Abstract
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the major cause of mortality among hospitalized acute lung injury (ALI) patients. Lung macrophages play an important role in maintaining the tissue-fluid homeostasis following injury. We recently showed that circulating monocytes recruited into the alveolar space suppressed the stimulator of type 1 interferon genes (STING) signaling in alveolar macrophages through sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). We used CD11b-DTR mice to deplete CD11b+ monocytes following LPS or Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Depletion of CD11b+ monocytes leads to the persistent inflammatory injury, infiltration of neutrophils, activation of STING signaling and mortality following lung infection. We demonstrated that adoptively transferred SPHK2-CD11b+ monocytes into CD11b-DTR mice after pathogenic infection rescue lung inflammatory injury.
Keywords: SPHK2, Lung injury, Macrophages, STING, ARDS
Author Commentary
Acute lung injury (ALI) is associated with bacterial and viral infection such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, SARSCOV2 virus, sepsis or drug toxicity which leads to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), predominantly in elderly patients. ARDS compromises survival of 40% of the patients but the cellular and molecular basis leading to ARDS remains unclear. Macrophages are crucial for a coordinated response to pathogenic insult and to the restoration of tissue homeostasis after triggering inflammatory signaling [1,2]. During any pathogenic infection, macrophages initiate host-defence by generation of pro-inflammatory cytokine and recruitment of neutrophil by activating transcription factor NF-κB via cell-surface toll-like receptor 4 [3,4]. Macrophages also suppress the inflammatory signaling pathway in a time dependent manner which is essential to restore tissue homeostasis. Thus, macrophages play a dual role by both initiating and suppressing inflammatory signaling and reinstating tissue-homeostasis [5, 6].
In the lung, two major subsets of macrophages are known to exist; the alveolar macrophages (AMφ), identified by expression of surface markers CD11c+/SiglecF+, while the other population, known as recruited macrophages originated from monocytes during injury and are identified as being CD11b+/SiglecF− [7–9].
AMφ trigger inflammatory signaling by releasing inflammatory cytokines and recruitment of neutrophils [10–13]. However, protracted inflammatory signaling from AMφ can itself damage vascular barrier function [13,14].
We showed that depletion of the recruited macrophage population, using diphtheria toxin (DT) in DTR-mice, during pathogenic insults induced proliferation and expansion of the inflammatory AMφ in the alveolar space [7]. We have shown that in CD11b+ monocytes depleted lungs, AMφ generated markedly higher IL6, IL-1β as well as IFN-β leading to the irreversible loss of lung vascular barrier function and rapid lethality of DTR mice. We demonstrated that, during lung injury, CD11b+Mφ alter the alveolar niche to cause AMφ to become anti-inflammatory, thereby preventing sustained inflammatory lung injury [7]. Our study demonstrated that adoptive transfer of CD11b+ monocytes from WT murine bone marrow into injured Mφdep mice rescued the anti-inflammatory function of AMφ and reversed lung vascular injury. Studies showed that monocytes can differentiate into AMφ [12] and CD11b+ CD11c+ macrophages in the lung represent a transitional pre-AMφ lineage [15,16]. Thus, an unanswered question is whether recruited CD11b+Mφ take on the AMφ signature and function after recruitment into the air space.
Upon sensing pathogens, cytokines released from AMφ can modulate the death of lung parenchymal cells depending on insult and its timing [17,18]. STING is a transmembrane homodimer located in the ER (endoplasmic reticulum) membrane and activated upon binding of the second messenger, cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) [19–21]. DNA liberated upon cell death is sensed by cGAS [22,23], which thereafter converts GMP and AMP into the second messenger cGAMP to activate STING [20]. Upon activation STING translocate to the perinuclear region, Golgi body and binds and phosphorylate to activates TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3). The phosphorylated IRF3 translocate to the nucleus and induces the generation of Type 1-IFN (Figure 1) [21,24]. We showed that depletion of CD11b+Mφ transiently increased cGAMP generation in control lungs while causing persistent increase in cGAMP levels in Mφdep lungs, resulting in enhanced STING signaling in these mice [7]. These findings indicate that recruited CD11b+Mφ in the airspace tightly control cGAMP-STING signaling in AMφ [7]. Macrophages are plastic in nature and can acquire either an inflammatory or anti-inflammatory phenotype depending on the inflammatory conditions [1]. The adoptive transfer of CD11b monocytes from WT or STING−/− mice into Mφdep mice reversed the AMφ inflammatory signaling. Also, STING null mice failed to exhibit the lung edema and characteristic inflammatory signaling as observed in control mice [7]. However, a caveat of this study was that it did not show the extent to which STING null CD11b+ macrophages facilitated anti-inflammatory function of existing AMφ or induce differentiation of Cd11b+Mφ into AMφ [7].
