Version Changes
Revised. Amendments from Version 1
In this new version, the methodology to evaluate key messages in papers about sporotrichosis was better detailed, replacing the "implications for practice", which, in fact, was not properly explored in the previous published version of this work. Also, the reasons behind database choices in this work were presented. Some references and small changes to the text were also performed, including the addition of % publications to Table 2, in order to clarify the meaning of our results and discussion.
Abstract
Background: Sporotrichosis has recently emerged as an important mycosis worldwide, with diverse transmission and epidemiologic profiles. For instance, in Brazil most cases are related to zoonotic transmission from naturally infected cats, and the majority of cases in China are due to external injury with environmental materials. Publications on sporotrichosis and on its etiologic agent may guide the direction of the research in this field. It can also define priorities for future studies.
Methods: In this study, we evaluated the trends of global research in Sporothrix and sporotrichosis, based on publications records retrieved from Scopus and Web of Science databases for the period of 1945 to 2018. The overall productivity in the field, its geographical and temporal distribution, research themes, co-authorship networks, funding sources, and if audience and research findings are addressed in the abstracts.
Results: A total of 4,007 unique publications involving 99 countries were retrieved, most of them published after 2000. Authors based on institutions from the United States of America and Brazil accounted for 57.4% of the publications. Brazil was the leading country in terms of research collaboration and networking, with co-authorship with 45 countries. The thematic mapping revealed a temporal shift from clinical to applied research. Despite the large number of countries publishing in this field, most of funded studies came from Brazil, Mexico, China, South Africa, or the United States of America. The analysis of content identified few specific public health recommendations for prevention, case-management, or research. Moreover, most papers do not have a clearly defined intended audience.
Conclusion: As the research in this field is emerging in several countries, with the generation of a large amount of data, it is necessary that scientists strengthen efforts to translate the research results into practice to curb this neglected infection.
Keywords: Bibliometrics, Network, Scientometry, Sporothrix, Sporotrichosis
Introduction
Sporotrichosis is a subcutaneous mycotic infection caused by dimorphic species of fungi belonging to the genus Sporothrix 1. It has a worldwide distribution, a broad range of clinical presentations, and can be fatal as an opportunistic infection in immunosuppressed patients 2. For more than one century, the etiological agent of sporotrichosis was identified as the sole species Sporothrix schenckii 3. However, in last years, using molecular biology techniques, it was possible to identify other sibling species that also cause sporotrichosis: Sporothrix brasiliensis, Sporothrix globosa, and, to a lesser extent, Sporothrix luriei, Sporothrix pallida, Sporothrix mexicana, and Sporothrix chilensis 4– 7. These agents can be found in the environment 1 and they present different clinical manifestations 8, virulence 9, drug susceptibility 10, and phenotypic characteristics 11.
The research about fungal diseases has been relatively neglected worldwide by public health authorities. The initiative “Global Action Fund for Fungal Infections” (GAFFI), an international non-governmental organization dedicated to combating fungal disease, was created to highlight gaps in diagnostics and treatments for fungal diseases as well as to fund raise and lobby global health agencies 12. GAFFI has identified some fungal infections as its highest priorities and sporotrichosis, along with other deep mycoses, is included 13. This organization has claimed that sporotrichosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, and fungal keratitis should be included in the WHO’s Neglected Tropical Diseases portfolio. This would be a big step towards increasing research funding and better care for patients with these serious diseases.
Bibliometric studies are frequently used to describe the global dynamics of knowledge generation and provide useful information on research discoveries, pointing at the strengths and weakness of new findings 14. As an example, through bibliometric analyses, based on quantitative and qualitative indicators, it was possible to assess the progress and collaboration in science, technology and innovation in the tuberculosis field 15. For instance, the co-authorship of scientific publications reveals collaborative patterns between individuals, organizations, or countries 16 and represents a formal statement of interaction between two or more researchers, being widely used to understand and assess collaboration profiles 17, 18. Bibliometric methods, however, have rarely been applied to the mycology field and not much is known about the extension and trends of Sporothrix research. Therefore, an assessment of the characteristics of the research focusing on sporotrichosis and its etiological agents is necessary to evaluate the progress of the findings in this field and the implications and impacts of sporotrichosis research for health practice.
Driven by the continued expansion of sporotrichosis in some countries such as Brazil, China, Mexico, and India 1, we analyzed the global scientific publications and scientific collaboration on the Sporothrix and sporotrichosis research field, with emphasis on the impact of the zoonotic epidemic of sporotrichosis in Brazil 2 and on the discovery of the new species genetically related to S. schenckii 5. We combined bibliometrics and social network analysis to generate evidence of the dynamics of the research community. Also, this research aims to evaluate a methodology to identify key messages and technical recommendations for action in the abstracts of the publications assessed, to check whether the research results were being translated into actions to curb sporotrichosis.
Methods
Source of data
Publications were retrieved from the Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus databases searching for the terms “ Sporothrix” or “sporotrichosis” on the title, abstract, and keyword fields. The review included original research articles, reviews, letters to the editor, and editorials from 1945 to 2018 (WoS Core Collection). For comparison purposes, the number of publications about other mycoses caused by dimorphic fungi (paracoccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, coccidiocomycosis, and blastomycosis) was also obtained, using the genus of the fungus and the name of the mycosis as the search query terms.
Cleaning and standardization of data
The data retrieved was imported into the text mining software VantagePoint 10.0 (Search Technology Inc. Norcross, GA, USA) and duplicate records were excluded. Names of institutions, countries, funding organizations, and journals were standardized using the VantagePoint list cleanup tool, and further manual processing. An open-access alternative for the use of VantagePoint 10.0 is the software OpenRefine 3.3.
Co-authorship network analyses
After cleaning and standardization, the data was formatted into adjacency matrixes to map co-authorship between countries and institutions based on authors’ professional affiliations. The matrixes were imported into the open-source software Gephi 0.9.1 for network visualization and calculation of metrics 19. Degree centrality was used to identify the most central institutions in the network, reflecting the significance of a network member (node) relative to all other nodes in the network. This metric takes into account the diverse means in which a node interacts and communicates with the rest of the network. The most important, or central ones, have a strategic impact in the network. The degree centrality can be explained as the number of direct links that a node has with other nodes. The more relational ties a node has, more power or prestige it may present in a network 20. Betweenness centrality was used to recognize organizations that mediated the connection between other institutions and their capacity to control the flow of information in the network 20. This metric reveals the extent to which a node works as a bridge among the other nodes in the network, which would otherwise be disconnected. For the spatial visualization of international collaboration, the authors’ professional affiliation country was manually geocoded and processed using the “ GeoLayout” 0.9.1.2 and “ Map of Countries” 1.5.1 plugins available within Gephi. In these networks, nodes represent countries or an institution, and two or more countries/institutions were connected if their researchers shared the authorship of one or more papers. As co-authorship involves reciprocal collaboration, all connections were considered as non-directional.
Mapping research themes
Term maps were created using the VOSviewer 1.6.6 software (Leiden University, the Netherlands) using terms obtained from titles and abstracts of all publications in the database. Each term was graphically denoted by a circle whose diameter and label size were directly proportional to their frequency. The software positions the circles closer to each other according to the power of the relationship and co-occurrence between terms. The mapping allowed a cluster analysis by research themes using a weighted and parameterized variant of modularity-based clustering to recognize groups of correlated terms 21.
