Abstract
Background
This study was undertaken to identify and functionally characterize virulence genes from Salmonella isolates in street food and stool cultures. From February 2017 to May 2018, clinical and food Salmonella strains were isolated in three regions in Burkina Faso. Salmonella was serotyped according to the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor method, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to detec invA, spvR, spvC, fimA and stn virulence genes commonly associated with salmonellosis in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Results
A total of 106 Salmonella isolates (77 human stools; 14 sandwiches) was analyzed using a serological identification with an O-group test reagent. The presence of Salmonella was confirmed in 86% (91/106) of the samples were reactive (OMA-positive/OMB-positive). Salmonella serogroup O:4,5 was the most common serogroup detected (40%; 36/91). Salmonella Enteritidis and Typhimurium represented 5.5% (5/91) and 3.3% (3/91), respectively and were identified only from clinical isolates. Furthermore, 14 serotypes of Salmonella (12/91 human strains and 2/15 sandwich strains) were evocative of Kentucky/Bargny serotype. For the genetic profile, 66% (70/106) of the Salmonella had invA and stn genes; 77.4% (82/106) had the fimA gene. The spvR gene was found in 36.8% (39/106) of the isolates while 48.1% (51/106) had the spvC gene. Among the identified Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhimurium isolated from stools, the virulence genes detected were invA (3/5) versus (2/3), fimA (4/5) versus (3/3), stn (3/5) versus (2/3), spvR (4/5) versus (2/3) and spvC (3/5) versus (2/3), respectively.
Conclusion
This study reports the prevalence of Salmonella serotypes and virulence genes in clinical isolates and in street foods. It shows that food could be a significant source of Salmonella transmission to humans. Our results could help decision-making by the Burkina Faso health authority in the fight against street food-related diseases, in particular by training restaurateurs in food hygiene.
Keywords: Salmonella, Serotypes, Virulence genes, Gastroenteritis, Sandwiches, Burkina Faso
Background
Salmonella is one of the most problematic foodborne and zoonotic pathogens that threaten general health and well-being [1]. Salmonella remains the leading cause of bacterial gastroenteritis and is also one of the most extensively studied and well-characterized bacterial species [2]. In spite of that Salmonella continue to be remains an important human pathogen and a serious public health concern worldwide [3]. Salmonellosis, caused by Salmonella, manifests mainly as mild diarrhea, also known as food poisoning [4].
In Europe, the number of non-typhoidal salmonellosis (NTS) is estimated at 690 cases per 100,000 inhabitants [5], and in the United States, 17.6 cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year [6]. In 2019, pathogens responsible for foodborne diseases, including Salmonella enterica (non-typhoid), caused 230,000 deaths in Africa [7]. In resource-limited countries, particularly in Sub-saharan Africa, NTS is endemic, with high rates in children under 3 years of age and immunocompromised individuals [8, 9]. These diseases have a significant negative economic impact in resource-limited countries amounting to $ 110 billion per year [10].
The pathogenicity of Salmonella is mediated by numerous genes comprising invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC, spiC and pipD [11]. The invasion gene (invA), located on the pathogenicity island 1 (SPI1), has been widely studied for its ability to promote virulence and also as a biomarker for the detection of Salmonella spp. [12]. The invA gene of Salmonella is also involved invasion of host epithelial cells [13, 14]. The Salmonella stn gene encode for an enterotoxin stn and is associated with infection with the serotypes of Salmonella Typhi, Typhimurium and Enteritidis [15]. Salmonella enterotoxin (stn) gene is a clinical important biomarker which is use to differentiate Salmonella enterica strains (stn+), from in Salmonella bongori and other Enterobacteriaceae [15]. The fimbriae (fimA) are Salmonella filamentous surface structures that contribute to colonization of the epithelium cells [16]. Salmonella virulence plasmids have been considered as a characteristic of Salmonella serotypes implicated in systemic disease. The Salmonella virulence plasmid carry several key virulence factors, including the spvABCD system and its spvR regulator, which are essential for systemic virulence [17]. These genes are also sufficient to restore systemic virulence in plasmid hardened strains [18]. Although Salmonella is a major cause of foodborne illness in developing countries, there is a scarcity of data on street found intake and Salmonella related diseases which undermined the real impact of salmonellosis on population health [19]. Other non-typhoidal Salmonella (NTS) serovars can also cause systemic infections, also known as invasive NTS (iNTS) disease [19–21]. This is predominantly due to the emergence of invasive clones of Enteritidis [22] and Typhimurium [23] serotypes that have spread throughout Africa. Despite being a serious public health concern, there are very few studies on salmonellosis, associated with food-borne illness, similarly, data on Salmonella virulence genes remain limited in Burkina Faso [24]. On the other hand, studies have been reported on the resistance genes of these bacteria [25, 26]. Therefore, there is a need to improve our understanding on the pathogenicity of these bacteria in regards to virulence genes and their impact on human health in Burkina Faso. This work aimed to address this lack of data on salmonellosis through determination of the prevalence of virulence genes of Salmonella strains isolated from street food and human stools in Burkina Faso.