Figure 1:
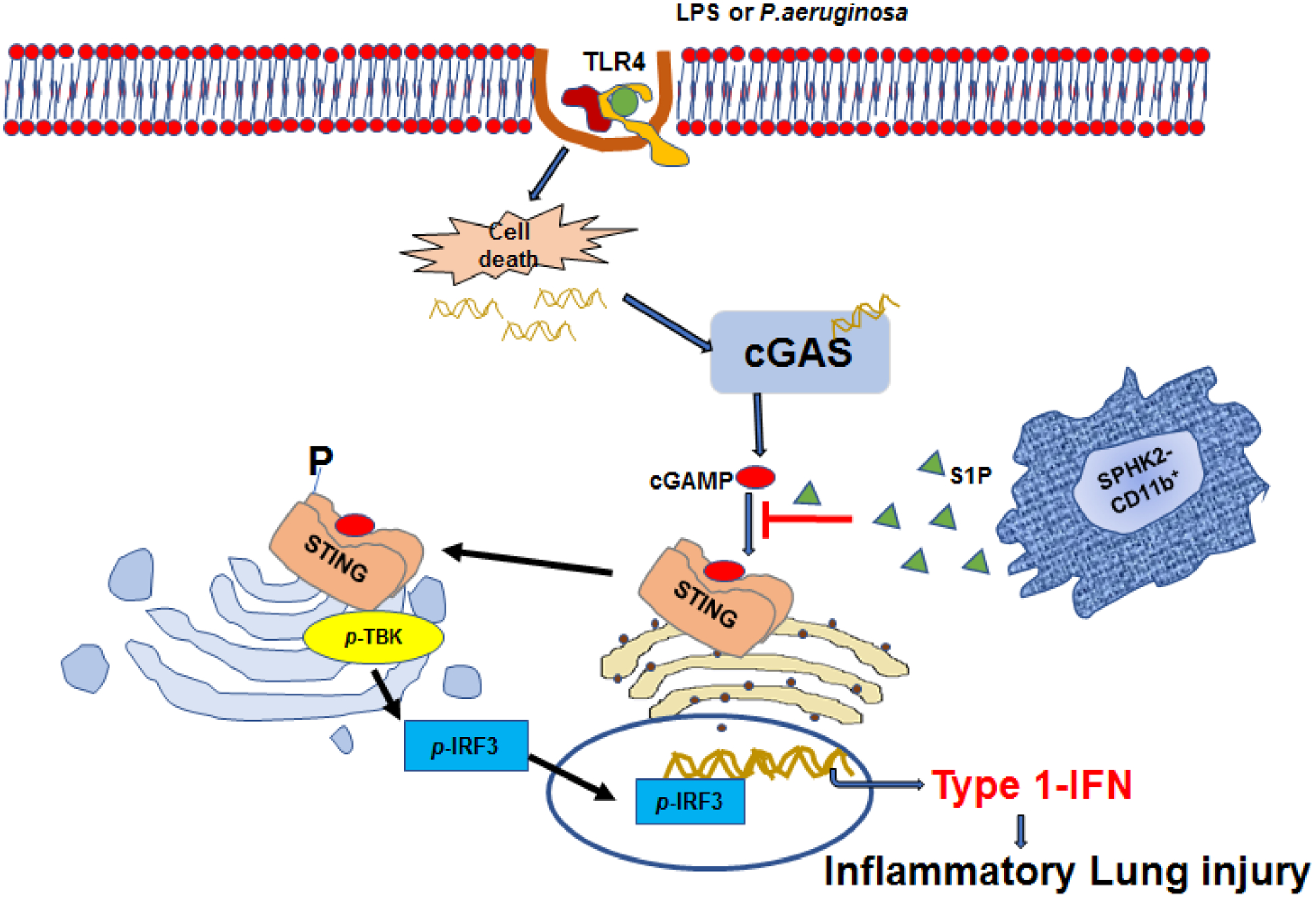
Upon recognition of LPS or Gram -ve bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosa by TLR4, there is cell death, which leads to the generation of dsDNA. This ds DNA is sensed by the DNA-sensing receptor cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) which acts as substrate to catalyze the formation of cGAMP, which is a second messenger to activate STING. Activated STING dimerizes and translocate from the ER to the perinuclear region via Golgi to recruit and promote phosphorylation of TBK1-IRF3, which subsequently drives translocation of p-IRF3 to the nucleus to produce type 1-IFN. The SPHK2-CD11b+ recruited macrophages release SIP which compete with cGAMP and inhibit binding of cGAMP to STING, thus blocks the translocation of STING and phosphorylation of TBK1 and IRF3 and generation of type 1-IFN.
