and Table 2). Overall, we observed that high LDL-C was not associated with the risk of MACE (RR: 1.12; 95% CI 0.80–1.55; P = 0.512; significant heterogeneity), all-cause mortality (RR: 1.01; 95% CI 0.21–4.77; P = 0.994; significant heterogeneity), and cardiac death (RR: 2.25; 95% CI 0.87–5.79; P = 0.093; moderate heterogeneity).
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
The number of studies (cohorts) available for the analysis of the association of each outcome with the per SD increase in HDL-C was 5, 4, and 4 for MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death, respectively (Fig. 2 and Table 2). We observed that the per SD increase in HDL-C was associated with a reduced risk of cardiac death (RR: 0.94; 95% CI 0.89–1.00; P = 0.048; significant heterogeneity), whereas it was not associated with the risk of MACE (RR: 0.86; 95% CI 0.67–1.11; P = 0.252; significant heterogeneity) and all-cause mortality (RR: 0.97; 95% CI 0.93–1.00; P = 0.065; significant heterogeneity). The sensitivity analysis indicated that the per SD increase in HDL-C might produce a protective effect against MACE (Additional file 2). No significant publication bias was observed (Additional file 3).
The number of studies (cohorts) available for the analysis of the association of each outcome with low versus high HDL-C was 7, 5, and 5 for MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death, respectively (Fig. 2 and Table 2). Overall, low HDL-C produced an excess risk of MACE (RR: 1.24; 95% CI 1.09–1.42; P = 0.002; with no evidence of heterogeneity), all-cause mortality (RR: 1.52; 95% CI 1.09–2.12; P = 0.014; significant heterogeneity), and cardiac death (RR: 1.44; 95% CI 1.11–1.87; P = 0.006; unimportant heterogeneity). The pooled results for MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death varied after excluding individual studies, owing to marginal 95% CI (Additional file 2). No significant publication bias was detected for MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death (Additional file 3).
Lipoprotein(a)
Data for the association of high versus low lipoprotein(a) with the risk of MACE was available in 3 studies (cohorts) (Fig. 2 and Table 2). The summary RR indicated that the risk of MACE was significantly increased in patients with CHD with high lipoprotein(a) (RR: 1.47; 95% CI 1.16–1.87; P = 0.001; with no evidence of heterogeneity).
Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies evaluated the role of the lipid profile on the risk of MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death in patients with CHD. This comprehensive quantitative study included a total of 76,221 patients with CHD from 21 prospective cohort studies with a wide range of patient characteristics. The results suggested that in patients with CHD, increased TG was associated with a reduced risk of MACE. Moreover, low HDL-C was associated with an increased risk of MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death. Finally, high lipoprotein(a) was associated with an increased risk of MACE in patients with CHD.
No previous systematic review and meta-analysis has focused on this topic, although numerous studies have illustrated the effects of lipid profile management in the secondary prevention of major cardiovascular outcomes. Gutierrez et al. conducted a meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials and found that the use of statin for lipid profile management significantly reduced the risk of cardiovascular events in both sexes, whereas statin therapy had no significant effect on the risk of stroke and all-cause mortality in women [40]. Navarese et al. conducted a meta-analysis of 34 trials and found more intensive versus less intensive LDL-C lowering could further reduction in risk of total and cardiovascular mortality for patients with higher baseline LDL-C levels [41]. However, they did not focused on CHD patients. A meta-analysis including 5 studies with 4351 diabetic patients with manifest CVD was conducted by de Vries et al. The authors pointed out that both intensive and standard-dose statin therapy could produce a significant reduction in the risk of any major cardiovascular or cerebrovascular event [42]. However, most patients with CHD routinely use lipid management agents, and whether the lipid profile should be monitored in these patients remains controversial. Afilalo et al. conducted a meta-analysis of 6 trials and found intensive statin therapy was associated with a reduction in MACE and admission to hospital for heart failure as compared with moderate statin therapy. Moreover, they point out intensive statin therapy significantly reduced all-cause mortality in patients with recent acute coronary syndrome, while this effect was not observed for patients with stable CHD [43]. A meta-analysis conducted by Yan et al. found intensive statin therapy could further reduction the recurrent risk of MACE [44]. The results of previous studies mainly focused on the reduction in LDL-C, and the potential role of other lipid profiles on the prognosis of CHD remains unclear. Moreover, the long-term event monitoring study found DM, hypertension, TG, and LDL-C should be controlled for patients treated with statin to avoid further vascular events [45]. Therefore, the current comprehensive quantitative meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the role of the lipid profile on the prognosis of patients with CHD.
