Abstract
Simple Summary
Recent research has enhanced our understanding of the diverse biological processes that occur in pediatric gliomas; and molecular genetic analysis has become essential to diagnose and treat these conditions. Because targetable molecular aberrations can be detected in pediatric gliomas, identifying these aberrations is very important. This review provides an overview of pediatric gliomas, and describes recent developments made in strategies for their diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, it presents a current picture of pediatric gliomas in light of advances in molecular genetics, and describes the current scientific progress in gliomas’ treatment using information from recently completed and ongoing clinical trials. The era of incorporating molecular genetic analysis into clinical practice is emerging.
Abstract
Recent research has promoted elucidation of the diverse biological processes that occur in pediatric central nervous system (CNS) tumors. Molecular genetic analysis is essential not only for proper classification, but also for monitoring biological behavior and clinical management of tumors. Ever since the 2016 World Health Organization classification of CNS tumors, molecular profiling has become an indispensable step in the diagnosis, prediction of prognosis, and treatment of pediatric as well as adult CNS tumors. These molecular data are changing diagnosis, leading to new guidelines, and offering novel molecular targeted therapies. The Consortium to Inform Molecular and Practical Approaches to CNS Tumor Taxonomy (cIMPACT-NOW) makes practical recommendations using recent advances in CNS tumor classification, particularly in molecular discernment of these neoplasms as morphology-based classification of tumors is being replaced by molecular-based classification. In this article, we summarize recent knowledge to provide an overview of pediatric gliomas, which are major pediatric CNS tumors, and describe recent developments in strategies employed for their diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: pediatric glioma, molecular profiling, next-generation sequencing, molecular targeted therapy, cIMPACT-NOW
1. Introduction
Central nervous system (CNS) tumors are the most frequent solid tumors in children, accounting for 21% of pediatric cancers and representing a primary cause of mortality [1]. Survivors of pediatric CNS tumors are at a high risk for late mortality and for developing subsequent neoplasms and chronic diseases [2]. The main secondary disorders are endocrine and cognitive disorders. In addition, only half of the patients are normally employed when they become adults, due to their complex disabilities [3]. Improvement of diagnosis and treatment of pediatric CNS tumors, and care of child-to-adult transition for these patients, are required [3].
Recent research has promoted our understanding of the complex biology of pediatric CNS tumors. Molecular genetic analysis is essential not only for proper classification but also for monitoring biological behavior and clinical management of tumors. Recent genome studies have revealed several unique genomic changes observed in pediatric CNS tumors, which were different from those observed in adults [4,5,6]. Since the 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of CNS tumors, molecular profiling has become an indispensable step in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of pediatric as well as adult tumors of this type [7]. These molecular data are changing the way tumors are being diagnosed. Specifically, morphology-based classification of tumors is being replaced by molecular-based classification, leading to new guidelines and offering novel molecular targeted therapies. The Consortium to Inform Molecular and Practical Approaches to CNS Tumor Taxonomy (cIMPACT-NOW) is making practical recommendations based on recent advances in CNS tumor classifications, particularly those based on molecular discernment of these neoplasms [8]. In this article, we summarize our current understanding of the most common pediatric gliomas, which are the major types of pediatric CNS tumors, and describe recent developments in strategies of their diagnosis and treatment.
2. Diagnostic Approach for Pediatric Brain Tumors
2.1. Integrated Diagnosis with Histological and Genetical Classification
In the past, conventional diagnosis of pediatric CNS tumors involved a pathologist’s histopathologic review, supported by radiological findings, such as magnetic resonance imaging, and standardized immunohistochemical testing for specific biomarkers. However, the importance of molecular genetic analysis has become a focus over the past decade, and the molecular profiling of tumors has revealed a number of important details including prognostic factors and predictive markers of drug sensitivity, resistance, and adverse events. This has allowed personalized therapy to become feasible. Molecular genetic analysis is required in order for pediatric CNS tumors to be incorporated into a histologically based tiered classification system and improve their diagnosis. In the 2016 CNS WHO classification of medulloblastomas, a histologically defined and a genetically defined lists of tumors were combined to produce an integrated list of parameters for improved diagnosis [9]. This provided great flexibility, while at the same time conveyed key diagnostic information in a layered concise format [10]. In cIMPACT-NOW update 6, the clinical utility of this combined two-list approach, has been proven to optimally categorize pediatric-type glial/glioneuronal tumors and ependymomas [8].
2.2. DNA Methylation Profiling
DNA methylation-based classification for CNS tumors is reported to be a reproducible and valuable approach, and is expected to reduce the substantial inter-observer variability that occurs in conventional morphology-based classification [11]. In cIMPACT-NOW update 6, although the committee did not recommend methylation profiling as the only method to identify specific tumor types or subtypes, they agreed that many CNS tumor types and subtypes can be reliably identified using this approach [8]. Methylation profiling for pediatric CNS tumors is a useful tool to identify specific subtypes with different clinical outcomes, and is expected to be a robust tool for diagnosis [11,12]. In pediatric CNS tumors, methylation profiling provides a reproducible modality for classification with high concordance to subtypes initially identified by gene expression profiling and genome sequencing [12].
2.3. Molecular Approaches for Precision Therapy
In recent years, advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS) and array-based genomic platforms have transformed analysis of the molecular landscapes of cancers, including pediatric CNS tumors [13]. NGS-based profiling allows analysis of some combinations of germline and/or somatic single nucleotide variants, small insertions, or deletions, and structure variants in the form of DNA copy number alterations, translocations, inversions, and other more complex alterations [13]. This novel method makes genomic-based precision therapy feasible. A national trial of pediatric cancer using molecular analysis for treatment decisions is currently being conducted by the Children’s Oncology Group [14]. Known as the National Cancer Institute-Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice (NCI-MATCH) trial, eligibility for assignment to treatment arms is determined based on predefined lists of genomic aberrations. In this trial, the tissue of solid tumors from pediatric and adolescent patients have undergone molecular profiling. If an aberration that has been defined as a driver mutation for a MATCH study drug targeting the identified aberration is identified, the patient has the opportunity to enroll in the relevant single agent treatment arm [14].
Liquid biopsy is also one of the current topics as a less invasive method using body fluid, such as plasma or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), for molecular diagnosis. Recent efforts including ours have developed digital PCR-based liquid biopsy targeting cell-free tumor DNA in CSF for detecting glioma-specific diagnostic mutations [15]. NGS-based liquid biopsy has been attempted. Miller et al. used NGS to analyze CSF samples from patients with diffuse gliomas, and identified glioma-related genetic alterations in 42 (49.2%) of 85 tumors [16]. Although they also detected these alterations from 3 (15.8%) of 19 plasma samples, all patients with positive plasma had radiological evidence for dissemination within the CNS [16]. These results indicated that the sensitivity of liquid biopsy is still an unsolved issue for the molecular diagnosis of CNS tumors. Accordingly, sufficient tissue samples obtained by conventional biopsy seems to be essential in the present state, especially for NGS or methylation profiling.
Because targetable molecular aberrations can be detected in pediatric CNS tumors, searching for these aberrations is essential for treating children with these tumors. However, most existing cancer multi-gene panel tests using NGS are currently performed only for adult cancer, resulting in undetectability of the rare genetic aberrations specific to pediatric cancer. Although molecular diagnosis is essential in cases of pediatric cancer, current cancer multi-gene panel tests cannot be used for the purpose of diagnosis. To resolve this issue, Kohsaka et al. reported the establishment of a comprehensive assay, the Todai OncoPanel, which consists of DNA and RNA hybridization capture-based NGS panels [17]. In this method, fusion genes, which are frequently detected in pediatric CNS tumors, can be accurately and cost-effectively identified because of the development of the junction capture method for RNA sequencing [17]. The development and implementation of NGS panels for pediatric cancer diagnosis is coming of age.
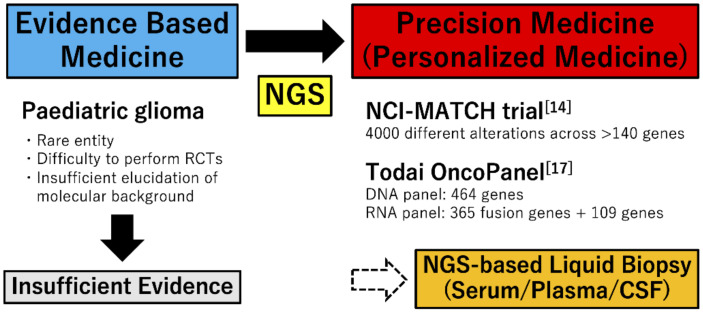
Currently, novel molecular profiling technologies, including whole-proteome, phosphoproteome, metabolome, and single-cell RNA-sequencing are also developing. Many of these technologies are being applied in current research to further characterize tumor biology [13]. In addition to development of the molecular-based diagnostic technologies, international cooperation to identify and approve new pediatric oncology drugs, such as ACCELERATE organized in Europe in 2015, has been advancing [18]. Many clinical trials for novel treatment are being conducted around the world. The era of incorporating molecular genetic analysis into clinical practice is beginning (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Change of treatment strategies for pediatric glioma. In treatment for pediatric glioma, because of advances of NGS, precision medicine is expected instead of evidence-based medicine. NCI-MATCH trial and Todai OncoPanel are representative precision medicine for pediatric glioma, and liquid biopsy is also expected in the future. RCT, randomized controlled trial; NGS, next-generation sequencing; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid.
