Key Points
Extended drug response assays are crucial for in vitro identification of treatments that selectively eradicate the cancer cells.
JAK inhibition in combination with selected inhibitors can effectively target aggressive NK-cell malignancies in a stratified manner.
Abstract
Mature natural killer (NK) cell neoplasms are rare but very aggressive types of cancers. With currently available treatments, they have a very poor prognosis and, as such, are an example of group of cancers in which the development of effective precision therapies is needed. Using both short- and long-term drug sensitivity testing, we explored novel ways to target NK-cell neoplasms by combining the clinically approved JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib with other targeted agents. We profiled 7 malignant NK-cell lines in drug sensitivity screens and identified that these exhibit differential drug sensitivities based on their genetic background. In short-term assays, various classes of drugs combined with ruxolitinib seemed highly potent. Strikingly, resistance to most of these combinations emerged rapidly when explored in long-term assays. However, 4 combinations were identified that selectively eradicated the cancer cells and did not allow for development of resistance: ruxolitinib combined with the mouse double-minute 2 homolog (MDM2) inhibitor idasanutlin in STAT3-mutant, TP53 wild-type cell lines; ruxolitinib combined with the farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib in TP53-mutant cell lines; and ruxolitinib combined with either the glucocorticoid dexamethasone or the myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL-1) inhibitor S63845 but both without a clear link to underlying genetic features. In conclusion, using a new drug sensitivity screening approach, we identified drug combinations that selectively target mature NK-cell neoplasms and do not allow for development of resistance, some of which can be applied in a genetically stratified manner.
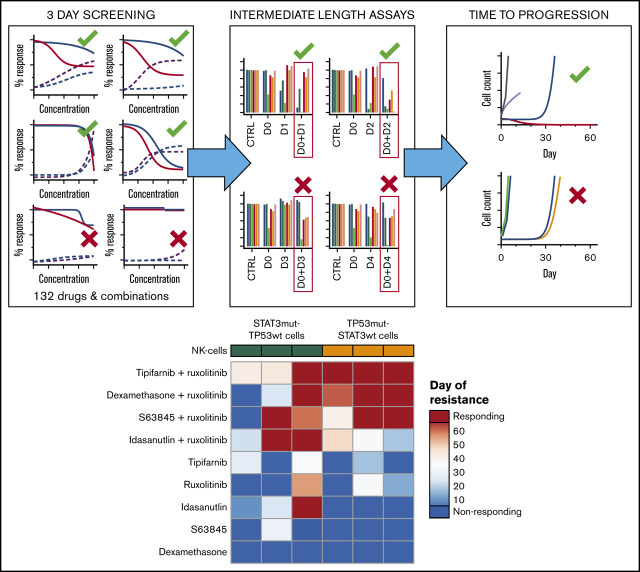
Visual Abstract
Introduction
Aggressive natural killer–cell leukemia (ANKL) and extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (NKTCL), are distinct diseases that exhibit overlap in genetic drivers, upregulated pathways, immunophenotypes, and sites of involvement.1-5 ANKL is a systemic malignancy, whereas NKTCL is present in the nasal cavity but in rare cases may present in extranodal sites (ie, lungs, skin, gastrointestinal track). Both malignancies are aggressive diseases with very poor prognosis. They have a higher prevalence in Asian and South American populations than in other populations and are associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection.1,5,6 NKTCL and ANKL share similarities with other EBV-positive leukemias and lymphomas, such as γδ-T-cell lymphoma,7 as well as with less aggressive T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia and chronic lymphoproliferative disorder of NK cells that are not associated with EBV infections.8,9
Cancer genome-sequencing efforts have revealed several recurrent mutations resulting in dysregulated signaling pathways in ANKL and NKTCL. These include mutations in the JAK/STAT pathway (JAK3, STAT3, and STAT5B), epigenetic modifiers (EP300, MLL2, ASXL3, and ARID1A), tumor suppressors (TP53), and transcription factors (MYC).2,3,10-12 In particular, high frequencies of mutations in STAT3 (8%-23%) and tumor protein p53 (TP53) (7%-35%) have been found in ANKL.1,3,13
Current treatment options for both ANKL and NKTCL involve l-asparaginase–containing combinatorial therapies such as SMILE (dexamethasone, methotrexate, ifosfamide, l-asparaginase, and etoposide).10,14 However, these treatments produce low complete response rates and, as a result, the median survival is no more than a few months. In the case of ANKL, fatal outcomes are considered a rule irrespective of treatment. Based on in vitro and preclinical efficacy, several targeted therapies have been suggested for ANKL and NKTCL. These include immune checkpoint inhibitors,15,16 as well as small-molecule inhibitors such as hypomethylating agents (decitabine), histone deacetylase inhibitors (vorinostat),17 combinations with ruxolitinib and the B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) family inhibitors venetoclax and navitoclax, or the aurora kinase inhibitor alisertib,3 as well as statins (lovastatin and simvastatin) combined with conventional cytotoxic chemotherapy (paclitaxel and topotecan).18 However, only a few patients have received immune checkpoint inhibitors in NKTCL,15,16 all the observations with small-molecule inhibitors are based on in vitro efficacy, and none of the novel targeted therapies has reportedly been tested in clinical settings.19
Combination with JAK inhibitors is a particularly appealing strategy for targeting NK-cell malignancies. JAK inhibitors selectively target NK-cell development, indicating the central role of JAK-STAT signaling in NK-cell biology. However, healthy NK-cell loss during the treatment is clinically manageable, and lymphocytes recover rapidly after treatment is interrupted.20,21 The JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib is approved to treat myelofibrosis, polycythemia vera, and acute graft-versus-host disease. Ruxolitinib is also under clinical investigation for relapsed/refractory T/NK-cell lymphoma (clinicaltrials.gov identifier #NCT02974647), and there is a wide interest in combining ruxolitinib or other JAK inhibitors with approved or investigational drugs for treatment of other hematologic disorders (clinicaltrials.gov identifiers #NCT03874052, #NCT03681561, and #NCT03795909).
In the current study, we found potential clinically translatable drug combinations for targeting ANKL and NKTCL cells in a stratified manner. Several drug combinations involving physiological doses of the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib were identified for which the cells do not develop resistance in long-term in vitro assays.
Methods
Cells and cell culture
NK-YS and SNK-6 cell lines were obtained from Wing C. Chan (City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA), NKL from Thomas P. Loughran, Jr. (University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA), YT, KHYG-1, and NK-92 from Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH (Braunschweig, Germany), and IMC-1 from I.-Ming Chen (University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM). NK-cell lines were cultured in RPMI 1640 (Gibco, Carlsbad, CA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA), 2 mM l-glutamine, 100 IU/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco), and 10 or 20 ng/mL human IL-2 (PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ) (supplemental Table 1). Cell lines were authenticated by using the GenePrint10 System (Promega, Madison, WI) and sequenced for mutations using the targeted next-generation sequencing SeqCap EZ Comprehensive Cancer Design panel (Roche NimbleGen, Pleasanton, CA) for the study by Dufva et al.3 The cell lines were prepared and cryopreserved as assay-ready cells. They were confirmed as Mycoplasma free based on the method described by Choppa et al,22,23 by the THL Biobank (Helsinki, Finland), and may be accessed from Cellosaurus (https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/) with the following accession numbers: IMC-1, CVCL_EQ57; KHYG-1, CVCL_2976; NK-92, CVCL_2142; NK-YS, CVCL_8461; NKL, CVCL_0466; SNK-6, CVCL_A673; and YT, CVCL_1797.
Drug sensitivity and resistance testing and synergy matrix screens
Drug sensitivity and resistance testing (DSRT) and synergy testing were adapted to screen NK-cell lines as previously described.24-26 The screen consisted of 132 approved and investigational oncology compounds (supplemental Data 1). All compounds were preplated at 5 or 7 different concentrations on black wall clear bottom 384-well plates (Corning, Corning, NY) using an acoustic dispenser (Echo 550; Labcyte Inc., San Jose, CA); 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 100 μM benzethonium chloride were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. The drugs were dissolved in 5 μL in cell culture medium with 1:400 CellTox Green (Promega) per well. Subsequently, 20 μL cell suspension per well was dispensed (supplemental Table 1) using a MultiFlo FX dispenser (BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT). Cells were incubated for 72 hours at 37°C and 5% carbon dioxide. After 72 hours, cell death (CellTox Green, Promega) and viability (CellTiter-Glo 2.0, Promega) were measured in a multiplexed manner by using a PHERAstar FS plate reader (BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany) as described previously.24
9-Day drug perturbation and drug combination reversibility tests
NK-cell lines (NK-YS, IMC-1, YT, NKL, NK-92, and SNK-6) were treated with compounds for 9 days on Nunc v-bottom 96-well plates (supplemental Table 1). Drugs and growth media were replenished every 72 hours: Cells were centrifuged at 200g for 5 minutes, supernatant was removed, cells were resuspended to 80 μL per well of growth media, and drugs were added at 20 μL per well diluted to growth media. In the 3-day treatment, 6-day drug recovery test, drug responses were also observed over 9 days, but cells were treated with drugs for 72 hours, after which the drugs were washed out and cells maintained in culture without drugs for another 6 days. Seventy-two hours before readout during growth media and/or drug replenishment, cells were transferred onto 96-well clear bottom black wall (#3904, Corning) plates. Cell viability was measured by using CellTiter-Glo 2.0 (Promega) and recorded by using a PHERAStar FS plate reader.
