Abstract
When subcloned into low‐copy‐number expression vectors, rumAB, encoding polVR391 (RumA′2B), is best characterized as a potent mutator giving rise to high levels of spontaneous mutagenesis in vivo. This is in dramatic contrast to the poorly mutable phenotype when polVR391 is expressed from the native 88.5 kb R391, suggesting that R391 expresses cis‐acting factors that suppress the expression and/or the activity of polVR391. Indeed, we recently discovered that SetRR391, an ortholog of λ cI repressor, is a transcriptional repressor of rumAB. Here, we report that CroSR391, an ortholog of λ Cro, also serves as a potent transcriptional repressor of rumAB. Levels of RumA are dependent upon an interplay between SetRR391 and CroSR391, with the greatest reduction of RumA protein levels observed in the absence of SetRR391 and the presence of CroSR391. Under these conditions, CroSR391 completely abolishes the high levels of mutagenesis promoted by polVR391 expressed from low‐copy‐number plasmids. Furthermore, deletion of croS R391 on the native R391 results in a dramatic increase in mutagenesis, indicating that CroSR391 plays a major role in suppressing polVR391 mutagenesis in vivo. Inactivating mutations in CroSR391 therefore have the distinct possibility of increasing cellular mutagenesis that could lead to the evolution of antibiotic resistance of pathogenic bacteria harboring R391.
Keywords: DNA polymerase V, integrating conjugative element, mutagenesis, R391, SOS response
When subcloned from R391 into low‐copy‐number expression vectors, polVR391 (RumA′2B) encoded by rumAB, is a potent mutator giving rise to high levels of spontaneous mutagenesis in vivo. This is in contrast to the poorly mutable phenotype when polVR391 is expressed from the native R391. Here, we report that CroSR391, an ortholog of λ Cro, serves as a potent transcriptional repressor of rumAB that plays a major role in suppressing polVR391 mutagenesis in vivo.
1. INTRODUCTION
The accelerating emergence of drug‐resistant pathogenic microorganisms is a critical global public health concern (https://www.who.int/news‐room/fact‐sheets/detail/antibiotic‐resistance). Antibiotic over‐use and prophylaxis, in both humans and livestock, for the treatment of disease‐causing bacteria has led to the selection and increased prevalence of so‐called “superbugs” that have often acquired resistance to multiple classes of antimicrobial compounds (Wendlandt et al., 2015). Estimates suggest a 10‐fold increase in mortality rates from untreatable bacterial infections within the next 30 years (https://amr‐review.org/sites/default/files/AMR%20Review%20Paper%20‐%20Tackling%20a%20crisis%20for%20the%20health%20and%20wealth%20of%20nations_1.pdf). The urgency of this impending crisis has recently led to a concerted effort to identify new synthetic compounds and natural products that might represent novel families of antibiotics (Bhattarai et al., 2020). In addition, the genetic mechanisms that give rise to antibiotic resistance, such as stress‐induced mutagenesis and broad‐host‐range drug‐resistance genetic elements (i.e., plasmids, genomic islands, and integrative and conjugative elements [ICE]), are being extensively studied as potential targets for mitigating the development of resistance.
Escherichia coli possesses five DNA polymerases, three of which, pol II (encoded by polB), pol IV (encoded by dinB), and polV (encoded by umuDC), are induced as part of the SOS response to stress and DNA damage (Simmons et al., 2008). Expression of these polymerases has previously been shown to contribute to the evolution of antibiotic drug resistance in many pathogenic strains of bacteria (Cirz et al., 2006a; 2006b; 2007; Cirz & Romesberg, 2006). PolV alone is responsible for up to a 100‐fold increase in spontaneous mutagenesis after SOS induction (Fijalkowska et al., 1997; Sweasy et al., 1990). As a consequence, the activity of polV is subject to multiple levels of regulation (Goodman et al., 2016). In addition to transcriptional repression by the SOS repressor, LexA (Bagg et al., 1981), the UmuD protein has to undergo activated RecA (RecA*)‐mediated posttranslational cleavage to UmuD′ (Burckhardt et al., 1988; Nohmi et al., 1988; Shinagawa et al., 1988), so that it can interact with UmuC (Woodgate et al., 1989) and generate polV (UmuD′2C) (Tang et al., 1999). Cleavage of UmuD to UmuD′ also leads to a change in the spatial location of polV inside the cell (Robinson et al., 2015). The polVs activity is further increased through an interaction with RecA and ATP to generate the polV Mutasome (polV Mut) (Jiang et al., 2009). Last, but not least, intracellular levels of UmuD, UmuD′, and UmuC are normally kept to a minimum through targeted proteolysis (Frank et al., 1996; Gonzalez et al., 1998, 2000).
The polV orthologs are found in many strains of bacteria, as well as bacteriophage, self‐transmissible R‐plasmids, and ICEs (Ho et al., 1993; McLenigan et al., 1999; Pinney, 1980; Upton & Pinney, 1983). Given that these orthologs are located on mobile genetic elements and are likely to find themselves in very different genetic environments, one might expect alternate mechanisms of regulation to keep their activity in check until needed.
A good example is the LexA‐regulated polV ortholog (encoded by rumAB) found on R391. R391 and a closely related ICE, SXT, exhibit 95% identity over 65 kb of their sequences (Hochhut et al., 2001). However, one notable difference between R391 and SXT is that rumB is inactivated in SXT due to the insertion of an ISCR2 element into the gene, and as a consequence, in contrast to R391, SXT does not possess an active polV.
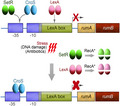
SetRSXT, a λ cI‐like repressor, has been shown to regulate genes involved in conjugation, integration, and excision of the SXT element (Beaber et al., 2004; Poulin‐Laprade & Burrus, 2015; Poulin‐Laprade et al., 2015). Previously, we examined the role of the related SetRR391 protein for its role in regulating polVR391 (Gonzalez et al., 2019). We found that the regulatory region of the rumAB R391 operon contains a single site that is highly similar to the known multiple SetRSXT 14‐bp operator sequences (Figure 1), leading us to suggest that SetRR391 could be involved in the repression of the rumAB R391 genes. We found that co‐expression of rumAB R391 and setR R391 from the same low‐copy plasmid reduced the levels of mutagenesis observed in a lexA defective SOS‐induced strain indicating that SetRR391 can regulate the rumAB R391 genes (Gonzalez et al., 2019). Moreover, the SetRR391 protein was shown to specifically bind to the 14‐bp operator sequence that overlaps with the −35 promoter element upstream of rumAB (Figure 1). However, we found that plasmid pRLH421, which contains ~21.5 kb of R391, including both setR R391 and rumAB, nevertheless exhibited very high levels of mutagenesis in an SOS‐induced strain [recA718 lexA51(Def)]. We argued that, in this SOS‐induced strain, the activated RecA co‐protease (encoded by recA718) cleaves the SetRR391 protein, in a similar fashion to LexA cleavage, inactivating SetRR391 and allowing expression of the rumAB operon. Indeed, when a non‐cleavable allele of setR R391 was cloned into pRLH421, we observed a significant decrease in mutagenesis (Gonzalez et al., 2019). Additional experiments revealed, however, that intact R391 exhibits even lower levels of mutagenesis in strains in which RecA is in a constitutively and highly activated state (recA730), suggesting that there is at least one additional negative regulator of the rumAB R391 genes encoded by R391 that is not affected by activated RecA (unpublished observations).
FIGURE 1.

Cartoon of the rumAB promoter region. A single SetR/CroS binding site is shown in blue color. This site partially overlaps with the −35 promoter element, shown in gold. A LexA binding site is shown in green, which partially overlaps with the −10 promoter element (also shown in gold). The ribosome binding site (RBS) is shown in purple, and the first two codons of RumA are shown in red
R391 also expresses a protein that is phylogenetically related to Cro‐like transcriptional repressor proteins (Figure S1) (Boltner et al., 2002). While the CroSR391 protein shows some phylogenetic divergence from related Cro‐like proteins, it is 100% identical to the CroSSXT protein (Figure S1). Previous studies on the CroSSXT and SetRSXT proteins revealed that they both bind to four conserved operator sequences: OL, O1, O2, and O3 (albeit with differing affinities) in the croS‐setR intergenic region that regulates their own expression from divergent promoters (Poulin‐Laprade & Burrus, 2015). In SXT, it is known that CroSSXT also regulates the setCD SXT genes and, similar to SetRSXT, is involved in regulating conjugative transfer (Poulin‐Laprade & Burrus, 2015; Poulin‐Laprade et al., 2015). The interplay between the ICE SetRSXT and CroSSXT proteins is therefore reminiscent of the λ cI and λ Cro proteins that govern the transition between lysogenic and lytic pathways during the bacteriophage life cycle (Johnson et al., 1978; Svenningsen et al., 2005; Takeda et al., 1977).
We hypothesized that like SetRR391, CroSR391 would function as a transcriptional regulator of the rumAB R391 operon and thereby play a role in regulating rumAB R391‐mediated mutagenesis. To test this hypothesis, we have constructed a series of plasmids expressing SetRR391 and/or CroSR391 and investigated their effects on rumAB expression and polVR391‐dependent mutagenesis in vivo. We report here that CroSR391 is a transcriptional repressor of rumAB and may be the major factor that suppresses polVR391 activity on R391.