Methods
Site and period of the study
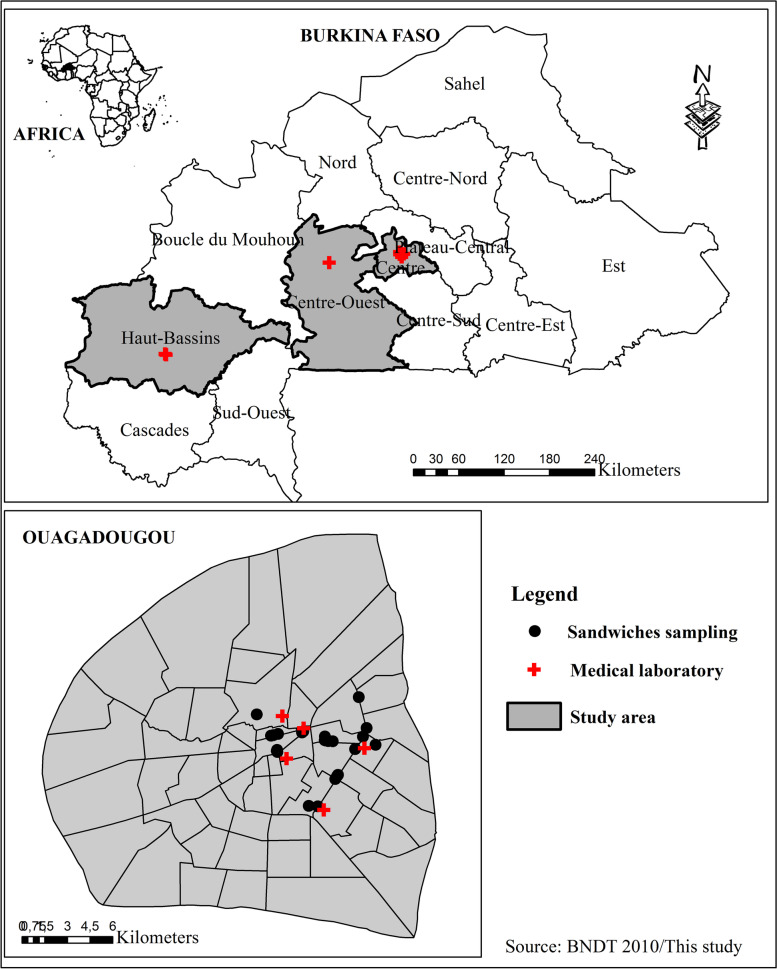
Samples were collected from February 2017 to May 2018 in Ouagadougou the capital, and Bobo-Dioulasso and Koudougou located in West and mid-western parts of Burkina Faso (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Geographic map of sample collection sites (health facilities and food sites)
Sample’s collection
Eighty-five (85) samples of ready-to-eat beef sandwiches were purchased in Ouagadougou and transported to the laboratory in a + 4 °C cooler for microbiological analysis. Analysis was carried out within 2 h after sampling. Ninety-one (91) Salmonella clinical strains, isolated from diarrheal stools samples from inpatients and out patients were collected from seven health care facilities in urban areas of three regions of Burkina Faso. Central region/Ouagadougou (“Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Yalgado Ouédraogo (CHU-YO)”, “Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Pédiatrique Charles De Gaulle (CHU-PCDG)”, “Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Bogodogo (CHU-B)”, “Hôpital Protestant Schiphra” and “Laboratoire d’analyse médical du Centre”), Hauts-Bassins region/ Bobo-Dioulasso (“Centre MURAZ”) and center-west region/ Koudougou (“Centre Hospitalier Régional de Koudougou”).
Sandwich samples were analyzed at the “Laboratoire de Biologie Moléculaire d’Epidémiologie et de Surveillance des Bactéries et Virus Transmis par les Aliments (LaBESTA, Université Joseph Ki-Zerbo)”.
Microbiological analyzes
Salmonella strains were isolated from eighty-five (85) samples of ready-to-eat beef sandwiches using ISO 6579-1:2017 standard - Horizontal method for Salmonella detection of Salmonella [27]. The Ninety-one (91) Salmonella clinical isolates collected from health facilities of three cities in Burkina Faso (83 in Ouagadougou, 2 in Koudougou and 6 in Bobo-Dioulasso) were submitted to API 20E identification system of Biomérieux France at the CHU-YO laboratory for verify that they are indeed Salmonella strains.
Pre-enrichment in non-selective broth
Prior to enrichment, 25 g from each sandwich sample were suspended in a sterile flask containing 225 mL of non-selective buffered peptone water (Liofilchem® Srl, Italy) and incubated at 37 °C for 16 to 20 h. This approach helps increase the number of bacterial cells of interest by enabling repair of lesions from damaged cells which regain their resistance to selective agents,
Selective enrichment in broth
Following the non-selective pre-enrichment stage, 1 mL and 0.1 mL of each sample suspension were transferred into 10 mL of Muller-Kauffmann Tetrathionate-Novobiocin Broth (MKTTn) (Liofilchem® Srl, Italy) and into 10 mL of Rappaport Vassiliadis Soy broth (Difco laboratories), respectively. Brilliant green at 0.95% was added to the Tetrathionate broth in order to inhibit the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and then incubated for 18 to 20 h at 37 ± 1 °C. The Rappaport Vassiliadis inoculate were incubated for 18 to 20 h at 42 ± 1 °C.
Selective isolation
During the third stage, a loopful of culture suspension from each selective media was placed on two different agar plates to identify individual colonies. The media chosen were Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate agar (XLD, HiMedia Laboratories, India) and Salmonella-Shigella agar (SS, HiMedia Laboratories, India). Typical Salmonella colonies on XLD are colorless, very light, slightly shiny and transparent (colour of the medium) with a dark tinted centre, surrounded by a light red area and yellow edge, but they can also appear as pink to red coloured, with or without a black centre. On the Salmonella-Shigella agar, typical Salmonella colonies are colourless or very light pink, opaque or semi-transparent, usually with a black centre.
Biochemical identification of characteristic colonies
At least five colonies suspicious for Salmonella were picked per plate and purified by growth on nutrient agar for 24 h. Then, colonies were sowed onto triple sugar iron agar (Difco laboratories) to observe sugar utilization, MR-VP broth for Voges Proskauer reaction, Christensen agar for urea utilization and peptone water broth for indole production. S. enterica serotype Typhimurium strain ATCC 14028 and S. enterica serotype Enteritidis strain ATCC 13076 were used as positive controls. Suspected colonies were purified on nutrient agar and then submitted to an API 20E (BioMérieux, Marcy Etoile, France) test for biochemical identification. The main biochemical tests are glucose fermentation, ortho phenyl beta galactosidase negative reaction, urease negative, lysine decarboxylase, negative indole test, H2S production, and fermentation of dulcitol [28]. Isolates of Salmonella spp. were stored in brain heart broth (BioMérieux, France) supplemented with 30% glycerol, in cryotubes at − 80 °C.
Serotyping
Serotyping and molecular characterization were performed at the Pasteur Institute in Côte d’Ivoire. All the strains were serotyped according to the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor scheme [29]. We purchased the anti-Salmonella agglutinating serums from Bio-Rad (Marnes-la-Coquette, France).