Funding data
Funding acknowledgments on publications were only available as a searchable field in WoS and Scopus from late 2008. In order to achieve reliable coverage, only papers published from 2012 onwards were selected for this purpose. Funding agencies were identified, their names standardized (whenever possible), and the number of publications per funding agency summarized.
Retrieving key messages from abstracts
In order to evaluate the applicability of a wording methodology to retrieve key messages, a screening was performed by two independent evaluators in the abstracts for statements or recommendations for sporotrichosis research, case-management, and prevention, searching keywords related to prescriptive, tentative or informative languages. In addition, the two evaluators also searched the audience mentioned in the abstracts. Titles and abstracts were tabulated on a Microsoft Excel 2010 spreadsheet, and searched for terms related to statements and recommendations for research, practice or public health. A set of words related to tentative language (“may”, “might”, “speculate”, “suggest”, or “potentially”), prescriptive language (“must”, “propose”, “should”, “stress”, or “recommend”) or related to minimal advice (“consider”, “advise”, “notify”, or “inform”) was used in this process 22. The audiences to whom the recommendations were directed to (medical doctors, nurses, laboratory staff, or veterinarians) were also identified.
Statistical analysis
The software GraphPad Prism 5 was used to build linear regressions, to check the frequency of publications over time and to compare slopes of different best-fit lines. The Chi-square test was used to test for differences in proportions of “tentative”, “prescriptive”, and “minimal advice” from research results according to the country of origin in an attempt to identify how explicit was the research message to the scientific community, practitioners and public health professionals. A p<0.05 was considered to be significant.
Results
The scientific literature on Sporothrix and sporotrichosis
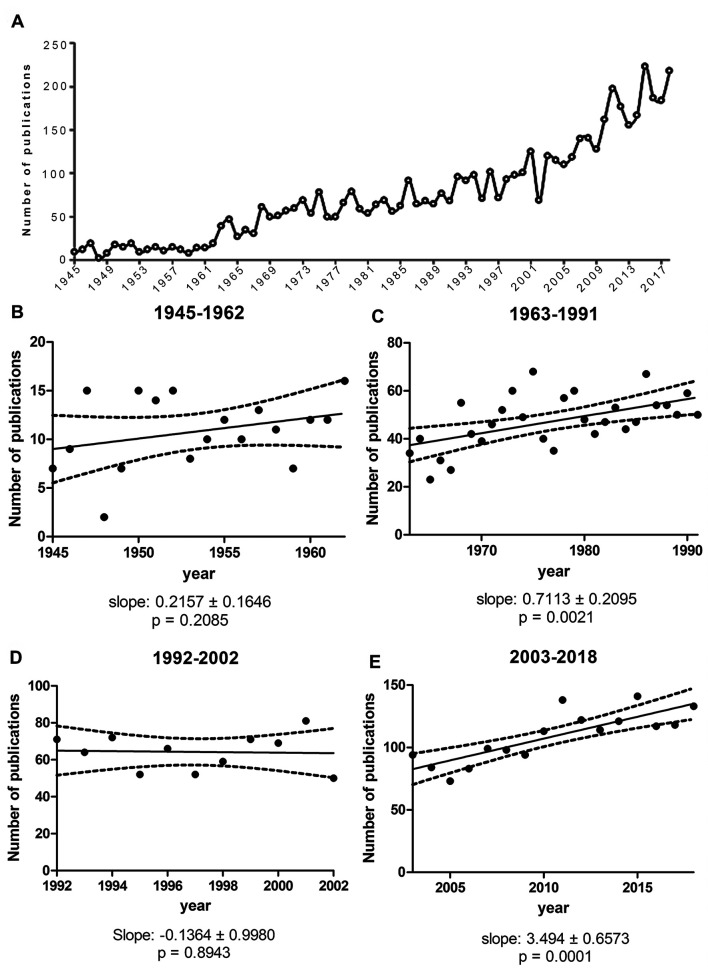
Sporotrichosis was found to be the mycosis caused by dimorphic fungi with the lowest number of publications in both databases used in this work ( Table 1). The literature search on the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field retrieved 1,868 publications from the WoS database and 3,660 publications from the Scopus database for the period of 1945 to 2018. After removing duplicate references present on both databases, new totals were 1,866 and 3,599 papers, respectively, with 1,458 publications present in both databases. The final data set resulted in 4,007 unique publications ( Figure 1; Underlying data 23). As depicted in Figure 2a, the overall number of publications on Sporothrix/sporotrichosis has increased steadily over the years. The frequency of publications reflecting the interest in the studied subject varied over time. Four periods could be identified: 1945 to 1962 ( Figure 2b), with an average of 10.8±3.7 publications per year; 1963 to 1991 ( Figure 2c), 47.2±11.3 papers per year; 1992 to 2002 ( Figure 2d), with 63.1±10.3 publications per year; and in the final period, 2003 to 2018 ( Figure 2e), 108.9±20.3 papers per year. Linear regressions of the number of publications per year were performed for each one of these periods and the results were as follows: In two of these periods, 1945–1962 and 1992–2002, the amount of publications per year was approximately constant (slopes of 0.2157 ± 0.1646 and -0.1364 ± 0.9980, p values of 0.2085 and 0.8943, respectively), whereas the two remaining periods, 1963–1991 and 2003–2018, presented increases in the publication numbers per year (slopes of 0.7113 ± 0.2095 and 3.494 ± 0.6573, p values of 0.0021 and 0.0001, respectively). The differences between the slopes were found to be extremely significant ( p < 0.0001).
Figure 1. Process of publication acquisition in the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field from the studied databases.
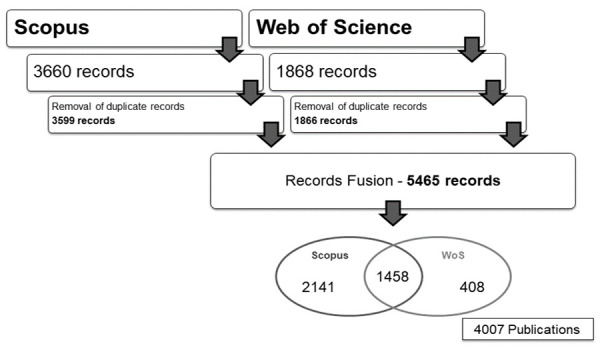
Figure 2. Global scientific production in the Sporothrix and Sporotrichosis field.
( a) Overall publication numbers per year (1945–2018). Trends in the number of publications on the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field are represented in a linear regression form for the following time periods: ( b) 1945–1962; ( c) 1963–1991; ( d) 1992–2002; ( e) 2003–2018. The continuous line represents the best-fit line for the linear regression. Dashed lines represent the 95% confidence interval of the best-fit line.
