Abstract
Although many genes are known to influence sleep, when and how they impact sleep-regulatory circuits remain ill-defined. Here, we show that insomniac (inc), a conserved adaptor for the autism-associated Cul3 ubiquitin ligase, acts in a restricted period of neuronal development to impact sleep in adult Drosophila. The loss of inc causes structural and functional alterations within the mushroom body (MB), a center for sensory integration, associative learning, and sleep regulation. In inc mutants, MB neurons are produced in excess, develop anatomical defects that impede circuit assembly, and are unable to promote sleep when activated in adulthood. Our findings link neurogenesis and postmitotic development of sleep-regulatory neurons to their adult function and suggest that developmental perturbations of circuits that couple sensory inputs and sleep may underlie sleep dysfunction in neurodevelopmental disorders.
Research organism: D. melanogaster
Introduction
A central goal of sleep research has been elucidating the mechanisms by which genes shape normal sleep patterns and cause sleep disorders. While numerous genes that strongly impact sleep have been identified in humans and in animals ranging from mammals to invertebrates (Chemelli et al., 1999; Chiu et al., 2016; Cirelli et al., 2005; Funato et al., 2016; He et al., 2009; Lin et al., 1999; Raizen et al., 2008), when these genes act to influence sleep is in many cases unresolved. Genes that act in the adult brain to modulate the activity of sleep-regulatory circuits in an ongoing manner have been intensively investigated (e.g. Chemelli et al., 1999; Lin et al., 1999), including with conditional gain-of-function, loss-of-function, and rescue in adult animals (Chiu et al., 2016; Clasadonte et al., 2017; Foltenyi et al., 2007; Guo et al., 2011; Ishimoto and Kitamoto, 2010; Joiner et al., 2006; Van Buskirk and Sternberg, 2007). In contrast, despite great progress in understanding neuronal development (Doe, 2008; Jessell and Sanes, 2000; Sanes and Zipursky, 2020; Tessier-Lavigne and Goodman, 1996; Weinstein and Hemmati-Brivanlou, 1999), developmental mechanisms by which genes influence sleep remain poorly explored, despite the likely relevance of such mechanisms to sleep disturbances in autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders (Angriman et al., 2015; Souders et al., 2017). Notably, the temporal contributions of genes that impact sleep are rarely assessed in a comprehensive manner, and a further challenge has been linking particular genes to developmental processes that control the structure and function of discrete sleep-regulatory circuits.
Here, we assess the temporal contributions of insomniac (inc), a gene whose mutation sharply curtails sleep in Drosophila (Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011). Pan-neuronal depletion of inc causes short sleep, while restoring inc solely to neurons is largely sufficient to rescue the sleep deficits of inc mutants, indicating that inc impacts sleep chiefly through neurons (Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011). inc is expressed in the larval, pupal, and adult brain (Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011), but when inc acts to influence sleep remains uncertain (Li and Stavropoulos, 2016; Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012). inc encodes an adaptor for the Cul3 ubiquitin ligase (Li et al., 2019), which, like inc, is required in neurons for normal sleep (Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011). Both inc and Cul3 are highly conserved, and mammalian inc orthologs restore sleep to inc mutants (Li et al., 2017), suggesting that functions and substrates of inc are conserved in mammals. Human Cul3 mutations are implicated as a cause of autism and its associated sleep dysfunction (Codina-Solà et al., 2015; Kong et al., 2012; O’Roak et al., 2012), but the underlying mechanisms are unknown. Studies of inc may thus reveal fundamental and conserved mechanisms underlying sleep regulation which are altered in sleep disorders.
Using conditional genetic manipulations of inc, we show that inc acts transiently in developing neurons to impact sleep in adulthood. We furthermore identify developmental defects in inc mutants within the mushroom body (MB), a brain structure that integrates sensory stimuli and regulates sleep. Loss of inc alters MB neurogenesis, causing the overproduction of late-born neurons and changes in postmitotic development that impair the assembly of MB circuits. These developmental alterations persist into adulthood and are associated with specific deficits in the ability of MB neurons to promote sleep in inc adults, in contrast to the anatomy and function of other sleep-regulatory circuits which remain intact. Together, these results elucidate an unexpected mechanism by which inc shapes the development and function of sleep-regulatory neurons to exert a lasting impact on sleep–wake behavior. Our findings additionally suggest that developmental alterations of neurogenesis and within brain centers that integrate sensory inputs may contribute to sleep dysfunction in autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders.
Results
inc acts transiently during a restricted developmental period to impact sleep in adulthood
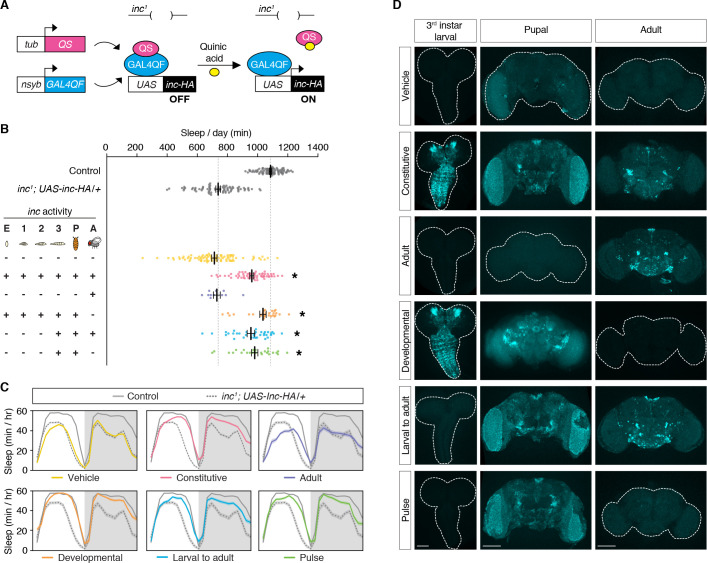
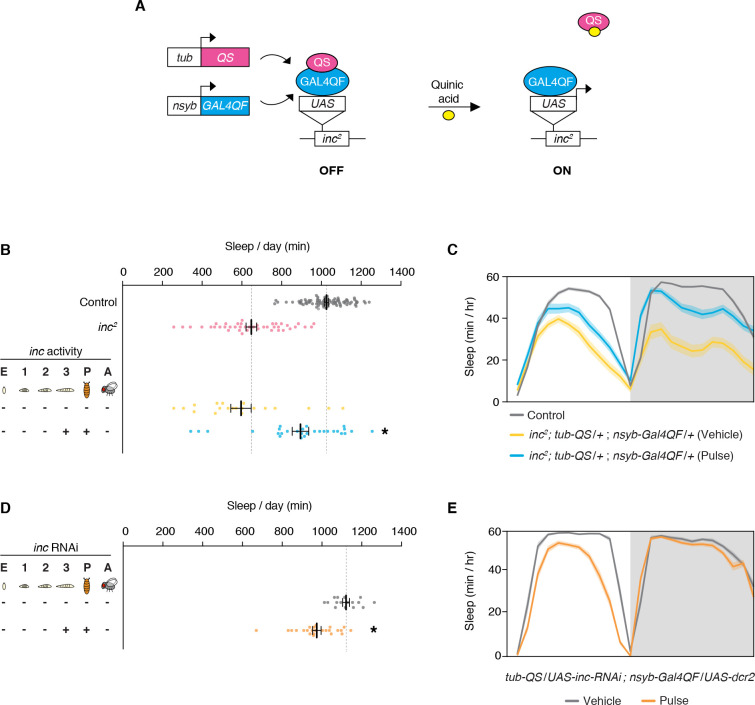
inc impacts sleep through neurons and is expressed in the developing and adult brain (Figure 1; Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011). To assess the temporal mechanisms by which inc impacts sleep, we manipulated inc expression in neurons using the ligand-inducible Q-system (Potter et al., 2010; Riabinina et al., 2015). The Q-system circumvents nonspecific perturbations of sleep caused by other inducible systems and allows constitutive, developmental, and adult manipulations of sleep (Li and Stavropoulos, 2016). We performed a series of conditional rescue experiments in short-sleeping inc1 null mutants bearing a UAS-inc-HA transgene whose expression is induced in neurons by the Q-system upon exposure to quinic acid (Figure 2A). Animals exposed to vehicle throughout development and adulthood slept indistinguishably from inc1 mutants, while animals exposed constitutively to quinic acid exhibited strongly rescued sleep (Figure 2B, C; Figure 2—figure supplement 1), consistent with the rescue conferred by constitutive neuronal expression of inc (Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011). Anti-HA staining of brains confirmed that the Q-system controlled inc expression as expected: vehicle-fed animals lacked inc-HA signal, while those exposed constitutively to quinic acid expressed inc-HA in the larval, pupal, and adult brain (Figure 2D). We next asked whether inc influences sleep through adult-specific or developmental mechanisms. Animals fed quinic acid in adulthood expressed inc-HA in the adult brain but exhibited no rescue of their sleep deficits (Figure 2B–D; Figure 2—figure supplement 1). In stark contrast, developmental induction of inc-HA from embryonic through pupal stages restored sleep to near wild-type levels (Figure 2B–D; Figure 2—figure supplement 1). These findings indicate that inc is dispensable in adult neurons and acts instead during neuronal development to ultimately impact sleep–wake behavior.
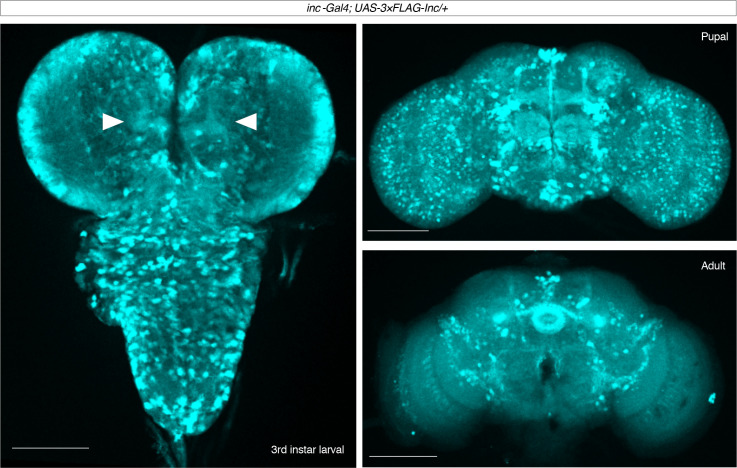
Figure 1. Expression of 3×FLAG-inc driven by inc-Gal4 in the larval, pupal, and adult brain.
Maximal projections are shown for male inc-Gal4; UAS-3×FLAG-inc/+ brains stained with anti-FLAG. For larval brain, projection from a partial z-stack is shown to allow visualization of signal in mushroom body projections (arrowheads). In pupae and adults, signal is prominent in the mushroom body, pars intercerebralis, fan-shaped body, and ellipsoid body. Scale bars, 100 μm.
Figure 2. inc acts in a restricted period of neuronal development to impact sleep in adulthood.
(A) Conditional rescue of inc1 mutants using the ligand-inducible Q-system. Quinic acid relieves QS suppression of the pan-neuronally expressed Gal4QF transcriptional activator, inducing UAS-inc-HA in neurons. (B) Total sleep duration of controls (gray) and inc1; UAS-inc-HA/tub-QS; nsyb-GAL4QF/+ animals exposed to quinic acid (+) or vehicle (−) at indicated life stages; embryos (E), larval stages (1–3), pupae (P), and adults (A). Bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). n = 11–86. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (F(7,397) = 86.73, p < 0.0001) and Tukey post hoc tests, *p < 0.01 for comparisons to inc1; UAS-inc-HA/+. (C) Average sleep profiles of flies in (B), with induction regimens indicated below. Shading indicates ± SEM. (D) Anti-HA staining of inc1; UAS-inc-HA/tub-QS; nsyb-GAL4QF/+ brains from indicated induction regimens. Scale bars, 100 μm.
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Additional sleep parameters for conditional rescue of inc1 mutants using the Q-system.
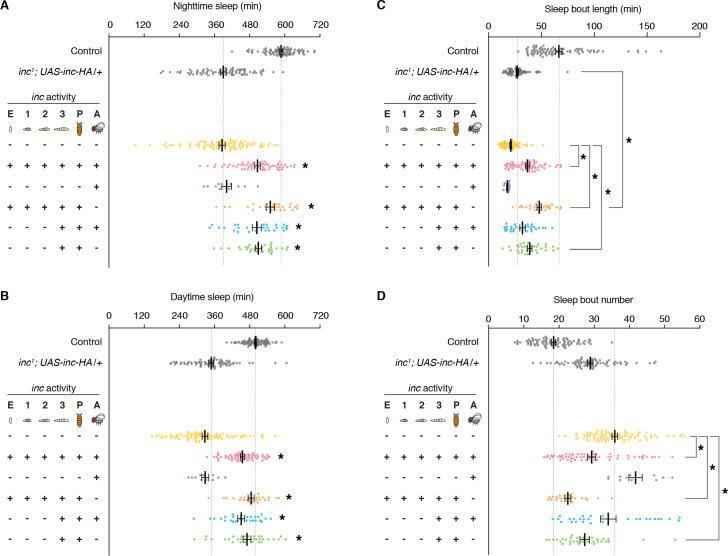
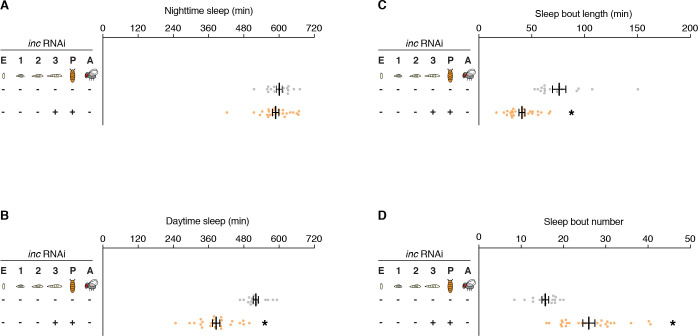
We further defined the developmental period in which inc functions, using more precise temporal manipulations. Neuronal induction of inc-HA from the late third instar larval stage through adulthood strongly rescued the inc sleep phenotype (Figure 2B–D; Figure 2—figure supplement 1), indicating that inc is dispensable in embryonic and early larval neurons. Induction of inc activity solely in late third instar larval and pupal neurons, using a pulse of quinic acid exposure (Figure 2D), restored sleep indistinguishably from constitutive neuronal induction (Figure 2B, C; Figure 2—figure supplement 1). The sleep deficits of inc2 animals, which bear an independent inc null allele that can be reverted by Gal4 (Stavropoulos and Young, 2011), were similarly rescued by this pulse of quinic acid (Figure 3A–C; Figure 3—figure supplement 1), confirming that inc activity in this developmental period is sufficient to restore sleep to inc mutants. We next assessed whether inc is required in late third instar larval and pupal neurons for normal sleep in adulthood, by using the Q-system to induce a pulse of inc RNAi. This manipulation markedly decreased sleep (Figure 3D, E; Figure 3—figure supplement 2). Together, these findings indicate that inc acts transiently in neurons of late third instar larvae and pupae to influence adult sleep–wake behavior. During these developmental stages, many neurons of the adult brain are born and assemble into circuits (Truman and Bate, 1988; White and Kankel, 1978).
