ABSTRACT
Streptococcus pneumoniae is an opportunistic pathogen that can alter its cell surface phenotype in response to the host environment. We demonstrated that the transcriptional regulator FabT is an indirect regulator of capsular polysaccharide, an important virulence factor of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Transcriptome analysis between the wild-type D39s and D39ΔfabT mutant strains unexpectedly identified a differentially expressed gene encoding a site-specific recombinase, PsrA. PsrA catalyzes the inversion of 3 homologous hsdS genes in a type I restriction-modification (RM) system SpnD39III locus and is responsible for the reversible switch of phase variation. Our study demonstrated that upregulation of PsrA in a D39ΔfabT mutant correlated with an increased ratio of transparent (T) phase variants. Inactivation of the invertase PsrA led to uniform opaque (O) variants. Direct quantification of allelic variants of hsdS derivatives and inversions of inverted repeats indicated that the recombinase PsrA fully catalyzes the inversion mediated by IR1 and IR3, and FabT mediated the recombination of the hsdS alleles in PsrA-dependent and PsrA-independent manners. In addition, compared to D39s, the ΔfabT mutant exhibited reduced nasopharyngeal colonization and was more resistant to phagocytosis and less adhesive to epithelial cells. These results indicated that phase variation in the ΔfabT mutant also affects other cell surface components involved in host interactions.
KEYWORDS: Streptococcus pneumoniae, capsular polysaccharide, phase variation, FabT, SpnD39III
INTRODUCTION
S. pneumoniae is a significant human-pathogenic bacterium and resides asymptomatically in healthy carriers, and infections are primarily a consequence of decreased immunity in children and the elderly (1, 2). The primary outcome of S. pneumoniae infections is pneumonia that can be accompanied by invasive disease such as meningitis, sepsis, otitis media, and bacteremia (3, 4). The capsular polysaccharide (CPS) plays a critical role in virulence and forms a protective barrier from mucosal agglutination and opsonophagocytosis (5). The phenotypic variation of the amounts of capsule on the cell surface are driven by fluctuating environmental conditions in the host and are associated with the well-characterized and reversible phase variation characterized by colony opacity (opaque and transparent) (6–8). Phenotypic variants can be identified by examination of colony morphology (8).
Phenotypic diversity in bacterial populations is complex and involves a variety of intrastrain variations in cell surface features, and these include virulence proteins (9, 10), the capsule (7, 11–13), and pili (14, 15), as well as cell wall teichoic acids (16, 17). Phase variation is a very powerful contingency strategy for generating a diverse population that contains individual variants that allow the pneumococcus to adapt to survive specific host niches. For instance, the transparent variants which express a high level of teichoic acid and surface proteins are able to establish stable colonization on the mucosal surface in the nasopharyngeal mucosa (18). In contrast, the opaque variants which express more capsular polysaccharides and fewer teichoic acids are more resistant to host clearance and more virulent in sepsis models (6). Although the capsule is a significant pathogenic determinant, the molecular mechanisms underlying the relationship between the capsule and the phenotypic variation need further investigation.
Recent works have focused on an epigenetic mechanism controlling the reversible opaque/transparent phenotypic forms in S. pneumoniae (19–21). The phenotypic variation is controlled by a type I restriction modification (RM) system, SpnD39III, that consists of three cotranscribed genes, hsdR (restriction enzyme), hsdM (methyltransferase), and three homologous hsdS sequence recognition proteins. The latter are composed of an hsdS gene at the active site accompanied by two truncated and transcriptionally silent genes, hsdS′ and hsdS″ (20). The hsdS gene consists of two variable regions encoding two target recognition domains (TRD), each of which identifies a specific sequence in the genome. The truncated hsdS homologs are responsible for providing additional alleles for both TRDs. Recombination between the hsdS genes is mediated by 3 pairs of inverted repeats, (IR) IR1 (85 bp), IR2 (298 bp), and IR3 (15 bp), that can recombine to form 6 unique hsdS alleles (19–23). The products of these alleles possess distinct DNA recognition specificities that generate distinct genomic DNA methylation patterns and thus control the phase variation of colony morphology. The DNA invertase PsrA is encoded within the SpnD39III locus and contributes to this site-specific DNA rearrangement (22, 23). This form of site-specific recombination is mediated by enzymes such as PsrA that catalyze the cleavage and rejoining of DNA fragments at specific recognition sequences without ATP or the synthesis of any new DNA. Indeed, SpnD39III TRD shuffling is not fully controlled by the site-specific recombinase PsrA. The inversion of a 15-bp IR3 bound sequence completely depends on PsrA, and the inversion within 85-bp IR1 and 298-bp IR2 bound sequences rely on factors in addition to PsrA (23), or for IR1 may be independent of PsrA (22). The regulation of psrA is unknown, and additional complexities are present in this system. For instance, the site-specific recombination can be mediated by direct repeats (19). The regulatory mechanisms underlying SpnD39III control of phase variation are far from clear.
Fatty acid biosynthesis transcriptional regulator FabT (SPD_0379) is a transcriptional repressor of membrane fatty acid synthesis in S. pneumoniae strains D39 and TIGR4 (24, 25). S. pneumoniae adopts the type II fatty acid synthesis pathway (FAS-II) for fatty acid synthesis, which is composed of 13 genes aligned in a single gene cluster, in which fabM encodes an enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase responsible for the synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs) (25), whereas fabK encodes an enoyl-ACP reductase involved in saturated fatty acid synthesis (26). The promoter regions of fabM, fabT, and fabK contain a consensus palindromic sequence, which is under the control of FabT (24). A fabT knockout leads to an increased expression of all FAS-II genes with the exception of fabM (24, 25, 27) and decreases the production of UFA with shortened chain lengths (24). The fatty acid composition of cytoplasmic membrane was shown to be related to phase variation of S. pneumoniae (28). Compared to the transparent variants, the opaque variants possessed less UFA in the cell membrane (28). As suggested above, the function of transcriptional regulator FabT appears to have a close relationship with phase variation in S. pneumoniae.
In this study, we found that deletion of fabT in S. penumoniae strain D39 resulted in significant decrease in CPS production as well as colony phenotype alteration. Site-specific recombinase PsrA was upregulated in the fabT-deleted strain, which changed the IR-mediated inversions. In addition, alteration of hsdS allele composition was also found in the fabT mutant, though it was not fully dependent on IR-mediated inversions.
RESULTS
Deletion of fabT decreases capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis in S. pneumoniae D39.
A knockout of the fabT was problematic due to its cotranscription with the essential gene fabH (24). To prevent the downstream fabH from polar effects, we retained the 3′ 54 bp of fabT through the introduction of a Janus cassette 1 (19) by allelic exchange into a streptomycin-resistant D39 derivative strain (D39s). This resulted in the strain D39ΔfabT::JC1. The latter was then employed to generate an unmarked in-frame deletion of fabT designated strain D39ΔfabT. The genomic ectopic complement strain CΔfabT was constructed by transformation of plasmid pPEPZ-Plac-RBS-fabT-FLAG3 encoding a Flag-tagged version of FabT. The absence of a lacI repressor in S. pneumoniae D39s ensured the constitutive expression of the construct. The fabT mRNA (Fig. S1A) and FabT protein (Fig. S1B) levels in this complementary strain were significantly lower than that in the parental strain D39s. These genomic manipulations did not result in any detectable differences in growth rates in Todd-Hewitt broth supplemented with yeast extract (THY) (data not shown).
Verification of fabT mutant strains. (A) Steady-state mRNA levels of fabT in fabT mutants; (B) FabT-Flag tag in complemented strain D39CΔfabT detected by Western blotting. Download FIG S1, TIF file, 0.08 MB (86.2KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
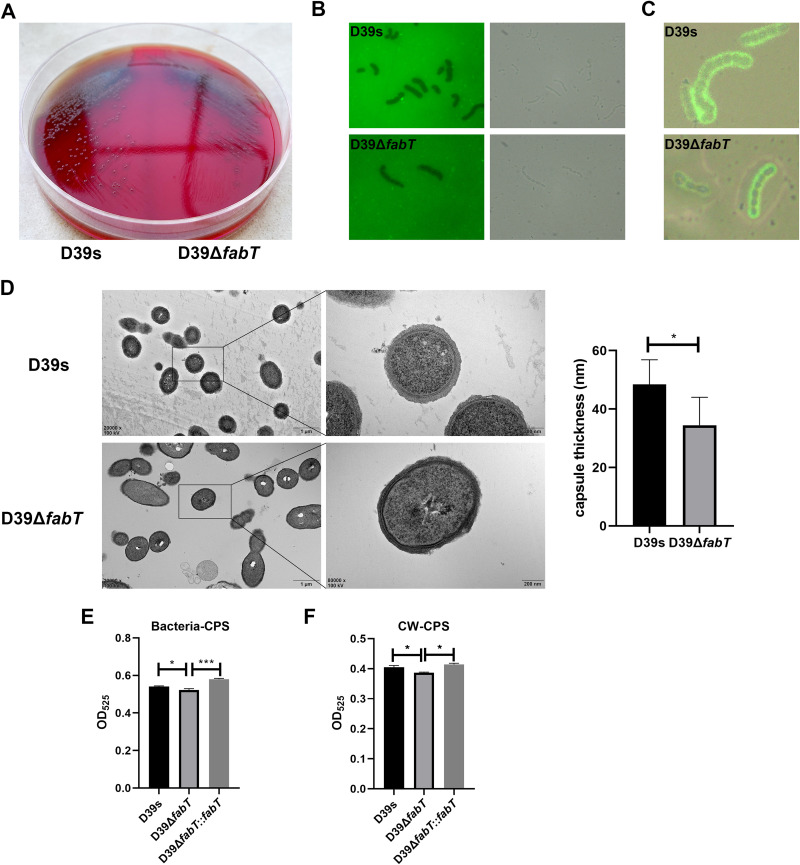
The fabT gene knockout strain was composed of small and rough colonies on blood agar plates (Fig. 1A). This indicated that the ΔfabT mutant produced less CPS than the wild-type D39s (29, 30). We measured the capsular thickness of the ΔfabT mutant by exposing the bacteria to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran, where the fluorescence-free area indicated the capsule boundary. The ΔfabT mutant displayed a smaller capsule size and a more transparent exclusion zone (Fig. 1B). Immunofluorescence microscopy revealed that the FabT-deficient strain showed a significant decrease in width of the fluorescence staining area with a smooth layer of capsule (Fig. 1C). This was verified by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and the mean capsule layer diameter of the ΔfabT mutant was only 71.2% of that of the parental strain, which was 34.5 ± 9.5 nm, compared with 48.4 ± 8.5 nm for the parental D39s (Fig. 1D). CPS production was also assessed by measurements of uronic acid content among these strains. The uronic acid levels for the ΔfabT mutant were significantly less than those of the parental strain, and restoration of the gene in the complemented strain fully restored the uronic acid content, either for whole-cell CPS or the cell wall-associated CPS (Fig. 1E and F). These results indicated that deletion of the fabT gene substantially decreased CPS production as well as the CPS attached on the cell surface.
FIG 1.
