Abstract
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an increasing and urgent issue for human health worldwide, as it leads to the reduction of available antibiotics to treat bacterial infections, in turn increasing hospital stays and lethality. Therefore, the study and genomic surveillance of bacterial carriers of resistance in and outside of clinical settings is of utter importance. A colony of multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria identified as Klebsiella spp., by 16S rDNA amplicon sequencing, has been isolated from an urban lake in Brazil, during a drug-degrading bacterial prospection. Genomic analyses revealed the bacteria as Klebsiella pneumoniae species. Furthermore, the in silico Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) identified the genome as a new sequence type, ST5236. The search for antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) detected the presence of genes against beta-lactams, fosfomycin, acriflavine and efflux pumps, as well as genes for heavy metal resistance. Of particular note, an extended-spectrum beta-lactamase gene (blaCTX-M-15) has been detected in close proximity to siphoviridae genes, while a carbapenemase gene (KPC-2) has been found in an extrachromosomal contig, within a novel non-Tn4401 genetic element (NTEKPC). An extrachromosomal contig found in the V3 isolate is identical to a contig of a K. pneumoniae isolate from a nearby hospital, which indicates a putative gene flow from the hospital network into Paranoá lake. The discovery of a MDR isolate in this lake is worrisome, as the region has recently undergone periods of water scarcity causing the lake, which receives treated wastewater effluent, and is already used for recreational purposes, to be used as an environmental buffer for drinking water reuse. Altogether, our results indicate an underrepresentation of environmental K. pneumoniae among available genomes, which may hamper the understanding of the population dynamics of the species in the environment and its consequences in the spread of ARGs and virulence genes.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae, antimicrobial resistance, strain type, MLST, one health, water scarcity
Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes antimicrobial resistance (AMR) as an urgent global issue with impending increases in mortality rates, hospitalization length and cross-contamination risks, as well as overall economic losses (World Health Organization [WHO], 2015). In spite of this problem, global antibiotic gross consumption and consumption per capita increased 65 and 39%, respectively, from 2000 to 2015. The broad-spectrum penicillins presented the highest increase, followed by cephalosporins, quinolones, and macrolides (Klein et al., 2018). In the current scenario, that antimicrobials are present in hospitals, animal production and communities, as well as, disposed of as wastewater in sewers, water and soil, the WHO emphasizes the need of a multidisciplinary, “One Health” approach to tackle this issue (World Health Organization [WHO], 2015).
Fortunately, ever since the seminal work of John Snow, pointing to a public water pump as a source of a cholera outbreak (Snow, 1855), several technologies in microbiology have been developed, from bacterial isolation and culture to next generation sequencing platforms (NGS). As such, different methodologies, in particular the so-called genomic surveillance, have become important to track the dissemination of infectious microbes and their genes of relevance among humans, humans and animals and these two and the environment. NGS can be particularly useful in order to track the ever-increasing dissemination of antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) (Mitchell and Simner, 2019; Ransom et al., 2020).
Among the most common ARGs, there are the beta-lactamase genes. Two of the most important classes of beta-lactamases are the extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) and the carbapenemases. The CTX-M enzymes are members of the ESBLs, able to hydrolyze expanded-spectrum cephalosporins and monobactams (Cantón et al., 2012). Prevalent worldwide, the CTX-M beta-lactamases are the most common ESBLs, especially CTX-M-15 (Bevan et al., 2017; Bush and Bradford, 2020). Infections with ESBL producers often drive the prescription of carbapenems, which may promote the selection and spread of potentially untreatable carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (Bevan et al., 2017). Among carbapenemases, the KPC-2 and KPC-3 are the most widespread and most commonly reported genes (Stoesser et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2020). These genes are frequently associated with mobile genetic elements (MGEs), such as plasmids and transposons. Thus far, the most common mobile element associated with blaKPC, at least for the species Klebsiella pneumoniae, is the transposon Tn4401 (Yang et al., 2021). However, different transposable elements, broadly termed non-Tn4401 genetic elements (NTEKPCs) were first described by Shen et al. (2009). Since then, several NTEKPCs sequences can be found deposited in GenBank, but the majority has not been formally described in articles (Yang et al., 2021). Thus, it becomes important for the study of blaKPC dispersal in hospitals and the community to describe them. There are reports of these elements in association with high-risk clonal group 258 lineages in Brazil (Cerdeira et al., 2019) as well as found in hospital-associated carbapenemase-resistant bacterial outbreaks in Colombia and Chile (Rada et al., 2020; Wozniak et al., 2020) and in wastewater (Gomi et al., 2018).
In an environmental perspective, Gillings et al. (2018) have coined the term xenogenetic DNA to represent novel gene arrangements, such as (MGEs) with ARGs, whose assembly and dispersion have been promoted by human activity, in analogy to xenobiotic chemical pollutants. In another analogy, xenogenetic DNA behave like invasive species in as much as their abundance is determined not only by release and transport, but also by replication. Thus, xenogenetic DNA could be understood as a novel type of pollutant, being able to replicate, but also being generated as a consequence of human activity.
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a gram-negative rod belonging to Enterobacterales. It is also part of the ESKAPEE group of pathogens (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, K. pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter spp. and Escherichia coli) known for their capacity of causing nosocomial infections and ability to resist to multiple classes of antibiotics (Rice, 2008; Partridge et al., 2018). Moreover, some strains of K. pneumoniae are also known as hypervirulent, are community-acquired and capable to promote metastatic infections (Shon et al., 2013). Many of such strains belong to the Cluster groups (CGs) 258 and CG11. Of note, there are also strains whose phenotype has converged into acquiring both multidrug resistance and hypervirulence traits (Wyres et al., 2020).
Wyres and Holt (2018) have shown that K. pneumoniae have a tendency to harbor more AMR genes and plasmids than other ESKAPEE pathogens. Furthermore, the species has a broad ecological distribution, ranging from gut colonization in mammals to insects, plants, water bodies and soil. Lastly, clinically relevant lineages have been isolated from non-clinical contexts, such as domestic animals. Hence, the authors suggest that K. pneumoniae may serve as an important hub for acquisition and transmission, via horizontal gene transfer, of AMR genes to microbes in different environments. Because of this capacity of colonizing the animal gut and the external environment (water and soil) and of being frequent carriers of acquired resistance, Berendonk et al. (2015) propose K. pneumoniae as a primary bacterial indicator of AMR spread in the environment.
Taking the context of water bodies in Brazil, Oliveira et al. (2014) have isolated a KPC-2 producing K. pneumoniae belonging to the Sequence type (ST)11 clonal complex from rivers, which is frequently associated with hypervirulent strains. Dropa et al. (2016) have described a, at the time, new K. pneumoniae ST harboring CTX-M-8 beta-lactamase from a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Moreover, carbapenemase resistant K. pneumoniae have also been found in recreational waters in Rio de Janeiro (Montezzi et al., 2015; de Araujo et al., 2016; Paschoal et al., 2017) and carbapenemase resistant Enterobacteriales have been found in Santos Bay (Andrade et al., 2020).
In the present study we describe a multidrug resistant (MDR) NTCKPC-bearing K. pneumoniae strain belonging to a novel ST that has been found during a prospection for xenobiotic-degrading bacteria in an artificial urban lake, next to a WWTP.