Table 1. Number of publications on dimorphic fungi and their respective mycoses retrieved from Web of Science and Scopus databases (1945 – 2018).
| Fungus / Disease | Number of publications per database | |
|---|---|---|
| Web of Science | Scopus | |
| Sporothrix / Sporotrichosis | 1,868 | 3,660 |
| Paracoccidioides / Paracoccidioidomycosis | 2,747 | 3,692 |
| Histoplasma / Histoplasmosis | 7,111 | 11,520 |
| Blastomyces / Blastomycosis | 2,513 | 6,491 |
| Coccidioides / Coccidiocomycosis | 3,312 | 5,786 |
Authorship by country
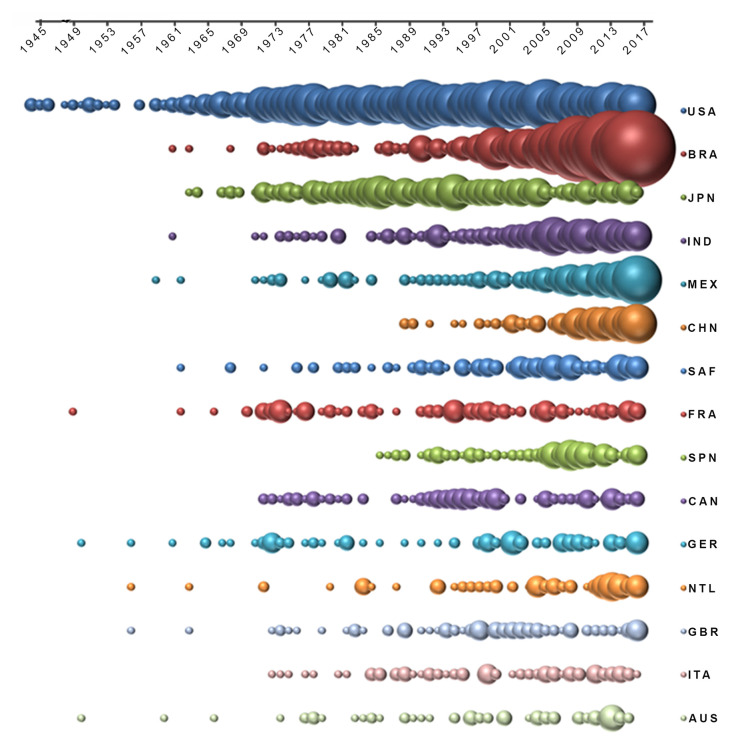
Authors from 99 countries accounted for the 4,007 publications on the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field. Table 2 lists the 20 most productive countries during the entire period studied and Figure 3 depicts the annual trends of the top 15 countries. The United States of America (USA) and Brazil were the leading countries, publishing together 2,300 publications (57.4% of all publications). The frequency of publications by these two countries differed considerably. After 1973, the USA showed a regular pattern of publications with a range of 15–44 and a median of 25 papers per year, while Brazil had up to 10 publications per year until 1999, with an exponential increase in the number of publications noticed after 2000. Overall, the frequency of publications from the Japan, France, and Canada remained stable throughout the studied period, whereas a significant increase was also observed for Mexico from 2007 onwards, and China from 2009 onwards.
Figure 3. Annual publication from the top 15 countries on numbers of articles in the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field.
The diameter of each circle is directly proportional to the annual number of publications. USA: United States of America; BRA: Brazil; JPN: Japan; IND: India; MEX: Mexico; CHN: China; SAF: South Africa; FRA: France; SPN: Spain; CAN: Canada; GER: Germany; NTL: The Netherlands; GBR: Great Britain; ITA: Italy; AUS: Australia.
Table 2. Top 20 countries in the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field (1945–2018) according to the author country of professional affiliation.
| Rank | Country | Number of publications | % publications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States of America | 1,315 | 32.8 |
| 2 | Brazil | 985 | 24.6 |
| 3 | Japan | 417 | 10.4 |
| 4 | India | 309 | 7.7 |
| 5 | Mexico | 275 | 6.9 |
| 6 | China | 190 | 4.7 |
| 7 | South Africa | 155 | 3.9 |
| 8 | France | 137 | 3.4 |
| 9 | Spain | 135 | 3.4 |
| 10 | Canada | 130 | 3.2 |
| 11 | The Netherlands | 106 | 2.6 |
| 12 | Germany | 105 | 2.6 |
| 13 | United Kingdom | 96 | 2.4 |
| 14 | Italy | 87 | 2.2 |
| 15 | Australia | 74 | 1.8 |
| 16 | Peru | 64 | 1.6 |
| 17 | Venezuela | 55 | 1.4 |
| 18 | Poland | 49 | 1.2 |
| 18 | South Korea | 49 | 1.2 |
| 19 | Colombia | 46 | 1.1 |
| 20 | Greece | 44 | 1.1 |
Scientific journals
Table 3 lists the top 15 journals (out of 1,182) with the highest number of articles on Sporothrix/sporotrichosis, along with their respective impact factors. Overall, the journals with most publications were Mycopathologia, Medical Mycology, Mycoses, the International Journal of Dermatology, and JAMA Dermatology. Since Brazil is the current leader on annual publications in this field ( Figure 3), the journals harboring these publications were also evaluated separately. When only publications with at least one Brazilian author were considered, in addition to Mycopathologia, Medical Mycology, Mycoses, and the International Journal of Dermatology, the journals PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, Frontiers in Microbiology, and four Brazilian scientific journals also appear listed among the top ten journals.
Table 3. Rank comparison scientific journals publishing global and Brazilian-based author articles on the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field (1945–2018).
The top 10 journals of each category are presented.
| Journal | Country | JIF Trend
2017/18 |
All Publications | Brazilian
Publications |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Papers (n) | Rank | Papers (n) | |||
| Mycopathologia | Netherlands | 1.476 | 1 | 283 | 2 | 68 |
| Medical Mycology | United Kingdom | 2.799 | 2 | 260 | 1 | 93 |
| Mycoses | Germany | 2.793 | 3 | 141 | 4 | 33 |
| International Journal of Dermatology | USA | 1.541 | 4 | 120 | 10 | 14 |
| JAMA Dermatology | USA | 8.107 | 5 | 96 | N/A | 0 |
| Clinical Infectious Diseases | USA | 9.117 | 6 | 80 | 13 | 11 |
| Journal of Clinical Microbiology | USA | 4.054 | 7 | 69 | 13 | 11 |
| Journal of the American Academy of
Dermatology |
USA | 6.898 | 8 | 57 | 21 | 3 |
| Revista Iberoamericana de
Micologia |
Spain | 0.989 | 9 | 51 | 14 | 10 |
| Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia | Brazil | 0.884 | 10 | 50 | 3 | 37 |
| Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de
Medicina Tropical |
Brazil | 1.358 | 22 | 26 | 5 | 26 |
| PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases | USA | 4.367 | 24 | 19 | 6 | 19 |
| Frontiers in Microbiology | Switzerland | 4.019 | 23 | 18 | 7 | 18 |
| Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz | Brazil | 2.833 | 21 | 16 | 8 | 16 |
| Revista do Instituto de Medicina
Tropical de São Paulo |
Brazil | 1.489 | 26 | 15 | 9 | 15 |
JIF – Journal Impact Factor N/A – Not available
Research trends
The analysis of term maps revealed five broad knowledge areas of the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis research ( Figure 4a): description of clinical aspects (green), treatment (yellow), epidemiology and taxonomy (blue), cellular biology (red), and susceptibility assays (pink). The most frequent topics throughout the period studied are represented in a heat map format ( Figure 4b), which shows that terms about clinical aspects were more frequent, followed by terms on taxonomy and cellular biology. Since we observed that in this century publications about Sporothrix and sporotrichosis increased considerably ( Figure 2e), we performed an analysis in two time periods - 1945–1999 ( Figure 4c) and 2000–2018 ( Figure 4d). This assessment revealed, in this last period of highly increasing publication numbers, a shift from research focused on treatment to other knowledge areas such as epidemiology and taxonomy.
