Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the prognostic value of the aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase (AST/ALT) ratio in primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) using propensity score matching (PSM) analysis.
Methods
We retrospectively collected the clinical and pathological data from 314 patients with primary NMIBC who underwent transurethral resection of bladder tumor. The full cohorts were divided into a low AST/ALT ratio group and a high AST/ALT ratio group according to the optimal cut-off value which was obtained based on the analysis of the receiver operating characteristic curve for the 3-year recurrence-free survival (RFS). After 1:1 PSM, the correlation between preoperative AST/ALT ratio and survival prognosis was evaluated by Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank tests. The independent prognostic factors for RFS and progression-free survival (PFS) were also analyzed.
Results
The optimum cutoff value of the preoperative AST/ALT ratio was 1.40. Before PSM, a high AST/ALT ratio was correlated with the larger proportion of age > 60 years (P = 0.007) and the worse pathological T stage (P < 0.001). After PSM, patients with a high AST/ALT ratio had poorer RFS and PFS than patients with a low AST/ALT ratio (all P < 0.001). In addition, multivariate Cox regression analysis indicated that preoperative AST/ALT ratio was considered as an independent prognostic factor of RFS (HR 2.865; 95%CI 1.873–4.381; P < 0.001) and PFS (HR 4.771; 95%CI 2.607–8.734; P < 0.001) in patients with primary NMIBC.
Conclusions
The high AST/ALT ratio group tended to have poorer RFS and PFS than the low AST/ALT ratio group. Our results also indicated that the elevated preoperative AST/ALT ratio could be seen as a useful prognostic biomarker for predicting early disease recurrence and progression in patients with primary NMIBC.
Keywords: Aspartate transaminase, Alanine transaminase, Primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer, Survival prognosis
Background
Bladder cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers in the urinary tract and the seventh most common tumor in the male population worldwide, while it drops to the 11th if both genders are considered [1, 2]. Approximately 75% of patients with bladder cancer present with disease confined to the mucosa or submucosa, which is referred to as non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) and this proportion is even higher in younger patients (< 40 years) [3]. The standard treatment for NMIBC is transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT), eventually followed by adjuvant intravesical therapy based on risk stratification [4]. However, the high recurrence rate of NMIBC patients is as high as 50–70% and one-third of recurrent patients will develop into muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) and eventually succumb to the disease [5, 6]. To better predict the recurrence and progression of NMIBC, several biomarkers, such as serum cholinesterase, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, plasma fibrinogen, and D-dimer, have been studied [7–9]. Nevertheless, our knowledge of plasma prognostic factors assessed preoperatively in NMIBC remains limited.
Aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) are found in the liver, heart, skeletal muscle, brain, kidney, and red blood cells, which are widely used to reflect hepatocellular damage in clinical practice. In 1957, the ratio of the serum activities of AST to ALT was first described as an important indicator for differentiating the etiology of acute hepatitis by De Ritis et al., which was also called the De Ritis ratio [10]. The AST/ALT ratio was widely used to identify various liver diseases such as viral hepatitis and alcoholic hepatitis. Meanwhile, the latest research shows that this ratio has been reported as a prognostic biomarker in several malignancies, such as renal cell carcinoma, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and colorectal cancer [11–15]. Similarly, this ratio has been demonstrated as a significant prognostic biomarker in patients undergoing radical cystectomy with bladder cancer [16–18]. Although their study was valuable for proposing the AST/ALT ratio as a new prognostic factor in BC, the molecular features and clinical outcomes between NMIBC and MIBC are highly distinct [19]. The prognostic predictive value of the AST/ALT ratio in primary NMIBC needs to be further clarified.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the prognostic predictive value of the AST/ALT ratio on the survival prognosis of patients with primary NMIBC. A propensity score-matching (PSM) methodology was performed to minimize the interference of other confounding factors.
Methods
Patient selection
We retrospectively reviewed the relevant medical records and collected clinical and pathological data of 314 patients with primary NMIBC who underwent TURBT at the Department of Urology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University from January 2013 to May 2017. Patient inclusion criteria as following: (1) biopsy of cystoscopy and postoperative pathological outcomes were consistent in confirming non-muscle-invasive bladder urothelial carcinoma, (2) laboratory data of AST and ALT were obtained within 5 days before the first surgical treatment, and (3) adequate follow-up information is available for prognostic analysis. Exclusion Criteria: (1) any concomitant malignancy and pelvic radiation, (2) present hematological disorders and chronic liver disease within the last 3 months, (3) perioperative death. All patients obtained and signed informed consent. This study has been approved by the Institutional Ethical Review Board and the study protocol was carried out following the guidelines of the Helsinki declaration.
