Abstract
Context
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a highly prevalent endocrine disorder characterized by hyperandrogenism, is the leading cause of anovulatory infertility.
Objective
This proof-of-concept study evaluated clinical efficacy and safety of the neurokinin 3 (NK3) receptor antagonist fezolinetant in PCOS.
Methods
This was a phase 2a, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study (EudraCT 2014-004409-34). The study was conducted at 5 European clinical centers. Women with PCOS participated in the study. Interventions included fezolinetant 60 or 180 mg/day or placebo for 12 weeks. The primary efficacy end point was change in total testosterone. Gonadotropins, ovarian hormones, safety and tolerability were also assessed.
Results
Seventy-three women were randomly assigned, and 64 participants completed the study. Adjusted mean (SE) changes in total testosterone from baseline to week 12 for fezolinetant 180 and 60 mg/day were −0.80 (0.13) and −0.39 (0.12) nmol/L vs −0.05 (0.10) nmol/L with placebo (P < .001 and P < .05, respectively). Adjusted mean (SE) changes from baseline in luteinizing hormone (LH) for fezolinetant 180 and 60 mg/d were −10.17 (1.28) and −8.21 (1.18) vs −3.16 (1.04) IU/L with placebo (P < .001 and P = .002); corresponding changes in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) were −1.46 (0.32) and −0.92 (0.30) vs −0.57 (0.26) IU/L (P = .03 and P = .38), underpinning a dose-dependent decrease in the LH-to-FSH ratio vs placebo (P < .001). Circulating levels of progesterone and estradiol did not change significantly vs placebo (P > .10). Fezolinetant was well tolerated.
Conclusion
Fezolinetant had a sustained effect to suppress hyperandrogenism and reduce the LH-to-FSH ratio in women with PCOS.
Keywords: polycystic ovary syndrome, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, neurokinin 3 receptor, neurokinin B, kisspeptin, dynorphin A neurons
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the leading cause of anovulatory infertility and the most common endocrine disorder in reproductive-aged women (1), with an estimated global prevalence of approximately 10% (2) and related annual medical costs exceeding $4 billion in the United States (3, 4). PCOS diagnostic criteria include clinical or biochemical hyperandrogenism, chronic oligoovulation or anovulation, and polycystic ovaries (5, 6). Diagnosis depends on identifying 2 of these 3 phenotypic features in the absence of other etiologies (Rotterdam criteria [6]). Metabolic features of PCOS, such as insulin resistance and dyslipidemia (7), also play a role in disease, although amelioration of these features is not the primary aim of treatments directed at hyperandrogenism and fertility. Subpopulations of patients with PCOS can be defined according to specific combinations of phenotypic, hormonal, and/or genomic features (7-9). Patients with PCOS present with complex symptomology, and the etiology of the disease remains unclear.
Altered signaling in the neuroendocrine circuits that regulate fertility is considered to be a preponderant feature of PCOS (10). The hypothalamic network of kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin A (KNDy) neurons has been identified as the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) pulse generator that governs the pattern of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion over the phases of the ovarian cycle (11-13). Patients with PCOS often express high-frequency pulses of LH, increased serum LH, and a high LH-to-FSH ratio (14-16). At the level of the ovary, high LH increases androgen synthesis, whereas (relatively) low FSH may contribute to follicular arrest, anovulation, and accumulation of cysts (10). Moreover, the androgen excess contributes to the impaired negative feedback of ovarian hormones on the LH pulse frequency and thereby fuels an arrhythmic reproductive cycle (17-20).
The current standard of care for PCOS is treatment with hormone contraceptives for managing menstrual irregularities and certain symptoms of hyperandrogenism (ie, hirsutism, acne, and alopecia) (5, 21, 22). The estrogen component of hormone contraceptives increases sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) and reduces LH and FSH, resulting in a decrease in androgen production and circulating free testosterone (21). Cyclic administration of progesterone (P4) is proposed to restore menstrual cycling and provide some additional benefit in the amelioration of PCOS symptoms (23). Metformin improves insulin sensitivity and is used in conjunction with dietary advice as additional therapy in women with PCOS who present with abnormal glucose tolerance or type 2 diabetes (5, 22). Spironolactone, a potassium-sparing diuretic with antiandrogen properties, is sometimes used in combination with hormone contraceptives to help alleviate the manifestations of hyperandrogenism (22, 24). In summary, all current treatments are aimed at ameliorating symptoms and correcting the biochemical imbalance of PCOS but do not address the central hormonal dysregulation.
Neurokinin 3 (NK3) receptor signaling has been shown to play a key role in positive and negative feedback loops regulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis (25, 26). In premenopausal women, NK3 receptor antagonism at the level of the KNDy neuron is understood to decrease the GnRH pulse frequency based on the downstream observations of reduced basal LH secretion, lower LH-to-FSH ratio, suppressed follicle development, and the modulation of the temporal dynamics of ovarian sex hormone production over the menstrual cycle (25-27). The pharmacology of NK3 receptor antagonists in the regulation of the HPG axis inspired us to investigate whether such compounds could correct the elevated GnRH pulse frequency attributed to the neuroendocrine impairments associated with PCOS and thereby improve clinical outcomes. In the interim, the NK3 receptor antagonist MLE4901 (formerly AZD4901) was investigated in exploratory phase 2 studies and was shown to reduce LH pulse frequency, as well as serum LH and testosterone levels, relative to placebo in women with PCOS who were treated for 28 days or less (28, 29); clinical development of MLE4901 has since been discontinued (30).
Fezolinetant (ESN364) is a novel oral small molecule that potently and selectively blocks the NK3 receptor (31). Preclinical data demonstrated that administration of fezolinetant decreased LH pulse frequency and lowered plasma LH without affecting FSH (32). Fezolinetant treatment for 21 days produced dose-dependent decreases in LH with no significant effect on FSH, leading to decreases in the LH-to-FSH ratio in healthy female volunteers with regular ovulatory menstrual cycles (26). Fezolinetant is now in phase 3 development for treatment of vasomotor symptoms in postmenopausal women, following promising efficacy and safety data for this indication in 2 phase 2 trials (33, 34). The present study was conducted to evaluate the effects of fezolinetant on the biochemical features of PCOS.
Materials and Methods
Study Design and Interventions
This phase 2, proof-of-concept, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study evaluated the efficacy and safety of fezolinetant vs placebo administered for 12 weeks in women with PCOS (EudraCT No.: 2014-004409-34). The study was conducted entirely at academic or clinical (hospital) sites from May 2015 through May 2017, in 5 European countries (Austria, Belgium, Georgia, Germany, and the Netherlands).
The study included a screening period (−28 to −7 days before first dose), during which baseline data were collected. Eligible women then entered a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment period and were randomly assigned 1:1:1 via computer-generated randomization schedule to receive fezolinetant 60 mg, fezolinetant 180 mg, or matching placebo. All study drugs were administered orally once daily after a light breakfast for up to 12 weeks. Patients visited the clinical center every 3 weeks for assessments and attended a follow-up visit 6 weeks after completing treatment. All in-study visits were to be planned within 2 to 8 hours after study drug intake, except for visit 2 (randomization visit; week 1, day 1) and visit 5 (week 9, day 63). These 2 visits were performed with patients in the fasted state in the morning to evaluate baseline parameters and, in the case of visit 5, to measure trough pharmacokinetics (PK) levels and hormonal effects at trough PK levels.
Ethical Considerations
The study protocol was reviewed and approved by an independent ethics committee and/or institutional review board at each study site, and the study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles defined in the Declaration of Helsinki and the International Council for Harmonisation guidance for Good Clinical Practice. All study patients provided written informed consent before any study-related procedure was performed.
Study Population
Patients were women aged 18 to 45 years with a diagnosis of PCOS according to the Rotterdam criteria (6), with the modification of mandatory biochemical hyperandrogenism (total testosterone: > 1.7 nmol/L). At least 1 of the following 2 other Rotterdam criteria were also required for diagnosis of PCOS: oligomenorrhea (≤ 6 menses per year) or oligoovulation and/or polycystic ovaries on ultrasound scan (at least 1 ovary with ≥ 12 antral follicles or ovarian volume ≥ 10 cm3). Additional inclusion criteria were normal thyroid function; normal levels of FSH, estradiol (E2), prolactin, and 17-hydroxyprogesterone; and good physical and mental health based on medical history and examination. Patients were also required to have negative cervical cytology within 36 months of screening, a negative urine test for drugs of abuse, and a negative pregnancy test and were required to use highly effective nonhormonal contraception through 42 days posttreatment if sexually active.