Materials and Methods
Strain Isolation
A 50 mL sample was collected from the surface water of Paranoá lake (Brasília, Brazil: 15°44′27.4″S 47°52′52.8″W) and an aliquot of 50 μL was used as inoculum onto M9 minimum media containing acetaminophen as its only carbon source (90 mM Na2SO4, 22 mM KH2SO4, 18 mM NH4Cl, 2 mM MgSO4, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 15 g.L–1 agar, 3.3 mM acetaminophen). The resulting medium plate was incubated at 25°C for 24 h. For storage, the bacterial colony was inoculated in 5 mL of M9 liquid medium and incubated under agitation at 25°C and 180 rpm for 18 h. From this culture, 1.5 mL 25% (v/v) glycerol stocks were prepared and kept at −80°C. All samples were collected in accordance with Brazilian regulations and registered in the National System for the Management of Genetic Heritage and Associated Traditional Knowledge – SISGen (A373E15).
Phenotypic Characterizations
An inoculum of 50 μL from the isolate culture, grown in LB medium at 25°C and 180 rpm for 18 h [10 g.L–1 triptone (Kasvi), 10 g.L–1 NaCl (Kasvi), 5 g.L–1 yeast extract (Kasvi)] was streaked onto MacConkey agar plates (Kasvi). Rugai medium was used for the presumptive biochemical identification, according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Laborclin).
The antibiotic sensitivity assay was performed using Müller-Hinton plates covered with different antibiotic-containing disks (Laborclin), including amikacin (30 μg), gentamicin (10 μg), tobramycin (10 μg), aztreonam (30 μg), cefepime (30 μg), ofloxacin (5 μg), norfloxacin (10 μg), ciprofloxacin (5 μg), levofloxacin (5 μg), lomefloxacin (10 μg), imipenem (10 μg), meropenem (10 μg), piperacillin/tazobactam (100/10 μg), and ticarcillin/clavulanic acid (85 μg). The antibiogram procedure was conducted and interpreted according to current EUCAST guidelines1, with E. coli ATCC 700336 as a negative control.
Genus Identification by 16S Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification and Sequencing
The isolate was grown in 5 mL of LB media overnight at 37°C and 180 rpm. Genomic DNA was extracted using Wizard® Genomic DNA purification kit (Promega), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Fragments of the 16S rRNA gene were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) from the genomic DNA using the primers RW01 (5′-AACTGGAGGAAGGTGGGGAT-3′) and DG74 (5′-AGGAGGTGATCCAACCGCA-3′), as described in Greisen et al. (1994). PCR reactions were performed in a 25 μL total volume incubated at 95°C for 4 min, 30 cycles of 95°C for 30 s, 58°C for 30 s, 72°C for 30 s and a final extension period of 72°C for 5 min. The resulting amplicons were subjected to Sanger sequencing in the High-Performance sequencing center at the Catholic University of Brasília.
Next Generation Genome Sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted following the same procedures for 16S amplification. Its integrity and purity were verified through 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and NanoDropTM Lite (Thermo Fisher Scientific) spectrophotometry. The DNA library was prepared using the rapid sequencing kit (RAD004) from Oxford Nanopore technologies (ONT) as per the manufacturer’s instructions and the sequencing reactions were performed in a R9.4.1 flowcell for 24 h, in a MinION device. Basecall was performed using Guppy 4.4.2.
Genome Assembly and Annotation
De novo genome assembly was performed with Flye v2.8 (Kolmogorov et al., 2019) using the MpGAP pipeline v1.02 using default parameters. Additionally, the assembled genome was polished (error correction step) with Medaka3 using the r941_min_high_g344 model. After Medaka the genome was polished once more by Homopolish using the parameters for bacteria and R9.4 flowcell models (Huang et al., 2020). Genome completeness was assessed with BUSCO v4.1.0, using the enterobacterales_odb10 dataset (Seppey et al., 2019).
Genome annotation was performed with the bacannot pipeline v2.24 using 85% gene coverage and identity thresholds for virulence gene (VG) annotations. With this pipeline, AMR genes were detected with CARD-RGI (database version 3.0.7) (Alcock et al., 2019), AMRFinderPlus v3.2.1 (Feldgarden et al., 2019) and ResFinder 4.0 (Bortolaia et al., 2020) tools, while VFDB (Liu et al., 2019) was used to identify virulence factors (accessed in July 2020). Prophage sequences were predicted with Phigaro v2.3.0 (Starikova et al., 2020). Capsule synthesis (K) and lipopolysaccharide (O) loci were further identified using Kaptive (Wick et al., 2018). Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) was performed with the K. pneumoniae MLST scheme (accessed in October 2020) (Diancourt et al., 2005). Plasmid replicons were detected with Plasmidfinder v2.1 (Carattoli et al., 2014) and Platon v1.5.0 (Schwengers et al., 2020).
Comparative Genomics
Genome-based taxonomy analysis was performed with the Type Strain Genome Server (TYGS) (Meier-Kolthoff and Göker, 2019). FastANI (Jain et al., 2018) was used to calculate the average nucleotide identity (ANI) index against all the K. pneumoniae genomes from NCBI (Accessed in April 2021). Using all the genomes with at least 99 ANI score, a core genome phylogeny was reconstructed with Parsnp (Treangen et al., 2014). The resulting phylogenetic tree was visualized with ggtree (Oliveira et al., 2014) and re-rooted at midpoint for a better display. Moreover, we have added a clinical K. pneumoniae sample (Kp-BSB-A) that has been previously studied by our group (de Campos et al., 2018) to the dataset for comparative purposes. In order to standardize the results, the Kp-BSB-A genome was reannotated as KpBSB31 following the same methods as for KpV3. GrapeTree (Zhou et al., 2018) was used via the BIGSdb database5 to reconstruct and visualize the relationships among K. pneumoniae STs using the Minimum Spanning tree v2 (MSTreeV2) algorithm. Moreover, GCluster v2.0.6 (Li et al., 2020) was used to draw the figure with the gene cluster comparison of the blaKPC genes.
Results
Biological Characterizations
The sequencing of 16S fragment amplicons and biochemical assays of the isolate (KpV3) were compatible with Klebsiella spp. It also presented characteristic pink mucoid colonies in Macconkey agar medium. Antibiotic resistance profiles revealed that the bacterial isolate was only susceptible to aminoglycosides (amikacin, gentamicin, and tobramycin) (Supplementary Table 1). Therefore, it can be classified as a multidrug-resistant isolate (Magiorakos et al., 2012).
Genomic Analyses
Sequence data obtained by long read nanopore DNA sequencing was used to assemble the genome of the studied strain. The resulting assembly comprised 5.4 Mb and showed great levels (98.5%) of gene space completeness based on BUSCO metrics (Table 1). The genome includes 5,132 CDS (coding sequences), 25 rRNA and 86 tRNA related sequences. Besides the chromosomal scaffold, two plasmid replicons, ColRNAI and IncU, have been detected. The genome was identified as K. pneumoniae by the TYGS, and this result was further validated with ANI analyses against available Klebsiella genomes in NCBI Refseq, showing the K. pneumoniae strain 2504 (GCF_011044895.1), from a study in Russia on hypervirulent K. pneumoniae isolates (PRJNA606163), as the closest genome available with 99.71 ANI index.
