Abstract
Background and Aims
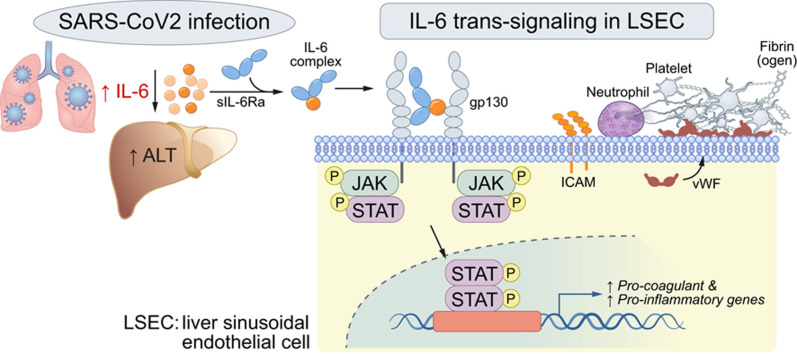
COVID-19 is associated with liver injury and elevated interleukin-6 (IL-6). We hypothesized that IL-6 trans-signaling in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) leads to endotheliopathy (a proinflammatory and procoagulant state) and liver injury in COVID-19.
Methods
Coagulopathy, endotheliopathy, and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were retrospectively analyzed in a subset (n = 68), followed by a larger cohort (n = 3,780) of patients with COVID-19. Liver histology from 43 patients with COVID-19 was analyzed for endotheliopathy and its relationship to liver injury. Primary human LSECs were used to establish the IL-6 trans-signaling mechanism.
Results
Factor VIII, fibrinogen, D-dimer, von Willebrand factor (vWF) activity/antigen (biomarkers of coagulopathy/endotheliopathy) were significantly elevated in patients with COVID-19 and liver injury (elevated ALT). IL-6 positively correlated with vWF antigen (p = 0.02), factor VIII activity (p = 0.02), and D-dimer (p <0.0001). On liver histology, patients with COVID-19 and elevated ALT had significantly increased vWF and platelet staining, supporting a link between liver injury, coagulopathy, and endotheliopathy. Intralobular neutrophils positively correlated with platelet (p <0.0001) and vWF (p <0.01) staining, and IL-6 levels positively correlated with vWF staining (p <0.01). IL-6 trans-signaling leads to increased expression of procoagulant (factor VIII, vWF) and proinflammatory factors, increased cell surface vWF (p <0.01), and increased platelet attachment in LSECs. These effects were blocked by soluble glycoprotein 130 (IL-6 trans-signaling inhibitor), the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib, and STAT1/3 small-interfering RNA knockdown. Hepatocyte fibrinogen expression was increased by the supernatant of LSECs subjected to IL-6 trans-signaling.
Conclusion
IL-6 trans-signaling drives the coagulopathy and hepatic endotheliopathy associated with COVID-19 and could be a possible mechanism behind liver injury in these patients.
Lay summary
Patients with SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) infection often have liver injury, but why this occurs remains unknown. High levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and its circulating receptor, which form a complex to induce inflammatory signals, have been observed in patients with COVID-19. This paper demonstrates that the IL-6 signaling complex causes harmful changes to liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and may promote blood clotting and contribute to liver injury.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, thrombosis, endothelial cell dysfunction, coagulopathy
Graphical abstract
See Editorial, pages 503–505
Introduction
COVID-19 has led to a global pandemic and has become the leading cause of death in the United States.1 Liver injury (elevated values of liver biochemical tests) is a common feature of COVID-192 associated with adverse outcomes such as intensive care unit admission/mechanical ventilation and death.3 , 4 Liver injury in COVID-19 has been associated with elevated interleukin 6 (IL-6)3 , 5 and some hypercoagulable parameters, with evidence of microthrombi on liver histopathology.3 , 6 , 7 These findings suggest a role for vascular pathology in liver injury in COVID-19, but mechanistic details are lacking.
Patients with COVID-19 exhibit coagulopathy8 , 9 and endotheliopathy, characterized by elevated levels of von Willebrand factor (vWF) and soluble thrombomodulin, which has been associated with disease severity and mortality.10 The same study also revealed significantly elevated activity of factor VIII, which is produced primarily by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs),11 in critically ill patients with COVID-19, supporting a role for hypercoagulable LSECs in COVID-19-related liver injury.
IL-6 is a hallmark cytokine of severe COVID-1912 , 13 and is associated with liver injury in the disease.14 IL-6 induces downstream signaling via Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) activation through 2 pathways. Classical IL-6 signaling is via IL-6 binding to the ligand-binding alpha subunit of its receptor (gp80/IL-6Ra) and subsequently recruiting the signaling beta subunit (glycoprotein 130 [gp130]) to induce downstream signaling.15 , 16 Trans-signaling occurs with IL-6 binding to a soluble form of the receptor alpha subunit (sIL-6R), which is typically increased in inflammatory conditions,17 to form an IL-6/sIL-6R complex, which then interacts with the beta subunit (gp130) on target cells that may not express IL-6Ra.18 , 19 IL-6 trans-signaling is thought to be the major route of IL-6 signaling to LSECs,20 and has been implicated in endotheliopathy in COVID-19.21 Basal levels of sIL-6R are relatively high22 and have been shown to increase in COVID-19,23 with a likely result of increased trans-signaling. Thus, IL-6 is an attractive potential mediator of endotheliopathy in the liver.
We now report a link between IL-6, endotheliopathy, coagulopathy, and liver injury in patients with COVID-19. This link was confirmed using histological analysis of post-mortem liver specimens and in vitro experiments. We implicate IL-6 trans-signaling in LSECs as a driver of this procoagulant endotheliopathy and liver injury. These results have important implications for treatment and prognosis of liver injury and endotheliopathy in COVID-19.
Materials and methods
COVID-19 patient data
Data from a previous cross-sectional study10 of 68 patients at Yale-New Haven Hospital with PCR-confirmed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection was reanalyzed with respect to alanine aminotransferase (ALT) checked within 5 days before and 5 days after coagulation parameters were assessed (peak value recorded). If no ALT was checked in this range, the ALT from the closest possible date was used, and patients with no ALT values were excluded (n = 1). The upper limit of normal for ALT was defined as 33 IU/L for males and 25 IU/L for females.24 Within this sample, thromboelastography (TEG) was performed for the 48 patients in the intensive care unit. A hypercoagulable TEG profile was defined as 2 parameters indicating hypercoagulability. Clinical data from the 6 delivery networks of the Yale-New Haven Health System were subsequently obtained via the Yale DOM-CovX database, a repository of clinical data for all admitted patients with first laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection between 14 days preceding admission and the date of discharge, from 3/10/2020 to 12/1/2020. Of 3,780 total adult (≥18 years old) patients with available data, 140 patients did not have data for ALT and were excluded from liver injury assessment. For this analysis, the maximum ALT value during hospitalization was compared to the maximum value for a given coagulation parameter. For IL-6 analysis, the initial IL-6 value was used to alleviate confounding from tocilizumab administration. Patients were only included in each analysis if they had a value for both variables being compared.
