Abstract
Autophagy is a core molecular pathway for the preservation of cellular and organismal homeostasis. Pharmacological and genetic interventions impairing autophagy responses promote or aggravate disease in a plethora of experimental models. Consistently, mutations in autophagy‐related processes cause severe human pathologies. Here, we review and discuss preclinical data linking autophagy dysfunction to the pathogenesis of major human disorders including cancer as well as cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, metabolic, pulmonary, renal, infectious, musculoskeletal, and ocular disorders.
Keywords: aging, cancer, inflammation, metabolic syndromes, neurodegeneration
Subject Categories: Autophagy & Cell Death
This review provides an exhaustive overview of the contribution of autophagy to multiple pathological phenotypes in vivo, and discusses the therapeutic potential of autophagy modulation in disease prevention and treatment.

Glossary
- AD
Alzheimer disease
- ALS
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- ARMD
age‐related macular degeneration
- ATG
autophagy related
- ATZ
mutant Z variant of SERPINA1/alpha‐1 antitrypsin
- CF
cystic fibrosis
- CMA
chaperone‐mediated autophagy
- CNS
central nervous system
- COPD
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CS
cigarette smoke
- CTLs
cytotoxic T lymphocyte
- DC
dendritic cell
- DKD
diabetic kidney disease
- FA
free fatty acid
- FTD
frontotemporal dementia
- GEMM
genetically engineered mouse model
- HD
Huntington disease
- HFD
high‐fat diet
- IBD
inflammatory bowel disease
- IFN
interferon
- IOP
intraocular pressure
- IRI
ischemia‐reperfusion injury
- LANDO
LC3‐associated endocytosis
- LAP
LC3‐associated phagocytosis
- LDs
lipid droplets
- LECs
lens epithelial cells
- mtDNA
mitochondrial DNA
- NAFLD
non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
- NK
natural killer
- NTG
normal tension glaucoma
- OA
osteoarthritis
- PD
Parkinson disease
- PDAC
pancreatic ductal carcinoma
- PDB
Paget disease of bone
- polyQ
polyglutamine
- PtdIns3K
class III phosphatidylinositol‐3‐kinase
- RGC
retinal ganglion cell
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- RPE
retinal pigment epithelium
- T2D
type 2 diabetes
- TECs
epithelial tubular cells
- TME
tumor microenvironment
- TREG
regulatory T cells
- UUO
unilateral ureteral obstruction
- WAT
white adipose tissue
Introduction
The staggering increase in life expectancy that has characterized the last century has progressively attenuated, until reaching an apparent plateau over the last decade. Conversely, aging increases the susceptibility to many chronic illnesses, a condition that poses a major threat to the socioeconomic stability of high‐ and low‐income countries (Kehler, 2019; Melzer et al, 2020). Consequently, the trajectories of human lifespan and healthspan are estimated to diverge in the near future. During the last decade, investigators have endeavored to put forward a holistic view of the biological principles underlying the general concepts of “health” and “disease” at the cellular and organismal levels, by framing them into archetypical “hallmarks” (Lopez‐Otin et al, 2013; Kennedy et al, 2014; Lopez‐Otin & Kroemer, 2021). On these bases, it has been possible to separate the quintessential processes that operate to maintain individual cells and multicellular entities in a “healthy” state, from those that perturb the status quo of cells and tissues, thereby hastening the clinical onset of life‐threatening diseases.
In this context, the process of autophagy can be considered as a bona fide health‐modifying agent (Choi et al, 2013; Mizushima & Levine, 2020). Indeed, a large body of evidence from the literature supports the view of autophagy as a pro‐longevity mechanism (Morselli et al, 2009; Morselli et al, 2010; Rubinsztein et al, 2011; Kaushik & Cuervo, 2015b; Madeo et al, 2015; Fernandez et al, 2018; Hansen et al, 2018; Leidal et al, 2018; Markaki et al, 2018) and as a cardinal regulator of cellular and organismal fitness in response to multiple endogenous or exogenous sources of stress (Mizushima, 2018; Morishita & Mizushima, 2019). Conversely, time‐dependent loss of autophagy proficiency is thought to critically contribute to the aged phenotype (Lopez‐Otin et al, 2013; Kennedy et al, 2014; Lopez‐Otin & Kroemer, 2021). Furthermore, several of the lifestyle changes that have been attributed a positive role in the regulation of longevity (including calorie restriction and physical exercise) are commonly noted for their capacity to stimulate autophagy (Lopez‐Otin et al, 2016).
Autophagy is also key in preventing stresses as one of the major quality control guardians in the cell (Mancias & Kimmelman, 2016; Conway et al, 2020). Noteworthy, the autophagy pathways acquire physiological relevance even under basal, non‐stressful conditions. In line with this notion, autophagy takes direct part in the regulation of developmental programs (Mizushima & Levine, 2010; Allen & Baehrecke, 2020), maintenance of stem cell self‐renewal potential (Chen et al, 2018c; Dong et al, 2021a), cellular differentiation and plasticity (Boya et al, 2018; Clarke & Simon, 2019). Concordant with this notion, the appearance of the “diseased” state associated with autophagy dysregulation may occur as a result of alterations in these central aspects of multicellular organism biology. Indeed, tissues that are mainly composed of cells that lay in a post‐mitotic/quiescent state exhibit higher sensitivity to loss of autophagy competence.
The term “autophagy” refers to composite molecular pathways in which intracellular components are conveyed to the lysosomal compartment for degradation and recycling. To date, three major forms of autophagy have been described (Galluzzi et al, 2017a). Macroautophagy (henceforth referred to as autophagy; Box 1) is a form of autophagy in which the cellular cargo becomes sequestered within a double‐membraned vesicle, termed an autophagosome. The choice of the autophagosomal content can proceed in a relatively nonselective manner (known as “bulk autophagy”) or involve the tightly regulated elimination of individual cellular components (known as “selective autophagy”), depending on the inducing factor (He & Klionsky, 2009; Sica et al, 2015; Dikic & Elazar, 2018; Gohel et al, 2020). By contrast, chaperone‐mediated autophagy (CMA) operates as a protein‐exclusive type of autophagy in which KFERQ‐like motif‐bearing proteins are first recognized by the heat‐shock cognate protein HSPA8/HSC70 and enter the lysosome for degradation, upon binding LAMP2A (lysosomal‐associated membrane protein 2A) and translocation through a channel formed by oligomerization of this protein (Kaushik & Cuervo, 2018). Finally, microautophagy involves the sequestration of cellular material (including KFERQ‐flagged proteins or bulk cytoplasmic content) directly via membranous invaginations formed at the surface of late endosomes or lysosomes (Sahu et al, 2011; Uytterhoeven et al, 2015; Mejlvang et al, 2018), in an ESCRT‐dependent (Sahu et al, 2011) or ESCRT‐independent (McNally & Brett, 2018) mode. Besides representing the terminal effector of the autophagy cascade, the lysosome operates as a primary regulator of the autophagy process, in light of its active role in nutrient sensing and signaling via the MTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase) complex 1 (MTORC1)‐TFEB (transcription factor EB) axis (Ballabio & Bonifacino, 2020).
Box 1. Core regulation of canonical autophagy.
Canonical autophagy is a multiphasic process that involves the sequential and selective recruitment of ATG (autophagy related) proteins (Galluzzi et al, 2017a). The initiation of the autophagic cascade is physiologically subjected to the repressive control of MTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase) complex 1 (MTORC1), which catalyzes the inactivating phosphorylation of ATG13 and ULK1 (unc‐51‐like autophagy‐activating kinase 1). ULK1 and ATG13 are found in a supramolecular complex that also contains RB1CC1 (RB1‐inducible coiled‐coil 1) and ATG101, which cooperates with ATG9 to promote autophagosome nucleation. The inhibitory action of MTORC1 is counterbalanced by AMP‐activated protein kinase (AMPK), which responds to dwindling ATP levels by phosphorylating ULK1 and BECN1 (Beclin 1). ULK1 favors the autophagic cascade by facilitating the phosphatidylinositol‐3‐kinase activity of a multiprotein complex formed by BECN1, PIK3C3/VPS34 (phosphatidylinositol‐3‐kinase catalytic subunit type 3), PIK3R4/VPS15 (phosphoinositide‐3‐kinase regulatory subunit 4), ATG14, and NRBF2 (nuclear receptor binding factor 2). Multiple regulatory interactors of the BECN1‐PIK3C3/VPS34 complex have been identified, including UVRAG (UV radiation resistance associated), SH3GLB1 (SH3 domain containing GRB2 like, endophilin B1), and AMBRA1 (autophagy and Beclin 1 regulator 1), which facilitate the catalytic activity of PIK3C3/VPS34, as well as RUBCN (rubicon autophagy regulator) and BCL2 (BCL2 apoptosis regulator), which inhibit it. The production of phosphatidylinositol‐3‐phosphate (PtdIns3P), followed by the engagement of PtdIns3P‐binding proteins of the WIPI (WD repeat domain, phosphoinositide interacting) family, is instrumental for the expansion of phagophores. This phase is promoted by two distinct ubiquitin‐like conjugation modules. The first relies upon the activity of ATG7 and ATG10 and enables the buildup of a multiprotein complex composed of ATG5, ATG12 and ATG16L1 (autophagy‐related 16‐like 1). The second one involves ATG3, ATG4, and ATG7 and is ultimately responsible for the cleavage of members of the Atg8‐family proteins, including mammalian MAP1LC3/LC3 (microtubule‐associated protein 1 light chain 3) and their conjugation to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). Lipidated LC3 (LC3‐II; which is experimentally employed for quantifying autophagy in vitro and in vivo) serves as a receptor for LC3‐interacting region (LIR)‐containing proteins, including autophagy substrates and receptors such as SQSTM1/p62 (sequestosome 1). Upon closure of the phagophore, the resulting autophagosome fuses with a lysosome to form an autolysosome, culminating with the degradation of autophagic substrates by acidic lysosomal hydrolases. AKT1S1, AKT1 substrate 1; DEPTOR, DEP domain containing MTOR interacting protein; MLST8, MTOR‐associated protein, LST8 homolog; RPTOR, regulatory‐associated protein of MTOR complex 1.
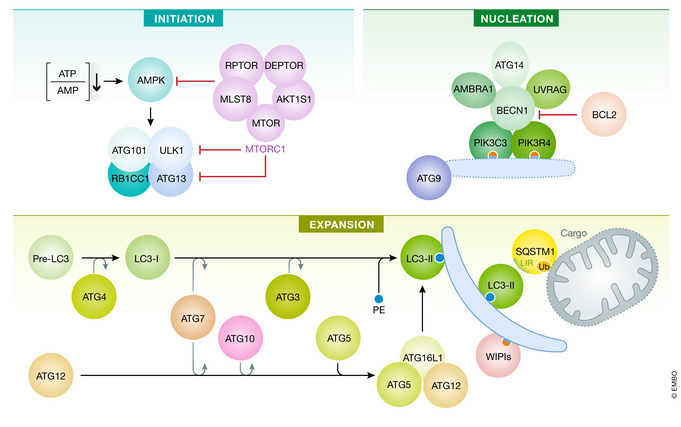
The complex molecular networks that underlie these distinct autophagic pathways, as well as other forms of canonical and non‐canonical autophagy that will be mentioned in this review, have been the object of thorough investigation and extensive reviewing over recent years (Dupont et al, 2017; Galluzzi et al, 2017a; Dikic & Elazar, 2018; Kaushik & Cuervo, 2018; Chu, 2019; Kirkin & Rogov, 2019; Nakatogawa, 2020; Klionsky et al, 2021). Whereas autophagy proceeds at a basal (yet cell type dependent) rate in virtually all eukaryotic cells—inherent to its housekeeping function in the turnover of superfluous or damaged organelles and long‐lived proteins—a prominent surge in the magnitude of the autophagic reaction occurs upon disturbance of the intracellular or environmental homeostasis (He & Klionsky, 2009; Mizushima & Komatsu, 2011). From an evolutionary perspective, autophagy primarily equips cells with the ability to maintain viability under nutrient‐restricted conditions, conferring autophagy‐competent cells a survival advantage over their autophagy‐defective counterparts (Galluzzi et al, 2014; Lahiri et al, 2019; Morishita & Mizushima, 2019). This notion is fully supported by the finding that whole‐body autophagy‐deficient mice undergo perinatal death due to their inability to withstand postnatal starvation (Kuma et al, 2004; Komatsu et al, 2005; Kuma et al, 2017). Moreover, insightful evidence generated from preclinical models of partial or tissue‐specific autophagy deficiency has contributed to broaden the physiological relevance of this pathway to several aspects of multicellular organism biology (Kuma et al, 2017; Levine & Kroemer, 2019). As selection pressure shifts from individual cell survival to reproductive fitness, however, autophagy regulation grows in complexity and the outcome of autophagy upregulation is less predictable (Cherra & Chu, 2008). For example, autophagy can engage in cell death (Fairlie et al, 2020; Miller et al, 2020), directly contributing to the pathogenesis of some human diseases (e.g., ischemia‐reperfusion injury, neuronal, and muscle atrophy) (Galluzzi et al, 2018b; Galluzzi et al, 2018c; Patel & Karch, 2020; Pervaiz et al, 2020).
The autophagy machinery participates in intercellular communication, mediating processes of non‐canonical protein secretion (an autophagy‐independent function of autophagy proteins) (Ponpuak et al, 2015; Zahoor & Farhan, 2018), regulation of tissue‐resident stem cells (Guan et al, 2013; Chang, 2020), modulation of immune cell functions (Deretic, 2021), and maintenance of tissue barrier integrity (Galluzzi & Green, 2019; Levine & Kroemer, 2019). As an example, in dendritic cells (DCs) autophagy and microautophagy serve the important role of feeding endogenous proteins to endosomal/lysosomal compartments for MHC class II molecule‐mediated immunosurveillance (Balan et al, 2019; Kotsias et al, 2019), and the biogenesis of endosomal microautophagy is tightly connected to exosomal production (Sahu et al, 2011). As yet another example, in phagocytic cells several components of the autophagy machinery (including the phosphatidylinositol‐3‐kinase [PtdIns3K] complex, but not ULK1 [unc‐51‐like autophagy‐activating kinase 1]) are recruited to the single‐layered phagosomal membrane, following the engagement of cell surface receptors (e.g., TLRs [Toll‐like receptors]) by pathogen‐associated molecules (Martinez et al, 2015), immune complexes (Henault et al, 2012), or phosphatidylserine exposed by apoptotic cells (Martinez et al, 2011). This process, defined as LC3‐associated phagocytosis (LAP) (Heckmann & Green, 2019), exquisitely relies upon CYBB/NOX2 (cytochrome b‐245, beta polypeptide), RUBCN (rubicon autophagy regulator), and the WD domain of ATG16L1 (autophagy‐related 16‐like 1), which are dispensable for the execution of canonical autophagy (Martinez et al, 2015).
The multitiered repercussions of autophagy on organismal homeostasis have spurred considerable efforts toward the identification of clinically actionable targets to modulate the autophagic pathway to prevent or treat diseases, in multiple pathological circumstances (Galluzzi et al, 2017c). Our current understanding about the contribution of autophagy in human disorders mostly derives from (i) the implementation of several mouse models of autophagy deficiency (Kuma et al, 2004), through which the role of autophagy can be interrogated at the whole body, or in a cell type‐specific manner, and (ii) from the discovery that several components of the autophagic machinery have been found mutated in human diseases (van Beek et al, 2018; Levine & Kroemer, 2019). Here, we discuss recent insights on the role of autophagy in the most penetrant human illnesses (Fig 1), placing particular emphasis on preclinical findings obtained in murine models of diseases in which autophagy has been genetically dismantled. In this regard, the involvement of virtually all ATG (autophagy related) proteins in autophagy‐independent tasks imposes a note of caution on the attribution of specific phenotypic effects to the mere inhibition of the autophagy process (Galluzzi & Green, 2019).
Figure 1. Common human disorders linked to dysregulated autophagic activity.
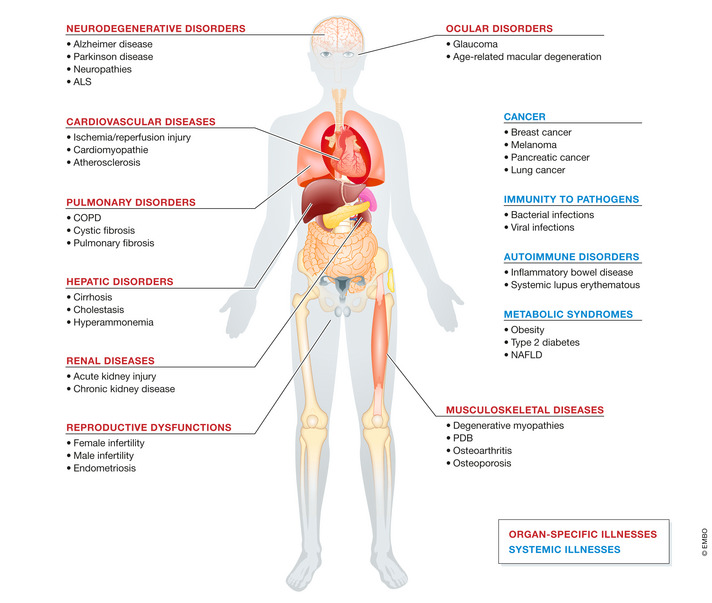
Representation of the main organ‐specific (red) and systemic (blue) human illnesses in which autophagy plays a critical role and that are discussed in this review. ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DKD, diabetic kidney disease; NAFLD, non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease; PDB, Paget disease of bone.
Neurodegenerative disorders
The autophagic process is essential in preserving the homeostatic requirements of post‐mitotic neurons, both at the central and at the peripheral nervous system levels (Menzies et al, 2017; Scrivo et al, 2018; Mallucci et al, 2020) (Table 1). Most neurodegenerative diseases are associated with the accumulation of aggregate‐prone proteins. Studies performed in diseases with Mendelian‐type inheritance suggest that these proteins are toxic drivers that are necessary and sufficient to cause pathology. A large body of evidence, supported by the demonstration that ATG genes are found mutated in multiple human neurodegenerative illnesses, indicates that autophagy directly intervenes in the clearance of those proteins (Nixon, 2013). In addition, MTOR p.Cys1483Tyr somatic mutation resulted in impaired autophagy, caused aberrant accumulation of OFD1, and disrupted neuronal ciliogenesis, which accounted for cortical dyslamination in Focal malformations of cortical development (Tang et al, 2013; Park et al, 2018). Furthermore, intact autophagy responses have been postulated to extinguish neuroinflammatory reactions, which directly contribute to the aetiopathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders (Rubinsztein et al, 2015). For these reasons, upregulation of autophagy has attracted particular interest as a potential therapeutic strategy for various neurodegenerative conditions (Menzies et al, 2017; Thangaraj et al, 2020).
Table 1.
Neurodegenerative disorders associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer disease | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Trim16 | Exacerbated endomembrane damage post‐infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Jia et al (2020) |
| Alzheimer disease | Whole‐body deletion of Sqstm1/p62 | Accumulation of hyperphosphorylated MAPT/tau and neurodegeneration | Ramesh Babu et al (2008) |
| Alzheimer disease | Whole‐body deletion of Nrf2 | Aberrant accumulation of phosphorylated and sarkosyl‐insoluble tau protein | Jo et al (2014) |
| Alzheimer disease | Conditional excitatory neuron‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced extracellular Aβ plaque burden, linked to cognitive dysfunction in APP transgenic mice | Nilsson et al (2013) |
| Alzheimer disease | Whole‐body deletion of Nrbf2 | Impaired cognitive fitness and increased Aβ plaque accumulation | Lachance et al (2019) |
| Alzheimer disease | Whole‐body deletion of Trem2 | Impaired metabolic fitness and increased accumulation of autophagic vesicles in the microglia of 5XFAD mice | Ulland et al (2017) |
| Alzheimer disease | Conditional myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 or Rubcn | Exacerbated Aβ plaque accumulation and inflammation within the hippocampus of young 5xFAD mice | Heckmann et al (2019) |
| Alzheimer disease | Whole‐body deletion of Atg16LΔWD | Exacerbated Aβ plaque accumulation, neuroinflammation and Tau hyperphosphorylation | Heckmann et al (2020) |
| Alzheimer disease | Neuron‐specific deletion of Lamp2 | Exacerbated Tau acetylation, extraneuronal release and propagation, linked to accelerated disease progression | Bourdenx et al (2021), Caballero et al (2021) |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | Whole‐body deletion of Epg5 | Muscle denervation, myofiber atrophy, late‐onset progressive paralysis, and reduced survival | Zhao et al (2013) |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | Conditional motoneuron‐specific deletion of Tbk1 | Accelerated early disease onset in SOD1G93A mice, linked to increased accumulation of ubiquitinated aggregates | Gerbino et al (2020) |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | Whole‐body knock‐in of mutant Tbk1G217R or Tbk1R228H | Accelerated early disease onset but extended lifespan in SOD1G93A mice, linked to reduced microglia IFN response | Gerbino et al (2020) |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | Whole‐body deletion of Grn | Exacerbated symptomatology linked to increased accumulation of pathological TDP‐43 in neurons | Chang et al (2017) |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | Conditional neuron‐specific deletion of Xbp1 | Reduced disease onset in SOD1G93A mice after inducing autophagy in motoneurons | Hetz et al (2009) |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | AAV‐mediated hippocampal‐specific deletion of C9orf72 | Exacerbated cognitive and motor deficits, hippocampal neuron loss, and DPR protein accumulation, after autophagy inhibition | Zhu et al (2020) |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 | Increased lifespan of mutant SOD1 transgenic mice | Nassif et al (2014) |
| Focal malformations of cortical development | Brain somatic mutations in MTOR | Cortical abnormalities that are highly associated with medically intractable epilepsy, intellectual disability, developmental delay, and autism‐spectrum disorders | Park et al (2018) |
| Axon growth | POMC neuron‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Abnormal development of POMC neuronal projections, associated with metabolic dysregulations | Coupe et al (2012) |
| Cognitive fitness | shRNA‐dependent hippocampal‐specific deletion of Becn1, Atg12 or Rb1cc1 | Impaired capacity to generate novel memories | Glatigny et al (2019) |
| Food intake and energy balance | AgRP neuron‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Increased neuronal lipid accumulation, associated with altered energy balance and food intake after starvation | Kaushik et al (2011) |
| Huntington disease | Conditional whole‐body deletion of WDFY3/ALFY | Accumulation of proteinaceous deposits, linked to accelerated onset and progression of Huntington disease pathogenesis | Fox et al (2020) |
| Ischemic brain damage | Whole‐body allelic loss of Sod2 | Increased infarct volume under hyperglycemic conditions, linked to increased oxidative DNA damage | Mehta et al (2011) |
| Ischemic brain damage | Neuron‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Complete protection from neonatal hypoxic/ischemic brain injury | Koike et al (2008), Xie et al (2016) |
| Nerve injury | Schwann cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Delayed myelin degradation and generation of repair cells after injury | Gomez‐Sanchez et al (2015) |
| Neurodegeneration | Neural cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Development of progressive deficits in motor function linked to cytoplasmic inclusion body accumulation in neurons | Hara et al (2006) |
| Neurodegeneration | Conditional CNS‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Behavioral defects and premature death, linked to massive neuronal loss and cytoplasmic inclusion body accumulation | Komatsu et al (2006) |
| Neurodegeneration | Conditional radial glial cell‐specific deletion of Rb1cc1 | Progressive loss of NSCs pool and impaired neuronal differentiation in the postnatal brain | Wang et al (2013) |
| Neurodegeneration | Conditional CNS‐specific deletion of Wdr45 | Reduced motor coordination, impaired learning and memory, and extensive axon swelling | Zhao et al (2015) |
| Neurodegeneration | Conditional neuron‐specific deletion of Wipi3 | Behavioral defects and cerebellar neuronal loss after non‐canonical autophagy inhibition | Yamaguchi et al (2020) |
| Neurodegeneration | Conditional telencephalon‐specific deletion of Vps15 | Severe progressive cortical atrophy associated with caspase‐induced apoptosis | Gstrein et al (2018) |
| Neurodegeneration | Whole‐body knock‐in of hypomorphic Atg16l1 | Developmental retention due to delayed differentiation of stem cells in the brain | Wu et al (2016) |
| Neurodegeneration | Conditional NSC‐specific co‐deletion of FoxO1, FoxO3 and FoxO4 | Initial proliferation of neural progenitor cells in early postnatal life, followed by NSC pool decline in adult brains | Paik et al (2009) |
| Neurodegeneration | Purkinje cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Progressive cell autonomous dystrophy and degeneration of the axon terminals | Komatsu et al (2007) |
| Neurodegeneration | Whole‐body deletion of TAX1BP1 | Aberrant accumulation of high molecular weight ubiquitin conjugates and lipofuscin | Sarraf et al (2020) |
| Neuropathies | Whole‐body deletion of Fam134b | Degeneration of sensory neurons after inhibition of ER‐phagy | Khaminets et al (2015) |
| Neuropathies | Whole‐body deletion of Tecpr2 | Exacerbated age‐dependent behavioral aberrations and neuroaxonal dystrophy, after accumulation of autophagosomes | Tamim‐Yecheskel et al (2020) |
| Neurotransmission | Post‐mitotic excitatory neuron‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Increased accumulation of tubular ER in axons, linked to increased excitatory neurotransmission and premature death | Kuijpers et al (2021) |
| Parkinson disease | Microglia‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Increased α‐synuclein accumulation and neurodegeneration | Choi et al (2020) |
| Parkinson disease | Whole‐body deletion of Rubcn | Reduced α‐synuclein accumulation in the brain, linked to reduced age‐related interstitial fibrosis in kidney | Nakamura et al (2019) |
| Parkinson disease | Conditional SN neuron‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Resistance to retrograde axonal degeneration | Cheng et al (2011) |
| Parkinson disease |
AAV‐mediated SN‐specific knock‐in of dominant‐negative Ulk1 |
Attenuated MPTP‐induced axonal neurodegeneration | Balke et al (2020) |
| Parkinson disease | Whole‐body deletion of Prkn | Impaired striatal neural plasticity, linked to increased sensitivity to oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction (exacerbated in Mutator mice but rescued by loss of STING) | Goldberg et al (2003), Palacino et al (2004), Kitada et al (2009), Pickrell et al (2015), Sliter et al (2018) |
| Parkinson disease | Whole‐body deletion of Pink1 | Increased sensitivity to oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction | Gautier et al (2008) |
AAV, adeno‐associated viral vector; AgRP, agouti‐related protein; APP, amyloid precursor protein; CNS, central nervous system; DPR, dipeptide‐repeated; MPTP, 1‐methyl‐4‐phenyl‐1,2,3,6‐tetrahydropyridine; NSCS, neural stem cell; OGD, oxygen glucose deprivation; POMC, proopiomelanocortin; SN, substantia nigra; TDP‐43, transactive response DNA‐binding protein of 43 kD.
The neuroprotective functions attributed to autophagy are estimated to transcend its well‐defined roles as proteostasis keeper and organelle turnover regulator. Indeed, several findings have underscored that the ATG machinery is functionally implicated in compartment‐specific tasks along the soma‐axon axis that include, among others, (i) the regulation of synaptic transmission (Kuijpers et al, 2021), (ii) the degradation of synaptic cargoes and vesicles, (iii) the anterograde/retrograde crosstalk between cell body and synaptic terminal, and (iv) myelination/demyelination events (Hill & Colon‐Ramos, 2020). With these compartment‐specific physiological functions, it is no surprise that both insufficient and overactive nonselective or selective autophagy responses contribute to neurodegeneration (Chu, 2019).
Due to perinatal lethality related to ubiquitous inhibition of autophagy, our current degree of knowledge regarding the relevance of autophagy within the neural lineage mostly stems from fruit flies (Juhasz et al, 2007; Simonsen et al, 2008) and mouse models in which essential (i.e., Atg5, Atg7, Rb1cc1/Fip200 [RB1‐inducible coiled‐coil 1]) (Hara et al, 2006; Komatsu et al, 2006; Wang et al, 2013) or non‐essential (i.e., Wdr45/Wipi4 [WD repeat domain 45], and Wdr45b/Wipi3) (Zhao et al, 2015; Ji et al, 2020; Yamaguchi et al, 2020) autophagic genes have been obliterated at the embryonic stage by virtue of Nes (nestin)‐driven Cre recombinase expression. Compared to their wild‐type littermates, mice that developmentally lack autophagy in the neuronal compartment display shortened lifespan and early‐onset neurodegenerative pathologies (whose severity varies depending on the targeted gene), associated with the pathological accumulation of proteinaceous aggregates in multiple neuronal populations (Hara et al, 2006; Komatsu et al, 2006; Metcalf et al, 2012). Neuronal dysfunctions account for the lethality associated with systemic autophagic deficiency, as testified to by the fact that overexpression of Atg5 in the neuronal compartment rescues perinatal mortality of atg5− / − mice (Yoshii et al, 2016). Blunted expression of PIK3R4/VPS15 (phosphoinositide‐3‐kinase regulatory subunit 4) is associated with neurodevelopmental impairment and cortical atrophy, matching the phenotype of patients bearing loss‐of‐function mutations in this gene (Gstrein et al, 2018). Along similar lines, de novo mutations in the autophagy gene WDR45 have been found in causal association with static encephalopathy of childhood with neurodegeneration in adulthood (also known as neurodegenerative disease β‐propeller protein‐associated neurodegeneration [BPAN]), a subtype of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) (Saitsu et al, 2013) and with human neurodegeneration (Suleiman et al, 2018). Supporting the possible involvement of autophagy in this pathology, abnormal early autophagosomal structures have been identified in patient‐derived lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) (Saitsu et al, 2013). In concordance with this result, CNS‐specific wdr45 knockout mice are defined by BPAN‐like features, including cognitive defects and impaired axonal homeostasis, but not other ones like iron accumulation in basal ganglia (Zhao et al, 2015). More recently, a mutation in Wipi2 (WD‐repeat protein interacting with phosphoinositide 2) has been identified, linking defective autophagy to the appearance of complex neurodevelopmental defects (Jelani et al, 2019). Impaired autophagosome–lysosome fusion, associated with loss‐of‐function mutations in EPG5 (ectopic P‐granule autophagy protein 5 homolog), causes autosomal recessive Vici syndrome (VICIS), pathologically defined by severe neurodevelopmental defects (Hori et al, 2017). The suppression of ATG5 expression during early brain development alters the differentiation trajectories and the rate of proliferation of neuronal progenitor cells, which eventually reflect into morphological defects in differentiated neurons. By analogy, a comparable phenotype has been described in Atg16l1 hypomorphic mice (Lv et al, 2014; Wu et al, 2016; Menzies et al, 2017). Recently, a missense mutation in ATG5 has been found in causal association with the manifestation of ataxia, with neurodevelopmental delay in human patients. Notably, the introduction of human mutated ATG5 in flies is sufficient to recapitulate the clinical feature of the human disorders (Kim et al, 2016).
Disturbance in the autophagic process also has an impact on neurogenesis, which testifies to the central role of autophagy in the maintenance of adult neural stem cell pools within the sub‐ventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricle wall and subgranular zone (SGZ) of the dentate gyrus (Fleming & Rubinsztein, 2020). Consistent with this finding, inhibition of autophagy elicited by Rb1cc1 ablation reduces differentiation potential and number of adult neural stem cells (Wang et al, 2013). Likewise, combined conditional deletion of genes coding for FOXO (forkhead box, sub‐group O; Foxo1, Foxo3, and Foxo4) in adult neural stem/progenitor cells correlates with abnormal morphological features of differentiated neurons (Paik et al, 2009).
Throughout the last decade, several mouse models of conditional autophagy disruption in specific populations of the CNS and peripheral nervous system have been implemented, revealing the cell type‐specific contribution of autophagy. These encompass Purkinje cells in the cerebellum (leading to progressive dystrophy) (Komatsu et al, 2007), hypothalamic AGRP (agouti‐related neuropeptide) neurons (evoking altered energy balance and food intake after starvation) (Kaushik et al, 2011), POMC (proopiomelanocortin) neurons (perturbing axon growth and decreasing α‐melanocyte‐stimulating hormone [MSH] levels) (Coupe et al, 2012; Kaushik et al, 2012), and Schwann cells (delaying the process of demyelination after injury) (Gomez‐Sanchez et al, 2015).
Functional autophagic responses are instrumental for preserving neuronal integrity upon circumstances of acute injury (Galluzzi et al, 2016). For example, it has been shown that a central role of autophagy is restraining the life‐threatening effect tied to brain ischemic challenge. In mice in which cerebral stroke was induced by transient middle carotid occlusion (MCAO), genetic interventions that undermine autophagy, including Sod2 (superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial) inactivation (Mehta et al, 2011) or shRNA‐mediated silencing of Tsc1 (TSC complex subunit 1) (Papadakis et al, 2013), aggravate the neurological sequelae instigated by the stroke episode. In apparent contrast with this finding, pharmacological inhibition of autophagy with 3‐methyladenine or bafilomycin A1 was observed to limit infarct size in a permanent MCAO, suggesting that autophagy may rather aggravate the ischemic injury (Zhang et al, 2013; Galluzzi et al, 2016). Although the reduced specificity of these pharmacological modulators limits the mechanistic interpretation of these results, it is nonetheless reasonable to propose that the actual contribution of autophagy in stroke‐associated neurotoxicity would vary depending upon the cerebral compartment affected and the developmental stage in which the ischemic episode occurs (Galluzzi et al, 2016). In support of this concept, brain‐specific deletion of Atg7 confers protection against neonatal hypoxia–ischemia injury in mice (Koike et al, 2008; Xie et al, 2016).
Intact hippocampal autophagy sustains the elevated degree of synaptic plasticity required to generate novel memories, as demonstrated by the fact that stereotactic delivery of shRNA targeting key autophagy genes (including Becn1 [Beclin 1, autophagy related], Rb1cc1, and Atg12) impairs cognitive fitness in mice (Glatigny et al, 2019). This effect, which can be phenocopied by pharmacological inhibition of autophagy (e.g., with spautin‐1, leupeptin, or chloroquine) and reversed by pharmacological activation of the ATG machinery with a Tat‐Beclin 1 peptide, supports the essential role of autophagy in dendritic spine formation and long‐term potentiation after stimuli (Glatigny et al, 2019). Of note, loss of autophagy performance may causally underlie the age‐dependent decline in memory tasks, as demonstrated by the fact that treatment of old mice with plasma derived from young donors improves cognitive fitness and restores normal levels of autophagy in the hippocampus (Glatigny et al, 2019). Further corroborating this result, dietary supplementation with spermidine, which also acts as an autophagy stimulator, mitigates age‐dependent cognitive impairment in mouse hippocampus and Drosophila heads, contingent upon intact autophagy and mitophagy responses (Schroeder et al, 2021).
In the recent past, autophagy has gained attention for its potential involvement in the pathogenesis of late‐onset neurodegenerative pathologies, owing to the historically rooted view of this pathway as a major determinant of long‐lived/aggregation‐prone protein disposal within the lysosome (Nixon, 2013; Menzies et al, 2017). Supporting this view, it has been demonstrated that the lack of the autophagic receptor TAX1BP1 (Tax1‐binding protein 1) results in aberrant protein aggregation in the brain (Sarraf et al, 2020). Although these disorders mainly follow a multifactorial pattern, evidence obtained from inherited variants of neurodegenerative illnesses has shed new light on the contribution of autophagy to the progressive loss of neural function.
Alzheimer disease
Alzheimer disease (AD) represents the most common form of dementia in humans, caused by the pathologically relevant accumulation of proteinaceous aggregates, i.e., intracellular MAPT/tau tangles and/or extracellular beta amyloid peptide [Aβ] plaques, which progressively leads to neuronal cell death and decline in cognitive functions. Connections between autophagy and AD originate from the observation of expansion of autophagic compartments in AD brains (Nixon et al, 2005). As recently revealed by multilayer brain proteomics analysis performed at different stages of AD in humans, the autophagic substrate SQSTM1/p62 (sequestosome 1) accumulates in AD, suggestive of impaired autophagic flux (Bai et al, 2020) similar to the one reported in AD experimental models (Yu et al, 2005). In support of this notion, functional autophagy is required to degrade soluble and aggregated variants of MAPT/tau (Berger et al, 2006; Silva et al, 2020). Lysosomal membrane lesions caused by MAPT/tau oligomers instigate an LGALS3 (galectin 3)‐coordinated program, which leads to autophagy activation (Jia et al, 2020). Genetic inactivation of SQSTM1/p62 in mice leads to accumulation of hyperphosphorylated MAPT/tau and neurodegeneration (Ramesh Babu et al, 2008). Supraphysiological accumulation of MAPT/tau tangles perturbs the retrograde axonal transport of autophagosomes by interfering with the dynein–DCTN (dynactin) complex, eventually instigating the detrimental accumulation of MAPT/tau‐containing autophagic vesicles (Butzlaff et al, 2015).
Notably, the NFE2L2/NRF2 (nuclear factor, erythroid‐derived 2, like 2)‐dependent transcription of the autophagy regulator CALCOCO2/NDP52 (calcium binding and coiled‐coil domain 2) is instrumental in promoting the degradation of MAPT/tau in response to oxidative stress (Jo et al, 2014). SQSTM1/p62 is also a target gene for NFE2L2/NRF2 (Jain et al, 2010), and it has been reported to mediate degradation of aggregated MAPT/tau (Xu et al, 2019b). In recent years, dysfunction of the endosomal‐sorting complex, the retromer, has been linked to a number of neurodegenerative diseases, including AD. Reduced expression of the retromer proteins and variants of the core retromer component VPS35 (vacuolar protein sorting 35) are associated with neurodegenerative diseases, often overlapping with MAPT/tau aggregation in the brain (Carosi et al, 2021; Seaman, 2021). Recent data demonstrate that the autophagy–lysosomal axis is central for the clearance of aggregated MAPT/tau and depletion of VPS35 blocks autophagy, whereas VPS35 overexpression has the opposite effect (Carosi et al, 2020; Carosi et al, 2021). Thus, the retromer–autophagy axis may play a relevant function in preventing multiple neurodegenerative diseases by ensuring that pathogenic protein aggregates are cleared as they arise.
In addition, multitiered connections have been established between autophagy and Aβ plaque formation. Aβ is targeted for autophagy‐dependent degradation within the lysosome, explaining why activation of autophagy reduces the burden of Aβ plaques in rodents (Boland et al, 2008; Menzies et al, 2017; Meng et al, 2019). However, autophagy appears to be causally implicated in the PSEN1 (presenilin 1)‐mediated conversion of APP (amyloid beta precursor protein) into Aβ (Yu et al, 2005), as well as in the non‐canonical secretion of Aβ into the extracellular space (Nilsson et al, 2013; Menzies et al, 2017). Mutations that alter PSEN1 function have been associated with defective autophagic vesicle clearance and early‐onset AD, due to impaired autophagosome–lysosome fusion and defective lysosomal acidification (Lee et al, 2010b; Chong et al, 2018). Similarly, loss‐of‐function mutations affecting PICALM (phosphatidylinositol‐binding clathrin assembly protein) impair autophagy dynamics, thus augmenting the risk for developing AD (Tian et al, 2013).
Additional autophagy modulators determine the cellular levels of Aβ protein. As an example, NRBF2 (nuclear receptor‐binding factor 2; a component of the PtdIns3K complex I) interacts with APP and favors its lysosomal disposal, as demonstrated by the fact that NRBF2 depletion leads to excessive levels of intracellular APP in cells (Yang et al, 2017b) and Aβ accumulation in AD mouse models (Lachance et al, 2019), whereas overexpression of NRBF2 reduces Aβ levels and improves mouse memory (Lachance et al, 2019). Recently, a possible link between autophagy activation in the microglial compartment and AD has been proposed. Importantly, ablation of the gene coding for TREM2 (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2), a surface receptor required for microglial responses to neurodegeneration, results in maladaptive accumulation of autophagosomes and disarray of microglia clustering around plaques (Ulland et al, 2017). This effect has been attributed to dysregulated MTORC1 activation, in turn evoking metabolic abnormalities in microglial cells. Consistent with this notion, normalization of autophagic flux by cyclocreatine decreases neuronal dystrophy in murine models of AD (5XFAD mice) (Ulland et al, 2017). In this landscape, defective mitophagy appears to be a major determinant of the functional decay of neurons in AD, in that its pharmacological stimulation (through NAD+ supplementation, urolithin A, and actinonin) is sufficient to retard memory impairment, while reducing the burden of amyloid aggregates upon stimulating microglial phagocytic capacity for extracellular Aβ plaques (Fang et al, 2019). In addition, non‐canonical functions of the ATG machinery in microglia contribute to alleviate the toxic effects associated with Aβ plaque deposition in the 5XFAD mouse model. Notably, the genetic ablation of Atg5 or Rubcn (but not that of Rb1cc1) in myeloid cells correlates with exacerbated Aβ plaque formation and aberrant production of inflammatory cytokines, while contributing to accelerate neuronal decay and cognitive impairment. Mechanistically, ATG5 and RUBCN take part in events of MAP1LC3/LC3 (microtubule‐associated protein 1 light chain 3) conjugation to Aβ–containing endosomal membranes positively marked by RAB5 and clathrin. This process, named LC3‐associated endocytosis (LANDO), appears to promote the recycling of putative Aβ receptors (e.g., TLR4, TREM2 [triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2]) from internalized endosomes to the plasma membrane of microglial cells. While it remains to be clarified whether LANDO mediates Aβ receptor degradation, its activation is instrumental to reduce Aβ burden and limit neuroinflammation in AD (Heckmann et al, 2019). Along similar lines, LANDO deficiency imposed on aged mice by deletion of the WD domain of ATG16L1 (which is dispensable for canonical autophagy), exacerbates the neuroinflammatory phenotype associated with an AD‐like symptomatology (Heckmann et al, 2020).
Chaperone‐mediated autophagy also contributes to degradation of a large fraction of neuronal MAPT/tau under physiological conditions (Caballero et al, 2018; Caballero et al, 2021). However, mutations and posttranslational modifications of this protein, such as acetylation, not only prevent MAPT/tau degradation by CMA but also inhibit normal CMA functioning (Caballero et al, 2018; Caballero et al, 2021). Blockage of CMA leads to rerouting of some of the pathogenic forms of MAPT/tau toward endosomal microautophagy, as both pathways share the same chaperone, HSPA8, and this promotes fusion of late endosomes with the plasma membrane and subsequent extraneuronal release of the MAPT/tau variants, thus contributing to MAPT/tau propagation (Caballero et al, 2021). Reduction in neuronal CMA activity has been recently shown in AD patient's brains (Bourdenx et al, 2021; Caballero et al, 2021), and pharmacological activation of CMA has been linked to ameliorated pathology in two different experimental models of tauopathies (Bourdenx et al, 2021).
Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease (PD) is pathologically defined by (i) the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) and (ii) the prevalence of proteinaceous Lewy bodies, mainly composed of SNCA/α‐synuclein (synuclein alpha) and other polyubiquitinated proteins but also vesicular structures. PD symptomatology is characterized by prominent motor and autonomic dysfunction, sometimes accompanied by cognitive and psychological deficits. Early evidence suggested roles for CMA and macroautophagy in degrading SNCA/α‐synuclein (Webb et al, 2003; Cuervo et al, 2004). High expression of wild‐type SNCA/α‐synuclein, mutations or unwanted posttranslational modifications on this protein (such as formation of dopamine adducts) is toxic to CMA by preventing multimerization of LAMP2A and subsequent lysosomal internalization of cargo proteins (Cuervo et al, 2004; Martinez‐Vicente et al, 2008). Recent evidence has demonstrated that selective autophagy clears neuron‐released SNCA/α‐synuclein through the autophagy receptor SQSTM1/p62 in microglia, offering protection of dopaminergic neurons (Choi et al, 2020). Consistent with this result, the activation of autophagy decreases the accumulation of SNCA/α‐synuclein (Nakamura et al, 2019). Conversely, uncontrolled expression of wild‐type or mutated variants of SNCA/α‐synuclein reduces autophagic flux or disturbs TFEB‐mediated lysosomal biogenesis by preventing the nuclear translocation of TFEB (Decressac et al, 2013). Pathologically meaningful levels of SNCA/α‐synuclein affect the intracellular localization of ATG9 via RAB1A (RAB1A, member RAS oncogene family), thereby perturbing autophagy dynamics in the brain of transgenic mice overexpressing SNCA/α‐synuclein (Winslow et al, 2010). Mutations in the gene GBA (glucosylceramidase beta) represent the most common genetic risk factor for PD. Of note, loss‐of‐function mutations in GBA disrupt the autophagic flux and lead to the aggregation of SNCA/α‐synuclein (Murphy et al, 2014). Likewise, an autosomal‐dominant mutation affecting VPS35 curtails autophagy by altering ATG9 localization (Zavodszky et al, 2014). A similar phenotype has also been described in the context of loss‐of‐function mutations in the P‐type ATPase gene ATP13A2, in which recessive, early‐onset PD has been linked to defective acidification of lysosomes and insufficient autophagy (Ramirez et al, 2006). Decreased autophagy in ATP13A2‐deficient neurons in turn leads to accumulation of damaged mitochondria with increased leakage of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Gusdon et al, 2012).
Dysregulated autophagy has also been associated with the expression of dominant mutants of LRRK2 (leucine‐rich repeat kinase 2) (Ramonet et al, 2011), the most common cause of familial PD. While it remains controversial whether LRRK2G2019S elicits increased or decreased autophagic flux, these differences may reflect the compartment (soma vs. dendrites vs. axons) being studied. Although autophagy upregulation may contribute to clearance of protein aggregates, the axo‐dendritic arbor is susceptible to autophagy‐mediated degeneration in cultured dopaminergic, sympathetic, and cortical neurons and in the axons of dopaminergic neurons in vivo as evidenced by Atg7 knockdown/knockout (Plowey et al, 2008; Cheng et al, 2011), expression of dominant‐negative ULK1 (Balke et al, 2020), or expression of an autophagy‐deficient LC3 phosphomimic, which protects against dendritic atrophy elicited by disease‐linked LRRK2 mutations and the PD toxin MPP+ (Cherra et al, 2010). Increased mitophagy, due to post‐synaptic mitochondrial calcium dysregulation, may contribute to dendritic degeneration (Verma et al, 2017). Emerging roles for LRRK2 in regulating RAB GTPases and other aspects of endolysosomal and vesicular transport may also complicate interpretation due to compensatory responses (Kuwahara & Iwatsubo, 2020).
A causal association has been established between autosomal recessive forms of PD and mutations affecting the mitophagy regulators PINK1 (PTEN‐induced putative kinase 1) and PRKN/PARK2 (Parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase) (Kitada et al, 1998; Valente et al, 2004; Narendra et al, 2008; Matsuda et al, 2010). Mouse models to monitor mitophagy show elevated basal mitophagy in dopaminergic neurons (McWilliams et al, 2018). Although PINK1 (McWilliams et al, 2018) and PRKN (Goldberg et al, 2003; Perez & Palmiter, 2005) deficiency do not elicit major defects under baseline conditions, defective striatal neural plasticity is observed in prkn− / − mice (Kitada et al, 2009). Importantly, mitophagy deficiency favored by ablation of Prkn (Palacino et al, 2004; Pickrell et al, 2015) or Pink1 (Gautier et al, 2008) sensitizes mice to oxidative stress, while worsening neural damage when combined with mitochondrial dysfunction (mitochondrial DNA [mtDNA] mutator‐prkn/parkin‐KO mice) (Pickrell et al, 2015). However, there are other pathways of mitophagy in neurons (Chu et al, 2013), and ablation of Pink1 or Prkn in mouse and fly mitophagy biosensor models suggests that neither protein is necessary to maintain normal basal levels of brain mitophagy (Lee et al, 2018a; McWilliams et al, 2018). Furthermore, serological markers of inflammation, which are also observed in individuals with Prkn mutations, are reduced leading to reversal of neuronal degeneration when these mice are crossed to STING1/STING (stimulator of interferon response cGAMP interactor 1)‐deficient mice (Sliter et al, 2018). These results match the original observation indicating a close association between PD and serum or cerebrospinal fluid markers of inflammation, further reinforcing the concept that neuroinflammation directly contributes to the pathogenesis of PD (Dzamko et al, 2015).
Polyglutamine diseases
Extensive experimental evidence has highlighted the role of autophagy in disorders caused by polyglutamine (polyQ) expansion, including Huntington disease (HD) and several forms of spinocerebellar ataxias (Jimenez‐Sanchez et al, 2012). The polyQ expansion in HTT (huntingtin) is the etiological driver of HD (Zheng et al, 2010), and the severity thereof is a direct function of polyQ length. Importantly, a significant dichotomy has emerged between the functions of wild‐type and mutated HTT toward the regulation of the autophagic process (Martin et al, 2015; Ashkenazi et al, 2017). Wild‐type HTT participates in the regulation of basal autophagy due to its role in the selection of the autophagic cargo (Ochaba et al, 2014; Rui et al, 2015). However, expression of mutant HTT (i) negatively affects autophagosomal cargo recognition through dysregulated interaction with SQSTM1/p62 (Martinez‐Vicente et al, 2010; Rui et al, 2015); (ii) sequesters the BECN1 interactor RASD2/RHES in the striatum (Mealer et al, 2014) and inhibits BECN1‐PIK3C3/VPS34 and ULK1 kinase activities (Lim et al, 2015; Wold et al, 2016); (iii) interferes with the regulatory interaction between ATXN3 (ataxin 3) and BECN1, compromising the response of neurons to starvation (Ashkenazi et al, 2017); (iv) disturbs axonal autophagosome transport (Wong & Holzbaur, 2014b); (v) drives a maladaptive unfolded protein response, which leads to ERN1/IRE1 (endoplasmic reticulum to nucleus signaling 1)‐dependent inhibition of autophagy (Lee et al, 2012); and (vi) disrupts the ability of wild‐type HTT to bind ULK1 and release it from the negative regulation of MTOR in order to activate autophagy (Rui et al, 2015). Notably, overexpression of wild‐type HTT in cells expressing its mutated variants restores autophagy and fosters the clearance of mutated HTT (Zheng et al, 2010). Of note, defective autophagy imposed by heterozygous depletion of the autophagy scaffold/adaptor WDFY3/ALFY (WD repeat and FYVE domain containing 3) accelerates the onset (and worsens the sequelae) of HD in mice (Fox et al, 2020). Interestingly, experimental rerouting of mutant HTT for degradation by CMA has proven effective in ameliorating disease phenotype in mice (Bauer et al, 2010).