Time to progression assay
Five million cells per treatment were seeded at 5 × 105 cells/mL with DMSO control, single drugs, and drug combinations. After the first splitting at day 3, the cells were maintained at 3.5 × 105 cells/mL (for NKL, YT, SNK-6, IMC-1, and NK-92) or 3 × 105 cells/mL (NK-YS) and counted every third or fourth day by using a Countess II Automated Cell Counter (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). After cell counting, cells were re-plated to 3 × 105 or 3.5 × 105 cells/mL in fresh interleukin-2 (IL-2) containing complete RPMI 1640 and drugs. The minimum volume at which cells were kept was 1 mL. After 30 days, drugs were washed out, and cells were maintained for another 30 to 32 days without drugs.
Healthy peripheral blood mononuclear cell enrichment and flow cytometry–based drug testing
Fresh healthy peripheral blood buffy coats were obtained from the Finnish Red Cross Blood Service (approval no. Veripalvelu 51/2019). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were enriched by using Ficoll-Paque Premium (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL) density gradient centrifugation. Cells were suspended to complete RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10 ng/mL IL-2 and plated to pre-drugged 96-well V-bottom plates. After 72 hours’ incubation, cells were stained with 25 μL antibody mix (supplemental Table 2) in staining buffer (10% fetal bovine serum and 0.02% sodium azide in RPMI 1640 medium). Cells were incubated 20 minutes with the antibodies and centrifuged at 500g for 5 minutes to remove supernatant. Apoptotic and dead cells were discriminated by 7-Aminoactinomycin D and PE-Annexin V (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ) and used at 25 μL per well. Cells were incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature before analysis using an iQue Screener PLUS flow cytometer (Sartorius, Göttingen, Germany). ForeCyt software (Sartorius) was used to gate cells and acquire population counts (as described elsewhere).27 Drug response was measured by calculating remaining viable cells after drug treatment of cell populations positive for the different markers. Absolute cell count was normalized to adjacent DMSO controls.
Data analysis
The DSRT data and synergy scores (ZIP) were processed and calculated by using the Web-based tools Breeze28 and Synergy Finder,29,30 respectively. Drug sensitivity score (DSS) values representing area under the drug response curve were prefiltered based on average DSS values and manual curation. The prefiltering cutoff for the CellTiter-Glo viability readout was 10, and for the CellTox Green toxicity readout it was 5. The average differential DSS values were analyzed as DSS values, but the cutoffs were for CellTiter-Glo readout 5 and for CellTox Green 2.5. The clustering was done in ClustVis.31 Synergy matrices were visualized in RStudio (Boston, MA), and statistical analyses were performed by using GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA).
Results
Mutational status of malignant NK-cell lines causes differential drug sensitivity
Seven malignant NK-cell lines were exposed to drug sensitivity testing to determine sensitivities to 132 mechanistically diverse approved and investigational oncology compounds (supplemental Data 1). We measured both viability and drug-induced cytotoxicity, allowing us to separate cytostatic from cytotoxic responses. For drug efficacy and potency evaluation, we calculated DSS, an area under the dose–response curve type metric, for each compound as previously described.26,32 Among the 7 cell lines tested, 4 carried TP53 mutations and the remaining 3 carried STAT3 mutations (supplemental Table 1). These findings reflect that STAT3 and TP53 mutations seem to be mutually exclusive or independent genetic events in the development of ANKL1 and NKTCL.11,33
We queried whether the drug responses differed between these 2 groups. Although most drugs showed similar effects against the 2 subsets of cell lines, differences in responses occurred in some compounds in both cell toxicity and cell viability readouts (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Data 1). Most of these compounds exhibited selective response in either viability or toxicity readout, and several selective viability-reducing drugs did not exhibit selective toxicities. Only filanesib and birinapant selectively affected TP53-mutant cells in both viability (Figure 1G,I) and toxicity (Figure 1H,J) readouts, whereas BCL-xL inhibition (A-1331852, navitoclax) showed greater effects toward STAT3-mutant cells with both readouts (Figure 1E-F,K-L). With several compounds, we observed mixed sensitivities toward drugs between cell lines within the same group.
Figure 1.
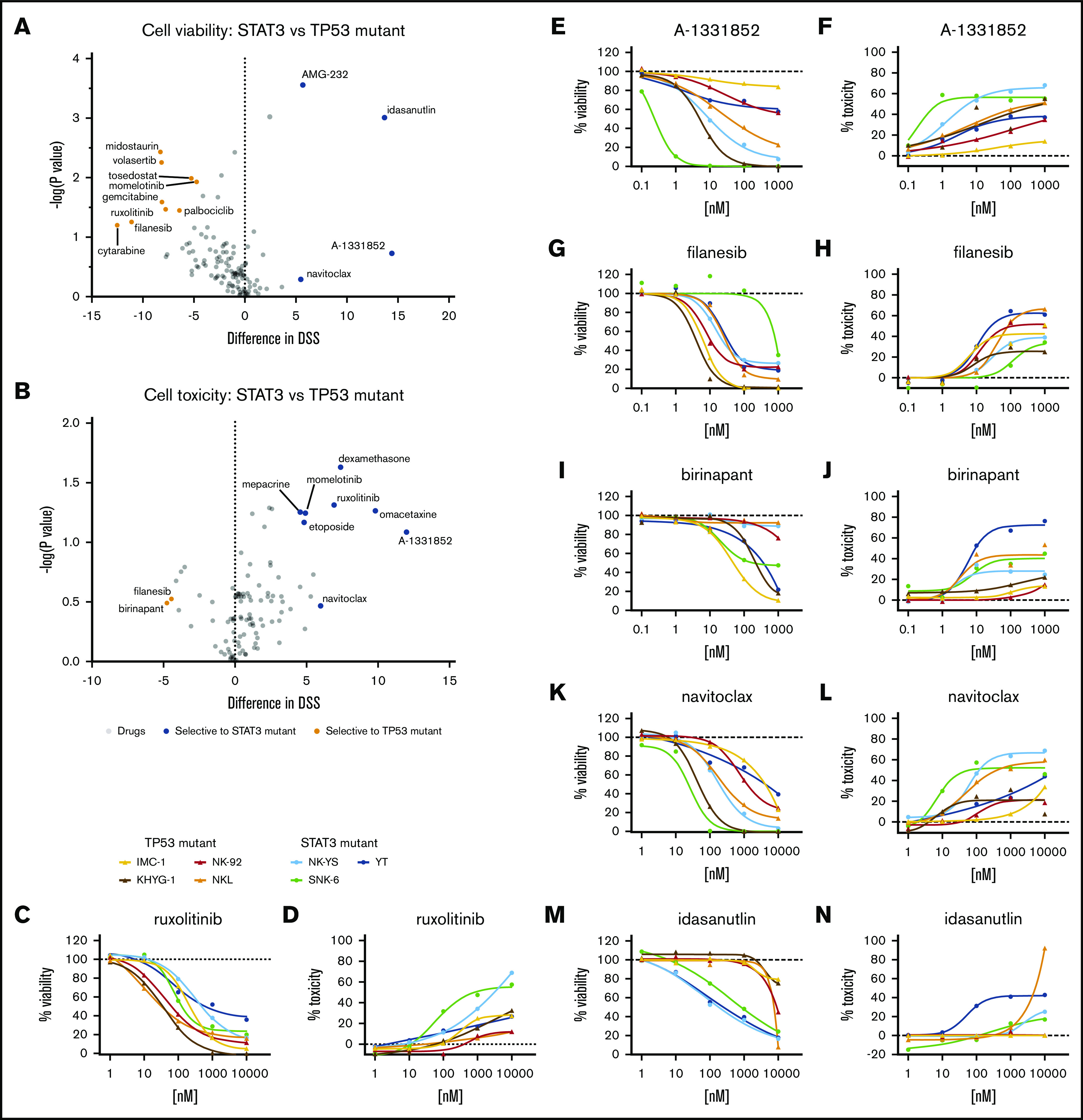
Drug responses in malignant NK-cell lines. Volcano plot of DSS of STAT3 (blue, n = 3) and TP53 (orange, n = 4) mutant cells in viability (A) and cytotoxicity (B) readouts. Drugs highlighted show selective sensitivity toward TP53 (orange) or STAT3 (blue) mutant NK cells. Dose–response curves of viability inhibition and toxicity in STAT3 and TP53 mutant NK-cell lines with ruxolitinib (C-D), A-1331852 (E-F), filanesib (G-H), birinapant (I-J), navitoclax (K-L), and idasanutlin (M-N). Drug responses were normalized to positive cell killing (benzethonium chloride) and negative (DMSO vehicle only) controls. Assays were conducted in single wells normalized plate-wise to negative (DMSO) and positive (BzCl) controls. Normalized cell viability, cell toxicity and resulting DSS values are provided in supplemental Data 1.
