Abstract
The limitation of inert N2 molecules with their high dissociation energy has ignited research interests in probing other nitrogen-containing species for ammonia synthesis. Nitrate ions, as an alternative feedstock with high solubility and proton affinity, can be facilely dissociated for sustainable ammonia production. Here we report a nitrate to ammonia photosynthesis route (NO3−RR) catalyzed by subnanometric alkaline-earth oxide clusters. The catalyst exhibits a high ammonia photosynthesis rate of 11.97 mol gmetal−1 h−1 (89.79 mmol gcat−1 h−1) with nearly 100% selectivity. A total ammonia yield of 0.78 mmol within 72 h is achieved, which exhibits a significant advantage in the area of photocatalytic NO3−RR. The investigation of the molecular-level reaction mechanism reveals that the unique active interface between the subnanometric clusters and TiO2 substrate is beneficial for the nitrate activation and dissociation, contributing to efficient and selective nitrate reduction for ammonia production with low energy input. The practical application of NO3−RR route in simulated wastewater is developed, which demonstrates great potential for its industrial application. These findings are of general knowledge for the functional development of clusters-based catalysts and could open up a path in the exploitation of advanced ammonia synthesis routes with low energy consumption and carbon emission.
Subject terms: Pollution remediation, Photocatalysis, Materials for energy and catalysis
Photocatalytic reduction of waste nitrate offers an alternative route for ammonia production. Here the authors report BaO clusters on TiO2 for nitrate-ammonia photosynthesis with high ammonia yield.
Introduction
As an essential chemical, ammonia (NH3) is industrially produced via the Haber-Bosch process, which consumes 1.0–2.0% of the world’s energy output and contributes to 1.6% of the world’s carbon emissions1–4. As an alternative, artificial electro-/photo-/photoelectrochemical nitrogen reduction reactions (N2RRs) for NH3 synthesis, inspired by the natural microbial N2 fixation, have attracted tremendous research interest5,6. Despite great achievements in recent decades, it is inconvenient to overlook that the future of N2RRs is plagued by the ultrahigh dissociation energy of the N≡N bond (941 kJ mol−1)7,8. Inferior catalytic performance is predictable, arising from the limited solubility and low proton affinity of the inert N2.
From an energy viewpoint, nitrate ions (NO3−), as a sustainable N-containing alternative, can be disintegrated at lower dissociation energy of 204 kJ mol−1, contributing to an accelerated reaction kinetics for NH3 synthesis9–13. Besides, the highest valence state of N-element in NO3− ensures that the deep reduction reaction can be achieved for selective NH4+ synthesis. The intermediate-valence N2 oxidation and reduction may proceed simultaneously when conducting N2RR, which restrains the NH4+ selectivity14–16. Another virtue of using NO3− feedstock lies in its rich distribution in wastewater. The abundant nitrate in wastewater offers sufficient reactants for NO3− reduction reaction (NO3−RR) routes17–20. Instead of the partial reduction of NO3− to N2 for its purification, the eight-electron transfer reaction for NO3− to NH4+ synthesis provides an opportunity for the value-added conversion of contaminative NO3− into ammonia as an economically competitive product. Also, the wide distribution of general organic matters such as aldehydes and phenols in wastewater is noted, which forms contaminant mixtures with nitrate21. These organic matters can serve as the hole sacrificial agents, which accelerates both the NO3− reduction for NH4+ synthesis and pollutants’ oxidation for their degradation. Thus, the development of a NO3−RR route for NH4+ production, which provides sustainable N-cycle utilization, has a profound effect in both reducing energy consumption and mitigating environmental anxieties.
Despite its advantages, NO3−RR also suffers from some inevitable difficulties as an active, yet challenging area of current research. In the eight-electron transfer reaction for NO3−-NH4+ synthesis, competitive side reactions may be fierce, mainly ascribed to five-electron transfer for the partial reduction of NO3− to N2 and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER)22–24. Moreover, it is well established that the yield rate and selectivity for NH4+ dominantly rely on the development of novel catalytic materials, precise regulation of the reaction parameters and systematic investigation of the reaction mechanism. In this scenario, a comprehensive catalysis system requires a rational design to sufficiently promote catalytic performance.
As a typical solid–liquid heterogeneous catalytic reaction, the interaction between catalysts and solvents is essential in the NO3−RR system. Generally, metal cations (Mx+) are introduced into solvents, serving as key functional components such as cocatalysts, ionic liquids or electrolytes25–27. With the catalytic reaction on stream, the dynamic evolution of Mx+ can be observed28,29. With the assistance of appropriate catalyst support and reaction conditions, the deposition of Mx+ on a solid surface is expected, which leads to the production of corresponding single atoms, nanoclusters or nanoparticles on a substrate surface30–32, thereby modifying the interfacial structure and in situ serving as the catalytic active sites. Key challenge lies in revealing the interfacial structure of active sites for facilitating the ammonia selectivity and suppressing the occurrence of side reactions (HER and NO3− to N2) to enhance the efficiency.
Here, we demonstrate a general strategy to accomplish the operando construction of subnanometric alkaline-earth oxide clusters (MONCs, M=Mg, Ca, Sr or Ba) as the active sites due to the nontoxicity and low price of alkaline-earth metals. Also, the widely investigated TiO2 nanosheets (TNS) is applied as the substrate since it is easy to be fabricated and characterized. After the operando construction of the BaONCs-TNS composite, a high ammonia photosynthesis rate of 11.97 mol gmetal−1 h−1 (89.79 mmol gcat−1 h−1) is reached with nearly 100% selectivity. A total ammonia yield of 0.78 mmol within 72 h is achieved. The local interfacial structure is precisely tailored to strengthen charge transfer at the MONCs/TNS interface. Then, it is revealed that the eight-electron transfer reaction for NO3−RR is notably accelerated to achieve a high rate for sustainable NH4+ photosynthesis. The practical application of NO3−RR route in simulated wastewater is also developed, which establishes an intriguing “sacrificial-agent-free” route for ammonia synthesis and demonstrates great potential for its real industrial application. The current ammonia photosynthesis route could provide an alternative route for nitrogen cycle utilization and promote the development of low-carbon technology.