Neuropathies
Neuropathies are disorders caused by the progressive degeneration and death of peripheral sensory (e.g., hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy [HSAN]) and motor (hereditary spastic paraplegia [HSP], Spastic paraplegia type 49 [SPG49]) neurons. Mutations in genes encoding several ER proteins involved in ER‐remodeling have been associated with hereditary neuropathies (Hubner & Dikic, 2020). For example, loss‐of‐function mutations in the reticulon type ER membrane protein RETREG1/FAM134B (reticulophagy regulator 1) are associated with the development of HSAN type II (HSAN2) (Kurth et al, 2009; Murphy et al, 2012), whereas mutations in RTN2 (reticulon 2) are linked with HSP (SPG12) (Montenegro et al, 2012). RETREG1 was identified as the first mammalian receptor for selective ER autophagy (reticulophagy) implicated in the delivery of ER fragments via autophagosomes for lysosomal degradation (Khaminets et al, 2015). RETREG1 also plays a role in the clearance of ER‐to‐lysosome‐associated degradation (ERAD)‐resistant SERPINA1/alpha‐1 antitrypsin Z variant polymers (Fregno et al, 2018) as well as endogenous procollagen (Forrester et al, 2019) within the ER. Some patients with mutations in RETREG1 suffer from cardiac arrhythmia, an‐ or hypohydrosis and other symptoms of autonomic malfunctions overlapping with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and myopathies (Eggermann et al, 2018). The HSAN‐related ATL3 (atlastin GTPase 3) Y192C mutation has been connected to reduced complexity of the endoplasmic reticulon network, disturbed connections between ER and mitochondria, and impaired mitochondrial function (Kornak et al, 2014; Behrendt et al, 2019; Krols et al, 2019; Xu et al, 2019a). Mutations in ATL1 paralog can also result in autosomal‐dominant spastic paraplegia (SPG3) (Zhao et al, 2001) or in HSAN type I (HSAN1) (Guelly et al, 2011). Atlastins in general are thought to remodel the ER for efficient autophagosomal degradation and functioning downstream of the reticulophagy receptor RETREG1 (Liang et al, 2018). As a caveat, it is worth mentioning that ATL1 and ATL3 are implicated in multiple ER‐related pathways. Therefore, additional studies are required to validate the hypothesis that dysfunctional autophagy primarily contributes to the phenotypic aberrations associated with mutations affecting these genes.
Spastic paraplegia type 49 (SPG49) is a severe neurodegenerative disorder that starts in infancy and is caused by several mutations in the TECPR2 (tectonin beta‐propeller repeat containing 2) gene. Frame‐shift mutations in exon 8 and exon 16 of TECPR2 (c.1319delT, c.3416delT) terminate in a premature stop codon (Oz‐Levi et al, 2012; Heimer et al, 2016), and an initial link between this gene to defects in autophagy was reported (Behrends et al, 2010; Oz‐Levi et al, 2012). All SPG49 patients share unique dysmorphic features such as microcephaly, dental crowding, short chubby appearance and a short, broad neck, and suffer from evolving spasticity, moderate to severe intellectual disability, decreased pain sensitivity and infantile onset of chronic respiratory disease (Oz‐Levi et al, 2012; Heimer et al, 2016). TECPR2 is a multi‐domain protein comprised of three WD repeats at the N terminus, the mostly unstructured middle region and six TECPR2 repeats terminating with an LC3‐interacting region (LIR) motif at its C terminus (Behrends et al, 2010; Stadel et al, 2015). TECPR2 was originally identified as an interactor of the Atg8‐family proteins, a detailed interactome of TECPR2 validated its interaction with Atg8‐family proteins through its functional LIR motif, and in addition identified its interaction with the biogenesis of lysosomal organelles complex 1 (BLOC1) and the homotypic fusion and protein sorting (HOPS) complex, two tethering protein complexes that mediate autophagosome–lysosome fusion (Stadel et al, 2015). A model for SPG49 was recently developed by creating a tecpr2 knockout mouse using CRISPR‐Cas9 (Tamim‐Yecheskel et al, 2020). This mouse exhibits behavioral aberrations accompanied by neuroaxonal dystrophy and autophagosome accumulation in the brainstem and spinal cord that is exacerbated in an age‐dependent manner. The accumulation of autophagosomes upon tecpr2 knockout suggests compromised targeting to lysosomes. Consistently, SPG49‐derived primary skin fibroblasts also exhibit accumulation of autophagosomes, strictly under basal growing conditions (Fraiberg et al, 2020). This phenotype is recovered by ectopically expressing the six carboxy‐terminal TECPR2 repeats, the full length TECPR2 protein or by inhibition of MTOR (Fraiberg et al, 2020). Mechanistically, TECPR2 has been suggested to facilitate targeting of autophagosomes to lysosomes, a process that is dependent on its C‐terminal LIR motif.
Recent studies of rare movement disorders have also provided links to autophagy. VPS13D is a rare disease gene, with mutations in VPS13D being associated with pediatric and young adult spastic ataxia or spastic paraplegia (Gauthier et al, 2018; Seong et al, 2018). Significantly, VPS13D is a regulator of autophagy, mitochondrial size, and mitochondrial clearance (Anding et al, 2018). These cellular phenotypes appear to be caused by altered mitochondria and ER contact, a phenotype that is conserved between flies and patient‐derived cells (Shen et al, 2021). Furthermore, a recent study indicated that mutations in VPS13D occur in 3 out of 64 children with Leigh syndrome features (Lee et al, 2020).
Further, a very recent study has identified a novel role for TRK‐fused gene (TFG) in autophagy (Carinci et al, 2021). TFG is an essential protein in the regulation of vesicular trafficking between endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi, and several TFG mutations have been associated with different neurological disorders, including hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with proximal dominant involvement (HMSN‐P), Charcot‐–Marie–Tooth disease, and recessive hereditary spastic paraparesis (Yagi et al, 2016). Indeed, under starvation conditions, TFG controls proper ULK1 localization and steady‐state levels by interacting with LC3C via a canonical LIR motif; this, in turn, regulates autophagy progression. These defects are also recapitulated in fibroblasts from a patient carrying an R106C TFG variant that has been previously associated with a complicated hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) phenotype (Beetz et al, 2013).
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is etiologically associated with the aberrant amassing of misfolded proteins, including SOD1 (superoxide dismutase 1), TARDBP/TDP‐43 (TAR DNA binding protein), or with the translation of dipeptide repeat proteins from the C9orf72 expanded repeat (the latter accounting for the most common variant of ALS) in motor neurons. ALS forms a genetic and pathological continuum with frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Interestingly, several FTD‐ALS genes code for autophagy receptors, including SQSTM1/p62 and OPTN (optineurin), lowering the capacity of neural cells to clear protein aggregates, as do mutations in VCP (valosin containing protein). As an example, SQSTM1/p62 mutants fail to dispose of aggregation‐prone SOD1 and TARDBP (Gal et al, 2009; Brady et al, 2011; Goode et al, 2016; Deng et al, 2020). Likewise, defective OPTN, leading to impaired binding to MYO6 (myosin VI), compromises autophagosomal trafficking (Tumbarello et al, 2012; Wong & Holzbaur, 2014a). Further supporting the role of OPTN in ALS, mutations in TBK1 (TANK binding kinase 1), which phosphorylates OPTN and promotes mitophagy, lead to detrimental accumulation of damaged mitochondria (Moore & Holzbaur, 2016). Of note, loss of TBK1 activity in SOD1G93A mouse models of ALS curtails autophagy and accelerates the clinical manifestation of ALS (Gerbino et al, 2020).
The strict nexus between ALS and autophagy is further strengthened by experimental evidence indicating that genetic deletion of central (e.g., VCP) (Johnson et al, 2010) or ancillary regulators of the autophagic cascade (e.g., GRN/progranulin, ALS2/alsin‐2) precipitate ALS symptomatology in mice and human patients (Yang et al, 2001; Chang et al, 2017). VCP also cooperates with PINK1 in regulating mitophagy and promoting PINK1‐dependent neuronal dendritogenesis through an independent mechanism (Kim et al, 2013b; Wang et al, 2018b). Mutations in the ESCRT‐III subunit CHMP2B (charged multivesicular body protein 2B)—required to sort integral membrane proteins into intraluminal vesicles of the multivesicular body (MVB)—have been causally linked to frontotemporal dementia and ALS. Mechanistically, mutated CHMP2B undermines autophagy‐mediated degradation, resulting in an elevated burden of SQSTM1/p62‐ and WDFY3‐containing protein aggregates in neurons. Further corroborating the central role of MVBs in the maintenance of neuronal proteostasis, MVBs are essential for the clearance of ubiquitinated TARDBP, which accumulates in ALS and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (Filimonenko et al, 2007). Mitophagy also appears to be defective in ALS (Wong & Holzbaur, 2014a). As result and in a non‐mutually exclusive manner, an impairment of ESCRT‐III function in phagophore sealing during mitophagy could contribute the ALS pathophysiology (Smith et al, 2019; Zhen et al, 2020). While these experimental observations suggest that defective autophagy may directly contribute to the phenotypic alterations linked to mutations in these genes, the fact that these proteins are involved in several autophagy‐unrelated processes imposes a note of caution on the interpretation of these results.
Conversely, genetic interventions that promote autophagy, such as the inactivation of the transcription factor XBP1 (X‐box binding protein 1) or restoration of HSPB8 expression in the nervous system, counteract ALS symptomatology by promoting the autophagy‐dependent disposal of SOD1G93A (Hetz et al, 2009; Crippa et al, 2010). Mutated forms of C9orf72 lead to the clinical manifestation of ALS through a number of different mechanisms. Because wild‐type C9orf72 is involved in central aspects of autophagosomes formation, maturation, and trafficking, it is likely that perturbations in autophagy contribute to the detrimental action of mutated C9orf72 in motor neuron dysfunction (Webster et al, 2016; Ho et al, 2019). Supporting this notion, genetic ablation of C9orf72 correlates with an increased burden of SQSTM1/p62 and TARDBP protein aggregation and synergizes with polyQ ATXN2 to induce the demise of motor neurons (Sellier et al, 2016). Consistently, it has been recently observed that loss of wild‐type C9orf72 function exacerbates the neurotoxic effects of a C9orf72 mutant allele, bearing hexanucleotide expansions, by repressing autophagy (Zhu et al, 2020). Conversely, the unexpected increase in lifespan elicited by BECN1 haploinsufficiency in the mutant SOD1 transgenic mouse model of ALS (Nassif et al, 2014) is difficult to reconcile. As for all the diseases discussed in this review, apparently conflicting, context‐dependent conclusions indicate a nuanced relationship between autophagy dysregulation and neurodegeneration.
Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disorders represent the leading cause of death worldwide. Cardiomyocytes, the essential cellular constituents of the cardiovascular system, mostly lay in the post‐mitotic state, implying that they are highly dependent upon intact autophagy and mitophagy to preserve their physiological functions and cope with harmful insults (Lavandero et al, 2015; Kaludercic et al, 2020) (Table 2). In view of the reduced regenerative potential of the cardiovascular system, autophagy operates at the forefront to promote survival of quiescent cells in the cardiovascular compartment, while counteracting events of apoptotic or necrotic cell death after injury (Henning & Brundel, 2017; Sciarretta et al, 2018).
Table 2.
Cardiovascular diseases associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atherosclerosis | Macrophage‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Enhanced atherogenic plaque progression due to hyperactivation of macrophage‐mediated inflammation and impaired lipid droplets catabolism | Ouimet et al (2011), Liao et al (2012), Razani et al (2012) |
| Atherosclerosis | Macrophage‐specific deletion of Rptor | Reduced development of atherogenic plaque upon high protein diet after restoration of mitophagy in macrophages | Zhang et al (2020) |
| Atherosclerosis | Macrophage‐specific overexpression of Tfeb | Reduced development of atherogenic plaque after stimulation of lysosomal biogenesis in macrophages | Sergin et al (2017) |
| Atherosclerosis | Vascular smooth muscle cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Enhanced atherogenic plaque progression, linked to increased CCL2‐mediated macrophage recruitment | Osonoi et al (2018) |
| Atherosclerosis | Endothelial cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 or Atg5 | Enhanced atherogenic plaque progression in hypercholesterolemic mice, linked to endothelial apoptosis, senescence, and inflammation | Vion et al (2017) |
| Atherosclerosis | Macrophage‐specific deletion of Rptor | Decreased atherogenic plaque formation with concomitant reductions in plaque macrophage content in Apoe− / − mice | Zhang et al (2020) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Conditional cardiomyocyte‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Exacerbated cardiac abnormalities and premature death, linked to increased ubiquitination and mitochondrial misalignment | Nakai et al (2007), Taneike et al (2010), Eisenberg et al (2016) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Whole‐body allelic loss of Atg5 | Exacerbated Ang‐II‐induced cardiac hypertrophy, linked to increased ROS production and NF‐κB activation in macrophages | Zhao et al (2014) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Cardiomyocyte‐specific overexpression of miR‐212/132 | Pathological cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, and premature death, after impaired autophagic response upon starvation | Ucar et al (2012) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Cardiomyocyte‐specific overexpression of miR‐199a | Pathological cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure and premature death, after impaired autophagic response upon starvation | Li et al (2017) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Cardiomyocyte‐specific knock‐in of mutant TSC2S1365A | Exacerbated cardiac hypertrophy and premature death from sustained PO after mTORC1 hyperactivation | Ranek et al (2019) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Cardiomyocyte‐specific deletion of Tsc2 | Exacerbated cardiac hypertrophy and premature death after mTORC1 hyperactivation | Taneike et al (2016) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Whole‐body deletion of Lamp2 | Accelerated development of a vacuolar cardioskeletal myopathy similar to Danon disease | Nishino et al (2000), Tanaka et al (2000) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Whole‐body deletion of Fbxo32 | Development of severe cardiomyopathy, with interstitial fibrosis, reduced diastolic function, and arrhythmias, after impaired autophagy | Zaglia et al (2014) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Conditional cardiomyocyte‐specific overexpression of Atg7 | Ameliorated signs of desmin‐related cardiomyopathy and prolonged survival after autophagy activation in CryABR120G Mice | Bhuiyan et al (2013) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 | Exacerbated signs of desmin‐related cardiomyopathy and reduced survival after autophagy inhibition in CryABR120G Mice | Bhuiyan et al (2013) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Whole‐body deletion of Tp53 | Decelerated cardiac aging, linked to improved mitophagic responses after stabilization of PRKN | Hoshino et al (2013) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Conditional cardiomyocyte knock‐in of mutant MNF2AA | Development of perinatal cardiomyopathy and premature death, after inhibition of mitochondrial PRKN translocation at birth | Gong et al (2015) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Conditional cardiomyocyte‐specific deletion of Prkn | Development of perinatal cardiomyopathy and premature death, linked to impaired mitochondrial biogenesis | Gong et al (2015) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Whole‐body deletion of Pink1 | Left ventricular dysfunction and cardiac hypertrophy by 2 months of age, linked to mitochondrial dysfunction | Billia et al (2011) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Cardiomyocyte‐specific co‐deletion of Bnip3 and Bnip3l | Cardiac hypertrophy and contractile dysfunction, linked to atypical mitochondrial morphology | Dorn (2010) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Cardiomyocyte‐specific deletion of Mnf2 | Progressive cardiomyopathy due to accumulation of morphologically and functionally abnormal mitochondria | Chen and Dorn (2013) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Conditional cardiomyocyte‐specific co‐deletion of Mnf2 and Mnf1 | Impaired myocardial contractile function due to malfunctional mitochondria, but protection against acute myocardial infarction | Hall et al (2016) |
| Cardiomyopathies | Cardiomyocyte‐specific deletion of Dnase2a | Left ventricular dilatation, severe contractile dysfunction, inflammation and premature death from sustained PO, linked to mitochondrial misalignment and aggregation | Oka et al (2012) |
| IRI | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 |
Reduced size of myocardial infarction/area after IRI But: Exacerbated ischemic damage upon HFD and resistance to rapamycin |
Matsui et al (2007), Sciarretta et al (2012) |
| IRI | Conditional cardiomyocyte‐specific deletion of mTORC1 | Exacerbated hypoxic injury and cardiomyocyte apoptosis after autophagy restoration | Sciarretta et al (2012) |
| IRI | Conditional cardiomyocyte‐specific overexpression of Rheb | Exacerbated hypoxic injury and cardiomyocyte apoptosis after autophagy restoration | Sciarretta et al (2012) |
| IRI | Whole‐body deletion of Mst1 | Reduced myocardial infarction after autophagy restoration | Maejima et al (2013) |
| IRI | Cardiomyocyte‐specific overexpression of DN‐Mst1 | Reduced myocardial infarction after autophagy restoration | Maejima et al (2013) |
| IRI | Whole‐body deletion of Pgam5 | Exacerbated necroptosis and ischemic injury after inhibition of mitophagy and accumulation of abnormal mitochondria | Lu et al (2016) |
| IRI | Conditional cardiomyocyte‐specific deletion of Dnm1l | Exacerbated size of myocardial infarction/area after inhibition of mitophagy | Cahill et al (2015), Ikeda et al (2015) |
| IRI | Whole‐body deletion of Prkn | Exacerbated size of myocardial infarction/area and reduced survival, after inhibition of mitophagy | Kubli et al (2013) |
| IRI | AAV‐mediated deletion of Atg7 with Mir188‐3p) | Reduced size of myocardial infarction/area | Wang et al (2015) |
| IRI | Cardiac‐specific overexpression of DN‐GSK‐3β | Exacerbated size of myocardial infarction/area after prolonged ischemia, after autophagy activation | Zhai et al (2011) |
| IRI | Cardiomyocyte‐specific deletion of Rubcn | Reduced IRI linked to autosis inhibition after restoration of normal autophagic flux | Nah et al (2020) |
AAV, adeno‐associated viral vector; Ang‐II, angiotensin II; DN, dominant negative; IRI, ischemia‐reperfusion injury; PO, pressure overload; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
Cardiomyopathies
As best illustrated by the genetic inhibition of essential or ancillary genes within the ATG machinery, autophagy deficiency renders mice prone to develop early‐onset cardiomyopathies, either under basal conditions or upon pre‐pathological circumstances of stress (e.g., pressure overload) (Bravo‐San Pedro et al, 2017). Consistently, mice with a cardiomyocyte‐specific conditional inactivation of Atg5, and challenged with transverse aortic constriction, display defects in sarcomere structure, aberrant aggregation of misfolded proteins, and altered mitochondrial dynamics, followed by prominent cardiac abnormalities (contractile dysfunction, maladaptive hypertrophy, left ventricular dilation) and early mortality (Nakai et al, 2007; Taneike et al, 2010). Likewise, the deletion of a single copy of Atg5 worsens angiotensin II‐induced cardiac hypertrophy (Zhao et al, 2014; Bravo‐San Pedro et al, 2017). Along similar lines, the cardiomyocyte‐specific overexpression of miRNAs invalidating the transcriptional activity of FOXO3 (Ucar et al, 2012) or activating MTORC1 (Li et al, 2017) precipitates cardiac function, leading to heart failure. In addition, broad‐spectrum autophagic defects tied to the systemic ablation of LAMP2 (causing Danon disease) account for the early development of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (Nishino et al, 2000; Tanaka et al, 2000). In this scenario, the persistent activation of MTORC1 lowers the capacity of cardiomyocytes to sustain pressure overload‐induced stress, as testified to by the fact that mice bearing knock‐in mutation in the MTORC1 inhibitor Tsc2 (TSC complex subunit 2) develop heart disease (Taneike et al, 2016), while succumbing to pressure overload (Ranek et al, 2019).
The detrimental effects associated with the inactivation of autophagy in cardiomyocytes are largely due to its involvement in the regulation of proteostatic adaptations and in the maintenance of mitochondrial fitness. Thus, the genetic knockout of the muscle‐specific ubiquitin ligase Fbxo32/atrogin‐1 (F‐box protein 32) prevents the proteasomal degradation of the autophagy regulator CHMP2B, possibly resulting in insufficient autophagic flux and aberrant protein aggregation, which are etiologically associated with the development of severe cardiomyopathy (Zaglia et al, 2014). Similarly, the overexpression of ATG7 ameliorates signs of DES (desmin)‐related cardiomyopathy in mice expressing the R120G mutant of CRYAB (crystallin, alpha B) (Bhuiyan et al, 2013), whereas the heterozygous loss of Becn1 accelerates heart failure under the same pathological setting (Tannous et al, 2008). However, defective mitophagy calls for major cardiac abnormalities. In particular, Trp53 (transformation‐related protein 53, for simplicity referred to as TP53) whole‐body deletion restrains the age‐dependent decline in cardiac performance by promoting the stabilization of the central mitophagy regulator PRKN (Hoshino et al, 2013). Accordingly, (i) cardiomyocyte‐restricted deletion of Prkn at birth (but not after weaning) hastens the manifestation of cardiac hypertrophy (Gong et al, 2015); (ii) whole‐body knockout of Pink1, another modulator of mitophagy, links to left ventricular defects and compensatory cardiac hypertrophy (Billia et al, 2011); and (iii) simultaneous deletion of genes coding for the mitophagy regulators BNIP3 (BCL2/adenovirus E1B interacting protein 3) and BNIP3L (BCL2/adenovirus E1B interacting protein 3‐like) leads to cardiac hypertrophy and impaired contractile functions, tied to ultrastructural mitochondrial alterations (Dorn, 2010).
Further highlighting the central role of proficient mitophagy in cardiac homeostasis, cardiomyocyte‐specific ablation of the gene encoding the PRKN regulator MFN2 (mitofusin 2) phenotypically manifests as lethal cardiomyopathy associated with insufficient mitophagy (Chen & Dorn, 2013), and co‐deletion of Mfn1 and Mfn2 in adult cardiomyocytes compromises optimal mitochondrial fusion, igniting dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure (Hall et al, 2016). Moreover, mice lacking Dnase2 (deoxyribonuclease II alpha), a gene coding for a lysosomal enzyme that catalyzes the autophagy‐dependent degradation of DNA released from damaged mitochondria), display major cardiac alterations when challenged with protocols of pressure overload (Oka et al, 2012). Finally, PINK1‐mediated mitophagy and PRKN‐mediated mitophagy are defective in the hearts of Duchenne muscular dystrophy model mice (Kang et al, 2018). Taken together, these data lay significant emphasis on the primordial role of autophagy in the safeguard of cardiovascular homeostasis. This concept is further reinforced by the demonstration that pharmacological preclinically harnessed to correct cardiovascular dysfunctions (e.g., spermidine, rapamycin) cannot prescind from intact autophagy to mediate their pro‐health effects (Sciarretta et al, 2012; Eisenberg et al, 2016).
Ischemia‐reperfusion injury
Pathological episodes that lead to the occlusion of coronary arteries impose on cardiomyocytes ischemic stress, peculiarly defined by temporally limited shortage of nutrients and exacerbated production of ROS, followed by a (mal)adaptive phase of reperfusion. Extensive evidence supports the view that autophagy is etiologically implicated in settings of ischemia‐reperfusion injury (IRI) (Martins et al, 2011; Lavandero et al, 2015; Bravo‐San Pedro et al, 2017; Sciarretta et al, 2018; Kaludercic et al, 2020). For example, a prominent surge in the autophagic flux, paralleling the inhibition of MTORC1, which in turn follows the activation of AMP‐activated protein kinase (AMPK) or the inhibition of RHEB (Ras homolog enriched in brain), occurs upon ischemic injury (Matsui et al, 2007; Sciarretta et al, 2012). Consistently, mice engineered to restore RHEB and MTORC1 functions display exacerbated hypoxic injury and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, suggesting that functional autophagy equips cardiomyocytes with a superior capacity to sustain the ischemic shock (Sciarretta et al, 2012). Likewise, cardiac‐selective deletion of Nox4 (NADPH oxidase 4), which impairs the autophagy response, aggravates the ischemic injury (Sciarretta et al, 2013). Conversely, mice lacking the pro‐apoptotic kinase MST1 show improved activation of cytoprotective autophagy and resistance to ischemic stress (Maejima et al, 2013).
In agreement with the notion that altered mitochondrial dynamics etiologically contribute to the ischemic damage, functional mitophagy appears to be required to support the survival of cardiomyocytes, presumably by limiting the burden of oxidative stress that accompanies the ischemic episode (Saito & Sadoshima, 2015; Bravo‐San Pedro et al, 2017). Consistently, whole‐body deletion of the mitophagy regulator Pgam5 (phosphoglycerate mutase family member 5) worsens the pathological outcome of myocardial infarction, inasmuch as it promotes events of necroptotic cell death (Lu et al, 2016). Furthermore, the cardiomyocyte‐specific ablation of the mitochondrial fission regulator Dnm1l/Drp1 (dynamin 1‐like) compromises optimal mitophagy and exacerbates the IRI (Cahill et al, 2015; Ikeda et al, 2015), and prkn− / − mice subjected to permanent ligation of the left descending cardiac artery exhibit more severe ischemic damage compared with their wild‐type littermates (Kubli et al, 2013). While these data lend robust support to the hypothesis that functional autophagy mitigates ischemic damage, this process appears to play a maladaptive role in the reperfusion phase, as demonstrated by the leading observation that Becn1 +/− mice display enhanced resistance to reperfusion damage compared with their autophagy‐competent counterparts (Ma et al, 2012a; Ma et al, 2012b). Of note, this finding can be functionally recapitulated by (i) the downregulation of Atg7 achieved via adenoviral delivery of Mir188‐3p, which appears to limit the size of myocardial infarction (Wang et al, 2015); and (ii) GSK3B (glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta) inhibition, which suppresses autophagy in an MTORC1‐dependent manner (Zhai et al, 2011). Conversely, it has been proposed that the accumulation of autophagosomes that defines the reperfusion stage may instead reflect defective autophagosomal clearance (Ma et al, 2012a; Ma et al, 2012b). The accurate assessment of the autophagy flux is hence instrumental to resolve this conundrum. In addition, IRI has been causally connected with autosis, a type of cell death ignited by the excessive activation of autophagy (Liu et al, 2013c). Autosis is upregulated during the reperfusion stage, alongside the enhanced expression of the negative autophagy regulator RUBCN, which results in the aberrant pile‐up of autophagosomes in cardiomyocytes (Nah et al, 2020). De facto, the genetic suppression of RUBCN, or the inhibition of autosis by treatment with cardiac glycosides, normalizes the autophagic flux and improves the response to IRI (Nah et al, 2020).
Atherosclerosis
As suggested above, persistent nutritional imbalance or overindulgent lifestyle behaviors undermine basal autophagy, thereby accelerating the occurrence of metabolic disorders. Importantly, excessive calorie intake impairs cardiovascular autophagy, in part accounting for the accrued propensity to manifest diabetic cardiomyopathy and atherosclerosis. Supporting this finding, Becn1+ / − mice receiving a high‐fat diet (HFD) exhibit heightened ischemic damage compared with wild‐type littermates in settings of prolonged ischemia (Sciarretta et al, 2012). Noteworthy, stimulation of BECN1‐dependent autophagy by physical exercise is sufficient to correct defects in the autophagic flux mediated by HFD feeding in cardiomyocytes (He et al, 2012).
Data obtained from preclinical models support the tenet that autophagy is a major disease‐modifying process during the different phases of atherogenesis (Martinet & De Meyer, 2009; Kaludercic et al, 2020). In apoe (apolipoprotein E)‐knockout mice fed a westernized diet, the macrophage‐specific ablation of Atg5 (Razani et al, 2012) or the vascular smooth muscle cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 (Osonoi et al, 2018) accelerates the acquisition of the atherogenic phenotype, linked to detrimental inflammasome activation or increased CCL2 (chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 2)‐mediated macrophage recruitment, respectively. This result matches the original observation, indicating that undissolved cholesterol crystals instigate lysosomal damage and promote NLRP3 inflammasome activation (Duewell et al, 2010). In line with the atheroprotective role of autophagy, the stimulation of autophagy in macrophage foam cells limits plaque buildup by favoring cholesterol efflux. Mechanistically, autophagy promotes the delivery of lipid droplets (LDs) to the lysosome, where resident lysosomal acid lipases hydrolyze cholesterol esters to free cholesterol prior to the ABCA1 (ATP‐binding cassette, subfamily A (ABC1), member 1)‐dependent release (Ouimet et al, 2011). Moreover, it has recently been observed that an excess of dietary proteins is sufficient to drive the atherogenic phenotype in apoe and ldlr (low‐density lipoprotein receptor) knockout mice, due to the overactivation of MTORC1 signaling and the consequent inhibition of mitophagy in macrophages (Zhang et al, 2020). In advanced stages of atherosclerosis, autophagy contributes to maintain plaque integrity by promoting macrophage survival, as witnessed by the fact that atg5 deletion in macrophages of ldlr− / − mice fed a HFD worsens the atherosclerotic phenotype due to exacerbated oxidative stress, impaired efferocytosis, and enhanced macrophage apoptosis (Liao et al, 2012). Corroborating this finding, stimulation of lysosomal biogenesis in macrophages by TFEB activation mitigates the atherogenic phenotype (Sergin et al, 2017). The atheropreventive functions of autophagy are not limited to macrophages. Indeed, defective endothelial autophagy in hypercholesterolemic mice dissipates the antiatherogenic effect of blood‐flow‐derived shear stress, worsening the burden of atherogenic plaques and exacerbating inflammatory reactions (Vion et al, 2017).
Musculoskeletal disorders
The proper functioning of the musculoskeletal system depends upon the tightly coordinated integration of signals that operate to maintain an adequate balance between mass and structural requirements of the skeletal muscles, but also bone and cartilage. Of note, defects in the musculoskeletal system yield tangible systemic consequences, due to (i) the pivotal role of skeletal muscle in the systemic regulation of INS (insulin) signaling and (ii) the hormone‐mediated crosstalk between the renal and osseous systems for Ca2+ homeostasis.
Muscular diseases
As briefly discussed above, intact autophagy is essential for the preservation of muscle structure and fitness at basal conditions (Sebastian & Zorzano, 2020) (Table 3). This observation is fully supported by experimental evidence revealing that autophagy‐incompetent muscle progressively degenerates as a direct consequence of aberrant proteostasis, leading to the development of severe myopathies (Masiero et al, 2009). Conversely, the stimulation of autophagy partially underlies the beneficial actions of physical exercise in maintaining muscle mass (He et al, 2012; Liu et al, 2020b), while retarding age‐dependent loss of muscle mass (sarcopenia) (Fan et al, 2016). In this regard, time‐dependent decline in autophagy proficiency has been functionally connected to accrued senescence of muscle satellite cells, suggesting that impaired autophagy is a key determinant of the sarcopenic phenotype (Garcia‐Prat et al, 2016). This tenet is further reinforced by recent observations demonstrating that suppression of the prostaglandin‐degrading enzyme HPGD/15‐PGDH (15‐hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase) restrains sarcopenia progression through the activation of autophagy (Palla et al, 2021) and that the anti‐atrophy action of SESNs (sestrins) depends on autophagy activation (Segales et al, 2020). Noteworthy, impaired mitochondrial dynamics play a central role in age‐dependent muscle decay, with levels of most fusion genes falling during aging and other atrophy conditions (Hood et al, 2019), as witnessed by the fact that age‐dependent loss or genetic ablation of Mfn2 in murine muscle precipitates sarcopenia via inhibition of mitophagy (Sebastian et al, 2016). However, the clinical relevance of mitochondrial dynamics in general in aging sarcopenia is unclear. In a cohort study, only levels of OPA1 (OPA1 mitochondrial dynamin‐like GTPase), a gene essential for inner mitochondrial membrane fusion and cristae remodeling (Giacomello et al, 2020), correlate with muscle mass, and its inducible deletion in the adult mouse triggers FOXO3‐dependent sarcopenia and FGF21 (fibroblast growth factor 21)‐induced systemic aging (Tezze et al, 2017).
Table 3.
Musculoskeletal disorders associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone loss | Chondrocyte‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced femoral and tibia lengths, linked to increased ER storage of PC2 and defective secretion of COL2A1, at the postnatal stage | Cinque et al (2015) |
| Bone loss | Osteoblast‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Reduced trabecular bone volume in 9‐month‐old mice, linked to reduced mineralization capacity | Nollet et al (2014) |
| Bone loss | Conditional osteoblast‐specific deletion of Fip200 | Exacerbated osteopenia due to defective osteoblast terminal differentiation | Liu et al (2013a) |
| Bone loss | Conditional osteoblast progenitor‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced bone mass at both developmental and adult age, linked to reduced mineralization capacity and promoted ER stress | Li et al (2018) |
| Bone loss | Conditional osteocyte‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced bone mass in 6‐month‐old mice linked to increased ROS levels and reduced osteoclast number | Onal et al (2013) |
| Bone loss | Osteoclast‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Increase trabecular bone volume and reduced ovariectomy‐induced bone loss | DeSelm et al (2011) |
| Bone loss | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced glucocorticoid‐ and ovariectomy‐induced osteoclast differentiation and bone loss | Lin et al (2016) |
| Exercise intolerance | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 | Decreased endurance and altered glucose metabolism during acute exercise, impaired exercise‐stimulated protection against HFD‐induced glucose intolerance | He et al (2012) |
| Exercise intolerance | Whole‐body knock‐in of mutant Bcl2AAA | Decreased endurance and altered glucose metabolism during acute exercise, impaired exercise‐stimulated protection against HFD‐induced glucose intolerance | He et al (2012) |
| Muscular dystrophy | Whole‐body deletion of Col6a1 | Myopathic defects associated with impaired autophagic flux and aberrant organelle accumulation |
Grumati et al (2010) Chrisam et al (2015) |
| Muscular dystrophy | Muscle‐specific knock‐in of Akt | Exacerbated muscular dystrophy after autophagy inhibition | Grumati et al (2010) |
| Muscular dystrophy | Whole‐body deletion of Trim32 | Exacerbated muscular atrophy associated with impaired autophagic induction | Di Rienzo et al (2019) |
| Osteoarthritis | Articular cartilage‐specific deletion of FoxO1 | Development of osteoarthritis‐like pathologies | Wang et al (2020a) |
| Osteoporosis | Whole‐body deletion of Optn | Early elevated osteoporotic bone loss, senescence of MSCs, and enhanced adipogenesis | Liu et al (2020c) |
| PDB | Whole‐body deletion of Optn | Bone lesions similar to PDB observed in patients, linked to increased osteoclastogenic potential and decreased type I IFN production | Wong et al (2020) |
| PDB | Whole‐body knock‐in of mutant p62P392L | Increased osteoclastogenic potential of bone microenvironment, but histologically normal bones | Hiruma et al (2008) |
| Sarcopenia | Muscle‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Exacerbated muscle loss during denervation and fasting, and abolished sestrin‐mediated protection against disuse‐induced muscle atrophy | Masiero et al (2009), Segales et al (2020) |
| Sarcopenia | shRNA‐mediated muscle‐specific deletion of 15‐PGDH | Increased aged muscle mass, strength, and exercise performance | Palla et al (2021) |
| Sarcopenia | Whole‐body deletion of Sesn1 | Exacerbated disuse‐induced muscle atrophy after constitutive mTORC1‐signaling activation | Segales et al (2020) |
| Sarcopenia | Muscle‐specific deletion of Mfn2 | Enhanced muscle atrophy and sarcopenia, linked to age‐induced mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production, after mitophagy inhibition | Sebastian et al (2016) |
| Sarcopenia | Conditional muscle‐specific deletion of Opa1 | Accelerated muscle atrophy linked to a precocious senescence phenotype and premature death | Tezze et al (2017) |
| Sarcopenia | Whole‐body deletion of Trim32 | Exacerbated muscle atrophy associated with impaired autophagic flux | Di Rienzo et al (2019) |
| XLMTM | Whole‐body deletion of Mtm1 | Myopathic defects associated with impaired autophagic flux and abnormal mitochondria | Fetalvero et al (2013) |
HFD, high‐fat diet; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; PC2, type II procollagen; PDB, Paget disease of bone; XLMTM, X‐linked myotubular myopathies.
In the light of these studies, whether autophagy ameliorates or exacerbates pathological settings of sarcopenia, remains controversial. Indeed, studies reported (i) pathological contexts in which deficient autophagy is pathognomonic to the disease; (ii) muscular illnesses in which supraphysiological levels of autophagy aggravate the degenerative phenotype; (iii) musculo‐degenerative conditions (e.g., lysosomal storage disorders) in which the lysosomal system is aberrantly altered (Vainshtein et al, 2014; Castets et al, 2016); and (iv) conditions in which pharmacological activation of muscular autophagy reinstalls functionality of the muscle (Chrisam et al, 2015).
In degenerative myopathies, such as collagen type VI‐related myopathies, failure in autophagy initiation is observed in the muscle of col6a1 (collagen, type VI, alpha‐1)‐knockout mice, resulting in aberrant organelle accumulation, mainly due to reduced expression of BECN1 (Grumati et al, 2010). More recently, a pathological role has been ascribed to dysfunctional autophagy in (i) Duchenne muscular dystrophy, as autophagy induction is hampered in adult mice displaying muscular dystrophy (Dmdmdx mutant mice) (De Palma et al, 2014); and (ii) X‐linked myotubular myopathies, as defective autophagy is detected in Mtm1 (X‐linked myotubular myopathy gene 1)‐deficient mouse muscle (Fetalvero et al, 2013). Limb‐girdle muscular dystrophy 2H (LGMD2H) is a muscle dystrophy caused by mutations in the ubiquitin ligase TRIM32, characterized by impaired muscle regrowth following atrophy (Kudryashova et al, 2012). Recently, it has been reported that TRIM32‐mutant muscle cells show a defective autophagy response to atrophic stimuli, associated with increased ROS and TRIM63/MuRF1 levels. The pro‐autophagy function of TRIM32 depends on its ability to bind to AMBRA1 (autophagy/Beclin 1 regulator 1) and ULK1 and stimulate ULK1 activity via unanchored K63‐linked polyubiquitin (Di Rienzo et al, 2019). In contrast with these findings, activated autophagy seems to accelerate the muscular dystrophic alterations observed in congenital myotonic dystrophy type I patients (Beffy et al, 2010). A large body of evidence supports the notion that impaired fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes exerts detrimental effects at the muscular level. This tenet has been confirmed in Danon disease, X‐linked myopathy with excessive autophagy and Pompe disease mouse models, in which autophagosomes are aberrantly accumulated due to impaired lysosomal degradation (Lieberman et al, 2012). Of note, strategies based on the enhancement of cellular waste disposal capacity (i.e., TFEB‐TFE3 gene therapy) hold promise of preclinical benefits in these pathological scenarios (Spampanato et al, 2013; Bajaj et al, 2019).
Bone disorders
Autophagy has a well‐recognized impact on the regulation of numerous aspects of bone biology, acting as a primary determinant of bone mass, structure, and functional remodeling (Shapiro et al, 2014; Yin et al, 2019) (Table 3). This is mainly due to the fact that autophagy is essential for the survival and landmark functions of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, which operate antagonistically to maintain a constant equilibrium between events of bone mineralization and bone resorption, respectively (Shapiro et al, 2014; Vrahnas et al, 2019; Yin et al, 2019). Furthermore, autophagy positively regulates chondrocyte functions, directly contributing to the secretion of COL2A1 (collagen, type II, alpha‐1; the major component of the cartilage matrix) in response to FGF18 at the postnatal stage (Cinque et al, 2015). Additionally, the autophagy pathway is directly modulated in response to hormonal and soluble signals (including bone morphogenetic proteins, TNFSF11/RANKL [tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11], and CTNNB1/β‐catenin) that intercept the central signaling pathway involved in bone mineralization dynamics. Based on this premise, it is not surprising that conditions that directly or indirectly disturb these processes evoke conditions of osteopetrosis, osteopenia, or osteoporosis (Shapiro et al, 2014; Dallas et al, 2018; Yin et al, 2019).
In line with the involvement of autophagy in events of bone mineralization, apatite crystals are detected within autophagic vacuoles in osteoblasts in vitro prior to their secretion. Furthermore, osteoblast‐restricted Atg5 ablation dampens their mineralization capacity, culminating in decreased trabecular bone mass (Nollet et al, 2014). In addition, several components of the ATG machinery support osteoclast secretory functions by promoting the polarized fusion of lysosomes with the plasma membrane. This phenomenon, which relies upon intact ATG5 and RAB7 expression, suggests that non‐canonical tasks of ATG proteins may contribute to osteoclast‐dependent bone resorption (DeSelm et al, 2011).
Moreover, deletion of Rb1cc1 compromises the differentiation of osteoblasts into osteocytes, instigating episodes of osteopenia (Liu et al, 2013a). Likewise, atg7 knockout in differentiated osteoblasts or osteoblast precursors in the bone marrow impairs mineralization, due to ramping ER stress in target cells (Li et al, 2018). Along similar lines, alterations in the activity of the transcription factor ATF4, which has been found mutated in two genetic diseases of the skeletal system (such as Coffin‐Lowry syndrome and neurofibromatosis type I), reduce the expression of key Atg genes and impair bone mineralization (Li et al, 2018). Aside from its role in osteoblasts, genetic inhibition of autophagy in terminally differentiated osteocytes, which primarily act as mechanosensors within the skeletal system, results in a significant bone mass reduction (Onal et al, 2013). A significant body of experimental evidence suggests that autophagy also affects bone resorptive capacity, by virtue of its involvement in the differentiation (which seems to rely on the HIF1A/HIF1α [hypoxia‐inducible factor 1, alpha subunit]‐BNIP3 axis, but is unaffected by atg5 deletion) (Zhao et al, 2012) and activity of osteoclasts (Shapiro et al, 2014; Dallas et al, 2018; Yin et al, 2019). In this regard, genetic inhibition of several autophagy genes in osteoclasts undermines the chain of events that lead to the release of acidic lysosomes at the contact site between bony surface and podosomes, resulting in increased bone volume (DeSelm et al, 2011). In view of the myriad actions in the skeletal tissue, researchers have investigated the role of autophagy in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis, which represents a significant health concern, especially among the elderly or post‐menopausal women. A genome‐wide association study established a correlation between genetic variants in several ATG proteins and wrist bone mineral density, suggesting that altered autophagy may predispose to the osteoporotic phenotype (Zhang et al, 2010). Considering that osteoporosis is a multifactorial disorder, establishing an etiological connection between autophagy and the onset of the disease remains a challenging task. In a rat model of osteoporosis, reduced levels of autophagy in osteoblasts have been reported (Tang et al, 2019). optn− / − mice show reduced ability to eliminate FABP3 (fatty acid binding protein 3, muscle and heart) by selective autophagy linked to impaired osteogenesis and increased bone loss, thus supporting the notion that decreased expression of OPTN during aging might lead to osteoporosis (Liu et al, 2020c). In contrast, genetic inactivation of autophagy in myeloid cells prevents osteoclastogenesis, while mitigating bone loss in mice treated with glucocorticoids or subjected to ovariectomy (Lin et al, 2016). This result fits well with the observation that exacerbated inflammatory signals, typified by TNF/TNF‐α‐mediated activation of autophagy in osteoclasts, are detrimental for bone loss (Lin et al, 2013).
A possible connection has also been put forward between disturbance in autophagy and Paget disease of bone (PDB), an age‐dependent pathology defined by altered bone turnover due to aberrant osteoclast activity. Mutations in the gene coding for SQSTM1/p62 have been found in approximately 10% of PDB patients, and a mouse model carrying the P394L mutation exhibits a PDB‐like bone disorder with focal bone lesions, linked to enhanced autophagy activation in osteoclasts and detrimental bone remodeling (Hiruma et al, 2008). Recently, genetic ablation of Optn in mice has been found to recapitulate the clinical features observed in human PBD patients. Mechanistically, OPTN deficiency maps to defective IFNB1/IFNβ1 (interferon beta 1) production and signaling, in turn linked to enhanced osteoclast differentiation and survival (Wong et al, 2020). Furthermore, mutations in VCP cause early‐onset Paget disease in conjunction with frontotemporal dementia and inclusion body myositis. The hallmark pathology of familial or sporadic inclusion body myositis consists of a massive accumulation of autophagy vacuoles and polyubiquitinated aggregates large enough to be visualized by routine histology as rimmed vacuoles (Nogalska et al, 2010).
Finally, dampened levels of ATG proteins (including ULK1, LC3, and BECN1) have been described in a mouse model of osteoarthritis (OA), the most prevalent joint pathology (Carames et al, 2010). This result lends further ground to the evidence that autophagy regulates central functions in chondrocytes, even at the adult stage. In support of this result, the induction of autophagy mediated by FOXO1 is instrumental for the activation of TFGB signaling and protects against OA. Conversely, the postnatal ablation of FoxO1 or its cartilage‐restricted suppression in adult mice is sufficient to drive an OA‐like symptomatology (Wang et al, 2020a). In this context, intact autophagy responses are instrumental to counteract the inflammatory burden that delineates OA pathogenesis, while concomitantly limiting IL1 (interleukin 1)‐induced erosion of cartilage matrix through efficiently dismantling inflammasomes and improving mitochondrial turnover (Sasaki et al, 2012; Kim et al, 2017). Because cellular senescence is functionally implicated in OA pathogenesis, it is plausible to speculate that defective autophagy contributes to OA by promoting chondrocyte senescence (Coryell et al, 2021).
Pulmonary disorders
Functional autophagy responses are required to fulfill multiple homeostatic tasks within the variety of cell types that forms the pulmonary tissue, thus ensuring a functional gas exchange in the lung. Of note, autophagy elicits cytoprotective or disease‐supporting roles in the most common pathologies affecting the lung tissues (Table 4).
Table 4.
Pulmonary disorders associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| COPD | Whole‐body deletion of Map1 lc3b | Decreased signs of emphysema and resistance to cilia shortening after CS exposure | Chen et al (2010), Lam et al (2013) |
| COPD | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 | Resistance to cilia shortening after CS exposure | Lam et al (2013) |
| COPD | X chromosome deletion of Hdac6 | Resistance to cilia shortening after CS exposure | Lam et al (2013) |
| COPD | Whole‐body deletion of miR‐21 | Improved pulmonary fitness after CS exposure by reducing autophagy activation in bronchiolar cells | Zeng et al (2018) |
| COPD | Whole‐body deletion of Pink1 | Improved lung function after subchronic CS exposure, linked to impaired mitophagy | Mizumura et al (2014) |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | Whole‐body deletion of Atg4b | Exacerbated bleomycin‐induced lung injury linked to increased lung inflammation | Cabrera et al (2015) |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | Conditional AEC‐specific deletion of Tsc1 | Exacerbated bleomycin‐induced lung injury after mTORC1 overactivation | Gui et al (2015) |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | Conditional A2T progenitor cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Exacerbated bleomycin‐induced lung injury by reducing A2T stemness | Li et al (2020a) |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | Whole‐body deletion of Anxa2 | Mitigated bleomycin‐induced lung injury via TFEB‐mediated autophagy activation | Wang et al (2018a) |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | Whole‐body deletion of Tlr4 | Exacerbated bleomycin‐induced lung injury and pulmonary inflammation after autophagy inhibition | Yang et al (2012) |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | Conditional myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 or Atg7 | Exacerbated bleomycin‐induced fibrosis and spontaneous lung inflammation by enhancing inflammasome activation | Abdel Fattah et al (2015), Jessop et al (2016) |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | Whole‐body deletion of Pink1 | Accelerated development of bleomycin‐induced lung fibrosis linked to accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria in AEC cells | Bueno et al (2015) |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | Whole‐body deletion of Prkn | Accelerated development of bleomycin‐induced lung fibrosis after mitophagy inhibition | Kobayashi et al (2016) |
| Sarcoidosis | Conditional myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Tsc2 | Exacerbated granuloma formation after mTORC1‐mediated hypertrophy and proliferation in macrophages | Linke et al (2017) |
| Cystic fibrosis | CFTRdel506 transgenic mice | Impaired autophagy through TG2‐mediated BECN1 inhibition | Luciani et al (2010) |
AEC, alveolar epithelial cell; A2T, alveolar type 2; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, CS, cigarette smoke.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressively debilitating disease caused by chronic exposure to cigarette smoke (CS), currently representing the fourth leading cause of death worldwide. The pathogenic features of COPD encompass airway obstruction and loss of alveolar cells (called emphysema), which lead to an aberrant remodeling of the lung parenchyma and irreversible decline of lung function. Preclinical models of CS exposure have delineated the pathological relevance of autophagy in COPD development (Nakahira et al, 2016). Consistently, partial autophagy deficiency imposed by map1lc3b deletion reduces signs of emphysema after 3‐month exposure to CS (Chen et al, 2010). In similar experimental settings, map1lc3b− / − and Becn1+ / − animals display enhanced resistance to CS‐induced mucociliary disruption, suggesting that autophagy‐dependent degradation of bronchial cilia (known as “ciliophagy”) elicits detrimental outcomes in COPD (Lam et al, 2013). Further corroborating the negative role of cilia resorption in COPD, genetic, or pharmacological inhibition of HDAC6 (histone deacetylase 6) with tubastatin A leads to decreased autophagy, followed by reduced cilia shortening and protection from CS‐induced lung dysfunction (Lam et al, 2013). In agreement with these results, mir21− / − mice exposed to CS exhibit improved pulmonary fitness compared with their wild‐type counterparts, alongside a reduction in markers of autophagy activation and decreased apoptosis of bronchiolar cells (Zeng et al, 2018). Recently, a possible correlation between selective lysosomal degradation of ferritin (known as “ferritinophagy”) and COPD has emerged, suggesting that NCOA4 (nuclear receptor coactivator 4)‐dependent ferritinophagy occurring upon CS exposure accelerates COPD progression by instigating parenchymal lung cell ferroptosis (Yoshida et al, 2019). Besides sensitizing parenchymal lung cells to death, the stimulation of autophagy by CS exposure precipitates neutrophil death, in turn resulting in the detrimental release of elastase in the lung. Mechanistically, this effect relies on the CS‐dependent activation of PAFR (platelet‐activating factor receptor), which in turn leads to autophagy upregulation in neutrophils (Lv et al, 2017).
In the recent past, a number of studies have investigated the contribution of mitophagy to COPD pathogenesis, leading to discordant findings (Cloonan & Choi, 2016). Defective mitophagy imposed on mice by pink1 deletion or by treatment with the mitophagy inhibitor Mdivi‐1 protects lung epithelial cells from CS‐induced necroptotic cell death, while improving lung function (Mizumura et al, 2014). Nonetheless, the inhibition of mitophagy associated with the genetic deletion of Prkn worsen the effect of CS, as it promotes the entry of epithelial alveolar cells in the senescent state (Ahmad et al, 2015). Because senescence operates as a major pathogenic mechanism in COPD and settings of derailed autophagy facilitate the installation of the senescent program (Antony & Thannickal, 2018), it is tempting to speculate that prolonged suppression of autophagy and mitophagy may instead contribute to the clinical manifestation of COPD. Further studies, addressing autophagy/mitophagy incompetency in selected cell types within the lung tissues, and triggered by additional manipulations, will be instrumental to clarify this conundrum.
