Abstract
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) has emerged as a mechanism that has been used to explain the formation of known organelles (e.g. nucleoli, promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies (PML NBs), etc) as well as other membraneless condensates (e.g. nucleosome arrays, DNA damage foci, X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) center, paraspeckles, stress granules, proteasomes, autophagosomes, etc). The formation of membraneless condensates could be triggered by proteins containing modular domains or intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) and nucleic acids. Multiple biological processes including transcription, chromatin organization, X-chromosome inactivation (XCI), DNA damage, tumorigenesis, autophagy, etc have been shown to utilize the principle of LLPS to facilitate these processes. This review will summarize the principle and components of LLPS, and describe how LLPS regulate these numerous biological processes and disruption of LLPS would cause disease formation. The role of LLPS in regulating normal cellular physiology and contributing to tumorigenesis will be discussed.
Keywords: Liquid-liquid phase separation, membraneless condensates, modular domains, intrinsically disordered regions
Introduction
Inside eukaryotic cells, many “membraneless” structures (e.g. nucleoli, Promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies (PML NBs), P bodies in C. elegans, etc) exist and perform critical functions [1,2]. Recently, these membraneless structures are shown to be formed through the principle of “liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS)” and they are renamed “membraneless condensates” or “biological condensates” [1-3]. Many important biological processes, including transcription, chromatin organization, X-chromosome inactivation (XCI), DNA damage response (DDR), tumorigenesis, autophagy, etc have been shown to utilize LLPS to generate the relevant membraneless condensates and achieve their specific functions [1-4]. However, the field of LLPS-mediated regulation of various biological processes is still in the primitive stage and the detailed molecular mechanisms and biological outcomes still require further intensive investigations.
In this review, the cell biological entities that constitute these membraneless condensates and the biophysical principles that generate these membraneless condensates inside cells will be discussed. In addition, the molecules that have been shown to trigger and regulate LLPS to facilitate the formation of membraneless condensates are described. Different biological processes, including chromatin organization and transcription, DNA damage repair, X-inactivation, protein turnover/degradation, ribonucleoprotein (RNP) particle formation, autophagy, tumorigenesis, synaptic vesicle active zone formation, etc will be discussed in the context of LLPS. The goal of the review will be to provide a concise and updated review of the field of LLPS since more detailed reviews have been published [1-3]. This review will try to present new perspectives so therapeutic approaches can be taken through further understanding of “membraneless condensates” and their role in crucial biological processes.
Cell biological entities as membraneless condensates
In contrast to the classical organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus that contain membranes surrounding their structure that can be easily discerned from a two-dimensional (2D) view, there are cellular compartments that are not contained by membranes [1-3]. These cellular compartments include nucleoli, P granules (C. elegans), Cajal bodies, nucleosome arrays, PML NBs, DNA damage foci, X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) compartment, paraspeckles, ribonucleoprotein (RNP) particles, stress granules, proteasomes, autophagosomes, synaptic vesicle active zones, etc [1-3]. These condensates assist the spatiotemporal control of many biological functions. For example, these condensates assemble proteins and/or nucleic acids via multivalent interactions to activate biochemical reactions [5] or to sequester biomolecules [6] via the increase of protein or RNA concentration. These condensates can also act as a sensor to respond to stresses, such as heat exposure or change of pH, as a survival strategy [7,8]. The questions become how these biomolecules can be held together inside the specific membraneless condensates so they can perform their specific functions.
Biophysical principles of liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) and critical components in inducing LLPS
From the examples of P granules in C. elegans, liquid-like properties similar to the behaviors of P granules have been shown in nucleoli, PML NBs, DNA repair foci, and stress granules [1,2]. From these studies, liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) is shown to be the biophysical principle governing the formation of membraneless condensates [1-3]. A single liquid phase can become two compositionally distinct liquid phases through LLPS, just like the “demixing” of oil and water as a classical example [1-3]. However, when condensates are observed in the cell-based studies, many aspects should be considered. It is common that the condensation in the cell milieu is aggregation as the proteins are overexpressed in this type of experiments. In this situation, the condensates will not have liquid-like properties. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) technique is a standard approach to demonstrate the liquid-like property of the condensates in a cell from a three-dimensional (3D) perspective [9]. When the target protein fused with a fluorescence label (e.g. GFP) condenses in live cells, the laser-bleached condensates will recover their fluorescence if the components inside the membraneless condensates can exchange with the surrounding medium in rapid time scales [9]. Furthermore, fusion and fission events among the condensates should be observed in the dynamic liquid-like condensates instead of aggregation [1-3]. Moreover, the biological relevance is the most critical aspect in interpreting the biomolecular condensates. Artificially, protein can condense at certain conditions as noticed in the field of crystallography for many years [10]. The biomolecular condensates observed in the cell might also be an artefact and thus one should carefully interpret whether the condensates have a functional relevance.