Exclusion criteria included evidence of diabetes based on World Health Organization criteria (35, 36); bariatric or ovarian surgery within 6 months of screening; hysterectomy and/or bilateral oophorectomy; Cushing syndrome; current or prior pelvic inflammatory disease; current or prior malignancy; known drug allergy or intolerance; active liver disease or jaundice, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase levels more than 1.3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), total bilirubin more than 1.3 times the ULN, or creatinine more than 1.25 times the ULN; hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL; positive hepatitis panel or HIV antibody test at screening; psychological disorder within 1 year before screening; symptomatic acute or chronic illness within 3 months of initial study drug administration; and significant blood loss or transfusion within 12 weeks of study drug administration.
Patients were excluded if they had received any of the following within 3 months before screening: antiandrogens, GnRH agonist/antagonists, selective estrogen receptor modulators, selective P4 receptor modulators, dienogest, danazol, aromatase inhibitors, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, or depot contraceptives. Any hormonal contraceptives were required to be stopped 1 month prior to screening, and any insulin sensitizers discontinued at screening. Any patient deemed by the investigator to be inappropriate for the study based on electrocardiographic abnormalities or an acute or chronic medical condition that could either interfere with drug PK or interpretation of the study outcomes was excluded.
End Points and Assessments
The primary efficacy end point was mean change in total testosterone from baseline to week 12 (end of treatment). Secondary efficacy end points included changes in levels of other gonadotropins and ovarian hormones (LH, FSH, LH-to-FSH ratio, P4, and E2) from baseline to weeks 6, 12, and 18 (follow-up); changes in total testosterone from baseline to weeks 6, 9, and 18; changes in menstrual cycle (frequency of menses, spotting, and intermenstrual bleeding); change in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Questionnaire (PCOSQ) score (37, 38); and changes in transvaginal ultrasound parameters (endometrial thickness, ovarian volume, number of follicles [cysts], and surface of the dominant follicle) from baseline to weeks 6 and 12.
Analysis of total testosterone was performed on frozen (−20°C) plasma samples by SGS Life Sciences, Wavre, Belgium, using a validated liquid chromatography with the tandem mass spectrometry method (39). The lower limit of quantitation was 25.0 pg/mL, percentage coefficient of variation ranged from 1.41% to 2.44%, and percentage relative error ranged from −3.77% to 2.08%. Other gonadotropin and ovarian hormone analyses were performed using validated analytical methods on frozen (< −70°C) plasma samples by BARC, Ghent, Belgium (LH, FSH, and P4) and CERBA, Paris, France (E2).
To allow assessment of changes in menstrual cycle, patients recorded start and end dates of any vaginal bleeding, as well as severity (none, spotting, light, normal, or heavy), in an electronic diary. They also completed the PCOSQ in an electronic diary every 3 weeks through week 12 and then at week 18. The PCOSQ is a validated health-related quality-of-life questionnaire comprising 26 questions in 5 domains: emotional, body hair, infertility, weight, and menstrual problems scored on a scale of 1 to 7 (37, 38). Two-dimensional transvaginal ultrasound was performed at screening, baseline, and weeks 6 and 12 using standardized instrument settings for beam focus, overall time-gain, and near-field and far-field gain. Central reading of the ultrasonography for ovarian volume, endometrial thickness, number of follicles, and dominant follicle development was performed by an independent radiologist at Biomedical Systems, Brussels, Belgium.
As an exploratory PK end point, fezolinetant plasma concentrations were assessed using sparse PK sampling. Blood samples for PK analysis were taken before study drug administration at weeks 1 and 9; at the latter time point, this sampling occurred approximately 24 hours after the previous administration of drug and is defined as the “trough” drug level. Additional sampling occurred approximately 2 to 8 hours after study drug administration at weeks 3, 6, and 12, compatible with the window of maximal pharmacodynamic effect after drug administration. Plasma was separated from the blood samples via centrifugation (4-8°C) for 10 minutes at approximately 1500g and shipped frozen (< −20°C) to the bioanalytic laboratory (SGS Life Sciences, Wavre, Belgium), where samples were analyzed using a validated liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method. The assay had a quantification limit of 5.00 ng/mL, a percentage coefficient of variation of 5.51% to 7.65%, and relative errors of −4.60% to 0.75%.
Exploratory pharmacodynamic end points, evaluated by the BARC laboratory using frozen (< −70°C) plasma samples at baseline and weeks 6, 12, and 18, included changes in levels of leptin, androstenedione, aldosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, SHBG, antimüllerian hormone (AMH), adrenocorticotropic hormone, prolactin, and cortisol.
Safety end points included adverse event (AE) frequency and severity, hematology and biochemistry assessments, changes in levels of bone density markers (bone alkaline phosphatase and beta-carboxy-terminal peptide of type I collagen), and change in Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) score from baseline to weeks 12 (end of treatment) and 18 (follow-up) (40, 41). Safety assessments also included physical examination, hematology and biochemistry testing, vital signs, and electrocardiographic findings.
Statistical Analysis
Planned total enrollment was 72 patients, with 24 randomly assigned to each treatment group; no formal power calculations were made. The safety population included all randomly assigned patients who received at least one dose of study medication. The intent-to-treat population included patients from the safety population who had at least one postbaseline efficacy assessment.
Statistical calculations were performed by SGS Life Sciences using SAS version 9.2 or higher (SAS Institute Inc) and/or WinNonlin version 5.2 or higher software (Pharsight Corp). All end points were summarized descriptively. A post hoc analysis was performed for sex steroid hormone parameters using an analysis of covariance model with treatment group as a fixed factor and baseline value as a covariate. A possible relationship between drug-plasma concentrations and clinical response, as measured by changes in LH, FSH, LH-to-FSH ratio, P4, E2, and total testosterone concentrations, was graphically explored. For safety end points, frequencies of AEs were tabulated and analyzed in a descriptive manner, with AEs coded according to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities version 18.0.
Results
Patient Disposition and Baseline Characteristics
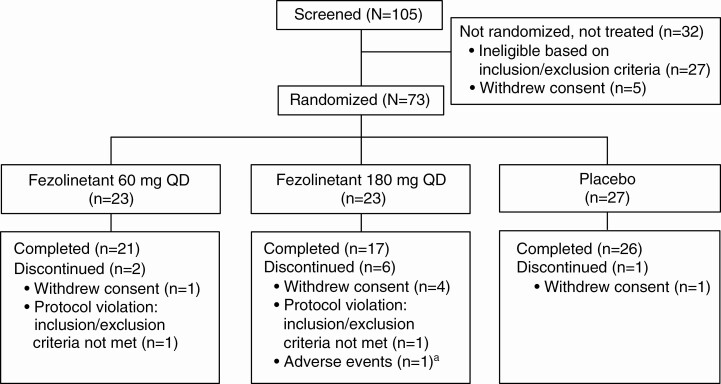
Of 105 patients screened, 73 were randomly assigned and included in the safety and intent-to-treat populations and 64 completed the study (Fig. 1). Treatment groups were well matched for demographics and baseline clinical characteristics (Table 1).
Figure 1.
Patient disposition. aPatient experienced depressed mood, mood swings, headache, and decreased libido considered by the investigator to be possibly related to treatment.
Table 1.
Demographics and baseline clinical characteristics
| Characteristic | Placebo (n = 27) | Fezolinetant 60 mg (n = 23) | Fezolinetant 180 mg (n = 23) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range), y | 27.0 (18-44) | 27.0 (21-41) | 26.0 (19-34) |
| Ht, median (range), cm | 166 (158-177) | 170 (157-178) | 170 (159-186) |
| Wt, median (range), kg | 84.7 (51.7-137.7) | 75.0 (61.0-125.4) | 80.0 (52.3-126.0) |
| BMI, median (range) | 31.2 (17.1-50.0) | 26.7 (19.5-42.0) | 26.6 (20.5-43.6) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 22 (81.5) | 16 (69.6) | 17 (73.9) |
| Black | 1 (3.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (4.3) |
| Asian | 0 (0) | 1 (4.3) | 0 (0) |
| American Indian/Alaskan native | 0 (0) | 1 (4.3) | 0 (0) |
| Not askeda | 4 (14.8) | 5 (21.7) | 5 (21.7) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic/Latino | 0 (0) | 1 (4.3) | 0 (0) |
| Not Hispanic/Latino | 26 (96.3) | 21 (91.3) | 22 (95.7) |
| Not askeda | 1 (3.7) | 1 (4.3) | 1 (4.3) |
Abbreviation: BMI, body mass index.
a Local regulations restricted asking.