Patients for clinicopathological study
Post-mortem liver biopsy samples from patients with COVID-19 were obtained in collaboration with Drs. Aurelio Sonzogni and Lisa Licini from Papa Giovanni XXIII Hospital – Bergamo as reported previously.6 No patient had a previous history of liver disease or portal hypertension nor developed clinical signs or symptoms of liver failure during their hospital stay. The highest serum ALT and IL-6 reached during the hospital stay were recorded. One patient with COVID-19 disease received tocilizumab and was excluded from analysis of IL-6 levels. HCV antibodies were negative in all patients; 1 patient was HBsAg positive/HBV DNA negative. The liver tissues from 12 healthy adults (6 cases from Johns Hopkins University Hospital [immunohistochemistry experiments] and 6 cases from Yale University [immunofluorescence experiments]) were used as controls.
Statistical analysis
Data are shown as the mean ± SEM or median ± IQR with box plot whiskers showing minimum to maximum. Statistical significance was determined by performing Tukey's test, Student's t-test, Welch's t-test, Mann-Whitney U test, or ANOVA as appropriate based on normality and variance. Normality was assessed as appropriate utilizing the D’Agostino-Pearson omnibus normality test. For categorical variables, statistical significance was determined utilizing the Chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test. Correlation was assessed using the Pearson correlation with the exception of IL-6/vWF correlation for which Spearman correlation was used. p values <0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance. Analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism7 (GraphPad, La Jolla, California, USA) or JMP15 (SAS Institute., NC, USA).
Supplementary materials and methods
For further details regarding the materials and methods used, please refer to the CTAT table and supplementary information, which provide further information on: histological examinations, immunofluorescence, human primary LSECs, primary mouse hepatocytes, platelets, chemicals and reagents, western blot analysis, quantitative reverse transcription PCR, flow cytometry, and small-interfering (si)RNA gene knockdown in human LSECs.
Results
Liver injury is associated with coagulopathy and elevated IL-6 in patients with COVID-19
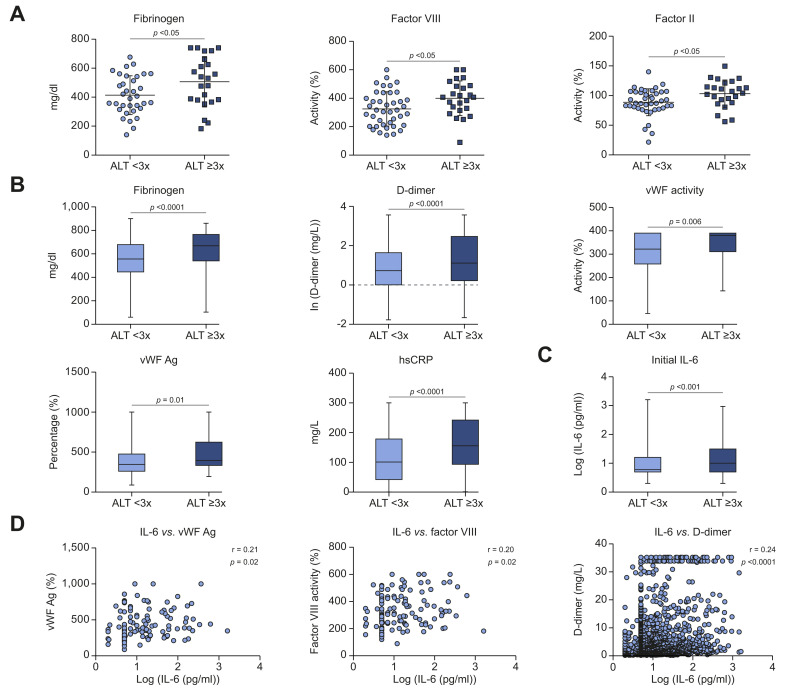
We initially interrogated coagulation data in patients (n = 68) with PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection (previously collected10), and found that patients with elevated ALT had significantly higher levels of fibrinogen (506.3 ± 36.34 mg/dl vs. 413.6 ± 22.98 mg/dl, p <0.05), factor VIII activity (399.9 ± 24.86% vs. 325.1 ± 18.81%, p <0.05), factor II activity (103.3 ± 4.71% vs. 88.75 ± 3.53%, p <0.05), and a trend toward a hypercoagulable TEG profile (p = 0.07) compared to those with lower ALT (Fig. 1 A, Table S4).
Fig. 1.
Procoagulant factors and IL-6 are significantly increased in COVID-19 patients with liver injury.
(A) Serum levels of fibrinogen (n = 57), factor VIII activity (n = 65), and factor II activity (n = 65) in patients with liver injury in an initial sample of patients with COVID-19 (n = 68). (B,C) Retrospective analysis using a large database of COVID-19 inpatients from 3/10/2020 to 12/1/2020 (n = 3,780). (B) Serum levels of fibrinogen (n = 3,344), D-dimer (n = 3,478), vWF activity (n = 129), vWF Ag (n = 131), and hsCRP (n = 2,828) in patients with COVID-19. (C) Initial IL-6 levels in patients with COVID-19. ALT <3x (n = 1,110) and ≥3x (n = 481). (D) Correlation between serum IL-6 and vWF antigen (n = 119), factor VIII activity (n = 126), and D-dimer (n = 1,600). Means compared with 2-tailed Student’s t test for (A) and medians compared with 2-tailed Mann-Whitney U test for (B), (C). Correlation in (D) assessed with Pearson correlation. Patients excluded in each analysis if necessary data not available. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; hsCRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IL-6, interleukin-6; vWF, von Willebrand factor; vWF Ag, VWF antigen.
To validate these findings, data for adult (≥18 years old) patients with laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in the Yale DOM-CovX database from 3/10/2020 to 12/1/2020 (n = 3,780) were retrospectively analyzed. Demographics and selected covariates are shown in Table S5. Consistent with the smaller cohort, significantly higher levels of fibrinogen (median 660 vs. 551.5 mg/dl, p <0.0001), D-dimer (median 0.98 vs. 0.67, p <0.0001), vWF activity (median 380% vs. 322%, p = 0.006), and vWF antigen (median 408% vs. 346%, p = 0.01) were present in patients with elevated ALT (Fig. 1B). High-sensitivity C-reactive protein, a possible procoagulant factor,25 was also significantly elevated in patients with elevated ALT (median 155.8 vs. 101.1 mg/L, p <0.0001). Because vWF and factor VIII are both released from LSECs, these data suggest that procoagulant and inflamed LSECs are central to liver injury in COVID-19.
We also found elevated IL-6 (n = 1,591, median 1.04 vs. 0.87, p <0.0001) (Fig. 1C) in patients with liver injury, consistent with prior reports.3 IL-6 additionally exhibited significant positive correlations with levels of vWF antigen (p = 0.02), factor VIII activity (p = 0.02), and D-dimer (p <0.0001) (Fig. 1D), generating the hypothesis that IL-6 may play a role in LSEC inflammation, activation of coagulation, and liver injury in COVID-19.
