Abstract
Background
The Botryosphaeriaceae are important plant pathogens, but also have the ability to establish asymptomatic infections that persist for extended periods in a latent state. In this study, we used comparative genome analyses to shed light on the genetic basis of the interactions of these fungi with their plant hosts. For this purpose, we characterised secreted hydrolytic enzymes, secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters and general trends in genomic architecture using all available Botryosphaeriaceae genomes, and selected Dothideomycetes genomes.
Results
The Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were rich in carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes), proteases, lipases and secondary metabolic biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) compared to other Dothideomycete genomes. The genomes of Botryosphaeria, Macrophomina, Lasiodiplodia and Neofusicoccum, in particular, had gene expansions of the major constituents of the secretome, notably CAZymes involved in plant cell wall degradation. The Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were shown to have moderate to high GC contents and most had low levels of repetitive DNA. The genomes were not compartmentalized based on gene and repeat densities, but genes of secreted enzymes were slightly more abundant in gene-sparse regions.
Conclusion
The abundance of secreted hydrolytic enzymes and secondary metabolite BGCs in the genomes of Botryosphaeria, Macrophomina, Lasiodiplodia, and Neofusicoccum were similar to those in necrotrophic plant pathogens and some endophytes of woody plants. The results provide a foundation for comparative genomic analyses and hypotheses to explore the mechanisms underlying Botryosphaeriaceae host-plant interactions.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12864-021-07902-w.
Keywords: Secretome, CAZyme, Secondary metabolism, Comparative genomics, Endophyte, Plant cell wall-degrading enzymes
Background
Secreted hydrolytic enzymes and fungal toxins play crucial roles in enabling fungal pathogens to establish successful infections on their plant hosts. Among the secreted proteins, carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes), protease and lipases are important for nutrient acquisition, as well as for the breakdown, manipulation (i.e effectors) or circumvention of host defences [1–7]. Fungal toxins are a diverse group of compounds and those most commonly found in fungal pathogens include polyketides, non-ribosomal peptides, terpenes and indole alkaloids [8]. These toxins are secondary metabolites that induce plant cell death, and for this reason, necrotrophic plant pathogens usually possess greater numbers of genes involved in secondary metabolite synthesis than biotrophic pathogens [9].
The genomes of many fungal and Oomycetes plant pathogens, especially those rich in repetitive elements, are not homogenous, but rather compartmentalized into repeat-rich, gene sparse regions and repeat poor, gene dense regions [10–13]. Genes localized to repeat-rich, gene sparse regions also have a higher rate of mutation and are often under stronger selective pressure [11, 14, 15]. This has given rise to a phenomenon referred to as ‘two-speed’ genomes, due to the stark differences in evolutionary rates between the two different types of genomic regions.
Fungi residing in the Botryosphaeriaceae include important plant pathogens. These fungi mostly cause diseases of woody plant species and they can impact negatively on the health of many economically and ecologically significant plant species [16, 17]. The Botryosphaeriaceae infect a wide range of plant hosts, most notably grapevine [18], pome and stone fruits [19], plantation forest trees such as Eucalyptus spp., Pinus spp. and Acacia mangium [20–22], as well as plants in their native habitats [23–26]. Many of these fungi (e.g. B. dothidea, M. phaseolina, Lasiodiplodia theobromae, Neofusicoccum parvum) have wide host ranges, while a few species (e.g. Diplodia sapinea on Pinus species) have narrower host ranges or are even very host-specific (e.g. Eutiarosporella darliae, E. pseudodarliae and E. tritici-australis on wheat) [27]. Many species of Botryopshaeriaceae are also known to occur endophytically in asymptomatic plant tissues or to have a latent pathogenic phase, where they inhabit their plant hosts in the absence of symptoms and cause disease only after the onset of stress, such as drought, frost or hail damage [16, 28].
A few recent studies have investigated secreted proteins and secondary metabolites in species of the Botryosphaeriaceae. Proteomic studies analyzing the secreted proteins of Diplodia seriata [29] and D. corticola [30] identified secreted proteins involved in pathogenesis. Studies of grapevine pathogens also predicted secreted CAZymes and genes involved in the production of secondary metabolites of D. seriata and Neofusicoccum parvum [31, 32], however no studies directly linking these genes to disease symptoms or plant interactions exist. Secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) have also been shown to play a role in host range determination, e.g. in E. darliae and E. pseudodarliae causing white grain disorder, where the presence of a secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene cluster is likely to allow woody hosts to be infected [27]. Despite the many publicly available genomes of species of Botryosphaeriaceae [31–38], no comprehensive comparative studies have been undertaken using these genomes; neither have analyses been conducted to characterise secreted proteins and secondary metabolites in most of these fungi. Such studies are also hampered by the lack of publicly available genome annotations.
The manner in which plants interact with beneficial microorganisms, while at the same time restricting the negative effects of pathogens, is an important and intriguing question in plant biology [39]. One proposed model referred to as the ‘balanced antagonism model’ [40] holds that endophytism is a result of both the host plant and the fungus employing antagonistic measures against each other, in such a way that neither overwhelms the other. Disruption of this balance either results in the pathogen causing disease or in the host plant successfully killing the fungus. The model thus predicts that known endophytic species should have similar genetic repertoires to their closely related plant pathogenic relatives. This appears to be the case when considering recent comparative genomics studies conducted on endophytic fungi [41–44], although some endophytic species, e.g. Xylonia heveae had fewer CAZymes than expected and were more similar to mutualistic species [45]. Indeed, the above-mentioned endophytes (other than X. heveae) commonly had high numbers of plant cell wall degrading enzymes and secondary metabolite genes.
Despite their ubiquity as endophytes and their importance as latent pathogens, very little is known regarding how Botryosphaeriaceae species interact with their diverse plant hosts at a molecular level. Studies have characterized this fungus-host interaction for the most prominent of Botryosphaeriaceae species [31, 46–50], but such knowledge remains lacking for most species. Key questions in this regard relate to the secreted hydrolytic enzymes and secondary metabolic biosynthesis genes present in their genomes. Based on the results of previous studies on Ascomycetes that are endophytes of woody plants, we have hypothesised that these genes and gene clusters in the Botryosphaeriaceae will resemble those of closely related plant pathogens. To test this hypothesis, we compared the predicted secreted hydrolytic enzyme and secondary metabolite genes of Botryosphaeriaceae species with those of other Dothideomycetes. We also characterised the genome architecture of the Botryosphaeriaceae in terms of gene density, repeat content and prevalence of repeat-induced point mutations (RIP), and considered how these associate with secreted hydrolytic enzymes and secondary metabolite BGCs.
Results
Genome sequencing, assembly and annotation
Nine genomes of Neofusicoccum and three genomes of Lasiodiplodia species were sequenced using Illumina sequencing (Table 1). These included two isolates each of N. cordaticola, N. kwambonambiense, N. parvum and N. ribis were sequenced. A single isolate was sequenced for L. gonubiensis, L. pseudotheobromae, L. theobromae and N. umdonicola.
Table 1.
List of genome sequences used in this studya
| Species | Reference collection/Isolate number | Assembly Size (Mbp) | Number of gene models | Genome accession number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dothideomycetes | |||||
| Botryosphaeriales | |||||
| Botryosphaeria kuwatsukai | LW030101 | 47.39 | 11,278 | MDSR01000000 | [35, 51] |
| Botryosphaeria dothidea | CMW8000 | 43.50 | 11,368 | http://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Botdo1_1/Botdo1_1.home.html | [36] |
| Diplodia corticola | CBS112549 | 34.99 | 9376 | MNUE01000001 | [30] |
| Diplodia sapinea | CBS117911 | 36.05 | 9589 | AXCF00000000 | [52] |
| CBS138184 | 35.24 | 9386 | JHUM00000000 | [52] | |
| Diplodia scrobiculata | CBS139796 | 34.93 | 9204 | LAEG00000000 | [53] |
| Diplodia seriata | UCDDS831 | 37.12 | 9759 | MSZU00000000 | [32] |
| F98.1 | 37.27 | 9832 | LAQI00000000 | [37] | |
| Eutiarosporella darliae | 2G6 | 27.27 | 7904 | GFXH01000000 | [27] |
| Eutiarosporella pseudodarliae | V4B6 | 26.74 | 7846 | GFXI01000000 | [27] |
| Eutiarosporella tritici-australis | 153 | 26.59 | 7783 | GFXG01000000 | [27] |
| Lasiodiplodia gonubiensis | CBS115812 | 41.14 | 10,649 | RHKH00000000 | Present study |
| Lasiodiplodia pseudotheobromae | CBS116459 | 43.01 | 10,964 | RHKG00000000 | Present study |
| Lasiodiplodia theobromae | CBS164.96 | 42.97 | 10,961 | RHKF00000000 | Present study |
| CSS01 | 43.28 | 11,017 | RHKB00000000 | [49] | |
| Macrophomina phaseolina | MS6 | 48.88 | 10,799 | AHHD00000000 | [34] |
| Neofusicoccum cordaticola | CBS123634 | 45.71 | 12,822 | RHKC00000000 | Present study |
| CBS123638 | 43.56 | 12,630 | RHKD00000000 | Present study | |
| Neofusicoccum kwambonambiense | CBS123639 | 44.17 | 12,839 | RHKE00000000 | Present study |
| CBS123642 | 44.21 | 12,904 | RKSS00000000 | Present study | |
| Neofusicoccum parvum | CMW9080 | 41.41 | 12,870 | RHJX00000000 | Present study |
| CBS123649 | 42.16 | 12,453 | RHJY00000000 | Present study | |
| UCRNP2 | 42.52 | 12,691 | AORE00000000 | [33] | |
| Neofusicoccum ribis | CBS115475 | 43.18 | 12,708 | RHJZ00000000 | Present study |
| CBS121.26 | 43.12 | 12,733 | RHKA00000000 | Present study | |
| Neofusicoccum umdonicola | CBS123644 | 42.29 | 12,816 | RHKB00000000 | Present study |
| Capnodiales | |||||
| Acidomyces richmondensis | meta | 26.82 | 10,338 | JOOL00000000 | [54] |
| Baudoinia panamericana | UAMH 10762 | 21.88 | 10,508 | AEIF00000000 | [4] |
| Cercospora berteroae | CBS538.71 | 33.89 | 11,903 | PNEN00000000 | [55] |
| Cercospora beticola | 09–40 | 37.06 | 12,463 | LKMD00000000 | [55] |
| Cercospora zeina | CMW25467 | 40.76 | 10,193 | MVDW00000000 | [56] |
| Dothistroma septosporum | NZE10 | 30.21 | 12,415 | AIEN00000000 | [4] |
| Pseudocercospora eumusae | CBS 114824 | 47.12 | 12,632 | LFZN01000000 | [57] |
| Pseudocercospora fijiensis | CIRAD86 | 29.98 | 13,066 | AIHZ00000000 | [4] |
| Pseudocercospora musae | CBS 116634 | 60.44 | 13,129 | LFZO00000000 | [57] |
| Ramularia collo-cygni | URUG2 | 32.25 | 11,612 | FJUY00000000 | [58] |
| Sphaerulina musiva | SO2202 | 29.35 | 10,233 | AEFD00000000 | [4] |
| Zymoseptoria tritici | IPO323 | 39.69 | 10,963 | ACPE00000000 | [59] |
| Dothideales | |||||
| Aureobasidium namibiae | CBS 147.97 | 25.43 | 10,259 | AYEM00000000 | [60] |
| Aureobasidium subglaciale | EXF-2481 | 25.80 | 10,792 | AYYB00000000 | [60] |
| Hysteriales | |||||
| Hysterium pulicare | CBS 123377 | 38.43 | 12,352 | AJFK00000000 | [4] |
| Rhytidhysteron rufulum | CBS 306.38 | 40.18 | 12,117 | AJFL00000000 | [4] |
| Myriangiales | |||||
| Elsinoe australis | NL1 | 23.34 | 9223 | NHZQ00000000 | [7] |
| Mytilinidiales | |||||
| Lepidopterella palustris | CBS 459.81 | 45.67 | 13,861 | LKAR00000000 | [61] |
| Pleosporales | |||||
| Alternaria alternata | SRC1lrK2f | 32.99 | 13,466 | LXPP00000000 | [62] |
| Ascochyta rabiei | ArDII | 34.66 | 10,596 | JYNV00000000 | [63] |
| Bipolaris maydis | ATCC 48331 | 32.93 | 12,705 | AIHU00000000 | [4] |
| Bipolaris oryzae | ATCC 44560 | 31.36 | 12,002 | AMCO00000000 | [64] |
| Bipolaris sorokiniana | ATCC 44560 | 34.41 | 12,214 | AEIN00000000 | [64] |
| Bipolaris victoriae | FI3 | 32.83 | 12,882 | AMCY00000000 | [64] |
| Bipolaris zeicola | 26-R− 13 | 31.27 | 12,853 | AMCN00000000 | [64] |
| Clohesyomyces aquaticus | CBS 115471 | 49.68 | 15,811 | MCFA00000000 | [65] |
| Corynespora cassiicola | CCP | 44.85 | 17,158 | NSJI00000000 | [66] |
| Epicoccum nigrum | ICMP 19927 | 34.74 | 12,025 | NCTX00000000 | [67] |
| Exserohilum turcicum | Et28A | 43.01 | 11,698 | AIHT00000000 | [4] |
| Leptosphaeria maculans | JN3 | 45.12 | 12,469 | FP929064:FP929139 | [12] |
| Paraphaeosphaeria sporulosa | AP3s5-JAC2a | 38.46 | 14,734 | LXPO00000000 | [62] |
| Parastagonospora nodorum | SN15 | 37.21 | 15,994 | AAGI00000000 | [68] |
| Periconia macrospinosa | DSE2036 | 54.99 | 18,735 | PCYO00000000 | [69] |
| Pyrenophora tritici-repentis | Pt-1C-BFP | 38.00 | 12,169 | AAXI00000000 | [70] |
| Stemphylium lycopersici | CIDEFI 216 | 35.17 | 8997 | LGLR00000000 | [71] |
| Venturiales | |||||
| Verruconis gallopava | CBS 43764 | 31.78 | 11,357 | JYBX00000000 | [72] |
| incertae sedis | |||||
| Cenococcum geophilum | 1.58 | 177.56 | 14,709 | LKKR00000000 | [61] |
| Coniosporium apollinis | CBS 100218 | 28.65 | 9308 | AJKL00000000 | [72] |
| Glonium stellatum | CBS 207.34 | 40.52 | 14,277 | LKAO00000000 | [61] |
| Eurotiomycetes | |||||
| Eurotiales | |||||
| Aspergillus nidulans | FGSC A4 | 30.28 | 9556 | AACD00000000 | [73] |
aEntries in boldface represent genomes that were sequenced as part of the present study
De novo genome assembly resulted in genome lengths of approximately 43 MB for both Lasiodiplodia spp. and Neofusicoccum spp. (Table 2). The number of scaffolds/contigs was variable between the sequenced genomes, but the three Lasiodiplodia genomes had a lower number of scaffolds (376–424) than the Neofusicoccum genomes (1343–5188). The N. parvum CMW9080 genome that was sequenced on the Miseq platform had a higher degree of fragmentation, as seen from the high total number of scaffolds (5188) and a large number of short contigs (N50: 897, L50:13.55 kb) and scaffolds (N50:830, L50: 14.81 kb). The percentage of repetitive elements of each genome was significantly greater in the Neofusicoccum genomes (6.84%) than in the Lasiodiplodia genomes (3.33%) (p = 0.004545, Wilcoxon rank sum test).