Figure 4. Thematic maps of Sporothrix/sporotrichosis research generated with the VOSviewer software.
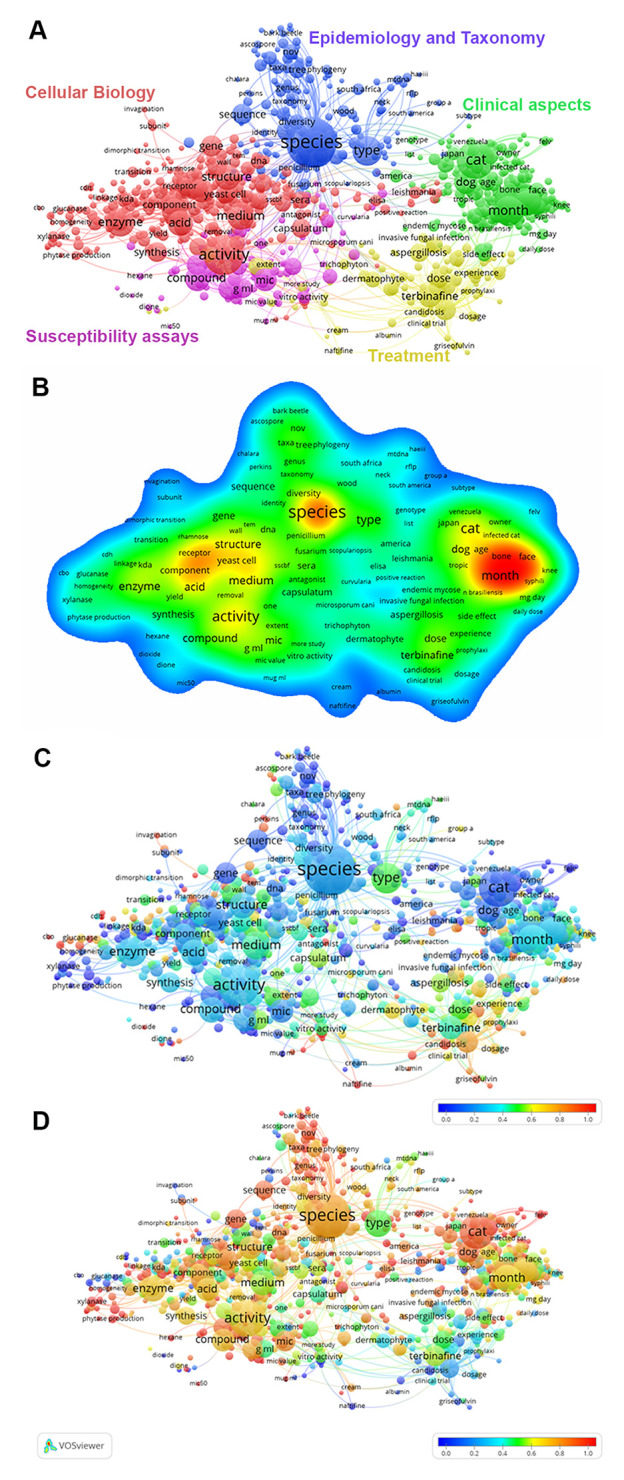
( a) Terms extracted from titles and abstracts clustered into five major research areas: cellular biology, epidemiology and taxonomy, clinical aspects, treatment, and susceptibility assays. Colors indicate clusters of terms that have co-occurred more frequently in the dataset. ( b) The heat map shows the most frequent terms in the period analyzed (1945–2018). The frequency was graded from blue to red; where red indicates a higher frequency. ( c) Research trends from 1945 to 1999. ( d) Research trends from 2000 to 2018. The diameters of the circles on a, c, and d panels are directly proportional to the occurrence of each term. Lines between different circles represent relationships between terms. The colors in c and d thematic maps indicate the occurrence of a term in each period. Blue represents a low occurrence, green an average occurrence, and red a high occurrence.
Network of countries
The international research network on Sporothrix and sporotrichosis was mapped according to the country affiliation of all authors. The network is formed by 99 countries, with a Brazilian leadership on collaborations. In fact, Brazilian authors have co-authorship with authors from 45 of the countries that compose the network ( Figure 5). The most frequent Brazilian collaborations were with institutions from the USA (84 publications), followed by the Netherlands (44 publications), Mexico (31 publications), Spain (23 publications), and France (16 publications).
Figure 5. Co-authorship map between Sporothrix/sporotrichosis researchers.
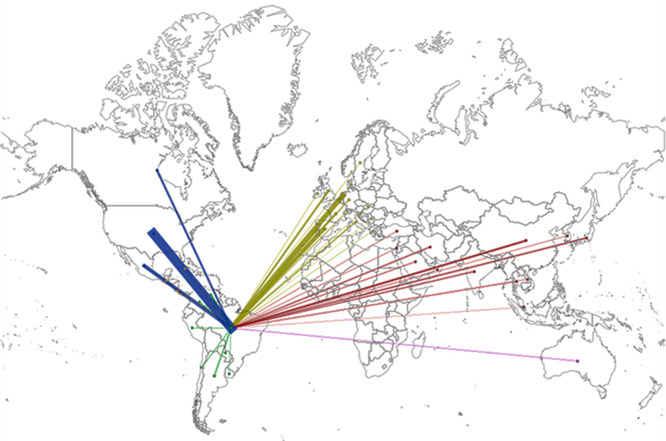
Brazilian network of scientific collaborations on the period studied. Country links were mapped based on the authors’ affiliations. Each node represents one country and two countries were considered connected if their researchers shared the authorship of a paper. Only relationships between the first author and their co-authors are shown. Links are color-coded according to the continent of the first author: North America – blue; Africa – dark green; Europe – yellow; South America – light green; Asia – red; Oceania – pink.