Study design
To evaluate the optimum thresholds for the AST/ALT ratio, the receiver operating characteristic curve for 3-year recurrence-free survival (RFS) was analyzed. The optimum threshold for the AST/ALT ratio was obtained when there was a maximum Youden index value. This threshold transforms the AST/ALT rate into a dichotomous variable that divides all patients into a high AST/ALT group and a low AST/ALT group. To balance the differences of the covariates of baseline data in both the group, PSM analysis was done using a multivariable logistic regression model based on age, gender, the history of smoking, tumor size, tumor number, restaging transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (Re-TURBT), pathological stage, pathological grade, concomitant carcinoma in situ, type of intravesical therapy. Pairs of patients were derived using 1:1 greedy nearest neighbor matching within a caliper size of 0.1. Further, the clinicopathological data of the two paired groups were analyzed and the predictive value of the AST/ALT ratio in primary NMIBC was evaluated.
Patient management and follow‑up
TURBT was performed by skilled urologists at our center. Indications for Re-TURBT in patients with NMIBC remain controversial [20]. Thus, Re-TURBT was not routinely performed in all patients. All patients received postoperative observation, early single instillation, adjuvant intravesical chemotherapy, or intravesical BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) treatment according to tumor characteristics. All pathological diagnoses were made by two pathologists after viewing and checking. In this study, the International Union Against Cancer tumor, node, metastasis classification system (2009) and the World Health Organization International Society of Urologic Pathology (2004) was used as the standard for bladder cancer staging and grading. The patient follow-up protocol which included surveillance cystoscopy or computerized tomography of the pelvis was performed at 3-month intervals for the initial 2 years, every 6 months in the next 3 years, and annually thereafter. RFS was defined as the time interval from initial TURBT to the first occurrence of local or distant recurrent disease. Progression-free survival (PFS) referred to the interval from initial surgery to first disease progression (any advance in tumor grade or stage).
Statistical analysis
All categorical data were presented as a percentage or an absolute number, while continuous variables were presented as the median and interquartile range (IQR). The difference in clinicopathologic factors between the two groups was taken by the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test before PSM, while the McNemar test was performed after PSM. The difference in survival was evaluated by Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank tests. The univariate and multivariate analyses were performed by a Cox proportional hazard model to identify the potential predictors of prognosis. PSM was performed using the MatchIt package in R software; all statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 26.0 Statistics software. P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Clinical and pathological characteristics in the full cohorts
A total of 314 patients newly diagnosed with NMIBC who underwent TURBT and were included in this study. The study population included 250 male and 64 female patients with a median age of 65 years (IQR 58–73 years), 137of whom had a history of smoking. 86 patients had a history of Re-TURBT. The tumor size was ≤ 3 cm in 247 (78.7%) patients, and > 3 cm in 67 (21.3%) patients. Multifocal tumors were found in 164 (52.2%) patients. Pathological T stage was Ta in 161 (51.3%) and T1 in 153 (48.7%) patients. Tumor grade was papillary urothelial neoplasms of low malignant potential in 13 (4.1%), low grade in157 (50.0%), and high grade in 144 (45.9%) patients. 29 (9.2%) patients had concomitant carcinoma in situ (CIS). 34 (10.8%) patients underwent early single instillation only and 48 (15.3%) patients were treated with postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy or BCG only, while 232 (73.9%) patients underwent combined therapy. Furthermore, 171 (54.5%) patients experienced recurrence, and 94 (29.9%) patients experienced progression after initial TURBT. The median follow-up time was 48 months (IQR 22.3–72 months).