Molecular characterization of Salmonella strains
Genomic DNA extraction
The extraction of total genomic DNA was carried out by the phenol/chloroform method [30] using Salmonella fresh growths from Luria Bertani (LB) broth. The Salmonella strains were grown in LB 1X broth incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. We incubated the mixture of 100 μL of enriched sample added to 300 μL of lysis buffer at 56 °C for 1 h. A total volume of 400 μL of the phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol mixture (25:24:1) was vortexed for 2 min and then centrifuged at 12500 rpm for 2 min. Then the supernatant was transferred in a new 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube and the pellet was discarded. The volume of the transferred supernatant was recorded and a double volume of absolute ethanol (100%) was added to the supernatant. The mixture was incubated for an hour at − 20 °C and then centrifuged at 12500 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was removed and the visible pellet was retained, washed with 200 μL of 70% of cold ethanol and centrifuged at 12500 rpm for 10 min. Finally, the pellet was dried for 20 min at room temperature and 60 μL of elution buffer was added to the pellet before storage at − 20 °C for PCR.
Detection of virulence genes by PCR
Salmonella isolates were tested for different virulent genes (invA, fimA, stn, spvR and spvC) using PCR with sets of specific primer pairs (Table 1) as described by Chaudhary et al. [31]. The amplification of the genes was carried out according to the method described by Li et al. [12] with minor modifications. Initially, the amplification of the invA gene also served as a specific biomarker for the identification of the genus Salmonella [12]. The amplifications of the invA, spvC genes were performed following simplex PCR at a different hybridization temperature of 63 °C using a thermocycler an Applied Biosystem GeneAmp PCR System 9700 type and GoTaq® G2 Flexi DNA Polymerase. The reaction mixture, with a final volume of 50 μL, consisted of 1X of 5X Green GoTaq® Flexi Buffer, 2 mM of MgCl2 Solution, 0.2 μM of each primer and PCR Nucleotide Mix, 27.75 μL of sterile distilled water, 1.25 U of GoTaq® G2 Flexi DNA Polymerase (Promega) and 5 μL of DNA extract. Gene amplification was performed as described by Kumar et al. [32] with minor modifications (volume of water and DNA). Then, the PCR conditions for amplification of virulence genes (invA, spvC) were as follows: 5 min of initial denaturation at 94 °C, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, hybridization at 63 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 30 s, ending with a final extension period of 72 °C for 10 min. Amplifications of the fimA, stn, spvR genes were performed in multiplex with slight variations in volume compared to the previous simplex PCR, using hybridization temperature of 56 °C. With a final volume of 50 μL, the reaction mixture has the same concentrations as described above for the kit GoTaq® G2 Flexi DNA Polymerase.
Table 1.
The primer pairs used for the characterization of virulence genes from isolates of Salmonella [31]
| Genes | Primer sequence (5′ → 3′) | TH (°C) | Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| invA |
F: GTG AAA TTA TCG CCA CGT TCG GGC AA R: TCA TCG CAC CGT CAA AGG AAC C |
63 | 284 | [32] |
| spvR |
F: CAG GTT CCT TCA GTA TCG CA R: TTT GGC CGG AAA TGG TCA GT |
57 | 310 | [33] |
| spvC |
F: ACT CCT TGC ACA ACC AAA TGC GGA R: TGT CTT CTG CAT TTC GCC ACC ATC A |
63 | 571 | [34] |
| fimA |
F: CCT TTC TCC ATC GTC CTG AA R: TGG TGT TAT CTG CCT GAC CA |
56 | 85 | [35] |
| stn |
F: CTT TGG TCG TAA AAT AAG GCG R: TGC CCA AAG CAG AGA GAT TC |
55 | 260 | [36] |
Electrophoresis and band visualization
The amplicons were separated by electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel containing 8 μg/mL of the intercalant Sybr safe DNA gel Strain (10,000X, Invitrogene, Carlsbad, CA 92008 USA). A volume of 8 μL of each of the PCR products was loaded into each well. Five microliters (5 μL) of a 100 bp DNA Ladder molecular weight marker (Promega, Madison, WI 53704 USA) was used to estimate the size of the amplicons. Electrophoresis was carried out at 110 V for 20 min using the Enduro gel XL electrophoresis system (Labnet, FL, USA). The bands were visualized using the GEL DOC EZ imaging system (Bio-Rad, USA).
Results
Salmonella strains isolated from food and clinical samples
Fifteen (15) Salmonella was isolated from sandwich samples and 91 from clinical samples. In total one hundred and six (106) Salmonella strains were involved in the analysis.
Serotyping of Salmonella strains
All 106 Salmonella isolates were agglutinated with antisera OMA and OMB. Ninety-one isolates (85.9%) gave a positive result (56 OMA + and 35 OMB +) and the remaining 15 isolates were negative to OMA and OMB. Salmonella of the antigenic groups OMA+/O:4.5 [39.6% (36/91)] and the antigenic group OMB+/O:6,7,8 [25.3% (23/91)] were the most frequent. Three (3) Salmonella Typhimurium serotypes (OMA+/O:4.5; HMB+/H:i H2:gm) and five (5) Salmonella Enteritidis serotypes (OMA+/O:9; HMB+/H1:gm H2:-) were found, only among clinical isolates. In addition, 14 strains of antigenic formulas (OMB+/O:6,7,8; HMA+/H:i) evocative of the Kentucky/Bargny serotype were isolated (2 from sandwiches and 12 from clinical isolates). These 14 Salmonella isolates were called suspected Kentucky serotypes because the serotyping was incomplete. All reported strains of Salmonella could not be completely serotyped by available sera as showed in Table 2.
Table 2.
Prevalence of Salmonella serotypes and virulence genes
| Origin strains | Salmonella serotypes (serogroups) | Number | Genetic markers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| invA | fimA | stn | spvR | spvC | |||
| Clinical | Enteritidis [D (9)] | 5 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| Typhimurium [B (4)] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Kentucky/Bargnya[C (8)] | 12 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 6 | |
| Salmonella spp. | 71 | 56 | 63 | 55 | 26 | 39 | |
| Total | 91 | 61 (67%) | 70 (76.9%) | 60 (65.9%) | 32 (35.2%) | 44 (48.4%) | |
| Food | Kentucky/Bargnya[C (8)] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Salmonella spp. | 13 | 9 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 7 | |
| Total | 15 | 9 (60%) | 12 (80%) | 10 (66.7%) | 7 (46.7%) | 7 (46.7%) | |
| Total (n = 106) | 70 (66%) | 82 (77.4%) | 70 (66%) | 39 (36.8%) | 51 (48.1%) | ||
aantigenic formula (OMB+/O:6,7,8; HMA H:i) suggestive of Salmonella Kentucky/Bargny
Molecular characterization of Salmonella strains
Molecular identification of Salmonella strains
The molecular identification of Salmonella strain showed that among the 106 Salmonella isolates, 70 (66%) carried invA genes, from which 61 (87.1%) were clinical isolates, and 9 (12.9%) were isolated from sandwich samples (Table 2).