Network evolution among Brazilian institutions
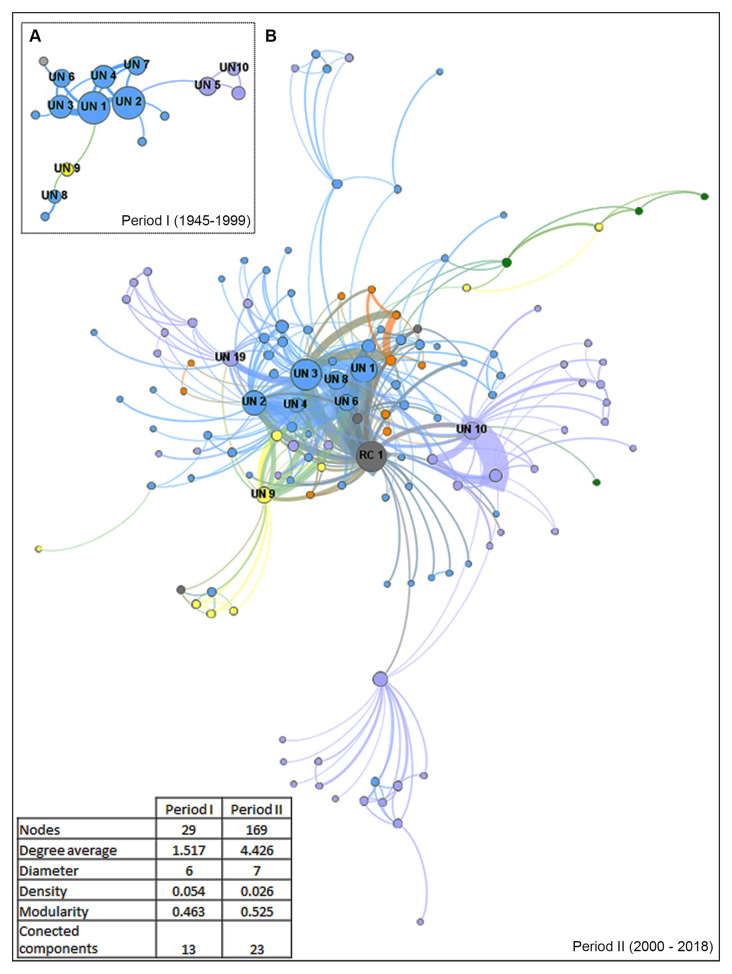
To further understand the dynamics of the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis research in the current leader country of publications, the evolution of Sporothrix research networks in Brazil was analyzed in the two-time intervals, 1945–1999 and 2000–2018, that is, before and after the beginning of the Brazilian zoonotic endemic of sporotrichosis ( Figure 6). In total, 29 institutions, mostly from the Southeast region, were present in the first period. The network core (giant component) was formed by 16 institutions: nine universities, one public foundation, and one private laboratory, all from the Southeast region, two universities and one hospital from the South region, one university from the Midwest region and one national research center. The network degree average was 1.5, indicating low connectivity in the network ( Figure 6a). The first three institutions with higher degree centrality in that period were federal universities located in the Brazilian Southeast region ( Table 4). For the second period, the number of institutions increased almost six times. The network was composed by 169 institutions, 135 of them within the giant component. The degree average increased four times (degree average: 4.426), showing a gain in the network connectivity ( Figure 6b). A national research center appears as the most central institution in the network, followed by three federal universities, central actors in the sporotrichosis network throughout the studied period. The ten most central organizations in these networks are shown in Table 4. Notably, most of them are from the Southeast region of the country (70% and 60% for 1945–1999 and 2000–2018, respectively).
Figure 6. Evolution of Sporothrix/sporotrichosis research networks involving Brazilian institutions.
( a) Research network from 1945 to 1999. ( b) Research network from 2000 to 2018. Each node represents one institution and two institutions were considered connected if their members shared the authorship of a paper. Nodes are color coded according to the geographic location of the institutions: North region - green; Northeast region – orange; Center-West region– yellow; Southeast region- blue; and South region – lilac. Multicampus National institutions are colored in gray. The size of the nodes is proportional to their centrality degree. For visualization purposes, only the giant component is shown. The top ten Brazilian organizations with highest degree centrality are labeled in each panel.
Table 4. Centrality Index of institutions in the Brazilian sporotrichosis collaboration network.
| Rank | Period I (1945–1999) | Period II (2000–2017) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Institutions | Degree | Betweenness
centrality |
Coauthored
Publications |
Institutions | Degree | Betweenness
centrality |
Coauthored
Publications |
|
| 1 |
UN1
(UFRJ) |
6 | 58.0 | 38 |
RC 1
(Fiocruz) |
44 | 3,041.99 | 313 |
| 2 |
UN2
(USP) |
6 | 57.0 | 26 |
UN 3
(UNIFESP) |
43 | 2,092.34 | 133 |
| 3 |
UN3
(UNIFESP) |
4 | 15.0 | 16 |
UN 1
(UFRJ) |
37 | 1,810.33 | 115 |
| 4 |
UN4
(UNESP) |
4 | 7.0 | 9 |
UN 2
(USP) |
32 | 797.79 | 93 |
| 5 |
UN5
(UFSM) |
3 | 26.0 | 6 |
UN 8
(UFMG) |
22 | 851.92 | 34 |
| 6 |
UN6
(UERJ) |
3 | 14.0 | 10 |
UN 10
(UFRGS) |
21 | 1,555.58 | 85 |
| 7 |
UN7
(UFF) |
3 | 0.0 | 4 |
UN 9
(UNB) |
18 | 694.66 | 27 |
| 8 |
UN8
(UFMG) |
2 | 14.0 | 10 |
UN 19
(UFPR) |
18 | 650.58 | 21 |
| 9 |
UN9
(UNB) |
2 | 26.0 | 2 |
UN 6
(UERJ) |
18 | 394.06 | 105 |
| 10 |
UN10
(UFRGS) |
2 | 0.0 | 2 |
UN 4
(UNESP) |
16 | 766.62 | 75 |
UFRJ: Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Southeast Brazil; USP: Universidade de São Paulo, Southeast Brazil; UNIFESP: Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Southeast Brazil; UNESP: Universidade Estadual Paulista, Southeast Brazil; UFSM: Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, South Brazil; UERJ: Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Southeast Brazil; UFF: Universidade Federal Fluminense, Southeast Brazil; UFMG: Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Southeast Brazil; UNB: Universidade de Brasília, Center Western Brazil; UFRGS: Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, South Brazil; UFPR: Universidade Federal do Paraná, South Brazil; Fiocruz: Fundação Oswaldo Cruz, Brazil.
Research funding
The analysis of funding acknowledgments was used as proxy information for research funding. A total of 457 (34%) articles out of 1,310 publications acknowledged funding during the period 2012 to 2018. Table 5 shows the top 10 funding agencies and the number of publications out of a total 236 funding organizations and initiatives. Five of them are from Brazil, two from Mexico, one from China, one from the USA, and one from South Africa.
Table 5. Top 10 funding organizations supporting publications on Sporothrix/sporotrichosis (2012 – 2018).
| Rank | Major Funding Organization | Number of funded
publications (%) |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CNPq - Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e
Tecnológico |
145 (11) | Brazil |
| 2 | CAPES - Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de
Nível Superior |
84 (6.4) | Brazil |
| 3 | FAPERJ - Fundação Carlos Chagas de Amparo à Pesquisa
do Estado do Rio de Janeiro |
64 (4.8) | Brazil |
| 4 | FAPESP - Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de
São Paulo |
61 (4.6) | Brazil |
| 5 | National Natural Science Foundation of China | 36 (2.7) | China |
| 6 | UG - Universidad de Guanajuato | 34 (2.6) | Mexico |
| 7 | CONACyT - Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología | 33 (2.5) | Mexico |
| 8 | FIOCRUZ - Fundação Oswaldo Cruz | 32 (2.4) | Brazil |
| 9 | NIH - National Institutes of Health | 22 (1.6) | United States of
America |
| 10 | DST/NRF Centre of Excellence in Tree Health Biotechnology
(CTHB) |
15 (1.1) | South Africa |
Statements about practice
An exploratory study on publications was conducted to assess the potential methodology for retrieve actionable messages. After excluding 1,262 articles with no published abstract, the type of language and the intended audience of the publications were assessed for 2,745 articles ( Table 6). Since Brazil was the current leading country publishing in the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field, we compared the frequency of statements related to research and practice on papers with at least one Brazilian author with those of authors from other countries exclusively. The proportion of papers presenting language compatible with tentative ( p = 0.0003) or minimal advice ( p = 0.0139) statements for sporotrichosis research was higher in the papers co-authored by Brazilians. The specific audience for the statements was mentioned in 167 abstracts. As depicted in Figure 7, most of the implications for practice were directed to medical doctors, followed by veterinarians, nurses, and laboratory technicians. Only 16 publications presented more than one audience, as indicated at the abstract. Some examples of actionable messages and their audiences are listed in Table 7.