Figure 3. Conditional rescue of inc2 mutants and conditional inc RNAi in larval and pupal neurons.
(A) Conditional neuronal rescue of inc2 mutants using the ligand-inducible Q-system. inc2 mutants contain a transposon insertion in the inc 5′UTR immediately upstream of the endogenous start codon. A UAS/TATA element within the transposon terminus permits Gal4-dependent restoration of inc expression (Stavropoulos and Young, 2011). (B) Total sleep duration in inc2; tub-QS/+; nysb-Gal4QF/+ animals exposed to vehicle or quinic acid at the late third instar larval and pupal stages. n = 20–83. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (F(3, 170) = 70.66, p > 0.0001) and Tukey post hoc tests, *p < 0.01 for comparisons to inc2. (C) Average sleep profiles of indicated genotypes from (B). (D) Total sleep duration in tub-QS/UAS-inc-RNAi; nsyb-Gal4QF/UAS-dcr2 animals exposed to vehicle or quinic acid at the late third instar larval and pupal stages. n = 16–24. Student’s t-test, *p < 0.01 for comparison to vehicle-treated control. (E) Average sleep profiles of animals from (D). For (B) and (D), bars represent mean ± SEM. For (C) and (E), shading represents ± SEM.
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Additional sleep parameters for conditional inc2 rescue in third instar larval and pupal neurons.
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Additional sleep parameters for conditional inc RNAi in larval and pupal neurons.
inc has a critical function in the MB that impacts sleep
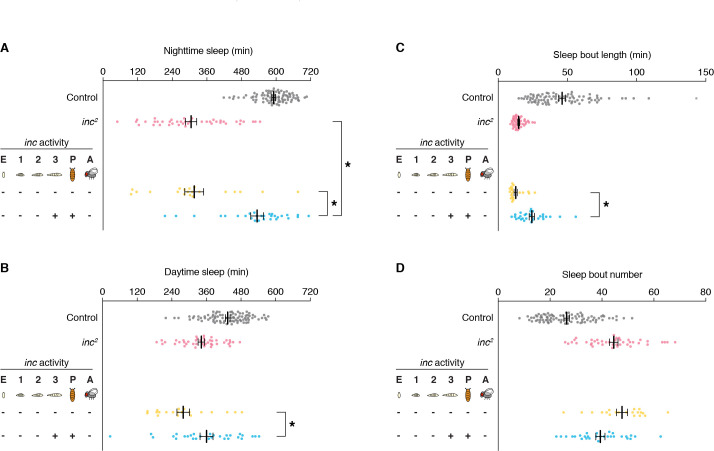
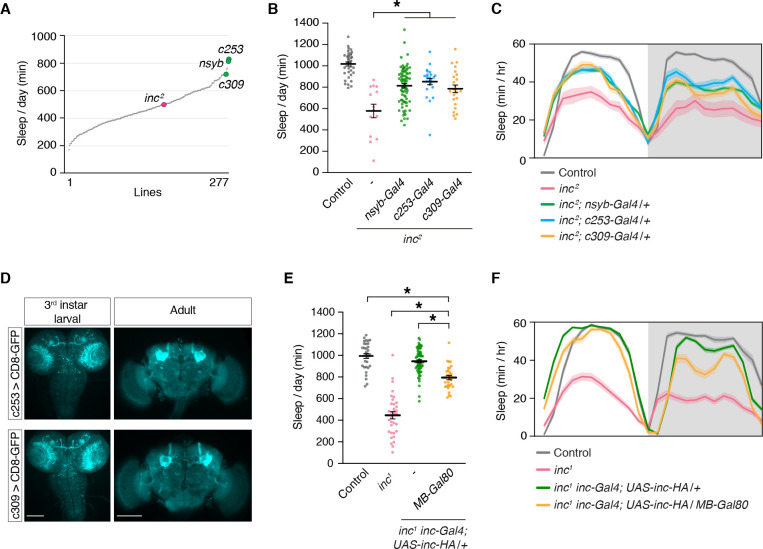
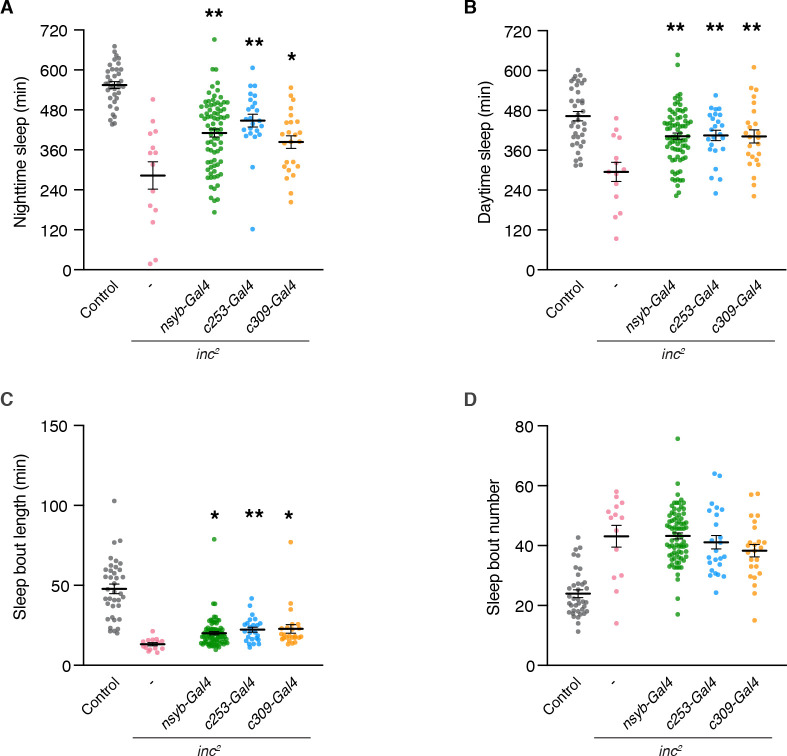
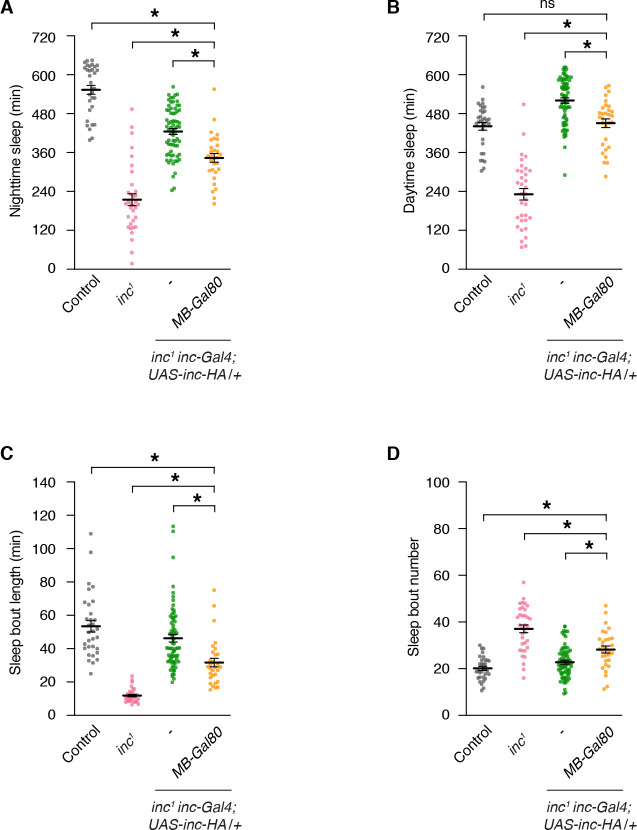
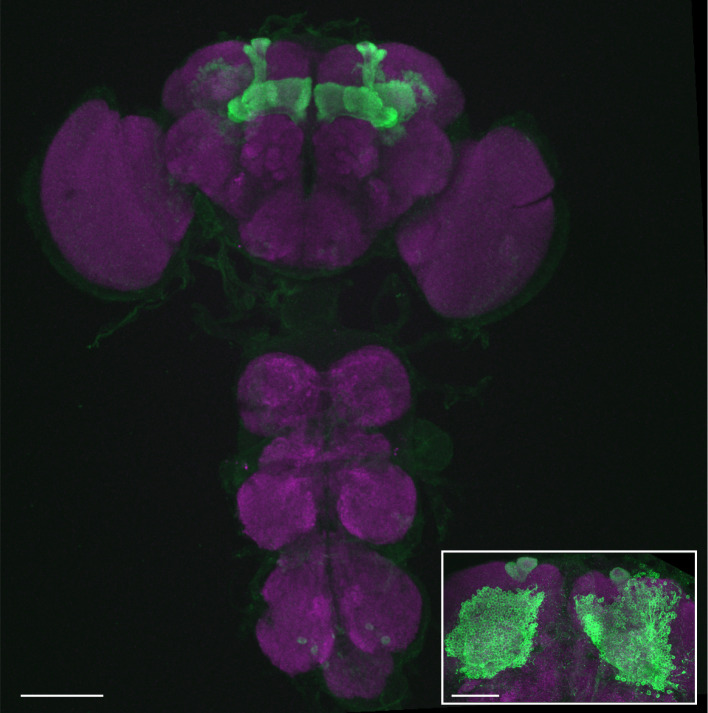
To identify neurons that might underlie the developmental impact of inc on sleep, we performed a rescue screen in inc2 mutants. We screened 277 Gal4 lines expressed in sleep-regulatory circuits or randomly selected populations of cells in the brain and identified two drivers, c253-Gal4 and c309-Gal4, that rescued sleep similarly to the pan-neuronal nsyb-Gal4 driver (Figure 4A). After backcrossing to an isogenic background, both drivers retained their ability to rescue most of the sleep phenotypes of inc2 mutants (Figure 4B, C; Figure 4—figure supplement 1). In late third instar larvae and adults, c253-Gal4 and c309-Gal4 are strongly expressed in the MB (Figure 4D), a structure important for sensory integration, associative learning, and sleep regulation (Heisenberg, 2003; Joiner et al., 2006; Pitman et al., 2006). Because c253-Gal4 and c309-Gal4 are also expressed outside of the MB, we used independent genetic manipulations to confirm that inc acts in the MB to influence sleep. inc-Gal4, a driver that bears inc regulatory sequences and fully rescues inc mutants when used to restore inc activity (Li et al., 2017; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011), is expressed in the larval, pupal, and adult MB (Figure 1). We tested whether the rescue conferred by inc-Gal4 was altered by MB-Gal80, a Gal4 suppressor expressed in MB neurons during development and adulthood (Krashes et al., 2007; Pauls et al., 2010). MB-Gal80 partially suppressed the ability of inc-Gal4 to restore sleep to inc1 mutants, indicating that while inc does not influence sleep solely through the MB, inc is required in MB neurons for normal sleep regulation (Figure 4E, F; Figure 4—figure supplement 2).
Figure 4. The mushroom body is a critical brain region through which inc impacts sleep.
(A) Mean sleep is plotted for each line in a Gal4 rescue screen of inc2 animals. n ≥ 5 per genotype. (B) c253-Gal4 and c309-Gal4 rescue sleep in inc2 mutants. n = 14–78. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (F(4, 172) = 20.36, p < 0.0001) and Tukey post hoc test, *p < 0.01 for comparisons to inc2. (C) Average sleep profiles of flies in (B). (D) Anti-GFP immunostaining of indicated genotypes. Scale bars, 100 μm. (E) MB-Gal80 suppresses sleep rescue in inc1 inc-Gal4; UAS-inc-HA/+ animals. n = 30–69. One-way ANOVA (F(3, 161) = 121.4, p < 0.0001) and Tukey post hoc tests, *p < 0.01. (F) Average sleep profiles of indicated genotypes from (E). For (B) and (E), bars represent mean ± SEM. For (C) and (F), shading represents ± SEM.
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Rescue of inc sleep phenotypes by c253-Gal4 and c309-Gal4.
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Additional parameters for suppression of sleep rescue in inc1 inc-Gal4; UAS-inc-HA animals by MB-Gal80.
Loss of inc abolishes the sleep-promoting functions of MB neurons but spares the functions of other sleep-regulatory circuits
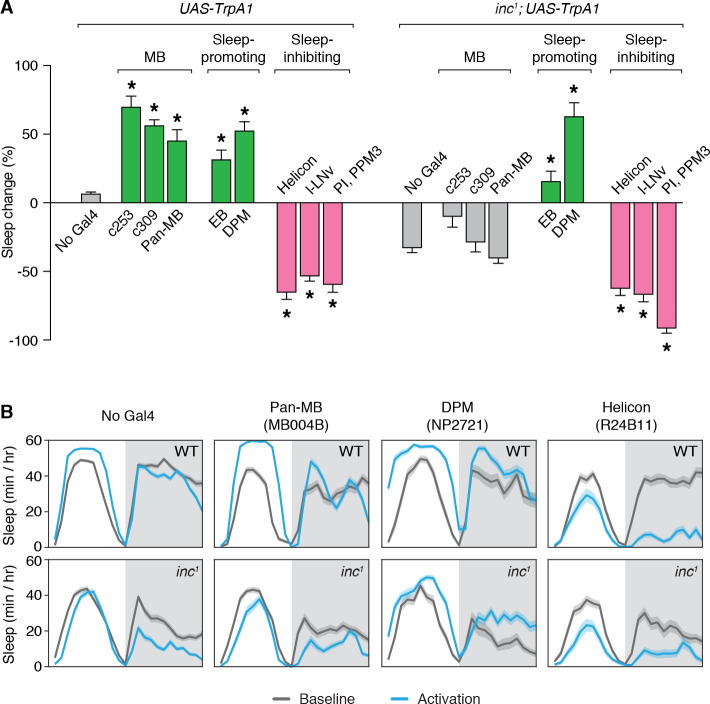
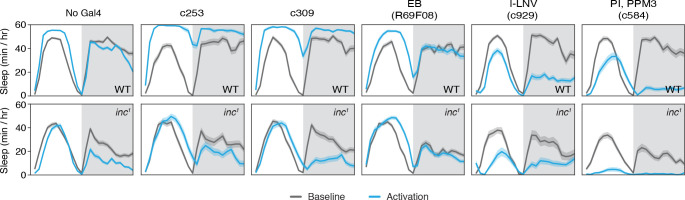
While different circuits within the MB can promote or inhibit sleep upon activation (Joiner et al., 2006; Pitman et al., 2006; Sitaraman et al., 2015a), ablation of the MB strongly reduces sleep (Joiner et al., 2006; Pitman et al., 2006), suggesting that the integrated activity of the MB is sleep-promoting. To assess whether the sleep-regulatory functions of the MB are altered in inc mutants, we activated MB neurons in adult wild-type and inc1 flies using the dTrpA1 heat-activated cation channel (Hamada et al., 2008). Wild-type control flies lacking Gal4 drivers exhibited no change in total sleep when shifted to 28.5°C for 24 hr, while inc1 flies lacking Gal4 drivers exhibited decreased sleep at this temperature (Figure 5A, B), suggesting that inc mutants are hyperarousable by thermal stimuli, as for mechanical stimuli (Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012). Activation of neurons expressing TrpA1 under the control of c253-Gal4 or c309-Gal4 strongly increased sleep in wild-type animals (Figure 5A, B; Figure 5—figure supplement 1), consistent with observations that inactivating synaptic output using the same drivers promotes wakefulness (Pitman et al., 2006). Because c253-Gal4 and c309-Gal4 are expressed in some cells outside of the MB, we also assessed a split-Gal4 driver expressed specifically in MB neurons (Figure 5—figure supplement 2). Using this driver to express TrpA1 and activate MB neurons increased sleep in wild-type animals (Figure 5A, B, ‘pan-MB’). Strikingly, using the same three drivers to activate neurons in inc1 mutants elicited no significant changes in sleep compared to inc1; UAS-TrpA1/+ controls (Figure 5A, B; Figure 5—figure supplement 1), indicating that the sleep-promoting effects of MB activation are abolished in inc mutants.