Membraneless condensates usually contain multivalent molecules that allow for intra- and inter-molecular interactions [11]. Heterotypic, multivalent interactions between proteins and/or nucleic acids are the basic biochemical principle of LLPS [12,13]. For LLPS to control and regulate the formation of membraneless condensates, there are many critical players involved. Proteins with modular domains (e.g. between SH3 domain and proline rich motifs (PRMs)) can interact and phase separate to form liquid droplets (Figure 1A) [11,14]. Valency (the number of interacting modules) and affinity determine the ability to control phase separation [15,16]. In contrast, proteins with intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) but still contain repeat sequences can also exhibit multivalent intermolecular interactions (Figure 1B) [12,17]. However, charged amino acids and aromatic amino acids are observed to be important for interactions between these IDRs [18]. IDRs can also go through homotypic or heterotypic interactions. Nucleic acids, especially RNAs, are shown to promote LLPS stimulated by interactions between IDRs and can exist in these membraneless condensates [1-3,19]. In these cases, RNA recognition motifs (RRMs) exist in these proteins in addition to the IDRs [1-3,19]. However, RNA itself can also promote LLPS, as shown in the trinucleotide RNA repeats in neurodegenerative diseases [20]. Finally, multiple functional roles of formation of these membraneless condensates include: 1) serving as reaction center to accelerate reaction kinetics, 2) regulating the specificity of biomolecular reactions, 3) sequestering “unfavored” molecules, 4) buffering biomolecule concentrations, and 5) rapid switching of biomolecular functions [1-3].
Figure 1.
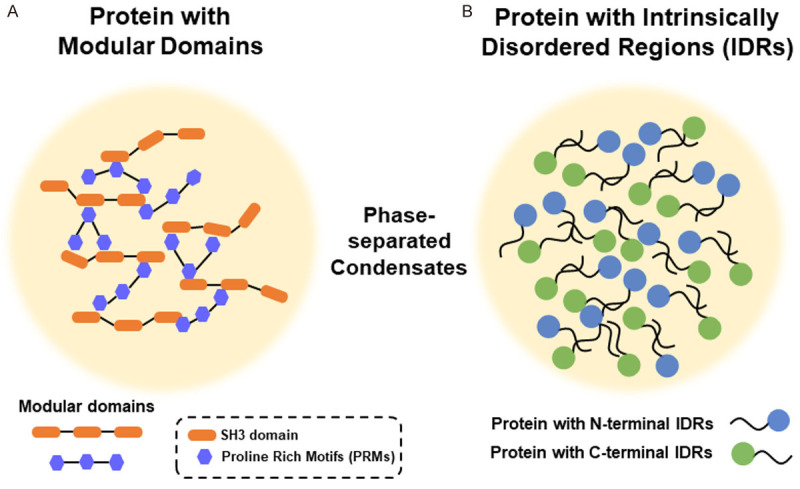
Proteins with either modular domains (A) or intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) (B) are able to form liquid-like phase-separated condensates. (A) Protein can form phase-separated condensates through the modular domains. One of the examples is SH3 domain (a typical modular domain) that interacts with proline rich motifs (PRMs). (B) Protein with intrinsically disordered domains (IDRs) can form phase-separated condensates through either N-terminal or C-terminal IDRs.
From the description of the above principles, this review will describe LLPS-induced organelles or genome organization in eukaryotic cells from three different aspects: 1) chromatin organization and gene transcription; 2) RNA or DNA-induced phase-separated condensates; 3) stress-induced or neural activity-induced organelles or condensates. We hope that categorization of membraneless condensates under this framework will help to better understand the principles of LLPS used by eukaryotic cells to carry out different physiological functions. In contrast, misregulation of LLPS has been shown to induce pathological consequences, including the tumorigenesis process [21]. The relationship between misregulated LLPS and tumorigenesis will be further discussed in later sections.
Nucleoli
Nucleoli are the first membraneless condensates observed, in contrast to the membrane-bound structures such as endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus [22]. Nucleoli are responsible for ribosome biogenesis and are where ribonucleoprotein particle assembly occurs [23]. It has been recently proposed that the formation of nucleoli undergoes LLPS and nucleoli represent a classical example of multilayered membraneless condensates [24].
Chromatin organization and transcription
LLPS has recently been shown to play a crucial role in chromatin organization and gene transcription [25-28]. In vitro reconstitution of chromatin undergoes histone tail-driven LLPS that can produce dense liquid droplets after injection into nucleus [29]. Acetylation of histone by p300 counteracts chromatin phase separation through dissolving and decreasing droplet formation [29]. In contrast, bromodomain proteins (e.g. BRD4) through binding to acetylated chromatin induce a new phase-separated chromatin state with droplets of distinct physical properties [29]. This new chromatin state can mix with unmodified chromatin droplets and together they mimic a nuclear chromatin subdomain [29]. Therefore, LLPS represents a principle driving either intrinsic or regulated states of chromatin organization [29].