Endotheliopathy in the liver is associated with liver inflammation and injury in COVID-19
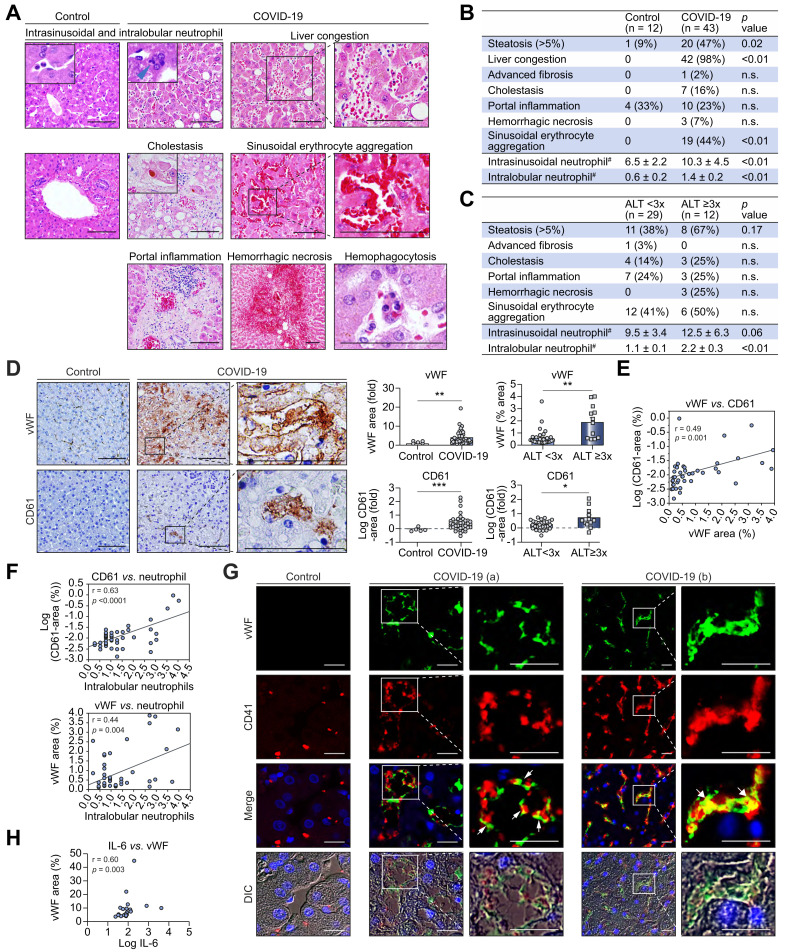
To explore the possible mechanisms of coagulopathy-related liver injury, we analyzed post-mortem liver tissue from patients with COVID-19. For general characterization, we compared the histology of patients with COVID-19 to normal controls (demographic and treatment information in Tables S6 [COVID-19 cohort] & S7 [Yale cohort]), no data available for de-identified Johns Hopkins cohort (n = 6, donor livers for transplantation). Dilated sinusoids with liver congestion, neutrophil infiltration in the hepatic parenchyma and accumulation in the sinusoids, steatosis, and sinusoidal erythrocyte aggregation – meaning erythrocyte aggregation and adherence to sinusoids predominantly in Zone 2 and atypical of congestion – were observed more frequently in the livers of patients with COVID-19 (Fig. 2 A,B). Because these findings may be related to severe inflammation in general, we characterized histological findings specifically related to liver injury in COVID-19 by defining patients with and without liver injury based on the same ALT cut-offs used previously and comparing histology between these groups. Neutrophil infiltration to the hepatic parenchyma (intralobular neutrophils) was significantly increased in patients with elevated ALT (Fig. 2C) and hepatic steatosis (Fig. S1), and neutrophil accumulation in the sinusoids (intrasinusoidal neutrophils) exhibited a strong trend toward an increase in patients with elevated ALT (Fig. 2C).
Fig. 2.
Expression of vWF in the liver is associated with increased platelet adhesion and liver injury in COVID-19.
(A) Representative liver histological features in patients with COVID-19 and controls. Scale bars:100 μm. (B) Summary of histological features (H&E staining) of the livers from patients with COVID-19 (n = 43) and controls (n = 12). #: Neutrophils per high-power field (C) Summary of histological features associated with liver injury: ALT <3x (n = 29) and ≥3x (n = 12). (D) Immunohistochemistry for vWF and CD61 in the liver from patients with COVID-19 and controls. Scale bars:100 μm. Comparisons of vWF and CD61 positive areas in the liver from patients with COVID-19 (n = 43) and controls (n = 5) (Upper and lower left graphs), as well as those from patients with liver injury (n = 12) and those without (n = 29) (upper and lower right graphs). (E) Correlation between vWF and CD61 positive areas in the livers of patients with COVID-19 (n = 43). (F) Correlation between intralobular neutrophils and CD61-positive area (n = 43) and vWF-positive area (n = 43) in the livers of patients with COVID-19. (G) Immunofluorescence of vWF and CD41 (a platelet marker) in the livers from patients with COVID-19 and controls. Scale bars: 25 μm. In patients with COVID-19, vWF is expressed mainly on LSECs, and CD41-positive platelets attach to these LSECs (arrow head). A lower level of vWF is expressed on CD41-positive platelets (arrow). (a) and (b) are different fields from the same patient. (H) Correlation between IL-6 and vWF-positive area in COVID-19 patients. Comparisons between 2 groups were obtained using Welch’s t test for continuous variables, Chi-squared test was used for categorical variables. Pearson’s correlation co-efficients were calculated to examine the correlation among vWF area, CD61 area, and intralobular neutrophils. Spearman correlation was used to examine the correlation between serum IL-6 level and vWF area. Biochemical liver injury in 2 patients with COVID-19 could not be classified (no available ALT value). Data are mean ± SEM. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; DIC, differential interference contrast; IL-6, interleukin-6; LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
Patients with COVID-19 (n = 43) had significantly increased staining for vWF (4.2-fold, p <0.01) compared with controls (n = 5), and patients with COVID-19 and elevated ALT (n = 12) had significantly increased vWF (Mean = 1.87+0.39 vs. 0.53+0.13, p <0.01) compared to those without (n = 29) (Fig. 2D). Because of the role of vWF in platelet adhesion and evidence suggesting thrombocytopathy in COVID-19,26 immunostaining was performed for CD61 (platelet marker). Patients with COVID-19 exhibited significantly increased CD61 staining (Mean = 0.44+0.09 vs. -0.02+0.06, p <0.001), and those with elevated ALT had a significant increase in CD61 compared to those without (mean = 0.72+0.20 vs. 0.25+0.06, p <0.05) (Fig. 2D). Additionally, in patients with COVID-19 (n = 43), vWF-positive area was correlated with platelet (CD61)-positive area (p = 0.001) (Fig. 2E). Further, neutrophil infiltration to the hepatic parenchyma is also positively correlated with CD61 (p <0.0001) and vWF (p = 0.004) (Fig. 2F), suggesting a link between the procoagulant state and liver inflammation. To further assess the relationship of vWF and platelets in the liver endothelium, immunofluorescence staining of vWF and an alternative platelet marker (CD41)27 was performed. Immunostaining for vWF was positive on the LSECs of dilated sinusoids and platelets attached to these LSECs (Fig. 2G) (though LSECs appear to be the main cell type expressing vWF). In concordance with our serological data, there was a significant correlation between IL-6 levels and vWF-positive areas in the livers of patients with COVID-19 (p = 0.003) (Fig. 2H). These results indicate that a procoagulant endotheliopathy is present in the livers of patients with COVID-19 and is likely mediating liver inflammation and injury. We then explored possible mechanisms.