2. RESULTS
2.1. Comparison of polVR391‐dependent mutagenesis when rumAB is expressed from R391 or subcloned onto a low‐copy‐number vector
Our studies examined the multifaceted nature of the regulation of the R391 mutagenic response. Regulation of the mutagenic activity of polVR391 when expressed in its native genetic environment promotes minimal levels of mutagenesis (Pinney, 1980), even in strains in which the LexA repressor is inactivated and RecA is constitutively activated (previous unpublished observations and Figure 2). However, when rumAB was subcloned onto a low‐copy‐number plasmid, there was a dramatic increase in polVR391 mutator activity, especially in strains with mutations in recA (recA718 and recA730) that lead to a constitutive RecA* phenotype (Ho et al., 1993) (Figure 2). Indeed, polVR391 is the most potent polV ortholog characterized to date (Kulaeva et al., 1995; Mead et al., 2007). The fact that polVR391 appears inactive when expressed from the native R391 indicates that there is likely to be cis‐acting factor(s) expressed from R391 that normally act to suppress the potent mutator activity of polVR391.
FIGURE 2.
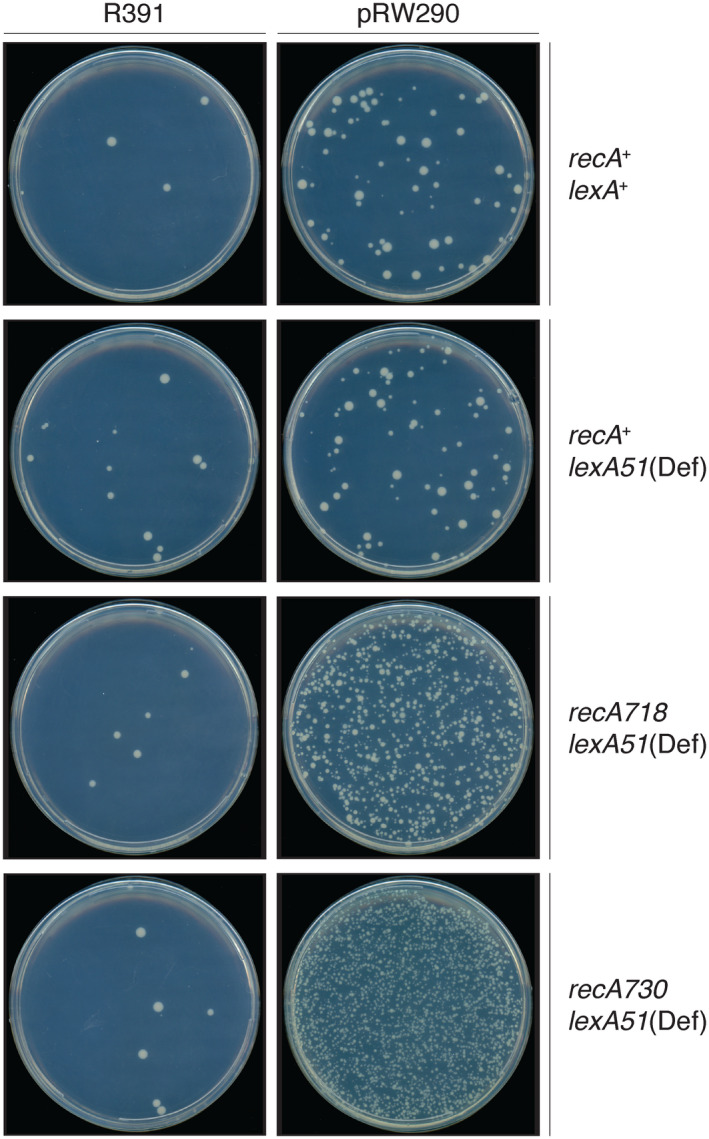
Spontaneous mutagenesis promoted by R391, or pRW290, in different genetic backgrounds. Cells were plated on minimal low histidine agar plates as described in Section 4.3: Qualitative analysis of spontaneous reversion of the hisG4(Oc) allele. His+ revertants appear as creamy white colonies against the dark background behind the agar plate. As observed, the 88.5‐kb R391 promotes low levels of spontaneous mutagenesis in all genetic backgrounds. This is in contrast to pRW290, which only expresses the rumAB R391 operon from a low‐copy‐number vector. Although the rumAB operon is subject to transcriptional regulation by the LexA repressor, there is little difference in mutagenesis between lexA + (RW120) and lexA51(Def) (RW546) strains. Mutagenesis increases significantly when RecA is partially activated for co‐protease functions (recA718; MVG114) or fully activated for co‐protease functions (recA730; RW578)
2.2. CroSR391 plays a major role in suppressing polVR391‐dependent mutagenesis
The rumAB operon was originally subcloned in 1993 into the low‐copy vector pGB2 (Churchward et al., 1984) as a partial EcoRI digest of R391 (Ho et al., 1993). R391 is normally chromosomally located and integrated into the 5′ end of prfC (Hochhut et al., 2001). However, the 21.5‐kb insert cloned into pGB2 to generate pRLH421 is clearly of episomal origin, since it contains both 5′ and 3′ ends of the linear R391. Unfortunately, sequence analysis of the insert in pRLH421 (Genbank: U13633) reveals that the croS R391 gene is truncated at an internal EcoRI site in the gene (Figure S2). We suspected that the croS_ΔC truncation could explain our disparate mutagenesis results with pRLH421 (high levels), versus intact R391 (low levels), if CroSR391 does indeed repress the rumAB R391 genes. To test this notion, we constructed a series of pRLH421‐derived plasmids with combinations of wild‐type croS R391 and setR R391, and/or deletions of croS R391 and setR R391 while still retaining the rumAB operon (Table 1) (Figure S2).
TABLE 1.
Plasmids used in this study
| Plasmid | Relevant characteristics | Source or reference |
|---|---|---|
| R391 | Integrated into prfC | (Ho et al., 1993) |
| R391ΔcroS | Integrated into prfC and with a deletion of croS R391 | This study |
| pRW290 | Low copy number, SpcR, ~2‐kb fragment of R391 expressing rumAB | (Szekeres et al., 1996) |
| pRLH421 | Low‐copy‐number, SpcR, ∼21.5‐kb fragment of R391 | Genbank:U13633 (Gonzalez et al., 2019) |
| pJM1355 | Low‐copy‐number, SpcR, ∼21.5‐kb fragment of R391 with ΔcroS R391 setR + R391 | This study |
| pJM1356 | Low‐copy‐number, SpcR, ∼21.5‐kb fragment of R391with croS + R391 setR + R391 | This study |
| pJM1359 | Low‐copy‐number, SpcR, ∼21.5‐kb fragment of R391 with ΔcroS R391 ΔsetR R391 | This study |
| pJM1360 | Low‐copy‐number, SpcR, ∼21.5‐kb fragment of R391 with croS + R391 ΔsetR R391 | This study |
| pJM1365 | Low‐copy‐number, SpcR, with ΔcroS R391 setR + R391 | This study |
| pJM1366 | Low‐copy‐number, SpcR, with croS + R391 setR + R391 | This study |
| pJM1367 | Low‐copy‐number, SpcR, with ΔcroS R391 ΔsetR R391 | This study |
| pJM1368 | Low‐copy‐number, SpcR, with croS + R391 ΔsetR R391 | This study |
| pCC1BacTM | Single‐copy‐number, CmR | Genscript |
| pJM1378 | pCC1‐based, CmR, with rumAB R391 | This study |
| pJM1467 | pCC1‐based, CmR, with recA‐promoter::rumAB R391 | This study |
| pRed/ET | Plasmid encoding the red gene cluster (redγβα) and recA TetR | (Wang et al., 2006) |
| pFLPe | Plasmid encoding the enhanced FLP recombinase, AmpR | Gen‐H |
The various plasmid iterations of croS R391 and setR R391 were transformed into MVG114 [∆umuDC596::ermGT, lexA51(Def), recA718, and hisG4(Oc)] in order to analyze RumAB‐dependent spontaneous mutagenesis utilizing the histidine reversion assay. In the lexA51(Def) background, the RecA718 protein is in a partially activated state (RecA*) (McCall et al., 1987) and promotes significant levels of polV‐dependent spontaneous mutagenesis in the absence of DNA damage (Sweasy et al., 1990). As with our earlier findings (Ho et al., 1993), pRLH421 gave very high levels of mutagenesis (Figure 3). Similarly, both the ΔcroS R391/setR + R391 construct (pJM1355) and the double ΔcroS R391/ΔsetR R391 construct (pJM1359) also gave high levels of mutagenesis revealing that the rumAB operon is not appreciably downregulated in the recA718 lexA51(Def) background. However, in strains harboring plasmid constructs that express CroSR391 the level of mutagenesis is significantly reduced. While the levels of mutagenesis with the croS + R391/setR + R391 construct (pJM1356) are reduced 2.7‐fold (cf. pJM1355) to 4.2‐fold (cf. pRLH421), the croS + R391/ΔsetR R391 construct (pJM1360) results in a 50‐ to 75‐fold reduction in mutagenesis (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3.