Diverse transcription factors can form phase-separated condensates with Mediator through their activation domains to activate gene expression [27]. The transcription factors (TFs) tested include OCT4 and GCN4 [27]. In addition, estrogen can enhance the phase separation between ligand-binding estrogen receptor and Mediator [27]. The relationship between Mediators and RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is revealed by the co-localization of Mediator and Pol II that show the properties of phase-separated condensates [30]. Clusters of Mediators recruited by transcription factors at enhancer elements interact with large Pol II clusters to form transcriptional condensates in vivo [30]. Super-enhancers (SEs) (i.e. clusters of enhancers) represent the assembly of a high-density transcriptional apparatus that drives gene activation [28]. Transcriptional co-activators BRD4 and MED1 are enriched at SEs and form transcriptional condensates that exhibit properties of liquid-droplets [28]. The formation of phase-separated droplets can be mediated by the IDRs of BRD4 and MED1 to concentrate the transcription apparatus [28]. Another report shows that a FET family protein, TAF15, interacts with the c-terminal domain (CTD) of Pol II through its unique charge distribution inside the protein that favors phase separation to enhance localized RNA transcription [31]. All the above results describe the underlying principle of chromatin organization and gene transcription mediated by LLPS. A figure summarizes the results described above is shown (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
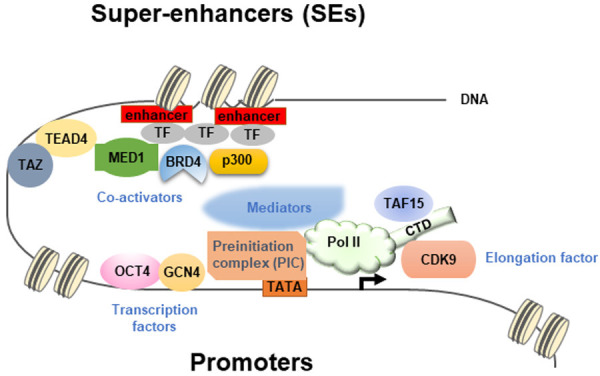
A summary of organization in the regions of promoters and super-enhancers (SEs) containing all the component proteins mediating gene transcription. The figure presents an overall picture of how the transcription factors, co-activators, mediators, and RNA Pol II work together to constitute a well-functional transcription apparatus. In the promoter region, OCT4 and GCN4 are representative transcription factors that interact with the preinitiation complex (PIC), Mediators, and RNA polymerase II (Pol II) to mediate gene transcription. The CTD domain of Pol II interacts with TAF15 and CDK9, a transcription elongation factor. In the super-enhancer region, the enhancer-binding transcription factors interact with MED1, BRD4, and p300 to further form a big transcription apparatus encompassing the promoter and enhancer regions. TAZ participates around the enhancer region through bridging by TEAD4 to MED1.
Inactivation of the Hippo signaling causes transcription factor TAZ to form phase-separated nuclear condensates with DNA-binding co-factor TEAD4, co-activators BRD4 and MED1, and transcription elongation factor CDK9 [32]. In contrast, activation of the Hippo signaling induces the phosphorylation of the coiled-coil (CC) domain in TAZ by LATS to prevent the phase-separation mediated by TAZ (Figure 3A) [32]. Deletion of the CC domain in TAZ also abolishes its phase-separation activity [32]. LLPS represents a mechanism for TAZ-mediated gene expression and its ability to promote tumorigenesis [32].
Figure 3.
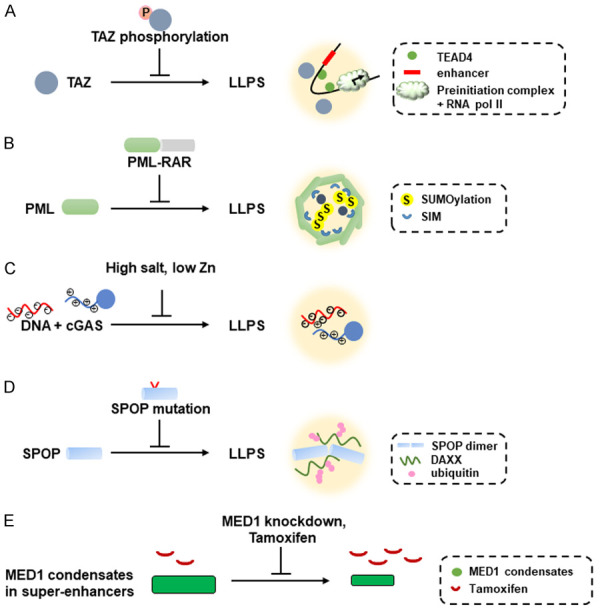
Disruption of LLPS through different mechanisms causes different human diseases as well as how chemotherapeutic drugs inhibit activation of oncogenes through shrinkage of MED1 condensates. The specific diseases are described in the text. A. Phosphorylation of the coiled-coil domain of TAZ inhibits the TAZ-mediated LLPS that involves TAZ, TEAD4, BRD4, and CDK9. B. PML-RAR chimeric proteins disrupt the formation of PML NBs that is mediated by SUMOylated PML proteins containing SIMs (SUMO-interacting motifs). C. Negatively-charged DNA interacts with positively-charged N-terminal domain of cGAS to form LLPS. High salt or low Zn concentration disfavor the LLPS formation between DNA and cGAS. D. Formation of LLPS between oligomerized SPOP and DAXX could be disrupted by mutated SPOP that is observed in prostate cancer and breast cancer. DAXX ubiquitination is also inhibited by SPOP mutations in cancer. E. Overexpression of MED1 in Tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells causes formation of large MED1 condensates and leads to dilution of Tamoxifen concentration in the condensates. Knockdown of MED1 or Tamoxifen treatment decreases the size of MED1 condensates and increases the concentration of Tamoxifen inside the MED1 condensates, leading to chemosensitivity to Tamoxifen.
PML
Promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies (PML NBs) are prototypic nuclear membraneless condensates that have been extensively investigated [33]. PML NBs are macromolecular multi-protein complexes. PML NBs exhibit the properties of phase-separated liquid-like droplets and have been speculated to undergo the LLPS process organized by heterotypic multivalent interactions between proteins and RNA molecules. PML is the essential component in PML NBs, which contains the RBCC motif (Ring finger domain, B box domain, coiled-coil domain) that is required for the assembly of PML NBs. The composition of PML NBs can switch rapidly through changes in scaffold concentration or valency [33]. Specifically, PML SUMOylation or mRNA concentration can control the compositions of PML NBs [33].