3. Histopathologic Subtypes of Pediatric CNS Tumors
Numerous entities comprise pediatric CNS tumors. The Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States (CBTRUS) Statistical Report showed the frequency of pediatric CNS tumors in a population-based study in the USA [19]. Gliomas were the most common. The majority of pediatric gliomas are pediatric low-grade glioma (pLGG) classified as WHO grade 1 or 2, but some develop in a short time period and progress rapidly, classified into WHO grade 3 or 4 as pediatric high-grade glioma (pHGG) [20]. According to the report, pilocytic astrocytoma (PA) accounted for 17.5%, other astrocytomas accounted for 8.9%, and mixed glioneuronal tumors accounted for 6.5% of pediatric CNS tumors. Oligodendroglial tumors were rare, with oligodendrogliomas at 0.9%, of cases and oligoastrocytic tumors at 0.6%. Glioblastoma (GBM) was also rare, accounting for 2.6% of cases. HGGs not otherwise specified (NOS) were 14.2% of cases. Ependymal tumors were 5.6%, and germ cell tumors were 3.7% of cases. As benign tumors, nerve sheath tumors, craniopharyngioma, and pituitary tumors comprised 4.8%, 4.0%, and 3.8% of cases, respectively. Others made up 9.3% of cases. Because these tumors are fundamentally different from those occurring in adults, specific treatment for (and management of) younger individuals are important.
4. Low Grade Gliomas
Compared to adult LGGs, isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutations are less observed in children, and malignant progression is extremely rare. These gliomas account for approximately 30% of pediatric CNS tumors [21,22]. The 10-year overall survival (OS) is high, over 95%, but 10-year progression-free survival (PFS) is only approximately 50%, and half of patients require adjuvant therapy [23]. Surgical resection is important for the management of pLGG, and complete resection is the most favorable predictor of survival in patients with pLGG [24]. In patients where gross tumor removal cannot be achieved, progression of the tumor has been treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation. However, patients with unresectable tumors have chronic clinical conditions and experience long-term reduction in quality of life [25]. In particular, radiation is associated with increased mortality [26,27,28].
4.1. Molecular Landscape in pLGG
4.1.1. RAS/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Pathway
In pLGG, the most common entity is pilocytic astrocytoma (PA) comprising >15% of tumors in patients aged 0 to 19 years [29]. PA is classified into WHO grade 1, and has a 10-year survival of over 90%, although a rare variant termed “pilomyxoid astrocytoma”, which occurs predominantly in children under 1 year of age, and in the hypothalamic/chiasmatic region, has been classified as WHO grade 2. As a molecular aberration of PA, KIAA1549-BRAF fusion by tandem duplication is historically well-known and the most frequently observed (>70%) [30]. However, high-throughput sequencing techniques that interrogate the whole genome have shown that a single aberration of the RAS/MAPK pathway is exclusively found in almost all cases, indicating that PA represents a one-pathway disease [30]. Recent studies have put forth an overview of the RAS/MAPK pathway alterations in pLGG [30,31,32,33]. Typical aberrations are reported as follows.
BRAF V600E mutation: in pLGG, patients with the BRAF V600E mutation demonstrated poor outcomes. Lassaletta et al. reported that the 10-year PFS is 27% and 60.2% for the BRAF V600E mutant and wild-type pLGG, respectively (p < 0.001) [34]. BRAF V600E mutations can be found in CNS tumors in any location, and are often detected in midline tumors, including the optic pathway, brainstem, and spinal cord [34]. The BRAF V600E mutation is commonly observed in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas (78%), followed by gangliogliomas (49%), and also in diffuse astrocytomas (43%) [34]. Astroblastomas are also known to harbor BRAF V600E [35]. However, this mutation is rare in PAs (3%) [34].
FGFR1: FGFRs are a family of receptor tyrosine kinases [36]. Their dysregulation has been detected in a wide variety of cancers, such as urothelial carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, ovarian cancer, and lung adenocarcinoma [37]. FGFR1-3 is identified in CNS tumors, including glioma, ependymoma, and medulloblastoma [37,38,39]. In pediatric gliomas, FGFR1 is well-noted and is expected to be a targetable aberration. FGFR1 aberrations include FGFR1 mutations, FGFR1-TACC1 fusions, and FGFR1-TKD duplications [33,40,41]. These aberrations cause FGFR1 autophosphorylation, resulting in upregulation of the RAS/MAPK pathway (Table 1) [33,40].
Table 1.
Summary of molecular landscape in pediatric gliomas.
| Molecular Alteration | Function | Tumor Type | Potential Biomarker |
|---|---|---|---|
| pLGG (RAS/MAPK pathway) | |||
| KIAA1549-BRAF fusion | Activation of BRAF kinase domain Deregulation of the RAS/MAPK pathway |
PA | Diagnostic marker Poor prognostic marker |
| BRAF V600E mutation | PA/PXA/GG/DA | ||
| FGFR1 | Upregulation of the RAS/MAPK pathway | CNS tumors | NA |
| NF-1 | Negative regulator of RAS | PA/DA | NA |
| pLGG (non-RAS/MAPK pathway) | |||
| MYB and MYBL1 | Control of proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic and other progenitor cells | DA | NA |
| CDKN2A homozygous deletion | Non-coding of the gene for tumor suppressors, protein p14ARF and p16INK4A | PXA | Poor prognostic marker |
| pHGG | |||
| H3K27M mutation | Decrease levels of lysine 27 methylation | GBM/DIPG | Diagnostic marker Poor prognostic marker |
| H3G34R/V mutation | Changes the distribution of lysine 36 methylation | ||
| Infantile glioma | |||
| NTRK fusions | Upregulation of the RAS/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways | Hemispheric HGG | Intermediate prognostic marker |
| ALK fusions | |||
| ROS1 fusions | |||
pLGG, pediatric low-grade glioma; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PA, pilocytic astrocytoma; PXA, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma; GG, ganglioglioma; DA, diffuse astrocytoma; CNS, central nervous system; NA, not available; pHGG, pediatric high-grade glioma; GBM, glioblastoma; DIPG, diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma.
NF-1: neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1) is a well-known inherited tumor predisposition syndrome caused by a germline mutation in the NF-1 tumor suppressor gene. This gene encodes neurofibromin, a GTPase-activating protein that functions as the negative regulator of RAS [42,43]. LGGs in the optic pathway are diagnosed in 10–15% of children with NF-1 [44,45]. Most LGGs associated with NF-1 are benign and require no treatment. However, LGGs associated with NF-1 in younger children under 2 years of age and/or outside of the optic pathway have risk of progression and poor outcomes [23,46].
4.1.2. Non-RAS/MAPK Pathway
pLGG, including PA, is considered a single RAS/MAPK pathway disease. However, some aberrations indirectly affect the RAS/MAPK pathway.
MYB and MYBL1 alterations: MYB alteration influences on control of proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic and other progenitor cells, and is associated with proto-oncogenic functions in both human leukemia and solid tumors [47,48]. Bandopadhayay et al. reported that 10% of pLGGs contained MYB alterations, and MYB-QKI fusion was specified as a driver aberration for angiocentric gliomas [49]. MYBL1 is a member of the MYB family. Although the biological function of MYBL1 is less known than that of MYB, MYBL1 is considered to function as a transcriptional regular critical for proliferation and differentiation [23]. MYBL1 alterations are rare and are detected in diffuse astrocytomas [41,49]. pLGGs frequently have alterations in MYB family genes, such as MYB and MYBL1 [33,50]. These alterations are detected more frequently in young children (median age, 5 years) and often occur in the cerebral hemispheres [51]. The clinical course is generally indolent in glioma patients with MYB and MYBL1 alterations, and Chiang et al. reported that the 10-year OS is 90%, and 10-year PFS is 95% [51].
CDKN2A homozygous deletion: CDKN2A is a gene encoding two tumor suppressors, protein p14ARF, and p16INK4A. Homozygous deletion of CDKN2A can contribute to uncontrolled tumor cell proliferation [52], and has been reported as a poor prognostic marker in adult glioma [53,54,55]. CDKN2A homozygous deletion is also observed in pediatric gliomas, and is a well-known hallmark lesion of pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. CDKN2A homozygous deletion co-occurs with the BRAF V600E mutation, demonstrating poor clinical outcomes [7,56].
4.2. Integrated Diagnosis of Pediatric Diffuse Gliomas in cIMPACT-NOW Update 4
In cIMPACT-NOW update 4, an integrated diagnosis of pediatric diffuse gliomas was reported. In this report, pediatric diffuse gliomas were classified by MYB, MYBL1, or FGFR1 alterations or BRAF V600E mutations [57]. These aberrations are not frequent; however, Qaddoumi et al. reported that a BRAF V600E mutation, FGFR alteration, or rearrangement of MYB or MYBL1 were detected in 84% of IDH-wild type/H3-wild type diffuse gliomas in a large pediatric cohort [41]. The following classifications were considered to provide valuable diagnostic and prognostic information, and for some entities, suggest targeted therapies [57]:
Diffuse glioma, MYB-altered;
Diffuse glioma, MYBL1-altered;
Diffuse glioma, FGFR1 TKD-duplicated;
Diffuse glioma, FGFR1-mutant;
Diffuse glioma, BRAF V600E-mutant;
Diffuse glioma, other MAPK pathway alteration.