Molecular detection of Salmonella virulence genes
The most prevalent virulence genes were fimA, 82/106 (77.4%) followed by stn and invA 70/106 (66%), spvC 51/106 (48.1%) and spvR 39/106 (36.8%).
The distribution of amplified genes according to strain origin (Table 2), showed that 67% (61/91) of clinical strains carried invA gene, 76.9% (70/91) fimA gene, 65.9% (60/91) stn gene, 35.2% (32/91) spvR gene and 48.4% (44/91) spvC gene.
Salmonella isolated from food (sandwich) carried fimA genes at 80% (12/15), stn genes at 66.7% (10/15), invA genes at 60% (9/15), spvR and spvC genes at 46.7% (7/15).
The distribution of virulence genes according to the serotypes from clinical isolates showed that 80% (4/5) of Salmonella Enteritidis strains carried fimA and spvR genes, and 60% (3/5) carried invA, stn and spvC. 100% (3/3) of Salmonella Typhimurium carried fimA and spvC genes, and 66.7% (2/3) carried invA, stn, fimA and spvR genes.
The majority of the 106 Salmonella isolates harbored at least one of the five genes associated with virulence (Table 3, Table 4). According to the presence of virulence genes, we classified the 106 isolates in eleven (11) different profiles (P) from clinical isolates and named as follows: P1, P2, P3, P10 to P11. The foodborne Salmonella had five (5) genetic profiles (P1, P3, P10, P7 and P11). For all isolates combined (food and human); profile P1 (positive for all five genes tested) was the most prevalent 38 (35.8%), follow by P2 (spvR absent), 12 (11.3%), profile P3 (spvR and spvC absent), 16 (15.1%), P10 (unique presence of fimA), 10 (9.4%) and P11 (negative for all five genes tested), 22 (20.8%).
Table 3.
Virulence genes and genetic profile of Salmonella spp. isolates from food in Burkina Faso
|
Salmonella Strain code |
Year | City | Source | Serotypes | Antigenic formule positive | Identified genes | Genetic profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 93 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:3,1,15; HMA | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 94 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 96 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; O:1,2; HMB Hgm | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 97 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8 | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 98 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMA | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 100 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMB+ | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 104 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi*a | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 92 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMA | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 95 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; O:1,2; HMB | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 103 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB Hgb | fimA, stn | P7 |
| 102 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB Hgc | fimA | P10 |
| 105 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | fimA | P10 |
| 99 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5 O1,2 | … | P11 |
| 101 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA-OMB- | … | P11 |
| 106 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Food | ICS | OMA+ O:3,1015; HMB | … | P11 |
ICS Incomplete serotyping, OMA Antiserum O mixture of group A, OMB Antiserum O mixture of group B, HMA Antiserum H mixture of group A, HMB Antiserum H mixture of group B; *antigenic formula (OMB+/O:6,7,8; HMA H:i) suggestive of Salmonella Kentucky/Bargny; P1: positive for all five genes tested; P3: spvR and spvC absent; P7: unique presence of fimA and stn; P10: unique presence of invA, P11: negative for all five genes test; a, b, coverlapping serotypes/genetic profile
Table 4.
Virulence genes and genetic profile of Salmonella spp. isolates from human stool in Burkina Faso
|
Salmonella Strain code |
Ye ar |
City | Source | Serotypes | Antigenic formule positive | Identified genes | Genetic profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 44 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8 | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 45 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 46 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMB Hgm | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 48 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 50 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMB Hg | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 51 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB Hg | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 53 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | Typhimurium | OMA+ O:4,5; HMA Hi; H1H2 | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 59 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 68 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB Hg | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 71 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 74 | 2017 | Koudougou | Human | Enteritidis | OMA+ O:9; HMB Hgm | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 75 | 2017 | Koudougou | Human | Enteritidis | OMA+ O:9; HMB Hgm | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 85 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMB Hgm | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 86 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 3 | 2017 | Bobo-Dioulasso | Human | Enteritidis | OMA+ O:9; HMB Hgm | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 17 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:9 | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 18 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8 | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 19 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 27 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB, Hg | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 28 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 29 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | Typhimurium | OMA+ O:4,5; HMA Hi; H1H2 | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 30 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:3,10,15; HMA Hi | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 32 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMB | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 34 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:9 | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 35 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 36 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 37 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 38 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 39 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:9 | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 40 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMA | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 43 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB | invA, fimA, stn, spvR, spvC | P1 |
| 1 | 2017 | Bobo-Dioulasso | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB Hg | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 4 | 2017 | Bobo-Dioulasso | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB,Hgm | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 20 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 21 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 22 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMB | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 23 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 24 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 25 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 26 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8 | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 80 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 81 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 84 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | invA, fimA, stn, spvC | P2 |