Deletion of fabT leads to decreased capsule production. (A) Colony morphology on a blood agar plate (BAP) of D39s (left) and D39ΔfabT (right) strains. (B) Fluorescence and bright-field microscopy of D39s (upper panel) and D39ΔfabT (lower panel) in the presence of FITC-dextran (×100 objective). (C) Overlay of bright-field and fluorescence microscopy of D39s and D39ΔfabT mutant strains showing the capsule in green (anti-type 2 capsule antibodies and FITC-goat anti-rabbit IgG). (D) Transmission electron microscopy of D39s and D39ΔfabT. The mean capsule layer diameters are indicated; n = 20. (E and F) Comparisons of whole-cell and cell wall-associated CPS using the uronic acid assay. Statistical analysis was performed using the unpaired t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.
Screening of FabT-regulated genes via transcriptomic analysis and qRT-PCR.
One potential mechanism for the capsule production defect in the ΔfabT mutant was downregulation of transcription at the cps locus. However, steady-state mRNA levels of the cps genes were unaffected by the fabT deletion (data not shown). Additionally, whole-genome transcriptome sequencing indicated that overall, 67 genes were upregulated and 66 were downregulated in the ΔfabT mutant (P < 0.05), and expression levels for the cps locus did not significantly vary between strains. As expected, the fab genes (SPD_0378-0390) were significantly increased from 1.7-fold to 4.4-fold in the ΔfabT mutant (Table 1). These results were inconsistent with previous studies (24, 27) in that fabM was also upregulated in the ΔfabT mutant, whereas this gene was previously shown to be independently regulated. The expression levels of fabH and acpP that are cotranscribed with fabT showed minor upregulation and no significant differences. This was supported by another study in which increased FabT expression resulted in a small decrease of fabH and did not affect acpP (31). These results were validated using a reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis of the fabM, fabT, and fabH genes (Fig. S2A).
TABLE 1.
Differential gene expression detected by transcriptome sequencing in the D39s relative to the D39ΔfabT mutanta
| Regulation status in D39ΔfabT and gene no.b | Gene | Description | Log2 fold change | P valuec |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | ||||
| SPD_0140 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 1.56 | 0.019 | |
| SPD_0185 | cls | Cardiolipin synthase | 0.72 | 0.008 |
| SPD_0201 | rpmC | 50S ribosomal protein L29 | 0.65 | 0.046 |
| SPD_0267 | NCS2 family permease | 0.63 | 0.012 | |
| SPD_0350 | vraT | Cell wall-active antibiotic response protein | 0.82 | 0.013 |
| SPD_0351 | vraS | Sensor histidine kinase | 0.94 | 0.002 |
| SPD_0354 | DNA alkylation repair protein | 1.16 | 0.032 | |
| SPD_0378 | fabM | Enoyl-CoA hydratase | 1.66 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0380 | fabH | Ketoacyl-ACP synthase III | 0.73 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0382 | fabK | Enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase FabK | 2.05 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0383 | fabD | ACP S-malonyltransferase | 1.77 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0384 | fabG | 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase | 1.70 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0385 | fabF | Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase II | 1.76 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0386 | accB | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase biotin carboxyl carrier protein | 1.79 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0387 | fabZ | 3-Hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase FabZ | 1.63 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0388 | accC | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase biotin carboxylase subunit | 2.00 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0389 | accD | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase carboxyltransferase subunit beta | 2.04 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0390 | accA | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase carboxyl transferase subunit alpha | 2.13 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0391 | briC | Biofilm-regulating peptide BriC | 1.19 | 0.004 |
| SPD_0392 | Hypothetical protein | 0.87 | 0.031 | |
| SPD_0452 | psrA d | Tyrosine-type DNA invertase PsrA | 3.03 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0453 | hsdS | Restriction endonuclease subunit S | 2.93 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0501 | licT | Transcription antiterminator Lict | 1.95 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0502 | PTS glucose transporter subunit IIA | 1.67 | 0.000 | |
| SPD_0503 | bglA-2 | 6-Phospho-beta-glucosidase | 1.69 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0646 | DegV family protein | 1.49 | 0.000 | |
| SPD_0670 | VanZ family protein | 0.62 | 0.042 | |
| SPD_0671 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 0.80 | 0.002 | |
| SPD_0684 | bioY | Biotin transporter BioY | 2.25 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0688 | ABC transporter permease | 0.61 | 0.020 | |
| SPD_0691 | PadR family transcriptional regulator | 0.71 | 0.014 | |
| SPD_0703 | DUF3270 domain-containing protein | 1.31 | 0.020 | |
| SPD_0745 | plsY | Glycerol-3-phosphate 1-O-acyltransferase PlsY | 1.20 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0772 | pfkB | 1-Phosphofructokinase | 0.86 | 0.002 |
| SPD_0858 | mutM | DNA-formamidopyrimidine glycosylase | 1.21 | 0.002 |
| SPD_0859 | coaE | Dephospho-CoA kinase | 1.24 | 0.007 |
| SPD_0860 | pmrA | Multidrug efflux MFS transporter PmrA | 1.16 | 0.019 |
| SPD_0888 | adcAII | Zinc-binding lipoprotein AdcAII | 0.81 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0889 | phtD | Pneumococcal histidine triad protein PhtD | 0.79 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0890 | phtE | Pneumococcal histidine triad protein PhtE | 1.51 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0913 | DUF1002 domain-containing protein | 1.77 | 0.014 | |
| SPD_0916 | piaB | Iron ABC transporter permease | 1.39 | 0.003 |
| SPD_0917 | piaC | Iron ABC transporter permease | 1.38 | 0.008 |
| SPD_0918 | piaD | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 1.20 | 0.015 |
| SPD_1037 | phtB | Pneumococcal-type histidine triad protein | 0.69 | 0.008 |
| SPD_1049 | lacT | Transcription antiterminator | 1.92 | 0.016 |
| SPD_1164 | cdd-2 | Cytidine deaminase | 2.18 | 0.000 |
| SPD_1165 | Phosphatidylglycerophosphatase A | 1.30 | 0.000 | |
| SPD_1166 | Hypothetical protein | 1.34 | 0.000 | |
| SPD_1167 | appD | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 1.43 | 0.000 |
| SPD_1168 | appC | ABC transporter permease | 1.54 | 0.000 |
| SPD_1169 | appB | ABC transporter permease | 1.54 | 0.000 |
| SPD_1170 | appA | ABC transporter substrate-binding protein | 1.16 | 0.007 |
| SPD_1171 | Cyclically permuted mutarotase family protein | 1.30 | 0.000 | |
| SPD_1264 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 1.35 | 0.015 | |
| SPD_1266 | Energy-coupling factor transporter transmembrane protein EcfT | 1.48 | 0.016 | |
| SPD_1267 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 1.32 | 0.003 | |
| SPD_1276 | EamA family transporter | 0.91 | 0.004 | |
| SPD_1277 | Serine hydrolase | 0.79 | 0.013 | |
| SPD_1490 | YesL family protein | 1.29 | 0.016 | |
| SPD_1492 | yjgK | Protein YjgK, linked to biofilm formation | 1.71 | 0.003 |
| SPD_1628 | xpt | Xanthine phosphoribosyltransferase | 1.11 | 0.003 |
| SPD_1629 | pbuX | Xanthine permease | 1.13 | 0.001 |
| SPD_2043 | pcsB | Secreted antigen GbpB/SagA/PcsB, putative peptidoglycan hydrolase | 1.41 | 0.033 |
| SPD_2068 | htrA | Serine protease, DegP/HtrA | 1.48 | 0.012 |
| Down | ||||
| SPD_0004 | ychF | Redox-regulated ATPase YchF | –0.59 | 0.037 |
| SPD_0024 | purA | Adenylosuccinate synthase | –0.55 | 0.019 |
| SPD_0033 | prsA | Ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase | –0.84 | 0.002 |
| SPD_0063 | strH | Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase | –0.67 | 0.037 |
| SPD_0074 | Nucleoside phosphorylase | –0.74 | 0.015 | |
| SPD_0079 | Hypothetical protein | –0.79 | 0.022 | |
| SPD_0098 | Glycosyltransferase family 2 protein | –0.63 | 0.009 | |
| SPD_0340 | rnpB | RNase P RNA component class B | –0.66 | 0.003 |
| SPD_0369 | zapA | Cell division protein ZapA | –0.68 | 0.010 |
| SPD_0373 | ahpD | Alkyl hydroperoxide reductase AhpD | –1.55 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0379 | fabT | MarR family transcriptional regulator | –15.50 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0422 | Hypothetical protein | –0.98 | 0.005 | |
| SPD_0423 | xylR | Xylose repressor protein | –0.69 | 0.008 |
| SPD_0450 | hsdS | Restriction endonuclease subunit S | –3.07 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0495 | DUF3883 domain-containing protein | –0.74 | 0.032 | |
| SPD_0534 | estA | Esterase family protein | –0.66 | 0.005 |
| SPD_0558 | prtA | Serine protease PrtA precursor | –1.19 | 0.005 |
| SPD_0582 | DUF3042 family protein | –0.99 | 0.032 | |
| SPD_0610 | Hypothetical protein | –2.67 | 0.000 | |
| SPD_0611 | Hypothetical protein | –2.17 | 0.002 | |
| SPD_0612 | Hypothetical protein | –1.94 | 0.001 | |
| SPD_0613 | Hypothetical protein | –1.64 | 0.001 | |
| SPD_0614 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | –1.71 | 0.000 | |
| SPD_0637 | lactoylglutathione lyase | –1.21 | 0.005 | |
| SPD_0649 | upp | Uracil phosphoribosyltransferase | –0.96 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0700 | pepN | M1 family metallopeptidase | –0.59 | 0.034 |
| SPD_0718 | YkuJ family protein | –1.13 | 0.002 | |
| SPD_0754 | DUF2969 domain-containing protein | –0.72 | 0.039 | |
| SPD_0853 | lytB | Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase | –2.67 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0957 | dnaG | DNA primase | –0.81 | 0.000 |
| SPD_0958 | rpoD | RNA polymerase sigma factor RpoD | –0.69 | 0.001 |
| SPD_0959 | Metal-sulfur cluster assembly factor | –0.85 | 0.012 | |
| SPD_0997 | hup | HU family DNA-binding protein | –0.87 | 0.003 |
| SPD_1141 | uraA | Uracil transporter | –2.52 | 0.002 |
| SPD_1212 | ywbD | Putative ribosomal RNA large subunit methyltransferase YwbD | –0.58 | 0.033 |
| SPD_1274 | guaA | Glutamine-hydrolyzing GMP synthase | –0.53 | 0.032 |
| SPD_1295 | Hemolysin III family protein | –0.80 | 0.022 | |
| SPD_1431 | gtrB | Bactoprenol glucosyl transferase | –0.80 | 0.007 |
| SPD_1461 | psaB | Manganese ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein | –1.98 | 0.009 |
| SPD_1462 | psaC | Manganese ABC transporter, permease protein, putative | –1.97 | 0.006 |
| SPD_1463 | psaA | Metal ABC transporter substrate-binding lipoprotein/adhesin PsaA | –1.88 | 0.022 |
| SPD_1468 | gpmA | Phosphoglycerate mutase | –0.98 | 0.001 |
| SPD_1483 | murF | UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-tripeptide–d-alanyl-d-alanine ligase | –0.78 | 0.000 |
| SPD_1548 | gmk | Guanylate kinase | –0.48 | 0.042 |
| SPD_1581 | tRNA-Lys-CUU | –1.11 | 0.000 | |
| SPD_1594 | XRE family transcriptional regulator | –0.69 | 0.009 | |
| SPD_1595 | Hypothetical protein | –0.76 | 0.014 | |
| SPD_1649 | piuB | Iron-compound ABC transporter, Permease protein | –2.13 | 0.011 |
| SPD_1650 | piuC | Iron-compound ABC transporter, permease protein | –4.54 | 0.000 |
| SPD_1651 | piuD | Iron-compound ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein | –2.98 | 0.000 |
| SPD_1652 | piuA | Iron-compound ABC transporter, iron-compound-binding protein | –2.88 | 0.018 |
| SPD_1775 | lysA | Diaminopimelate decarboxylase | –0.71 | 0.024 |
| SPD_1790 | rpmH | 50S ribosomal protein L34 | –0.82 | 0.048 |
| SPD_1899 | Gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate hydrolase family protein | –1.35 | 0.022 | |
| SPD_1903 | mutS | DNA mismatch repair protein MutS | –0.54 | 0.041 |
| SPD_1922 | hipO | N-acetyldiaminopimelate deacetylase | –0.59 | 0.043 |
| SPD_1923 | dapD | 2,3,4,5-Tetrahydropyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate N-acetyltransferase | –0.85 | 0.004 |
| SPD_1926 | tyrS | Tyrosine-tRNA ligase | –1.07 | 0.002 |
| SPD_1927 | ctpC | Heavy metal translocating P-type ATPase | –0.96 | 0.000 |
| SPD_1931 | Membrane protein | –0.74 | 0.020 | |
| SPD_1984 | ybbK | Putative stomatin/prohibitin-family membrane protease subunit YbbK | –1.09 | 0.003 |
| SPD_2018 | Isoprenylcysteine carboxyl methyltransferase family protein | –0.80 | 0.033 | |
| SPD_2055 | guaB | IMP dehydrogenase | –0.86 | 0.003 |
Log2 fold change in gene expression as assessed by RNA-seq.
