Abstract
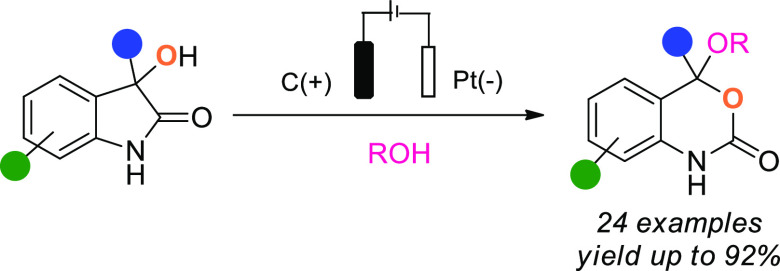
We report an unexpected rearrangement of 3-hydroxyoxindoles into benzoxazinones using electrochemistry. Our reaction employs mild and environmentally friendly conditions, and the benzoxazinone products are obtained in moderate to excellent yields. Mechanistic experiments suggest that a peroxide intermediate is likely involved.
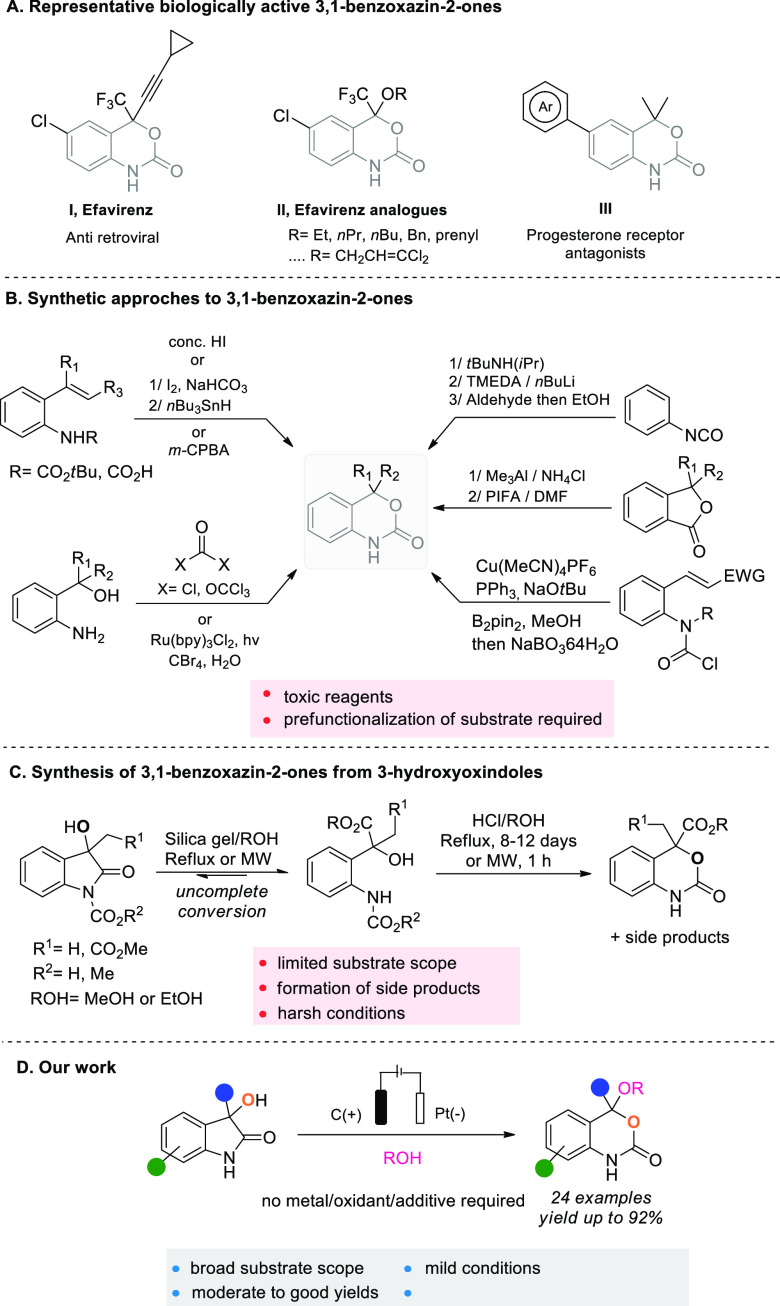
3,1-Benzoxazin-2-ones constitute a privileged scaffold within the carbamate family, present in a large number of pharmaceuticals and biologically active compounds,1 such as the well-known antiretroviral efavirenz (I)1a and its analogues (II) as well as (III) that are known to be progesterone receptor antagonists.1b (Scheme 1A).