| 2 | 2017 | Bobo-Dioulasso | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8 | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 5 | 2017 | Bobo-Dioulasso | Human | ICS | OMB+ | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 6 | 2017 | Bobo-Dioulasso | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 7 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB,Hgm | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 8 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 9 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA, Hi* | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 10 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB,H1 | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 11 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 14 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 15 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 16 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:9 | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 54 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 55 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB Hg | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 73 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB Hg | invA, fimA, stn | P3 |
| 72 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8 | fimA, stn, spvC | P4 |
| 13 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMB | invA, fimA | P5 |
| 31 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | invA, fimA | P5 |
| 33 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:3,10,15 | invA, stn | P6 |
| 58 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMB Hgmb | fimA, stn | P7 |
| 57 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | Enteritidis | OMA+ O:9; HMB Hgm | fimA, spvR | P8 |
| 12 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ | invA | P9 |
| 42 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:3,10,15 | fimA | P10 |
| 56 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | Typhimurium | OMA+ O:4,5; HMA Hi; H1H2 | fimA | P10 |
| 60 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB Hg | fimA | P10 |
| 62 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB Hg | fimA | P10 |
| 63 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMB Hgmc | fimA | P10 |
| 65 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMA Hi | fimA | P10 |
| 66 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ | fimA | P10 |
| 67 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMB Hgm | fimA | P10 |
| 41 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5, HMB Hgm | … | P11 |
| 47 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | … | P11 |
| 49 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:3,10,15 | … | P11 |
| 52 | 2018 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA + O:3,10,15 | … | P11 |
| 61 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5; HMB | … | P11 |
| 64 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA-OMB- | … | P11 |
| 69 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMB Hgm | … | P11 |
| 70 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | … | P11 |
| 76 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | … | P11 |
| 77 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | … | P11 |
| 78 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ | … | P11 |
| 79 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8; HMA Hi* | … | P11 |
| 82 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5 | … | P11 |
| 83 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMA+ O:4,5 | … | P11 |
| 87 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ | … | P11 |
| 88 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ O:6,7,8 | … | P11 |
| 89 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ | … | P11 |
| 90 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | Enteritidis | OMA+ O:9; HMB Hgm | … | P11 |
| 91 | 2017 | Ouagadougou | Human | ICS | OMB+ | … | P11 |
ICS Incomplete serotyping, OMA Antiserum O mixture of group A, OMB Antiserum O mixture of group B, HMA Antiserum H mixture of group A, HMB Antiserum H mixture of group B; *antigenic formula (OMB+/O:6,7,8; HMA H:i) suggestive of Salmonella Kentucky/Bargny; P1: positive for all five genes tested; P2: spvR absent; P3: spvR and spvC absent; P9: unique presence of fimA; P10: unique presence of invA, P11: negative for all five genes test; a, b, c:overlapping serotypes/genetic profile
Discussion
The present study investigated the frequency of serotypes of Salmonella, the prevalence and genetic characteristics of Salmonella virulence genes from human diarrheal stools and street-vended sandwiches in Burkina Faso. This is the first study that reports the distribution of Salmonella virulence factors isolated from ready-to-eat sandwiches sold in the street in Burkina Faso. Analyses showed that only 15 (17.7%) out of 85 samples from street-vended sandwiches in Ouagadougou were positive for Salmonella. Our result is different from those found by other researchers. Hassanin et al. [37] isolated Salmonella in 31.1% of shawarmas samples in Egypt, while Abd-El-Malek et al. [38] isolated 7% in kibdas. In Chad, Djibrine et al. [39] did not isolate any Salmonella from beef minced sandwiches vended in streets. These variation rates might be linked to the diversity of cooking process in these different countries.
Serotyping revealed the presence of Salmonella Enteritidis (5/91), Salmonella Typhimurium (3/91), and Salmonella Kentucky/Bargny (12/91) serotypes (Table 2). The remaining isolates that have been not identified completely were categorized as Salmonella spp. (71/91). Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis serotypes were from clinical strains. Indeed, Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis, are the most serotypes involved in human infections and frequently isolated from farm animals [40]. In Sub-saharan Africa, non-typhoid salmonellosis is endemic and the serogroups B (4), D (9) and C (8) have been identified from Salmonella isolated in this study (Table 2). An earlier study argued that more than 2500 serovars of Salmonella enterica were identified by using the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor scheme; about 20 serovars were found primarily in antigen groups B, C, D and E [41]. The serogroups B, D and C are the main causes of human infections, including gastroenteritis and bacteremia [42]. Also, they are widely distributed among farm animals and enter the food chain [40]. Our study reported suspected Kentucky serotypes. This ubiquitous serotype has been closely linked to poultry since 1937 and is now spread in several African countries [43]. In the current decade in West Africa, the finding of the expansion of Salmonella Kentucky in the poultry sector has also been reported by Igomu et al. [44] and Kagambèga et al. [45].
The virulence of Salmonella is linked to a combination of chromosomal and plasmid factors; the invA gene serves also as a specific biomarker for the identification of the genus Salmonella [12]. Elsewhere, published papers [31, 46–48] reveal that invA gene has already been detected in 100% of Salmonella strains. However, in our study we found a lower rate (66%) to 100%. Other authors like Mthembu et al. [49] reported lower rates of (54.4%; 106/195) and Somda et al. [24] reported the presence of the invA gene in 91% (52/57) of nontyphoidal Salmonella isolates from human diarrhea, environment and lettuce samples in Burkina Faso. In our study, 34% of Salmonella isolates do not have the invA gene and therefore would be unable to induce host cell invasion. Then, Salmonella may be in a virulent (invA) or non-virulent state [50]. In addition, asymptomatic animals’ carrying these virulent or non-virulent strains could be potential sources of their transmission to humans via the food chain, promiscuity between human and animals, and the poor management of animal effluents [49, 50]. In clinical isolates and in food (sandwich) isolates, the invA, fimA and stn genes found have approximately high percentages and the presence of one would predict the presence of the other. Several authors previously revealed the constant presence of invA, fimA and stn gene in all Salmonella isolates analyzed in their study [31, 47, 48]. As observed by Foley et al. [11, 49], the difference in frequency of the virulence genes observed in our study could be related to the topology of the gene in Salmonella; despite their different locations, they remain responsible for virulence in salmonellosis. The virulence plasmid gene spvR was present in 36.8% of strains, giving them the ability to cause systemic infections. This frequency of spvR is significantly higher than those reported by several authors [24, 31, 48]. The spvC gene was detected in 48.1% of all the isolates (106) tested, 44/106 were clinical isolates and 7/106 came from sandwiches (Table 2). Krzyzanowski et al. [51] found out a low rate of Salmonella strains with the spvC gene, suggesting its particularity in the virulence of Salmonella. Amini et al. [52] found out the presence of spvC in Salmonella strains isolated from humans and cattle and reported 100 and 90%, respectively.
