Abstract
Ferroptosis has recently attracted much interest because of its relevance to human diseases such as cancer and ischemia‐reperfusion injury. We have reported that prolonged severe cold stress induces lipid peroxidation‐dependent ferroptosis, but the upstream mechanism remains unknown. Here, using genome‐wide CRISPR screening, we found that a mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake regulator, mitochondrial calcium uptake 1 (MICU1), is required for generating lipid peroxide and subsequent ferroptosis under cold stress. Furthermore, the gatekeeping activity of MICU1 through mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) is suggested to be indispensable for cold stress‐induced ferroptosis. MICU1 is required for mitochondrial Ca2+ increase, hyperpolarization of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and subsequent lipid peroxidation under cold stress. Collectively, these findings suggest that the MICU1‐dependent mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostasis‐MMP hyperpolarization axis is involved in cold stress‐induced lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis.
Keywords: Ca2+, cold stress‐induced ferroptosis, CRISPR screening, MICU1, mitochondria
Subject Categories: Autophagy & Cell Death, Membrane & Intracellular Transport
This study identifies MICU1 as a key regulator for lipid peroxidation and subsequent ferroptosis under cold stress, suggesting that MICU1 can be a potential target for preventing cell death in organ preservation.
Introduction
Ferroptosis, an iron‐dependent and lipid peroxidation‐induced regulated necrosis, has been defined (Dixon et al, 2012) and has received much attention because of its relevance to various diseases, such as cancer, neurodegeneration, and ischemia‐reperfusion injury (Angeli et al, 2017; Stockwell et al, 2017; Friedmann Angeli et al, 2019; Nakamura et al, 2019). Ferroptosis is caused by the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), particularly lipid ROS. In addition, it has recently been proposed that in cysteine deprivation‐induced ferroptosis, the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) is hyperpolarized associated with lipid ROS accumulation (Gao et al, 2019). Upon lipid ROS accumulation, glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) and ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1, also known as AIFM2) play important roles in scavenging lipid ROS and preventing ferroptosis (Yang et al, 2014; Ingold et al, 2018; Bersuker et al, 2019; Doll et al, 2019). Therefore, inhibitors targeting GPX4 or FSP1 and reagents disrupting the cellular metabolism of their substrates, e.g., glutathione or coenzyme Q10, are known to induce ferroptosis (Dixon et al, 2012; Yang et al, 2014; Shimada et al, 2016; Doll et al, 2019). Without using these artificial inducers, we have recently reported that cold stress also induces lipid ROS‐dependent ferroptosis (Hattori et al, 2017), but the molecular mechanisms by which cold stress leads to accumulated lipid ROS remain largely unknown.
Changes in extracellular temperature affect various cellular functions, such as proteostasis, metabolism, and membrane fluidity. Cold stress‐induced tissue damage during organ preservation is an example of clinical environment. Recently, some organ preservation methods have been developed, including a machine perfusion system (Jing et al, 2018) and preservation solution supplemented with iron chelators (Lautenschläger et al, 2018). However, there are few drugs targeting the molecules or mechanisms of cold stress‐induced tissue damage. We have reported that severe cold stress drives the lipid ROS accumulation and subsequent activation of the ASK1‐p38 pathway, which culminates in ferroptosis (Hattori et al, 2017).
In this study, using genome‐wide CRISPR screening, we identified mitochondrial calcium uptake 1 (MICU1), as one of the regulators of ferroptosis under cold stress. MICU1 has been characterized as an essential molecule for gatekeeping and activating mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) during mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake (Perocchi et al, 2010; Mallilankaraman et al, 2012; Csordás et al, 2013; Kamer & Mootha, 2014; Patron et al, 2014). We found that some domains, which have been shown to be necessary for MICU1‐dependent MCU activation, are also required for cold stress‐induced lipid ROS accumulation and subsequent cell death. Moreover, as observed in typical ferroptosis induced by cysteine deprivation (Gao et al, 2019), MMP was hyperpolarized with mitochondrial Ca2+ influx under cold stress. Collectively, we demonstrate that MICU1‐dependent mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and the resultant MMP hyperpolarization facilitate lipid ROS accumulation, which plays a central role in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
Results and Discussion
MICU1 deficiency suppresses cold stress‐induced ferroptosis
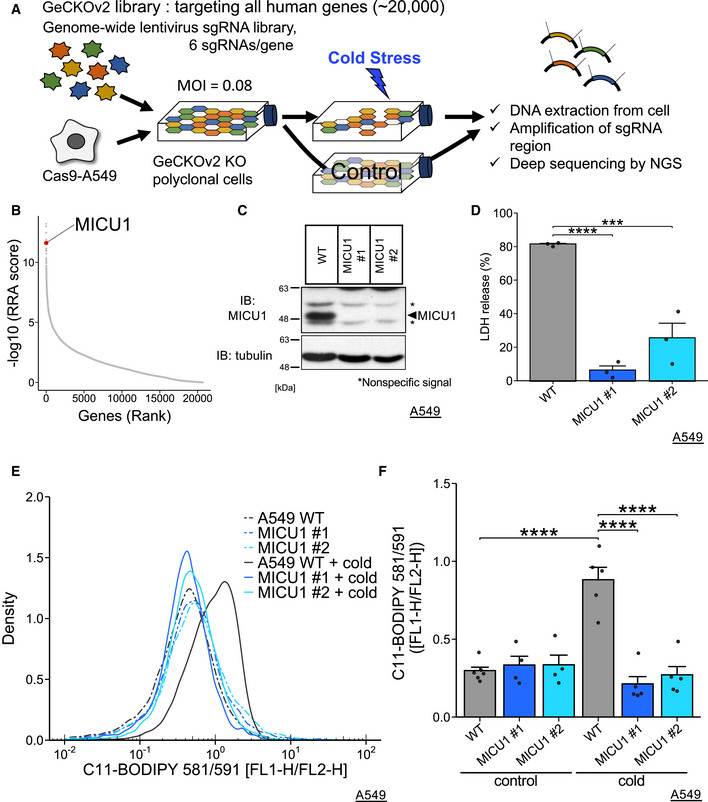
To identify the genes required for cold stress‐induced ferroptosis, we performed a genome‐wide CRISPR screening (Fig 1A) of A549 cells stably expressing Cas9 (Cas9‐A549 cells). We chose A549 cells because cold stress‐induced ferroptosis of A549 cells was readily reproducible and well characterized (Hattori et al, 2017). The cells were infected with an extremely low infection ratio (MOI = 0.08) with a lentivirus‐based GeCKOv2 library (Sanjana et al, 2014; Shalem et al, 2014). The cells were divided into two groups after puromycin selection for 3 days; then, cold stress was applied for 30 h and repeated twice (for details, see methods). Then, the surviving cells were harvested, and genomic DNA was deep‐sequenced to obtain reads counts for each sgRNA. The reads counts were analyzed by the MAGeCK program (Li et al, 2014). Evaluating by a beta score, a well‐known ferroptosis inducer (ACSL4) and ferroptosis suppressors (GPX4, AIFM2, and SLC7A11) were found outside the ± 2 × SD range as genes required for cell death and cell survival, respectively (Fig EV1A).
Figure 1. MICU1 deficiency suppresses cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
-
ASchematic model showing the design of the screening.
-
BMICU1 was identified using the MAGeCK program with a robust ranking aggregation (RRA) score.
-
CImmunoblots of endogenous MICU1 for validating gene knockout. *Nonspecific signals.
-
DLDH assay was performed after 24 h of cold stress on ice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001 by one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.
-
E,FLipid peroxidation was measured by C11‐BODIPY 581/591 after cold stress for 5 h. Representative plots are shown in (E), and the data (F) are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4–6, biological replicates. ****P < 0.0001, *** P < 0.001 by two‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test
Source data are available online for this figure.
Figure EV1. Analysis of screening, and mitochondria itself is involved in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis, related to Fig 1.
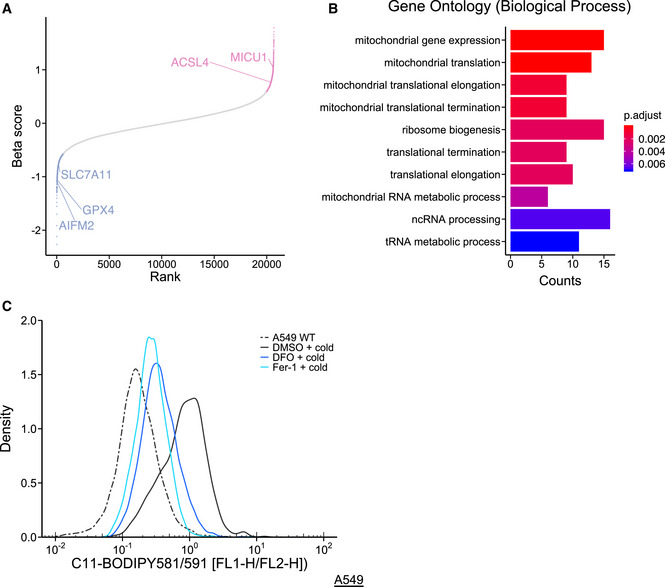
- Some genes are described as ferroptosis inducer or suppressors for the adequate evaluation of this screening. A well‐known ferroptosis inducer, acyl‐CoA synthetase long‐chain family member 4 (ACSL4) and ferroptosis suppressors, ferroptosis suppressor 1 (FSP1 also known as AIFM2), glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), and solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11), are highlighted after analyzing the count data from CRISPR screening using the MAGeCK program. Red and blue genes are outside of the 2 × SD range and candidates of ferroptosis inducers and suppressors, respectively, which are enriched in MAGeCKFlute packages.
- Results of Gene Ontology (GO) analysis with biological process. After analysis of count data using MAGeCK, positive genes (cut‐off of P < 0.01, see also Dataset EV1) were analyzed by GO analysis using clusterProfiler packages for R.
- Lipid peroxidation was measured by C11‐BODIPY 581/591 after cold stress for 5 h. Representative density plot is presented as reported previously (Hattori et al, 2017). Deferoxamine (DFO, 200 µM) and ferrostatin‐1 (Fer‐1, 1 µM) were pretreated for 30 min before cold stress.
Evaluated by a robust ranking aggregation (RRA) score using the MAGeCK program, the genes required for cold stress‐induced cell death were determined on the basis of the requirements for a P < 0.01 (Dataset EV1). When these genes were analyzed by GO analysis (Yu et al, 2012), mitochondria‐related genes were found to be highly enriched (Fig EV1B). Although a recent report suggests that the mitochondria play an important role in ferroptosis (Gao et al, 2019), the molecular mechanisms remained largely unknown. In terms of mitochondrial function and high RRA score, we were interested in MICU1 (Fig 1B). MICU1 was reported to be involved in apoptosis (Mallilankaraman et al, 2012; Csordás et al, 2013; Hall et al, 2014) but not necrosis.