Scheme 1. Biologically Active Compounds Containing Benzoxazinone Moieties, Relevant Synthetic Methods to Access These Motifs and Work Presented Herein.
Given the prevalence of this motif in medicinal chemistry, there remains a general need for divergent methodologies that facilitate the preparation of a range of benzoxazin-2-one derivatives to support drug discovery. Classical methods to access such structures generally involve either the annulation of o-vinylaniline derivatives2 or the carbonylation of amino alcohols3 (Scheme 1B, left), relying on the use of reagents such as tributyltin hydride or phosgene and its derivatives, respectively. Other approaches form the desired carbamates either by double-lithiation of a transient urea, formed from an isocyanate, followed by reaction with an aldehyde,4 or by an aminolysis–Hofmann rearrangement starting from phthalides5 (Scheme 1B, right). These methods require the use of strong bases or stoichiometric organometallic reagents and are often step intensive. Recently, the Lautens group reported a novel procedure for the formation of 3,1-benzoxazin-2-ones which, while using considerably milder conditions, still requires a complicated system as well as complex and expensive starting materials (Scheme 1B, bottom right).6
While derivatization of 3-hydroxy-2-oxindoles through action of a Brønsted or a Lewis acid in combination with a range of nucleophiles, such as alcohols,7e,7f thiols,7,7f−7h malonates,7g and aryl groups,7a,7c,7d,7f is well-known, the use of 3-hydroxy-2-oxindole to access other heteroaromatic structures is more scarcely reported (Scheme 1D).8 The sole example of formation of 3,1-benzoxazin-2-ones from 3-hydroxy-2-oxindole involves ring-opening alkoxylation in the presence of an alcohol, followed by a second step of cyclization. However, the reaction is limited to carbamate-protected 3-hydroxyoxindoles and to methanol or ethanol as the nucleophiles and, moreover, proved comparatively sluggish and unselective.
As part of a research program focused on novel approaches to drug design, we became interested in the reactivity of 3-hydroxyoxindole derivatives, which seemed particularly amenable to electrochemical transformation. Electrochemical synthesis provides a multitude of advantages as an environmentally friendly tool, generally featuring mild conditions, good functional group tolerance, and high chemoselectivity.9 In the event, we observed an unexpected rearrangement of 3-hydroxy-2-oxindoles to 3,1-benzoxazin-2-ones under electrochemical conditions (Scheme 1D).
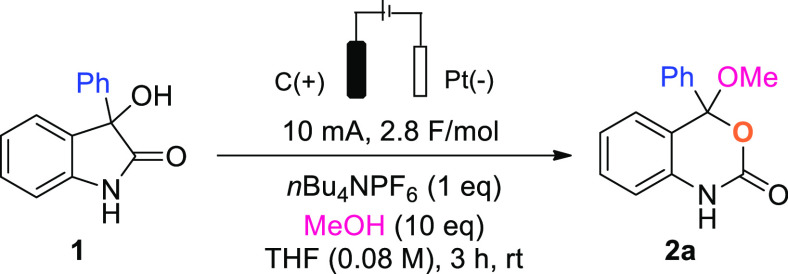
The initial reaction was performed using 1 as the starting material with the commercially available ElectraSyn 2.0 in an undivided cell (Table 1). A graphite (C) anode and a platinum (Pt) cathode were used as electrodes under a constant current of 10 mA, with tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate (nBu4PF6) as the supporting electrolyte and 10 equiv of MeOH in THF as the solvent. Encouragingly, under these unoptimized conditions, product 2a was obtained in 62% yield (Table 1, entry 1). Increasing the concentration (entry 2) or the reaction time (entry 3) led to a decrease in the yield of 2a, and it was noted that prolonged reaction times led to decomposition of the product (see the SI for details). Neither the addition of 4 Å MS (entry 4) nor the use of AgPF6 as a sacrificial oxidant (entry 5) proved beneficial for the reaction and the use of TFA (entry 6) or TEMPO (entry 7) as additives gave lower isolated yields due to substantial degradation. Subsequently, various solvents were examined, with DMF and CH3CN giving slightly decreased yields, and CH2Cl2, reported to be reduced at the cathode and act as an electron sink,10 also led to no improvement (entries 8–10). Gratifyingly, it was found that using a 1:1 mixture of MeOH and THF allowed us to successfully improve the yield to 91% (entry 11). Finally, a control reaction in the absence of electricity was conducted, and no product was observed (entry 12).