The current study indicated that in patients with CHD, low TC was not associated with the risk of MACE and cardiac death. The potential reason for this result could be the twice higher prevalence of noncardiac death in the low TC group and cancer being the most frequent cause of noncardiac death. Moreover, we observed that patients with increased TG and LDL-C was not associated with the risk of MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death. The result for TG was based on another study [46] that included the same population as that in the study by Behar et al. [21]. The authors pointed out that the association risk was balanced after adjusting for other risk factors and comorbidities [46].
The summary results indicated that CHD patients with low HDL-C have an excess risk of MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death. Several included studies reported consistent results. Seo et al. found that patients with low HDL-C had a significantly increased risk of MACE after 832 days of follow-up, whereas low HDL-C had no significant impact on all-cause mortality and cardiac death [27]. The potential reason for this could be the shorter duration of follow-up than what was needed to show a clinical benefit, especially for the lower-than-expected all-cause mortality and cardiac death rates, which always yielded broad confidence intervals (i.e., no statistically significant difference). Ghazzal et al. found that low serum HDL-C was an independent risk factor for 1-year mortality, and used 35 mg/dL as a cutoff value for defining high and low HDL-C levels [26]. De Bacquer et al. suggested that the risk of cardiac death was significantly increased in patients with CHD with low HDL-C [28]. Lin et al. indicated that low HDL-C level did not affect the risk of all-cause mortality and cardiac death in patients with CHD with a body mass index of > 25.0 kg/m2, whereas an increased risk of all-cause mortality and cardiac death was noted with low HDL-C level when the body mass index was < 25.0 kg/m2 [29]. Ding et al. found that the risk of all-cause mortality and cardiac death had a U-shaped correlation with HDL-C after adjusting for major CVD risk factors [31]. They pointed out that the antiatherogenic effect of HDL-C could reverse macrophage cholesterol transport, which, in turn, could stimulate nitric oxide production, inhibit endothelial apoptosis, and induce endothelial homeostasis [47, 48].
This study showed that the risk of MACE was significantly increased in CHD patients with high lipoprotein(a), which was consistent with the result of a previous study that found that the reduction in lipoprotein(a) was independently correlated with a reduced risk of MACE [49]. Furthermore, lipoprotein(a) level was not associated with the risk of all-cause mortality and cardiac death [33]. Finally, we noted LDL-C was not associated with the risk of MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death in CHD patients. The potential reason for this could be CHD patients with strictly lipid profile management strategies to prevent the progression of major adverse cardiovascular outcomes.
The limitations of this meta-analysis are as follows: (1) the cutoff values of lipid profile variables varied among the included studies, which could affect the effect size of the risk of MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death in patients with CHD; (2) the dose–response analysis were not conducted owing to it requires that the distributions of cases and persons or person-years and effect estimate (RRs or HRs) with the variance estimates for at least 3 quantitative exposure categories; (3) several outcomes were reported in only a few studies, and stratified analyses according to patients’ characteristics were not described; (4) heterogeneity among included studies were substantial, which not fully interpret by using a sensitivity analyses. These results could introduce by various disease status, background therapies, cutoff value of lipid profiles, and adjusted factors; (5) the adjusted factors were different among the included studies, which could affect the prognosis of patients with CHD; (6) unpublished data were not identified, which might cause an overestimation of the summary effect estimate; and (7) the role of apolipoprotein in patients with CHD was not investigated in the included studies. Further studies investigating any potential role of apolipoprotein on the progression of major cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CHD are needed.
Conclusions
The results of this study suggested that the lipid profile could affect the progression of MACE, all-cause mortality, and cardiac death in patients with CHD. Further large-scale prospective studies should be conducted with a focus on patients with specific characteristics to investigate the secondary prevention of major cardiovascular outcomes and mortality.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Search strategy in PubMed.
Additional file 2. Sensitivity analysis.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CHD
Coronary heart disease
- CIs
Confidence intervals
- CVD
Cardiovascular disease
- HDL
High-density lipoprotein
- LDL
Low-density lipoprotein
- MACE
Major adverse cardiovascular events
- SD
Standard deviation
- TC
Total cholesterol
- TG
Triglyceride
- WHO
World Health Organization
Authors’ contributions
XMZ developed the concept and drafted the manuscript. DYW and XMZ researched the literatures and collected the data. LJQ contributed to the data analysis and made the final revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Henan Provincial Science and Technology Department [Grant Number 172102310066].
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12872-020-01835-0.