Figure 5. Sleep-promoting functions of the mushroom body are impaired in inc mutants.
(A) Thermogenetic activation of neuronal populations expressing TrpA1 in control and inc1 animals. Percent change in sleep (mean ± SEM) elicited by activation is shown. n = 31–144. Control and inc1 animals expressing dTrpA1 are compared to no-Gal4 controls (UAS-dTrpA1/+ and inc1; UAS-dTrpA1/+, respectively). *p < 0.01 for Dunnet’s post hoc comparisons after one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for control animals (F(8, 528) = 92.12, p < 0.0001) or inc1 mutants (F(8, 452) = 50.01, p < 0.0001). Green and pink bars indicate drivers that significantly promote or inhibit sleep, respectively; gray bars indicate no significant change with respect to controls. (B) Average sleep profiles of animals from (A) on the baseline day and during thermogenetic activation. Shading represents ± SEM.
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Sleep profiles during baseline and neuronal activation.
Figure 5—figure supplement 2. A split-Gal4 driver expressed specifically in mushroom body (MB) neurons.
To test whether the loss of inc specifically impairs the sleep-regulatory functions of MB neurons or causes more general deficits in sleep regulation, we assessed other neuronal populations that influence sleep. Activation of sleep-promoting populations that include ellipsoid body R5 (EB) (Liu et al., 2016) or Dorsal Paired Medial (DPM) neurons (Haynes et al., 2015) increased sleep similarly in wild-type and inc1 animals (Figure 5A, B; Figure 5—figure supplement 1). Conversely, activation of sleep-inhibiting populations that include Helicon (Donlea et al., 2018), l-LNv (Sheeba et al., 2008), or pars intercerebralis and dopaminergic PPM3 neurons (PI, PPM3) (Dubowy et al., 2016) strongly decreased sleep in wild-type and inc1 animals (Figure 5A, B; Figure 5—figure supplement 1). The functions of these populations thus appear to be intact in inc mutants, suggesting that the loss of inc specifically impairs the sleep-regulatory functions of MB neurons. These findings, together with the developmental time-of-action of inc and its requirement within the MB for normal sleep, suggest that inc acts developmentally in MB neurons to have a lasting impact on their sleep-regulatory functions in adulthood.
inc regulates the production and anatomy of late-born MB neurons
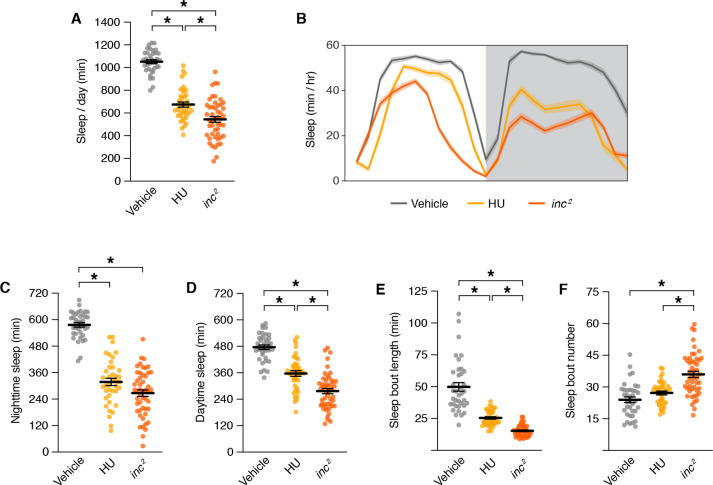
During the critical developmental period through which inc impacts sleep, MB neurons are born and assemble into adult circuits (Ito and Hotta, 1992; Lee et al., 1999). In each brain hemisphere, four MB neuroblasts proliferate to yield ~2000 neurons comprising seven sequentially born subtypes (γd, γm, α´/β´ap, α´/β´m, α/βp, α/βs, and α/βc) that project axons into distinct lobes (γ, α´/β´, and α/β) (Aso et al., 2014a; Ito et al., 1997; Ito and Hotta, 1992; Kurusu et al., 2002; Lee and Luo, 1999; Tanaka et al., 2008; Truman and Bate, 1988; Zhu et al., 2003). Chemical ablation of the MB by exposing first instar larvae to hydroxyurea, an inhibitor of DNA replication, causes sleep deficits in adulthood (Joiner et al., 2006; Pitman et al., 2006). The sleep deficits caused by MB ablation are similar to but less severe than those of inc mutants, including reductions in sleep across the day and decreased sleep consolidation (Figure 6A–F). These findings and the partial suppression of inc rescue by MB-Gal80 (Figure 4E, F; Figure 4—figure supplement 2) support the notion that reduced sleep in inc mutants results from impairments in the MB, alongside effects in additional neuronal populations.
Figure 6. Sleep phenotypes for mushroom body ablation and inc mutants.
Sleep parameters for inc2 mutants and animals exposed to vehicle or hydroxyurea (HU). For all panels, n = 37–49; *p < 0.01 for post hoc tests. (A) Total sleep. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (F(2, 122) = 132.9, p < 0.0001) and Tukey post hoc tests. (B) Average daily sleep profiles. Shading represents ± SEM. (C) Nighttime sleep. One-way ANOVA (F(2, 122) = 126.6, p < 0.0001) and Tukey post hoc tests. (D) Daytime sleep. One-way ANOVA (F(2, 122) = 74.32, p < 0.0001) and Tukey post hoc tests. (E) Sleep bout length. Kruskal–Wallis (p < 0.0001) and Dunn’s post hoc tests. (F) Sleep bout number. One-way ANOVA (F(2, 122) = 24.89, p < 0.0001) and Tukey post hoc tests. For (A) and (C–F), bars represent mean ± SEM.
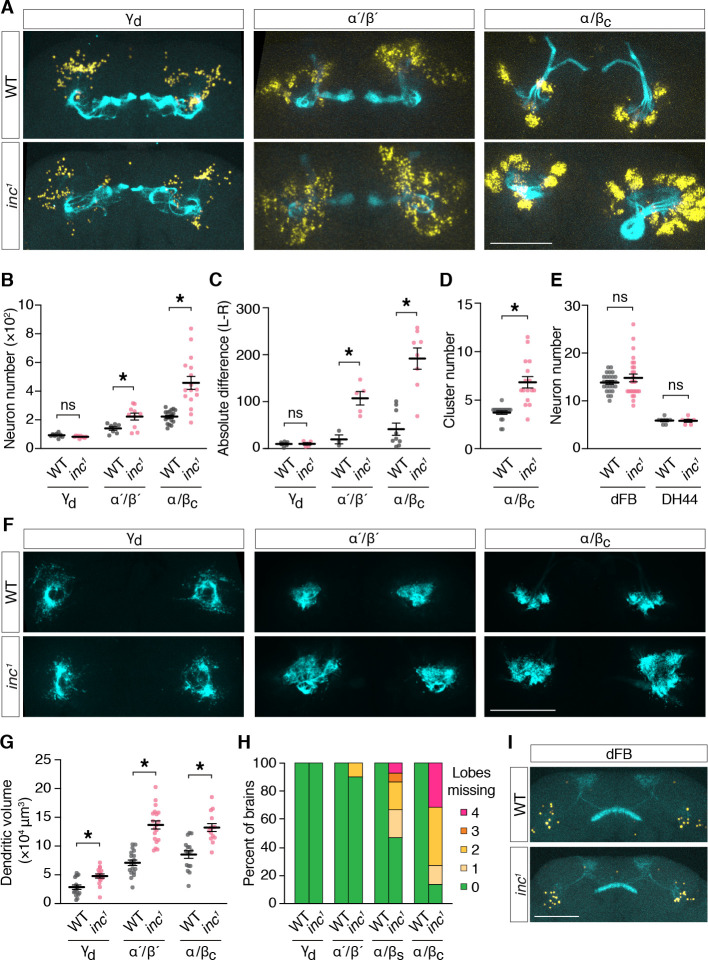
To determine whether inc mutants have anatomical changes in the adult MB that might disrupt its sleep-regulatory functions, we examined MB neurons expressing UAS-Myr-GFP-2A-RedStinger, a bicistronic reporter that marks projections and nuclei (Daniels et al., 2014). Specifically, we used split-Gal4 drivers that label MB neuron subtypes born in embryos (γd), late larval stages (α´/β´), and in pupae (α/βc) (Aso et al., 2014a), to assess whether the loss of inc might preferentially alter subtypes whose birth and development coincides with the critical period through which inc impacts sleep. Consistent with this notion, we observed prominent changes in the number and anatomy of larval- and pupal-born MB neurons in inc mutants. While embryonic-born γd neurons were present in similar numbers in adult brains of controls and inc1 mutants (control, 102 ± 4; inc1, 94 ± 2) (Figure 7A, B), the number of larval-born α´/β´ neurons was increased 58% in inc1 animals (control, 141 ± 13; inc1, 223 ± 24), and the number of pupal-born α/βc neurons was doubled (control, 223 ± 11; inc1, 458 ± 45). The surplus of α´/β´ and α/βc neurons varied between left and right hemispheres in individual inc1 brains and this variation was greatest for α/βc neurons, the last-born in the MB (Figure 7A, C; Figure 7—figure supplement 1), indicating that inc mutants have a stochastic and cumulative defect in MB neurogenesis. Four clusters of α/βc neurons were present in control animals, reflecting their birth from four MB neuroblasts (Ito et al., 1997; Ito and Hotta, 1992; Truman and Bate, 1988), whereas inc1 mutants exhibited an average of nearly seven clusters (control, 3.7 ± 0.2; inc1, 6.8 ± 0.6) (Figure 7A, D; Figure 7—figure supplement 1), suggesting an origin from aberrant or excess neuroblasts. The numbers of other sleep-regulatory neurons, including those of the dorsal fan-shaped body (dFB) and DH44+ neurons, were unchanged in inc mutants (Figure 7A, I), indicating that neuronal overproduction in inc mutants is specific to the MB or manifests preferentially within this neuronal lineage. These findings indicate that inc regulates neurogenesis, a fundamental process regulated by proteins conserved from flies to mammals (Doe, 2008; Knoblich, 2008), and suggest that alterations in early nervous system development can exert a lasting impact on sleep.
Figure 7. inc regulates neurogenesis and anatomy of late-born mushroom body (MB) neurons.
(A) Adult control and inc1 brains expressing UAS-MyrGFP-2A-RedStinger in indicated MB neuron subtypes, stained with anti-GFP (cyan) and anti-dsRed (yellow). (B) MB neuron number per hemisphere. γd, n = 10–11; α ´/β ´, n = 7–10; α/βc, n = 16–18. *p < 0.01, Welch’s t-test. (C) Absolute difference in MB neuron number between left and right brain hemispheres; γd, n = 5–6; α ´/β ´, n = 3–5; α/βc, n = 8–9. *p < 0.01, Welch’s t-test. (D) Number of α/βc neuron clusters per hemisphere. n = 16–18. *p < 0.01, Welch’s t-test. (E) Numbers of dorsal fan-shaped body (dFB) and DH44+ neurons. dFB, n = 26; DH44+, n = 6–8. ns, p > 0.01, Welch’s t-test. (F) Adult control and inc1 brains expressing UAS-DenMark-smGdP-V5 in indicated MB neuron subtypes, stained with anti-GFP. (G) Dendrite volume per hemisphere. γd, n = 16–17; α ´/β ´, n = 19; α/βc, n = 14–16. *p < 0.01, Welch’s t-test. (H) Quantification of axonal projection defects for MB neuron subtypes. Colored bars represent the number of MB lobes in each brain entirely lacking axonal myr-GFP signal. See also panel (A). n = 10–25. (I) Adult control and inc1 brains expressing UAS-MyrGFP-2A-RedStinger in dFB neurons. All scale bars represent 100 μm. For (B–E) and (G), bars represent mean ± SEM.
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Analysis of α/βc neuron clusters and projections.
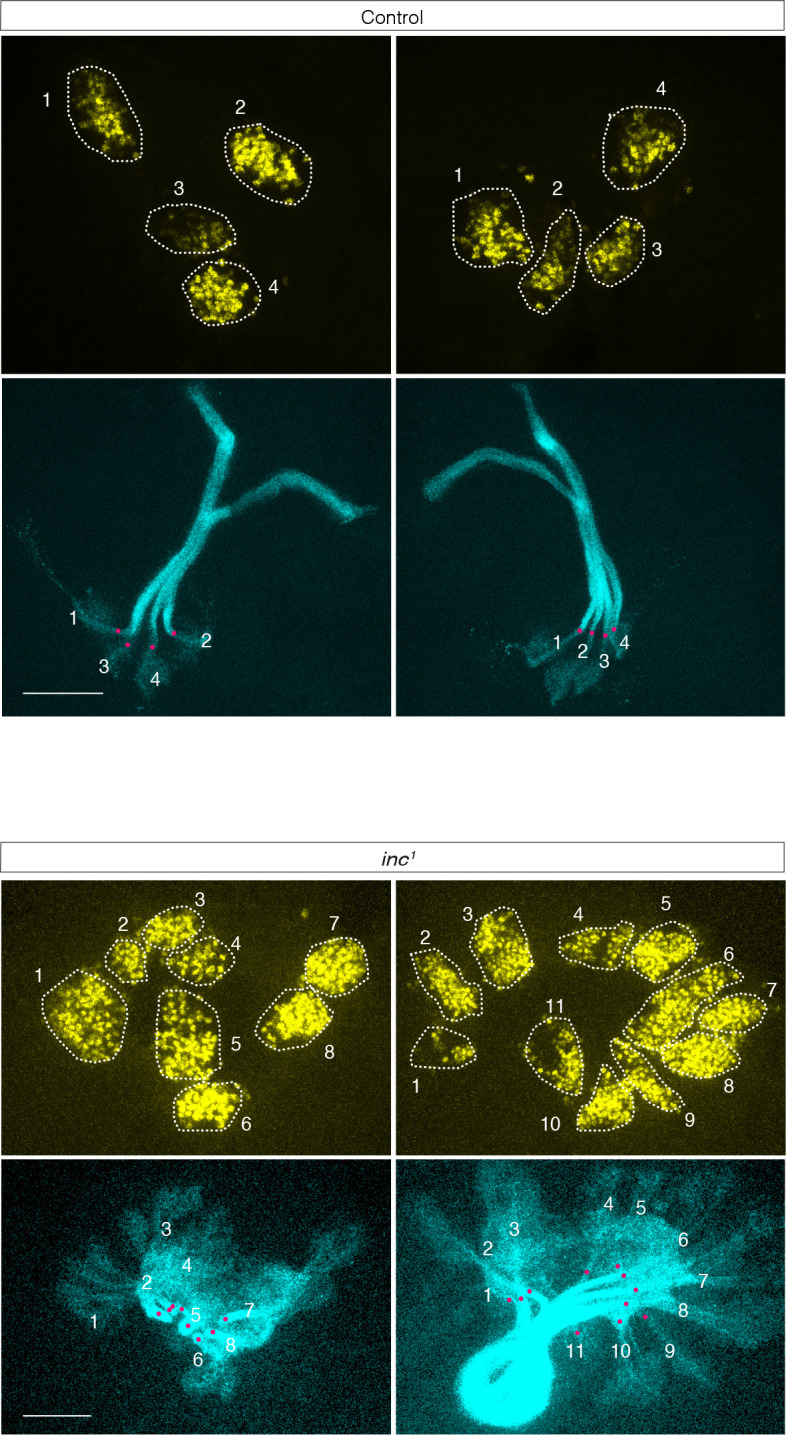
Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Analysis of dendrites in additional sleep-regulatory circuits.