PML NBs have been shown to have physical contacts with chromatin. PML NBs contain chromatin associated factors such as histones (e.g. H3.3) and histone chaperones (e.g. H3.3 HIRA complex) [33]. PML NBs can be associated with the regulatory regions of active genes [33]. Regulation of transcription factor activity by modification, modulation of the availability of chromatin-associated factors, and establishment of permissive or restrictive chromatin domains are three mechanisms mediated by PML NBs in regulating transcription [33]. PML NBs have been shown to control specific cellular chromatin assembly pathways that regulate senescence and telomere maintenance [33].
Translocation between PML and RAR has been shown to be the event leading to acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) formation [33]. Due to the phase separation behavior induced by PML NBs, it is conceivable that chimeric protein PML-RAR would disrupt the phase-separated behaviors induced by PML (Figure 3B) [33]. Remission of APL induced by retinoic acid treatment would reflect the restoration of the phase-separation properties of PML NBs [33]. Therefore, LLPS that triggers the formation of PML NBs serves as a mechanism that could be disrupted by the PML-RAR chimeric protein, thus explaining the tumorigenesis mechanism of APL [33].
DNA damage response (DDR)
DNA damage response (DDR) induces damage-induced lncRNAs (dilncRNAs) that are synthesized by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) at DNA double strand break sites [34]. The synthesis of these dilncRNAs requires a RNA Pol II preinitiation complex, MED1, and CDK9, which are necessary for the formation of double strand break (DSB) foci [34]. In addition, dilncRNAs recruit other DDR proteins, such as 53BP1, into damage foci that exhibit the properties of phase-separated condensates [34]. DilncRNAs thereby trigger phase separation of DDR factors in DSB damage foci formation [34].
Another report shows that lncRNA LINP1 facilitates the formation of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) complex by competing with PAXX [35]. LINP1 goes through self-triggered phase separation via RNA-RNA interactions and forms filamentous Ku70/Ku80-containing condensates. Structural motifs in LINP1 that bind Ku are identified, which promote Ku multimerization and stabilization of the initial events of NHEJ by substituting PAXX [35]. For human tumors, LINP1 is overexpressed in multiple tumor types and mediates resistance to chemotherapy and ionizing radiation through RNA-dependent DNA repair mechanism (i.e. NHEJ) in tumors [35]. This report demonstrates the role of LINP1-induced LLPS in recruiting multiple Ku-NHEJ assemblies and promoting DNA-end joining in NHEJ in tumor cells [35].
lncRNAs (Xist, NEAT1) in LLPS
X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is an important biological process to regulate gene silencing in inactivated X chromosome [36]. One of the important players, lncRNA Xist, binds multiple proteins such as PTBP1, MATR3, TDP-43, and CELF1 through its multivalent E-repeat elements followed by self-aggregation and heterotypic protein-protein interactions to form a condensate in the inactive X (Xi)-compartment. Formation of the condensate is required for gene silencing and for anchoring Xist [37]. These E-repeat binding proteins, but not Xist, are essential for transition into Xist-independent XCI [37]. This result provides a novel mechanism for heritable gene silencing [37].
Another lncRNA, NEAT1, has been shown to serve as an architectural RNA to construct paraspeckles that exhibit the properties of phase-separated condensates [38]. The domains in NEAT1 that construct paraspeckles have been mapped, which shows that the middle domain of NEAT1 containing functionally redundant subdomains are important for paraspeckle assembly [38]. The subdomains in NEAT1 bind NONO/SFPQ and lead to in vitro formation of phase-separated condensates [38]. However, linking of NONO by an artificial method to mutant NEAT1 still triggers paraspeckle formation, indicating that enrichment of NONO dimers initiates the construction of phase-separated paraspeckles [38]. The example of NEAT1-triggered paraspeckle formation provides a good example of lncRNA-induced phase-separated condensates.
DEAD-box ATPases (DDXs) and organelle regulation
RNA-dependent DEAD-box ATPases (DDXs) have been shown to regulate the formation of RNA-containing phase-separated organelles in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes [39]. This process requires that DDXs stay in their ATP-bound form. ATP hydrolysis of the ATP-bound DDXs will result in compartment turnover and initiate the release of RNA into another DDX-containing compartment [39]. Therefore, RNA flux into and out of phase-separated condensates can be regulated by DDXs and change the composition and fate of RNP particles [39].
Stress granules
Eukaryotic cells under stress will form stress granules (SG) by shutting down translation and releasing mRNA molecules from polysomes [40,41]. Stress granule is a prominent type of RNP granule that responds to stress to form a dynamic and reversible cytoplasmic condensate in eukaryotic cells [40,41]. Under non-stress condition, the SG protein G3BP1 exists in an auto-inhibited state through intramolecular interactions between its IDRs and the arginine-rich region [40]. Under stress condition, unfolded mRNAs release the auto-inhibited conformation of G3BP1 that results in clustering of G3BP1 through protein-RNA interactions [40]. This process is followed by formation of G3BP1/RNA phase-separated condensates [40]. G3BP1 impedes RNA entanglement and recruits the client proteins to promote stress granule assembly [40]. Stress granules formation through LLPS arises from interactions across a core protein-RNA interaction network [40]. G3BP1 represents a molecular switch that responds to a rise in free RNA concentrations and triggers RNA-dependent LLPS [41]. Three IDRs located in G3BP1 regulate the intrinsic LLPS-forming tendency that can be modulated by phosphorylation inside the IDRs [41]. Extrinsic G3BP1-binding proteins can exert positive or negative regulation of the stress granule network [41]. RNP stress granule assembly also occurs through heterotypic multivalent interactions [40,41].