IL-6 trans-signaling in LSECs mediates endotheliopathy, cell surface expression of vWF, and platelet attachment
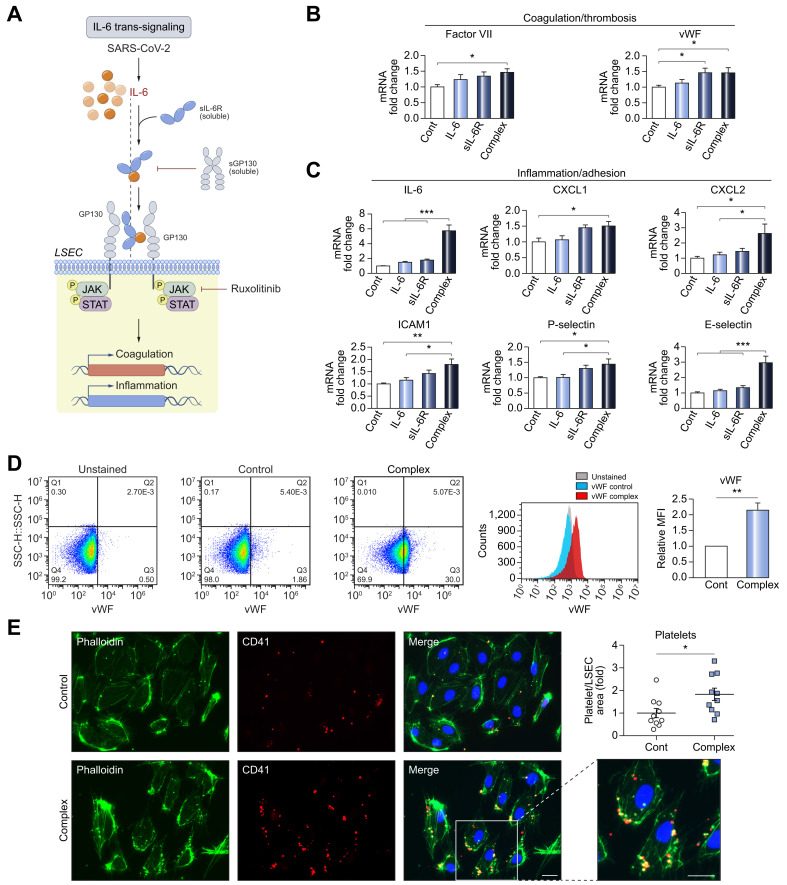
We hypothesized that the coagulopathy and endotheliopathy leading to liver injury in COVID-19 could be caused by IL-6 signaling to LSECs due to the elevated IL-6 levels seen in patients with COVID-19 (Fig. 1C,D, Fig. 2D-H). Classical IL-6 signaling occurs via an oligomeric receptor consisting of an 80 kDa ligand-binding alpha subunit (gp80/IL-6Ra) and a 130 kDa signal-transducing beta subunit (gp130).15 , 16 Because endothelial cells including LSECs do not express IL-6Ra, the primary mechanism of IL-6 signaling to LSECs is thought to be trans-signaling, in which IL-6 binds to a soluble form of the receptor alpha subunit (sIL-6R) and forms a complex which subsequently recruits the beta subunit (gp130, which is expressed by LSECs).20 Elevation of sIL-6R in COVID-19 has been previously reported,23 which would facilitate such trans-signaling. Additionally, basal levels of sIL-6R are relatively high22 and have been shown to increase in influenza infection28 and other inflammatory conditions,29 so the inflammation linked to COVID-19 is likely to increase trans-signaling as well. To test this hypothesis in vitro, we treated primary human LSECs with culture medium alone, IL-6 alone, sIL-6R alone, and the IL-6/sIL-6R complex, and found a significant increase in expression of procoagulant factors, such as factor VIII (1.52-fold, p <0.05) and vWF (1.50-fold, p <0.05), in LSECs treated with IL-6/sIL-6R complex (trans-signaling; Fig. 3 A,B). IL-6/sIL-6R complex treatment also significantly increased expression of proinflammatory mediators, such as IL-6 (5.80-fold, p <0.001), CXCL1/2 (1.50/2.62-folds, p <0.05), ICAM1 (1.8-fold, p <0.01), P-selectin (1.43-fold, p <0.05), and E-selectin (3.0-fold, p <0.001) (Fig. 3C). Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) treated in the same way exhibited similar results (Fig. S2). We next examined cell surface vWF on LSECs in response to complex treatment by flow cytometry and found a significant increase (2.15-fold, p <0.01) (Fig. 3D) and platelet attachment to LSECs was also significantly enhanced by complex treatment (1.83-fold, p <0.05) (Fig. 3E). Taken together, these results indicate that IL-6 trans-signaling promotes a procoagulant and proinflammatory phenotype in LSECs, which in turn may promote neutrophil recruitment and liver injury.
Fig. 3.
IL-6 trans-signaling induces endotheliopathy and increases cell surface levels of vWF and platelet attachment to LSECs.
(A) Schema of IL-6 trans-signaling and blocking by soluble gp130 or ruxolitinib. (B,C) qPCR of markers for (B) procoagulant and (C) proinflammatory endotheliopathy. Human primary LSECs were incubated with control, human recombinant IL-6 (20 ng/ml), human recombinant sIL-6R (20 ng/ml) or IL-6/sIL-6R complex (20 ng/ml) for 1 hour. Graphs show the fold-change (control is set to 1). n
= 6. (D) Flow cytometry for cell surface levels of vWF in LSECs treated with control or IL-6/sIL-6R complex (20 ng/ml) for 6 hours. n = 3. (E) Platelet attachment to LSECs. Phalloidin (Green, F-actin for cell structure), CD41 (Red, platelet). LSECs were treated with control or IL-6/sIL-6R complex (20 ng/ml) for 4 hours and incubated with platelets for 2 hours. Scale bar = 10 μm n = 10. Data are mean ± SEM of at least 3 experiments. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple groups, or 2-tailed unpaired t test for 2 groups was used. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001. CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; ICAM1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL-6, interleukin-6; LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; qPCR, quantitative PCR; sIL-6R, soluble IL-6 receptor; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
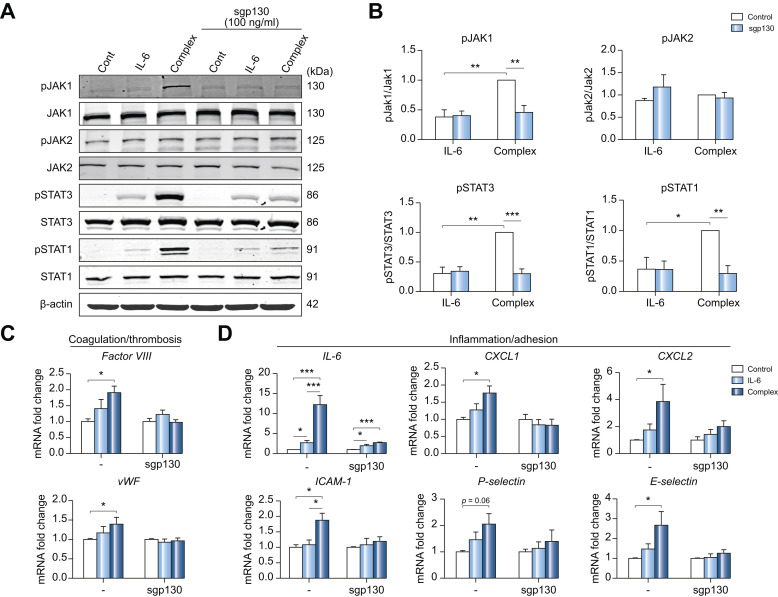
Soluble gp130 (sgp130) blocks JAK1 and STAT3 phosphorylation induced by IL-6 trans-signaling in LSECs
Treatment of human primary LSECs with IL-6 alone (classical signaling) or the IL-6/sIL-6R complex (trans-signaling; Fig. 3A) was used to define downstream signaling. We found that the proportion of phosphorylated STAT1/3 is higher and persists for a longer duration with complex treatment compared to IL-6 alone (Fig. S3A,B). We observed similar results in HUVECs (Fig. S3C). To further confirm the causative role of IL-6 trans-signaling in LSECs, we used soluble gp130 protein (Fc) that can bind to the IL-6/sIL-6R complex and specifically block IL-6 trans-signaling without blocking classical signaling. The concentration of sgp130 Fc was optimized using HUVECs (Fig. S4). As shown in Fig. 4 A,B, IL-6/sIL-6R complex treatment significantly increased the phosphorylation of JAK1 and STAT1/3, which was blocked by sgp130 Fc. Of note, sgp130 Fc did not affect JAK2, suggesting that STAT1/3 is phosphorylated downstream of JAK1. Importantly, increased mRNA expression of factor VIII, vWF (Fig. 4C), IL-6, CXCL1/2, ICAM1, P-selectin, and E-selectin (Fig. 4D) induced by the IL-6/sIL-6R complex, were blocked by sgp130 treatment. These results support IL-6 trans-signaling as the mechanism for LSEC endotheliopathy in SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Fig. 4.