Pulmonary fibrosis
Unlike COPD, autophagy appears to elicit protective functions in murine models of pulmonary fibrosis induced by chemotherapeutics (i.e., bleomycin) or silica (Patel et al, 2012; Zhao et al, 2019; Zhao et al, 2020). Of note, induction of lung injury produced by these agents leads to adverse inflammatory events, which may causally contribute to an excessive healing process and fibrogenesis (Racanelli et al, 2018). Although these preclinical systems present inherent limitations, because they fail to recapitulate key features of human interstitial lung disorders, they are currently employed to study the pathological underpinnings of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, and lung injury. Partial autophagy incompetency driven by type II alveolar epithelial cell‐specific knockdown of Tsc1 or whole‐body atg4b knockout exacerbates bleomycin‐induced lung injury (Cabrera et al, 2015; Gui et al, 2015). Moreover, activation of MTORC1 in macrophages by selective deletion of Tsc2 leads to excessive granuloma formation, a clinical implication for sarcoidosis (Linke et al, 2017). In addition, defective autophagy in progenitor alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells aggravates bleomycin‐induced lung injury, as it reduces AT2 cell stemness by reprogramming their metabolism (Li et al, 2020a). Consistently, bleomycin‐induced upregulation of ANXA2 (Annexin A2) perturbs the autophagic flux by limiting TFEB nuclear translocation (Wang et al, 2018a). Supporting these results, TLR4‐dependent activation of autophagy in a mouse model of silicosis is required to resolve chronic lung injury (Yang et al, 2012).
The antifibrotic properties attributed to autophagy in the context of acute or chronic lung injury are presumably tied to (i) enhanced resistance of alveolar epithelial cells to programmed death; (ii) reduced TGFB/TGFβ (transforming growth factor, beta)‐dependent fibroblast differentiation; and (iii) suppression of the inflammatory cascade (Patel et al, 2012; Mora et al, 2017; Zhao et al, 2019; Zhao et al, 2020). As an example, mice characterized by autophagy deficiency in myeloid cells display exacerbated inflammation and fibrosis compared with their autophagy‐competent littermates in the context of bleomycin‐ or silica‐induced fibrosis (Abdel Fattah et al, 2015; Jessop et al, 2016). Derailed mitochondrial fitness participates in the fibrogenic process in pulmonary fibrosis. In accordance with this notion, genetic loss of Pink1 and Prkn accelerates the development of the fibrotic phenotype in bleomycin‐treated mice, linked to alveolar epithelial cell II (AECII) loss and accrued inflammation (Bueno et al, 2015; Kobayashi et al, 2016). Of note, the levels of PINK1 decline with age, suggesting that a time‐dependent drop in mitophagy proficiency may contribute to the development of pulmonary fibrosis in aged individuals (Bueno et al, 2015).
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic autosomal recessive disease, due to mutations in the CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) gene, with the most frequent one being CFTRdel506 (Rowntree & Harris, 2003). Loss‐of‐function mutations of CFTR lead to its reduced expression or affect its correct transport to the plasma membrane. The production of abnormally viscous mucus, associated with declining functions of lung epithelial cells and macrophages, renders CF patients susceptible to infections and aberrant inflammation, which eventually account for the fatal outcome of this disease. Of note, a large body of evidence indicates that CFTR defects impair autophagy, through mechanisms that include the sequestration of BECN1 (and its interactome) in aggresomes (Luciani et al, 2010; Luciani et al, 2011) and an impairment in xenophagy. Treatment of mice bearing the Cftrdel506 mutation with a combination of EGCG (an inhibitor of the autophagy repressor EP300) and cysteamine (which restores the trafficking of CFTRdel506 to the membrane by inhibiting TGM2 [transglutaminase 2, C polypeptide]) yield to tangible clinical and preclinical benefits in autophagy‐competent mice, yet fail to do so in their autophagy‐deficient counterparts, further emphasizing the key involvement of autophagy in CF pathogenesis (Tosco et al, 2016). Mechanistically, it has been demonstrated that TGM2 triggers the trimerization and activation of HSF1 (heat‐shock transcription factor 1) regulating adaptation to stress and proteostasis impairment. TG2 loss of function correlates with a defect in the nuclear translocation of HSF1 and restores the imbalance in the HSF1‐HSPA/HSP70 pathway in CF leading to an increase in approximately 40% in CFTR function in a CF mouse model lacking TGM2 (Rossin et al, 2018). Interestingly, mice bearing defective CFTR are abnormally susceptible to a celiac disease‐like enteropathy as a consequence of inflammatory response induced by oral challenge with the gluten‐derivative gliadin (Villella et al, 2019b). Further, stimulation of autophagy by restored expression of BECN1 attenuates this gliadin‐induced inflammation (Villella et al, 2019a).
Kidney diseases
Intact autophagic responses are essential to regulate baseline functions of resident kidney cells, while exerting renoprotective effects under conditions of acute or chronic damage (Choi, 2020; Tang et al, 2020) (Table 5). Unlike the conditional deletion of essential autophagic genes at the embryonic stage, which does not significantly have an impact on normal kidney development, the promoter‐specific invalidation of autophagy in adult mice severely affects kidney physiology, depending upon the targeted cell type. As an example, the Six2 (sine oculis‐related homeobox 2) promoter‐driven expression of Cre recombinase in Atg5fl / fl or Atg7fl / fl mice, which renders the entire nephron incompetent for autophagy, is accompanied by the detrimental remodeling of tubular and glomerular structures and leads to irreversible renal failure (Kawakami et al, 2015). Likewise, atg5 deletion in both distal and proximal tubular epithelial cells (TECs) results in progressive kidney damage and tubulointerstitial fibrosis (Liu et al, 2012). The same result is not observed in settings of autophagy deficiency in distal TECs only, suggesting that proximal TECs are more reliant upon basal autophagy than their distal counterparts (Liu et al, 2012). Importantly, disturbance of the autophagy flux in podocytes, by podocyte‐specific deletion of Atg5 (Hartleben et al, 2010), Pik3c3/Vps34 (Bechtel et al, 2013), or Ctsd (cathepsin D) (Yamamoto‐Nonaka et al, 2016), underpins events of glomerulosclerosis and proteinuria, culminating in severe glomerulopathy and kidney dysfunction. Of note, the phenotypic alterations associated with the suppression of autophagy within multiple components of the renal system become clinically manifest (or exhibit worsened features) with age, implying that defective autophagy is a primary driver of kidney aging (Tang et al, 2020). This result seems to corroborate the observations that the expression of the autophagy suppressor protein RUBCN increases over time, alongside exacerbated markers of defective lysosomal function (Matsuda et al, 2020).
Table 5.
Kidney diseases associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute kidney injury | Distal and proximal TEC‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Impaired kidney function and increased sensitivity to ischemic injury, linked to accumulation of damaged mitochondria | Liu et al (2012) |
| Acute kidney injury | Proximal TEC‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Exacerbated nephropathy induced by oxalate crystals | Nakamura et al (2020) |
| Acute kidney injury | Proximal TEC‐specific deletion of Rubcn | Increased sensitivity to ischemic injury, linked to increased fat efflux from cells to circulation, after autophagy activation | Matsuda et al (2020) |
| Acute kidney injury | Whole‐body deletion of Pink1 and/or Prkn | Increased sensitivity to ischemic injury linked to damaged mitochondria, ROS production, and inflammatory response, after mitophagy inhibition | Tang et al (2018) |
| Acute kidney injury | Proximal TEC‐specific deletion of Tfeb | Enhanced progression of kidney injury induced by oxalate crystals, linked to exacerbation of lysosomal damage. | Nakamura et al (2020) |
| Diabetic kidney disease | Podocyte‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Accelerated diabetes‐induced podocytopathy with a leaky GFB and glomerulosclerosis | Lenoir et al (2015) |
| Diabetic kidney disease | Proximal TEC‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Exacerbated renal hypertrophy, tubular damage, fibrosis, inflammation, and albuminuria in diabetic mice | Lenoir et al (2015), Ma et al (2020) |
| Diabetic kidney disease | Whole‐body deletion of Sglt2 | Reduced glomerular hyperfiltration, linked to decreased accumulation of SQSTM1 in streptozotocin‐treated mice | Vallon et al (2013) |
| Diabetic kidney disease | Proximal TEC‐specific deletion of miR‐214 or Tp53 | Reduced renal hypertrophy and albuminuria, by preventing autophagy impairment in diabetic kidneys | Ma et al (2020) |
| Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis | Nephron‐specific deletion of Atg5 or Atg7 | Development of kidney dysfunction by 2 months and organ failure by 6 months | Kawakami et al (2015) |
| Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis | Podocyte‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Development of early glomerulopathy and proteinuria in aging mice, resulting in late‐onset glomerulosclerosis | Hartleben et al (2010) |
| Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis | Conditional podocyte‐specific deletion of Vps34 | Premature death, development of early‐onset proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis | Bechtel et al (2013) |
| Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis | Podocyte‐specific deletion of Ctsd | Development of late‐onset glomerulosclerosis and proteinuria in aging mice | Yamamoto‐Nonaka et al (2016) |
| Kidney fibrosis | Proximal TEC (S3 segment)‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Reduced tubular atrophy, senescence, and inflammation, linked to superior renal function 30 days after IRI | Baisantry et al (2016) |
| Kidney fibrosis | Conditional proximal TEC‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced tubular atrophy, nephron loss, and macrophages infiltration, during UUO‐induced fibrosis | Livingston et al (2016) |
| Kidney fibrosis | Whole‐body deletion of Map1 lc3b | Exacerbated UUO‐induced fibrosis, linked to increased collagen deposition and TGF‐β production | Ding et al (2014) |
| Kidney fibrosis | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 | Exacerbated UUO‐induced fibrosis, linked to increased collagen deposition and TGF‐β production | Ding et al (2014) |
| Kidney fibrosis | Conditional distal TEC‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Exacerbated UUO‐induced fibrosis, linked to accumulation of damaged mitochondria and TGF‐β production | Nam et al (2019) |
| Kidney fibrosis | Whole‐body deletion of Pink1 or Prkn | Exacerbated UUO‐induced fibrosis, linked to impaired macrophage mitochondrial homeostasis | Bhatia et al (2019) |
| Kidney fibrosis | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Mfn2 | Exaggerated kidney fibrosis after inhibition of macrophage mitophagy | Bhatia et al (2019) |
| Kidney fibrosis | Whole‐body αKlotho haploinsufficiency | Exacerbated renal fibrosis and accelerated CKD progression upon high phosphate diet following UNX | Shi et al (2016) |
| Kidney insufficiency | Conditional proximal TEC‐specific deletion of Vps34/PI3KC3 | Impaired autophagy flux, causing a Fanconi‐like syndrome and renal insufficiency | Grieco et al (2018) |
| Proteinuria | Podocyte‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Higher levels of proteinuria and ultrastructural changes following UNX | Oliva Trejo et al (2014) |
CKD, chronic kidney disease; IRI, ischemia‐reperfusion injury; GFB, glomerular filtration barrier; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TEC, tubular epithelial cell; UNX, unilateral nephrectomy; UUO, unilateral ureteric obstruction.
Acute kidney injury
The capacity of tubular cells to activate autophagy elicits protection against various forms of acute kidney injury, including IRI driven by kidney artery clamping, cisplatin treatment, oxalate crystals, and infectious agents (Kaushal & Shah, 2016; Choi, 2020; Nakamura et al, 2020; Tang et al, 2020). Regardless of the experimental setting, inactivation of autophagy in TECs exacerbates the noxious effects of IRI, sensitizing kidney‐resident cells to death (Kaushal & Shah, 2016; Choi, 2020; Tang et al, 2020). By contrast, uncontrolled activation of autophagy as mediated by rubcn deletion fails to elicit renoprotective effects against IRI, possibly indicating autophagy‐independent function of the protein or because of autosis induction (Matsuda et al, 2020). The maintenance of mitochondrial integrity is central to mount an adequate response to kidney IRI, as demonstrated by the observations that mitophagy is robustly activated in proximal TECs during IRI and that defective mitophagy imposed by pink1 or prkn deletion aggravates kidney damage (Tang et al, 2018; Choi, 2020).
Diabetic kidney disease
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) represents one of the most common forms of chronic kidney pathologies. Dysfunctional autophagy plays a major contributing role in the pathogenesis of DKD. For example, streptozotocin‐induced chronic hyperglycemia leads to glomerulopathy, whose phenotypic manifestation is more severe in Atg5‐deficient podocytes than their wild‐type counterparts (Lenoir et al, 2015). In proximal TEC, an inverse correlation has been established between autophagy levels and the expression of SLC5A2/SGLT2 (solute carrier family 5 member 2), which mediates glucose reabsorption. Accordingly, slc5a2 deletion reduces the pathological accumulation of SQSTM1/p62 in streptozotocin‐treated mice (Vallon et al, 2013). Supporting this notion, recent results indicate that autophagy is impaired in DKD through TP53‐Mir214‐dependent downregulation of ULK1 (Ma et al, 2020). Ablation of Mir214 from proximal TEC or TP53 block rescues kidney hypertrophy and albuminuria, restoring autophagy (Ma et al, 2020). Furthermore, HDAC6‐mediated deacetylation of TFEB, which triggers transcriptional autophagy activation, improves the outcome of DKD in rats (Brijmohan et al, 2018). Along similar lines, OPTN‐dependent activation of mitophagy improves signs of diabetic nephropathy by counteracting premature senescence (Chen et al, 2018b) and reducing NRLP3 inflammasome activation (Chen et al, 2019), hence supporting the hypothesis that autophagy may exert beneficial effects via the suppression of inflammatory reactions. Along similar lines, OPTN‐dependent activation of mitophagy improves signs of diabetic nephropathy by counteracting premature senescence (Chen et al, 2018b) and reducing NRLP3 inflammasome activation (Chen et al, 2019), hence supporting the hypothesis that autophagy may exert beneficial effects via the suppression of inflammatory reactions.
Polycystic kidney disease
Autosomal‐dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most common genetic form of chronic renal disease. The appearance of the pathological phenotype is causally linked to mutations in the cilia‐regulating genes PKD1 (polycystin 1, transient receptor potential channel interacting) or PKD2, coding for calcium channels (Choi, 2020), which have been linked to functional autophagy and maintenance of a physiological catabolic state (Pena‐Oyarzun et al, 2020). Cyst expansion observed in the ADPKD mouse model occurs along with an elevated MTOR activity, which is counteracted by treatment with rapamycin (Zafar et al, 2010; Choi, 2020). In keeping with this result, rapamycin treatment mitigates the pathological phenotype in a rat model of ADPKD when administered to male animals, yet fails to elicit renoprotective effects in female rats (Belibi et al, 2011). Interestingly, in a pkd1 mutant zebrafish model of ADPKD, the genetic suppression of autophagy accelerates cystogenesis, whereas pharmacological stimulation of autophagy by BECN1‐activating peptide, rapamycin, or carbamazepine ameliorates kidney function (Zhu et al, 2017).
Kidney fibrosis
In stark contrast with settings of acute kidney injury, the role of autophagy in the transition from acute to chronic kidney disease, which comes along with aberrant tissue repair and fibrosis, remains to be clarified. Because the recovery of kidney architecture entails a proliferative burst of resident kidney tubular cells, the suppression of autophagy responses after acute injury may be instrumental for regenerative repair (Li et al, 2014; Choi, 2020; Tang et al, 2020). Consistently, prolonged activation of autophagy during the reperfusion phase has been associated with events of autophagy‐dependent cell death and kidney fibrosis (Baisantry et al, 2016). Further corroborating the biphasic role of autophagy during IRI, whereas atg5 deletion in TECs within the S3 segment predisposes proximal TECs to death, the inhibition of autophagy during the reperfusion phase instead facilitates the recovery of kidney function, accompanied by reduced markers of tubular cellular senescence (Baisantry et al, 2016). Hence, the pro‐fibrotic role of autophagy during the reperfusion phase seems to be tied to pro‐senescence actions of autophagy, possibly linked to the TOR‐autophagy spatial coupling compartment (TASCC)‐mediated production of pro‐fibrotic soluble mediators (Narita et al, 2011).
The contribution of autophagy to events of tubulointerstitial fibrosis has been extensively investigated in mouse models subjected to unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) or settings of TGFB administration/overexpression. The role of autophagy in the establishment of kidney fibrosis is controversial (Choi, 2020; Tang et al, 2020). Numerous reports validate the hypothesis that autophagy activation in UUO‐treated mice (Li et al, 2010; Livingston et al, 2016) or in murine models of TGFB overexpression in proximal TECs promotes fibrotic injury (Koesters et al, 2010). These results are supported by the observation that genetic or pharmacological inhibition of autophagy by chloroquine and 3‐methyladenine reduces the fibrotic burden in the kidney, suggesting that autophagy retains pro‐fibrotic effects in these pathological circumstances (Livingston et al, 2016; Tang et al, 2020).
By contrast, antifibrotic functions of autophagy have also been reported in mouse models of UUO‐induced fibrosis. Of note, map1 lc3b deletion in proximal TECs leads to accrued COL1A (collagen, type I, alpha) production and severe fibrotic injury compared with autophagy‐competent animals (Ding et al, 2014). It is plausible to speculate that this effect could be associated with the anti‐inflammatory properties of autophagy, inasmuch as intact autophagy restrains NF‐κB (nuclear factor kappa B) signaling and NRLP3 inflammasome activation in UUO‐treated mice, thereby limiting noxious infiltration of inflammatory cells and decreasing fibrotic damage (Nam et al, 2019). Notably, dysfunctional mitophagy evoked by single or double pink and prkn knockout aggravates the fibrotic phenotype in UUO‐treated mice, by promoting macrophage reprogramming toward a pro‐fibrotic “M2‐like” phenotype (Bhatia et al, 2019). Maladaptive compensatory renal hypertrophy following surgical procedures, modeled in mice through unilateral nephrectomy (UNX), accelerates the transition from acute to chronic kidney injury, while enhancing the burden of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Convergent evidence indicates that the autophagy flux is reduced during UNX (Brown et al, 2021). Concordant with this result, podocyte‐specific Atg7‐deficient mice display higher levels of proteinuria and ultrastructural changes following UNX (Oliva Trejo et al, 2014). In addition, KL/αKlotho‐haploinsufficient mice (which display reduced levels of autophagy) subjected to UNX plus contralateral ischemia‐reperfusion injury, exhibit elevated levels of fibrosis compared with their wild‐type counterparts. Conversely, restauration of autophagy flux mediated by KL overexpression or recombinant KL administration improves kidney functions after UNX (Shi et al, 2016).
Metabolic syndromes
The ATG machinery has been evolutionarily devised to react to minimal oscillations in the intracellular and extracellular metabolic rheostat, with the purpose of maintaining a tightly regulated balance between anabolic and catabolic pathways (Rabinowitz & White, 2010; Galluzzi et al, 2014). In support of this tenet, essential molecular players of the cellular energetic state, such as MTORC1 and AMPK, are epistatic to autophagy initiation induced by nutritional changes (Jewell et al, 2013; Galluzzi et al, 2014). Because the lysosomal disposal of intracellular macromolecules invariably leads to their breakdown into essential metabolic intermediates, including amino acids, glucose, nucleotides, and free fatty acids (FAs), autophagy stands out as a key coordinator of the response to energetic stresses, at both the tissue‐specific and systemic levels (Rabinowitz & White, 2010; Galluzzi et al, 2014). Thus, autophagy fulfills tissue‐inherent metabolic tasks within the major organs involved in the maintenance of organismal energetic balance, including adipose tissue, liver, and exocrine pancreas (Kim & Lee, 2014; Lim et al, 2014). Additionally, intact autophagic responses directly interfere with the composition of the extracellular metabolome, thus contributing to the metabolic interconnectedness between different tissues that is essential in fine tuning an efficient response to bioenergetics cues (Galluzzi et al, 2014; Kim & Lee, 2014). In this context, autophagy exerts a crucial role in the adaptation to short‐ and long‐term metabolic stresses, while paving the way to compensatory systemic responses. For example, depletion of acetyl‐CoA promotes autophagy and blocks anabolic reactions, via activation of AMPK and consequent MTORC1 inhibition (Pietrocola et al, 2015). Consistently, the autophagy‐dependent release of DBI/ACBP/acyl‐CoA‐binding protein (diazepam binding inhibitor), which occurs upon starvation, leads to paracrine inhibition of autophagy in target cells accompanied by enhanced lipogenesis and food intake (Bravo‐San Pedro et al, 2019).
Circumstances of sustained energetic unbalance (encompassing excessive calorie assumption, dysregulated macronutrient intake, and reduced energy expenditure), mirrored by the aberrant activation of trophic axes (e.g., insulin signaling), contribute to the clinical manifestation of metabolic syndromes. These infirmities include type II diabetes (T2D), obesity and non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and their associated complications.
Commensurate with the multipronged layers of control over cellular bioenergetics, alterations in the autophagic flux affect the pathogenesis and progression of metabolic disorders (Ryter et al, 2014; Zhang et al, 2018; Menikdiwela et al, 2020) (Table 6). A large body of evidence supports the view that insufficient autophagy is pathognomonic to metabolic syndromes. In agreement with this notion, the genetic invalidation of several autophagy‐associated genes, including Atg7 (Lim et al, 2014), Atg4b (Fernandez et al, 2017), Becn2 (He et al, 2013), and Tfeb (Settembre et al, 2013), at the whole‐body level or in a tissue‐restricted manner, predisposes to the occurrence of metabolic disorders, both under a normal dietary regimen and obesogenic diets. Conversely, experimental settings of autophagy induction, for example, by ATG5 (Pyo et al, 2013) or TFEB overexpression (Settembre et al, 2013), or genetic or antibody‐mediated neutralization of DBI/ACBP (Bravo‐San Pedro et al, 2019), are sufficient to alleviate the metabolic anomalies tied to systemic energetic dysregulation and to mitigate characteristic signs of metabolic syndromes. Although these results support the hypothesis that autophagy‐stimulating therapies may lead to therapeutic advantages for the prevention and treatment of metabolic disorders, it is worth mentioning that autophagy inhibition in specific tissues (e.g., adipose tissue) may instead antagonize metabolic anomalies (Romero & Zorzano, 2019). Therefore, the overall phenotypic features that emerge from the systemic ablation of Atg genes are likely the net result of specialized functions of autophagy in metabolically relevant tissues. In this respect, the causal nexus between autophagy and metabolic syndrome can be explained by the multitiered actions of autophagy on (i) adipocyte differentiation (Singh et al, 2009b; Romero & Zorzano, 2019), (ii) accumulation of fat deposits in the liver, (iii) maintenance of pancreatic β‐cell fitness (Jung et al, 2008), (iv) central nervous system (CNS)‐mediated regulation of food intake (Kaushik et al, 2011), (v) inflammatory reactions (Zhong et al, 2016; Zhang et al, 2018), among other processes.
Table 6.
Metabolic syndromes associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Whole‐body allelic loss of Atg7 | Development of obesity‐induced diabetes linked to augmented inflammation and lipid accumulation | Lim et al (2014) |
| Diabetes | Whole‐body deletion of Atg4b | Development of experimentally induced type I diabetes, linked to increased body weight gain upon HFD | Fernandez et al (2017) |
| Diabetes | Whole‐body knock‐in of mutant Becn1F121A | Improved insulin sensitivity, but impaired glucose tolerance upon HFD, after autophagy hyperactivation | Yamamoto et al (2018) |
| Diabetes | β cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced glucose tolerance due to reduced β‐cell mass, and development of obesity‐induced diabetes | Ebato et al (2008), Jung et al (2008), Quan et al (2012) |
| Diabetes | shRNA‐mediated liver‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced systemic glucose tolerance in obese mice linked to aberrant ER stress | Yang et al (2010) |
| NAFLD | shRNA‐mediated liver‐specific deletion of Tfeb | Increased development of severe ethanol‐induced liver injury, steatosis, and impaired lysosomal biogenesis | Chao et al (2018) |
| NAFLD | siRNA‐mediated liver‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Increased ethanol‐induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury | Ding et al (2010) |
| NAFLD | Hepatocyte‐specific deletion of Rubcn | Ameliorated liver steatosis and injury upon HFD, linked to activation of lipophagy | Tanaka et al (2016) |
| NAFLD | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Enhanced toxin‐induced liver injury linked to production of pro‐inflammatory cytokines | Ilyas et al (2016) |
| NAFLD | Hepatocyte‐specific deletion of Rb1cc1 | Increased endotoxin‐induced liver injury, inflammation, and hepatic fibrosis in FILKO mice | Ma et al (2013a) |
| NAFLD / Obesity | Hepatocyte‐specific deletion of Tfeb | Increased body weight gain upon HFD due to defects in lipid degradation | Settembre et al (2013) |
| NASH | Endothelial cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Development of NASH and liver fibrosis, linked to enhanced inflammation | Hammoutene et al (2020) |
| Hepatic fibrosis | Hepatic stellate cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced experimentally induced fibrogenesis and matrix accumulation in the liver | Hernandez‐Gea et al (2012) |
| Hepatic steatosis | Hepatocyte‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Marked increase in liver size, linked to increased lipid accumulation and impaired FA oxidation | Singh et al (2009a), Saito et al (2019) |
| Hepatic steatosis | Conditional hepatocyte‐specific deletion of Lamp2 | Exacerbation of liver steatosis due to impaired lipophagy and FA oxidation, after CMA inhibition | Schneider et al (2014), Kaushik and Cuervo (2015a) |
| Hepatic steatosis | Whole‐body deletion of BNip3 | Reduced β‐oxidation of fatty acids and impaired response to fasting. Elevated, inflammation, and steatohepatitis. | Glick et al (2012) |
| Hepatic steatosis | Hepatocyte‐specific deletion of Vsp15 | Exacerbation of liver steatosis due to mitochondrial depletion and impaired FA oxidation | Iershov et al (2019) |
| Hepatic steatosis | Hepatocyte‐specific deletion of Acox1 | Reduced hepatic steatosis caused by starvation or HFD after induction of autophagy | He et al (2020) |
| Metabolic syndrome | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn2 | Increased body weight gain upon HFD, impaired glucose tolerance, and decreased insulin sensitivity | He et al (2013) |
| Metabolic syndrome | Whole‐body overexpression of Atg5 | Anti‐aging phenotypes, including leanness and increased insulin sensitivity | Pyo et al (2013) |
| Metabolic syndrome | Conditional whole‐body deletion of Acbp | Increase ability to maintain glucose levels in the normoglycemic range, by inducing lipid catabolism | Bravo‐San Pedro et al (2019) |
| Obesity | AgRP neurons‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced food intake, body weight, total fat, and WAT mass | Kaushik et al (2011) |
| Obesity | Adipocyte‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced body weight and WAT mass linked to enhanced insulin sensitivity and features of brown adipocytes | Singh et al (2009b), Zhang et al (2009) |
| Obesity | Adipocyte‐specific deletion of Atg5 or Atg12 | Reduced adipogenesis and body weight gain upon HFD, linked to enhanced insulin sensitivity and maintenance of beige adipocyte | Baerga et al (2009), Altshuler‐Keylin et al (2016) |
| Obesity | Whole‐body deletion of Prkn | Reduced maintenance of beige adipocyte due to mitophagy inhibition | Lu et al (2018) |
| Obesity | Conditional adipocyte‐specific deletion of Atg3 or Atg16L1 | Reduced adipose and systemic insulin resistance, linked to dysfunctional mitochondria and increased adipose tissue inflammation | Cai et al (2018) |
| Obesity | Adipocyte‐specific deletion of Rubcn | Increased systemic fat atrophy and hepatic lipid accumulation, after induction of excessive autophagy | Yamamuro et al (2020) |
AgRP, agouti‐related peptide; CMA, chaperone‐mediated autophagy; FA, fatty acid; HFD, high‐fat diet; NAFLD, non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis; WAT, white adipose tissue.
Obesity
Convergent evidence supports the hypothesis that autophagy also co‐regulates the program of adipogenesis in white adipose tissue (WAT). Accordingly, adipocyte‐restricted knockout of Atg5 (Baerga et al, 2009) or Atg7 (Singh et al, 2009b; Zhang et al, 2009) correlates with decreased expression of adipogenic factors, significant reduction in fat mass and increased UCP1 (uncoupling protein 1 [mitochondrial, proton carrier])‐dependent thermogenic capacity, commonly known as “browning”, which systemically map to a lean phenotype and heightened insulin sensitivity (Cairo & Villarroya, 2020). The anti‐obesogenic effect observed upon experimental settings of autophagy inhibition appears to be linked to the overaccumulation of mitochondria in WAT due to the impairment in mitophagy (Wrighton, 2016). Owing to its capacity to dispose of aged or damaged mitochondria, autophagy favors the plastic transition of “beige” adipocytes (i.e., brown‐like adipocytes within WAT deposits) toward a “white” phenotype (Cairo & Villarroya, 2020). Therefore, the UCP1‐specific deletion of Atg5 or Atg12 compromises the “beige‐to‐white” conversion under β‐adrenergic stimuli withdrawal, enabling mice to better cope with conditions of diet‐induced obesity and insulin resistance (Altshuler‐Keylin et al, 2016). Supporting the pro‐whitening function of mitophagy, the systemic inactivation of the mitophagy regulator PRKN promotes the maintenance of the beige phenotype through a mechanism that involves the β‐3 adrenergic‐mediated stimulation of PRKA (protein kinase, cAMP dependent), independently of UCP1 (Lu et al, 2018). Consistently, downregulation of the transcriptional program of lysosomal biogenesis orchestrated by the transcription factor family MITF (melanogenesis‐associated transcription factor)‐TFE prevents beige‐to‐white adipocyte transition leading to higher thermogenic capacity and protection against diet‐induced obesity and insulin resistance (Altshuler‐Keylin et al, 2016). While the transient inactivation of autophagy in adipocytes is instrumental to foster the systemic response to nutritional dysregulation, prolonged autophagy inhibition may nonetheless precipitate the obese phenotype, ultimately leading to defective differentiation, proteotoxic stress, and accrued inflammation (Cai et al, 2018; Zhang et al, 2018). Indeed, a systemic partial autophagy defect, as observed in Atg4b‐deficient mice, predisposes to diet‐induced obesity (Fernandez et al, 2017), and obesity is associated with increased plasma levels of autophagy‐inhibitory factors including DBI/ACBP, both in humans and in mice (Bravo‐San Pedro et al, 2019; Joseph et al, 2020). Adding to the complexity, the overactivation of autophagy through adipocyte‐specific knockout of Rubcn, a negative regulator of autophagy, markedly impairs the systemic metabolic balance by promoting adipose tissue atrophy and detrimental pile‐up of fat deposits in the liver (Yamamuro et al, 2020).
Non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
In the liver, autophagy takes active part in the orchestration of the metabolic response to opposite instances of metabolic stress, because it gets activated under both conditions of nutrient excess and scarcity (Ueno & Komatsu, 2017; Allaire et al, 2019; Hazari et al, 2020; Springer et al, 2021). Under conditions of nutritional overload, the acute induction of autophagy appears to primarily serve (i) to counteract the lipotoxic effect of free FAs, in particular those linked to dietary intake of saturated and trans‐unsaturated FAs, thus preserving the proteostatic and mitochondrial fitness of hepatocytes (Niso‐Santano et al, 2015; Madrigal‐Matute & Cuervo, 2016; Nguyen & Olzmann, 2017; Hazari et al, 2020); (ii) to prevent the aberrant expansion of triglyceride‐containing LDs by promoting their selective breakdown in the lysosome (Singh et al, 2009a; Singh & Cuervo, 2012); (iii) to reduce the acute toxicity associated with elevated alcohol consumption (Ding et al, 2010; Chao et al, 2018); and (iv) to counteract excessive lipid accumulation in hepatitis C virus‐infected hepatocytes (Vescovo et al, 2012). De facto, sustained nutritional imbalance over time and aberrant activation of the insulin signaling route abrogates the autophagic flux in the liver, leading to the onset of NAFLD, whose clinical manifestations span from non‐alcoholic steatosis to fibrosing non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) (Allaire et al, 2019). Dampened levels of ATG proteins have been described in the liver of NASH patients or animals fed a methionine‐choline‐deficient diet (Allaire et al, 2019). In line with this result, the levels of the negative autophagy regulator RUBCN and SQSTM1/p62 are found increased in these pathological contexts (Tanaka et al, 2016).
The genetic inhibition of autophagy in the parenchymal (Settembre et al, 2013), stromal (e.g., endothelial cells) (Hammoutene et al, 2020), and immune (Ilyas et al, 2016) compartment of the liver sensitizes mice to the development of NAFLD via both cell autonomous (Yang et al, 2010) and non‐cell autonomous effects, linked to aberrant inflammatory reactions (Aghajan et al, 2012). Similarly, excessive generation of hepatic acetyl‐CoA in the liver via peroxisomal β‐oxidation inhibits autophagy, while accelerating the manifestation of hepatic steatosis (He et al, 2020).
Conversely, genetic interventions that enhance the autophagic flux (such as the increased expression of Tfeb) mitigate the induction of NAFLD favored by HFD regimens through activation of PPARGC1A/PGC‐1α (peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, gamma, coactivator 1 alpha) and PPARA/PPARα (peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor alpha) transcriptional programs (Settembre et al, 2013) and/or through activation of lipophagy (Tanaka et al, 2016). In spite of these experimental lines of evidence, controversy still exist about the role of selective ATG proteins in NAFLD pathogenesis. As an example, the hepatocyte‐restricted deletion of Rb1cc1 reduces triglyceride accumulation in NAFLD mouse models (Ma et al, 2013a).
Whereas autophagy downregulation generally predisposes to the development of NAFLD, such downregulation appears to limit fibrogenic responses in the liver. In this respect, a proficient autophagy flux is required for the transdifferentiation of hepatic stellate cells into extracellular matrix‐producing myofibroblasts, as illustrated by the fact that hepatic stellate cell‐specific ablation of Atg5 protects mice from hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride (Thoen et al, 2011; Hernandez‐Gea et al, 2012).
In response to nutrient deprivation, BNIP3‐dependent mitophagy also plays a critical role in GCG (glucagon)‐induced metabolic responses of the liver (Springer et al, 2021). Zonal expression of BNIP3 and zonal patterning of mitophagy in liver parenchyma in response to nutrient deprivation contributes to zonal metabolic compartmentalization in the liver, and BNIP3 loss causes increased mitochondrial mass and disruption of urea cycle and glutamate–glutamine metabolism in particular (Springer et al, 2021).
Under nutrient shortage, hepatic autophagy maintains the organismal energetic balance through its crucial action of energy mobilization from nutrient stores, by hydrolyzing glycogen granules (a process known as “glycophagy”) and LDs in the lysosome. Whereas glycophagy defines the early phases after nutrient shortage, lipophagy operates (along with cytosolic lipases) as a crucial mechanism of resistance to sustained fasting (Singh & Cuervo, 2012; Madrigal‐Matute & Cuervo, 2016). Of note, the CMA‐mediated removal of PLINs (perilipins; which cover LDs) is epistatic to the initiation of lipophagy (Kaushik & Cuervo, 2015a) and may explain the upregulation of this type of autophagy early after a lipid challenge (Rodriguez‐Navarro et al, 2012). Consistently, the liver‐specific deficiency of CMA precipitates hepatic steatosis (Schneider et al, 2014), and the suppression of hepatic autophagy correlates with defective ketogenesis linked to the accumulation of the autophagy substrate NCOR1 (nuclear receptor co‐repressor 1), which suppresses the PPARA‐dependent transcriptional program of free FA oxidation (Iershov et al, 2019; Saito et al, 2019).
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) clinically manifests with the appearance of insulin resistance in insulin‐responsive target cells, progressively accompanied by compromised function of insulin‐producing pancreatic β cells in Langerhans islets. Notably, autophagy appears to be etiologically implicated in both aspects of T2D pathogenesis. Defective autophagy in insulin‐responsive tissues (e.g., liver) fails to counteract the exacerbated levels of oxidative stress and ER stress upon persistent stimulation of the insulin‐signaling axis (Yang et al, 2010; Yamamoto et al, 2018; Zhang et al, 2018; Pietrocola & Bravo‐San Pedro, 2021). Autophagy also operates as a pivotal process in the regulation of pancreatic β cell homeostatic functions (Ebato et al, 2008; Jung et al, 2008). Under basal conditions, a selective form of autophagy (known as “crinophagy”) dedicated to the degradation of insulin‐containing granules contributes to regulate physiological levels of insulin in β cells (Lee et al, 2019). Unlike in the majority of cell types, short‐term starvation inhibits autophagy in pancreatic β cells through mechanisms of starvation‐induced nascent granule degradation (Goginashvili et al, 2015) and Golgi membrane‐associated degradation (Yamaguchi et al, 2016), thus serving as a buffer against the production of insulin in nutrient‐depleted conditions. Interestingly, the cell surface pyruvate transporter SLC16A11 is associated with risk of T2D (Rusu et al, 2017), and regulates autophagy (Velentzas et al, 2018).
A prominent surge in autophagy is detected in pancreatic β cells under conditions of nutritional challenges (e.g., HFD) or genetic LEP (leptin) deficiency. Such an increase in autophagy is required for the compensatory increase in β cell mass and survival of insulin‐producing cells, as witnessed by the fact that genetic ablation of Atg7 in β cells promotes their demise, leading to impaired insulin production and glucose intolerance (Ebato et al, 2008). Mechanistically, defective autophagy maps to the incapacity of β cells to mount an adequate unfolded protein response/UPR, which is instrumental to sustain the hypersecretory phenotype of insulin‐producing β cells (Quan et al, 2012). Additionally, proficient autophagic response may contribute to the anti‐oxidative program elicited by NFE2L2/NRF2 activation in β cells, thus enabling them to withstand accrued oxidative burden associated with HFD (Abebe et al, 2017). In agreement with the concept that autophagy is essential for β‐cell survival, the interaction between C3 (complement component 3) and ATG16L1 underlies the maintenance of a functional autophagic flux during T2D, limiting the deleterious effects of nutritional stress on pancreatic β cells (King et al, 2019). Along similar lines, functional autophagy allows pancreatic β cells to sustain the detrimental proteotoxic stress linked to the intracellular accumulation and aggregation of IAPP (islet amyloid polypeptide), which is co‐secreted with insulin (Shigihara et al, 2014; King et al, 2019). While these experimental lines of evidence emphasize the positive role of autophagy in the regulation of β‐cell homeostasis, it is worth mentioning that constitutive activation of autophagy, by the expression of the knock‐in Becn1F121A dominant mutant, produces the paradoxical outcomes in the context of diet‐induced T2D of reducing glucose tolerance (due to the uncontrolled degradation of insulin granules) yet improving the responsiveness to insulin in peripheral tissues (Yamamoto et al, 2018). Future investigation is warranted to clarify this unexpected duality and to assess the clinical impact of autophagy‐inducing interventions in the prevention and management of metabolic syndromes.
Other liver pathologies
Autophagy mediates widespread actions of control over the activity of the parenchymal and stromal components of the liver. Therefore, alterations in the autophagy flux are sufficient to instigate or modify hepatic pathological phenotypes (Hazari et al, 2020) (Table 7). As a consequence, the pharmacological targeting of autophagy is progressively emerging as a valuable translational approach for the prevention or treatment of hepatic disorders (Allaire et al, 2019).
Table 7.
Other liver pathologies associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| AATD | Liver‐specific knock‐in of human Tfeb | Reduced liver apoptosis and fibrosis, lined to promoted clearance of hepatotoxic ATZ in PiZ mice after autophagy activation | Pastore et al (2013) |
| Acute liver failure | Conditional liver‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Development of hepatomegaly and hepatic cell swelling, and enhanced APAP‐induced liver injury | Komatsu et al (2005), Igusa et al (2012) |
| Acute liver failure | Liver‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Development of hepatomegaly and basal liver injury, but resistance to APAP‐induced liver injury due to compensatory Nrf2 activation | Ni et al (2012b) |
| Acute liver failure | Conditional whole‐body deletion of Atg5 | Development of hepatomegaly and hepatic cell swelling | Cassidy et al (2018) |
| Acute liver failure | Liver‐specific co‐deletion of Ulk1 and Ulk2 | Resistance to APAP‐induced liver injury independently of the autophagic process | Ni et al (2012b) |
| Cirrhosis | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Exacerbated CCl4‐induced liver fibrosis linked to enhanced inflammatory infiltrate | Lodder et al (2015), Habib et al (2019) |
| Cirrhosis | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Rubcn | Exacerbated CCl4‐induced liver fibrosis linked to enhanced inflammatory infiltrate | Wan et al (2020) |
| Hyperammonemia | HDAd‐mediated liver‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Higher levels of serum ammonia after ammonium chloride challenge | Soria et al (2018) |
AATD, Alpha‐1 antitrypsin deficiency; APAP, acetaminophen; ATZ, alpha‐1‐antitrypsin; HDAd, helper‐dependent adenoviral.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a late‐stage liver disease and a major health problem worldwide, in which liver tissue is permanently replaced by scar tissue, known as “fibrosis”, starting as a pathological consequence of chronic liver injury (such as hepatitis or alcoholic liver disease). Advances in the understanding of liver fibrosis have identified (i) sustained inflammation originating from macrophages as a driving force in the fibrogenic process (Krenkel & Tacke, 2017) and (ii) autophagy as a limiting factor to a pro‐inflammatory phenotype in macrophages. In particular, atg5 deletion (Lodder et al, 2015; Habib et al, 2019) and genetic inhibition of LAP components (Wan et al, 2020) in the myeloid compartment exacerbate hepatic inflammation in mice with chronic liver injury, thus enhancing liver fibrosis. Accordingly, pharmacological blockade of LAP increases the inflammatory signature in human monocytes from patients with cirrhosis (Wan et al, 2020). These data are in line with the reported role of autophagy in limiting the pro‐fibrotic effects of macrophages in models of kidney (Bhatia et al, 2019) and lung fibrosis (Abdel Fattah et al, 2015; Jessop et al, 2016), thus suggesting that canonical and non‐canonical forms of autophagy prevent the reprogramming of macrophages to a pro‐inflammatory phenotype during events of fibrosis.
Acute liver failure
The genetic suppression of basal autophagy in hepatocytes leads to hepatomegaly and exacerbated liver injury (Komatsu et al, 2005; Ni et al, 2012b; Cassidy et al, 2018). In addition, the induction of autophagy is required to counteract the aberrant levels of oxidative stress induced by acetaminophen (APAP) overdose, thus preventing APAP‐mediated necrotic death (Ni et al, 2012a). Conversely, genetic removal of Atg7 precipitates the demise of hepatocytes exposed to a high APAP dose (Igusa et al, 2012). In contrast with these findings, the hepatocyte‐restricted deletion of Atg5 protects liver parenchymal cells from APAP‐induced toxicity, casting the hepatoprotective role of autophagy in APAP‐induced toxicity into doubt (Ni et al, 2012b). Adding to the complexity, autophagy‐independent functions of ULK1/2 kinases (which mediate activation of MAPK8/c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase) appear to support the damaging actions of APAP in the liver (Sun et al, 2018; Allaire et al, 2019). Hence, it is tempting to speculate that gene‐dependent effects dictate the role of autophagy in this pathological context. Likewise, the role of autophagy in ischemia‐reperfusion hepatic injury remains controversial. Whereas autophagy seems to prevent liver injury shortly after ischemia‐reperfusion, the positive or negative contribution of autophagy during the reperfusion phase largely varies depending upon the experimental setting of ischemia (e.g., warm vs. cold) adopted (Gracia‐Sancho & Guixe‐Muntet, 2018).
Genetic liver disorders
Wilson disease (WD) is a genetically inherited condition characterized by the toxic accumulation of copper in hepatocytes, which lead to hepatocyte poisoning and death, and eventually culminates in liver failure. The pathological phenotype emerges as a consequence of loss‐of‐function mutations in the gene coding for the intracellular copper export transporter ATP7B. Copper overload perturbs mitochondrion structure and dynamics, leading to the detrimental accumulation of non‐disposable mitochondria within the cell (Zischka & Einer, 2018). A compensatory/cytoprotective surge in the autophagy flux occurs in the liver of WD patients and in ATP7B‐deficient animals (Polishchuk et al, 2019). Consistent with this result, the genetic obliteration of Atg7 (or the pharmacological inhibition of autophagy by spautin‐1) in copper‐challenged hepatocytes precipitates their death, supporting the view that autophagy is required to promote hepatocyte survival in WD (Polishchuk et al, 2019). Intriguingly, treatment of mice with the copper chelator triethylenetetramine promotes the activation of autophagy in the liver, further reinforcing the idea that autophagy activation may improve liver phenotype in WD patients (Pietrocola et al, 2020).
Alpha‐1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is caused by loss‐of‐function mutations in SERPINA1/alpha‐1 antitrypsin mutant Z protein (ATZ), which compromises the ability of ATZ to properly fold and leads to its accumulation in the ER of hepatocytes. The toxic effect of ATZ inclusions pathologically manifests as liver injury, progressively leading to fibrosing liver disease (Allaire et al, 2019). The compensatory increase in autophagy is insufficient to reduce the pathological accumulation of ATZ inclusions, whereas the genetic ablation of Atg5 precipitates hepatocyte death (Kamimoto et al, 2006). In this scenario, the increase in lysosomal biogenesis imposed on hepatocytes by Tfeb gene transfer in mice (Pastore et al, 2013), or the pharmacological activation of autophagy by carbamazepine or rapamycin, reduces the burden of fibrotic lesions in AATD mouse liver (Allaire et al, 2019).
Hyperammonemia
Hepatic urea biosynthesis is required to minimize the neurotoxic effects associated with excessive accumulation of nitrogen waste in the blood. In a mouse model of acute hyperammonemia induced by ammonium chloride administration, autophagy is required for ammonia detoxification (Soria et al, 2018). Mechanistically, autophagy promotes hepatic ureagenesis and ammonia clearance by providing key urea cycle intermediates. In keeping with this result, pharmacological stimulation of autophagy by rapamycin, Tat‐Beclin 1 peptide, or Tfeb‐hepatic gene transfer improves the fitness of ammonium chloride‐challenged animals. In line with these data, Tat‐beclin 1‐mediated activation of autophagy improves the hepatic phenotype in two distinct urea cycle disorder mouse models (Soria et al, 2021).
Cholestasis
The detrimental accumulation of bile acids is associated with severe hepatic damage and systemic clinical sequalae. Reduced bile acid flow compromises autophagy in patients with cholestasis. Mechanistically, bile acid overload impairs autophagosome‐to‐lysosome fusion depending upon the activation of NR1H4/farnesoid X receptor (nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 4), which in turn controls the expression of the negative autophagy regulator RUBCN. In support of this result, the genetic ablation of RUBCN corrects bile acid‐mediated impairment of autophagy in an in vitro model of cholestasis (Panzitt et al, 2020).
Cancer
Autophagy operates at the homeostatic forefront to preserve the genomic integrity of quiescent and proliferating cells in tissues (Hewitt & Korolchuk, 2017). From a mere cell intrinsic standpoint, autophagy generally prevents the neoplastic transformation of healthy cells (Galluzzi et al, 2015b). In support of this notion, pharmacological or genetic interventions hampering autophagic flux result in the appearance of early neoplastic lesions in a variety or preclinical tumor models (Galluzzi et al, 2015b). Thus, it is likely that autophagy in healthy cells operates as a tumor suppressor mechanism to counteract the effects of pro‐oncogenic stimuli (Rybstein et al, 2018). Supporting this concept, the activation of autophagy appears to be an essential step for the activation of the oncogene‐induced senescence program (Young et al, 2009). However, this reductionist standpoint needs to be framed within a more complex scenario, in which the actual contribution of autophagy to the biology of cancer depends on several aspects, including tumor type, disease stage, and host factors (Santana‐Codina et al, 2017). Indeed, proficient autophagy fosters the metabolic fitness of neoplastic cells, endowing them with the ability to cope with dwindling levels of energetic supply within the tumor bed (White, 2015; Kimmelman & White, 2017; Mukhopadhyay et al, 2021). Variations in the magnitude of the autophagy flux have been reported in the context of tumor metastatic recurrence, although the final outcome of autophagy modulation in these conditions strongly varies depending upon the type of cancer and the Atg object of investigation (Dower et al, 2018; Vera‐Ramirez et al, 2018; Marsh et al, 2020). In addition, autophagy is thought to participate in events of tumor relapse and resistance to therapy (Huang et al, 2020; Mele et al, 2020), in light of its direct involvement in the maintenance of a functional pool of cancer stem cells (Nazio et al, 2019; Smith & Macleod, 2019). Adding a further layer of complexity, autophagy in non‐transformed cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME; including stromal cells and resident or infiltrating leukocytes) plays a critical role in supporting cancer growth (Sousa et al, 2016; Katheder et al, 2017; Poillet‐Perez et al, 2018; Yang et al, 2018; Amaravadi et al, 2019). Moreover, perturbations in autophagy in immune cells that infiltrate the tumor niche also affect cancer dynamics in a highly context‐dependent manner, evoking immunostimulatory or immunosuppressive effects depending upon leukocyte subtypes involved, tumor stage, and therapeutic regimen (Amaravadi et al, 2019; Xia et al, 2021; Yamazaki et al, 2021). The development of mouse models in which genes encoding molecules involved in the autophagy machinery are deleted, and the mice are challenged with established protocols of chemical carcinogenesis or they are crossed with genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs) of oncogene‐driven cancers, has enabled investigators to delve into the pathophysiological functions of autophagy in oncogenesis, tumor progression, and response to anticancer therapy (Galluzzi et al, 2015b; Amaravadi et al, 2016; Santana‐Codina et al, 2017) (Table 8). Because whole‐body knockout of essential Atg genes leads to perinatal lethality (Kuma et al, 2004; Komatsu et al, 2005), whole‐body knockout strategies to study the role of autophagy in cancer are limited to heterozygous deletion models such as Becn1+ / −, which achieves only partial autophagy incompetence. In order to achieve complete autophagy suppression, conditional knockout mice and inducible conditional knockout mice have been used. As an important disclaimer, the vast majority of these studies is based on the deletion of Atg genes that are functionally implicated in the regulation of pathways other than autophagy (e.g., LAP) (Xia et al, 2021), opening the possibility that alternative mechanisms would underlie the tumor‐modulating properties of the autophagy pathway.
Table 8.