Determination of optimal cutoff values regarding prediction of 3-year RFS
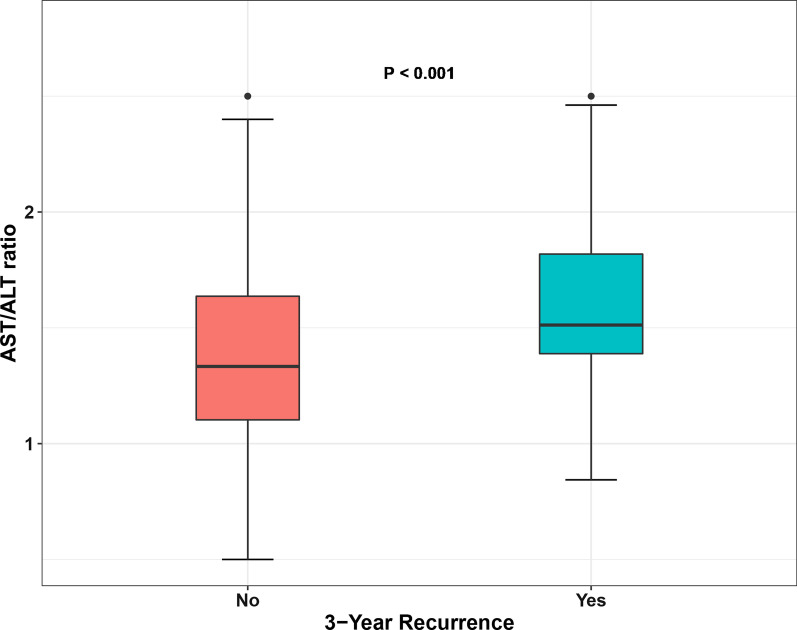
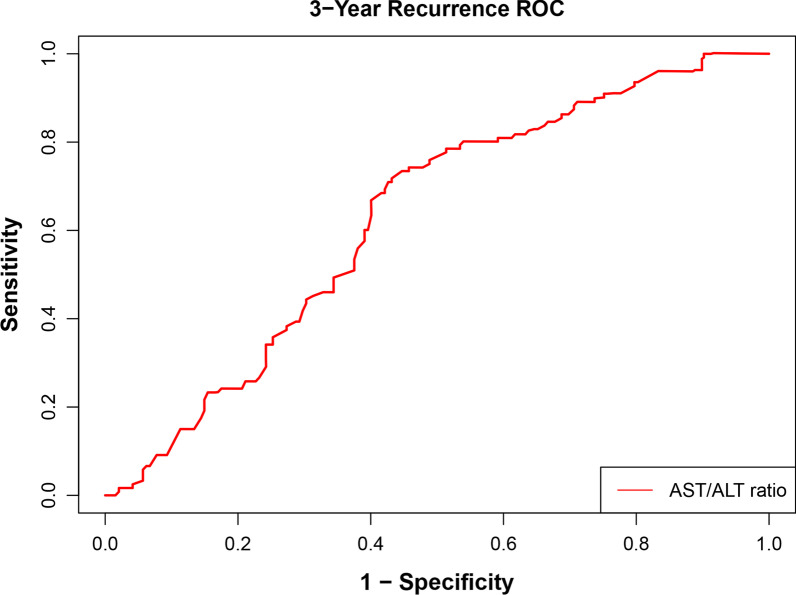
The median ALT, AST, and the AST/ALT ratio were 16.0 U/L (IQR 12.0–21.0 U/L), 22.0 U/L (IQR 19.0–27.0 U/L), and 1.4 (IQR 1.2–1.8), respectively. Patients who relapsed within 3 years after initial TURBT was more tend to have a high AST/ALT ratio (P < 0.001) (Fig. 1). According to the receiver operating characteristic curve for 3-year recurrence-free survival, when there is a maximum value of the Youden index, the optimal cutoff value for the AST/ALT ratio is 1.40 (area under the curve 0.627, sensitivity 0.746, specificity 0.541) (Fig. 2). In the full cohorts, there were 139 (44.3%) patients in the high AST/ALT group and 175 (55.7%) patients in the low AST/ALT group.
Fig. 1.
Comparison of the AST/ALT ratio between 3-year recurrence group and 3-year nonrecurrence group
Fig. 2.
ROC curve analysis for determination of optimal cutoff values of the AST/ALT ratio in 3-year RFS
Relationship between preoperative AST/ALT ratio and Clinical and pathological characteristics in the full and PSM cohorts
With regard to the clinical characteristics of the two groups in the full cohorts, there was no statistical difference between the two groups in gender, history of smoking, Re-TURBT, tumor size, tumor number, pathological grade, concomitant carcinoma in situ (CIS), and type of intravesical therapy (all P ≥ 0.05). However, the pathological T stage of the high AST/ALT ratio group was worse than those of the low AST/ALT ratio group (P < 0.001), and the proportion of those aged > 60 years was also higher (P = 0.007) (Table 1). After 1:1 PSM, the cohort included 100 patients, of which 102 (50.0%) were in the high AST/ALT group and 102 (50.0%) in the low AST/ALT group. There were no statistically significant differences in reported baseline covariates in PSM cohorts (Table 1).
Table1.