In the viability readout, all cell lines responded to the JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib, reflecting the general dependence on cytokine-JAK-STAT signaling in NK cells (Figure 1C-D). However, in the toxicity readout, only 2 of the 7 cell lines exhibited a strong cytotoxicity response. Similar to the toxicity readout, BCL-2 homology domain 3 profiling34 in ruxolitinib-treated cells (16 hours) showed greater BIM-, BID-, and HRK-dependent apoptotic priming in NK-YS cells than in NKL cells (supplemental figure 1; supplemental Materials). As expected, the TP53-mouse double-minute 2 homolog (MDM2) inhibitor idasanutlin exhibited selectivity toward the TP53 wild-type cells in the viability readout (Figure 1M-N). However, as with JAK inhibition, it primarily appeared to be a cytostatic effect because there was much less induction of cytotoxicity.
Combination testing reveals sensitivity to farnesyltransferase inhibitors, glucocorticoids, and anti-apoptotic inhibitors in the presence of JAK inhibition
We next tested whether these JAK-STAT signaling-dependent cells have increased sensitivity toward specific drug classes when treated in combination with ruxolitinib. A collection of 132 targeted and cytotoxic small molecules were screened in the presence and absence of 300 nM ruxolitinib to look for potential synergistic interactions (supplemental Data 1). In the presence of ruxolitinib, increased sensitivity toward several drug classes was observed, including farnesyltransferase inhibitors, glucocorticoids, and several pro-apoptotic agents (BCL-2 family, myeloid cell leukemia-1 [MCL-1], and MDM2 inhibitors). Furthermore, in the viability readout, ruxolitinib increased sensitivity toward several anti-mitotics, as well as topoisomerase I and II, aurora kinase (that behave as anti-mitotics in our assays24,26), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors, and the antimetabolites cytarabine and methotrexate (Figure 2A).
Figure 2.
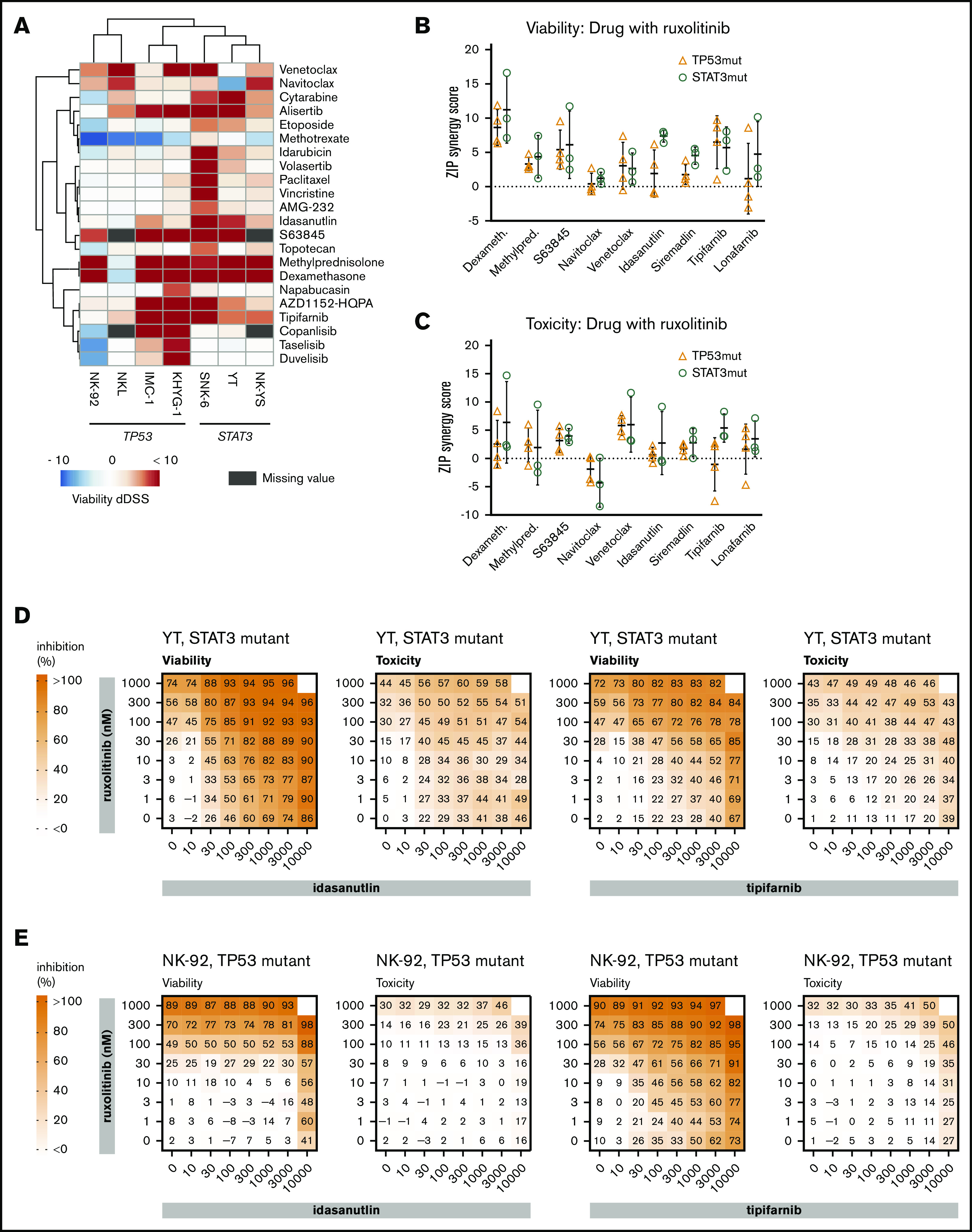
Drug combinations in malignant NK-cell lines. (A) Differential DSS (dDSS) values comparing the response to compounds in the presence vs absence of 300 nM ruxolitinib. ZIP scores represent the drug synergies based on viability (B) and cytotoxicity (C) readout. Each dot represents a different cell line; the bar represents the variability between cell lines, and the line represents the median of TP53-mutant (orange) and STAT3-mutant (teal) NK-cell lines. Drug combination matrices in viability and toxicity readouts with ruxolitinib and idasanutlin or tipifarnib in TP53-mutant NK-92 cell line (D) and STAT3-mutant YT cell line (E) are shown. Assays were conducted in single wells normalized plate-wise to negative (DMSO) and positive (BzCl) controls. dDSS values were calculated by subtracting the DSS(DMSO) from the DSS(ruxo). DSS values are provided in supplemental Data 1, and drug combination matrix figures for all tested cell lines and drugs are provided in supplemental Data 2.
Based on differential DSS values, we selected 9 combinations for testing in dose–response matrices to identify synergistic or additive relationships. Lower dose ranges were selected for the dose–response matrices to better identify combinatory relationships at physiologically relevant intermediate doses. As expected, TP53-mutant lines did not exhibit synergistic responses to the combination of ruxolitinib and idasanutlin (Figure 2B-E; supplemental Data 2). Broad synergies across both TP53- and STAT3-mutant cell lines were observed in combinations between ruxolitinib and tipifarnib, glucocorticoids, or BCL-2 family inhibitors (Figure 2B-C; supplemental Data 2; supplemental Table 3).