TABLE 1.
KpV3 genome assembly statistics.
| Strain | Genome accession (NCBI) | Estimated long read Coverage | Assembly size (Mb) | Contigs (≥200 bp) | N50 | BUSCO C; CS/CD/F/M | Plasmid replicons |
| KpV3 | GCA_019038575.1 | 475 | 5.4 | 7 | 5,363,194 | 98.5%; 98.0/0.5/0.7/0.8 | ColRNAI, IncU |
The BUSCO Enterobacterales database (440 genes) was used to evaluate the completeness of the assembly. BUSCO numbers reported are percentage complete (C) followed by the percentages of complete single-copy (CS), complete duplicated (CD), fragmented (F), and missing (M) out of 440 genes.
Molecular Typing
Since some Klebsiella K and O serotypes are related to increased virulence particularly K1 and O1 serotypes, the identification of these loci is important for the rapid detection of high-risk clones (Paschoal et al., 2017; Andrade et al., 2020). Genome analysis enabled the classification of KpV3 strain as a KL45:O1v2 K. pneumoniae strain. The O1 serotype is one of the most common serotypes in clinically relevant K. pneumoniae isolates and is often associated with increased virulence (Hsieh et al., 2012; Fang et al., 2016), thus the identification of an O1 strain in an urban lake near the hospital is worrisome. Moreover, using the public BIGSdb K. pneumoniae MLST scheme the strain KpV3 was classified as a novel ST: 5236.
Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Virulence Genes
We performed the search for ARGs using three different tools and databases, namely AMRFinderPlus, CARD-RGI and Resfinder, in order to have a more comprehensive overview of the annotation, due to differences in database gene content and curation, as well as prediction schemes. All three software, in concert, detected genes for beta-lactams (blaSHV-121, blaCTX-M-15, and blaKPC-2) and fosfomycin (fosA) (Table 2). Moreover, several multidrug efflux pumps (kdeA, emrD, oqxAB, and acrAB) were also detected by at least one database. The efflux pump oqxAB has been regularly implicated in low to intermediate resistance to quinoxalines, quinolones, tigecycline, nitrofurantoin, several detergents and disinfectants (Li et al., 2019). Furthermore, the acrAB is an important intrinsic virulence factor, which have been shown to provide resistance to host-derived antimicrobial peptides in E. coli (Swick et al., 2011) and when overexpressed, contributes to multidrug resistance. Additionally, AMRFinderPlus also detected in the genome, genes conferring heavy metal resistance (fieF and arsC). Resfinder has identified multiple point mutations in the acrR, ompK36, and ompK37 genes which are predicted to confer together resistance to fluoroquinolones, carbapenems and cephalosporins.
TABLE 2.
Summary of KpV3 and KpBSB31 genes related to virulence and antimicrobial resistance.
| Characteristics | KpV3 | KpBSB31 |
| Sequence type (ST) | 5236 | 11 |
| Antimicrobial resistance to: | ||
| Beta-lactams | blaCTX-M-15, blaSHV-121, blaKPC-2 | blaSHV-182, blaKPC-2, blaLAP-2 |
| (Fluoro) quinolones | oqxA, oqxB | oqxA, oqxB, qnrS1 |
| Fosfomycin | fosA | fosA |
| Sulfonamide | sul1, sul2 | |
| Tetracycline | tetA, tetD | |
| Trimethoprim | dfrA1 | |
| Efflux pumps | emrD, kdeA, acrA, acrB | emrD, kdeA, acrA, acrB |
| Heavy metal resistance genes to: | ||
| Iron stress | fieF | fieF |
| Arsenic | arsC | arsC |
| Quaternary ammonium compounds | qacEdelta1 | |
| Acid resistance | asr | |
| Virulence genes to: | ||
| Type 1 fimbriae | fimABCDEFGHIK | fimABCDEFGHIK |
| Type 3 fimbriae | mrkABCDFHIJ | mrkABCDFHIJ |
| Type VI secretion system | tssBCDFGHIJKLM, tli1, tle1 | tssABCDFGHIJKLM, tli1, tle1 |
| Enterobactin | entABCEF, fepABCDG, fes, ybdA | entABCEF, fepABCDG, fes, ybdA |
| Salmochelin | iroE | iroE |
| Yersiniabactin | fyuA, irp1, ipr2, ybtAEPQSTUX | |
| Plasmids | ColRNAI, IncU | Col440I, ColRNAI, IncA/C2, IncFIB(pKPHS1), IncN, IncR |
| Prophage-related sequences | 5 | 5 |
| GenBank accession number | SAMN19730657 | SAMEA104554881 |
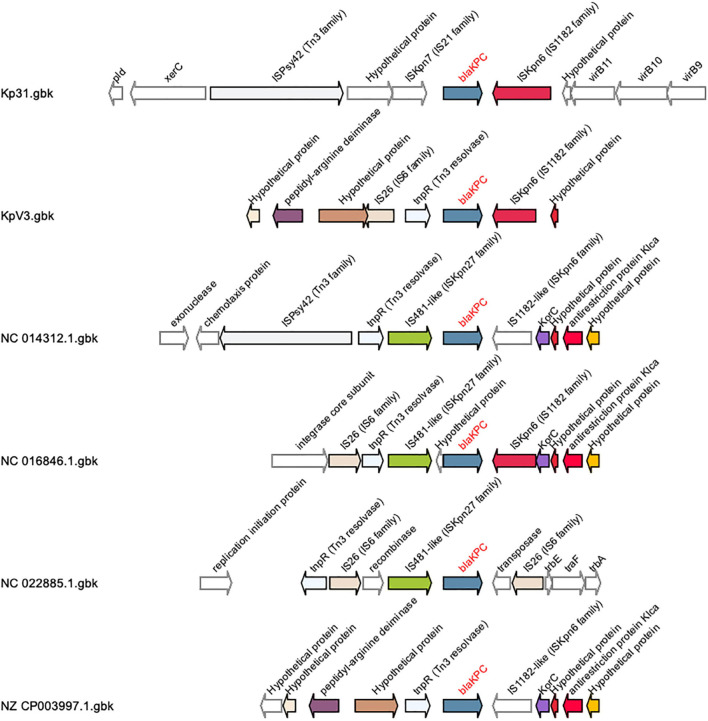
In terms of acquired resistance genes, a bla-CTX-M-15 gene was found within the flanking region (3.3 kb distance) of a 39.2 kb Siphoviridae gene cluster in the bacterial chromosome, which could be a putative source to mobility to this gene. As originally discussed by Chen et al. (2014), the most common MGE associated with blaKPC in K. pneumoniae is the 4401 transposon (tn), while other MGEs were classified NTEKPC. Most NTEKPCs share at least a truncated version of the ISkpn6 insertion sequence gene downstream of blaKPC, with sub-type divisions depending on the gene composition found upstream of blaKPC, such as the presence of blaTEM. In KpV3, the blaKPC-2 gene was found in association with a truncated insertion sequence (IS) ISKpn6, a Tn3 resolvase and an IS26, forming a putative NTEKPC of approximately 3 kb (Figure 1). In this element, the IS 26 and tnpR resolvase are upstream of blaKPC, without blaTEM sequences, as it occurs with NTEKPC-Ib and NTEKPC-Id. However, the ISkpn8 sequence is absent in the observed NTEKPC, which indicates that the element found in KpV3 is a putative novel group I NTEKPC. Furthermore, the IS26 is found in an opposite orientation when compared to the other NTEKPC sequences, which could indicate an independent transposition event with this IS alone (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of group I NTEKPCs gene clusters and its flanking genome contexts. This analysis was created with GCluster using different Klebsiella pneumoniae genomes, found in the literature, and the genomes of the strains KpV3 and Kp31. The blaKPC gene is represented in blue, the insertion sequences ISkpn6 are colored in purple and it is located downstream the blaKPC gene, as in most NTEKPCs. The insertion sequence IS26 is represented in pink and is located upstream the blaKPC, but in the KpV3 this IS26 sequence is found in an opposite orientation when compared to the other group I NTEKPCs.