4.3. Targeted Therapy for pLGG
We summarize recently reported clinical trials of targeted therapy for pediatric glioma in Table 2 and ongoing clinical trials in Table 3. Successful treatment with BRAF inhibitors for BRAF-mutated gliomas has been recently reported [58,59,60,61]. Dabrafenib, one of those agents, is expected to improve clinical outcomes with few adverse events and good tolerance in patients with BRAF-mutated gliomas [60,61,62]. Despite high initial response rates, acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors occurs in a majority of patients, and one of the most frequent causes of this resistance is reactivation of the MAPK pathway [63]. However, an additional MEK inhibitor that inhibits the MAPK pathway to BRAF inhibitors, trametinib, overcame BRAF inhibitor resistance, and demonstrated superiority over a BRAF inhibitor alone in phase III clinical trials in patients with BRAF mutant metastatic melanoma [64,65]. In CNS tumors, including gliomas, clinical experience with a combination of BRAF and MEK inhibitors has also been reported [61,66,67]. To evaluate the efficacy and safety of dabrafenib in combination with trametinib for pediatric gliomas, a nationwide phase II pediatric study is in progress. In a recent phase II study of patients with pLGG in the United States, the efficacy of selumetinib, a MEK1/2 inhibitor, was assessed [68]. In this study, children with PA harboring either one of the two most common BRAF aberrations, KIAA1549-BRAF fusion or the BRAF V600E mutation, and NF-1 associated LGG, participated. Selumetinib was found to be active in cases of recurrent or progressive BRAF aberrated PA and NF-1 associated LGG [68]. In Japan, a selumetinib pediatric NF-1 phase I study is in progress, although this study does not include CNS tumors. Early clinical approval and expanded indication for selumetinib in treating CNS tumors is expected. In addition, in a phase I study, vemurafenib, a BRAF V600E inhibitor approved for metastatic melanoma, was determined to be acceptable for recurrent or refractory BRAF V600E mutant glioma [69,70]. In the near future, these targeted therapies may be included among standard chemotherapies for treatment of BRAF-mutated tumors.
Table 2.
Summary of recent clinical trials of targeted therapies for pediatric glioma.
| Author | Year | ClinicalTrials.gov ID | Phase | Patients | Disease | Molecular Target | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGG | ||||||||
| Fangusaro et al. [68] | 2019 | NCT01089101 | II | 3–21 y n = 38 |
Recurrent/refractory LGG | MEK | Selumetinib | Positive antitumor activity Well-tolerated |
| Hargrave et al. [62] | 2019 | NCT01677741 | I/II | 2–18 y n = 32 |
Recurrent/refractory LGG | BRAF V600E mutant | Dabrafenib | Positive antitumor activity Well-tolerated |
| Nicolaides et al. [70] | 2020 | NCT01748149 | I | 3–17 y n = 19 |
Recurrent/refractory gliomas | BRAF V600E mutant | Vemurafenib | Positive antitumor activity Well-tolerated |
| HGG | ||||||||
| Wetmore et al. [73] | 2016 | NCT01462695 | II | 18 m–22 y n = 30 |
HGG or ependymoma |
VEGFR
PDGFR KIT |
Sunitinib | No antitumor activity Well-tolerated |
| Becher et al. [74] | 2017 | NCT01049841 | I | 4–24 y n = 23 |
Recurrent/refractory brain tumor |
AKT
mTOR |
Perifosine Temsirolimus |
Well-tolerated |
| Broniscer et al. [75] | 2018 | NCT01644773 | I | 2–21 y n = 25 |
Recurrent/progressive HGG or DIPG |
PDGFRA
c-Met |
Dasatinib Crizotinib |
Minimal antitumor activity Poorly tolerated |
| Chi et al. [76] | 2019 | NCT03134131 | II | 3–42 y n = 18 |
H3K27M mutant diffuse midline glioma/DIPG | DRD2/3 | ONC201 | Positive antitumor activity |
LGG, low-grade glioma; y, years; HGG, high-grade glioma; m, months; DIPG, diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma; DRD2/3, dopamine receptor type 2/3.
Table 3.
Summary of ongoing clinical trials for targeted therapies in pediatric glioma.
| ClinicalTrials.gov ID | Phase | Patients | Disease | Molecular Target | Treatment | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAS/MAPK pathway targeted therapy | ||||||
| NCT01734512 | II | 3–21 y | Recurrent/progressive LGG | mTOR | Everolimus | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT01748149 | I | Up to 25 y | Recurrent/refractory glioma | BRAF V600E mutant | Vemurafenib | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT02684058 | II | 12 m–17 y | LGG or relapsed/refractory HGG |
BRAF V600E mutant MEK |
Dabrafenib Trametinib | Recruiting |
| NCT03363217 | I/II | 1 m–25 y | NF-1, Recurrent/refractory LGG |
MAPK/ERK pathway BRAF fusion |
Trametinib | Recruiting |
| NCT04485559 | I | 1–25 y | Recurrent grade 2 glioma |
MAPK/ERK pathway mTOR |
Trametinib Everolimus |
Recruiting |
| NCT03429803 | I | 1–25 y | Recurrent/progressive LGG | BRAF fusion | TAK-580 | Recruiting |
| NCT02285439 | I/II | 1–18 y | NF-1, Recurrent/refractory LGG | MEK | MEK162 | Recruiting |
| NCT03696355 | I | 2–21 y | DIPC or other diffuse midline H3K27M mutant gliomas | PI3K/Akt/mTOR | GDC-0084 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT02650401 | I/II | Up to 18 y | CNS tumor | NTRK or ROS1 fusion | Entrectinib | Recruiting |
| NCT04655404 | I | Up to 21 y | Newly diagnosed HGG | NTRK fusion | Larotrectinib | Not yet recruiting |
| Other targeted therapy | ||||||
| NCT03749187 | I | 13–25 y | Gliomas, IDH1/2 mutant | PARP | BGB-290 + TMZ | Recruiting |
| NCT03416530 | I | 2–18 y | Newly diagnosed DIPG Recurrent/refractory H3K27M gliomas |
DRD2 | ONC201 | Recruiting |
| NCT01922076 | I | 37 m–21 y | Newly diagnosed DIPG | Tyrosine kinase WEE1 | Adavosertib | Active, not recruiting |
MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; y, years; LGG, low-grade glioma; m, months; HGG, high-grade glioma; NF-1, neurofibromatosis type 1; DIPG, diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma; CNS, central nervous system; PARP, poly ADP ribose polymerase; TMZ, temozolomide; DRD2, dopamine receptor type 2.
FGFR kinase inhibitors are currently in clinical development. AZD4547 is an orally bioavailable FGFR1-3 inhibitor [71]. In the NCI-MATCH trial, AZD4547 was administered to patients with tumors harboring FGFR1-3 mutations or fusions. In this phase II trial, the CNS tumor was only one case out of a total of 20, and AZD4547 was not found to meet the primary end point. However, this trial showed modest activity of AZD4547 in patients with FGFR mutations and fusions, suggesting the possibility of clinical use in the future [72].
5. High Grade Gliomas
pHGGs account for 8–12% of pediatric CNS tumors, including anaplastic astrocytoma (WHO grade 3) and GBM (WHO grade 4), both types malignant, diffuse, infiltrating astrocytic tumors [7,77,78]. Current management of pHGG consists of maximal surgical resection followed by radiotherapy with concurrent and adjuvant alkylator therapy. These gliomas have a 3-year PFS of 10% and 3-year OS of 20% [79]. Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG), which is an exceptionally unresectable tumor, has an aggressive clinical course, even when the histological findings demonstrate low-grade [80]. This feature is reflected in the 2016 WHO classification—diffuse midline gliomas with K27M histone mutations, including most DIPGs, are classified as WHO grade 4, regardless of histological findings [7,81].
5.1. Molecular Landscape in pHGG (Table 1)
G34R/V and K27M mutations are well-known mutations in pHGG. In an integrated molecular meta-analysis of pHGG, the distribution of recurrently mutated genes was 47% TP53, 36% H3.3, 24% ATRX, and 7% BRAF V600E [82]. These tumors included presence of mutually exclusive G34 and K27M mutations, and co-occurring mutations of ATRX with G34R of NF1 [83,84].
H3K27M mutation: histone H3 (H3F3A and HIST1H3B) pK27M mutations are frequently observed in DIPGs, which arise in the brainstem almost exclusively in children, and in pHGGs in midline structures such as the thalamus and spinal cord [85,86,87,88,89]. This tumor type was classified as a separate entity, “diffuse midline glioma, H3K27M-mutant” (WHO grade 4), in the 2016 WHO classification [7]. H3K27M mutation results in a global H3K27me3 reduction by multiple mechanisms, such as aberrant polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) interactions and hampered H3K27me3 spreading. It is also thought to suppress neuroglial differentiation through deregulation of epigenetic modifications [90,91,92,93]. Although additional mechanisms have not been revealed to date, the H3K27M mutation is an important key for pHGG treatment.
H3G34R/V mutation: in cIMPACT-NOW update 6, diffuse glioma, H3.3 G34-mutant was reported as a novel tumor type separated from the established gliomas as well as from diffuse midline glioma, H3K27M-mutant. It was also found to correspond with WHO grade 4 [8]. When compared with the K27M mutation, how the G34 mutation affects the epigenome remains unclear. G34R/V in H3F3A, which encodes non-canonical histone H3.3, occurs in pHGGs of the cerebral cortex [85,86,88], whereas the G34W mutation is prevalent in bone tumors [94]. Neumann et al. analyzed data from 77 patients with GBM under the age of 30, and found that the frequency of G34R/V and K27M mutations was 16% and 32%, respectively [95]. Among our 411 consecutive glioma patients, 14 (3.4%) harbored H3F3A mutations, of which 4 had G34R mutations and 10 K27M mutations [96]. We recently reported that G34 mutations exerted characteristic methylomic effects, regardless of the tumor tissue of origin, and this mutation could affect chromosome instability [97]. Although G34R/V mutations are relatively rare in pHGG, this genotype is likely to have specific methylomic signals and show extensive infiltration and various histological phenotypes [96,97].
5.2. Targeted Therapy for pHGG
Clinical trials of targeted therapy for pHGG are summarized in Table 2 and Table 3. H3K27M has been shown to inhibit PRC2, a multiprotein complex responsible for the methylation of H3 at lysin 27, by binding to its catalytic subunit, EZH2 [98]. Mohammad et al. demonstrated that H3K27M mutated tumors require PRC2 for proliferation, and EZH2 inhibitors cease tumor cell growth [99]. EZH2 is a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of H3K27M mutated tumors, and the pediatric MATCH study included this targeted therapy. In Japan, a phase I clinical trial of a dual EZH1/2 inhibitor for pediatric, adolescent, and young adult patients with malignant solid tumors is in progress.