Table 2.
Genome statistics of new draft Botryosphaeriaceae genomes
| # scaffolds | # contigs | Scaffold length (Mb) | Contig length (Mb) | Genome scaffold N50/L50 (#/kb) | Genome contig N50/L50 (#/kb) | Maximum scaffold length (Mb) | Maximum contig length (kb) | % main genome in scaffolds > 50 KB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lasiodiplodia gonubiensis CBS115812 | 376 | 1578 | 41.14 | 40.97 | 50/234.83 | 267/45.4 | 1.06 | 226.76 | 0.92 |
| Lasiodiplodia pseudotheobromae CBS116459 | 403 | 1285 | 43.01 | 42.89 | 48/236.23 | 218/61.88 | 1.03 | 416.59 | 0.91 |
| Lasiodiplodia theobromae CBS164.96 | 424 | 1093 | 42.97 | 42.88 | 48/223.84 | 163/81.56 | 1.69 | 591.21 | 0.91 |
| Neofusicoccum cordaticola CBS123634 | 1912 | 8698 | 45.71 | 45.10 | 276/47.38 | 1218/10.76 | 680.02 | 143.71 | 0.48 |
| Neofusicoccum cordaticola CBS123638 | 2393 | 3252 | 43.56 | 43.44 | 254/51.16 | 386/33.04 | 274.15 | 152.21 | 0.51 |
| Neofusicoccum kwambonambiense CBS123639 | 1560 | 2839 | 44.17 | 43.99 | 219/59.44 | 363/34.21 | 344.53 | 186.24 | 0.58 |
| Neofusicoccum kwambonambiense CBS123642 | 1717 | 2871 | 44.21 | 44.06 | 210/61.88 | 352/34.6 | 387.07 | 262.94 | 0.58 |
| Neofusicoccum parvum CBS123649 | 2185 | 6686 | 42.16 | 41.76 | 312/39.13 | 995/12.5 | 439.22 | 92.09 | 0.40 |
| Neofusicoccum parvum CMW9080 | 5188 | 5739 | 41.41 | 41.39 | 830/14.81 | 897/13.55 | 99.22 | 80.57 | 0.04 |
| Neofusicoccum ribis CBS115475 | 1994 | 3261 | 43.18 | 43.03 | 301/42.08 | 474/26.80 | 231.82 | 186.29 | 0.43 |
| Neofusicoccum ribis CBS121.26 | 2417 | 3145 | 43.12 | 43.03 | 245/51.65 | 371/33.92 | 280.49 | 167.59 | 0.51 |
| Neofusicoccum umdonicola CBS123644 | 1343 | 2424 | 42.29 | 42.15 | 165/73.88 | 345/36.48 | 422.57 | 210.10 | 0.67 |
Twenty-six Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were annotated by predicting protein-coding genes with MAKER using BRAKER trained profiles. BUSCO analysis using the Ascomycota ortholog library (Table 3) indicated that all Botryosphaeriaceae genomes had a high degree of completeness (average of 98.%, minimum of 95.1%). The genome annotations that were generated also had a high BUSCO completeness score (average of 97.8.%, minimum of 94.3%). When comparing theses BUSCO results to those of species with existing genome annotations on NCBI/JGI, it was clear that in five out of the six cases the genome annotations from the present study had a higher BUSCO completeness score than the existing genome annotations.
Table 3.
Genome and genome annotation completeness assesmenta
| Genome BUSCO % | Current annotation BUSCO % | Prior annotation BUSCO % | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genome | C | S | D | F | M | C | S | D | F | M | C | S | D | F | M |
| Botryosphaeria kuwatsukai LW030101 | 99.2 | 98.9 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 98.4 | 98.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.0 | |||||
| Botryosphaeria dothidea CMW8000 | 99.0 | 98.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 98.5 | 98.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 98.1 | 97.7 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.6 |
| Diplodia corticola CBS112549 | 98.9 | 98.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 98.7 | 98.6 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 99.4 | 99.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Diplodia sapinea CBS117911 | 98.0 | 97.8 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 97.6 | 97.5 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.5 | |||||
| Diplodia sapinea CBS138184 | 96.0 | 95.8 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 95.6 | 95.4 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 3.2 | |||||
| Diplodia scrobiculata CBS139796 | 95.4 | 95.2 | 0.2 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 95.0 | 94.8 | 0.2 | 1.8 | 3.2 | |||||
| Diplodia seriata UCDDS831 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 98.8 | 98.7 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 87 | 86.9 | 0.1 | 5.9 | 7.1 |
| Diplodia seriata F98.1 | 99.3 | 98.9 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 98.9 | 98.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 90.1 | 89.9 | 0.2 | 2.6 | 7.3 |
| Eutiarosporella darliae 2G6 | 98.1 | 97.8 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 98.5 | 97.8 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |||||
| Eutiarosporella pseudodarliae V4B6 | 98.2 | 98.0 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 98.1 | 97.8 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 1.2 | |||||
| Eutiarosporella tritici-australis 153 | 98.3 | 98.0 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 98.6 | 98.4 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 1.0 | |||||
| Lasiodiplodia gonubiensis CBS115812 | 97.2 | 97.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.6 | 98.3 | 98.2 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.9 | |||||
| Lasiodiplodia pseudotheobromae CBS116459 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 98.3 | 98.0 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.9 | |||||
| Lasiodiplodia theobromae CBS164.96 | 97.2 | 97.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 2.6 | 98.6 | 98.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.9 | |||||
| Lasiodiplodia theobromae CSS01 | 99.1 | 98.7 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 99.1 | 98.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |||||
| Macrophomina phaseolina MS6 | 98.9 | 98.7 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 98.1 | 97.9 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 91.2 | 91 | 0.2 | 4.5 | 4.3 |
| Neofusicoccum cordaticola CBS123634 | 97.0 | 94.9 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2.1 | 96.1 | 94.2 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 2.3 | |||||
| Neofusicoccum cordaticola CBS123638 | 98.5 | 98.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 98.3 | 97.9 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.1 | |||||
| Neofusicoccum kwambonambiense CBS123639 | 99.0 | 98.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 98.6 | 98.2 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.7 | |||||
| Neofusicoccum kwambonambiense CBS123642 | 98.9 | 98.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 98.8 | 98.3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 | |||||
| Neofusicoccum parvum CMW9080 | 95.4 | 95.0 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 2.6 | 94.3 | 93.9 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 3.7 | |||||
| Neofusicoccum parvum CBS123649 | 95.1 | 94.5 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 4.0 | 96.4 | 95.9 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 2.3 | |||||
| Neofusicoccum parvum UCRNP2 | 98.1 | 97.9 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 97.8 | 97.6 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 84.9 | 84.8 | 0.1 | 6.6 | 8.5 |
| Neofusicoccum ribis CBS115475 | 98.3 | 97.9 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 97.6 | 97.2 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 1.1 | |||||
| Neofusicoccum ribis CBS121.26 | 98.7 | 98.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 98.2 | 97.7 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |||||
| Neofusicoccum umdonicola CBS123644 | 98.7 | 98.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 98.1 | 97.5 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 0.8 | |||||
aBUSCO percentages for Complete (C), single (S), duplicated (D), fragmented (F) and missing (M) genes. Assesments were done using the Ascomycota ortholog library
Phylogenomic analyses
We identified 207 core orthologous genes from the collection of 26 Botryosphaeriaceae, 39 other Dothideomycetes and the outgroup (Aspergillus nidulans) genomes. Only orthologous genes that were represented by a single gene per species were retained. The results of the phylogenomic analyses corresponded well to previous phylogenies for the Dothideomycetes [74–76]. The phylogeny indicated the early divergence of the Dothideomycetidae (Dothideales, Capnodiales and Myrangiales) from the lineage containing the Pleosporomycetidae (Pleosporales, Hysteriales and Mytilinidiales) and other Dothideomycetes without current subclass designation (Fig. 1). This phylogeny further supported the early divergence of the Botryosphaeriales from the ancestral Dothideomycetes lineage after the divergence of the Dothideomycetidae and Venturiales. The phylogenetic relationships between the Botryosphaeriacaeae were well defined and the phylogenetic placement of species and genera corresponded with that found in previous studies [77, 78].
Fig. 1.
Phylogenomic tree and functional annotation summary of 26 Botryosphaeriaceae, 39 Dothideomycetes and one outgroup (Aspergillus nidulans). The supermatrix maximum likelihood phylogeny was determined using the sequence data of 207 single-copy core orthologous genes. Branches with 100% bootstrap support are indicated in black, those with less than 100% support are indicated in grey. This phylogeny illustrates the how the Botryosphaeriaceae taxa are related to one another, as well as how the Botryosphaeriaceae relates to the other Dothideomycetes. The number of genes (secreted and non-secreted) annotated with CAZyme, proteases or lipase activity, as well as the number of gene cluster types involved in secondary metabolite biosynthesis are indicated using bar graphs. These bar graphs depict that the number of these functional annotations are generally conserved within each Botryosphaeriaceae genus but that these values vary widely across this family. The Botryosphaeriaceae contains some of the largest (Neofusicoccum) as well as some of the smallest (Eutiarosporella) amounts of these functional annotations among the Dothideomycetes. Further statistical analyses of these values are provided in Additional file 2
Functional annotation
In the Botryosphaeriaceae, both genome size and the total gene number were strongly correlated with the number of secreted proteins, CAZymes, proteases, lipases and secondary metabolite gene clusters (Additional files 1 and 2). Within the Dothideomycetes, however, the numbers of secreted proteins, CAZymes, proteases, lipases, and secondary metabolite BGCs present within a genome were correlated with one another (i.e. species that contained large numbers of secreted proteins also contained large numbers of CAZymes, proteases, lipases and secondary metabolite BGCs), but only weakly correlated with genome size and the total number of genes (Additional file 2).
Among the Botryosphaeriaceae, the Eutiarosporella spp. had the lowest number of each of functional annotation category, followed in increasing order by Diplodia spp. and Botryosphaeria, Lasiodiplodia, Macrophomina, and Neofusicoccum species (Fig. 1, Additional file 1). This observation was also evident when considering the different classes of CAZymes/proteases/lipases and the different types of secondary metabolite BGCs (Fig. 2). Furthermore, for many functional annotation categories the Botryosphaeriaceae were more similar to the Pleosporomycetidae than the Dothideomycetidae.
Fig. 2.
Box-and-whisker plots of the number of prominent CAZyme, protease and lipase classes (total and secreted) and secondary metabolite BGC types present within the genomes of the considered Botryosphaeriaceae and other Dothideomycetes taxa. Represented data is scaled using the mean of each class/type and is indicated by the number appearing at the top of each facet. Taxa are placed into three categories: Dothideomycetidae, Pleosporomycetidae (plus related taxa without subclass designation) and Botryosphaeriaceae. The upper and lower bounds of the box represent the 1st and 3rd quartiles (respectively) and the bar inside represent the median. The error lines (whiskers) represents 1.5 times the interquartile range (IQR) and outliers are indicated as dots. Additionally, the genera of the Botryosphaeriaceae are indicated by means of a scatterplot overlain on the Botryosphaeriaceae box-and-whisker plot. These graphs visually compares the variance of each functional annotation class between the Botryosphaeriaceae and other Dothideomycetes subclasses. It also depicts that, among the Botryosphaeriaceae, the Eutiarosporella and Diplodia have smaller amounts of most functional annotation classes than the other genera
The genomes of the Botryosphaeriaceae genera differed significantly (p-value < 0.05) for many of the annotation categories (Additional file 2). All genera were significantly different (Neofusicoccum > Botryosphaeria-clade > Lasiodiplodia > Diplodia > Eutiarosporella) for the number of secreteted genes, number of total CAZymes and secreted CAZymes. This trend also existed for the other annotation categories with a few exceptions: Among the proteases and lipases, the Neofusicoccum and Botryosphaeria-clade were not significantly different. When considering the secreted proteases, species in the Botryosphaeria-clade were not significantly different to those of Lasiodiplodia, Eutiarosporella or Diplodia. The secreted lipases were not significantly different between Eutiarosporella and Diplodia. The secondary metabolite BGCs were not significantly different between the Neofusicoccum and species in the Botryosphaeria-clade.
Significant differences also existed when comparing the functional annotation categories of the Botryosphaeriaceae to the rest of the Dothideomycetes (Additional file 2). The Botryosphaeriaceae had significantly greater numbers of secreted genes, total CAZymes and total proteases than the Dothideomycetidae. Furthermore, the Botryosphaeriaceae had significantly greater numbers of secreted CAZymes, secreted proteases, both total and secreted lipases and secondary metabolite BGCs than both Dothideomycetidae and Pleosporomycetidae.