References
- 1.WHO . The top 10 causes of death. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Antithrombotic TC. Collaborative meta-analysis of randomised trials of antiplatelet therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in high risk patients. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 2002;324(7329):71–86. doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7329.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ettehad D, Emdin CA, Kiran A, Anderson SG, Callender T, Emberson J, et al. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet (London, England) 2016;387(10022):957–967. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chou R, Dana T, Blazina I, Daeges M, Jeanne TL. Statins for prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: evidence report and systematic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA. 2016;316(19):2008–2024. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.15629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Karimi F, Rayani M, Akbarzade S, Tahmasebi R, Khakzade M, Arab J. The prevalence of hyperlipidemia in persons over 19 years of Bushehr in 1378. Iran South Med J. 2000;3(2):98–106. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Esmaeili NA, Ahmadi KJ. Lipid abnormalities in urban population of Rafsanjan (Rafsanjan coronary risk factors study phase 1). 2004.
- 7.Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25 Pt B):2889–2934. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Catapano AL, Graham I, De Backer G, Wiklund O, Chapman MJ, Drexel H, et al. 2016 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(39):2999–3058. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kinoshita M, Yokote K, Arai H, Iida M, Ishigaki Y, Ishibashi S, et al. Japan Atherosclerosis Society (JAS) guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases 2017. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018;25(9):846–984. doi: 10.5551/jat.GL2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Ge P, PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non randomised studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 12.DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7(3):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ades AE, Lu G, Higgins JP. The interpretation of random-effects meta-analysis in decision models. Med Decis Mak Int J Soc Med Decis Mak. 2005;25(6):646–654. doi: 10.1177/0272989X05282643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Deeks JJ, Higgins J, Altman DG. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins J, Green S, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Oxford: Wiley; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 2003;327(7414):557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tobias A. Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Tech Bull. 1999;47:15–17. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 1997;315(7109):629–634. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994;50(4):1088–1101. doi: 10.2307/2533446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sigurdsson E, Sigfusson N, Agnarsson U, Sigvaldason H, Thorgeirsson G. Long-term prognosis of different forms of coronary heart disease: the Reykjavik Study. Int J Epidemiol. 1995;24(1):58–68. doi: 10.1093/ije/24.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tervahauta M, Pekkanen J, Nissinen A. Risk factors of coronary heart disease and total mortality among elderly men with and without preexisting coronary heart disease. Finnish cohorts of the Seven Countries Study. JACC. 1995;26(7):1623–1629. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00395-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Behar S, Graff E, Reicher-Reiss H, Boyko V, Benderly M, Shotan A, et al. Low total cholesterol is associated with high total mortality in patients with coronary heart disease. The Bezafibrate Infarction Prevention (BIP) Study Group. Eur Heart J. 1997;18(1):52–59. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a015117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mabuchi H, Kita T, Matsuzaki M, Matsuzawa Y, Nakaya N, Oikawa S, et al. Large scale cohort study of the relationship between serum cholesterol concentration and coronary events with low-dose simvastatin therapy in Japanese patients with hypercholesterolemia and coronary heart disease: secondary prevention cohort study of the Japan Lipid Intervention Trial (J-LIT) Circ J. 2002;66(12):1096–1100. doi: 10.1253/circj.66.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vittinghoff E, Shlipak MG, Varosy PD, Furberg CD, Ireland CC, Khan SS, et al. Risk factors and secondary prevention in women with heart disease: the Heart and Estrogen/progestin Replacement Study. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(2):81–89. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-138-2-200301210-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Leander K, Wiman B, Hallqvist J, Andersson T, Ahlbom A, de Faire U. Primary risk factors influence risk of recurrent myocardial infarction/death from coronary heart disease: results from the Stockholm Heart Epidemiology Program (SHEEP) Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2007;14(4):532–537. doi: 10.1097/HJR.0b013e328012e3cc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Al-Mallah MH, Hatahet H, Cavalcante JL, Khanal S. Low admission LDL-cholesterol is associated with increased 3-year all-cause mortality in patients with non ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Cardiol J. 2009;16(3):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ghazzal ZB, Dhawan SS, Sheikh A, Douglas JS, Veledar E, Mavromatis K, et al. Usefulness of serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level as an independent predictor of one-year mortality after percutaneous coronary interventions. Am J Cardiol. 2009;103(7):902–906. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.11.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Seo SM, Choo EH, Koh YS, Park MW, Shin DI, Choi YS, et al. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a predictor of clinical outcomes in patients achieving low-density lipoprotein cholesterol targets with statins after percutaneous coronary intervention. Heart. 2011;97(23):1943–1950. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2011.225466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.De Bacquer D, Dallongeville J, Kotseva K, Cooney MT, Pajak A, Deckers JW, et al. Residual risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with coronary heart disease: the EUROASPIRE risk categories. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(2):910–914. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.10.