In the treatment of patients with DIPG, the Individualized Therapy For Relapsed Malignancies in Childhood (INFORM) registry study offered comprehensive molecular profiling of high-risk tumors to identify targetable alterations for precision therapy [100]. In this study, tumor material was obtained from brainstem biopsy, and molecular information was used for initiation of targeted therapy in 5 of 21 patients [100]. In addition to the INFORM study, the Pacific Pediatric Neuro-Oncology Consortium (PNOC003) study demonstrated the feasibility of genomic-based precision therapy for DIPG using NGS [101]. This study revealed that the molecular profiling of DIPGs changed the therapy and course of tumor progression [101]. More interventional molecular matching studies for DIPG are expected in the near future.
Some recent clinical trials of targeted therapy for pHGG have failed to prove its efficacy and safety. Sunitinib, a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), and stem cell factor receptor (KIT), had no antitumor activity against HGG and ependymoma [73]. Although the combination of perifosine, an AKT inhibitor, and temsirolimus, an mTOR inhibitor, for CNS tumors, including HGG, was well tolerated, sufficient antitumor activity was not demonstrated [74]. The combination of dasatinib, PDGFR-A inhibitor, crizotinib, and c-Met inhibitor, for recurrent/progressive HGG or DIPG was poorly tolerated and its antitumor activity was minimal [75]. However, as the other targeted therapy for DIPG, phase II studies of ONC201, a dopamine receptor D2 antagonist for patients with newly diagnosed DIPG harboring the H3K27M mutation, demonstrated clinical efficacy [76]. Dopamine receptor D2 is a G protein-coupled receptor that promotes tumor growth [102]. In gliomas harboring the H3K27M mutation, dopamine receptor D2 is overexpressed and dopamine receptor D5 is suppressed, resulting in enhancement of sensitivity to a dopamine receptor D2 antagonist [103].
In addition, immune checkpoint inhibitors have been expected to bring a paradigm shift in treatment for gliomas. These have been shown effective in treatments for other malignancies, such as melanoma [104,105]. However, previous clinical trials failed to prove the outcome impact of immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of adult GBMs [106,107]. On the other hand, microsatellite instability, which is used as a molecular marker for defective DNA mismatch repair genes, is detected more frequently in pediatric gliomas than in adult gliomas [108,109], suggesting that pediatric gliomas have a promising response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
6. Infantile Gliomas
Compared to gliomas in children and adults, infantile gliomas have paradoxical clinical behavior. Whereas HGGs have a better clinical course [82,110], LGGs have a higher mortality rate [111,112,113]. Infantile pediatric gliomas have been reported to be subclassified into the following three molecular groups [114]:
Group 1, hemispheric receptor tyrosine kinase-driven gliomas, including ALK, ROS1, NTRK, and MET fusions, which are enriched for high-grade glioma, and have an intermediate clinical outcome.
Group 2, hemispheric RAS/MAPK-driven gliomas, which demonstrate excellent long-term survival with minimal post-surgery clinical intervention.
Group 3, midline RAS/MAPK-driven gliomas, which are enriched for LGG, such as PA, with BRAF alternations, and have a poor outcome.
Because each subtype indicates the clinical and molecular features, updating the diagnosis and treatment of these gliomas is necessary. Additionally, because these molecular features can be targetable, novel molecular targeted therapies are expected to develop. The involvement of the RAS/MAPK pathway in infantile gliomas has been revealed, and current molecular profiling have identified novel alterations regarding this pathway.
6.1. Fusion Genes in Infantile Gliomas (Table 1)
NTRK fusions: NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3 are actionable drivers of tumor growth [115,116], and these genes encode the tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) family of receptor tyrosine kinases, proteins TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC, respectively. The TRK family plays a role in neuronal development, cell survival, and cellular proliferation [117]. NTRK fusions affect both the RAS/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways, and are considered to be associated with tumorigenesis [118,119]. Wu et al. reported that 40% (4/10) of non-brainstem high-grade gliomas in children under 3 years of age contained NTRK1-3 fusion genes [89]. NTRK1-3 fusion genes have not been identified frequently in pLGG and adult GBM [33,40,120]. However, NTRK fusions can be detected in histologically diagnosed glioneuronal tumors [121], and cancer multi-gene panel tests should be widely and frequently performed.
ALK fusions: the ALK gene is thought to be associated with development and function of the nervous system. ALK fusion is reported to cause ectopic expression of the ALK fusion protein [23,122], resulting in upregulation of the RAS/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways [114]. Although gliomas with ALK fusion are rare and the published literature is limited to several case studies, CCDC88A-ALK and PPP1CB-ALK were reported as the most frequent alterations [114,123,124,125]. In our institution, we encountered a case of HGG that harbored VCL as a novel partner of the ALK fusion gene [126].
ROS1 fusions: ROS1 is an orphan tyrosine receptor, which is considered to be associated with cell proliferation and differentiation. Although ROS1 fusion in glioma is quite rare, several reports have highlighted it as a targetable genetic alteration [127,128,129]. GOPC-ROS1 was reported as the most common ROS1 alteration in glioma. In addition, CEP85L-ROS1, ZCCHC8-ROS1, and KLC1-ROS1 have also been identified [127,128,129]. The targeted agents for lung cancer with ROS1 has shown significant antitumor activity [130,131].
6.2. Treatment for Each Group in Infantile Gliomas
Clinical trials of targeted therapy for infantile glioma are summarized in Table 2 and Table 3. As infantile gliomas are mostly single-driver tumors, they are suitable for precision therapy [114]. The efficacy of some types of targeted kinase inhibitors has already been demonstrated.
Group 1 tumors: group 1 tumors harbored ALK/ROS1/NTRK/MET alterations, and 5-year OS was 53.8, 25.0, and 42.9% for tumors with ALK, ROS1, and NTRK fusions, respectively [114]. Entrectinib, an oral inhibitor of the tyrosine kinases TRKA/B/C, ROS1 and ALK, was evaluated in two phase I studies, and shown to be well tolerated. Only reversible grade 1/2 adverse events and active against gene fusions of NTRK1-3, ROS1, and ALK were found in adult patients with solid tumors, including CNS tumors [132]. Response was observed as early as 4 weeks after administration, and lasted as long as >2 years [132]. A phase I clinical trial, using larotrectinib for newly diagnosed pHGG with NTRK fusion, is planned in the United States. NTRK1-3, ROS1, and ALK fusion genes in infantile glioma are targetable, therefore, nationwide adaptation of NGS to evaluate these fusion genes and more extensive accumulation of clinical data are required.
Group 2 tumors: because group 2 tumors show excellent long-term survival, a safe resection and careful follow-up are recommended [114].
Group 3 tumors: Because most group 3 tumors result in poor outcomes after conventional chemotherapy, targeted therapy, such as BRAF/MEK inhibitors, should be administered as soon after initial diagnosis as possible [114]. In the treatment of these tumors, dabrafenib, a BRAF inhibitor, and selumetinib, an MEK inhibitor, have been reported to be effective and tolerable [68,133,134].