MICU1‐knockout single clones were established by CRISPR/Cas9 knockout using two different sgRNAs (Fig 1C). Wild‐type (WT) A549 cells and MICU1‐knockout cells were exposed to sustained cold stress for 24 h, and cell death was measured by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release (Fig 1D). MICU1 deficiency attenuated cold‐induced cell death. Moreover, MICU1 knockdown by siRNA also reduced the rate of cell death induced by cold stress (Fig EV2A and B).
Figure EV2. MCU deficiency does NOT suppress cold stress‐induced ferroptosis, related to Figures 1 and 2.
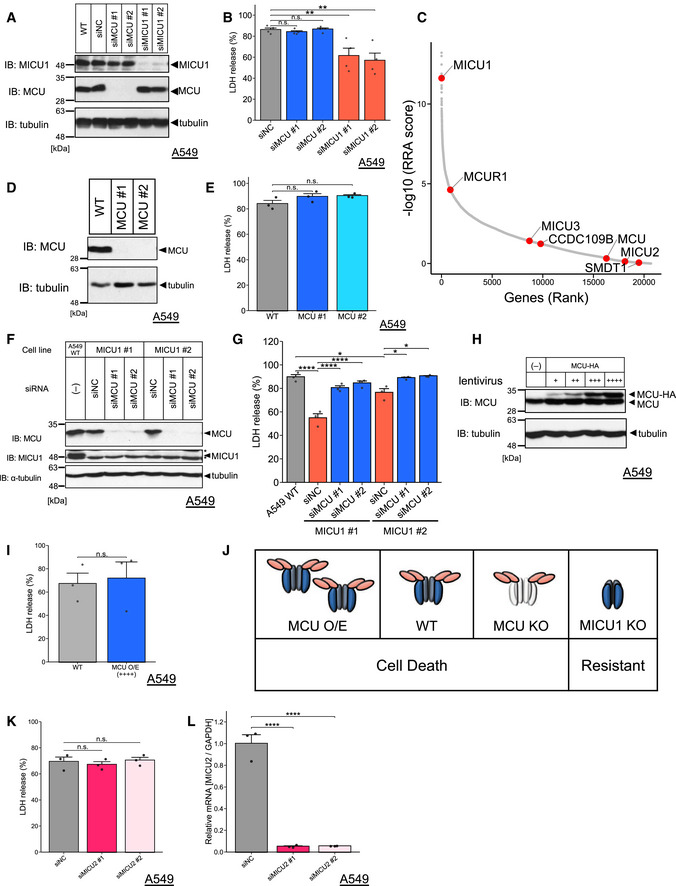
- Immunoblots of endogenous MICU1 or MCU signals after siRNAs transfection in the WT A549 cells.
- LDH release was measured after cold stress for 24 h. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4 (B), biological replicates, **P < 0.01, n.s.: not significant, one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test.
- Components of the MCU complex (MCU, MCUR1, MCUb (CCDC109B), MICU1, MICU2, MICU3, and EMRE (SMDT1)) are highlighted in red in the RRA score plot calculated by the MAGeCK program.
- Immunoblots of endogenous MCU signals after Cas9/sgRNA lentivirus infection in the WT A549 cells.
- LDH release was measured after cold stress for 24 h. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates, n.s.: not significant, one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test.
- Immunoblots of endogenous MICU1 or MCU signals after siRNAs transfection in the WT A549 cells and MICU1‐KO cells.
- LDH release was measured after cold stress for 24 h. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates, ****P < 0.0001, *P < 0.05, one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.
- Immunoblots of endogenous and overexpressing MCU signals after MCU‐HA lentivirus infection in the WT A549 cells.
- LDH release was measured after cold stress for 24 h. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates, n.s.: not significant, unpaired t‐test.
- Schematic model for MICU1 and MCU expression and its effect on cell death induced by cold stress.
- LDH release was measured after cold stress for 16 h. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates, n.s.: not significant, one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test.
- MICU2 mRNA was quantified by RT–qPCR. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates, ****P < 0.0001, one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test.
To investigate the requirement of MICU1 for lipid peroxidation, we used C11‐BODIPY 581/591 to measure lipid peroxidation (Drummen et al, 2002). Lipid peroxidation was clearly increased in WT A549 cells after cold stress for 5 h, but not in the presence of iron chelator: deferoxamine (DFO), or a radical trapping antioxidant: ferrostatin‐1 (Fer‐1) as previously shown (Fig EV1C) (Hattori et al, 2017). The lipid peroxidation under cold stress was not observed in the MICU1‐deficient A549 cells (Fig 1E and F). ASK1 is known to be activated by cold stress‐dependent lipid peroxidation (Hattori et al, 2017). Cold stress‐induced ASK1 activation was also suppressed in MICU1‐deficient A549 cells (Fig EV4A). Together, these results suggest that MICU1 is necessary for the lipid peroxidation and subsequent cell death in the context of cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
Figure EV4. ASK1 activity in various conditions and hyperpolarization of MMP under cold stress, related to Figs 1, 3 and 4.
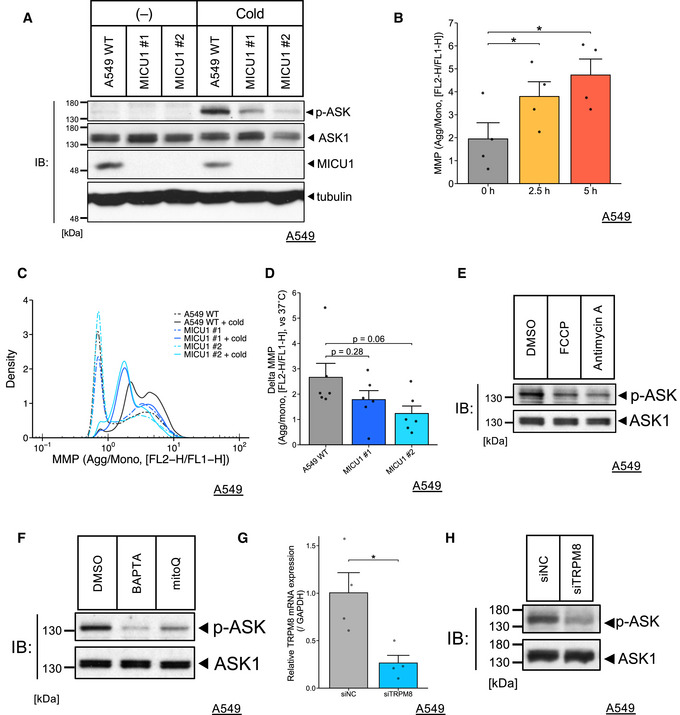
-
AImmunoblots of endogenous phospho‐ASK signals after cold stress for 5 h of the WT A549 cells, cloned MICU1‐KO cells.
-
BMitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) was measured by JC‐1 after cold stress at the indicated time points. Quantification data for the WT A549 cells are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4, biological replicates, *P < 0.05, one‐way ANOVA followed by William’s test.
-
C,DMitochondrial membrane potential was measured by JC‐1 after cold stress for 5 h. Representative (C) and quantification data (D) are represented as mean ± SEM; n = 6, one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. Delta MMP was shown by the MMP of the WT A549 or MICU1 KO cells subtracted from that of each control condition.
-
E,FImmunoblots of endogenous phospho‐ASK signals after cold stress for 5 h of the WT A549 cells. Inhibitors (FCCP: 200 µM, Antimycin A: 50 µM, BAPTA: 10 µM, mitoQ: 0.5 µM) were used as pretreatments for 30 min.
-
GTRPM8 mRNA was quantified by RT–qPCR. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4, *P < 0.05, unpaired t‐test.
-
HImmunoblots of endogenous phospho‐ASK signals after cold stress for 5 h of the WT A549 cells or TRPM8‐KD cells by siRNA transfection.
DIME interaction and dimerization domains of MICU1 are necessary for cold stress‐induced ferroptosis
MICU1 plays an essential role in gatekeeping and activating MCU through its interaction with some components of the MCU complex (Fig 2A). MICU1 has two EF hand domains for sensing Ca2+ concentration (Perocchi et al, 2010; Mallilankaraman et al, 2012), the DIME interaction domain (DID) for interacting with the D‐ring of the MCU pore to regulate mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake (Paillard et al, 2018), the homo‐ or heterodimerization domain of MICU1 for appropriate gatekeeping and MCU‐MICU1 rearrangements (Patron et al, 2014; Petrungaro et al, 2015; Gottschalk et al, 2019), and the EMRE binding domain for tethering MICU1 to the MCU complex without affecting mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake (Sancak et al, 2013; Paillard et al, 2018).
Figure 2. DIME interaction and dimerization domains of MICU1 are necessary for cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
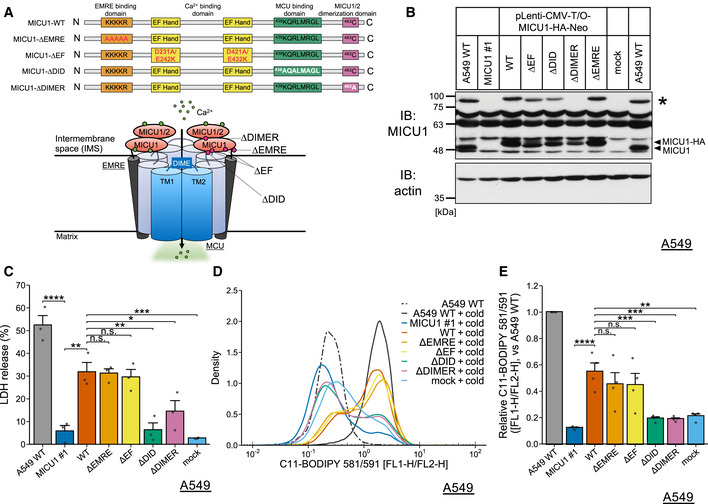
-
ASchematic model describing the domains of MICU1 and the brief structure of the MCU complex green points describing Ca2+ and red points describing mutants.
-
BImmunoblots of MICU1 and its mutants rescued by the lentivirus. Arrows indicate MICU1 or the dimer. * indicates the potential DTT‐resistant dimer.
-
CLDH assay was performed after 16 h of cold stress on ice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, n.s.: not significant, by one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test
-
D,ELipid peroxidation was measured by C11‐BODIPY 581/591 after cold stress for 5 h. Representative plots are shown in (D). Quantification data (E), whose raw value were normalized by the C11‐BODIPY 581/591 of the WT A549 cells after cold stress application, are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4, biological replicates. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, n.s.: not significant, by one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
Source data are available online for this figure.
Thus, we next determined which domain of MICU1 was involved in cold stress‐induced cell death. We preformed rescue experiments in the MICU1‐KO A549 cells (MICU1 #1) by reconstituting various MICU1 mutants, including ∆EF (D231A, E242K, D421A, and E432K), ∆DID (438KQRLMRGL > AQALMAGL), ∆DIMER (C463A), and ∆EMRE (99KKKKR > AAAAA) (Fig 2B). First, we examined the effect of the reconstituted MICU1 mutants on cell death, which was determined by LDH release. Re‐expression of MICU1 WT, ∆EF, and ∆EMRE but not ∆DID or ∆DIMER rescued cell death of MICU1 KO cells in cold stress, suggesting that the interaction of MICU1 with MCU and MICU1/2 would be required for cold stress‐induced cell death (Fig 2C).