The Botryosphaeriaceae, had significantly more CAZymes of the auxiliary activities (AA), carbohydrate-binding modules (CBM), carbohydrate esterases (CE) and glycoside hydrolases (GH) classes than Dothideomycetidae (Fig. 2, Additional file 2). Additionally, the Botryosphaeriaceae had significantly more polysaccharide lyase (PL) genes than both Dothideomycetidae and Pleosporomycetidae. Conversely, significantly fewer CEs were present in the Botryosphaeriaceae than in the Pleosporomycetidae, as well as fewer glycosyltransferases (GT) than the other two Dothideomycetes sub-classes.
When considering the secreted CAZyme classes, the Botryosphaeriaceae had significantly more CAZymes of the AA, CBM and CE classes than Dothideomycetidae and significantly more GH and PL classes than both Dothideomycetidae and Pleosporomycetidae (Fig. 2, Additional file 2). The most abundant secreted CAZyme families in the Botryosphaeriaceae were CBM1, AA3, GH3, GH43, GH5, AA9, CBM18, AA1, GH28 and CBM13 (Additional file 1).
The Botryosphaeriaceae had above-average numbers of aspartic- (A), metallo- (M) and serine- (S) proteases, especially in the species of Botryosphaeria, Lasiodiplodia, Macrophomina, and Neofusicoccum (Fig. 2). For both the total and secreted number of predicted aspartic and serine proteases, the Botrosphaeriaceae had significantly greater levels than the Dothideomycetidae and Pleosporomycetidae (Fig. 2, Additional file 2). The total and secreted metallo-proteases of the Botryosphaeriaceae were significantly higher than those of the Dothideomycetidae. These three protease classes were also the dominant proteases in the secretome. Furthermore, the Botryosphaeriaceae had significantly fewer secreted cysteine (C) proteases and protease inhibitors (I) than the other Dothideomycetes. Notably, the Botryosphaeriaceae possessed a single secreted protease inhibitor family, namely I51.001 (serine carboxypeptidase Y inhibitor), whereas many other Dothideomycetes secreted protease inhibitors were of this family, as well as I09.002 (peptidase A inhibitor 1) or I09.003 (peptidase B inhibitor). Diplodia sapinea and D. scrobiculata had no secreted protease inhibitors. The most abundant secreted protease families among the Botryosphaeriaceae were S09, A01, S10, S08, M28, S53, S33, M43, M35 and S12 (Additional file 1).
In the Botryosphaeriaceae and the Dothideomycetes, the most abundant lipases/lipase-like families were abH04 (Moraxella lipase 2 like), abH03 (Candida rugosa lipase-like), abH36, (cutinase) and abH23 (Filamentous fungi lipases) (Fig. 2). The abH03, abH36 and abH23 lipase families were the main constituents of the predicted secretomes among the Dothideomycetes and the Botryosphaeriaceae had significantly more of these secreted enzymes than the Dothideomycetidae and Pleosporomycetidae (Additional file 2).
The Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were rich in gene clusters involved in the synthesis of secondary metabolites (Fig. 2). Type 1 polyketide synthases (t1PKS) were the most abundant type of gene cluster, followed by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) and NRPS-like, terpene synthases (TS) and t1PKS-NRPS hybrid clusters. The Botryosphaeriaceae had significantly more t1PKS clusters than the Dothideomycetidae and more NRPS-like, TS and betalactone clusters than both Dothideomycetidae and Pleosporomycetidae (Additional file 2). Certain Dothideomycetes genomes, predominantly those of the Pleosporomycetidae also contained indole and type 3 PKS BGCs, however, these were not present in any of the Botryosphaeriaceae genomes.
The most abundant secreted CAZyme, protease and lipase families of the Botryosphaeriaceae were also those that had the greatest difference from the rest of the Dothideomycetes (Table 4, Additional file 2). The twenty most abundant secreted hydrolytic enzyme families of the Botryosphaeriaceae were all significantly greater that both the Dothideomycetidae and Pleosporomycetidae, with the exception of the secreted CBM1 and AA9 CAZymes and the M28 metalloprotease families of the Botryosphaeriaceae that were not significantly greater than those of the Pleosporomycetidae. Furthermore, these twenty most abundant secreted families of the Botryosphaeriaceae were also those that had, on average, the highest deviation from the Dothideomycetes average. The number of genes in these gene families were not increased among the non-secreted proteins. Consequently, the ratio of secreted to total proteins for these gene families was higher among the Botryosphaeriaceae than in the the Dothideomycetidae and Pleosporomycetidae.
Table 4.
Comparison between the secreted and non-secreted amounts of the twenty most abundant secreted enzyme families in the Botryosphaeriaceae
| Enzyme family | CBM1 | S09 | AA3 | abH03 | abH36 | GH3 | GH43 | GH5 | A01 | AA9 | CBM18 | S10 | AA1 | GH28 | S08 | CBM13 | M28 | PL1 | CE5 | PL3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount of secreted proteins | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Botryosphaeriaceae average | 42.85 | 28.96 | 22.62 | 20.50 | 13.62 | 12.92 | 12.54 | 11.38 | 11.38 | 10.92 | 10.73 | 10.50 | 9.81 | 8.73 | 8.23 | 7.69 | 7.38 | 7.35 | 7.23 | 5.96 |
| Deviation from the Dothideomycetes averagea | 13.77 | 12.19 | 8.85 | 11.04 | 5.08 | 5.15 | 5.97 | 3.08 | 5.77 | 0.33 | 4.01 | 2.09 | 3.86 | 4.09 | 2.10 | 3.05 | 0.90 | 3.12 | 2.85 | 3.45 |
| Significantly greater thanb | D | D, P | D, P | D, P | D, P | D, P | D, P | D, P | D, P | D | D, P | D, P | D, P | D, P | D, P | D, P | D | D, P | D, P | D, P |
| Significantly less thanb | P | |||||||||||||||||||
| Amount of non-secreted proteins | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Botryosphaeriaceae average | 4.73 | 52.00 | 12.50 | 6.85 | 0.62 | 10.58 | 2.12 | 4.65 | 10.92 | 0.85 | 1.73 | 3.42 | 9.54 | 0.77 | 3.42 | 1.15 | 3.96 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 1.46 |
| Deviation from the Dothideomycetes averagea | −0.60 | 6.49 | 0.47 | −1.03 | −1.38 | 3.47 | −2.68 | −1.17 | 1.87 | −1.08 | −2.91 | 0.63 | 4.26 | −0.41 | −0.91 | 0.08 | −1.78 | −0.17 | −0.99 | 1.00 |
| Significantly greater thanb | D, P | D | D | D, P | P | P | D, P | D, P | ||||||||||||
| Significantly less thanb | P | D, P | P | D, P | P | P | D | P | D, P | P | D, P | |||||||||
| Ratio of secreted to total predicted amounts | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Dothideomycetidae | 0.79 | 0.23 | 0.48 | 0.61 | 0.75 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.88 | 0.54 | 0.71 | 0.48 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.73 | 0.43 | 0.94 | 0.76 | 0.30 |
| Pleosporomycetidae | 0.81 | 0.29 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.79 | 0.46 | 0.53 | 0.59 | 0.42 | 0.85 | 0.61 | 0.76 | 0.54 | 0.88 | 0.56 | 0.83 | 0.55 | 0.91 | 0.76 | 0.94 |
| Botryosphaeriaceae | 0.90 | 0.36 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.95 | 0.56 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.51 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.76 | 0.51 | 0.93 | 0.72 | 0.88 | 0.65 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.81 |
| Eutiarosporella | 0.94 | 0.42 | 0.61 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.59 | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.47 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 0.95 | 0.67 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.89 |
| Diplodia | 0.91 | 0.32 | 0.56 | 0.74 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 0.67 | 0.49 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.54 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.65 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.81 |
| Lasiodiplodia | 0.88 | 0.36 | 0.61 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0.59 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 0.49 | 0.81 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.49 | 0.90 | 0.68 | 0.83 | 0.59 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.75 |
| Botryosphaeria-clade | 0.88 | 0.32 | 0.67 | 0.70 | 0.94 | 0.61 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 0.59 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.71 | 0.52 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 0.80 | 0.61 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.71 |
| Neofusicoccum | 0.90 | 0.37 | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.97 | 0.49 | 0.88 | 0.74 | 0.52 | 0.99 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.48 | 0.89 | 0.66 | 0.90 | 0.68 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.84 |
a Deviation from the Dothideomycetes average excluding the Botryosphaeriaceae
b Dothideomycete subclass designation: D Dothideomycetidae, P Pleosporomycetidae
Gene family evolution
These results of the CAFE analyses (Additional file 3) indicated that expansions and contractions of CAZyme gene families occurred at roughly similar levels. This was after the divergence of the Botryosphaeriales ancestor from the Pleosporomycetidae until the formation of the Botryosphaeriaceae crown group (61 MYA) [79]. During this time, protease gene families experienced more contractions than expansions, lipase gene families had slightly more expansions than contractions and secondary metabolite BGCs experienced a large amount of gene family contractions. Several CAZyme gene families (AA1, AA3, AA7, AA8, AA9, CBM1, CBM18, CE4, CE5, GH3, GH10, GH28, GH43, GH78, GT1, GT2, GT25, PL1 and PL3) experienced rapid expansion (i.e. greater than expected under the birth/death model of gene family evolution) prior to the divergence of the Botryosphaeriaceae crown group.
After the divergence of the Botryosphaeriaceae, the genera Botryosphaeria, Lasiodiplodia, Macrophomina and Neofusicoccum experienced more gene family expansions than contractions, whereas the opposite was observed for the Diplodia and Eutiariosporella. Among the Neofusicoccum spp., the AA3, AA7, GH3 and GT2 gene families were rapidly expanding. Similarly, among the Lasiodiplodia spp., the AA7 and GH106 gene families were rapidly expanding. Conversely, among the Diplodia spp. the AA7 gene family was rapidly contracting, as were the AA1, AA3, AA7, GH28, PL1 and PL3 gene families among the Eutiarosporella spp.
Principal component analysis and hierarchical clustering
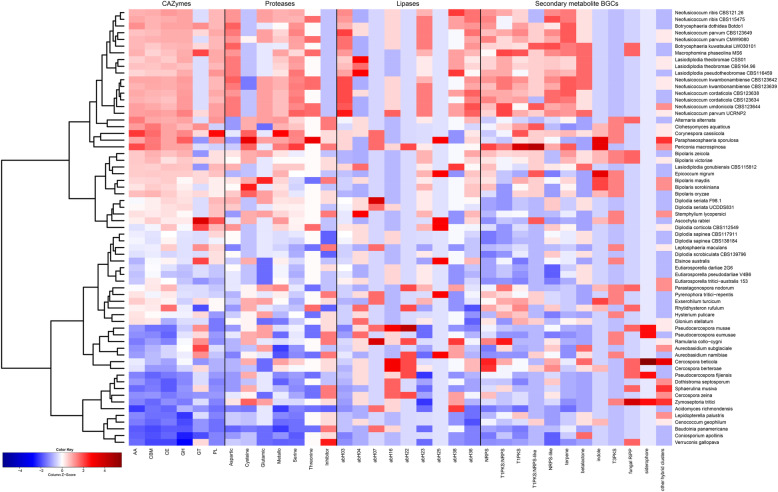
Hierarchical clustering separated the taxa into four groups (Fig. 3). The taxa in the Pleosporomycetidae and Dothideomycetidae generally clustered separately, however, there was no overall clustering based on taxonomic placement. Botryosphaeriaceae species were present in three of the four dominant clusters.
Fig. 3.
Hierarchical clustering and heatmap of Botryosphaeriaceae and other representative Dothideomycetes species based on the number of functional annotation categories of secreted and secondary metabolite BGCs. Overrepresented (red and dark red) and underrepresented (blue and dark blue) values are scaled relative to the column mean
A first cluster included B. dothidea, B. kuwatsukai, M. phaseolina, L. theobromae, L. pseudotheobromae and Neofusicoccum spp., as well as several Pleosporales (Alternaria alternata, Clohesyomyces aquaticus, Corynespora cassiicola Paraphaeosphaeria sporulosa and Periconia macrospinosa). A second cluster mostly contained taxa from the Pleosporales (Aschochyta rabiei, Bipolaris spp., Epicoccum nigrum and Stemphylium lycopersici), but also contained D. seriata, D. corticola and L. gonubiensis. A third cluster contained taxa from both the Dothideomycetidae and Pleosporomycetidae, as well as D. sapinea, D. scrobiculata and Eutiarosporella spp. A fourth cluster was dominated by taxa from the Dothideomycetidae with the exception of L. palustris, C. geophilum, C. apollinis and V. gallopava.
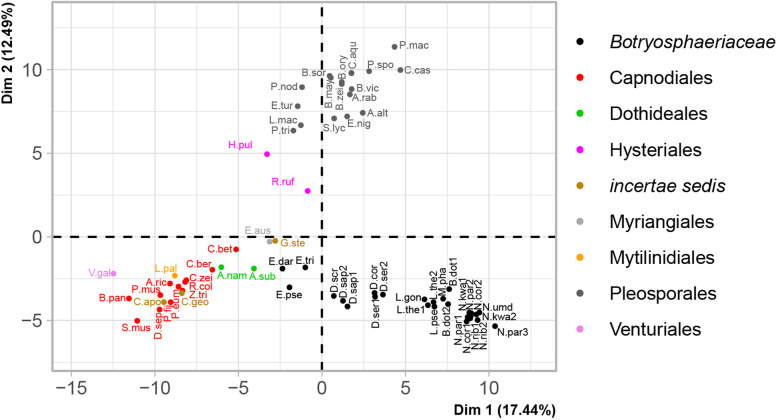
PCA of the functional annotation categories clustered the data along 65 dimensions/principal components. The first two dimensions (Fig. 4) accounted for 29.9% of the variance among the taxa. The first dimension accounted for 17.4% and the second dimension for 12.5% of the variance. The first dimension was most strongly influenced by several secreted CAZyme (AA3, CBM1, GH131, PL3, CBM13, CBM18, CE8, CE12, AA7, GH43, PL4, PL1, CE5 and CBM63), cutinase (abH36) and lipase (abH03 and abH23) and protease (S09 and A01) families, as well as terpene BGCs. The second dimension was most strongly influenced by CAZyme (GH145, CBM3, GH6, GH11, PL26, CBM60, GH7, AA12, AA9, CBM2, GH16, CBM6, CBM87 and CE18), protease (S01, M14 and M36) families, as well as the indole and T3PKS BGC types.