7. Conclusions
Because the molecular characteristics of pediatric gliomas are different from those of adult gliomas, molecular genetic analysis is essential to diagnose and treat pediatric gliomas. Because targetable molecular aberrations can be detected in pediatric gliomas, searching for these aberrations is very important. Moreover, sufficient evidence of the novel targeted therapies has not been demonstrated in the present clinical trials. However, efficient targeted therapies are expected to be feasible even for rare subtypes in CNS tumors because of multi-gene panel analysis using NGS in the near future. Although the era of incorporating molecular genetic analysis into clinical practice is beginning, the search for specific molecular aberrations in pediatric gliomas is insufficient. How to administer molecular genetic analysis in clinical practice may be a future issue.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Aki Sako for her technical assistance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.F. (Yusuke Funakoshi) and N.H.; original draft preparation, Y.F. (Yusuke Funakoshi); review and editing, N.H., D.K., R.H., Y.S., Y.F. (Yutaka Fujioka), and K.T.; supervision, M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (JSPS KAKENHI) Award (Grant No. JP20K09392, JP18K08970, JP19K17673, and JP20K17972).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Ward E., DeSantis C., Robbins A., Kohler B., Jemal A. Childhood and Adolescent Cancer Statistics, 2014. C.A. Cancer J. Clin. 2014;64:83–103. doi: 10.3322/caac.21219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Armstrong G.T., Liu Q., Yasui Y., Huang S., Ness K.K., Leisenring W., Hudson M.M., Donaldson S.S., King A.A., Stovall M., et al. Long-Term Outcomes Among Adult Survivors of Childhood Central Nervous System Malignancies in the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009;101:946–958. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vinchon M., Baroncini M., Leblond P., Delestret I. Morbidity and Tumor-Related Mortality Among Adult Survivors of Pediatric Brain Tumors: A Review. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2011;27:697–704. doi: 10.1007/s00381-010-1385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Glod J., Rahme G.J., Kaur H., Raabe E., Hwang E.I., Israel M.A. Pediatric Brain Tumors: Current Knowledge and Therapeutic Opportunities. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2016;38:249–260. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000000551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lassaletta A., Zapotocky M., Bouffet E., Hawkins C., Tabori U. An Integrative Molecular and Genomic Analysis of Pediatric Hemispheric Low-Grade Gliomas: An Update. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2016;32:1789–1797. doi: 10.1007/s00381-016-3163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Park S.H., Won J., Kim S.I., Lee Y., Park C.K., Kim S.K. Molecular Testing of Brain Tumor. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2017;51:205–223. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2017.03.08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Louis D.N., Perry A., Reifenberger G., von Deimling A., Figarella-Branger D., Cavenee W.K., Ohgaki H., Wiestler O.D., Kleihues P., Ellison D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Louis D.N., Wesseling P., Aldape K., Brat D.J., Capper D., Cree I.A., Eberhart C., Figarella-Branger D., Fouladi M., Fuller G.N., et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 6: New Entity and Diagnostic Principle Recommendations of the cIMPACT-Utrecht Meeting on Future CNS Tumor Classification and Grading. Brain Pathol. 2020;30:844–856. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Louis D.N., Perry A., Burger P., Ellison D.W., Reifenberger G., von Deimling A., Aldape K., Brat D., Collins V.P., Eberhart C., et al. International Society of Neuropathology—Haarlem Consensus Guidelines for Nervous System Tumor Classification and Grading. Brain Pathol. 2014;24:429–435. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Louis D.N., Wesseling P., Brandner S., Brat D.J., Ellison D.W., Giangaspero F., Hattab E.M., Hawkins C., Judge M.J., Kleinschmidt-DeMasters B., et al. Data Sets for the Reporting of Tumors of the Central Nervous System. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019;144:196–206. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2018-0565-OA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Capper D., Jones D.T.W., Sill M., Hovestadt V., Schrimpf D., Sturm D., Koelsche C., Sahm F., Chavez L., Reuss D.E., et al. DNA Methylation-Based Classification of Central Nervous System Tumours. Nature. 2018;255:469–474. doi: 10.1038/nature26000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kumar R., Liu A.P.Y., Orr B.A., Northcott P.A., Robinson G.W. Advances in the Classification of Pediatric Brain Tumors Through DNA Methylation Profiling: From Research Tool to Frontline Diagnostic. Cancer. 2018;124:4168–4180. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mack S.C., Northcott P.A. Genomic Analysis of Childhood Brain Tumors: Methods for Genome-Wide Discovery and Precision Medicine Become Mainstream. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017;35:2346–2354. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.9921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Seibel N.L., Janeway K., Allen C.E., Chi S.N., Cho Y.J., Glade Bender J.L., Kim A., Laetsch T.W., Irwin M.S., Takebe N., et al. Pediatric Oncology Enters an Era of Precision Medicine. Curr. Probl. Cancer. 2017;41:194–200. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2017.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fujioka Y., Hata N., Akagi Y., Kuga D., Hatae R., Sangatsuda Y., Michiwaki Y., Amemiya T., Takigawa K., Funakoshi Y., et al. Molecular diagnosis of diffuse glioma using a chip-based digital PCR system to analyze IDH, TERT, and H3 mutations in the cerebrospinal fluid. J. Neurooncol. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03682-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Miller A.M., Shah R.H., Pentsova E.I., Pourmaleki M., Briggs S., Distefano N., Zheng Y., Skakodub A., Mehta S.A., Campos C., et al. Tracking tumour evolution in glioma through liquid biopsies of cerebrospinal fluid. Nature. 2019;565:654–658. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0882-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kohsaka S., Tatsuno K., Ueno T., Nagano M., Shinozaki-Ushiku A., Ushiku T., Takai D., Ikegami M., Kobayashi H., Kage H., et al. Comprehensive Assay for the Molecular Profiling of Cancer by Target Enrichment from Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Specimens. Cancer Sci. 2019;110:1464–1479. doi: 10.1111/cas.13968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.About Us—Accelerate Platform. [(accessed on 5 February 2021)]; Available online: https://www.accelerate-platform.org/about-us/
- 19.Ostrom Q.T., Gittleman H., Farah P., Ondracek A., Chen Y., Wolinsky Y. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010. Neuro Oncol. 2013;15(Suppl. 2):ii1–ii56. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sturm D., Pfister S.M., Jones D.T.W. Pediatric Gliomas: Current Concepts on Diagnosis, Biology, and Clinical Management. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017;35:2370–2377. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.0242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ostrom Q.T., De Blank P.M., Kruchko C., Petersen C.M., Liao P., Finlay J.L., Stearns D.S., Wolff J.E., Wolinsky Y., Letterio J.J., et al. Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation Infant and Childhood Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2007–2011. Neuro. Oncol. 2015;16(Suppl. 10):x1–x36. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ostrom Q.T., Gittleman H., Truitt G., Boscia A., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro. Oncol. 2018;20(Suppl. 4):iv1–iv86. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noy131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ryall S., Tabori U., Hawkins C. Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma in the Era of Molecular Diagnostics. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020;8:30. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-00902-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wisoff J.H., Sanford R.A., Heier L.A., Sposto R., Burger P.C., Yates A.J., Holmes E.J., Kun L.E. Primary Neurosurgery for Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas: A Prospective Multi-Institutional Study from the Children’s Oncology Group. Neurosurgery. 2011;68:1548–1555. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e318214a66e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Armstrong G.T., Conklin H.M., Huang S., Srivastava D., Sanford R., Ellison D.W., Merchant T.E., Hudson M.M., Hoehn M.E., Robison L.L. Survival and Long-Term Health and Cognitive Outcomes After Low-Grade Glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2011;13:223–234. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noq178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Erkal H.S., Serin M., Çakmak A. Management of Optic Pathway and Chiasmatic-Hypothalamic Gliomas in Children with Radiation Therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 1997;45:11–15. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8140(97)00102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Merchant T.E., Conklin H.M., Wu S., Lustig R.H., Xiong X. Late Effects of Conformal Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Patients with Low-Grade Glioma: Prospective Evaluation of Cognitive, Endocrine, and Hearing Deficits. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009;27:3691–3697. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Krishnatry R., Zhukova N., Guerreiro Stucklin A.S., Pole J.D., Mistry M., Fried I., Ramaswamy V., Bartels U., Huang A., Laperriere N., et al. Clinical and Treatment Factors Determining Long-Term Outcomes for Adult Survivors of Childhood Low-Grade Glioma: A Population-Based Study. Cancer. 2016;122:1261–1269. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ostrom Q.T., Gittleman H., Xu J., Kromer C., Wolinsky Y., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro. Oncol. 2016;18(Suppl. 5):v1–v75. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Collins V.P., Jones D.T.W., Giannini C. Pilocytic Astrocytoma: Pathology, Molecular Mechanisms and Markers. Acta Neuropathol. 2015;129:775–788. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1410-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jones D.T.W., Gronych J., Lichter P., Witt O., Pfister S.M. MAPK Pathway Activation in Pilocytic Astrocytoma. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012;69:1799–1811. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0898-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Northcott P.A., Pfister S.M., Jones D.T.W. Next-Generation (Epi)Genetic Drivers of Childhood Brain Tumours and the Outlook for Targeted Therapies. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:e293–e302. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang J., Wu G., Miller C.P., Tatevossian R.G., Dalton J.D., Tang B., Orisme W., Punchihewa C., Parker M., Qaddoumi I., et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies Genetic Alterations in Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas. Nat. Genet. 2013;45:602–612. doi: 10.1038/ng.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lassaletta A., Zapotocky M., Mistry M., Ramaswamy V., Honnorat M., Krishnatry R., Guerreiro Stucklin A., Zhukova N., Arnoldo A., Ryall S., et al. Therapeutic and Prognostic Implications of BRAF V600E in Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017;35:2934–2941. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.71.8726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hatae R., Hata N., Suzuki S.O., Yoshimoto K., Kuga D., Murata H., Akagi Y., Sangatsuda Y., Iwaki T., Mizoguchi M., et al. A Comprehensive Analysis Identifies BRAF Hotspot Mutations Associated with Gliomas with Peculiar Epithelial Morphology. Neuropathology. 2017;37:191–199. doi: 10.1111/neup.12347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Goetz R., Mohammadi M. Exploring Mechanisms of FGF Signalling Through the Lens of Structural Biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013;14:166–180. doi: 10.1038/nrm3528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dai S., Zhou Z., Chen Z., Xu G., Chen Y. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs): Structures and Small Molecule Inhibitors. Cells. 2019;8:614. doi: 10.3390/cells8060614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lehtinen B., Raita A., Kesseli J., Annala M., Nordfors K., Yli-Harja O., Zhang W., Visakorpi T., Nykter M., Haapasalo H., et al. Clinical Association Analysis of Ependymomas and Pilocytic Astrocytomas Reveals Elevated FGFR3 and FGFR1 Expression in Aggressive Ependymomas. BMC Cancer. 2017;17:310. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3274-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Holzhauser S., Lukoseviciute M., Andonova T., Ursu R.G., Dalianis T., Wickström M., Kostopoulou O.N. Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR) and Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K) Signaling Pathways in Medulloblastoma Cell Lines. Anticancer Res. 2020;40:53–66. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jones D.T.W., Hutter B., Jäger N., Korshunov A., Kool M., Warnatz H.J., Zichner T., Lambert S.R., Ryzhova M., Quang D.A.K., et al. Recurrent Somatic Alterations of FGFR1 and NTRK2 in Pilocytic Astrocytoma. Nat. Genet. 2013;45:927–932. doi: 10.1038/ng.2682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Qaddoumi I., Orisme W., Wen J., Santiago T., Gupta K., Dalton J.D., Tang B., Haupfear K., Punchihewa C., Easton J., et al. Genetic Alterations in Uncommon Low-Grade Neuroepithelial Tumors: BRAF, FGFR1, and MYB Mutations Occur at High Frequency and Align with Morphology. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:833–845. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1539-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Friedman J.M. Epidemiology of Neurofibromatosis type 1. Am. J. Med. Genet. Semin. Med. Genet. 1999;89:1–6. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19990326)89:1<1::AID-AJMG3>3.0.CO;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rasmussen S.A., Friedman J.M. NF1 Gene and Neurofibromatosis 1. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000;151:33–40. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a010118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Blanchard G., Lafforgue M.P., Lion-François L., Kemlin I., Rodriguez D., Castelnau P., Meyer P., Rivier F., Barbarot S., Chaix Y., et al. Systematic MRI in NF1 Children Under Six Years of Age for the Diagnosis of Optic Pathway Gliomas. Study and Outcome of a French Cohort. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016;20:275–281. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2015.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Uusitalo E., Rantanen M., Kallionpää R.A., Pöyhönen M., Leppävirta J., Ylä-Outinen H., Riccardi V.M., Pukkala E., Pitkäniemi J., Peltonen S., et al. Distinctive Cancer Associations in Patients with Neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016;34:1978–1986. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.3576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fisher M.J., Loguidice M., Gutmann D.H., Listernick R., Ferner R.E., Ullrich N.J., Packer R.J., Tabori U., Hoffman R.O., Ardern-Holmes S.L., et al. Visual Outcomes in Children with Neurofibromatosis type 1-Associated Optic Pathway Glioma Following Chemotherapy: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis. Neuro. Oncol. 2012;14:790–797. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pattabiraman D.R., Gonda T.J. Role and Potential for Therapeutic Targeting of MYB in Leukemia. Leukemia. 2013;27:269–277. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhou Y., Ness S.A. Myb Proteins: Angels and Demons in Normal and Transformed Cells. Front. Biosci. 2011;16:1109–1131. doi: 10.2741/3738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bandopadhayay P., Ramkissoon L.A., Jain P., Bergthold G., Wala J., Zeid R., Schumacher S.E., Urbanski L., O’Rourke R., Gibson W.J., et al. MYB-QKI Rearrangements in Angiocentric Glioma Drive Tumorigenicity Through a Tripartite Mechanism. Nat. Genet. 2016;48:273–282. doi: 10.1038/ng.3500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ramkissoon L.A., Horowitz P.M., Craig J.M., Ramkissoon S.H., Rich B.E., Schumacher S.E., McKenna A., Lawrence M.S., Bergthold G., Brastianos P.K., et al. Genomic Analysis of Diffuse Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas Identifies Recurrent Oncogenic Truncating Rearrangements in the Transcription Factor MYBL1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:8188–8193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300252110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chiang J., Harreld J.H., Tinkle C.L., Moreira D.C., Li X., Acharya S., Qaddoumi I., Ellison D.W. A Single-Center Study of the Clinicopathologic Correlates of Gliomas with a MYB or MYBL1 Alteration. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;138:1091–1092. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-02081-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Appay R., Dehais C., Maurage C.A., Alentorn A., Carpentier C., Colin C., Ducray F., Escande F., Idbaih A., Kamoun A., et al. CDKN2A Homozygous Deletion Is a Strong Adverse Prognosis Factor in Diffuse Malignant IDH-Mutant Gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2019;21:1519–1528. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noz126.000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Reis G.F., Pekmezci M., Hansen H.M., Rice T., Marshall R.E., Molinaro A.M., Phillips J.J., Vogel H., Wiencke J.K., Wrensch M.R., et al. CDKN2A Loss Is Associated with Shortened Overall Survival in Lower-Grade (World Health Organization Grades II–III) Astrocytomas. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015;74:442–452. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Brat D.J., Aldape K., Colman H., Figrarella-Branger D., Fuller G.N., Giannini C., Holland E.C., Jenkins R.B., Kleinschmidt-DeMasters B., Komori T., et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 5: Recommended Grading Criteria and Terminologies for IDH-Mutant Astrocytomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;139:603–608. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02127-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ma S., Rudra S., Campian J.L., Dahiya S., Dunn G.P., Johanns T., Goldstein M., Kim A.H., Huang J. Prognostic Impact of CDKN2A/B Deletion, Tert Mutation, and EGFR Amplification on Histological and Molecular IDH-Wildtype Glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol. Adv. 2020;2:vdaa126. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdaa126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mistry M., Zhukova N., Merico D., Rakopoulos P., Krishnatry R., Shago M., Stavropoulos J., Alon N., Pole J.D., Ray P.N., et al. BRAF Mutation and CDKN2A Deletion Define a Clinically Distinct Subgroup of Childhood Secondary High-Grade Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:1015–1022. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.3922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ellison D.W., Hawkins C., Jones D.T.W., Onar-Thomas A., Pfister S.M., Reifenberger G., Louis D.N. cIMPACT-NOW update 4: Diffuse Gliomas Characterized by MYB, MYBL1, or FGFR1 Alterations or BRAF V600E Mutation. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;137:683–687. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-01987-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hofer S., Berthod G., Riklin C., Rushing E., Feilchenfeldt J. BRAF V600E Mutation: A Treatable Driver Mutation in Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) Acta Oncol. 2016;55:122–123. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2015.1021428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lee E.Q., Ruland S., Leboeuf N.R., Wen P.Y., Santagata S. Successful Treatment of a Progressive BRAF V600E-Mutated Anaplastic Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma with Vemurafenib Monotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016;34:e87–e89. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.51.1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Usubalieva A., Pierson C.R., Kavran C.A., Huntoon K., Kryvenko O.N., Mayer T.G., Zhao W., Rock J., Ammirati M., Puduvalli V.K., et al. Primary Meningeal Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma with Anaplastic Features: A Report of 2 Cases, One with BRAFV600E Mutation and Clinical Response to the BRAF Inhibitor Dabrafenib. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015;74:960–969. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Brown N.F., Carter T., Kitchen N., Mulholland P. Dabrafenib and Trametinib in BRAFV600E Mutated Glioma. CNS Oncol. 2017;6:291–296. doi: 10.2217/cns-2017-0006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hargrave D.R., Bouffet E., Tabori U., Broniscer A., Cohen K.J., Hansford J.R., Geoerger B., Hingorani P., Dunkel I.J., Russo M.W., et al. Efficacy and Safety of Dabrafenib in Pediatric Patients with BRAF V600 Mutation–Positive Relapsed or Refractory Low-Grade Glioma: Results from a phase I/IIa Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019;25:7303–7311. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Solit D.B., Rosen N. Resistance to BRAF Inhibition in Melanomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;364:772–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcibr1013704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Robert C., Karaszewska B., Schachter J., Rutkowski P., Mackiewicz A., Stroiakovski D., Lichinitser M., Dummer R., Grange F., Mortier L., et al. Improved Overall Survival in Melanoma with Combined Dabrafenib and Trametinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015;72:30–39. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1412690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Long G.V., Stroyakovskiy D., Gogas H., Levchenko E., De Braud F., Larkin J., Garbe C., Jouary T., Hauschild A., Grob J.J., et al. Dabrafenib and Trametinib Versus Dabrafenib and Placebo for Val600 BRAF-Mutant Melanoma: A Multicentre, Double-Blind, phase 3 Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet. 2015;386:444–451. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60898-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Brastianos P.K., Shankar G.M., Gill C.M., Taylor-Weiner A., Nayyar N., Panka D.J., Sullivan R.J., Frederick D.T., Abedalthagafi M., Jones P.S., et al. Dramatic Response of BRAF V600E Mutant Papillary Craniopharyngioma to Targeted Therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016;108:djv310. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Migliorini D., Aguiar D., Vargas M.I., Lobrinus A., Dietrich P.Y. BRAF/MEK Double Blockade in Refractory Anaplastic Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma. Neurology. 2017;88:1291–1293. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Fangusaro J., Onar-Thomas A., Young Poussaint T., Wu S., Ligon A.H., Lindeman N., Banerjee A., Packer R.J., Kilburn L.B., Goldman S., et al. Selumetinib in Paediatric Patients with BRAF-Aberrant or Neurofibromatosis type 1-Associated Recurrent, Refractory, or Progressive Low-Grade Glioma: A Multicentre, phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:1011–1022. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30277-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wang H., Long-Boyle J., Winger B.A., Nicolaides T., Mueller S., Prados M., Ivaturi V. Population Pharmacokinetics of Vemurafenib in Children with Recurrent/Refractory BRAF Gene V600E-Mutant Astrocytomas. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020;60:1209–1219. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Nicolaides T., Nazemi K.J., Crawford J., Kilburn L., Minturn J., Gajjar A., Gauvain K., Leary S., Dhall G., Aboian M., et al. Phase I Study of Vemurafenib in Children with Recurrent or Progressive BRAFV600E Mutant Brain Tumors: Pacific Pediatric Neuro-Oncology Consortium Study (PNOC-002) Oncotarget. 2020;11:1942–1952. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Gavine P.R., Mooney L., Kilgour E., Thomas A.P., Al-Kadhimi K., Beck S., Rooney C., Coleman T., Baker D., Mellor M.J., et al. AZD4547: An Orally Bioavailable, Potent, and Selective Inhibitor of the Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Family. Cancer Res. 2012;72:2045–2056. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Chae Y.K., Hong F., Vaklavas C., Cheng H.H., Hammerman P., Mitchell E.P., Zwiebel J.A., Ivy S.P., Gray R.J., Li S., et al. Phase II Study of AZD4547 in Patients with Tumors Harboring Aberrations in the FGFR Pathway: Results from the NCI-MATCH Trial (EAY131) Subprotocol W. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020;38:2407–2417. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wetmore C., Daryani V.M., Billups C.A., Boyett J.M., Leary S., Tanos R., Goldsmith K.C., Stewart C.F., Blaney S.M., Gajjar A. Phase II Evaluation of Sunitinib in the Treatment of Recurrent or Refractory High-Grade Glioma or Ependymoma in Children: A Children’s Oncology Group Study ACNS1021. Cancer Med. 2016;5:1416–1424. doi: 10.1002/cam4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Becher O.J., Gilheeney S.W., Khakoo Y., Lyden D.C., Haque S., De Braganca K.C., Kolesar J.M., Huse J.T., Modak S., Wexler L.H., et al. A Phase I Study of Perifosine with Temsirolimus for Recurrent Pediatric Solid Tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2017;64 doi: 10.1002/pbc.26409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Broniscer A., Jia S., Mandrell B., Hamideh D., Huang J., Onar-Thomas A., Gajjar A., Raimondi S.C., Tatevossian R.G., Stewart C.F. Phase 1 Trial, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of Dasatinib Combined with Crizotinib in Children with Recurrent or Progressive High-Grade and Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2018;65:e27035. doi: 10.1002/pbc.27035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Chi A.S., Tarapore R.S., Hall M.D., Shonka N., Gardner S., Umemura Y., Sumrall A., Khatib Z., Mueller S., Kline C., et al. Pediatric and Adult H3 K27M-Mutant Diffuse Midline Glioma Treated with the Selective DRD2 Antagonist ONC201. J. Neuro Oncol. 2019;145:97–105. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03271-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bondy M.L., Scheurer M.E., Malmer B., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S., Davis F.G., Il’yasova D., Kruchko C., McCarthy B.J., Rajaraman P., Schwartzbaum J.A., et al. Brain Tumor Epidemiology: Consensus from the Brain Tumor Epidemiology Consortium. Cancer. 2008;113:1953–1968. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.McCrea H.J., Bander E.D., Venn R.A., Reiner A.S., Iorgulescu J.B., Puchi L.A., Schaefer P.M., Cederquist G., Greenfield J.P. Sex, Age, Anatomic Location, and Extent of Resection Influence Outcomes in Children with High-Grade Glioma. Neurosurgery. 2015;77:443–453. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Cohen K.J., Pollack I.F., Zhou T., Buxton A., Holmes E.J., Burger P.C., Brat D.J., Rosenblum M.K., Hamilton R.L., Lavey R.S., et al. Temozolomide in the Treatment of High-Grade Gliomas in Children: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Neuro Oncol. 2011;13:317–323. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noq191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Buczkowicz P., Bartels U., Bouffet E., Becher O., Hawkins C. Histopathological Spectrum of Paediatric Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;128:573–581. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1319-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Okuda T., Hata N., Suzuki S.O., Yoshimoto K., Arimura K., Amemiya T., Akagi Y., Kuga D., Oba U., Koga Y., et al. Pediatric Ganglioglioma with an H3 K27M Mutation Arising from the Cervical Spinal Cord. Neuropathology. 2018 doi: 10.1111/neup.12471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Mackay A., Burford A., Carvalho D., Izquierdo E., Fazal-Salom J., Taylor K.R., Bjerke L., Clarke M., Vinci M., Nandhabalan M., et al. Integrated Molecular Meta-Analysis of 1,000 Pediatric High-Grade and Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:520–537.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.08.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.D’Angelo F., Ceccarelli M., Tala , Garofano L., Zhang J., Frattini V., Caruso F.P., Lewis G., Alfaro K.D., Bauchet L., et al. The molecular landscape of glioma in patients with Neurofibromatosis 1. Nat. Med. 2019;25:176–187. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0263-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Korshunov A., Capper D., Reuss D., Schrimpf D., Ryzhova M., Hovestadt V., Sturm D., Meyer J., Jones C., Zheludkova O., et al. Histologically Distinct Neuroepithelial Tumors with Histone 3 G34 Mutation Are Molecularly Similar and Comprise a Single Nosologic Entity. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:137–146. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1493-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Schwartzentruber J., Korshunov A., Liu X.Y., Jones D.T.W., Pfaff E., Jacob K., Sturm D., Fontebasso A.M., Quang D.A., Tönjes M., et al. Driver Mutations in Histone H3.3 and Chromatin Remodelling Genes in Paediatric Glioblastoma. Nature. 2012;482:226–231. doi: 10.1038/nature10833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Wu G., Broniscer A., McEachron T.A., Lu C., Paugh B.S., Becksfort J., Qu C., Ding L., Huether R., Parker M., et al. Somatic Histone H3 Alterations in Pediatric Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Gliomas and Non-Brainstem Glioblastomas. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:251–253. doi: 10.1038/ng.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Khuong-Quang D.A., Buczkowicz P., Rakopoulos P., Liu X.Y., Fontebasso A.M., Bouffet E., Bartels U., Albrecht S., Schwartzentruber J., Letourneau L., et al. K27M Mutation in Histone H3.3 Defines Clinically and Biologically Distinct Subgroups of Pediatric Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;124:439–447. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-0998-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Sturm D., Witt H., Hovestadt V., Khuong-Quang D.A., Jones D.W., Konermann C., Pfaff E., Tönjes M., Sill M., Bender S., et al. Hotspot Mutations in H3F3A and IDH1 Define Distinct Epigenetic and Biological Subgroups of Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:425–437. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.08.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Wu G., Diaz A.K., Paugh B.S., Rankin S.L., Ju B., Li Y., Zhu X., Qu C., Chen X., Zhang J., et al. The Genomic Landscape of Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma and Pediatric Non-Brainstem High-Grade Glioma. Nat. Genet. 2014;46:444–450. doi: 10.1038/ng.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Bender S., Tang Y., Lindroth A.M., Hovestadt V., Jones D.W., Kool M., Zapatka M., Northcott P., Sturm D., Wang W., et al. Reduced H3K27me3 and DNA Hypomethylation Are Major Drivers of Gene Expression in K27M Mutant Pediatric High-Grade Gliomas. Cancer Cell. 2013;24:660–672. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Chan K.M., Fang D., Gan H., Hashizume R., Yu C., Schroeder M., Gupta N., Mueller S., James C.D., Jenkins R., et al. The Histone H3.3K27M Mutation in Pediatric Glioma Reprograms H3K27 Methylation and Gene Expression. Genes Dev. 2013;27:985–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.217778.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Stafford J.M., Lee C.H., Voigt P., Descostes N., Saldaña-Meyer R., Yu J.R., Leroy G., Oksuz O., Chapman J.R., Suarez F., et al. Multiple Modes of PRC2 Inhibition Elicit Global Chromatin Alterations in H3K27M Pediatric Glioma. Sci. Adv. 2018;4:eaau5935. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau5935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Chung C., Sweha S.R., Pratt D., Tamrazi B., Panwalkar P., Banda A., Bayliss J., Hawes D., Yang F., Lee H.J., et al. Integrated Metabolic and Epigenomic Reprogramming by H3K27M Mutations in Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Gliomas. Cancer Cell. 2020;38:334–349.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Amary F., Berisha F., Ye H., Gupta M., Gutteridge A., Baumhoer D., Gibbons R., Tirabosco R., O’Donnell P., Flanagan A. H3F3A (Histone 3.3) G34W Immunohistochemistry: A Reliable Marker Defining Benign and Malignant Giant Cell Tumor of Bone. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017;41:1059–1068. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Neumann J.E., Dorostkar M.M., Korshunov A., Mawrin C., Koch A., Giese A., Schüller U. Distinct Histomorphology in Molecular Subgroups of Glioblastomas in Young Patients. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016;75:408–414. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlw015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Yoshimoto K., Hatae R., Sangatsuda Y., Suzuki S.O., Hata N., Akagi Y., Kuga D., Hideki M., Yamashita K., Togao O., et al. Prevalence and Clinicopathological Features of H3.3 G34-Mutant High-Grade Gliomas: A Retrospective Study of 411 Consecutive Glioma Cases in a Single Institution. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2017;34:103–112. doi: 10.1007/s10014-017-0287-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Sangatsuda Y., Miura F., Araki H., Mizoguchi M., Hata N., Kuga D., Hatae R., Akagi Y., Amemiya T., Fujioka Y., et al. Base-Resolution Methylomes of Gliomas Bearing Histone H3.3 Mutations Reveal a G34 Mutant-Specific Signature Shared with Bone Tumors. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:16162. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73116-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Lewis P.W., Müller M.M., Koletsky M.S., Cordero F., Lin S., Banaszynski L.A., Garcia B.A., Muir T.W., Becher O.J., Allis C.D. Inhibition of PRC2 Activity by a Gain-of-Function H3 Mutation Found in Pediatric Glioblastoma. Science. 2013;340:857–861. doi: 10.1126/science.1232245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Mohammad F., Weissmann S., Leblanc B., Pandey D.P., Højfeldt J.W., Comet I., Zheng C., Johansen J.V., Rapin N., Porse B.T., et al. EZH2 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target for H3K27M-Mutant Pediatric Gliomas. Nat. Med. 2017;23:483–492. doi: 10.1038/nm.4293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Pfaff E., El Damaty A., Balasubramanian G.P., Blattner-Johnson M., Worst B.C., Stark S., Witt H., Pajtler K.W., van Tilburg C.M., Witt R., et al. Brainstem Biopsy in Pediatric Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma in the Era of Precision Medicine: The INFORM Study Experience. Eur. J. Cancer. 