Soluble gp130 blocks JAK1 and STAT3 phosphorylation induced by IL-6 trans-signaling in LSECs.
Human primary LSECs were treated with control, IL-6 (20 ng/ml) or IL-6/sIL-6R complex (20 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of sgp130 Fc (100 ng/ml) for 15 minutes (western blot) and 1 hour (qPCR). (A) A representative blot. β-actin (loading control). n = 3. (B) Activation (phosphorylation) of JAK1, JAK2, STAT3 and STAT1. The fold-change for quantification of western blot. (complex without sgp130 is set to 1). n = 3. qPCR of markers for (C) procoagulant and (D) proinflammatory endotheliopathy in LSECs with or without sgp130 Fc (100 ng/ml). n = 6. Control is set to 1 for each experiment and data presented as fold-change vs. complex. Data are mean ± SEM of at least 3 experiments. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple groups, or 2-tailed unpaired t test for 2 groups was used. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001. CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; gp130, glycoprotein 130; ICAM1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL-6, interleukin-6; JAK, Janus kinase; LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; qPCR, quantitative PCR; sgp130, soluble gp130; sIL-6R, soluble IL-6 receptor; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.
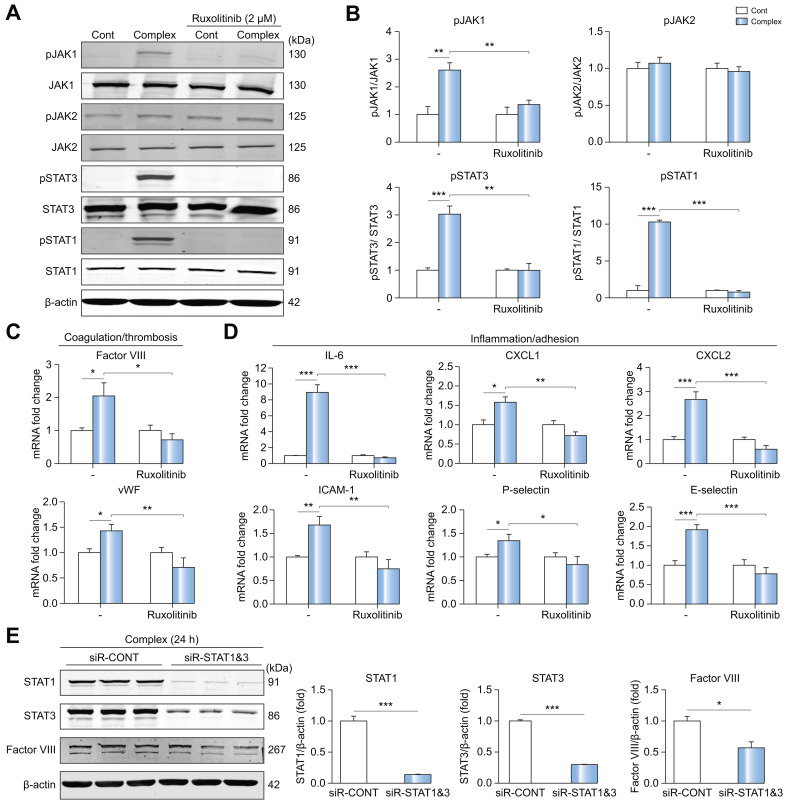
JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib efficiently blocks JAK/STAT induction by IL-6 trans-signaling and procoagulant endotheliopathy in LSECs
We examined the efficacy of JAK inhibitors ruxolitinib and filgotinib in blocking IL-6 trans-signaling in LSECs and HUVECs. Ruxolitinib blocked phosphorylation of JAK1 and STAT1/3 at 2 μM more effectively than filgotinib (Fig. S5). As shown in Fig. 5 A,B, ruxolitinib blocked JAK1 and STAT1/3 activation by IL-6/sIL-6R complex treatment in LSECs. Of note, ruxolitinib did not affect JAK2, again suggesting that STAT1/3 is downstream of JAK1 in IL-6 trans-signaling. Importantly, increased mRNA expression of factor VIII and vWF induced by complex treatment were both blocked by ruxolitinib. Similarly, increased mRNA expression of proinflammatory factors, such as IL-6, CXCL1/2, ICAM1, P-selectin and E-selectin, induced by IL-6/sIL-6R complex treatment, were significantly inhibited by ruxolitinib (Fig. 5D). We next investigated whether knockdown of STAT1/3 affects the protein expression of factor VIII.30 In LSECs treated with complex, protein expression of factor VIII (0.57-fold, p <0.05) was inhibited by siR-STAT1/3 (Fig. 5E). These results indicate that JAK1-STAT1/3 signaling is essential for inducing a procoagulant (Fig. 5C) and proinflammatory (Fig. 5D) LSEC phenotype due to IL-6 trans-signaling.
Fig. 5.
JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib blocks JAK1/STAT3 induction by IL-6 trans-signaling and blocks procoagulant endotheliopathy in LSECs.
Human primary LSECs were treated with control or IL-6/sIL-6R complex (20 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of ruxolitinib (2 μM) for 15 minutes (western blot) and 1 hour (qPCR). Cells were incubated with ruxolitinib for 20 minutes before treatment with complex. (A) Representative western blot. (B) Quantification of western blot. Control is set to 1 for each experiment and data presented as fold-change vs. complex. n = 3. qPCR of markers for (C) procoagulant and (D) proinflammatory endotheliopathy in LSECs with or without ruxolitinib. The graphs show the fold-change (control is set to 1). n = 6. (E) Representative western blot and its quantification. LSECs were treated with siRNA-STAT1 & 3 [STAT1 (10 nM), STAT3 (20 nM) for 64 hours] and then incubated with control or IL-6/sIL-6R complex for 24 hours. n = 3. Data are mean ± SEM of at least 3 experiments. Two-tailed unpaired t test was used. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001. IL-6, interleukin-6; JAK, Janus kinase; LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; qPCR, quantitative PCR; sIL-6R, soluble IL-6 receptor; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.