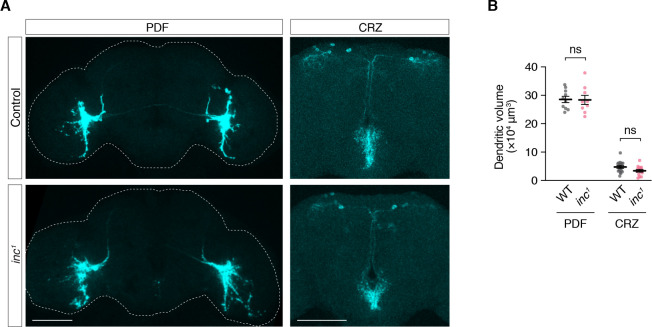
To further assess MB anatomy in inc mutants, we examined axons marked with myr-GFP and separately examined dendrites by expressing DenMark (Nicolaï et al., 2010). Axons of embryonic-born γd neurons exhibited no obvious changes in inc1 mutants (Figure 7A, H). In contrast, axons of larval- and pupal-born MB neurons exhibited morphological defects whose severity correlated with neuronal overproduction and birth order (Figure 7A, H). While α´/β´ axons were absent from MB lobes in a minority (10%) of inc1 brains, axons of α/βs neurons, the penultimate to be born, were missing from MB lobes in 53% of inc1 brains (1.07 ± 0.33 missing lobes per brain) (Figure 7H). Axons of last-born α/βc neurons showed the most severe defects; they failed to project into lobes in 86% of inc brains (2.23 ± 0.3 missing lobes per brain), fasciculated from ectopic neuronal clusters, and often aggregated near the peduncle (Figure 7A, H; Figure 7—figure supplement 1). The dendrites of γd, α´/β´, and α/βc neurons occupied enlarged territories in inc mutants but otherwise appeared normal (Figure 7F, G). Expansions in dendritic volume for α´/β´ and α/βc subtypes paralleled increases in the numbers of these neurons (Figure 7A, B), while increases for γd dendrites occurred independently of neuron number, consistent with functions of inc in postmitotic γd neurons or non-cell autonomous mechanisms. Axons and dendrites of other sleep-regulatory circuits, including those of the dFB, CRZ+ neurons, and PDF+ circadian pacemaker neurons, exhibited no obvious changes in inc mutants (Figure 7I; Figure 7—figure supplement 2), suggesting that alterations of neuronal anatomy in inc mutants are specific to the MB. These findings indicate that increases in the numbers of late-born MB neurons in inc mutants are associated with changes in postmitotic development expected to perturb circuit assembly and function. In particular, the altered axons of multiple MB neuron subtypes are unlikely to form normal circuits with their targets that influence sleep, including dopaminergic neurons, MB output neurons, and recurrent connections to the MB (Aso et al., 2014b; Sitaraman et al., 2015a; Sitaraman et al., 2015b).
Discussion
Here, we have used temporally restricted genetic manipulations to show that inc acts during neuronal development to ultimately impact sleep in adulthood. While many genes are known to act in adults to impact sleep, developmental mechanisms underlying sleep regulation have only recently gained attention (Chakravarti Dilley et al., 2020; Gong et al., 2021; Iwasaki et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2019). Our results underscore the importance of unbiased temporal genetic manipulations to define critical periods through which genes impact sleep, and suggest that genes may influence sleep through unappreciated developmental mechanisms. A clear implication of these findings is that variations in human sleep patterns, including pathological disruptions of sleep, may have a developmental origin.
Reciprocal conditional manipulations have been critical in revealing surprising developmental and adult contributions of genes to neuronal function and behavior. In one notable example, anxiety-like behaviors in mice caused by mutations of the 5-HT1A serotonin receptor were found to be rescued by developmental expression of the receptor (Gross et al., 2002). Withdrawal of receptor expression in adulthood had no measurable consequences on anxiety-like behavior, and adult-specific receptor expression failed to provide rescue, indicating the necessity and sufficiency of the receptor during development (Gross et al., 2002). A second noteworthy example is provided by a mouse model of Rett syndrome, a neurodevelopmental disorder caused by mutation of MECP2, a transcriptional regulator. Conditional MeCP2 expression solely in adulthood was found to be sufficient to rescue mutant phenotypes, indicating a critical period for MeCP2 function in adults rather than during brain development (Guy et al., 2007; Guy et al., 2012). Inactivation of MECP2 specifically in adulthood causes MECP2 mutant phenotypes (McGraw et al., 2011), confirming its adult requirement. By analogy, various genes that influence sleep might act developmentally or in adulthood in a manner that cannot be anticipated in the absence of conditional manipulations.
inc activity is required in neurons for normal sleep, and conversely, restoring inc solely to neurons is largely sufficient to rescue the short sleep of inc mutants (Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011). Our conditional neuronal manipulations of inc span embryonic development through adulthood and indicate that inc expression in neurons of late third instar larvae and pupae is sufficient to rescue sleep in inc mutants to near wild-type levels, indistinguishable from the rescue provided by constitutive neuronal inc expression (Pfeiffenberger and Allada, 2012; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011). Extending this developmental pulse of neuronal inc expression into adulthood does not augment the rescue of inc sleep phenotypes, nor does expressing inc only in adult neurons restore sleep to inc animals. inc expression in embryonic, early larval, and adult neurons thus appears dispensable for normal sleep. Instead, inc is required at a time coincident with the birth and development of many adult neurons, including those of the MB (Ito and Hotta, 1992; Lee et al., 1999; White and Kankel, 1978). While our findings suggest that the MB is not the sole brain structure through which inc impacts sleep, they establish a vital role for inc in regulating MB development and its sleep-regulatory functions.
Our findings reveal that inc governs neurogenesis, a fundamental process regulated by genes and pathways conserved from flies to mammals (Doe, 2008; Knoblich, 2008), and suggest that alterations of neurogenesis can cause lasting changes in sleep–wake behavior. The cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying altered neurogenesis in inc mutants, including the stochastic nature of these phenotypes and their apparent restriction to the MB, are of particular interest. inc null mutations are viable (Stavropoulos and Young, 2011), in contrast to the lethality of mutations that globally alter neurogenesis (Betschinger et al., 2006; Lee et al., 2006a; Lee et al., 2006b; Rolls et al., 2003; Vaessin et al., 1991), consistent with the notion that altered neurogenesis in inc mutants manifests preferentially or specifically within the MB. The stochastic nature of neurogenic defects in inc mutants and the overproduction of neurons with projection defects are reminiscent of phenotypes of mushroom body defect (mud) mutants (Guan et al., 2000; Hovhanyan and Raabe, 2009; Prokop and Technau, 1994). In mud mutants, infrequent errors in asymmetric neuroblast division give rise to excess neuroblasts and MB neurons (Bowman et al., 2006; Siller et al., 2006). Similar alterations in neuroblast proliferation in inc mutants may account for the stochastic and cumulative defects in the production of late-born MB neurons; a subtle defect in neuroblast proliferation would be expected to manifest particularly in the MB lineage, the longest in the fly brain. Our results do not yet distinguish the cellular populations through which inc regulates neurogenesis. One possibility is that inc acts in neurons to promote their differentiation, analogous to lola and midlife crisis, genes whose absence causes neurons to dedifferentiate and acquire the proliferative character of neuroblasts (Carney et al., 2013; Southall et al., 2014). Another possibility is that inc functions in neuroblasts, like mud, to govern their asymmetric division.
Our studies and recent findings (Gong et al., 2021) suggest that proper regulation of neurogenesis is essential for normal sleep and that altered neurogenesis in discrete circuits can cause lifelong sleep dysfunction. Intriguing but fragmentary evidence suggests that other genes whose mutation impacts sleep might similarly alter neurogenesis. wide awake (wake), whose mutation causes short sleep in Drosophila (Liu et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2015), was characterized in an independent study as banderuola (bnd) and shown to regulate the asymmetric division of neuroblasts (Mauri et al., 2014). An interesting possibility yet to be assessed is whether sleep phenotypes of wake/bnd mutants might arise developmentally or through neuroblasts. Similarly, while short sleep phenotypes caused by mutations in the potassium channel subunits encoded by Shaker and Hyperkinetic (Bushey et al., 2007; Cirelli et al., 2005) are thought to reflect their role in regulating excitability in specific adult neurons (Kempf et al., 2019; Pimentel et al., 2016), developmental functions that could contribute to their impact on sleep remain unexplored. Notably, mutations in the Shaker ortholog Kv1.1 analogous to those that strongly reduce sleep in Drosophila (Cirelli et al., 2005; Gisselmann et al., 1989) cause megencephaly and neuronal overproduction in mammals, implicating Kv1.1 in regulating neurogenesis (Chou et al., 2021; Donahue et al., 1996; Petersson et al., 2003; Yang et al., 2012). Explicit tests of whether wake/bnd and Shaker impact sleep through adult or developmental mechanisms, or through a combination of the two, await conditional temporal analysis.
While further manipulations of inc are required to elucidate the precise developmental mechanisms by which it impacts sleep, Cul3 is known to regulate various aspects of neuronal development. Clonal analysis of Cul3 mutations in Drosophila indicates that Cul3 is required for normal axonal arborization and dendritic elaboration within the MB, as well as axonal fasciculation (Zhu et al., 2005). These phenotypes overlap those of inc mutants, although direct comparisons are complicated by the pleiotropic nature of Cul3 mutations, which dysregulate multiple adaptor and substrate pathways. Mosaic analysis of inc is required to discern its developmental functions in postmitotic neurons, to compare its phenotypes with Cul3, and to distinguish cell autonomous and non-cell autonomous mechanisms. In mammals, Cul3 mutations alter neurogenesis, cortical lamination, neuronal migration, synaptic development, and cause behavioral deficits (Amar et al., 2021; Dong et al., 2020; Fischer et al., 2020; Rapanelli et al., 2021). inc and Cul3 are present at synapses in flies and mammals (Kikuma et al., 2019; Li et al., 2017) and are required at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction for synaptic homeostasis (Kikuma et al., 2019), a process proposed to be a core function of sleep (Tononi and Cirelli, 2003). The impact of inc on the development and function of central synapses has yet to be assessed, and whether such functions contribute to inc sleep phenotypes remains unknown. As a Cul3 adaptor, inc may engage multiple molecular targets and cellular pathways. Identifying and manipulating inc substrates are thus important goals in elucidating the mechanisms through which inc impacts neuronal development and sleep–wake behavior.
The loss of inc causes enduring developmental and functional impairments in the MB, a structure important for sensory integration, learning, and sleep regulation. The MB integrates olfactory (de Belle and Heisenberg, 1994; Heisenberg et al., 1985), gustatory (Keene and Masek, 2012; Masek and Scott, 2010), visual (Li et al., 2020; Vogt et al., 2016), and thermal inputs (Frank et al., 2015; Hong et al., 2008; Shih et al., 2015), and its activity is altered by sleep pressure (Bushey et al., 2015; Sitaraman et al., 2015a). The MB may thus integrate and filter sensory stimuli to promote sleep in appropriate environmental conditions, in a manner modulated by learning and sleep history. The anatomical defects in inc mutants may render the MB hypersensitive to sensory stimuli, alter functions of the MB that link learning and sleep (Berry et al., 2015; Cervantes-Sandoval et al., 2017; Haynes et al., 2015; Seugnet et al., 2011; Seugnet et al., 2008), or impair the relay of sensory input from MB neurons to downstream sleep-promoting circuits (Aso et al., 2014b; Sitaraman et al., 2015a). While MB circuits and genetic pathways that act in the MB to influence sleep have been manipulated with increasing precision (Aso et al., 2014b; Cavanaugh et al., 2016; Guo et al., 2011; Joiner et al., 2006; Pitman et al., 2006; Sitaraman et al., 2015a; Sitaraman et al., 2015b; Yi et al., 2013), much remains unknown about the function of the MB in sleep regulation, and additional analysis is required to elucidate how inc lesions might alter discrete circuits within the MB and signaling to their targets.
While sensory hypersensitivity and sleep dysfunction are hallmarks of autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders, the underlying mechanisms remain obscure. Given the conserved functions of Cul3–inc complexes and the associations of Cul3 lesions with autism (Kong et al., 2012; Li et al., 2017; O’Roak et al., 2012), elucidating inc substrates and their contributions to neurogenesis and neuronal anatomy may provide insights into brain development, tumorigenesis, and sleep disorders.