The reference genome under GenBank accession numbers NC_008533.2 and CP027540.1.
Adjusted P values, P values were adjusted using the Benjamini and Hochberg method.
SpnD39III type I restriction-modification system genes are indicated in bold.
(A to D) The qRT-PCR results for the (A) fab gene cluster (B) adcAII (C) hsdM, and (D) mutS in the D39s and D39s derivative strains. Download FIG S2, TIF file, 0.1 MB (109.1KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
The zinc transporter lipoprotein AdcAII was recently found to affect capsule thickness (32) and was upregulated 1.75-fold in ΔfabT mutants as detected using transcriptome analysis. However, the quantitative RT-PCR analysis did not reproduce this difference in our study (Fig. S2B). We also found that a variety of membrane-associated ABC transporters were altered in the transcriptome analysis. These included iron-ABC transporters PiaABC (SPD_0916-0918) and piuABC (SPD_1650-1652), manganese-ABC transporter PsaABC (SPD_1641-1643), and oligopeptide ABC transporter (SPD_1168-1170) (33–35). These alterations were most likely the result of the overall cellular response to the changes in membrane fatty acid composition as previously reported (24, 36).
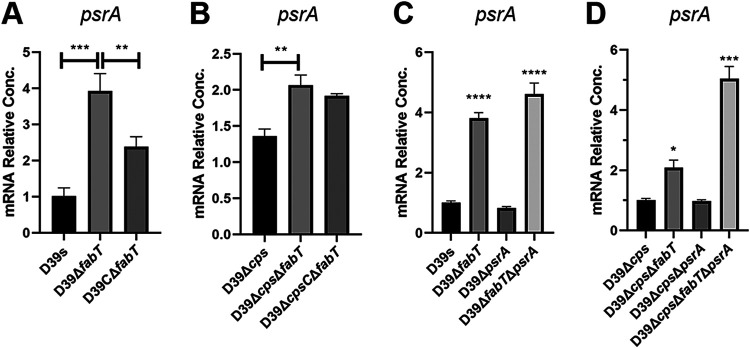
Of particular interest, the ΔfabT mutant also displayed a significant upregulation of psrA as well as hsdS′ and an associated downregulation of hsdS. The transcriptional upregulation of psrA was validated by qRT-PCR and was less obvious in the unencapsulated ΔcpsΔfabT strain. The complemented FabT strain displayed psrA levels that were partially reduced (Fig. 2A and B).
FIG 2.
psrA gene expression in fabT and psrA mutant strains. (A to D) Related abundance of the psrA mRNA in the (A and C) encapsulated and (B and D) unencapsulated fabT and psrA mutant strains was detected by qRT-PCR. Results were normalized to gyrB. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM of a representative experiment. Each experiment was replicated at least three times. Statistical analysis was performed using the unpaired t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0005.
To further confirm the linkage between FabT and PsrA, we constructed frameshift psrA mutants in strains D39s and D39Δcps by truncating the PsrA protein at amino acid 6 without altering the size of the gene, and mRNA levels did not vary even though no functional PsrA was expressed. The mutation of psrA in the ΔfabT mutant resulted in high-level psrA expression in both encapsulated and unencapsulated strains (Fig. 2C and D). This result indicated that FabT might participate in the negative feedback regulation of PsrA that inhibited its own expression when FabT was present.
Deletion of fabT drives pneumococci toward the T phase by the PsrA-dependent mechanism.
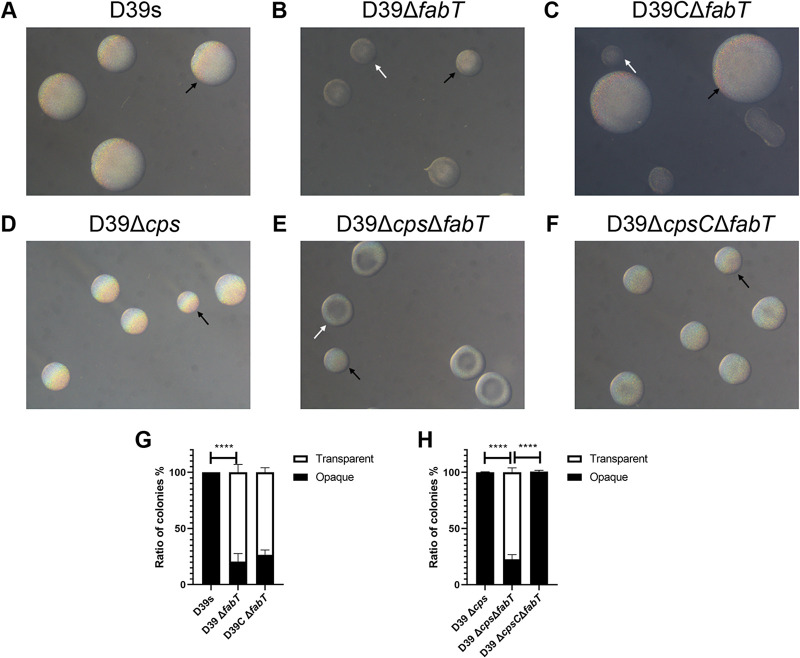
S. pneumoniae colonies can switch between transparent (T) and opaque (O) phenotypes known as phase variation. These variants differ in expression of surface virulence proteins, CPS, and teichoic acids. We examined whether FabT regulates CPS production through phase variation. We first investigated whether the differentially expressed psrA and hsdS in the ΔfabT mutant affect phase variation. The colony phenotypes and the ratio between O and T colonies in a single clonally derived population were characterized for D39s and the ΔfabT mutant on tryptic soy agar (TSA) plates. Parental strain D39s was uniformly composed of O colonies (100% O) after 24 h. In contrast, fabT deletion led to a significantly increased proportion of T colonies compared with the parental strain (79.3% T). Interestingly, the D39CΔfabT strain generated two colony types. The shape and size of large colonies were similar to those of D39s and were uniform and opaque and accompanied by small colonies that were predominantly the T phenotype (Fig. 3C). Moreover, these distinct variants in D39CΔfabT were unable to switch phases with extensive passaging (Table S1). Mechanisms of adaptation leading to pneumococcal irreversible mutations and to readjustment of regulatory networks have been described (37). The complemented D39CΔfabT strain was present as two stable and heritable variant colonies that may be related to this type of readjustment process.
FIG 3.
Colony morphology of fabT mutants. (A to C) Encapsulated D39 and derivatives and (D to F) unencapsulated D39Δcps and derivatives were grown on TSA plates supplemented with catalase. Phase variation of colony opacity of S. pneumoniae was visualized under an inverted microscope through oblique lighting after 24 h (encapsulated) and 26 h (unencapsulated). Representative opaque (O) and transparent (T) colonies in each strain are highlighted with black and white arrowheads, respectively. (G) O/T ratio of encapsulated strains. (H) O/T ratio of unencapsulated strains. All pictures are to the same scale. Original magnification = ×40.
Quantitative assessment of the stability in the colony opacity phenotypes among the D39s derivatives. Download Table S1, PDF file, 0.05 MB (54.2KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Previous reports have indicated that the thick capsule in D39 derivatives may blur the observation of colony opacity, resulting in an incorrect interpretation of the O/T phenotype (19). To eliminate the potential for this in our experiments, we generated unencapsulated D39Δcps and ΔcpsΔfabT strains and then evaluated colony phenotypes. Though it is typically assumed that unencapsulated pneumococci undergo spontaneous phase variation in colony opacity, unencapsulated D39Δcps still produced a uniformly opaque colony after 26 h of cultivation (100% O). In contrast, the ΔcpsΔfabT mutant presented a mixture at 26 h (77.3% T) (Fig. 3D and E). The colony morphology of unencapsulated CΔfabT reverted to a uniformly opaque variant (Fig. 3F). These results indicated that FabT regulated the phase variation in S. pneumoniae independently of CPS expression.
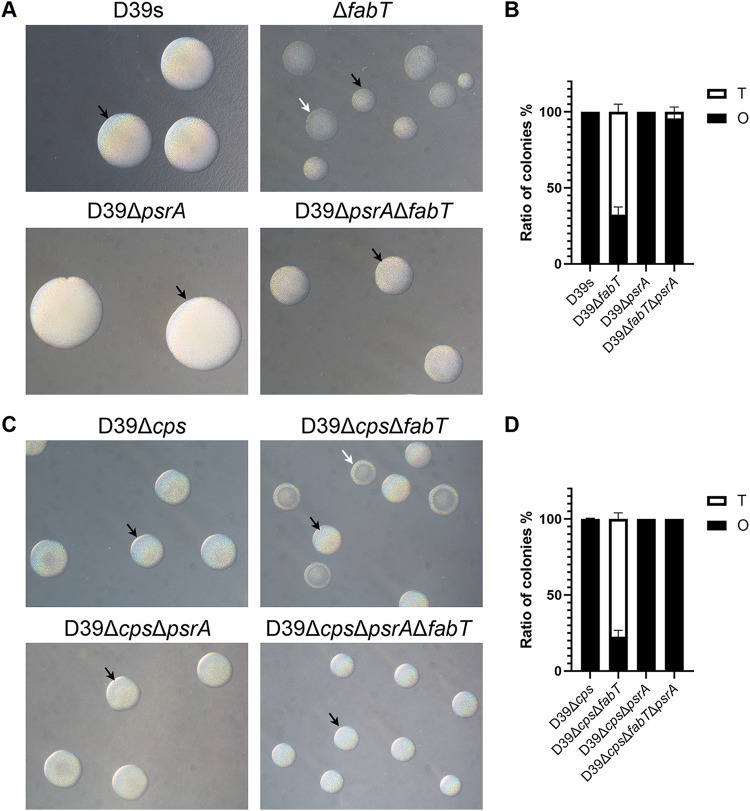
To further determine whether the variation of colony morphology in the ΔfabT mutant was due to the upregulated PsrA, we determined the phase variation in inactivated psrA mutants. The psrA mutants that were generated from ΔfabT mutants produced almost completely opaque colonies (Fig. 4). These results indicated that FabT was able to regulate colony opacity in a PsrA-dependent manner. However, complemented ΔcpsCΔfabT did not downregulate the expression of psrA significantly, indicating that FabT was also able to regulate colony opacity in a PsrA-independent manner.