In searching of the mechanism by which CD11b+Mφ suppressed STING signaling in AMφ, we focused on their paracrine role. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) generated by sphingosine kinases (SPHK1 and SPHK2) is a well-known bioactive lipid that protects vascular injury in various murine models of lung injury [25–27]. We showed that SPHK2 expression was higher in CD11b+Mφ than AMφ. Further, we showed that SPHK2 was required for maintaining SPHK activity and S1P levels in macrophages following LPS injury [7]. Adoptive transfer of WT-CD11b+ bone marrow monocytes blocked AMφ STING activity in Mφ depleted mice while transfer of SPHK2-deficient CD11b+ bone marrow monocytes failed to do so. In this case, AMφ remained inflammatory and led to non-resolvable lung injury. We also showed that SPHK2, but not SPHK1, was required for LPS stimulated S1P generation and that inhibition of SPHK2 kinase activity enhanced STING signaling in WT-BMDM as well as human macrophages. AMφ and CD11b+Mφ sorted from naïve WT and SPHK2-null lungs by flow cytometry were also assessed for SPHK1 and SPHK2 protein expression and differences in SPHK2 activity in CD11b+Mφ versus AMφ. Interestingly, we found that SPHK2 activity was 2-fold higher in CD11b+Mφ compared to AMφ whereas SPHK1 was expressed to the same extent in both macrophage subsets. Whereas the SPHK activity and S1P generation in macrophages isolated from bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) of WT or Sphk2−/−mice were significantly reduced after LPS challenge in macrophages during peak of injury [7]. In human macrophages (U937 cell line), inhibition of SPHK2 activity using specific SPHK2 inhibitor, ABC294640 [28,29] increased TBK1, IRF3 and NF-κB-p65 phosphorylation. These findings suggested that recruited CD11b+Mφ functioned in a SPHK2 dependent manner.
Evidence indicates that activation of plasmalemmal S1P receptors respond to S1P generated by SPHK1 [25,26,30], whereas SPHK2-mediated S1P generation regulates cellular functions in a localized manner [31,32]. We showed that SPHK2 suppressed STING redistribution, indicating compartmentalized action of SPHK2 in targeting ER-STING signaling [7]. Consistent with this C-terminus of STING to induce STING signaling [33]. To assess S1P interaction with C-terminus of STING we used lysates from HEK cells transducing HA-full-length STING (1–379 aa) or the C-terminus of STING (HA-STING-CTD: aa149–379-STING). While CTD-STING was expressed to a lower extent than FL-STING in HEK, it did interact with S1P. Molecular docking predicted that S1P can competitively inhibit binding of cGAMP to STING C-terminal domain and thereby blocks down stream signaling [7]. However, several questions remain unanswered. First, how SPHK2 blocked STING translocation to Golgi? We expect that SPHK2 generated S1P might modulate the STING dimerization and making it unavailable for translocation. Second, what is the affinity of S1P towards STING in absence or presence of cGAMP and what are these binding sites? In order to check the binding affinity of S1P to STING, cGAMP binding and other possible sites in STING could be mutated thereafter its signaling can be assessed following pathogenic insult and/or in the presence of S1P. In addition, it is unclear whether this effect of S1P would be only on CD11b+ macrophages, or also in other cell types in the lung. To confirm the action of SPHK2 generated S1P in other cell type it would be required to perform in vitro studies using specific cell lines or shorted primary cells and targeted delivery of SPHK2 cDNA in mice following lung injury. How SPHK2-S1P→STING would be regulated in the context of inflammation? The possibility of the regulation of SPHK2 activation and generation of S1P following lung infection is depend upon the generation of NF-κB or generation of cGAMP. Answer to all of these questions need critical experiment design and execution in future.