Materials and methods
Key resources table.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | α-HA (rat monoclonal) | Roche | Cat# 11867431001, RRID:AB_390919 | (1:100) |
| Antibody | α-Brp (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | Cat# nc82, RRID:AB_2314866 | (1:20 and 1:50) |
| Antibody | α-FLAG (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# F1804, RRID:AB_262044 | (1:100) |
| Antibody | α-GFP (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | Cat# GFP-G1, RRID:AB_2619561 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | α-GFP (rabbit polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A11122, RRID:AB_221569 | (1:2000) |
| Antibody | α-dsRed (rabbit polyclonal) | Takara Bio | Cat# 632496, RRID:AB_10013483 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | α-FasII (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | Cat# 8 C6, RRID:AB_2314391 | (1:50) |
| Antibody | α-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 (donkey polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A21202, RRID:AB_141607 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | α-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 (donkey polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A21206, RRID:AB_2535792 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | α-rat Alexa Fluor 488 (donkey polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A21208, RRID:AB_2535794 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | α-rabbit Alexa Fluor 568 (donkey polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A10042, RRID:AB_2534017 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | α-mouse Alexa Fluor 647 (donkey polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A31571, RRID:AB_162542 | (1:1000) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hydroxyurea | Sigma-Aldrich | H8627 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w 1118 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_5905 | Ryder et al., 2004 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | inc 1 | Stavropoulos lab | FLYB:FBal0266013 | Stavropoulos and Young, 2011; BDSC #5,905 background |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | inc 2 | Stavropoulos lab | FLYB:FBal0162225 | Stavropoulos and Young, 2011; BDSC #5,905 background |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | tub-QS; nsyb-Gal4QF | Christopher Potter | Riabinina et al., 2015; Li and Stavropoulos, 2016; BDSC #5,905 background | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | inc-Gal4 | Stavropoulos lab | Stavropoulos and Young, 2011; BDSC #5,905 background | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | inc1inc-Gal4 | Stavropoulos lab | Li et al., 2017; BDSC #5,905 background | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nsyb-Gal4 | Julie Simpson | Simpson, 2016; BDSC #5,905 background | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | c253-Gal4 (MB) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_6980 | Pitman et al., 2006; BDSC #5,905 background; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | c309-Gal4 (MB) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_6906 | Connolly et al., 1996; Pitman et al., 2006 Joiner et al., 2006; Aso et al., 2009; BDSC #5,905 background; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | c929-Gal4 (l-LNv) | Amita Sehgal | Hewes et al., 2000; Hewes et al., 2003; Sheeba et al., 2008; Parisky et al., 2008; Shang et al., 2008; iso31 background; used in inc[2] rescue screen | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | c584-Gal4 (PI, PPM3) | Amita Sehgal | Martin et al., 1999; Dubowy et al., 2016; iso31 background; used in inc[2] rescue screen | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | R69F08-Gal4 (EB) | Mark Wu | Liu et al., 2016; used in inc[2] rescue screen | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | R24B11-Gal4 (Helicon) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49070 | Donlea et al., 2018 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | R23E10-Gal4 (dFB) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49032 | Donlea et al., 2014 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | NP2721-Gal4 (DPM) | Leslie Griffith | Wu et al., 2011; Haynes et al., 2015; used in inc[2] rescue screen | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | DH44-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39347 | Cavanaugh et al., 2014 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | pdf-Gal4 | Stavropoulos lab | Renn et al., 1999 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | crz-Gal4 | Stavropoulos lab | Tayler et al., 2012 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MB004B (pan-MB) | Yoshinori Aso | Sitaraman et al., 2015a | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MB607B (ɣd) | Yoshinori Aso | Sitaraman et al., 2015a | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MB370B (α'β'm + α'β'ap) | Yoshinori Aso | Sitaraman et al., 2015a | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MB185B (αβs) | Yoshinori Aso | Sitaraman et al., 2015a | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MB594B (αβc) | Yoshinori Aso | Sitaraman et al., 2015a | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MB-Gal80 | Michael Young | Krashes et al., 2007 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-3xFLAG-Inc | Stavropoulos lab | Li et al., 2017; BDSC #5,905 background | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-inc-HA | Stavropoulos lab | Li et al., 2017; BDSC #5,905 background | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-inc-RNAi | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | FLYB:FBst0453067 | Dietzl et al., 2007; Stavropoulos and Young, 2011 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-dcr2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_24651 | Dietzl et al., 2007; BDSC #5,905 background |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-TrpA1 | Stavropoulos lab | Hamada et al., 2008; BDSC #5,905 background | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-MyrGFP-2A-RedStinger | Barry Ganetzky | Daniels et al., 2014 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 5xUAS-DenMark::smGdP-V5 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_62138 | Nern et al., 2015 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 5xUAS-IVS-Syt1::smGdP-HA | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_62142 | Nern et al., 2015 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 20xUAS-IVS-CD8-GFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_32194 | Pfeiffer et al., 2010 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | NP1227-Gal4 | Kathy Nagel | Okada et al., 2009; used in inc[2] rescue screen | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | R2-Split Gal4 | Greg Suh | Liu et al., 2016; used in inc[2] rescue screen | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | R72G06-Gal4 | Mark Wu | used in inc[2] rescue screen | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | VT64246-Gal4 | Leslie Griffith | used in inc[2] rescue screen | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | c305a-Gal4 | Leslie Griffith | used in inc[2] rescue screen | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR49E09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_38692 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR49F01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_38694 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR49F02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_38695 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR49G06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_38707 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR51G05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_38797 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR53B06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_38863 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR53C04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_38871 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR54F06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39081 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR55A03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39095 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR55B12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39103 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR55D01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39110 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR55D05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39112 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR55F07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39128 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR55G11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39132 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR56H02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39164 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR56H09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39166 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR58E10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39184 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR58H05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39198 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR59B10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39209 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR59E09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39220 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR59H05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39229 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR60C01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39240 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR60D05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39247 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR60H12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39268 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR64A11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39289 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR64F03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39309 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR64G05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39316 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR65B04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39336 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR65D06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39352 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR65D07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39353 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR67A04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39396 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR69C02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39483 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR71D01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39579 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR72H03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39799 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR74H01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39872 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR76F06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39937 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR77H03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39976 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR78A01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39985 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR78G06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40013 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR79A01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40021 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR79B08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40029 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR83H01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40368 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR85C07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40422 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR87A08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40473 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR92G09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40629 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR93C06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40647 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR93G05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40662 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR93H07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40669 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR94D04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40681 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR94E07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40688 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR94F06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40694 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR95E08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40710 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR95F11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40714 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR40B09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41235 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR40E08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41238 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR41G11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41244 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR42F06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41253 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR60D10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41284 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR65C03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41290 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR74B11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41301 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR87B02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41316 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR65B09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41353 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR34C12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_45219 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR45D10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_45323 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR60G12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_45360 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR23G07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_45493 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR26C01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_45518 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48D06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_45774 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR20E01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_45837 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR25G01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_45851 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR53G07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46041 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR55G02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46070 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR35H03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46205 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR46H09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46275 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR58G05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46410 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR59H01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46423 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR64D08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46539 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR65C05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46554 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR65H08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46566 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR69H02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46620 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR70G11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46641 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR71E04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46658 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR72A04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46665 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR73D06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46692 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR56F05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46714 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR77A04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_46976 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR80C12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47059 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR81C04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47087 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR81D04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47094 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR91A08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47148 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR91G01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47175 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR92H11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47211 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR93B04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47215 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR93D01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47221 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR93D06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47224 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR93G11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47238 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR94H10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47268 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR16D12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47325 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR16H05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47327 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR10E03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47447 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR42E09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47589 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR52A01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47634 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR70A09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47720 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR72F10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47731 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR74G04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47742 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR10A11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47839 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR10A12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47840 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR13C06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47860 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR19G10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47887 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR21C11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47898 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR30F07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47911 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR44G12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47933 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR52F09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_47943 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR28F06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48083 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR33H11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48119 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR50A07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48179 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR51B08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48183 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR52C05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48190 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR54H12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48205 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR58F01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48213 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR59B11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48215 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR59C12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48219 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR59E04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48221 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR10D10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48261 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR10H09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48277 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR67B06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48294 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR73H09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48318 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR87C01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48389 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR89C02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48404 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR92A08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48414 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR93C08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48417 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR93F02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48422 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR95F03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48433 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR10E07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48440 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR11C07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48448 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR12B10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48490 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR12D12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48506 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR12G09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48525 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR13B10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48548 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR13D09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48561 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR13E04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48565 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR13E06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48566 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR13F04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48573 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR14C08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48606 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR20F01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48610 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR14E05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48642 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR14E06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48643 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR14E09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48645 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR14E12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48647 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR14F11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48653 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR14G08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48661 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR14H02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48664 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR15B07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48678 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR15D11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48690 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR15E09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48696 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR16E03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48727 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR17B12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48759 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR17D02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48764 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR17G05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48782 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR18D04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48811 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR18D07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48813 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR18F04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48820 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR18G06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48826 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR19F05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48855 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR20F04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48904 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR21C09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48936 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR21D02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48939 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR21D06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48942 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR22C12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48978 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR22E06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_48986 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR22H10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49005 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR23B04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49016 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR23C06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49023 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR23E10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49032 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR23F05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49035 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR24A08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49058 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR24B11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49070 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR24C06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49073 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR24C07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49074 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR24C10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49075 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR24E05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49081 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR24F03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49086 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR24H03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49098 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR25A01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49102 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR25A06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49105 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR25C01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49115 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR25C03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49117 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR25E04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49125 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR25H06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49144 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR26B04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49158 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR26B11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49164 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR26B12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49165 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR26C11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49171 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR26E02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49179 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR26E07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49182 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR26F09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49194 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR27A02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49207 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR10E06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49236 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR14B11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49255 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR15B03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49261 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR18G02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49278 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR32D08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49357 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR35F09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49371 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR60F05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49405 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR28E01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49457 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR29A12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49478 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR30B10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49522 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR43D09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49553 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR47E07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49568 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48D07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49572 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR52F11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49579 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR59A05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49593 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR65H10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49614 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR66A03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49615 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR30G03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49646 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR31F06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49684 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR31G04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49686 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR31H05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49692 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR32E04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49717 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR33H07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49760 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR34B11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49774 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR34C08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49780 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR35B08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49818 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR10G02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49825 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR11E05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49827 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR19C10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49831 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR19E12-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49835 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR20D07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49848 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR20E08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49851 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR21H06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49866 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR22F03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49875 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR35D07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49908 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR37E08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49958 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR37F05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49961 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR38A11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49980 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR38B06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_49986 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR38E08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50008 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR39C07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50039 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR39E10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50053 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR39G09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50064 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR40C07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50080 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR42D11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50156 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR44B03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50200 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR44B10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50202 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR44D02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50205 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR45D05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50227 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR45G01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50241 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR45G05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50243 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR45H11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50248 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR46B05-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50253 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR47D07-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50304 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR47F04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50319 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR47G08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50328 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR47H01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50330 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48A03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50339 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48A08-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50341 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48B10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50352 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48C06-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50357 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48E02-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50367 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48G01-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50381 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48G04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50383 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48H04-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50392 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48H10-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50395 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR48H11-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50396 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR49A09-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50403 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{GMR49C03-GAL4}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50414 | Jenett et al., 2012; used in inc[2] rescue screen |
Fly food and culture
Fly food was prepared in batches containing the following ingredients: 1800 g cornmeal (Labscientific, FLY-8010-20), 1800 ml molasses (Labscientific, FLY-8008-16), 744 g yeast (Labscientific, FLY-8040-20F), 266 g agar (Mooragar, 41084), 56 g methyl paraben (Sigma, H3647), 560 ml alcohol (Fisher, A962P4), 190 ml propionic acid (Fisher, A258500), and 47 l of water. Unless indicated otherwise, crosses were performed with five females and three males in vials (28.5 mm diameter × 95 mm height) containing standard fly food supplemented with dry yeast (Fleischmann, B000LRFVHE). Crosses were cultured at 25°C in 12 hr light–dark (LD) cycles.
To prepare food for conditional induction of the Q-system, solid fly food was melted in a microwave oven and allowed to cool before addition of quinic acid or vehicle. Quinic acid solution was freshly prepared essentially as described (Riabinina et al., 2015). 10 g of quinic acid (Sigma, 138622) was dissolved in 30 ml of water and the pH was adjusted to 6.5 with 10 mM NaOH. A volume of quinic acid solution containing the equivalent of 0.66 g of quinic acid (~2.4 ml) was added for each 10 ml of melted fly food and mixed well; ~12.4 ml was distributed to each empty vial. Food was allowed to cool and subsequently stored at 4°C prior to use. Vehicle food was prepared similarly, substituting an equal volume of water.
Conditional Q-system induction
Three sets of conditional induction experiments were performed. The first set contained vehicle treatment and constitutive, developmental-specific, and adult-specific induction regimens. The second set included vehicle, constitutive induction, and induction from the late third instar larval stage through adulthood. The third set included vehicle, constitutive induction, and a pulse of induction from the late third instar larval stage through pupal stages. Initiation, maintenance, or termination of induction at desired developmental stages was achieved by transferring larvae, pupae, and/or adults to food containing quinic acid or vehicle as described below. Within each set of experiments, w1118 and inc1 controls were exposed to vehicle and quinic acid induction regimens, and all animals underwent the same physical transfers in parallel. Sleep of w1118 and inc1 animals was not altered by exposure to vehicle or quinic acid, as described previously (Li and Stavropoulos, 2016), nor by physical transfer at larval, pupal, or adult stages. Vehicle-treated w1118 and inc1 animals, pooled across all three sets of experiments, are shown in Figure 2B. Two to three independent biological replications were performed for all induction experiments.
In the first set of experiments, developmental-specific induction was achieved by setting crosses on food containing quinic acid, allowing animals to develop and pupate in the same vials, and transferring adult males within 2–3 hr of eclosion to fresh vials with vehicle-containing food to terminate Q-system induction. Adult animals were maintained in these vials for 3–4 days, anesthetized with CO2, and transferred to DAM tubes with vehicle-containing food for measurement of sleep. For adult-specific induction, crosses were set on vehicle food and animals developed in the same vials. Adult males eclosing from these cultures were transferred within 2–3 hr of eclosion to fresh vials with food containing quinic acid, maintained on this food for 3–4 days, and transferred to DAM tubes containing food with quinic acid for measurement of sleep. For constitutive induction and vehicle treatment, food containing quinic acid or vehicle, respectively, was used throughout, along with the same transfer procedure.
In the second set of experiments, induction from the late third instar larval stage through adulthood was achieved as follows: crosses were set on vehicle-containing food and wandering third instar larvae from these cultures were gently collected with blunt forceps and examined under brief phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) immersion to select males by visual identification of gonads as described (Kerkis, 1931). Larvae were transferred to recipient vials containing isogenic w1118 larvae and pre-churned quinic acid food; these recipient cultures were initiated in parallel with experimental crosses to allow food consistency to be maintained during Q-system induction. Adult animals bearing mini-white-marked transgenes were transferred within 2–3 hr of eclosion to fresh vials containing quinic acid food to maintain Q-system induction. Three- to four-day-old adults were subsequently transferred to DAM tubes with food containing quinic acid for measurement of sleep. Constitutive induction and vehicle treatment were performed similarly, using appropriate food and the same transfer procedure.
In the third set of experiments, a pulse of Q-system induction specific to late third instar larval and pupal stages was achieved as follows: crosses were set on vehicle food and male wandering third instar larval progeny were selected and transferred to w1118 recipient vials containing pre-churned quinic acid food as described above. To prevent adult exposure to quinic acid, pupae bearing mini-white-marked transgenes were identified at approximately the P13–P14 stage by pigmented eyes and black wings (Ashburner et al., 2005; Bainbridge and Bownes, 1981) and gently dislodged from vial walls with a paintbrush and transferred to the walls of fresh vials containing vehicle food. Three- to four-day-old adults eclosing from these vials were transferred to DAM tubes containing vehicle food for measurements of sleep. Constitutive induction and vehicle treatment were performed similarly, using appropriate food and the same transfer procedure.
inc2 rescue screen
inc2 virgins were crossed to male flies carrying Gal4 transgenes and a minimum of five male progeny were screened for each genotype. A total of 277 Gal4 lines were screened, including 266 randomly selected drivers and 11 drivers previously characterized for expression in sleep-regulatory circuits. To select random lines, 4088 lines from the FlyLight collection available from the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center were assigned sample numbers. Using the randperm command in Matlab, 300 lines were randomly selected. Expression patterns for these lines in the Janelia Flylight database were examined; 84 lines were excluded due to very low levels of expression, very broad expression patterns unlikely to be useful for functional mapping, or because expression data were unavailable. Expression patterns for the remaining 216 lines ranged from broad to sparse. This procedure for random selection was applied iteratively to yield 266 lines. Top-ranking hits from the initial screen were rescreened in independent crosses. Rescreening of c253-Gal4 and c309-Gal4 was performed after backcrossing each line six generations to an isogenic w1118 stock (BDSC #5905) (Ryder et al., 2004).