Table 1. Optimization of Reaction Conditionsa.
| entry | variation from initial conditionsa | yieldb (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | none | 62 |
| 2 | 0.16 M instead of 0.08 M | 47c |
| 3 | 5 h instead of 3 h | 20 |
| 4 | 4 Å MS as an additive | 53 |
| 5 | AgPF6 (1.5 equiv) as an additive | 23d |
| 6 | TFA (1:4 v/v with THF) as an additive | 25d |
| 7 | TEMPO (10 mol %) as an additive | 25d |
| 8 | MeCN instead of THF | 37e |
| 9 | DMF instead of THF | 38 |
| 10 | CH2Cl2 instead of THF | 55 |
| 11 | MeOH/THF(1:1v/v, 0.08 M) | 91 |
| 12 | without current | nr |
Initial conditions: undivided cell, Pt cathode, C-SK50 anode, constant current = 10 mA, 1 (0.4 mmol), nBu4PF6 (1.0 equiv), MeOH (10 equiv), THF (0.08 M), rt, 3 h.
Isolated yield.
50% conversion.
Partial decomposition was observed.
59% conversion.
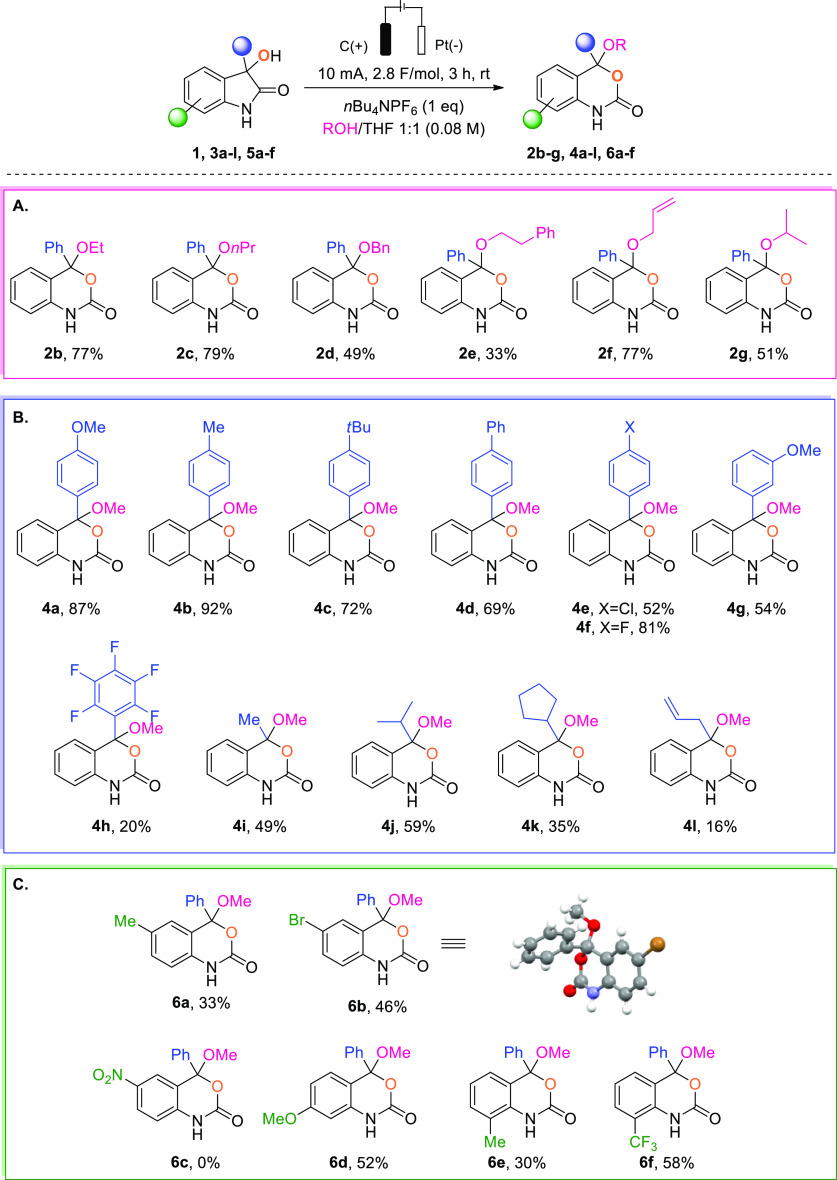
After identifying suitable reaction conditions, we set out to explore the versatility of this reaction in the presence of a variety of alcohol nucleophiles (Scheme 2). Aliphatic alcohols such as EtOH and nPrOH were well tolerated and yielded the corresponding products 2b and 2c in 77% and 79% yield, respectively (Scheme 2A). Similarly, when benzyl alcohol, 2-phenylethanol, or allyl alcohol was employed, the desired compounds 2d–f were obtained in moderate to good yields. A secondary alcohol such as 2-propanol was also a competent nucleophile and afforded 2g in 51% yield. We then examined the scope of this reaction using various 3-substituted 3-hydroxyoxindoles 3a–n (Scheme 3B) and were pleased to observe broad tolerance of different substituents at the C-3 position. Substitution with electron-donating groups (OMe, Me, tBu, and Ph) led to products 4a–d in yields up to 92%, and halogens at the para position (4e,f) or a meta-OMe substituent (4g) resulted in moderate to good yields. Compound 4h bearing a pentafluoroaryl substituent was formed in a lower yield of 20%, and a range of aliphatic substituents (4i–4l) was also tolerated. Additionally, we investigated the substrate scope using various oxindoles substituted on the aromatic (5a–f, forming 6a–f) (Scheme 2C). All modifications, with the exception of substrate 5c carrying a nitro group, were well tolerated and provided the desired products in moderate yields. Unambiguous confirmation of the benzoxazinone core was possible through X-ray diffraction of a single crystal obtained from compound 6b.