Total Testosterone
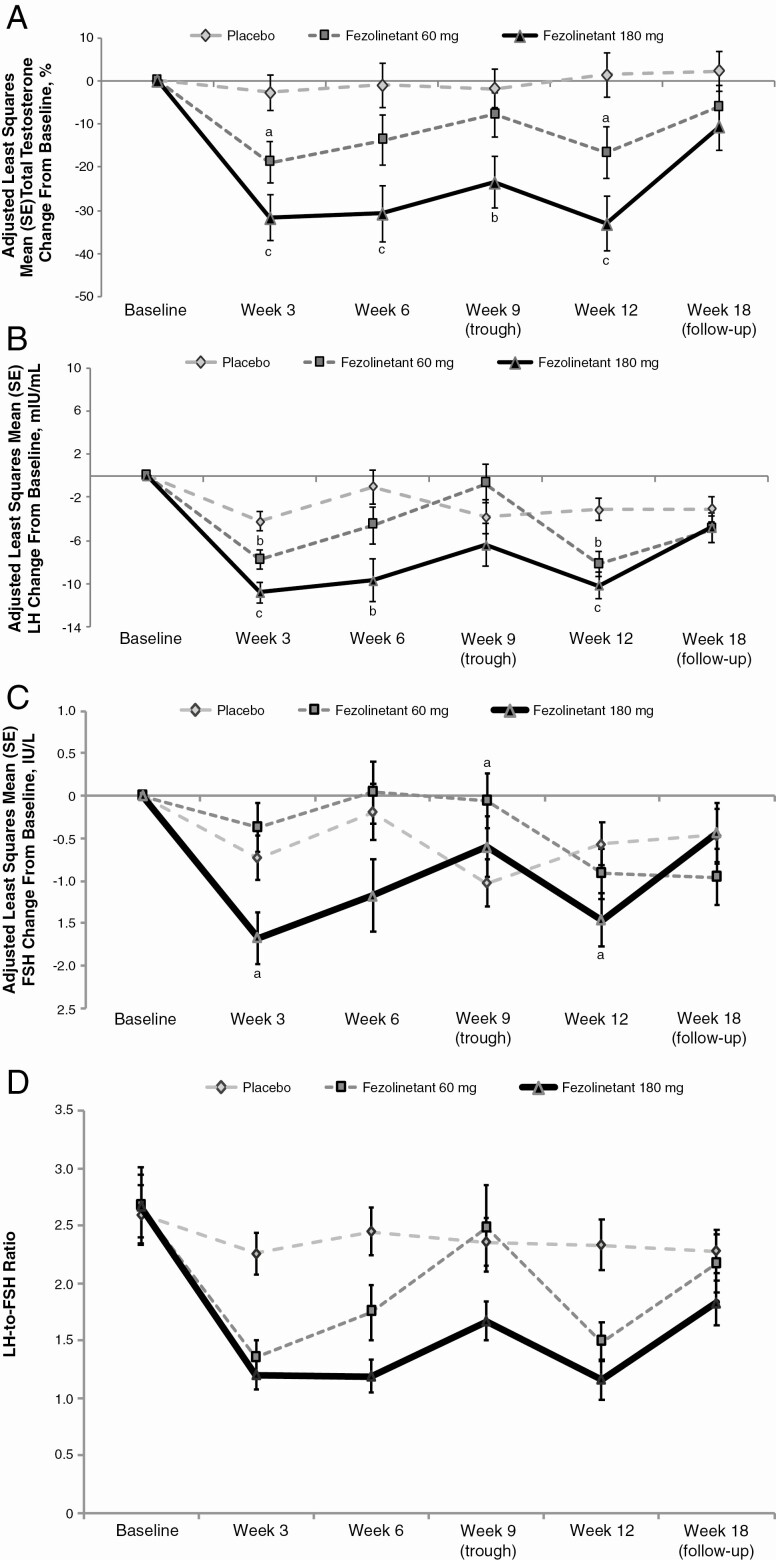
Both doses of fezolinetant significantly reduced total testosterone relative to placebo at week 12 (Table 2), the primary end point. A dose-related effect showed that the 180 mg dose significantly (P < .001) reduced total testosterone relative to placebo at all time points during treatment, whereas the 60 mg dose significantly (P < .05) reduced total testosterone at only weeks 3 and 12. Specifically, change (95% CI) from baseline in total testosterone at weeks 3, 6, and 12 were −19% (−28.7 to −9.0), −14% (−25.6 to −1.8), and −17% (−28.7 to −4.6), respectively, with fezolinetant 60 mg; −32% (−42.1 to −21.3), −31% (−43.9 to −17.7), and −33% (−45.91 to −20.4), respectively, with fezolinetant 180 mg; and −3% (−11.1 to 5.7), −1% (−11.4 to 9.4), and 1% (−8.8 to 11.7), respectively, with placebo (Fig. 2A). The reduction (95% CI) from baseline in total testosterone at trough PK concentrations (week 9) was 8% (−18.0 to 2.3) with 60 mg and 24% (−35.5 to −11.7) with 180 mg; the latter was also significant vs placebo (P = .005), indicating that fezolinetant 180 mg suppresses androgen throughout the day.
Table 2.
Effect of fezolinetant on sex hormones (primary and secondary end points), intent-to-treat population
| Hormone | Treatment | Mean (SD) level at baseline | Mean (SD) level at week 12 | Adjusted Mean (SE) change from baseline to week 12a | P vs placebo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total testosterone, nmol/L | Placebo | 2.01 (0.80) | 1.92 (0.78) | −0.05 (0.10) | — |
| Fezolinetant 60 mg | 1.65 (0.66) | 1.38 (0.59) | −0.39 (0.12) | .04 | |
| Fezolinetant 180 mg | 2.16 (1.01) | 1.39 (0.60) | −0.80 (0.13) | < .001 | |
| LH, IU/L | Placebo | 14.43 (6.51) | 12.51 (6.62) | −3.16 (1.04) | — |
| Fezolinetant 60 mg | 17.64 (16.83) | 7.84 (4.31) | −8.21 (1.18) | .002 | |
| Fezolinetant 180 mg | 14.43 (8.60) | 5.72 (4.47) | −10.17 (1.28) | < .001 | |
| FSH, IU/L | Placebo | 5.95 (1.86) | 5.53 (1.68) | −0.57 (0.26) | — |
| Fezolinetant 60 mg | 6.61 (4.41) | 5.29 (1.40) | −0.92 (0.30) | .38 | |
| Fezolinetant 180 mg | 5.67 (2.35) | 4.65 (1.14) | −1.46 (0.32) | .03 | |
| LH-to-FSH ratio | Placebo | 2.60 (1.32) | 2.33 (1.10) | −0.31 (0.16) | — |
| Fezolinetant 60 mg | 2.67 (1.62) | 1.49 (0.77) | −1.24 (0.18) | < .001 | |
| Fezolinetant 180 mg | 2.67 (1.30) | 1.16 (0.73) | −1.45 (0.19) | < .001 | |
| P4, ng/mL | Placebo | 1.31 (3.19) | 2.12 (5.60) | 0.42 (0.73) | — |
| Fezolinetant 60 mg | 2.56 (4.03) | 1.00 (1.74) | −0.77 (0.83) | .29 | |
| Fezolinetant 180 mg | 0.83 (1.10) | 0.34 (0.20) | −1.28 (0.91) | .15 | |
| E2, pmol/L | Placebo | 239.26 (203.37) | 357.31 (632.70) | 81.98 (82.35) | — |
| Fezolinetant 60 mg | 366.52 (256.01) | 255.50 (216.51) | −32.64 (93.94) | .36 | |
| Fezolinetant 180 mg | 233.48 (137.33) | 140.59 (40.38) | −135.5 (102.75) | .10 |
Abbreviations: ANCOVA, analysis of covariance; E2, estradiol; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; LH, luteinizing hormone; P4, progesterone.
a Least squares mean change from ANCOVA model using treatment group as a fixed factor and baseline value as a covariate.
Figure 2.
A, Adjusted mean (SE) percentage change from baseline in total testosterone levels during treatment with fezolinetant vs placebo. B, Adjusted mean (SE) change from baseline in LH during treatment with fezolinetant vs placebo. C, Adjusted mean (SE) change from baseline in FSH during treatment with fezolinetant vs placebo. D, Effects of fezolinetant on LH-to-FSH ratio. All ITT population. Changes in these hormone levels were analyzed post hoc using an analysis of covariance model with treatment group as a fixed factor and baseline value as a covariate. aP < .05; bP < .01; cP < .001 vs placebo. Between-treatment statistical comparisons were not made on absolute LH-to-FSH ratios. Abbreviations: FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; ITT, intent-to-treat; LH, luteinizing hormone.