MB ablation
MB ablation was performed essentially as described previously (de Belle and Heisenberg, 1994). Egg collection was performed on grape juice agar plates containing a spot of rehydrated dry yeast. w1118 larvae at the first instar stage were transferred to a well of a 24-well plate bearing a spot of rehydrated dry yeast paste, containing water vehicle or 50 mg/ml hydroxyurea (Sigma, H8627). After 4–5 hr, larvae were collected and washed briefly with distilled water on a Nitex mesh filter (Genesee Scientific, 57–102) to remove yeast and subsequently transferred to vials containing standard food. Vials were cultured at 25°C in LD cycles and adult animals eclosing from these cultures were assayed for sleep as described below. MB ablation was verified in adult brains in a separate cohort of animals by staining with anti-FasII primary antibody (1:50, DSHB) and Alexa 488-conjugated donkey anti-mouse secondary as described below. Vehicle-treated animals exhibited MB lobes demarcated with FasII signal (100%, n = 9), while hydroxyurea-treated animals exhibited complete MB ablation as indicated by the lack of residual FasII staining (100%, n = 12); FasII signal within the EB was observed in all brains, providing a control for staining of the MB.
Immunohistochemistry
All fixing, washing, and incubation steps for immunohistochemistry were performed on a nutator. To assess conditional induction of inc-HA using the Q-system, larval, pupal, and adult brains were dissected from inc1; UAS-inc-HA/tub-QS; nsyb-Gal4QF/+ males. Wandering third instar male larvae were selected by visual identification of gonads as described above. Larval brains were dissected in ice-cold PBS, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 30 min at room temperature, and washed 3× 15 min in PBS containing 0.2% Triton X-100 (PBST). Male pupae at stage P13–P14 were identified by the staging criteria described above and the presence of sex combs. Pupal brains were dissected in ice-cold PBST, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBST for 30 min at room temperature, and washed 3× 15 min in PBST. To prepare adult brains, 2- or 4-day-old whole male adults were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBST for 3 hr at 4°C and washed 3× 15 min in PBST at room temperature prior to brain dissection in PBST. After dissection, all brains were blocked with 5% normal donkey serum (NDS) (Lampire Biological, 7332500) in PBST at room temperature for 30–60 min. Samples were incubated overnight at 4°C in rat anti-HA (1:100; Sigma, 11867431001) and mouse anti-Brp (1:20, DSHB, nc82) antibodies prepared in 5% NDS in PBST. Brains were subsequently washed 3× 15 min in PBST at room temperature, incubated overnight at 4°C in Alexa 488 donkey anti-rat (1:1000; Life Technologies, A21208) and Alexa 647 donkey anti-mouse (1:1000, Life Technologies A31571) antibodies prepared in 5% NDS in PBST, washed 3× 15 min at room temperature in PBST, and mounted on microscope slides (Fisher, 1255015) in Vectashield (Vector Labs, H-1000).
For all other immunohistochemistry, adult brains of 4-day-old males were dissected in PBST, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBST for 30 min at room temperature, and washed 3× 20 min in PBST at room temperature. Brains of male wandering third instar larvae and stage P13–P14 pupae were dissected, fixed, and stained as described above for Q-system experiments. Primary antibodies were mouse anti-FLAG (1:100; Sigma, F1804), rabbit anti-GFP (1:2000; Fisher, A11122), mouse anti-GFP (1:1000; DSHB, GFP-G1), rabbit anti-dsRed (1:1000; Takara, 632496), and mouse anti-Brp (1:50, DSHB, nc82). Secondary antibodies were Alexa 488 donkey anti-rabbit (1:1000; Life Technologies, A21206), Alexa 488 donkey anti-mouse (1:1000; Life Technologies, A21202), and Alexa 568 donkey anti-rabbit (1:1000; Life Technologies, A10042).
Imaging and quantitation of neuron number and cluster number
All imaging was performed on a Zeiss LSM800 confocal microscope, using a 10X air objective to capture z-stacks at 512 × 512 pixel resolution with 1 μM z-slices, unless indicated otherwise. All imaging settings were identical for each experiment comprising control and experimental brains stained in parallel.
To quantify MB neuron numbers, wild-type and inc1 brains expressing UAS-MyrGFP-2A-RedStinger under the control of split-Gal4 drivers were imaged as described above. For each neuron subtype, wild-type and inc1 brains were assigned sample numbers and a subset, randomly selected using the randperm command in Matlab, was imaged at higher resolution with a 63X oil objective. Both hemispheres of brains were imaged, capturing dsRed and myr-GFP channels separately. Only a single hemisphere could be imaged for two wild-type brains, one each in the γd and α´/β´ groups, due to sample compression by the objective. z-stacks encompassing nuclei were captured at 512 × 512 resolution for γd neurons and at 1024 × 1024 resolution for α´/β´ and α/βc neurons; 2 μM z-slices were used to ensure that all nuclei (diameter ~3 μM) were segmented in at least one optical section.
High resolution z-stacks were assigned a random letter code and neurons were counted in a single-blind manner by two independent experimenters. Nuclei of γd and α´/β´ neurons exhibited minimal overlap along the z-axis, allowing nuclei to be counted in maximum intensity z-projections using the Cell Counter plug-in in ImageJ; visual inspection of z-stacks in parallel allowed overlapping nuclei to be differentiated. Dense distribution of α/βc neurons prohibited accurate counting in single maximum intensity z-projections; maximum intensity z-projections were generated for every 10 z-slices, yielding three to four maximum intensity z-projections representing 20 μM each. To improve visualization of densely clustered α/βc nuclei, background was subtracted using a rolling ball/sliding paraboloid algorithm (radius set to the size of the largest nucleus: 50 pixels) and image intensity display range was adjusted (minimum: 5; maximum: 175). Processed maximum intensity z-projections representing 20 μM each were then merged into a single z-stack for manual counting using the Cell Counter plug-in in ImageJ; to avoid double-counting of nuclei segmented in adjacent z-projections, the original unprocessed z-stack was examined in parallel. The variation in MB neuron counts between experimenters, calculated as the absolute difference between the two counts divided by their mean, was (mean ± SEM) 2.0% ± 0.2% for γd; 1.5% ± 0.3% for α´/β´; and 2.6% ± 0.3% for α/βc. Where neuron counts were different for a given hemisphere, the average was plotted. Numbers of γd neurons in wild-type animals were intermediate between those reported in prior studies (Aso et al., 2014a; Shih et al., 2019), while numbers of α´/β´ and α/βc neurons were lower, likely reflecting conservative assignment of nuclei in our study and the use of different antibodies and reporters (Aso et al., 2014a; Shih et al., 2019). α´/β´ counts obtained using the MB370B driver were similar to previously reported numbers of α´/β´m neurons; because MB370B labels α´/β´m neurons strongly and α´/β´ap neurons weakly, the lower absolute numbers of α´/β´ neurons in our studies may reflect detection sensitivity and correspond chiefly to α´/β´m neurons.
To count the number of α/βc neuron clusters in wild-type and inc1 brains, the same randomly selected samples used to quantify neuron numbers were assessed in a single-blind manner by two independent experimenters. Each z-stack was analyzed using a combination of visual inspection of z-sections and rotating the image stack in three dimensions using the 3D Viewer plug-in in ImageJ (threshold: 0; resampling factor: 2). A group of nuclei distributed continuously along all axes was classified as a cluster; a continuous gap at least one nuclear diameter in width across all axes was used to define cluster edges and discrete clusters. Cluster counts were identical for wild-type brains; total cluster counts for inc1 brains differed by 8.2% ± 0.2% (mean ± SEM) between experimenters. Where cluster counts were different for a given hemisphere, the average was plotted.
DH44 and dFB somata were counted in a single-blind manner by two independent experimenters as described for γd and α´/β´ neurons, using DH44-Gal4 to drive UAS-MyrGFP-2A-RedStinger and 23E10-Gal4 to drive 5× UAS-IVS-Syt1::smGdP-HA. Numbers of dFB and DH44 neurons were identical between two independent experimenters.
Analysis of axonal projections and dendritic volume
To analyze axonal projections and dendritic volume, image stacks were captured using a 10X objective at 512 × 512 resolution with 1 μM z-slices. Axonal projection defects were assessed in maximum intensity z-projections. The number of horizontal and/or vertical lobes missing myr-GFP signal entirely was counted for each brain. To quantify dendritic volume, the Threshold command in ImageJ was applied to z-stacks to select dendrites based on DenMark immunofluorescence; high signal to noise allowed unambiguous demarcation of dendrites and clear separation from background. The same minimum and maximum threshold values were applied to all wild-type and inc1 brains stained in parallel in an experiment and captured the entirety of dendritic signal for all samples. A single rectangular region of interest of minimal area encompassing dendritic signals from both brain hemispheres across all z-slices was drawn for each z-stack. Dendritic volume was quantified using the Voxel Counter plug-in in ImageJ.
Sleep analysis
Three- to four-day-old male flies eclosing from LD-entrained cultures raised at 25°C were loaded in glass tubes (5 mm diameter × 65 mm length) containing standard food or appropriate food for Q-system experiments as described above. Animals were monitored for 5–7 days at 25°C in LD cycles using DAM2 monitors (Trikinetics). Locomotor activity data were collected in 1 min bins. Inactive periods of 5 min or longer were classified as sleep. The first 36–48 hr of data were discarded to allow acclimation of animals to tubes, and 3–5 integral days of data were analyzed beginning with ZT0. Dead animals were excluded from analysis by a combination of automated filtering and visual inspection of locomotor traces. Matlab code used to analyze sleep is available in Source code 1.
Thermogenetic activation
Crosses were set on standard fly food as described above and cultured at 21.5°C. One- to four-day-old male flies eclosing from these cultures were assayed for 5 days in LD cycles. Animals were maintained at 21.5°C for the first 60–72 hr of the assay, including 36–48 hr of acclimation and the subsequent baseline day beginning at ZT0. Temperature was increased to 28.5°C for 24 hr to activate dTrpA1, followed by 24 hr of recovery at 21.5°C. The percent change in sleep was calculated for each animal by subtracting the amount of sleep on the baseline day from the amount of sleep on the activation day and dividing this difference by the amount of sleep on the baseline day. The percent change in sleep for individual animals was averaged for each genotype.
Gal4 drivers used to express TrpA1 were as follows: pan-MB, MB004B split-Gal4; MB, c253-Gal4 and c309-Gal4; EB, R69F08-Gal4; DPM, NP2721-Gal4; Helicon, R24B11-Gal4; l-LNV, c929-Gal4; PI, PPM3, c584-Gal4.
Statistics
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey post hoc tests were used for comparisons between more than two groups of animals for total sleep, daytime sleep, nighttime sleep, and sleep bout number; for comparisons of these sleep parameters between two groups, unpaired two-sided Student’s t-tests were used. Kruskal–Wallis tests and Dunn’s post hoc tests were used for comparisons of sleep bout length between more than two groups of animals; for comparison between two groups, Mann–Whitney tests were used. One-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post hoc tests were used for comparisons of percent change in sleep. Unpaired two-sided Welch’s t-tests were used for pairwise comparisons of neuron number, cluster number, and dendrite volume.
Acknowledgements
We thank C Desplan, N Ringstad, M Shirasu-Hiza, and members of the Stavropoulos lab for comments on the manuscript; Y Aso, B Ganetzky, L Griffith, W Joiner, W Li, K Nagel, C Potter, A Sehgal, J Simpson, G Suh, M Wu, M Young, the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, the Vienna Drosophila Resource Center, and the Janelia Flylight collection for fly stocks; and DSHB for antibodies. This work was supported by an International Student Research Fellowship from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) to QL and by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01NS112844 and R21NS111304), the Mathers Foundation, Whitehall Foundation grant 2013-05-78, fellowships from the Alfred P Sloan and Leon Levy Foundations, a NARSAD Young Investigator Award from the Brain and Behavior Foundation, the J Christian Gillin, M.D. Research Award from the Sleep Research Society Foundation, and a Career Scientist Award from the Irma T Hirschl/Weill-Caulier Trust to NS.
Funding Statement
The funders had no role in study design, data collection, and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Contributor Information
Nicholas Stavropoulos, Email: stavropoulos@waksman.rutgers.edu.
Ronald L Calabrese, Emory University, United States.
Ronald L Calabrese, Emory University, United States.
Funding Information
This paper was supported by the following grants:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute International Student Research Fellowship to Qiuling Li.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke R01NS112844 to Nicholas Stavropoulos.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke R21NS111304 to Nicholas Stavropoulos.
G. Harold and Leila Y. Mathers Foundation to Nicholas Stavropoulos.
Whitehall Foundation 2013-05-78 to Nicholas Stavropoulos.
Alfred P. Sloan Foundation to Nicholas Stavropoulos.
Leon Levy Foundation to Nicholas Stavropoulos.
Brain and Behavior Research Foundation NARSAD Young Investigator to Nicholas Stavropoulos.
Sleep Research Society Foundation J. Christian Gillin, M.D. Research Grant to Nicholas Stavropoulos.
Irma T. Hirschl Trust Career Scientist Award to Nicholas Stavropoulos.
Additional information
Competing interests
No competing interests declared.
No competing interests declared.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing.
Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing.
Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing.
Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Additional files
Data availability
Data for all figures and code used to analyze sleep are included in the supporting files.