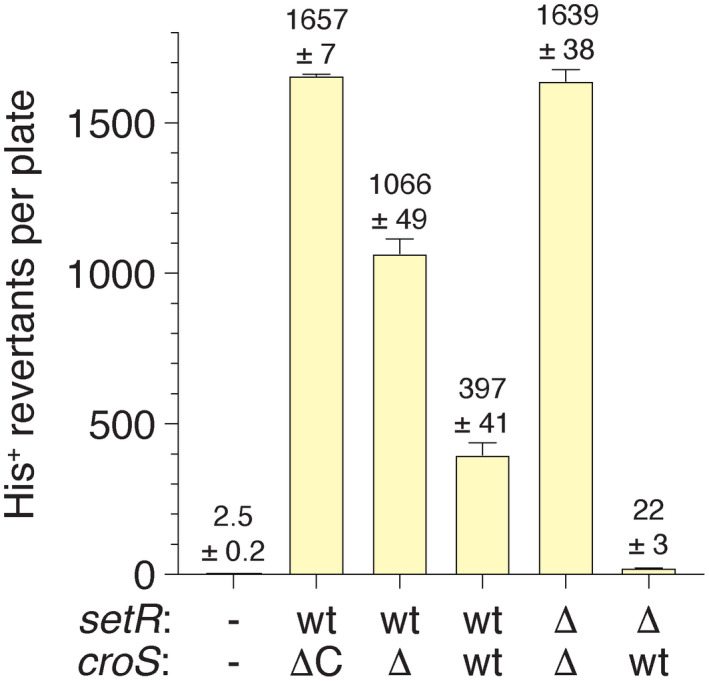
RumABR391‐dependent mutagenesis is regulated by croS R391. The histidine reversion assay was performed on the E. coli strain MVG114 or MVG114 strains transformed with pRLH421 or various croS R391 or setR R391 wild‐type or deletion combinations. (wt/ΔC) represents MVG114 transformed with the plasmid pRLH421 that contains ~21.5 kb of R391 and harbors a C‐terminal deletion of the croS R391 gene. MVG114 was transformed with plasmids pJM1355, pJM1356, pJM1359 and pJM1360, and the croS R391 or setR R391 genotypes are indicated. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM)
2.3. CroSR391 repression can operate in trans and is specific for the rumAB promoter
To demonstrate that the regulation of rumAB‐dependent mutagenesis was specifically due to CroSR391 and not some other factor encoded in the R391 DNA cloned in the pRLH421 derivatives described above, we deleted ~20.3 kb from ScaI to SmaI of the R391 DNA leaving only the various croS R391 and setR R391 operons (Figure S2). The pJM1378 (Table 1), a pCC1 derivative (Epicenter/Genscript), carrying the rumAB R391 operon, including the rumAB promoter, was transformed alone or in combination with pJM1365 (ΔcroS R391/setR+ R391), pJM1366 (croS + R391/setR + R391), pJM1367 (ΔcroS R391/ΔsetR R391), and pJM1368 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391) into MVG114 [∆umuDC596::ermGT, lexA51(Def), recA718, and hisG4(Oc)]. Again, utilizing the histidine reversion mutagenesis assay, we found that rumAB‐dependent mutagenesis was lower when expressing both wild‐type CroSR391 and SetRR391 (pJM1366) corresponding to our above finding with plasmid pJM1356 (croS + R391/setR + R391) (Figures 4a and S3). In contrast, when setR R391 is deleted such that only CroSR391 is expressed (pJM1368), rumAB‐dependent mutagenesis is virtually eliminated (Figures 4a and S3), again in agreement with the results with pJM1360 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391). Furthermore, we found that in all strains where there is no CroSR391 expressed (pJM1378 alone or with pJM1365, or pJM1367), there is a very high level of spontaneous mutagenesis. These results confirm that regulation of rumAB‐dependent mutagenesis occurs during an interplay between SetRR391 and CroSR391 and that this regulation can operate in trans.
FIGURE 4.
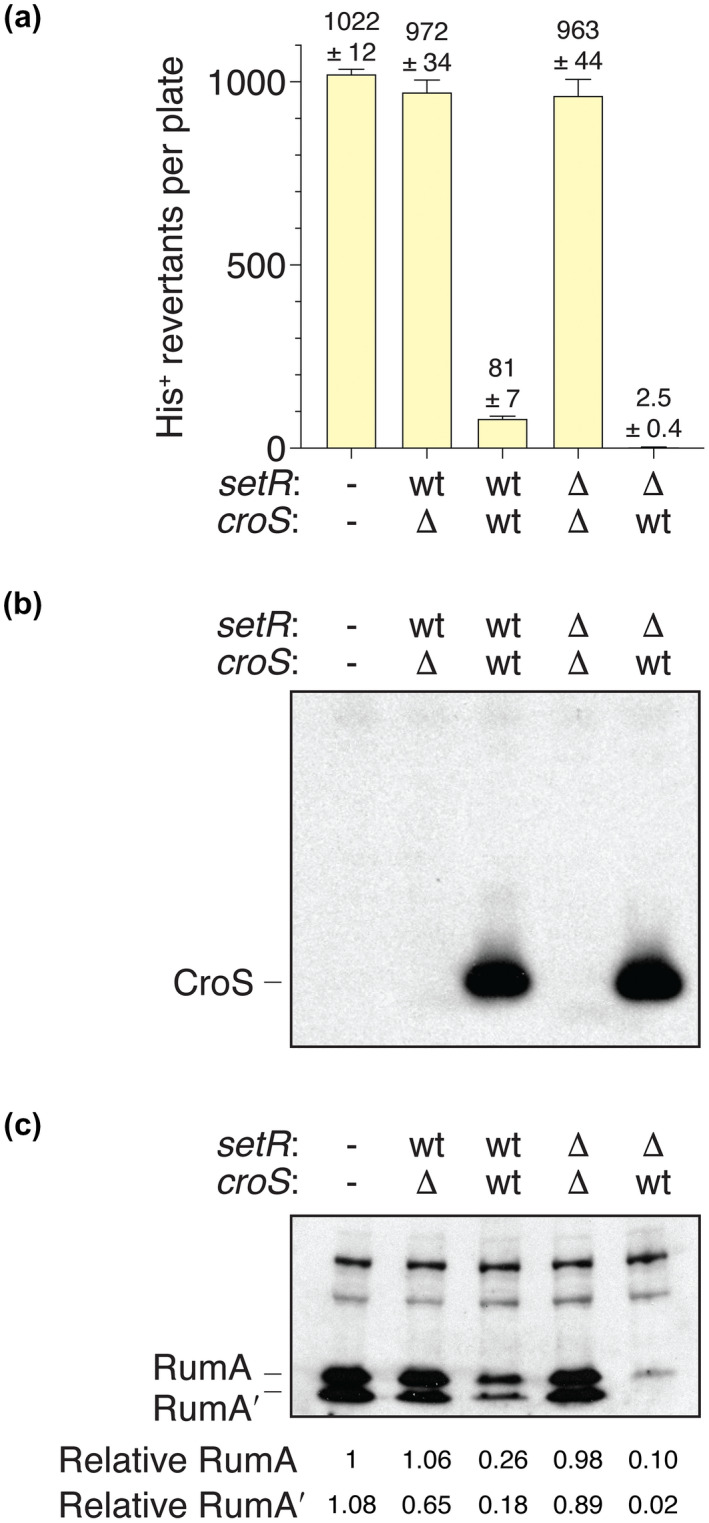
CroSR391 trans‐regulation of RumABR391‐dependent mutagenesis. (a) Spontaneous histidine reversion mutagenesis assays utilizing MVG114 strains harboring pJM1378 alone (−/−), a pCC1 derivative (copy‐control plasmid) carrying the rumAB R391 operon, were transformed with low‐copy pGB2 derivatives (pJM1365, pJM1366, pJM1367, and pJM1368) carrying various iterations of the croS R391/setR R391 operon (Table 1). The genotypes of croS R391 or setR R391, either wild‐type or deleted, are indicated. (b) Western blot analysis using an anti‐CroS antibody indicating that only strains harboring a plasmid with a wild‐type croS R391 gene express any CroS protein. (c) Western blot using an anti‐RumA antibody indicating that strains that express the CroS protein have significantly reduced levels of the RumA protein. However, strains that express only SetR show no reduction in the level of RumA protein. Numbers reported for the levels of RumA and RumA′ are relative to RumA in track 1
Knowing that there is a single SetRR391 binding site upstream of the rumAB R391 operon (Figure 1) (Gonzalez et al., 2019) and that the four SetR binding sites in the setR‐croS intergenic region of the SXT element are also bound by CroSSXT (Poulin‐Laprade & Burrus, 2015), we wanted to show that the CroSR391 repression of rumAB R391 was dependent on the rumAB promoter region. We therefore replaced the rumAB R391 promoter region in pJM1378 with the promoter region of the E. coli recA gene, to create plasmid pJM1467 (recA‐promoter::rumAB R391) (Table 1). As before, pJM1467 was transformed alone or in combination with pJM1365 (ΔcroS R391/setR + R391), pJM1366 (croS + R391/setR + R391), pJM1367 (ΔcroS R391/ΔsetR R391), and pJM1368 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391) into MVG114, and histidine reversion mutagenesis was performed (Figures 5a and S3). Most plasmid combinations gave uniformly high levels of mutagenesis. The exception was pJM1467 together with pJM1368 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391) that gave ~85% of the level of mutagenesis observed with the other plasmid combinations. It should be emphasized that this is in dramatic contrast to when RumABR391 is expressed from the native SetR/CroS binding site‐containing rumAB promoter, where CroSR391 expressed from pJM1368 eliminated virtually all RumAB‐dependent mutagenesis (cf. Figures 4a, 5a, and S3).
FIGURE 5.