Clinical and pathological data of all patients and propensity score-matched cohorts
| Variables | Before PSM | After PSM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low AST/ALT ratio (n = 139) | High AST/ALT ratio (n = 175) | P valuea | Low AST/ALT ratio (n = 102) | High AST/ALT ratio (n = 102) | P valueb | |
| Age, n (%) | 0.007* | 0.597 | ||||
| ≤ 60 year | 59 (42.4) | 49 (28.0) | 31 (30.4) | 35 (34.3) | ||
| > 60 year | 80 (57.6) | 126 (72.0) | 71 (69.6) | 67 (65.7) | ||
| Gender, n (%) | 0.133 | 0.728 | ||||
| Female | 23 (16.5) | 41 (23.4) | 18 (17.6) | 21 (20.6) | ||
| Male | 116 (83.5) | 134 (76.6) | 84 (82.4) | 81 (79.4) | ||
| Smoking, n (%) | 67 (48.2) | 70 (40.0) | 0.146 | 49 (48.0) | 52 (51.0) | 0.736 |
| Tumor size, n (%) | 0.117 | 1.000 | ||||
| ≤ 3 cm | 115 (82.7) | 132 (75.4) | 83 (81.4) | 83 (81.4) | ||
| > 3 cm | 24 (17.3) | 43 (24.6) | 19 (18.6) | 19 (18.6) | ||
| Tumor number, n (%) | 0.084 | 0.711 | ||||
| Solitary | 74 (53.2) | 76 (43.4) | 50 (49.0) | 53 (52.0) | ||
| Multiple | 65 (46.8) | 99 (56.6) | 52 (51.0) | 49 (48.0) | ||
| Re-TURBT, n (%) | 37 (26.6) | 49 (28.0) | 0.785 | 27 (26.5) | 28 (27.5) | 1.000 |
| Pathological stage, n (%) | < 0.001* | 1.000 | ||||
| pTa | 94 (67.6) | 67 (38.3) | 57 (55.9) | 58 (56.9) | ||
| pT1 | 45 (32.4) | 108 (61.7) | 45 (44.1) | 44 (43.1) | ||
| Pathological grade, n (%) | 0.954 | 0.291 | ||||
| LG or less | 75 (54.0) | 95 (54.3) | 50 (49.0) | 58 (56.9) | ||
| HG | 64 (46.0) | 80 (45.7) | 52 (51.0) | 44 (43.1) | ||
| Concomitant carcinoma in situ, n (%) | 11 (7.9) | 18 (10.3) | 0.471 | 11 (10.8) | 9 (8.8) | 0.815 |
| Type of intravesical therapy, n (%) | 0.331 | 0.076 | ||||
| Early single instillation | 17 (12.2) | 17 (9.7) | 7 (6.9) | 16 (15.7) | ||
| Adjuvant chemotherapy or BCG | 25 (18.0) | 23 (13.1) | 19 (18.6) | 14 (13.7) | ||
| Combined therapy | 97 (69.8) | 135 (77.1) | 76 (74.5) | 72 (70.6) | ||
PSM, Propensity score-matched; Re-TURBT, restaging transurethral resection of the bladder tumor; LG or less, low grade or papillary urothelial neoplasms of low malignant potential; HG, high grade; BCG, bacillus Calmette-Guerin
*Indicates P < 0.05
aχ2 test or Fisher’s exact test
bMcNemar test
Relationship between preoperative AST/ALT ratio and RFS in the PSM cohorts
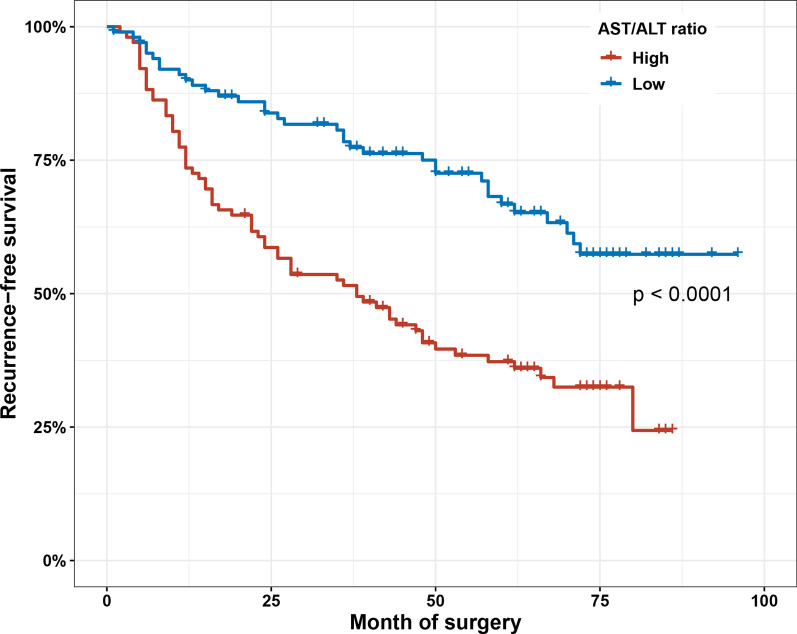
Kaplan–Meier survival analysis was performed to assess the relationship between preoperative AST/ALT ratio and risk of recurrence. The results showed that the low AST/ALT ratio group had significantly better RFS than the high AST/ALT ratio group (P < 0.001) (Fig. 3). The univariate Cox analysis of RFS showed that several prognostic factors including age (P = 0.010), tumor size (P = 0.008), Re-TURBT (P = 0.001), pathological stage (P = 0.011) and the AST/ALT ratio (P < 0.001) were related to the RFS of patients. In multivariate Cox analyses, these related prognostic factors including tumor size (HR 1.879; 95%CI 1.180–2.993; P = 0.008), tumor number (HR 1.728; 95%CI 1.140–2.619; P = 0.010), Re-TURBT (HR 0.305; 95%CI 0.177–0.526; P < 0.001), pathological stage (HR 1.601; 95%CI 1.036–2.474; P = 0.034), and the elevated AST/ALT ratio (HR 2.865; 95%CI 1.873–4.381; P < 0.001) continued independent association with RFS in multivariate Cox analysis (Table 2).