FIG 4.
Colony morphology of fabT and psrA mutants. (A) Encapsulated D39 and derivatives and (C) unencapsulated D39Δcps and derivatives cultured on TSA supplemented with catalase. Phase variation was visualized through oblique lighting after 24 h (encapsulated) and 26 h (unencapsulated). (B) O/T ratio of encapsulated strains. (D) O/T ratio of unencapsulated strains. See Fig. 3 for abbreviations and additional information.
Interestingly, the capsule produced by ΔpsrA mutants was not significantly different from its parental strain (Fig. S3). In addition, the unencapsulated fabT and psrA mutants showed consistent colony opacity variation, indicating that lower levels of expressed capsule in the ΔfabT mutant were not associated with increased numbers of T variants (Fig. 1E to H).
Capsule production in inactivated psrA mutants. (A and B) Amounts of (A) whole-cell and (B) cell wall CPS using the uronic acid assay. Download FIG S3, TIF file, 0.09 MB (90.3KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
The inversion of inverted repeats catalyzed by PsrA is influenced by deletion of fabT.
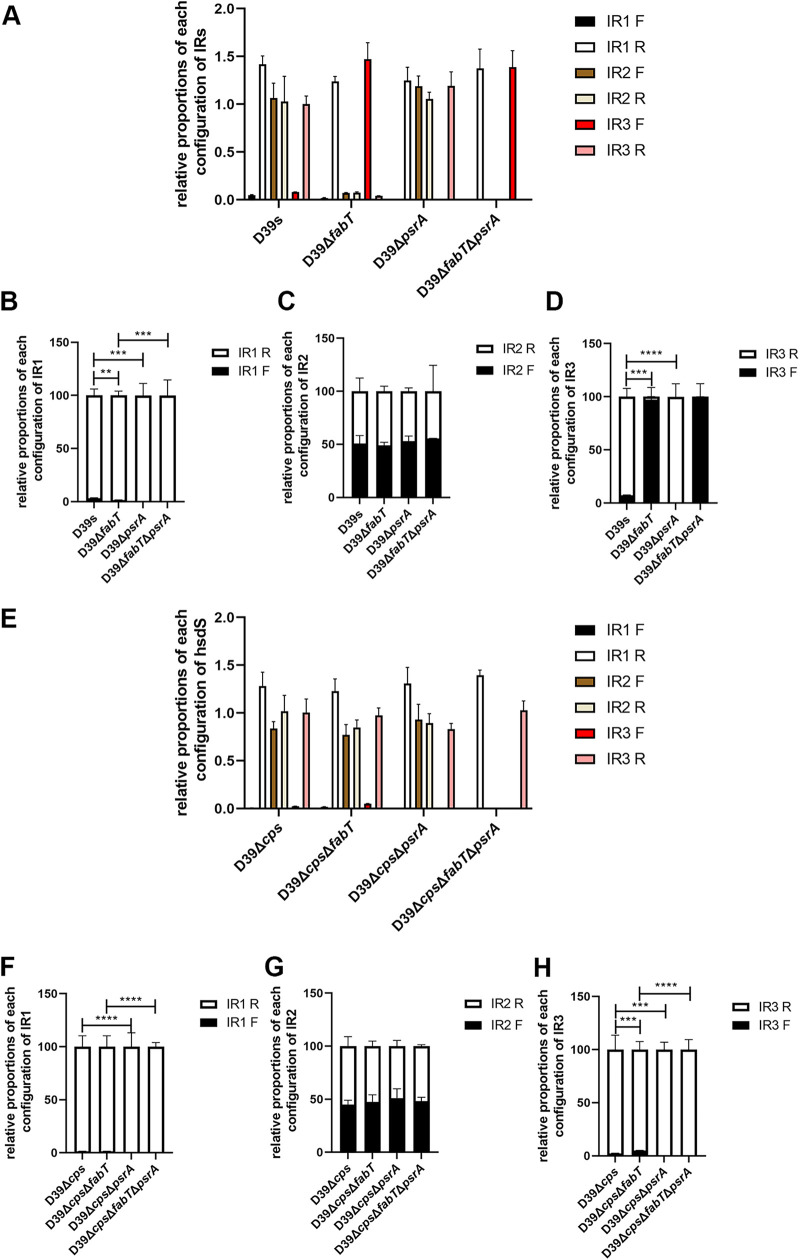
A recent study has shown that inactivation of recombinase PsrA resulted in the loss of all IR3-mediated inversion events and a partial loss of IR2- and IR1-mediated inversions (19). We therefore examined these inversion events in our experimental strains (Fig. S4A). We found that both encapsulated and unencapsulated ΔpsrA mutants lacked significant levels of the inverted IR1-bound sequences. The encapsulated strains of D39s generated 3.2% of the forward configuration of IR1, while the level for the ΔfabT mutant was 1.5% (Fig. 5B). The levels for the ΔcpsΔfabT mutant were similar to those of D39Δcps (1.5%) (Fig. 5F). These results suggested that IR1-mediated inversion was not related to the upregulated expression of psrA in the ΔfabT mutant but also was consistent with the finding that PsrA is indispensable for inversions of sequences bound by IR1 (22, 23).
FIG 5.
Impact of PsrA and FabT on the inversion forms of IR1, IR2, and IR3. (A to H) Configurations (forward and reverse) of the target sequence flanked by (B and F) IR1, (C and G) IR2 (D and H), and IR3 in (A to D) encapsulated and (E to H) unencapsulated strains were determined by qPCR using 20 ng genomic DNA as the templates. Relative abundance of the configuration of each IR was normalized to IR3R in (A) D39s or (E) D39Δcps, respectively. The sum of 2ΔΔCT-For and 2ΔΔCT-Rev of each pair of inverted repeats in panels A and E was defined as 100%, and relative compositions of each orientation were compared in (B to D) encapsulated and (F to H) unencapsulated strains. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM of a representative experiment. Each experiment was replicated at least three times. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0005.
Detection of IRs mediated inversion. (A) Positions of the primers used for detection of the orientation of IRs in the SpnD39III locus. (B) Primers for detecting IR inversion and corresponding hsdS alleles. (C and E) The relative abundance of the configuration of each IR was normalized to the IR3R in (C) D39s and (E) D39Δcps. (D and F) Forward and reverse configurations of the target sequence flanked by IR1, IR2, and IR3 in (D) encapsulated and (F) unencapsulated strains. Download FIG S4, TIF file, 0.3 MB (281.1KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
The inversion of IR3 was also completely abrogated in both encapsulated and unencapsulated ΔpsrA mutants. This suggested that PsrA completely catalyzed the IR3-mediated inversions (Fig. 5D and H). In encapsulated strains, the form of IR3-mediated inversion in the reverse orientation (92.6%) in D39s switched to forward (97.3%) in the ΔfabT mutant. The reverse configuration of IR3-mediated inversion was also fully abrogated in ΔfabTΔpsrA (Fig. 5D). In unencapsulated strains, the forward configuration of IR3 was also increased in the fabT strain from 2.2 to 4.9% (Fig. 5H). Likewise, IR3-mediated inversions were not present in the ΔpsrA mutant. Moreover, the inversion of IR3-bound sequences was partially restored in the complemented strain, indicating that the elevated levels of PsrA that were regulated by FabT were responsible for the IR3-mediated inversion (Fig. S4D).
In contrast, mutation of psrA did not affect the inverse configuration for IR2. The ratio of IR2F to IR2R was 50.8 to 49.1% in D39s and 53.0 to 47.0% in the psrA mutants (Fig. 5C and G). Additionally, levels of IR2 fragments were significantly decreased for the encapsulated FabT mutants regardless of fragment direction. Moreover, the IR2 fragments could not be amplified in the D39ΔfabTΔpsrA mutant (Fig. 5A). This result was confirmed by replacing primer Pr1974 with Pr2042 (data not shown). Moreover, we determined that the IR2.1 downstream sequence was recombined into the genome but not excised due to the existence of a TRD2.1 fragment using primers pr2013/1975 (Fig. S5). However, the matter was more complex because in the unencapsulated strain, the content and the proportions of IR2-mediated inversion were consistent with the parental strain for the ΔcpsΔfabT mutants, while the IR2 fragment disappeared in strains ΔcpsΔfabTΔpsrA, consistent with D39ΔfabTΔpsrA (Fig. 5E). This was most likely the result of the action of an unknown endonuclease or recombinase in TRD2.1 ectopic recombination. The observed disappearance of the IR2 fragment also paralleled PsrA mRNA levels. Thus, there may be an unknown endonuclease/recombinase which was regulated by both FabT and PsrA in the same way as PsrA. When the endonuclease was highly expressed, the sequence downstream of IR2.1 was sheared and ectopic integration was favored (Fig. 6).
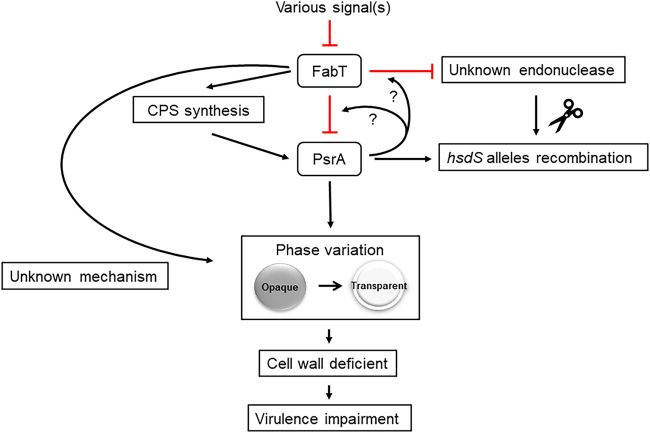
FIG 6.
A model of repressor FabT and its modulation of pneumococcal capsule production and colony phase. Once the expression of FabT is repressed by unspecified signals, the production of CPS of S. pneumoniae is significantly downregulated. Meanwhile, FabT is involved in the negative feedback regulation of PsrA and an unknown endonuclease by unknown mechanism. Overexpressed PsrA acts to catalyze the recombination of hsdS alleles as well as the phase variation of colony morphology, which seems to be irrelevant with the specific hsdS configuration. Besides the PsrA-mediated phase variation, downregulated FabT is able to drive the opaque colony phase to transparent phase directly by unknown mechanism.