Ruxolitinib combined with tipifarnib or idasanutlin maintains the inhibitory effect in extended drug response assays
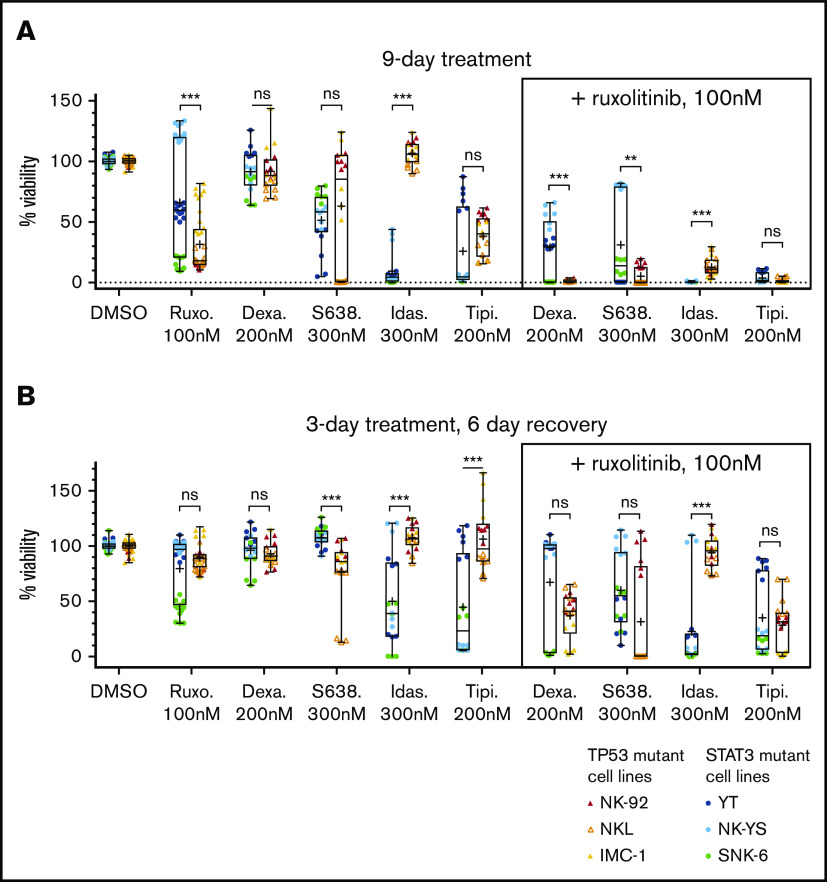
We next assessed whether the drug combinations completely eradicate the cells or if resistance emerges over time. First, we followed up the 9 combinations in 2 types of extended assays, observing the drug-treated cells for 9 days (supplemental Figure 2): one in which cells were continuously treated with the selected compounds for 9 days (Figure 3A) and another in which the cells were treated for 3 days and then were allowed to recover without drugs for the next 6 days (Figure 3B). We observed that in the 9-day drug treatment, dexamethasone (200 nM) combined with ruxolitinib (100 nM) resulted in stronger inhibition in the TP53-mutant cells, whereas idasanutlin (300 nM) and ruxolitinib caused stronger inhibition in STAT3-mutant cells. Tipifarnib (200 nM) and ruxolitinib (100 nM) caused similar inhibition in both cell line groups. When testing the cell recovery after a 3-day drug perturbation, cells in all combinations recovered to varying degrees after 6 days except for idasanutlin and ruxolitinib, in which the median viability was 2.5% of DMSO control in the STAT3-mutant cells. We further confirmed dexamethasone, idasanutlin, and tipifarnib combination responses, with additional compounds having the same mechanism of action (the glucocorticoid methylprednisolone, the TP53-MDM2 inhibitor siremadlin, and the farnesyltransferase inhibitor lonafarnib) (supplemental Figure 2). Ruxolitinib combined with MCL-1 and BCL-2 inhibitors exhibited variability between cell lines, but ruxolitinib combined with the MCL-1 inhibitor S63845 generally caused a stronger decrease in viability than with the BCL-2/BCL-xL inhibitor navitoclax or the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax.
Figure 3.
Effects of drugs and drug reversibility in NK-cell lines in a 9-day assay. (A) Six NK-cell lines were treated with single drugs and combinations with indicated concentrations for 9 days. (B) Drug reversibility after 3-day drug perturbation in NK-cell lines. Cells were observed for 6 days after drug removal. Cell viabilities are normalized to positive and negative controls. Box indicates standard deviation; line, median; plus sign, mean; and bars, minimum and maximum of STAT3- and TP53-mutant cell lines (color labeled). Data are from 2 individual experiments performed at least in triplicate. Each dot represents a single assay point. **P < .01; ***P < .001 (Student t test). Dexa., dexamethasone; Idas., idasanutlin; ns, nonsignificant; Ruxo., ruxolitinib; S638., S63845; Tipi., tipifarnib.
Long-term time-to-progression assays identify several combinations with persisting responses without regrowth of cells
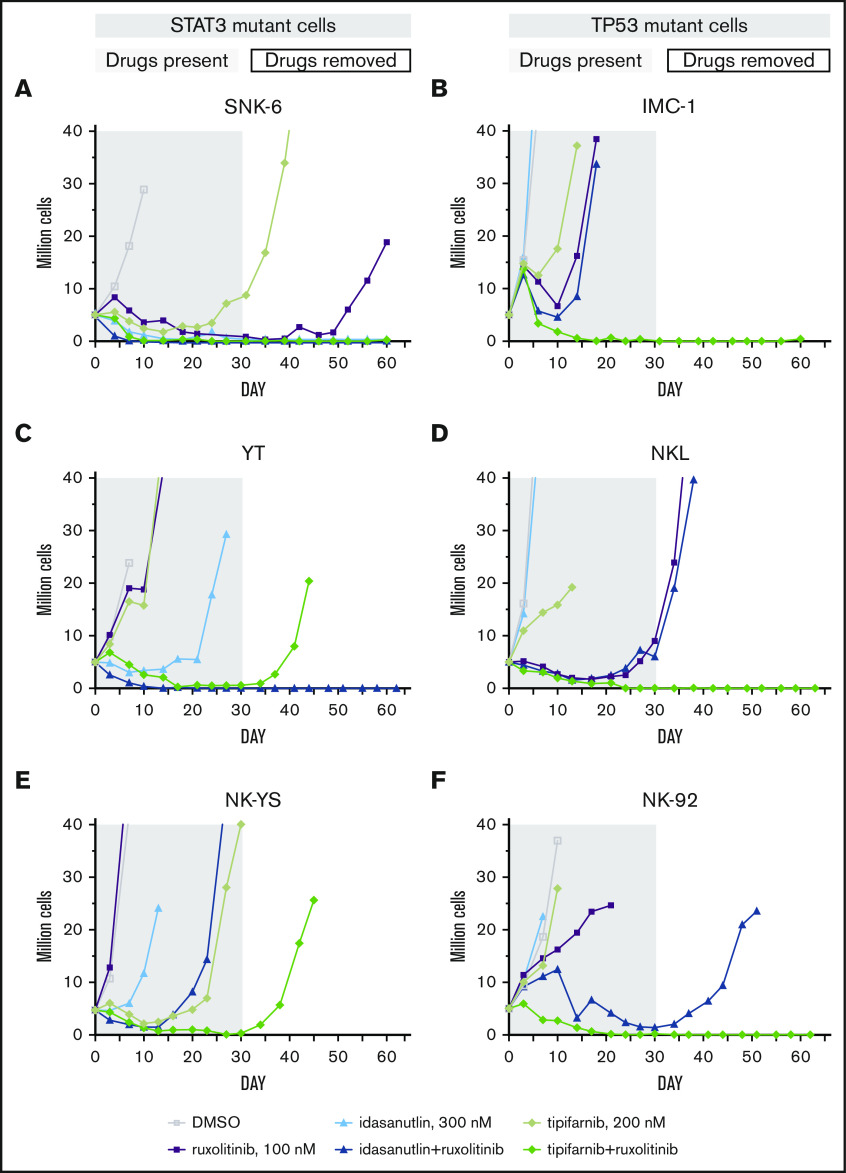
From the extended drug response assays, we selected the most potent drug combinations that may have clinical relevance and observed them in 6 cell lines with an in vitro time-to-progression (TTP) assay.35 We treated the STAT3-mutant YT, SNK-6, and NK-YS cell lines and the TP53-mutant NK-92, NKL, and IMC-1 cell lines with 4 combinations that were controlled with single drug treatments (Table 1; supplemental Figure 3) for up to 30 days and continued the culture for an additional 30 to 32 days without compounds or until regrowth occurred. The cell lines were not eradicated by single drugs (ruxolitinib, dexamethasone, tipifarnib, S63845, or idasanutlin) with the exception of the SNK-6 cells, and no combination blocked emergence of resistance/regrowth in all of the cell line models. However, the tipifarnib and ruxolitinib combination eradicated 4 of 6 cell lines; in the remaining 2 cell lines, the recovery only occurred after 42 or 44 days. Tipifarnib combined with ruxolitinib eradicated all the TP53-mutant cell lines (Figure 4B,D,F), whereas it was only fully effective in 1 of the 3 STAT3-mutant cell lines (Figure 4A,C,E). Idasanutlin combined with ruxolitinib was most effective in STAT3-mutant cells. Ruxolitinib combinations with dexamethasone or S63845 did not exhibit STAT3 or TP53 mutation-specific response patterns, although in both cases, 3 of 6 cell lines were eradicated by the combinations.
Table 1.