Fig. 4.
Principal component analysis of functional annotation categories of secreted proteins and secondary metabolite BGCs from Botryosphaeriaceae and other Dothideomycetes. Taxa are indicated using abbreviated names (Additional file 1) and colours indicate their Order/Family. The percentage variation accounted for by each principal component is indicated at each axis. The Botrosphaeriaceae varied mostly based on Dimension 1, with Eutiarosporella spp. clustered at the lower ranges of the first dimension (x-axis) followed by clusters accomodating the Diplodia species towards the middle ranges and the other genera of Botryosphaeriaceae clustered at the high ranges of the x-axis
The Botryosphaeriaceae were distributed mainly along the first dimension of the PCA and clustered into three groups. Eutiarosporella spp. clustered at the lower ranges of the first dimension (x-axis) followed by clusters accomodating the Diplodia species towards the middle ranges and the other genera of Botryosphaeriaceae clustered at the high ranges of the x-axis. The Botryosphaeriaceae clustered along a relatively narrow range along the second dimension (y-axis) compared to the other Dothideomycetes. The clustering of the other Dothideomycetes along the x-axis was correlated to their clustering on the y-axis: taxa towards the higher end of the x-axis also occurred towards the higher end of the y-axis. The clustering of taxa did not correspond to their nutritional lifestyle, but their taxonomic placement was reflected in their clustering.
Genome architecture
Two-dimensional heatmaps of the 5′ and 3′ FIRs of the 26 Botryosphaeriaceae genomes indicated no genome compartmentalization (Fig. 5 and Additional file 4). This was evident from the unimodal gene density distributions of these genomes. Genomes of Botryosphaeria, Lasiodiplodia and Macrophomina had a higher proportion of genes in gene sparse regions than the other species in this family. Eutiarosporella spp., D. sapinea, D. scrobiculata and Neofusicoccum spp. had fewer genes in gene sparse regions.
Fig. 5.

Gene density landscape of the genera of Botryosphaeriaceae. The two-dimensional heatmap shows the distribution of genes to gene dense or sparse regions of the genome based on their 5′ and 3′ flanking intergenic regions (FIRs). Two-dimensional heatmaps of each genus is the average across bins of all genomes in the group. The heatmaps labelled as “Botryosphaeria-clade” include the genomes of B. dothidea, B. kuwatsukai and M. phaseolina. The values on the axes are distances in base pairs and signify the upper limit of each bin. The median bin is indicated by dotted lines to assist in comparison between plots. The colours of the heatmap represents the number of genes present within each two-dimensional bin. All Botryosphaeriaceae had unimodal gene density distributions, with Eutiarosporella, Diplodia and Neofusicoccum with a greater overall gene density (smaller intergenic regions) than the other genera
The predicted secreted proteins of the Botryosphaeriaceae contained a greater number of genes in gene sparse regions than the total predicted genes (Additional file 4). The total CAZymes contained a higher proportion of genes in gene sparse regions than the total predicted genes. The secreted CAZyme gene density distribution was very similar to that of the total CAZymes. The secreted lipases and cutinases, however, occurred more frequently in gene sparse regions than the total lipases and cutinases (Additional file 4). This trend was also observed for the secreted proteases, although not as strongly. Genes associated with secondary metabolite BGCs were less prevalent in gene sparse regions.
The levels of repetitive sequences for most Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were between 3 and 8% of the total genome size (Table 5). The two Botryosphaeria spp. differed considerably in their repeat content (3.48 vs. 11.88%). The genome of M. phaseolina also had a higher than average repeat content (16.37%). Among the Neofusicoccum species, the genomes of N. parvum and N. umdonicola had less repetitive sequences than the other genomes of this genus. The genomes of D. sapinea and D. scrobiculata also contained less repetitive sequences than the other two Diplodia species.
Table 5.
Summary of genomic architecture features of Botryosphaeriaceae genomes
| Genome size (Mb) | Repetitive sequences (bp) | % of repetitive sequences | Genome GC % | % genome that is GC rich (> 50%) | Genes in TA rich regions | Secreted genes in TA rich regions | % genome affected by RIP | Number of LRARs | Total size (bp) of all LRARs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eutiarosporella darliae 2G6 | 27.27 | 1,415,283 | 5.19 | 61 | 98.3 | 3 | 0 | 0.91 | 4 | 32,276 |
| E. pseudodarliae V4B6 | 26.74 | 1,290,421 | 4.83 | 61.53 | 98.6 | 7 | 0 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 |
| E. tritici-australis 153 | 26.59 | 1,544,103 | 5.81 | 61.66 | 97.3 | 0 | 0 | 2.54 | 14 | 95,508 |
| Diplodia sapinea CBS117911 | 36.05 | 1,344,948 | 3.73 | 56.84 | 95 | 73 | 4 | 1.12 | 2 | 9500 |
| D. sapinea CBS138184 | 35.24 | 1,305,464 | 3.7 | 56.73 | 94.7 | 68 | 6 | 0.96 | 2 | 12,500 |
| D. scrobiculata CBS139796 | 34.93 | 1,110,716 | 3.18 | 57.01 | 95.6 | 63 | 6 | 0.82 | 1 | 13,000 |
| D. seriata UCDDS831 | 37.27 | 1,711,911 | 4.61 | 56.6 | 96.8 | 29 | 2 | 2.63 | 21 | 125,537 |
| D. seriata F98.1 | 37.12 | 1,593,160 | 4.27 | 48.47 | 94.5 | 51 | 1 | 1.87 | 34 | 554,000 |
| D. corticola CBS112549 | 34.99 | 2,102,085 | 6.01 | 47.92 | 94.5 | 31 | 3 | 3.39 | 42 | 690,014 |
| Lasiodiplodia theobromae CBS164.96 | 42.97 | 1,498,597 | 3.49 | 54.74 | 89.9 | 354 | 32 | 0.72 | 3 | 59,500 |
| L. theobromae CSS01 | 43.28 | 1,543,231 | 3.57 | 48.15 | 89.8 | 306 | 33 | 1.04 | 18 | 375,000 |
| L. pseudotheobromae CBS116459 | 43.01 | 1,402,977 | 3.26 | 54.66 | 89.2 | 377 | 36 | 0.92 | 12 | 375,000 |
| L. gonubiensis CBS115812 | 41.14 | 1,330,240 | 3.23 | 54.72 | 92.1 | 223 | 24 | 1.18 | 12 | 345,500 |
| Botryosphaeria dothidea CMW8000 | 43.5 | 1,515,197 | 3.48 | 54.3 | 89.8 | 385 | 53 | 0.88 | 1 | 5000 |
| B. kuwatsukai LW030101 | 47.39 | 5,628,118 | 11.88 | 53.09 | 81.1 | 406 | 41 | 9.65 | 170 | 1,387,657 |
| Macrophomina phaseolina MS6 | 48.88 | 8,000,688 | 16.37 | 52.33 | 80.2 | 228 | 23 | 12.92 | 172 | 2,658,966 |
| Neofusicoccum cordaticola CBS123634 | 45.71 | 3,594,350 | 7.86 | 54.9 | 86.5 | 566 | 54 | 3.7 | 105 | 1,071,347 |
| N. cordaticola CBS123638 | 43.56 | 3,614,552 | 8.3 | 55.92 | 88.7 | 393 | 40 | 3.99 | 47 | 324,966 |
| N. kwambonambiense CBS123639 | 44.17 | 3,369,216 | 7.62 | 55.92 | 89.1 | 408 | 40 | 2.75 | 64 | 693,395 |
| N. kwambonambiense CBS123642 | 44.21 | 3,592,960 | 8.13 | 56.04 | 89.2 | 459 | 49 | 2.35 | 56 | 554,628 |
| N. parvum CMW9080 | 41.41 | 1,944,617 | 4.7 | 56.54 | 91.3 | 406 | 40 | 1.36 | 11 | 63,557 |
| N. parvum CBS123649 | 42.16 | 2,032,314 | 4.82 | 56.06 | 91.8 | 360 | 36 | 1.65 | 14 | 88,222 |
| N. parvum UCRNP2 | 42.52 | 2,167,908 | 5.1 | 56.76 | 91.4 | 407 | 35 | 1.59 | 11 | 72,874 |
| N. ribis CBS115475 | 43.18 | 3,241,261 | 7.51 | 55.71 | 89.6 | 379 | 38 | 4.52 | 79 | 911,957 |
| N. ribis CBS121.26 | 43.12 | 3,171,232 | 7.35 | 55.88 | 89.1 | 423 | 51 | 4.71 | 25 | 153,638 |
| N. umdonicola CBS123644 | 42.29 | 2,237,372 | 5.29 | 56.51 | 91.6 | 415 | 48 | 1.38 | 11 | 76,232 |
On average, the Botryosphaeriaceae genomes had less than 10% of their genomes composed of TA rich regions (GC < 50%) (Table 5). The genomes of B. kuwatsukai LW030101 and M. phaseolina had 18.9 and 19.8% of their genomes as TA rich regions, respectively. The genomes of Diplodia and Eutiarosporella had fewer TA rich regions (approximately 5% of the genome) compared to the other genera. Less than 5% of genes were present in TA rich regions and secreted genes were not found to be over-represented among these genes (Additional file 4). The genomes of Diplodia and Eutiarosporella had considerably fewer genes associated with TA rich regions, than the other taxa of this family.
Analysis of the prevalence of RIP in the genomes of Botryosphaeriaceae indicated that this has occurred to varying degrees in these genomes (Table 5). Neofusicoccum spp. had between 1.36 and 4.71% of their genome affected by RIP. The level of RIP was similar between different genomes of the same Neofusicoccum species. Neofusicoccum parvum and N. umdonicola had lower proportions of RIP affected sequences than the other species of the genus. There was a large (> 10-fold) difference in the level of RIP between B. dothidea and B. kuwatsukai. The genome of M. phaseolina had the highest (12.92%) amount of RIP of all the Botryosphaeriaceae. Lasiodiplodia spp. had RIP levels between 0.72 and 1.18%. The level of RIP in the genomes of D. sapinea and D. scrobiculata was lower than in D. seriata and D. corticola. The genome of E. tritici-australis had more than double the level of RIP affected regions than the other two species of the genus.
Discussion
This study represents the first large-scale comparative genomics-level consideration of all available genomes of Botryosphaeriaceae. The results showed that the included Botryosphaeriaceae genomes, especially those of Botryosphaeria, Macrophomina, Lasiodiplodia and Neofusicoccum, encode high numbers of secreted hydrolytic enzymes and secondary metabolite BGCs. This emerges due to these fungi having increased numbers of genes associated with plant interactions in their secretome. The results also indicate that the Botryosphaeriaceae are most similar to species of the Pleosporomycetidae based on secreted enzyme and secondary metabolite profiles. Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were furthermore determined not to be compartmentalized based on gene density or GC-content.
There was a strong correlation between the number of hydrolytic enzymes and secondary metabolite BGCs, and the genome size and gene number of the Botryosphaeriaceae considered in this study. This correlation between genome size and gene number has generally not been seen in other fungi [4, 11, 80], because transposable elements and repetitive DNA vary significantly among species [11]. A recent comparison of Dothideomycetes genomes [81] also showed that genome size and gene number were not correlated to the abundance of functional annotation classes; neither to the lifestyle or phylogenetic placement of a species.
The genomes of Botryosphaeria, Macrophomina, Lasiodiplodia and Neofusicoccum had abundant secreted hydrolytic enzyme and secondary metabolite BGCs. This is a pattern that is most similar to prominent necrotrophic plant pathogens (A. alternata, C. casiicola), saprobes (C. aquaticus, P. sporulosa) and the endophyte/latent pathogen P. macrospinosa in the Pleosporales. The pattern was consistent with reports that necrotrophic pathogens tend to have higher numbers of hydrolytic enzymes and secondary metabolite toxins than biotrophs and symbiotic fungi [7, 82]. An abundance of secreted hydrolytic enzymes and secondary metabolite BGCs found in the Botryosphaeriaceae is also similar to that of other species of woody endophytes. Studies on such endophytic species have shown that they have similar or higher amounts of various secreted enzymes (notably plant cell wall degrading enzymes) or secondary metabolites than closely related plant pathogenic species [41–44]. The specific gene families that are enriched, however, differ among endophytic lineages, due to the evolutionary independent origins of endophytism [41–44]. It has furthermore been noted that fungi with dual lifestyles (e.g. fungi with endophytic and pathogenic phase) have large numbers of CAZymes [83, 84], however, few studies have investigated this. These observations also emerging from the present study are consistent with the known dual-lifestyle of Botryosphaeriaceae as latent pathogens.
The Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were rich in CAZymes, especially those involved in plant cell wall degradation (PCWD), although at lower numbers in the genomes of Diplodia and Eutiarosporella species. CAZymes involved in the degradation of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin were present in all Botryosphaeriaceae. The genomes of Botryosphaeria, Macrophomina, Lasiodiplodia and Neofusicoccum were particularly rich in CAZyme families involved in cell wall degradation. Specifically, CAZymes involved in plant, general and fungal cell wall degradation [4, 85, 86] were abundant in the genomes of the above-mentioned genera.
The Botryosphaeriaceae secretomes were rich in CAZyme families involved in the recognition of cellulose (CBM1) and chitin (CBM18). Although carbohydrate-binding domains have no catalytic activity of their own they play important roles in substrate recognition and binding of other CAZymes [87, 88], they are also involved in the protection of fungal cell walls from degradation by host enzymes and prevention of host detection [1, 89]. High numbers of secreted CAZymes involved with PCWD have also been found in previous studies of N. parvum and D. seriata [31, 32] and in other, especially necrotrophic, Dothideomycetes [62, 63, 66, 70, 85]. The abundance of these CAZyme families in some genera of Botryosphaeriaceae suggests that cell wall degradation plays an important role in the biology of these fungi.