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lin GM, Li YH, Lin CL, Wang JH, Han CL. Low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and low/normal body mass index are associated with increased mortality in coronary artery disease patients in Taiwan. Circ J. 2013;77(8):2079–2087. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-12-1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.van de Woestijne AP, Wassink AM, Monajemi H, Liem AH, Nathoe HM, van der Graaf Y, et al. Plasma triglyceride levels increase the risk for recurrent vascular events independent of LDL-cholesterol or nonHDL-cholesterol. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ding D, Li X, Qiu J, Li R, Zhang Y, Su D, et al. Serum lipids, apolipoproteins, and mortality among coronary artery disease patients. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:709756. doi: 10.1155/2014/709756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Martin SS, Khokhar AA, May HT, Kulkarni KR, Blaha MJ, Joshi PH, et al. HDL cholesterol subclasses, myocardial infarction, and mortality in secondary prevention: the Lipoprotein Investigators Collaborative. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(1):22–30. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Park SH, Rha SW, Choi BG, Park JY, Jeon U, Seo HS, et al. Impact of high lipoprotein(a) levels on in-stent restenosis and long-term clinical outcomes of angina pectoris patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents in Asian population. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015;42(6):588–595. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li JJ, Zhang Y, Li S, Cui CJ, Zhu CG, Guo YL, et al. Large HDL subfraction but not HDL-C is closely linked with risk factors, coronary severity and outcomes in a cohort of nontreated patients with stable coronary artery disease: a prospective observational study. Medicine. 2016;95(4):e2600. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu HH, Guo YL, Wu NQ, Zhu CG, Gao Y, Qing P, et al. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels are associated with coronary severity but not with outcomes in new-onset patients with stable coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2017;263:104–111. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tsai IT, Wang CP, Lu YC, Hung WC, Wu CC, Lu LF, et al. The burden of major adverse cardiac events in patients with coronary artery disease. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017;17(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12872-016-0436-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nordenskjold AM, Baron T, Eggers KM, Jernberg T, Lindahl B. Predictors of adverse outcome in patients with myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronary artery (MINOCA) disease. Int J Cardiol. 2018;261:18–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.03.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Dai W, Zhang Z, Zhao S. Baseline levels of serum high sensitivity C reactive protein and lipids in predicting the residual risk of cardiovascular events in Chinese population with stable coronary artery disease: a prospective cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0923-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Winter MP, Wiesbauer F, Blessberger H, Pavo N, Sulzgruber P, Huber K, et al. Lipid profile and long-term outcome in premature myocardial infarction. Eur J Clin Investig. 2018;48(10):e13008. doi: 10.1111/eci.13008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Gutierrez J, Ramirez G, Rundek T, Sacco RL. Statin therapy in the prevention of recurrent cardiovascular events: a sex-based meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(12):909–919. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.2145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Navarese EP, Robinson JG, Kowalewski M, Kolodziejczak M, Andreotti F, Bliden K, et al. Association between baseline LDL-C level and total and cardiovascular mortality after LDL-C lowering: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2018;319(15):1566–1579. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.de Vries FM, Kolthof J, Postma MJ, Denig P, Hak E. Efficacy of standard and intensive statin treatment for the secondary prevention of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in diabetes patients: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(11):e111247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Afilalo J, Majdan AA, Eisenberg MJ. Intensive statin therapy in acute coronary syndromes and stable coronary heart disease: a comparative meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Heart. 2007;93(8):914–921. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2006.112508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yan YL, Qiu B, Hu LJ, Jing XD, Liu YJ, Deng SB, et al. Efficacy and safety evaluation of intensive statin therapy in older patients with coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;69(12):2001–2009. doi: 10.1007/s00228-013-1570-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Morishita R, Itakura H, Nakaya N, Yoshida M, Odawara M, Ichihara A, et al. Risk factors for cardiovascular events in Japanese patients treated with fluvastatin from the long-term event monitoring (LEM) study. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2012;10(2):178–186. doi: 10.2174/157016112799305049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Klempfner R, Erez A, Sagit BZ, Goldenberg I, Fisman E, Kopel E, et al. Elevated triglyceride level is independently associated with increased all-cause mortality in patients with established coronary heart disease: twenty-two-year follow-up of the bezafibrate infarction prevention study and registry. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2016;9(2):100–108. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.115.002104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Besler C, Luscher TF, Landmesser U. Molecular mechanisms of vascular effects of high-density lipoprotein: alterations in cardiovascular disease. EMBO Mol Med. 2012;4(4):251–268. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201200224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mineo C, Deguchi H, Griffin JH, Shaul PW. Endothelial and antithrombotic actions of HDL. Circ Res. 2006;98(11):1352–1364. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000225982.01988.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Shlipak MG, Simon JA, Vittinghoff E, Lin F, Barrett-Connor E, Knopp RH, et al. Estrogen and progestin, lipoprotein(a), and the risk of recurrent coronary heart disease events after menopause. JAMA. 2000;283(14):1845–1852. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.14.1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Search strategy in PubMed.
Additional file 2. Sensitivity analysis.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].