Gonadotropins and Female Sex Hormones
Changes in LH and FSH at week 12 are shown in Table 2 and Fig. 2B and 2C, respectively. Both doses of fezolinetant significantly reduced concentrations of LH to a greater extent than FSH, thereby significantly (P < .001) decreasing the LH-to-FSH ratio relative to placebo at week 12. A dose-dependent effect was also seen in reductions in the LH-to-FSH ratio, which were better sustained with fezolinetant 180 mg, especially at trough PK concentrations (week 9) (see Fig. 2D).
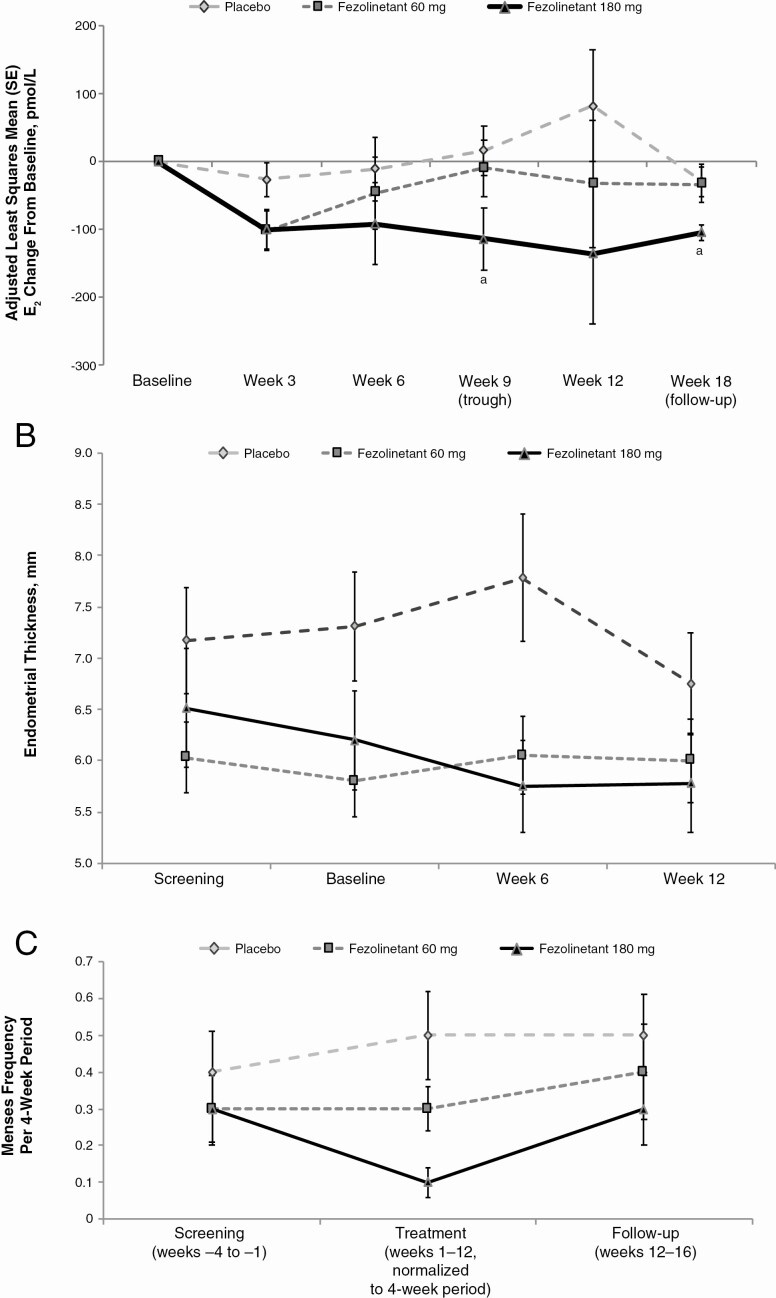
For both doses of fezolinetant, changes in E2 and P4 concentrations at week 12 were not significantly different from placebo (see Table 2). Fezolinetant 180 mg reduced E2 from baseline, but these changes were not significant at weeks 3, 6, or 12 compared with changes seen with placebo (Fig. 3A). As shown in Table 2, P4 sampling on the same schedule indicated a tendency for fezolinetant 180 mg to reduce P4 from baseline to week 12, but this change was not statistically significant. Ten patients (placebo: n = 7; fezolinetant 60 mg: n = 3; fezolinetant 180 mg: n = 0) had P4 concentrations greater than 6.0 ng/mL at any time during active treatment, indicative of ovulation (42); however, the small number of patients and sporadic timing of these elevated P4 readings precludes any clear relationship to treatment.
Figure 3.
Effects of fezolinetant on A, adjusted mean change in E2 based on ANCOVA; B, endometrial thickness over time; and C, menses frequency, ITT population. aP < .05; bP < .01. Change in E2 is based on least squares mean percentage change from the ANCOVA model with treatment group as a fixed factor and baseline value as a covariate. ANCOVA, analysis of covariance; E2, estradiol; ITT, intent-to-treat.
Clinical Outcomes
Fezolinetant was not associated with clinically meaningful changes in PCOSQ scores (Table 3). On transvaginal ultrasound examinations, endometrial thickness for both fezolinetant groups was similar to or lower than for the placebo group throughout the treatment duration (Fig. 3B). Treatment with fezolinetant did not regularize the menstrual cycles (Fig. 3C).
Table 3.
Change from baseline to week 12 in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Questionnaire total scores, intent-to-treat population
| PCOSQ domain | Mean (SE) total score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | Fezolinetant 60 mg | Fezolinetant 180 mg | |
| Emotions | |||
| Baseline | 4.57 (0.25) | 4.57 (0.27) | 4.78 (0.28) |
| Wk 12 change | −0.1 (0.17) | 0 (0.19) | −0.6 (0.29) |
| Body hair | |||
| Baseline | 3.97 (0.36) | 3.76 (0.39) | 4.06 (0.45) |
| Wk 12 change | −0.3 (0.17) | −0.1 (0.17) | −0.3 (0.26) |
| Weight | |||
| Baseline | 3.92 (0.42) | 3.74 (0.45) | 4.10 (0.41) |
| Wk 12 change | −0.3 (0.22) | −0.4 (0.19) | 0 (0.27) |
| Infertility problemsa | |||
| Baseline | 4.70 (0.36) | 4.37 (0.35) | 4.77 (0.39) |
| Wk 12 change | 0.1 (0.24) | 0.1 (0.26) | −0.6 (0.35) |
| Menstrual problems | |||
| Baseline | 4.38 (0.28) | 3.67 (0.30) | 4.14 (0.28) |
| Wk 12 change | 0.3 (0.26) | 0.6 (0.26) | 0.3 (0.30) |
Abbreviation: PCOSQ, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Questionnaire.
a Participants were required to use contraception during the trial if they were sexually active. However, the PCOSQ was administered in full, including the 4 items relating to infertility.
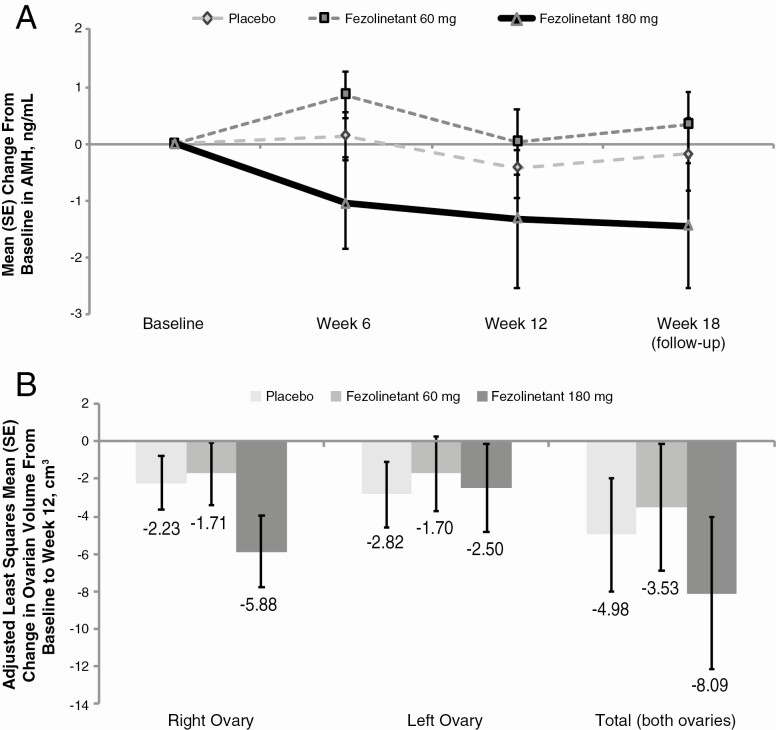
Antimüllerian Hormone, Ovarian Function, and Volume
A decrease in AMH over the duration of the study was observed in the 180 mg group, although this finding was not statistically significant (Fig. 4A). Change from baseline in ovarian volume based on transvaginal ultrasound was not significantly different for fezolinetant vs placebo, although total ovarian volume trended downward at week 12 in the fezolinetant 180 mg group (Fig. 4B). There were no significant changes observed in the number of follicles nor surface size of the dominant follicle (Table 4).