2019;114:27–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.03.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Mueller S., Jain P., Liang W.S., Kilburn L., Kline C., Gupta N., Panditharatna E., Magge S.N., Zhang B., Zhu Y., et al. A Pilot Precision Medicine Trial for Children with Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma—PNOC003: A Report from the Pacific Pediatric Neuro-Oncology Consortium. Int. J. Cancer. 2019;145:1889–1901. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Li J., Zhu S., Kozono D., Ng K., Futalan D., Shen Y., Akers J.C., Steed T., Kushwaha D., Schlabach M., et al. Genome-Wide shRNA Screen Revealed Integrated Mitogenic Signaling Between Dopamine Receptor D2 (DRD2) and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) in Glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5:882–893. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Hall M.D., Odia Y., Allen J.E., Tarapore R., Khatib Z., Niazi T.N., Daghistani D., Schalop L., Chi A.S., Oster W., et al. First Clinical Experience with DRD2/3 Antagonist ONC201 in H3 K27M–Mutant Pediatric Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma: A Case Report. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019 doi: 10.3171/2019.2.PEDS18480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Robert C., Ribas A., Schachter J., Arance A., Grob J.J., Mortier L., Daud A., Carlino M.S., McNeil C.M., Lotem M., et al. Pembrolizumab Versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma (KEYNOTE-006): Post-hoc 5-Year Results from an Open-Label, Multicentre, Randomised, Controlled, phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:1239–1251. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30388-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Wolchok J.D., Chiarion-Sileni V., Gonzalez R., Rutkowski P., Grob J.-J., Cowey C.L., Lao C.D., Wagstaff J., Schadendorf D., Ferrucci P.F., et al. Overall Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;377:1345–1356. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Omuro A., Vlahovic G., Lim M., Sahebjam S., Baehring J., Cloughesy T., Voloschin A., Ramkissoon S.H., Ligon K.L., Latek R., et al. Nivolumab with or Without Ipilimumab in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma: Results from Exploratory Phase i Cohorts of CheckMate. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20:674–686. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Filley A.C., Henriquez M., Dey M. Recurrent Glioma Clinical Trial, CheckMate-143: The Game Is Not Over Yet. Oncotarget. 2017;8:91779–91794. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Mizoguchi M., Hata N., Suzuki S.O., Fujioka Y., Murata H., Amano T., Nakamizo A., Yoshimoto K., Iwaki T., Sasaki T. Pediatric Glioblastoma with Oligodendroglioma Component: Aggressive Clinical Phenotype with Distinct Molecular Characteristics. Neuropathology. 2013;33:652–657. doi: 10.1111/neup.12029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Szybka M., Bartkowiak J., Zakrzewski K., Polis L., Liberski P.P., Kordek R. Microsatellite Instability and Expression of DNA Mismatch Repair Genes in Malignant Astrocytic Tumors from Adult and Pediatric Patients. Clin. Neuropathol. 2003;22:180–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Duffner P.K., Krischer J.P., Burger P.C., Cohen M.E., Backstrom J.W., Horowitz M.E., Sanford R., Friedman H., Kun L. Treatment of Infants with Malignant Gliomas: The Pediatric Oncology Group Experience. J. Neurooncol. 1996;28:245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00250203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Ater J.L., Zhou T., Holmes E., Mazewski C.M., Booth T.N., Freyer D.R., Lazarus K.H., Packer R.J., Prados M., Sposto R., et al. Randomized Study of Two Chemotherapy Regimens for Treatment of Low-Grade Glioma in Young Children: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:2641–2647. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.6054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Mirow C., Pietsch T., Berkefeld S., Kwiecien R., Warmuth-Metz M., Falkenstein F., Diehl B., von Hornstein S., Gnekow A.K. Children <1 year show an inferior outcome when treated according to the traditional LGG treatment strategy: A report from the german multicenter trial HIT-LGG 1996–2003 for children with low grade glioma (LGG) Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2014;61:457–463. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Gnekow A.K., Walker D.A., Kandels D., Picton S., Perilongo G., Grill J., Stokland T., Sandstrom P.E., Warmuth-Metz M., Pietsch T., et al. A European Randomised Controlled Trial of the Addition of Etoposide to Standard Vincristine and Carboplatin Induction as Part of an 18-Month Treatment Programme for Childhood (≤16 Years) Low Grade Glioma—A Final Report. Eur. J. Cancer. 2017;81:206–225. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.04.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Guerreiro Stucklin A.S., Ryall S., Fukuoka K., Zapotocky M., Lassaletta A., Li C., Bridge T., Kim B., Arnoldo A., Kowalski P.E., et al. Alterations in ALK/ROS1/NTRK/MET Drive a Group of Infantile Hemispheric Gliomas. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:4343. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12187-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Vaishnavi A., Le A.T., Doebele R.C. TRKing down an Old Oncogene in a New Era of Targeted Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:25–34. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Amatu A., Sartore-Bianchi A., Siena S. NTRK Gene Fusions as Novel Targets of Cancer Therapy Across Multiple Tumour Types. ESMO Open. 2016;1:e000023. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2015-000023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Chao M.V. Neurotrophins and Their Receptors: A Convergence Point for Many Signalling Pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003;4:299–309. doi: 10.1038/nrn1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Khotskaya Y.B., Holla V.R., Farago A.F., Mills Shaw K.R., Meric-Bernstam F., Hong D.S. Targeting TRK Family Proteins in Cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017;173:58–66. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Nguyen N., Lee S.B., Lee Y.S., Lee K.H., Ahn J.Y. Neuroprotection by NGF and BDNF Against Neurotoxin-Exerted Apoptotic Death in Neural Stem Cells Are Mediated Through TRK Receptors, Activating PI3-Kinase and MAPK Pathways. Neurochem. Res. 2009;34:942–951. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9848-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Frattini V., Trifonov V., Chan J.M., Castano A., Lia M., Abate F., Keir S.T., Ji A.X., Zoppoli P., Niola F., et al. The Integrated Landscape of Driver Genomic Alterations in Glioblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2013;45:1141–1149. doi: 10.1038/ng.2734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Kurozumi K., Nakano Y., Ishida J., Tanaka T., Doi M., Hirato J., Yoshida A., Washio K., Shimada A., Kohno T., et al. High-Grade Glioneuronal Tumor with an ARHGEF2-NTRK1 Fusion Gene. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2019;36:121–128. doi: 10.1007/s10014-019-00345-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Armstrong F., Duplantier M.M., Trempat P., Hieblot C., Lamant L., Espinos E., Racaud-Sultan C., Allouche M., Campo E., Delsol G., et al. Differential Effects of X-ALK Fusion Proteins on Proliferation, Transformation, and Invasion Properties of NIH3T3 Cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:6071–6082. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Aghajan Y., Levy M.L., Malicki D.M., Crawford J.R. Novel PPP1CB-ALK Fusion Protein in a High-Grade Glioma of Infancy. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016 doi: 10.1136/bcr-2016-217189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Ng A., Levy M.L., Malicki D.M., Crawford J.R. Unusual High-Grade and Low-Grade Glioma in an Infant with PPP1CB-ALK Gene Fusion. BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12 doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-228248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Olsen T.K., Panagopoulos I., Meling T.R., Micci F., Gorunova L., Thorsen J., Due-Tønnessen B., Scheie D., Lund-Iversen M., Krossnes B., et al. Fusion Genes with ALK as Recurrent Partner in Ependymoma-Like Gliomas: A New Brain Tumor Entity? Neuro. Oncol. 2015;17:1365–1373. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Yamamoto S., Koga Y., Ono H., Asai H., Ono K., Hatae R., Hata N., Mizoguchi M., Yamamoto H., Suzuki O.S., et al. High-grade glioma with a novel fusion gene of VCL-ALK. Neuro. Oncol. 2020;22:iii348. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa222.309. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Coccé M.C., Mardin B.R., Bens S., Stütz A.M., Lubieniecki F., Vater I., Korbel J.O., Siebert R., Alonso C.N., Gallego M.S. Identification of ZCCHC8 as Fusion Partner of ROS1 in a Case of Congenital Glioblastoma multiforme with a t(6;12) (q21;q24.3) Genes Chromosom. Cancer. 2016;55:677–687. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Davare M.A., Henderson J.J., Agarwal A., Wagner J.P., Iyer S.R., Shah N., Woltjer R., Somwar R., Gilheeney S.W., DeCarvalo A., et al. Rare but Recurrent ROS1 Fusions Resulting from chromosome 6q22 Microdeletions Are Targetable Oncogenes in Glioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018;24:6471–6482. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Nakano Y., Tomiyama A., Kohno T., Yoshida A., Yamasaki K., Ozawa T., Fukuoka K., Fukushima H., Inoue T., Hara J., et al. Identification of a Novel KLC1-ROS1 Fusion in a Case of Pediatric Low-Grade Localized Glioma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2019;36:14–19. doi: 10.1007/s10014-018-0330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Drilon A., Somwar R., Wagner J.P., Vellore N.A., Eide C.A., Zabriskie M.S., Arcila M.E., Hechtman J.F., Wang L., Smith R.S., et al. A Novel Crizotinib-Resistant Solvent-Front Mutation Responsive to Cabozantinib Therapy in a Patient with ROS1-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;22:2351–2358. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Shaw A.T., Ou S.-H.I., Bang Y.-J., Camidge D.R., Solomon B.J., Salgia R., Riely G.J., Varella-Garcia M., Shapiro G.I., Costa D., et al. Crizotinib in ROS1-Rearranged Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;371:1963–1971. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1406766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Drilon A., Siena S., Ou S.H.I., Patel M., Ahn M.J., Lee J., Bauer T.M., Farago A.F., Wheler J.J., Liu S.V., et al. Safety and Antitumor Activity of the Multitargeted Pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK Inhibitor Entrectinib: Combined Results from Two Phase I Trials (ALKA-372-001 and STARTRK-1) Cancer Discov. 2017;7:400–409. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Lassaletta A., Guerreiro Stucklin A., Ramaswamy V., Zapotocky M., McKeown T., Hawkins C., Bouffet E., Tabori U. Profound Clinical and Radiological Response to BRAF Inhibition in a 2-Month-Old Diencephalic Child with Hypothalamic/Chiasmatic Glioma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2016;63:2038–2041. doi: 10.1002/pbc.26086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Banerjee A., Jakacki R.I., Onar-Thomas A., Wu S., Nicolaides T., Young Poussaint T., Fangusaro J., Phillips J., Perry A., Turner D., et al. A phase i Trial of the MEK Inhibitor Selumetinib (AZD6244) in Pediatric Patients with Recurrent or Refractory Low-Grade Glioma: A Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium (PBTC) Study. Neuro. Oncol. 2017;19:1135–1144. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.