Taken together, our findings suggest that during acute lung injury, CD11b+Mφ in the air space can educate AMφ to resolve ALI through suppressing STING signaling. Our study showed that inhibition of SPHK1 expression in SPHK2 null BMDM had no effect on STING activity [7].
Our finding also showed that SPHK2 regulate STING distribution to Golgi body following its activation, while inhibition of SPHK2 promoted STING interaction with TBK1, leading to its activation. Further studies showed that S1P formed a complex with STING in LPS treated bone-marrow derived macrophages (BMDM). We further showed S1P inhibited cGAMP induced IFN-β production in SPHK2-null BMDM nearly to the levels of WT-BMDM, indicating SPHK2-induced S1P binds STING and inhibits cGAMP activation of STING inflammatory signaling [7] (Figure 1). cGAMP interacts with downstream of SPHK2-mediated S1P generation. These findings could be the basis for future study where SPHK2 generated S1P in CD11b+ macrophages may be a targeted delivery option for the therapeutics of lung inflammatory injury.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants HL77806, HL060678, HL84153 and HL137179.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest Disclosure
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
References
- 1.Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013. Apr;496(7446):445–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gautier EL, Shay T, Miller J, Greter M, Jakubzick C, Ivanov S, et al. Gene-expression profiles and transcriptional regulatory pathways that underlie the identity and diversity of mouse tissue macrophages. Nature Immunology. 2012. Nov;13(11):1118–28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Newton K, Dixit VM. Signaling in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 2012. Mar 1;4(3):a006049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mogensen TH. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 2009. Apr 1;22(2):240–73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Matthay MA, Ware LB, Zimmerman GA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2012. Aug 1;122(8):2731–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Randolph AG. Management of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome in children. Critical Care Medicine. 2009. Aug 1;37(8):2448–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Joshi JC, Joshi B, Rochford I, Rayees S, Akhter MZ, Baweja S, et al. SPHK2-Generated S1P in CD11b+ Macrophages Blocks STING to Suppress the Inflammatory Function of Alveolar Macrophages. Cell Reports. 2020. Mar 24;30(12):4096–109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schyns J, Bureau F, Marichal T. Lung interstitial macrophages: past, present, and future. Journal of Immunology Research. 2018. Apr 30;2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ward PA. Acute lung injury: how the lung inflammatory response works. Eur Respiratory Soc. 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bosmann M, Grailer JJ, Russkamp NF, Ruemmler R, Zetoune FS, Sarma JV, ET AL. CD11c+ alveolar macrophages are a source of IL-23 during LPS-induced acute lung injury. Shock (Augusta, Ga.) 2013. May;39(5):447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Byrne AJ, Maher TM, Lloyd CM. Pulmonary macrophages: a new therapeutic pathway in fibrosing lung disease?. Trends in Molecular Medicine. 2016. Apr 1;22(4):303–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Westphalen K, Gusarova GA, Islam MN, Subramanian M, Cohen TS, Prince AS, et al. Sessile alveolar macrophages communicate with alveolar epithelium to modulate immunity. Nature. 2014. Feb;506(7489):503–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Duan M, Li WC, Vlahos R, Maxwell MJ, Anderson GP, Hibbs ML. Distinct macrophage subpopulations characterize acute infection and chronic inflammatory lung disease. The Journal of Immunology. 2012. Jul 15;189(2):946–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gibbings SL, Thomas SM, Atif SM, McCubbrey AL, Desch AN, Danhorn T, et al. Three unique interstitial macrophages in the murine lung at steady state. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. 2017. Jul;57(1):66–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schneider C, Nobs SP, Kurrer M, Rehrauer H, Thiele C, Kopf M. Induction of the nuclear receptor PPAR-γ by the cytokine GM-CSF is critical for the differentiation of fetal monocytes into alveolar macrophages. Nature Immunology. 2014. Nov;15(11):1026–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Makris S, Paulsen M, Johansson C. Type I interferons as regulators of lung inflammation. Frontiers in Immunology. 