Figure 4.
Effect of fezolinetant on A, AMH and B, adjusted mean change in ovarian volume based on transvaginal ultrasound at week 12, ITT population. AMH, antimüllerian hormone; ITT, intent-to-treat.
Table 4.
Number of ovarian follicles and surface of dominant follicle, assessed by transvaginal ultrasound
| Placebo (n = 27) | Fezolinetant 60 mg (n = 23) | Fezolinetant 180 mg (n = 23) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of follicles, left ovary | |||
| Baseline | 16.9 (11.2) | 14.4 (6.9) | 17.8 (7.8) |
| Wk 6 change | −2.0 (8.7) | 0.1 (7.3) | −0.4 (11.2) |
| Wk 12 change | −0.7 (10.1) | −1.8 (8.2) | 3.7 (13.1) |
| No. of follicles, right ovary | |||
| Baseline | 19.1 (12.8) | 13.9 (7.0) | 18.7 (12.8) |
| Wk 6 change | −2.1 (11.4) | −1.0 (4.2) | −2.1 (8.6) |
| Wk 12 change | −1.2 (9.8) | 0.6 (6.6) | 3.1 (12.4) |
| Surface of dominant follicle, mm 3 | |||
| Baseline | 102.8 (103.6) | 220.0 (354.4) | 140.4 (255.5) |
| Wk 6 change | −54.7 (113.9) | −145.8 (349.9) | −19.8 (151.3) |
| Wk 12 change | −24.0 (153.6) | −99.2 (311.9) | 15.6 (43.7) |
All results are reported as mean (SD).
Other Exploratory End Points
Fezolinetant plasma concentrations are shown in Table 5. Mean plasma concentrations at weeks 3, 6, and 12 ranged from 417 to 469 ng/mL in the 60 mg group and from 1362 to 1434 ng/mL in the 180 mg group. Trough concentrations (measured at week 9) were 58 and 362 ng/mL in the 60 and 180 mg groups, respectively.
Table 5.
Fezolinetant plasma concentrations, safety population
| Fezolinetant 60 mg (n = 23) | Fezolinetant 180 mg (n = 23) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Mean (SE), ng/mL | Median, ng/mL | Range, ng/mL | No. | Mean (SE), ng/mL | Median, ng/mL | Range, ng/mL | |
| Predose samplesa | ||||||||
| Wk 1 (baseline) | 23 | 0 (0) | 0 | — | 22 | 0 (0) | 0 | — |
| Wk 9 (trough) | 20 | 57.51 (28.04) | 19.2 | 0-576.0 | 17 | 362.06 (121.84) | 153.0 | 0-1815.0 |
| Postdose (peak) samplesb | ||||||||
| Wk 3 | 22 | 423.35 (57.53) | 395.5 | 13.5-1023.0 | 18 | 1371.20 (149.55) | 1431.5 | 9.7-2266.0 |
| Wk 6 | 21 | 468.91 (43.94) | 440.0 | 0-847.0 | 17 | 1433.59 (110.24) | 1415.0 | 753.0-2401.0 |
| Wk 12 | 21 | 417.24 (59.07) | 424.0 | 0-927.0 | 17 | 1361.88 (153.53) | 1299.0 | 0-2428.0 |
a Blood samples for fezolinetant concentrations were taken before intake of study drug.
b Blood samples for fezolinetant concentrations were taken 2 to 8 hours after intake of study drug.
Fezolinetant produced no clinically relevant changes in SHBG, leptin, prolactin, or hormones in the pituitary–adrenal axis (adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol, aldosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate) (data not shown). As expected, a small but consistent decrease in androstenedione was observed in the fezolinetant 180 mg group, which correlated with the changes in total testosterone levels.
Safety
Overall, treatment with fezolinetant for 12 weeks was safe and well tolerated. Treatment-emergent AEs (TEAEs) occurring in at least 3 patients are listed in Table 6. TEAEs that occurred in at least 3 patients exposed to fezolinetant were headache, paresthesia, rash, nausea, and nasopharyngitis. The most frequently reported TEAEs considered at least possibly related to treatment by the investigator were headache (placebo: 18.5%, fezolinetant 60 mg: 13.0%, and fezolinetant 180 mg: 39.1%) and paresthesia (0%, 0%, and 17.4%, respectively).
Table 6.
Treatment-emergent adverse events occurring in 3 or more patients and effects on liver function, safety population
| TEAE, n (%) | Placebo (n = 27) | Fezolinetant 60 mg (n = 23) | Fezolinetant 180 mg (n = 23) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Any TEAE | 20 (74.1) | 17 (73.9) | 21 (91.3) |
| Treatment-related TEAEs | 13 (48.1) | 12 (52.2) | 13 (56.5) |
| TEAEs of any severity or causality occurring in ≥ 3 patients in any treatment group | |||
| Headache | 7 (25.9) | 5 (21.7) | 9 (39.1) |
| Paresthesia | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 (21.7) |
| Rash | 1 (3.7) | 0 (0) | 3 (13.0) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 5 (18.5) | 3 (13.0) | 2 (8.7) |
| Fatigue | 3 (11.1) | 2 (8.7) | 0 (0) |
| Nausea | 1 (3.7) | 3 (13.0) | 0 (0) |
| Treatment-emergent AST or ALT ≥ 3 × ULNa | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; ULN, upper limit of normal.
a Based on laboratory testing; all increases were transient and resolved spontaneously during treatment.
Three serious TEAEs were reported in 3 fezolinetant-treated patients. One patient in the fezolinetant 60 mg group experienced superficial thrombophlebitis that was determined to be possibly related to treatment; the drug was temporarily stopped and then restarted without incident. The other 2 serious TEAEs, both in the 180 mg group, were an ankle fracture associated with a horse-riding accident that required temporary study drug discontinuation during surgery (n = 1) and severe sciatica (n = 1), neither of which was deemed related to treatment. All other TEAEs were mild to moderate in severity.
One patient in the fezolinetant 180 mg group discontinued the study drug because of AEs of depressed mood, headache, decreased libido, and mood swings. These AEs were determined by the study sponsor to be potentially related to treatment, and the study drug was permanently discontinued.
No clinically relevant changes in clinical laboratory parameters, vital signs, electrocardiographic values, or bone density markers were observed. The most frequently reported treatment-emergent laboratory abnormalities (observed in ≥ 4 patients in any treatment group) were elevated ALT, calcium, creatinine, urate, and hemoglobin and lower than normal levels of leukocytes and neutrophils. There was an apparent dose-related increase in creatinine seen in 3.7% of patients in the placebo group, 4.3% of the fezolinetant 60 mg group, and 18.2% of the fezolinetant 180 mg group.
Treatment-emergent ALT increases, based on laboratory monitoring, were equally distributed over the treatment groups. All reported increases were less than 3 times the ULN except for 1 patient in the placebo group who had ALT values of 5.5 times the ULN at week 12 and 1 patient in the 180 mg group with an ALT of 3.2 times the ULN at week 3. All increases were transient and resolved spontaneously. In the 180 mg group, 1 patient had an ALT of 8.6 times the ULN at week 3, but her baseline value was 14.3 times the ULN. Thus, the on-treatment ALT elevation was a preexisting condition, and because her liver test values normalized during treatment and in the absence of any concomitant signs or symptoms, this event was not regarded as treatment emergent.
C-SSRS scores were negative in all but one patient who developed moderate treatment-emergent depression possibly related to treatment; the patient recovered from this TEAE by day 61 with a negative C-SSRS score at follow-up.