The proteasome shuttle protein UBQLN2 contains IDRs and exists inside stress granules. UBQLN2 can induce LLPS that requires its oligomerization [42]. Ubiquitin or polyubiquitin binding eliminates LLPS induced by UBQLN2 [42], reflecting the ability of UBQLN2 to act as shuttle protein and enable shuttling of clients out of stress granules after the interaction of UBQLN2 with ubiquitinated client proteins and reversal of phase separation induced by UBQLN2 [42].
DNA-induced LLPS
One prominent example of DNA-induced phase separation is that cytoplasmic DNA binds to cGAS to produce secondary messenger cGAMP and activates innate immune response [43]. Recent results show that DNA binding to cGAS induces phase-separated condensates where cGAS is activated (Figure 3C) [43]. The N-terminal IDRs of cGAS is identified to enhance phase separation and long DNA as well as Zn ion promotes DNA-induced cGAS phase separation (Figure 3C) [43]. Salt concentration also affects the cGAS enzymatic activity after binding to cytoplasmic DNA to cGAS (Figure 3C) [43].
Proteasome and autophagosomes
Proteasomes can form as nuclear foci that display liquid droplet properties under stress conditions (e.g. hyperosmotic stress) [44]. These foci are membraneless condensates containing ubiquitinated protein, p97 (Valosin-containing protein (VCP)), and numerous proteasome-interacting proteins. Improperly-assembled ribosomal proteins are the major substrates for degradation by proteasome. The substrate-shuttling factor, RAD23B, and ubiquitinated proteins are necessary for proteasome foci formation [44]. Multivalent interactions of two ubiquitin-associated domains (UBA) of RAD23B and K48-linked polyubiquitin (K48Ub) chains are important to trigger LLPS [44]. This result demonstrates the formation of nuclear proteasomes through ubiquitin-chain-mediated phase separation [44].
In another report, the scaffold protein, p62, assembles ubiquitin-tagged misfolded proteins into aggregates followed by engulfment and degradation by autophagosomes [45]. K63-linked polyubiquitination of p62 is required form p62 to form liquid-like droplets [45]. Similarly, polyubiquitin chain-mediated phase separation requires the PB1 domain and UBA domain of p62, leading to the degradation of p62 in autophagosomes [45]. Mutations of p62 discovered in patients with PDB (Padget’s disease of bone) that are located in the UBA domain of p62 affects p62-mediated phase separation [45]. This result links the anomaly of p62-induced phase separation to human disease [45].
Tumor suppressor SPOP (speckle-type POZ protein) gene has been shown to be mutated in multiple tumor types, especially in prostate cancer and breast cancer [46]. SPOP is localized in nuclear speckles and functions as a substrate adaptor of cullin3-Ring ubiquitin ligase (CRL3) [46]. SPOP and DAXX undergo phase separation and colocalize in membraneless condensates, which can be promoted by SPOP oligomerization [46]. SPOP mutations disrupt its phase separation and colocalization with DAXX as well as DAXX ubiquitination (Figure 3D) [46]. This report demonstrates that the tumorigenesis mechanism of SPOP mutations is caused by disruption of substrate-induced phase separation and colocalization of SPOP and DAXX.
Synaptic vesicle active zones
Neural circuits formation during neuronal development requires formation of synapses [47]. Every presynapse contains an active zone structure where ion channels and synaptic vesicles co-exist [47]. During the stage of presynpase development in C. elegans, LLPS is utilized by active zone scaffold proteins SYD-2 and ELKS-1 to form active zone that subsequently mature into a solid structure [47]. Mutant SYD-2 and ELKS-1 proteins show defects in active zone assembly and synapse function [47]. In vitro reconstitution of SYD-2 and ELKS-1 establishes liquid-phase scaffold which is essential for recruiting and incorporating downstream active zone proteins [47]. Therefore, LLPS is a crucial principle governing pre-synaptic active zone assembly that is important for subsequent synaptic functions [47].
LLPS in cancer therapy
Chemotherapy has been used for decades to treat cancer patients with certain degree of efficacy [48]. Recent results show that chemotherapeutic drugs partition selectively into condensates, which influences drug activity [48]. This partitioning behavior occurs through physicochemical properties independent of their molecular targets [48]. Drug resistance can occur through mechanisms that alter drug-partitioning condensates [48]. For example, MED1 condensates on the MYC oncogene are observed in ER+ breast cancer cells and can be enhanced by estrogen, whereas Tamoxifen treatment reduces these MED1 condensates (Figure 3E) [48]. For breast cancer cells containing ER mutations, Tamoxifen could not reduce these MED1 condensates [48]. Alternatively, MED1 overexpression in Tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells form larger MED1 condensates that dilute out the concentration of Tamoxifen in these condensates [48]. Knockdown of MED1 causes the shrinkage of the MED1 condensates and elevates the concentration of Tamoxifen inside these condensates (Figure 3E) and restores the chemosensitivity of these breast cancer cells to Tamoxifen [48]. Therefore, drug partitioning into condensates emerges as a novel mechanism that can be used to modulate drug activity.
Conclusions
For this review, we have tried to describe the basic principle of LLPS and summarize recent researches in the field of LLPS. More comprehensive reviews can be found in previous reviews [1-3]. As many cell biological processes have been extensively investigated, LLPS has been demonstrated to play a significant role in regulating and/or modulating these processes. Since the field of LLPS is still in the primitive stage, identifying crucial players involved in this process that may regulate or modulate critical biological processes will be important at this stage.