Ruxolitinib combinations and single-agents tested in TTP assay
| Treatment/cell line | YT | NK-YS | SNK-6 | NK-92 | NKL | IMC-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutation in STAT3 or TP53 | STAT3 | STAT3 | STAT3 | TP53 | TP53 | TP53 |
| Dexamethasone + ruxolitinib | Regrowth (day 24) | Non-responding | Responding | Regrowth (day 62) | Responding | Responding |
| Tipifarnib + ruxolitinib | Regrowth (day 44) | Regrowth (day 42) | Responding | Responding | Responding | Responding |
| S63845 + ruxolitinib | Responding | Nonresponding | Regrowth (day 60) | Regrowth (day 41) | Responding | Responding |
| Idasanutlin + ruxolitinib | Responding | Regrowth (day 23) | Responding | Regrowth (day 48) | Regrowth (day 34) | Regrowth (day 18) |
| Ruxolitinib, 100 nM | Nonresponding | Nonresponding | Regrowth (day 56) | Nonresponding | Regrowth (day 34) | Regrowth (day 14) |
| Dexamethasone, 200 nM | Nonresponding | Nonresponding | Nonresponding | Nonresponding | Nonresponding | Nonresponding |
| Tipifarnib, 200 nM | Nonresponding | Regrowth (day 27) | Regrowth (day 35) | Nonresponding | Regrowth (day 17) | Nonresponding |
| S63845, 300 nM | Regrowth (day 30) | Nonresponding | Regrowth (day 24) | Nonresponding | Nonresponding | Nonresponding |
| Idasanutlin, 300 nM | Regrowth (day 24) | Regrowth (day 10) | Responding | Nonresponding | Nonresponding | Nonresponding |
Cells were considered fully responding when no sign of regrowth was visible at the end of the assay. Regrowth day marked in brackets was based on when cells reached 10 million (one doubling). Cells were considered nonresponding when expansion occurred within 9 days of starting treatment.
Figure 4.
In vitro TTP assay reveals differential drug sensitivities toward ruxolitinib combinations in STAT3- and TP53-mutant cell lines. Concurrent treatment with ruxolitinib and tipifarnib or idasanutlin in STAT3-mutant (A-C) or TP53-mutant (D-F) NK-cell lines. Treatments were maintained for 30 days (gray area) with single drugs and their combinations, and observed for another 30 to 32 days after drug removal (white area). Cells were counted, and drug and media were replenished every third to fourth day and set to 3 to 3.5 × 105 cells/mL cell density. Cultures were stopped when reaching 20 million (2 duplications from start).
Short-term drug responses are poorly predictive of long-term responses
With the long-term responses at hand, we compared the consistency of the long-term responses vs those with the same treatments in 3-day assays, in the extended 9-day assays, the 3-day treatment + 6-day recovery assays, and the synergy scores achieved in 3-day combination testing. The short-term (3-day) DSRT assays were not predictive of long-term complete responses, and the short-term responses alone could therefore not be used to effectively predict for treatments with long-term responses (Figure 5A-B). Conversely, the end point results of the extended 9-day assays (both the 9-day treatment and the 3-day treatment + 6-day recovery) could have been used to strongly enrich for long-term complete responses, but some false-positive findings would be selected also (Figure 5C-D). Strikingly, there was no correlation between short-term synergy scores and long-term responses (Figure 5E-F), although all effective combinations except for one showed some synergy in the viability readout.
Figure 5.
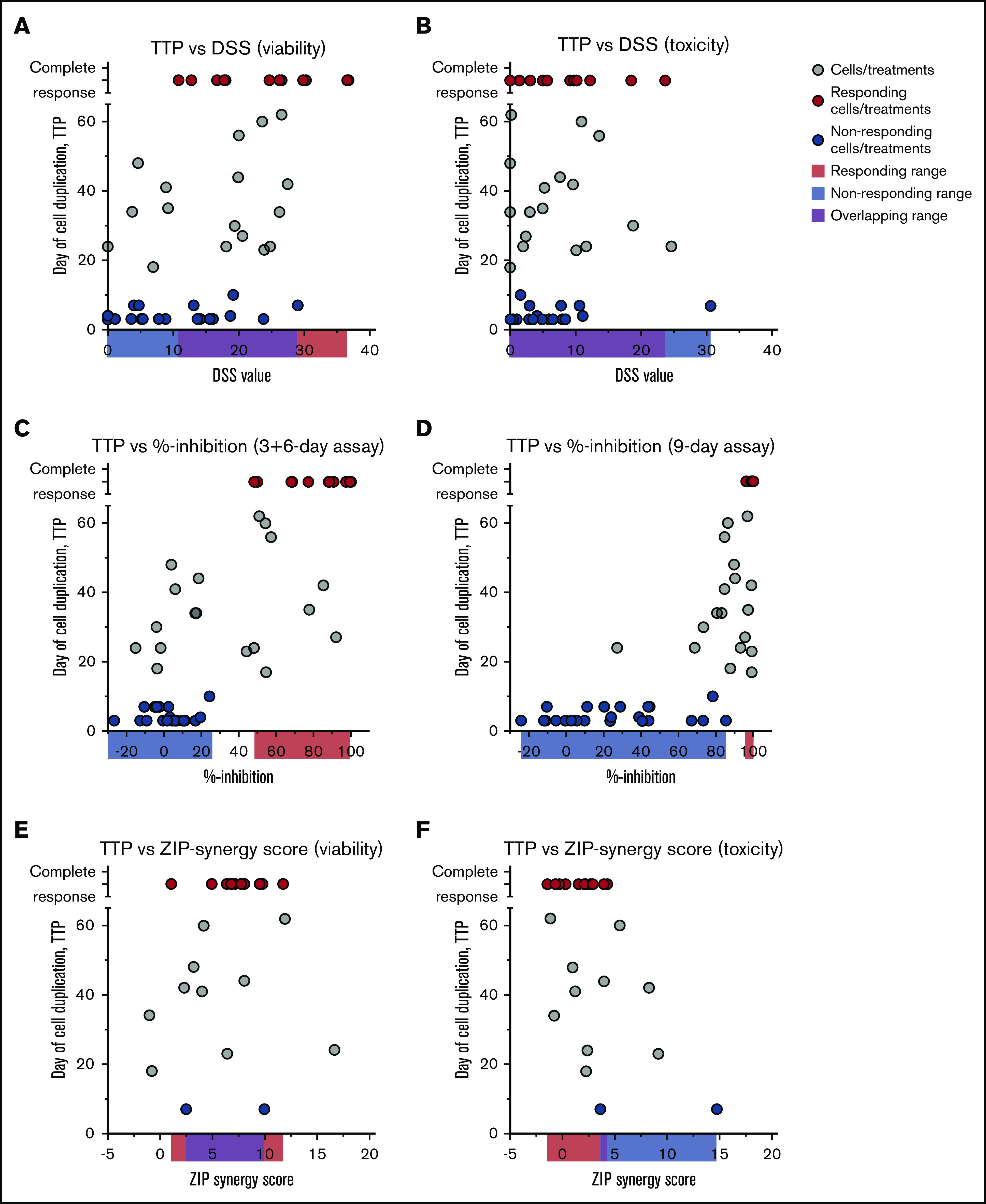
Comparison of TTP assay vs short and extended time assays. Day when cells reached 10 million (one duplication) in the TTP assay correlated with DSS values from short-term assays (3 days) based on viability (A) and toxicity (B) readout, % inhibition values from extended 3-day treatment, 6-day recovery (C) and 9-day treatment assays (D), and ZIP synergy scores based on viability (E) and toxicity (F) readout. Red dots represent cell/treatment combinations that responded in the TTP assay; blue dots, treatments that did not respond; and gray cells, treatments that did not fall into either group. Cutoff for nonresponders was 10 days in the TTP assay and for the responders no growth at the end of the assay. Data are from Figures 1 to 4.
Key drug combinations are not broadly toxic in normal blood mononuclear cells
To elucidate the effect of ruxolitinib combinations on different types of healthy leukocytes, we tested the top combinations on healthy PBMCs. In dose–response matrix testing, none of the combinations caused as strong cytostatic or cytotoxic responses for the PBMCs as for the malignant NK-cell lines (Figure 6A-F; supplemental Figure 4; supplemental Data 2).
Figure 6.