Malignancies associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder cancer | Conditional whole‐body deletion of Atg7 or Atg5 | Impaired growth of allografted MB49 urothelial cancer cells, linked to reduced circulating arginine, and increased antitumor CD8+ T‐cell response | Poillet‐Perez et al (2018), Poillet‐Perez et al (2020) |
| Bone cancer | Deletion of Atg7 or Atg5 in transplantable MCA205 cells | Resistance to chemotherapy, linked to impaired release of immunogenic danger signals and reduced antitumor T‐cell response | Michaud et al (2011) |
| Breast cancer | Conditional deletion of Atg5 or Atg12 in transplantable PyMT‐driven MaEC cells | Increased recurrence and size of spontaneous metastases when injected intravenously in syngeneic mice | Marsh et al (2020) |
| Breast cancer | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 | Development of spontaneous mammary tumors, linked to augmented mammary stem and progenitor cell activities | Cicchini et al (2014) |
| Breast cancer | Whole‐body deletion of Bnip3 | Accelerated PyMT‐driven tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis, linked to mitochondrial dysfunction | Chourasia et al (2015) |
| Breast cancer | Conditional deletion of Fip200 in PyMT‐driven MaEC cells | Reduced PyMT‐driven tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis, linked to increased IFN‐mediated T‐cell infiltration in the TME | Wei et al (2011) |
| Breast cancer | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 | Reduced pro‐tumorigenic effect associated with Palb2 ablation in Tp53 wild‐type mice | Huo et al (2013) |
| Breast cancer | Deletion of Becn1 in transplantable 4T1 cells | Improved NK‐mediated tumor regression | Baginska et al (2013), Li et al (2020b) |
| Breast cancer | Deletion of Lamp2 in transplantable breast cancer cells | Reduced tumor growth and formation of metastasis when injected in nude mice | Han et al (2017) |
| Breast cancer | Deletion of Atg5 in transplantable 4T1 cells | Accelerated tumor growth and resistance to T‐cell‐mediated antitumor immunity after ICIs treatment | Li et al (2020b) |
| Breast cancer | Deletion of Atg5 or Atg7 in transplantable TS/A cells | Improved radiosensitivity and control of non‐irradiated lesions, linked to enhanced type I IFN‐mediated antitumor immunity | Yamazaki et al (2020) |
| Breast cancer | Conditional whole‐body deletion of Atg5 or Atg16L1 or Atg14 | Reduced tumor growth of allografted syngeneic E0771 breast cancer cells, coupled with increased antitumor CD8+ T‐cell response | DeVorkin et al (2019) |
| Colorectal cancer | Conditional deletion of Atg7 in intestinal epithelial cells | Reduced Apc loss‐driven tumor development and progression, coupled with increased antitumor CD8+ T‐cell response | Levy et al (2015) |
| Colorectal cancer | Deletion of Atg7 in transplantable CT26 cells | Reduced tumor growth, linked to increased antitumor CD8+ T‐cell response | Arensman et al (2020) |
| Colorectal cancer | Deletion of Atg5 or Becn1 in transplantable CT26 cells | Resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, linked to impaired release of immunogenic danger signals, and reduced antitumor T‐cell response | Michaud et al (2011), Ko et al (2014) |
| Hepatic tumor | Liver‐specific mosaic deletion of Atg5 or Atg7 | Increased number of spontaneous tumors, linked to increased p62 accumulation and dysfunctional mitochondria | Takamura et al (2011) |
| Hepatic tumor | Liver‐specific deletion of Lamp2 | Increased tumor incidence linked to increased vulnerability to oxidative stress | Schneider et al (2015) |
| Hepatic tumor | Knock‐in of Lamp2 in transplantable HCC cells | Increased tumor growth when injected subcutaneously in nude mice | Ding et al (2016) |
| Intestinal cancer | Intestinal epithelia cell‐specific deletion of Stat3 | Reduced initiation of sporadic intestinal tumorigenesis linked to enhanced mitophagy | Ziegler et al (2018) |
| Lung cancer | Deletion of Ambra1 in transplantable iMEFs | Accelerated tumor development | Cianfanelli et al (2015) |
| Lung cancer | Conditional whole‐body deletion of Atg7 or Atg5 | Impaired growth of allografted 71.8 NSCLC cells, linked to reduced circulating arginine | Poillet‐Perez et al (2018) |
| Lung cancer | Conditional deletion of Atg5 in KrasG12D ‐driven lung tumors | Prolonged OS linked to dysfunctional mitochondria, but accelerated tumor development linked to increased tumor infiltration by TREG | Rao et al (2014), Pietrocola et al (2016) |
| Lung cancer | Conditional deletion of Atg7 in KrasG12D ‐driven lung tumors | Prolonged OS and reduced tumor progression of established tumors, linked to dysfunctional mitochondria and reduced FA oxidation | Guo et al (2013), Karsli‐Uzunbas et al (2014) |
| Lung cancer | Conditional deletion of Atg7 in BrafV600E ‐driven lung tumors | Prolonged OS and reduced tumor progression due to dysfunctional mitochondria, but accelerated tumor development | Strohecker et al (2013) |
| Lung cancer | Deletion of Lamp2 in transplantable lung cancer cells | Reduced tumor growth and formation of metastasis when injected in nude mice | Kon et al (2011) |
| Lung cancer | Knock‐in of mutant PKM2K305Q in transplantable lung cancer cells | Increased tumor growth when injected in nude mice, linked to accumulation of glycolytic intermediates | Lv et al (2011) |
| Melanoma | Conditional whole‐body deletion of Atg7 or Atg5 deletion | Impaired growth of allografted YUMM1.1‐9 melanoma cells, linked to reduced circulating arginine, and increased antitumor CD8+ T‐cell response | Poillet‐Perez et al (2018), Poillet‐Perez et al (2020, 883) |
| Melanoma | Conditional deletion of Atg7 in BrafV600E ‐driven, Pten‐competent melanomas | Reduced OS and accelerated melanoma onset | Rosenfeldt et al (2021) |
| Melanoma | Conditional deletion of Atg7 in BrafV600E ‐driven, Pten‐null melanomas | Prolonged OS and reduced tumor development, linked to increased oxidative stress and senescence | Xie et al (2015) |
| Melanoma | Deletion of Becn1 in transplantable B16–F10 cells | Improved NK‐mediated tumor regression in a CCL5‐dependent manner | Baginska et al (2013), Mgrditchian et al (2017) |
| Melanoma | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Becn1 or Atg5 | Reduced growth of subcutaneously engrafted murine B16F10 melanoma | Cunha et al (2018) |
| Melanoma | Whole‐body deletion of Rubcn | Reduced growth of subcutaneously engrafted murine B16F10 melanoma | Cunha et al (2018) |
| Multiple malignancies | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 | Development of spontaneous malignancies | Qu et al (2003), Yue et al (2003) |
| Multiple malignancies | Whole‐body allelic loss of Ambra1 | Development of spontaneous malignancies | Cianfanelli et al (2015) |
| Multiple malignancies | Conditional whole‐body deletion of Atg5 | Accelerated development of spontaneous tumors after temporal autophagy inhibition | Cassidy et al (2020) |
| Multiple malignancies | Conditional whole‐body deletion of Atg7 | Accelerated development of p53 loss‐driven spontaneous tumors | Yang et al (2020) |
| Pancreatic cancer | Deletion of Atg5 or Atg7 in PSCs | Delayed tumor growth of co‐injected PDAC cells linked to reduced alanine production by PSCs | Sousa et al (2016) |
| Pancreatic cancer | Conditional whole‐body Knock‐in of mutant Atg4BC74A | Tumor regression in an autochthonous mouse model of PDAC | Yang et al (2018) |
| Pancreatic cancer | Pancreas‐specific mosaic deletion of Atg7 or Atg5 | Accelerated KRASG12D ‐driven tumor development in the absence of p53 | Rosenfeldt et al (2013), Yang et al (2014) |
| Pancreatic cancer | Conditional knock‐in of mutant Atg4bC74A in transplantable PDAC cells | Reduced tumor growth, linked to enhanced expression of MHC class I molecules and a potentiated antitumor CD8+ T‐cell response | Yamamoto et al (2020) |
| Pancreatic cancer | Conditional pancreas‐specific deletion of Bnip3l | Delayed tumor progression, linked to restauration in mitochondrial content, and improved respiratory capacity | Humpton et al (2019) |
| Prostate cancer | Conditional whole‐body deletion of Atg5 | Reduced tumor growth of allografted syngeneic Tramp‐C2 prostate cancer cells, coupled with increased antitumor CD8+ T‐cell response | DeVorkin et al (2019) |
| Renal cancer | Allelic loss of Becn1 or deletion of Atg5 in transplantable iBMK cells | Accelerated tumor growth linked to increased p62 accumulation and dysfunctional mitochondria | Mathew et al (2009) |
FA, fatty acid; iBMK, immortalized baby mouse kidney; iMEF: immortalized mouse embryonic fibroblast; MaEC, mammary epithelial carcinoma; NSCLC, non‐small‐cell lung cancer; OS, overall survival; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PSC, pancreatic stellate cell; PyMT, polyoma middle tumor antigen; TME, tumor microenvironment.
Oncosuppressive functions of autophagy: cancer initiation
Becn1+ /− mice are more susceptible to develop spontaneous or oncogene‐activation‐driven malignancies than their wild‐type counterparts (Qu et al, 2003; Yue et al, 2003; Cicchini et al, 2014). In addition, the appearance of (in most cases benign) tumor lesions is accelerated by the deletion of multiple genes that intercept the autophagy pathway (White, 2015; Amaravadi et al, 2016; Amaravadi et al, 2019). Examples of autophagy genes for which this has been observed include (i) systemic deletion of Ambra1 (Cianfanelli et al, 2015; Di Leo et al, 2021; Maiani et al, 2021), (ii) shRNA‐dependent temporal suppression of Atg5 expression (Cassidy et al, 2020), (iii) liver‐specific mosaic deletion of Atg5 (Takamura et al, 2011), or (iv) conditional knockout of Atg5 or Atg7 in the lung and the pancreas of GEMMs (Rosenfeldt et al, 2013; Strohecker et al, 2013; Rao et al, 2014). Whereas in specific circumstances (i.e., Becn1+ / − mice, or temporal suppression of Atg5 expression), derailed autophagy evokes the appearance of advanced malignancies, in other cases neoplastic lesions originating from suppressed autophagy fail to transition from the benign to the malign state. Data inferred from patients affected by primary melanoma suggest that low expression levels of Atg5 correlate with reduced progression‐free survival. Of note, Atg5 downregulation hinders the induction of oncogene‐induced senescence promoting BRAFV600E‐driven melanogenesis in vitro (Liu et al, 2013b). As further corroboration of this result, deletion of Atg7 accelerates melanogenesis in animals in which the expression of BRAFV600E is restricted to the skin, depending upon the expression of functional Pten (phosphatase and tensin homolog) (Rosenfeldt et al, 2021).
In evaluating the sum total of these preclinical findings, the implications are that for patients who are treated with chemical autophagy inhibitors, it is unlikely that secondary cancers will arise during the earliest stages of treatment, but monitoring for polyp formation in certain organs may need to be considered if autophagy inhibitors are used for longer periods of time or as chemoprevention agents.
Autophagy‐dependent removal of selective organelles has been also linked to tumor‐preventive functions (Miller & Thorburn, 2021). As an example, the mitophagy regulator BNIP3 limits the formation and progression of primary polyomavirus middle T antigen/PyMT‐driven mammary tumors in mice (Chourasia et al, 2015). Recently, selective autophagy has also been reported to prevent genomic instability derived by aberrant mitoses, which are frequent in tumors. In this case, autophagy selectively targets the non‐membranous organelles centriolar satellites, which safeguard mitosis accuracy by preserving centrosome integrity (Holdgaard et al, 2019). In addition, alternative autophagy routes participate in the tumor‐preventive action of the autophagy pathway. Growing evidence supports the idea that chaperone‐mediated autophagy (CMA) contributes to the prevention of cellular malignant transformation under physiological conditions. Indeed, mouse models with selective blockage of CMA in the liver result in higher rates of malignant transformation in this organ (Schneider et al, 2015). CMA protects against oncogenic transformation, on the one hand by actively promoting degradation of pro‐oncogenic proteins such as MYC (MYC proto‐oncogene, bHLH transcription factor) (Gomes et al, 2017), TPT1/TCTP (tumor protein, translationally controlled 1) (Bonhoure et al, 2017), or MDM2 (Lu et al, 2010), and on the other hand by contributing to the immuno‐oncogenic response (Garg et al, 2013).
Besides the well‐recognized capacity to safeguard the homeostasis of parenchymal cells, it appears plausible to speculate that part of the oncosuppressive functions of autophagy are due to its ability to attenuate the inflammatory response (Zhong et al, 2016; Monkkonen & Debnath, 2018). In particular, autophagy counteracts the establishment of an inflammatory microenvironment (i) by disposing of dysfunctional mitochondria and the oxidatively damaged proteome (Cannizzo et al, 2012; Palikaras et al, 2018) and reducing SQSTM1/p62 accumulation (Mathew et al, 2009; Moscat et al, 2016), therefore dampening aberrant intracellular ROS burden, or (ii) by degrading inflammasomes (which are required for the maturation and secretion of IL1B/IL1β and IL18), or preventing their activation (e.g., through the elimination of cytosolic mtDNA) (Lamkanfi & Dixit, 2014; Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al, 2018). In addition, proficient mitophagy appears to be required to stimulate CD8+ T‐cell‐dependent immunity in the context of intestinal tumorigenesis, thereby enabling the establishment of anticancer immunosurveillance over pre‐cancerous lesions (Ziegler et al, 2018; Rao et al, 2019).
Tumor‐promoting functions of autophagy: cancer initiation
Although the experimental lines of evidence mentioned above support the concept that autophagy limits neoplastic transformation, notable exceptions to this paradigm have been described. As an example, conditional deletion of the gene coding for the ULK1/Atg1 interactor RB1CC1/FIP200 in mammalian epithelial cells restrains the growth of mammary carcinoma tumors induced by polyomavirus middle T antigen, associated with the induction of a prominent type I IFN response (Wei et al, 2011). Likewise, allelic loss of Becn1 suppresses the pro‐tumorigenic effect linked to the loss of the hereditary breast cancer susceptibility gene Palb2 (partner and localizer of BRCA2), in the presence of an intact TP53 signaling (Huo et al, 2013). In addition, conditions of “leaky gut” associated with the conditional ablation of Atg7 in epithelial colon cells predispose a local immune response that is instrumental for limiting the number of pre‐tumoral lesions in Apc+ / − colonocytes (Levy et al, 2015). Consistently, CT26 cells knocked out for Atg7 show increased expression of chemokines involved in the recruitment of CD8+ T lymphocytes, and depletion of CD8+ T cells significantly restores the growth of tumors in immunocompetent hosts (Arensman et al, 2020).
Tumor‐promoting functions of autophagy: cancer progression
Compelling evidence obtained from a large variety GEMMs of cancer contributed to advocate the hypothesis that autophagy is required to sustain the increasing metabolic demand of cancer cells during the earliest stages of neoplastic transformation, explaining why the genetic inhibition of autophagy in malignant cells restrains progression from normal to benign tumors and arrests it into a benign state (Galluzzi et al, 2015b; Kimmelman & White, 2017). Such an effect seems to occur irrespectively of cancer type and driver mutation, as it has been documented in preclinical models of lung and pancreatic ductal carcinomas driven by KrasG12D (Guo et al, 2013; Rosenfeldt et al, 2013; Rao et al, 2014; Yang et al, 2014), BrafV600E ‐driven lung cancer (Strohecker et al, 2013), and melanoma (upon simultaneous loss of Pten) (Xie et al, 2015). In the context of Kras G12D ‐driven pancreatic ductal carcinoma (PDAC), pharmacological inhibition of KRAS or its downstream effector MAPK1/ERK2 (mitogen‐activated protein kinase 1) further increases the autophagic flux, while enhancing the dependency of cancer cells to intact autophagy (Bryant et al, 2019; Kinsey et al, 2019). Therefore, pharmacological inhibition of autophagy by chloroquine or genetic suppression of autophagy synergistically improves the efficacy of MAPK/ERK inhibitors in restraining PDAC progression (Bryant et al, 2019). Autophagy‐deficient tumor lesions are peculiarly characterized by the inability to process and oxidize metabolic substrates (e.g., glutamine, fatty acids) within mitochondria, suggesting that autophagy preserves the metabolic fitness of malignant cells via proficient mitophagy (Karsli‐Uzunbas et al, 2014; Kimmelman & White, 2017; Poillet‐Perez & White, 2019; Vara‐Perez et al, 2019). In this scenario, accumulating evidence supports the tenet that the removal of specific organelles (Miller & Thorburn, 2021) or proteins (Deng et al, 2021) via autophagy contributes to the tumor‐supportive function of autophagy in established tumor lesions. Of note, while deletion of essential autophagic genes impairs the outgrowing performance of cancer cells, autophagy‐deficient tumors evolve the capacity to bypass autophagy loss via the upregulation of NFE2L2/NRF2. Importantly, NFE2L2/NRF2 activation appears to compensate for the loss of proteostasis imposed on neoplastic cells by autophagy deficiency, yet renders autophagy‐deficient cells more sensitive to proteasomal inhibition (Towers et al, 2019).
A pro‐oncogenic mechanism has also been described for CMA in established tumor lesions (Arias & Cuervo, 2020). Most types of solid tumor cells display abnormally upregulated levels of CMA that are required to sustain tumor growth (Kon et al, 2011; Ding et al, 2016; Han et al, 2017). Multiple mechanisms seem to contribute to this pro‐tumorigenic function of CMA including the participation of CMA in the regulation of cancer cellular energetics (Kon et al, 2011; Lv et al, 2011; Xia et al, 2015), protein translation (Hao et al, 2019) and cell cycle (Hubbi et al, 2014; Zhou et al, 2016), the direct degradation by CMA of antitumoral proteins such as RND3 (Rho family GTPase 3) or MCL1 (MCL1 apoptosis regulator, BCL2 family member) (Zhou et al, 2016; Suzuki et al, 2017), and the participation of CMA in the cellular response to stressors (Ali et al, 2011; Saha, 2012; Hubbi et al, 2013). CMA in cells within the TME has also recently been shown to contribute to tumorigenesis (Valdor et al, 2019; Wang et al, 2019) although the specific mechanisms require future clarification. Targeting CMA in cancer is gaining growing interest since the development of drugs that selectively activate this type of autophagy (Anguiano et al, 2013) that could be used preventively in situation at risk of transformation; some groups have even proposed utilizing further upregulation of CMA in cancer to induce a metabolic crisis (Xia et al, 2015). However, because in more cancer types, experimental blockage of CMA has demonstrated to efficiently reduce the tumor size, efforts are now focused on development of drugs capable of selectively inhibiting CMA.
Autophagy in anticancer immunosurveillance
As discussed above, autophagy operates at the interface between the transformed and non‐transformed compartments of the tumor. Interestingly, perturbations in the autophagic flux paradoxically enable malignant cells to bypass immune system‐mediated control or instead impose on tumor cells a superior control by the immune system, in a highly context‐dependent fashion. Extracellular release of KRASG12D by cancer cells succumbing to autophagy‐dependent ferroptosis is essential for pancreatic tumor‐associated macrophages (TAM) to switch to an “M2‐like” immunosuppressive phenotype (Dai et al, 2020). Importantly, M2 TAMs have been linked to tumor progression, metastases (Han et al, 2021), and resistance to conventional chemotherapeutics (Larionova et al, 2019) in multiple tumors. Consistent with this finding, chloroquine and its derivative hydroxychloroquine improve TAM‐mediated anticancer immune response by promoting the establishment of an “M1‐like” phenotype (Chen et al, 2018a; Sharma et al, 2020).
Pancreatic ductal carcinoma tumors expressing an ATG4B dominant‐negative mutant exhibit increased sensitivity to CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)‐mediated lysis (Yamamoto et al, 2020). Of note, PDAC cells in which autophagy is inhibited show an increased expression of MHC class I molecules at the surface, improving antigen presentation. This study found that MHC class I molecules are specific autophagy substrates. Therefore, autophagy promotes immune evasion via the lysosomal degradation of MHC class I molecule (Yamamoto et al, 2020). Consistently, Atg5 deficiency promotes the formation of effector memory CD8+ T cells, resulting in production of higher levels of IFNG and TNF/TNF‐α and enhanced tumor rejection (DeVorkin et al, 2019). In addition, autophagy restrains anticancer immune response in highly antigenic tumors by limiting a STING1‐dependent type I IFN response, thereby reducing T‐cell infiltration (Poillet‐Perez et al, 2020). Similarly, enhanced levels of autophagy in malignant cells are favored by a hypoxic environment, which in turn correlates with increased resistance of tumor cells to natural killer (NK)‐mediated lysis through multipronged mechanisms (Baginska et al, 2013; Tittarelli et al, 2015). Inhibition of autophagy (i.e., by shRNA silencing Becn1) induces a massive CCL5‐dependent infiltration of NK cells into melanoma tumors, thereby reducing tumor volume (Mgrditchian et al, 2017). In addition, loss of autophagy in the tumor or in the host modulates the intra‐tumoral infiltration of regulatory T (TREG) cells (Ladoire et al, 2016; Poillet‐Perez et al, 2020), which are associated with poor disease outcome in cohorts of patients affected by multiple tumor types (Tanchot et al, 2013). Administration of lysosomotropic agents (e.g., hydroxychloroquine) boosts the activity of an immune checkpoint inhibitor in preclinical models of melanoma (Sharma et al, 2020). Similarly, chloroquine also phenocopies the effect of an ATG4B dominant‐negative mutant in PDAC cells by restoring the surface expression of MHC class I molecules and synergizes with immune checkpoint blockade treatment in restraining PDAC outgrowth (Yamamoto et al, 2020). This result has been further reinforced in a CRISPR‐Cas9 screen performed across multiple cell lines, indicating that autophagy proficiency entails the inherent ability to evade immune detection (Lawson et al, 2020). Supporting this finding, lysosomotropic agents or small molecules targeting the PtdIns3K PIK3C3/VSP34 have been efficiently combined with therapeutic regimens that promote the activation of the immune system against cancer cells (Janji et al, 2020; Noman et al, 2020). Along similar lines, pharmacological or genetic inhibition of autophagy in syngeneic TS/A breast cancer models is sufficient to enhance the secretion of type I IFN by tumor cells exposed to focal radiation (Yamazaki et al, 2020). This effect follows the mtDNA‐mediated activation of the cGAS (cyclic GMP‐AMP synthase)‐STING1 pathway and in turn promotes long‐lasting local and systemic immunosurveillance (Vanpouille‐Box et al, 2018; Sprooten et al, 2019; Yamazaki et al, 2020).
Autophagy‐independent functions of the ATG machinery have also been implicated in the crosstalk between immune and cancer cells. As an example, functional LAP in myeloid cells supports tumor progression by promoting the establishment of an immune tolerant microenvironment upon phagocytosis of dying tumor cells, which eventually hinders T‐cell activation. Accordingly, genetic suppression of LAP in myeloid cells enables an improved immune control over tumor outgrowth (Cunha et al, 2018). In addition, the extracellular release of potassium by dying cancer cells leads to the induction of autophagy in CD8+ T cells, thus resulting in the acquisition of a stem cell‐like phenotype and ultimately improving tumor clearance. This effect can be further potentiated by treatment with caloric restriction mimetics (Vodnala et al, 2019), thus suggesting dietary interventions stimulating autophagy can be combined with certain antineoplastic therapies to achieve durable anticancer immunosurveillance (Levesque et al, 2019b; Pietrocola & Kroemer, 2019).
In contrast to these findings, intact autophagy responses regulate (i) the adjuvanticity (e.g., the capacity to emit danger signals that are preliminary to the recruitment of immune cells to the tumor bed) (Michaud et al, 2011; Zitvogel et al, 2015; Garg et al, 2016) and (ii) antigenicity of tumor cells (Caron et al, 2011; Ma et al, 2013c; Pietrocola et al, 2017), thereby promoting the establishment of the cancer‐immunity cycle leading to the CTL‐dependent elimination of malignant cells (Yamazaki et al, 2020). In line with this observation, autophagy‐deficient tumors transplanted into immunocompetent mice escape immunosurveillance, due to their inability to secrete immunostimulatory ATP (Michaud et al, 2011), and the absence of markers of autophagy (i.e., LC3B) in cancer cells has been correlated to reduced intra‐tumoral infiltration of CTLs (but higher infiltration of TREGs and CD68+ macrophages) and poor prognosis in women with breast cancer (Ladoire et al, 2016). In addition, in this setting, functional autophagy accounts for the ability of selected chemotherapeutics to elicit immunogenic cell death (Galluzzi et al, 2015a; Galluzzi et al, 2020b), an effect that is intimately related to the autophagy‐dependent release of ATP in the tumor bed (Kroemer et al, 2013; Martins et al, 2014; Galluzzi et al, 2017d) and that in turn promotes the recruitment of DC precursors and the priming of antitumor T cells (Ma et al, 2013b; Lee & Radford, 2019; Martinek et al, 2019; Galluzzi et al, 2020a). Of note, overactivation of autophagy by time‐restricted fasting or fasting mimetic agents potentiates the anticancer activity of immunogenic cell death inducers when used as a standalone regimen (Pietrocola et al, 2016; Galluzzi et al, 2017b; Castoldi et al, 2019) or in combination with antibodies targeting CTLA4 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte‐associated protein 4) or the immunosuppressive molecule CD274/PD‐L1 (Levesque et al, 2019a). Likewise, defective autophagy underlies the increased resistance of triple‐negative breast cancer cells to CTL lysis after immune checkpoint blocker treatment (Li et al, 2020b), while reducing the radiosensitivity of colorectal CT26 tumors transplanted into immunocompetent (but not immunodeficient) hosts (Ko et al, 2014).
Autophagy and cancer: clinical implications
Targeting autophagy‐dependent vulnerabilities of cancer cells has progressively gained attraction in the last decade, strongly advocating for the use of autophagy inhibitors (Amaravadi et al, 2019) in combination with regimens of targeted therapy (Bryant et al, 2019; Liu et al, 2020a), radiotherapy (Yamazaki et al, 2020), and immunotherapy (Galluzzi et al, 2018a; Yamamoto et al, 2020; Xia et al, 2021). Conditional deletion of autophagy essential genes in the host curtails the availability of metabolic substrates for hyperproliferating tumor cells, thereby impairing tumor progression (Karsli‐Uzunbas et al, 2014; Poillet‐Perez et al, 2018; Poillet‐Perez & White, 2019).
In this scenario, the field would certainly benefit from the expansion of the pharmacological toolbox to restrain autophagy in established neoplasia (Egan et al, 2015), in light of the limited specificity of autophagy inhibitors used in clinics (Manic et al, 2014). In addition to this aspect, further analyses performed in human studies are in need to assess the safety profile of prolonged/systemic inhibition of autophagy, as stable or transient inhibition of autophagy not only can limit antitumor immune responses mediated by chemotherapy, radiation therapy (Galluzzi et al, 2017b; Galluzzi et al, 2020a), and/or targeted therapy (Petroni et al, 2021), but may accelerate organismal decay (Guo et al, 2013; Yang et al, 2020), while precipitating episodes of secondary transformation (Cassidy et al, 2020). Hence, it is tempting to speculate that research efforts will be re‐energized toward the implementation of pharmacological modalities to selectively modulate autophagy in the transformed compartment.
The translation of autophagy‐targeted therapy into the clinic has just begun. Data from clinical studies are needed to clarify to which degree autophagy is active in specific tumors, either at the basal level or in response to distinct anticancer regimens. Owing to the high context‐dependency of the autophagy pathway in cancer, therapy‐oriented decisions based on autophagy modulation can only be adopted by taking into consideration the type and stage of tumor, and host‐related characteristics.
Immunity to pathogens, autoimmunity, and inflammation
Autophagy, or selected ATG functional modules, participates in the defensive response to pathogen invasion. Robust evidence demonstrates that maneuvers that hamper the autophagy reaction predispose cells to specific bacterial, protozoan, viral, or fungal infections (Levine et al, 2011; Gomes & Dikic, 2014; Keller et al, 2020b) (Table 9). The causes underlying the accrued propensity of autophagy‐incompetent cells to microbial infections lay in the multitude of actions exerted by the autophagic machinery within specialized (i.e., adaptive and innate immune cells) and parenchymal cells (Ma et al, 2013c; Clarke & Simon, 2019; Deretic, 2021). First, autophagy mediates quintessential (and cell type defining) functions in virtually all the immune cell subtypes, both at sites of hematopoiesis and in peripheral tissues (Ma et al, 2013c; Clarke & Simon, 2019). Accordingly, autophagy deficiency affects generation, survival, maturation, and effector properties of central cellular components of innate and adaptive immunity (Ma et al, 2013c; Clarke & Simon, 2019; Deretic, 2021). Second, impaired autophagy responses undermine the capacity of infected cells to dispose of invading pathogens (or components thereof) within the lysosome (Levine et al, 2011; Gomes & Dikic, 2014; Keller et al, 2020b; Deretic, 2021). Pathogen invasion entails the activation of bulk or selective autophagy modalities as a first‐line defense strategy. Nonetheless, infectious microorganisms utilize evasive strategies to bypass autophagy‐dependent degradation, or even subvert autophagosomal membranes as a preferential replication site (Gomes & Dikic, 2014). In addition, certain intracellular parasites such as Toxoplasma gondii or bacteria such as Francisella tularensis hijack host autophagy to harness nutrients they are auxotrophic for, such as fatty acids or amino acids (Steele et al, 2013; Pernas et al, 2018). Third, instances of derailed autophagy exacerbate the organismal response to infection, as it alters the extinction of the inflammatory cascade, thereby exacerbating the noxious local and systemic effects tied to invading pathogen infection (Deretic, 2021).
Table 9.
Immunity, inflammation, and immune‐related disorders associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial infection | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Enhanced susceptibility to infection mediated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Watson et al (2012), Kimmey et al (2015) |
| Bacterial infection | Whole‐body deletion of Prkn | Enhanced susceptibility to infection mediated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Manzanillo et al (2013) |
| Bacterial infection | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Abrogated autophagic killing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. bovis | Pilli et al (2012) |
| Bacterial infection | Conditional myeloid cell‐specific knock‐in of mutant Mcu Δmye | Improved control of Listeria monocytogenes infection, linked to enhanced LAP formation improved | Li et al (2021) |
| Bacterial infection | Intestinal epithelial cell‐specific deletion of Atg16l1 | Enhanced susceptibility to infection mediated by Listeria monocytogenes | Tan et al (2018) |
| Bacterial infection | Whole‐body deletion of Map1lc3b or knock‐in of hypomorphic Atg16l1 | Enhanced susceptibility to systemic and lung infection mediated by Staphylococcus aureus | Maurer et al (2015), Keller et al (2020a) |
| Bacterial infection | Endothelial cell deletion of Atg16l1 | Enhanced lethality due to exacerbated susceptibility to systemic and lung infection mediated by Staphylococcus aureus | Maurer et al (2015) |
| Bacterial infection | T‐cell‐specific deletion of Lamp2 | Impaired adaptive response to immunization with OVA peptide or Listeria infection | Valdor et al (2014) |
| Fungal infection | Whole‐body deletion of Rubcn | Enhanced susceptibility to infection mediated by Aspergillus fumigatus and granuloma formation, linked to increased pro‐inflammatory cytokines secretion | Martinez et al (2015) |
| Fungal infection | Myeloid cell‐specific deletion of Becn1 or Atg7 | Enhanced susceptibility to infection mediated by A. fumigatus and granuloma formation, linked to increased pro‐inflammatory cytokines secretion | Martinez et al (2015) |
| IBD | Whole‐body knock‐in of mutant Atg16l1T316A | Impaired clearance of the ileal pathogen Y. enterocolitica and elevated inflammatory cytokine response | Lassen et al (2014), Murthy et al (2014), Bel et al (2017) |
| IBD | Whole‐body knock‐in of hypomorphic Atg16l1 | Disruption of the Paneth cell granule exocytosis pathway and enhanced susceptibility to infection by commensal MNV | Cadwell et al (2008), Cadwell et al (2009), Cadwell et al (2010) |
| IBD | IEC‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Disruption of the Paneth cell granule exocytosis pathway linked to impaired lipid metabolism | Cadwell et al (2008) |
| IBD | IEC‐specific deletion of Atg16l1 | More severe colon histopathology and increased susceptibility to GVHD | Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al (2017), Aden et al (2018), Pott et al (2018) |
| IBD | IEC‐specific deletion of Tsc1 | Disrupted intestinal homeostasis and highly susceptibility to DSS‐induced colitis | Xie et al (2020) |
| IBD | IEC‐specific co‐deletion of Atg7 and Xbp1 | Worsening of Crohn disease‐like ileitis linked to defective ER stress response | Adolph et al (2013) |
| IBD | IEC‐specific co‐deletion of Atg16l1 and Xbp1 | Worsening of Crohn disease‐like ileitis linked to defective ER stress response | Adolph et al (2013), Aden et al (2018) |
| IBD | T‐cell‐specific deletion of Atg16l1 | Development of spontaneous intestinal inflammation | Kabat et al (2016) |
| IBD | CD4+ T‐cell‐specific deletion of Atg16l1 | Increased susceptibility to T‐cell‐mediated experimental IBD and elevated TH2‐mediated responses | Kabat et al (2016) |
| IBD | FOXP3+ T‐cell‐specific deletion of Atg16l1 | Development of spontaneous multiorgan inflammation | Kabat et al (2016) |
| IBD | CD11c+ DC‐specific deletion of Atg16l1 | Increased susceptibility to Bacteroides fragilis‐mediated colitis, linked to reduced induction of TREG cells | Chu et al (2016) |
| Lung fibrosis | Whole‐body deletion of Atg4b | Exacerbated bleomycin‐induced lung fibrosis, linked to alterations in pro‐inflammatory cytokines, and increased neutrophilic infiltration | Cabrera et al (2015) |
| Multiple sclerosis | Conditional CD11c+ DC‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Reduced development of EAE linked to limited CNS accumulation of CD4+ T cells | Keller et al (2017) |
| Multiple sclerosis | CD11c+ DC‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced incidence and severity of EAE by reducing CD4+ T‐cell priming | Bhattacharya et al (2014) |
| Multiple sclerosis | Microglia‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Increased accumulation of phagocytosed myelin and lack of recovery from multiple sclerosis‐like disease | Berglund et al (2020) |
| SLE | B cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Extended OS and reduced markers of SLE in Tlr7.1 transgenic mice | Weindel et al (2015) |
| SLE | DC‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Extended OS and reduced markers of SLE in Tlr7.1 transgenic mice | Weindel et al (2017) |
| SLE | DC and B cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Development of a rapid and lethal inflammatory condition in Tlr7.1 transgenic mice | Weindel et al (2017) |
| SLE | Whole‐body deletion of Nox2 or Rubcn | Development of symptoms of autoinflammatory disorder | Martinez et al (2016) |
| SLE | Whole‐body deletion of Nox2 or Rubcn | Development of symptoms of autoinflammatory disorder | Martinez et al (2016) |
| Viral infection | Neuron‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Increased susceptibility of neonatal mice to lethal CNS infection with SIN | Orvedahl et al (2010) |
| Viral infection | Whole‐body deletion of Fancc | Increased susceptibility to lethal CNS infection with SIN or HSV‐1, after mitophagy inhibition | Sumpter et al (2016) |
| Viral infection | Whole‐body deletion of Snx5 | Increased susceptibility of neonatal mice to lethal CNS infection with SIN, CHIKV, or WNV, after virus‐induced autophagy inhibition | Dong et al (2021b) |
| Viral infection | Whole‐body knock‐in of mutant Atg16l1E230 | Increased susceptibility low‐pathogenicity IAV, exacerbated pneumonia, and high mortality, after LAP inhibition | Wang et al (2021) |
| Viral infection | Conditional activated CD8+ T‐cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 or Atg5 | Impaired CD8+ T‐cell memory formation in response to chronic LCMV infection | Wang et al (2021) |
| Viral infection | Conditional CD11c+ cDC‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Increased susceptibility to HSV‐2 infection, linked to impaired antigen presentation and CD4+ T‐cell priming by cDCs | Lee et al (2010a) |
| Viral infection | T‐cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Impaired CD8+ T‐cell memory formation in response to MCMV infection | Wang et al (2021) |
| Viral infection | Pancreatic acinar cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Reduced CVB3 titer in the pancreas and diminished pancreatic pathology | Alirezaei et al (2012) |
| Viral infection | Whole‐body knock‐in of hypomorphic Atg16l1 | Limited ZIKV vertical transmission and placental and fetal damage in pregnant mice | Alirezaei et al (2012) |
CHIKV, chikungunya virus; CNS, central nervous system; CVB3, coxsackievirus B3; cDC, conventional dendritic cell; DSS, dextran sulfate sodium; EAE, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; GVHD, graft‐versus‐host disease; HSV, herpes simplex virus; IAV, influenza A virus; IEC, intestinal epithelial cell; LCMV, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus; MCMV, murine cytomegalovirus; MNV, murine norovirus; OVA, ovalbumin; SIN, Sindbis virus; SLE, systemic lupus erythematous; WNV, West Nile virus; ZIKV, Zika virus
Bacterial infections
A large variety of bacterial species with intracellular tropism (including Shigella flexneri, Listeria monocytogenes and Group A Streptococcus) are targeted for autophagy‐mediated elimination (Gomes & Dikic, 2014; Keller et al, 2020b). From a mere cell autonomous standpoint, the autophagosome‐generating machinery perceives intracellular microbes of bacterial origin (especially those escaping their membranes of internalization) as a substrate, thereby triggering a selective form of autophagy known as “xenophagy”, which has been extensively typified for infections mediated by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (Birmingham et al, 2006) or Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Gutierrez et al, 2004; Watson et al, 2012). In the context of M. tuberculosis infection, a positive correlation has been established between successful IFNG and IL17A antibacterial immune response and levels of autophagy in patients (Rovetta et al, 2014; Tateosian et al, 2017). Along similar lines, M. tuberculosis‐induced expression of signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family member 1 (SLAMF1) contributes to the activation of autophagy in neutrophils (Pellegrini et al, 2020). Pattern‐recognition receptor sensing of bacterial components is instrumental for the ignition of the autophagy cascade that leads to the sequestration of intracellular pathogens within autophagosomes. As an example, the interaction of lipopolysaccharide with TLR4 precedes the autophagy‐mediated engulfment of Salmonella Typhimurium (Liu et al, 2019). Likewise, MYD88 (myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88)‐ and TICAM1/TRIF (Toll‐like receptor adaptor molecule 1)‐dependent signaling downstream of TLR activation causes the dissociation of BECN1 from BCL2, hence triggering xenophagy in macrophages (Shi & Kehrl, 2008). Cardiolipin, which recruits LC3 during mitophagy (Chu et al, 2013), contributes to Shigella xenophagy by recruiting septins that form cages colocalizing with LC3 (Krokowski et al, 2018).
Along similar lines, detection of cytosolic peptidoglycans by NOD1 (nucleotide‐binding oligomerization domain containing 1) and NOD2 enables the spatiotemporal coordinated localization of the autophagy machinery at the site of bacterial ingress (Travassos et al, 2010). The mechanistic underpinnings of xenophagy appear to recapitulate key fundamentals of PRKN‐dependent mitophagy, in that host E3 ubiquitin ligases (including PRKN, SMURF1 [SMAD‐specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1] and LRSAM1 [leucine‐rich repeat and sterile alpha motif containing 1]) (Huett et al, 2012; Manzanillo et al, 2013; Fiskin et al, 2016) and linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC) catalyze the ubiquitination of cytoplasmic bacteria prior to their interaction with autophagy receptors, such as SQSTM1/p62 and CALCOCO2 (Fiskin et al, 2016; Noad et al, 2017; van Wijk et al, 2017). Corroborating this finding, prkn knockout mice are more sensitive to M. tuberculosis infection than their wild‐type littermates (Manzanillo et al, 2013). Importantly, exposure to LGALS8/galectin‐8 (evoked by pathogen‐induced phagosomal membrane rupture) is preparatory for the recognition by CALCOCO2, which in turn enables the autophagy‐regulated disposal of pathogen‐leaky vacuoles (Thurston et al, 2012). In contrast with this finding, Coxiella burnetii promotes the recruitment of the autophagy machinery to reseal intracellular damaged membranes (Mansilla Pareja et al, 2017).
In settings of S. Typhimurium infection, TLR4‐dependent activation of xenophagy involves the sequential activation of ULK1 by MAP3K7/TAK1 (mitogen‐activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7) (Liu et al, 2019) and TBK1‐dependent phosphorylation of OPTN, which augments its binding to ubiquitin‐decorated bacteria (Wild et al, 2011). A similar sequence of events occurs upon infection of macrophages with M. tuberculosis, after the STING1‐dependent recognition of extracellular DNA (Watson et al, 2012) and the subsequent recruitment of SQSTM1/p62, CALCOCO2, and TBK1 (Pilli et al, 2012). Although pattern‐recognition receptor activation triggers cytoprotective autophagy, the stimulation of autophagy is instrumental to prevent excessive IL1B production by sequestering lipopolysaccharide and preventing its recognition in the cytosol through the CASP4/CASP11 (caspase 4, apoptosis‐related cysteine peptidase) inflammasome (Meunier et al, 2014).
Intracellular pathogens have elaborated a variety of mechanisms to evade xenophagy (Mestre et al, 2010; Gomes & Dikic, 2014; Cong et al, 2020; Keller et al, 2020b; Gauron et al, 2021). For example, Salmonella and mycobacteria restrain the maturation of the phagosome, in order to foster their replication. In the case of L. monocytogenes (Birmingham et al, 2008) or Legionella (Yang et al, 2017a), evasive modalities involve the production of virulence factors that inactivate key components of the ATG machinery, blocking their recruitment to pathogen‐containing vacuoles (Gomes & Dikic, 2014; Cong et al, 2020). More recently, it has been reported that L. monocytogenes retains the capacity to subvert LAP (through modulation of mitochondrial calcium signaling), as a survival strategy (Li et al, 2021).
The induction of canonical autophagy pathway promotes the survival of cells exposed to pore forming cytolysin produced by Vibrio cholerae (Gutierrez et al, 2007). However, the functions of ATG proteins in non‐canonical processes participate in the immune response against pathogens (Mauthe & Reggiori, 2016). For instance, ATG5 mediates exclusive instances of cell death in neutrophils upon infection by M. tuberculosis (Kimmey et al, 2015). Autophagy‐independent functions of the ATG16L1 complex limit cell‐to‐cell spreading of L. monocytogenes infections by repairing listeriolysin O‐mediated rupture in the plasma membrane (Tan et al, 2018) and protect cells from α‐toxin‐dependent cytolysis in the context of Staphylococcus aureus infection (Maurer et al, 2015). In addition to soluble cargo such as IL1B and Aβ, ATG proteins mediate the secretion of toxin‐binding transmembrane receptors through extracellular vesicles in response to bacteria (Keller et al, 2020a). Of note, in phagocytic cells several components of the ATG machinery contribute to the internalization and elimination of microbes by participating in the LAP pathway in phagocytic cells (Martinez et al, 2015; Cunha et al, 2018; Galluzzi & Green, 2019; Heckmann & Green, 2019; Li et al, 2021). Unlike canonical autophagy, LAP acquires significant relevance for microbial cargos originating from the extracellular space, and it is thought to boost the rate of delivery of engulfed pathogens to the lysosome, after extracellular TLR stimulation, while simultaneously enabling cytokine production and antigen presentation in myeloid cells (Henault et al, 2012; Cunha et al, 2018; Galluzzi & Green, 2019; Heckmann & Green, 2019).
Viral infections
Whereas the mechanistic insights of xenophagy have extensively been characterized in the context of bacterial infections, viruses are also targeted for autophagy‐dependent degradation, often referred to as virophagy (Choi et al, 2018; Cong et al, 2020). Virophagy has been typified by the lysosomal degradation of the Sindbis virus capsid upon interaction with SQSTM1/p62, an event that is required to protect neurons from virus‐induced death (Orvedahl et al, 2010; Sumpter et al, 2016). As discussed above in the context of bacterial infections, the selection of the viral cargo impinges on the usage of factors involved in the mitophagic process, including Fanconi anemia‐related proteins (Sumpter et al, 2016). Recently, a genome‐wide siRNA screening identified the endosomal protein SNX5 (sorting nexin 5) as an essential factor for virus‐induced autophagy, and knockout of Snx5 in mice enhances lethality in response to infection by several human viruses (Dong et al, 2021b). Supporting the notion that autophagy enables cells to cope with viral infections, interventions that stimulate the autophagy reaction (such as the administration of the Tat‐Beclin 1 peptide) reduce the viral load and enhance the survival of mice infected by chikungunya and West Nile virus (Shoji‐Kawata et al, 2013). Besides enhancing the resistance of parenchymal cells to virus‐induced death, the induction of autophagy, which occurs downstream of viral sensing modules (including MAVS [mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein], implicated in cytosolic RNA detection, and STING1), concurrently restrains the excessive activation of type I IFN‐ and IL1B‐dependent signaling pathways, thus limiting tissue‐injury effects linked to an over‐persistent immune response (Cadwell, 2016; Choi et al, 2018; Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al, 2018). Conversely, systemic loss of the wild‐type linker domain of ATG16L1 makes mice more sensitive to lethal influenza A virus, due to LAP deficiency and reduced IFN signaling (Wang et al, 2021). Of note, accumulating evidence shows that the production of type I IFN can be influenced by ER stress/UPR during viral infections (Sprooten & Garg, 2020) and that downregulation of autophagy and LAP in leukocytes involved in the adaptive immune response to viral pathogens renders mice susceptible to viral infections. As an example, obliteration of Atg5 in ITGAX/CD11c+ antigen‐presenting cells hinders the efficient presentation of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV‐1)‐associated antigens to cognate T cells (Lee et al, 2010a). In addition, sustained autophagy responses in B and T cells are required to meet the metabolic demands associated with events of differentiation, clonal expansion, and acquisition of the memory phenotype, as described for CD8+ memory T cells generated in response to prolonged lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection (Hubbard et al, 2010; Ma et al, 2013c; Xu et al, 2014) and influenza (Puleston et al, 2014). CMA is also required for T‐cell activation through selective elimination of the negative regulators ITCH and RCAN (Valdor et al, 2014).
Notably, viruses have developed the capacity to block or subvert autophagy at multiple stages of their replication cycle (Cong et al, 2020). For example, (i) the murine gammaherpesvirus 68/MHV68 and HSV‐1 have been proposed to exploit BECN1 mimicry strategies to bypass autophagy‐mediated disruption (Orvedahl et al, 2007; E et al, 2009); (ii) the papain‐like protease domain of CoV‐NL63 binds BECN1 and STING1, thus hindering BECN1‐mediated autophagosome formation and inhibiting IFN production (Devaraj et al, 2007; Chen et al, 2014); while (iii) the Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)‐CoV promotes BECN1 degradation (Oudshoorn et al, 2017; Gassen et al, 2019); (iv) human papilloma virus inhibits autophagy in oropharyngeal squamous cells through E7‐mediated degradation of AMBRA1 (Antonioli et al, 2020); and (v) human cytomegalovirus suppresses autophagy flux in epithelial renal cells (Lopez Giuliani et al, 2020). Recently, it has been shown that ORF3a of the COVID‐19 virus SARS‐CoV‐2 may suppress autophagy activity. Individual ORF3a expression causes lysosomal damage, while preventing the interaction between the homotypic fusion and protein sorting (HOPS) complex and the autophagosomal soluble N‐ethylmaleimide‐sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) protein STX17 (syntaxin 17), eventually undermining the assembly of the STX17‐SNAP29‐VAMP8 SNARE macro‐complex, which regulates the fusion of the autophagosome with the lysosome (Miao et al, 2021). In this scenario, it is tempting to speculate that autophagy hijacking by SARS‐CoV‐2 contributes to exacerbate the inflammatory burden associated with viral infection, possibly contributing to the aberrant type I IFN response observed in COVID‐19 patients (Deretic, 2021). Upon picornavirus (e.g., coxsackievirus and rhinovirus) infection, the host lipid‐modifying enzyme PLAAT3/PLA2G16 promotes the delivery of the single‐stranded RNA viral genome to the cytosol before autophagy‐dependent degradation (Staring et al, 2017). In addition, mice in which Atg5 is selectively deleted in pancreatic acinar cells display resistance to coxsackievirus‐induced pancreatitis (Alirezaei et al, 2012). Although it is unclear whether picornavirus and herpesviruses hijack the autophagy pathway, components of the ATG machinery have been found in association with membranous platforms utilized by these viruses for replication. Interestingly, these viruses also appear to even subvert non‐canonical autophagy secretion to promote virion egress (Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al, 2018; Keller et al, 2020b). A pro‐viral function of autophagy has been described in circumstances of Junín virus (JUNV) infection (the etiological agent of Argentine hemorrhagic fever), as suggested by the fact that the replication capacity of JUNV was markedly reduced upon Atg5 or Beclin 1 genetic suppression (Roldan et al, 2019). Likewise, proficient autophagy responses appear to support the replicative capacity of Dengue virus (Heaton et al, 2010; Lee et al, 2018b). In addition, hepatitis C virus (HCV) stimulates the induction of autophagy via multipronged mechanisms to promote its replication and egress from infected cells (Shrivastava et al, 2012; Hansen et al, 2017).
Inflammatory disorders of the bowel
In view of the multifaceted implications of autophagy in the systemic and local responses to infectious cues, intense research has been dedicated to delineate the role of the autophagy pathway in non‐infectious inflammatory disorders, with particular emphasis on supraphysiological inflammatory responses affecting the gastrointestinal tract (Table 9). In particular, a significant body of literature has established a robust nexus between defective autophagy and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as Crohn disease and ulcerating colitis (Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al, 2018). The most common mutant variant ATG16L1T300A, which renders the protein a target for CASP3‐dependent cleavage, increases the risk of developing Crohn disease (Lassen et al, 2014; Murthy et al, 2014). Supporting a role for compromised autophagy in preventing the “leaky gut” and dysbiosis associated with IBD pathogenesis, Crohn disease patients harboring the ATG16L1T300A variant and various autophagy gene mutant mice exhibit defective secretion of antimicrobials and production of secretory granules in Paneth cells, a specialized epithelial cell type that protects the intestinal stem cell niche (Cadwell et al, 2008; Cadwell et al, 2009; Cabrera et al, 2015; Bel et al, 2017). Hypomorphic expression of ATG16L1 or knock‐in T300A mutation sensitizes mice to infection by commensal virus, while intensifying the inflammatory response to dextran sulfate sodium‐induced intestinal injury (Cadwell et al, 2010; Kernbauer et al, 2014; Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al, 2017). Through preserving organelle homeostasis, ATG proteins have a conserved function in mice and humans in promoting the resilience of the intestinal barrier to metabolic and immune‐mediated damage and preventing necrotic cell death of the epithelium (Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al, 2017; Aden et al, 2018; Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al, 2020; Xie et al, 2020). This concept is reinforced by the finding that Paneth cell‐specific deletion of multiple Atg genes, especially when deleted together with the ER stress gene Xbp1, leads to intestinal inflammation (Adolph et al, 2013). In support of the tenet that autophagy represses the inflammatory cascade in IBD, susceptibility genes associated with Crohn disease (i.e., Nod2, see also above) stimulate autophagy downstream of bacterial invasion to dampen inflammasome overactivation (Travassos et al, 2010; Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al, 2018). Because IBD‐sensitizing mutations occur at the germline level, it is presumed that a generalized impairment of autophagy, affecting also immune cells that infiltrate the gastrointestinal tract, contributes to the clinical outcomes of IBD, such as TREG cells (Kabat et al, 2016) and epithelial cells (Pott et al, 2018). In this scenario, it cannot be discounted that non‐canonical tasks of ATG proteins contribute to the aetiopathogenesis of IBD. As an example, commensal Bacteroides fragilis‐induced activation of LAP drives a transcriptionally tolerogenic program of differentiation in antigen‐presenting cells, which is required to generate immunosuppressive TREG cells in the context of colitis (Chu et al, 2016). Recently, it has been shown that functional IRGM1 (immunity‐related GTPase family M member 1), a Crohn disease risk factor (Parkes et al, 2007) which participates in the autophagy‐dependent elimination of intracellular pathogens (Singh et al, 2006; Kumar et al, 2020), dampens IL1B maturation by interfering in NRLP3 inflammasome assembly. Mechanistically, IRGM promotes the autophagy‐mediated degradation of NLRP3 and PYCARD/ASC, while reducing signs of accrued inflammation in a mouse model of Crohn disease (Mehto et al, 2019).