Steady-state mRNA levels of TRD2.1 quantified using qRT-PCR. (A) Schematic map representing the hsdSA variant with primers indicated. (B) qRT-PCR detection of TRD2.1. Download FIG S5, TIF file, 0.09 MB (97.1KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
The site-specific recombinant of the SpnD39III locus is altered in fabT-deficient mutants.
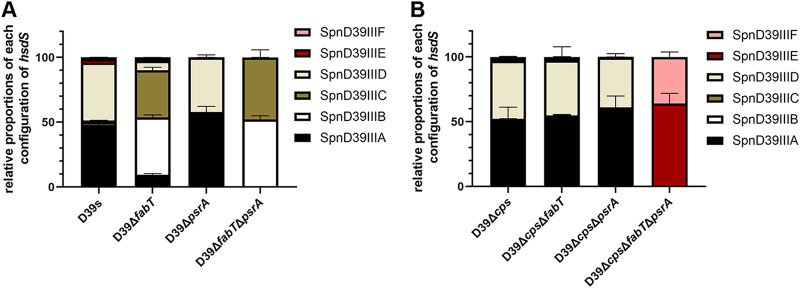
Recombinase PsrA catalyzes the inversion of IRs and mediates recombination of the 3 homologous hsdS genes. The recombination process results from the rearrangement of 5 different TRDs within homologous hsdS genes and was associated with distinct DNA methylation patterns. Recent studies revealed the relationship between hsdS allelic inversion and methylation of distinct DNA motifs in genomes catalyzed by the type I RM system SpnD39III. The different methylomes led to the reversible switching between O and T colony phases, although previous results were not consistent with each other (19–21). To evaluate the existence of shuffled TRDs, we designed a qRT-PCR assay that amplified distinct sequences on the mRNA of each allelic hsdS gene to evaluate the frequency of hsdS inversions in the SpnD39III locus using a 5′ noninvertible region shared by the six hsdS alleles as an internal reference (Fig. S6). We confirmed that the expression levels of hsdM that lies upstream of hsdS and is cotranscribed with hsdS, was not affected in fabT and psrA mutants (Fig. S2C). These results demonstrated that the D39s stocks held within our laboratory collection expressed a mixture of the SpnD39III variants. SpnD39IIIA (47.9%) and D (44.8%) were the predominant variants in D39s, whereas SpnD39IIIB (44.2%) and C (36.5%) were predominant for the ΔfabT mutant. In the absence of the PsrA recombinase, only SpnD39IIIA/D or SpnD39IIIB/C were detected in D39s and ΔfabT (Fig. 7A).
FIG 7.
Impact of PsrA and FabT on the hsdS allelic configuration. (A and B) Relative proportions of hsdS allelic genes in (A) encapsulated and (B) unencapsulated D39 derivatives were determined by qRT-PCR with cDNA as the templates. The transcripts of the 5′ noninvertible sequence of hsdS were detected in all strains as a reference to calculate the ΔCT values. ΔCT values of each hsdS allele were normalized again with the mean value of hsdSA as a reference in each strain to obtain ΔΔCT. The sum of the ΔΔCT of all six hsdS alleles was defined as 100%, and the relative composition of each hsdS allelic gene was calculated. Primers are listed in Fig. S6.
Methods used for hsdS allelic detection. (A) Schematic map of the organization in the SpnD39III locus and six alternative hsdS genes. (B) The proportions of hsdS alleles in the mixed population. The red line indicates the two transcripts in the SpnD39III locus. The cDNA of the mixed population was used as the template. (C) Primer pairs used to detect the hsdS alleles. Download FIG S6, TIF file, 0.2 MB (217.2KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
In unencapsulated stains, the levels for D39Δcps were consistent with the presence of hsdS alleles in D39s in which SpnD39IIIA (50.9%) and D (44.6%) were the predominant variants. The ΔcpsΔfabT double mutant displayed no deviation with SpnD39IIIA (52.8%) and D (42.4%). However, in the ΔcpsΔfabTΔpsrA mutant, the formation of the hsdS allele was locked in SpnD39IIIE (64.0%) and F (35.9%). In the different psrA mutants, the hsdS gene was locked in all six hsdS alleles, indicating that the intrastrain phase variation was dependent on the activity of invertase PsrA (Fig. 7B).
The ΔfabT mutant impaired pneumococcal virulence.
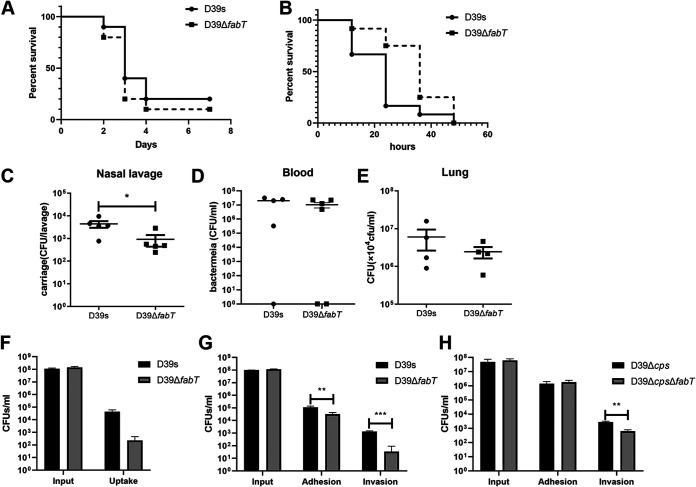
Recent studies demonstrated that distinct SpnD39III variants diversify the capacity of pneumococcal adhesion and invasion in the upper respiratory tract and for nasopharyngeal colonization (19–21). We used a mouse intranasal infection assay to investigate the role of FabT in S. pneumoniae D39. Mice that were intranasally infected with ΔfabT showed an improved survival rate compared to the parental S. pneumoniae D39s strain, while mice infected with D39s appeared visibly sick and had considerable weight loss, yet the difference was not statistically significant (Fig. 8A). During invasive infection, the numbers of bacteria in the nasal lavage fluid from ΔfabT-infected mice were lower than those in the WT-infected mice at 48 h after challenge (Fig. 8C). However, the bacterial loads in their blood or lung homogenates did not show significant differences (Fig. 8D and E). A slightly lower virulence was also present in the bacteremia model (Fig. 8B). The most important pathogenic determinant of S. pneumoniae is the thick pneumococcal capsule that minimizes phagocytosis. We also evaluated the bacterial survival rate after incubation with human macrophages in the absence of serum. To our surprise, the ΔfabT mutant showed an increase in antiphagocytosis against macrophages (Fig. 8F). The adherence of the ΔfabT mutant to the epithelial A549 cells was significantly decreased compared to D39 (Fig. 8G). This was consistent with the decrease in bacterial loads in nasal lavage specimens of the ΔfabT mutant. To avoid potential impact of the capsule, unencapsulated strains were used to verify the adhesion capacity. The unencapsulated ΔfabT mutant displayed a lower level of invasion (Fig. 8H). Taken together, these results indicated that FabT attenuated the virulence of S. pneumoniae by altering the phenotypic variation, and this had a significant impact on pneumococcal colonization and persistence.
FIG 8.
In vivo and in vitro phenotypes of fabT mutant strains. (A) Survival experiments were performed by intranasal inoculation of 1 × 108 CFU S. pneumoniae into C57BL/6 mice. (B) Survival in the mouse septicemia model. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with 776 and 600 CFU of strains D39s and D39ΔfabT, respectively. (C to E) Intranasal infection with 1.5 × 107 CFU of S. pneumoniae. Bacterial loads were evaluated by cultures of (C) nasal lavage, (D) blood, and (E) lung homogenates. (F) Infection of mouse peritoneal primary macrophages with D39s and D39ΔfabT. MOI = 100:1. The input and the intracellular (uptake) bacteria were counted by plating from serial dilutions. (G and H) A549 epithelial cells were infected at an MOI of 100:1 with (G) D39s and (H) D39Δcps. Input, cell-associated (adhesion), and intracellular (invasion) bacteria were counted by plating from serial dilutions.
DISCUSSION
This work demonstrated that mutation of the transcriptional repressor FabT in the S. pneumoniae D39 strain led to an unexpected decrease in capsule production that was accompanied by a novel rough colony morphology on blood agar plates. Complementation of the fabT strain restored capsule production and normal colony morphology. Although the capsule production for the D39ΔfabT mutant was significantly impaired, the expression levels from the cps locus were unaffected. It is unknown how the fatty acid biosynthesis transcriptional regulator FabT impacts the pneumococcal capsule. A site-specific recombinase PsrA was identified in transcriptome analysis, and this played a dominant role in specific alleles of the SpnD39III (Spn5556II) type I RM system and contributed to TRD rearrangements of hsdS alleles that further affected colony phase variation. Capsule production is an enormous energetic burden for the cell and can compete directly with central metabolism for energy (30, 38). The encapsulated ΔfabT mutant might be under higher metabolic stress when its CPS and fatty acid production are altered. Thus, in the absence of an energy demand by CPS production, the demand of altered expression of PsrA to regulate the SpnD39III epigenetic switching machine was much less for the unencapsulated ΔfabT mutant (Fig. 6). Our initial expectation was that the differences in the amount of CPS correlated with the colony morphology in the fabT-deficient strain, and this has been demonstrated previously (6, 39). However, we found that 100% O psrA mutants produced CPS at the same level as the parental strain. This confirmed that CPS production was not only affected by the variation of colony opacity, but FabT deletion was able to reduce the capsule thickness through an unknown mechanism (Fig. 6). This result was supported by previous experiments what utilized fixed SpnD39III alleles that were transformed into the hyper-encapsulated ΔadcAII mutant and were unable to alter that phenotype (32).
Our results demonstrated that the highly expressed recombinase PsrA contributed to the presence of more T colonies in the ΔfabT mutant. In agreement with previous studies, the psrA frameshift-deficient mutant strains diminished the tendency to generate T colonies and were fully restored to the O colony phase in both encapsulated and unencapsulated parental strains. Therefore, deletion of FabT may promote the T colony phase of S. pneumoniae by transcriptional activation of recombinase PsrA (Fig. 6).
To further investigate the underlying mechanism, we examined IR inversions and the resulting disposition of hsdS alleles catalyzed by PsrA at the SpnD39III locus. We found that the absence of PsrA completely abrogated the inversion of IR1- and IR3-mediated TRDs, and the inversion mediated by IR2 was not affected. This outcome conflicted with previous reports that had indicated that the absence of PsrA in the D39 derivative eliminated all IR3 shuffling and partially affected the inversion of IR2 while leaving inversions mediated by IR1 intact (22). A complete dependence of IR3 on PsrA as well as IR1- and IR2-mediated inversions has also been reported (23).
As the recombination within the S. pneumoniae SpnD39III loci leads to epigenetic regulation of genome DNA methylation, we further investigated the composition of the mRNA of hsdS alleles. However, our results were not consistent with the IR inversions detected using genomic DNA (gDNA). All TRD recombinations that shuffled between IR3 were halted in psrA frameshift mutants (i.e., D39ΔfabTΔpsrA consisted of hsdSB and C variants, and IR3 was fully in the forward configuration). The configuration of IR1 conflicts with our IR detection results and hsdS quantification results (i.e., D39s contained approximately 50% hsdSA variants, which were IR1 forward configuration). One potential explanation was that the transcription occurred at the hsdS″ gene that led to mRNA amplicons that were not solely present in the transcript of a specific hsdS variant. The transcription of hsdS″ has been previously verified (23).