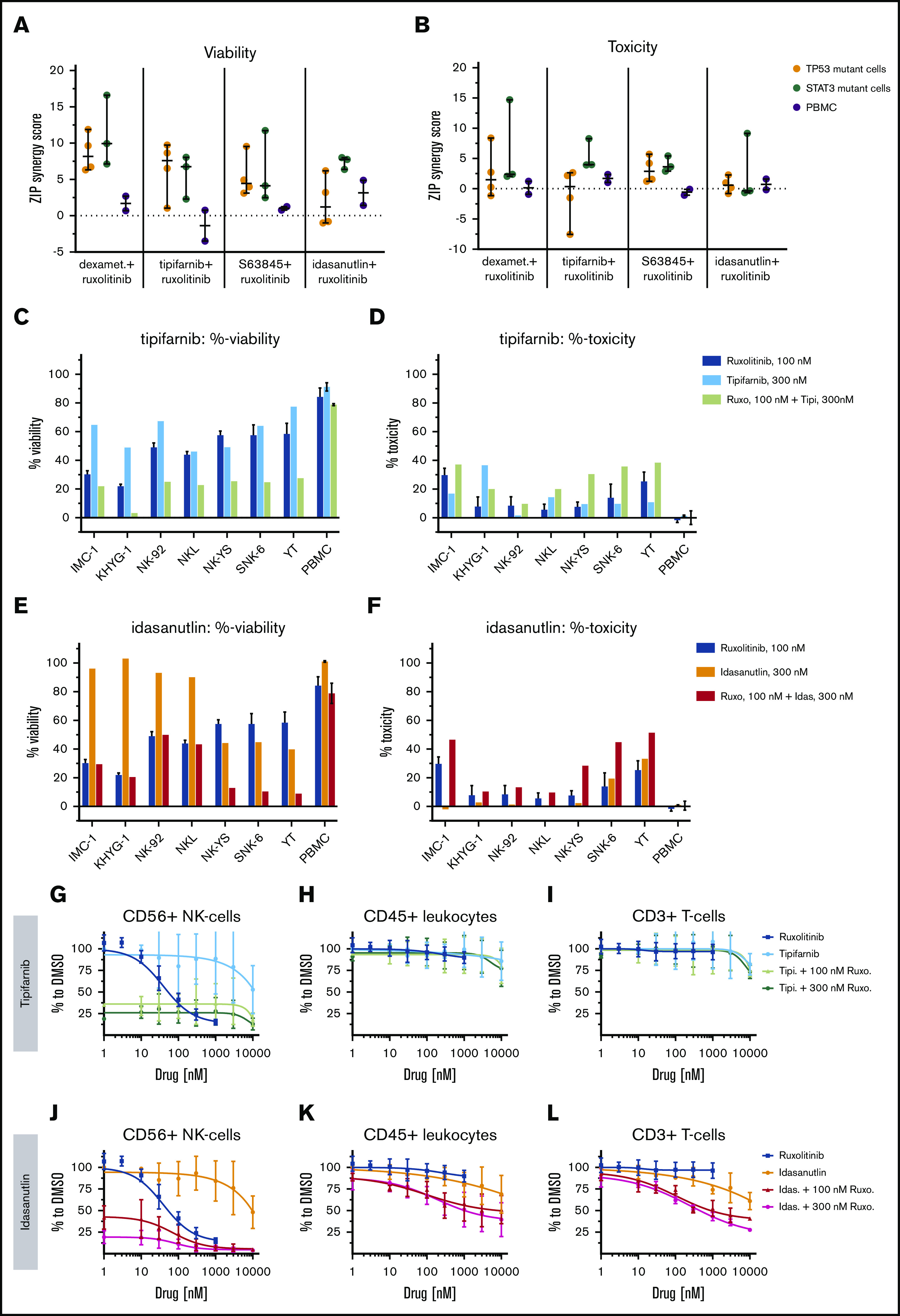
Single compounds and ruxolitinib combinations across malignant NK-cell lines and healthy PBMCs. ZIP scores are given, representing the drug synergies across malignant NK-cell lines and PBMCs in viability (A) and toxicity (B) readout. PBMCs from 2 individuals (gray) are compared with either TP53-mutant (orange) or STAT3-mutant (teal) NK-cell lines. Each dot represents one NK-cell line or in PBMCs. Line is set to median, and bar represents standard deviation. %-viability and %-toxicity of 300 nM tipifarnib (C-D) or 300 nM idasanutlin (E-F) combined with 100 nM ruxolitinib are shown. Single measurement per cell line. Mean and standard deviation represent, in ruxolitinib single treatment, 6 technical replicates and in “PBMC,” mean of PBMCs from 2 individuals. Dose responses and 8 × 8 dose-range synergy matrices are provided in supplemental Data 2. Drug combinations and single-drug dose–response curves of PBMC populations in the presence of 10 ng/mL IL-2: NK cells (G,J), total leukocytes (H,K), and T cells (I,L). Each dot represents mean and error bars represent the range from single wells of 2 experiments of PBMCs from different individuals.
We further used a flow cytometry–based readout to detect responses in separate cell populations. In these assays, CD56+ NK cells exhibited a strong dose-dependent sensitivity toward ruxolitinib alone, confirming that these cells are dependent on IL-2–induced JAK-STAT signaling. Due to the potent ruxolitinib response, healthy NK cells were also strongly affected by all tested combinations, leaving ∼20% of the cells intact, but no synergies were seen (Figure 6G,J). CD3+ T cells and total CD45+ leukocytes were not affected by ruxolitinib or the tested drug combinations (Figure 6H-I,K-L; supplemental Figure 5). Thus, in agreement with previously published data,3 our results show that both malignant and healthy NK cells are sensitive to JAK inhibition. However, the tested combinations were only synergistic in the malignant NK-cell lines, thus providing a good rationale to use ruxolitinib combinations to treat NK-cell malignancies.
Discussion
In the current study, high-throughput drug sensitivity screens combined with follow-up long-term assays were used to identify effective drug combinations against which malignant NK cells did not develop resistance. We started with the type of short-term assays (3 days) that are common in drug response profiling of cell lines and primary patient cells, followed these up with 9-day assays, and finally tested key combination long-term TTP assays in which the cells were treated for 30 days and subsequently followed up by another month of recovery while observing any regrowth of cells.
A key finding from these tests was that short-term drug responses often failed to predict long-term responses. In most cases, the treatments reduced the number of viable cells initially but eventually did not hold back the regrowth of resistant cells. Interestingly, in some cases, the cells acquired resistance quickly in the presence of the drugs, whereas in others, a few cells persisted in the long-term treatment and regrew after drug removal. As a consequence, our data strongly suggest that selection based on short-term drug response assays is often going to result in treatments for which resistance will develop relatively quickly in vitro and presumably also in vivo. Nine-day assays were more predictive than the 3-day assays but still did not fully reflect the long-term in vitro TTP assay responses. As an example, the 9-day assay suggested that STAT3-mutant lines responded stronger to the combination of ruxolitinib and tipifarnib, whereas the long-term assays proved that the TP53-mutant lines exhibit the best responses. In the case of 3 other ruxolitinib combinations (dexamethasone, idasanutlin, and S63845), the 3-day perturbation, 6-day recovery assays were able to predict the long-term outcome. This may indicate the different perturbation times needed for each drug but also emphasizes the importance of validating the drug screening results in long-term in vitro assays before in vivo assessment to observe whether resistance emerges.
Several studies have shown in both solid and hematologic malignancies that cancer cells quickly develop resistance to targeted drugs.36-38 This resistance can occur from drug-tolerant “persister” cells that slowly arise at the presence of drugs.35,37 Similar to our in vitro data on malignant NK-cell lines, others have shown that concomitant blockade of endothelial growth factor receptor and MEK in colorectal cancer prevents resistance development in both in vitro and in vivo TTP assays.35 Together, these data suggest that in vitro long-term assays reveal the emergence of resistance development, and this can allow for better prediction of in vivo efficacy, whether the starting point is a short-term drug sensitivity screen or a treatment strategy identified through other means such as genetic information.
We observed that the NK cells have differential drug responses depending on TP53 or STAT3 mutation status. Based on previous reports, TP53 and STAT3 mutations appear mutually exclusive or independent in ANKL and NKTCL,1,3,13,33 and others have suggested that mutations in STAT3, BCOR, and DDX3X are nearly mutually exclusive in NKTCL.13 A molecular subtype–based classification for NKTCL has been proposed.33 In this classification, JAK-STAT and TP53 dysregulated NKTCL are in one group and the other two groups consist of NKTCL patients with dysregulated MYC or EP300. Our data suggest that the JAK-STAT and TP53 group can be further subdivided. To our knowledge, others have not studied differences in drug responses based on TP53 or STAT3 mutations in mature T-cell/NK-cell leukemias, and there are likely further ways to genetically stratify the patients; this subject requires further study, however, with larger cohorts.