Several important CAZyme families that are common among Dothideomycetes were absent from all the Botryosphaeriaceae genomes, i.e. Acetyl xylan esterase (CE3) [90], Pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent oxidoreductase (AA12) [91], endo-α-1,4-polygalactosaminidase (GH114) [92] and α-L-arabinofuranosidase/β-xylosidase (GH54) [93]. The absence of these CAZyme families in the Botryosphaeriaceae does not necessarily indicate a gap in the metabolic repertoire of these fungi because a large degree of functional redundancy is commonly seen in fungal CAZyme repertoires [94–96]. Interestingly, some of the CAZyme families that can functionally compensate for the absence of the above-mentioned CAZyme families are those that were found to be among the most abundant secreted CAZyme families of the Botryosphaeriaceae (e.g. CE16, AA3, AA7, GH15 and GH3).
The Botryosphaeriaceae were rich in secreted serine-, metallo- and aspartic-proteases. Protease families (A01, S08, S09, S10) that were previously identified as the most common secreted proteases among Dothideomycetes [4] were also the most abundant in the Botryosphaeriaceae. Secreted proteases play important roles in nutrient acquisition, signalling and degradation of plant defences [3, 97–99]. Although secreted proteases are abundant in several necrotrophic pathogens, e.g. Corynespora cassiicola [66] and several Colletotrichum spp. [100], no patterns between nutritional lifestyle and the abundance of secreted proteases could be distinguished. The precise function of most of these proteases in the Botryosphaeriaceae are unknown and their role during infection and disease expression remains to be determined.
A lower abundance and diversity of secreted protease inhibitors of the Botryosphaeriaceae suggests a reduced capacity and/or need for extracellular enzyme inhibition. Plant pathogenic fungi secrete protease inhibitors to inhibit plant proteases involved in defence responses [101] and several protease inhibitors are known virulence factors, e.g. avr2 of Cladosporium fulvum [102, 103] and Pit2 of Ustilago maydis [104]. However, the exact role of many fungal protease inhibitors, such as those secreted by the Botryosphaeriaceae and Dothideomycetes, remains unknown [105].
Botryosphaeriaceae, especially species of Botryosphaeria, Macrophomina, Lasiodiplodia and Neofusicoccum possessed high numbers of secreted lipases. Three lipase families were present in high numbers in the secretomes of the Dothideomycetes, i.e. Candida rugosa lipase-like (abH03), cutinases (abH36 and CE5) and Filamentous fungi lipases (abH23). The Botryosphaericeae genomes were rich in secreted enzymes for these three families. Lipases and cutinases are important for fungal penetration of host tissue [6, 106], growth and adhesion [107, 108] and manipulation of host defences [5]. The abundance of these secreted lipases and cutinases emphasises their potentially important role during the infection process in the Botryosphaeriaceae.
The genomes of Botryosphaeria, Macrophomina, Lasiodiplodia and Neofusicoccum contained many BGCs, especially t1PKS, NRPS, NRPS-like and TS type clusters. The products produced by most of these clusters are unknown, however, the products of some clusters could be determined. These compounds included melanin, phytotoxins (ACT-Toxin II, (−)-Mellein), siderophores (dimethylcoprogen) and antioxidants (pyranonigrin E). Many phytotoxic secondary metabolites have been identified in the Botryosphaeriaceae [109–114]. Of these, the most commonly identified phytotoxic compounds are mellein and its derivatives [115, 116]. The presence of a predicted ACT-toxin producing gene cluster in the Botryosphaeriaceae is interesting as it is a host selective toxin from citrus infecting A. alternata [117]. This toxin is part of the Epoxy-decatrienoic acid (EDA) family, however, neither this type of toxin or any in this family has been isolated from the Botryosphaeriaceae. The ability to produce secondary metabolite toxins have been associated with pathogenic fungi’s lifestyle, host range and virulence [4, 118, 119]. Many plant pathogenic fungi have large numbers of secondary metabolite BGCs, e.g. Bipolaris spp. [120], Corynespora cassiicola [66], Colletotrichum spp. [100] and Pyrenophora teres [4], but so also do fungi with other lifestyles such as the saprobic Annulohypoxylon stygium [121], Hysterium pulicare, and Rhytidhysteron rufulum [4]. Despite the observation that the total abundance of secondary metabolite BGCs does not predict lifestyle, several fungal toxins are able to modulate a fungal species’ host range or virulence, e.g. the AF-toxin of A. alternata [118], the Hybrid-1,2 and 3 genes of Eutiarosporella darliae and E. pseudodarliae [27] and the HC-toxins of Bipolaris zeicola [122].
The Botryosphaeriaceae genera were shown to possess non-compartmentalized genomes. These species were characterized as having moderate to high % GC, RIP-affected genomes with low amounts of repetitive DNA, a slight preferential localization of secreted genes to gene sparse regions and no preferential localization of secreted genes to TA rich regions. Most Dothideomycetes do not have compartmentalized genomes, but several important pathogenic species (e.g. L. maculans and Pseudocercospora spp.), have genomes with high levels of repetitive DNA (often transposable elements) [12, 57] enriched for fast-evolving genes related to pathogenicity or virulence [57, 123, 124]. However, not all rapidly evolving fungal phytopathogens have this characteristic ‘two-speed’ genome architecture [13]. Where ‘two-speed’ genomes rely on the action of leaky RIP to generate variation for selection to act on, ‘one-speed’ genomes of fast-evolving plant pathogens rely on the absence of RIP that allows gene duplication/copy number variation to generate variation [13]. The Botryosphaeriaceae are not like those species with ‘two-speed’ genomes as they don’t have compartmentalized genomes, but RIP is also not completely absent as seen in species with ‘one-speed’ fast-evolving genomes.
Conclusions
This study is the first large-scale comparative genomics study to consider all available genomes of Botryosphaeriaceae. It has illustrated large variability in the secreted hydrolytic enzyme and secondary metabolite biosynthetic repertoire between genera of this family. Most importantly, we have demonstrated similarities between the Botryosphaeriaceae and necrotrophic plant pathogens and endophytes of woody plants, emphasising their role as latent pathogens. This study highlights the importance of these genes in the infection biology of Botryosphaeriaceae species and their interaction with plant hosts. This knowledge will be useful in future studies aimed at understanding the mechanisms of endophytic infections and how these transition to a pathogenic state. The results should also help to better understand the genetic factors involved in determining the complex question of host range in the Botryosphaeriaceae.
Materials and methods
Genomic data
All available, published Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were retrieved from public databases (NCBI and JGI). Additionally, we sequenced and assembled 12 genomes representing three Lasiodiplodia spp. and five Neofusicoccum spp. (Table 1). To standardize protein annotations for downstream application, all of the above Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were annotated using the same pipeline described below. Additionally, the genomes and protein annotations of 41 Dothideomycetes and Aspergillus nidulans (Eurotiales), which had both genomic sequences and annotated protein sequences available on NCBI, were retrieved (Table 1). These genomes were used for comparative purposes in the phylogenomic analyses, hydrolytic enzyme and secondary metabolite BGC analyses and in the statistical clustering analyses, described below.
DNA extraction, genome sequencing and assembly
Cultures of three Lasiodiplodia and five Neofusicoccum species (Table 1) were inoculated onto cellophane covered 2% malt extract agar (MEA; Biolab, Merck) and incubated at 22 °C. After 5 days, mycelium was harvested from the surface of the cellophane using a sterile scalpel and DNA was extracted using a modified phenol/chloroform protocol, that included the addition of potassium acetate to precipate protein. Mycelium was ground to a fine powder using liquid nitrogen and mortar and pestle. Approximately 500 mg of ground mycelium was used for DNA extraction. To the ground mycelia, 18 ml of a 200 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, 25 mM EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, pH 8.0) and 0.5% SDS (Sodium dodecyl sulfate) solution and 125 μl of 20 mg/ml Proteinase K was added and incubated at 60 °C for 2 h. This was followed by addition of 6 ml of 5 M potassium acetate and 30 min incubation at 0 °C. Samples were then centrifuged at 5000 g for 20 min. The aqueous phase was kept and 24 ml of a 1:1 phenol:chloroform solution was added; samples were then centrifuged as above. Two chloroform washes were performed on the aqueous phase, followed by addition of 100 μl of 10 mg/ml Rnase A and incubated for 2 h. DNA was precipitated using one volume isopropanol and centrifuged for 30 min. The pellet was cleaned with two 70% ethanol washes and resuspended in 1 x Tris-EDTA buffer.
The extracted DNA was used for paired-end sequencing (average fragment size of 500 bp). All samples were sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform, except for N. parvum (isolate CMW9080) that was sequenced on a Miseq platform. The quality of the resulting reads was assessed using FastQC 0.10.1 [125] and low quality and short reads were trimmed or discarded using Trimmomatic 0.30 [126]. De novo genome assembly was performed by Velvet 1.2.10 [127] and Velvetoptimiser 2.2.5 [128]. Paired-end reads were used to scaffold the assembly and insert size statistics were determined by Velvet for each genome assembly. Genome assembly summary statistics were calculated with the AssemblyStatsWrapper tool of BBtools 38.00 [129].
Genome annotation
The twelve sequenced genomes described above, as well as the fourteen Botryosphaeriaceae genomes retrieved from public databases, were annotated as follows: Custom repeat libraries were constructed for each genome assembly using RepeatModeler 1.0.10 [130]. BRAKER 1.10 [131] was used to create trained GeneMark-ET 4.29 [132] and AUGUSTUS 3.2.3 [133] profiles using previously published N. parvum transcriptome data (SRR3992643 and SRR3992649) [31]. Genomes were annotated through the MAKER2 2.31.8 [134] pipeline using the custom repeat libraries and the BRAKER trained GeneMark-ET 4.29 and AUGUSTUS profiles. Genomes and genome annotations were assessed for completeness with BUSCO 4.0.5 [135] using the Ascomycota ortholog library (Creation date 2020-09-10, 1706 core orthologous genes). The annotations for six Botryosphaeriaceae genomes available on public databases prior to this study were also assessed using BUSCO and compared to those of the annotations generated in this study.
Phylogenomic analyses
To illustrate the relationships between species and genera of the Botryosphaeriaceae, as well as the relationship of this family to the rest of the Dothideomycetes, a robust phylogeny was created from the genome data. Single copy core orthologous genes were identified from individual genomes (Table 1) using BUSCO (as described above). The BUSCO genes present in all taxa (207 genes) were selected for further analysis. Each orthogroup was aligned using MAFFT 7.407 [136] before being concatenated into a single matrix. RAxML 8.2.4 [137] was used to perform maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference using the PROTGAMMAAUTO option and a thousand bootstrap replicates were performed. Trees were rooted using sequences from Aspergillus nidulans.
Functional annotation
The genome annotation data for the Botryosphaeriaceae, the other Dothideomycetes and the outgroup A. nidulans were used to perform functional annotation for hydrolytic enzymes and secondary metabolite BGCs. CAZymes were predicted by searching the total predicted proteins of each genome against the CAZy database [138] using dbCAN2 (HMMdb release v9.0) [139]. Only those CAZyme predictions supported by two or more tools (HMMR, DIAMOND, Hotpep) were retained. Proteases and protease inhibitors were predicted by subjecting the predicted protein sequences to a BLASTP [140] search against the MEROPS protease database 12.0 [141] using a cut off E-value of 1E-04. Lipases and cutinases were predicted by searching protein sequences against lipase and cutinase hidden Markov model (HMM) profiles retrieved from the Lipase Engineering Database v 3.0 [142] using HMMER 3.1b2 [143]. Secondary metabolite BGCs were identified from all annotated genomes using AntiSMASH v5.1.1 [144].
The total predicted proteins were also analyzed for the presence of signal peptides, involved in protein secretion. Phobius 1.01 [145] and SignalP 4.1 [146] were used to assess the presence of signal peptides and TMHMM 2.0 [147] was used to determine if any transmembrane regions occurred within these proteins. Only proteins with a signal peptide predicted by both Phobius and SignalP, as well as no transmembrane domains outside of the signal peptide predicted by both Phobius and TMHMM were regarded here as predicted secreted proteins.
Statistical analyses were performed using the total number of annotations, as well as the number of each enzyme class/secondary metabolite BGC type. Statistical tests were done comparing the genera of the Botrysphaeriaceae, but also for comparisons between Dothideomycetidae, Pleosporomycetidae and Botryosphaeriaceae. Due to the small number of representative genomes for Botryosphaeria (2) and Macrophomina (1) and their close phylogenetic placement, they were combined in a single group (i.e. Botryosphaeria-clade) for the purpose of statistical analyses. We further also included Cenococcum geophilum, Coniosporium apollinis and Glonium stellatum in the Pleosporomycetidae, based on their phylogenetic placement (Fig. 1).
We calculated pairwise Pearsons correlation coefficients [148] in order to test whether genome size, the number of predicted genes or any of the functional annotation categories were correlated. The Shapiro-Wilk test [149] was performed in order to test for a normal distribution using the byf.shapiro function of the RVAideMemoire R-package [150]. Pairwise comparisons to test for significant differences were done using one-tailed Wilcoxon rank-sum tests [151] in R using the pairwise.wilcox.test function of the R stats package [152] with either the ‘greater’ or ‘less’ alternative hypothesis options. This is a non-parametric test to determine whether two independent sets of values have the same distribution. Unlike the t-test, the Wilcoxon rank sum test does not assume a normal distribution [153] and thus was better suited to our data. These same tests as above were done using the total number of predicted, as well as the number of secreted genes, associated with hydrolytic enzyme families to test if specific CAZyme, protease or lipase families within the secretomes of the Dothideomycetidae, Pleosporomycetidae and Botryosphaeriaceae were significantly different.