The search for VGs detected, in the chromosome of KpV3, the presence of VGs related to some classical K. pneumoniae virulence factors such as the phenolate siderophore enterobactin (entABCEF, fepABCDG, fes, and ybdA) and types I and III fimbriae (fimABCDEFGHIK and mrkABCDFHIJ) (Table 2). Moreover, the iroE (salmochelin siderophore) gene was also detected in the genome. The production of more than one type of siderophore is a characteristic of more virulent bacterium (Marr and Russo, 2019). Furthermore, several genes (tssBCDFGHIJKLM) related to the Type VI secretion system (T6SS) have also been detected. The T6SS is an apparatus related to bacterial competition, cell invasion and in vivo colonization, as well as DNA acquisition from other bacteria or metal acquisition from the environment, thus, capable of enhancing the bacterium environment fitness (Ho et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2017; Barbosa and Lery, 2019; Coulthurst, 2019). Upon visual inspection in Artemis genome browser and domain prediction from their putative proteins in CDvist (Adebali et al., 2015), we have found three VgrG4-like genes, which are T6SS effectors.
Comparative Genomics
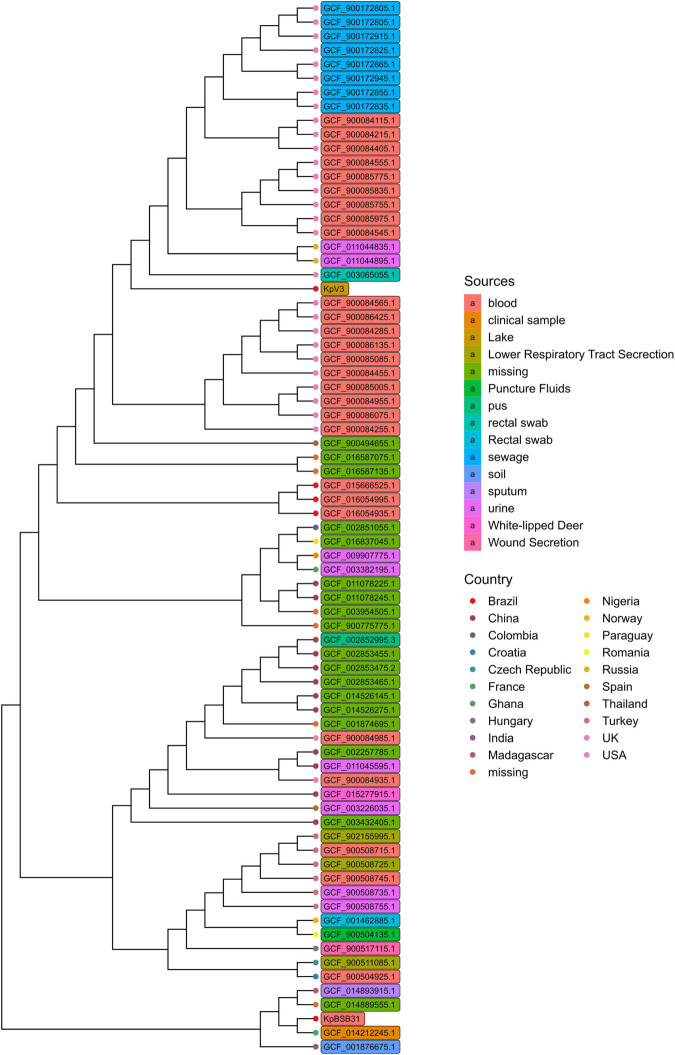
A total of 74 K. pneumoniae genomes have been used to reconstruct a core genome phylogeny with Parsnp (Treangen et al., 2014; Figure 2). As expected, the KpV3 sample was placed as the single representative of a tree branch, meaning that closer genomes may exist but have not yet been identified. Most of the strains in the tree were isolated from clinical environments, which further indicates a bias toward sequencing of clinical isolates. Interestingly, although collected from very near locations, the KpV3 and KpBSB31 samples are placed distantly to each other, highlighting the genetic difference among clinical and environmental samples. In summary, these results emphasize the diversity of the K. pneumoniae species and underscore the need of more sequencing efforts on clinical and non-clinical samples to better understand the true extent of phylogenetic relationships in the species.
FIGURE 2.
Core genome phylogeny reconstructed with Parsnp using genomes with at least 99 ANI score with KpV3. Branch tips and genome names have been respectively colored based on country and isolation sources.
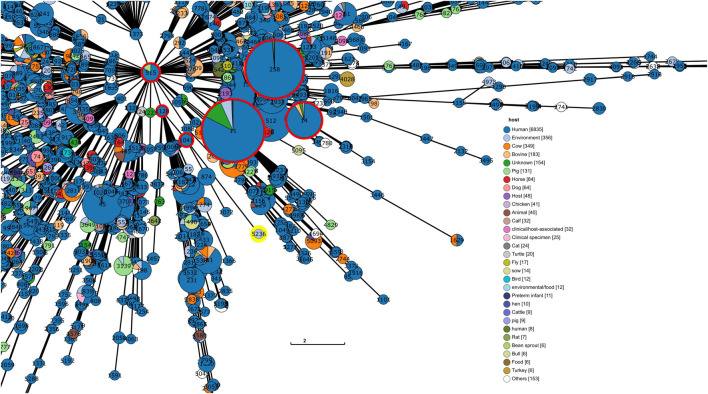
The reconstruction and visualization of relationships among K. pneumoniae STs enabled the observation that the ST 5236 (KpV3) does not have close relationships to worldwide threat STs such as ST 11, 14, and 258 (Figure 3). In fact, the results show the ST 5236 placed in a branch closer to STs 874, 1041, 1072, and 1128, in a bigger group of STs with 515 as founder. Among the closest STs, the majority of the deposited isolates comes from human hosts. This could indicate that either there is a bias toward isolation of hospital-born bacteria and/or that KpV3 could share important genomic features with hospital-born isolates.
FIGURE 3.
Section of the tree representation of genetic relationships among the different profiles of the K. pneumoniae MLST scheme. This analysis was produced via GrapeTree with the minimum spanning tree algorithm (MSTree V2). The ST identified in this study is highlighted with a yellow circle and high-risk lineages (CG 11, 14, and 258) are highlighted with red circles. For readability purposes, only the section of the tree where the ST is placed is shown. (The tree containing the whole analysis is in Supplementary Figure 1).