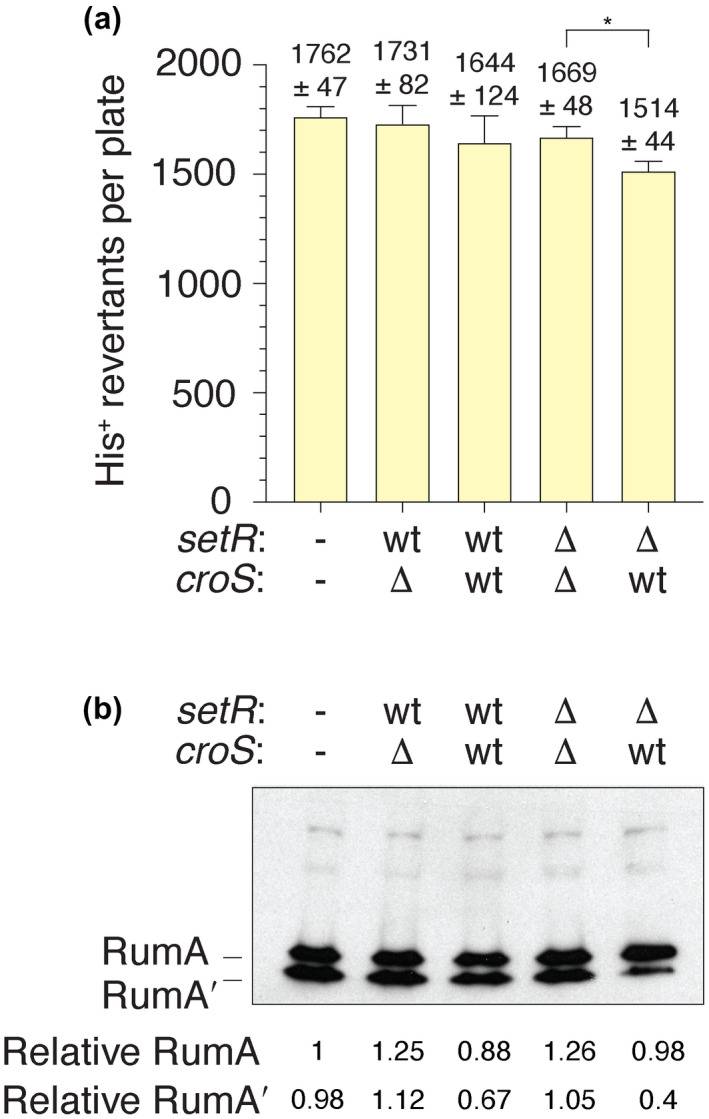
CroSR391 regulation of RumABR391‐dependent mutagenesis is dependent on the rumAB R391 promoter region. (a) Spontaneous histidine reversion mutagenesis assays utilizing MVG114 strains harboring pJM1467 (−/−), a pCC1 derivative carrying the rumAB R391 operon under the control of the recA promoter, were transformed with low‐copy pGB2 derivatives (pJM1365, pJM1366, pJM1367, and pJM1368) carrying various iterations of the croS R391‐setR R391 operon (Table 1). The genotypes of croS R391 or setR R391, either wild‐type or deleted, are indicated. The histogram illustrates the mean colony count for each indicated strain (n = 5). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). An unpaired two‐tailed t test was used to compare the mean colony counts for the ΔsetR ΔcroS and the ΔsetR croS + strains. * = p < .05. (b) Western blot using an anti‐RumA antibody indicating that the level of RumA expressed from the E. coli recA promoter does not change appreciably in the presence, or absence, of SetR or CroS. Numbers reported for the expression levels of RumA and RumA′ are relative to RumA in the left‐hand lane
2.4. CroSR391 regulation of RumAR391 protein level is specific to the rumAB R391 promoter
In order to demonstrate that the CroSR391 protein regulates mutagenesis by repressing the rumAB genes, we performed western blot analysis using rabbit anti‐CroSR391 (this study) and anti‐RumAR391 antibodies. Whole cell protein extracts were made from MVG114 strains harboring pJM1378 (rumAB) alone or in combination with pJM1365 (ΔcroS R391/setR + R391), pJM1366 (croS + R391/setR + R391), pJM1367 (ΔcroS R391/ΔsetR R391), or pJM1368 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391). As expected, only the strains harboring the pJM1366 (croS + R391/setR + R391) and pJM1368 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391) constructs expressed any CroSR391 protein (Figure 4b), and the level of CroS was identical in the presence or absence of SetR, suggesting that the phenotypic differences observed with the two plasmids (Figure 4a) are dependent on the presence of the SetR protein and not the level of CroS protein. When compared to strains lacking CroS, the levels of RumAR391/RumA′R391 proteins are significantly reduced in the strains harboring the pJM1366 (croS + R391/setR + R391) and pJM1368 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391) constructs (Figure 4c). Moreover, in the strain harboring pJM1368, which expresses only CroSR391, the level of RumAR391 protein is less than in the strain harboring pJM1366, despite expressing the same amount of CroS (Figure 4b), and the RumA′R391 protein is close to the limits of detection (Figure 4c). These findings demonstrate that the CroSR391 protein does indeed regulate the expression of the RumAR391 protein and that its regulation can be modulated in the presence of SetRR391. In addition, in the absence of the SetRR391 protein (pJM1368), CroSR391 protein may also have some inhibitory effect on RecA‐mediated cleavage of RumAR391 to RumA′R391 (see below for more discussion).
Next, we wanted to show that the CroSR391 regulation of RumA protein expression is specific to the rumAB promoter region. Plasmid pJM1467 (recA‐prom::rumAB R391), which expresses RumABR391 from the E. coli recA promoter, was co‐transformed into MVG114 along with pJM1365 (ΔcroS R391/setR + R391), pJM1366 (croS + R391/setR + R391), pJM1367 (ΔcroS R391/ΔsetR R391), or pJM1368 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391). Western blot analysis using the anti‐RumA antibodies was performed (Figure 5b). We found that the levels of RumAR391/RumA′R391 proteins are enhanced when expressed from the E. coli recA promoter as compared to RumAR391/RumA′R391 protein expressed from the native rumAB R391 promoter. However, unlike the previous results, the levels of RumAR391 protein expressed from the recA promoter are not affected by the presence of the CroSR391 protein (pJM1366 and pJM1368) indicating that CroSR391 transcriptional repression is specific to the rumAB R391 promoter. Again, in the absence of the SetRR391 protein (pJM1368), we observed a reduction in cleavage of RumAR391 to RumA′R391 (Figure 5). We believe that the reduction in RumA cleavage is due to an indirect inhibitory effect of CroSR391 on the spontaneous generation of RecA* in the recA718 strain, since significantly more RumA cleavage was observed in the same recA718 strain exposed to the DNA damaging agent, Mitomycin C, or in the highly proficient RecA*‐forming recA730 strain (± Mitomycin C) (Figure S4).
2.5. Expression of RumA/RumA′ in a recA + lexA + strain expressing SetR ± and CroS ± after antibiotic‐induced SOS induction
Based on the known interplay between CroS and SetR (Poulin‐Laprade & Burrus, 2015; Poulin‐Laprade et al., 2015), we hypothesized that rumAB would be the most repressed upon conditions that activate R391 transfer, namely at low SetR concentrations and high CroS levels, after damage‐ or stress‐induced induction of the SOS response. We were therefore interested in assaying expression of RumA in a wild‐type recA + lexA + strain (RW520) harboring the various setR‐croS plasmids, which also encode the rumAB R391 operon (pJM1355, pJM1356, pJM1359, and pJM1360), in which the SOS response was stress induced by treatment with the antibiotic, Ciprofloxacin, for up to 3 hr (Figure 6). Ciprofloxacin‐mediated induction of the SOS response was followed by western blot analysis of the LexA‐regulated RecA and RumA proteins. With all plasmid combinations, a strong induction of RecA was observed after treatment with Ciprofloxacin, indicating that the chromosomally encoded LexA repressor had been inactivated in vivo (Figure 6). The lack of any effect of the various setR‐croS plasmids on RecA expression also indicates that recA is not negatively regulated by either SetR or CroS. In contrast, the timing of the induction of RumAR391 was dependent upon the presence, or absence, of SetR or CroS (Figure 6). For example, in strains harboring pJM1359 (ΔcroS R391/ΔsetR R391), where rumA is only regulated by LexA, there was a time‐dependent induction of RumA, which peaked around 1 hr after Ciprofloxacin treatment, followed by conversion of RumA to RumA′ 2‐ to 3‐hr posttreatment. By comparison, the peak of RumA induction in the presence of pJM1355 (ΔcroS R391/setR + R391) was around 2 hr, suggesting that the presence of SetR delays RumA expression by an hour. However, there was no effect on the conversion of RumA to RumA′ that nevertheless occurred 2–3 hr posttreatment. (Figure 6). In contrast, no Ciprofloxacin‐induced expression of RumA was observed in the presence of pJM1360 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391), consistent with our earlier observations (Figure 4c). Interestingly, in the presence of pJM1356 (expressing both croS + R391/setR + R391), expression of RumA peaked at 1 hr post‐Ciprofloxacin treatment; from that point on, RumA levels decrease and by 3 hr, they are barely detectable. Such observations can readily be explained by the interplay and hierarchy of the three transcriptional repressors. We know that LexA is cleaved just a few minutes after DNA damage, so as to induce the 40+ protein SOS regulon (Fernández de Henestrosa et al., 2000). In contrast, SetR, which we have previously shown to be cleaved much slower than LexA in vitro (Gonzalez et al., 2019), would be expected to be cleaved and inactivated by RecA* in vivo around the 1‐ to 2‐hr point, which would then allow CroSR391 sole access to the SetR/CroS binding site in the rumAB promoter, thereby effectively eliminating residual expression of the RumA protein. The fact that RumA is detected in the croS + R391/setR + R391 strain, but not in the croS + R391/ΔsetR R391 strain, implies that SetRR391 normally competes with CroSR391 in vivo and to some degree blocks its access to the SetR‐CroS binding site in the rumAB promoter. Such a scenario explains why polVR391, encoded by the stably integrated R391, promotes such low levels of mutagenesis after DNA damage, or in constitutively activated RecA* strains, where both LexA and SetR repressors are inactivated and rumAB is repressed solely by CroS (Figure 2).