Next, we examined the effect of these mutants on lipid peroxidation. Similar to the findings on cell death, the reintroduction of the MICU1 WT, ∆EF, and ∆EMRE rescued the cold stress‐induced lipid peroxidation, but the reintroduction of ∆DID or ∆DIMER did not have this effect (Fig 2D and E). The C‐terminus of MICU1 is required for MCU‐MICU1 complex rearrangement and the subsequent regulations for MCU as a gatekeeper in mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake (Patron et al, 2014; Wang et al, 2014; Paillard et al, 2018; Gottschalk et al, 2019). ∆DID (K438A;R440A;R443A) and ∆DIMER (C463A) mutations are located in the C‐terminus (Fig 2A) and lack MICU1‐MCU/MICU2 interactions necessary for gatekeeping MCU complex. On the other hand, EF hand mutation of MICU1 impairs its Ca2+‐dependent activating but not gatekeeping activity of MCU (Perocchi et al, 2010; Gottschalk et al, 2019). One of the interpretations of these data would be that the ability of MICU1 to interact with MCU and/or MICU2 and to serve as a gatekeeper for MCU may be necessary for cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
Next, we examined the effect of MICU1 deficiency on Ca2+ concentration in mitochondria and cytosol under cold stress. Firstly, we tried measuring Ca2+ by imaging experiments using mt‐pericam and CEPIA2mt for mitochondria Ca2+ (Nagai et al, 2001; Suzuki et al, 2014), and Fura‐2 AM and Fura‐8 AM for cytosol Ca2+. However, we could not construct a reliable measuring system, because we did not have an equipment to keep cold circumstances on confocal microscopy. Instead, we used Rhod‐2 for mitochondria Ca2+ and by Cal‐520 for cytosol Ca2+ in plate reader‐based measuring system, because these Ca2+ probes showed better signal intensity. The mitochondrial Ca2+ concentration measured by Rhod‐2 AM was increased after cold stress. The increased Rhod‐2 signal at 1 h after cold stress was partially but significantly reduced in the MICU1‐KO cells compared with the level in the WT cells, while the basal mitochondrial Ca2+ showed a slight increase without significant difference in MICU1‐KO cells (Fig EV4, EV3, EV5). Cytosolic Ca2+ measured by Cal‐520 was also increased after cold stress, and it was rather enhanced in MICU1‐deficient cells, while the basal cytosolic Ca2+ showed a slight increase without significant difference in MICU1‐KO cells (Fig EV4, EV3, EV5). Some reports show that mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake by MICU1 deficiency was reduced in high Ca2+ conditions or after Ca2+ mobilizing agonists treatment(Csordás et al, 2013; Liu et al, 2016). Thus, it seems that MICU1‐deficient cells may decrease mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake from cytosol after cold stress. However, since Rhod‐2 and Cal‐520 may have some technical problems to measure precise Ca2+ concentration, further investigations may be required for precise conclusion.
Figure EV3. Cold stress‐induced Ca2+ increase in matrix and cytosol, related to Figs 1–4.
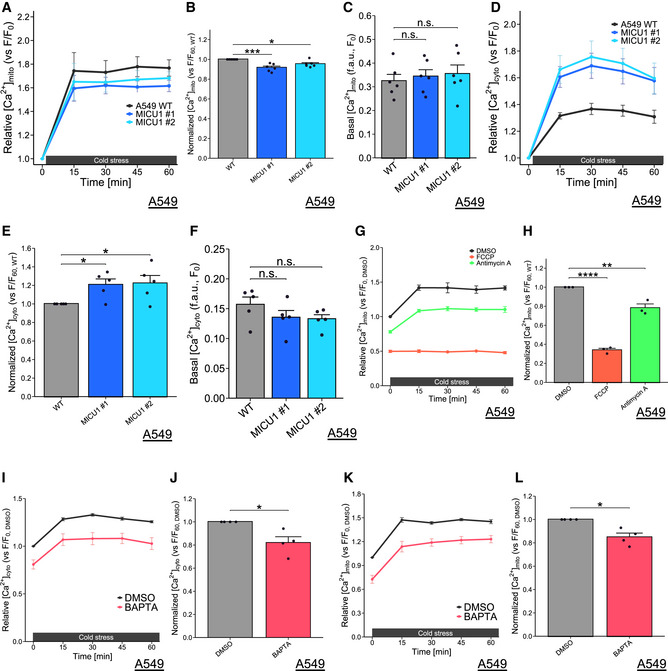
-
A‐FMitochondrial Ca2+ concentration (A‐C) and cytosolic Ca2+ concentration (D‐F) were monitored by Rhod‐2 AM and Cal‐520 AM, respectively, at every 15 min. Data (A,B, D and E) were normalized by data of before cold stress. The data before cold stress (C, F) and at 60 min (B, E) are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 6 (A‐C), 5 (D‐F), biological replicates, ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05, n.s.: not significant, by one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.
-
G,HMitochondrial Ca2+ concentration was monitored by Rhod‐2 AM at every 15 min. FCCP (200 µM) and antimycin A (50 µM) were used as pretreatments for 30 min. Data were normalized by data of DMSO before cold stress and the data at 60 min (H) are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates, ****P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01, by one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.
-
I‐LCytosolic Ca2+ concentration (I‐J) and mitochondrial Ca2+ concentration (K‐L) were monitored by Cal‐520 AM and Rhod‐2 AM, respectively, at every 15 min. BAPTA‐AM (10 µM) were used as pretreatments for 30 min. Data were normalized by data of DMSO before cold stress, and the data at 60 min (J, L) are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4, biological replicates, *P < 0.05, by paired T‐test.
Figure EV5. MICU1 can be one of potential targets for cold‐induced cell death, but MICU1 and cytosolic Ca2+ may not be involve in other ferroptotic cell death.
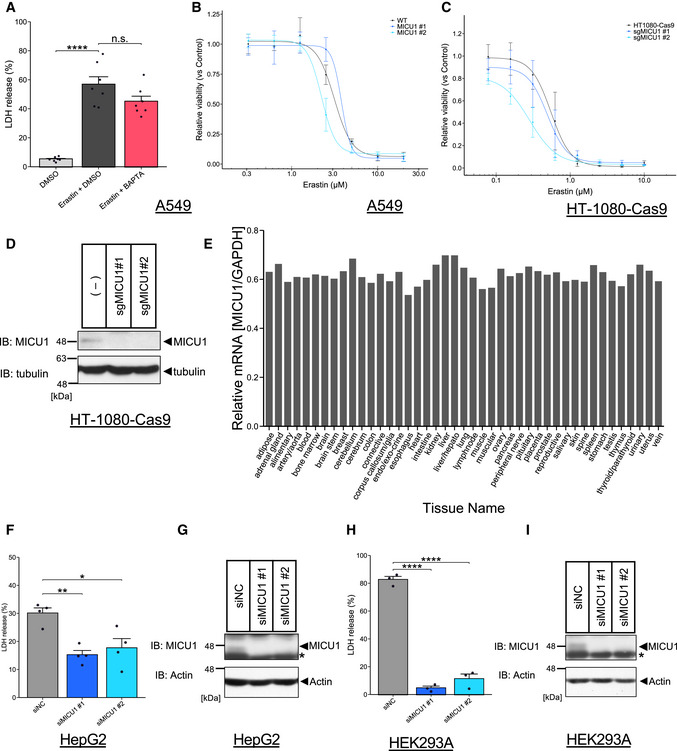
-
ALDH release was measured after DMSO or erastin (10 µM) treatment with DMSO or BAPTA‐AM (10 µM) for 24 h. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 7, biological replicates, ****P < 0.0001, n.s.: not significant, one‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s test.
-
B,CCell viability was measured after erastin treatment as indicated concentrations for 24 hours in A549 cells and MICU1 #1/#2 KO A549 cells or Cas9‐HT‐1080 cells and Cas9‐HT‐1080 cells infected with lentivirus containing sgRNA of MICU1 #1/#2. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3 biological replicates.
-
DImmunoblots of MICU1 were present for knockout confirmation in Cas9‐HT‐1080 cells after lentivirus infection.
-
ERelative mRNA expression of MICU1 in normal human tissue was normalized by GAPDH mRNA expression. Data was obtained from Refex database.
-
FLDH release was measured after cold stress for 24 h in indicated cell lines. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4, biological replicates, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test.
-
GImmunoblots of MICU1 were present for knockdown confirmation in HepG2 cells after siRNA transfection.
-
HLDH release was measured after cold stress for 24 h in indicated cell lines. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates, ****P < 0.0001, one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test.
-
IImmunoblots of MICU1 were present for knockdown confirmation in HEK293A cells after siRNA transfection.
MCU and MICU2 are not necessary for cold stress‐induced ferroptosis
Although MICU1‐dependent regulation of MCU appeared to be important for cold stress‐induced ferroptosis, other components of the MCU complex were not enriched in our screening (Fig EV2C). Moreover, the MCU deficiency induced by CRISPR/Cas9 or siRNA could not suppress cell death (Fig EV2A, B, D and E). Interestingly, when MCU was silenced by siRNA in the MICU1‐KO cells, the MICU1‐KO‐induced suppression of cell death was abrogated (Fig EV2F and G). These data indicate that MCU deficiency per se did not suppress cold stress‐induced ferroptosis but could cancel the effect of MICU1 deficiency. This may be because the complete MCU deficiency may activate alternative Ca2+ uptake pathways in cold stress or MICU1 has MCU‐independent functions. These hypotheses may be supported by some reports indicating that MCU‐knockout mice are viable (Pan et al, 2013), and that MCU‐independent Ca2+ uptake is also induced by ryanodine receptors, TRPC3, UCP2/3, and LETM1 (Trenker et al, 2007; Jiang et al, 2009; Ryu et al, 2010; Feng et al, 2013). Moreover, MICU1 controls cristae structure in a MCU‐independent manner (Gottschalk et al, 2019; Tomar et al, 2019). Thus, the cell death mediated by MICU1/MCU double deficiency might be caused by the mitochondrial Ca2+ regulation in a MCU complex‐independent manner.
Another hypothesis is that activation of MCU rather suppresses cell death via buffering cytosolic Ca2+ as previously discussed (Marchi et al, 2020). To investigate this point, we overexpressed MCU in A549 WT cells, but there was no effect on cell death (Fig EV2, EV4, EV3, EV5). In addition, the cytosolic Ca2+ buffering hypothesis seems inconsistent, because MICU1 deficiency rather increased cytosolic Ca2+ but suppressed cold stress‐induced ferroptosis (Fig EV4, EV3, EV5).