For comparative purposes, we contrasted the presence/absence of ARGs and VGs with KpBSB31 (Table 2). The KpBSB31 (Kp-BSB-A) was isolated from the blood of a 60- to 70-year-old patient deceased 18 days after hospitalization (de Campos et al., 2018). The hospital from which the KpBSB31 sample was collected is very near to the KpV3 isolation site. Although we are analyzing and comparing only two isolates, the comparison between these samples could highlight the putative horizontal gene transfer between clinical and environmental samples. As expected, in terms of predicted gene content, the clinical sample KpBSB31 is more virulent and more resistant to antibiotics than the environmental sample KpV3, however it is possible to observe the presence and maintenance of relevant genes in KpV3 such as iroE, blaCTX-M, and blaKPC. Interestingly, the ColRNAI plasmid has been found to be almost identical (>99% identity) between samples. The maintenance of plasmids, VGs and ARGs in environmental strains is worrisome as they can act as a reservoir, playing a key role in the dissemination of different genetic traits (Huijbers et al., 2019; Fouz et al., 2020).
Discussion
In the present study we have identified an environmental K. pneumoniae isolate belonging to a novel sequence type, ST 5236 and displaying capsular serotype (K) KL45 and LPS serotype (O) O1v2. With respect to the K antigens, there are currently 78 serotypes, despite having more than 130 allelic combinations in its biosynthetic locus (KLs) (Wick et al., 2018; Wyres et al., 2020). Among these serotypes, K1 and K2 are both most commonly isolated from patients, more virulent in mice experiments and more resistant to phagocytosis and intercellular killing by phagocytes (Paczosa and Mecsas, 2016). On the other hand, regarding the O antigens, there are nine serotypes and 12 O-loci, with serotypes O1 and O2 being the most common for clinical isolates (Wyres et al., 2020). Storey et al. (2020) have recently characterized a novel T6SS effector for K. pneumoniae, termed VgrG4. The presence of this gene in bacterial strains contributed to toxicity against bacterial and fungal species. Within this gene, the portion coding for the DUF2345 domain was responsible for the intoxication. In our study, we have found three genes with DUF2345 conserved regions, alongside a nearly complete T6SS gene cluster. The presence of multiple copies of DUF2345-bearing genes could represent a competitive edge for K. pneumoniae isolates directly against microbiotas from different environments or a strategy for quickly acquiring genes from them.
Although this notion has been long known by Brazilian indigenous people (Krenak, 2020), the “One World-One health” concept was established in 2004 as a form to understand human health. As this concept goes, human health is dependent on animal health, both domestic and wild, and on environmental health. Increasing, modern anthropic pressures on the environment, such as pollution, habitat destruction and others, promote changes in its composition, which ultimately leads to the increase in frequency and intensity of disease-states in humans (Destoumieux-Garzón et al., 2018).
Nevertheless, the sequencing efforts for K. pneumoniae are mainly focused on clinical samples, a bias reflected in the phylogenetic analysis presented in Figure 3 where KpV3 has been placed in an undivided branch and the majority of bacterial isolates in the tree come from human samples. Besides, the samples derived from the sewer were actually taken from hospital effluents. Not only the AMR gene profile found in WWTPs reflects that of clinical settings (Pärnänen et al., 2019), but surveillance in WWTPs could represent a more accurate perspective of AMR spread at a populational level (Sims and Kasprzyk-Hordern, 2020). Moreover, a similar pattern was also observed in the MLST tree analysis (Figure 3) where the branch length represents the distance between groups. The analysis shows that the ST 5236 (KpV3) has a reasonable distance to its closest ST (ST 1041), which means that closer STs might exist, but are not yet identified. It is important to observe that this new ST is not related to other worldwide threat STs such as ST 11 and 258, meaning that this new ST might not be a threat in terms of hypervirulence.
It is disturbing that we have found an environmental K. pneumoniae strain containing both an ESBL (CTX-M-15) and a carbapenemase (KPC-2) enzyme, which raises concern about the selective pressure applied in the region. Of special note, both genes have been found inside or very near MGEs. The bla-CTX-M-15 was found in the bacterial chromosome, close to a putative Siphoviridae prophage sequence. This viral family has been associated with human fecal pollution in water bodies and with beta-lactamase gene transfer (Colomer-Lluch et al., 2011). Furthermore, the blaKPC2 gene was found in association with a transposase gene, forming a small gene cluster with two other genes. Klebsiella spp. ISs are often associated with AMR genes (Razavi et al., 2020) and transposition events can be an important factor in spreading these genes in contexts of positive selection among different plasmids, strains and species (Sheppard et al., 2016).
When comparing the genomes of the environmental KpV3 and the clinical isolate KpBSB31, we have detected that the ColRNAI plasmid is identical between the samples, which indicates a putative genetic flow of mobile elements between clinical and environmental isolates in the lake near the hospital. Similar observations of gene flows from hospitals water bodies have been made elsewhere (Ekwanzala et al., 2019; Lepuschitz et al., 2019; Bleichenbacher et al., 2020). However, it is unclear whether KpV3 isolate represents a clonal dispersion of hospital K. pneumoniae or if it has acquired genetic features from hospital-borne isolates via HGT. The extent of this genetic flow should be addressed by sampling different parts of the hospital system wastewater treatment. Thorough analyses of microbes discharged from the WWTPs into Paranoá lake are required to access the extent of their contribution to dissemination of AMR. Furthermore, the quantification of antibiotics and heavy metals in WWTPs, which may select/co-select resistant microbes (Hernando-Amado et al., 2019), is also of relevance, though fecal pollution alone may be the main factor in AMR spread (Karkman et al., 2019). Finally, Ekwanzala et al. (2019) have shown that in a river which receives WWTP effluent, a larger ratio of carbapenem resistant versus susceptible K. pneumoniae strains was found in its sediment, in contrast to surface waters. Thus, different portions of a given water body could weigh more in AMR maintenance. Danko et al. (2021) have analyzed >4,000 metagenomic samples from 60 cities around the world, as to characterize their urban microbiomes. Even with these many samples, the rarefaction curves for microbial species and ARGs did not saturate, indicating there is a considerable amount of diversity to be explored, particularly when considering the selective pressures for the formation of new ARGs and MGEs.
Brasília is located in a morphoclimatic domain, termed Cerrado, with two well-defined seasons, wet and dry. As a consequence of the dry season, the city has undergone into situations of water scarcity in recent years. As a response, Paranoá lake, which receives treated effluent from two WWTPs, has been turned into an environmental buffer for water reuse, including drinking water (Sodré and Sampaio, 2020). Hence, the discovery of an ESBL producer carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae isolate in this lake is of great concern, as regions undergoing water scarcity might become more susceptible to AMR spread, despite the presence of downstream water treatment processes. Additionally, climate change models based upon Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) scenarios predict increases in temperature and dry season duration as well as precipitation decreases for the Cerrado biome (Bustamante et al., 2012). MacFadden et al. (2018) have shown that increases in minimal local temperatures are associated with higher frequency of infections caused by antimicrobial-resistant E. coli, S. aureus, and K. pneumoniae. Also, Anderson et al. (2008) have shown that K. pneumoniae blood stream infections occur more commonly with higher temperatures and dew point. There are many, non-excluding hypotheses for the causes of this correlation, from bacterial physiology to human societal changes (Rodríguez-Verdugo et al., 2020). Collignon et al. (2018) point that socioeconomical factors such poor infrastructure and governance, low health expenditure and high GDP and education were associated with higher AMR levels around the world. As the authors discuss, while temperature was positively correlated with AMR, this could be a correlation by proxy (Such as poor infrastructure) or a direct correlation. As water reuse may become more common as a result of climate change (Tram et al., 2014), this phenomenon may play a key role in AMR spread and warrants further inquiry.