FIGURE 6.
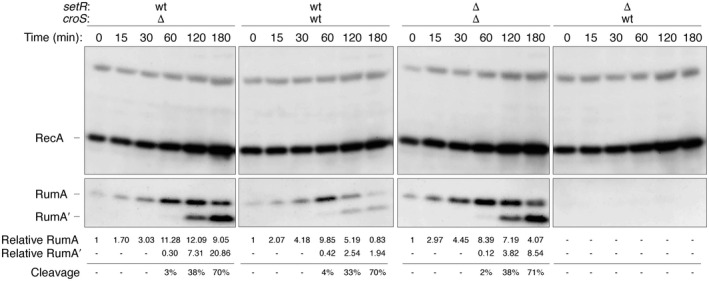
Expression of RecA, RumA, and RumA′ in wild‐type recA + lexA + cells after exposure to the SOS‐inducing antibiotic, Ciprofloxacin. Western blot analysis was performed on whole‐cell protein extracts from RW520 (recA + lexA +) harboring pRLH421 derivatives (pJM1355, pJM1356, pJM1359, or pJM1360), with various croS R391 or setR R391 wild type, or deletion combinations as indicated. To induce the SOS response, cells were treated with 30 ng ml–1 Ciprofloxacin for various times, as indicated in the figure. Levels of RecA and RumA/ RumA′ were detected using affinity purified polyclonal rabbit antibodies to RecA and RumA proteins. The number reported for the level of RumA or RumA’ is relative to a cross‐reacting band in the same track
2.6. Deletion of croS R391 on R391 leads to enhanced mutagenesis
Since R391 stably integrates into the E. coli chromosome at the 5′ end of the prfC gene (Hochhut et al., 2001), we were able to construct a croS R391 deletion mutant in the MVG114 genetic background and compare mutagenesis between the R391 and the R391ΔcroS strains. First, we examined mutagenesis using a galK2(Oc) reversion papillation assay in which orange‐red Gal+ mutant “papillae” grow up within bacterial colonies plated on MacConkey‐galactose agar media. Representative colonies from the R391 and R391ΔcroS strains are shown in Figure 7. The R391 strains gave 0–3 Gal+ mutant papillae per colony, whereas the R391ΔcroS gave 30–50 Gal+ mutant papillae per colony. Second, we utilized a rifampicin mutagenesis assay in which cells are plated on LB agar plates containing 100 μg ml–1 rifampicin. R391 ΔcroS strains exhibited a 10‐fold increase in rifampicin resistant mutagenesis, as compared to the strains harboring the wild‐type R391 (Figure 8). Both of these results demonstrate that the CroS protein, expressed from its native locus within an intact R391, downregulates rumAB and tightly controls mutagenesis in strains carrying the R391 element.
FIGURE 7.
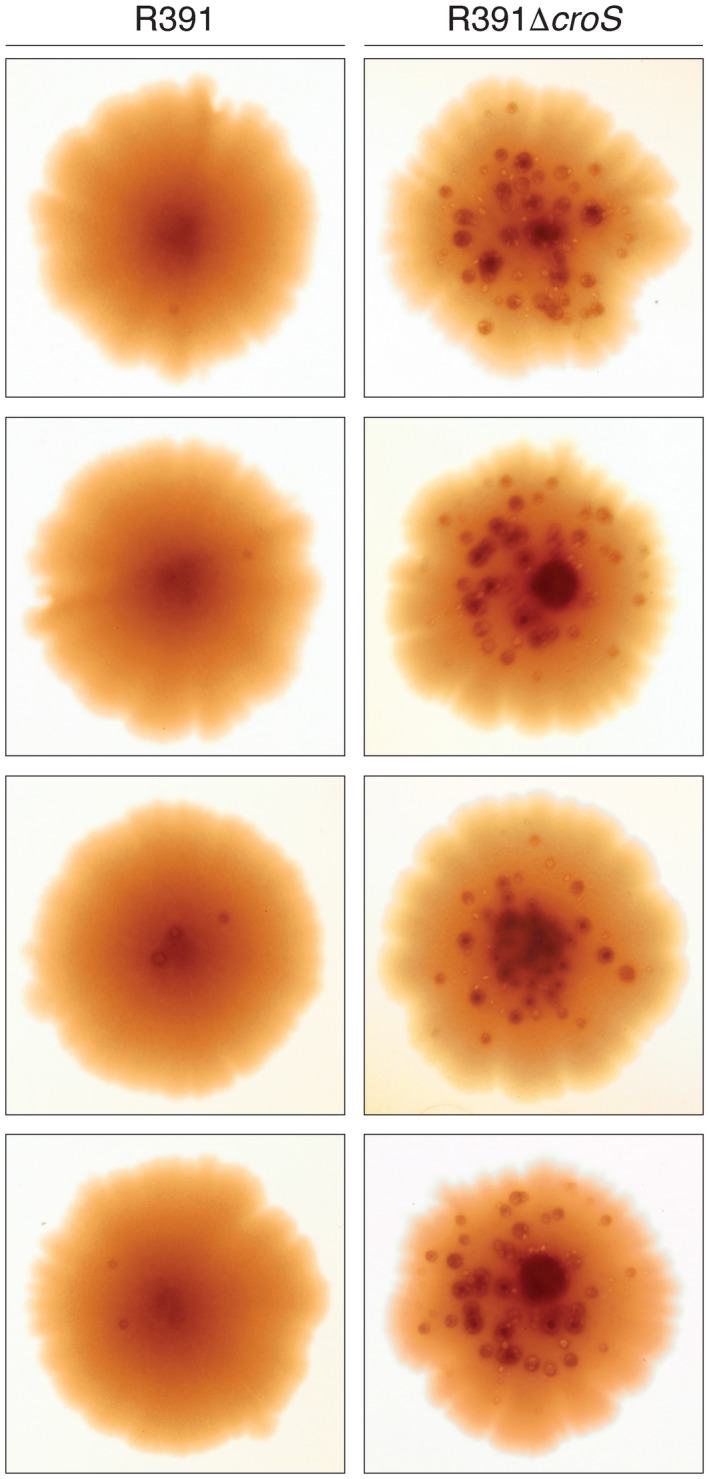
The galK2(Oc) reversion papillation assay of R391 or R391ΔcroS strains. R391 or R391ΔcroS were moved into MVG114 by conjugal transfer. Cells were plated onto MacConkey‐galactose agar media and grown for 8 days at 37℃. Pictures of representative colonies from each strain were taken showing the appearance of Gal+ papillae indicating the level of mutagenesis occurring within the colonies. The MVG114/R391ΔcroS colonies contain approximately 10−50 times the number of revertant papillae, when compared to the MVG114/R391 colonies
FIGURE 8.
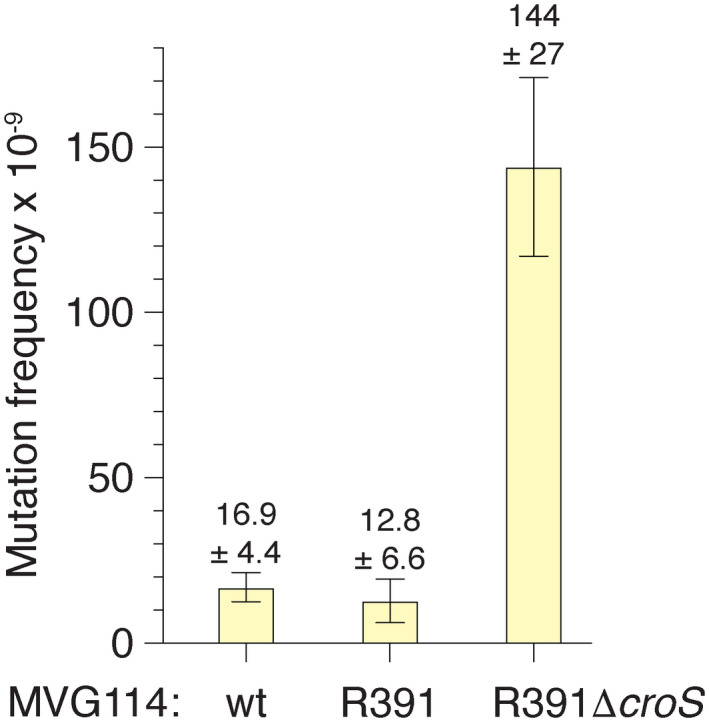
Rifampicin mutagenesis in R391 and R391ΔcroS strains. MVG114, MVG114/R391, and MVG114/R391ΔcroS cultures were started from with approximately 1,000 cells, or less, and grown overnight to stationary phase. Cells were plated onto LB agar plates containing rifampicin to select for rifampicin‐resistant mutants. Appropriate dilutions were plated to LB agar plates to determine viable counts, and the frequency of mutagenesis to rifampicin resistance was calculated. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). The MVG114/R391ΔcroS strain exhibits an ~10‐fold higher frequency of mutagenesis to rifampicin resistance than the MVG114/R391 strain
3. DISCUSSION
3.1. Unprecedented transcriptional regulation of R391 encoded rumAB
Previous studies have shown that chromosomally encoded E. coli polV is tightly regulated via a combination of transcriptional, posttranslational, and spatial regulation (Goodman et al., 2016). It is therefore likely that polV orthologs are also subject to strict regulation. Indeed, since the mid‐1990s, when the R391 rumAB operon was sequenced, it has been known that rumAB‐encoded polVR391 is regulated by the LexA transcriptional repressor (Kulaeva et al., 1995). Recently, we reported that the rumAB operon is also regulated by the λ cI‐like transcriptional repressor, SetRR391 (Gonzalez et al., 2019). Here, we provide in vivo data that are compelling and consistent with CroSR391 as acting as a third and potentially the most potent transcriptional regulator of the rumAB operon. For example, when expressed in cis‐ or trans‐ with rumAB, CroSR391 completely inhibits polVR391‐dependent mutagenesis (Figures 3 and 4). The lack of polVR391 mutagenesis in vivo is attributed to extremely low‐level expression of RumA (Figure 4) and RumB (unpublished observations) from its native promoter in the presence of CroSR391. The most reasonable explanation for such a phenotype is the unhindered access that CroSR391 has to the single SetR‐CroS binding site in the promoter region of the rumAB operon (Figure 1), where it acts as a strong transcriptional repressor of the rumAB operon. Interestingly, expression of RumA actually increases when CroSR391 and SetRR391 are co‐expressed (Figures 4 and 6), implying that SetRR391 may at least partially block CroSR391 access and binding to the SetR‐CroS binding site, thereby preventing it from acting as a potent transcriptional repressor. Indeed, expression of RumA in a wild‐type strain after antibiotic‐induced SOS induction appears to result from an interplay of all three transcriptional repressors—LexA, SetRR391, and CroSR391—such that extremely low levels of polVR391 are only present, even after full induction of the SOS response (Figure 6).