Another potential explanation was the ectopic recombination generated from direct repeats (DRs) mediated excision on the hsdS genes. Li et al. found that besides three pairs of IRs mediating hasS recombination events, two pairs of DRs can mediate hsdS deletion events (19). Likewise, we found that the detection fragments for IR2 that included DR2 were lost in FabT and PsrA double knockouts. However, we do not as yet understand the reason for the loss of IR2 in the ΔfabT and ΔfabTΔpsrA mutants. Recently, the presence of an uncharacterized recombination system in the S. pneumoniae genome was hypothesized to play a role in PsrA-independent inversions (22, 23). Our results strongly imply that there are unknown mechanisms or specific recombination systems playing an important role in SpnD39III locus inversion. ΔfabT, ΔfabTΔpsrA, and ΔcpsΔfabTΔpsrA mutants displayed significant increases in psrA expression levels, and the decreased IR2 fragment levels indicated a similar trend. Thus, we hypothesized that this unknown recombinase can mediate the ectopic integration of the sequence downstream of IR2.1 into other homologous positions on the genome in the absence of fabT and that FabT may work as a repressor of the unknown recombinase in the same manner as PsrA (Fig. 6). The precise mechanism or a specific recombination system of the FabT-dependent recombination awaits further investigation.
The relationship between the locked hsdS allele and the colony opacity were quite different in recent studies. For instance, Li et al. found that only hsdSE allele strains were opaque and the others led to transparent variants (19). Manso et al. found that the hsdSA, E allele strains were opaque (20), and not any of them were completely transparent. Oliver et al. demonstrated that hsdSA and B alleles were completely opaque, while the others were transparent (21). Our results of quantitatively detected hsdS alleles demonstrated that D39ΔpsrA and ΔcpsΔpsrA mutants were locked in hsdSA and D alleles; the ΔfabTΔpsrA mutant was locked in hsdSB and C alleles, whereas the ΔcpsΔfabTΔpsrA mutant was locked in hsdSE and F alleles. The presumed mechanism of phase variation regulation by the SpnD39III system might be affected directly by recombinase PsrA rather than the unique sequence specificity protein HsdS that mediated variations in genome DNA methylation patterns, though this needs further investigation.
TRD shuffling at the SpnD39III locus was also controlled by a PsrA-independent mechanism, though recent studies have ruled out site-specific or RecA-mediated recombination in S. pneumoniae (22, 23). The gene encoding a DNA mismatch repair protein, MutS, was slightly upregulated in our D39ΔfabT mutant, indicating a putative mechanism for inversion repair. However, the qRT-PCR results did not support this hypothesis (Fig. S2D).
Existing evidence strongly suggests that PsrA is indirectly regulated by FabT. FabT is a MarR family transcription factor, and the latter are characterized by possession of a conserved winged-helix-turn-helix (wHTH) DNA-binding motif that is widespread in all prokaryotes from archaea to bacteria (40). FabT globally regulates the fatty acid synthesis pathway via binding the distinct DNA palindromes (ANTTTGACTGTNAAATT) located in the promoters upstream of FAS genes (24, 27, 41). Our study demonstrated that the expression level of psrA was significantly upregulated in the fabT deletion mutant, but there was no consensus on predicted DNA palindrome sequences located in the promoter region of psrA.
FabT is a transcriptional regulator in the fab gene cluster and thus regulates the transcription of fatty acid synthesis and controls the membrane fatty acid composition in S. pneumoniae (24, 42, 43). The role of FabT in the regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis is well established. Opaque and transparent variants carry the same types of fatty acids but differ in their proportions (28). The opaque variants possess a relatively lower degree of UFAs in the cell membrane. The fabT knockout can also upregulate the entire fab gene cluster, with the exception of fabM, and leads to decreased levels of UFAs coupled with an increase of saturated fatty acids (SFAs) (24). However, there is a putative FabT-binding sequence upstream the fabM, and FabT can generate a FabT-DNA complex with the FabT-binding site upstream of fabM (31). This indicated that FabT can regulate fabM expression. Indeed, we found that fabM expression levels were increased using both transcriptome and qRT-PCR analyses. FabM is an essential enzyme responsible for UFA synthesis in pneumococci. Therefore, a possible explanation for the higher proportion of transparent variants might be associated with the upregulated fabM in the D39ΔfabT mutant.
Colonization of the nasopharyngeal mucosa is an essential initiative step in the pathogenesis of pneumococcal disease and involves direct interaction between pneumococcal adhesins and specific receptors on host epithelial cells. During colonization, S. pneumoniae expresses low levels of CPS (transparent type) to enhance the exposure of cell surface proteins and promote binding to epithelial cells. In contrast, S. pneumoniae expresses high-level CPS (opaque type) during systemic infection to evade complement-mediated opsonophagocytosis (6). Based on the colony morphology and impaired capsule phenotypes we observed in the ΔfabT mutant, we hypothesized that deletion of fabT most likely resulted in enhanced adherence to epithelial cells and increased nasopharynx colonization in mice. However, the result was quite counterintuitive since the encapsulated ΔfabT mutant displayed reduced adherence to A549 cells and colonization in the mouse nasopharynx. These results suggested that in addition to the reduction of the capsule caused by the phase variable ΔfabT mutant, other components of surface structures related to adhesion and invasion, such as teichoic acids or surface proteins, were also affected.
Although the precise intermediate steps remain to be identified, the results of the present study describe a new function of transcriptional regulator FabT during the process of phase variation and the expression of capsule, resulting in attenuated bacterial virulence. The site-specific recombinase PsrA in the type I RM system SpnD39III was able to catalyze the inversion of IR1 and IR3 but not IR2. The phenotypic variation depends only on the activity of PsrA, not the recombination of hsdS alleles. FabT is essential for the negative feedback regulation of PsrA and an unknown endonuclease. The underlying mechanism of how FabT affects the recombinase PsrA and what virulence factors besides capsule are affected in the different variation phases will be further investigated in our future study.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains and growth conditions.
The strains used in this study are derivatives of strain D39 (Table S2). For growth in liquid cultures, S. pneumoniae strains were incubated in Todd-Hewitt broth (Difco, BD Diagnostics, Sparks, MD, USA) or supplemented with 0.5% yeast extract (THY medium) broth at pH 7.4 unless otherwise stated. For transformation, cultures growing in C+Y medium (C medium supplemented with 0.8% yeast extract) (pH 8.0) were induced with synthetic competence-stimulating peptide (CSP-1; China Peptides, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China) as previously described (44). For growth on solid medium, blood agar plates (Chongqing Pangtong, Chongqing, People’s Republic of China) or tryptic soy agar (TSA; BD Diagnostics) were used. Broth and plates were cultivated at 37°C with 5% CO2. Antibiotic selection was used at the following concentrations: streptomycin, 150 μg/ml; kanamycin, 200 μg/ml; spectinomycin, 50 μg/ml for Escherichia coli and 200 μg/ml for S. pneumoniae.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study. Download Table S2, PDF file, 0.1 MB (149.5KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Strain constructions.
The construction of pneumococcal mutants was carried out in D39s, a streptomycin-resistant derivative of strain D39 (45). Unencapsulated D39Δcps mutants were constructed by unmarked deletion of the entire cps2A promoter region dexB-cps2A as previously described (46). In brief, the up- and downstream sequences of the dexB-cps2A intergenic region were amplified with primer pairs Pr1901/1902 and Pr1903/1904 from D39s, and the new Janus cassette (referred to as JC1) was amplified with Pr1905/1906 from the strain TH7457 (19). The overlap extension fusion PCR was performed with Pr1901/1904 before being transformed into D39s to generate D39ΔdexB-cps2A::JC1. The up- and downstream sequences of the dexB-cps2A region were then amplified with Pr1901/1907 and Pr1908/1904 from D39s and fused by overlap primer Pr1901/1904. The fusion PCR product was transformed into D39ΔdexB-cps2A::JC1 to generate unmarked D39Δcps mutant.
To construct the unmarked deletion mutant ΔfabT, first the upstream (primers Pr1917/1910) and downstream (primers Pr1913/1914) sequences of the fabT gene were fused with JC1 (primers Pr1911/1912) with primers Pr1917/1914 and transformed into the background strain to generate the ΔfabT::JC1 mutant. Strain ΔfabT was then constructed by transforming the amplicon of the fusion PCR product, in which upstream (primers Pr1917/1915) and downstream (primers Pr1916/1914) sequences were overlapped with primers Pr1917/1914.
The complemented FabT was constructed by using suicide vector pPEPZ (47), which integrates efficiently in S. pneumoniae. Through the homologous fragment carried on the plasmid, the insert can be integrated upstream of spd_1736 and is a nonessential pseudogene. Upstream of the pPEPZ multiple cloning site, the expression of the insert is regulated by a Plac promoter, and the lack of LacI repressor in S. pneumoniae enabled constitutive expression from the construct. The sequence fabT-FLAG3 was amplified with primers Pr2043/2034 and Pr2035/2044 and then overlapped with Pr2043/2044. The plasmid and DNA fragment were digested with BglII and XhoI, followed by ligation with T4 DNA ligase. To construct the complementary strains, the resulting plasmid pPEPZ-Plac-RBS-fabT-FLAG3 was used to transform into the ΔfabT mutants.
For the psrA frameshift mutants, in order to create the mutant in all six hsdS alleles, the homologous sequence was amplified in the intergenic region of IR3.1-IR3.2 (primers Pr1994/2010 and Pr2013/1975) that does not undergo inversion. After fusion PCR of JC1 (primers Pr2011/2012) with primers Pr1994/1975, the amplicon was transformed into the background strains to insert the JC1 into the invertase PsrA. The frameshift mutant sequence was amplified with Pr1994/2008 and Pr2007/1975. The resulting fusion PCR amplicons were transformed into the corresponding JC1 replacement derivatives to generate psrA frameshift mutants (22). All of the primers used in this study are listed in Table S3. The transformation of S. pneumoniae was carried out by natural transformation essentially as previously described (48).
Primers used in this work. Download Table S3, PDF file, 0.04 MB (46.7KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran exclusion assay.
The thickness of capsule was determined by measuring the zone of exclusion of FITC-dextran (2,000 kDa; Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) based on published methods (49, 50). In brief, bacteria were cultured in 5 ml THY, harvested during the exponential growth phase by centrifugation at 3,000 × g for 5 min, and washed once with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and 20 μl of bacteria was mixed with 2 μl of a 10-mg/ml stock solution of FITC-dextran for staining. The stained sample was mounted on slides and visualized using a ×100 objective.
Immunofluorescence microscopy.
Capsular polysaccharides of the D39s and D39ΔfabT mutant were detected by immunofluorescence microscopy as previously described (51). Briefly, pneumococcus type 2 serum (SSI Diagnostica, Denmark) was used as the primary antibody at a dilution of 1:50, and goat anti-mouse IgG-PE (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) was used as the secondary antibody at a dilution of 1:500. Finally, images were obtained with a Nikon Eclipse 80i microscope.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
To determine the capsule morphology, bacteria were grown to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.5 in THY and harvested by centrifugation. The bacterial pellets were fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 24 h, embedded into 2% agarose, and processed by the Electron Microscopy Research Service of Chongqing Medical University. Capsule thickness was determined by measuring 20 randomly chosen cells using Image J software (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/download.html).