Scheme 2. Scope of the Reaction.
Scheme 3. Mechanistic Investigations.
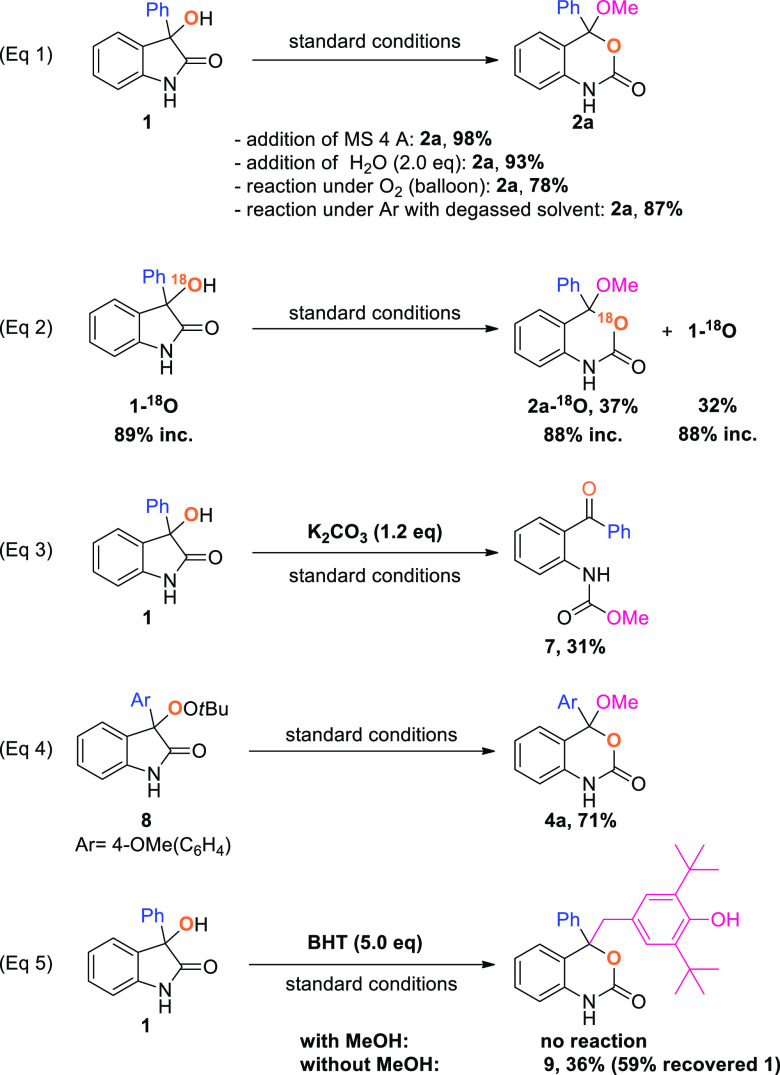
The observed formation of 3,1-benzoxazin-2-ones from 3-hydroxy-2-oxindoles raised questions regarding the mechanism of this transformation. In order to shed light on the intricacies of this transformation, several control experiments were conducted (Scheme 3). Initial experiments focused on determining the source of the endocyclic oxygen of the 3,1-benzoxazin-2-one. Water and atmospheric oxygen were ruled out as possible sources after it was found that neither the addition of molecular sieves, water, or molecular oxygen nor conducting the reaction under an inert atmosphere with degassed solvents had a significant impact on the yield (Scheme 3, eq 1). In addition, these results highlight the robustness of our protocol which proved to be tolerant of water as well as oxygen. Suspecting the endocyclic oxygen to stem from the hydroxy group of 1, the substrate was labeled with 18O (Scheme 3, eq 2). Under standard conditions, the corresponding labeled 3,1-benzoxazin-2-one 2a-[18O] was isolated without loss of the label, suggesting that the oxygen indeed stems from the hydroxy group of 1. Additional information was obtained when we recovered unreacted starting material with an unchanged degree of incorporation, pointing to the fact that the carbon–oxygen bond is not affected during the reaction. Surprisingly, the reaction of 1 under the standard conditions in the presence of K2CO3 led to an oxidative fragmentation followed by skeletal rearrangement (Scheme 3, eq 3). A transformation employing similar reaction conditions and starting from the corresponding peroxide was previously reported by Stoltz12 and prompted us to investigate the formation of a peroxide as a possible intermediate. A positive control of peroxide involvement was achieved when 8 was subjected to the electrochemical conditions, yielding 4a in 71% yield (Scheme 3, eq 4). Finally, the reaction was performed in the presence of BHT as a radical scavenger (Scheme 3, eq 5), affording a BHT-benzoxazinone adduct 9 as the exclusive product, suggesting the formation of a benzoxazinone benzylic radical.
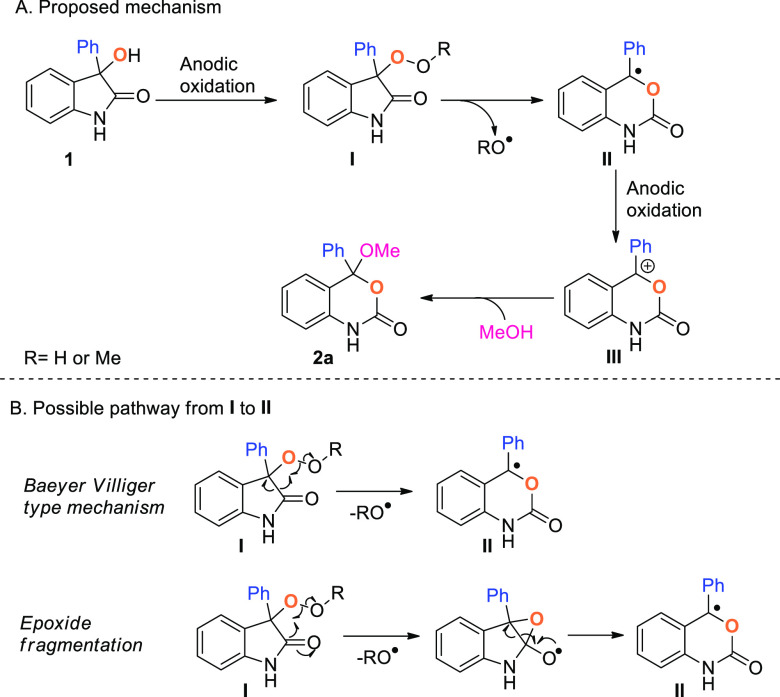
On the basis of these results, a possible mechanism is described in Scheme 4A. Initially 1 could be oxidized at the anode to form the peroxide intermediate I that could rearrange to give a benzoxazinone benzylic radical IIvia two possible pathways (Scheme 4B). A Baeyer–Villiger type rearrangement involving a concomitant cleavage of the C–C bond and liberation of an alkoxy radical could directly lead to ring enlargement, or the intramolecular formation on an epoxide could generate intermediate II through an oxa-Dowd–Beckwith-type rearrangement. It should be noted that the “Epoxide fragmentation” pathway could also be accessible from an oxygen-centered radical derived from 1. Radical II is then proposed to undergo a second favorable anodic oxidation to form a highly stabilized benzylic carbocation III, which can be finally trapped by MeOH leading to product 2a.
Scheme 4. Proposed Mechanism.