Altogether, we have little evidence in favor of KpV3 as an isolate with high virulence. However, our observations suggest that there is a gene flow from hospitals into the lake, likely through WWTPs. While our findings point toward this hypothesis, it has been based so far on a single isolate. Therefore, the extent of ARG dissemination into the lake and how it may be represented in other isolates are a matter of future studies. Furthermore, there may be a positive selective pressure being applied in the Paranoá lake that may promote the selection and spread of potentially untreatable carbapenemase-producing bacteria while turning the region as a possible reservoir for ARGs. Thus, genomic surveillance and quality assessment programs with the wastewaters that are dumped in the lake are required to control and mitigate such pressure.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset whole genome sequencing data for the KpV3 isolate is available under the NCBI Bioproject PRJNA738490, and for the Kp-BSB-A (KpBSB31) is available under the NCBI Bioproject PRJEB24576 (de Campos et al., 2018).
Author Contributions
LJ and TD performed the strain isolation and phenotypic characterizations. LJ, FA, and RB performed the genome sequencing and bioinformatics analyses. GP, TC, and VM conceived and supervised the study. LJ, FA, GP, TC, and VM wrote the manuscript and analyzed the data. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Distrito Federal (FAPDF), grant 00193-00000129/2019-80 to GP and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), grant 205555/2018-7 and grant 433790/2018-0 to VM. This study was partially financed by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) as a fellowship to LJ (140826/2017-3) and to FA (140576/2020-7).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.732324/full#supplementary-material
Tree representation of genetic relationships among the different profiles of the K. pneumoniae MLST scheme. This analysis was produced via GrapeTree with the minimum spanning tree algorithm (MSTree V2). The ST identified in this study is highlighted with a yellow circle and a red arrow. High-risk lineages (CG 11, 14, and 258) are highlighted with red circles.
References
- Adebali O., Ortega D. R., Zhulin I. B. (2015). CDvist: a webserver for identification and visualization of conserved domains in protein sequences. Bioinformatics 31 1475–1477. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcock B. P., Raphenya A. R., Lau T. T. Y., Tsang K. K., Bouchard M., Edalatmand A., et al. (2019). CARD 2020: antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 48 D517–D525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Richet H., Chen L. F., Spelman D. W., Hung Y., Huang A. T., et al. (2008). Seasonal variation in Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection on 4 continents. J. Infect. Dis. 197 752–756. 10.1086/527486 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade V. C., Caetano T., Mendo S., Oliveira A. J. F. C. (2020). Carbapenem resistant Enterobacteriaceae from port areas in São Paulo State (Brazil): isolation and molecular characterization. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 159:111329. 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111329 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa V. A. A., Lery L. M. S. (2019). Insights into Klebsiella pneumoniae type VI secretion system transcriptional regulation. BMC Genomics. 20:506. 10.1186/s12864-019-5885-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendonk T. U., Manaia C. M., Merlin C., Fatta-Kassinos D., Cytryn E., Walsh F., et al. (2015). Tackling antibiotic resistance: the environmental framework. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 13 310–317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan E. R., Jones A. M., Hawkey P. M. (2017). Global epidemiology of CTX-M β-lactamases: temporal and geographical shifts in genotype. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 72 2145–2155. 10.1093/jac/dkx146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleichenbacher S., Stevens M. J. A., Zurfluh K., Perreten V., Endimiani A., Stephan R., et al. (2020). Environmental dissemination of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in rivers in Switzerland. Environ. Pollut. 265:115081. 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115081 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolaia V., Kaas R. S., Ruppe E., Roberts M. C., Schwarz S., Cattoir V., et al. (2020). ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75 3491–3500. 10.1093/jac/dkaa345 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Bradford P. A. (2020). Epidemiology of β-Lactamase-Producing pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 33 e47–e19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante M., Nardoto G., Pinto A., Resende J., Takahashi F., Vieira L. (2012). Potential impacts of climate change on biogeochemical functioning of Cerrado ecosystems. Braz. J. Biol. 72(Suppl. 3) 655–671. 10.1590/s1519-69842012000400005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantón R., González-Alba J. M., Galán J. C. (2012). CTX-M enzymes: origin and diffusion. Front. Microbiol. 3:110. 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carattoli A., Zankari E., García-Fernández A., Voldby Larsen M., Lund O., Villa L., et al. (2014). In Silico detection and typing of plasmids using plasmidfinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58 3895–3903. 10.1128/AAC.02412-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdeira L. T., Lam M. M. C., Wyres K. L., Wick R. R., Judd L. M., Lopes R., et al. (2019). Small IncQ1 and Col-like plasmids harboring bla KPC–2 and Non-Tn 4401 elements (NTE KPC -IId) in high-risk lineages of Klebsiella pneumoniae CG258. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63 1–4. 10.1128/AAC.02140-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Mathema B., Chavda K. D., DeLeo F. R., Bonomo R. A., Kreiswirth B. N. (2014). Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: molecular and genetic decoding. Trends Microbiol. 22 686–696. 10.1016/j.tim.2014.09.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collignon P., Beggs J. J., Walsh T. R., Gandra S., Laxminarayan R. (2018). Anthropological and socioeconomic factors contributing to global antimicrobial resistance: a univariate and multivariable analysis. Lancet Planetary Health. 2 e398–e405. 10.1016/S2542-5196(18)30186-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colomer-Lluch M., Jofre J., Muniesa M. (2011). Antibiotic resistance genes in the bacteriophage DNA fraction of environmental samples. Aziz R, organizador. PLoS One 6:e17549. 10.1371/journal.pone.0017549 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulthurst S. (2019). The Type VI secretion system: a versatile bacterial weapon. Microbiology 165 503–515. 10.1099/mic.0.000789 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danko D., Bezdan D., Afshin E. E., Ahsanuddin S., Bhattacharya C., Butler D. J., et al. (2021). A global metagenomic map of urban microbiomes and antimicrobial resistance. Cell 184 3376.e17–3393.e17. 10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Araujo C. F. M., Silva D. M., Carneiro M. T., Ribeiro S., Fontana-Maurell M., Alvarez P., et al. (2016). Detection of carbapenemase genes in aquatic environments in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60 4380–4383. 10.1128/AAC.02753-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Campos T. A., Gonçalves L. F., Magalhães K. G., de Paulo Martins V., Pappas Júnior G. J., Peirano G., et al. (2018). A fatal bacteremia caused by hypermucousviscous KPC-2 producing extensively drug-resistant K64-ST11 Klebsiella pneumoniae in Brazil. Front Med. 5:265. 10.3389/fmed.2018.00265 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Destoumieux-Garzón D., Mavingui P., Boetsch G., Boissier J., Darriet F., Duboz P., et al. (2018). The one health concept: 10 years old and a long road ahead. Front. Vet. Sci. 5:14. 10.3389/fvets.2018.00014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diancourt L., Passet V., Verhoef J., Grimont P. A. D., Brisse S. (2005). Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43 4178–4182. 10.1128/JCM.43.8.4178-4182.