The polVR391 is a potent mutator DNA polymerase when uncoupled from its normal regulatory pathways (Figure 2). Its unprecedented regulation by three separate transcriptional repressors, two of which (LexA and SetR) are cleaved and inactivated after DNA damage, therefore only allows for the very limited expression of the highly error‐prone DNA polymerase (Figure 6), before the third (non‐cleavable) repressor (CroS), curtails RumAB expression, and provides a mechanism whereby the cell returns to a resting state, with low levels of cellular mutagenesis.
3.2. Inactivation of croS R391 increases the potential of enhanced mutagenesis
Deletion of croS R391 on the intact R391 stably integrated into the E. coli genome allowed us to evaluate the effect of the CroSR391 protein on repression of the rumAB R391 operon and mutagenesis from R391 in its native locus. Utilizing both a qualitative galK2(Oc) reversion papillation assay (Figure 7) and a quantitative assay rifampicin resistance assay (Figure 8), we found that mutagenesis is significantly increased in MVG114 strains harboring R391 ΔcroS as compared with strains harboring wild‐type R391. These results confirm our assertion that the CroSR391 protein is the major R391‐encoded negative regulator of the rumAB R391 operon and indicate that there are likely no additional rumAB R391 regulators encoded on the full‐length R391.
R391 is widely distributed in enterobacteriaceae that are opportunistic pathogens that cause a variety of infections in humans (Bie et al., 2017; Fang et al., 2018; Kong et al., 2020; Slattery et al., 2020; Song et al., 2013). Given that CroSR391 appears to be the “master regulator” to switch off rumAB expression, naturally occurring inactivating mutations in croS therefore have the potential of increasing the development and proliferation of polVR391‐dependent antibiotic resistance in a wide range of pathogenic microorganisms.
4. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
4.1. Bacterial strains and plasmids
Plasmids are listed in Table 1. Bacterial strains are listed in Table 2.
TABLE 2.
E. coli strains used in this study
| Strain | Relevant genotype | Source or reference |
|---|---|---|
| RW120 a | ∆umuDC595::cat hisG4(Oc) galK2(Oc) | (Ho et al., 1993) |
| RW546 a | ∆umuDC595::cat lexA51(Def) hisG4(Oc) galK2(Oc) | (Fernández de Henestrosa et al., 2000) |
| RW578 a | ∆umuDC595::cat lexA51(Def) recA730 hisG4(Oc) galK2(Oc) | (Mead et al., 2007) |
| RW520 a | ∆umuDC596::ermGT hisG4(Oc) galK2(Oc) | LGI stocks |
| RW584 a | ∆umuDC596::ermGT lexA51(Def) recA730 hisG4(Oc) galK2(Oc) | (McDonald et al., 2012) |
| MVG114 a | ∆umuDC596::ermGT lexA51(Def) recA718 hisG4(Oc) galK2(Oc) | (Gonzalez et al., 2019) |
| MVG114 a | R391 | This study |
| RW1766 b | ΔdinB61::ble | This study |
| MVG114 a | R391 ΔcroS | This study |
Full genotype: thr‐1 araD139 Δ(gpt‐proA)62 lacY1 tsx‐33 glnV44 rpsL31 xyl‐5 mtl‐1 argE3 thi‐1 sulA211.
ΔdinB61::ble derivative of MG1655 (F− λ− rph‐1).
Previously, R391 DNA (formerly known as the IncJ plasmid, R391) was isolated in its unintegrated episomal form in an E. coli strain harboring the recA718 allele (RW96) (Ho et al., 1993). This episomal R391 DNA was partially digested with EcoRI, and an ~21.5‐kb fragment was cloned into the low‐copy‐number vector pGB2 (Churchward et al., 1984) to generate pRLH421 (Genbank U13633) (Gonzalez et al., 2019). Unfortunately, the pRLH421 plasmid contains a truncation of the croS R391 gene in the divergent operon with setR R391 at an internal EcoRI within the croS R391 gene. To reconstruct the croS R391 gene, a fragment, designated “croS complete NarI‐PmeI‐Bsu36I,” was synthesized (Genscript) that includes from the NarI site to the EcoRI site of pGB2, the complete croS R391 open reading frame, the upstream promoter sequences, and a Bsu36I site replacing the start of the setR R391 gene. The croS complete fragment was subcloned into pRLH421 from the NarI (in pGB2) to PmeI (in the promoter region) to create an intact croS + R391 setR + R391 operon (pJM1356). Further, the croSR391 complete fragment was subcloned into pRLH421 from the NarI to Bsu36I (in setR R391) to create a croS + R391/ΔsetR R391 operon within only 222 bp of the 3′ end of the setR R391 gene (pJM1360). Another fragment designated “croS deletion NarI‐PmeI‐Bsu36I,” was synthesized (Genscript) from the NarI site to the first five bases of the EcoRI site of pGB2, the promoter sequences upstream of the croS R391 start ATG and a Bsu36I site replacing the start of the setR R391 gene. The croS deletion fragment was subcloned into pRLH421 from the NarI to PmeI to create a ΔcroS R391/setR + R391 operon (pJM1355). Further, the croS R391 deletion fragment was subcloned into pRLH421 from the NarI to Bsu36I to create a ΔcroS R391/ΔsetR R391 operon (pJM1359).
To create plasmids that carry just these four iterations of the croS R391/setR R391 operon, the plasmids pJM1355, pJM1356, pJM1359, and pJM1360 were digested with ScaI and SmaI and re‐ligated, which deletes ~20.3 kb of R391, leaving only the croS R391/setR R391 region including about 200 bases downstream of the end of the setR R391 gene. These plasmids are designated pJM1365 (ΔcroS R391/setR + R391), pJM1366 (croS+ R391/setR + R391), pJM1367 (ΔcroS R391/ΔsetR R391), and pJM1368 (croS + R391/ΔsetR R391).
The rumAB operon and the rumAB promoter region were cloned into the copy control plasmid, pCC1 (Genscript), to generate pJM1378. In addition, the rumAB operon fused to the E. coli recA promoter region was cloned into pCC1 to generate pJM1467 (recA‐prom::rumAB) (Genscript). These low‐copy pCC1Bac plasmids are compatible with the pGB2‐based croS R391/setR R391 plasmids described above, such that the various iterations of the croS R391/setR R391 operon can be co‐expressed with the rumAB operon.
4.2. Generation of R391ΔcroS
RW1766/R391 was constructed by inoculating an individual colony of RW1766 and RW120/R391 into 5‐ml LB and incubating overnight at 37℃ without shaking. The next morning, the culture was streaked on to plates containing Zeocin (25 μg ml–1) and Kanamycin (50 μg ml–1) to select for isolates of RW1766 that had acquired R391 via bacterial conjugation.
The marker‐less removal of the croS gene from the R391 element of E. coli RW1766/R391 was performed according to Zhang et al. (1998) (see Figure S5). In a first recombination step, a linear knock out cassette, generated with primers listed in Table 3, was used to replace the croS gene via Red/ET recombination by using plasmid pRed/ET. This resulted in a chloramphenicol‐resistant intermediate strain with the genotype ΔcroS::FRT‐CmR‐FRT (Figure S5). In a second recombination step, the selection marker was removed in a FLP recombinase‐mediated fashion, leaving a single FRT site at the former croS locus (genotype: ΔcroS::FRT). The intermediate and final clones were analyzed by Sanger sequencing using primers listed in Table 3 covering the complete modified and adjacent regions.
TABLE 3.
Oligonucleotides used in this study
| Name | Sequence | Source |
|---|---|---|
| P1 a | CTCGCTTTTGTGTTTACGTAAAATGCTGACCATTATTTGCCCTTAATCCTAAATTAACCCTCACTAAAGGGCGG | BioSpring |
| P2 a | CAGTTTAAACTGTAACATTCAATCTTGTAACAGTTATTATTGTAACAGGAGACGGTTAGCACGGAGTTCATTAGGGCTC | Biospring |
| cp01 b | GCGATGCCATACCAATGAAGTCG | BioSpring |
| cp02 b | CAACGTAACCAATCGGCAGTCG | BioSpring |
| cp03 b | CCAGTGACTTCACGCCACTCC | BioSpring |
| cp04 b | CAGGATCAACAACGATCACTGCC | BioSpring |
Used in the generation of linear knock out cassette.
Used in the amplification of the modified region and subsequent DNA sequencing.