Loss of MICU1 can increase MCU‐dependent heavy metals uptake such as Fe2+ (Wettmarshausen et al, 2018). Considering that Fe2+ is required for ferroptosis, it may be possible that loss of MICU1 can reduce cytosolic Fe2+ through MCU‐dependent permeability. However, if heavy metals increase in mitochondria, it would generally result in cell death (Wettmarshausen et al, 2018), inconsistent with our observed phenotype. Nonetheless, we tried to measure cytosolic Fe2+ in MICU1 deficiency using the specific Fe2+ probe (Hirayama et al, 2017), but the probe appeared to be affected by cold temperature and we could not properly measure the Fe2+ concentration (Appendix Fig S1B).
In addition, MICU2 plays an opposing role to MICU1 on MCU in histamine‐induced mitochondrial Ca2+ influx (Patron et al, 2014). We thus investigated the role of MICU2 in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis. MICU2 depletion by siRNAs resulted in neither promotion nor inhibition of cell death (Fig EV2K and L). Since MICU2 silencing is reported to reduce MICU1’s gatekeeping activity (Patron et al, 2014), our results suggest the cold stress‐induced ferroptosis may be regulated not only by the gatekeeping activity of MICU1.
Altogether, the gatekeeping activity and/or the potential MCU‐independent functions of MICU1 may be important for cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
Cold stress‐induced mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) hyperpolarization contributes to lipid ROS accumulation and ferroptosis
Ca2+ influx into mitochondria can promote electron transport chain (ETC) activity and activates tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, thereby increasing the MMP (Rizzuto et al, 2012) (Fig 3A). It is also known that the MMP itself drives mitochondrial Ca2+ entry through its electronic force (Giorgi et al, 2018). Therefore, the MMP and mitochondrial Ca2+ are mutually regulated. It was previously reported that MMP hyperpolarization associates with lipid peroxidation in cysteine deprivation‐induced ferroptosis (Gao et al, 2019). Thus, we investigated the involvement of the MMP in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
Figure 3. Cold stress‐induced mitochondrial membrane potential hyperpolarization contributes to lipid ROS accumulation and ferroptosis.
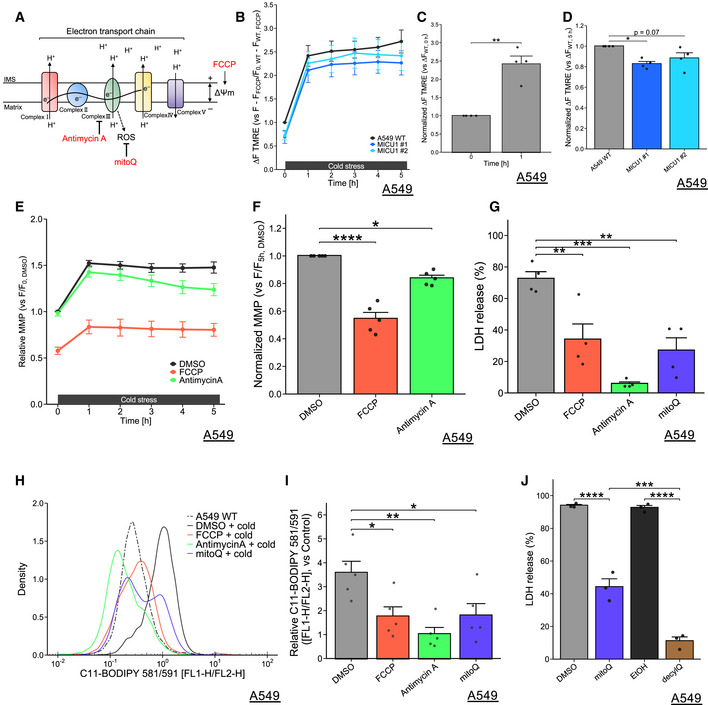
-
ASchematic model of the electron transport chain (ETC) and targets of the inhibitors used.
-
B‐FMMP was monitored by TMRE fluorescence at every 1 h. FCCP (200 µM) and antimycin A (50 µM) were used as pretreatments for 30 min. Data were normalized by basal state of WT A549 cells (B‐D) or WT A549 cells with DMSO (E‐F) before cold stress. Data at 1 h (C), 5 h (D, F) are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4 (B‐D) and n = 5 (E‐F), biological replicates, ****P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 by paired T‐test (C), or one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (D, F).
-
G‐J(G, J) LDH release was measured after cold stress for 24 h. FCCP (200 µM), antimycin A (50 µM), mitoQ, and decylQ (500 nM) were used as pretreatments for 30 min. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4 (G) and n = 3 (J), biological replicates, ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, by one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s or Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. (H, I) Lipid peroxidation was measured by C11‐BODIPY 581/591 after cold stress for 5 h. Representative plots are shown in (H). Quantification data (I), whose raw value were normalized by the C11‐BODIPY 581/591 without cold stress of non‐treatment, are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 5, biological replicates. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, by one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.
Hyperpolarization of the MMP was observed by the fluorescence of tetramethyl rhodamine, ethyl ester, perchlorate (TMRE) in the A549 WT cells within 1 h after cold stress (Fig 3B and C). This hyperpolarization was also confirmed with a different MMP probe: JC‐1 (Fig EV4B). The MMP was low in basal state of MICU1 depleted cells and was also maintained low level all thorough the challenge of cold stress for 5 h (Figs 3B and EV4C). The relative increment of MMP was also reduced by MICU1 deficiency (Figs 3D and EV4D).
In addition to mitochondrial Ca2+ regulation, MICU1 deficiency is proposed to change the integrity of cristae, leading to leak H+ to cristae lumen and resulting in decreasing MMP (Gottschalk et al, 2019). Thus, it would be possible that MMP under cold stress would not increase in MICU1‐KO cells compared to WT. Moreover, since ferroptosis shows the loss of cristae and the disruption of mitochondrial structure (Dixon et al, 2012), loss of MICU1 may alter mitochondria into cytoprotective structures possibly through dependence on MCU activity. It will be defined in future researches whether or not these proposed structural changes in MICU1 deficiency are responsible for Ca2+ regulation and our observed phenotype.
Inhibitors of the MMP hyperpolarization, such as antimycin A (a complex III inhibitor) and FCCP (an uncoupler), suppressed not only the MMP hyperpolarization after cold stress for 5 h (Fig 3E and F) but also Ca2+ influx into mitochondria (Fig EV3G and H). These data confirmed the previous notion that MMP contributes Ca2+ uptake of mitochondria (Giorgi et al, 2018). Furthermore, the pretreatment of antimycin A and FCCP suppressed their death (Fig 3G) and lipid peroxidation (Fig 3H and I) under cold stress, suggesting that inhibiting either mitochondrial Ca2+ increase or the MMP hyperpolarization, or both are required for cell death and lipid peroxidation, presumably through ETC activation.
Given the ETC is activated by cold stress, ROS will be generated in mitochondria; in particular, complex III is one of the major sources of ROS production (Fig 3A). Therefore, we investigated the role of mitochondrial ROS in this cell death. MitoQ is a mitochondria‐targeted antioxidant and a partial inhibitor of GPX4 deficiency‐ or cysteine deprivation‐induced ferroptosis (Friedmann Angeli et al, 2014). Pretreatment with mitoQ suppressed both cell death (Fig 3G) and lipid peroxidation (Fig 3H and I) after cold stress. Consistent with these observations, MMP inhibitors (antimycin A and FCCP) and mitoQ suppressed cold stress‐induced activation of ASK1 (Fig EV4E and F).
Activation of ETC by mitochondrial Ca2+ results in the generation of ROS in the intermembrane space (IMS) and matrix via the respiratory chain. ROS in matrix may generate lipid ROS via the Fenton reaction such as ROS attacking iron‐sulfur clusters (ISCs) and subsequently generating free iron (Nakamura et al, 2019). Considering that ASK1 but not GPX4 are present in matrix and that mitoQ can localize in matrix, the initial inadequate elimination of lipid ROS in matrix may be the source of these series of ferroptosis signaling. To emphasize the role of mitochondrial lipid ROS in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis, we compared the effect of mitoQ with its analog, non‐selectively localized antioxidant (decyl ubiquinone; decylQ) on cell death. As shown before (Friedmann Angeli et al, 2014), decylQ protected cell death more efficiently than mitoQ (Fig 3J). These results suggest that the major source of ROS to induce this ferroptosis is derived from mitochondria with some other additional sources. Thus, mitochondria may be one of the main subcellular compartments to induce cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
Cold‐sensing Ca2+ channel, TRPM8, is partly involved in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis
To investigate a source of mitochondrial Ca2+ increase, we focused on cytosolic Ca2+ concentration, as the relative cytosolic Ca2+ immediately increased after cold stress (Fig EV3D), consistent with previous report (Bautista et al, 2007). The high Ca2+ concentration after cold stress was diminished by the cytosolic Ca2+ chelator, BAPTA‐AM (Fig EV3I and J). Importantly, the cold stress‐induced mitochondrial Ca2+ increase was also suppressed by BAPTA‐AM (Fig EV3K and L). Moreover, similar to the action of the MMP inhibitors, BAPTA‐AM suppressed cold stress‐induced ferroptosis (Fig 4A), lipid peroxidation (Fig 4B and C), and ASK1 activation (Fig EV4F).
Figure 4. Cytosolic Ca2+ is involved in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
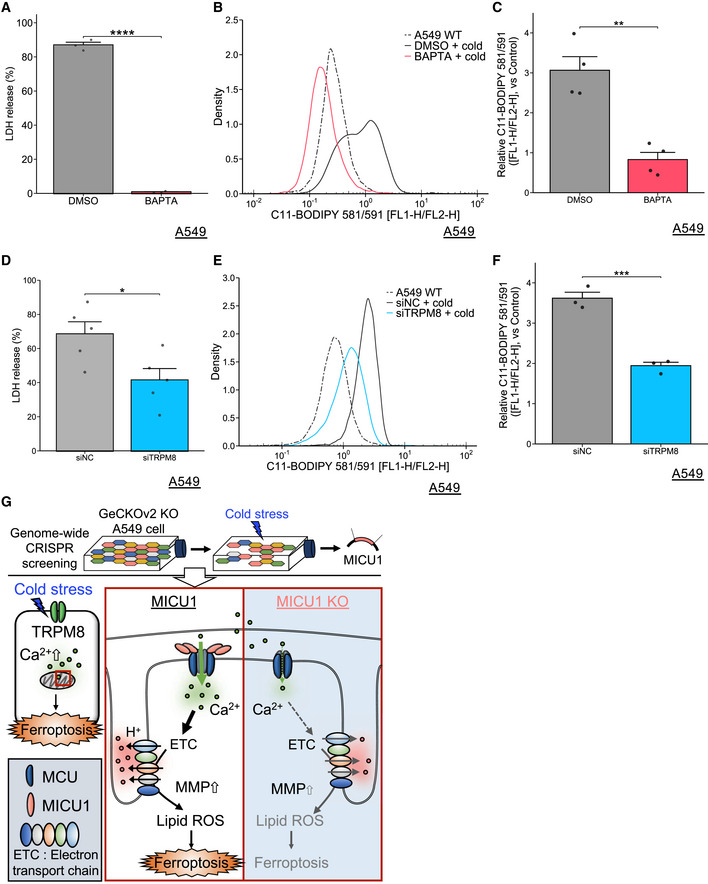
-
ALDH release was measured after cold stress for 24 h. BAPTA‐AM (10 µM) was used as pretreatments for 30 min. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, biological replicates, ****P < 0.0001, by unpaired T‐test.