References
- Amar M, Pramod AB, Yu NK, Herrera VM, Qiu LR, Moran-Losada P, Zhang P, Trujillo CA, Ellegood J, Urresti J, Chau K, Diedrich J, Chen J, Gutierrez J, Sebat J, Ramanathan D, Lerch JP, Yates JR, Muotri AR, Iakoucheva LM. Autism-linked Cullin3 germline haploinsufficiency impacts cytoskeletal dynamics and cortical neurogenesis through RhoA signaling. Molecular Psychiatry. 2021;26:3586–3613. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01052-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angriman M, Caravale B, Novelli L, Ferri R, Bruni O. Sleep in children with neurodevelopmental disabilities. Neuropediatrics. 2015;46:199–210. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1550151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M, Golic KG, Hawley RS. Drosophila: A Laboratory Handbook. 2nd ed. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Aso Y, Grübel K, Busch S, Friedrich AB, Siwanowicz I, Tanimoto H. The mushroom body of adult Drosophila characterized by GAL4 drivers. Journal of Neurogenetics. 2009;23:156–172. doi: 10.1080/01677060802471718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aso Y, Hattori D, Yu Y, Johnston RM, Iyer NA, Ngo TTB, Dionne H, Abbott LF, Axel R, Tanimoto H, Rubin GM. The neuronal architecture of the mushroom body provides a logic for associative learning. eLife. 2014a;3:e04577. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aso Y, Sitaraman D, Ichinose T, Kaun KR, Vogt K, Belliart-Guérin G, Plaçais PY, Robie AA, Yamagata N, Schnaitmann C, Rowell WJ, Johnston RM, Ngo TTB, Chen N, Korff W, Nitabach MN, Heberlein U, Preat T, Branson KM, Tanimoto H, Rubin GM. Mushroom body output neurons encode valence and guide memory-based action selection in Drosophila. eLife. 2014b;3:e04580. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainbridge SP, Bownes M. Staging the metamorphosis of Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Embryology and Experimental Morphology. 1981;66:57–80. doi: 10.1242/dev.66.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry JA, Cervantes-Sandoval I, Chakraborty M, Davis RL. Sleep Facilitates Memory by Blocking Dopamine Neuron-Mediated Forgetting. Cell. 2015;161:1656–1667. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betschinger J, Mechtler K, Knoblich JA. Asymmetric segregation of the tumor suppressor brat regulates self-renewal in Drosophila neural stem cells. Cell. 2006;124:1241–1253. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman SK, Neumüller RA, Novatchkova M, Du Q, Knoblich JA. The Drosophila NuMA Homolog Mud regulates spindle orientation in asymmetric cell division. Developmental Cell. 2006;10:731–742. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushey D, Huber R, Tononi G, Cirelli C. Drosophila Hyperkinetic mutants have reduced sleep and impaired memory. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2007;27:5384–5393. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0108-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushey D, Tononi G, Cirelli C. Sleep- and wake-dependent changes in neuronal activity and reactivity demonstrated in fly neurons using in vivo calcium imaging. PNAS. 2015;112:4785–4790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1419603112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney TD, Struck AJ, Doe CQ. midlife crisis encodes a conserved zinc-finger protein required to maintain neuronal differentiation in Drosophila. Development. 2013;140:4155–4164. doi: 10.1242/dev.093781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh DJ, Geratowski JD, Wooltorton JRA, Spaethling JM, Hector CE, Zheng X, Johnson EC, Eberwine JH, Sehgal A. Identification of a circadian output circuit for rest:activity rhythms in Drosophila. Cell. 2014;157:689–701. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh DJ, Vigderman AS, Dean T, Garbe DS, Sehgal A. The Drosophila Circadian Clock Gates Sleep through Time-of-Day Dependent Modulation of Sleep-Promoting Neurons. Sleep. 2016;39:345–356. doi: 10.5665/sleep.5442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervantes-Sandoval I, Phan A, Chakraborty M, Davis RL. Reciprocal synapses between mushroom body and dopamine neurons form a positive feedback loop required for learning. eLife. 2017;6:e23789. doi: 10.7554/eLife.23789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti Dilley L, Szuperak M, Gong NN, Williams CE, Saldana RL, Garbe DS, Syed MH, Jain R, Kayser MS. Identification of a molecular basis for the juvenile sleep state. eLife. 2020;9:2. doi: 10.7554/eLife.52676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chemelli RM, Willie JT, Sinton CM, Elmquist JK, Scammell T, Lee C, Richardson JA, Williams SC, Xiong Y, Kisanuki Y, Fitch TE, Nakazato M, Hammer RE, Saper CB, Yanagisawa M. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell. 1999;98:437–451. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81973-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu CN, Rihel J, Lee DA, Singh C, Mosser EA, Chen S, Sapin V, Pham U, Engle J, Niles BJ, Montz CJ, Chakravarthy S, Zimmerman S, Salehi-Ashtiani K, Vidal M, Schier AF, Prober DA. A Zebrafish Genetic Screen Identifies Neuromedin U as a Regulator of Sleep/Wake States. Neuron. 2016;89:842–856. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou SM, Li KX, Huang MY, Chen C, Lin King YH, Li GG, Zhou W, Teo CF, Jan YN, Jan LY, Yang SB. Kv1.1 channels regulate early postnatal neurogenesis in mouse hippocampus via the TrkB signaling pathway. eLife. 2021;10:e58779. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirelli C, Bushey D, Hill S, Huber R, Kreber R, Ganetzky B, Tononi G. Reduced sleep in Drosophila Shaker mutants. Nature. 2005;434:1087–1092. doi: 10.1038/nature03486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clasadonte J, Scemes E, Wang Z, Boison D, Haydon PG. Connexin 43-Mediated Astroglial Metabolic Networks Contribute to the Regulation of the Sleep-Wake Cycle. Neuron. 2017;95:1365–1380. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.08.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina-Solà M, Rodríguez-Santiago B, Homs A, Santoyo J, Rigau M, Aznar-Laín G, Del Campo M, Gener B, Gabau E, Botella MP, Gutiérrez-Arumí A, Antiñolo G, Pérez-Jurado LA, Cuscó I. Integrated analysis of whole-exome sequencing and transcriptome profiling in males with autism spectrum disorders. Molecular Autism. 2015;6:21. doi: 10.1186/s13229-015-0017-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly JB, Roberts IJ, Armstrong JD, Kaiser K, Forte M, Tully T, O’Kane CJ. Associative learning disrupted by impaired Gs signaling in Drosophila mushroom bodies. Science. 1996;274:2104–2107. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5295.2104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels RW, Rossano AJ, Macleod GT, Ganetzky B. Expression of multiple transgenes from a single construct using viral 2A peptides in Drosophila. PLOS ONE. 2014;9:e100637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Belle JS, Heisenberg M. Associative odor learning in Drosophila abolished by chemical ablation of mushroom bodies. Science. 1994;263:692–695. doi: 10.1126/science.8303280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzl G, Chen D, Schnorrer F, Su KC, Barinova Y, Fellner M, Gasser B, Kinsey K, Oppel S, Scheiblauer S, Couto A, Marra V, Keleman K, Dickson BJ. A genome-wide transgenic RNAi library for conditional gene inactivation in Drosophila. Nature. 2007;448:151–156. doi: 10.1038/nature05954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe CQ. Neural stem cells: balancing self-renewal with differentiation. Development. 2008;135:1575–1587. doi: 10.1242/dev.014977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue LR, Cook SA, Johnson KR, Bronson RT, Davisson MT. Megencephaly: a new mouse mutation on chromosome 6 that causes hypertrophy of the brain. Mammalian Genome. 1996;7:871–876. doi: 10.1007/s003359900259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Z, Chen W, Chen C, Wang H, Cui W, Tan Z, Robinson H, Gao N, Luo B, Zhang L, Zhao K, Xiong WC, Mei L. CUL3 Deficiency Causes Social Deficits and Anxiety-like Behaviors by Impairing Excitation-Inhibition Balance through the Promotion of Cap-Dependent Translation. Neuron. 2020;105:475–490. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.10.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlea JM, Pimentel D, Miesenböck G. Neuronal machinery of sleep homeostasis in Drosophila. Neuron. 2014;81:860–872. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlea JM, Pimentel D, Talbot CB, Kempf A, Omoto JJ, Hartenstein V, Miesenböck G. Recurrent Circuitry for Balancing Sleep Need and Sleep. Neuron. 2018;97:378–389. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.12.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowy C, Moravcevic K, Yue Z, Wan JY, Van Dongen HPA, Sehgal A. Genetic Dissociation of Daily Sleep and Sleep Following Thermogenetic Sleep Deprivation in Drosophila. Sleep. 2016;39:1083–1095. doi: 10.5665/sleep.5760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S, Schlotthauer I, Kizner V, Macartney T, Dorner-Ciossek C, Gillardon F. Loss-of-function Mutations of CUL3, a High Confidence Gene for Psychiatric Disorders, Lead to Aberrant Neurodevelopment In Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Neuroscience. 2020;448:234–254. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.08.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foltenyi K, Greenspan RJ, Newport JW. Activation of EGFR and ERK by rhomboid signaling regulates the consolidation and maintenance of sleep in Drosophila. Nature Neuroscience. 2007;10:1160–1167. doi: 10.1038/nn1957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank DD, Jouandet GC, Kearney PJ, Macpherson LJ, Gallio M. Temperature representation in the Drosophila brain. Nature. 2015;519:358–361. doi: 10.1038/nature14284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funato H, Miyoshi C, Fujiyama T, Kanda T, Sato M, Wang Z, Ma J, Nakane S, Tomita J, Ikkyu A, Kakizaki M, Hotta-Hirashima N, Kanno S, Komiya H, Asano F, Honda T, Kim SJ, Harano K, Muramoto H, Yonezawa T, Mizuno S, Miyazaki S, Connor L, Kumar V, Miura I, Suzuki T, Watanabe A, Abe M, Sugiyama F, Takahashi S, Sakimura K, Hayashi Y, Liu Q, Kume K, Wakana S, Takahashi JS, Yanagisawa M. Forward-genetics analysis of sleep in randomly mutagenized mice. Nature. 2016;539:378–383. doi: 10.1038/nature20142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisselmann G, Sewing S, Madsen BW, Mallart A, Angaut-Petit D, Müller-Holtkamp F, Ferrus A, Pongs O. The interference of truncated with normal potassium channel subunits leads to abnormal behaviour in transgenic Drosophila melanogaster. The EMBO Journal. 1989;8:2359–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong NN, Dilley LC, Williams CE, Moscato EH, Szuperak M, Wang Q, Jensen M, Girirajan S, Tan TY, Deardorff MA, Li D, Song Y, Kayser MS. The chromatin remodeler ISWI acts during Drosophila development to regulate adult sleep. Science Advances. 2021;7:eabe2597. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abe2597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross C, Zhuang X, Stark K, Ramboz S, Oosting R, Kirby L, Santarelli L, Beck S, Hen R. Serotonin1A receptor acts during development to establish normal anxiety-like behaviour in the adult. Nature. 2002;416:396–400. doi: 10.1038/416396a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan Z, Prado A, Melzig J, Heisenberg M, Nash HA, Raabe T. Mushroom body defect, a gene involved in the control of neuroblast proliferation in Drosophila, encodes a coiled-coil protein. PNAS. 2000;97:8122–8127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.14.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo F, Yi W, Zhou M, Guo A. Go Signaling in Mushroom Bodies Regulates Sleep in Drosophila. Sleep. 2011;34:273–281. doi: 10.1093/sleep/34.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy J, Gan J, Selfridge J, Cobb S, Bird A. Reversal of neurological defects in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Science. 2007;315:1143–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.1138389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy J, McKay L, Brockett E, Spike RC, Selfridge J, De Sousa D, Merusi C, Riedel G, Bird A. Morphological and functional reversal of phenotypes in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Brain: A Journal of Neurology. 2012;135:2699–2710. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada FN, Rosenzweig M, Kang K, Pulver SR, Ghezzi A, Jegla TJ, Garrity PA. An internal thermal sensor controlling temperature preference in Drosophila. Nature. 2008;454:217–220. doi: 10.1038/nature07001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes PR, Christmann BL, Griffith LC. A single pair of neurons links sleep to memory consolidation in Drosophila melanogaster. eLife. 2015;4:e3868. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Y, Jones CR, Fujiki N, Xu Y, Guo B, Holder JL, Rossner MJ, Nishino S, Fu YH. The transcriptional repressor DEC2 regulates sleep length in mammals. Science. 2009;325:866–870. doi: 10.1126/science.1174443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisenberg M, Borst A, Wagner S, Byers D. Drosophila mushroom body mutants are deficient in olfactory learning. Journal of Neurogenetics. 1985;2:1–30. doi: 10.3109/01677068509100140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisenberg M. Mushroom body memoir: from maps to models. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 2003;4:266–275. doi: 10.1038/nrn1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewes RS, Schaefer AM, Taghert PH. The cryptocephal gene (ATF4) encodes multiple basic-leucine zipper proteins controlling molting and metamorphosis in Drosophila. Genetics. 2000;155:1711–1723. doi: 10.1093/genetics/155.4.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewes RS, Park D, Gauthier SA, Schaefer AM, Taghert PH. The bHLH protein Dimmed controls neuroendocrine cell differentiation in Drosophila. Development. 2003;130:1771–1781. doi: 10.1242/dev.00404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong ST, Bang S, Hyun S, Kang J, Jeong K, Paik D, Chung J, Kim J. cAMP signalling in mushroom bodies modulates temperature preference behaviour in Drosophila. Nature. 2008;454:771–775. doi: 10.1038/nature07090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovhanyan A, Raabe T. Structural brain mutants: mushroom body defect (mud): a case study. Journal of Neurogenetics. 2009;23:42–47. doi: 10.1080/01677060802471700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto H, Kitamoto T. The steroid molting hormone Ecdysone regulates sleep in adult Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 2010;185:269–281. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.114587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K, Hotta Y. Proliferation pattern of postembryonic neuroblasts in the brain Drosophila melanogaster. Developmental Biology. 1992;149:134–148. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90270-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K, Awano W, Suzuki K, Hiromi Y, Yamamoto D. The Drosophila mushroom body is a quadruple structure of clonal units each of which contains a virtually identical set of neurones and glial cells. Development. 1997;124:761–771. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki K, Fujiyama T, Nakata S, Park M, Miyoshi C, Hotta-Hirashima N, Ikkyu A, Kakizaki M, Sugiyama F, Mizuno S, Abe M, Sakimura K, Takahashi S, Funato H, Yanagisawa M. Induction of Mutant Sik3Sleepy Allele in Neurons in Late Infancy Increases Sleep Need. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2021;41:2733–2746. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1004-20.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenett A, Rubin GM, Ngo TTB, Shepherd D, Murphy C, Dionne H, Pfeiffer BD, Cavallaro A, Hall D, Jeter J, Iyer N, Fetter D, Hausenfluck JH, Peng H, Trautman ET, Svirskas RR, Myers EW, Iwinski ZR, Aso Y, DePasquale GM, Enos A, Hulamm P, Lam SCB, Li HH, Laverty TR, Long F, Qu L, Murphy SD, Rokicki K, Safford T, Shaw K, Simpson JH, Sowell A, Tae S, Yu Y, Zugates CT. A GAL4-driver line resource for Drosophila neurobiology. Cell Reports. 2012;2:991–1001. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.09.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell TM, Sanes JR. Development: The decade of the developing brain. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2000;10:599–611. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(00)00136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner WJ, Crocker A, White BH, Sehgal A. Sleep in Drosophila is regulated by adult mushroom bodies. Nature. 2006;441:757–760. doi: 10.1038/nature04811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene AC, Masek P. Optogenetic induction of aversive taste memory. Neuroscience. 2012;222:173–180. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.07.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempf A, Song SM, Talbot CB, Miesenböck G. A potassium channel β-subunit couples mitochondrial electron transport to sleep. Nature. 2019;568:230–234. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1034-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkis J. The Growth of the Gonads in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1931;16:212–224. doi: 10.1093/genetics/16.3.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuma K, Li X, Perry S, Li Q, Goel P, Chen C, Kim D, Stavropoulos N, Dickman D. Cul3 and insomniac are required for rapid ubiquitination of postsynaptic targets and retrograde homeostatic signaling. Nature Communications. 2019;10:2913–2998. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10992-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoblich JA. Mechanisms of asymmetric stem cell division. Cell. 2008;132:583–597. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong A, Frigge ML, Masson G, Besenbacher S, Sulem P, Magnusson G, Gudjonsson SA, Sigurdsson A, Jonasdottir A, Jonasdottir A, Wong WSW, Sigurdsson G, Walters GB, Steinberg S, Helgason H, Thorleifsson G, Gudbjartsson DF, Helgason A, Magnusson OT, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K. Rate of de novo mutations and the importance of father’s age to disease risk. Nature. 2012;488:471–475. doi: 10.1038/nature11396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krashes MJ, Keene AC, Leung B, Armstrong JD, Waddell S. Sequential use of mushroom body neuron subsets during Drosophila odor memory processing. Neuron. 2007;53:103–115. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.11.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurusu M, Awasaki T, Masuda-Nakagawa LM, Kawauchi H, Ito K, Furukubo-Tokunaga K. Embryonic and larval development of the Drosophila mushroom bodies: concentric layer subdivisions and the role of fasciclin II. Development. 2002;129:409–419. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T, Lee A, Luo L. Development of the Drosophila mushroom bodies: sequential generation of three distinct types of neurons from a neuroblast. Development. 1999;126:4065–4076. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.18.4065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T, Luo L. Mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker for studies of gene function in neuronal morphogenesis. Neuron. 1999;22:451–461. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80701-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee CY, Robinson KJ, Doe CQ. Lgl, Pins and aPKC regulate neuroblast self-renewal versus differentiation. Nature. 2006a;439:594–598. doi: 10.1038/nature04299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee CY, Wilkinson BD, Siegrist SE, Wharton RP, Doe CQ. Brat is a Miranda cargo protein that promotes neuronal differentiation and inhibits neuroblast self-renewal. Developmental Cell. 2006b;10:441–449. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q, Stavropoulos N. Evaluation of Ligand-Inducible Expression Systems for Conditional Neuronal Manipulations of Sleep in Drosophila. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics. 2016;6:3351–3359. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.034132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q, Kellner DA, Hatch HAM, Yumita T, Sanchez S, Machold RP, Frank CA, Stavropoulos N. Conserved properties of Drosophila Insomniac link sleep regulation and synaptic function. PLOS Genetics. 2017;13:e1006815. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q, Lim KYY, Stavropoulos N. Structural and Behavioral Analysis Reveals That Insomniac Impacts Sleep by Functioning as a Cul3 Adaptor. bioRxiv. 2019 doi: 10.1101/689471. [DOI]