Eight (08) Salmonella spp. isolated from the sandwiches indicated a simultaneous presence of spvC and spvR. Three of the Salmonella serotype Enteritidis and two of the Salmonella serotype Typhimurium identified from clinical isolates also harbored these two genes (spvC and spvR) (Table 2). Derakhshandeh et al. [53] also found out two human serotypes of Salmonella Enteritidis indicating a simultaneous presence of spvC and spvR. However, Chaudhary et al. [31] reported the complete absence of spvC gene in all their analyzed isolates. The spvR locus is strongly associated with strains that cause non-typhoid bacteremia, but are not present in typhoid strains [54]. However, in Senegal, none of Salmonella serotype Keurmassar investigated (human and poultry origin) harbored a virulence plasmid [46]. This gene is not commonly found in the genome of Salmonella, but is of paramount importance when present. In addition, most Salmonella Typhimurium strains contain a self-transmissible virulence plasmid (pSLT) such as the spv operon [18]. Salmonella’s genetic variations could be derived from transfer of this organism between human-origin and animal/food-origin strains [55]. Whether this can transfer virulence plasmid from animal-origin strains to human-origin strains or vice versa remains to be investigated. These genes (spvR and spvC) are carried by mobile genetic elements that are lost over the time: their distribution, which appears low, does not reflect the clinical reality [56]. Despite our study’s antigenic similarities among the Salmonella isolates, the genetic profile was different for all strains. Although all serotypes of Salmonella can be considered potentially pathogenic, there have some differences in their virulence [57]. Salmonella isolated from sandwiches share same types of virulence genes with clinical isolates. Six Salmonella (food and human) isolates overlapped (a, b,c) due to their partial antigenic formulas, genetic profiles and locality (Table 3, Table 4). We also found that these overlaps are in city of Ouagadougou, which may justify because food samples were collected in Ouagadougou only and in the vicinity of medical centers (Fig. 1). We could be led to verify the fact that clinical Salmonella’s derive from meal contaminations and vice versa. It was possible to characterize the isolates according to different genetic profiles [47]. The P1 profile (positive for all five genes tested) had the highest frequency necessary for a very successful infection, demonstrating that these genes are widely distributed in Salmonella population (Table 3, Table 4). Detection of several genetic profiles may suggest gene acquisitions or deletions in different clones, which could favor different levels of adaptation of strains to the host [58]. Then, genetic variations in Salmonella could be derived from the transfer of virulence plasmid from animal-origin strains to human-origin strains or vice versa, which remains to be investigated [55]. The P11 profile indicates that strains do not harbor any of the five virulence genes. Our study reported the P11 profile in 20.75% (22/106) of the Salmonella (Table 3, Table 4), even though these strains were confirmed by serotyping. Theoretically, in clinical Salmonella, the invA and stn genes should be present. However, the acquisition of the lactose operon by Salmonella reduces its virulence potential [59]. The hypothesis would be that these isolates have lost their virulence genes during their evolution, or are avirulent and the low sensitivity of the PCR.
Conclusion
This study highlighted the most serotypes frequently involved salmonellosis in Burkina Faso. Salmonella Enteritidis and Typhimurim were mainly isolated in human stool. Additional analysis is needed to confirm the plausible presence of the Kentucky/Bargny serotype among the food and clinical isolates. The presence of Salmonella virulence genes was equally important in food and clinical isolates. The presence of virulence genes among isolates from sandwich samples alerted on the potential risk of contamination of the population and probably a possible community health crisis. In addition, the results of this study support that there is genetic differentiation between isolates of the same serotype in the distribution of virulent genes. This provides a basis for the criteria for determining possible variations in the virulence of different strains in vivo, as well as further studies in full serotyping and phylogenetic analysis. These results could enable Burkina Faso’s health authority to better orient their programs to fight diseases associated with street food, notably through the training of restaurateurs in food hygiene.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful the mobility grant of the “West African Research Association”, and its corollary institution, the “West African Research Center” (WARA / WARC) and Department of Bacteriology, Molecular Biology Platform of Pasteur Institute from Côte d’Ivoire for their cooperation while carrying out this work. Special thanks are given to Dr. Solange KAKOU-NGAZOA for welcoming me to his team and for his considerable support in this work.
Abbreviations
- NTS
Non-typhoidal Salmonella
- stn
Salmonella enterotoxin
- XLD
Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate
- SS
Salmonella-Shigella
- MR-VP Broth
Methyl-red Voges-Proskauer Broth
- LB Broth
Luria Bertani Broth
- PCR
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- ICS
Incomplete serotyping
- OMA
Antiserum O mixture of group A
- OMB
Antiserum O mixture of group B
- HMA
Antiserum H mixture of group A
- HMB
Antiserum H mixture of group B
- pSLT
self-transmissible virulence plasmid
- spv
Salmonella plasmid virulence
Authors’ contributions
MEMN: Conceptualization, Investigation, formal analysis, result analysis, writing-review& editing. Data analysis: MEMN, SK, AK, AS. Strains isolation and processing data collection: MEMN, AS, ES, KG, AS, AYAA, RO. Manuscript writing and editing: SK, AK, EB, JBO, OZ, AKT, IJO. All authors contributed to manuscript editing. NB, LS: Conceptualization, supervision, Director of thesis, review. All authors have helped in revision and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval by the “Comité d’éthique pour la recherche en santé (CERS)” by decision N° 2021–11-266. The Institutional Agreement of CHU-Yalgado Ouédraogo N°2017–480/MS/SG/CHU-YO/DG and the collaboration of other health centers in Burkina Faso. This study is part of the surveillance and epidemiology of Salmonella in Burkina Faso.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have not declared any conflict of interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Balasubramanian R, Im J, Lee JS, Jeon HJ, Mogeni OD, Kim JH, et al. The global burden and epidemiology of invasive non-typhoidal Salmonella infections. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(6):1421–1426. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1504717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chami B, Bao S. Tech Published/books/Salmonella-Distribution, Adaptation, Control Measures and Molecular Technologies. 2012. Salmonella: Invasion, Evasion & Persistence; pp. chp16–cp313. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hardy A. Salmonella: a continuing problem. Postgrad Med J. 2004;80(947):541–545. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.2003.016584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hennekinne JA, Herbin S, Firmesse O, Auvray F. European food poisoning outbreaks involving meat and meat-based products. Procedia Food Sci. 2015;5:93–96. doi: 10.1016/j.profoo.2015.09.024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tran Dien A.. Génomique épidémiologique de Salmonella (Doctoral dissertation, Paris, Institut agronomique, vétérinaire et forestier de France). 2018. p.22.. https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-02006644/document. Accessed date May 2020.
- 6.Mather A, Reid S, Maskell D, Parkhill J, Fookes M, Harris S, et al. Distinguishable epidemics of multidrug-resistant Salmonella typhimurium DT104 in different hosts. Science. 2013;341(6153):1514–1517. doi: 10.1126/science.1240578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Havelaar AH. Première Conférence internationale FAO/OMS/UA sur la sécurité sanitaire des aliments. Addis-Abeba. 12 et 13 février 2019. http://www.fao.org/3/CA3056FR/ca3056fr.pdf. Accessed date May 2020.