Discussion
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study supports the concept that NK3 antagonist therapy offers potential benefit in the treatment of PCOS. Fezolinetant produced significant reductions in hyperandrogenemia during 12 weeks of treatment in women with PCOS, reducing total testosterone with daily doses of 60 and 180 mg by 14% to 19% and 31% to 33% at peak drug concentrations, for each dose, respectively. Fezolinetant 180 mg produced a sustained reduction of total testosterone over the 24-hour dose interval (24% at trough drug concentrations [P = .005]) and also consistently lowered the LH-to-FSH ratio to within a normal range so that LH and FSH, as well as estrogen, were maintained at levels comparable to those in healthy women in the early to midfollicular phase (15, 26).
Results are consistent with the hypothesis that antagonism of NK3 receptor signaling affects the GnRH pulse generator (43). Thus, fezolinetant is proposed to modulate KNDy neuron signaling in the infundibular nucleus to reduce GnRH pulse frequency, which is consistent with the observed decrease in plasma LH concentrations (and the LH-to-FSH ratio) as well as lesser LH-induced production of sex hormones by the ovaries (26, 32). The GnRH pulse generator is regulated by negative feedback from the ovarian hormones P4 and E2 (44). Across the range of clinical studies conducted to date, it is interesting to observe a similar sensitivity in response to fezolinetant on the gonadotropins, LH and FSH, under conditions of normal feedback from ovarian hormones (26), negligible feedback from ovarian hormones (eg, menopause [33]), and disordered feedback from ovarian hormones (eg, PCOS [18]), as shown here. These data provide further empirical evidence for the functional hierarchy of hypothalamic NK3 over kisspeptin signaling pathways in mediating feedback mechanisms on the HPG axis (25).
Exogenous administration of a kisspeptin agonist does not change the dynamics of LH secretion in PCOS patients relative to healthy controls (45), indicating that any neuroendocrine basis of PCOS is at a hierarchical level above that of kisspeptin signaling. Thus, altered KNDy neuron signaling and resultant changes in the pattern of endogenous kisspeptin secretion may be relevant to disease. In the present study, fezolinetant significantly decreased FSH in patients with PCOS, as previously observed only during the midcycle gonadotrophin surge in premenopausal healthy female volunteers (26). Thus, perhaps the distinct neuroendocrine dynamics relevant to surge (13) also pertain to the etiology of PCOS. In primates, the surge generator is reliant on estrogen-positive feedback at the level of the pituitary and/or involves distinct neuronal circuits in the mediobasal hypothalamus (44, 46). Although kisspeptin is involved in estrogen-induced surge, the specific role of KNDy neurons in this phenomenon is unclear (47). Notably, it is only under estrogen-positive feedback that NK3 antagonist treatment improved the regularity and orderliness of kisspeptin-stimulated LH pulses in premenopausal women (25). Further research is required to determine whether NK3 antagonists may correct the abnormal temporal coupling between pulses of kisspeptin and LH distinctively evident in oligomenorrheic PCOS patients (29, 48).
The sustained reduction in total testosterone and LH over the entire treated population in the current 12-week study compares well with the preliminary findings from a trial of MLE4901 (formerly AZD4901), another NK3 antagonist, in which similar findings were apparent in all patients at day 7 but only in suspected anovulatory patients at day 28 (28). In this previous study, the authors acknowledge that P4 concentrations in the treatment phase were higher than expected for PCOS patients in general, and the suspected ovulatory patients (ie, those with P4 > 6 ng/mL [42]) were removed from post hoc analyses (28). In contrast, our findings indicate that NK3 antagonist treatment tends to lower the incidence of P4 elevation and subsequent post hoc analyses were not obliged. MLE4901 has since been discontinued, as the risk/benefit profile no longer supported continued development (30). The duration of this initial, exploratory study with MLE4901 was acknowledged to be insufficient to assess clinical outcomes, and such findings were not reported (28).
A secondary objective of the present study was to determine whether targeted modulation of the hypothalamic KNDy-HPG axis combined with a sustained decrease in plasma total testosterone and normalization of the LH-to-FSH ratio would affect clinical outcomes in PCOS. However, there was no improvement in menstrual cycle regularity, follicle counts, or PCOSQ scores. The 12-week duration of treatment in this trial may be inadequate to affect these parameters as positive clinical outcomes in PCOS clinical trials are typically detected after 6 to 9 months of treatment (49, 50). However, the small but consistent dose-related decreases in serum AMH levels, together with the associated decreases in ovarian volume (51-53), may be an early sign of improved clinical outcomes with prolonged treatment. The time course required to lower AMH levels could relate to the necessity to replace the whole follicle cohort against a background of reduced androgen (50).
Diverse approaches ranging from retrospective clinical studies to mathematical modeling converge to conclude that androgenic effects both at the pituitary and the ovaries contribute to the etiology of PCOS (54, 55). High total testosterone correlates with a larger number of small antral follicles (56), leading to increased AMH production (57) and follicular development arrest (58). AMH also inhibits cytochrome P450 aromatase (CYP19, the enzyme that converts androgens to E2) in the granulosa cells to further elevate androgen levels (59).
Furthermore, both total testosterone and AMH modulate hypothalamic-pituitary circuits to elevate the LH-to-FSH ratio. A positive correlation between LH and AMH serum levels is evident in women with PCOS (53), a finding consistent with recent mechanistic studies in rodent models demonstrating that AMH has direct, positive feedback on GnRH neuronal activation to increase LH pulsatility (60, 61). Also, genome-wide association analyses conclude that testosterone has an etiologic role in PCOS (62) in accordance with mechanistic studies demonstrating that elevated androgens affect the plasticity of key neuroendocrine circuits (63, 64). The latter finding is consistent with the pharmacologic demonstration that long-term androgen receptor blockade restores the negative feedback of estrogen and P4 on LH pulse frequency in women with PCOS (19). Thus, the trends toward lower levels of both total testosterone and AMH shown here in response to fezolinetant suggest that longer-term studies would be of interest to confirm whether improved clinical outcomes are achievable.
This study has focused on the neuroendocrine axis as the target site for interpreting NK3 antagonist effects in PCOS. However, the NKB-NK3 receptor signaling pathway is also present in human granulosa and cumulus cells (65), where a significant decrease in NK3 receptor expression (eg, TACR3 messenger RNA) (66-68) may contribute to the decreased aromatase levels in women with PCOS (69). Any direct actions of fezolinetant at the level of the ovary were not evaluated in this trial.
Further clinical development of fezolinetant is focused on potential benefits in treating vasomotor symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats. NK3 receptor antagonism is potentially a novel therapeutic strategy targeting the underlying central mechanisms causing vasomotor symptoms. In 2 phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in postmenopausal women with vasomotor symptoms, fezolinetant significantly reduced vasomotor symptom frequency and severity and was well tolerated (33, 34). The PK profile of fezolinetant in women with PCOS was similar to that reported in healthy female volunteers and postmenopausal women (26, 33). The stable exposure levels over the duration of the study indicate that there is no drug accumulation or modulation of PK processes consequent to repeated dosing.
Fezolinetant was generally well tolerated in women with PCOS. The only serious, potentially treatment-related AE was superficial thrombophlebitis, which occurred in one patient in the fezolinetant 60 mg group. One patient in the 180 mg dose group discontinued treatment because of mood-related effects considered to be potentially treatment related, and one patient had a transiently positive C-SSRS score. No patients discontinued treatment because of elevated liver enzymes, and the incidences of treatment-emergent increases in liver enzymes were similarly distributed over the placebo and fezolinetant-treatment groups.
Women with PCOS may have an increased risk of endometrial cancer (70). Endometrial health was assessed and, as previously demonstrated in premenopausal and menopausal women (26, 34), fezolinetant treatment had no estrogen-like stimulatory or proliferative effects on the endometrium.
Limitations of this proof-of-concept study include the exploratory nature of the statistical analyses, the focus on biochemical biomarkers (eg, total testosterone, LH-to-FSH ratio) over clinical outcomes as influenced by the short duration of the study, the sufficiency of the 1-month stop interval of any oral contraceptives prior to screening, and the small sample size. Although a hyperandrogenemic population was selected, other factors (eg, incidence of oligomenorrhea, metabolic markers, body mass index, SHBG) potentially relevant to PCOS patient clustering were uncontrolled in this study, so heterogeneity in the study population may be a confounding factor in the interpretation of results (8, 9). At the time that this study was launched, there was no precedence for this type of therapy in a PCOS trial, and therefore no formal power calculation was performed to define the sample size. However, an estimate of sample size was made based on assumptions regarding a projected effect size of 30% to lower both total testosterone and LH on the basis of the response to fezolinetant measured in healthy volunteers (26).