-
B‐F(B‐C, E‐F) Lipid peroxidation was measured by C11‐BODIPY 581/591 after cold stress for 5 h. Representative plots are shown in (B, E). Quantification data (C, F), whose raw value were normalized by the C11‐BODIPY 581/591 without cold stress of non‐treatment, are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4 (C), 3 (F), biological replicates. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 by unpaired t‐test. (D) LDH release was measured after cold stress for 16 h. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 5, biological replicates, *P < 0.05, by unpaired T‐test.
-
GBrief strategy for finding regulators for cold stress‐induced ferroptosis and summary of molecular mechanism of lipid peroxidation mediated by MICU1.
Although it has been reported that cytosolic Ca2+ chelation by BAPTA‐AM has no effect on erastin‐induced ferroptosis in HT‐1080 cells (Dixon et al, 2012) and A549 cells (Fig EV5A), BAPTA‐AM suppressed both cell death and lipid peroxidation during cold stress‐induced ferroptosis (Fig 4B and C). Moreover, MICU1 deficiency by CRISPR/Cas9 did not protect erastin‐induced ferroptosis (Fig EV5B and C). Thus, MICU1 and Ca2+ may be selectively involved in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
Previous reports have characterized some thermoreceptors that respond to the temperature range similar to that investigated in our study (~ 5°C). Among the cold‐sensing Ca2+ channels, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 8 (TRPM8) is one of the candidates for cytosolic Ca2+ increase (Bautista et al, 2007). TRPM8 knockdown by siRNA (Fig EV4G) partially but significantly suppressed cell death (Fig 4D), lipid peroxidation (Fig 4E and F), and ASK1 activation (Fig EV4H). Thus, these results suggest that, in contrast to other stimuli‐induced ferroptosis (Dixon et al, 2012), cytosolic Ca2+ influx, at least in part through TRPM8, plays an important role in lipid peroxidation and cell death in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
It is also known that there are other cold‐sensing Ca2+ channels, TRPA1 (Karashima et al, 2008) and GRIK2 (Gong et al, 2019); however, none of these molecules, including TRPM8, were enriched in our screening. We focused on TRPM8 because of its relevance to the response to the temperature range (Patapoutian et al, 2003; Hattori et al, 2017). Nevertheless, since the suppression of cold stress‐induced cell death by TRPM8 depletion was partial compared with that induced by BAPTA‐AM treatment, other Ca2+ channels regulating cytosolic Ca2+ may also be involved, in a redundant manner, in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis.
In summary, using genome‐wide CRISPR screening, we identified the involvement of MICU1 in cold stress‐induced ferroptosis (Fig 4G). Cold stress induces MICU1‐dependent mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and subsequent MMP hyperpolarization, which is required for cold stress‐dependent lipid peroxidation. As a source of cytosolic Ca2+ increase under cold stress, we also suggest the involvement of TRPM8‐dependent influx of extracellular Ca2+.
These findings may provide new perspectives on the molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and ferroptosis‐related diseases. MICU1 is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues and organs (Fig EV5E) (Ono et al, 2017), and we found that MICU1 knockdown by siRNAs could suppress cold stress‐induced ferroptosis in kidney‐ and liver‐derived cell lines (Fig EV5F–I). Considering a MICU1 specific inhibitor has recently been reported (Di Marco et al, 2020), MICU1 can be a novel and promising drug target for organ preservation and/or other human diseases.
Material and Methods
Reagents and Tools table
| Reagent/Resource | Reference or Source | Identifier or Catalog Number |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental Models | ||
| Human: A549 cells | ATCC | N/A |
| Human: Cas9‐stably‐expressing A549 cells (Cas9‐A549) | This paper | N/A |
| Human: MICU1 KO #1 A549 cells | This paper | N/A |
| Human: MICU1 KO #2 A549 cells | This paper | N/A |
| Human: MCU KO #1 A549 cells | This paper | N/A |
| Human: MCU KO #2 A549 cells | This paper | N/A |
| Human: HepG2 cells | ATCC | N/A |
| Human: HEK293A cells | ATCC | N/A |
| Human: HEK293T cells | ATCC | N/A |
| Human: Cas9‐stably‐expressing HT‐1080 cells (Cas9‐HT‐1080) | This paper | N/A |
| Recombinant DNA | ||
| pLenti CMV/TO Puro DEST (670‐1) | Addgene | Cat#17293 |
| pLenti CMV/TO Neo DEST | This paper | N/A |
| pLenti CMV T/O MICU1‐WT‐HA Neo DEST (CDS of NM_001195518.2) | This paper | N/A |
| pLenti CMV T/O MICU1‐∆EF‐HA Neo DEST | This paper | N/A |
| pLenti CMV T/O MICU1‐∆DID‐HA Neo DEST | This paper | N/A |
| pLenti CMV T/O MICU1‐∆DIMER‐HA Neo DEST | This paper | N/A |
| pLenti CMV T/O MICU1‐∆EMRE‐HA Neo DEST | This paper | N/A |
| GeCKOv2 human library (A/B) | Addgene | Cat#1000000048 |
| lentiCas9‐Blast | Addgene | Cat#52962 |
| pCMV‐VSV‐G | Addgene | Cat#8454 |
| psPAX2 | Addgene | Cat#12260 |
| lentiCRISPRv2 | Addgene | Cat#52961 |
| lentiGuide‐Puro | Addgene | Cat#52963 |
| Antibodies | ||
| Mouse monoclonal anti‐Actin (Actin; AC‐40) | Sigma‐Aldrich | Cat#A3853 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti‐CCDC109A (MCU; E‐9) | Santa Cruz | Cat#sc‐515930 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti‐ASK1 (ASK1; EP553Y) | Abcam | Cat#ab45178 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti‐MICU1 | Sigma‐Aldrich | Cat#HPA037480 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti‐phospho‐ASK (p‐ASK; Thr838 in human ASK1) | Tobiume et al, 2002 | N/A |
| Rat monoclonal anti‐α Tubulin (α Tubulin; YL1/2) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat#sc‐53029 |
| Oligonucleotides and sequence‐based reagents | ||
| Primers for sgRNAs | This paper | Table EV1 |
| Primers for cloning and subcloning | This paper | Table EV1 |
| Primers for qRT‐PCR | Bidaux et al, 2015 | Table EV1 |
| Control siRNA (ON‐TARGET plus Non‐targeting siRNA #4, target sequence: 5’‐UGGUUUACAGUUUUCCUA‐3’) | Dharmacon | Cat#D‐001810‐04‐05 |
| MICU1 siRNA #1 (ON‐TARGET plus MICU1 siRNA, target sequence: 5’‐GCAGUUUGGUGGCAUGCUA‐3’) | Dharmacon | Cat#J‐012720‐18 |
| MICU1 siRNA #2 (ON‐TARGET plus MICU1 siRNA, target sequence: 5’‐UCCUCGAAUUUCAGCGUAA‐3’) | Dharmacon | Cat#J‐012720‐19 |
| MCU siRNA #1 (ON‐TARGET plus MCU siRNA, target sequence: 5’‐GUUUUGACCUAGAGAAAUA −3’) | Dharmacon | Cat#J‐015519‐18 |
| MCU siRNA #2 (ON‐TARGET plus MCU siRNA, target sequence: 5’‐GUAAUGACACGCCAGGAAU‐3’) | Dharmacon | Cat#J‐015519‐20 |
| MICU2 siRNA#1 (ON‐TARGET plus MICU2 siRNA, target sequence: 5’‐GCAUCGAGGUUUAUGGGUA‐3’) | Dharmacon | Cat#J‐015468‐17 |
| MICU2 siRNA#2 (ON‐TARGET plus MICU2 siRNA, target sequence: 5’‐UGAGCAAAUGGAACGUAAA‐3’) | Dharmacon | Cat#J‐015468‐18 |
| Control siRNA (Stealth RNAi Negative Control Medium GC Duplex #2) | Invitrogen | Cat#12935‐112 |
| TRPM8 siRNA #1 (Stealth RNAi siRNA, target sequence: 5’‐AGGAGUACUGCAGCCGCCUCAAUAU‐3’) | Invitrogen | Cat#HSS128188 |
| Chemicals, enzymes and other reagents | ||
| Antimycin A | Sigma‐Ardrich | Cat#A8674 |
| BAPTA‐AM | Dojindo | Cat#B035 |
| Blastcidin S HCl | Invitrogen | Cat#A1113903 |
| C11‐BODIPY 581/591 | Invitrogen | Cat#D3861 |
| Cal‐520 AM | Abcam | Cat#ab171868 |
| Cell Counting Kit‐8 | Dojindo | Cat#CK04 |
| Carbonyl cyanide 4‐(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone (FCCP) | Cayman | Cat#15218 |
| Deferoxiamine | Cayman | Cat#14595 |
| Decylubiquinone (decylQ) | Cayman | Cat#21027 |
| Erastin | Sigma‐Ardrich | Cat#E7781 |
| Ferrostain‐1 | Sigma‐Ardrich | Cat#SML0583 |
| FerroFarRed | Gryoukayaku | Cat#GC903‐01 |
| G418 | Invitrogen | Cat#10131‐035 |
| Gateway LR Clonase ll Enzyme Mix | Invitrogen | Cat#11791‐100 |
| Hexadimethrine Bromide (Polybrene) | Nakarai tesque | Cat#17736‐44 |
| JC‐1 | Cayman | Cat#10009172 or Cat#15003 |
| Lipofectamine 3000 reagent | Invitrogen | Cat#130469 |
| Lipofectamine RNAiMAX | Invitrogen | Cat#13778‐150 |
| Mitoquinone mesylate (mitoQ) | MCH | Cat#HY‐100116A |
| Puromycin | Gibco | Cat#A11138‐03 |
| Rhod‐2 AM | Abcam | Cat#ab142780 |
| Tetramethyl rhodamine, Ethyl Ester, Perchlorate (TMRE) | Invitrogen | Cat#T669 |
| Pluronic F127 | Invitrogen | Cat#31382W |
| LDH‐Cytotoxic Test | Wako | Cat#299‐50601 |
| Software | ||
| MAGeCK (ver. 0.5.9) | Li et al, 2014 | https://sourceforge.net/projects/mageck/ |
| FlowCal (ver. 1.2.1) | Castillo‐Hair et al, 2016 | https://pypi.org/project/FlowCal/ |
| MAGeCKFlute | Wang et al, 2019 | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/MAGeCKFlute.html |
| clusterProfiler | Yu et al, 2012 | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/clusterProfiler.html |
| Other | ||
| 96‐well imaging microplate with lid | Falcon | Cat# 353219 |
| Varioskan Flash | Thermo Fisher Scientifc | |
| FACSCalibur | BD Biosciences | |
| QuantStadio1 Real‐Time PCR System | ABI |
Methods and Protocols
Cell lines and cell culture
A549 cells and HEK293A cells were cultured in DMEM‐high glucose (Sigma, Cat#D5796) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). HepG2 cells were cultured in DMEM‐low glucose (Sigma, Cat#D5796) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). FLAG‐Cas9‐stably expressing A549 cells were cultured in DMEM‐high glucose with 10% FBS, 5 µg/ml blasticidin. FLAG‐Cas9 stably expressing HT‐1080 cells were cultured with DMEM‐high glucose with 10% FBS, 5 µg/ml blasticidin, and MEM Non‐Essential Amino Acids Solution (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat#11140050). All cells were cultured in 5% CO2 at 37°C and verified to be negative for mycoplasma.