In our data set, both malignant and healthy NK cells showed sensitivity toward ruxolitinib inhibition, highlighting that NK cells are generally dependent on cytokine-based JAK-STAT signaling. This is in line with previous observations in which both healthy NK cells and malignant NK-cell lines exhibit moderate cytostatic sensitivity to ruxolitinib.3 It has been reported that JAK inhibition induces apoptosis in malignant NK-cell lines by reducing MCL-1 expression,39,40 and ruxolitinib seems to have JAK3-STAT5 inhibition capacity in NK cells.21
Inhibition of JAK kinases with ruxolitinib combined with farnesyltransferase inhibition in the current study resulted in long-term efficacy in all TP53-mutant malignant NK-cell lines, whereas ruxolitinib combined with idasanutlin was effective in STAT3-mutant cell lines. Tipifarnib has been shown to inhibit IL6-STAT3 signaling in pancreatic cancer41 and STAT3 expression levels in acute myeloid leukemia.42 Tipifarnib has been explored as a monotherapy in a phase 2 clinical trial to treat large granular lymphocytic leukemia, a closely related nonaggressive NK/T-cell malignancy (clinicaltrials.gov identifier #NCT00360776).43 The tipifarnib and ruxolitinib combination has not previously been tested in NK-cell malignancies, but both drugs have been clinically tested as single agents in multiple types of hematologic malignancies.44,45
STAT3-mutant, TP53 wild-type NK-cell lines exhibited long-term sensitivity toward the combination of the TP53-MDM2 interaction inhibitor idasanutlin and ruxolitinib. Idasanutlin monotherapy was not effective, on the other hand, as resistance developed quickly in responding cell lines. Analogous to our results, TP53 wild-type osteosarcoma and breast cancer cell lines that are initially sensitive to idasanutlin have been described as developing resistance through selection of resistant clones.46
The combination of the MCL-1 inhibitor S63845 and ruxolitinib exhibited long-term effects independently of STAT3 vs TP53 mutations. Notably, levels of phospho-Y705-STAT3 and MCL-1 have been shown to correlate in patients with NKTCL.39 This may explain why some of the phospho-Y705-STAT3–positive NK-cell lines47 responded to MCL-1 inhibition, but the differences in sensitivities to the S63845 and ruxolitinib combination might also be explained by differing anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family protein expression. Finally, the combination of the glucocorticoid dexamethasone and ruxolitinib was effective long term in multiple cell lines, but responses did not seem to be linked to TP53 vs STAT3 mutational status. The combinatorial potential of glucocorticoids and JAK inhibition has also been shown in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia models, in which JAK-STAT signaling can mediate resistance to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis.48-50 Furthermore, the same combinatorial effect was recently described for controlling cytotoxic T cells in hyperinflammation such as cytokine storm syndromes.51 Importantly, in our study, the T cells in peripheral blood did not respond strongly to ruxolitinib, dexamethasone, or their combination, suggesting that the combination does not act on normal, non-hyperactivated T cells. The potential advantage of glucocorticoids and ruxolitinib is that both are well tolerated, are used to treat cancer and autoimmune diseases,52,53 and are actively researched as combination treatments for inflammatory and hematologic diseases. This research includes a phase 3 clinical trial for treating glucocorticoid-refractory graft-versus-host disease (clinicaltrials.gov identifier #NCT02913261) and phase 1 and 2 clinical trials for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (clinicaltrials.gov identifiers #NCT03613428 and #NCT02723994). Hence, combining ruxolitinib and dexamethasone seems safe and has notable potential for clinical translation for NK-cell neoplasms.
A limitation of this study is the small number of cell lines studied, which most certainly cannot represent the full heterogeneity of NK-cell malignancies. However, we believe this is close to the state-of-the-art in this disease setting. Generation of cell lines from ANKL and NKTCL have proven exceptionally challenging, and only 12 cell lines have been described,54-65 many of which are not publicly available. No primary patient cell culture systems have been documented. Only a handful of xenograft mouse models from cell lines66,67 and one single case of a patient-derived xenograft model from a patient with NKTCL68 have been described, and they all tend to be unstable models, questioning their relevance.
In conclusion, stratifying ANKL and NKTCL based on mutations might be a promising approach to reach better therapeutic outcomes. Cotargeting JAK1/2 together with TP53-MDM2 inhibitors can be a feasible way to target aggressive NK-cell malignancies that carry STAT3 mutations but are TP53 wild type. Patients with TP53 mutations may benefit from JAK1/2 and farnesyltransferase inhibition. The combination of ruxolitinib with either a glucocorticoid or an MCL-1 inhibitor also seems relevant for further translational studies to identify predictive biomarkers. These findings shed light on novel therapy options for ANKL and NKTCL that warrant further studies in larger data sets or in clinical settings. Finally, our results highlight the importance of performing extended drug response assays for in vitro identification of treatments that selectively eradicate the cancer cells and do not easily allow for development of resistance, a common problem with many targeted therapies.
Supplementary Material
The full-text version of this article contains a data supplement.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Thomas P. Loughran, Jr, I.-Ming Chen, and Wing C. Chan for providing the cell lines used in this study. Laura Turunen, Maria Nurmi, Jani Saarela, and other members of the FIMM High Throughput Biomedicine unit are acknowledged for technical assistance with drug screening (supported by the University of Helsinki/Biocenter Finland Research infrastructure funds). The authors also thank Riku Turkki for technical assistance regarding data analysis and visualization, and Amanda Ranta for technical assistance.
This work was supported through a center grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation (Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Stem Cell Biology [DanStem], Grant Number NNF17CC0027852), grants from the Academy of Finland (277293 [K.W.] and 331256 [S.M.]), Sigrid Jusélius Foundation, Cancer Society of Finland, Finnish Blood Disease Research Foundation, Finnish Hematology Association, and the European Research Council (M-IMM project [S.M.]).
Footnotes
Requests for original data may be submitted to the corresponding author (Krister Wennerberg; e-mail: krister.wennerberg@bric.ku.dk). Drug-screening data may be found in supplemental Data 1 and 2.
Authorship
Contribution: E.P. and K.W. designed the study and wrote the manuscript; E.P. designed and performed the experiments and analyzed data; H.K. performed the flow cytometry experiments; D.B. performed the BCL-2 homology domain 3 profiling; S.M. provided the cell lines and performed critical revision of the manuscript; K.W. edited the manuscript and supervised the work; and all the authors contributed to the writing and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.M. has received honoraria and research funding from BMS and research funding from Pfizer and Novartis (unrelated to this project). K.W. has received honoraria from Pfizer and research funding from Novartis (unrelated to this project). The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests
Correspondence: Krister Wennerberg, Biotech Research & Innovation Centre (BRIC), University of Copenhagen, Ole Maaløes Vej 5, DK-2200 Copenhagen, Denmark; e-mail: krister.wennerberg@bric.ku.dk.
References
- 1.Huang L, Liu D, Wang N, et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies deregulated JAK/STAT-MYC-biosynthesis axis in aggressive NK-cell leukemia. Cell Res. 2018;28(2):172-186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jiang L, Gu ZH, Yan ZX, et al. Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DDX3X in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Nat Genet. 2015;47(9):1061-1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dufva O, Kankainen M, Kelkka T, et al. Aggressive natural killer-cell leukemia mutational landscape and drug profiling highlight JAK-STAT signaling as therapeutic target. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Küçük C, Jiang B, Hu X, et al. Activating mutations of STAT5B and STAT3 in lymphomas derived from γδ-T or NK cells. Nat Commun. 2015;6(1):6025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016;127(20):2375-2390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Haverkos BM, Pan Z, Gru AA, et al. Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL-NT): an update on epidemiology, clinical presentation, and natural history in North American and European cases. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2016;11(6):514-527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Iqbal J, Weisenburger DD, Chowdhury A, et al. ; International Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma Project . Natural killer cell lymphoma shares strikingly similar molecular features with a group of non-hepatosplenic γδ T-cell lymphoma and is highly sensitive to a novel aurora kinase A inhibitor in vitro [published correction appears in Leukemia. 2011;25(8):1377]. Leukemia. 2011;25(2):348-358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rajala HL, Olson T, Clemente MJ, et al. The analysis of clonal diversity and therapy responses using STAT3 mutations as a molecular marker in large granular lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 2015;100(1):91-99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jerez A, Clemente MJ, Makishima H, et al. STAT3 mutations unify the pathogenesis of chronic lymphoproliferative disorders of NK cells and T-cell large granular lymphocyte leukemia. Blood. 2012;120(15):3048-3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tang YT, Wang D, Luo H, et al. Aggressive NK-cell leukemia: clinical subtypes, molecular features, and treatment outcomes. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7(12):660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Song TL, Nairismägi ML, Laurensia Y, et al. Oncogenic activation of the STAT3 pathway drives PD-L1 expression in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2018;132(11):1146-1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.de Mel S, Soon GS, Mok Y, et al. The genomics and molecular biology of natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: opportunities for translation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):E1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Montes-Mojarro IA, Chen BJ, Ramirez-Ibarguen AF, et al. Mutational profile and EBV strains of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type in Latin America. Mod Pathol. 2020;33(5):781-791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yamaguchi M, Suzuki R, Oguchi M. Advances in the treatment of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood. 2018;131(23):2528-2540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li X, Cheng Y, Zhang M, et al. Activity of pembrolizumab in relapsed/refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kwong YL, Chan TSY, Tan D, et al. PD1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing l-asparaginase. Blood. 2017;129(17):2437-2442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Karube K, Tsuzuki S, Yoshida N, et al. Comprehensive gene expression profiles of NK cell neoplasms identify vorinostat as an effective drug candidate. Cancer Lett. 2013;333(1):47-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Henslee AB, Steele TA. Combination statin and chemotherapy inhibits proliferation and cytotoxicity of an aggressive natural killer cell leukemia. Biomark Res. 2018;6(1):26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ishida F. Aggressive NK-cell leukemia. Front Pediatr. 