- Li J, Mahoney BD, Jacob MS, Caron SJC. Visual Input into the Drosophila melanogaster Mushroom Body. Cell Reports. 2020;32:108138. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L, Faraco J, Li R, Kadotani H, Rogers W, Lin X, Qiu X, de Jong PJ, Nishino S, Mignot E. The sleep disorder canine narcolepsy is caused by a mutation in the hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2 gene. Cell. 1999;98:365–376. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81965-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S, Lamaze A, Liu Q, Tabuchi M, Yang Y, Fowler M, Bharadwaj R, Zhang J, Bedont J, Blackshaw S, Lloyd TE, Montell C, Sehgal A, Koh K, Wu MN. WIDE AWAKE mediates the circadian timing of sleep onset. Neuron. 2014;82:151–166. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S, Liu Q, Tabuchi M, Wu MN. Sleep Drive Is Encoded by Neural Plastic Changes in a Dedicated Circuit. Cell. 2016;165:1347–1360. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin JR, Raabe T, Heisenberg M. Central complex substructures are required for the maintenance of locomotor activity in Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Comparative Physiology. A, Sensory, Neural, and Behavioral Physiology. 1999;185:277–288. doi: 10.1007/s003590050387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masek P, Scott K. Limited taste discrimination in Drosophila. PNAS. 2010;107:14833–14838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009318107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauri F, Reichardt I, Mummery-Widmer JL, Yamazaki M, Knoblich JA. The conserved discs-large binding partner Banderuola regulates asymmetric cell division in Drosophila. Current Biology. 2014;24:1811–1825. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw CM, Samaco RC, Zoghbi HY. Adult neural function requires MeCP2. Science. 2011;333:186. doi: 10.1126/science.1206593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nern A, Pfeiffer BD, Rubin GM. Optimized tools for multicolor stochastic labeling reveal diverse stereotyped cell arrangements in the fly visual system. PNAS. 2015;112:E2967–E2976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506763112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaï LJJ, Ramaekers A, Raemaekers T, Drozdzecki A, Mauss AS, Yan J, Landgraf M, Annaert W, Hassan BA. Genetically encoded dendritic marker sheds light on neuronal connectivity in Drosophila. PNAS. 2010;107:20553–20558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010198107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada R, Awasaki T, Ito K. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mediated neural connections in the Drosophila antennal lobe. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 2009;514:74–91. doi: 10.1002/cne.21971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Roak BJ, Vives L, Girirajan S, Karakoc E, Krumm N, Coe BP, Levy R, Ko A, Lee C, Smith JD, Turner EH, Stanaway IB, Vernot B, Malig M, Baker C, Reilly B, Akey JM, Borenstein E, Rieder MJ, Nickerson DA, Bernier R, Shendure J, Eichler EE. Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature. 2012;485:246–250. doi: 10.1038/nature10989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisky KM, Agosto J, Pulver SR, Shang Y, Kuklin E, Hodge JJL, Kang K, Kang K, Liu X, Garrity PA, Rosbash M, Griffith LC. PDF cells are a GABA-responsive wake-promoting component of the Drosophila sleep circuit. Neuron. 2008;60:672–682. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.10.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D, Selcho M, Gendre N, Stocker RF, Thum AS. Drosophila larvae establish appetitive olfactory memories via mushroom body neurons of embryonic origin. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2010;30:10655–10666. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1281-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersson S, Persson AS, Johansen JE, Ingvar M, Nilsson J, Klement G, Arhem P, Schalling M, Lavebratt C. Truncation of the Shaker-like voltage-gated potassium channel, Kv1.1, causes megencephaly. The European Journal of Neuroscience. 2003;18:3231–3240. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2003.03044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffenberger C, Allada R. Cul3 and the BTB adaptor insomniac are key regulators of sleep homeostasis and a dopamine arousal pathway in Drosophila. PLOS Genetics. 2012;8:e1003003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer BD, Ngo TTB, Hibbard KL, Murphy C, Jenett A, Truman JW, Rubin GM. Refinement of tools for targeted gene expression in Drosophila. Genetics. 2010;186:735–755. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.119917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel D, Donlea JM, Talbot CB, Song SM, Thurston AJF, Miesenböck G. Operation of a homeostatic sleep switch. Nature. 2016;536:333–337. doi: 10.1038/nature19055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman JL, McGill JJ, Keegan KP, Allada R. A dynamic role for the mushroom bodies in promoting sleep in Drosophila. Nature. 2006;441:753–756. doi: 10.1038/nature04739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter CJ, Tasic B, Russler EV, Liang L, Luo L. The Q system: a repressible binary system for transgene expression, lineage tracing, and mosaic analysis. Cell. 2010;141:536–548. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokop A, Technau GM. Normal function of the mushroom body defect gene of Drosophila is required for the regulation of the number and proliferation of neuroblasts. Developmental Biology. 1994;161:321–337. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raizen DM, Zimmerman JE, Maycock MH, Ta UD, You Y, Sundaram MV, Pack AI. Lethargus is a Caenorhabditis elegans sleep-like state. Nature. 2008;451:569–572. doi: 10.1038/nature06535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapanelli M, Tan T, Wang W, Wang X, Wang ZJ, Zhong P, Frick L, Qin L, Ma K, Qu J, Yan Z. Behavioral, circuitry, and molecular aberrations by region-specific deficiency of the high-risk autism gene Cul3. Molecular Psychiatry. 2021;26:1491–1504. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0498-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renn SC, Park JH, Rosbash M, Hall JC, Taghert PH. A pdf neuropeptide gene mutation and ablation of PDF neurons each cause severe abnormalities of behavioral circadian rhythms in Drosophila. Cell. 1999;99:791–802. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81676-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabinina O, Luginbuhl D, Marr E, Liu S, Wu MN, Luo L, Potter CJ. Improved and expanded Q-system reagents for genetic manipulations. Nature Methods. 2015;12:219–222. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolls MM, Albertson R, Shih HP, Lee CY, Doe CQ. Drosophila aPKC regulates cell polarity and cell proliferation in neuroblasts and epithelia. The Journal of Cell Biology. 2003;163:1089–1098. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200306079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder E, Blows F, Ashburner M, Bautista-Llacer R, Coulson D, Drummond J, Webster J, Gubb D, Gunton N, Johnson G, O’Kane CJ, Huen D, Sharma P, Asztalos Z, Baisch H, Schulze J, Kube M, Kittlaus K, Reuter G, Maroy P, Szidonya J, Rasmuson-Lestander A, Ekström K, Dickson B, Hugentobler C, Stocker H, Hafen E, Lepesant JA, Pflugfelder G, Heisenberg M, Mechler B, Serras F, Corominas M, Schneuwly S, Preat T, Roote J, Russell S. The DrosDel collection: a set of P-element insertions for generating custom chromosomal aberrations in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 2004;167:797–813. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.026658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes JR, Zipursky SL. Synaptic Specificity, Recognition Molecules, and Assembly of Neural Circuits. Cell. 2020;181:536–556. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seugnet L, Suzuki Y, Vine L, Gottschalk L, Shaw PJ. D1 receptor activation in the mushroom bodies rescues sleep-loss-induced learning impairments in Drosophila. Current Biology. 2008;18:1110–1117. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.07.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seugnet L, Suzuki Y, Merlin G, Gottschalk L, Duntley SP, Shaw PJ. Notch signaling modulates sleep homeostasis and learning after sleep deprivation in Drosophila. Current Biology. 2011;21:835–840. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang Y, Griffith LC, Rosbash M. Light-arousal and circadian photoreception circuits intersect at the large PDF cells of the Drosophila brain. PNAS. 2008;105:19587–19594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809577105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheeba V, Fogle KJ, Kaneko M, Rashid S, Chou YT, Sharma VK, Holmes TC. Large ventral lateral neurons modulate arousal and sleep in Drosophila. Current Biology. 2008;18:1537–1545. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.08.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih HW, Wu CL, Chang SW, Liu TH, Lai JSY, Fu TF, Fu CC, Chiang AS. Parallel circuits control temperature preference in Drosophila during ageing. Nature Communications. 2015;6:7775. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih MFM, Davis FP, Henry GL, Dubnau J. Nuclear Transcriptomes of the Seven Neuronal Cell Types That Constitute the Drosophila Mushroom Bodies. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics. 2019;9:81–94. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siller KH, Cabernard C, Doe CQ. The NuMA-related Mud protein binds Pins and regulates spindle orientation in Drosophila neuroblasts. Nature Cell Biology. 2006;8:594–600. doi: 10.1038/ncb1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson JH. Rationally subdividing the fly nervous system with versatile expression reagents. Journal of Neurogenetics. 2016;30:185–194. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2016.1248761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitaraman D, Aso Y, Jin X, Chen N, Felix M, Rubin GM, Nitabach MN. Propagation of Homeostatic Sleep Signals by Segregated Synaptic Microcircuits of the Drosophila Mushroom Body. Current Biology. 2015a;25:2915–2927. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitaraman D, Aso Y, Rubin GM, Nitabach MN. Control of Sleep by Dopaminergic Inputs to the Drosophila Mushroom Body. Frontiers in Neural Circuits. 2015b;9:73. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2015.00073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souders MC, Zavodny S, Eriksen W, Sinko R, Connell J, Kerns C, Schaaf R, Pinto-Martin J. Sleep in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Current Psychiatry Reports. 2017;19:34. doi: 10.1007/s11920-017-0782-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southall TD, Davidson CM, Miller C, Carr A, Brand AH. Dedifferentiation of neurons precedes tumor formation in Lola mutants. Developmental Cell. 2014;28:685–696. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.01.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavropoulos N, Young MW. insomniac and Cullin-3 regulate sleep and wakefulness in Drosophila. Neuron. 2011;72:964–976. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka NK, Tanimoto H, Ito K. Neuronal assemblies of the Drosophila mushroom body. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 2008;508:711–755. doi: 10.1002/cne.21692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tayler TD, Pacheco DA, Hergarden AC, Murthy M, Anderson DJ. A neuropeptide circuit that coordinates sperm transfer and copulation duration in Drosophila. PNAS. 2012;109:20697–20702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218246109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessier-Lavigne M, Goodman CS. The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science. 1996;274:1123–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5290.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tononi G, Cirelli C. Sleep and synaptic homeostasis: a hypothesis. Brain Research Bulletin. 2003;62:143–150. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2003.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truman JW, Bate M. Spatial and temporal patterns of neurogenesis in the central nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster. Developmental Biology. 1988;125:145–157. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessin H, Grell E, Wolff E, Bier E, Jan LY, Jan YN. prospero is expressed in neuronal precursors and encodes a nuclear protein that is involved in the control of axonal outgrowth in Drosophila. Cell. 1991;67:941–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90367-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Buskirk C, Sternberg PW. Epidermal growth factor signaling induces behavioral quiescence in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature Neuroscience. 2007;10:1300–1307. doi: 10.1038/nn1981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt K, Aso Y, Hige T, Knapek S, Ichinose T, Friedrich AB, Turner GC, Rubin GM, Tanimoto H. Direct neural pathways convey distinct visual information to Drosophila mushroom bodies. eLife. 2016;5:e14009. doi: 10.7554/eLife.14009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein DC, Hemmati-Brivanlou A. Neural induction. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 1999;15:411–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.15.1.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K, Kankel DR. Patterns of cell division and cell movement in the formation of the imaginal nervous system in Drosophila melanogaster. Developmental Biology. 1978;65:296–321. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu CL, Shih MFM, Lai JSY, Yang HT, Turner GC, Chen L, Chiang AS. Heterotypic gap junctions between two neurons in the Drosophila brain are critical for memory. Current Biology. 2011;21:848–854. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.02.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie X, Tabuchi M, Corver A, Duan G, Wu MN, Kolodkin AL. Semaphorin 2b Regulates Sleep-Circuit Formation in the Drosophila Central Brain. Neuron. 2019;104:322–337. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.07.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang SB, Mclemore KD, Tasic B, Luo L, Jan YN, Jan LY. Kv1.1-dependent control of hippocampal neuron number as revealed by mosaic analysis with double markers. The Journal of Physiology. 2012;590:2645–2658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.228486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi W, Zhang Y, Tian Y, Guo J, Li Y, Guo A. A subset of cholinergic mushroom body neurons requires Go signaling to regulate sleep in Drosophila. Sleep. 2013;36:1809–1821. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S, Ross KD, Seidner GA, Gorman MR, Poon TH, Wang X, Keithley EM, Lee PN, Martindale MQ, Joiner WJ, Hamilton BA. Nmf9 Encodes a Highly Conserved Protein Important to Neurological Function in Mice and Flies. PLOS Genetics. 2015;11:e1005344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu S, Chiang AS, Lee T. Development of the Drosophila mushroom bodies: elaboration, remodeling and spatial organization of dendrites in the calyx. Development. 2003;130:2603–2610. doi: 10.1242/dev.00466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu S, Perez R, Pan M, Lee T. Requirement of Cul3 for axonal arborization and dendritic elaboration in Drosophila mushroom body neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2005;25:4189–4197. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0149-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]