Analysis of gene family evolution
CAFE (Computational Analysis of gene Family Evolution) v4.2 [154] was used to study the evolution of gene family size in the hydrolytic enzymes and secondary metabolite BGCs. To this end, the phylogeny described above was converted to an ultrametric tree using r8s v1.81 [155]. This was then calibrated by fixing the age of the Botrosphaeriaceae to 61 million years [79] and constraining the age of the Dothideomycetes to 303–357 million years [156]. Gene family sizes for the total predicted CAZymes, proteases, lipases and secondary metabolite BGCs (Additional file 1) were used as input for the CAFE analyses. CAFE was run using separate lambda (birth) and mu (death) rate parameters. Additionally, two separate rate classes were allowed in that the rate parameters were calculated independently for the Botryosphaeriaceae and the remaining Dothideomycete taxa. CAFE was run using a P-value cutoff of 0.01 and Viterbi P-values were calculated to significant expansions/contractions across branches.
Hierarchical clustering and principal component analysis
Hierarchical clustering was done to determine the similarity between taxa based on the secreted hydrolytic enzyme classes and secondary metabolite BGC types. The heatmap.2 function of the gplots [157] R package was used to perform the analysis. Additionally, principal component analysis (PCA) was performed using the same functional annotations as used in the hierarchical clustering, with the exception that for CAZymes and proteases the number of genes associated with each family (e.g AA1, A01) was used instead of those of each class (e.g AA, Aspartic). The FactoMineR [158] R package was used to perform the analysis and Factoshiny [159] was used to generate PCA plots.
Genome architecture
Gene densities were analyzed for each Botryosphaeriaceae genome to assess the level of genome compartmentalization. Intergenic distances were used as a measure of gene density, by considering the 5′ and 3′ flanking intergenic regions (FIRs) of each gene. FIR lengths were used for two-dimensional data binning to construct gene density heat maps [160] using R [152]. Possible differences in the gene density distributions between the total and secreted CAZymes, proteases and lipases were also considered. We compared the relative amounts (i.e. the percentage) of these genes located in gene-sparse regions. In this case, gene sparse regions were defined as genes with both 5′ and 3′ FIRs larger than 1500 bp, as previously used by S Raffaele and S Kamoun [11].
The repeat contents of the Botryosphaeriaceae genomes were determined using RepeatMasker [161] with custom repeat libraries created by RepeatModeler. The presence of TA rich regions and the genes present therein were determined using OcculterCut [124]. Specifically, the numbers of the total secreted genes, the secreted CAZymes, proteases and lipases, as well as the number of secondary metabolite BGCs associated with TA rich regions were determined. The occurrence of RIP, including large regions affected by RIP (LRARs), was determined in each genome using TheRIPper [162].
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the University of Pretoria, The Department of Science and Technology (DST)/National Research Foundation (NRF) Centre of Excellence in Tree Health Biotechnology and members of the Tree Protection Cooperative Program for financial support of this study. The authors acknowledge the Centre for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, University of Pretoria and the Centre for High Performance Computing (CHPC), South Africa for providing computational resources to this research project. Lastly, our sincere thanks to Alisa Postma for her guidance during the genome assembly and annotation process and to Dr. Tuan Duong for his critical comments on this manuscript.
Authors’ contributions
BS and MJW were supervisors for the doctoral research by JHN. All authors contributed to the study conception, data interpretation and the revision of the manuscript. JHN performed the laboratory work, data analyses and visualizations, and wrote the draft manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The South African National Research Foundation (NRF) funded the Doctoral research of the first author. This project was financed by the University of Pretoria, the Department of Science and Innovation (DSI)/National Research Foundation (NRF) Centre of Excellence in Tree Health Biotechnology. The Grant holders acknowledge that opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in any publication generated by NRF-supported research are that of the author(s) and that the NRF accepts no liability whatsoever in this regard.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files). Genomic data used in this study (Table 1) are available from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome) and the JGI Genome Portal (http://genome.jgi.doe.gov). Raw sequencing reads of the de novo genomes described in this study linked to Bioproject PRJNA497969 (Biosample Accessions SAMN10319569 - SAMN10319580) have been deposited to the Sequence Read Archive (SRA, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) database and are awaiting accession numbers.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.De Jonge R, Thomma BPHJ. Fungal LysM effectors: extinguishers of host immunity? Trends Microbiol. 2009;17(4):151–157. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jia Y, McAdams SA, Bryan GT, Hershey HP, Valent B. Direct interaction of resistance gene and avirulence gene products confers rice blast resistance. EMBO J. 2000;19(15):4004–4014. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.15.4004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Carlile AJ, Bindschedler LV, Bailey AM, Bowyer P, Clarkson JM, Cooper RM. Characterization of SNP1, a cell wall-degrading trypsin, produced during infection by Stagonospora nodorum. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2000;13(5):538–550. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.5.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ohm RA, Feau N, Henrissat B, Schoch CL, Horwitz BA, Barry KW, Condon BJ, Copeland AC, Dhillon B, Glaser F. Diverse lifestyles and strategies of plant pathogenesis encoded in the genomes of eighteen Dothideomycetes fungi. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(12):e1003037. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Christensen SA, Kolomiets MV. The lipid language of plant–fungal interactions. Fungal Genet Biol. 2011;48(1):4–14. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2010.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Voigt CA, Schäfer W, Salomon S. A secreted lipase of Fusarium graminearum is a virulence factor required for infection of cereals. Plant J. 2005;42(3):364–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhao Z, Liu H, Wang C, Xu J-R. Correction: comparative analysis of fungal genomes reveals different plant cell wall degrading capacity in fungi. BMC Genomics. 2014;15(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Keller NP, Turner G, Bennett JW. Fungal secondary metabolism—from biochemistry to genomics. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3(12):937–947. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Howlett BJ. Secondary metabolite toxins and nutrition of plant pathogenic fungi. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2006;9(4):371–375. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dong S, Raffaele S, Kamoun S. The two-speed genomes of filamentous pathogens: waltz with plants. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2015;35:57–65. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2015.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Raffaele S, Kamoun S. Genome evolution in filamentous plant pathogens: why bigger can be better. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012;10(6):417–430. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rouxel T, Grandaubert J, Hane JK, Hoede C, van de Wouw AP, Couloux A, Dominguez V, Anthouard V, Bally P, Bourras S. Effector diversification within compartments of the Leptosphaeria maculans genome affected by repeat-induced point mutations. Nat Commun. 2011;2(1):202. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Frantzeskakis L, Kusch S, Panstruga R. The need for speed: compartmentalized genome evolution in filamentous phytopathogens. Mol Plant Pathol. 2019;20(1):3–7. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stukenbrock EH, Jorgensen FG, Zala M, Hansen TT, McDonald BA, Schierup MH. Whole-genome and chromosome evolution associated with host adaptation and speciation of the wheat pathogen Mycosphaerella graminicola. PLoS Genet. 2010;6(12):e1001189. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Möller M, Stukenbrock EH. Evolution and genome architecture in fungal plant pathogens. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017;15(12):756. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Slippers B, Wingfield MJ. Botryosphaeriaceae as endophytes and latent pathogens of woody plants: diversity, ecology and impact. Fungal Biol Rev. 2007;21(2):90–106. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mehl JWM, Slippers B, Roux J, Wingfield MJ. Cankers and Other Diseases Caused by the Botryosphaeriaceae. In: Gonthier P, Nico G, editors. Infectious Forest Diseases: CABI; 2013:298–317.
- 18.Urbez-Torres JR. The status of Botryosphaeriaceae species infecting grapevines. Phytopathol Mediterr. 2011;50(4):5–45. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Slippers B, Smit WA, Crous PW, Coutinho TA, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ. Taxonomy, phylogeny and identification of Botryosphaeriaceae associated with pome and stone fruit trees in South Africa and other regions of the world. Plant Pathol. 2007;56(1):128–139. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Alves A, Barradas C, Phillips AJL, Correia A. Diversity of Botryosphaeriaceae species associated with conifers in Portugal. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2013;135(4):791–804. doi: 10.1007/s10658-012-0122-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mohali S, Slippers B, Wingfield MJ. Identification of Botryosphaeriaceae from Eucalyptus, Acacia and Pinus in Venezuela. Fungal Divers. 2007;25:103–125. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rodas CA, Slippers B, Gryzenhout M, Wingfield MJ. Botryosphaeriaceae associated with Eucalyptus canker diseases in Colombia. For Pathol. 2009;39(2):110–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0329.2008.00569.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jami F, Slippers B, Wingfield MJ, Gryzenhout M. Botryosphaeriaceae species overlap on four unrelated, native south African hosts. Fungal Biology. 2014;118(2):168–179. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2013.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Marincowitz S, Groenewald JZ, Wingfield MJ, Crous PW. Species of Botryosphaeriaceae occurring on Proteaceae. Persoonia. 2008;21(1):111–118. doi: 10.3767/003158508X372387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pavlic D, Wingfield MJ, Barber P, Slippers B, Hardy GESJ, Burgess TI. Seven new species of the Botryosphaeriaceae from baobab and other native trees in Western Australia. Mycologia. 2008;100(6):851–866. doi: 10.3852/08-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jami F, Wingfield MJ, Gryzenhout M, Slippers B. Diversity of tree-infecting Botryosphaeriales on native and non-native trees in South Africa and Namibia. Australas Plant Pathol. 2017;46(6):529–545. doi: 10.1007/s13313-017-0516-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Thynne E, Mead OL, Chooi Y-H, McDonald MC, Solomon PS. Acquisition and loss of secondary metabolites shaped the evolutionary path of three emerging phytopathogens of wheat. Genome Biol Evol. 2019;11(3):890–905. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bihon W, Burgess T, Slippers B, Wingfield MJ, Wingfield BD. Distribution of Diplodia pinea and its genotypic diversity within asymptomatic Pinus patula trees. Australas Plant Pathol. 2011;40(5):540–548. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cobos R, Barreiro C, Mateos RM, Coque J-JR. Cytoplasmic-and extracellular-proteome analysis of Diplodia seriata: a phytopathogenic fungus involved in grapevine decline. Proteome Sci. 2010;8(1):46. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-8-46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fernandes I, Alves A, Correia A, Devreese B, Esteves AC. Secretome analysis identifies potential virulence factors of Diplodia corticola, a fungal pathogen involved in cork oak (Quercus suber) decline. Fungal Biol. 2014;118(5–6):516–523. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2014.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Massonnet M, Morales-Cruz A, Figueroa-Balderas R, Lawrence DP, Baumgartner K, Cantu D. Condition-dependent co-regulation of genomic clusters of virulence factors in the grapevine trunk pathogen Neofusicoccum parvum. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016;19(1):21–34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Morales-Cruz A, Amrine KCH, Blanco-Ulate B, Lawrence DP, Travadon R, Rolshausen PE, Baumgartner K, Cantu D. Distinctive expansion of gene families associated with plant cell wall degradation, secondary metabolism, and nutrient uptake in the genomes of grapevine trunk pathogens. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1624-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Blanco-Ulate B, Rolshausen P, Cantu D. Draft genome sequence of Neofusicoccum parvum isolate UCR-NP2, a fungal vascular pathogen associated with grapevine cankers. Genome announcements. 2013;1(3):e00339–e00313. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00339-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Islam MS, Haque MS, Islam MM, Emdad EM, Halim A, Hossen QMM, Hossain MZ, Ahmed B, Rahim S, Rahman MS. Tools to kill: genome of one of the most destructive plant pathogenic fungi Macrophomina phaseolina. BMC Genomics. 2012;13(1):493. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu Z, Lian S, Li B, Lu H, Dong X, Wang C. Draft genome sequence of Botryosphaeria dothidea, the pathogen of apple ring rot. Genome Announc. 2016;4(5):e01142–e01116. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01142-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Marsberg A, Kemler M, Jami F, Nagel JH, Postma-Smidt A, Naidoo S, Wingfield MJ, Crous PW, Spatafora JW, Hesse CN, Robbertse B, Slippers B. Botryosphaeria dothidea: a latent pathogen of global importance to woody plant health. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016;18(4):477–488. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Robert-Siegwald G, Vallet J, Abou-Mansour E, Xu J, Rey P, Bertsch C, Rego C, Larignon P, Fontaine F, Lebrun M-H. Draft genome sequence of Diplodia seriata F98.1, a fungal species involved in grapevine trunk diseases. Genome Announc. 2017;5(14):e00061–e00017. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00061-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.van der Nest MA, Bihon W, De Vos L, Naidoo K, Roodt D, Rubagotti E, Slippers B, Steenkamp ET, Wilken PM, Wilson A. Draft genome sequences of Diplodia sapinea, Ceratocystis manginecans, and Ceratocystis moniliformis. IMA Fungus. 2014;5(1):135–140. doi: 10.5598/imafungus.2014.05.01.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Southworth D. Biocomplexity of plant-fungal interactions: Wiley; 2012. 10.1002/9781118314364.