2018;6:292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Borella L, Green AA, Webster RG. Immunologic rebound after cessation of long-term chemotherapy in acute leukemia. Blood. 1972;40(1):42-51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schönberg K, Rudolph J, Vonnahme M, et al. JAK inhibition impairs NK cell function in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Cancer Res. 2015;75(11):2187-2199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Choppa PC, Vojdani A, Tagle C, Andrin R, Magtoto L. Multiplex PCR for the detection of Mycoplasma fermentans, M. hominis and M. penetrans in cell cultures and blood samples of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Mol Cell Probes. 1998;12(5):301-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vojdani A, Choppa PC, Tagle C, Andrin R, Samimi B, Lapp CW. Detection of Mycoplasma genus and Mycoplasma fermentans by PCR in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1998;22(4):355-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gautam P, Karhinen L, Szwajda A, et al. Identification of selective cytotoxic and synthetic lethal drug responses in triple negative breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2016;15(1):34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Parri E, Kuusanmäki H, van Adrichem AJ, Kaustio M, Wennerberg K. Identification of novel regulators of STAT3 activity. PLoS One. 2020;15(3):e0230819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pemovska T, Kontro M, Yadav B, et al. Individualized systems medicine strategy to tailor treatments for patients with chemorefractory acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2013;3(12):1416-1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kuusanmäki H, Leppä AM, Pölönen P, et al. Phenotype-based drug screening reveals association between venetoclax response and differentiation stage in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2020;105(3):708-720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Potdar S, Ianevski A, Mpindi JP, et al. Breeze: an integrated quality control and data analysis application for high-throughput drug screening. Bioinformatics. 2020;36(11):3602-3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yadav B, Wennerberg K, Aittokallio T, Tang J. Searching for drug synergy in complex dose-response landscapes using an interaction potency model [published correction appears in Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2017;15:387]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2015;13:504-513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ianevski A, He L, Aittokallio T, Tang J. SynergyFinder: a web application for analyzing drug combination dose-response matrix data. Bioinformatics. 2017;33(15):2413-2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Metsalu T, Vilo J. ClustVis: a web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using principal component analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(W1):W566-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yadav B, Pemovska T, Szwajda A, et al. Quantitative scoring of differential drug sensitivity for individually optimized anticancer therapies. Sci Rep. 2014;4(1):5193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Xiong J, Cui BW, Wang N, et al. Genomic and transcriptomic characterization of natural killer T cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2020;37(3):403-419.e6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ryan J, Letai A. BH3 profiling in whole cells by fluorimeter or FACS. Methods. 2013;61(2):156-164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Misale S, Bozic I, Tong J, et al. Vertical suppression of the EGFR pathway prevents onset of resistance in colorectal cancers. Nat Commun. 2015;6(1):8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Garraway LA, Jänne PA. Circumventing cancer drug resistance in the era of personalized medicine. Cancer Discov. 2012;2(3):214-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Boumahdi S, de Sauvage FJ. The great escape: tumour cell plasticity in resistance to targeted therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19(1):39-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sharma SV, Lee DY, Li B, et al. A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell. 2010;141(1):69-80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tsutsui M, Yasuda H, Suto H, et al. Frequent STAT3 activation is associated with Mcl-1 expression in nasal NK-cell lymphoma. Int J Lab Hematol. 2010;32(4):419-426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Epling-Burnette PK, Liu JH, Catlett-Falcone R, et al. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling leads to apoptosis of leukemic large granular lymphocytes and decreased Mcl-1 expression. J Clin Invest. 2001;107(3):351-362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Venkatasubbarao K, Choudary A, Freeman JW. Farnesyl transferase inhibitor (R115777)-induced inhibition of STAT3(Tyr705) phosphorylation in human pancreatic cancer cell lines require extracellular signal-regulated kinases. Cancer Res. 2005;65(7):2861-2871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Raponi M, Belly RT, Karp JE, Lancet JE, Atkins D, Wang Y. Microarray analysis reveals genetic pathways modulated by tipifarnib in acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Cancer. 2004;4(1):56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Epling-Burnette PK, Sokol L, Chen X, et al. Clinical improvement by farnesyltransferase inhibition in NK large granular lymphocyte leukemia associated with imbalanced NK receptor signaling. Blood. 2008;112(12):4694-4698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sweet K, Hazlehurst L, Sahakian E, et al. A phase I clinical trial of ruxolitinib in combination with nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia patients with molecular evidence of disease. Leuk Res. 2018;74:89-96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fenaux P, Raza A, Mufti GJ, et al. A multicenter phase 2 study of the farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib in intermediate- to high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 2007;109(10):4158-4163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Skalniak L, Kocik J, Polak J, et al. Prolonged idasanutlin (RG7388) treatment leads to the generation of p53-mutated cells. Cancers (Basel). 2018;10(11):E396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kuusanmäki H, Dufva O, Parri E, et al. Drug sensitivity profiling identifies potential therapies for lymphoproliferative disorders with overactive JAK/STAT3 signaling. Oncotarget. 2017;8(57):97516-97527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Delgado-Martin C, Meyer LK, Huang BJ, et al. JAK/STAT pathway inhibition overcomes IL7-induced glucocorticoid resistance in a subset of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Leukemia. 2017;31(12):2568-2576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kam JC, Szefler SJ, Surs W, Sher ER, Leung DY. Combination IL-2 and IL-4 reduces glucocorticoid receptor-binding affinity and T cell response to glucocorticoids. J Immunol. 1993;151(7):3460-3466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Meyer LK, Huang BJ, Delgado-Martin C, et al. Glucocorticoids paradoxically facilitate steroid resistance in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias and thymocytes. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(2):863-876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Meyer LK, Verbist KC, Albeituni S, et al. JAK/STAT pathway inhibition sensitizes CD8 T cells to dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in hyperinflammation. Blood. 2020;136(6):657-668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Loh ML, Tasian SK, Rabin KR, et al. A phase 1 dosing study of ruxolitinib in children with relapsed or refractory solid tumors, leukemias, or myeloproliferative neoplasms: a Children’s Oncology Group phase 1 consortium study (ADVL1011). Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62(10):1717-1724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pufall MA. Glucocorticoids and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;872:315-333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Chen IM, Whalen M, Bankhurst A, et al. A new human natural killer leukemia cell line, IMC-1. A complex chromosomal rearrangement defined by spectral karyotyping: functional and cytogenetic characterization. Leuk Res. 2004;28(3):275-284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Drexler HG, Matsuo Y. Malignant hematopoietic cell lines: in vitro models for the study of natural killer cell leukemia-lymphoma. Leukemia. 2000;14(5):777-782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gong JH, Maki G, Klingemann HG. Characterization of a human cell line (NK-92) with phenotypical and functional characteristics of activated natural killer cells. Leukemia. 1994;8(4):652-658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Nagata H, Konno A, Kimura N, et al. Characterization of novel natural killer (NK)-cell and gammadelta T-cell lines established from primary lesions of nasal T/NK-cell lymphomas associated with the Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 2001;97(3):708-713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Robertson MJ, Cochran KJ, Cameron C, Le JM, Tantravahi R, Ritz J. Characterization of a cell line, NKL, derived from an aggressive human natural killer cell leukemia. Exp Hematol. 1996;24(3):406-415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Tsuchiyama J, Yoshino T, Mori M, et al. Characterization of a novel human natural killer-cell line (NK-YS) established from natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Blood. 1998;92(4):1374-1383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yagita M, Huang CL, Umehara H, et al. A novel natural killer cell line (KHYG-1) from a patient with aggressive natural killer cell leukemia carrying a p53 point mutation. Leukemia. 2000;14(5):922-930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Yoneda N, Tatsumi E, Kawano S, et al. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus genome in natural-killer-like cell line, YT. Leukemia. 1992;6(2):136-141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Nagata H, Numata T, Konno A, et al. Presence of natural killer-cell clones with variable proliferative capacity in chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Pathol Int. 2001;51(10):778-785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zhang Y, Nagata H, Ikeuchi T, et al. Common cytological and cytogenetic features of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive natural killer (NK) cells and cell lines derived from patients with nasal T/NK-cell lymphomas, chronic active EBV infection and hydroa vacciniforme-like eruptions. Br J Haematol. 2003;121(5):805-814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Loong SL, Hwang JS, Lim ST, et al. An Epstein-Barr virus positive natural killer lymphoma xenograft derived for drug testing. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49(6):1161-1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yang HG, Kang MC, Kim TY, et al. Discovery of a novel natural killer cell line with distinct immunostimulatory and proliferative potential as an alternative platform for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kawada J, Ito Y, Iwata S, et al. mTOR inhibitors induce cell-cycle arrest and inhibit tumor growth in Epstein-Barr virus-associated T and natural killer cell lymphoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(21):5412-5422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Xue W, Li W, Shang Y, et al. One method to establish Epstein-Barr virus-associated NK/T cell lymphoma mouse models. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(2):1509-1516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zhao S, Tang QL, He MX, et al. A novel nude mice model of human extranodal nasal type NK/T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2008;22(1):170-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.