New strains containing wild‐type R391 or R391ΔcroS were made by conjugal transfer of the ICE from RW1766 (Table 2) to the desired recipient strain by selecting on plates containing Streptomycin (100 μg ml–1) and Kanamycin (50 μg ml–1).
4.3. Qualitative analysis of spontaneous reversion of the hisG4(Oc) allele
The E. coli strain MVG114 was transformed with various plasmid constructs expressing CroSR391, SetRR391, and RumAB, either alone or in various iterations (Table 1). To assay for reversion of the hisG4(Oc) allele, three to five isolates of each strain were grown overnight at 37℃ in LB medium containing the appropriate antibiotic(s). Five hundred microliters of the cultures were centrifuged, and the pellets were resuspended in an equal volume of SM buffer. One hundred microliters of the resuspended pellets were spread on each of the five low‐histidine minimal plates (Davis and Mingioli minimal agar plates; Davis & Mingioli, 1950): plus glucose (0.4% wt/vol); agar (1.0% wt/vol); proline, threonine, valine, leucine, and isoleucine (all at 100 μg ml–1); thiamine (0.25 μg ml–1); and histidine (1 μg ml–1). After incubating the plates for 4 days at 37℃, the His+ mutant colonies were counted and averaged between the independent cultures and standard error of the mean calculated.
4.4. The galK2(Oc) reversion papillation assay
The galK2(Oc) papillation is a visual reversion mutagenesis assay that was previously used to identify genes from R‐plasmids that encode orthologs of the E. coli umuDC genes including rumAB from R391 (Ho et al., 1993). Briefly, ~ 50–75 E. coli cells harboring the galK2(Oc) allele are plated onto MacConkey‐galactose agar media and grown for 8 days at 37℃. A number of small orange‐red Gal+ papillae that grow up within a bacterial colony are noted from multiple colonies. Comparison of the number of papillae allows the assessment of the level of mutagenesis in the MVG114 strains harboring R391 versus MVG114 harboring R391ΔcroS.
4.5. Rifampicin mutagenesis assay
Selection for rifampicin resistance is another generally used mutagenesis assay. Base‐pair substitution mutations arising within the central 202 bp of the rpoB gene can give rise to resistance to the rifampicin antibiotic. Five milliliter cultures of MVG114/R391 and MVG114/R391ΔcroS were started, in triplicate, from an initial inoculum containing ~1,000 viable cells and grown for 24 hr at 37℃. One hundred microliters of these cultures were spread on five LB agar plates containing 100 μg ml–1 rifampicin. In addition, these cultures were serially diluted, and appropriate volumes were plated to LB agar plates to determine viable cell counts. Subsequently, frequencies of rifampicin mutations arising within the cultures were calculated.
4.6. Western blot analysis of CroSR391, RumAR391, and RecA proteins
E. coli cultures were grown in Luria‐Bertani media at 37℃ until exponential phase (OD600 ~0.5). For the experiments shown in Figure 6, Ciprofloxacin (30 ng ml–1) was added to the culture and cells were harvested by centrifugation at subsequent time points (as indicated in Figure 6). For all other experiments, undamaged cells were harvested at an OD600 ~0.5. The cell pellet was resuspended in NuPage LDS sample buffer (Novex) and freeze‐thawed to produce the whole cell extracts. Cell extracts were electrophoresed on NuPage 4%–12% Bis‐Tris gels (Novex). Proteins were transferred to an Invitrolon polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (Novex) that was probed with appropriate dilutions of affinity purified rabbit anti‐CroSR391, anti‐RumAR391, or anti‐E. coli RecA antibodies and subsequently probed with an appropriate dilution of Goat Anti‐Rabbit IgG (H+L)‐AP Conjugate (Bio‐Rad). Using the CDP‐Star chemiluminescent assay (Tropix), the CroSR391, RumAR391/A′R391, or RecA proteins were visualized on Carestream Biomax XAR Film after various exposure times. Digital images were also captured using an Alpha Innotech FluorChem HD2. These images were then imported as .tif files into LI‐COR Biosciences Image Studio Lite software, where band density was quantified using the Data Analysis tool. Relative protein levels for bands of interest were calculated by normalizing band density to that of nonspecific bands within each lane and then expressed relative to a cross‐reacting reference band.
4.7. Overexpression and purification of CroS
The gene encoding R391 croS was codon optimized for expression in E. coli and chemically synthesized (Genscript) as a 309 bp NdeI‐PstI fragment and cloned into pUC57 (Genscript). The NdeI‐PstI fragment was subsequently subcloned into the same sites of pCF2. pCF2 is a medium copy plasmid that expresses Isopropyl ß‐D‐1‐thiogalactopyranoside‐inducible glutathione‐S transferase (GST). The construct also contains a PreScission (GE Healthcare) protease site immediately downstream of the GST protein and upstream of the unique NdeI site. When the target gene is cloned into the NdeI site of pCF2, a GST‐fusion protein is generated with a PreScission site immediately upstream of the target protein. CroS was initially purified as a GST‐CroS fusion protein as a custom service by scientists at Eurofins, as previously described (Poulin‐Laprade & Burrus, 2015), and the GST‐affinity tag subsequently removed after the PreScission protease treatment (Eurofins).
4.8. CroS antibodies
Polyclonal antibodies to the purified CroS protein were raised in rabbits as a custom service (Covance) and affinity purified. These antibodies are highly specific with very few cross‐reacting bands in western blots of E. coli extracts lacking CroS.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with the content of this article.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: JPM, MG, and RW
Funding Acquisition: MG and RW
Investigation: JPM, DRQ, AV, ARM, JR, MS, MG, and RW
Writing‐Original Draft: JPM and RW
Writing‐Review and Editing: JPM, DRQ, AV, ARM, JR, MS, MG, and RW.
Supporting information
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was funded in part by the NICHD/NIH Intramural Research Program to RW, and the Southwestern University Faculty‐Student Collaborative Projects Fund and the Lizanell and Colbert Coldwell Foundation to MG. We thank Nicholas Ashton, LGI/NIH, for his assistance in generating the figures shown herein, as well as quantifying the levels of RumA and RumA′ reported in Figures 4, 5, 6, and S5.
McDonald, J.P. , Quiros, D.R. , Vaisman, A. , Mendez, A.R. , Reyelt, J. , Schmidt, M. , et al. (2021) CroSR391, an ortholog of the λ Cro repressor, plays a major role in suppressing polVR391‐dependent mutagenesis. Molecular Microbiology, 116, 877–889. 10.1111/mmi.14777
Contributor Information
Martín Gonzalez, Email: gonzale2@southwestern.edu.
Roger Woodgate, Email: woodgate@nih.gov.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
REFERENCES
- Bagg, A. , Kenyon, C.J. & Walker, G.C. (1981) Inducibility of a gene product required for UV and chemical mutagenesis in Escherichia coli . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 78, 5749–5753. 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5749 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaber, J.W. , Hochhut, B. & Waldor, M.K. (2004) SOS response promotes horizontal dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Nature, 427, 72–74. 10.1038/nature02241 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, K. , Bastola, R. & Baral, B. (2020) Antibiotic drug discovery: challenges and perspectives in the light of emerging antibiotic resistance. Advances in Genetics, 105, 229–292. 10.1016/bs.adgen.2019.12.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bie, L. , Wu, H. , Wang, X.H. , Wang, M. & Xu, H. (2017) Identification and characterization of new members of the SXT/R391 family of integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) in Proteus mirabilis . International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 50, 242–246. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.01.045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boltner, D. , MacMahon, C. , Pembroke, J.T. , Strike, P. & Osborn, A.M. (2002) R391: a conjugative integrating mosaic comprised of phage, plasmid, and transposon elements. Journal of Bacteriology, 184, 5158–5169. 10.1128/JB.184.18.5158-5169.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt, S.E. , Woodgate, R. , Scheuermann, R.H. & Echols, H. (1988) UmuD mutagenesis protein of Escherichia coli: overproduction, purification and cleavage by RecA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 85, 1811–1815. 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1811 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchward, G. , Belin, D. & Nagamine, Y. (1984) A pSC101‐derived plasmid which shows no sequence homology to other commonly used cloning vectors. Gene, 31, 165–171. 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90207-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirz, R.T. , Gingles, N. & Romesberg, F.E. (2006a) Side effects may include evolution. Nature Medicine, 12, 890–891. 10.1038/nm0806-890 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirz, R.T. , Jones, M.B. , Gingles, N.A. , Minogue, T.D. , Jarrahi, B. , Peterson, S.N. et al. (2007) Complete and SOS‐mediated response of Staphylococcus aureus to the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Journal of Bacteriology, 189, 531–539. 10.1128/JB.01464-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirz, R.T. , O'Neill, B.M. , Hammond, J.A. , Head, S.R. & Romesberg, F.E. (2006b) Defining the Pseudomonas aeruginosa SOS response and its role in the global response to the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Journal of Bacteriology, 188, 7101–7110. 10.1128/JB.00807-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirz, R.T. & Romesberg, F.E. (2006) Induction and inhibition of ciprofloxacin resistance‐conferring mutations in hypermutator bacteria. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 50, 220–225. 10.1128/AAC.50.1.220-225.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis, B.D. & Mingioli, E.S. (1950) Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. Journal of Bacteriology, 60, 17–28. 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y. , Wang, Y. , Li, Z. , Liu, Z. , Li, X. , Diao, B. et al. (2018) Distribution and genetic characteristics of SXT/R391 integrative conjugative elements in Shewanella spp. from China. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 920. 