In conclusion, this is the first study to demonstrate that an NK3 receptor antagonist has a sustained effect in women with PCOS to normalize the LH-to-FSH ratio and reduce the hyperandrogenic state. However, these changes in hormones did not translate into improved clinical outcomes in this 12-week study. These data suggest that therapy principally targeting the hypothalamic KNDy-HPG axis elicits positive changes in biochemical biomarkers but that the expected, consequent changes in the plasticity of relevant, neuroendocrine circuits and ovarian physiology correct slowly; therefore, prolonged therapy may be required to demonstrate clinical benefit.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all members of the OGEDA Drug Discovery Team and Astellas Pharma Inc, which acquired 100% of the equity of OGEDA SA on May 17, 2017. Development of this manuscript, including editorial support provided by Lauren Cerruto and Traci Stuve, MA, of Echelon Brand Communications (Parsippany, NJ, USA), an OPEN Health company, was sponsored by Astellas Pharma Global Development. The authors would like to thank Joyce Kingsbury, Principal Biostatistician and PHASTAR (Derry, NH, USA), and Richard S. Legro (Penn State Health Obstetrics and Gynecology, Hershey, PA, USA) for consulting related to the study design.
Financial Support and Role of the Sponsor: This study was sponsored by OGEDA SA (Gosselies, Belgium), a wholly owned subsidiary of Astellas Pharma Inc. Employees of OGEDA SA (Gosselies, Belgium) were involved in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Employees of Astellas Pharma US Inc, were involved in the analysis and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Clinical Trial Information: EudraCT registration No.: 2014-004409-34 (registered January 21, 2015).
Glossary
Abbreviations
- AE
adverse event
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- AMH
antimüllerian hormone
- C-SSRS
Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale
- E2
estradiol
- FSH
follicle-stimulating hormone
- GnRH
gonadotropin-releasing hormone
- HPG
hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal
- KNDy
kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin A
- LH
luteinizing hormone
- NK3
neurokinin 3
- P4
progesterone
- PCOS
polycystic ovary syndrome
- PK
pharmacokinetics
- SHBG
sex hormone–binding globulin
- TEAE
treatment-emergent adverse event
- ULN
upper limit of normal
Additional Information
Disclosures: G.L.F. has served as a consultant to Astellas Pharma, was formerly employed by OGEDA SA during the conduct of the study, is an employee of EPICS Therapeutics, and is a coauthor of patent WO 2014/154897 licensed to Astellas Pharma. B.O.-P. has nothing to disclose. J.L. received grants from Astellas Pharma during the conduct of the study and has received grants and personal fees from Ansh Labs and Ferring, personal fees from Danone and Titus Healthcare, and grants from Merck Serono and ZonMw. G.G. received compensation for the conduct of the study and has received honoraria and/or nonfinancial support from Abbott, Ferring, Finox, Gedeon Richter, Glycotope GmbH, Guerbet, Merck Serono, MSD, ObsEva, ReprodWissen GmbH, and Theramex. A.P. received fees (paid to University Hospital Liège) from Astellas Pharma during the conduct of the study and is a consultant for Bayer, Ceres, and Gedeon Richter. D.T. received fees (paid to University Hospitals Leuven) from Astellas Pharma during the conduct of the study. B.C.J.M.F. has received fees or grant support from the following organizations (in alphabetic order): Bain Capital, Controversies in Obstetrics, Gynecology & Infertility (COGI), Dutch Heart Foundation (Nederlandse Hartstichting), Elsevier, European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE), OGEDA (wholly owned subsidiary of Astellas), Ferring, International Federation of Fertility Societies (IFFS), London Women’s Clinic (LWC), Menogenix, Myovant, Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (ZonMw), Pantarhei Bioscience, Partners Group, PregLem/Gedeon Richter, Reproductive Biomedicine Online (RBMO), and the World Health Organization. C.L. is an employee of Astellas Pharma. J.C. is an employee of EPICS Therapeutics. H.R.H. and S.R. are former employees of OGEDA SA.
Data Availability
The data sets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
- 1. Duncan WC. A guide to understanding polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2014;40(3):217-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Bozdag G, Mumusoglu S, Zengin D, Karabulut E, Yildiz BO. The prevalence and phenotypic features of polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(12):2841-2855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Azziz R, Marin C, Hoq L, Badamgarav E, Song P. Health care-related economic burden of the polycystic ovary syndrome during the reproductive life span. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(8):4650-4658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Jason J. Polycystic ovary syndrome in the United States: clinical visit rates, characteristics, and associated health care costs. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(13):1209-1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Legro RS, Arslanian SA, Ehrmann DA, et al. ; Endocrine Society . Diagnosis and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(12):4565-4592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS Consensus Workshop Group. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Hum Reprod. 2004;19(1):41-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Lizneva D, Suturina L, Walker W, Brakta S, Gavrilova-Jordan L, Azziz R. Criteria, prevalence, and phenotypes of polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2016;106(1):6-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Huang CC, Tien YJ, Chen MJ, Chen CH, Ho HN, Yang YS. Symptom patterns and phenotypic subgrouping of women with polycystic ovary syndrome: association between endocrine characteristics and metabolic aberrations. Hum Reprod. 2015;30(4):937-946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Dapas M, Lin FTJ, Nadkarni GN, et al. Distinct subtypes of polycystic ovary syndrome with novel genetic associations: an unsupervised, phenotypic clustering analysis. PloS Med. 2020;17(6):e1003132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Ruddenklau A, Campbell RE. Neuroendocrine impairments of polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrinology. 2019;160(10):2230-2242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Clarkson J, Han SY, Piet R, et al. Definition of the hypothalamic GnRH pulse generator in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(47):E10216-E10223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Lippincott MF, León S, Chan YM, et al. Hypothalamic reproductive endocrine pulse generator activity independent of neurokinin B and dynorphin signaling. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104(10):4304-4318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Herbison AE. A simple model of estrous cycle negative and positive feedback regulation of GnRH secretion. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2020;57:100837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Blank SK, McCartney CR, Marshall JC. The origins and sequelae of abnormal neuroendocrine function in polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod Update. 2006;12(4):351-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Waldstreicher J, Santoro NF, Hall JE, Filicori M, Crowley WF Jr. Hyperfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis in women with polycystic ovarian disease: indirect evidence for partial gonadotroph desensitization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988;66(1):165-172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Taylor AE, McCourt B, Martin KA, et al. Determinants of abnormal gonadotropin secretion in clinically defined women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(7):2248-2256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Daniels TL, Berga SL. Resistance of gonadotropin releasing hormone drive to sex steroid-induced suppression in hyperandrogenic anovulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(12):4179-4183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Pastor CL, Griffin-Korf ML, Aloi JA, Evans WS, Marshall JC. Polycystic ovary syndrome: evidence for reduced sensitivity of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse generator to inhibition by estradiol and progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83(2):582-590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Eagleson CA, Gingrich MB, Pastor CL, et al. Polycystic ovarian syndrome: evidence that flutamide restores sensitivity of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse generator to inhibition by estradiol and progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(11):4047-4052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Chang RJ. The reproductive phenotype in polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007;3(10):688-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Barthelmess EK, Naz RK. Polycystic ovary syndrome: current status and future perspective. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2014;6:104-119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Teede H, Misso M, Costello M, et al. , on behalf of the International PCOS Network and Collaborating Organizations. International Evidence-based Guideline for the Assessment and Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome 2018. Monash University; 2018, https://www.monash.edu/__data/assets/pdf_file/0004/1412644/PCOS_Evidence-Based-Guidelines_20181009.pdf. Accessed May 25, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Briden L, Shirin S, Prior JC. The central role of ovulatory disturbances in the etiology of androgenic polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)—evidence for treatment with cyclic progesterone. Drug Discov Today Dis Models. 2020;32(Pt B):71-82. [Google Scholar]