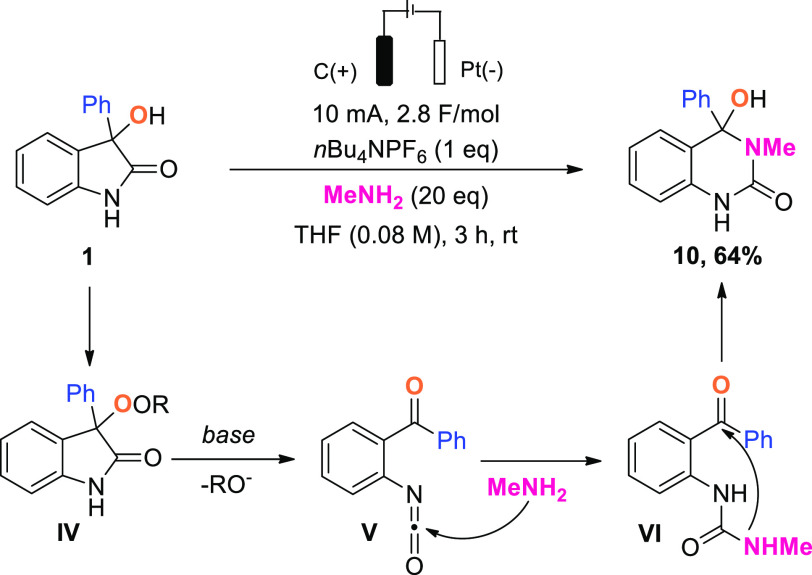
Under our standard conditions, in the presence of additional methylamine, 1 is converted into a 3,3-disubstituted quinazolinone derivative 10 in 64% yield (Scheme 5). This result, reminiscent of that obtained with K2CO3 (cf. Scheme 3, eq 3), can similarly be explained by the basic character of methylamine, enabling possible fragmentation of the peroxyoxindole (IV) to form an isocyanate intermediate (V). Subsequent addition of methylamine to form a urea (VI) followed by intramolecular nucleophilic collapse then accounts for the formation of 10.
Scheme 5. Reaction of 3-Hydroxyoxindole 1 with Methylamine.
In conclusion, we have developed a practical strategy to access 3,1-benzoxazin-2-one derivatives by electrochemical skeletal reorganization of 3-hydroxy-2-oxindoles. The reaction boasts broad functional-group tolerance and experimental simplicity, being conducted in a setup open to air with nonanhydrous solvents and is a mechanistically intriguing process.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Daniel Kaiser for useful discussions and careful proofreading. We thank Vincent Porte for his help during the revisions of the manuscript. We are very grateful to A. Prado-Roller and N. Gajic for measuring the single-crystal X-ray structures. Financial support by the Austrian Federal Ministry for Digital and Economic Affairs, the National Foundation for Research, Technology and Development, and the Christian Doppler Research Association is gratefully acknowledged. We are grateful to the University of Vienna for its continued support of our research programs.
Supporting Information Available
The Supporting Information is available free of charge at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03569.
Additional optimization tables, experimental procedures, 1H and 13C NMR spectra, and characterization data of compounds (PDF)
Accession Codes
CCDC 2102358 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif, or by emailing data_request@ccdc.cam.ac.uk, or by contacting The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, 12 Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1EZ, UK; fax: +44 1223 336033.
Author Contributions
‡ M.V. and M.P. contributed equally.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- a Rizzo R. C.; Udier-Blagovic M.; Wang D.-P.; Watkins E. K.; Smith M. B. K.; Smith R. H. Jr.; Tirado-Rives J.; Jorgensen W. L. Prediction of Activity for Nonnucleoside Inhibitors with HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Based on Monte Carlo Simulations. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2970–2987. 10.1021/jm010580q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Zhang P.; Terefenko E. A.; Fensome A.; Wrobel J.; Winneker R.; Lundeen S.; Marschke K. B.; Zhang Z. 6-Aryl-1,4-dihydro-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-2-ones: A Novel Class of Potent, Selective, and Orally Active Nonsteroidal Progesterone Receptor Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 4379–4382. 10.1021/jm025555e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Collins M. A.; Hudak V.; Bender R.; Fensome A.; Zhang P.; Miller L.; Winneker R. C.; Zhang Z.; Zhu Y.; Cohen J.; Unwallaa R. J.; Wrobel J. Novel Pyrrole Containing Progesterone Receptor Modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 2185–2189. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.02.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d Zhang P.; Kern J.. 6-Amino-1,4-dihydrobenzo[d][1,3]oxazin-2-ones and Analogs Useful as Progesterone Receptor Modulators. US 20050085470, 2005.; e Zhang P.; Kern J. C.; Terefenko E. A.; Fensome A.; Unwalla R.; Zhang Z.; Cohen J.; Berrodin T. J.; Yudt M. R.; Winneker R. C.; Wrobel J. 7-Aryl 1,5-dihydro-benzo[e][1,4]oxazepin-2-ones and Analogs as Non-steroidal Progesterone Receptor Antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 6589–6600. 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.05.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; f Girard C.; Liu S.; Cadepond F.; Adams D.; Lacroix C.; Verleye M.; Gillardin J.-M.; Baulieu E.-E.; Schumacher M.; Schweizer-Groyer G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008, 105, 20505–20510. 10.1073/pnas.0811201106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; g Commons T. J.; Jenkins D. J.; Trybulski E. J.; Fensome A.. Substituted Benzo[d]- [1,3]oxazin-2(4H)-ones and Related Derivatives and Their Uses for Modulating the Progesterone Receptor. US 20090197878, 2009.; h Mizutani T.; Ishikawa S.; Nagase T.; Takahashi H.; Fujimura T.; Sasaki T.; Nagumo A.; Shimamura K.; Miyamoto Y.; Kitazawa H.; Kanesaka M.; Yoshimoto R.; Aragane K.; Tokita S.; Sato N. Discovery of Novel Benzoxazinones as Potent and Orally Active Long Chain Fatty Acid Elongase 6 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7289–7300. 