Figure 7. Identification of specified audiences in publications about Sporothrix or sporotrichosis.
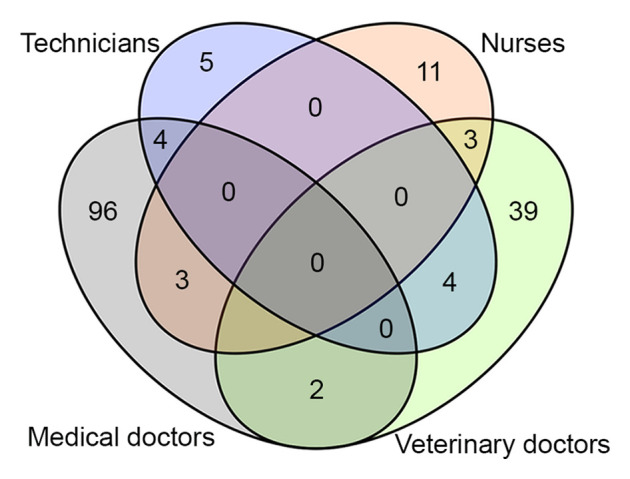
The Venn diagram was constructed based on four different audiences observed in the abstracts of the publications studied. Numbers on diagrams indicate how many abstracts reporting advice for medical doctors, veterinary doctors, nurses, and/or lab technicians were identified.
Table 6. Type of language statements and identified audience from Sporothrix and sporotrichosis articles (1945–2018).
| Statements with | Brazil | Other countries | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prescriptive language | 52 (9.5%) | 226 (10.3%) | 0.6576 |
| Tentative language | 195 (35.7%) | 613 (27.9%) | 0.0003 |
| Minimal advice | 78 (14.3%) | 230 (10.4%) | 0.0139 |
| Audience specified | 37 (6.8%) | 122 (5.5%) | 0.2714 |
Table 7. Examples of actionable messages found in article abstracts from papers evaluated in this study.
| Title of publication | PMID | Type of
language |
Audience
Specified |
actionable message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histopathology of canine
sporotrichosis: A morphological study of 86 cases from Rio de Janeiro |
19360480 | Prescriptive | No | Specific staining of serial sections is
recommended in the case of dogs with skin lesions whose histopathological presentation is consistent with sporotrichosis. |
| Sporotrichosis in cats: ABCD
guidelines on prevention and management |
23813827 | Prescriptive | Yes | Professionals must wear gloves when handling
cats with skin nodules and ulcers and dealing with diagnostic samples |
| Molecular cloning,
characterization and differential expression of DRK1 in Sporothrix schenckii |
23175272 | Tentative | No | SsDRK1 may be involved in the dimorphic
switch in S. schenckii. |
| Disseminated sporotrichosis
with extensive cutaneous involvement in a patient with AIDS |
10025867 | Tentative | Yes | It is important that clinicians be aware of the
presentation of this unusual opportunistic infection |
| Sporotrichosis in Himachal
Pradesh (north India) |
10492787 | Minimal advice | No | This study identifies Kangra district and
adjoining areas in Himachal Pradesh as an endemic region for sporotrichosis and highlights the need for evaluation of geo-climatically similar areas. |
| Unsuspected sporotrichosis in
childhood |
11332673 | Minimal advice | Yes | We urge clinicians to consider sporotrichosis
in the differential diagnosis of a solitary skin nodule. |
Discussion
The results herein presented demonstrate that research on Sporothrix and sporotrichosis is increasing worldwide. This increase could be even greater, because some regional or specialized journals may possibly not be indexed in the databases reviewed. However, considering the proposed focus, the authors believe that the study material was a comprehensive representation of the scientific production in the field.
The apparent fast engagement of authors from several countries in the late 90s can be explained by the global increase in the incidence of sporotrichosis 1, especially in Brazil 2 and China 24, two of the major countries currently publishing on this field. Historically, Brazil and China are also the leading countries reporting sporotrichosis cases, followed by South Africa, all of them with more than 3,000 human and animal cases reported 25. In this study, South Africa ranked as the seventh country on number of publications with no increasing trend. Most of the cases in this country occurred during an outbreak in the 1940’s 26. Although a new mine-related outbreak occurred more recently 27, there is no evidence that there is a re-emergence of sporotrichosis occurring in South Africa, which may explain its apparently constant number of publications in this field.
The number of publications on the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field usually followed crucial events that have driven to a shift on typical clinical cases of sporotrichosis. In the 1980s, with the development of ketoconazole, the first oral antifungal azole drug 28, and the emergence of AIDS, there was an increase in papers reporting results of sporotrichosis treatment 29, 30 and unusual severe forms of sporotrichosis related to immunosuppression 31– 33, coherent with the predominant thematic at the time. After 2007, the advances in polyphasic taxonomy of Sporothrix spp., driven by the worldwide increasing numbers of clinical cases 5, resulted in the description of several new pathogenic Sporothrix species 5– 7, which may explain the shift for epidemiology and taxonomy occurred in this century.
Authors from Brazil and the USA authored around 57% of the papers on the subject studied. Also, a high-level of collaboration between these two countries was seen, as occurred in other knowledge areas 34, 35. While the number of publications authored by researchers from the USA showed a consistent trend in the studied period, Brazilian authors have emerged as very productive in this field. Some factors that may have influenced the strong commitment of Brazilian researchers in the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis field include: (i) the zoonotic sporotrichosis epidemic, that begun in Rio de Janeiro state in 2000 36 and now is spreading to almost the totality of the Brazilian territory 37– 39; (ii) the increasing numbers of national and international Brazilian collaboration networks 40; and (iii) the beginning and still discrete recognition of the relevance of this research field by Brazilian funding agencies, which was detected in the funding analysis of this study.
The evaluation of co-authorship networks in sporotrichosis identified structural patterns of research involving Brazilian scientists. USA, Netherlands, Mexico, Spain, and France were Brazil’s most frequent collaborators. Government collaboration and research programs supported by the USA are in place since 1950’s, explaining the robust scientific collaboration between the countries 34.