Cold stress application
Cell culture plates or flasks were placed on top of metal covered with ice or directly on ice in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at ~ 25°C. The ice was added or replaced when it was melted.
LDH assay
Cell death rate was measured using the LDH‐Cytotoxic Test (Wako, Cat#299‐50601) basically following the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, culture medium was collected and centrifuged for 3 min at 400 × g (medium sample). Cells were lysed with PBS containing 0.1% Triton X‐100, and then, cell lysate was centrifuged for 10 min at 17,700 × g (lysate sample). Medium and lysate samples were individually mixed with reagents on microplates, and the absorbance was measured at 570 nm using Varioskan Flash (Thermo Fisher Scientific) after around 5 min incubation at room temperature. Cell death ratio was calculated by LDH release (%) as follows: (absorbance (abs) of medium samples – background)/((abs of lysate samples – background) + (abs of medium samples – background)).
Cell viability assay
Cell viability was measured by a Cell Counting Kit‐8 (Dojindo, Cat#CK04), following the manufacture’s protocol. Dose‐response curve prediction was performed by R with drc package.
Lipid peroxidation assay
Cells were preloaded with 5 µM C11‐BODIPY 581/591 (Invitrogen, Cat#D3861) to the culture media and incubated for an hour in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. Cell culture medium was replaced with fresh one right before inhibitor treatment or cold stress application. After cold stress application, cells were washed with PBS and trypsinized. Then, cells were suspended in PBS and cell suspension was filtered through a cell strainer (40 µm, Falcon, Cat#352340). Finally, each cell samples were subjected to flow cytometer analysis (FACSCalibur, BD Biosciences) measuring 10,000 cells. The fluorescence of BODIPY from fcs file was extracted by FlowCal (Castillo‐Hair et al, 2016) and calculated using Microsoft Excel, and followed by depicting figures by R with RStudio. Ratio of fluorescence of C11‐BODIPY 581/591 (lipid peroxidation) [FL1/FL2 ratio (oxidized / reduced ratio)] was calculated as follows: (FL1‐H fluorescence of each cell ‐ median of FL1‐H fluorescence of unstained cells) / (FL2‐H fluorescence of each cell ‐ median of FL2‐H fluorescence of unstained cells). Statistical analysis was performed by median of [FL1/FL2 ratio (oxidized / reduced ratio)] of each experiments. Relative C11‐BODIPY 581/591 was calculated by FL1/FL2 ratio divided by samples without cold stress of non‐treatment.
Mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) assay
Microplate reader: Cells were seeded in 96‐well black plate (Falcon, Cat# 353219) and preloaded with 200 nM tetramethylrhodamine, ethyl ester, perchlorate (TMRE) (Invitrogen, Cat#T669) for 30 min. Subsequently, cells were washed with PBS to remove TMRE from the media and pretreated with indicated compounds for 30 min. The fluorescence of TMRE before and after cold stress application at indicated time was quickly measured at the wavelength (Ex/Em = 545/575 nm) using Varioskan Flash (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The cold stress was continued to the endpoint. During measurements, the temperature was set at 10.2°C (minimum). For calibrations of MMP for comparison of WT and MICU1 KO cells lines, 2 x 400 µM FCCP culture medium was added to each well and cells were incubated on ice for 30 min; then, the fluorescence of TMRE was measured. For Appendix Fig S1A, the temperature was measured as previous paper shown (Hattori et al, 2017). For experiments of MICU1 KO cells, all data were shown as ∆F TMRE [(F ‐FFCCP) / (F0,WT ‐FWT, FCCP)] and calculated as follows: the mean fluorescence of each cell (F) was subtracted from the value of each cell after FCCP treatment (FFCCP) [F ‐FFCCP], then divided by mean fluorescence of WT of time 0 h (F0, WT) subtracted from the value of WT after FCCP treatment (FWT, FCCP) [F0,WT ‐FWT, FCCP]. All other all data were normalized by each control condition of before cold stress application (indicated as “0 h”).
Flow Cytometry: Cells were preloaded with JC‐1 (Cayman, Cat#10009172; 1/500 or Cat#15003; 1 µM) for 30 min. Cell culture medium was replaced with fresh one right before cold stress application. After stimulation, cells were washed with PBS and trypsinized, followed by suspension in PBS. The cell suspension was filtered through a cell strainer (40 µm, Falcon) and then subjected to flow cytometer analysis (FACSCalibur, BD Biosciences) measuring 10,000 cells. The raw data were extracted by FlowCal and calculated using Microsoft Excel or R, followed by depicting figures by R and RStudio. MMP [FL2/FL1 ratio (multimer / monomer ratio)] was calculated as follows: (FL2‐H fluorescence of each cell ‐ median of FL2‐H fluorescence of unstained cells) / (FL1‐H fluorescence of each cell ‐ median of FL1‐H fluorescence of unstained cells). Statistical analysis was performed by median of MMP of each experiment. Delta MMP was calculated by FL2/FL1 ratio subtracted by control condition of each cell lines.
Calcium quantification assay
Mitochondrial Ca2+ concentration quantification: Cells were seeded in 96‐well black plate (Falcon, Cat# 353219) and preloaded with 2 µM Rhod‐2 AM (Abcam, Cat#ab142780) and Pluronic F127 (0.02%, Invitrogen, Cat#31382W) diluted in HHBS (Hank's Buffer with Hepes) for one hour. Subsequently, cells were washed with HHBS once to remove Rhod‐2 from the media and normal medium with 10% FBS and 200 µM MnCl2 in order to quench cytosolic signals of Rhod‐2 (Pan et al, 2013). In experiments of inhibitors, cells were pretreated with indicated inhibitors for 30 min. The fluorescence of Rhod‐2 before and after cold stress application at indicated time was quickly measured at the wavelength (Ex/Em = 552/581 nm) using Varioskan Flash (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Cold stress was continued to the endpoint. During measurements, the temperature was set at 10.2°C (minimum). All data were normalized by control condition of several minutes before cold stress application (indicated as “0 min”). In case of using KO cells, data were normalized by control condition of several minutes before cold stress application of each cell lines. For comparisons of time 60 min among deferent cells or conditions, all data were normalized by the control conditions (WT or DMSO) of time 60 min of each experiment.
Cytosolic Ca2+ concentration quantification: Cells were seeded in 96‐well black plate (Falcon, Cat# 353219) and preloaded with 4 µM Cal‐520 AM (Abcam, Cat#ab171868) and Pluronic F127 (0.02%) diluted in HHBS (Hank's Buffer with Hepes) for two hours. Subsequently, cells were washed with HHBS once to remove trace Cal‐520 and medium was changed to normal medium with 10% FBS. All inhibitors were pretreated for 30 min at indicated concentrations. The fluorescence of Cal‐520 before and after cold stress application at indicated time was quickly measured at the wavelength (Ex/Em = 492/514 nm) using Varioskan Flash (Thermo Fisher Scientific). During measurements, the temperature was set at 10.2°C (minimum). Cold stress was continued to the endpoint. All data were normalized by control condition of several minutes before cold stress application (indicated as “0 min”). For comparisons of time 60 min among deferent cells or conditions, all data were normalized by the control conditions (WT or DMSO) of time 60 min of each experiment.
Fe2+ quantification assay
Cells were preloaded with 5 µM FerroFarRed (Goryokaku, Cat#GC903‐01) to the serum‐free culture media and incubated for an hour in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. Cell culture medium was replaced with fresh serum‐free medium right before inhibitor treatment or cold stress application. 100 µM Fe(II)SO4 solution diluted in serum‐free DMEM was added during cold stress as a control stimulus. After cold stress for 5 h, cells were washed with PBS and trypsinized, followed by suspension in PBS. The cell suspension was filtered through a cell strainer (40 µm, Falcon) and then subjected to flow cytometer analysis (FACSCalibur, BD Biosciences, FL4‐H channel) measuring 10,000 cells.
Expression and sgRNA plasmids construction
Lentiviral plasmids for this study were constructed by standard molecular biology techniques, and all constructs were verified by sequencing. A human MICU1 cDNA (CDS of NM_001195518.2) and MCU cDNA (CSD of NM_138357.2) were cloned from cDNA derived from A549 cells and subcloned into the entry vector (pENTR) with an C‐terminal HA‐tag. Moreover, wild type of MICU1 resistant to sgRNA#1 was constructed by mutagenesis from full‐length MICU1 cDNA and subcloned into pENTR. Then, ∆EF (D231A/E242K/D421A/E432K), ∆DID (438KQRLMRGL > 438AQALMAGL), ∆DIMER (C463A), and ∆EMRE (99KKKKR > 99AAAAA) as previously shown(Perocchi et al, 2010; Paillard et al, 2018) were constructed from MICU1 wild‐type resistant to sgRNA#1 and subcloned into pENTR with an C‐terminal HA‐tag. pLenti CMV/TO Neo DEST vector is constructed by in Fusion HD cloning Kit (Takara, Cat#Z9648N) from pLenti CMV/TO Puro DEST (670‐1) (Addgene, Cat#17293) for the backbone of destination vector and pEGFP‐C1 (Addgene, Cat#6084‐1) for neomycin resistant marker. Finally, recombination between pENTR and pLenti CMV/TO Neo DEST was performed with Gateway LR Clonase ll Enzyme Mix (Invitrogen, Cat#11791‐100). Vectors containing sgRNAs were subcloned into LentiCRISPRv2 (Addgene, Cat#52961) and lentiGuide‐Puro (Addgene, Cat#52963). Firstly, these vectors were digested by FastDigest Fsp3I (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat# FD0454) and FastAP (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat#EF0654) for 30 min at 37°C. Then, digested vectors were purified by using Wizard SV Gel&PCR Clean‐up System (Promega, Cat#A9285) and eluted in TE buffer. Each pair of oligo nucleotides were phosphorylated by T4 PNK (NEB, Cat#M0201S or Toyobo, Cat#PNK‐111) with T4 ligation buffer (Takara, Cat#A1901) for 30 min at 37°C and annealed for 30 min at room temperature after incubation for 2 min at 98°C. Then, ligation reactions were performed by Ligation‐Convenience Kit (Nippongene, Cat#319‐05961). All lentiviral plasmids were transformed into homemade Stbl3 bacteria (propagated from Invitrogen, Cat#C737303). Primer sequences are listed in Table EV1.