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dropa M., Lincopan N., Balsalobre L. C., Oliveira D. E., Moura R. A., Fernandes M. R., et al. (2016). Genetic background of novel sequence types of CTX-M-8- and CTX-M-15-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from public wastewater treatment plants in São Paulo, Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23 4953–4958. 10.1007/s11356-016-6079-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekwanzala M. D., Dewar J. B., Kamika I., Momba M. N. B. (2019). Tracking the environmental dissemination of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae using whole genome sequencing. Sci. Tot. Environ. 691 80–92. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.533 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang C.-T., Shih Y.-J., Cheong C.-M., Yi W.-C. (2016). Rapid and accurate determination of lipopolysaccharide O-antigen types in Klebsiella pneumoniae with a Novel PCR-based O-genotyping method. Munson E, organizador. J. Clin. Microbiol. 54 666–675. 10.1128/JCM.02494-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldgarden M., Brover V., Haft D. H., Prasad A. B., Slotta D. J., Tolstoy I., et al. (2019). Validating the AMRFinder tool and resistance gene database by using antimicrobial resistance genotype-phenotype correlations in a collection of isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63 e483–e419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouz N., Pangesti K. N. A., Yasir M., Al-Malki A. L., Azhar E. I., Hill-Cawthorne G. A., et al. (2020). The contribution of wastewater to the transmission of antimicrobial resistance in the environment: implications of mass gathering settings. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 5:33. 10.3390/tropicalmed5010033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillings M. R., Westoby M., Ghaly T. M. (2018). Pollutants that replicate: xenogenetic DNAs. Trends Microbiol. 26 975–977. 10.1016/j.tim.2018.08.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomi R., Matsuda T., Yamamoto M., Chou P.-H., Tanaka M., Ichiyama S., et al. (2018). Characteristics of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in wastewater revealed by genomic analysis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62 e2501–e2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisen K., Loeffelholz M., Purohit A., Leong D. (1994). PCR primers and probes for the 16S rRNA gene of most species of pathogenic bacteria, including bacteria found in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Clin. Microbiol. 32 335–351. 10.1128/jcm.32.2.335-351.1994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernando-Amado S., Coque T. M., Baquero F., Martínez J. L. (2019). Defining and combating antibiotic resistance from One Health and Global Health perspectives. Nat. Microbiol. 4 1432–1442. 10.1038/s41564-019-0503-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho B. T., Dong T. G., Mekalanos J. J. (2014). A view to a kill: the bacterial type VI secretion system. Cell Host Microbe 15 9–21. 10.1016/j.chom.2013.11.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P.-F., Lin T.-L., Yang F.-L., Wu M.-C., Pan Y.-J., Wu S.-H., et al. (2012). Lipopolysaccharide O1 antigen contributes to the virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae causing pyogenic liver abscess. Forestier C, organizador. PLoS One. 7:e33155. 10.1371/journal.pone.0033155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y.-T., Liu P.-Y., Shih P.-W. (2020). Homopolish: a method for the removal of systematic errors in nanopore sequencing by homologous polishing. Genome Biol. 22:95. 10.1186/s13059-021-02282-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huijbers P. M. C., Flach C.-F., Larsson D. G. J. (2019). A conceptual framework for the environmental surveillance of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance. Environ. Int. 130:104880. 10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.074 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain C., Rodriguez-R L. M., Phillippy A. M., Konstantinidis K. T., Aluru S. (2018). High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 9:5114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkman A., Pärnänen K., Larsson D. G. J. (2019). Fecal pollution can explain antibiotic resistance gene abundances in anthropogenically impacted environments. Nat. Commun. 10:80. 10.1038/s41467-018-07992-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E. Y., Van Boeckel T. P., Martinez E. M., Pant S., Gandra S., Levin S. A., et al. (2018). Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115 E3463–E3470. 10.1073/pnas.1717295115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov M., Yuan J., Lin Y., Pevzner P. A. (2019). Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 37:12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenak A. (2020). Ideas to Postpone the End of the World. Toronto: House of Anansi Press, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Lepuschitz S., Schill S., Stoeger A., Pekard-Amenitsch S., Huhulescu S., Inreiter N., et al. (2019). Whole genome sequencing reveals resemblance between ESBL-producing and carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Austrian rivers and clinical isolates from hospitals. Sci. Tot. Environ. 662 227–235. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Zhang H., Ning J., Sajid A., Cheng G., Yuan Z., et al. (2019). The nature and epidemiology of OqxAB, a multidrug efflux pump. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 8:44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Chen F., Chen Y. (2020). Gcluster: a simple-to-use tool for visualizing and comparing genome contexts for numerous genomes. Robinson P, organizador. Bioinformatics. 36 3871–3873. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa212 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Zheng D., Jin Q., Chen L., Yang J. (2019). VFDB 2019: a comparative pathogenomic platform with an interactive web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 D687–D692. 10.1093/nar/gky1080 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L., Ye M., Li X., Li J., Deng Z., Yao Y.-F., et al. (2017). Identification and characterization of an antibacterial Type VI secretion system in the carbapenem-resistant strain Klebsiella pneumoniae HS11286. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 7:442. 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00442 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacFadden D. R., McGough S., Fisman D., Santillana M., Brownstein J. (2018). Antibiotic resistance increases with local temperature. Nat. Clim. Change 8:6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos A.-P., Srinivasan A., Carey R. B., Carmeli Y., Falagas M. E., Giske C. G., et al. (2012). Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 18 268–281. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr C. M., Russo T. A. (2019). Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: a new public health threat. Expert Rev. Anti-Infective Ther. 17 71–73. 10.1080/14787210.2019.1555470 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier-Kolthoff J. P., Göker M. (2019). TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 10:2182. 10.1038/s41467-019-10210-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell S. L., Simner P. J. (2019). Next-Generation sequencing in clinical microbiology. Clin. Lab. Med. 39 405–418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montezzi L. F., Campana E. H., Corrêa L. L., Justo L. H., Paschoal R. P., da Silva I. L. V. D., et al. (2015). Occurrence of carbapenemase-producing bacteria in coastal recreational waters. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 45 174–177. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.10.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira S., Moura R., Silva K., Pavez M., McCulloch J., Dropa M. (2014). Isolation of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains belonging to the high-risk multiresistant clonal complex 11 (ST437 and ST340) in urban rivers. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69 849–851. 10.1093/jac/dkt431 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paczosa M. K., Mecsas J. (2016). Klebsiella pneumoniae: going on the offense with a strong defense. Microb. Mol. Biol. Rev. 80 629–661. 10.1128/MMBR.00078-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pärnänen K. M. M., Narciso-da-Rocha C., Kneis D., Berendonk T. U., Cacace D., Do T. T., et al. (2019). Antibiotic resistance in European wastewater treatment plants mirrors the pattern of clinical antibiotic resistance prevalence. Sci. Adv. 5:eaau9124. 