Fig. 3.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves of RFS according to the AST/ALT ratio in propensity score-matched cohorts
Table 2.
Univariate and multivariate cox proportional regression analysis for RFS in propensity score-matched cohorts
| Variables | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | P value | HR (95%CI) | P value | |
| Age, n (%) | ||||
| ≤ 60 year | Ref | Ref | ||
| > 60 year | 0.596 (0.402–0.884) | 0.010* | 0.713 (0.476–1.068) | 0.101 |
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
| Female | Ref | |||
| Male | 1.039 (0.631–1.712) | 0.880 | ||
| Smoking, n (%) | 1.171 (0.792–1.730) | 0.429 | ||
| Tumor size | ||||
| ≤ 3 cm | Ref | Ref | ||
| > 3 cm | 1.838 (1.168–2.892) | 0.008* | 1.879 (1.180–2.993) | 0.008* |
| Tumor number, n (%) | ||||
| Solitary | Ref | Ref | ||
| Multiple | 1.428 (0.962–2.119) | 0.077 | 1.728 (1.140–2.619) | 0.010* |
| Re-TURBT, n (%) | 0.399 (0.233–0.681) | 0.001* | 0.305 (0.177–0.526) | < 0.001* |
| Pathological stage, n (%) | ||||
| pTa | Ref | Ref | ||
| pT1 | 1.659 (1.121–2.457) | 0.011* | 1.601 (1.036–2.474) | 0.034* |
| Pathological grade, n (%) | ||||
| LG or less | Ref | Ref | ||
| HG | 1.301 (0.880–1.923) | 0.187 | 1.336 (0.857–2.081) | 0.201 |
| Concomitant carcinoma in situ, n (%) | 1.458 (0.814–2.614) | 0.205 | ||
| Type of intravesical therapy, n (%) | ||||
| Early single instillation | Ref | |||
| Adjuvant chemotherapy or BCG | 1.467 (0.633–3.401) | 0.371 | ||
| Combined therapy | 1.611 (0.777–3.338) | 0.200 | ||
| AST/ALT ratio | ||||
| Low | Ref | Ref | ||
| High | 2.445 (1.620–3.691) | < 0.001* | 2.865 (1.873–4.381) | < 0.001* |
RFS, Recurrence-free survival; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; Ref, Reference; Re-TURBT, restaging transurethral resection of the bladder tumor; LG or less, low grade or papillary urothelial neoplasms of low malignant potential; HG, high grade; BCG, bacillus Calmette-Guerin
*Indicates P < 0.05
Relationship between preoperative AST/ALT ratio and PFS in the PSM cohorts
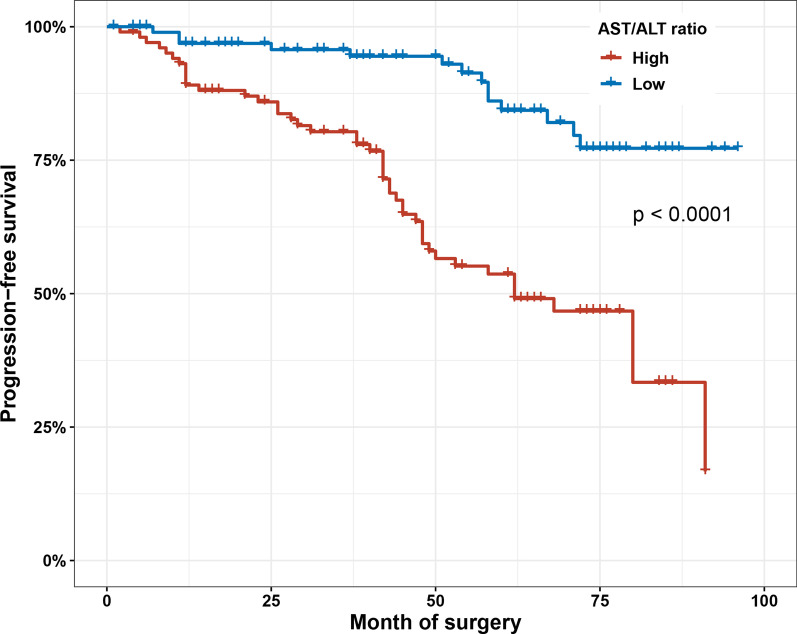
Kaplan–Meier survival analysis demonstrated that the high AST/ALT ratio group tended to have poorer PFS than the low AST/ALT ratio group (P < 0.001) (Fig. 4). In univariate Cox proportional hazard model, the prognostic indicators of RFS in primary NMIBC included Re-TURBT (P = 0.006), pathological stage (P = 0.047), pathological grade (P = 0.023), and the AST/ALT ratio (P < 0.001). According to Cox multivariate analysis, the independent prognostic indicators of RFS in primary NMIBC involved Re-TURBT (HR 0.301; 95%CI 0.147–0.617; P = 0.001), pathological grade (HR 1.893; 95%CI 1.076–3.329; P = 0.027), and the AST/ALT ratio (HR 4.771; 95%CI 2.607–8.734; P < 0.001) (Table 3).