LSEC-hepatocyte crosstalk amplifies hyperfibrinogenemia in COVID-19
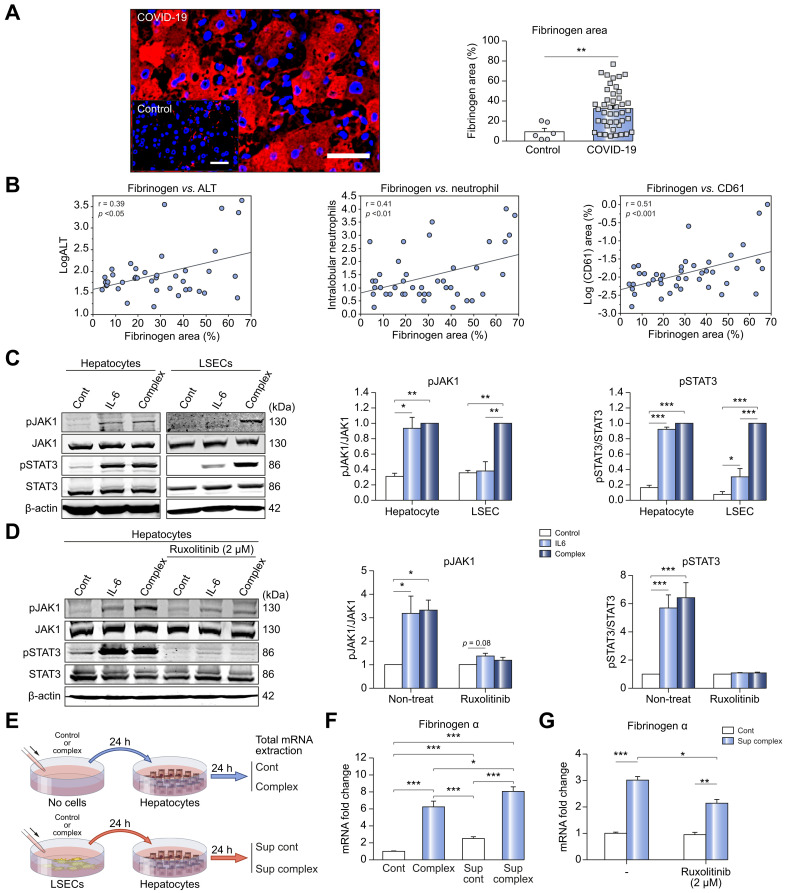
Because fibrinogen is elevated in COVID-19 liver injury (Fig. 1) and may play a role in platelet adhesion31 and neutrophil activation,32 we performed immunostaining for fibrinogen in the livers of patients with COVID-19. Fibrinogen positive areas were significantly increased in patients with COVID-19 (n = 43) compared with controls (n = 6) (%, 9.292±3.392 vs. 32.47±3.08, p <0.01) (Fig. 6 A). Additionally, we found a positive correlation between fibrinogen positive area and serum ALT level (p <0.05) as well as fibrinogen positive area and neutrophil infiltration (p <0.01) (Fig. 6B). Fibrinogen positive areas also significantly correlated with CD61 (platelet) positive area (p <0.001) (Fig. 6B), linking hyperfibrinoginemia and procoagulant endotheliopathy in COVID-19 livers.
Fig. 6.
Fibrinogen levels are increased in livers of patients with COVID-19 by IL-6 signaling amplified by LSEC-hepatocyte crosstalk.
(A) Representative immunolabeling of fibrinogen (Red) in livers from patients with COVID-19. Scale bar: 50 μm. Quantification of fibrinogen positive area (right panel) in patients with COVID-19 (n = 43) and controls (n = 6). (B) Correlation between fibrinogen area and ALT (n = 41), neutrophil infiltration (n = 43), and CD61 (n = 43) in livers of patients with COVID-19. (C) Western blot analyses in primary hepatocytes and primary LSECs treated with control, IL-6 alone (20 ng/ml) or IL-6/sIL-6R complex (20 ng/ml). Representative western blot (left) and its quantification (right panel). n = 3. Complex is set to 1 for each experiment and data presented as fold-change. (D) Western blot analyses in mouse primary hepatocytes treated with control, IL-6 alone (20 ng/ml) or IL-6/sIL-6R complex (20 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of ruxolitinib (2 μM) for 15 minutes. Ruxolitinib was added 20 minutes before treatment with IL-6 alone or complex. n = 3. The graphs show the fold-change (control is set to 1). (E) Experimental scheme for (F & G). (F) mRNA expression of fibrinogen. n = 9. The graphs show the fold-change (control is set to 1). (G) mRNA expression of fibrinogen in mouse primary hepatocytes treated with control medium or supernatant from LSECs treated with IL-6/sIL-6R complex for 24 hours in the presence or absence of ruxolitinib. n = 3. The graphs show the fold-change (control is set to 1). Data are the mean ± SEM of at least 3 experiments. Pearson’s correlation coefficients were calculated to examine the correlation among fibrinogen area, ALT, neutrophil infiltration and CD61 area. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple groups, or two-tailed unpaired t test for 2 groups was used. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; IL-6, interleukin-6; LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; sIL-6R, soluble IL-6 receptor.
We then investigated JAK/STAT signaling downstream of IL-6 in primary mouse hepatocytes. IL-6 alone produced the same levels of JAK1 and STAT3 phosphorylation as complex treatment, suggesting hepatocytes respond primarily to classical IL-6 signaling, in contrast to LSECs (Fig. 6C). Ruxolitinib blocked this effect (Fig. 6D). We next investigated LSEC-hepatocyte crosstalk after IL-6 trans-signaling in LSECs. Primary hepatocytes were treated with control medium, complex alone, supernatant from LSECs treated with control medium for 24 hours, or supernatant from LSECs treated with complex for 24 hours (Fig. 6E). The mRNA expression of fibrinogen was significantly increased by the supernatant from complex-treated LSECs compared with complex alone (1.3-fold, 6.25±0.67 vs. 8.06±0.54, p <0.05) (Fig. 6F), and this increase was mitigated by ruxolitinib (Fig. 6G). Therefore, LSEC-hepatocyte crosstalk, most likely mediated by IL-6 (Fig. 3C), results in hepatocyte JAK/STAT activation and fibrinogen production, which may further worsen liver inflammation and injury.
Discussion
Endotheliopathy and a procoagulant state are highly prevalent in COVID-19, and thrombotic complications are a key cause of morbidity and mortality.26 Our study demonstrates an association between liver injury in COVID-19 and endotheliopathy, and defines a potential thromboinflammatory mechanism likely driven by IL-6 trans-signaling in LSECs.
Our study advances the understanding of the liver injury associated with COVID-19 on several fronts. First, our patient data defines a coagulopathy (higher levels of fibrinogen, factor II, factor VIII, vWF, and D-dimer) in patients with COVID-19 and liver injury. As described previously,10 these findings are discordant from a consumptive coagulopathy and suggest a procoagulant endotheliopathy. Second, our data linking elevated IL-6 levels to elevations of vWF, factor VIII, and D-dimer generated the hypothesis that an IL-6-mediated procoagulant endotheliopathy is driving liver injury in COVID-19. Third, our demonstration of elevated factor VIII and vWF in patients with liver injury suggests LSEC endotheliopathy in particular, because LSECs are the major producer of factor VIII in the body and vWF upregulation is a well-established phenomenon in liver pathology.33
On liver histology, steatosis and mild inflammatory infiltration in the hepatic lobule and portal tract have been previously observed in patients with COVID-19,6 , 34 and several papers have shown sinusoidal thrombosis.6 , 35 Our data defines the presence of a procoagulant endotheliopathy in the liver, linking increased hepatic vWF expression and platelet accumulation with both liver injury and liver inflammation (elevated ALT, neutrophil infiltration), suggesting that endotheliopathy and platelet attachment mediating neutrophil recruitment is a key mechanism of liver injury in COVID-19. We also demonstrated a significant correlation between maximal IL-6 levels and vWF levels in the sinusoidal endothelium, bolstering the potential causative role for IL-6 in intrahepatic endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. This causative role was supported by experiments in primary human LSECs demonstrating an IL-6-mediated procoagulant endotheliopathy occurring via JAK/STAT activation.