Lentiviral production and infection
All lentivirus clones for stably overexpressing or re‐expressing genes were obtained as follows.
Lentivirus was produced in HEK293T cells. In brief, HEK293T cells were cultured with DMEM‐high glucose with 10% FBS were transfected with pCMV‐VSV‐G (Addgene, Cat#8454), psPAX2 (Addgene, Cat#12260), and lentiviral vectors (MICU1 and MCU expression or sgRNA vectors) using Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen, Cat#130469), according to manufacturer’s protocols with minor optimization. To reduce cytotoxicity, after 4–6 h the medium of cells was replaced with fresh one. Lentiviral supernatants were harvested at 48–60 h post‐transfection and filtered through a 0.45 µm PVDF filter (Millipore, Cat#SLHV033RS). A549 cells or Cas9‐A549 cells and Cas9‐HT‐1080 cells were seeded into 12‐well plates (1.0 × 105 cells per well) with medium supplemented with 10 µg/ml polybrene (Nakarai tesque, Cat#17736‐44), and reverse transduction with lentivirus for overnight was performed. Next day, the culture medium was replaced with fresh one containing appropriate antibiotics (puromycin (Gibco, Cat#A11138‐03; 1.5 µg/ml), blasticidin (Invitrogen, Cat#A1113903; 10 µg/ml), or G418 (Invitrogen, Cat#10131‐035; 2 mg/mL)) for more than 2–7 days until control cells were dead.
Stably CRISPR/Cas9‐mediated gene knockout and Cas9 expression cells
A549 cells were infected with LentiCRISPRv2 which have sgRNAs targeting MICU1 and selected by puromycin as described above. Then, polyclonal KO cells were seeded onto 10 cm dish at low density to pick single colony. Single clones of MICU1 knockout cells were confirmed by immunoblotting.
Then, polyclonal KO clones of MICU1 knockout cells in HT‐1080 cells were confirmed by immunoblotting for further cell viability assays.
Stably‐FLAG‐Cas9‐A549 cells and FLAG‐Cas9‐HT‐1080 cells were established by lentiviral infection produced from lentiCas9‐Blast (Addgene, Cat#52962), and single cloned cells were picked as described above, and FLAG‐Cas9 expression was validated by immunoblotting.
Gene silencing by siRNA transfection and analysis of TRPM8 mRNA expression by qRT–PCR
Knockdown experiment with siRNA was carried out by reverse transfection using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX (Invitrogen, Cat#133778‐150), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. After transfection for around 48 hours, each experiment was performed.
Total RNA was isolated from A549 cells using Isogen (Wako, Cat#319‐90211) and reverse transcribed with ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Master Mix with gDNA Remover (Toyobo, Cat#FSQ‐301). Primers (GAPDH and TRPM8) were used as previously described(Bidaux et al, 2015). Quantitative reverse transcription–PCR was performed using KAPA SYBR Fast qPCR Kit (KAPABIO, Cat#KK4602) with a QuantStadio1 Real‐Time PCR System (ABI). Data were normalized to GAPDH. Primer sequences are listed in Table EV1.
Cell lysis and immunoblotting
Cells were lysed with IP lysis buffer (10 mM EDTA pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.5, 1% w/v sodium deoxycholate, 1% v/v Triton X‐100, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 5 µg/ ml leupeptin) supplemented with phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (6.25 µM cantharidin, 2.5 mM imidazole, 15 mM b‐glycerophosphatase, 10 mM NaF, 1.25 mM Na3VO4 and 1.5 mM Na2MoO4). Cell extracts were centrifuged for 10 min at 17,700 × g, and supernatants were sampled by adding 2 x SDS sample buffer (80 µg/ml bromophenol blue, and 10 mM dithiothreitol, 28.8% glycerol, 4% SDS, and 80 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.8). After boiling at 98°C for 3 min, the samples were resolved by SDS–PAGE and electroblotted onto Immobilon‐P membrane (Millipore, Cat#IPVH00010). The membranes were blocked with 2% skim milk (Megmilk Snow Brand) in TBS‐T (137 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.0, and 0.1% Tween 20) and probed with the appropriate primary antibodies diluted by 1st antibody‐dilution buffer (TBS‐T with 5% BSA (Iwai Chemicals, Cat#A001) and 0.1% NaN3 (Nacalai Tesque, Cat#312‐33)) for overnight. After replacing and probing the appropriate secondary antibodies diluted with 2% skim milk in TBS‐T, antibody‐antigen complexes were detected on X‐ray films (FUJIFILM, Cat#47410‐26615 or Cat#47410‐22617) using an ECL system (ECL select, diluted in 1/200, GE Healthcare, Cat#RPN2235). Representative images were shown after the adjustment to the appropriate brightness and contrast using the ImageJ software (ver.1.52 t) by enhancing contrast option (saturated pixels: 0.1%).
Genome‐wide CRISPR screening
A genome‐wide CRISPR screening was performed as described (Wang et al, 2016; Joung et al, 2017) with minor optimization. Firstly, HEK293T cells were seeded into 6‐well plates (7.5 x 105 cells per well). Then, next day, cells were transfected with pCMV‐VSV‐G, psPAX2, and with GeCKO v2 Human sgRNA library A and B (Addgene, Cat#1000000048) with the ratio of 0.1 µg : 0.9 µg : 1 µg using Lipofectamine 3000, according to manufacturer’s protocols. To reduce cytotoxicity, after 8 hours the medium of cells was replaced with fresh one. Lentiviral supernatants were harvested at 2 days post‐transfection and filtered through a 0.45 µm PVDF filter.
Cas9‐A549 cells were seeded into 6‐well plates (3.0 × 106 cells per well, 3.0 × 108 cells in total, i.e., 500 times of its library) with medium containing 10 µg/ml polybrene and, at the same time, reverse transduction with lentivirus containing GeCKOv2 libraries (119,412 sgRNAs) with extremely low infection efficiency (MOI = 0.08 & SIP = 96%, calculated as described (Pan et al, 2018)). The next day, the medium was replaced with fresh medium containing puromycin (1.5 µg/ml). After puromycin selection for 2 days, cells were collected and re‐seeded into T‐225 flasks (2.0 × 107 cells per flasks in total six). The next day, one group (three flasks) was applied to cold stress for 30 hours and the other was cultured in normal conditions. After cold stress application, cells were cultured for 43 hours and re‐seeded into new flasks and the same cold stress application was performed once again (in total twice). Then, cells were cultured for 18 hours after normal conditions, cells were collected and centrifuged for 3 min at 400 × g, and cell pellets were harvested. The extraction of gDNA, sgRNA amplification, and identification by NGS (Illumina Hiseq) was performed by Genewiz.
Identification of positive genes and analysis of screening
After deep‐sequencing sgRNAs, we obtained count data of each sgRNAs with control sample and cold stress application sample. To get more statistically significant genes, the low expression sgRNAs were omitted (threshold of count < 20; total 5233 sgRNAs were omitted), and the count data were analyzed by MAGeCK software as described (Li et al, 2014). The plots of RRA score as positive selection were depicted by using R with Rstudio, and the plot of beta score was depicted by MAGeCKFlute (Wang et al, 2019). In addition to MICU1, a well‐known ferroptosis regulator (ACSL4) and ferroptosis suppressors (GPX4, SLC7A11, and AIFM2) were highlighted.
mRNA expression data among different tissues mined from database
Gene expression data of MICU1 (CBARB1) and GAPDH in human normal tissues samples are mined from Reference Expression dataset (RefEx) (Ono et al, 2017).
Statistical analysis
All data are shown as the mean ± SEM, and number (n) in each figure legend represents biological replicates. All experiments were performed at least three times independently. Two‐tailed Student’s t‐test, one‐way or two‐way ANOVA followed by William’s, Dunnett’s, or Tukey’s multiple comparisons test were performed using R with RStudio, and stars indicates *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, see figure legend for further detail. All data obtained by probes (Cal‐520‐AM, Rhod‐2‐AM, TMRE) measured by Varioskan and JC‐1 measured by FACSCalibur are considered as paired samples with control ones in each experiment; thus, all data were normalized by each control as 1. The results of the statistical analysis are represented in each figure. P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Author contributions
IN and HI co‐conceived of and supervised this project. TN, MO, KK, ST, SI designed and performed the experiments and TN analyzed and visualized the data. TN, KH, IN, and HI drafted the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting information
Appendix
Expanded View Figures PDF
Table EV1
Dataset EV1
Source Data for Expanded View
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 1
Source Data for Figure 2
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Y. Sekine (the Department of Medicine at the University of Pittsburgh) for helpful advices with the screening. This work was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) under the Project for Elucidating and Controlling Mechanisms of Aging and Longevity (grant number JP20gm5010001 to HI), by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) Moonshot R&D–MILENNA program (grant number JPMJMS2022‐18 to HI)by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) under the Grant‐in‐Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (KAKENHI; grant number JP17H06419 to IN) and the Grants‐in‐Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI; grant numbers JP18H03995 JP18K19469 to HI, JP18H02569 and JP15K14445 to IN) and by the Yakugaku‐shinkoukai Foundation.
EMBO reports (2021) 22: e51532.
Contributor Information
Isao Naguro, Email: nagurois@mol.f.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Hidenori Ichijo, Email: ichijo@mol.f.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of the present study are available from the corresponding authors upon request. No data were deposited in a public database.