Fig. 4.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves of PFS according to the AST/ALT ratio in propensity score-matched cohorts
Table 3.
Univariate and multivariate cox proportional regression analysis for PFS in propensity score-matched cohorts
| Variables | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | P value | HR (95%CI) | P value | |
| Age, n (%) | ||||
| ≤ 60 year | Ref | |||
| > 60 year | 0.859 (0.505–1.462) | 0.576 | ||
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
| Female | Ref | |||
| Male | 0.748 (0.379–1.477) | 0.403 | ||
| Smoking, n (%) | 1.128 (0.680–1.872) | 0.641 | ||
| Tumor size | ||||
| ≤ 3 cm | Ref | |||
| > 3 cm | 1.666 (0.911–3.044) | 0.097 | ||
| Tumor number, n (%) | ||||
| Solitary | Ref | Ref | ||
| Multiple | 0.982 (0.591–1.632) | 0.943 | 1.877 (0.997–3.532) | 0.051 |
| Re-TURBT, n (%) | 0.372 (0.183–0.758) | 0.006* | 0.301 (0.147–0.617) | 0.001* |
| Pathological stage, n (%) | ||||
| pTa | Ref | Ref | ||
| pT1 | 1.687 (1.007–2.828) | 0.047* | 1.534 (0.873–2.694) | 0.137 |
| Pathological grade, n (%) | ||||
| LG or less | Ref | Ref | ||
| HG | 1.820 (1.085–3.053) | 0.023* | 1.893 (1.076–3.329) | 0.027* |
| Concomitant carcinoma in situ, n (%) | 1.752 (0.859–3.575) | 0.123 | ||
| Type of intravesical therapy, n (%) | ||||
| Early single instillation | Ref | |||
| Adjuvant chemotherapy or BCG | 1.061 (0.385–2.920) | 0.909 | ||
| Combined therapy | 1.191 (0.507–2.798) | 0.688 | ||
| AST/ALT ratio | ||||
| Low | Ref | Ref | ||
| High | 4.165 (2.283–7.599) | < 0.001* | 4.771 (2.607–8.734) | < 0.001* |
PFS, Progression-free survival; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; Ref, Reference; Re-TURBT, restaging transurethral resection of the bladder tumor; LG or less, low grade or papillary urothelial neoplasms of low malignant potential; HG, high grade; BCG, bacillus Calmette-Guerin
*Indicates P < 0.05
Discussion
The serum levels of AST and ALT are biochemical markers widely used in clinical treatment to determine the liver function and to identify liver diseases such as viral hepatitis and alcoholic hepatitis. The AST is widely expressed in several organs, but ALT is s considered more liver-specific and enriched [21]. Thus, pathological conditions leading to a higher proliferative state, tissue damage, and high tumor cell turnover are likely to elevate AST rather than ALT, at least not to the same extent, making the AST/ALT ratio a novel potential biomarker in tumors.
In the present study, we find that the high AST/ALT ratio has independent predicting early disease relapse and progression value in primary NIMBC after PSM. In fact, several recent studies about the AST/ALT ratio all demonstrated that it could be considered as a significant prognostic biomarker in renal cell carcinoma, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and colorectal cancer. [11–15]. Lee et al. indicated that the AST/ALT ratio (≥ 1.5) is an independent prognostic factor associated with a worse prognosis of disease progression, overall mortality, and cancer-specific mortality in patients with nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma [12]. Moreover, Nishikawa et al. also first reported that the AST/ALT ratio was considered as an independent prognostic factor in upper tract urothelial cancer [22]. Similarly, Gorgel et al. [16] Ha et al. [17] and Yuk et al. [18] all concluded that the AST/ALT ratio was an independent prognostic predictor in patients undergoing radical cystectomy with bladder urothelial carcinoma. These findings are consistent with the results of our study. On the contrary, Cho et al. showed that the AST/ALT ratio was not significantly associated with RFS in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma [23]. This might be related to different diseases, different pathological states, as well as the selected population.