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández de Henestrosa, A.R. , Ogi, T. , Aoyagi, S. , Chafin, D. , Hayes, J.J. , Ohmori, H. et al. (2000) Identification of additional genes belonging to the LexA‐regulon in Escherichia coli . Molecular Microbiology, 35, 1560–1572. 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01826.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fijalkowska, I.J. , Dunn, R.L. & Schaaper, R.M. (1997) Genetic requirements and mutational specificity of the Escherichia coli SOS mutator activity. Journal of Bacteriology, 179, 7435–7445. 10.1128/jb.179.23.7435-7445.1997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank, E.G. , Ennis, D.G. , Gonzalez, M. , Levine, A.S. & Woodgate, R. (1996) Regulation of SOS mutagenesis by proteolysis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 93, 10291–10296. 10.1073/pnas.93.19.10291 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, M. , Frank, E.G. , Levine, A.S. & Woodgate, R. (1998) Lon‐mediated proteolysis of the Escherichia coli UmuD mutagenesis protein: in vitro degradation and identification of residues required for proteolysis. Genes & Development, 12, 3889–3899. 10.1101/gad.12.24.3889 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, M. , Huston, D. , McLenigan, M.P. , McDonald, J.P. , Garcia, A.M. , Borden, K.S. et al. (2019) SetRICE391, a negative transcriptional regulator of the integrating conjugative element 391 mutagenic response. DNA Repair, 73, 99–109. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.11.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, M. , Rasulova, F. , Maurizi, M.R. & Woodgate, R. (2000) Subunit‐specific degradation of the UmuD/D' heterodimer by the ClpXP protease: the role of trans recognition in UmuD' stability. EMBO Journal, 19, 5251–5258. 10.1093/emboj/19.19.5251 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, M.F. , McDonald, J.P. , Jaszczur, M.M. & Woodgate, R. (2016) Insights into the complex levels of regulation imposed on Escherichia coli DNA polymerase V. DNA Repair, 44, 42–50. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C. , Kulaeva, O.I. , Levine, A.S. & Woodgate, R. (1993) A rapid method for cloning mutagenic DNA repair genes: isolation of umu‐complementing genes from multidrug resistance plasmids R391, R446b, and R471a. Journal of Bacteriology, 175, 5411–5419. 10.1128/jb.175.17.5411-5419.1993 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochhut, B. , Beaber, J.W. , Woodgate, R. & Waldor, M.K. (2001) Formation of chromosomal tandem arrays of the SXT element and R391, two conjugative chromosomally integrating elements that share an attachment site. Journal of Bacteriology, 183, 1124–1132. 10.1128/JB.183.4.1124-1132.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q. , Karata, K. , Woodgate, R. , Cox, M.M. & Goodman, M.F. (2009) The active form of DNA polymerase V is UmuD'2C‐RecA‐ATP. Nature, 460, 359–363. 10.1038/nature08178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A. , Meyer, B.J. & Ptashne, M. (1978) Mechanism of action of the cro protein of bacteriophage λ. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 75, 1783–1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.H. , Xiang, R. , Wang, Y.L. , Wu, S.K. , Lei, C.W. , Kang, Z.Z. et al. (2020) Integration of the blaNDM‐1 carbapenemase gene into a novel SXT/R391 integrative and conjugative element in Proteus vulgaris . Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 75, 1439–1442. 10.1093/jac/dkaa068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaeva, O.I. , Wootton, J.C. , Levine, A.S. & Woodgate, R. (1995) Characterization of the umu‐complementing operon from R391. Journal of Bacteriology, 177, 2737–2743. 10.1128/jb.177.10.2737-2743.1995 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall, J.O. , Witkin, E.M. , Kogoma, T. & Roegner‐Maniscalco, V. (1987) Constitutive expression of the SOS response in recA718 mutants of Escherichia coli requires amplification of RecA718 protein. Journal of Bacteriology, 169, 728–734. 10.1128/jb.169.2.728-734.1987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, J.P. , Vaisman, A. , Kuban, W. , Goodman, M.F. & Woodgate, R. (2012) Mechanisms employed by Escherichia coli to prevent ribonucleotide incorporation into genomic DNA by pol V. PLoS Genetics, 8, e1003030. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLenigan, M.P. , Kulaeva, O.I. , Ennis, D.G. , Levine, A.S. & Woodgate, R. (1999) The bacteriophage P1 HumD protein is a functional homolog of the prokaryotic UmuD'‐like proteins and facilitates SOS mutagenesis in Escherichia coli . Journal of Bacteriology, 181, 7005–7013. 10.1128/JB.181.22.7005-7013.1999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead, S. , Vaisman, A. , Valjavec‐Gratian, M. , Karata, K. , Vandewiele, D. & Woodgate, R. (2007) Characterization of polVR391: a Y‐family polymerase encoded by rumA'B from the IncJ conjugative transposon, R391. Molecular Microbiology, 63, 797–810. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05561.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohmi, T. , Battista, J.R. , Dodson, L.A. & Walker, G.C. (1988) RecA‐mediated cleavage activates UmuD for mutagenesis: mechanistic relationship between transcriptional derepression and posttranslational activation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 85, 1816–1820. 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1816 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney, R.J. (1980) Distribution among incompatibility groups of plasmids that confer UV mutability and UV resistance. Mutation Research, 72, 155–159. 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90232-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulin‐Laprade, D. & Burrus, V. (2015) A λ Cro‐Like repressor is essential for the induction of conjugative transfer of SXT/R391 elements in response to DNA damage. Journal of Bacteriology, 197, 3822–3833. 10.1128/JB.00638-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulin‐Laprade, D. , Matteau, D. , Jacques, P.E. , Rodrigue, S. & Burrus, V. (2015) Transfer activation of SXT/R391 integrative and conjugative elements: unraveling the SetCD regulon. Nucleic Acids Research, 43, 2045–2056. 10.1093/nar/gkv071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, A. , McDonald, J.P. , Caldas, V.E. , Patel, M. , Wood, E.A. , Punter, C.M. et al. (2015) Regulation of mutagenic DNA polymerase V: activation in space and time. PLoS Genetics, 11, e1005482. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005482 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa, H. , Iwasaki, H. , Kato, T. & Nakata, A. (1988) RecA protein‐dependent cleavage of UmuD protein and SOS mutagenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 85, 1806–1810. 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, L.A. , Foti, J.J. , Cohen, S.E. & Walker, G.C. (2008) The SOS regulatory network. EcoSal Plus, 2008. 10.1128/ecosalplus.5.4.3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slattery, S. , Pembroke, J.T. , Murnane, J.G. & Ryan, M.P. (2020) Isolation, nucleotide sequencing and genomic comparison of a novel SXT/R391 ICE mobile genetic element isolated from a municipal wastewater environment. Scientific Reports, 10, 8716. 10.1038/s41598-020-65216-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y. , Yu, P. , Li, B. , Pan, Y. , Zhang, X. , Cong, J. et al. (2013) The mosaic accessory gene structures of the SXT/R391‐like integrative and conjugative elements derived from Vibrio spp. isolated from aquatic products and environment in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. BMC Microbiology, 13, 214. 10.1186/1471-2180-13-214 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenningsen, S.L. , Costantino, N. , Court, D.L. & Adhya, S. (2005) On the role of Cro in λ prophage induction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 4465–4469. 10.1073/pnas.0409839102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweasy, J.B. , Witkin, E.M. , Sinha, N. & Roegner‐Maniscalco, V. (1990) RecA protein of Escherichia coli has a third essential role in SOS mutator activity. Journal of Bacteriology, 172, 3030–3036. 10.1128/jb.172.6.3030-3036.1990 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekeres, E.S.J. , Woodgate, R. & Lawrence, C.W. (1996) Substitution of mucAB or rumAB for umuDC alters the relative frequencies of the two classes of mutations induced by a site‐specific T‐T cyclobutane dimer and the efficiency of translesion DNA synthesis. Journal of Bacteriology, 178, 2559–2563. 10.1128/jb.178.9.2559-2563.1996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, Y. , Folkmanis, A. & Echols, H. (1977) Cro regulatory protein specified by bacteriophage λ. Structure, DNA‐binding, and repression of RNA synthesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 252, 6177–6183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M. , Shen, X. , Frank, E.G. , O'Donnell, M. , Woodgate, R. & Goodman, M.F. (1999) UmuD'2C is an error‐prone DNA polymerase, Escherichia coli, DNA pol V. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96, 8919–8924. 10.1073/pnas.96.16.8919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton, C. & Pinney, R.J. (1983) Expression of eight unrelated Muc+ plasmids in eleven DNA repair‐deficient E. coli strains. Mutation Research, 112, 261–273. 10.1016/0167-8817(83)90002-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. , Sarov, M. , Rientjes, J. , Fu, J. , Hollak, H. , Kranz, H. et al. (2006) An improved recombineering approach by adding RecA to λ Red recombination. Molecular Biotechnology, 32, 43–53. 10.1385/MB:32:1:043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendlandt, S. , Shen, J. , Kadlec, K. , Wang, Y. , Li, B. , Zhang, W.J. et al. (2015) Multidrug resistance genes in staphylococci from animals that confer resistance to critically and highly important antimicrobial agents in human medicine. Trends in Microbiology, 23, 44–54. 10.1016/j.tim.2014.10.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgate, R. , Rajagopalan, M. , Lu, C. & Echols, H. (1989) UmuC mutagenesis protein of Escherichia coli: purification and interaction with UmuD and UmuD'. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 86, 7301–7305. 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7301 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. , Buchholz, F. , Muyrers, J.P. & Stewart, A.F. (1998) A new logic for DNA engineering using recombination in Escherichia coli . Nature Genetics, 20, 123–128. 10.1038/2417 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Material
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.