- 40.Schulz B, Boyle C. The endophytic continuum. Mycol Res. 2005;109(6):661–686. doi: 10.1017/S095375620500273X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hacquard S, Kracher B, Hiruma K, Münch PC, Garrido-Oter R, Thon MR, Weimann A, Damm U, Dallery J-F, Hainaut M. Survival trade-offs in plant roots during colonization by closely related beneficial and pathogenic fungi. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1):1–13. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schlegel M, Münsterkötter M, Güldener U, Bruggmann R, Duò A, Hainaut M, Henrissat B, Sieber CMK, Hoffmeister D, Grünig CR. Globally distributed root endophyte Phialocephala subalpina links pathogenic and saprophytic lifestyles. BMC Genomics. 2016;17(1):1015. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3369-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Xu X-H, Su Z-Z, Wang C, Kubicek CP, Feng X-X, Mao L-J, Wang J-Y, Chen C, Lin F-C, Zhang C-L. The rice endophyte Harpophora oryzae genome reveals evolution from a pathogen to a mutualistic endophyte. Sci Rep. 2014;4:5783. doi: 10.1038/srep05783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yang Y, Liu X, Cai J, Chen Y, Li B, Guo Z, Huang G. Genomic characteristics and comparative genomics analysis of the endophytic fungus Sarocladium brachiariae. BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):1–20. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6095-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gazis R, Kuo A, Riley R, LaButti K, Lipzen A, Lin J, Amirebrahimi M, Hesse CN, Spatafora JW, Henrissat B. The genome of Xylona heveae provides a window into fungal endophytism. Fungal Biol. 2016;120(1):26–42. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2015.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Paolinelli-Alfonso M, Villalobos-Escobedo JM, Rolshausen P, Herrera-Estrella A, Galindo-Sánchez C, López-Hernández JF, Hernandez-Martinez R. Global transcriptional analysis suggests Lasiodiplodia theobromae pathogenicity factors involved in modulation of grapevine defensive response. BMC Genomics. 2016;17(1):615. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2952-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gonçalves MFM, Nunes RB, Tilleman L, Van de Peer Y, Deforce D, Van Nieuwerburgh F, Esteves AC, Alves A. Dual RNA sequencing of Vitis vinifera during Lasiodiplodia theobromae infection unveils host–pathogen interactions. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6083. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ali SS, Asman A, Shao J, Balidion JF, Strem MD, Puig AS, Meinhardt LW, Bailey BA. Genome and transcriptome analysis of the latent pathogen Lasiodiplodia theobromae, an emerging threat to the cacao industry. Genome. 2020;63(1):37–52. doi: 10.1139/gen-2019-0112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yan JY, Zhao WS, Chen Z, Xing QK, Zhang W, Chethana KW, Xue MF, Xu JP, Phillips AJL, Wang Y. Comparative genome and transcriptome analyses reveal adaptations to opportunistic infections in woody plant degrading pathogens of Botryosphaeriaceae. DNA Res. 2017;25(1):87–102. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsx040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bellée A, Comont G, Nivault A, Abou-Mansour E, Coppin C, Dufour MC, Corio-Costet MF. Life traits of four Botryosphaeriaceae species and molecular responses of different grapevine cultivars or hybrids. Plant Pathol. 2017;66(5):763–776. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang B, Liang X, Gleason ML, Zhang R, Sun G. Comparative genomics of Botryosphaeria dothidea and B. kuwatsukai, causal agents of apple ring rot, reveals both species expansion of pathogenicity-related genes and variations in virulence gene content during speciation. IMA fungus. 2018;9(2):243–257. doi: 10.5598/imafungus.2018.09.02.02. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bihon W, Wingfield MJ, Slippers B, Duong TA, Wingfield BD. MAT gene idiomorphs suggest a heterothallic sexual cycle in a predominantly asexual and important pine pathogen. Fungal Genet Biol. 2014;62:55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2013.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wingfield BD, Ades PK, Al-Naemi FA, Beirn LA, Bihon W, Crouch JA, De Beer WZ, De Vos L, Doung TA, Fields CJ, et al. Draft genome sequences of Chrysoporthe austroafricana, Diplodia scrobiculata, Fusarium nygamai, Leptographium lundbergii, Limonomyces culmigenus, Stagonosporopsis tanaceti, and Thielaviopsis punctulata. IMA Fungus. 2015;6(1):233–248. doi: 10.5598/imafungus.2015.06.01.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mosier AC, Miller CS, Frischkorn KR, Ohm RA, Li Z, LaButti K, Lapidus A, Lipzen A, Chen C, Johnson J. Fungi contribute critical but spatially varying roles in nitrogen and carbon cycling in acid mine drainage. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:238. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.de Jonge R, Ebert MK, Huitt-Roehl CR, Pal P, Suttle JC, Spanner RE, Neubauer JD, Jurick WM, Stott KA, Secor GA. Gene cluster conservation provides insight into cercosporin biosynthesis and extends production to the genus Colletotrichum. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2018;115(24):E5459–E5466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1712798115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wingfield BD, Berger DK, Steenkamp ET, Lim H-J, Duong TA, Bluhm BH, De Beer ZW, De Vos L, Fourie G, Naidoo K. Draft genome of Cercospora zeina, Fusarium pininemorale, Hawksworthiomyces lignivorus, Huntiella decipiens and Ophiostoma ips. IMA Fungus. 2017;8(2):385–396. doi: 10.5598/imafungus.2017.08.02.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chang T-C, Salvucci A, Crous PW, Stergiopoulos I. Comparative genomics of the Sigatoka disease complex on banana suggests a link between parallel evolutionary changes in Pseudocercospora fijiensis and Pseudocercospora eumusae and increased virulence on the banana host. PLoS Genet. 2016;12(8):e1005904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.McGrann GRD, Andongabo A, Sjökvist E, Trivedi U, Dussart F, Kaczmarek M, Mackenzie A, Fountaine JM, Taylor JMG, Paterson LJ. The genome of the emerging barley pathogen Ramularia collo-cygni. BMC Genomics. 2016;17(1):584. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2928-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Goodwin SB, M’barek SB, Dhillon B, Wittenberg AH, Crane CF, Hane JK, Foster AJ, Van der Lee TA, Grimwood J, Aerts A. Finished genome of the fungal wheat pathogen Mycosphaerella graminicola reveals dispensome structure, chromosome plasticity, and stealth pathogenesis. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(6):e1002070. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gostinčar C, Ohm RA, Kogej T, Sonjak S, Turk M, Zajc J, Zalar P, Grube M, Sun H, Han J. Genome sequencing of four Aureobasidium pullulans varieties: biotechnological potential, stress tolerance, and description of new species. BMC Genomics. 2014;15(1):549. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Peter M, Kohler A, Ohm RA, Kuo A, Krützmann J, Morin E, Arend M, Barry KW, Binder M, Choi C. Ectomycorrhizal ecology is imprinted in the genome of the dominant symbiotic fungus Cenococcum geophilum. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1):12662. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Zeiner CA, Purvine SO, Zink EM, Paša-Tolić L, Chaput DL, Haridas S, Wu S, LaButti K, Grigoriev IV, Henrissat B. Comparative analysis of secretome profiles of manganese (II)-oxidizing ascomycete fungi. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0157844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Verma S, Gazara RK, Nizam S, Parween S, Chattopadhyay D, Verma PK. Draft genome sequencing and secretome analysis of fungal phytopathogen Ascochyta rabiei provides insight into the necrotrophic effector repertoire. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):24638. doi: 10.1038/srep24638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Condon BJ, Leng Y, Wu D, Bushley KE, Ohm RA, Otillar R, Martin J, Schackwitz W, Grimwood J, MohdZainudin N. Comparative genome structure, secondary metabolite, and effector coding capacity across Cochliobolus pathogens. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Mondo SJ, Dannebaum RO, Kuo RC, Louie KB, Bewick AJ, LaButti K, Haridas S, Kuo A, Salamov A, Ahrendt SR. Widespread adenine N6-methylation of active genes in fungi. Nat Genet. 2017;49(6):964–968. doi: 10.1038/ng.3859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lopez D, Ribeiro S, Label P, Fumanal B, Venisse J-S, Kohler A, De Oliveira RR, Labutti K, Lipzen A, Lail K. Genome-wide analysis of Corynespora cassiicola leaf fall disease putative effectors. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:276. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Fokin M, Fleetwood D, Weir BS, Villas-Boas S. Genome sequence of the saprophytic ascomycete Epicoccum nigrum strain ICMP 19927, isolated from New Zealand. Genome Announc. 2017;5(24):e00557–e00517. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00557-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hane JK, Lowe RGT, Solomon PS, Tan K-C, Schoch CL, Spatafora JW, Crous PW, Kodira C, Birren BW, Galagan JE. Dothideomycete–plant interactions illuminated by genome sequencing and EST analysis of the wheat pathogen Stagonospora nodorum. Plant Cell. 2007;19(11):3347–3368. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.052829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Knapp DG, Németh JB, Barry K, Hainaut M, Henrissat B, Johnson J, Kuo A, Lim JHP, Lipzen A, Nolan M. Comparative genomics provides insights into the lifestyle and reveals functional heterogeneity of dark septate endophytic fungi. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):6321. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24686-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Manning VA, Pandelova I, Dhillon B, Wilhelm LJ, Goodwin SB, Berlin AM, Figueroa M, Freitag M, Hane JK, Henrissat B. Comparative genomics of a plant-pathogenic fungus, Pyrenophora tritici-repentis, reveals transduplication and the impact of repeat elements on pathogenicity and population divergence. G3. 2013;3(1):41–63. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.004044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Franco MEE, López S, Medina R, Saparrat MCN, Balatti P. Draft genome sequence and gene annotation of Stemphylium lycopersici strain CIDEFI-216. Genome Announc. 2015;3(5):e01069–e01015. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01069-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Teixeira MM, Moreno LF, Stielow BJ, Muszewska A, Hainaut M, Gonzaga L, Abouelleil A, JSL P, Priest M, Souza R. Exploring the genomic diversity of black yeasts and relatives (Chaetothyriales, Ascomycota) Stud Mycol. 2017;86:1–28. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2017.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Galagan JE, Calvo SE, Cuomo C, Ma L-J, Wortman JR, Batzoglou S, Lee S-I, Baştürkmen M, Spevak CC, Clutterbuck J. Sequencing of Aspergillus nidulans and comparative analysis with a. fumigatus and A. oryzae. Nature. 2005;438(7071):1105–1115. doi: 10.1038/nature04341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Zhang Y, Crous PW, Schoch CL, Bahkali AH, Guo LD, Hyde KD. A molecular, morphological and ecological re-appraisal of Venturiales—a new order of Dothideomycetes. Fungal Divers. 2011;51(1):249–277. doi: 10.1007/s13225-011-0141-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Schoch CL, Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Boehm EWA, Burgess TI, De Gruyter J, De Hoog GS, Dixon LJ, Grube M, Gueidan C. A class-wide phylogenetic assessment of Dothideomycetes. Stud Mycol. 2009;64:1–15. doi: 10.3114/sim.2009.64.01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Schoch CL, Shoemaker RA, Seifert KA, Hambleton S, Spatafora JW, Crous PW. A multigene phylogeny of the Dothideomycetes using four nuclear loci. Mycologia. 2006;98(6):1041–1052. doi: 10.1080/15572536.2006.11832632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Yang T, Groenewald JZ, Cheewangkoon R, Jami F, Abdollahzadeh J, Lombard L, Crous PW. Families, genera, and species of Botryosphaeriales. Fungal Biol. 2017;121(4):322–346. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2016.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Slippers B, Boissin E, Phillips AJL, Groenewald JZ, Lombard L, Wingfield MJ, Postma A, Burgess T, Crous PW. Phylogenetic lineages in the Botryosphaeriales: a systematic and evolutionary framework. Stud Mycol. 2013;76:31–49. doi: 10.3114/sim0020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Phillips AJL, Hyde KD, Alves A, Liu J-KJ. Families in Botryosphaeriales: a phylogenetic, morphological and evolutionary perspective. Fungal Divers. 2019;94(1):1–22. doi: 10.1007/s13225-018-0416-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Mohanta TK, Bae H. The diversity of fungal genome. Biol Proced Online. 2015;17(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12575-015-0020-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Haridas S, Albert R, Binder M, Bloem J, LaButti K, Salamov A, Andreopoulos B, Baker SE, Barry K, Bills G. 101 Dothideomycetes genomes: a test case for predicting lifestyles and emergence of pathogens. Stud Mycol. 2020;96:141–153. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2020.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lyu X, Shen C, Fu Y, Xie J, Jiang D, Li G, Cheng J. Comparative genomic and transcriptional analyses of the carbohydrate-active enzymes and secretomes of phytopathogenic fungi reveal their significant roles during infection and development. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):15565. doi: 10.1038/srep15565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wang X, Zhang X, Liu L, Xiang M, Wang W, Sun X, Che Y, Guo L, Liu G, Guo L. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis fici reveals its lifestyle and high potential for synthesis of natural products. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12864-014-1190-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Queiroz CB, Santana MF. Prediction of the secretomes of endophytic and nonendophytic fungi reveals similarities in host plant infection and colonization strategies. Mycologia. 2020:1–13. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 85.Zhao Z, Liu H, Wang C, Xu J-R. Comparative analysis of fungal genomes reveals different plant cell wall degrading capacity in fungi. BMC Genomics. 2013;14(1):274. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Levasseur A, Drula E, Lombard V, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B. Expansion of the enzymatic repertoire of the CAZy database to integrate auxiliary redox enzymes. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013;6(1):41. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-6-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Christiansen C, Abou Hachem M, Janeček Š, Viksø-Nielsen A, Blennow A, Svensson B. The carbohydrate-binding module family 20–diversity, structure, and function. FEBS J. 2009;276(18):5006–5029. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Boraston AB, Bolam DN, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ. Carbohydrate-binding modules: fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition. Biochem J. 2004;382(3):769–781. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Marshall R, Kombrink A, Motteram J, Loza-Reyes E, Lucas J, Hammond-Kosack K, et al. Analysis of two in planta expressed LysM effector homologues from the fungus Mycosphaerella graminicola reveals novel functional properties and varying contributions to virulence on wheat. Plant Physiol. 2011:111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 90.Biely P, Puls J, Schneider H. Acetyl xylan esterases in fungal cellulolytic systems. FEBS Lett. 1985;186(1):80–84. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Takeda K, Matsumura H, Ishida T, Samejima M, Ohno H, Yoshida M, Igarashi K, Nakamura N. Characterization of a novel PQQ-dependent quinohemoprotein pyranose dehydrogenase from Coprinopsis cinerea classified into auxiliary activities family 12 in carbohydrate-active enzymes. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0115722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Bamford NC, Le Mauff F, Subramanian AS, Yip P, Millán C, Zhang Y, Zacharias C, Forman A, Nitz M, Codée JDC. Ega3 from the fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus is an endo-α-1, 4-galactosaminidase that disrupts microbial biofilms. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(37):13833–13849. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Miyanaga A, Koseki T, Miwa Y, Mese Y, Nakamura S, Kuno A, Hirabayashi J, Matsuzawa H, Wakagi T, Shoun H. The family 42 carbohydrate-binding module of family 54 α-L-arabinofuranosidase specifically binds the arabinofuranose side chain of hemicellulose. Biochem J. 2006;399(3):503–511. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Couturier M, Tangthirasunun N, Ning X, Brun S, Gautier V, Bennati-Granier C, Silar P, Berrin J-G. Plant biomass degrading ability of the coprophilic ascomycete fungus Podospora anserina. Biotechnol Adv. 2016;34(5):976–983. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Goulet KM, Saville BJ. Carbon acquisition and metabolism changes during fungal biotrophic plant pathogenesis: insights from Ustilago maydis. Can J Plant Pathol. 2017;39(3):247–266. doi: 10.1080/07060661.2017.1354330. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Couger MB, Youssef NH, Struchtemeyer CG, Liggenstoffer AS, Elshahed MS. Transcriptomic analysis of lignocellulosic biomass degradation by the anaerobic fungal isolate Orpinomyces sp. strain C1A. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2015;8(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s13068-015-0390-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Olivieri F, Zanetti ME, Oliva CR, Covarrubias AA, Casalongué CA. Characterization of an extracellular serine protease of Fusarium eumartii and its action on pathogenesis related proteins. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2002;108(1):63–72. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Plummer KM, Clark SJ, Ellis LM, Loganathan A, Al-Samarrai TH, Rikkerink EHA, Sullivan PA, Templeton MD, Farley PC. Analysis of a secreted aspartic peptidase disruption mutant of Glomerella cingulata. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2004;110(3):265–274. doi: 10.1023/B:EJPP.0000019796.78598.8c. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Thon MR, Nuckles EM, Takach JE, Vaillancourt LJ. CPR1: a gene encoding a putative signal peptidase that functions in pathogenicity of Colletotrichum graminicola to maize. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2002;15(2):120–128. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.2.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Baroncelli R, Amby DB, Zapparata A, Sarrocco S, Vannacci G, Le Floch G, Harrison RJ, Holub E, Sukno SA, Sreenivasaprasad S. Gene family expansions and contractions are associated with host range in plant pathogens of the genus Colletotrichum. BMC Genomics. 2016;17(1):555. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2917-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Jashni MK, Mehrabi R, Collemare J, Mesarich CH, De Wit PJGM. The battle in the apoplast: further insights into the roles of proteases and their inhibitors in plant–pathogen interactions. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:584. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.van Esse HP, van't Klooster JW, Bolton MD, Yadeta KA, Van Baarlen P, Boeren S, Vervoort J, de Wit PJGM, Thomma BPHJ. The Cladosporium fulvum virulence protein Avr2 inhibits host proteases required for basal defense. Plant Cell. 2008;20(7):1948–1963. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.059394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Rooney HCE, van't Klooster JW, van der Hoorn RAL, Joosten MHAJ, Jones JDG, de Wit PJGM. Cladosporium Avr2 inhibits tomato Rcr3 protease required for Cf-2-dependent disease resistance. Science. 2005;308(5729):1783–1786. doi: 10.1126/science.1111404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Mueller AN, Ziemann S, Treitschke S, Aßmann D, Doehlemann G. Compatibility in the Ustilago maydis–maize interaction requires inhibition of host cysteine proteases by the fungal effector Pit2. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(2):e1003177. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Dunaevsky YE, Popova VV, Semenova TA, Beliakova GA, Belozersky MA. Fungal inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes: classification, properties, possible biological roles, and perspectives for practical use. Biochimie. 2014;101:10–20. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Kolattukudy PE. Enzymatic penetration of the plant cuticle by fungal pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 1985;23(1):223–250. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Feng J, Wang F, Liu G, Greenshields D, Shen W, Kaminskyj S, Hughes GR, Peng Y, Selvaraj G, Zou J. Analysis of a Blumeria graminis-secreted lipase reveals the importance of host epicuticular wax components for fungal adhesion and development. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009;22(12):1601–1610. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-22-12-1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Gácser A, Stehr F, Kröger C, Kredics L, Schäfer W, Nosanchuk JD. Lipase 8 affects the pathogenesis of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 2007;75(10):4710–4718. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00372-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Reveglia P, Savocchia S, Billones-Baaijens R, Masi M, Cimmino A, Evidente A. Phytotoxic metabolites by nine species of Botryosphaeriaceae involved in grapevine dieback in Australia and identification of those produced by Diplodia mutila, Diplodia seriata, Neofusicoccum australe and Neofusicoccum luteum. Nat Prod Res. 2019;33(15):2223–2229. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1497631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Reveglia P, Savocchia S, Billones-Baaijens R, Masi M, Evidente A. Spencertoxin and spencer acid, new phytotoxic derivatives of diacrylic acid and dipyridinbutan-1, 4-diol produced by Spencermartinsia viticola, a causal agent of grapevine Botryosphaeria dieback in Australia. Arab J Chem. 2020;13(1):1803–1808. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.01.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Masi M, Reveglia P, Baaijens-Billones R, Górecki M, Pescitelli G, Savocchia S, Evidente A. Phytotoxic metabolites from three Neofusicoccum species causal agents of Botryosphaeria dieback in Australia, luteopyroxin, neoanthraquinone, and luteoxepinone, a disubstituted furo-α-pyrone, a hexasubstituted anthraquinone, and a trisubstituted oxepi-2-one from Neofusicoccum luteum. J Nat Prod. 2020;83(2):453–460. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Evidente A, Punzo B, Andolfi A, Cimmino A, Melck D, Luque J. Lipophilic phytotoxins produced by Neofusicoccum parvum, a grapevine canker agent. Phytopathol Mediterr. 2010;49(1):74–79. [Google Scholar]
- 113.Burruano S, Giambra S, Mondello V, Dellagreca M, Basso S, Tuzi A, et al. Naphthalenone polyketides produced by Neofusicoccum parvum, a fungus associated with grapevine Botryosphaeria dieback. Phytopathol Mediterr. 2016:197–206.
- 114.Andolfi A, Basso S, Giambra S, Conigliaro G, Lo Piccolo S, Alves A, Burruano S. Lasiolactols a and B produced by the grapevine fungal pathogen Lasiodiplodia mediterranea. Chem Biodivers. 2016;13(4):395–402. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201500104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Muria-Gonzalez MJ, Chooi YH, Breen S, Solomon PS. The past, present and future of secondary metabolite research in the Dothideomycetes. Mol Plant Pathol. 2015;16(1):92–107. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Reveglia P, Masi M, Evidente A. Melleins—intriguing natural compounds. Biomolecules. 2020;10(5):772. doi: 10.3390/biom10050772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Tsuge T, Harimoto Y, Akimitsu K, Ohtani K, Kodama M, Akagi Y, Egusa M, Yamamoto M, Otani H. Host-selective toxins produced by the plant pathogenic fungus Alternaria alternata. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2013;37(1):44–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Ito K, Tanaka T, Hatta R, Yamamoto M, Akimitsu K, Tsuge T. Dissection of the host range of the fungal plant pathogen Alternaria alternata by modification of secondary metabolism. Mol Microbiol. 2004;52(2):399–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Stergiopoulos I, Collemare J, Mehrabi R, De Wit PJGM. Phytotoxic secondary metabolites and peptides produced by plant pathogenic Dothideomycete fungi. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2013;37(1):67–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Zaccaron AZ, Bluhm BH. The genome sequence of Bipolaris cookei reveals mechanisms of pathogenesis underlying target leaf spot of sorghum. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):17217. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17476-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Wingfield BD, Bills GF, Dong Y, Huang W, Nel WJ, Swalarsk-Parry BS, Vaghefi N, Wilken PM, An Z, de Beer ZW. Draft genome sequence of Annulohypoxylon stygium, Aspergillus mulundensis, Berkeleyomyces basicola (syn. Thielaviopsis basicola), Ceratocystis smalleyi, two Cercospora beticola strains, Coleophoma cylindrospora, Fusarium fracticaudum, Phialophora cf. hyalina, and Morchella septimelata. IMA Fungus. 2018;9(1):199. doi: 10.5598/imafungus.2018.09.01.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Wolpert TJ, Dunkle LD, Ciuffetti LM. Host-selective toxins and avirulence determinants: what's in a name? Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2002;40(1):251–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.40.011402.114210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Grandaubert J, Lowe RG, Soyer JL, Schoch CL, Van de Wouw AP, Fudal I, Robbertse B, Lapalu N, Links MG, Ollivier B. Transposable element-assisted evolution and adaptation to host plant within the Leptosphaeria maculans-Leptosphaeria biglobosa species complex of fungal pathogens. BMC Genomics. 2014;15(1):891. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Testa AC, Oliver RP, Hane JK. OcculterCut: a comprehensive survey of AT-rich regions in fungal genomes. Genome biology and evolution. 2016;8(6):2044–2064. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Andrews S. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 126.Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(15):2114–2120. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008;18(5):821–829. doi: 10.1101/gr.074492.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Gladman S, Seemann T. VelvetOptimiser. Victorian Bioinformatics Consortium, Clayton, Australia. 2012.https://github.com/tseemann/VelvetOptimiser.
- 129.Bushnell B, Rood J, Singer E. BBMerge–accurate paired shotgun read merging via overlap. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0185056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Smit A, Hubley R. RepeatModeler-1.0.10. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 131.Hoff KJ, Lange S, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M, Stanke M. BRAKER1: unsupervised RNA-Seq-based genome annotation with GeneMark-ET and AUGUSTUS. Bioinformatics. 2015;32(5):767–769. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Lomsadze A, Burns PD, Borodovsky M. Integration of mapped RNA-Seq reads into automatic training of eukaryotic gene finding algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(15):e119. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Stanke M, Schöffmann O, Morgenstern B, Waack S. Gene prediction in eukaryotes with a generalized hidden Markov model that uses hints from external sources. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006;7(1):62. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Holt C, Yandell M. MAKER2: an annotation pipeline and genome-database management tool for second-generation genome projects. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12(1):491. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Waterhouse RM, Seppey M, Simão FA, Manni M, Ioannidis P, Klioutchnikov G, et al. BUSCO applications from quality assessments to gene prediction and phylogenomics. Mol Biol Evol. 2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 136.Katoh K, Standley DM. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(4):772–780. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(9):1312–1313. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Lombard V, Golaconda Ramulu H, Drula E, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;42(D1):D490–D495. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Zhang H, Yohe T, Huang L, Entwistle S, Wu P, Yang Z, Busk PK, Xu Y, Yin Y. dbCAN2: a meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(W1):W95–W101. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10(1):421. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ, Thomas PD, Huang X, Bateman A, Finn RD. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;46(D1):D624–D632. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Fischer M, Pleiss J. The lipase engineering database: a navigation and analysis tool for protein families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(1):319–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Eddy SR. Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011;7(10):e1002195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Blin K, Shaw S, Steinke K, Villebro R, Ziemert N, Lee SY, Medema MH, Weber T. antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W81–W87. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Käll L, Krogh A, Sonnhammer ELL. Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction—the Phobius web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(suppl_2):W429–W432. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H. SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods. 2011;8(10):785–786. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Krogh A, Larsson B, Von Heijne G, Sonnhammer ELL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: application to complete genomes1. J Mol Biol. 2001;305(3):567–580. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Pearson K. Notes on Regression and Inheritance in the Case of Two Parents Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 58, 240–242. 1895. [Google Scholar]
- 149.Shapiro SS, Francia RS. An approximate analysis of variance test for normality. J Am Stat Assoc. 1972;67(337):215–216. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1972.10481232. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Hervé M, Hervé MM. Package ‘RVAideMemoire’. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 151.Wilcoxon F. Individual comparisons by ranking methods. In: Breakthroughs in statistics: Springer; 1992. p. 196–202.
- 152.Team RC: R: a language and environment for statistical computing. 2013.
- 153.Conover WJ. Practical nonparametric statistics, vol. 350: Wiley; 1998.
- 154.Han MV, Thomas GWC, Lugo-Martinez J, Hahn MW. Estimating gene gain and loss rates in the presence of error in genome assembly and annotation using CAFE 3. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(8):1987–97. 10.1093/molbev/mst100. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 155.Sanderson MJ. r8s: inferring absolute rates of molecular evolution and divergence times in the absence of a molecular clock. Bioinformatics. 2003;19(2):301–302. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/19.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Hyde KD, Maharachchikumbura SSN, Hongsanan S, Samarakoon MC, Lücking R, Pem D, Harishchandra D, Jeewon R, Zhao R-L, Xu J-C. The ranking of fungi: a tribute to David L. Hawksworth on his 70th birthday. Fungal Divers. 2017;84(1):1–23. [Google Scholar]
- 157.Warnes GR, Bolker B, Bonebakker L, Gentleman R, WHA L, Lumley T, Maechler M, Magnusson A, Moeller S, Schwartz M. gplots: various R programming tools for plotting data. R package version 3.0. 1. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 158.Lê S, Josse J, Husson F. FactoMineR: an R package for multivariate analysis. J Stat Softw. 2008;25(1):1–18. [Google Scholar]
- 159.Vaissie P, Monge A, Husson F. Factoshiny: perform factorial analysis from FactoMineR with a shiny application. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 160.Saunders DGO, Win J, Kamoun S, Raffaele S. Two-dimensional data binning for the analysis of genome architecture in filamentous plant pathogens and other eukaryotes. In: Plant-Pathogen Interactions: Springer; 2014. p. 29–51. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 161.Smit AFA, Hubley R, Green P. RepeatMasker Open-4.0.5. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 162.Van Wyk S, Harrison CH, Wingfield BD, De Vos L, van Der Merwe NA, Steenkamp ET. The RIPper, a web-based tool for genome-wide quantification of repeat-induced point (RIP) mutations. PeerJ. 2019;7:e7447. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files). Genomic data used in this study (Table 1) are available from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome) and the JGI Genome Portal (http://genome.jgi.doe.gov). Raw sequencing reads of the de novo genomes described in this study linked to Bioproject PRJNA497969 (Biosample Accessions SAMN10319569 - SAMN10319580) have been deposited to the Sequence Read Archive (SRA, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) database and are awaiting accession numbers.