This study describes the AST/ALT ratio as a novel significant biomarker for predicting recurrence and progression in patients with primary NMIBC. However, the mechanism behind the relationship between NMIBC and AST/ALT ratio remains obscure and requires further research. Several hypotheses have been presented to explain this mechanism. The most famous of these hypotheses is the “Warburg effect.” In tumor cell metabolism, it produces enough adenosine triphosphatase (ATP) by increasing glucose uptake and anaerobic glycolysis to promote the multiplying of cancer cells [24]. Meanwhile, the accelerated glycolysis will promote the secretion of lactate. The study suggested that increased lactate plays an important role in maintaining glycolysis, affecting the ratio of lactate dehydrogenase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH)/NAD+ as well as the glucose transporter. [25]. It is known that AST plays an essential role in glycolysis by relocating NADH into the mitochondria by the malate-aspartate shuttle pathway. Consequently, cancer cell metabolism might be connected with the AST/ALT ratio in many glucose-using malignancies. Bladder cancer is considered as a glucose-reliant malignant tumor [26, 27]. Whyard et al. used fluorescence microscopy to investigate the uptake of fluorescent glucose by bladder cancer cells and found that there was a big difference in glucose consumption between normal urothelial and malignant urothelial cells [26]. Therefore, it is highly likely that the AST/ALT ratio is correlated with the prognosis of patients with primary NMIBC after TURBT, but our understanding of the mechanism behind it is so far limited.
Despite the current study showed novel findings, it has some limitations. First, this study was a retrospective analysis. Although all included patients received alike treatment, there were inevitably various inherent biases. Second, the AST/ALT rate was performed only once on the patient before TURBT and no comparative analysis was conducted at the interval of follow-up. Finally, it has the disadvantage of a single-center study and a small sample size. The results of this study need prospective larger studies to further consolidate, but this finding also would help clinicians in clinical decision making.
Conclusions
This study has shown that the high AST/ALT ratio group tended to have poorer RFS and PFS than the low AST/ALT ratio group. Meanwhile, our results also indicated that the elevated preoperative AST/ALT ratio could be regarded as a significant prognostic biomarker for predicting early disease recurrence and progression of patients with primary NMIBC after TURBT. The findings would further help clinicians in making clinical decisions.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ALT
Alanine transaminase
- AST
Aspartate transaminase
- CI
Confidence interval
- HR
Hazard ratio
- IQR
Interquartile range
- MIBC
Muscle invasive bladder cancer
- NMIBC
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
- PFS
Progression-free survival
- PSM
Propensity score-matched analysis
- Re-TURBT
Restaging transurethral resection of the bladder tumor
- RFS
Recurrence-free survival
- TURBT
Transurethral resection of bladder tumor
Authors' contributions
XFC and GXW: project development, data analysis, manuscript writing; XCZ, MY, and SX: project development, manuscript editing; GXW and CZ: project development, operation performance. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was approved by the ethics board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University Review Board and all patients signed the preoperative informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34. doi: 10.3322/caac.21551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.May M, Protzel C, Vetterlein MW, Gierth M, Noldus J, Karl A, Grimm T, Wullich B, Grimm MO, Nuhn P, et al. Is there evidence for a close connection between side of intravesical tumor location and ipsilateral lymphatic spread in lymph node-positive bladder cancer patients at radical cystectomy? Results of the PROMETRICS 2011 database. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017;49(2):247–254. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1469-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Compérat E, Larré S, Roupret M, Neuzillet Y, Pignot G, Quintens H, Houéde N, Roy C, Durand X, Varinot J, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of urothelial bladder cancer in patients less than 40 years old. Virchows Arch. 2015;466(5):589–594. doi: 10.1007/s00428-015-1739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Babjuk M, Böhle A, Burger M, Capoun O, Cohen D, Compérat EM, Hernández V, Kaasinen E, Palou J, Rouprêt M, et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2016. Eur Urol. 2017;71(3):447–461. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.van Rhijn BW, Burger M, Lotan Y, Solsona E, Stief CG, Sylvester RJ, Witjes JA, Zlotta AR. Recurrence and progression of disease in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: from epidemiology to treatment strategy. Eur Urol. 2009;56(3):430–442. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.06.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kim YH, Kim WT, Jeong P, Ha YS, Kang HW, Yun SJ, Moon SK, Choi YH, Kim IY, Kim WJ. Novel combination markers for predicting survival in patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer: USP18 and DGCR2. J Korean Med Sci. 2014;29(3):351–356. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li X, Shu K, Zhou J, Yu Q, Cui S, Liu J, Zhou R, Ding D. Preoperative plasma fibrinogen and D-dimer as prognostic biomarkers for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2020;18(1):11–19.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2019.10.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kimura S, Soria F, D'Andrea D, Foerster B, Abufaraj M, Vartolomei MD, Karakiewicz PI, Mathieu R, Moschini M, Rink M, et al. Prognostic value of serum cholinesterase in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018;16(6):e1123–e1132. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2018.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Getzler I, Bahouth Z, Nativ O, Rubinstein J, Halachmi S. Preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio improves recurrence prediction of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 2018;18(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12894-018-0404-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.De Ritis F, Coltorti M, Giusti G. An enzymic test for the diagnosis of viral hepatitis; the transaminase serum activities. Clin Chim Acta. 1957;2(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(57)90027-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bezan A, Mrsic E, Krieger D, Stojakovic T, Pummer K, Zigeuner R, Hutterer GC, Pichler M. The preoperative AST/ALT (De Ritis) ratio represents a poor prognostic factor in a cohort of patients with nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2015;194(1):30–35. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.01.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee H, Lee SE, Byun SS, Kim HH, Kwak C, Hong SK. De Ritis ratio (aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase ratio) as a significant prognostic factor after surgical treatment in patients with clear-cell localized renal cell carcinoma: a propensity score-matched study. BJU Int. 2017;119(2):261–267. doi: 10.1111/bju.13545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rawson NS, Peto J. An overview of prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer. A report from the subcommittee for the management of lung cancer of the United Kingdom coordinating committee on cancer research. Br J Cancer. 1990;61(4):597–604. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stocken DD, Hassan AB, Altman DG, Billingham LJ, Bramhall SR, Johnson PJ, Freemantle N. Modelling prognostic factors in advanced pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;99(6):883–893. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lindmark G, Gerdin B, Påhlman L, Bergström R, Glimelius B. Prognostic predictors in colorectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994;37(12):1219–1227. doi: 10.1007/BF02257785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gorgel SN, Kose O, Koc EM, Ates E, Akin Y, Yilmaz Y. The prognostic significance of preoperatively assessed AST/ALT (De Ritis) ratio on survival in patients underwent radical cystectomy. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017;49(9):1577–1583. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1648-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ha YS, Kim SW, Chun SY, Chung JW, Choi SH, Lee JN, Kim BS, Kim HT, Yoo ES, Kwon TG, et al. Association between De Ritis ratio (aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase) and oncological outcomes in bladder cancer patients after radical cystectomy. BMC Urol. 2019;19(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12894-019-0439-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yuk HD, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim HH, Ku JH. De Ritis Ratio (Aspartate Transaminase/Alanine Transaminase) as a significant prognostic factor in patients undergoing radical cystectomy with bladder urothelial carcinoma: a propensity score-matched study. Dis Markers. 2019;2019:6702964. doi: 10.1155/2019/6702964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Knowles MA, Hurst CD. Molecular biology of bladder cancer: new insights into pathogenesis and clinical diversity. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(1):25–41. doi: 10.1038/nrc3817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zapała P, Dybowski B, Poletajew S, Białek Ł, Niewczas A, Radziszewski P. Clinical rationale and safety of restaging transurethral resection in indication-stratified patients with high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1310-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Botros M, Sikaris KA. The de ritis ratio: the test of time. Clin Biochem Rev. 2013;34(3):117–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nishikawa M, Miyake H, Fujisawa M. De Ritis (aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase) ratio as a significant predictor of recurrence-free survival in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma following nephroureterectomy. Urol Oncol. 2016;34(9):417.e419–417.e415. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cho YH, Hwang JE, Chung HS, Kim MS, Hwang EC, Jung SI, Kang TW, Kwon DD, Choi SH, Kim HT, et al. The De Ritis (aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase) ratio as a predictor of oncological outcomes in patients after surgery for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017;49(8):1383–1390. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1613-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Warburg O. On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science. 1956;124(3215):269–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dorward A, Sweet S, Moorehead R, Singh G. Mitochondrial contributions to cancer cell physiology: redox balance, cell cycle, and drug resistance. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1997;29(4):385–392. doi: 10.1023/A:1022454932269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Whyard T, Waltzer WC, Waltzer D, Romanov V. Metabolic alterations in bladder cancer: applications for cancer imaging. Exp Cell Res. 2016;341(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tai YS, Chen CH, Huang CY, Tai HC, Wang SM, Pu YS. Diabetes mellitus with poor glycemic control increases bladder cancer recurrence risk in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015;31(3):307–314. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.