10.1021/jm900915x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; i Cox P. M.; Bumpus N. N. Single Heteroatom Substitutions in the Efavirenz Oxazinone Ring Impact Metabolism by CYP2B6. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2630–2637. 10.1002/cmdc.201600519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Kobayashi K.; Fukamachi S.; Nakamura D.; Morikawa O.; Konishi H. Convenient Synthesis of 1,4-Dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-ones by Iodocyclization of t-Butyl 2-Vinylphenylcarbamate. Heterocycles 2008, 75, 95–105. 10.3987/COM-07-11186. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; b Kobayashi K.; Fukamachi S.; Konishi H. Synthesis of 1,4-Dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-ones by Hydriodic Acid Mediated Cyclization of tert-Butyl 2-Vinylphenylcarbamates. Heterocycles 2008, 75, 2301–2307. 10.3987/COM-08-11399. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; c Yu Y.-M.; Huang Y.-N.; Deng J. Catalytic Asymmetric Chlorocyclization of 2-Vinylphenylcarbamates for Synthesis of 1,4-Dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1224–1227. 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d Sun S.; Zhou C.; Yu J.-T.; Cheng J. Visible-Light-Driven Palladium-Catalyzed Oxy-Alkylation of 2-(1-Arylvinyl)anilines by Unactivated Alkyl Bromides and CO2: Multicomponent Reactions toward 1,4-Dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-ones. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6579–6583. 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b02700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; e Fan H.; Wan Y.; Pan P.; Cai W.; Liu S.; Liu C.; Zhang Y. A Cascade Approach to 3D Cyclic Carbamates via an Ionic Decarboxylative Functionalization of Olefinic Oxamic Acids. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 86–89. 10.1039/C9CC07709J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Nikam S. S.; Yuen P.-W.; Kornberg B. E.; Tobias B.; Rafferty M. F. Novel Use of Substituted 1,4-Dihydrobenz[d][1,3]oxazin-2-ones in the Synthesis of Important Aminomethyl o-Nitroanilines. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 9331–9334. 10.1021/jo9707491. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; b Zhao Y.; Huang B.; Yang C.; Chen Q.; Xia W. Sunlight-Driven Forging of Amide/Ester Bonds from Three Independent Components: An Approach to Carbamates. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5572–5575. 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b02811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Nishiyama Y.; Naitoh Y.; Sonoda N. A New Synthetic Method of 1,4-Dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-ones: Selenium-Catalyzed Reductive Carbonylation of Aromatic Nitro Compounds with Carbon Monoxide. Synlett 2004, 886–888. 10.1055/s-2004-820018. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; d Xiong H.; Wu X.; Wang H.; Sun S.; Yu J.-T.; Cheng J. The Reaction of oAminoacetophenone N-Tosylhydrazone and CO2 toward 1,4-Dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-ones. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 3538–3542. 10.1002/adsc.201900341. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Houlden C. E.; Lloyd-Jones G. C.; Booker-Milburn K. I. Facile Double-Lithiation of a Transient Urea: Vicarious ortho-Metalation of Aniline Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3090–3092. 10.1021/ol101102y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández E.; Vélez J. M.; Vlaar C. P. Synthesis of 1,4-Dihydro-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-2-ones from Phthalides via an Aminolysis-Hofmann Rearrangement Protocol. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 8972–8975. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.10.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larin E. M.; Torelli A.; Loup J.; Lautens M. One-Pot, Three-Step Synthesis of Benzoxazinones via Use of the Bpin Group as a Masked Nucleophile. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 2720–2725. 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Nicolaou K. C.; Chen D. Y.-K.; Huang X.; Ling T.; Bella M.; Snyder S. A. Chemistry and Biology of Diazonamide A: First Total Synthesis and Confirmation of the True Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12888–12896. 