Our initial analysis of the four periods revealed that two of them, 1945-1962 and 1992-2002, publications remained without significant variation. The strongest variation occurred after 2002, which coincides with the start of publications about the Brazilian zoonotic epidemics of sporotrichosis. Therefore, for subsequent analysis, we chose to separate the articles only in two periods: before and after the beginning of the Brazilian sporotrichosis epidemics. The Brazilian sporotrichosis research network has grown, almost six times in size, from the first (initial 54 years of low productivity) to the second period (last 18 years with a high level of publications), over the seven decades evaluated. This fact, together with the increase in the average degree and size of the giant component, that is, the network core, indicated a strengthening of network cohesion for collaboration over the years. It is worth noting that the measure of centrality is not related to the volume of publications, but to the capacity to aggregate collaboration. The centrality analysis of the interinstitutional network highlighted the current role of one national research center in promoting collaboration and knowledge spreading in the sporotrichosis field. This same research center also has a centrality on the research of other infectious diseases 15, 41. High degree centrality from a research center indicated a strong collaborative pattern in research 15. Together with other institutions, the Federal Universities in Southeast Brazil had a vital role in maintaining the connection between the overall research network and in ensuring that the less well-connected organizations gained access to new knowledge and information on sporotrichosis during the period studied. It is interesting to note that just recently, sporotrichosis has spread to the Northeast 39 and Midwest regions of the country 38, which means that, in the future, institutions from these regions may have a more important role in the collaboration network.
The network evolution was accompanied by a shift in the research trends. When comparing the first period to the 2000 onwards, the basic biomedical research profile gained more importance and became most frequent. The diversity of research trends may be related to the continued increase of institutions engagement in the Sporothrix/sporotrichosis network, providing new insights through new collaborations, showing the effectiveness of the research network in knowledge generation, sharing and diffusion. A similar scenario was observed in dengue research networks 42.
The current funding scenario for fungal infections has a negative perspective. Only cryptococcal meningitis was classified within the most poorly funded neglected diseases by the G-Finder survey (a reference publication for research funding flows on neglected infectious), receiving less than 0.5% of global funding 43. Other clinically relevant fungal infections (paracoccidioidomycosis, mycetoma, sporotrichosis, and chromoblastomycosis) were not even quoted in the G-Finder report. In fact, a recent study noticed that some fungal diseases, including sporotrichosis, have received negligible funding 44. Our study corroborates these findings, showing that, with the exception of Brazil, possibly because of the expanding sporotrichosis endemic areas 37– 39, other countries are not strongly committed to sporotrichosis funding research.
This work aimed to evaluate the applicability of a methodology proposed to retrieve key messages from abstracts. Traditionally, the scientific publication is the most frequent method of disseminating research results for a possible transfer of knowledge. In the ideal scenario, scientific articles and their abstracts should present a summary of the results, as well as the main conclusions and recommendations, when appropriate. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), five aspects should be taken into account for knowledge transfer: i) the presence of a clear message; ii) defined target audience; iii) communication strategy; iv) the method of transfer and, finally; v) the evaluation of the effect of the transferred message. Identifying the first two of these five points in a publication is key to bringing the results to action 45. In our analysis, we recovered in publications co-authored by Brazilian researchers more words related to tentative and minimal advice than in papers written by authors from other countries. This could be related to a concern of Brazilian researchers to address the major public health problem that sporotrichosis has become in the country 2, 37, which has certainly affected the overall number of publications. The screening method proved to be an efficient tool to identify and recovery recommendation messages in the abstracts. New words should be added to the recovery method to improve its sensitivity (For example: need, ought, necessary, reinforce, advice, highlight).
The fact that some journals have a specific audience (for instance, four of the top ten journals are directed to medical doctors interested in dermatology) may bias the nature of recommendations. However, as abstracts are the first contact for the readers with a publication, we believe mentioning statements or recommendations for practice in this section can improve the visibility of the research. Also, the analysis of contents revealed that a minor proportion of publications is directed to more than one specific audience, which is one indicator of a poor translational research in the studied field.
This study is based on a bibliometric approach to observe the evolution of the world scientific literature and identify research trends of sporotrichosis field, focusing in the Brazilian scenario. As a methodological approach, some national, regional or specialized journals indexed in regional databases such as SciELO and LILACS were not included, due to the difficulty to obtain total equivalence for a global analysis, since other regional databases should be included as well, making data harmonization difficult.
The retrieving key messages wording review based solely on abstracts is another limitation of this study. However, abstracts are the most widely read summaries of research findings and are an important source of information for clinicians and policy makers; particularly abstracts published in high profile journals. In this work, the proposal was validate the methodology of recovering. Future analysis is necessary to understand the translation scientific research into policies and practical applications.
Despite cases being reported all around the globe 1, sporotrichosis remains a neglected disease in terms of research interest, funding and medical attention. The growth of research on sporotrichosis needs to be translated into practical applications on diagnosis, treatment, and prevention, given the limited tools available for rapid tests 2, the cost-effective treatment 46, and the lack of effective vaccines 47. The challenge is to share and advance knowledge to curb this disease. The funding agencies have a critical role to play in this context.
Data availability
Underlying data generated in this study are available at Open Science Framework: Bibliometric assessment of sporotrichosis research. https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/MXU6V 23
This project contains the following underlying data:
-
-
(F1_T1) Countries publication by years.xlsx (All countries with sporotrichosis publications)
-
-
(F2) MapVoS.txt (Map file for VOSViewer software)
-
-
(F2) NetVoS.txt (Network file for VOSViewer software)
-
-
(F3) CountryNet.gephi (Country map file for Gephi software)
-
-
(F4) Period I.gephi (Network file for Gephi Software)
-
-
(F4) Period II.gephi (Network file for Gephi Software)
-
-
(T2) Source.xlsx (All Journals with retrieved publications about sporotrichosis)
-
-
(T3) Funding BR 12_18.xlsx (Funding agencies supporting sporotrichosis research)
-
-
(T4) Actionable messages.xlsx (implications for practice on retrieved articles)
Data are available under the terms of the Creative Commons Zero "No rights reserved" data waiver (CC0 1.0 Public domain dedication).