In addition to the normal physiological processes, disruption of LLPS has been shown to be involved in the tumorigenic mechanisms as described in this review. In contrast, disruption of LLPS-mediated MED1 condensates by knockdown of MED1 restores chemosensitivity of these tumor cells to Tamoxifen by shrinking MED1 condensates (Figure 3E) [48]. A summary of how disruption of LLPS that lead to tumorigenesis is presented (Figure 3A, 3B and 3D). It is foreseeable that many more examples of involvement of LLPS that contribute to tumorigenesis will be demonstrated in the future. Therefore, better understanding of LLPS and discovering the ways to manipulate LLPS will become important issues for researches in tumor biology. It is also important that the principle of LLPS may be mixed with other biological principles to co-regulate crucial cellular biology. A summary of different biological functions of LLPS-mediated membraneless condensates is presented (Figure 4). The interface between LLPS and other biological principles may become important issues for future biomedical researches.
Figure 4.
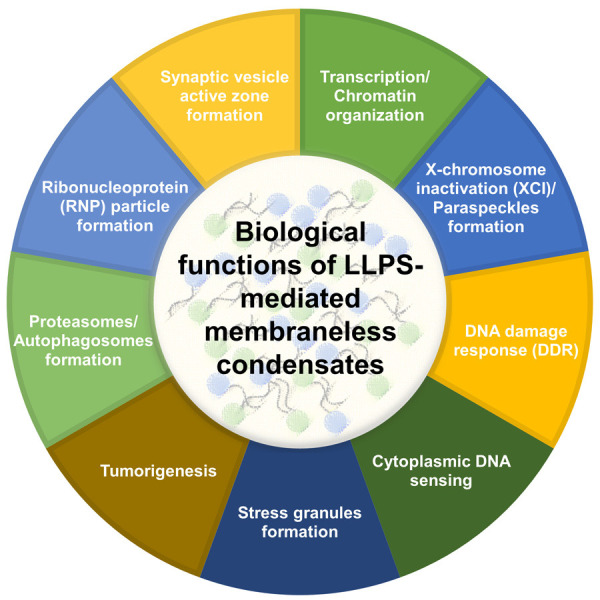
All the biological functions of LLPS-mediated membraneless condensates are summarized, which include transcription/chromatin organization, X-chromosome inactivation (XCI)/paraspeckles formation, DNA damage response (DDR), cytoplasmic DNA sensing, stress granule formation, tumorigenesis, proteasomes/autophagosomes formation, ribonucleoprotein (RNP) formation, and synaptic vesicle active zone formation.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Jie-Rong Huang (National Yang-Ming Chiaotong Univ.) for his input in the revised manuscript. This work was supported in part to K.J.W. by Ministry of Science and Technology Summit and Frontier grants (MOST 108-2321-B-182A-005, MOST 109-2326-B-182A-002), Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (OMRPG3I0012, NMRPG3J6192, CORPG3J0232, NMRPG3J0672); to K.W.H. by Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 109-2628-B-039-006), China Medical University (CMU109-MF-12), and the “Drug Development Center, China Medical University” from The Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project (Ministry of Education, Taiwan); and to P.H.P. by Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 109-2320-B-182A-022), Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (NMRPG3K0511).
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Shin Y, Brangwynne CP. Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science. 2017;357:eaaf4382. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf4382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Banani SF, Lee HO, Hyman AA, Rosen MK. Biomolecular condensates: organizers of cellular biochemistry. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18:285–298. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang H, Ji X, Li P, Liu C, Lou J, Wang Z, Wen W, Xiao Y, Zhang M, Zhu X. Liquid-liquid phase separation in biology: mechanisms, physiological functions and human diseases. Sci China Life Sci. 2020;63:953–985. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1702-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nozawa RS, Yamamoto T, Takahashi M, Tachiwana H, Maruyama R, Hirota T, Saitoh N. Nuclear microenvironment in cancer: control through liquid-liquid phase separation. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:3155–3163. doi: 10.1111/cas.14551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sheu-Gruttadauria J, MacRae IJ. Phase transitions in the assembly and function of human miRISC. Cell. 2018;173:946–957. e916. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Woodruff JB, Ferreira Gomes B, Widlund PO, Mahamid J, Honigmann A, Hyman AA. The centrosome is a selective condensate that nucleates microtubules by concentrating tubulin. Cell. 2017;169:1066–1077. e1010. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Franzmann TM, Jahnel M, Pozniakovsky A, Mahamid J, Holehouse AS, Nuske E, Richter D, Baumeister W, Grill SW, Pappu RV, Hyman AA, Alberti S. Phase separation of a yeast prion protein promotes cellular fitness. Science. 2018;359:eaao5654. doi: 10.1126/science.aao5654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Riback JA, Katanski CD, Kear-Scott JL, Pilipenko EV, Rojek AE, Sosnick TR, Drummond DA. Stress-triggered phase separation is an adaptive, evolutionarily tuned response. Cell. 2017;168:1028–1040. e1019. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Alberti S, Gladfelter A, Mittag T. Considerations and challenges in studying liquid-liquid phase separation and biomolecular condensates. Cell. 2019;176:419–434. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Asherie N. Protein crystallization and phase diagrams. Methods. 2004;34:266–272. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2004.03.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Li P, Banjade S, Cheng HC, Kim S, Chen B, Guo L, Llaguno M, Hollingsworth JV, King DS, Banani SF, Russo PS, Jiang QX, Nixon BT, Rosen MK. Phase transitions in the assembly of multivalent signalling proteins. Nature. 2012;483:336–340. doi: 10.1038/nature10879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nott TJ, Petsalaki E, Farber P, Jervis D, Fussner E, Plochowietz A, Craggs TD, Bazett-Jones DP, Pawson T, Forman-Kay JD, Baldwin AJ. Phase transition of a disordered nuage protein generates environmentally responsive membraneless organelles. Mol Cell. 2015;57:936–947. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lin Y, Protter DS, Rosen MK, Parker R. Formation and maturation of phase-separated liquid droplets by RNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell. 2015;60:208–219. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.08.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zeng M, Chen X, Guan D, Xu J, Wu H, Tong P, Zhang M. Reconstituted postsynaptic density as a molecular platform for understanding synapse formation and plasticity. Cell. 2018;174:1172–1187. e1116. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.06.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Martin EW, Holehouse AS, Peran I, Farag M, Incicco JJ, Bremer A, Grace CR, Soranno A, Pappu RV, Mittag T. Valence and patterning of aromatic residues determine the phase behavior of prion-like domains. Science. 2020;367:694–699. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw8653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang J, Choi JM, Holehouse AS, Lee HO, Zhang X, Jahnel M, Maharana S, Lemaitre R, Pozniakovsky A, Drechsel D, Poser I, Pappu RV, Alberti S, Hyman AA. A molecular grammar governing the driving forces for phase separation of prion-like RNA binding proteins. Cell. 2018;174:688–699. e616. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.06.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chiu YP, Sun YC, Qiu DC, Lin YH, Chen YQ, Kuo JC, Huang JR. Liquid-liquid phase separation and extracellular multivalent interactions in the tale of galectin-3. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1229. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15007-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pak CW, Kosno M, Holehouse AS, Padrick SB, Mittal A, Ali R, Yunus AA, Liu DR, Pappu RV, Rosen MK. Sequence determinants of intracellular phase separation by complex coacervation of a disordered protein. Mol Cell. 2016;63:72–85. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Banani SF, Rice AM, Peeples WB, Lin Y, Jain S, Parker R, Rosen MK. Compositional control of phase-separated cellular bodies. Cell. 2016;166:651–663. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jain A, Vale RD. RNA phase transitions in repeat expansion disorders. Nature. 2017;546:243–247. doi: 10.1038/nature22386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhu G, Xie J, Kong W, Xie J, Li Y, Du L, Zheng Q, Sun L, Guan M, Li H, Zhu T, He H, Liu Z, Xia X, Kan C, Tao Y, Shen HC, Li D, Wang S, Yu Y, Yu ZH, Zhang ZY, Liu C, Zhu J. Phase separation of disease-associated SHP2 mutants underlies MAPK hyperactivation. Cell. 2020;183:490–502. e418. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wilson EB. The structure of protoplasm. Science. 1899;10:33–45. doi: 10.1126/science.10.237.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lafontaine DLJ, Riback JA, Bascetin R, Brangwynne CP. The nucleolus as a multiphase liquid condensate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:165–182. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brangwynne CP, Mitchison TJ, Hyman AA. Active liquid-like behavior of nucleoli determines their size and shape in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:4334–4339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017150108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Larson AG, Elnatan D, Keenen MM, Trnka MJ, Johnston JB, Burlingame AL, Agard DA, Redding S, Narlikar GJ. Liquid droplet formation by HP1alpha suggests a role for phase separation in heterochromatin. Nature. 2017;547:236–240. doi: 10.1038/nature22822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Strom AR, Emelyanov AV, Mir M, Fyodorov DV, Darzacq X, Karpen GH. Phase separation drives heterochromatin domain formation. Nature. 2017;547:241–245. doi: 10.1038/nature22989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Boija A, Klein IA, Sabari BR, Dall’Agnese A, Coffey EL, Zamudio AV, Li CH, Shrinivas K, Manteiga JC, Hannett NM, Abraham BJ, Afeyan LK, Guo YE, Rimel JK, Fant CB, Schuijers J, Lee TI, Taatjes DJ, Young RA. Transcription factors activate genes through the phase-separation capacity of their activation domains. Cell. 2018;175:1842–1855. e1816. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sabari BR, Dall’Agnese A, Boija A, Klein IA, Coffey EL, Shrinivas K, Abraham BJ, Hannett NM, Zamudio AV, Manteiga JC, Li CH, Guo YE, Day DS, Schuijers J, Vasile E, Malik S, Hnisz D, Lee TI, Cisse II, Roeder RG, Sharp PA, Chakraborty AK, Young RA. Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers links phase separation and gene control. Science. 2018;361:eaar3958. doi: 10.1126/science.aar3958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gibson BA, Doolittle LK, Schneider MWG, Jensen LE, Gamarra N, Henry L, Gerlich DW, Redding S, Rosen MK. Organization of chromatin by intrinsic and regulated phase separation. Cell. 2019;179:470–484. e421. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cho WK, Spille JH, Hecht M, Lee C, Li C, Grube V, Cisse II. Mediator and RNA polymerase II clusters associate in transcription-dependent condensates. Science. 2018;361:412–415. doi: 10.1126/science.aar4199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wei MT, Chang YC, Shimobayashi SF, Shin Y, Strom AR, Brangwynne CP. Nucleated transcriptional condensates amplify gene expression. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:1187–1196. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-00578-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lu Y, Wu T, Gutman O, Lu H, Zhou Q, Henis YI, Luo K. Phase separation of TAZ compartmentalizes the transcription machinery to promote gene expression. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:453–464. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0485-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Corpet A, Kleijwegt C, Roubille S, Juillard F, Jacquet K, Texier P, Lomonte P. PML nuclear bodies and chromatin dynamics: catch me if you can! Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:11890–11912. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pessina F, Giavazzi F, Yin Y, Gioia U, Vitelli V, Galbiati A, Barozzi S, Garre M, Oldani A, Flaus A, Cerbino R, Parazzoli D, Rothenberg E, d’Adda di Fagagna F. Functional transcription promoters at DNA double-strand breaks mediate RNA-driven phase separation of damage-response factors. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21:1286–1299. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0392-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Thapar R, Wang JL, Hammel M, Ye R, Liang K, Sun C, Hnizda A, Liang S, Maw SS, Lee L, Villarreal H, Forrester I, Fang S, Tsai MS, Blundell TL, Davis AJ, Lin C, Lees-Miller SP, Strick TR, Tainer John A. Mechanism of efficient double-strand break repair by a long non-coding RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:10953–10972. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cerase A, Armaos A, Neumayer C, Avner P, Guttman M, Tartaglia GG. Phase separation drives X-chromosome inactivation: a hypothesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019;26:331–334. doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0223-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pandya-Jones A, Markaki Y, Serizay J, Chitiashvili T, Mancia Leon WR, Damianov A, Chronis C, Papp B, Chen CK, McKee R, Wang XJ, Chau A, Sabri S, Leonhardt H, Zheng S, Guttman M, Black DL, Plath K. A protein assembly mediates Xist localization and gene silencing. Nature. 2020;587:145–151. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2703-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yamazaki T, Souquere S, Chujo T, Kobelke S, Chong YS, Fox AH, Bond CS, Nakagawa S, Pierron G, Hirose T. Functional domains of NEAT1 architectural lncRNA induce paraspeckle assembly through phase separation. Mol Cell. 2018;70:1038–1053. e1037. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hondele M, Sachdev R, Heinrich S, Wang J, Vallotton P, Fontoura BMA, Weis K. DEAD-box ATPases are global regulators of phase-separated organelles. Nature. 2019;573:144–148. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1502-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Guillén-Boixet J, Kopach A, Holehouse AS, Wittmann S, Jahnel M, Schlüßler R, Kim K, Trussina IREA, Wang J, Mateju D, Poser I, Maharana S, Ruer-Gruß M, Richter D, Zhang X, Chang Y-T, Guck J, Honigmann A, Mahamid J, Hyman AA, Pappu RV, Alberti S, Franzmann TM. RNA-induced conformational switching and clustering of G3BP drive stress granule assembly by condensation. Cell. 2020;181:346–361. e317. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yang P, Mathieu C, Kolaitis RM, Zhang P, Messing J, Yurtsever U, Yang Z, Wu J, Li Y, Pan Q, Yu J, Martin EW, Mittag T, Kim HJ, Taylor JP. G3BP1 is a tunable switch that triggers phase separation to assemble stress granules. Cell. 2020;181:325–345. e328. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dao TP, Kolaitis RM, Kim HJ, O’Donovan K, Martyniak B, Colicino E, Hehnly H, Taylor JP, Castañeda CA. Ubiquitin modulates liquid-liquid phase separation of UBQLN2 via disruption of multivalent interactions. Mol Cell. 2018;69:965–978. e966. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Du M, Chen ZJ. DNA-induced liquid phase condensation of cGAS activates innate immune signaling. Science. 2018;361:704–709. doi: 10.1126/science.aat1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yasuda S, Tsuchiya H, Kaiho A, Guo Q, Ikeuchi K, Endo A, Arai N, Ohtake F, Murata S, Inada T, Baumeister W, Fernandez-Busnadiego R, Tanaka K, Saeki Y. Stress- and ubiquitylation-dependent phase separation of the proteasome. Nature. 2020;578:296–300. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1982-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sun D, Wu R, Zheng J, Li P, Yu L. Polyubiquitin chain-induced p62 phase separation drives autophagic cargo segregation. Cell Res. 2018;28:405–415. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0017-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bouchard JJ, Otero JH, Scott DC, Szulc E, Martin EW, Sabri N, Granata D, Marzahn MR, Lindorff-Larsen K, Salvatella X, Schulman BA, Mittag T. Cancer mutations of the tumor suppressor SPOP disrupt the formation of active, phase-separated compartments. Mol Cell. 2018;72:19–36. e18. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.McDonald NA, Fetter RD, Shen K. Assembly of synaptic active zones requires phase separation of scaffold molecules. Nature. 2020;588:454–458. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2942-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Klein IA, Boija A, Afeyan LK, Hawken SW, Fan M, Dall’Agnese A, Oksuz O, Henninger JE, Shrinivas K, Sabari BR, Sagi I, Clark VE, Platt JM, Kar M, McCall PM, Zamudio AV, Manteiga JC, Coffey EL, Li CH, Hannett NM, Guo YE, Decker TM, Lee TI, Zhang T, Weng JK, Taatjes DJ, Chakraborty A, Sharp PA, Chang YT, Hyman AA, Gray NS, Young RA. Partitioning of cancer therapeutics in nuclear condensates. Science. 2020;368:1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz4427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