References
- Angeli JPF, Shah R, Pratt DA, Conrad M (2017) Ferroptosis Inhibition: Mechanisms and Opportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38: 489–498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautista DM, Siemens J, Glazer JM, Tsuruda PR, Basbaum AI, Stucky CL, Jordt SE, Julius D (2007) The menthol receptor TRPM8 is the principal detector of environmental cold. Nature 448: 204–208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li Z, Magtanong L, Ford B, Tang PH, Roberts MA, Tong B, Maimone TJ, Zoncu R et al (2019) The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 575: 688–692 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidaux G, Borowiec AS, Gordienko D, Beck B, Shapovalov GG, Lemonnier L, Flourakis M, Vandenberghe M, Slomianny C, Dewailly E et al (2015) Epidermal TRPM8 channel isoform controls the balance between keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation in a cold‐dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112: E3345–E3354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo‐Hair SM, Sexton JT, Landry BP, Olson EJ, Igoshin OA, Tabor JJ (2016) FlowCal: A User‐Friendly, Open Source Software Tool for Automatically Converting Flow Cytometry Data from Arbitrary to Calibrated Units. ACS Synthetic Biology 5: 774–780 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csordás G, Golenár T, Seifert EL, Kamer KJ, Sancak Y, Perocchi F, Moffat C, Weaver D, de la Fuente PS, Bogorad R et al (2013) MICU1 controls both the threshold and cooperative activation of the mitochondrial Ca2⁺ uniporter. Cell Metab 17: 976–987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS et al (2012) Ferroptosis: An iron‐dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149: 1060–1072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll S, Freitas FP, Shah R, Aldrovandi M, da Silva MC, Ingold I, Grocin AG, Xavier da Silva TN, Panzilius E, Scheel CH et al (2019) FSP1 is a glutathione‐independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 575: 693–698 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummen GPC, Van Liebergen LCM, Op den Kamp JAF, Post JA (2002) C11‐BODIPY581/591, an oxidation‐sensitive fluorescent lipid peroxidation probe: (Micro)spectroscopic characterization and validation of methodology. Free Radic Biol Med 33: 473–490 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S, Li H, Tai Y, Huang J, Su Y, Abramowitz J, Zhu MX, Birnbaumer L, Wang Y (2013) Canonical transient receptor potential 3 channels regulate mitochondrial calcium uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: 11011–11016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann Angeli JP, Krysko DV, Conrad M (2019) Ferroptosis at the crossroads of cancer‐acquired drug resistance and immune evasion. Nat Rev Cancer 19: 405–414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, Herbach N, Aichler M, Walch A, Eggenhofer E et al (2014) Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol 16: 1180–1191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao M, Yi J, Zhu J, Minikes AM, Monian P, Thompson CB, Jiang X (2019) Role of Mitochondria in Ferroptosis. Mol Cell 73: 354–363.e353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi C, Marchi S, Pinton P (2018) The machineries, regulation and cellular functions of mitochondrial calcium. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19: 713–730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong J, Liu J, Ronan EA, He F, Cai W, Fatima M, Zhang W, Lee H, Li Z, Kim G‐H et al (2019) A Cold‐Sensing Receptor Encoded by a Glutamate Receptor Gene. Cell 1–12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk B, Klec C, Leitinger G, Bernhart E, Rost R, Bischof H, Madreiter‐Sokolowski CT, Radulović S, Eroglu E, Sattler W et al (2019) MICU1 controls cristae junction and spatially anchors mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter complex. Nat Commun 10: 3732 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall DD, Wu Y, Domann FE, Spitz DR, Anderson ME (2014) Mitochondrial calcium uniporter activity is dispensable for MDA‐MB‐231 breast carcinoma cell survival. PLoS One 9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori K, Ishikawa H, Sakauchi C, Takayanagi S, Naguro I, Ichijo H (2017) Cold stress‐induced ferroptosis involves the ASK1‐p38 pathway. EMBO Rep 18: e201744228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama T, Tsuboi H, Niwa M, Miki A, Kadota S, Ikeshita Y, Okuda K, Nagasawa H (2017) A universal fluorogenic switch for Fe(II) ion based on N‐oxide chemistry permits the visualization of intracellular redox equilibrium shift towards labile iron in hypoxic tumor cells. Chemical Science 8: 4858–4866 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingold I, Berndt C, Schmitt S, Doll S, Poschmann G, Buday K, Roveri A, Peng X, Porto Freitas F, Seibt T et al (2018) Selenium Utilization by GPX4 Is Required to Prevent Hydroperoxide‐Induced Ferroptosis. Cell 172: 409–422.e421 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang D, Zhao L, Clapham DE (2009) Genome‐wide RNAi screen identifies Letm1 as a mitochondrial Ca2+/H+ antiporter. Science (New York, NY) 326: 144–147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jing L, Yao L, Zhao M, Peng L‐P, Liu M (2018) Organ preservation: from the past to the future. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39: 845–857 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joung J, Konermann S, Gootenberg JS, Abudayyeh OO, Platt RJ, Brigham MD, Sanjana NE, Zhang F (2017) Genome‐scale CRISPR‐Cas9 knockout and transcriptional activation screening. Nat Protoc 12: 828–863 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamer KJ, Mootha VK (2014) MICU1 and MICU2 play nonredundant roles in the regulation of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter. EMBO Rep 15: 299–307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karashima Y, Talavera K, Everaerts W, Janssens A, Kwan KY, Vennekens R, Nilius B, Voets T (2008) TRPA1 acts as a cold sensor in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106: 1273–1278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautenschläger I, Pless‐Petig G, Middel P, De Groot H, Rauen U, Stojanovic T (2018) Cold Storage Injury to Rat Small‐bowel Transplants ‐ Beneficial Effect of a Modified HTK Solution. Transplantation 102: 1666–1673 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W, Xu H, Xiao T, Cong L, Love MI, Zhang F, Irizarry RA, Liu JS, Brown M, Liu XS (2014) MAGeCK enables robust identification of essential genes from genome‐scale CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screens. Genome Biol 15: 554 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu JC, Liu J, Holmström KM, Menazza S, Parks RJ, Fergusson MM, Yu ZX, Springer DA, Halsey C, Liu C et al (2016) MICU1 Serves as a Molecular Gatekeeper to Prevent In Vivo Mitochondrial Calcium Overload. Cell Rep 16: 1561–1573 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallilankaraman K, Doonan P, Cárdenas C, Chandramoorthy HC, Müller M, Miller R, Hoffman NE, Gandhirajan RK, Molgó J, Birnbaum MJ et al (2012) MICU1 is an essential gatekeeper for MCU‐mediated mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake that regulates cell survival. Cell 151: 630–644 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchi S, Giorgi C, Galluzzi L, Pinton P (2020) Ca Fluxes and Cancer. Molecular Cell 78: 1055–1069 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Marco G, Vallese F, Jourde B, Bergsdorf C, Sturlese M, De Mario A, Techer‐Etienne V, Haasen D, Oberhauser B, Schleeger S et al (2020) A High‐Throughput Screening Identifies MICU1 Targeting Compounds. Cell Rep 30: 2321–2331.e2326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai T, Sawano A, Eun Sun P, Miyawaki A (2001) Circularly permuted green fluorescent proteins engineered to sense Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 3197–3202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T, Naguro I, Ichijo H (2019) Iron homeostasis and iron‐regulated ROS in cell death, senescence and human diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) ‐ General Subjects 1863: 1398–1409 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono H, Ogasawara O, Okubo K, Bono H (2017) RefEx, a reference gene expression dataset as a web tool for the functional analysis of genes. Scientific Data 4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paillard M, Csordás G, Huang KT, Várnai P, Joseph SK, Hajnóczky G (2018) MICU1 Interacts with the D‐Ring of the MCU Pore to Control Its Ca 2+ Flux and Sensitivity to Ru360. Mol Cell 72: 778–785.e773 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D, Kobayashi A, Jiang P, Ferrari de Andrade L, Tay RE, Luoma AM, Tsoucas D, Qiu X, Lim K, Rao P et al (2018) A major chromatin regulator determines resistance of tumor cells to T cell‐mediated killing. Science (New York, NY) 359: 770–775 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan X, Liu J, Nguyen T, Liu C, Sun J, Teng Y, Fergusson MM, Rovira II, Allen M, Springer DA et al (2013) The physiological role of mitochondrial calcium revealed by mice lacking the mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Nat Cell Biol 15: 1464–1472 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patapoutian A, Peier AM, Story GM, Viswanath V (2003) ThermoTRP channels and beyond: mechanisms of temperature sensation. Nat Rev Neurosci 4: 529–539 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patron M, Checchetto V, Raffaello A, Teardo E, Vecellio Reane D, Mantoan M, Granatiero V, Szabò I, De Stefani D, Rizzuto R (2014) MICU1 and MICU2 finely tune the mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter by exerting opposite effects on MCU activity. Mol Cell 53: 726–737 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perocchi F, Gohil VM, Girgis HS, Bao XR, McCombs JE, Palmer AE, Mootha VK (2010) MICU1 encodes a mitochondrial EF hand protein required for Ca(2+) uptake. Nature 467: 291–296 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrungaro C, Zimmermann KM, Küttner V, Fischer M, Dengjel J, Bogeski I, Riemer J (2015) The Ca2+‐dependent release of the Mia40‐induced MICU1‐MICU2 dimer from MCU regulates mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. Cell Metab 22: 721–733 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R, De Stefani D, Raffaello A, Mammucari C (2012) Mitochondria as sensors and regulators of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13: 566–578 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S‐Y, Beutner G, Dirksen RT, Kinnally KW, Sheu S‐S (2010) Mitochondrial ryanodine receptors and other mitochondrial Ca2+ permeable channels. FEBS Lett 584: 1948–1955 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancak Y, Markhard AL, Kitami T, Kovács‐bogdán E, Kamer KJ, Udeshi ND, Carr SA, Chaudhuri D, Clapham DE, Li AA et al (2013) EMRE Is an Essential Component. Science 147: 1379–1382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjana NE, Shalem O, Zhang F (2014) Improved vectors and genome‐wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat Methods 11: 783–784 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalem O, Sanjana NE, Hartenian E, Shi X, Scott DA, Mikkelson T, Heckl D, Ebert BL, Root DE, Doench JG et al (2014) Genome‐scale CRISPR‐Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science (New York, NY) 343: 84–87 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K, Skouta R, Kaplan A, Yang WS, Hayano M, Dixon SJ, Brown LM, Valenzuela CA, Wolpaw AJ, Stockwell BR (2016) Global survey of cell death mechanisms reveals metabolic regulation of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 12: 497–503 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK, Kagan VE et al (2017) Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 171: 273–285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki J, Kanemaru K, Ishii K, Ohkura M, Okubo Y, Iino M (2014) Imaging intraorganellar Ca2+ at subcellular resolution using CEPIA. Nat Commun 5: 1–13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomar D, Thomas M, Garbincius JF, Kolmetzky DW, Jadiya P, Carpenter AC, Elrod JW (2019) MICU1 regulates mitochondrial cristae structure and function independent of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter channel. bioRxiv [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Trenker M, Malli R, Fertschai I, Levak‐Frank S, Graier WF (2007) Uncoupling proteins 2 and 3 are fundamental for mitochondrial Ca2+ uniport. Nat Cell Biol 9: 445–452 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B, Wang M, Zhang W, Xiao T, Chen C‐H, Wu A, Wu F, Traugh N, Wang X, Li Z et al (2019) Integrative analysis of pooled CRISPR genetic screens using MAGeCKFlute. Nat Protoc : 1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Yang X, Li S, Wang Z, Liu Y, Feng J, Zhu Y, Shen Y (2014) Structural and mechanistic insights into MICU1 regulation of mitochondrial calcium uptake. EMBO J 33: 594–604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T, Lander ES, Sabatini DM (2016) Viral packaging and cell culture for CRISPR‐based screens. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols 2016: 289–296 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettmarshausen J, Goh V, Huang KT, Arduino DM, Tripathi U, Leimpek A, Cheng Y, Pittis AA, Gabaldón T, Mokranjac D et al (2018) MICU1 Confers Protection from MCU‐Dependent Manganese Toxicity. Cell Rep 25: 1425–1435.e1427 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang WS, Sriramaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji AF, Clish CB et al (2014) Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 156: 317–331 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G, Wang L‐G, Han Y, He Q‐Y (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16: 284–287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Appendix
Expanded View Figures PDF
Table EV1
Dataset EV1
Source Data for Expanded View
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 1
Source Data for Figure 2
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the findings of the present study are available from the corresponding authors upon request. No data were deposited in a public database.