- 8.Dembélé R, Konaté A, Bonkoungou IJO, Kagambega A, Konaté K, Bagré TS, et al. Serotyping and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella isolated from children under five years of age with diarrhea in rural Burkina Faso. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2014;8(34):3157–3163. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2014.7002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Langendorf C, Le Hello S, Moumouni A, Gouali M, Mamaty AA, Grais RF, et al. Enteric bacterial pathogens in children with diarrhea in Niger: diversity and antimicrobial resistance. Plos One. 2015;10(3):e0120275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jaffee S, Henson S, Unnevehr L, Grace D, Cassou E. The safe food imperative: Accelerating progress in low-and middle-income countries: The World Bank; 2018. 10.1596/978-1-4648-1345-0. Accessed date April 2021
- 11.Foley SL, Johnson TJ, Ricke SC, Nayak R, Danzeisen J. Salmonella pathogenicity and host adaptation in chicken-associated serovars. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013;77(4):582–607. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00015-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li Q, Cheng W, Zhang D, Yu T, Yin Y, Ju H, et al. Rapid and sensitive strategy for Salmonella detection using an InvA gene-based electrochemical DNA sensor. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2012;7(1):844–856. [Google Scholar]
- 13.El-Sebay NA, Abu Shady H, El-Rashed El-Zeedy S, Samy A. InvA gene sequencing of Salmonella typhimurium isolated from Egyptian poultry. Asian J Sci Res. 2017;10:194–202. doi: 10.3923/ajsr.2017.194.202. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Galán JE. Molecular genetic bases of Salmonella entry into host cells. Mol Microbiol. 1996;20(2):263–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Prager R, Fruth A, Tschäpe H. Salmonella enterotoxin (stn) gene is prevalent among strains of Salmonella enterica, but not among Salmonella bongori and other Enterobacteriaceae. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1995;12(1):47–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1995.tb00173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Collinson SK, Liu SL, Clouthier SC, Banser PA, Doran JL, Sanderson KE, et al. The location of four fimbrin-encoding genes, agfA, fimA, sefA and sefD, on the Salmonella Enteritidis and/or Salmonella typhimurium XbaI-BlnI genomic restriction maps. Gene. 1996;169(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00763-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gulig PA, Doyle TJ, Hughes JA, Matsui H. Analysis of host cells associated with the Spv-mediated increased intracellular growth rate of Salmonella typhimurium in mice. Infect Immun. 1998;66(6):2471–2485. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.6.2471-2485.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gulig PA, Danbara H, Guiney DG, Lax AJ, Norel F, Rhen M. Molecular analysis of spv virulence genes of the Salmonella virulence plasmids. Mol Microbiol. 1993;7(6):825–830. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Marks F, Von Kalckreuth V, Aaby P, Adu-Sarkodie Y, El Tayeb MA, Ali M, et al. Incidence of invasive Salmonella disease in sub-Saharan Africa: a multicentre population-based surveillance study. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5(3):e310–e323. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30022-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Langridge GC, Nair S, Wain J. Nontyphoidal Salmonella serovars cause different degrees of invasive disease globally. J Infect Dis. 2009;199:602–603. doi: 10.1086/596208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kariuki S, Gordon MA, Feasey N, Parry CM. Antimicrobial resistance and management of invasive Salmonella disease. Vaccine. 2015;33 Suppl 3(0 3):C21–C29. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.03.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Feasey NA, Hadfield J, Keddy KH, Dallman TJ, Jacobs J, Deng X, et al. Distinct Salmonella Enteritidis lineages associated with enterocolitis in high-income settings and invasive disease in low-income settings. Nat Genet. 2016;48:1211–1217. doi: 10.1038/ng.3644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pulford CV, Perez-Sepulveda BM, Canals R, Bevington JA, Bengtsson RJ, Wenner N, et al. Stepwise evolution of Salmonella typhimurium ST313 causing bloodstream infection in Africa. Nat Microbiol. 2021;6:327–338. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-00836-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Somda NS, Bonkoungou JIO, Sambe-Ba B, Drabo MS, Wane AA, Sawadogo-Lingani H, et al. Diversity and antimicrobial drug resistance of non-typhoid Salmonella serotypes isolated in lettuce, irrigation water and clinical samples in Burkina Faso. J Agri Food Res. 2021;100167. 10.1016/j.jafr.2021.100167.
- 25.Kagambèga A, Lienemann T, Frye JG, Barro N, Haukka K. Whole genome sequencing of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium isolated from humans and poultry in Burkina Faso. Trop Med Health. 2018;46:4. doi: 10.1186/s41182-018-0086-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dembélé R, Konaté A, Traoré O, Kaboré WA, Soulama I, Kagambèga A, et al. Extended spectrum beta-lactamase and fluoroquinolone resistance genes among Escherichia coli and Salmonella isolates from children with diarrhea. Burkina Faso BMC Pediatr. 2020;20(1):459. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-02342-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 6579–1. Microbiology of the food chain — Horizontal method for the detection, enumeration and serotyping of Salmonella— Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. 2017. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Odumeru JA, León-velarde CG. Salmonella Detection Methods for Food and Food Ingredients. 2000;(Williams 1981):374–92. 10.5772/29526.