Capsule preparation and quantification of the glucuronic acid content.
Samples for the determination of the capsular glucuronic acid amounts were prepared as follows. Bacteria were grown in THY under semiaerobic conditions as described above. The whole-cell CPS were prepared in PBS, and cultures were harvested at an OD600 of 0.5. An aliquot of 6 ml was pelleted at 6000 × g for 5 min and washed with PBS and then suspended in 500 μl Tris-HCl, pH 7, and 1 mM MgSO4 as whole-cell CPS samples. To determine the amount of CPS attached to the cell wall, pellets were suspended in 1 ml PBS with 2% wt/vol SDS preheated to 100°C. Cells were heated at 100°C for 30 min. The cell walls were washed 3 times in PBS to completely remove SDS and then suspended in 300 μl Tris-HCl/MgSO4 buffer, treated with 40 units of mutanolysin (Sigma), and incubated overnight at 37°C. The samples were then treated with 100 μg proteinase K at 56°C for 4 h. The glucuronic acid of the cell wall-associated CPS or whole-cell CPS was quantified using the method for quantitative determination of uronic acids as previously described (52).
RNAseq analysis.
The RNAprotect bacterial reagent and RNeasy Protect bacterial kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) were employed for RNA extraction according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNAseq was performed at Novogene Bioinformatics Technology (Beijing, People’s Republic of China). Trimmed reads were mapped to the genome of S. pneumoniae D39 as the reference genome (GenBank Accession number NC_008533.2). Differential expression analysis of two groups (two biological replicates per group) was performed using the DESeq R package 1.18.0. The resulting P values were adjusted using Benjamini and Hochberg’s approach for controlling the false-discovery rate. Genes with an adjusted P value of <0.05 found by DESeq were assigned as differentially expressed.
qRT-PCR.
RNA extraction was performed as described above. PrimeScript RT master mix (TaKaRa, Beijing) was used to prepare cDNA from total RNA according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The primers used in this study are listed in Table S3. gyrB was amplified with primers Pr1930/1931 as an internal control for the constitutively expressed gene. The relative expression level was calculated using the average mean cycle threshold value for the target gene for each sample and gyrB. The results of representative experiments are presented as the means of three replicates ± standard deviations.
Colony phase variation observation.
Observation of pneumococcal colony opacity was carried out with TSA plates supplemented with catalase (Sigma) as described previously (53). Briefly, S. pneumoniae was grown to an OD600 of 0.5 in THY. The culture was then diluted with PBS at 1:10,000 to approximately 104 CFU/ml. Then, 50 μl of diluted bacteria was mixed with 100 μl of catalase work solution (20 mg/ml) and spread on TSA plates and incubated in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C for the indicated times. The observation of pneumococcal colonies was carried out with a Nikon Eclipse Ti inverted microscope. The plate was put on the stage with the open side up and an LED spotlight placed diagonally above was used to provide an oblique and transmitted light to observe the colony. Each experiment was repeated at least three times.
Determination of the inversion configuration of IRs in genomic DNA.
Forward and reverse configurations of IRs in the hsdS locus were detected by qPCR as described previously (23). Briefly, the template genomic DNA (gDNA) of each strain was extracted using a TIANamp bacterial DNA kit (Tiangen, Beijing, People’s Republic of China), and 20 ng of genomic DNA was used as the template for each reaction. The primers used to determine the inversions of three IRs are listed in Table S3. To determine the relative configuration of a particular IR, the average cycle threshold (CT) of each inverted repeat was first normalized by subtracting the CT of the internal reference Pr2001/1995 to obtain ΔCT. ΔCT values for each IR in the forward and reverse states were normalized again with the mean value of IR3R as a reference in each strain to obtain ΔΔCT. The relative amplification level was then calculated according to the equation 2ΔΔCT-For and 2ΔΔCT-Rev, and the total amplification level was defined as 100%, which was the total value of 2ΔΔCT-For and 2ΔΔCT-Rev.
hsdS quantification.
The hsdS′ and hsdS″ genes lack independent transcription and are almost transcriptionally silent (23). Thus, the specific sequence in the transcript of hsdS was quantitated to assess the relative abundance of allelic hsdS genes in the mixture population. The cDNA prepared above was used as the template. Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed with primer pairs Pr2005/1974, Pr2005/1970, Pr1992/1970, Pr1994/1974, Pr2005/1971, and Pr1992/1971 to detect the specific sequence in hsdSA to -F, respectively. As an internal reference for PCR, the 5′ noninvertible region shared by the six hsdS alleles was also amplified with primers Pr2001/1995. The amplification efficiency between different primers was almost the same. The average CT of each hsdS allele was first normalized by subtracting the CT of the internal reference Pr2001/1995 to obtain ΔCT. ΔCT values for hsdS alleles were normalized again with the mean value of hsdSA as a reference in each strain to obtain ΔΔCT. The data from one representative experiment are presented as the mean value of triplicate samples ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) for each strain. Each experiment was repeated at least three times.
Adhesion and antiphagocytic assay.
Pneumococcal adherence and invasion assays with A549 human type II pneumocytes were performed in 24-well plates. Confluent epithelial cells (∼2 × 105 cells/well) were inoculated with 2 × 107 CFU pneumococci at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1:100 and incubated in Dulbecco’s minimal essential medium (DMEM) at 37°C in the presence of 5% CO2 for 1 h. Subsequently, the cells were rinsed five times with PBS to remove unbound bacteria. For isolation of pneumococci that were taken up by the cells, extracellular bacteria were killed by treatment with gentamicin (100 μg/ml) and penicillin G (10 μg/ml). The intracellular pneumococci were recovered after lysing of the cells with double-distilled water (ddH2O) and plated on blood agar plates with the appropriate dilution. The amount of intracellular surviving bacteria per well was then determined. Each experiment was repeated at least three times. The results of representative experiments are presented as the means of three replicates ± standard errors. Phagocytosis of pneumococci was determined with mouse peritoneal primary macrophages. The remaining steps were the same as described above.
Mouse infection assays.
Mouse infection assays were performed as previously described (51, 54, 55). Mice were obtained and raised at the experimental animal center of Chongqing Medical University. All the animal experiments were discussed with and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Chongqing Medical University. All procedures were performed according to the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and conformed to animal protection laws of the People’s Republic of China and applicable guidelines. The D39s and D39ΔfabT mutant used for infection were grown to an OD600 of 0.5 in THY. Bacteria were washed and suspended in PBS. For the lung infection model, C57BL/6 mice (6 to 8 weeks old, male) were infected intratracheally with 1.5 × 107 CFU and 1 × 108 CFU of S. pneumoniae for pneumonia model and survival assay, respectively. To determine the organ involvement, blood aliquots and nasal lavage samples were collected from mice following induction of general euthanasia at 48 h after infection. Lung and spleen whole tissues were homogenized. Bacterial counts in the blood as well as organ homogenates were determined by separately plating serial dilutions. The results were presented as the means of three replicates ± the standard deviation (SD). Mouse survival was monitored daily for 7 days.
For the sepsis model, C57BL/6 mice (6 to 8 weeks old, male) were infected intraperitoneally with 100-μl volumes of S. pneumoniae. The CFU/mouse were 776 and 600 for D39s and the D39ΔfabT mutant, respectively. Survival was recorded every 12 h until death.
Statistical analysis.
All analyses were performed with Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). The data were statistically analyzed with two-tailed unpaired Student’s test or the nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test. Statistical significance was defined by P < 0.05 (*), <0.01 (**), and <0.001 (***).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Jingren Zhang for providing strain D39 and synthetic Janus cassette 1.
This work was supported by Projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81772153 and 81871698), and J.Z. was supported by a Chongqing graduate scientific research innovation project (CYB19163).
Footnotes
Citation Zhang J, Ye W, Wu K, Xiao S, Zheng Y, Shu Z, Yin Y, Zhang X. 2021. Inactivation of transcriptional regulator FabT influences colony phase variation of Streptococcus pneumoniae. mBio 12:e01304-21. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01304-21.
Contributor Information
Xuemei Zhang, Email: zhangxuemei@cqmu.edu.cn.
Craig R. Roy, Yale University School of Medicine
REFERENCES
- 1.Der Poll TV, Opal SM. 2009. Pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia. Lancet 374:1543–1556. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lee CJ, Banks SD, Li JP. 1991. Virulence, immunity, and vaccine related to Streptococcus pneumoniae. Crit Rev Microbiol 18:89–114. doi: 10.3109/10408419109113510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Black RE, Cousens S, Johnson HL, Lawn JE, Rudan I, Bassani DG, Jha P, Campbell H, Walker CF, Cibulskis R, Eisele T, Liu L, Mathers C. 2010. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2008: a systematic analysis. Lancet 375:1969–1987. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60549-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jedrzejas MJ. 2001. Pneumococcal virulence factors: structure and function. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:187–207. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.65.2.187-207.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Paton JC, Trappetti C. 2019. Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharide. Microbiol Spectr 7:7.2.33. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0019-2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kim JO, Weiser JN. 1998. Association of intrastrain phase variation in quantity of capsular polysaccharide and teichoic acid with the virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis 177:368–377. doi: 10.1086/514205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Waite RD, Penfold DW, Struthers JK, Dowson CG. 2003. Spontaneous sequence duplications within capsule genes cap8E and tts control phase variation in Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes 8 and 37. Microbiology (Reading) 149:497–504. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Weiser JN. 1998. Phase variation in colony opacity by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb Drug Resist 4:129–135. doi: 10.1089/mdr.1998.4.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tauseef I, Ali YM, Bayliss CD. 2013. Phase variation of PorA, a major outer membrane protein, mediates escape of bactericidal antibodies by Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun 81:1374–1380. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01358-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chopra-Dewasthaly R, Spergser J, Zimmermann M, Citti C, Jechlinger W, Rosengarten R. 2017. Vpma phase variation is important for survival and persistence of Mycoplasma agalactiae in the immunocompetent host. PLoS Pathog 13:e1006656. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Waite RD, Struthers JK, Dowson CG. 2001. Spontaneous sequence duplication within an open reading frame of the pneumococcal type 3 capsule locus causes high-frequency phase variation. Mol Microbiol 42:1223–1232. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McEllistrem MC, Ransford JV, Khan SA. 2007. Characterization of in vitro biofilm-associated pneumococcal phase variants of a clinically relevant serotype 3 clone. J Clin Microbiol 45:97–101. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01658-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hilton T, Rosche T, Froelich B, Smith B, Oliver J. 2006. Capsular polysaccharide phase variation in Vibrio vulnificus. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6986–6993. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00544-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.De Angelis G, Moschioni M, Muzzi A, Pezzicoli A, Censini S, Delany I, Lo Sapio M, Sinisi A, Donati C, Masignani V, Barocchi MA. 2011. The Streptococcus pneumoniae pilus-1 displays a biphasic expression pattern. PLoS One 6:e21269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hiramune T, Onishi K, Kikuchi N, Yanagawa R. 1991. Phase variation of pili of Corynebacterium pilosum. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B 38:303–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1991.tb00875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.van Putten JP. 1993. Phase variation of lipopolysaccharide directs interconversion of invasive and immuno-resistant phenotypes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. EMBO J 12:4043–4051. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weiser JN, Love JM, Moxon ER. 1989. The molecular mechanism of phase variation of H. influenzae lipopolysaccharide. Cell 59:657–665. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Weiser JN, Austrian R, Sreenivasan PK, Masure HR. 1994. Phase variation in pneumococcal opacity: relationship between colonial morphology and nasopharyngeal colonization. Infect Immun 62:2582–2589. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.6.2582-2589.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Li J, Li JW, Feng Z, Wang J, An H, Liu Y, Wang Y, Wang K, Zhang X, Miao Z, Liang W, Sebra R, Wang G, Wang WC, Zhang JR. 2016. Epigenetic switch driven by DNA inversions dictates phase variation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. PLoS Pathog 12:e1005762. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Manso AS, Chai MH, Atack JM, Furi L, De Ste Croix M, Haigh R, Trappetti C, Ogunniyi AD, Shewell LK, Boitano M, Clark TA, Korlach J, Blades M, Mirkes E, Gorban AN, Paton JC, Jennings MP, Oggioni MR. 2014. A random six-phase switch regulates pneumococcal virulence via global epigenetic changes. Nat Commun 5:5055. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Oliver MB, Basu Roy A, Kumar R, Lefkowitz EJ, Swords WE. 2017. Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4 phase-locked opacity variants differ in virulence phenotypes. mSphere 2:e00386-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00386-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.De Ste Croix M, Chen KY, Vacca I, Manso AS, Johnston C, Polard P, Kwun MJ, Bentley SD, Croucher NJ, Bayliss CD, Haigh RD, Oggioni MR. 2019. Recombination of the phase-variable spnIII locus is independent of all known pneumococcal site-specific recombinases. J Bacteriol 201:e00233-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00233-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li JW, Li J, Wang J, Li C, Zhang JR. 2019. Molecular mechanisms of hsdS inversions in the cod locus of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 201:e00581-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00581-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lu YJ, Rock CO. 2006. Transcriptional regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol 59:551–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Marrakchi H, Choi KH, Rock CO. 2002. A new mechanism for anaerobic unsaturated fatty acid formation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Biol Chem 277:44809–44816. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208920200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Marrakchi H, Dewolf WE Jr, Quinn C, West J, Polizzi BJ, So CY, Holmes DJ, Reed SL, Heath RJ, Payne DJ, Rock CO, Wallis NG. 2003. Characterization of Streptococcus pneumoniae enoyl-(acyl-carrier protein) reductase (FabK). Biochem J 370:1055–1062. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jerga A, Rock CO. 2009. Acyl-Acyl carrier protein regulates transcription of fatty acid biosynthetic genes via the FabT repressor in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Biol Chem 284:15364–15368. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C109.002410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Aricha B, Fishov I, Cohen Z, Sikron N, Pesakhov S, Khozin-Goldberg I, Dagan R, Porat N. 2004. Differences in membrane fluidity and fatty acid composition between phenotypic variants of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 186:4638–4644. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.14.4638-4644.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Carvalho SM. 2012. Understanding the relationship between central metabolism and virulence in the human pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae. https://core.ac.uk/reader/303718342.