In addition to endothelial factors, elevated fibrinogen levels were associated with liver injury, and fibrinogen production from hepatocytes was amplified by crosstalk with LSECs following IL-6 trans-signaling. It remains to be fully explored whether this is playing a direct role in liver injury, perhaps via neutrophil activation,36 or is a parallel phenomenon worsening hyperfibrinoginemia in COVID-19.
Our study has implications for the global coagulopathy and endotheliopathy of COVID-19. Endotheliopathy has been observed not only in the liver but also in the lung,37 and markers of systemic endotheliopathy, such as plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and soluble thrombomodulin, are elevated in COVID-19.10 , 21 LSECs have been previously shown to react to IL-6 trans-signaling with increased angiogenesis,38 but our data also show that they can adopt a proinflammatory, procoagulant phenotype similar to that of other endothelial cells in response to IL-6 trans-signaling.18 , 39 Because the global endotheliopathy of COVID-19 has shown a response to IL-6 inhibition,21 the mechanism of endotheliopathy we identify in LSECs is likely applicable to other vascular beds in the body. Clinical trials of JAK and IL-6 inhibitors have shown promising results in COVID-19,[40], [41], [42] and the mechanism we have defined of IL-6/JAK/STAT-driven endotheliopathy in LSECs may be driving thromboinflammation in other vascular beds and may provide a framework for identifying those patients who will benefit from therapy.
Our study has several limitations. Future studies are needed to define the specificity of our findings to COVID-19 vs. other inflammatory conditions. Additionally, because of a lack of well-defined experimental models, completely definitive mechanistic studies of endotheliopathy as the key cause of liver injury in COVID-19 could not be performed. Data from the Yale DOM-CovX database and all histologic data were obtained via a retrospective cross-sectional study design, and access to our variables of interest was not available for all patients. Changes in therapeutic recommendations for COVID-19 over the course of the study resulted in variation of treatment across our patient sample. Further, given the nature of our tissue samples, we cannot definitively determine the role of LSECs vs. other cell types in producing IL-6 in vivo. The strengths of our study include data from multiple centers, histologic analysis of a relatively large sample of patients with COVID-19, and the fact that most mechanistic experiments were conducted in primary human cells for a high degree of translational relevance.
In conclusion, our study establishes a mechanism by which liver injury may occur in COVID-19 due to an IL-6-mediated procoagulant endotheliopathy. Our findings provide a new level of mechanistic detail to aid in the clinical assessment of liver injury in these patients, and a context in which to understand any long-term consequences of COVID-19 on the liver, which remain unknown. In addition, the mechanistic insights into the coagulopathy and endotheliopathy of COVID-19 provided by this study suggest that the IL-6/JAK/STAT pathway may be a novel target for mitigating the thrombotic complications of COVID-19.
Abbreviations
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; ICAM1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL-6, interleukin 6; LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; gp130, glycoprotein 130; JAK, Janus kinase; mIL-6R, membrane-bound IL-6 receptor; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; sIL-6R, soluble IL-6 receptor; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TEG, thromboelastography; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
Financial support
This study was supported by NIH grants (R56DK121511 & R01DK117597) to YI, (R24 AA025017) to ZS, (R01HL115247, R01HL122815, R01HL150515) to JH, (R01HL142818) to HJC; AASLD Clinical, Translational, and Outcomes Research Award to MM.
Authors’ contributions
YI designed the study, interpreted results, study supervision, wrote the manuscript; MM, NK, RK designed the study, performed experiments, analyzed and interpreted results and wrote the manuscript; AS, LL, CV, PAB, SS, MGA, GP, MS technical and material support, sample analysis; XZ, ZS technical and material support; CF, AW technical and material support, study supervision; TU, XZ, HQ performed animal experiments; AL, ABP, HJC, CP technical and material support; MS study supervision; JH critical revision of the manuscript regarding important intellectual content.
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information.
Ethics approval
This study was reviewed and approved by the institutional review board of the authors hospital/institutions and conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Protocols utilized were IRB#2000028972 (Yale), HIC#2000027792 (Yale), HIC#1005006865 (Yale), IRB# https://e-irb.jhmi.edu/eirb2/sd/Rooms/DisplayPages/LayoutInitial?Container=com.webridge.entity.Entity[OID[543BB818229EE34D99697F551DC8332A]]. Click or tap if you trust this link.">IRB00107893 (Johns Hopkins), and Resolution number 1935/2020 concerning LIVER COVID19/HPG23-YALE UNIVERSITY STUDY (approved by Ethical Committee reference number 2020-0201), issued by Chief Executive Manager of Papa Giovanni XXIII Hospital- Bergamo on October 20, 2020. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects when required by the relevant oversight committee.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest that pertain to this work.
Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Richard Pierce (Yale University) for providing us materials, the Yale Department of Medicine COVID Explorer data repository made possible by funding from the Department of Medicine, the George M. O’Brien Kidney Center at Yale (P30DK079310), resources from the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator and collaboration with the Yale Center for Clinical Investigation, Drs. Maria Ciarleglio & Yanhong Deng for statistical consultation (Yale Liver Center), and the Clinical and Molecular Core of the Silvio O. Conte Digestive Diseases Research Core Center (NIH 30 DK034989).
Footnotes
Author names in bold designate co-first authorship
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.050.