- 29.Grimont PA, Weill FX. WHO collaborating centre for reference and research on Salmonella. 2007. Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serovars; pp. 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sambrook J, Russell DW. Purification of nucleic acids by extraction with phenol:chloroform. CSH Protoc. 2006;2006(1):pdb.prot4455. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot4455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chaudhary J, Nayak J, Brahmbhatt M, Makwana P. Virulence genes detection of Salmonella serovars isolated from pork and slaughterhouse environment in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Vet World. 2015;8(1):121–124. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2015.121-124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kumar R, Surendran PK, Thampuran N. Evaluation of culture, ELISA and PCR assays for the detection of Salmonella in seafood. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2008;46(2):221–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2007.02286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pasmans F, Immerseel FV, Heyndrickx M, Godard C, Wildemauwe C, Ducatelle R, et al. Host adaptation of pigeon isolates of Salmonella serovar typhimurium var. Copenhagen PT99 is associated with macrophage cytotoxicity. Infect Immun. 2003;71(10):6068–6074. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.10.6068-6074.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Oliveira SD, Rodenbusch CR, Michae GB, Cardoso MI, Canal CW, Brandelli A. Detection of virulence genes in Salmonella Enteritidis isolated from different sources. Braz J Microbiol. 2003;34(1):123–124. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822003000500042. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Naravaneni R, Jamil K. Rapid detection of food-borne pathogens by using molecular techniques. J Med Microbiol. 2005;54(1):51–54. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.45687-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Makino S, Kurazono H, Chongsanguam M, Hayashi H, Cheun H, Suzuki S, et al. Establishment of the PCR system specific to Salmonella spp. and its application for the inspection of food and fecal samples. J Vet Med Sci. 1999;61(11):1245–1247. doi: 10.1292/jvms.61.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hassanin F, Reham AA, Shawky N, Gomaa W. Incidence of Escherichia coli and Salmonella in ready to eat foods. Benha Vet Med J. 2014;27(1):84–91. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Abd-El-Malek AM. Microbiological quality of ready-to-eat liver sandwiches (Kibda) Global Vet. 2014;13(6):1097–1102. doi: 10.5829/idosi.gv.2014.13.06.91141. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Djibrine MA, Tidjani A, Ngandolo BN, Nadlaou B, Barro N. Microbiological quality of some street foods in N'Djamena, Chad: case of sandwiches. Int J Biol Chem Sci. 2018;12(3):1113–1122. doi: 10.4314/ijbcs.v12i3.3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Foley S, Lynne A, Nayak R. Salmonella challenges: prevalence in swine and poultry and potential pathogenicity of such isolates. J Anim Sci. 2008;86(14 Suppl):E149–E162. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jones TF, Ingram LA, Cieslak PR, Vugia DJ, Tobin-d'angelo M, Hurd S, et al. Salmonellosis outcomes differ substantially by serotype. J Infect Dis. 2008;198(1):109–114. doi: 10.1086/588823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kariuki S, Revathi G, Kariuki N, Kiiru J, Mwituria J, Hart CA. Characterisation of community acquired non-typhoidal Salmonella from bacteraemia and diarrhoeal infections in children admitted to hospital in Nairobi, Kenya. BMC Microbiol. 2006;6:101. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-6-101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Le Hello S, Hendriksen RS, Doublet B, Fisher I, Nielsen EM, Whichard JM, et al. International spread of an epidemic population of Salmonella enterica serotype Kentucky ST198 resistant to ciprofloxacin. J Infect Dis. 2011;204:675–684. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Igomu EE. Salmonella Kentucky: prevalence and challenges in Nigeria and the Africa continent. Afr J Clin Exper Microbiol. 2020;21(4):272–283. doi: 10.4314/ajcem.v21i4.3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kagambèga A, Hiott LM, Boyle DS, McMillan EA, Sharma P, Gupta SK, et al. Serotyping of sub-Saharan Africa Salmonella strains isolated from poultry feces using multiplex PCR and whole genome sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2021;21(1):1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02085-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gassama-Sow A, Wane AA, Canu NA, Uzzau S, Aidara-Kane A, Rubino S. Characterization of virulence factors in the newly described Salmonella enterica serotype Keurmassar emerging in Senegal (sub-Saharan Africa) Epidemiol Infect. 2006;134(4):741–743. doi: 10.1017/S0950268805005807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Borges KA, Furian TQ, Borsoi A, Moraes HL, Salle CT, Nascimento VP. Detection of virulence-associated genes in Salmonella Enteritidis isolates from chicken in south of Brazil. Pesq Vet Bras. 2013;33(12):1416–1422. doi: 10.1590/S0100-736X2013001200004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Deguenon E, Dougnon V, Lozes E, Maman N, Agbankpe J, Abdel-Massih RM, et al. Resistance and virulence determinants of faecal Salmonella spp. isolated from slaughter animals in Benin. BMC Res Notes. 2019;12(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4341-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mthembu TP, Zishiri OT, El Zowalaty ME. Detection and molecular identification of Salmonella virulence genes in livestock production Systems in South Africa. Pathogens. 2019;8(3):124. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8030124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ahmer BMM, Gunn JS. Interaction of Salmonella spp with the intestinal microbiota. Front Microbiol. 2011;2:101. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Krzyzanowski F, Zappelini L, Martone-Rocha S, Dropa M, Matté MH, Nacache F, et al. Quantification and characterization of Salmonella spp isolates in sewage sludge with potential usage in agriculture. BMC Microbiol. 2014;14:263. doi: 10.1186/s12866-014-0263-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Amini K, Salehi TZ, Nikbakht G, Ranjbar R, Amini J, Ashrafganjooei SB. Molecular detection of invA and spv virulence genes in Salmonella Enteritidis isolated from human and animals in Iran. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2010;4(21):2202–2210. doi: 10.5897/AJMR.9000508. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Derakhshandeh A, Firouzi R, Khoshbakht R. Association of Three Plasmid-Encoded spv genes among different Salmonella serotypes isolated from different origins. Indian J Microbiol. 2013;53(1):106–110. doi: 10.1007/s12088-012-0316-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Guiney DG, Fierer J. The role of the spv genes in Salmonella pathogenesis. Front Microbiol. 2011;2:129. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Chiu CH, Su LH, Chu CH, Wang MH, Yeh CM, Weill FX, et al. Detection of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium phage types DT102, DT104, and U302 by multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44(7):2354–2358. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00171-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gebreyes WA, Thakur S, Dorr P, Tadesse DA, Post WL. Occurrence of spvA virulence gene and clinical significance for multidrug-resistant Salmonella strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47(3):777–780. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01660-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Karasova D, Havlickova H, Sisak F, Rychlik I. Deletion of sodCI and spvBC in Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis reduced its virulence to the natural virulence of serovars Agona, Hadar and Infantis for mice but not for chickens early after infection. Vet Microbiol. 2009;139(3–4):304–309. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.06.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Moussa IM, Aleslamboly YS, Al-arfaj AA, Hessain AM, Gouda AS, Kamal RM. Molecular characterization of Salmonella virulence genes isolated from different sources relevant to human health. J Food Agric Environ. 2013;11(2):197–201. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Eswarappa SM, Karnam G, Nagarajan AG, Chakraborty S, Chakravortty D. lac repressor is an antivirulence factor of Salmonella enterica: its role in the evolution of virulence in Salmonella. Plos One. 2009;4(6):e5789. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.