Funding Statement
Software licenses were funded by the Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia de Inovação em Doenças de Populações Negligenciadas (INCT-IDPN). RMZ-O was supported in part by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico [CNPq 302796/2017-7] and Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro [FAPERJ E-26/202.527/2019]. This work was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
[version 2; peer review: 2 approved
References
- 1. Chakrabarti A, Bonifaz A, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, et al. : Global epidemiology of sporotrichosis. Med Mycol. 2015;53(1):3–14. 10.1093/mmy/myu062 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Orofino-Costa R, Macedo PM de, Rodrigues AM, et al. : Sporotrichosis: an update on epidemiology, etiopathogenesis, laboratory and clinical therapeutics. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92(5):606–20. 10.1590/abd1806-4841.2017279 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Lopes-Bezerra LM, Schubach A, Costa RO: Sporothrix schenckii and sporotrichosis. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2006;78(2):293–308. 10.1590/s0001-37652006000200009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Morrison AS, Lockhart SR, Bromley JG, et al. : An environmental Sporothrix as a cause of corneal ulcer. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2013;2:88–90. 10.1016/j.mmcr.2013.03.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Marimon R, Cano J, Gené J, et al. : Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana, three new Sporothrix species of clinical interest. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45(10):3198–206. 10.1128/JCM.00808-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Marimon R, Gené J, Cano J, et al. : Sporothrix luriei: a rare fungus from clinical origin. Med Mycol. 2008;46(6):621–5. 10.1080/13693780801992837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Rodrigues AM, Cruz Choappa R, Fernandes GF, et al. : Sporothrix chilensis sp. nov. (Ascomycota: Ophiostomatales), a soil-borne agent of human sporotrichosis with mild-pathogenic potential to mammals. Fungal Biol. 2016;120(2):246–64. 10.1016/j.funbio.2015.05.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Almeida-Paes R, de Oliveira MME, Freitas DFS, et al. : Sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Sporothrix brasiliensis is associated with atypical clinical presentations. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8(9):e3094. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Arrillaga-Moncrieff I, Capilla J, Mayayo E, et al. : Different virulence levels of the species of Sporothrix in a murine model. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009;15(7):651–5. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02824.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Marimon R, Serena C, Gené J, et al. : In vitro antifungal susceptibilities of five species of Sporothrix. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52(2):732–4. 10.1128/AAC.01012-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Almeida-Paes R, de Oliveira LC, Oliveira MME, et al. : Phenotypic characteristics associated with virulence of clinical isolates from the Sporothrix complex. BioMed Res Int. 2015;2015: 212308. 10.1155/2015/212308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Global Action Fund for Fungal Infections: 95–95 by 2025. Improving outcomes for patients with fungal infections across the world: a roadmap for the next decade.2015. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 13. Global Action Fund for Fungal Infections: Gaffi - fact sheet: sporotrichosis. [cited 2019 Aug 14].2018. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 14. Joshi MA: Bibliometric indicators for evaluating the quality of scientifc publications. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2014;15(2):258–62. 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Fonseca BPF, da Silva MV, de Araújo KM, et al. : Network analysis for science and technology management: Evidence from tuberculosis research in Fiocruz, Brazil. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0181870. 10.1371/journal.pone.0181870 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Melin G, Persson O: Studying research collaboration using co-authorships. Scientometrics. 1996;36(3):363–77. 10.1007/BF02129600 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Fonseca BPF, Sampaio RB, Fonseca MVA, et al. : Co-authorship network analysis in health research: method and potential use. Health Res Policy Syst. 2016;14(1):34. 10.1186/s12961-016-0104-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Sampaio RB, Fonseca BPF, Bahulkar A, et al. : Network analysis to support public health: evolution of collaboration among leishmaniasis researchers. Scientometrics. 2017;111(3):2001–21. 10.1007/s11192-017-2346-6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M: Gephi : An Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks.2009;2. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 20. Freeman LC: Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc Netw. 1978;1(3):215–39. 10.1016/0378-8733(78)90021-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Waltman L, van Eck NJ, Noyons ECM: A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks. J Informetr. 2010;4(4):629–35. 10.1016/j.joi.2010.07.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Lynn J, Owens AP, Bartunek JM: Clarity and strength of implications for practice in medical journal articles: an exploratory analysis. BMJ Qual Saf. 2011;20(Suppl 1):i52–57. 10.1136/bmjqs.2010.046532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Albuquerque PC, Almeida-Paes R: Bibliometric assessment of sporotrichosis research.2020. 10.17605/OSF.IO/MXU6V [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Chen M, Xu Y, Hong N, et al. : Epidemiology of fungal infections in China. Front Med. 2018;12(1):58–75. 10.1007/s11684-017-0601-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Zhang Y, Hagen F, Stielow B, et al. : Phylogeography and evolutionary patterns in Sporothrix spanning more than 14 000 human and animal case reports. Persoonia. 2015;35:1–20. 10.3767/003158515X687416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Quintal D: Sporotrichosis infection on mines of the Witwatersrand. J Cutan Med Surg. 2000;4(1):51–4. 10.1177/120347540000400113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Govender NP, Maphanga TG, Zulu TG, et al. : An outbreak of lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis among mine-workers in South Africa. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9(9):e0004096. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Gupta AK, Lyons DCA: The rise and fall of oral ketoconazole. J Cutan Med Surg. 2015;19(4):352–7. 10.1177/1203475415574970 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Martins JE, Mendonça PR, Cucé LC: Tratamento da esporotricose com cetoconazol. Rev Hosp Clin. 1982;37(2):92–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Samorodin CS, Sina B: Ketoconazole-treated sporotrichosis in a veterinarian. Cutis. 1984;33(5):487–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Fitzpatrick JE, Eubanks S: Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome presenting as disseminated cutaneous sporotrichosis. Int J Dermatol. 1988;27(6):406–7. 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1988.tb02389.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Lipstein-Kresch E, Isenberg HD, Singer C, et al. : Disseminated Sporothrix schenckii infection with arthritis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1985;12(4):805–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Penn CC, Goldstein E, Bartholomew WR: Sporothrix schenckii meningitis in a patient with AIDS. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;15(4):741–3. 10.1093/clind/15.4.741 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Albuquerque PC, Fonseca BPF, Girard-Dias W, et al. : Mapping the Brazilian microscopy landscape: A bibliometric and network analysis. Micron. 2019;116:84–92. 10.1016/j.micron.2018.10.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. González-Alcaide G, Salinas A, Ramos JM: Scientometrics analysis of research activity and collaboration patterns in Chagas cardiomyopathy. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018;12(6):e0006602. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006602 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. de Lima Barros MB, Schubach TM, Galhardo MC, et al. : Sporotrichosis: an emergent zoonosis in Rio de Janeiro. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2001;96(6):777–9. 10.1590/s0074-02762001000600006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Freitas DFS, do Valle ACF, et al. : Epidemiological aspects of sporotrichosis epidemic in Brazil. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2015;9(4):238–45. 10.1007/s12281-015-0237-y [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Araújo LTR, Silva WA, Juliano RS: Região fronteriça e epidemiologia: Estudo da esporotricose e sua relação na dinâmica da fronteira Brasil-Bolívia. Rev GeoPantanal. 2017;12:97–105. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 39. Silva GM, Howes JCF, Leal CAS, et al. : Surto de esporotricose felina na região metropolitana do Recife. Pesq Vet Bras 2018;38(9):1767–71. 10.1590/1678-5150-pvb-5027 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Lang PB, Gouveia FC, Leta J: Health research networks on the web: an analysis of the Brazilian presence. Cad Saude Publica. 2014;30(2):369–78. 10.1590/0102-311X00136812 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Mota FB, Fonseca BPFE, Galina AC, et al. : Mapping the dengue scientific landscape worldwide: a bibliometric and network analysis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2017;112(5):354–63. 10.1590/0074-02760160423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Fonseca BPFE, Zicker F: Dengue research networks: building evidence for policy and planning in Brazil. Health Res Policy Syst. 2016;14(1):80. 10.1186/s12961-016-0151-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Chapman DN, Doubell A, Oversteegen L, et al. : Policy cures research.121. [Google Scholar]
- 44. Rodrigues ML, Albuquerque PC: Searching for a change: The need for increased support for public health and research on fungal diseases. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018;12(6):e0006479. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006479 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Nedjat S, Nedjat S, Gholami J, et al. : How much importance do we give to target audiences in article writing? Int J Prev Med. 2010;1(1):11–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Mahajan VK: Sporotrichosis: An Overview and Therapeutic Options. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014: 272376. 10.1155/2014/272376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. García-Carnero LC, Pérez-García LA, Martínez-Álvarez JA, et al. : Current trends to control fungal pathogens: exploiting our knowledge in the host-pathogen interaction. Infect Drug Resist. 2018;11:903–13. 10.2147/IDR.S170337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]