2017. Mar 10;8:259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hiruma T, Tsuyuzaki H, Uchida K, Trapnell BC, Yamamura Y, Kusakabe Y, et al. IFN-β improves sepsis-related alveolar macrophage dysfunction and postseptic acute respiratory distress syndrome-related mortality. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. 2018. Jul;59(1):45–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Li X, Shu C, Yi G, Chaton CT, Shelton CL, Diao J, Zuo X, Kao CC, Herr AB, Li P. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is activated by double-stranded DNA-induced oligomerization. Immunity. 2013. Dec 12;39(6):1019–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cai X, Chiu YH, Chen ZJ. The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing and signaling. Molecular Cell. 2014. Apr 24;54(2):289–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Barber GN. STING: infection, inflammation and cancer. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2015. Dec;15(12):760–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Burdette DL, Monroe KM, Sotelo-Troha K, Iwig JS, Eckert B, Hyodo M, et al. STING is a direct innate immune sensor of cyclic di-GMP. Nature. 2011. Oct;478(7370):515–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ishikawa H, Barber GN. STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature. 2008. Oct;455(7213):674–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chen Q, Sun L, Chen ZJ. Regulation and function of the cGAS–STING pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing. Nature immunology. 2016. Oct;17(10):1142–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tauseef M, Kini V, Knezevic N, Brannan M, Ramchandaran R, Fyrst H, et al. Activation of sphingosine kinase-1 reverses the increase in lung vascular permeability through sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling in endothelial cells. Circulation research. 2008. Nov 7;103(10):1164–72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Natarajan V, Dudek SM, Jacobson JR, Moreno-Vinasco L, Huang LS, Abassi T, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate, FTY720, and Sphingosine-1–phosphate receptors in the pathobiology of acute lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. 2013. Jul;49(1):6–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Szczepaniak WS, Zhang Y, Hagerty S, Crow MT, Kesari P, Garcia JG, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate rescues canine LPS-induced acute lung injury and alters systemic inflammatory cytokine production in vivo. Translational Research. 2008. Nov 1;152(5):213–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xun C, Chen MB, Qi L, Tie-Ning Z, Peng X, Ning L, et al. Targeting sphingosine kinase 2 (SphK2) by ABC294640 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. 2015. Dec;34(1):1–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Xu L, Jin L, Yang B, Wang L, Xia Z, Zhang Q, Xu J. The sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor ABC294640 inhibits cervical carcinoma cell growth. Oncotarget. 2018. Jan 5;9(2):2384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Spiegel S, Milstien S. The outs and the ins of sphingosine-1-phosphate in immunity. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2011. Jun;11(6):403–15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Park K, Elias PM, Shin KO, Lee YM, Hupe M, Borkowski AW, et al. A novel role of a lipid species, sphingosine-1-phosphate, in epithelial innate immunity. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2013. Feb 15;33(4):752–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang L, Urtz N, Gaertner F, Legate KR, Petzold T, Lorenz M, et al. Sphingosine kinase 2 (Sphk2) regulates platelet biogenesis by providing intracellular sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P). Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology. 2013. Aug 1;122(5):791–802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lau L, Gray EE, Brunette RL, Stetson DB. DNA tumor virus oncogenes antagonize the cGAS-STING DNA-sensing pathway. Science. 2015. Oct 30;350(6260):568–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wu X, Yang J, Na T, Zhang K, Davidoff AM, Yuan BZ, Wang Y. RIG-I and IL-6 are negative-feedback regulators of STING induced by double-stranded DNA. PloS One. 2017. Aug 14;12(8):e0182961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Li Y, James SJ, Wyllie DH, Wynne C, Czibula A, Bukhari A, et al. TMEM203 is a binding partner and regulator of STING-mediated inflammatory signaling in macrophages. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2019. Aug 13;116(33):16479–88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