10.1126/sciadv.aau9124 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. R., Kwong S. M., Firth N., Jensen S. O. (2018). Mobile genetic elements associated with antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 31 e88–e17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschoal R. P., Campana E. H., Corrêa L. L., Montezzi L. F., Barrueto L. R. L., da Silva I. R., et al. (2017). Concentration and variety of carbapenemase producers in recreational coastal waters showing distinct levels of pollution. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61 e1963–e1917. 10.1128/AAC.01963-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rada A. M., De La Cadena E., Agudelo C., Capataz C., Orozco N., Pallares C., et al. (2020). Dynamics of bla KPC–2 dissemination from Non-CG258 Klebsiella pneumoniae to other Enterobacterales via IncN plasmids in an area of high endemicity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 64 e1743–e1720. 10.1128/AAC.01743-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom E. M., Potter R. F., Dantas G., Burnham C.-A. D. (2020). Genomic Prediction of antimicrobial resistance: ready or not, here it comes! Clin. Chem. 66 1278–1289. 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razavi M., Kristiansson E., Flach C.-F., Larsson D. G. J. (2020). The association between insertion sequences and antibiotic resistance genes. mSphere 5 e418–e420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice L. B. (2008). Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: no eskape. J. Infect. Dis. 197 1079–1081. 10.1086/533452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Verdugo A., Lozano-Huntelman N., Cruz-Loya M., Savage V., Yeh P. (2020). Compounding effects of climate warming and antibiotic resistance. iScience 23:101024. 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwengers O., Barth P., Falgenhauer L., Hain T., Chakraborty T., Goesmann A. (2020). Platon: identification and characterization of bacterial plasmid contigs in short-read draft assemblies exploiting protein sequence-based replicon distribution scores. Microb. Genom. 1–12. 10.1099/mgen.0.000398 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppey M., Manni M., Zdobnov E. M. (2019). “BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness,” in Gene Prediction (Methods in Molecular Biology, Vol. 1962 ed. Kollmar M. (New York, NY: Springer; ), 227–245. 10.1007/978-1-4939-9173-0_14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen P., Wei Z., Jiang Y., Du X., Ji S., Yu Y., et al. (2009). Novel genetic environment of the carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-Lactamase KPC-2 among Enterobacteriaceae in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 4333–4338. 10.1128/AAC.00260-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard A. E., Stoesser N., Wilson D. J., Sebra R., Kasarskis A., Anson L. W., et al. (2016). Nested russian doll-like genetic mobility drives rapid dissemination of the carbapenem resistance gene bla KPC. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60 3767–3778. 10.1128/AAC.00464-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shon A. S., Bajwa R. P. S., Russo T. A. (2013). Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: a new and dangerous breed. Virulence 4 107–118. 10.4161/viru.22718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims N., Kasprzyk-Hordern B. (2020). Future perspectives of wastewater-based epidemiology: monitoring infectious disease spread and resistance to the community level. Environ. Int. 139:105689. 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105689 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow J. (1855). On the Mode of Communication of Cholera. London: Macmillan. [Google Scholar]
- Sodré F. F., Sampaio T. R. (2020). Development and application of a SPE-LC-QTOF method for the quantification of micropollutants of emerging concern in drinking waters from the Brazilian capital. Emerg. Contaminants 6 72–81. 10.1016/j.emcon.2020.01.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Starikova E. V., Tikhonova P. O., Prianichnikov N. A., Zdobnov E. M., Govorun V. M. (2020). Phigaro: high throughput prophage sequence annotation. Bioinformatics 36, 3882–3884. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa250 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoesser N., Sheppard A. E., Peirano G., Anson L. W., Pankhurst L., Sebra R., et al. (2017). Genomic epidemiology of global Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 7:5917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D., McNally A., Åstrand M., sa-Pessoa Graca Santos J., Rodriguez-Escudero I., Elmore B. (2020). Klebsiella pneumoniae type VI secretion system-mediated microbial competition is PhoPQ controlled and reactive oxygen species dependent. PLoS Pathog. 16:e1007969. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007969 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick M. C., Morgan-Linnell S. K., Carlson K. M., Zechiedrich L. (2011). Expression of multidrug efflux pump genes acrAB-tolC, mdfA, and norE in Escherichia coli clinical isolates as a function of fluoroquinolone and multidrug resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55 921–924. 10.1128/AAC.00996-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tram V. O. P., Ngo H. H., Guo W., Zhou J. L., Nguyen P. D., Listowski A., et al. (2014). A mini-review on the impacts of climate change on wastewater reclamation and reuse. Sci. Tot. Environ. 494–495 9–17. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treangen T. J., Ondov B. D., Koren S., Phillippy A. M. (2014). The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol. 15:524. 10.1186/s13059-014-0524-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick R. R., Heinz E., Holt K. E., Wyres K. L. (2018). Kaptive web: user-friendly capsule and lipopolysaccharide serotype prediction for Klebsiella genomes. Diekema DJ, organizador. J. Clin. Microbiol. 56 e197–e118. 10.1128/JCM.00197-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization [WHO] (2015). Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance [Internet]. Disponível Em. Available online at: www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/193736 (accessed April, 2021).
- Wozniak A., Figueroa C., Moya-Flores F., Guggiana P., Castillo C., Rivas L., et al. (2020). A multispecies outbreak of carbapenem-resistant bacteria harboring the blaKPC gene in a non-classical transposon element. BMC Microbiol. 21:107. 10.1186/s12866-021-02169-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyres K. L., Holt K. E. (2018). Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 45 131–139. 10.1016/j.mib.2018.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyres K. L., Lam M. M. C., Holt K. E. (2020). Population genomics of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat Rev Microbiol. 18 344–359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X., Dong N., Chan E. W.-C., Zhang R., Chen S. (2021). Carbapenem resistance-encoding and virulence-encoding conjugative plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Trends Microbiol. 29 65–83. 10.1016/j.tim.2020.04.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Li F., Cui S., Mao L., Li X., Awan F., et al. (2020). Prevalence and distribution characteristics of blaKPC–2 and blaNDM–1 genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 13 2901–2910. 10.2147/idr.s253631 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Alikhan N.-F., Sergeant M. J., Luhmann N., Vaz C., Francisco A. P., et al. (2018). GrapeTree: visualization of core genomic relationships among 100,000 bacterial pathogens. Genome Res. 28 1395–1404. 10.1101/gr.232397.117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Tree representation of genetic relationships among the different profiles of the K. pneumoniae MLST scheme. This analysis was produced via GrapeTree with the minimum spanning tree algorithm (MSTree V2). The ST identified in this study is highlighted with a yellow circle and a red arrow. High-risk lineages (CG 11, 14, and 258) are highlighted with red circles.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset whole genome sequencing data for the KpV3 isolate is available under the NCBI Bioproject PRJNA738490, and for the Kp-BSB-A (KpBSB31) is available under the NCBI Bioproject PRJEB24576 (de Campos et al., 2018).