Other autoimmune disorders
In contrast with the protective role of autophagy in IBD, overexuberant autophagy may exacerbate autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis (Xu et al, 2013; Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto et al, 2018). Mechanistically, this phenomenon appears to be linked to aberrant self‐antigen presentation, maladaptive survival of T helper 17 (TH17)‐CD4+ T cells and exacerbated response to IL17‐derived inflammatory signals (Ireland & Unanue, 2011; van Loosdregt et al, 2016; Kim et al, 2017). In large‐scale genome‐wide association studies, a significant correlation has emerged between multiple ATG genes and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disorder characterized by autoantibody production, aberrant inflammation and multiorgan injury (Qi et al, 2019). In human, autophagy is hyperactive and required for autoantibody‐producing B cells (Clarke et al, 2015). Abnormal upregulation of CMA has also been described in systemic lupus erythematosus, and a phosphopeptide that significantly ameliorates clinical manifestations of the disease has CMA‐inhibitory properties (Macri et al, 2015; Wang et al, 2020b). While these results may highlight the hyperactivation of autophagy as a common feature of different autoimmune disorders, additional studies are required to solve this enigma. As an example, conflicting evidence can be inferred from murine models of systemic lupus erythematous. On the one hand, the activation of autophagy in B cells supports the production of autoantibodies in two distinct murine models of systemic lupus erythematous (Weindel et al, 2015); on the other hand, concomitant deletion of Atg5 in DCs and B cells precipitates the inflammatory phenotype, lending further support to the hypothesis that autophagy can mediate cell type‐exclusive function in distinct autoimmune pathologies (Weindel et al, 2017). Adding a further layer of complexity, non‐canonical autophagy is implicated in similar autoimmune processes, as testified to by the fact that LAP is necessary for the type I IFN response during internalization of DNA–antibody complexes by plasmacytoid DCs (Henault et al, 2012; Hayashi et al, 2018; Leylek & Idoyaga, 2019), while also mediating the turnover of dying cells by myeloid cells to prevent the generation of such antibody complexes (Martinez et al, 2016). A non‐canonical role for ATG proteins has been also described in a model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (a CD4+ T‐cell‐mediated mouse model of multiple sclerosis) where targeted knockout of Atg5 or Atg7 in DCs abrogates myelin presentation to myelin‐specific CD4+ T cells, hence preventing the accumulation of autoimmune T cells within the CNS and the consequent CNS damage (Bhattacharya et al, 2014; Keller et al, 2017; Berglund et al, 2020).
Ocular diseases
Visual impairment is among the leading disorders in developed countries, being that aging is the major cause for its clinical manifestation. In support of the involvement of autophagy in the age‐dependent decay of eye function, reduced mRNA expression of essential autophagy regulators, accompanied by increased markers of defective autophagy flux, has been reported in the retina of old mice (Rodriguez‐Muela et al, 2015). In view of its inherent function of cytoprotection elicited in neuronal precursors and in the multitude of differentiated cell types that form the eyeball, bulk and selective types of autophagy operate at the frontline to preserve visual integrity (Boya et al, 2016) (Table 10).
Table 10.
Ocular diseases associated with genetic intervention of autophagy in mice.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADOA | RGC‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Ameliorated visual defects driven by Opa1 ablation by normalizing the autophagic flux | Zaninello et al (2020) |
| ARMD | RPE‐specific deletion of Rubcn | Prevention of the inflammatory response to chronic blue light exposure by limiting autophagy impairment | Ando et al (2021) |
| ARMD | Whole‐body deletion of Lamp2 | Accelerated age‐associated formation of basal laminar deposits in the retina | Notomi et al (2019) |
| Cataract | LEC‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Development of lens clouding by 21 months of age | Morishita et al (2013) |
| Cataract | LEC‐specific deletion of Vps34 | Development of congenital cataract and microphthalmia, through an autophagy‐independent mechanism | Morishita et al (2013) |
| Glaucoma | Overexpression of mutant OptnE50K | Increased RGC death and reduced retinal thickness, linked to profound gliosis in the retina | Chi et al (2010), Minegishi et al (2013) |
| Retinal development | Whole‐body deletion of Atg5 or Bnip3l | Inhibited RGC differentiation after mitophagy inhibition | Esteban‐Martinez et al (2017) |
| Retinal degeneration | Whole‐body deletion of Atg4b | Reduced numbers of surviving RGCs after optic nerve transection | Rodriguez‐Muela et al (2012) |
| Retinal degeneration | Conditional RGC‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Reduced numbers of surviving RGCs after optic nerve transection | Rodriguez‐Muela et al (2012) |
| Retinal degeneration | Whole‐body allelic loss of Becn1 | Increased susceptibility to light‐induced retinal damage | Chen et al (2013) |
| Retinal degeneration | Whole‐body deletion of Prkn | Exacerbated light‐induced retinopathy linked to accumulation of damaged mitochondria | Chen et al (2013) |
| Retinal degeneration | Conditional rod photoreceptor‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Increased susceptibility to light‐induced retinal damage linked to increased photoreceptor cell death | Chen et al (2013) |
| Retinal degeneration | Conditional RPE‐specific deletion of Rb1cc1 | Increased age‐dependent degeneration of the RPE, and secondary degeneration of the overlying photoreceptors | Yao et al (2015) |
| Retinal degeneration | Conditional RPE‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Decreased photoreceptor responses to light stimuli linked to disrupted lysosomal processing | Kim et al (2013a) |
| Retinal degeneration | Conditional rod photoreceptor‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Progressive degeneration of rod photoreceptors by 8 weeks of age, independently of light exposure | Zhou et al (2015a) |
| Retinal degeneration | Cone cell‐specific deletion of Atg5 | Increased susceptibility to light‐induced retinal damage linked to accumulation of damaged mitochondria | Zhou et al (2015b) |
AOA, autosomal‐dominant optic atrophy; ARMD; age‐related macular degeneration; LEC, lens epithelial cell; RGC, retinal ganglion cell; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.
Intact autophagy supports the regression of the hyaloid artery that accompanies eye maturation (Kim et al, 2010). Because the constitutive knockout of key autophagy genes results in embryonic or perinatal lethality, the retinal phenotype of these animal models has not been characterized in detail, although the specific deletion of Atg5 in neuronal precursors results in a very dramatic phenotype of photoreceptor death and night vision loss already at 7 weeks of age (Rodriguez‐Muela et al, 2013). Ambra1‐deficient zebrafish models exhibit ocular dysfunction during embryonic development (Benato et al, 2013). In addition, Atg5‐deficient mouse retinas display a reduced number of retinal ganglion cells during development and alterations in retina metabolism (Esteban‐Martinez et al, 2017). Whereas models of partial autophagy deficiency (i.e., atg4b− / − mice) do not display visual impairment under baseline conditions, they are characterized by accrued sensitivity to axonal damage (Rodriguez‐Muela et al, 2012). Likewise, Becn1+ / − animals exhibit exacerbated retinal damage upon prolonged exposure to bright light (Chen et al, 2013), and old ambra1+ / gt exhibit accrued sensitivity to optic nerve crush (Bell et al, 2020). Conditional rb1cc1 deletion in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) leads to severe visual impairment, linked to reduced RPE proteostatic functions (Yao et al, 2015). In line with these observations, conditional deletion of Atg5 in the RPE does not affect eye function at birth, yet manifests as declining photoreceptor functions at old age, linked to impaired lysosomal degradation of photoreceptor outer segments. In this context, autophagy‐independent functions of the ATG machinery are instrumental in regulating the vision cycle, as shown by the fact that the ATG5‐ and BECN1‐dependent (but ULK1 independent) conjugation of LC3 to phagosomal membranes is required for phagocytosis and degradation of photoreceptor outer segments (POS) in RPE (Kim et al, 2013a). The conditional knockout of Atg7 in rod cells causes severe degeneration of the superior retina only upon exposure to bright light (Chen et al, 2013). However, conditional Atg5 deficiency in rod photoreceptors results in age‐dependent rod degeneration, even in animals raised in darkness, implying a gene‐specific degree of severity (Zhou et al, 2015a). Along similar lines, deletion of Atg5 in cone cells progressively affects cone number and function across mouse lifespan, making animals more sensitive to light‐induced degeneration (Zhou et al, 2015b). In addition, deletion of Atg5 in cone cells progressively affects cone number and function across mouse lifespan, making animals more sensitive to light‐induced degeneration (Zhou et al, 2015b). In animal models of retinitis pigmentosa, lysosomal membrane rupture and overexuberant MTOR pathway activation causally contribute to photoreceptor decay (Rodriguez‐Muela et al, 2015). Conversely, the activation of autophagy promoted by HDAC3 inhibition (Samardzija et al, 2020) and trehalose treatment limits photoreceptor degeneration, thus preserving visual acuity (Lotfi et al, 2018).
Alterations in the ATG machinery contribute to the pathogenesis of ocular diseases caused by dysfunction in different cellular components forming the eyeball. Mice harboring LEC‐specific atg5 deletion develop lens clouding by 21 months of age (Morishita et al, 2013). A similar effect occurs upon pik3c3/vps34 deletion in LECs, which also leads to age‐dependent cataracts (Morishita et al, 2013). Of note, this effect does not rely on the autophagy‐dependent degradation of organelles, which is postulated to be essential to generate an organelle‐free transparent zone. Recent findings rather suggest that organelle degradation in LECs depends upon functional PLAAT/HRASLS (phospholipase A and acyltransferase) phospholipases, which induce organelles rupture followed by their complete degradation (Morishita et al, 2021).
Congenital forms of cataracts have been associated with mutations in the LC3 and RAB7 binding protein FYCO1 (FYVE and coiled‐coil domain autophagy adaptor 1), which also takes part in autophagosome trafficking and fusion with lysosomes (Chen et al, 2011). Likewise, a knock‐in mouse model bearing the R120G mutation in CRYAB/αB‐crystallin, which leads to human congenital cataracts, displays an impaired autophagy flux (Wignes et al, 2013).
Experimental findings (mostly in vitro studies) showed that autophagy elicits protective functions in age‐related macular degeneration (ARMD), which manifests in humans in a dry or wet form. ARMD pathogenesis is linked to events of altered proteostasis and aberrant oxidative stress, associated with the prominent accumulation of lysosomal lipofuscin granules and extracellular proteinaceous deposits (known as “drusen”) in RPE of the basal layer, which cause progressive degeneration of post‐mitotic RPE. In two different mouse models of ARDM (Sod2 knockdown and the apoe/APOE4‐HFC model), autophagy is upregulated at the early stage of the disease, yet declines at advanced stages of the pathology (Mitter et al, 2014; Song et al, 2017). In support of this result, the induction of autophagy is required to dispose of the lipofuscin component A2E in RPE, which progressively accumulates with age (Zhang et al, 2015). A2E in RPE inhibits autophagy partly through upregulation of RUBCN (Ando et al, 2021). In this scenario, treatment with rapamycin improves A2E degradation (Zhang et al, 2015). Further corroborating the idea that impaired lysosomal function is pathognomonic to ARMD, animal models deficient in CRYBA1/bA3/A1‐crystallin display impaired lysosomal acidification in RPE, culminating in RPE degeneration and signs of ARMD (Valapala et al, 2014). Moreover, the pathogenesis of human dry ARMD is characterized by the loss of LAMP2 expression by RPE cells, and the knockout of Lamp2 suffices to cause an ARMD‐like disease in mice (Notomi et al, 2019).
Glaucoma, a progressive optic neuropathy that leads to retinal ganglion cell (RGC) degeneration, is among the leading causes of blindness. Primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) is commonly associated with elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) and aging. The occlusion of the trabecular meshwork that regulates aqueous humor outflow from the anterior chamber of the eye is a major cause for POAG; yet, genetic factors, vascular alterations, and autoimmune reactions have also ascribed a causative role. A second form of glaucoma, called normal tension glaucoma (NTG), is not associated with elevated IOP. The clinical outcome of both glaucoma subtypes is visual loss caused by RGC degeneration. Autophagy has been implicated in both the etiological phase of elevated IOP generation in POAG and the etiological phase of RGC loss in both POAG and NTG. Commonly, outflow from the eye anterior chamber is inhibited by mutations in MYOC (myocilin) that can be recapitulated in the mouse. Interestingly, stimulation of autophagy can clear mutant MYOC accumulation and correct IOP elevation (Kasetti et al, 2021). Decreased autophagy flux has been reported in RGC upon chronic IOP elevation (Hirt et al, 2018). In contrast, others have reported that autophagy is chronically activated in RGCs of aged mice with elevated IOP (Nettesheim et al, 2020). In line with these controversies, autophagy appears to protect or promote RGC death depending on the experimental model and the time point analyzed (Koch & Lingor, 2016). For example, the expression of a GFP‐LC3 transgene exacerbates optic nerve degeneration in a mouse model of spontaneous IOP, pointing to a detrimental role for excess autophagy (Hirt et al, 2018). A similar situation has been reported in the case of autosomal‐dominant optic atrophy (ADOA), a genetic form of RGC degeneration caused by dominant‐negative mutations in, or haploinsufficiency of, the mitochondrial dynamic‐regulating gene OPA1. In vitro and in vivo experiments have demonstrated that the pathological phenotype of ADOA depends on excessive autophagy, and genetic normalization of the autophagy flux fully corrects the visual loss observed in the ADOA mouse model (Zaninello et al, 2020). A role for reduced mitophagy has been identified in NTG, associated with mutations in the autophagy receptor gene Optn (the most common being E50K and M98K). Transgenic mice overexpressing the OPTNE50K mutation, which instigates the formation of insoluble OPTN aggregates and results in autophagy blockade, display RGC loss and reduced retinal thickness (Chi et al, 2010; Minegishi et al, 2013). In these settings, pharmacological stimulation of autophagy by rapamycin mitigates OPTNE50K‐induced RGC death (Chalasani et al, 2014).
Retinal ganglion cell death can be mimicked in mice by optic nerve axotomy (an acute model of glaucoma) and causes retrograde RGC degeneration in a BCL2‐inhibitable manner (Cenni et al, 1996; Porciatti et al, 1996). Not surprisingly, adenovirus‐mediated depletion of Atg5 in RGCs sensitizes RGCs to optic nerve axotomy‐induced death (Rodriguez‐Muela et al, 2012). Therefore, upon optic nerve axotomy autophagy is activated (via canonical and non‐canonical routes) to promote RGC survival (Rodriguez‐Muela et al, 2012). Supporting this finding, pharmacological activation of autophagy by rapamycin shows protective effects in multiple experimental models of glaucoma. (Rodriguez‐Muela et al, 2012; Kitaoka et al, 2013; Su et al, 2014; Russo et al, 2018; Wen et al, 2019; Lee et al, 2021).
As ocular disorders are in the vast majority of the cases multifactorial, or associated with concurrent pathologies, it is tempting to speculate that lifestyle factors or chronic diseases that undermine autophagy (i.e., diabetes) contribute to the pathological phenotype in the eye also via autophagy downregulation, as in the case of diabetic retinopathy (Boya et al, 2016).
Reproductive system dysfunctions
Endometriosis is a benign gynecological disease, associated with dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain, and infertility in women. Accumulating evidence reveals a pivotal role for autophagy in the pathogenesis of endometriosis (Yang et al, 2017c). While in normal endometrium autophagy is induced as a pro‐apoptotic mechanism in glandular epithelial and stromal cells during menstruation (Choi et al, 2012), increased autophagy mediates hyperplasia of murine endometriotic tissue and stromal cells (Ruiz et al, 2016), thus limiting apoptosis and promoting abnormal immune responses (Yu et al, 2016). Consistently, genetic or pharmacological inhibition of autophagy prevents the formation of endometriotic lesions (Liu et al, 2017) (Table 11).
Table 11.
Reproductive system dysfunctions.
| Setting | Genetic intervention | Effects on disease phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male infertility | Germ cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 | Reduced motility of spermatozoa with malformed head, linked to impaired cytoskeleton organization | Shang et al (2016) |
| Male infertility | Sertoli cell‐specific deletion of Atg7 or Atg5 | Disorganized seminiferous tubules and spermatozoa with malformed heads, linked to impaired cytoskeleton organization | Liu et al (2016) |
Dysfunctional autophagy has also been linked to ovarian insufficiency due to inflammatory aging and miscarriage, as well as to male infertility. For example, inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome leads to increased levels of autophagy markers in the ovary of 12‐month‐old female mice and is linked to improved reproductive pregnancy rate (Navarro‐Pando et al, 2021), whereas pharmacological induction of autophagy (by rapamycin) promotes endometrium autophagy (and NK cell infiltration), thus decreasing the risk of spontaneous abortion in mice (Lu et al, 2020). In addition, functional autophagy sustains correct spermiogenesis. For example, atg7 −/− mice show defects in cytoskeleton organization limiting the differentiation of spermatids (Shang et al, 2016) and autophagy disruption in Sertoli cell results in the formation of disorganized tubules and production of low motility malformed spermatozoa (Liu et al, 2016; Shang et al, 2016).
Concluding remarks
Taken together, these observations point to autophagy as a primordial determinant of human health, thus delineating autophagy‐modulating interventions as promising approaches to prevent or mitigate phenotypic anomalies of the most common human illnesses. While the introduction of conditional knockout murine models of disease has enabled researchers to shed new light on the cell type inherent functions of autophagy, these models still present important limitations, in that they fall short in capturing the multidimensional relationships among cell types, which often rely upon non‐cell autonomous effects of the autophagy route, at the tissue and systemic level. Moreover, the majority of the genetic models employed in autophagy research are not inducible, and hence establish an autophagy defect either at fecundation or upon activation of the tissue‐restricted promoter employed to control Cre expression. Even in the latter scenario, this generally occurs during development, and hence fails to recapitulate an acute autophagic defect in the adult. Autophagy also intersects with other pathways (e.g., LAP, LANDO, RCD) at multiple signaling nodes. As most of the results discussed herein were obtained upon the deletion or downregulation of single components of the autophagic apparatus, the observed phenotypes may actually originate from non‐autophagic pathways that share core regulators with autophagy. Thus, future studies examining the role of autophagy in disease should rely on genetic deletions of more than one autophagy gene, preferably encompassing early and late functions, and on recently derived genetic models that can differentiate canonical from non‐canonical autophagy phenotypes. Finally, evidence from human clinical studies, possibly inferred at pre‐pathological stages of the diseases, would ignite the field with important insights about autophagy dynamics in relevant human pathologies.
Despite these caveats, a few general concepts emerge from the abundant preclinical literature discussed herein. First, autophagy defects are particularly detrimental for post‐mitotic cells (e.g., neurons, cardiomyocytes, memory T cells), largely linked to their accrued demands for long‐term proteostasis. Second, autophagy defects in healthy cells are often connected to disease as a consequence of lost cellular homeostasis rather than failed adaptation to dwindling nutrients. Instead, cancer cells generally harness autophagy as a measure to withstand intracellular stress linked to the malignant status and challenging microenvironmental conditions. Third, autophagic proficiency declines with age, hence contributing to multiple pathologies of the elderly. Finally, a number of commonly accepted lifespan‐ and healthspan‐extending habits (e.g., exercise, caloric restriction) share the ability of activating autophagy. Thus, although much remains to be done, the modulation of autophagy for therapeutic purposes remains a promising strategy for the management of multiple human disorders (Fig 2). The future will tell which specific conditions will be the first to benefit from clinically usable pharmacological autophagy modulators.
Figure 2. Basic principles of autophagy modulation as a therapeutic strategy for human disease.
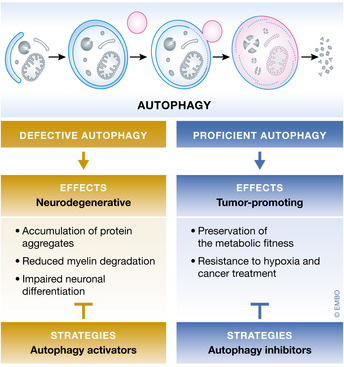
In multiple settings including various neurodegenerative conditions, autophagy defects contribute to disease onset and progression, suggesting that autophagy activators may mediate beneficial effects. Conversely, proficient autophagic responses support tumor progression and resistance to therapy, pointing to autophagy inhibition as an appropriate therapeutic approach. In both scenarios, the effect of autophagy modulation on non‐diseased cells must be carefully considered to enable safety and superior therapeutic efficacy.
Author contributions
DJK, LG and FP conceived and wrote the manuscript, centralized and integrated comments from co‐authors, and revised the review upon editorial feedback. GP designed the figure, performed bibliographic searches, and helped with table preparation. All authors corrected the article and provided valuable input to obtain a unified view. With the exception of DJK, GP, LG and FP, authors are listed alphabetically, which does not reflect their relative contribution to the preparation of this article.
Conflict of interest
A.B. is cofounder of CASMA Therapeutics Inc., Advisory Board member of Next Generation Diagnostics and of Avilar Therapeutics. K.C. has received research support from Pfizer, Takeda, Pacific Biosciences, and AbbVie; consulted for or received an honorarium from PureTech Health, Genentech, and AbbVie; and holds U.S. patent 10,722,600 and provisional patents 62/935,035 and 63/157,225. A.M.K.C. is a cofounder, stock holder and serves on the Scientific Advisory Board for Proterris, which develops therapeutic uses for carbon monoxide. A.M.K.C. also has a use patent on CO. G.K is a cofounder and advisor of EverImmune, Samsara Therapeutics, and Therafast Bio as well as advisor for The Longevity Labs (TLL). F.M. is a founder, is advisor, and has equity interests in The Longevity Labs (TLL) and Samara Therapeutics. D.C.R is a consultant for Aladdin Healthcare Technologies SE, Drishti Discoveries, and Nido Biosciences. L.G. has received research funding from Lytix Biopharma and Phosplatin, as well as consulting/advisory honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, OmniSEQ, Onxeo, The Longevity Labs, Inzen, and the Luke Heller TECPR2 Foundation. RKA is cofounder of Pinpoint Therapeutics and advisor for Deciphera, Sprint Biosciences, Merck, and Immunacell. He gets research funding for clinical trials from Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Deciphera. J.Y. is a consultant for Denali Therapeutics, Sanofi, and Nido. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
The EMBO Journal (2021) 40: e108863.
See the Glossary for abbreviations used in this article.
Contributor Information
Lorenzo Galluzzi, Email: deadoc80@gmail.com.
Federico Pietrocola, Email: federico.pietrocola@ki.se.
References
- Abdel Fattah E, Bhattacharya A, Herron A, Safdar Z, Eissa NT (2015) Critical role for IL‐18 in spontaneous lung inflammation caused by autophagy deficiency. J Immunol 194: 5407–5416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abebe T, Mahadevan J, Bogachus L, Hahn S, Black M, Oseid E, Urano F, Cirulli V, Robertson RP (2017) Nrf2/antioxidant pathway mediates beta cell self‐repair after damage by high‐fat diet‐induced oxidative stress. JCI Insight 2: e92854 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aden K, Tran F, Ito GO, Sheibani‐Tezerji R, Lipinski S, Kuiper JW, Tschurtschenthaler M, Saveljeva S, Bhattacharyya J, Häsler Ret al (2018) ATG16L1 orchestrates interleukin‐22 signaling in the intestinal epithelium via cGAS‐STING. J Exp Med 215: 2868–2886 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adolph TE, Tomczak MF, Niederreiter L, Ko H‐J, Böck J, Martinez‐Naves E, Glickman JN, Tschurtschenthaler M, Hartwig J, Hosomi Set al (2013) Paneth cells as a site of origin for intestinal inflammation. Nature 503: 272–276 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aghajan M, Li N, Karin M (2012) Obesity, autophagy and the pathogenesis of liver and pancreatic cancers. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27(Suppl 2): 10–14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad T, Sundar IK, Lerner CA, Gerloff J, Tormos AM, Yao H, Rahman I (2015) Impaired mitophagy leads to cigarette smoke stress‐induced cellular senescence: implications for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. FASEB J 29: 2912–2929 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali AB, Nin DS, Tam J, Khan M (2011) Role of chaperone mediated autophagy (CMA) in the degradation of misfolded N‐CoR protein in non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. PLoS One 6: e25268 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alirezaei M, Flynn CT, Wood MR, Whitton JL (2012) Pancreatic acinar cell‐specific autophagy disruption reduces coxsackievirus replication and pathogenesis in vivo . Cell Host Microbe 11: 298–305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allaire M, Rautou PE, Codogno P, Lotersztajn S (2019) Autophagy in liver diseases: time for translation? J Hepatol 70: 985–998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen EA, Baehrecke EH (2020) Autophagy in animal development. Cell Death Differ 27: 903–918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altshuler‐Keylin S, Shinoda K, Hasegawa Y, Ikeda K, Hong H, Kang Q, Yang Y, Perera RM, Debnath J, Kajimura S (2016) Beige adipocyte maintenance is regulated by autophagy‐induced mitochondrial clearance. Cell Metab 24: 402–419 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaravadi R, Kimmelman AC, White E (2016) Recent insights into the function of autophagy in cancer. Genes Dev 30: 1913–1930 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaravadi RK, Kimmelman AC, Debnath J (2019) Targeting autophagy in cancer: recent advances and future directions. Cancer Discov 9: 1167–1181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anding AL, Wang C, Chang TK, Sliter DA, Powers CM, Hofmann K, Youle RJ, Baehrecke EH (2018) Vps13D encodes a ubiquitin‐binding protein that is required for the regulation of mitochondrial size and clearance. Curr Biol 28: 287–295.e286 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando S, Hashida N, Yamashita D, Kawabata T, Asao K, Kawasaki S, Sakurai K, Yoshimori T, Nishida K (2021) Rubicon regulates A2E‐induced autophagy impairment in the retinal pigment epithelium implicated in the pathology of age‐related macular degeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 551: 148–154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anguiano J, Garner TP, Mahalingam M, Das BC, Gavathiotis E, Cuervo AM (2013) Chemical modulation of chaperone‐mediated autophagy by retinoic acid derivatives. Nat Chem Biol 9: 374–382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonioli M, Pagni B, Vescovo T, Ellis R, Cosway B, Rollo F, Bordoni V, Agrati C, Labus M, Covello Ret al (2020) HPV sensitizes OPSCC cells to cisplatin‐induced apoptosis by inhibiting autophagy through E7‐mediated degradation of AMBRA1. Autophagy 1–14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antony VB, Thannickal VJ (2018) Cellular senescence in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: multifaceted and multifunctional. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 59: 135–136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arensman MD, Yang XS, Zhong W, Bisulco S, Upeslacis E, Rosfjord EC, Deng S, Abraham RT, Eng CH (2020) Anti‐tumor immunity influences cancer cell reliance upon ATG7. Oncoimmunology 9: 1800162 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias E, Cuervo AM (2020) Pros and cons of chaperone‐mediated autophagy in cancer biology. Trends Endocrinol Metab 31: 53–66 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A, Bento CF, Ricketts T, Vicinanza M, Siddiqi F, Pavel M, Squitieri F, Hardenberg MC, Imarisio S, Menzies FMet al (2017) Polyglutamine tracts regulate beclin 1‐dependent autophagy. Nature 545: 108–111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baerga R, Zhang Y, Chen PH, Goldman S, Jin S (2009) Targeted deletion of autophagy‐related 5 (atg5) impairs adipogenesis in a cellular model and in mice. Autophagy 5: 1118–1130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baginska J, Viry E, Berchem G, Poli A, Noman MZ, van Moer K, Medves S, Zimmer J, Oudin A, Niclou SPet al (2013) Granzyme B degradation by autophagy decreases tumor cell susceptibility to natural killer‐mediated lysis under hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: 17450–17455 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai B, Wang X, Li Y, Chen P‐C, Yu K, Dey KK, Yarbro JM, Han X, Lutz BM, Rao Set al (2020) Deep multilayer brain proteomics identifies molecular networks in Alzheimer's disease progression. Neuron 106: 700 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baisantry A, Bhayana S, Rong S, Ermeling E, Wrede C, Hegermann J, Pennekamp P, Sörensen‐Zender I, Haller H, Melk Aet al (2016) Autophagy induces prosenescent changes in proximal tubular s3 segments. J Am Soc Nephrol 27: 1609–1616 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj L, Lotfi P, Pal R, Ronza AD, Sharma J, Sardiello M (2019) Lysosome biogenesis in health and disease. J Neurochem 148: 573–589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balan S, Saxena M, Bhardwaj N (2019) Dendritic cell subsets and locations. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 348: 1–68 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balke D, Tatenhorst L, Dambeck V, Ribas VT, Vahsen BF, Michel U, Bahr M, Lingor P (2020) AAV‐mediated expression of dominant‐negative ULK1 increases neuronal survival and enhances motor performance in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Mol Neurobiol 57: 685–697 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A, Bonifacino JS (2020) Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21: 101–118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer PO, Goswami A, Wong HK, Okuno M, Kurosawa M, Yamada M, Miyazaki H, Matsumoto G, Kino Y, Nagai Yet al (2010) Harnessing chaperone‐mediated autophagy for the selective degradation of mutant huntingtin protein. Nat Biotechnol 28: 256–263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel W, Helmstädter M, Balica J, Hartleben B, Kiefer B, Hrnjic F, Schell C, Kretz O, Liu S, Geist Fet al (2013) Vps34 deficiency reveals the importance of endocytosis for podocyte homeostasis. J Am Soc Nephrol 24: 727–743 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beek N, Klionsky DJ, Reggiori F (2018) Genetic aberrations in macroautophagy genes leading to diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1865: 803–816 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beetz C, Johnson A, Schuh AL, Thakur S, Varga R‐E, Fothergill T, Hertel N, Bomba‐Warczak E, Thiele H, Nurnberg Get al (2013) Inhibition of TFG function causes hereditary axon degeneration by impairing endoplasmic reticulum structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: 5091–5096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beffy P, Del Carratore R, Masini M, Furling D, Puymirat J, Masiello P, Simili M (2010) Altered signal transduction pathways and induction of autophagy in human myotonic dystrophy type 1 myoblasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42: 1973–1983 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP, Harper JW (2010) Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature 466: 68–76 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrendt L, Kurth I, Kaether C (2019) A disease causing ATLASTIN 3 mutation affects multiple endoplasmic reticulum‐related pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci 76: 1433–1445 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bel S, Pendse M, Wang Y, Li Y, Ruhn KA, Hassell B, Leal T, Winter SE, Xavier RJ, Hooper LV (2017) Paneth cells secrete lysozyme via secretory autophagy during bacterial infection of the intestine. Science 357: 1047–1052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belibi F, Ravichandran K, Zafar I, He Z, Edelstein CL (2011) mTORC1/2 and rapamycin in female Han:SPRD rats with polycystic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 300: F236–F244 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell K, Rosignol I, Sierra‐Filardi E, Rodriguez‐Muela N, Schmelter C, Cecconi F, Grus F, Boya P (2020) Age related retinal Ganglion cell susceptibility in context of autophagy deficiency. Cell Death Discov 6: 21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benato F, Skobo T, Gioacchini G, Moro I, Ciccosanti F, Piacentini M, Fimia GM, Carnevali O, Dalla Valle L (2013) Ambra1 knockdown in zebrafish leads to incomplete development due to severe defects in organogenesis. Autophagy 9: 476–495 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger Z, Ravikumar B, Menzies FM, Oroz LG, Underwood BR, Pangalos MN, Schmitt I, Wullner U, Evert BO, O'Kane CJet al (2006) Rapamycin alleviates toxicity of different aggregate‐prone proteins. Hum Mol Genet 15: 433–442 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglund R, Guerreiro‐Cacais AO, Adzemovic MZ, Zeitelhofer M, Lund H, Ewing E, Ruhrmann S, Nutma E, Parsa R, Thessen‐Hedreul Met al (2020) Microglial autophagy‐associated phagocytosis is essential for recovery from neuroinflammation. Sci Immunol 5: eabb5077 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia D, Chung KP, Nakahira K, Patino E, Rice MC, Torres LK, Muthukumar T, Choi AM, Akchurin OM, Choi ME (2019) Mitophagy‐dependent macrophage reprogramming protects against kidney fibrosis. JCI Insight 4: e132826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya A, Parillon X, Zeng S, Han S, Eissa NT (2014) Deficiency of autophagy in dendritic cells protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Biol Chem 289: 26525–26532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan MS, Pattison JS, Osinska H, James J, Gulick J, McLendon PM, Hill JA, Sadoshima J, Robbins J (2013) Enhanced autophagy ameliorates cardiac proteinopathy. J Clin Invest 123: 5284–5297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billia F, Hauck L, Konecny F, Rao V, Shen J, Mak TW (2011) PTEN‐inducible kinase 1 (PINK1)/Park6 is indispensable for normal heart function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 9572–9577 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmingham CL, Smith AC, Bakowski MA, Yoshimori T, Brumell JH (2006) Autophagy controls Salmonella infection in response to damage to the Salmonella‐containing vacuole. J Biol Chem 281: 11374–11383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmingham CL, Canadien V, Kaniuk NA, Steinberg BE, Higgins DE, Brumell JH (2008) Listeriolysin O allows Listeria monocytogenes replication in macrophage vacuoles. Nature 451: 350–354 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland B, Kumar A, Lee S, Platt FM, Wegiel J, Yu WH, Nixon RA (2008) Autophagy induction and autophagosome clearance in neurons: relationship to autophagic pathology in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 28: 6926–6937 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonhoure A, Vallentin A, Martin M, Senff‐Ribeiro A, Amson R, Telerman A, Vidal M (2017) Acetylation of translationally controlled tumor protein promotes its degradation through chaperone‐mediated autophagy. Eur J Cell Biol 96: 83–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdenx M, Martin‐Segura A, Scrivo A, Rodriguez‐Navarro JA, Kaushik S, Tasset I, Diaz A, Storm NJ, Xin Q, Juste YRet al (2021) Chaperone‐mediated autophagy prevents collapse of the neuronal metastable proteome. Cell 184: 2696–2714.e2625 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boya P, Esteban‐Martinez L, Serrano‐Puebla A, Gomez‐Sintes R, Villarejo‐Zori B (2016) Autophagy in the eye: development, degeneration, and aging. Prog Retin Eye Res 55: 206–245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boya P, Codogno P, Rodriguez‐Muela N (2018) Autophagy in stem cells: repair, remodelling and metabolic reprogramming. Development 145: dev146506 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady OA, Meng P, Zheng Y, Mao Y, Hu F (2011) Regulation of TDP‐43 aggregation by phosphorylation and p62/SQSTM1. J Neurochem 116: 248–259 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2017) Autophagy and mitophagy in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 120: 1812–1824 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Sica V, Martins I, Pol J, Loos F, Maiuri MC, Durand S, Bossut N, Aprahamian F, Anagnostopoulos Get al (2019) Acyl‐CoA‐binding protein is a lipogenic factor that triggers food intake and obesity. Cell Metab 30: 754–767.e759 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brijmohan AS, Batchu SN, Majumder S, Alghamdi TA, Thieme K, McGaugh S, Liu Y, Advani SL, Bowskill BB, Kabir MGet al (2018) HDAC6 inhibition promotes transcription factor EB activation and is protective in experimental kidney disease. Front Pharmacol 9: 34 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown CN, Atwood D, Pokhrel D, Holditch SJ, Altmann C, Skrypnyk NI, Bourne J, Klawitter J, Blaine J, Faubel Set al (2021) Surgical procedures suppress autophagic flux in the kidney. Cell Death Dis 12: 248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant KL, Stalnecker CA, Zeitouni D, Klomp JE, Peng S, Tikunov AP, Gunda V, Pierobon M, Waters AM, George SDet al (2019) Combination of ERK and autophagy inhibition as a treatment approach for pancreatic cancer. Nat Med 25: 628–640 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno M, Lai Y‐C, Romero Y, Brands J, St. Croix CM, Kamga C, Corey C, Herazo‐Maya JD, Sembrat J, Lee JSet al (2015) PINK1 deficiency impairs mitochondrial homeostasis and promotes lung fibrosis. J Clin Invest 125: 521–538 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzlaff M, Hannan SB, Karsten P, Lenz S, Ng J, Voßfeldt H, Prüßing K, Pflanz R, Schulz JB, Rasse Tet al (2015) Impaired retrograde transport by the Dynein/Dynactin complex contributes to Tau‐induced toxicity. Hum Mol Genet 24: 3623–3637 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caballero B, Wang Y, Diaz A, Tasset I, Juste YR, Stiller B, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E, Cuervo AM (2018) Interplay of pathogenic forms of human tau with different autophagic pathways. Aging Cell 17: e12692 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caballero B, Bourdenx M, Luengo E, Diaz A, Sohn PD, Chen XU, Wang C, Juste YR, Wegmann S, Patel Bet al (2021) Acetylated tau inhibits chaperone‐mediated autophagy and promotes tau pathology propagation in mice. Nat Commun 12: 2238 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera S, Maciel M, Herrera I, Nava T, Vergara F, Gaxiola M, Lopez‐Otin C, Selman M, Pardo A (2015) Essential role for the ATG4B protease and autophagy in bleomycin‐induced pulmonary fibrosis. Autophagy 11: 670–684 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadwell K, Liu JY, Brown SL, Miyoshi H, Loh J, Lennerz JK, Kishi C, Kc W, Carrero JA, Hunt Set al (2008) A key role for autophagy and the autophagy gene Atg16l1 in mouse and human intestinal Paneth cells. Nature 456: 259–263 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadwell K, Patel KK, Komatsu M, Virgin HW, Stappenbeck TS (2009) A common role for Atg16L1, Atg5 and Atg7 in small intestinal Paneth cells and Crohn disease. Autophagy 5: 250–252 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadwell K, Patel KK, Maloney NS, Liu TC, Ng AC, Storer CE, Head RD, Xavier R, Stappenbeck TS, Virgin HW (2010) Virus‐plus‐susceptibility gene interaction determines Crohn's disease gene Atg16L1 phenotypes in intestine. Cell 141: 1135–1145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadwell K (2016) Crosstalk between autophagy and inflammatory signalling pathways: balancing defence and homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol 16: 661–675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill TJ, Leo V, Kelly M, Stockenhuber A, Kennedy NW, Bao L, Cereghetti G, Harper AR, Czibik G, Lao Cet al (2015) Resistance of dynamin‐related protein 1 oligomers to disassembly impairs mitophagy, resulting in myocardial inflammation and heart failure. J Biol Chem 290: 25907–25919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai J, Pires KM, Ferhat M, Chaurasia B, Buffolo MA, Smalling R, Sargsyan A, Atkinson DL, Summers SA, Graham TEet al (2018) Autophagy ablation in adipocytes induces insulin resistance and reveals roles for lipid peroxide and Nrf2 signaling in adipose‐liver crosstalk. Cell Rep 25: 1708–1717.e1705 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairo M, Villarroya J (2020) The role of autophagy in brown and beige adipose tissue plasticity. J Physiol Biochem 76: 213–226 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzo E, Clement C, Morozova K, Valdor R, Kaushik S, Almeida L, Follo C, Sahu R, Cuervo A, Macian Fet al (2012) Age‐related oxidative stress compromises endosomal proteostasis. Cell Rep 2: 136–149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carames B, Taniguchi N, Otsuki S, Blanco FJ, Lotz M (2010) Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal cartilage, and its aging‐related loss is linked with cell death and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62: 791–801 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carinci M, Testa B, Bordi M, Milletti G, Bonora M, Antonucci L, Ferraina C, Carro M, Kumar M, Ceglie Det al (2021) TFG binds LC3C to regulate ULK1 localization and autophagosome formation. EMBO J 40: e103563 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron E, Vincent K, Fortier M‐H, Laverdure J‐P, Bramoullé A, Hardy M‐P, Voisin G, Roux PP, Lemieux S, Thibault Pet al (2011) The MHC I immunopeptidome conveys to the cell surface an integrative view of cellular regulation. Mol Syst Biol 7: 533 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carosi JM, Hein LK, van den Hurk M, Adams R, Milky B, Singh S, Bardy C, Denton D, Kumar S, Sargeant TJ (2020) Retromer regulates the lysosomal clearance of MAPT/tau. Autophagy 1–21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carosi JM, Denton D, Kumar S, Sargeant TJ (2021) Retromer dysfunction at the nexus of tauopathies. Cell Death Differ 28: 884–899 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy LD, Young AR, Perez‐Mancera PA, Nimmervoll B, Jaulim A, Chen HC, McIntyre DJO, Brais R, Ricketts T, Pacey Set al (2018) A novel Atg5‐shRNA mouse model enables temporal control of autophagy in vivo . Autophagy 14: 1256–1266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy LD, Young ARJ, Young CNJ, Soilleux EJ, Fielder E, Weigand BM, Lagnado A, Brais R, Ktistakis NT, Wiggins KAet al (2020) Temporal inhibition of autophagy reveals segmental reversal of ageing with increased cancer risk. Nat Commun 11: 307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castets P, Frank S, Sinnreich M, Ruegg MA (2016) "Get the Balance Right": pathological significance of autophagy perturbation in neuromuscular disorders. J Neuromuscul Dis 3: 127–155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castoldi F, Vacchelli E, Zitvogel L, Maiuri MC, Pietrocola F, Kroemer G (2019) Systemic autophagy in the therapeutic response to anthracycline‐based chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology 8: e1498285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenni MC, Bonfanti L, Martinou JC, Ratto GM, Strettoi E, Maffei L (1996) Long‐term survival of retinal ganglion cells following optic nerve section in adult bcl‐2 transgenic mice. Eur J Neurosci 8: 1735–1745 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalasani ML, Kumari A, Radha V, Swarup G (2014) E50K‐OPTN‐induced retinal cell death involves the Rab GTPase‐activating protein, TBC1D17 mediated block in autophagy. PLoS One 9: e95758 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang MC, Srinivasan K, Friedman BA, Suto E, Modrusan Z, Lee WP, Kaminker JS, Hansen DV, Sheng M (2017) Progranulin deficiency causes impairment of autophagy and TDP‐43 accumulation. J Exp Med 214: 2611–2628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang NC (2020) Autophagy and stem cells: self‐eating for self‐renewal. Front Cell Dev Biol 8: 138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao X, Wang S, Zhao K, Li Y, Williams JA, Li T, Chavan H, Krishnamurthy P, He XC, Li Let al (2018) Impaired TFEB‐mediated lysosome biogenesis and autophagy promote chronic ethanol‐induced liver injury and steatosis in mice. Gastroenterology 155: 865–879.e812 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen ZH, Lam HC, Jin Y, Kim HP, Cao J, Lee SJ, Ifedigbo E, Parameswaran H, Ryter SW, Choi AM (2010) Autophagy protein microtubule‐associated protein 1 light chain‐3B (LC3B) activates extrinsic apoptosis during cigarette smoke‐induced emphysema. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 18880–18885 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J, Ma Z, Jiao X, Fariss R, Kantorow W, Kantorow M, Pras E, Frydman M, Pras E, Riazuddin Set al (2011) Mutations in FYCO1 cause autosomal‐recessive congenital cataracts. Am J Hum Genet 88: 827–838 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Dorn GW 2nd (2013) PINK1‐phosphorylated mitofusin 2 is a Parkin receptor for culling damaged mitochondria. Science 340: 471–475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Sawada O, Kohno H, Le YZ, Subauste C, Maeda T, Maeda A (2013) Autophagy protects the retina from light‐induced degeneration. J Biol Chem 288: 7506–7518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X, Wang K, Xing Y, Tu J, Yang X, Zhao Q, Li K, Chen Z (2014) Coronavirus membrane‐associated papain‐like proteases induce autophagy through interacting with Beclin 1 to negatively regulate antiviral innate immunity. Protein Cell 5: 912–927 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D, Xie J, Fiskesund R, Dong W, Liang X, Lv J, Jin X, Liu J, Mo S, Zhang Tet al (2018a) Chloroquine modulates antitumor immune response by resetting tumor‐associated macrophages toward M1 phenotype. Nat Commun 9: 873 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K, Dai H, Yuan J, Chen J, Lin L, Zhang W, Wang L, Zhang J, Li K, He Y (2018b) Optineurin‐mediated mitophagy protects renal tubular epithelial cells against accelerated senescence in diabetic nephropathy. Cell Death Dis 9: 105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X, He Y, Lu F (2018c) Autophagy in stem cell biology: a perspective on stem cell self‐renewal and differentiation. Stem Cells Int 2018: 9131397 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K, Feng L, Hu W, Chen J, Wang X, Wang L, He Y (2019) Optineurin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation by enhancing mitophagy of renal tubular cells in diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J 33: 4571–4585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H‐C, Kim SR, Oo TF, Kareva T, Yarygina O, Rzhetskaya M, Wang C, During M, Talloczy Z, Tanaka Ket al (2011) Akt suppresses retrograde degeneration of dopaminergic axons by inhibition of macroautophagy. J Neurosci 31: 2125–2135 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherra SJ 3rd, Chu CT (2008) Autophagy in neuroprotection and neurodegeneration: a question of balance. Future Neurol 3: 309–323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherra SJ 3rd, Kulich SM, Uechi G, Balasubramani M, Mountzouris J, Day BW, Chu CT (2010) Regulation of the autophagy protein LC3 by phosphorylation. J Cell Biol 190: 533–539 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi Z‐L, Akahori M, Obazawa M, Minami M, Noda T, Nakaya N, Tomarev S, Kawase K, Yamamoto T, Noda Set al (2010) Overexpression of optineurin E50K disrupts Rab8 interaction and leads to a progressive retinal degeneration in mice. Hum Mol Genet 19: 2606–2615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi J, Jo M, Lee E, Oh YK, Choi D (2012) The role of autophagy in human endometrium. Biol Reprod 86: 70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi AM, Ryter SW, Levine B (2013) Autophagy in human health and disease. N Engl J Med 368: 651–662 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y, Bowman JW, Jung JU (2018) Autophagy during viral infection ‐ a double‐edged sword. Nat Rev Microbiol 16: 341–354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi I, Zhang Y, Seegobin SP, Pruvost M, Wang Q, Purtell K, Zhang B, Yue Z (2020) Microglia clear neuron‐released alpha‐synuclein via selective autophagy and prevent neurodegeneration. Nat Commun 11: 1386 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi ME (2020) Autophagy in kidney disease. Annu Rev Physiol 82: 297–322 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong CM, Ke M, Tan Y, Huang Z, Zhang K, Ai N, Ge W, Qin D, Lu JH, Su H (2018) Presenilin 1 deficiency suppresses autophagy in human neural stem cells through reducing gamma‐secretase‐independent ERK/CREB signaling. Cell Death Dis 9: 879 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chourasia AH, Tracy K, Frankenberger C, Boland ML, Sharifi MN, Drake LE, Sachleben JR, Asara JM, Locasale JW, Karczmar GSet al (2015) Mitophagy defects arising from BNip3 loss promote mammary tumor progression to metastasis. EMBO Rep 16: 1145–1163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrisam M, Pirozzi M, Castagnaro S, Blaauw B, Polishchuck R, Cecconi F, Grumati P, Bonaldo P (2015) Reactivation of autophagy by spermidine ameliorates the myopathic defects of collagen VI‐null mice. Autophagy 11: 2142–2152 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu CT, Ji J, Dagda RK, Jiang JF, Tyurina YY, Kapralov AA, Tyurin VA, Yanamala N, Shrivastava IH, Mohammadyani Det al (2013) Cardiolipin externalization to the outer mitochondrial membrane acts as an elimination signal for mitophagy in neuronal cells. Nat Cell Biol 15: 1197–1205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu H, Khosravi A, Kusumawardhani IP, Kwon AHK, Vasconcelos AC, Cunha LD, Mayer AE, Shen Y, Wu W‐L, Kambal Aet al (2016) Gene‐microbiota interactions contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Science 352: 1116–1120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu CT (2019) Mechanisms of selective autophagy and mitophagy: implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Dis 122: 23–34 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianfanelli V, Fuoco C, Lorente M, Salazar M, Quondamatteo F, Gherardini PF, De Zio D, Nazio F, Antonioli M, D’Orazio Met al (2015) AMBRA1 links autophagy to cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by promoting c‐Myc dephosphorylation and degradation. Nat Cell Biol 17: 20–30 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchini M, Chakrabarti R, Kongara S, Price S, Nahar R, Lozy F, Zhong H, Vazquez A, Kang Y, Karantza V (2014) Autophagy regulator BECN1 suppresses mammary tumorigenesis driven by WNT1 activation and following parity. Autophagy 10: 2036–2052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinque L, Forrester A, Bartolomeo R, Svelto M, Venditti R, Montefusco S, Polishchuk E, Nusco E, Rossi A, Medina DLet al (2015) FGF signalling regulates bone growth through autophagy. Nature 528: 272–275 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke AJ, Ellinghaus U, Cortini A, Stranks A, Simon AK, Botto M, Vyse TJ (2015) Autophagy is activated in systemic lupus erythematosus and required for plasmablast development. Ann Rheum Dis 74: 912–920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke AJ, Simon AK (2019) Autophagy in the renewal, differentiation and homeostasis of immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol 19: 170–183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloonan SM, Choi AM (2016) Mitochondria in lung disease. J Clin Invest 126: 809–820 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cong Y, Dinesh Kumar N, Mauthe M, Verlhac P, Reggiori F (2020) Manipulation of selective macroautophagy by pathogens at a glance. J Cell Sci 133: jcs240440 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway O, Akpinar HA, Rogov VV, Kirkin V (2020) Selective autophagy receptors in neuronal health and disease. J Mol Biol 432: 2483–2509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coryell PR, Diekman BO, Loeser RF (2021) Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 17: 47–57 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupe B, Ishii Y, Dietrich MO, Komatsu M, Horvath TL, Bouret SG (2012) Loss of autophagy in pro‐opiomelanocortin neurons perturbs axon growth and causes metabolic dysregulation. Cell Metab 15: 247–255 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crippa V, Sau D, Rusmini P, Boncoraglio A, Onesto E, Bolzoni E, Galbiati M, Fontana E, Marino M, Carra Set al (2010) The small heat shock protein B8 (HspB8) promotes autophagic removal of misfolded proteins involved in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Hum Mol Genet 19: 3440–3456 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo AM, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R, Lansbury PT, Sulzer D (2004) Impaired degradation of mutant alpha‐synuclein by chaperone‐mediated autophagy. Science 305: 1292–1295 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha LD, Yang M, Carter R, Guy C, Harris L, Crawford JC, Quarato G, Boada‐Romero E, Kalkavan H, Johnson MDLet al (2018) LC3‐associated phagocytosis in myeloid cells promotes tumor immune tolerance. Cell 175: 429–441.e416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai E, Han L, Liu J, Xie Y, Kroemer G, Klionsky DJ, Zeh HJ, Kang R, Wang J, Tang D (2020) Autophagy‐dependent ferroptosis drives tumor‐associated macrophage polarization via release and uptake of oncogenic KRAS protein. Autophagy 16: 2069–2083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas SL, Xie Y, Shiflett LA, Ueki Y (2018) Mouse cre models for the study of bone diseases. Curr Osteoporos Rep 16: 466–477 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Palma C, Morisi F, Cheli S, Pambianco S, Cappello V, Vezzoli M, Rovere‐Querini P, Moggio M, Ripolone M, Francolini Met al (2014) Autophagy as a new therapeutic target in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cell Death Dis 5: e1363 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decressac M, Mattsson B, Weikop P, Lundblad M, Jakobsson J, Bjorklund A (2013) TFEB‐mediated autophagy rescues midbrain dopamine neurons from alpha‐synuclein toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: E1817–E1826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Z, Lim J, Wang Q, Purtell K, Wu S, Palomo GM, Tan H, Manfredi G, Zhao Y, Peng Jet al (2020) ALS‐FTLD‐linked mutations of SQSTM1/p62 disrupt selective autophagy and NFE2L2/NRF2 anti‐oxidative stress pathway. Autophagy 16: 917–931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Z, Li X, Blanca Ramirez M, Purtell K, Choi I, Lu JH, Yu Q, Yue Z (2021) Selective autophagy of AKAP11 activates cAMP/PKA to fuel mitochondrial metabolism and tumor cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118: e2020215118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V (2021) Autophagy in inflammation, infection, and immunometabolism. Immunity 54: 437–453 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSelm CJ, Miller BC, Zou W, Beatty WL, van Meel E, Takahata Y, Klumperman J, Tooze SA, Teitelbaum SL, Virgin HW (2011) Autophagy proteins regulate the secretory component of osteoclastic bone resorption. Dev Cell 21: 966–974 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaraj SG, Wang N, Chen Z, Chen Z, Tseng M, Barretto N, Lin R, Peters CJ, Tseng C‐T, Baker SCet al (2007) Regulation of IRF‐3‐dependent innate immunity by the papain‐like protease domain of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J Biol Chem 282: 32208–32221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVorkin L, Pavey N, Carleton G, Comber A, Ho C, Lim J, McNamara E, Huang H, Kim P, Zacharias LGet al (2019) Autophagy regulation of metabolism is required for CD8(+) T cell anti‐tumor immunity. Cell Rep 27: 502–513.e505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Leo L, Bodemeyer V, Bosisio FM, Claps G, Carretta M, Rizza S, Faienza F, Frias A, Khan S, Bordi Met al (2021) Loss of Ambra1 promotes melanoma growth and invasion. Nat Commun 12: 2550 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rienzo M, Antonioli M, Fusco C, Liu Y, Mari M, Orhon I, Refolo G, Germani F, Corazzari M, Romagnoli Aet al (2019) Autophagy induction in atrophic muscle cells requires ULK1 activation by TRIM32 through unanchored K63‐linked polyubiquitin chains. Sci Adv 5: eaau8857 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikic I, Elazar Z (2018) Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19: 349–364 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding WX, Li M, Chen X, Ni HM, Lin CW, Gao W, Lu B, Stolz DB, Clemens DL, Yin XM (2010) Autophagy reduces acute ethanol‐induced hepatotoxicity and steatosis in mice. Gastroenterology 139: 1740–1752 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding Y, Kim S, Lee SY, Koo JK, Wang Z, Choi ME (2014) Autophagy regulates TGF‐beta expression and suppresses kidney fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Am Soc Nephrol 25: 2835–2846 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding Z‐B, Fu X‐T, Shi Y‐H, Zhou J, Peng Y‐F, Liu W‐R, Shi G‐M, Gao Q, Wang X‐Y, Song Ket al (2016) Lamp2a is required for tumor growth and promotes tumor recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol 49: 2367–2376 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong S, Wang Q, Kao YR, Diaz A, Tasset I, Kaushik S, Thiruthuvanathan V, Zintiridou A, Nieves E, Dzieciatkowska Met al (2021a) Chaperone‐mediated autophagy sustains haematopoietic stem‐cell function. Nature 591: 117–123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X, Yang Y, Zou Z, Zhao Y, Ci B, Zhong L, Bhave M, Wang L, Kuo YC, Zang Xet al (2021b) Sorting nexin 5 mediates virus‐induced autophagy and immunity. Nature 589: 456–461 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn GW 2nd (2010) Mitochondrial pruning by Nix and BNip3: an essential function for cardiac‐expressed death factors. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 3: 374–383 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower CM, Wills CA, Frisch SM, Wang HG (2018) Mechanisms and context underlying the role of autophagy in cancer metastasis. Autophagy 14: 1110–1128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duewell P, Kono H, Rayner KJ, Sirois CM, Vladimer G, Bauernfeind FG, Abela GS, Franchi L, Nuñez G, Schnurr Met al (2010) NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature 464: 1357–1361 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont N, Nascimbeni AC, Morel E, Codogno P (2017) Molecular mechanisms of noncanonical autophagy. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 328: 1–23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzamko N, Geczy CL, Halliday GM (2015) Inflammation is genetically implicated in Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience 302: 89–102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E X, Hwang S, Oh S, Lee JS, Jeong JH, Gwack Y, Kowalik TF, Sun R, Jung JU, Liang C (2009) Viral Bcl‐2‐mediated evasion of autophagy aids chronic infection of gammaherpesvirus 68. PLoS Pathog 5: e1000609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebato C, Uchida T, Arakawa M, Komatsu M, Ueno T, Komiya K, Azuma K, Hirose T, Tanaka K, Kominami Eet al (2008) Autophagy is important in islet homeostasis and compensatory increase of beta cell mass in response to high‐fat diet. Cell Metab 8: 325–332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan D, Chun M, Vamos M, Zou H, Rong J, Miller C, Lou H, Raveendra‐Panickar D, Yang C‐C, Sheffler Det al (2015) Small molecule inhibition of the autophagy kinase ULK1 and identification of ULK1 substrates. Mol Cell 59: 285–297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggermann K, Gess B, Hausler M, Weis J, Hahn A, Kurth I (2018) Hereditary neuropathies. Dtsch Arztebl Int 115: 91–97 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg T, Abdellatif M, Schroeder S, Primessnig U, Stekovic S, Pendl T, Harger A, Schipke J, Zimmermann A, Schmidt Aet al (2016) Cardioprotection and lifespan extension by the natural polyamine spermidine. Nat Med 22: 1428–1438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban‐Martínez L, Sierra‐Filardi E, McGreal RS, Salazar‐Roa M, Mariño G, Seco E, Durand S, Enot D, Graña O, Malumbres Met al (2017) Programmed mitophagy is essential for the glycolytic switch during cell differentiation. EMBO J 36: 1688–1706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairlie WD, Tran S, Lee EF (2020) Crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy signaling pathways. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 352: 115–158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J, Kou X, Jia S, Yang X, Yang Y, Chen N (2016) Autophagy as a potential target for sarcopenia. J Cell Physiol 231: 1450–1459 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang EF, Hou Y, Palikaras K, Adriaanse BA, Kerr JS, Yang B, Lautrup S, Hasan‐Olive MM, Caponio D, Dan Xet al (2019) Mitophagy inhibits amyloid‐beta and tau pathology and reverses cognitive deficits in models of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Neurosci 22: 401–412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez AF, Barcena C, Martinez‐Garcia GG, Tamargo‐Gomez I, Suarez MF, Pietrocola F, Castoldi F, Esteban L, Sierra‐Filardi E, Boya Pet al (2017) Autophagy couteracts weight gain, lipotoxicity and pancreatic beta‐cell death upon hypercaloric pro‐diabetic regimens. Cell Death Dis 8: e2970 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández ÁF, Sebti S, Wei Y, Zou Z, Shi M, McMillan KL, He C, Ting T, Liu Y, Chiang W‐Cet al (2018) Disruption of the beclin 1‐BCL2 autophagy regulatory complex promotes longevity in mice. Nature 558: 136–140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetalvero KM, Yu Y, Goetschkes M, Liang G, Valdez RA, Gould TY, Triantafellow E, Bergling S, Loureiro J, Eash Jet al (2013) Defective autophagy and mTORC1 signaling in myotubularin null mice. Mol Cell Biol 33: 98–110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filimonenko M, Stuffers S, Raiborg C, Yamamoto A, Malerod L, Fisher EM, Isaacs A, Brech A, Stenmark H, Simonsen A (2007) Functional multivesicular bodies are required for autophagic clearance of protein aggregates associated with neurodegenerative disease. J Cell Biol 179: 485–500 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiskin E, Bionda T, Dikic I, Behrends C (2016) Global analysis of host and bacterial ubiquitinome in response to Salmonella Typhimurium infection. Mol Cell 62: 967–981 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming A, Rubinsztein DC (2020) Autophagy in neuronal development and plasticity. Trends Neurosci 43: 767–779 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester A, De Leonibus C, Grumati P, Fasana E, Piemontese M, Staiano L, Fregno I, Raimondi A, Marazza A, Bruno Get al (2019) A selective ER‐phagy exerts procollagen quality control via a Calnexin‐FAM134B complex. EMBO J 38: e99847 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox LM, Kim K, Johnson CW, Chen S, Croce KR, Victor MB, Eenjes E, Bosco JR, Randolph LK, Dragatsis Iet al (2020) Huntington's disease pathogenesis is modified in vivo by Alfy/Wdfy3 and selective macroautophagy. Neuron 105: 813–821.e816 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraiberg M, Tamim‐Yecheskel BC, Kokabi K, Subic N, Heimer G, Eck F, Nalbach K, Behrends C, Ben‐Zeev B, Shatz Oet al (2020) Lysosomal targeting of autophagosomes by the TECPR domain of TECPR2. Autophagy: 1–13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fregno I, Fasana E, Bergmann TJ, Raimondi A, Loi M, Solda T, Galli C, D'Antuono R, Morone D, Danieli Aet al (2018) ER‐to‐lysosome‐associated degradation of proteasome‐resistant ATZ polymers occurs via receptor‐mediated vesicular transport. EMBO J 37: e99259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal J, Strom AL, Kwinter DM, Kilty R, Zhang J, Shi P, Fu W, Wooten MW, Zhu H (2009) Sequestosome 1/p62 links familial ALS mutant SOD1 to LC3 via an ubiquitin‐independent mechanism. J Neurochem 111: 1062–1073 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Levine B, Kroemer G (2014) Metabolic control of autophagy. Cell 159: 1263–1276 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Buque A, Kepp O, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2015a) Immunological effects of conventional chemotherapy and targeted anticancer agents. Cancer Cell 28: 690–714 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Amaravadi RK, Baehrecke EH, Cecconi F, Codogno P, Debnath J, Gewirtz DA, Karantza Vet al (2015b) Autophagy in malignant transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J 34: 856–880 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Blomgren K, Kroemer G (2016) Autophagy in acute brain injury. Nat Rev Neurosci 17: 467–484 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Baehrecke EH, Ballabio A, Boya P, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Cecconi F, Choi AM, Chu CT, Codogno P, Colombo MIet al (2017a) Molecular definitions of autophagy and related processes. EMBO J 36: 1811–1836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Demaria S, Formenti SC, Kroemer G (2017b) Activating autophagy to potentiate immunogenic chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14: 247–258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Levine B, Green DR, Kroemer G (2017c) Pharmacological modulation of autophagy: therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16: 487–511 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Buque A, Kepp O, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2017d) Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol 17: 97–111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Chan TA, Kroemer G, Wolchok JD, Lopez‐Soto A (2018a) The hallmarks of successful anticancer immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med 10: eaat7807 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Amelio I, Andrews DWet al (2018b) Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ 25: 486–541 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Yamazaki T, Kroemer G (2018c) Linking cellular stress responses to systemic homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19: 731–745 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Green DR (2019) Autophagy‐independent functions of the autophagy machinery. Cell 177: 1682–1699 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Humeau J, Buque A, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2020a) Immunostimulation with chemotherapy in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17: 725–741 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Warren S, Adjemian S, Agostinis P, Martinez AB, Chan TA, Coukos G, Demaria S, Deutsch Eet al (2020b) Consensus guidelines for the definition, detection and interpretation of immunogenic cell death. J Immunother Cancer 8: e000337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García‐Prat L, Martínez‐Vicente M, Perdiguero E, Ortet L, Rodríguez‐Ubreva J, Rebollo E, Ruiz‐Bonilla V, Gutarra S, Ballestar E, Serrano ALet al (2016) Autophagy maintains stemness by preventing senescence. Nature 529: 37–42 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg AD, Dudek AM, Agostinis P (2013) Calreticulin surface exposure is abrogated in cells lacking, chaperone‐mediated autophagy‐essential gene, LAMP2A. Cell Death Dis 4: e826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg AD, Krysko DV, Vandenabeele P, Agostinis P (2016) Extracellular ATP and P(2)X(7) receptor exert context‐specific immunogenic effects after immunogenic cancer cell death. Cell Death Dis 7: e2097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassen NC, Niemeyer D, Muth D, Corman VM, Martinelli S, Gassen A, Hafner K, Papies J, Mösbauer K, Zellner Aet al (2019) SKP2 attenuates autophagy through Beclin 1‐ubiquitination and its inhibition reduces MERS‐Coronavirus infection. Nat Commun 10: 5770 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauron MC, Newton AC, Colombo MI (2021) PKCalpha is recruited to Staphylococcus aureus‐containing phagosomes and impairs bacterial replication by inhibition of autophagy. Front Immunol 12: 662987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier J, Meijer IA, Lessel D, Mencacci NE, Krainc D, Hempel M, Tsiakas K, Prokisch H, Rossignol E, Helm MHet al (2018) Recessive mutations in VPS13D cause childhood onset movement disorders. Ann Neurol 83: 1089–1095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier CA, Kitada T, Shen J (2008) Loss of PINK1 causes mitochondrial functional defects and increased sensitivity to oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 11364–11369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbino V, Kaunga E, Ye J, Canzio D, O'Keeffe S, Rudnick ND, Guarnieri P, Lutz CM, Maniatis T (2020) The loss of TBK1 kinase activity in motor neurons or in all cell types differentially impacts ALS disease progression in SOD1 mice. Neuron 106: 789–805.e785 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomello M, Pyakurel A, Glytsou C, Scorrano L (2020) The cell biology of mitochondrial membrane dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21: 204–224 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatigny M, Moriceau S, Rivagorda M, Ramos‐Brossier M, Nascimbeni AC, Lante F, Shanley MR, Boudarene N, Rousseaud A, Friedman AKet al (2019) Autophagy is required for memory formation and reverses age‐related memory decline. Curr Biol 29: 435–448.e438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick D, Zhang W, Beaton M, Marsboom G, Gruber M, Simon MC, Hart J, Dorn GW 2nd, Brady MJ, Macleod KF (2012) BNip3 regulates mitochondrial function and lipid metabolism in the liver. Mol Cell Biol 32: 2570–2584 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goginashvili A, Zhang Z, Erbs E, Spiegelhalter C, Kessler P, Mihlan M, Pasquier A, Krupina K, Schieber N, Cinque Let al (2015) Insulin granules. Insulin secretory granules control autophagy in pancreatic beta cells. Science 347: 878–882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gohel R, Kournoutis A, Petridi S, Nezis IP (2020) Molecular mechanisms of selective autophagy in Drosophila . Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 354: 63–105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg MS, Fleming SM, Palacino JJ, Cepeda C, Lam HA, Bhatnagar A, Meloni EG, Wu N, Ackerson LC, Klapstein GJet al (2003) Parkin‐deficient mice exhibit nigrostriatal deficits but not loss of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem 278: 43628–43635 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes LC, Dikic I (2014) Autophagy in antimicrobial immunity. Mol Cell 54: 224–233 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes LR, Menck CFM, Cuervo AM (2017) Chaperone‐mediated autophagy prevents cellular transformation by regulating MYC proteasomal degradation. Autophagy 13: 928–940 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez‐Sanchez JA, Carty L, Iruarrizaga‐Lejarreta M, Palomo‐Irigoyen M, Varela‐Rey M, Griffith M, Hantke J, Macias‐Camara N, Azkargorta M, Aurrekoetxea Iet al (2015) Schwann cell autophagy, myelinophagy, initiates myelin clearance from injured nerves. J Cell Biol 210: 153–168 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong G, Song M, Csordas G, Kelly DP, Matkovich SJ, Dorn GW 2nd (2015) Parkin‐mediated mitophagy directs perinatal cardiac metabolic maturation in mice. Science 350: aad2459 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goode A, Butler K, Long J, Cavey J, Scott D, Shaw B, Sollenberger J, Gell C, Johansen T, Oldham NJet al (2016) Defective recognition of LC3B by mutant SQSTM1/p62 implicates impairment of autophagy as a pathogenic mechanism in ALS‐FTLD. Autophagy 12: 1094–1104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracia‐Sancho J, Guixe‐Muntet S (2018) The many‐faced role of autophagy in liver diseases. J Hepatol 68: 593–594 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieco G, Janssens V, Gaide Chevronnay HP, N’Kuli F, Van Der Smissen P, Wang T, Shan J, Vainio S, Bilanges B, Jouret Fet al (2018) Vps34/PI3KC3 deletion in kidney proximal tubules impairs apical trafficking and blocks autophagic flux, causing a Fanconi‐like syndrome and renal insufficiency. Sci Rep 8: 14133 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumati P, Coletto L, Sabatelli P, Cescon M, Angelin A, Bertaggia E, Blaauw B, Urciuolo A, Tiepolo T, Merlini Let al (2010) Autophagy is defective in collagen VI muscular dystrophies, and its reactivation rescues myofiber degeneration. Nat Med 16: 1313–1320 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gstrein T, Edwards A, Přistoupilová A, Leca I, Breuss M, Pilat‐Carotta S, Hansen AH, Tripathy R, Traunbauer AK, Hochstoeger Tet al (2018) Mutations in Vps15 perturb neuronal migration in mice and are associated with neurodevelopmental disease in humans. Nat Neurosci 21: 207–217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan JL, Simon AK, Prescott M, Menendez JA, Liu F, Wang F, Wang C, Wolvetang E, Vazquez‐Martin A, Zhang J (2013) Autophagy in stem cells. Autophagy 9: 830–849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guelly C, Zhu P‐P, Leonardis L, Papić L, Zidar J, Schabhüttl M, Strohmaier H, Weis J, Strom TM, Baets Jet al (2011) Targeted high‐throughput sequencing identifies mutations in atlastin‐1 as a cause of hereditary sensory neuropathy type I. Am J Hum Genet 88: 99–105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gui Y‐S, Wang L, Tian X, Li X, Ma A, Zhou W, Zeng NI, Zhang JI, Cai B, Zhang Het al (2015) mTOR overactivation and compromised autophagy in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One 10: e0138625 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo JY, Karsli‐Uzunbas G, Mathew R, Aisner SC, Kamphorst JJ, Strohecker AM, Chen G, Price S, Lu W, Teng Xet al (2013) Autophagy suppresses progression of K‐ras‐induced lung tumors to oncocytomas and maintains lipid homeostasis. Genes Dev 27: 1447–1461 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusdon AM, Zhu J, Van Houten B, Chu CT (2012) ATP13A2 regulates mitochondrial bioenergetics through macroautophagy. Neurobiol Dis 45: 962–972 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez MG, Master SS, Singh SB, Taylor GA, Colombo MI, Deretic V (2004) Autophagy is a defense mechanism inhibiting BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in infected macrophages. Cell 119: 753–766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez MG, Saka HA, Chinen I, Zoppino FC, Yoshimori T, Bocco JL, Colombo MI (2007) Protective role of autophagy against Vibrio cholerae cytolysin, a pore‐forming toxin from V. cholerae . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 1829–1834 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habib A, Chokr D, Wan JH, Hegde P, Mabire M, Siebert M, Ribeiro‐Parenti L, Le Gall M, Lettéron P, Pilard Net al (2019) Inhibition of monoacylglycerol lipase, an anti‐inflammatory and antifibrogenic strategy in the liver. Gut 68: 522–532 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall AR, Burke N, Dongworth RK, Kalkhoran SB, Dyson A, Vicencio JM, Dorn GW II, Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ (2016) Hearts deficient in both Mfn1 and Mfn2 are protected against acute myocardial infarction. Cell Death Dis 7: e2238 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammoutene A, Biquard L, Lasselin J, Kheloufi M, Tanguy M, Vion A‐C, Mérian J, Colnot N, Loyer X, Tedgui Aet al (2020) A defect in endothelial autophagy occurs in patients with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis and promotes inflammation and fibrosis. J Hepatol 72: 528–538 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han QI, Deng Y, Chen S, Chen R, Yang M, Zhang Z, Sun X, Wang W, He Y, Wang Fet al (2017) Downregulation of ATG5‐dependent macroautophagy by chaperone‐mediated autophagy promotes breast cancer cell metastasis. Sci Rep 7: 4759 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C, Zhang C, Wang H, Zhao L (2021) Exosome‐mediated communication between tumor cells and tumor‐associated macrophages: implications for tumor microenvironment. Oncoimmunology 10: 1887552 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen MD, Johnsen IB, Stiberg KA, Sherstova T, Wakita T, Richard GM, Kandasamy RK, Meurs EF, Anthonsen MW (2017) Hepatitis C virus triggers Golgi fragmentation and autophagy through the immunity‐related GTPase M. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114: E3462–E3471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M, Rubinsztein DC, Walker DW (2018) Autophagy as a promoter of longevity: insights from model organisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19: 579–593 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao Y, Kacal M, Ouchida AT, Zhang B, Norberg E, Vakifahmetoglu‐Norberg H (2019) Targetome analysis of chaperone‐mediated autophagy in cancer cells. Autophagy 15: 1558–1571 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T, Nakamura K, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakahara Y, Suzuki‐Migishima R, Yokoyama M, Mishima K, Saito I, Okano Het al (2006) Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature 441: 885–889 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartleben B, Gödel M, Meyer‐Schwesinger C, Liu S, Ulrich T, Köbler S, Wiech T, Grahammer F, Arnold SJ, Lindenmeyer MTet al (2010) Autophagy influences glomerular disease susceptibility and maintains podocyte homeostasis in aging mice. J Clin Invest 120: 1084–1096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K, Taura M, Iwasaki A (2018) The interaction between IKKalpha and LC3 promotes type I interferon production through the TLR9‐containing LAPosome. Sci Signal 11: eaan4144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazari Y, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Hetz C, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G (2020) Autophagy in hepatic adaptation to stress. J Hepatol 72: 183–196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He C, Klionsky DJ (2009) Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet 43: 67–93 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He C, Bassik MC, Moresi V, Sun K, Wei Y, Zou Z, An Z, Loh J, Fisher J, Sun Qet al (2012) Exercise‐induced BCL2‐regulated autophagy is required for muscle glucose homeostasis. Nature 481: 511–515 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He C, Wei Y, Sun K, Li B, Dong X, Zou Z, Liu Y, Kinch L, Khan S, Sinha Set al (2013) Beclin 2 functions in autophagy, degradation of G protein‐coupled receptors, and metabolism. Cell 154: 1085–1099 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He A, Chen X, Tan M, Chen Y, Lu D, Zhang X, Dean JM, Razani B, Lodhi IJ (2020) Acetyl‐CoA derived from hepatic peroxisomal beta‐oxidation inhibits autophagy and promotes steatosis via mTORC1 activation. Mol Cell 79: 30–42.e34 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton NS, Perera R, Berger KL, Khadka S, Lacount DJ, Kuhn RJ, Randall G (2010) Dengue virus nonstructural protein 3 redistributes fatty acid synthase to sites of viral replication and increases cellular fatty acid synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 17345–17350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann BL, Green DR (2019) LC3‐associated phagocytosis at a glance. J Cell Sci 132: jcs222984 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann BL, Teubner BJW, Tummers B, Boada‐Romero E, Harris L, Yang M, Guy CS, Zakharenko SS, Green DR (2019) LC3‐associated endocytosis facilitates beta‐amyloid clearance and mitigates neurodegeneration in murine Alzheimer's disease. Cell 178: 536–551.e514 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann BL, Teubner BJW, Boada‐Romero E, Tummers B, Guy C, Fitzgerald P, Mayer U, Carding S, Zakharenko SS, Wileman Tet al (2020) Noncanonical function of an autophagy protein prevents spontaneous Alzheimer's disease. Sci Adv 6: eabb9036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer G, Oz‐Levi D, Eyal E, Edvardson S, Nissenkorn A, Ruzzo EK, Szeinberg A, Maayan C, Mai‐Zahav M, Efrati Oet al (2016) TECPR2 mutations cause a new subtype of familial dysautonomia like hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy with intellectual disability. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 20: 69–79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henault J, Martinez J, Riggs J, Tian J, Mehta P, Clarke L, Sasai M, Latz E, Brinkmann M, Iwasaki Aet al (2012) Noncanonical autophagy is required for type I interferon secretion in response to DNA‐immune complexes. Immunity 37: 986–997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning RH, Brundel B (2017) Proteostasis in cardiac health and disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 14: 637–653 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez‐Gea V, Ghiassi‐Nejad Z, Rozenfeld R, Gordon R, Fiel MI, Yue Z, Czaja MJ, Friedman SL (2012) Autophagy releases lipid that promotes fibrogenesis by activated hepatic stellate cells in mice and in human tissues. Gastroenterology 142: 938–946 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetz C, Thielen P, Matus S, Nassif M, Court F, Kiffin R, Martinez G, Cuervo AM, Brown RH, Glimcher LH (2009) XBP‐1 deficiency in the nervous system protects against amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by increasing autophagy. Genes Dev 23: 2294–2306 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt G, Korolchuk VI (2017) Repair, reuse, recycle: the expanding role of autophagy in genome maintenance. Trends Cell Biol 27: 340–351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt J, Porter K, Dixon A, McKinnon S, Liton PB (2018) Contribution of autophagy to ocular hypertension and neurodegeneration in the DBA/2J spontaneous glaucoma mouse model. Cell Death Discov 4: 14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill SE, Colon‐Ramos DA (2020) The journey of the synaptic autophagosome: a cell biological perspective. Neuron 105: 961–973 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiruma Y, Kurihara N, Subler MA, Zhou H, Boykin CS, Zhang H, Ishizuka S, Dempster DW, Roodman GD, Windle JJ (2008) A SQSTM1/p62 mutation linked to Paget's disease increases the osteoclastogenic potential of the bone microenvironment. Hum Mol Genet 17: 3708–3719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho WY, Tai YK, Chang J‐C, Liang J, Tyan S‐H, Chen S, Guan J‐L, Zhou H, Shen H‐M, Koo Eet al (2019) The ALS‐FTD‐linked gene product, C9orf72, regulates neuronal morphogenesis via autophagy. Autophagy 15: 827–842 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdgaard SG, Cianfanelli V, Pupo E, Lambrughi M, Lubas M, Nielsen JC, Eibes S, Maiani E, Harder LM, Wesch Net al (2019) Selective autophagy maintains centrosome integrity and accurate mitosis by turnover of centriolar satellites. Nat Commun 10: 4176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood DA, Memme JM, Oliveira AN, Triolo M (2019) Maintenance of skeletal muscle mitochondria in health, exercise, and aging. Annu Rev Physiol 81: 19–41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori I, Otomo T, Nakashima M, Miya F, Negishi Y, Shiraishi H, Nonoda Y, Magara S, Tohyama J, Okamoto Net al (2017) Defects in autophagosome‐lysosome fusion underlie Vici syndrome, a neurodevelopmental disorder with multisystem involvement. Sci Rep 7: 3552 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino A, Mita Y, Okawa Y, Ariyoshi M, Iwai‐Kanai E, Ueyama T, Ikeda K, Ogata T, Matoba S (2013) Cytosolic p53 inhibits Parkin‐mediated mitophagy and promotes mitochondrial dysfunction in the mouse heart. Nat Commun 4: 2308 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X, Zhang G, Bai X, Liang T (2020) Reviving the role of MET in liver cancer therapy and vaccination: an autophagic perspective. Oncoimmunology 9: 1818438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard VM, Valdor R, Patel B, Singh R, Cuervo AM, Macian F (2010) Macroautophagy regulates energy metabolism during effector T cell activation. J Immunol 185: 7349–7357 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbi ME, Hu H, Kshitiz AI, Levchenko A, Semenza GL (2013) Chaperone‐mediated autophagy targets hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1alpha (HIF‐1alpha) for lysosomal degradation. J Biol Chem 288: 10703–10714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbi ME, Gilkes DM, Hu H, Kshitiz AI, Semenza GL (2014) Cyclin‐dependent kinases regulate lysosomal degradation of hypoxia‐inducible factor 1alpha to promote cell‐cycle progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111: E3325–E3334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubner CA, Dikic I (2020) ER‐phagy and human diseases. Cell Death Differ 27: 833–842 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huett A, Heath RJ, Begun J, Sassi SO, Baxt LA, Vyas JM, Goldberg MB, Xavier RJ (2012) The LRR and RING domain protein LRSAM1 is an E3 ligase crucial for ubiquitin‐dependent autophagy of intracellular Salmonella Typhimurium. Cell Host Microbe 12: 778–790 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humpton TJ, Alagesan B, DeNicola GM, Lu D, Yordanov GN, Leonhardt CS, Yao MA, Alagesan P, Zaatari MN, Park Yet al (2019) Oncogenic KRAS induces NIX‐mediated mitophagy to promote pancreatic cancer. Cancer Discov 9: 1268–1287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huo Y, Cai H, Teplova I, Bowman‐Colin C, Chen G, Price S, Barnard N, Ganesan S, Karantza V, White Eet al (2013) Autophagy opposes p53‐mediated tumor barrier to facilitate tumorigenesis in a model of PALB2‐associated hereditary breast cancer. Cancer Discov 3: 894–907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iershov A, Nemazanyy I, Alkhoury C, Girard M, Barth E, Cagnard N, Montagner A, Chretien D, Rugarli EI, Guillou Het al (2019) The class 3 PI3K coordinates autophagy and mitochondrial lipid catabolism by controlling nuclear receptor PPARalpha. Nat Commun 10: 1566 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igusa Y, Yamashina S, Izumi K, Inami Y, Fukada H, Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Ikejima K, Watanabe S (2012) Loss of autophagy promotes murine acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. J Gastroenterol 47: 433–443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y, Shirakabe A, Maejima Y, Zhai P, Sciarretta S, Toli J, Nomura M, Mihara K, Egashira K, Ohishi Met al (2015) Endogenous Drp1 mediates mitochondrial autophagy and protects the heart against energy stress. Circ Res 116: 264–278 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas G, Zhao E, Liu K, Lin Y, Tesfa L, Tanaka KE, Czaja MJ (2016) Macrophage autophagy limits acute toxic liver injury in mice through down regulation of interleukin‐1beta. J Hepatol 64: 118–127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland JM, Unanue ER (2011) Autophagy in antigen‐presenting cells results in presentation of citrullinated peptides to CD4 T cells. J Exp Med 208: 2625–2632 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain A, Lamark T, Sjottem E, Larsen KB, Awuh JA, Overvatn A, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Johansen T (2010) p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element‐driven gene transcription. J Biol Chem 285: 22576–22591 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janji B, Hasmim M, Parpal S, Berchem G, Noman MZ (2020) Firing up the cold tumors by targeting Vps34. Oncoimmunology 9: 1809936 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelani M, Dooley HC, Gubas A, Mohamoud HSA, Khan MTM, Ali Z, Kang C, Rahim F, Jan A, Vadgama Net al (2019) A mutation in the major autophagy gene, WIPI2, associated with global developmental abnormalities. Brain 142: 1242–1254 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessop F, Hamilton RF, Rhoderick JF, Shaw PK, Holian A (2016) Autophagy deficiency in macrophages enhances NLRP3 inflammasome activity and chronic lung disease following silica exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 309: 101–110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell JL, Russell RC, Guan KL (2013) Amino acid signalling upstream of mTOR. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14: 133–139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji C, Zhao H, Li D, Sun H, Hao J, Chen R, Wang X, Zhang H, Zhao YG (2020) Role of Wdr45b in maintaining neural autophagy and cognitive function. Autophagy 16: 615–625 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia J, Claude‐Taupin A, Gu Y, Choi SW, Peters R, Bissa B, Mudd MH, Allers L, Pallikkuth S, Lidke KAet al (2020) Galectin‐3 coordinates a cellular system for lysosomal repair and removal. Dev Cell 52: 69–87.e68 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez‐Sanchez M, Thomson F, Zavodszky E, Rubinsztein DC (2012) Autophagy and polyglutamine diseases. Prog Neurogibol 97: 67–82 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jo C, Gundemir S, Pritchard S, Jin YN, Rahman I, Johnson GV (2014) Nrf2 reduces levels of phosphorylated tau protein by inducing autophagy adaptor protein NDP52. Nat Commun 5: 3496 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson JO, Mandrioli J, Benatar M, Abramzon Y, Van Deerlin VM, Trojanowski JQ, Gibbs JR, Brunetti M, Gronka S, Wuu Jet al (2010) Exome sequencing reveals VCP mutations as a cause of familial ALS. Neuron 68: 857–864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph A, Moriceau S, Sica V, Anagnostopoulos G, Pol J, Martins I, Lafarge A, Maiuri MC, Leboyer M, Loftus Jet al (2020) Metabolic and psychiatric effects of acyl coenzyme A binding protein (ACBP)/diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI). Cell Death Dis 11: 502 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhasz G, Erdi B, Sass M, Neufeld TP (2007) Atg7‐dependent autophagy promotes neuronal health, stress tolerance, and longevity but is dispensable for metamorphosis in Drosophila . Genes Dev 21: 3061–3066 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung HS, Chung KW, Won Kim J, Kim J, Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Nguyen YH, Kang TM, Yoon KH, Kim JWet al (2008) Loss of autophagy diminishes pancreatic beta cell mass and function with resultant hyperglycemia. Cell Metab 8: 318–324 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat AM, Harrison OJ, Riffelmacher T, Moghaddam AE, Pearson CF, Laing A, Abeler‐Dorner L, Forman SP, Grencis RK, Sattentau Qet al (2016) The autophagy gene Atg16l1 differentially regulates Treg and TH2 cells to control intestinal inflammation. Elife 5: e12444 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaludercic N, Maiuri MC, Kaushik S, Fernández ÁF, de Bruijn J, Castoldi F, Chen Y, Ito J, Mukai R, Murakawa Tet al (2020) Comprehensive autophagy evaluation in cardiac disease models. Cardiovasc Res 116: 483–504 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimoto T, Shoji S, Hidvegi T, Mizushima N, Umebayashi K, Perlmutter DH, Yoshimori T (2006) Intracellular inclusions containing mutant alpha1‐antitrypsin Z are propagated in the absence of autophagic activity. J Biol Chem 281: 4467–4476 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C, Badr MA, Kyrychenko V, Eskelinen EL, Shirokova N (2018) Deficit in PINK1/PARKIN‐mediated mitochondrial autophagy at late stages of dystrophic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res 114: 90–102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsli‐Uzunbas G, Guo JY, Price S, Teng X, Laddha SV, Khor S, Kalaany NY, Jacks T, Chan CS, Rabinowitz JDet al (2014) Autophagy is required for glucose homeostasis and lung tumor maintenance. Cancer Discov 4: 914–927 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasetti RB, Maddineni P, Kiehlbauch C, Patil S, Searby CC, Levine B, Sheffield VC, Zode GS (2021) Autophagy stimulation reduces ocular hypertension in a murine glaucoma model via autophagic degradation of mutant myocilin. JCI Insight 6: e143359 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katheder NS, Khezri R, O’Farrell F, Schultz SW, Jain A, Rahman MM, Schink KO, Theodossiou TA, Johansen T, Juhász Get al (2017) Microenvironmental autophagy promotes tumour growth. Nature 541: 417–420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal GP, Shah SV (2016) Autophagy in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 89: 779–791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik S, Rodriguez‐Navarro JA, Arias E, Kiffin R, Sahu S, Schwartz GJ, Cuervo AM, Singh R (2011) Autophagy in hypothalamic AgRP neurons regulates food intake and energy balance. Cell Metab 14: 173–183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik S, Arias E, Kwon H, Lopez NM, Athonvarangkul D, Sahu S, Schwartz GJ, Pessin JE, Singh R (2012) Loss of autophagy in hypothalamic POMC neurons impairs lipolysis. EMBO Rep 13: 258–265 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik S, Cuervo AM (2015a) Degradation of lipid droplet‐associated proteins by chaperone‐mediated autophagy facilitates lipolysis. Nat Cell Biol 17: 759–770 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik S, Cuervo AM (2015b) Proteostasis and aging. Nat Med 21: 1406–1415 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik S, Cuervo AM (2018) The coming of age of chaperone‐mediated autophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19: 365–381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T, Gomez IG, Ren S, Hudkins K, Roach A, Alpers CE, Shankland SJ, D'Agati VD, Duffield JS (2015) Deficient autophagy results in mitochondrial dysfunction and FSGS. J Am Soc Nephrol 26: 1040–1052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehler DS (2019) Age‐related disease burden as a measure of population ageing. Lancet Public Health 4: e123–e124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller CW, Sina C, Kotur MB, Ramelli G, Mundt S, Quast I, Ligeon LA, Weber P, Becher B, Munz Cet al (2017) ATG‐dependent phagocytosis in dendritic cells drives myelin‐specific CD4(+) T cell pathogenicity during CNS inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114: E11228–E11237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller MD, Ching KL, Liang FX, Dhabaria A, Tam K, Ueberheide BM, Unutmaz D, Torres VJ, Cadwell K (2020a) Decoy exosomes provide protection against bacterial toxins. Nature 579: 260–264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller MD, Torres VJ, Cadwell K (2020b) Autophagy and microbial pathogenesis. Cell Death Differ 27: 872–886 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy BK, Berger SL, Brunet A, Campisi J, Cuervo AM, Epel ES, Franceschi C, Lithgow GJ, Morimoto RI, Pessin JEet al (2014) Geroscience: linking aging to chronic disease. Cell 159: 709–713 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernbauer E, Ding Y, Cadwell K (2014) An enteric virus can replace the beneficial function of commensal bacteria. Nature 516: 94–98 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaminets A, Heinrich T, Mari M, Grumati P, Huebner AK, Akutsu M, Liebmann L, Stolz A, Nietzsche S, Koch Net al (2015) Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum turnover by selective autophagy. Nature 522: 354–358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JH, Kim JH, Yu YS, Mun JY, Kim KW (2010) Autophagy‐induced regression of hyaloid vessels in early ocular development. Autophagy 6: 922–928 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JY, Zhao H, Martinez J, Doggett TA, Kolesnikov AV, Tang PH, Ablonczy Z, Chan CC, Zhou Z, Green DRet al (2013a) Noncanonical autophagy promotes the visual cycle. Cell 154: 365–376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim NC, Tresse E, Kolaitis RM, Molliex A, Thomas RE, Alami NH, Wang B, Joshi A, Smith RB, Ritson GPet al (2013b) VCP is essential for mitochondrial quality control by PINK1/Parkin and this function is impaired by VCP mutations. Neuron 78: 65–80 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim KH, Lee MS (2014) Autophagy–a key player in cellular and body metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10: 322–337 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M, Sandford E, Gatica D, Qiu Y, Liu X, Zheng Y, Schulman BA, Xu J, Semple I, Ro SHet al (2016) Mutation in ATG5 reduces autophagy and leads to ataxia with developmental delay. Elife 5: e12245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim EK, Kwon JE, Lee SY, Lee EJ, Kim DS, Moon SJ, Lee J, Kwok SK, Park SH, Cho ML (2017) IL‐17‐mediated mitochondrial dysfunction impairs apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through activation of autophagy. Cell Death Dis 8: e2565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmelman AC, White E (2017) Autophagy and tumor metabolism. Cell Metab 25: 1037–1043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmey JM, Huynh JP, Weiss LA, Park S, Kambal A, Debnath J, Virgin HW, Stallings CL (2015) Unique role for ATG5 in neutrophil‐mediated immunopathology during M. tuberculosis infection. Nature 528: 565–569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King BC, Kulak K, Krus U, Rosberg R, Golec E, Wozniak K, Gomez MF, Zhang E, O'Connell DJ, Renstrom Eet al (2019) Complement component C3 is highly expressed in human pancreatic islets and prevents beta cell death via ATG16L1 interaction and autophagy regulation. Cell Metab 29: 202–210.e206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsey CG, Camolotto SA, Boespflug AM, Guillen KP, Foth M, Truong A, Schuman SS, Shea JE, Seipp MT, Yap JTet al (2019) Protective autophagy elicited by RAF–>MEK–>ERK inhibition suggests a treatment strategy for RAS‐driven cancers. Nat Med 25: 620–627 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkin V, Rogov VV (2019) A diversity of selective autophagy receptors determines the specificity of the autophagy pathway. Mol Cell 76: 268–285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392: 605–608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada T, Pisani A, Karouani M, Haburcak M, Martella G, Tscherter A, Platania P, Wu B, Pothos EN, Shen J (2009) Impaired dopamine release and synaptic plasticity in the striatum of parkin‐/‐ mice. J Neurochem 110: 613–621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaoka Y, Munemasa Y, Kojima K, Hirano A, Ueno S, Takagi H (2013) Axonal protection by Nmnat3 overexpression with involvement of autophagy in optic nerve degeneration. Cell Death Dis 4: e860 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky DJ, Abdel‐Aziz AK, Abdelfatah S, Abdellatif M, Abdoli A, Abel S, Abeliovich H, Abildgaard MH, Abudu YP, Acevedo‐Arozena Aet al (2021) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition). Autophagy 17: 1–382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko A, Kanehisa A, Martins I, Senovilla L, Chargari C, Dugue D, Mariño G, Kepp O, Michaud M, Perfettini J‐let al (2014) Autophagy inhibition radiosensitizes in vitro, yet reduces radioresponses in vivo due to deficient immunogenic signalling. Cell Death Differ 21: 92–99 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K, Araya J, Minagawa S, Hara H, Saito N, Kadota T, Sato N, Yoshida M, Tsubouchi K, Kurita Yet al (2016) Involvement of PARK2‐mediated mitophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis pathogenesis. J Immunol 197: 504–516 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch JC, Lingor P (2016) The role of autophagy in axonal degeneration of the optic nerve. Exp Eye Res 144: 81–89 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koesters R, Kaissling B, Lehir M, Picard N, Theilig F, Gebhardt R, Glick AB, Hahnel B, Hosser H, Grone HJet al (2010) Tubular overexpression of transforming growth factor‐beta1 induces autophagy and fibrosis but not mesenchymal transition of renal epithelial cells. Am J Pathol 177: 632–643 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M, Shibata M, Tadakoshi M, Gotoh K, Komatsu M, Waguri S, Kawahara N, Kuida K, Nagata S, Kominami Eet al (2008) Inhibition of autophagy prevents hippocampal pyramidal neuron death after hypoxic‐ischemic injury. Am J Pathol 172: 454–469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu M, Waguri S, Ueno T, Iwata J, Murata S, Tanida I, Ezaki J, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Uchiyama Yet al (2005) Impairment of starvation‐induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7‐deficient mice. J Cell Biol 169: 425–434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, Murata S, Iwata J‐I, Tanida I, Ueno T, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Kominami Eet al (2006) Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature 441: 880–884 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu M, Wang QJ, Holstein GR, Friedrich VL Jr, Iwata J, Kominami E, Chait BT, Tanaka K, Yue Z (2007) Essential role for autophagy protein Atg7 in the maintenance of axonal homeostasis and the prevention of axonal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 14489–14494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kon M, Kiffin R, Koga H, Chapochnick J, Macian F, Varticovski L, Cuervo AM (2011) Chaperone‐mediated autophagy is required for tumor growth. Sci Transl Med 3: 109ra117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornak U, Mademan I, Schinke M, Voigt M, Krawitz P, Hecht J, Barvencik F, Schinke T, Gießelmann S, Beil FTet al (2014) Sensory neuropathy with bone destruction due to a mutation in the membrane‐shaping atlastin GTPase 3. Brain 137: 683–692 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotsias F, Cebrian I, Alloatti A (2019) Antigen processing and presentation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 348: 69–121 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenkel O, Tacke F (2017) Liver macrophages in tissue homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 17: 306–321 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Zitvogel L (2013) Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol 31: 51–72 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krokowski S, Lobato‐Márquez D, Chastanet A, Pereira PM, Angelis D, Galea D, Larrouy‐Maumus G, Henriques R, Spiliotis ET, Carballido‐López Ret al (2018) Septins recognize and entrap dividing bacterial cells for delivery to lysosomes. Cell Host Microbe 24: 866–874.e864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krols M, Asselbergh B, De Rycke R, De Winter V, Seyer A, Muller FJ, Kurth I, Bultynck G, Timmerman V, Janssens S (2019) Sensory neuropathy‐causing mutations in ATL3 affect ER‐mitochondria contact sites and impair axonal mitochondrial distribution. Hum Mol Genet 28: 615–627 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubli DA, Zhang X, Lee Y, Hanna RA, Quinsay MN, Nguyen CK, Jimenez R, Petrosyan S, Murphy AN, Gustafsson AB (2013) Parkin protein deficiency exacerbates cardiac injury and reduces survival following myocardial infarction. J Biol Chem 288: 915–926 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudryashova E, Kramerova I, Spencer MJ (2012) Satellite cell senescence underlies myopathy in a mouse model of limb‐girdle muscular dystrophy 2H. J Clin Invest 122: 1764–1776 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers M, Kochlamazashvili G, Stumpf A, Puchkov D, Swaminathan A, Lucht MT, Krause E, Maritzen T, Schmitz D, Haucke V (2021) Neuronal autophagy regulates presynaptic neurotransmission by controlling the axonal endoplasmic reticulum. Neuron 109: 299–313.e299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuma A, Hatano M, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakaya H, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y, Tokuhisa T, Mizushima N (2004) The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period. Nature 432: 1032–1036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuma A, Komatsu M, Mizushima N (2017) Autophagy‐monitoring and autophagy‐deficient mice. Autophagy 13: 1619–1628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S, Jain A, Choi SW, da Silva GPD, Allers L, Mudd MH, Peters RS, Anonsen JH, Rusten T‐E, Lazarou Met al (2020) Mammalian Atg8 proteins and the autophagy factor IRGM control mTOR and TFEB at a regulatory node critical for responses to pathogens. Nat Cell Biol 22: 973–985 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurth I, Pamminger T, Hennings JC, Soehendra D, Huebner AK, Rotthier A, Baets J, Senderek J, Topaloglu H, Farrell SAet al (2009) Mutations in FAM134B, encoding a newly identified Golgi protein, cause severe sensory and autonomic neuropathy. Nat Genet 41: 1179–1181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara T, Iwatsubo T (2020) The emerging functions of LRRK2 and Rab GTPases in the endolysosomal system. Front Neurosci 14: 227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachance V, Wang Q, Sweet E, Choi I, Cai C‐Z, Zhuang X‐X, Zhang Y, Jiang JL, Blitzer RD, Bozdagi‐Gunal Oet al (2019) Autophagy protein NRBF2 has reduced expression in Alzheimer's brains and modulates memory and amyloid‐beta homeostasis in mice. Mol Neurodegener 14: 43 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladoire S, Enot D, Senovilla L, Ghiringhelli F, Poirier‐Colame V, Chaba K, Semeraro M, Chaix M, Penault‐Llorca F, Arnould Let al (2016) The presence of LC3B puncta and HMGB1 expression in malignant cells correlate with the immune infiltrate in breast cancer. Autophagy 12: 864–875 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri V, Hawkins WD, Klionsky DJ (2019) Watch what you (self‐) eat: autophagic mechanisms that modulate metabolism. Cell Metab 29: 803–826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam HC, Cloonan SM, Bhashyam AR, Haspel JA, Singh A, Sathirapongsasuti JF, Cervo M, Yao H, Chung AL, Mizumura Ket al (2013) Histone deacetylase 6‐mediated selective autophagy regulates COPD‐associated cilia dysfunction. J Clin Invest 123: 5212–5230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM (2014) Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell 157: 1013–1022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larionova I, Cherdyntseva N, Liu T, Patysheva M, Rakina M, Kzhyshkowska J (2019) Interaction of tumor‐associated macrophages and cancer chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology 8: 1596004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen KG, Kuballa P, Conway KL, Patel KK, Becker CE, Peloquin JM, Villablanca EJ, Norman JM, Liu T‐C, Heath RJet al (2014) Atg16L1 T300A variant decreases selective autophagy resulting in altered cytokine signaling and decreased antibacterial defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111: 7741–7746 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavandero S, Chiong M, Rothermel BA, Hill JA (2015) Autophagy in cardiovascular biology. J Clin Invest 125: 55–64 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson KA, Sousa CM, Zhang X, Kim E, Akthar R, Caumanns JJ, Yao Y, Mikolajewicz N, Ross C, Brown KRet al (2020) Functional genomic landscape of cancer‐intrinsic evasion of killing by T cells. Nature 586: 120–126 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee HK, Mattei LM, Steinberg BE, Alberts P, Lee YH, Chervonsky A, Mizushima N, Grinstein S, Iwasaki A (2010a) In vivo requirement for Atg5 in antigen presentation by dendritic cells. Immunity 32: 227–239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JH, Yu WH, Kumar A, Lee S, Mohan PS, Peterhoff CM, Wolfe DM, Martinez‐Vicente M, Massey AC, Sovak Get al (2010b) Lysosomal proteolysis and autophagy require presenilin 1 and are disrupted by Alzheimer‐related PS1 mutations. Cell 141: 1146–1158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H, Noh JY, Oh Y, Kim Y, Chang JW, Chung CW, Lee ST, Kim M, Ryu H, Jung YK (2012) IRE1 plays an essential role in ER stress‐mediated aggregation of mutant huntingtin via the inhibition of autophagy flux. Hum Mol Genet 21: 101–114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JJ, Sanchez‐Martinez A, Martinez Zarate A, Beninca C, Mayor U, Clague MJ, Whitworth AJ (2018a) Basal mitophagy is widespread in Drosophila but minimally affected by loss of Pink1 or parkin. J Cell Biol 217: 1613–1622 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee YR, Kuo SH, Lin CY, Fu PJ, Lin YS, Yeh TM, Liu HS (2018b) Dengue virus‐induced ER stress is required for autophagy activation, viral replication, and pathogenesis both in vitro and in vivo . Sci Rep 8: 489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee YH, Kim J, Park K, Lee MS (2019) beta‐cell autophagy: mechanism and role in beta‐cell dysfunction. Mol Metab 27S: S92–S103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee YS, Radford KJ (2019) The role of dendritic cells in cancer. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 348: 123–178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JS, Yoo T, Lee M, Lee Y, Jeon E, Kim SY, Lim BC, Kim KJ, Choi M, Chae JH (2020) Genetic heterogeneity in Leigh syndrome: highlighting treatable and novel genetic causes. Clin Genet 97: 586–594 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee SH, Shim KS, Kim CY, Park TK (2021) Characterization of the role of autophagy in retinal ganglion cell survival over time using a rat model of chronic ocular hypertension. Sci Rep 11: 5767 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidal AM, Levine B, Debnath J (2018) Autophagy and the cell biology of age‐related disease. Nat Cell Biol 20: 1338–1348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir O, Jasiek M, Hénique C, Guyonnet L, Hartleben B, Bork T, Chipont A, Flosseau K, Bensaada I, Schmitt Aet al (2015) Endothelial cell and podocyte autophagy synergistically protect from diabetes‐induced glomerulosclerosis. Autophagy 11: 1130–1145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque S, Le Naour J, Pietrocola F, Paillet J, Kremer M, Castoldi F, Baracco EE, Wang Y, Vacchelli E, Stoll Get al (2019a) A synergistic triad of chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and caloric restriction mimetics eradicates tumors in mice. Oncoimmunology 8: e1657375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque S, Pol JG, Ferrere G, Galluzzi L, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2019b) Trial watch: dietary interventions for cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology 8: 1591878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B, Mizushima N, Virgin HW (2011) Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature 469: 323–335 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B, Kroemer G (2019) Biological functions of autophagy genes: a disease perspective. Cell 176: 11–42 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy J, Cacheux W, Bara MA, L’Hermitte A, Lepage P, Fraudeau M, Trentesaux C, Lemarchand J, Durand A, Crain A‐Met al (2015) Intestinal inhibition of Atg7 prevents tumour initiation through a microbiome‐influenced immune response and suppresses tumour growth. Nat Cell Biol 17: 1062–1073 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leylek R, Idoyaga J (2019) The versatile plasmacytoid dendritic cell: function, heterogeneity, and plasticity. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 349: 177–211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L, Zepeda‐Orozco D, Black R, Lin F (2010) Autophagy is a component of epithelial cell fate in obstructive uropathy. Am J Pathol 176: 1767–1778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L, Wang ZV, Hill JA, Lin F (2014) New autophagy reporter mice reveal dynamics of proximal tubular autophagy. J Am Soc Nephrol 25: 305–315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z, Song Y, Liu L, Hou N, An X, Zhan D, Li Y, Zhou L, Li P, Yu Let al (2017) miR‐199a impairs autophagy and induces cardiac hypertrophy through mTOR activation. Cell Death Differ 24: 1205–1213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Li D, Ma Z, Qian Z, Kang X, Jin X, Li F, Wang X, Chen Q, Sun Het al (2018) Defective autophagy in osteoblasts induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and causes remarkable bone loss. Autophagy 14: 1726–1741 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X, Wu J, Sun X, Wu Q, Li Y, Li K, Zhang Q, Li Y, Abel ED, Chen H (2020a) Autophagy reprograms alveolar progenitor cell metabolism in response to lung injury. Stem Cell Rep 14: 420–432 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li ZL, Zhang HL, Huang Y, Huang JH, Sun P, Zhou NN, Chen YH, Mai J, Wang Y, Yu Yet al (2020b) Autophagy deficiency promotes triple‐negative breast cancer resistance to T cell‐mediated cytotoxicity by blocking tenascin‐C degradation. Nat Commun 11: 3806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T, Kong L, Li X, Wu S, Attri KS, Li Y, Gong W, Zhao B, Li L, Herring LEet al (2021) Listeria monocytogenes upregulates mitochondrial calcium signalling to inhibit LC3‐associated phagocytosis as a survival strategy. Nat Microbiol 6: 366–379 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Liang JR, Lingeman E, Ahmed S, Corn JE (2018) Atlastins remodel the endoplasmic reticulum for selective autophagy. J Cell Biol 217: 3354–3367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao X, Sluimer JC, Wang Y, Subramanian M, Brown K, Pattison JS, Robbins J, Martinez J, Tabas I (2012) Macrophage autophagy plays a protective role in advanced atherosclerosis. Cell Metab 15: 545–553 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman AP, Puertollano R, Raben N, Slaugenhaupt S, Walkley SU, Ballabio A (2012) Autophagy in lysosomal storage disorders. Autophagy 8: 719–730 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim Y‐M, Lim H, Hur KY, Quan W, Lee H‐Y, Cheon H, Ryu D, Koo S‐H, Kim HL, Kim Jet al (2014) Systemic autophagy insufficiency compromises adaptation to metabolic stress and facilitates progression from obesity to diabetes. Nat Commun 5: 4934 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim J, Lachenmayer ML, Wu S, Liu W, Kundu M, Wang R, Komatsu M, Oh YJ, Zhao Y, Yue Z (2015) Proteotoxic stress induces phosphorylation of p62/SQSTM1 by ULK1 to regulate selective autophagic clearance of protein aggregates. PLoS Genet 11: e1004987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin NY, Stefanica A, Distler JH (2013) Autophagy: a key pathway of TNF‐induced inflammatory bone loss. Autophagy 9: 1253–1255 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin NY, Chen CW, Kagwiria R, Liang R, Beyer C, Distler A, Luther J, Engelke K, Schett G, Distler JH (2016) Inactivation of autophagy ameliorates glucocorticoid‐induced and ovariectomy‐induced bone loss. Ann Rheum Dis 75: 1203–1210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke M, Pham HTT, Katholnig K, Schnöller T, Miller A, Demel F, Schütz B, Rosner M, Kovacic B, Sukhbaatar Net al (2017) Chronic signaling via the metabolic checkpoint kinase mTORC1 induces macrophage granuloma formation and marks sarcoidosis progression. Nat Immunol 18: 293–302 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S, Hartleben B, Kretz O, Wiech T, Igarashi P, Mizushima N, Walz G, Huber TB (2012) Autophagy plays a critical role in kidney tubule maintenance, aging and ischemia‐reperfusion injury. Autophagy 8: 826–837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F, Fang F, Yuan H, Yang D, Chen Y, Williams L, Goldstein SA, Krebsbach PH, Guan JL (2013a) Suppression of autophagy by FIP200 deletion leads to osteopenia in mice through the inhibition of osteoblast terminal differentiation. J Bone Miner Res 28: 2414–2430 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H, He Z, von Rutte T, Yousefi S, Hunger RE, Simon HU (2013b) Down‐regulation of autophagy‐related protein 5 (ATG5) contributes to the pathogenesis of early‐stage cutaneous melanoma. Sci Transl Med 5: 202ra123 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y, Shoji‐Kawata S, Sumpter RM Jr, Wei Y, Ginet V, Zhang L, Posner B, Tran KA, Green DR, Xavier RJet al (2013c) Autosis is a Na+, K+‐ATPase‐regulated form of cell death triggered by autophagy‐inducing peptides, starvation, and hypoxia‐ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: 20364–20371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C, Wang H, Shang Y, Liu W, Song Z, Zhao H, Wang L, Jia P, Gao F, Xu Zet al (2016) Autophagy is required for ectoplasmic specialization assembly in sertoli cells. Autophagy 12: 814–832 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H, Zhang Z, Xiong W, Zhang L, Xiong Y, Li N, He H, Du Y, Liu Y (2017) Hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1alpha promotes endometrial stromal cells migration and invasion by upregulating autophagy in endometriosis. Reproduction 153: 809–820 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W, Zhuang J, Jiang Y, Sun J, Prinz RA, Sun J, Jiao X, Xu X (2019) Toll‐like receptor signalling cross‐activates the autophagic pathway to restrict Salmonella Typhimurium growth in macrophages. Cell Microbiol 21: e13095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P, Zhao L, Ferrere G, Alves‐Costa‐Silva C, Ly P, Wu Q, Tian AL, Derosa L, Zitvogel L, Kepp Oet al (2020a) Combination treatments with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin are compatible with the therapeutic induction of anticancer immune responses. Oncoimmunology 9: 1789284 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y, Nguyen PT, Wang X, Zhao Y, Meacham CE, Zou Z, Bordieanu B, Johanns M, Vertommen D, Wijshake Tet al (2020b) TLR9 and beclin 1 crosstalk regulates muscle AMPK activation in exercise. Nature 578: 605–609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu ZZ, Hong CG, Hu WB, Chen ML, Duan R, Li HM, Yue T, Cao J, Wang ZX, Chen CYet al (2020c) Autophagy receptor OPTN (optineurin) regulates mesenchymal stem cell fate and bone‐fat balance during aging by clearing FABP3. Autophagy 1–17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston MJ, Ding HF, Huang S, Hill JA, Yin XM, Dong Z (2016) Persistent activation of autophagy in kidney tubular cells promotes renal interstitial fibrosis during unilateral ureteral obstruction. Autophagy 12: 976–998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodder J, Denaes T, Chobert MN, Wan J, El‐Benna J, Pawlotsky JM, Lotersztajn S, Teixeira‐Clerc F (2015) Macrophage autophagy protects against liver fibrosis in mice. Autophagy 11: 1280–1292 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdregt J, Rossetti M, Spreafico R, Moshref M, Olmer M, Williams GW, Kumar P, Copeland D, Pischel K, Lotz Met al (2016) Increased autophagy in CD4(+) T cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients results in T‐cell hyperactivation and apoptosis resistance. Eur J Immunol 46: 2862–2870 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez‐Otin C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G (2013) The hallmarks of aging. Cell 153: 1194–1217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez‐Otin C, Galluzzi L, Freije JMP, Madeo F, Kroemer G (2016) Metabolic control of longevity. Cell 166: 802–821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López Giuliani AC, Hernández E, Tohmé MJ, Taisne C, Roldán JS, García Samartino C, Lussignol M, Codogno P, Colombo MI, Esclatine Aet al (2020) Human cytomegalovirus inhibits autophagy of renal tubular epithelial cells and promotes cellular enlargement. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10: 474 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez‐Otin C, Kroemer G (2021) Hallmarks of health. Cell 184: 33–63 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotfi P, Tse DY, Di Ronza A, Seymour ML, Martano G, Cooper JD, Pereira FA, Passafaro M, Wu SM, Sardiello M (2018) Trehalose reduces retinal degeneration, neuroinflammation and storage burden caused by a lysosomal hydrolase deficiency. Autophagy 14: 1419–1434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu TL, Huang GJ, Wang HJ, Chen JL, Hsu HP, Lu TJ (2010) Hispolon promotes MDM2 downregulation through chaperone‐mediated autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 398: 26–31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu W, Sun J, Yoon JS, Zhang Y, Zheng L, Murphy E, Mattson MP, Lenardo MJ (2016) Mitochondrial protein PGAM5 regulates mitophagic protection against cell necroptosis. PLoS One 11: e0147792 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X, Altshuler‐Keylin S, Wang Q, Chen Y, Henrique Sponton C, Ikeda K, Maretich P, Yoneshiro T, Kajimura S (2018) Mitophagy controls beige adipocyte maintenance through a Parkin‐dependent and UCP1‐independent mechanism. Sci Signal 11: eaap8526 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H, Yang HL, Zhou WJ, Lai ZZ, Qiu XM, Fu Q, Zhao JY, Wang J, Li DJ, Li MQ (2020) Rapamycin prevents spontaneous abortion by triggering decidual stromal cell autophagy‐mediated NK cell residence. Autophagy 1–17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciani A, Villella VR, Esposito S, Brunetti‐Pierri N, Medina D, Settembre C, Gavina M, Pulze L, Giardino I, Pettoello‐Mantovani Met al (2010) Defective CFTR induces aggresome formation and lung inflammation in cystic fibrosis through ROS‐mediated autophagy inhibition. Nat Cell Biol 12: 863–875 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciani A, Villella VR, Esposito S, Brunetti‐Pierri N, Medina DL, Settembre C, Gavina M, Raia V, Ballabio A, Maiuri L (2011) Cystic fibrosis: a disorder with defective autophagy. Autophagy 7: 104–106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lv L, Li D, Zhao DI, Lin R, Chu Y, Zhang H, Zha Z, Liu Y, Li ZI, Xu Yet al (2011) Acetylation targets the M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase for degradation through chaperone‐mediated autophagy and promotes tumor growth. Mol Cell 42: 719–730 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lv X, Jiang H, Li B, Liang Q, Wang S, Zhao Q, Jiao J (2014) The crucial role of Atg5 in cortical neurogenesis during early brain development. Sci Rep 4: 6010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lv XX, Liu SS, Li K, Cui B, Liu C, Hu ZW (2017) Cigarette smoke promotes COPD by activating platelet‐activating factor receptor and inducing neutrophil autophagic death in mice. Oncotarget 8: 74720–74735 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X, Liu H, Foyil SR, Godar RJ, Weinheimer CJ, Diwan A (2012a) Autophagy is impaired in cardiac ischemia‐reperfusion injury. Autophagy 8: 1394–1396 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X, Liu H, Foyil SR, Godar RJ, Weinheimer CJ, Hill JA, Diwan A (2012b) Impaired autophagosome clearance contributes to cardiomyocyte death in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation 125: 3170–3181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma D, Molusky MM, Song J, Hu CR, Fang F, Rui C, Mathew AV, Pennathur S, Liu F, Cheng JXet al (2013a) Autophagy deficiency by hepatic FIP200 deletion uncouples steatosis from liver injury in NAFLD. Mol Endocrinol 27: 1643–1654 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y, Adjemian S, Mattarollo SR, Yamazaki T, Aymeric L, Yang H, Portela Catani JP, Hannani D, Duret H, Steegh Ket al (2013b) Anticancer chemotherapy‐induced intratumoral recruitment and differentiation of antigen‐presenting cells. Immunity 38: 729–741 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y, Galluzzi L, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2013c) Autophagy and cellular immune responses. Immunity 39: 211–227 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Z, Li L, Livingston MJ, Zhang D, Mi Q, Zhang M, Ding HF, Huo Y, Mei C, Dong Z (2020) p53/microRNA‐214/ULK1 axis impairs renal tubular autophagy in diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest 130: 5011–5026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macri C, Wang F, Tasset I, Schall N, Page N, Briand JP, Cuervo AM, Muller S (2015) Modulation of deregulated chaperone‐mediated autophagy by a phosphopeptide. Autophagy 11: 472–486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madeo F, Zimmermann A, Maiuri MC, Kroemer G (2015) Essential role for autophagy in life span extension. J Clin Invest 125: 85–93 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrigal‐Matute J, Cuervo AM (2016) Regulation of liver metabolism by autophagy. Gastroenterology 150: 328–339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maejima Y, Kyoi S, Zhai P, Liu T, Li H, Ivessa A, Sciarretta S, Del Re DP, Zablocki DK, Hsu C‐Pet al (2013) Mst1 inhibits autophagy by promoting the interaction between Beclin1 and Bcl‐2. Nat Med 19: 1478–1488 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiani E, Milletti G, Nazio F, Holdgaard SG, Bartkova J, Rizza S, Cianfanelli V, Lorente M, Simoneschi D, Di Marco Met al (2021) AMBRA1 regulates cyclin D to guard S‐phase entry and genomic integrity. Nature 592: 799–803 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallucci GR, Klenerman D, Rubinsztein DC (2020) Developing therapies for neurodegenerative disorders: insights from protein aggregation and cellular stress responses. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 36: 165–189 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancias JD, Kimmelman AC (2016) Mechanisms of selective autophagy in normal physiology and cancer. J Mol Biol 428: 1659–1680 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manic G, Obrist F, Kroemer G, Vitale I, Galluzzi L (2014) Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for cancer therapy. Mol Cell Oncol 1: e29911 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansilla Pareja ME, Bongiovanni A, Lafont F, Colombo MI (2017) Alterations of the Coxiella burnetii replicative vacuole membrane integrity and interplay with the autophagy pathway. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7: 112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzanillo PS, Ayres JS, Watson RO, Collins AC, Souza G, Rae CS, Schneider DS, Nakamura K, Shiloh MU, Cox JS (2013) The ubiquitin ligase parkin mediates resistance to intracellular pathogens. Nature 501: 512–516 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markaki M, Palikaras K, Tavernarakis N (2018) Novel insights into the anti‐aging role of mitophagy. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 340: 169–208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh T, Kenific CM, Suresh D, Gonzalez H, Shamir ER, Mei W, Tankka A, Leidal AM, Kalavacherla S, Woo Ket al (2020) Autophagic degradation of NBR1 restricts metastatic outgrowth during mammary tumor progression. Dev Cell 52: 591–604.e596 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin DD, Ladha S, Ehrnhoefer DE, Hayden MR (2015) Autophagy in Huntington disease and huntingtin in autophagy. Trends Neurosci 38: 26–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinet W, De Meyer GR (2009) Autophagy in atherosclerosis: a cell survival and death phenomenon with therapeutic potential. Circ Res 104: 304–317 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J, Almendinger J, Oberst A, Ness R, Dillon CP, Fitzgerald P, Hengartner MO, Green DR (2011) Microtubule‐associated protein 1 light chain 3 alpha (LC3)‐associated phagocytosis is required for the efficient clearance of dead cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 17396–17401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Martinez J, Malireddi RK, Lu Q, Cunha LD, Pelletier S, Gingras S, Orchard R, Guan JL, Tan H, Peng Jet al (2015) Molecular characterization of LC3‐associated phagocytosis reveals distinct roles for Rubicon, NOX2 and autophagy proteins. Nat Cell Biol 17: 893–906 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Martinez J, Cunha LD, Park S, Yang M, Lu Q, Orchard R, Li Q‐Z, Yan M, Janke L, Guy Cet al (2016) Noncanonical autophagy inhibits the autoinflammatory, lupus‐like response to dying cells. Nature 533: 115–119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Martinek J, Wu TC, Cadena D, Banchereau J, Palucka K (2019) Interplay between dendritic cells and cancer cells. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 348: 179–215 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez‐Vicente M, Talloczy Z, Kaushik S, Massey AC, Mazzulli J, Mosharov EV, Hodara R, Fredenburg R, Wu DC, Follenzi Aet al (2008) Dopamine‐modified alpha‐synuclein blocks chaperone‐mediated autophagy. J Clin Invest 118: 777–788 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez‐Vicente M, Talloczy Z, Wong E, Tang G, Koga H, Kaushik S, de Vries R, Arias E, Harris S, Sulzer Det al (2010) Cargo recognition failure is responsible for inefficient autophagy in Huntington's disease. Nat Neurosci 13: 567–576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins I, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G (2011) Hormesis, cell death and aging. Aging (Albany NY) 3: 821–828 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins I, Wang Y, Michaud M, Ma Y, Sukkurwala AQ, Shen S, Kepp O, Métivier D, Galluzzi L, Perfettini J‐let al (2014) Molecular mechanisms of ATP secretion during immunogenic cell death. Cell Death Differ 21: 79–91 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masiero E, Agatea L, Mammucari C, Blaauw B, Loro E, Komatsu M, Metzger D, Reggiani C, Schiaffino S, Sandri M (2009) Autophagy is required to maintain muscle mass. Cell Metab 10: 507–515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew R, Karp CM, Beaudoin B, Vuong N, Chen G, Chen H‐Y, Bray K, Reddy A, Bhanot G, Gelinas Cet al (2009) Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis through elimination of p62. Cell 137: 1062–1075 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda N, Sato S, Shiba K, Okatsu K, Saisho K, Gautier CA, Sou Y‐S, Saiki S, Kawajiri S, Sato Fet al (2010) PINK1 stabilized by mitochondrial depolarization recruits Parkin to damaged mitochondria and activates latent Parkin for mitophagy. J Cell Biol 189: 211–221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda J, Takahashi A, Takabatake Y, Sakai S, Minami S, Yamamoto T, Fujimura R, Namba‐Hamano T, Yonishi H, Nakamura Jet al (2020) Metabolic effects of RUBCN/Rubicon deficiency in kidney proximal tubular epithelial cells. Autophagy 16: 1889–1904 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, Abdellatif M, Sakoda H, Asano T, Levine B, Sadoshima J (2007) Distinct roles of autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: roles of AMP‐activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy. Circ Res 100: 914–922 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto YU, Shono Y, Gomez LE, Hubbard‐Lucey VM, Cammer M, Neil J, Dewan MZ, Lieberman SR, Lazrak A, Marinis JMet al (2017) Autophagy protein ATG16L1 prevents necroptosis in the intestinal epithelium. J Exp Med 214: 3687–3705 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto Y, Hwang S, Cadwell K (2018) Autophagy and Inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol 36: 73–101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto YU, Hine A, Shono Y, Rudensky E, Lazrak A, Yeung F, Neil JA, Yao X, Chen Y‐H, Heaney Tet al (2020) An intestinal organoid‐based platform that recreates susceptibility to T‐cell‐mediated tissue injury. Blood 135: 2388–2401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer K, Reyes‐Robles T, Alonzo F 3rd, Durbin J, Torres VJ, Cadwell K (2015) Autophagy mediates tolerance to Staphylococcus aureus alpha‐toxin. Cell Host Microbe 17: 429–440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauthe M, Reggiori F (2016) Using microbes as a key tool to unravel the mechanism of autophagy and the functions of the ATG proteins. Microb Cell 4: 1–5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally EK, Brett CL (2018) The intralumenal fragment pathway mediates ESCRT‐independent surface transporter down‐regulation. Nat Commun 9: 5358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWilliams TG, Prescott AR, Montava‐Garriga L, Ball G, Singh F, Barini E, Muqit MMK, Brooks SP, Ganley IG (2018) Basal mitophagy occurs independently of pink1 in mouse tissues of high metabolic demand. Cell Metab 27: 439–449.e435 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mealer RG, Murray AJ, Shahani N, Subramaniam S, Snyder SH (2014) Rhes, a striatal‐selective protein implicated in Huntington disease, binds beclin‐1 and activates autophagy. J Biol Chem 289: 3547–3554 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta SL, Lin Y, Chen W, Yu F, Cao L, He Q, Chan PH, Li PA (2011) Manganese superoxide dismutase deficiency exacerbates ischemic brain damage under hyperglycemic conditions by altering autophagy. Transl Stroke Res 2: 42–50 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehto S, Jena KK, Nath P, Chauhan S, Kolapalli SP, Das SK, Sahoo PK, Jain A, Taylor GA, Chauhan S (2019) The Crohn's disease risk factor IRGM limits NLRP3 inflammasome activation by impeding its assembly and by mediating its selective autophagy. Mol Cell 73: 429–445.e427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mejlvang J, Olsvik H, Svenning S, Bruun J‐A, Abudu YP, Larsen KB, Brech A, Hansen TE, Brenne H, Hansen Tet al (2018) Starvation induces rapid degradation of selective autophagy receptors by endosomal microautophagy. J Cell Biol 217: 3640–3655 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mele L, Del Vecchio V, Liccardo D, Prisco C, Schwerdtfeger M, Robinson N, Desiderio V, Tirino V, Papaccio G, La Noce M (2020) The role of autophagy in resistance to targeted therapies. Cancer Treat Rev 88: 102043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer D, Pilling LC, Ferrucci L (2020) The genetics of human ageing. Nat Rev Genet 21: 88–101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng T, Lin S, Zhuang H, Huang H, He Z, Hu Y, Gong Q, Feng D (2019) Recent progress in the role of autophagy in neurological diseases. Cell Stress 3: 141–161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menikdiwela KR, Ramalingam L, Rasha F, Wang S, Dufour JM, Kalupahana NS, Sunahara KKS, Martins JO, Moustaid‐Moussa N (2020) Autophagy in metabolic syndrome: breaking the wheel by targeting the renin‐angiotensin system. Cell Death Dis 11: 87 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzies FM, Fleming A, Caricasole A, Bento CF, Andrews SP, Ashkenazi A, Füllgrabe J, Jackson A, Jimenez Sanchez M, Karabiyik Cet al (2017) Autophagy and Neurodegeneration: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Neuron 93: 1015–1034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestre MB, Fader CM, Sola C, Colombo MI (2010) Alpha‐hemolysin is required for the activation of the autophagic pathway in Staphylococcus aureus‐infected cells. Autophagy 6: 110–125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf DJ, Garcia‐Arencibia M, Hochfeld WE, Rubinsztein DC (2012) Autophagy and misfolded proteins in neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol 238: 22–28 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier E, Dick MS, Dreier RF, Schürmann N, Broz DK, Warming S, Roose‐Girma M, Bumann D, Kayagaki N, Takeda Ket al (2014) Caspase‐11 activation requires lysis of pathogen‐containing vacuoles by IFN‐induced GTPases. Nature 509: 366–370 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mgrditchian T, Arakelian T, Paggetti J, Noman MZ, Viry E, Moussay E, Van Moer K, Kreis S, Guerin C, Buart Set al (2017) Targeting autophagy inhibits melanoma growth by enhancing NK cells infiltration in a CCL5‐dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114: E9271–E9279 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao G, Zhao H, Li Y, Ji M, Chen Y, Shi Y, Bi Y, Wang P, Zhang H (2021) ORF3a of the COVID‐19 virus SARS‐CoV‐2 blocks HOPS complex‐mediated assembly of the SNARE complex required for autolysosome formation. Dev Cell 56: 427–442.e425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud M, Martins I, Sukkurwala AQ, Adjemian S, Ma Y, Pellegatti P, Shen S, Kepp O, Scoazec M, Mignot Get al (2011) Autophagy‐dependent anticancer immune responses induced by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science 334: 1573–1577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller DR, Cramer SD, Thorburn A (2020) The interplay of autophagy and non‐apoptotic cell death pathways. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 352: 159–187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller DR, Thorburn A (2021) Autophagy and organelle homeostasis in cancer. Dev Cell 56: 906–918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minegishi Y, Iejima D, Kobayashi H, Chi ZL, Kawase K, Yamamoto T, Seki T, Yuasa S, Fukuda K, Iwata T (2013) Enhanced optineurin E50K‐TBK1 interaction evokes protein insolubility and initiates familial primary open‐angle glaucoma. Hum Mol Genet 22: 3559–3567 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitter SK, Song C, Qi X, Mao H, Rao H, Akin D, Lewin A, Grant M, Dunn W, Ding Jet al (2014) Dysregulated autophagy in the RPE is associated with increased susceptibility to oxidative stress and AMD. Autophagy 10: 1989–2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizumura K, Cloonan SM, Nakahira K, Bhashyam AR, Cervo M, Kitada T, Glass K, Owen CA, Mahmood A, Washko GRet al (2014) Mitophagy‐dependent necroptosis contributes to the pathogenesis of COPD. J Clin Invest 124: 3987–4003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima N, Levine B (2010) Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 12: 823–830 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima N, Komatsu M (2011) Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 147: 728–741 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima N (2018) A brief history of autophagy from cell biology to physiology and disease. Nat Cell Biol 20: 521–527 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima N, Levine B (2020) Autophagy in human diseases. N Engl J Med 383: 1564–1576 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monkkonen T, Debnath J (2018) Inflammatory signaling cascades and autophagy in cancer. Autophagy 14: 190–198 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro G, Rebelo AP, Connell J, Allison R, Babalini C, D’Aloia M, Montieri P, Schüle R, Ishiura H, Price Jet al (2012) Mutations in the ER‐shaping protein reticulon 2 cause the axon‐degenerative disorder hereditary spastic paraplegia type 12. J Clin Invest 122: 538–544 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore AS, Holzbaur EL (2016) Dynamic recruitment and activation of ALS‐associated TBK1 with its target optineurin are required for efficient mitophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113: E3349–E3358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora AL, Rojas M, Pardo A, Selman M (2017) Emerging therapies for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a progressive age‐related disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16: 755–772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita H, Eguchi S, Kimura H, Sasaki J, Sakamaki Y, Robinson ML, Sasaki T, Mizushima N (2013) Deletion of autophagy‐related 5 (Atg5) and Pik3c3 genes in the lens causes cataract independent of programmed organelle degradation. J Biol Chem 288: 11436–11447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita H, Mizushima N (2019) Diverse cellular roles of autophagy. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 35: 453–475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita H, Eguchi T, Tsukamoto S, Sakamaki Y, Takahashi S, Saito C, Koyama‐Honda I, Mizushima N (2021) Organelle degradation in the lens by PLAAT phospholipases. Nature 592: 634–638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morselli E, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Criollo A, Maiuri MC, Tavernarakis N, Madeo F, Kroemer G (2009) Autophagy mediates pharmacological lifespan extension by spermidine and resveratrol. Aging (Albany NY) 1: 961–970 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morselli E, Maiuri MC, Markaki M, Megalou E, Pasparaki A, Palikaras K, Criollo A, Galluzzi L, Malik SA, Vitale Iet al (2010) Caloric restriction and resveratrol promote longevity through the Sirtuin‐1‐dependent induction of autophagy. Cell Death Dis 1: e10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscat J, Karin M, Diaz‐Meco MT (2016) p62 in cancer: signaling adaptor beyond autophagy. Cell 167: 606–609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay S, Biancur DE, Parker SJ, Yamamoto K, Banh RS, Paulo JA, Mancias JD, Kimmelman AC (2021) Autophagy is required for proper cysteine homeostasis in pancreatic cancer through regulation of SLC7A11. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118: e2021475118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy SM, Davidson GL, Brandner S, Houlden H, Reilly MM (2012) Mutation in FAM134B causing severe hereditary sensory neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83: 119–120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy KE, Gysbers AM, Abbott SK, Tayebi N, Kim WS, Sidransky E, Cooper A, Garner B, Halliday GM (2014) Reduced glucocerebrosidase is associated with increased alpha‐synuclein in sporadic Parkinson's disease. Brain 137: 834–848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy A, Li Y, Peng I, Reichelt M, Katakam AK, Noubade R, Roose‐Girma M, DeVoss J, Diehl L, Graham RRet al (2014) A Crohn's disease variant in Atg16l1 enhances its degradation by caspase 3. Nature 506: 456–462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nah J, Zhai P, Huang CY, Fernandez AF, Mareedu S, Levine B, Sadoshima J (2020) Upregulation of Rubicon promotes autosis during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 130: 2978–2991 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahira K, Pabon Porras MA, Choi AM (2016) Autophagy in pulmonary diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 194: 1196–1207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, Higuchi Y, Hikoso S, Taniike M, Omiya S, Mizote I, Matsumura Y, Asahi Met al (2007) The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med 13: 619–624 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S, Oba M, Suzuki M, Takahashi A, Yamamuro T, Fujiwara M, Ikenaka K, Minami S, Tabata N, Yamamoto Ket al (2019) Suppression of autophagic activity by Rubicon is a signature of aging. Nat Commun 10: 847 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S, Shigeyama S, Minami S, Shima T, Akayama S, Matsuda T, Esposito A, Napolitano G, Kuma A, Namba‐Hamano Tet al (2020) LC3 lipidation is essential for TFEB activation during the lysosomal damage response to kidney injury. Nat Cell Biol 22: 1252–1263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatogawa H (2020) Mechanisms governing autophagosome biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21: 439–458 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nam SA, Kim WY, Kim JW, Park SH, Kim HL, Lee MS, Komatsu M, Ha H, Lim JH, Park CWet al (2019) Autophagy attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis through regulating transforming growth factor‐beta and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 10: 78 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Youle RJ (2008) Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol 183: 795–803 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita M, Young ARJ, Arakawa S, Samarajiwa SA, Nakashima T, Yoshida S, Hong S, Berry LS, Reichelt S, Ferreira Met al (2011) Spatial coupling of mTOR and autophagy augments secretory phenotypes. Science 332: 966–970 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassif M, Valenzuela V, Rojas‐Rivera D, Vidal R, Matus S, Castillo K, Fuentealba Y, Kroemer G, Levine B, Hetz C (2014) Pathogenic role of BECN1/Beclin 1 in the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Autophagy 10: 1256–1271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro‐Pando JM, Alcocer‐Gomez E, Castejon‐Vega B, Navarro‐Villaran E, Condes‐Hervas M, Mundi‐Roldan M, Muntane J, Perez‐Pulido AJ, Bullon P, Wang Cet al (2021) Inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome prevents ovarian aging. Sci Adv 7: eabc7409 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazio F, Bordi M, Cianfanelli V, Locatelli F, Cecconi F (2019) Autophagy and cancer stem cells: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Cell Death Differ 26: 690–702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nettesheim A, Dixon A, Shim MS, Coyne A, Walsh M, Liton PB (2020) Autophagy in the aging and experimental ocular hypertensive mouse model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 61: 31 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen TB, Olzmann JA (2017) Lipid droplets and lipotoxicity during autophagy. Autophagy 13: 2002–2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni HM, Bockus A, Boggess N, Jaeschke H, Ding WX (2012a) Activation of autophagy protects against acetaminophen‐induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 55: 222–232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni HM, Boggess N, McGill MR, Lebofsky M, Borude P, Apte U, Jaeschke H, Ding WX (2012b) Liver‐specific loss of Atg5 causes persistent activation of Nrf2 and protects against acetaminophen‐induced liver injury. Toxicol Sci 127: 438–450 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson P, Loganathan K, Sekiguchi M, Matsuba Y, Hui K, Tsubuki S, Tanaka M, Iwata N, Saito T, Saido TC (2013) Abeta secretion and plaque formation depend on autophagy. Cell Rep 5: 61–69 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino I, Fu J, Tanji K, Yamada T, Shimojo S, Koori T, Mora M, Riggs JE, Oh SJ, Koga Yet al (2000) Primary LAMP‐2 deficiency causes X‐linked vacuolar cardiomyopathy and myopathy (Danon disease). Nature 406: 906–910 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niso‐Santano M, Malik SA, Pietrocola F, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Mariño G, Cianfanelli V, Ben‐Younès A, Troncoso R, Markaki M, Sica Vet al (2015) Unsaturated fatty acids induce non‐canonical autophagy. EMBO J 34: 1025–1041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon RA, Wegiel J, Kumar A, Yu WH, Peterhoff C, Cataldo A, Cuervo AM (2005) Extensive involvement of autophagy in Alzheimer disease: an immuno‐electron microscopy study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64: 113–122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon RA (2013) The role of autophagy in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med 19: 983–997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noad J, von der Malsburg A, Pathe C, Michel MA, Komander D, Randow F (2017) LUBAC‐synthesized linear ubiquitin chains restrict cytosol‐invading bacteria by activating autophagy and NF‐kappaB. Nat Microbiol 2: 17063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogalska A, D'Agostino C, Terracciano C, Engel WK, Askanas V (2010) Impaired autophagy in sporadic inclusion‐body myositis and in endoplasmic reticulum stress‐provoked cultured human muscle fibers. Am J Pathol 177: 1377–1387 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nollet M, Santucci‐Darmanin S, Breuil V, Al‐Sahlanee R, Cros C, Topi M, Momier D, Samson M, Pagnotta S, Cailleteau Let al (2014) Autophagy in osteoblasts is involved in mineralization and bone homeostasis. Autophagy 10: 1965–1977 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noman MZ, Parpal S, Van Moer K, Xiao M, Yu Y, Arakelian T, Viklund J, De Milito A, Hasmim M, Andersson Met al (2020) Inhibition of Vps34 reprograms cold into hot inflamed tumors and improves anti‐PD‐1/PD‐L1 immunotherapy. Sci Adv 6: eaax7881 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notomi S, Ishihara K, Efstathiou NE, Lee J‐J, Hisatomi T, Tachibana T, Konstantinou EK, Ueta T, Murakami Y, Maidana DEet al (2019) Genetic LAMP2 deficiency accelerates the age‐associated formation of basal laminar deposits in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116: 23724–23734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochaba J, Lukacsovich T, Csikos G, Zheng S, Margulis J, Salazar L, Mao K, Lau AL, Yeung SY, Humbert Set al (2014) Potential function for the Huntingtin protein as a scaffold for selective autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111: 16889–16894 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T, Hikoso S, Yamaguchi O, Taneike M, Takeda T, Tamai T, Oyabu J, Murakawa T, Nakayama H, Nishida Ket al (2012) Mitochondrial DNA that escapes from autophagy causes inflammation and heart failure. Nature 485: 251–255 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva Trejo JA, Asanuma K, Kim EH, Takagi‐Akiba M, Nonaka K, Hidaka T, Komatsu M, Tada N, Ueno T, Tomino Y (2014) Transient increase in proteinuria, poly‐ubiquitylated proteins and ER stress markers in podocyte‐specific autophagy‐deficient mice following unilateral nephrectomy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 446: 1190–1196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onal M, Piemontese M, Xiong J, Wang Y, Han LI, Ye S, Komatsu M, Selig M, Weinstein RS, Zhao Het al (2013) Suppression of autophagy in osteocytes mimics skeletal aging. J Biol Chem 288: 17432–17440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvedahl A, Alexander D, Talloczy Z, Sun Q, Wei Y, Zhang W, Burns D, Leib DA, Levine B (2007) HSV‐1 ICP34.5 confers neurovirulence by targeting the Beclin 1 autophagy protein. Cell Host Microbe 1: 23–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvedahl A, MacPherson S, Sumpter R Jr, Talloczy Z, Zou Z, Levine B (2010) Autophagy protects against Sindbis virus infection of the central nervous system. Cell Host Microbe 7: 115–127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osonoi Y, Mita T, Azuma K, Nakajima K, Masuyama A, Goto H, Nishida Y, Miyatsuka T, Fujitani Y, Koike Met al (2018) Defective autophagy in vascular smooth muscle cells enhances cell death and atherosclerosis. Autophagy 14: 1991–2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudshoorn D, Rijs K, Limpens R, Groen K, Koster AJ, Snijder EJ, Kikkert M, Barcena M (2017) Expression and cleavage of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus nsp3‐4 polyprotein induce the formation of double‐membrane vesicles that mimic those associated with coronaviral RNA replication. MBio 8: e01658‐17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouimet M, Franklin V, Mak E, Liao X, Tabas I, Marcel YL (2011) Autophagy regulates cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells via lysosomal acid lipase. Cell Metab 13: 655–667 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oz‐Levi D, Ben‐Zeev B, Ruzzo E, Hitomi Y, Gelman A, Pelak K, Anikster Y, Reznik‐Wolf H, Bar‐Joseph I, Olender Tet al (2012) Mutation in TECPR2 reveals a role for autophagy in hereditary spastic paraparesis. Am J Hum Genet 91: 1065–1072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik J‐H, Ding Z, Narurkar R, Ramkissoon S, Muller F, Kamoun WS, Chae S‐S, Zheng H, Ying H, Mahoney Jet al (2009) FoxOs cooperatively regulate diverse pathways governing neural stem cell homeostasis. Cell Stem Cell 5: 540–553 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacino JJ, Sagi D, Goldberg MS, Krauss S, Motz C, Wacker M, Klose J, Shen J (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in parkin‐deficient mice. J Biol Chem 279: 18614–18622 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palikaras K, Lionaki E, Tavernarakis N (2018) Mechanisms of mitophagy in cellular homeostasis, physiology and pathology. Nat Cell Biol 20: 1013–1022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palla AR, Ravichandran M, Wang YX, Alexandrova L, Yang AV, Kraft P, Holbrook CA, Schurch CM, Ho ATV, Blau HM (2021) Inhibition of prostaglandin‐degrading enzyme 15‐PGDH rejuvenates aged muscle mass and strength. Science 371: eabc8059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzitt K, Jungwirth E, Krones E, Lee JM, Pollheimer M, Thallinger GG, Kolb‐Lenz D, Xiao R, Thorell A, Trauner Met al (2020) FXR‐dependent Rubicon induction impairs autophagy in models of human cholestasis. J Hepatol 72: 1122–1131 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadakis M, Hadley G, Xilouri M, Hoyte LC, Nagel S, McMenamin MM, Tsaknakis G, Watt SM, Drakesmith CW, Chen Ret al (2013) Tsc1 (hamartin) confers neuroprotection against ischemia by inducing autophagy. Nat Med 19: 351–357 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park SM, Lim JS, Ramakrishina S, Kim SH, Kim WK, Lee J, Kang H‐C, Reiter JF, Kim DS, Kim Het al (2018) Brain somatic mutations in MTOR disrupt neuronal ciliogenesis, leading to focal cortical dyslamination. Neuron 99: 83–97.e87 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes M, Barrett JC, Prescott NJ, Tremelling M, Anderson CA, Fisher SA, Roberts RG, Nimmo ER, Cummings FR, Soars Det al (2007) Sequence variants in the autophagy gene IRGM and multiple other replicating loci contribute to Crohn's disease susceptibility. Nat Genet 39: 830–832 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastore N, Blomenkamp K, Annunziata F, Piccolo P, Mithbaokar P, Maria Sepe R, Vetrini F, Palmer D, Ng P, Polishchuk Eet al (2013) Gene transfer of master autophagy regulator TFEB results in clearance of toxic protein and correction of hepatic disease in alpha‐1‐anti‐trypsin deficiency. EMBO Mol Med 5: 397–412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel AS, Lin L, Geyer A, Haspel JA, An CH, Cao J, Rosas IO, Morse D (2012) Autophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One 7: e41394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P, Karch J (2020) Regulation of cell death in the cardiovascular system. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 353: 153–209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini JM, Sabbione F, Morelli MP, Tateosian NL, Castello FA, Amiano NO, Palmero D, Levi A, Ciallella L, Colombo MIet al (2020) Neutrophil autophagy during human active tuberculosis is modulated by SLAMF1. Autophagy 1–10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pena‐Oyarzun D, Batista‐Gonzalez A, Kretschmar C, Burgos P, Lavandero S, Morselli E, Criollo A (2020) New emerging roles of Polycystin‐2 in the regulation of autophagy. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 354: 165–186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez FA, Palmiter RD (2005) Parkin‐deficient mice are not a robust model of parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 2174–2179 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernas L, Bean C, Boothroyd JC, Scorrano L (2018) Mitochondria restrict growth of the intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii by limiting its uptake of fatty acids. Cell Metab 27: 886–897.e884 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pervaiz S, Bellot GL, Lemoine A, Brenner C (2020) Redox signaling in the pathogenesis of human disease and the regulatory role of autophagy. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 352: 189–214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petroni G, Buque A, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2021) Immunomodulation by targeted anticancer agents. Cancer Cell 39: 310–345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell AM, Huang CH, Kennedy SR, Ordureau A, Sideris DP, Hoekstra JG, Harper JW, Youle RJ (2015) Endogenous parkin preserves dopaminergic substantia nigral neurons following mitochondrial DNA mutagenic stress. Neuron 87: 371–381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrocola F, Galluzzi L, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Madeo F, Kroemer G (2015) Acetyl coenzyme A: a central metabolite and second messenger. Cell Metab 21: 805–821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrocola F, Pol J, Vacchelli E, Rao S, Enot D, Baracco E, Levesque S, Castoldi F, Jacquelot N, Yamazaki Tet al (2016) Caloric restriction mimetics enhance anticancer immunosurveillance. Cancer Cell 30: 147–160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrocola F, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G (2017) Autophagy in natural and therapy‐driven anticancer immunosurveillance. Autophagy 13: 2163–2170 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrocola F, Kroemer G (2019) Caloric restriction promotes the stemness and antitumor activity of T lymphocytes. Oncoimmunology 8: e1616153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrocola F, Castoldi F, Zischka H, Kroemer G (2020) Extending the mode of action of triethylenetetramine (trientine): autophagy besides copper chelation. J Hepatol 73: 970–972 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrocola F, Bravo‐San Pedro JM (2021) Targeting autophagy to counteract obesity‐associated oxidative stress. Antioxidants (Basel) 10: 102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilli M, Arko‐Mensah J, Ponpuak M, Roberts E, Master S, Mandell MA, Dupont N, Ornatowski W, Jiang S, Bradfute SBet al (2012) TBK‐1 promotes autophagy‐mediated antimicrobial defense by controlling autophagosome maturation. Immunity 37: 223–234 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowey ED, Cherra SJ 3rd, Liu YJ, Chu CT (2008) Role of autophagy in G2019S‐LRRK2‐associated neurite shortening in differentiated SH‐SY5Y cells. J Neurochem 105: 1048–1056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poillet‐Perez L, Xie X, Zhan LE, Yang Y, Sharp DW, Hu ZS, Su X, Maganti A, Jiang C, Lu Wet al (2018) Autophagy maintains tumour growth through circulating arginine. Nature 563: 569–573 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poillet‐Perez L, White E (2019) Role of tumor and host autophagy in cancer metabolism. Genes Dev 33: 610–619 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poillet‐Perez L, Sharp DW, Yang Y, Laddha SV, Ibrahim M, Bommareddy PK, Hu ZS, Vieth J, Haas M, Bosenberg MWet al (2020) Autophagy promotes growth of tumors with high mutational burden by inhibiting a T‐cell immune response. Nature Cancer 1: 923–934 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polishchuk EV, Merolla A, Lichtmannegger J, Romano A, Indrieri A, Ilyechova EY, Concilli M, De Cegli R, Crispino R, Mariniello Met al (2019) Activation of autophagy, observed in liver tissues from patients with Wilson disease and from ATP7B‐deficient animals, protects hepatocytes from copper‐induced apoptosis. Gastroenterology 156: 1173–1189.e1175 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponpuak M, Mandell MA, Kimura T, Chauhan S, Cleyrat C, Deretic V (2015) Secretory autophagy. Curr Opin Cell Biol 35: 106–116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porciatti V, Pizzorusso T, Cenni MC, Maffei L (1996) The visual response of retinal ganglion cells is not altered by optic nerve transection in transgenic mice overexpressing Bcl‐2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 14955–14959 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pott J, Kabat AM, Maloy KJ (2018) Intestinal epithelial cell autophagy is required to protect against TNF‐induced apoptosis during chronic colitis in mice. Cell Host Microbe 23: 191–202.e194 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puleston DJ, Zhang H, Powell TJ, Lipina E, Sims S, Panse I, Watson AS, Cerundolo V, Townsend AR, Klenerman Pet al (2014) Autophagy is a critical regulator of memory CD8(+) T cell formation. Elife 3: e03706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyo JO, Yoo SM, Ahn HH, Nah J, Hong SH, Kam TI, Jung S, Jung YK (2013) Overexpression of Atg5 in mice activates autophagy and extends lifespan. Nat Commun 4: 2300 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi YY, Zhou XJ, Zhang H (2019) Autophagy and immunological aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Immunol 49: 523–533 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu X, Yu J, Bhagat G, Furuya N, Hibshoosh H, Troxel A, Rosen J, Eskelinen E‐L, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Yet al (2003) Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin 1 autophagy gene. J Clin Invest 112: 1809–1820 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan W, Hur KY, Lim Y, Oh SH, Lee J‐C, Kim KH, Kim GH, Kim S‐W, Kim HL, Lee M‐Ket al (2012) Autophagy deficiency in beta cells leads to compromised unfolded protein response and progression from obesity to diabetes in mice. Diabetologia 55: 392–403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz JD, White E (2010) Autophagy and metabolism. Science 330: 1344–1348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racanelli AC, Kikkers SA, Choi AMK, Cloonan SM (2018) Autophagy and inflammation in chronic respiratory disease. Autophagy 14: 221–232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh Babu J, Lamar Seibenhener M, Peng J, Strom A‐L, Kemppainen R, Cox N, Zhu H, Wooten MC, Diaz‐Meco MT, Moscat Jet al (2008) Genetic inactivation of p62 leads to accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau and neurodegeneration. J Neurochem 106: 107–120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez A, Heimbach A, Gründemann J, Stiller B, Hampshire D, Cid LP, Goebel I, Mubaidin AF, Wriekat A‐L, Roeper Jet al (2006) Hereditary parkinsonism with dementia is caused by mutations in ATP13A2, encoding a lysosomal type 5 P‐type ATPase. Nat Genet 38: 1184–1191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramonet D, Daher JPL, Lin BM, Stafa K, Kim J, Banerjee R, Westerlund M, Pletnikova O, Glauser L, Yang Let al (2011) Dopaminergic neuronal loss, reduced neurite complexity and autophagic abnormalities in transgenic mice expressing G2019S mutant LRRK2. PLoS One 6: e18568 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranek MJ, Kokkonen‐Simon KM, Chen A, Dunkerly‐Eyring BL, Vera MP, Oeing CU, Patel CH, Nakamura T, Zhu G, Bedja Det al (2019) PKG1‐modified TSC2 regulates mTORC1 activity to counter adverse cardiac stress. Nature 566: 264–269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S, Tortola L, Perlot T, Wirnsberger G, Novatchkova M, Nitsch R, Sykacek P, Frank L, Schramek D, Komnenovic Vet al (2014) A dual role for autophagy in a murine model of lung cancer. Nat Commun 5: 3056 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S, Gharib K, Han A (2019) Cancer Immunosurveillance by T Cells. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 342: 149–173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razani B, Feng C, Coleman T, Emanuel R, Wen H, Hwang S, Ting JP, Virgin HW, Kastan MB, Semenkovich CF (2012) Autophagy links inflammasomes to atherosclerotic progression. Cell Metab 15: 534–544 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez‐Muela N, Germain F, Marino G, Fitze PS, Boya P (2012) Autophagy promotes survival of retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve axotomy in mice. Cell Death Differ 19: 162–169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez‐Muela N, Koga H, Garcia‐Ledo L, de la Villa P, de la Rosa EJ, Cuervo AM, Boya P (2013) Balance between autophagic pathways preserves retinal homeostasis. Aging Cell 12: 478–488 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez‐Muela N, Hernandez‐Pinto AM, Serrano‐Puebla A, Garcia‐Ledo L, Latorre SH, de la Rosa EJ, Boya P (2015) Lysosomal membrane permeabilization and autophagy blockade contribute to photoreceptor cell death in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. Cell Death Differ 22: 476–487 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez‐Navarro JA, Kaushik S, Koga H, Dall'Armi C, Shui G, Wenk MR, Di Paolo G, Cuervo AM (2012) Inhibitory effect of dietary lipids on chaperone‐mediated autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109: E705–E714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldan JS, Candurra NA, Colombo MI, Delgui LR (2019) Junin virus promotes autophagy to facilitate the virus life cycle. J Virol 93: e02307‐18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero M, Zorzano A (2019) Role of autophagy in the regulation of adipose tissue biology. Cell Cycle 18: 1435–1445 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeldt MT, O’Prey J, Morton JP, Nixon C, MacKay G, Mrowinska A, Au A, Rai TS, Zheng L, Ridgway Ret al (2013) p53 status determines the role of autophagy in pancreatic tumour development. Nature 504: 296–300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeldt MT, O'Prey J, Lindsay CR, Nixon C, Roth S, Sansom OJ, Ryan KM (2021) Loss of autophagy affects melanoma development in a manner dependent on PTEN status. Cell Death Differ 28: 1437–1439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossin F, Villella VR, D'Eletto M, Farrace MG, Esposito S, Ferrari E, Monzani R, Occhigrossi L, Pagliarini V, Sette Cet al (2018) TG2 regulates the heat‐shock response by the post‐translational modification of HSF1. EMBO Rep 19: e45067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovetta AI, Pena D, Hernandez Del Pino RE, Recalde GM, Pellegrini J, Bigi F, Musella RM, Palmero DJ, Gutierrez M, Colombo MIet al (2014) IFNG‐mediated immune responses enhance autophagy against Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens in patients with active tuberculosis. Autophagy 10: 2109–2121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowntree RK, Harris A (2003) The phenotypic consequences of CFTR mutations. Ann Hum Genet 67: 471–485 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein DC, Marino G, Kroemer G (2011) Autophagy and aging. Cell 146: 682–695 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein DC, Bento CF, Deretic V (2015) Therapeutic targeting of autophagy in neurodegenerative and infectious diseases. J Exp Med 212: 979–990 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rui Y‐N, Xu Z, Patel B, Chen Z, Chen D, Tito A, David G, Sun Y, Stimming EF, Bellen HJet al (2015) Huntingtin functions as a scaffold for selective macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol 17: 262–275 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz A, Rockfield S, Taran N, Haller E, Engelman RW, Flores I, Panina‐Bordignon P, Nanjundan M (2016) Effect of hydroxychloroquine and characterization of autophagy in a mouse model of endometriosis. Cell Death Dis 7: e2059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo R, Varano GP, Adornetto A, Nazio F, Tettamanti G, Girardello R, Cianfanelli V, Cavaliere F, Morrone LA, Corasaniti MTet al (2018) Rapamycin and fasting sustain autophagy response activated by ischemia/reperfusion injury and promote retinal ganglion cell survival. Cell Death Dis 9: 981 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusu V, Hoch E, Mercader JM, Tenen DE, Gymrek M, Hartigan CR, DeRan M, von Grotthuss M, Fontanillas P, Spooner Aet al (2017) Type 2 diabetes variants disrupt function of SLC16A11 through two distinct mechanisms. Cell 170: 199–212.e120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybstein MD, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2018) The autophagic network and cancer. Nat Cell Biol 20: 243–251 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter SW, Koo JK, Choi AM (2014) Molecular regulation of autophagy and its implications for metabolic diseases. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 17: 329–337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha T (2012) LAMP2A overexpression in breast tumors promotes cancer cell survival via chaperone‐mediated autophagy. Autophagy 8: 1643–1656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahu R, Kaushik S, Clement CC, Cannizzo ES, Scharf B, Follenzi A, Potolicchio I, Nieves E, Cuervo AM, Santambrogio L (2011) Microautophagy of cytosolic proteins by late endosomes. Dev Cell 20: 131–139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T, Sadoshima J (2015) Molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial autophagy/mitophagy in the heart. Circ Res 116: 1477–1490 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T, Kuma A, Sugiura Y, Ichimura Y, Obata M, Kitamura H, Okuda S, Lee H‐C, Ikeda K, Kanegae Yet al (2019) Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism through selective turnover of NCoR1. Nat Commun 10: 1567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitsu H, Nishimura T, Muramatsu K, Kodera H, Kumada S, Sugai K, Kasai‐Yoshida E, Sawaura N, Nishida H, Hoshino AIet al (2013) De novo mutations in the autophagy gene WDR45 cause static encephalopathy of childhood with neurodegeneration in adulthood. Nat Genet 45: 445–449, 449e441 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samardzija M, Corna A, Gomez‐Sintes R, Jarboui MA, Armento A, Roger JE, Petridou E, Haq W, Paquet‐Durand F, Zrenner Eet al (2020) HDAC inhibition ameliorates cone survival in retinitis pigmentosa mice. Cell Death Differ 28: 1317–1332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santana‐Codina N, Mancias JD, Kimmelman AC (2017) The role of autophagy in cancer. Annu Rev Cancer Biol 1: 19–39 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarraf SA, Shah HV, Kanfer G, Pickrell AM, Holtzclaw LA, Ward ME, Youle RJ (2020) Loss of TAX1BP1‐directed autophagy results in protein aggregate accumulation in the brain. Mol Cell 80: 779–795.e710 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H, Takayama K, Matsushita T, Ishida K, Kubo S, Matsumoto T, Fujita N, Oka S, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2012) Autophagy modulates osteoarthritis‐related gene expression in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 64: 1920–1928 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider JL, Suh Y, Cuervo AM (2014) Deficient chaperone‐mediated autophagy in liver leads to metabolic dysregulation. Cell Metab 20: 417–432 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider JL, Villarroya J, Diaz‐Carretero A, Patel B, Urbanska AM, Thi MM, Villarroya F, Santambrogio L, Cuervo AM (2015) Loss of hepatic chaperone‐mediated autophagy accelerates proteostasis failure in aging. Aging Cell 14: 249–264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder S, Hofer SJ, Zimmermann A, Pechlaner R, Dammbrueck C, Pendl T, Marcello GM, Pogatschnigg V, Bergmann M, Müller Met al (2021) Dietary spermidine improves cognitive function. Cell Rep 35: 108985 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciarretta S, Zhai P, Shao D, Maejima Y, Robbins J, Volpe M, Condorelli G, Sadoshima J (2012) Rheb is a critical regulator of autophagy during myocardial ischemia: pathophysiological implications in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Circulation 125: 1134–1146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciarretta S, Zhai P, Shao D, Zablocki D, Nagarajan N, Terada LS, Volpe M, Sadoshima J (2013) Activation of NADPH oxidase 4 in the endoplasmic reticulum promotes cardiomyocyte autophagy and survival during energy stress through the protein kinase RNA‐activated‐like endoplasmic reticulum kinase/eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha/activating transcription factor 4 pathway. Circ Res 113: 1253–1264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciarretta S, Maejima Y, Zablocki D, Sadoshima J (2018) The role of autophagy in the heart. Annu Rev Physiol 80: 1–26 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrivo A, Bourdenx M, Pampliega O, Cuervo AM (2018) Selective autophagy as a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol 17: 802–815 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman MNJ (2021) The retromer complex: from genesis to revelations. Trends Biochem Sci 46: 608–620 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastián D, Sorianello E, Segalés J, Irazoki A, Ruiz‐Bonilla V, Sala D, Planet E, Berenguer‐Llergo A, Muñoz JP, Sánchez‐Feutrie Met al (2016) Mfn2 deficiency links age‐related sarcopenia and impaired autophagy to activation of an adaptive mitophagy pathway. EMBO J 35: 1677–1693 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian D, Zorzano A (2020) Self‐eating for muscle fitness: autophagy in the control of energy metabolism. Dev Cell 54: 268–281 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segalés J, Perdiguero E, Serrano AL, Sousa‐Victor P, Ortet L, Jardí M, Budanov AV, Garcia‐Prat L, Sandri M, Thomson DMet al (2020) Sestrin prevents atrophy of disused and aging muscles by integrating anabolic and catabolic signals. Nat Commun 11: 189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellier C, Campanari ML, Julie Corbier C, Gaucherot A, Kolb‐Cheynel I, Oulad‐Abdelghani M, Ruffenach F, Page A, Ciura S, Kabashi Eet al (2016) Loss of C9ORF72 impairs autophagy and synergizes with polyQ Ataxin‐2 to induce motor neuron dysfunction and cell death. EMBO J 35: 1276–1297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong E, Insolera R, Dulovic M, Kamsteeg EJ, Trinh J, Bruggemann N, Sandford E, Li S, Ozel AB, Li JZet al (2018) Mutations in VPS13D lead to a new recessive ataxia with spasticity and mitochondrial defects. Ann Neurol 83: 1075–1088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergin I, Evans TD, Zhang X, Bhattacharya S, Stokes CJ, Song E, Ali S, Dehestani B, Holloway KB, Micevych PSet al (2017) Exploiting macrophage autophagy‐lysosomal biogenesis as a therapy for atherosclerosis. Nat Commun 8: 15750 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settembre C, De Cegli R, Mansueto G, Saha PK, Vetrini F, Visvikis O, Huynh T, Carissimo A, Palmer D, Jürgen Klisch Tet al (2013) TFEB controls cellular lipid metabolism through a starvation‐induced autoregulatory loop. Nat Cell Biol 15: 647–658 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang Y, Wang H, Jia P, Zhao H, Liu C, Liu W, Song Z, Xu Z, Yang L, Wang Yet al (2016) Autophagy regulates spermatid differentiation via degradation of PDLIM1. Autophagy 12: 1575–1592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro IM, Layfield R, Lotz M, Settembre C, Whitehouse C (2014) Boning up on autophagy: the role of autophagy in skeletal biology. Autophagy 10: 7–19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma G, Ojha R, Noguera‐Ortega E, Rebecca VW, Attanasio J, Liu S, Piao S, Lee JJ, Nicastri MC, Harper SLet al (2020) PPT1 inhibition enhances the antitumor activity of anti‐PD‐1 antibody in melanoma. JCI Insight 5: e133225 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen JL, Fortier TM, Zhao YG, Wang R, Burmeister M, Baehrecke EH (2021) Vmp1, Vps13D, and Marf/Mfn2 function in a conserved pathway to regulate mitochondria and ER contact in development and disease. Curr Biol 31: 3028–3039.e7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi CS, Kehrl JH (2008) MyD88 and Trif target Beclin 1 to trigger autophagy in macrophages. J Biol Chem 283: 33175–33182 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi M, Flores B, Gillings N, Bian A, Cho HJ, Yan S, Liu Y, Levine B, Moe OW, Hu MC (2016) alphaKlotho mitigates progression of AKI to CKD through activation of autophagy. J Am Soc Nephrol 27: 2331–2345 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigihara N, Fukunaka A, Hara A, Komiya K, Honda A, Uchida T, Abe H, Toyofuku Y, Tamaki M, Ogihara Tet al (2014) Human IAPP‐induced pancreatic beta cell toxicity and its regulation by autophagy. J Clin Invest 124: 3634–3644 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji‐Kawata S, Sumpter R, Leveno M, Campbell GR, Zou Z, Kinch L, Wilkins AD, Sun Q, Pallauf K, MacDuff Det al (2013) Identification of a candidate therapeutic autophagy‐inducing peptide. Nature 494: 201–206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava S, Bhanja Chowdhury J, Steele R, Ray R, Ray RB (2012) Hepatitis C virus upregulates Beclin1 for induction of autophagy and activates mTOR signaling. J Virol 86: 8705–8712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica V, Galluzzi L, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Izzo V, Maiuri MC, Kroemer G (2015) Organelle‐specific initiation of autophagy. Mol Cell 59: 522–539 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva MC, Nandi GA, Tentarelli S, Gurrell IK, Jamier T, Lucente D, Dickerson BC, Brown DG, Brandon NJ, Haggarty SJ (2020) Prolonged tau clearance and stress vulnerability rescue by pharmacological activation of autophagy in tauopathy neurons. Nat Commun 11: 3258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen A, Cumming RC, Brech A, Isakson P, Schubert DR, Finley KD (2008) Promoting basal levels of autophagy in the nervous system enhances longevity and oxidant resistance in adult Drosophila . Autophagy 4: 176–184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh SB, Davis AS, Taylor GA, Deretic V (2006) Human IRGM induces autophagy to eliminate intracellular mycobacteria. Science 313: 1438–1441 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Novak I, Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Cuervo AM, Czaja MJ (2009a) Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature 458: 1131–1135 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R, Xiang Y, Wang Y, Baikati K, Cuervo AM, Luu YK, Tang Y, Pessin JE, Schwartz GJ, Czaja MJ (2009b) Autophagy regulates adipose mass and differentiation in mice. J Clin Invest 119: 3329–3339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R, Cuervo AM (2012) Lipophagy: connecting autophagy and lipid metabolism. Int J Cell Biol 2012: 282041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliter DA, Martinez J, Hao L, Chen XI, Sun N, Fischer TD, Burman JL, Li Y, Zhang Z, Narendra DPet al (2018) Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING‐induced inflammation. Nature 561: 258–262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Smith AG, Macleod KF (2019) Autophagy, cancer stem cells and drug resistance. J Pathol 247: 708–718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith EF, Shaw PJ, De Vos KJ (2019) The role of mitochondria in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurosci Lett 710: 132933 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C, Mitter SK, Qi X, Beli E, Rao HV, Ding J, Ip CS, Gu H, Akin D, Dunn WA Jret al (2017) Oxidative stress‐mediated NFkappaB phosphorylation upregulates p62/SQSTM1 and promotes retinal pigmented epithelial cell survival through increased autophagy. PLoS One 12: e0171940 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria LR, Allegri G, Melck D, Pastore N, Annunziata P, Paris D, Polishchuk E, Nusco E, Thöny B, Motta Aet al (2018) Enhancement of hepatic autophagy increases ureagenesis and protects against hyperammonemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115: 391–396 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria LR, Gurung S, De Sabbata G, Perocheau DP, De Angelis A, Bruno G, Polishchuk E, Paris D, Cuomo P, Motta Aet al (2021) Beclin‐1‐mediated activation of autophagy improves proximal and distal urea cycle disorders. EMBO Mol Med 13: e13158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sousa CM, Biancur DE, Wang X, Halbrook CJ, Sherman MH, Zhang LI, Kremer D, Hwang RF, Witkiewicz AK, Ying Het al (2016) Pancreatic stellate cells support tumour metabolism through autophagic alanine secretion. Nature 536: 479–483 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spampanato C, Feeney E, Li L, Cardone M, Lim J‐A, Annunziata F, Zare H, Polishchuk R, Puertollano R, Parenti Get al (2013) Transcription factor EB (TFEB) is a new therapeutic target for Pompe disease. EMBO Mol Med 5: 691–706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer MZ, Poole LP, Drake LE, Bock‐Hughes A, Boland ML, Smith AG, Hart J, Chourasia AH, Liu I, Bozek Get al (2021) BNIP3‐dependent mitophagy promotes cytosolic localization of LC3B and metabolic homeostasis in the liver. Autophagy 1–17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprooten J, Agostinis P, Garg AD (2019) Type I interferons and dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 348: 217–262 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprooten J, Garg AD (2020) Type I interferons and endoplasmic reticulum stress in health and disease. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 350: 63–118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel D, Millarte V, Tillmann K, Huber J, Tamin‐Yecheskel B‐C, Akutsu M, Demishtein A, Ben‐Zeev B, Anikster Y, Perez Fet al (2015) TECPR2 cooperates with LC3C to regulate COPII‐dependent ER export. Mol Cell 60: 89–104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staring J, von Castelmur E, Blomen VA, van den Hengel LGBrockmann M, Baggen J, Thibaut HJ, Nieuwenhuis J, Janssen H, van Kuppeveld FJMet al (2017) PLA2G16 represents a switch between entry and clearance of Picornaviridae. Nature 541: 412–416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele S, Brunton J, Ziehr B, Taft‐Benz S, Moorman N, Kawula T (2013) Francisella tularensis harvests nutrients derived via ATG5‐independent autophagy to support intracellular growth. PLoS Pathog 9: e1003562 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohecker AM, Guo JY, Karsli‐Uzunbas G, Price SM, Chen GJ, Mathew R, McMahon M, White E (2013) Autophagy sustains mitochondrial glutamine metabolism and growth of BrafV600E‐driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov 3: 1272–1285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W, Li Z, Jia Y, Zhuo Y (2014) Rapamycin is neuroprotective in a rat chronic hypertensive glaucoma model. PLoS One 9: e99719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suleiman J, Allingham‐Hawkins D, Hashem M, Shamseldin HE, Alkuraya FS, El‐Hattab AW (2018) WDR45B‐related intellectual disability, spastic quadriplegia, epilepsy, and cerebral hypoplasia: a consistent neurodevelopmental syndrome. Clin Genet 93: 360–364 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumpter R, Sirasanagandla S, Fernández ÁF, Wei Y, Dong X, Franco L, Zou Z, Marchal C, Lee M, Clapp Det al (2016) Fanconi anemia proteins function in mitophagy and immunity. Cell 165: 867–881 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y, Li TY, Song L, Zhang C, Li J, Lin ZZ, Lin SC, Lin SY (2018) Liver‐specific deficiency of unc‐51 like kinase 1 and 2 protects mice from acetaminophen‐induced liver injury. Hepatology 67: 2397–2413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki J, Nakajima W, Suzuki H, Asano Y, Tanaka N (2017) Chaperone‐mediated autophagy promotes lung cancer cell survival through selective stabilization of the pro‐survival protein, MCL1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482: 1334–1340 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamura A, Komatsu M, Hara T, Sakamoto A, Kishi C, Waguri S, Eishi Y, Hino O, Tanaka K, Mizushima N (2011) Autophagy‐deficient mice develop multiple liver tumors. Genes Dev 25: 795–800 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamim‐Yecheskel B‐C, Fraiberg M, Kokabi K, Freud S, Shatz O, Marvaldi L, Subic N, Brenner O, Tsoory M, Eilam‐Altstadter Ret al (2020) A tecpr2 knockout mouse exhibits age‐dependent neuroaxonal dystrophy associated with autophagosome accumulation. Autophagy 1–14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan JMJ, Mellouk N, Osborne SE, Ammendolia DA, Dyer DN, Li R, Brunen D, van Rijn JM, Huang JU, Czuczman MAet al (2018) An ATG16L1‐dependent pathway promotes plasma membrane repair and limits Listeria monocytogenes cell‐to‐cell spread. Nat Microbiol 3: 1472–1485 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y, Guhde G, Suter A, Eskelinen EL, Hartmann D, Lullmann‐Rauch R, Janssen PM, Blanz J, von Figura K, Saftig P (2000) Accumulation of autophagic vacuoles and cardiomyopathy in LAMP‐2‐deficient mice. Nature 406: 902–906 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S, Hikita H, Tatsumi T, Sakamori R, Nozaki Y, Sakane S, Shiode Y, Nakabori T, Saito Y, Hiramatsu Net al (2016) Rubicon inhibits autophagy and accelerates hepatocyte apoptosis and lipid accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatology 64: 1994–2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanchot C, Terme M, Pere H, Tran T, Benhamouda N, Strioga M, Banissi C, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G, Tartour E (2013) Tumor‐infiltrating regulatory T cells: phenotype, role, mechanism of expansion in situ and clinical significance. Cancer Microenviron 6: 147–157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneike M, Yamaguchi O, Nakai A, Hikoso S, Takeda T, Mizote I, Oka T, Tamai T, Oyabu J, Murakawa Tet al (2010) Inhibition of autophagy in the heart induces age‐related cardiomyopathy. Autophagy 6: 600–606 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneike M, Nishida K, Omiya S, Zarrinpashneh E, Misaka T, Kitazume‐Taneike R, Austin R, Takaoka M, Yamaguchi O, Gambello MJet al (2016) mTOR hyperactivation by ablation of tuberous sclerosis complex 2 in the mouse heart induces cardiac dysfunction with the increased number of small mitochondria mediated through the down‐regulation of autophagy. PLoS One 11: e0152628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Z, Lin MG, Stowe TR, Chen S, Zhu M, Stearns T, Franco B, Zhong Q (2013) Autophagy promotes primary ciliogenesis by removing OFD1 from centriolar satellites. Nature 502: 254–257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C, Han H, Yan M, Zhu S, Liu J, Liu Z, He L, Tan J, Liu YU, Liu Het al (2018) PINK1‐PRKN/PARK2 pathway of mitophagy is activated to protect against renal ischemia‐reperfusion injury. Autophagy 14: 880–897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang N, Zhao H, Zhang H, Dong Y (2019) Effect of autophagy gene DRAM on proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy of osteoblast in osteoporosis rats. J Cell Physiol 234: 5023–5032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C, Livingston MJ, Liu Z, Dong Z (2020) Autophagy in kidney homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 16: 489–508 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannous P, Zhu H, Johnstone JL, Shelton JM, Rajasekaran NS, Benjamin IJ, Nguyen L, Gerard RD, Levine B, Rothermel BAet al (2008) Autophagy is an adaptive response in desmin‐related cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 9745–9750 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateosian NL, Pellegrini JM, Amiano NO, Rolandelli A, Casco N, Palmero DJ, Colombo MI, Garcia VE (2017) IL17A augments autophagy in Mycobacterium tuberculosis‐infected monocytes from patients with active tuberculosis in association with the severity of the disease. Autophagy 13: 1191–1204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tezze C, Romanello V, Desbats MA, Fadini GP, Albiero M, Favaro G, Ciciliot S, Soriano ME, Morbidoni V, Cerqua Cet al (2017) Age‐associated loss of OPA1 in muscle impacts muscle mass, metabolic homeostasis, systemic inflammation, and epithelial senescence. Cell Metab 25: 1374–1389.e1376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thangaraj A, Sil S, Tripathi A, Chivero ET, Periyasamy P, Buch S (2020) Targeting endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy as therapeutic approaches for neurological diseases. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 350: 285–325 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoen LF, Guimaraes EL, Dolle L, Mannaerts I, Najimi M, Sokal E, van Grunsven LA (2011) A role for autophagy during hepatic stellate cell activation. J Hepatol 55: 1353–1360 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurston TL, Wandel MP, von Muhlinen N, Foeglein A, Randow F (2012) Galectin 8 targets damaged vesicles for autophagy to defend cells against bacterial invasion. Nature 482: 414–418 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Y, Chang JC, Fan EY, Flajolet M, Greengard P (2013) Adaptor complex AP2/PICALM, through interaction with LC3, targets Alzheimer's APP‐CTF for terminal degradation via autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: 17071–17076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tittarelli A, Janji B, Van Moer K, Noman MZ, Chouaib S (2015) The selective degradation of synaptic connexin 43 protein by hypoxia‐induced autophagy impairs natural killer cell‐mediated tumor cell killing. J Biol Chem 290: 23670–23679 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosco A, De Gregorio F, Esposito S, De Stefano D, Sana I, Ferrari E, Sepe A, Salvadori L, Buonpensiero P, Di Pasqua Aet al (2016) A novel treatment of cystic fibrosis acting on‐target: cysteamine plus epigallocatechin gallate for the autophagy‐dependent rescue of class II‐mutated CFTR. Cell Death Differ 23: 1380–1393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towers CG, Fitzwalter BE, Regan D, Goodspeed A, Morgan MJ, Liu CW, Gustafson DL, Thorburn A (2019) Cancer cells upregulate NRF2 signaling to adapt to autophagy inhibition. Dev Cell 50: 690–703.e696 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travassos LH, Carneiro LAM, Ramjeet M, Hussey S, Kim Y‐G, Magalhães JG, Yuan L, Soares F, Chea E, Le Bourhis Let al (2010) Nod1 and Nod2 direct autophagy by recruiting ATG16L1 to the plasma membrane at the site of bacterial entry. Nat Immunol 11: 55–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumbarello DA, Waxse BJ, Arden SD, Bright NA, Kendrick‐Jones J, Buss F (2012) Autophagy receptors link myosin VI to autophagosomes to mediate Tom1‐dependent autophagosome maturation and fusion with the lysosome. Nat Cell Biol 14: 1024–1035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucar A, Gupta SK, Fiedler J, Erikci E, Kardasinski M, Batkai S, Dangwal S, Kumarswamy R, Bang C, Holzmann Aet al (2012) The miRNA‐212/132 family regulates both cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte autophagy. Nat Commun 3: 1078 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno T, Komatsu M (2017) Autophagy in the liver: functions in health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14: 170–184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulland TK, Song WM, Huang S‐C, Ulrich JD, Sergushichev A, Beatty WL, Loboda AA, Zhou Y, Cairns NJ, Kambal Aet al (2017) TREM2 maintains microglial metabolic fitness in Alzheimer's disease. Cell 170: 649–663.e613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uytterhoeven V, Lauwers E, Maes I, Miskiewicz K, Melo M, Swerts J, Kuenen S, Wittocx R, Corthout N, Marrink S‐Jet al (2015) Hsc70‐4 deforms membranes to promote synaptic protein turnover by endosomal microautophagy. Neuron 88: 735–748 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainshtein A, Grumati P, Sandri M, Bonaldo P (2014) Skeletal muscle, autophagy, and physical activity: the menage a trois of metabolic regulation in health and disease. J Mol Med (Berl) 92: 127–137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valapala M, Wilson C, Hose S, Bhutto IA, Grebe R, Dong A, Greenbaum S, Gu L, Sengupta S, Cano Met al (2014) Lysosomal‐mediated waste clearance in retinal pigment epithelial cells is regulated by CRYBA1/betaA3/A1‐crystallin via V‐ATPase‐MTORC1 signaling. Autophagy 10: 480–496 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdor R, Mocholi E, Botbol Y, Guerrero‐Ros I, Chandra D, Koga H, Gravekamp C, Cuervo AM, Macian F (2014) Chaperone‐mediated autophagy regulates T cell responses through targeted degradation of negative regulators of T cell activation. Nat Immunol 15: 1046–1054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdor R, Garcia‐Bernal D, Riquelme D, Martinez CM, Moraleda JM, Cuervo AM, Macian F, Martinez S (2019) Glioblastoma ablates pericytes antitumor immune function through aberrant up‐regulation of chaperone‐mediated autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116: 20655–20665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valente EM, Abou‐Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MM, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Del Turco D, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DGet al (2004) Hereditary early‐onset Parkinson's disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science 304: 1158–1160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallon V, Rose M, Gerasimova M, Satriano J, Platt KA, Koepsell H, Cunard R, Sharma K, Thomson SC, Rieg T (2013) Knockout of Na‐glucose transporter SGLT2 attenuates hyperglycemia and glomerular hyperfiltration but not kidney growth or injury in diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 304: F156–F167 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanpouille‐Box C, Demaria S, Formenti SC, Galluzzi L (2018) Cytosolic DNA sensing in organismal tumor control. Cancer Cell 34: 361–378 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara‐Perez M, Felipe‐Abrio B, Agostinis P (2019) Mitophagy in cancer: a tale of adaptation. Cells 8: 493 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velentzas PD, Zhang L, Das G, Chang TK, Nelson C, Kobertz WR, Baehrecke EH (2018) The proton‐coupled monocarboxylate transporter hermes is necessary for autophagy during cell death. Dev Cell 47: 281–293.e284 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vera‐Ramirez L, Vodnala SK, Nini R, Hunter KW, Green JE (2018) Autophagy promotes the survival of dormant breast cancer cells and metastatic tumour recurrence. Nat Commun 9: 1944 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma M, Callio J, Otero PA, Sekler I, Wills ZP, Chu CT (2017) Mitochondrial calcium dysregulation contributes to dendrite degeneration mediated by PD/LBD‐associated LRRK2 mutants. J Neurosci 37: 11151–11165 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vescovo T, Romagnoli A, Perdomo AB, Corazzari M, Ciccosanti F, Alonzi T, Nardacci R, Ippolito G, Tripodi M, Garcia–Monzon Cet al (2012) Autophagy protects cells from HCV‐induced defects in lipid metabolism. Gastroenterology 142: 644–653.e643 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villella VR, Esposito S, Ferrari E, Monzani R, Tosco A, Rossin F, Castaldo A, Silano M, Marseglia GL, Romani Let al (2019a) Autophagy suppresses the pathogenic immune response to dietary antigens in cystic fibrosis. Cell Death Dis 10: 258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villella VR, Venerando A, Cozza G, Esposito S, Ferrari E, Monzani R, Spinella MC, Oikonomou V, Renga G, Tosco Aet al (2019b) A pathogenic role for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in celiac disease. EMBO J 38: e100101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vion A‐C, Kheloufi M, Hammoutene A, Poisson J, Lasselin J, Devue C, Pic I, Dupont N, Busse J, Stark Ket al (2017) Autophagy is required for endothelial cell alignment and atheroprotection under physiological blood flow. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114: E8675–E8684 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodnala SK, Eil R, Kishton RJ, Sukumar M, Yamamoto TN, Ha N‐H, Lee P‐H, Shin MH, Patel SJ, Yu Zet al (2019) T cell stemness and dysfunction in tumors are triggered by a common mechanism. Science 363: eaau0135 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrahnas C, Blank M, Dite TA, Tatarczuch L, Ansari N, Crimeen‐Irwin B, Nguyen H, Forwood MR, Hu Y, Ikegame Met al (2019) Increased autophagy in EphrinB2‐deficient osteocytes is associated with elevated secondary mineralization and brittle bone. Nat Commun 10: 3436 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan JH, Weiss E, Ben Mkaddem S, Mabire M, Choinier P‐M, Picq O, Thibault‐Sogorb T, Hegde P, Pishvaie D, Bens Met al (2020) LC3‐associated phagocytosis protects against inflammation and liver fibrosis via immunoreceptor inhibitory signaling. Sci Transl Med 12: eaaw8523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C, Liang CC, Bian ZC, Zhu Y, Guan JL (2013) FIP200 is required for maintenance and differentiation of postnatal neural stem cells. Nat Neurosci 16: 532–542 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K, Liu C‐Y, Zhou L‐Y, Wang J‐X, Wang M, Zhao B, Zhao W‐K, Xu S‐J, Fan L‐H, Zhang X‐Jet al (2015) APF lncRNA regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting miR‐188‐3p. Nat Commun 6: 6779 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K, Zhang T, Lei Y, Li X, Jiang J, Lan J, Liu Y, Chen H, Gao W, Xie Net al (2018a) Identification of ANXA2 (annexin A2) as a specific bleomycin target to induce pulmonary fibrosis by impeding TFEB‐mediated autophagic flux. Autophagy 14: 269–282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang KZQ, Steer E, Otero PA, Bateman NW, Cheng MH, Scott AL, Wu C, Bahar I, Shih YT, Hsueh YPet al (2018b) PINK1 interacts with VCP/p97 and activates PKA to promote NSFL1C/p47 phosphorylation and dendritic arborization in neurons. eNeuro 5: ENEURO.0466‐18.2018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R, Liu Y, Liu L, Chen M, Wang X, Yang J, Gong Y, Ding BS, Wei Y, Wei X (2019) Tumor cells induce LAMP2a expression in tumor‐associated macrophage for cancer progression. EBioMedicine 40: 118–134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C, Shen J, Ying J, Xiao D, O'Keefe RJ (2020a) FoxO1 is a crucial mediator of TGF‐beta/TAK1 signaling and protects against osteoarthritis by maintaining articular cartilage homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117: 30488–30497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F, Tasset I, Cuervo AM, Muller S (2020b) In vivo remodeling of altered autophagy‐lysosomal pathway by a phosphopeptide in lupus. Cells 9: 2328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Sharma P, Jefferson M, Zhang W, Bone B, Kipar A, Bitto D, Coombes JL, Pearson T, Man Aet al (2021) Non‐canonical autophagy functions of ATG16L1 in epithelial cells limit lethal infection by influenza A virus. EMBO J 40: e105543 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson RO, Manzanillo PS, Cox JS (2012) Extracellular M. tuberculosis DNA targets bacteria for autophagy by activating the host DNA‐sensing pathway. Cell 150: 803–815 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb JL, Ravikumar B, Atkins J, Skepper JN, Rubinsztein DC (2003) Alpha‐Synuclein is degraded by both autophagy and the proteasome. J Biol Chem 278: 25009–25013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster CP, Smith EF, Bauer CS, Moller A, Hautbergue GM, Ferraiuolo L, Myszczynska MA, Higginbottom A, Walsh MJ, Whitworth AJet al (2016) The C9orf72 protein interacts with Rab1a and the ULK1 complex to regulate initiation of autophagy. EMBO J 35: 1656–1676 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei H, Wei S, Gan B, Peng X, Zou W, Guan JL (2011) Suppression of autophagy by FIP200 deletion inhibits mammary tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 25: 1510–1527 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weindel CG, Richey LJ, Bolland S, Mehta AJ, Kearney JF, Huber BT (2015) B cell autophagy mediates TLR7‐dependent autoimmunity and inflammation. Autophagy 11: 1010–1024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weindel CG, Richey LJ, Mehta AJ, Shah M, Huber BT (2017) Autophagy in dendritic cells and b cells is critical for the inflammatory state of TLR7‐mediated autoimmunity. J Immunol 198: 1081–1092 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen YT, Zhang JR, Kapupara K, Tsai RK (2019) mTORC2 activation protects retinal ganglion cells via Akt signaling after autophagy induction in traumatic optic nerve injury. Exp Mol Med 51: 1–11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E (2015) The role for autophagy in cancer. J Clin Invest 125: 42–46 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wignes JA, Goldman JW, Weihl CC, Bartley MG, Andley UP (2013) p62 expression and autophagy in alphaB‐crystallin R120G mutant knock‐in mouse model of hereditary cataract. Exp Eye Res 115: 263–273 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijk SJL, Fricke F, Herhaus L, Gupta J, Hotte K, Pampaloni F, Grumati P, Kaulich M, Sou YS, Komatsu Met al (2017) Linear ubiquitination of cytosolic Salmonella Typhimurium activates NF‐kappaB and restricts bacterial proliferation. Nat Microbiol 2: 17066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild P, Farhan H, McEwan DG, Wagner S, Rogov VV, Brady NR, Richter B, Korac J, Waidmann O, Choudhary Cet al (2011) Phosphorylation of the autophagy receptor optineurin restricts Salmonella growth. Science 333: 228–233 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow AR, Chen CW, Corrochano S, Acevedo‐Arozena A, Gordon DE, Peden AA, Lichtenberg M, Menzies FM, Ravikumar B, Imarisio Set al (2010) alpha‐Synuclein impairs macroautophagy: implications for Parkinson's disease. J Cell Biol 190: 1023–1037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold MS, Lim J, Lachance V, Deng Z, Yue Z (2016) ULK1‐mediated phosphorylation of ATG14 promotes autophagy and is impaired in Huntington's disease models. Mol Neurodegener 11: 76 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong YC, Holzbaur EL (2014a) Optineurin is an autophagy receptor for damaged mitochondria in parkin‐mediated mitophagy that is disrupted by an ALS‐linked mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111: E4439–E4448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong YC, Holzbaur EL (2014b) The regulation of autophagosome dynamics by huntingtin and HAP1 is disrupted by expression of mutant huntingtin, leading to defective cargo degradation. J Neurosci 34: 1293–1305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S‐W, Huang B‐W, Hu X, Ho Kim E, Kolb JP, Padilla RJ, Xue P, Wang L, Oguin TH, Miguez PAet al (2020) Global deletion of Optineurin results in altered type I IFN signaling and abnormal bone remodeling in a model of Paget's disease. Cell Death Differ 27: 71–84 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton KH (2016) Metabolism: mitophagy turns beige adipocytes white. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17: 607 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X, Fleming A, Ricketts T, Pavel M, Virgin H, Menzies FM, Rubinsztein DC (2016) Autophagy regulates Notch degradation and modulates stem cell development and neurogenesis. Nat Commun 7: 10533 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia H‐G, Najafov A, Geng J, Galan‐Acosta L, Han X, Guo Y, Shan B, Zhang Y, Norberg E, Zhang Tet al (2015) Degradation of HK2 by chaperone‐mediated autophagy promotes metabolic catastrophe and cell death. J Cell Biol 210: 705–716 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia H, Green DR, Zou W (2021) Autophagy in tumour immunity and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 21: 281–297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie X, Koh JY, Price S, White E, Mehnert JM (2015) Atg7 overcomes senescence and promotes growth of BrafV600E‐driven melanoma. Cancer Discov 5: 410–423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie C, Ginet V, Sun Y, Koike M, Zhou K, Li T, Li H, Li Q, Wang X, Uchiyama Yet al (2016) Neuroprotection by selective neuronal deletion of Atg7 in neonatal brain injury. Autophagy 12: 410–423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Y, Zhao Y, Shi L, Li W, Chen K, Li M, Chen X, Zhang H, Li T, Matsuzawa‐Ishimoto YUet al (2020) Gut epithelial TSC1/mTOR controls RIPK3‐dependent necroptosis in intestinal inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest 130: 2111–2128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu K, Xu P, Yao JF, Zhang YG, Hou WK, Lu SM (2013) Reduced apoptosis correlates with enhanced autophagy in synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res 62: 229–237 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X, Araki K, Li S, Han J‐H, Ye L, Tan WG, Konieczny BT, Bruinsma MW, Martinez J, Pearce ELet al (2014) Autophagy is essential for effector CD8(+) T cell survival and memory formation. Nat Immunol 15: 1152–1161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H, Zhang C, Cao L, Song J, Xu X, Zhang B, Chen B, Zhao G (2019a) ATL3 gene mutation in a Chinese family with hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1F. J Peripher Nerv Syst 24: 150–155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y, Zhang S, Zheng H (2019b) The cargo receptor SQSTM1 ameliorates neurofibrillary tangle pathology and spreading through selective targeting of pathological MAPT (microtubule associated protein tau). Autophagy 15: 583–598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T, Ito D, Suzuki N (2016) TFG‐related neurologic disorders: new insights into relationships between endoplasmic reticulum and neurodegeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 75: 299–305 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H, Arakawa S, Kanaseki T, Miyatsuka T, Fujitani Y, Watada H, Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2016) Golgi membrane‐associated degradation pathway in yeast and mammals. EMBO J 35: 1991–2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H, Honda S, Torii S, Shimizu K, Katoh K, Miyake K, Miyake N, Fujikake N, Sakurai HT, Arakawa Set al (2020) Wipi3 is essential for alternative autophagy and its loss causes neurodegeneration. Nat Commun 11: 5311 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S, Kuramoto K, Wang N, Situ X, Priyadarshini M, Zhang W, Cordoba‐Chacon J, Layden BT, He C (2018) Autophagy differentially regulates insulin production and insulin sensitivity. Cell Rep 23: 3286–3299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K, Venida A, Yano J, Biancur DE, Kakiuchi M, Gupta S, Sohn ASW, Mukhopadhyay S, Lin EY, Parker SJet al (2020) Autophagy promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer by degrading MHC‐I. Nature 581: 100–105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto‐Nonaka K, Koike M, Asanuma K, Takagi M, Oliva Trejo JA, Seki T, Hidaka T, Ichimura K, Sakai T, Tada Net al (2016) Cathepsin D in podocytes is important in the pathogenesis of proteinuria and CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 27: 2685–2700 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamuro T, Kawabata T, Fukuhara A, Saita S, Nakamura S, Takeshita H, Fujiwara M, Enokidani Y, Yoshida G, Tabata Ket al (2020) Age‐dependent loss of adipose Rubicon promotes metabolic disorders via excess autophagy. Nat Commun 11: 4150 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki T, Kirchmair A, Sato AI, Buqué A, Rybstein M, Petroni G, Bloy N, Finotello F, Stafford L, Navarro Manzano Eet al (2020) Mitochondrial DNA drives abscopal responses to radiation that are inhibited by autophagy. Nat Immunol 21: 1160–1171 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki T, Bravo‐San Pedro JM, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G, Pietrocola F (2021) Autophagy in the cancer‐immunity dialogue. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 169: 40–50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang YI, Hentati A, Deng H‐X, Dabbagh O, Sasaki T, Hirano M, Hung W‐Y, Ouahchi K, Yan J, Azim ACet al (2001) The gene encoding alsin, a protein with three guanine‐nucleotide exchange factor domains, is mutated in a form of recessive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet 29: 160–165 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L, Li P, Fu S, Calay ES, Hotamisligil GS (2010) Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab 11: 467–478 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H‐Z, Wang J‐P, Mi SU, Liu H‐Z, Cui B, Yan H‐M, Yan J, Li Z, Liu H, Hua Fet al (2012) TLR4 activity is required in the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis after acute and chronic lung injury. Am J Pathol 180: 275–292 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A, Rajeshkumar NV, Wang X, Yabuuchi S, Alexander BM, Chu GC, Von Hoff DD, Maitra A, Kimmelman AC (2014) Autophagy is critical for pancreatic tumor growth and progression in tumors with p53 alterations. Cancer Discov 4: 905–913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A, Pantoom S, Wu YW (2017a) Elucidation of the anti‐autophagy mechanism of the Legionella effector RavZ using semisynthetic LC3 proteins. Elife 6: e23905 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C, Cai CZ, Song JX, Tan JQ, Durairajan SSK, Iyaswamy A, Wu MY, Chen LL, Yue Z, Li Met al (2017b) NRBF2 is involved in the autophagic degradation process of APP‐CTFs in Alzheimer disease models. Autophagy 13: 2028–2040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang HL, Mei J, Chang KK, Zhou WJ, Huang LQ, Li MQ (2017c) Autophagy in endometriosis. Am J Transl Res 9: 4707–4725 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A, Herter‐Sprie G, Zhang H, Lin EY, Biancur D, Wang X, Deng J, Hai J, Yang S, Wong K‐Ket al (2018) Autophagy sustains pancreatic cancer growth through both cell‐autonomous and nonautonomous mechanisms. Cancer Discov 8: 276–287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y, Karsli‐Uzunbas G, Poillet‐Perez L, Sawant A, Hu ZS, Zhao Y, Moore D, Hu W, White E (2020) Autophagy promotes mammalian survival by suppressing oxidative stress and p53. Genes Dev 34: 688–700 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao J, Jia L, Khan N, Lin C, Mitter SK, Boulton ME, Dunaief JL, Klionsky DJ, Guan JL, Thompson DAet al (2015) Deletion of autophagy inducer RB1CC1 results in degeneration of the retinal pigment epithelium. Autophagy 11: 939–953 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin X, Zhou C, Li J, Liu R, Shi B, Yuan Q, Zou S (2019) Autophagy in bone homeostasis and the onset of osteoporosis. Bone Res 7: 28 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M, Minagawa S, Araya J, Sakamoto T, Hara H, Tsubouchi K, Hosaka Y, Ichikawa A, Saito N, Kadota Tet al (2019) Involvement of cigarette smoke‐induced epithelial cell ferroptosis in COPD pathogenesis. Nat Commun 10: 3145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii S, Kuma A, Akashi T, Hara T, Yamamoto A, Kurikawa Y, Itakura E, Tsukamoto S, Shitara H, Eishi Yet al (2016) Systemic analysis of Atg5‐null mice rescued from neonatal lethality by transgenic ATG5 expression in neurons. Dev Cell 39: 116–130 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young AR, Narita M, Ferreira M, Kirschner K, Sadaie M, Darot JF, Tavare S, Arakawa S, Shimizu S, Watt FMet al (2009) Autophagy mediates the mitotic senescence transition. Genes Dev 23: 798–803 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu WH, Cuervo AM, Kumar A, Peterhoff CM, Schmidt SD, Lee JH, Mohan PS, Mercken M, Farmery MR, Tjernberg LOet al (2005) Macroautophagy–a novel Beta‐amyloid peptide‐generating pathway activated in Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Biol 171: 87–98 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J‐J, Sun H‐T, Zhang Z‐F, Shi R‐X, Liu L‐B, Shang W‐Q, Wei C‐Y, Chang K‐K, Shao J, Wang M‐Yet al (2016) IL15 promotes growth and invasion of endometrial stromal cells and inhibits killing activity of NK cells in endometriosis. Reproduction 152: 151–160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue Z, Jin S, Yang C, Levine AJ, Heintz N (2003) Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 15077–15082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafar I, Ravichandran K, Belibi FA, Doctor RB, Edelstein CL (2010) Sirolimus attenuates disease progression in an orthologous mouse model of human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 78: 754–761 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaglia T, Milan G, Ruhs A, Franzoso M, Bertaggia E, Pianca N, Carpi A, Carullo P, Pesce P, Sacerdoti Det al (2014) Atrogin‐1 deficiency promotes cardiomyopathy and premature death via impaired autophagy. J Clin Invest 124: 2410–2424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahoor M, Farhan H (2018) Crosstalk of autophagy and the secretory pathway and its role in diseases. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 337: 153–184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaninello M, Palikaras K, Naon D, Iwata K, Herkenne S, Quintana‐Cabrera R, Semenzato M, Grespi F, Ross‐Cisneros FN, Carelli Vet al (2020) Inhibition of autophagy curtails visual loss in a model of autosomal dominant optic atrophy. Nat Commun 11: 4029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavodszky E, Seaman MN, Moreau K, Jimenez‐Sanchez M, Breusegem SY, Harbour ME, Rubinsztein DC (2014) Mutation in VPS35 associated with Parkinson's disease impairs WASH complex association and inhibits autophagy. Nat Commun 5: 3828 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng Z, He S, Lu J, Liu C, Lin H, Xu C, Xie L, Sun S (2018) MicroRNA‐21 aggravates chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by promoting autophagy. Exp Lung Res 44: 89–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai P, Sciarretta S, Galeotti J, Volpe M, Sadoshima J (2011) Differential roles of GSK‐3beta during myocardial ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion. Circ Res 109: 502–511 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Goldman S, Baerga R, Zhao Y, Komatsu M, Jin S (2009) Adipose‐specific deletion of autophagy‐related gene 7 (atg7) in mice reveals a role in adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 19860–19865 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L, Guo Y‐F, Liu Y‐Z, Liu Y‐J, Xiong D‐H, Liu X‐G, Wang L, Yang T‐L, Lei S‐F, Guo Yet al (2010) Pathway‐based genome‐wide association analysis identified the importance of regulation‐of‐autophagy pathway for ultradistal radius BMD. J Bone Miner Res 25: 1572–1580 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Yan H, Yuan Y, Gao J, Shen Z, Cheng Y, Shen Y, Wang R‐R, Wang X, Hu W‐Wet al (2013) Cerebral ischemia‐reperfusion‐induced autophagy protects against neuronal injury by mitochondrial clearance. Autophagy 9: 1321–1333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J, Bai Y, Huang L, Qi Y, Zhang Q, Li S, Wu Y, Li X (2015) Protective effect of autophagy on human retinal pigment epithelial cells against lipofuscin fluorophore A2E: implications for age‐related macular degeneration. Cell Death Dis 6: e1972 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Sowers JR, Ren J (2018) Targeting autophagy in obesity: from pathophysiology to management. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14: 356–376 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Sergin I, Evans TD, Jeong S‐J, Rodriguez‐Velez A, Kapoor D, Chen S, Song E, Holloway KB, Crowley JRet al (2020) High‐protein diets increase cardiovascular risk by activating macrophage mTOR to suppress mitophagy. Nat Metab 2: 110–125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X, Alvarado D, Rainier S, Lemons R, Hedera P, Weber CH, Tukel T, Apak M, Heiman‐Patterson T, Ming Let al (2001) Mutations in a newly identified GTPase gene cause autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia. Nat Genet 29: 326–331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y, Chen G, Zhang W, Xu N, Zhu JY, Jia J, Sun ZJ, Wang YN, Zhao YF (2012) Autophagy regulates hypoxia‐induced osteoclastogenesis through the HIF‐1alpha/BNIP3 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 227: 639–648 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao H, Zhao YG, Wang X, Xu L, Miao L, Feng D, Chen Q, Kovacs AL, Fan D, Zhang H (2013) Mice deficient in Epg5 exhibit selective neuronal vulnerability to degeneration. J Cell Biol 200: 731–741 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao W, Li Y, Jia L, Pan L, Li H, Du J (2014) Atg5 deficiency‐mediated mitophagy aggravates cardiac inflammation and injury in response to angiotensin II. Free Radic Biol Med 69: 108–115 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao YG, Sun L, Miao G, Ji C, Zhao H, Sun H, Miao L, Yoshii SR, Mizushima N, Wang Xet al (2015) The autophagy gene Wdr45/Wipi4 regulates learning and memory function and axonal homeostasis. Autophagy 11: 881–890 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X, Wei S, Li Z, Lin C, Zhu Z, Sun D, Bai R, Qian J, Gao X, Chen Get al (2019) Autophagic flux blockage in alveolar epithelial cells is essential in silica nanoparticle‐induced pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Dis 10: 127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao H, Wang Y, Qiu T, Liu W, Yao P (2020) Autophagy, an important therapeutic target for pulmonary fibrosis diseases. Clin Chim Acta 502: 139–147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhen Y, Spangenberg H, Munson MJ, Brech A, Schink KO, Tan K‐W, Sørensen V, Wenzel EM, Radulovic M, Engedal Net al (2020) ESCRT‐mediated phagophore sealing during mitophagy. Autophagy 16: 826–841 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng S, Clabough EB, Sarkar S, Futter M, Rubinsztein DC, Zeitlin SO (2010) Deletion of the huntingtin polyglutamine stretch enhances neuronal autophagy and longevity in mice. PLoS Genet 6: e1000838 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z, Sanchez‐Lopez E, Karin M (2016) Autophagy, inflammation, and immunity: a troika governing cancer and its treatment. Cell 166: 288–298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z, Doggett TA, Sene A, Apte RS, Ferguson TA (2015a) Autophagy supports survival and phototransduction protein levels in rod photoreceptors. Cell Death Differ 22: 488–498 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z, Vinberg F, Schottler F, Doggett TA, Kefalov VJ, Ferguson TA (2015b) Autophagy supports color vision. Autophagy 11: 1821–1832 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J, Yang J, Fan X, Hu S, Zhou F, Dong J, Zhang S, Shang Y, Jiang X, Guo Het al (2016) Chaperone‐mediated autophagy regulates proliferation by targeting RND3 in gastric cancer. Autophagy 12: 515–528 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu P, Sieben CJ, Xu X, Harris PC, Lin X (2017) Autophagy activators suppress cystogenesis in an autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease model. Hum Mol Genet 26: 158–172 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Q, Jiang J, Gendron TF, McAlonis‐Downes M, Jiang L, Taylor A, Diaz Garcia S, Ghosh Dastidar S, Rodriguez MJ, King Pet al (2020) Reduced C9ORF72 function exacerbates gain of toxicity from ALS/FTD‐causing repeat expansion in C9orf72. Nat Neurosci 23: 615–624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler PK, Bollrath J, Pallangyo CK, Matsutani T, Canli Ö, De Oliveira T, Diamanti MA, Müller N, Gamrekelashvili J, Putoczki Tet al (2018) Mitophagy in intestinal epithelial cells triggers adaptive immunity during tumorigenesis. Cell 174: 88–101.e116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zischka H, Einer C (2018) Mitochondrial copper homeostasis and its derailment in Wilson disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 102: 71–75 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitvogel L, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Smyth MJ, Kroemer G (2015) Type I interferons in anticancer immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 15: 405–414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