- 24. Sirmans SM, Pate KA. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Epidemiol. 2013;6:1-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Skorupskaite K, George JT, Veldhuis JD, Millar RP, Anderson RA. Interactions between neurokinin B and kisspeptin in mediating estrogen feedback in healthy women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(12):4628-4636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Fraser GL, Ramael S, Hoveyda HR, Gheyle L, Combalbert J. The NK3 receptor antagonist ESN364 suppresses sex hormones in men and women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(2):417-426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Skorupskaite K, George JT, Veldhuis JD, Anderson RA. Neurokinin B regulates gonadotropin secretion, ovarian follicle growth, and the timing of ovulation in healthy women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(1):95-104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. George JT, Kakkar R, Marshall J, et al. Neurokinin B receptor antagonism in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(11):4313-4321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Skorupskaite K, George JT, Veldhuis JD, Millar RP, Anderson RA. Kisspeptin and neurokinin B interactions in modulating gonadotropin secretion in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod. 2020;35(6):1421-1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Modi M, Dhillo WS. Neurokinin B and neurokinin-3 receptor signaling: promising developments in the management of menopausal hot flushes. Semin Reprod Med. 2019;37(3):125-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Hoveyda HR, Fraser GL, Dutheuil G, et al. Optimization of novel antagonists to the neurokinin-3 receptor for the treatment of sex-hormone disorders (Part II). ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015;6(7):736-740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Fraser GL, Hoveyda HR, Clarke IJ, et al. The NK3 receptor antagonist ESN364 interrupts pulsatile LH secretion and moderates levels of ovarian hormones throughout the menstrual cycle. Endocrinology. 2015;156(11):4214-4225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Depypere H, Timmerman D, Donders G, et al. Treatment of menopausal vasomotor symptoms with fezolinetant, a neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist: a phase 2a trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104(12):5893-5905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Fraser GL, Lederman S, Waldbaum A, et al. A phase 2b, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, dose-ranging study of the neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist fezolinetant for vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. Menopause. 2020;27(4):382-392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. World Health Organization. Definition and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus and Intermediate Hyperglycemia: Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation. World Health Organization; 2006, http://www.who.int/diabetes/publications/Definition%20and%20diagnosis%20of%20diabetes_new.pdf. Accessed May 25, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 36. World Health Organization. Use of Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) in the Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus. Advanced Report of a WHO Consultation. World Health Organization; 2011, http://www.who.int/diabetes/publications/report-hba1c_2011.pdf. Accessed May 25, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 37. Cronin L, Guyatt G, Griffith L, et al. Development of a health-related quality-of-life questionnaire (PCOSQ) for women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83(6):1976-1987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Jones GL, Benes K, Clark TL, et al. The polycystic ovary syndrome health-related quality of life questionnaire (PCOSQ): a validation. Hum Reprod. 2004;19(2):371-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. SGS Life Science Services. Validation of an LC/MS-MS Method for the Determination of Testosterone in Lithium Heparinised Human Plasma [Validation Report No. B1121044]. SGS Life Science, division of SGS Belgium NV; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 40. Posner K, Brown GK, Stanley B, et al. The Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale: initial validity and internal consistency findings from three multisite studies with adolescents and adults. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168(12):1266-1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. The Columbia Scale (C-SSRS). A Unique Suicide Risk Assessment Tool: the Columbia Lighthouse Project. 2016, http://cssrs.columbia.edu/the-columbia-scale-c-ssrs/about-the-scale/. Accessed May 25, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 42. Welt CK. Evaluation of the Menstrual Cycle and Timing of Ovulation. UpToDate; 2019, https://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-the-menstrual-cycle-and-timing-of-ovulation. Accessed May 25, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 43. Herbison AE. The gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse generator. Endocrinology. 2018;159(11):3723-3736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Plant TM. A comparison of the neuroendocrine mechanisms underlying the initiation of the preovulatory LH surge in the human, Old World monkey and rodent. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2012;33(2):160-168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Abbara A, Eng PC, Phylactou M, et al. Kisspeptin receptor agonist has therapeutic potential for female reproductive disorders. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(12):6739-6753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Kenealy BP, Keen KL, Garcia JP, Kohlenberg LK, Terasawa E. Obligatory role of hypothalamic neuroestradiol during the estrogen-induced LH surge in female ovariectomized rhesus monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(52):13804-13809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Marques P, Skorupskaite K, George JT, Anderson RA. Physiology of GNRH and gonadotropin secretion. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, et al. , eds. Endotext. MDText.com Inc; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 48. Katulski K, Podfigurna A, Czyzyk A, Meczekalski B, Genazzani AD. Kisspeptin and LH pulsatile temporal coupling in PCOS patients. Endocrine. 2018;61(1):149-157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Ibáñez L, Ong K, Ferrer A, Amin R, Dunger D, de Zegher F. Low-dose flutamide-metformin therapy reverses insulin resistance and reduces fat mass in nonobese adolescents with ovarian hyperandrogenism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(6):2600-2606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Fleming R, Harborne L, MacLaughlin DT, et al. Metformin reduces serum mullerian-inhibiting substance levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome after protracted treatment. Fertil Steril. 2005;83(1):130-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Ortega MT, Carlson L, McGrath JA, et al. AMH is higher across the menstrual cycle in early postmenarchal girls than in ovulatory women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105(4):e1762-e1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Chun S. Inter-ovarian differences in ultrasound markers of ovarian size in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2019;46(4):197-201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Laven JS, Mulders AG, Visser JA, Themmen AP, De Jong FH, Fauser BC. Anti-Müllerian hormone serum concentrations in normoovulatory and anovulatory women of reproductive age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(1):318-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Lv PP, Jin M, Rao JP, et al. Role of anti-Müllerian hormone and testosterone in follicular growth: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2020;20(1):101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Hendrix AO, Selgrade JF. Bifurcation analysis of a menstrual cycle model reveals multiple mechanisms linking testosterone and classical PCOS. J Theor Biol. 2014;361:31-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Vendola KA, Zhou J, Adesanya OO, Weil SJ, Bondy CA. Androgens stimulate early stages of follicular growth in the primate ovary. J Clin Invest. 1998;101(12):2622-2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Andersen CY, Schmidt KT, Kristensen SG, Rosendahl M, Byskov AG, Ernst E. Concentrations of AMH and inhibin-B in relation to follicular diameter in normal human small antral follicles. Hum Reprod. 2010;25(5):1282-1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Pigny P, Merlen E, Robert Y, et al. Elevated serum level of anti-mullerian hormone in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: relationship to the ovarian follicle excess and to the follicular arrest. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(12):5957-5962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Grossman MP, Nakajima ST, Fallat ME, Siow Y. Müllerian-inhibiting substance inhibits cytochrome P450 aromatase activity in human granulosa lutein cell culture. Fertil Steril. 2008;89(5 Suppl):1364-1370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Cimino I, Casoni F, Liu X, et al. Novel role for anti-Müllerian hormone in the regulation of GnRH neuron excitability and hormone secretion. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Tata B, Mimouni NEH, Barbotin AL, et al. Elevated prenatal anti-Müllerian hormone reprograms the fetus and induces polycystic ovary syndrome in adulthood. Nat Med. 2018;24(6):834-846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Ruth KS, Day FR, Tyrrell J, et al. ; Endometrial Cancer Association Consortium . Using human genetics to understand the disease impacts of testosterone in men and women. Nat Med. 2020;26(2):252-258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Pielecka J, Quaynor SD, Moenter SM. Androgens increase gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron firing activity in females and interfere with progesterone negative feedback. Endocrinology. 2006;147(3):1474-1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Silva MS, Prescott M, Campbell RE. Ontogeny and reversal of brain circuit abnormalities in a preclinical model of PCOS. JCI Insight. 2018;3(7):e99405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. García-Ortega J, Pinto FM, Fernández-Sánchez M, et al. Expression of neurokinin B/NK3 receptor and kisspeptin/KISS1 receptor in human granulosa cells. Hum Reprod. 2014;29(12):2736-2746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Qi X, Salem M, Zhou W, et al. Neurokinin B exerts direct effects on the ovary to stimulate estradiol production. Endocrinology. 2016;157(9):3355-3365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Blasco V, Pinto FM, Fernández-Atucha A, et al. Altered expression of the kisspeptin/KISS1R and neurokinin B/NK3R systems in mural granulosa and cumulus cells of patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2019;36(1):113-120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Blasco V, Pinto FM, Fernández-Atucha A, González-Ravina C, Fernández-Sánchez M, Candenas L. Female infertility is associated with an altered expression of the neurokinin B/neurokinin B receptor and kisspeptin/kisspeptin receptor systems in ovarian granulosa and cumulus cells. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(4):869-878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Yang F, Ruan YC, Yang YJ, et al. Follicular hyperandrogenism downregulates aromatase in luteinized granulosa cells in polycystic ovary syndrome women. Reproduction. 2015;150(4):289-296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Barry JA, Azizia MM, Hardiman PJ. Risk of endometrial, ovarian and breast cancer in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2014;20(5):748-758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data sets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.