- 30.Carvalho SM, Kloosterman TG, Manzoor I, Caldas J, Vinga S, Martinussen J, Saraiva LM, Kuipers OP, Neves AR. 2018. Interplay between capsule expression and uracil metabolism in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39. Front Microbiol 9:321. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Eijkelkamp BA, Begg SL, Pederick VG, Trapetti C, Gregory MK, Whittall JJ, Paton JC, McDevitt CA. 2018. Arachidonic acid stress impacts pneumococcal fatty acid homeostasis. Front Microbiol 9:813. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Durmort C, Ercoli G, Ramos-Sevillano E, Chimalapati S, Haigh RD, De Ste Croix M, Gould K, Hinds J, Guerardel Y, Vernet T, Oggioni M, Brown JS. 2020. Deletion of the zinc transporter lipoprotein AdcAII causes hyperencapsulation of Streptococcus pneumoniae associated with distinct alleles of the type I restriction-modification system. mBio 11:e00445-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00445-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Honsa ES, Johnson MD, Rosch JW. 2013. The roles of transition metals in the physiology and pathogenesis of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 3:92. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ogunniyi AD, Mahdi LK, Jennings MP, McEwan AG, McDevitt CA, Van der Hoek MB, Bagley CJ, Hoffmann P, Gould KA, Paton JC. 2010. Central role of manganese in regulation of stress responses, physiology, and metabolism in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 192:4489–4497. doi: 10.1128/JB.00064-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Whalan RH, Funnell SG, Bowler LD, Hudson MJ, Robinson A, Dowson CG. 2005. PiuA and PiaA, iron uptake lipoproteins of Streptococcus pneumoniae, elicit serotype independent antibody responses following human pneumococcal septicaemia. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 43:73–80. doi: 10.1016/j.femsim.2004.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Meiers M, Volz C, Eisel J, Maurer P, Henrich B, Hakenbeck R. 2014. Altered lipid composition in Streptococcus pneumoniae cpoA mutants. BMC Microbiol 14:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Claverys JP, Prudhomme M, Mortier-Barriere I, Martin B. 2000. Adaptation to the environment: Streptococcus pneumoniae, a paradigm for recombination-mediated genetic plasticity? Mol Microbiol 35:251–259. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hathaway LJ, Brugger SD, Morand B, Bangert M, Rotzetter JU, Hauser C, Graber WA, Gore S, Kadioglu A, Muhlemann K. 2012. Capsule type of Streptococcus pneumoniae determines growth phenotype. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002574. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Weiser JN, Bae D, Epino H, Gordon SB, Kapoor M, Zenewicz LA, Shchepetov M. 2001. Changes in availability of oxygen accentuate differences in capsular polysaccharide expression by phenotypic variants and clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun 69:5430–5439. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5430-5439.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Grove A. 2013. MarR family transcription factors. Curr Biol 23:R142–R143. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zuo G, Chen ZP, Jiang YL, Zhu Z, Ding C, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Zhou CZ, Li Q. 2019. Structural insights into repression of the pneumococcal fatty acid synthesis pathway by repressor FabT and co-repressor acyl-ACP. FEBS Lett 593:2730–2741. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Eraso JM, Olsen RJ, Beres SB, Kachroo P, Porter AR, Nasser W, Bernard PE, DeLeo FR, Musser JM. 2016. Genomic landscape of intrahost variation in group A streptococcus: repeated and abundant mutational inactivation of the fabT gene encoding a regulator of fatty acid synthesis. Infect Immun 84:3268–3281. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00608-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Faustoferri RC, Hubbard CJ, Santiago B, Buckley AA, Seifert TB, Quivey RG Jr.. 2015. Regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis by the global regulator CcpA and the local regulator FabT in Streptococcus mutans. Mol Oral Microbiol 30:128–146. doi: 10.1111/omi.12076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Håvarstein LS, Coomaraswamy G, Morrison DA. 1995. An unmodified heptadecapeptide pheromone induces competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:11140–11144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.24.11140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sung CK, Li H, Claverys JP, Morrison DA. 2001. An rpsL cassette, Janus, for gene replacement through negative selection in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5190–5196. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.11.5190-5196.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wen Z, Sertil O, Cheng Y, Zhang S, Liu X, Wang WC, Zhang JR. 2015. Sequence elements upstream of the core promoter are necessary for full transcription of the capsule gene operon in Streptococcus pneumoniae strain D39. Infect Immun 83:1957–1972. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02944-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Keller LE, Rueff AS, Kurushima J, Veening JW. 2019. Three new integration vectors and fluorescent proteins for use in the opportunistic human pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae. Genes 10:394. doi: 10.3390/genes10050394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yother J, McDaniel LS, Briles DE. 1986. Transformation of encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 168:1463–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1463-1465.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gates MA, Thorkildson P, Kozel TR. 2004. Molecular architecture of the Cryptococcus neoformans capsule. Mol Microbiol 52:13–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2003.03957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schaffner TO, Hinds J, Gould KA, Wuthrich D, Bruggmann R, Kuffer M, Muhlemann K, Hilty M, Hathaway LJ. 2014. A point mutation in cpsE renders Streptococcus pneumoniae nonencapsulated and enhances its growth, adherence and competence. BMC Microbiol 14:210. doi: 10.1186/s12866-014-0210-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zheng Y, Zhang X, Wang X, Wang L, Zhang J, Yin Y. 2017. ComE, an essential response regulator, negatively regulates the expression of the capsular polysaccharide locus and attenuates the bacterial virulence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Front Microbiol 8:277. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G. 1973. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem 54:484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Li J, Wang J, Jiao F, Zhang J-R. 2017. Observation of pneumococcal phase variation in colony morphology. Bio-Protocol 7:e2434. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ye W, Zhang J, Shu Z, Yin Y, Zhang X, Wu K. 2018. Pneumococcal LytR protein is required for the surface attachment of both capsular polysaccharide and teichoic acids: essential for pneumococcal virulence. Front Microbiol 9:1199. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wu K, Xu H, Zheng Y, Wang L, Zhang X, Yin Y. 2016. CpsR, a GntR family regulator, transcriptionally regulates capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and governs bacterial virulence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Sci Rep 6:29255. doi: 10.1038/srep29255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Verification of fabT mutant strains. (A) Steady-state mRNA levels of fabT in fabT mutants; (B) FabT-Flag tag in complemented strain D39CΔfabT detected by Western blotting. Download FIG S1, TIF file, 0.08 MB (86.2KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
(A to D) The qRT-PCR results for the (A) fab gene cluster (B) adcAII (C) hsdM, and (D) mutS in the D39s and D39s derivative strains. Download FIG S2, TIF file, 0.1 MB (109.1KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Quantitative assessment of the stability in the colony opacity phenotypes among the D39s derivatives. Download Table S1, PDF file, 0.05 MB (54.2KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Capsule production in inactivated psrA mutants. (A and B) Amounts of (A) whole-cell and (B) cell wall CPS using the uronic acid assay. Download FIG S3, TIF file, 0.09 MB (90.3KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Detection of IRs mediated inversion. (A) Positions of the primers used for detection of the orientation of IRs in the SpnD39III locus. (B) Primers for detecting IR inversion and corresponding hsdS alleles. (C and E) The relative abundance of the configuration of each IR was normalized to the IR3R in (C) D39s and (E) D39Δcps. (D and F) Forward and reverse configurations of the target sequence flanked by IR1, IR2, and IR3 in (D) encapsulated and (F) unencapsulated strains. Download FIG S4, TIF file, 0.3 MB (281.1KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Steady-state mRNA levels of TRD2.1 quantified using qRT-PCR. (A) Schematic map representing the hsdSA variant with primers indicated. (B) qRT-PCR detection of TRD2.1. Download FIG S5, TIF file, 0.09 MB (97.1KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Methods used for hsdS allelic detection. (A) Schematic map of the organization in the SpnD39III locus and six alternative hsdS genes. (B) The proportions of hsdS alleles in the mixed population. The red line indicates the two transcripts in the SpnD39III locus. The cDNA of the mixed population was used as the template. (C) Primer pairs used to detect the hsdS alleles. Download FIG S6, TIF file, 0.2 MB (217.2KB, tif) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study. Download Table S2, PDF file, 0.1 MB (149.5KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Primers used in this work. Download Table S3, PDF file, 0.04 MB (46.7KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2021 Zhang et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.