Supplementary data
The following are the supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Woolf S.H., Chapman D.A., Lee J.H. COVID-19 as the leading cause of death in the United States. JAMA. 2021;325:123–124. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.24865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Saviano A., Wrensch F., Ghany M.G., Baumert T.F. Liver disease and COVID-19: from pathogenesis to clinical care. Hepatology. 2020 doi: 10.1002/hep.31684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Phipps M.M., Barraza L.H., LaSota E.D., Sobieszczyk M.E., Pereira M.R., Zheng E.X., et al. Acute liver injury in COVID-19: prevalence and association with clinical outcomes in a large U.S. Cohort. Hepatology. 2020;72:807–817. doi: 10.1002/hep.31404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hundt M.A., Deng Y., Ciarleglio M.M., Nathanson M.H., Lim J.K. Abnormal liver tests in COVID-19: a retrospective observational cohort study of 1,827 patients in a major U.S. Hospital network. Hepatology. 2020;72:1169–1176. doi: 10.1002/hep.31487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Romana P.F., Antonio N., Fabio D.Z., Francesco S., Maurizio P., Antonio G. Correlation between liver function tests abnormalities and interleukin-6 serum levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Gastroenterology. 2020 doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sonzogni A., Previtali G., Seghezzi M., Grazia Alessio M., Gianatti A., Licini L., et al. Liver histopathology in severe COVID 19 respiratory failure is suggestive of vascular alterations. Liver Int. 2020;40:2110–2116. doi: 10.1111/liv.14601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tsutsumi T., Saito M., Nagai H., Yamamoto S., Ikeuchi K., Lim L.A., et al. Association of coagulopathy with liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19. Hepatol Res. 2020 doi: 10.1111/hepr.13577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tang N., Li D., Wang X., Sun Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:844–847. doi: 10.1111/jth.14768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Panigada M., Bottino N., Tagliabue P., Grasselli G., Novembrino C., Chantarangkul V., et al. Hypercoagulability of COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit: a report of thromboelastography findings and other parameters of hemostasis. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:1738–1742. doi: 10.1111/jth.14850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Goshua G., Pine A.B., Meizlish M.L., Chang C.H., Zhang H., Bahel P., et al. Endotheliopathy in COVID-19-associated coagulopathy: evidence from a single-centre, cross-sectional study. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7:e575–e582. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30216-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shahani T., Covens K., Lavend'homme R., Jazouli N., Sokal E., Peerlinck K., et al. Human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells but not hepatocytes contain factor VIII. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12:36–42. doi: 10.1111/jth.12412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhu J., Pang J., Ji P., Zhong Z., Li H., Li B., et al. Elevated interleukin-6 is associated with severity of COVID-19: a meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020 doi: 10.1002/jmv.26085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Aziz M., Fatima R., Assaly R. Elevated interleukin-6 and severe COVID-19: a meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92:2283–2285. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Effenberger M., Grander C., Grabherr F., Griesmacher A., Ploner T., Hartig F., et al. Systemic inflammation as fuel for acute liver injury in COVID-19. Dig Liver Dis. 2021;53:158–165. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vermes C., Jacobs J.J., Zhang J., Firneisz G., Roebuck K.A., Glant T.T. Shedding of the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor (gp80) determines the ability of IL-6 to induce gp130 phosphorylation in human osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:16879–16887. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200546200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ward L.D., Hammacher A., Howlett G.J., Matthews J.M., Fabri L., Moritz R.L., et al. Influence of interleukin-6 (IL-6) dimerization on formation of the high affinity hexameric IL-6.receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20138–20144. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.33.20138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Magro G. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: is interleukin-6 (IL-6) the 'culprit lesion' of ARDS onset? What is there besides Tocilizumab? SGP130Fc. Cytokine X. 2020;2:100029. doi: 10.1016/j.cytox.2020.100029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zegeye M.M., Lindkvist M., Falker K., Kumawat A.K., Paramel G., Grenegard M., et al. Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways are crucial for IL-6 trans-signaling-mediated pro-inflammatory response in human vascular endothelial cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2018;16:55. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0268-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chatterjee P.K., Al-Abed Y., Sherry B., Metz C.N. Cholinergic agonists regulate JAK2/STAT3 signaling to suppress endothelial cell activation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;297:C1294–C1306. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00160.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schmidt-Arras D., Rose-John S. IL-6 pathway in the liver: from physiopathology to therapy. J Hepatol. 2016;64:1403–1415. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kang S., Tanaka T., Inoue H., Ono C., Hashimoto S., Kioi Y., et al. IL-6 trans-signaling induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 from vascular endothelial cells in cytokine release syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117:22351–22356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2010229117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nishimoto N., Terao K., Mima T., Nakahara H., Takagi N., Kakehi T. Mechanisms and pathologic significances in increase in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-6 receptor after administration of an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Castleman disease. Blood. 2008;112:3959–3964. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-155846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Patra T., Meyer K., Geerling L., Isbell T.S., Hoft D.F., Brien J., et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes IL-6 trans-signaling by activation of angiotensin II receptor signaling in epithelial cells. Plos Pathog. 2020;16 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kwo P.Y., Cohen S.M., Lim J.K. ACG clinical guideline: evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:18–35. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fay W.P. Linking inflammation and thrombosis: role of C-reactive protein. World J Cardiol. 2010;2:365–369. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v2.i11.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gu S.X., Tyagi T., Jain K., Gu V.W., Lee S.H., Hwa J.M., et al. Thrombocytopathy and endotheliopathy: crucial contributors to COVID-19 thromboinflammation. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00469-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kondo R., Yano H., Nakashima O., Tanikawa K., Nomura Y., Kage M. Accumulation of platelets in the liver may be an important contributory factor to thrombocytopenia and liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol. 2013;48:526–534. doi: 10.1007/s00535-012-0656-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang J., Wang Q., Han T., Li Y.K., Zhu S.L., Ao F., et al. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor is elevated during influenza A virus infection and mediates the IL-6 and IL-32 inflammatory cytokine burst. Cell Mol Immunol. 2015;12:633–644. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jones S.A., Horiuchi S., Topley N., Yamamoto N., Fuller G.M. The soluble interleukin 6 receptor: mechanisms of production and implications in disease. FASEB J. 2001;15:43–58. doi: 10.1096/fj.99-1003rev. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Do H., Healey J.F., Waller E.K., Lollar P. Expression of factor VIII by murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:19587–19592. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.28.19587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ruggeri Z.M., Mendolicchio G.L. Adhesion mechanisms in platelet function. Circ Res. 2007;100:1673–1685. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000267878.97021.ab. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rubel C., Fernandez G.C., Dran G., Bompadre M.B., Isturiz M.A., Palermo M.S. Fibrinogen promotes neutrophil activation and delays apoptosis. J Immunol. 2001;166:2002–2010. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.3.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lisman T., Bongers T.N., Adelmeijer J., Janssen H.L., de Maat M.P., de Groot P.G., et al. Elevated levels of von Willebrand Factor in cirrhosis support platelet adhesion despite reduced functional capacity. Hepatology. 2006;44:53–61. doi: 10.1002/hep.21231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Falasca L., Nardacci R., Colombo D., Lalle E., Di Caro A., Nicastri E., et al. Postmortem findings in Italian patients with COVID-19: a descriptive full autopsy study of cases with and without comorbidities. J Infect Dis. 2020;222:1807–1815. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rapkiewicz A.V., Mai X., Carsons S.E., Pittaluga S., Kleiner D.E., Berger J.S., et al. Megakaryocytes and platelet-fibrin thrombi characterize multi-organ thrombosis at autopsy in COVID-19: a case series. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;24:100434. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rubel C., Fernandez G.C., Rosa F.A., Gomez S., Bompadre M.B., Coso O.A., et al. Soluble fibrinogen modulates neutrophil functionality through the activation of an extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent pathway. J Immunol. 2002;168:3527–3535. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.7.3527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ackermann M., Verleden S.E., Kuehnel M., Haverich A., Welte T., Laenger F., et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:120–128. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2015432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bergmann J., Muller M., Baumann N., Reichert M., Heneweer C., Bolik J., et al. IL-6 trans-signaling is essential for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology. 2017;65:89–103. doi: 10.1002/hep.28874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Montgomery A., Tam F., Gursche C., Cheneval C., Besler K., Enns W., et al. Overlapping and distinct biological effects of IL-6 classic and trans-signaling in vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00323.2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cao Y., Wei J., Zou L., Jiang T., Wang G., Chen L., et al. Ruxolitinib in treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;146:137–146 e133. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Vannucchi A.M., Sordi B., Morettini A., Nozzoli C., Poggesi L., Pieralli F., et al. Compassionate use of JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib for severe COVID-19: a prospective observational study. Leukemia. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-01018-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Salama C., Han J., Yau L., Reiss W.G., Kramer B., Neidhart J.D., et al. Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with covid-19 pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:20–30. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2030340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information.