10.1021/ja040092i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b England D. B.; Merey G.; Padwa A. Substitution and Cyclization Reactions Involving the Quasi-Antiaromatic 2H-Indol-2-one Ring System. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 3805–3807. 10.1021/ol7016438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Zhou F.; Cao Z.-Y.; Zhang J.; Yang H.-B.; Zhou J. A Highly Efficient Friedel-Crafts Reaction of 3-Hydroxyoxindoles and Aromatic Compounds to 3,3-Diaryl and 3-Alkyl-3-aryloxindoles Catalyzed by Hg(ClO4)2-3H2O. Chem. - Asian J. 2012, 7, 233–241. 10.1002/asia.201100773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d Wang X.; Liu J.; Xu L.; Hao Z.; Wang L.; Xiao J. Friedel-Crafts alkylation of heteroarenes and arenes with indolyl alcohols for construction of 3,3-disubstituted oxindoles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 101713–101717. 10.1039/C5RA21919A. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; e Zhu F.; Zhou F.; Cao Z.-Y.; Wang C.; Zhang Y.-X.; Wang C.-H.; Zhou J. A Facile Method for the Synthesis of 3-Substituted 3-(Alkylthio)oxindoles or 3-Alkoxyoxindoles. Synthesis 2012, 44, 3129–3144. 10.1055/s-0032-1316772. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; f Piemontesi C.; Wang Q.; Zhu J. Synthesis of 3,3-disubstituted oxindoles by one-pot integrated Brønsted base-catalyzed trichloroacetimidation of 3-hydroxyoxindoles and Brønsted acid-catalyzed nucleophilic substitution reaction. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 1533–1536. 10.1039/c2ob27196f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; g Naresh Babu K.; Kariyandi N. R.; Saheeda M. K. S.; Kinthada L. K.; Bisai A. Lewis Acid-Catalyzed Malonate Addition onto 3-Hydroxy-2-oxindoles: Mechanistic Consideration and Synthetic Approaches to the Pyrroloindoline Alkaloids. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 12664–12682. 10.1021/acs.joc.8b02017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; h Sharma N. Peddinti Experimental and theoretical investigations of regioselective functionalization of 3-hydroxy bisindoles with thiols. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 9259–9268. 10.1039/C8OB02118J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Castillo O. R.; Bautista-Hernández C. I.; Sánchez-Zavala M.; Meléndez-Rodríguez M.; Sierra-Zenteno A.; Morales-Ríos M. S.; Joseph-Nathan P. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of 3,1-Benzoxazin-2-ones from 3-Hydroxyoxindoles. Heterocycles 2012, 85, 2147–2171. 10.3987/COM-12-12472. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- a Horn E. J.; Rosen B. R.; Baran P. S. Synthetic Organic Electrochemistry: An Enabling and Innately Sustainable Method. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 302–308. 10.1021/acscentsci.6b00091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Yan M.; Kawamata Y.; Baran P. S. Organic Electrochemical Methods Since 2000: On the Verge of a Renaissance. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13230–13319. 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Wiebe A.; Gieshoff T.; Möhle S.; Rodrigo E.; Zirbes M.; Waldvogel S. R. Electrifying Organic Synthesis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5594–5619. 10.1002/anie.201711060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d Kärkäs M. D. Electrochemical strategies for C-H functionalization and C-N bond formation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5786–5865. 10.1039/C7CS00619E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; e Jiang Y.; Xu K.; Zeng C. Use of Electrochemistry in the Synthesis of Heterocyclic Structures. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4485–4540. 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; f Phillips A. M. F.; Pombeiro A. J. L. Electrochemical asymmetric synthesis of biologically active substances. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 7026–7055. 10.1039/D0OB01425G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang J.; Shang M.; Kawamata Y.; Lundberg H.; Reisberg S.; Chen M.; Mykhailiuk P.; Beutner G.; Collins M.; Davies A.; Del Bel M.; Gallego G.; Spangler J.; Starr J. T.; Yang S.; Blackmond D.; Baran P. S. Hindered dialkyl ether synthesis with electrogenerated carbocations. Nature 2019, 573, 398–402. 10.1038/s41586-019-1539-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klare H. F. T.; Goldberg A. F. G.; Duquette D. C.; Stoltz B. M. Oxidative Fragmentations and Skeletal Rearrangements of Oxindole Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 988–991. 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.