Results
Operando construction of the subnanometric clusters
Alkaline-earth ions (50 mg/L) are first injected into the reaction mixture for the NO3−RR on TNS. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) results demonstrate that the morphology and crystal structure of TNS is well maintained after alkaline-earth ion incorporation (Supplementary Figs. 1–3). To reveal the operando evolution of the alkaline-earth ions, the mixture is extracted from the reaction on stream. As identified by the quasi in situ high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM), the operando evolution of the alkaline-earth species on the catalyst surface is observed (Fig. 1).
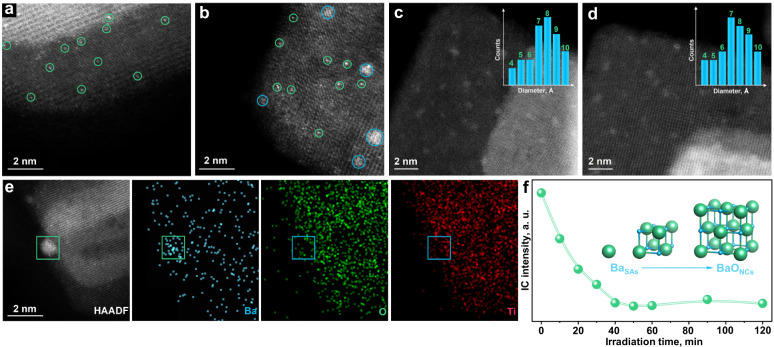
Fig. 1. Structure identification of subnanometric BaO nanoclusters (BaONCs) operando construction on TiO2 nanosheets (TNS) support.
a–d Quasi in situ high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) images showing the evolution course from isolated Ba single atoms (BaSAs) to subnanometric (BaONCs) at the irradiation time of 5 min (a), 10 min (b), 60 min (c) and 120 min (d) respectively. The related size distribution is labeled as insets (c, d), in which the range of both x (0.4–1.0) and y (0–7) axes are set consistently. e, HAADF-STEM image (left) and respective elemental mapping images (right) verifying the component of Ba elements on the BaONCs-TNS surface. f Variation of Ba2+ concentration during the operando construction of BaONCs detected by ion chromatography.
Taking Ba2+ as an example, once the BaCl2·2H2O is introduced into the reaction mixture, single atoms (BaSAs) are constructed on the TNS surface after 5 min of irradiation (Fig. 1a). The subsequent growth and agglomeration of BaSAs lead to the generation of subnanometric BaO clusters (BaONCs) with a size of ~0.6 nm (Fig. 1b). With prolonged irradiation time (Fig. 1c, d for 60 and 120 min respectively), uniformly dispersed BaONCs with a mean size of 0.7 ± 0.3 nm are formed on TNS. In addition, the HAADF-STEM elemental mappings (Fig. 1e) confirm that the MONCs are mainly composed of Ba. It is worth noting that the variation of the Ba2+ concentration is revealed by ion chromatography (IC) detection (Fig. 1f). A continuous decrease in the Ba2+ concentration is observed within the first 60 min of irradiation. Then, equilibrium is reached to guarantee the subnanometric size of the BaONCs, thereby preventing excessive agglomeration and further growth. In addition, the operando construction of MgONCs, CaONCs and SrONCs is accomplished under the same procedure as that for the BaONCs (Supplementary Figs. 4–8), indicating that this is a general strategy to form the MONCs.
Characterization and electronic properties of the MONCs-TNS composites
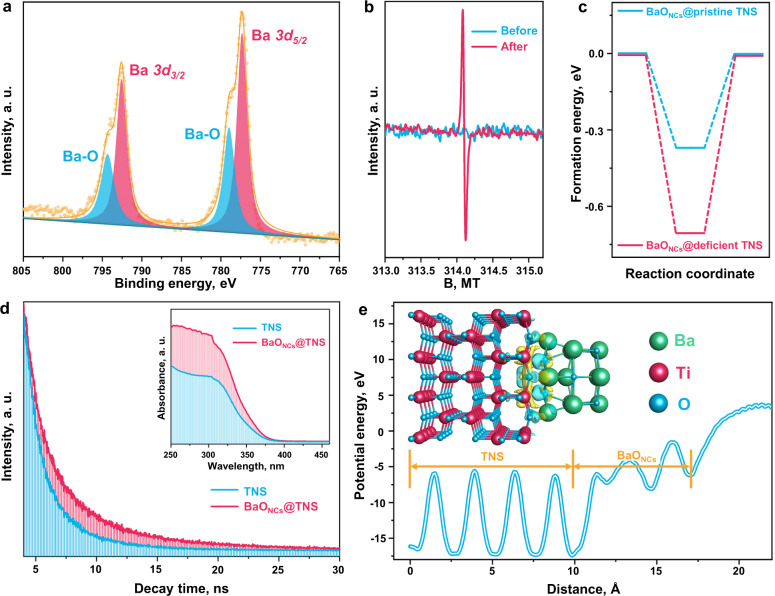
The chemical components and valence states of the BaONCs were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Fig. 2a and Supplementary Fig. 9). The deconvolution of the Ba 3d XPS spectrum illustrates that the four characteristic peaks are fitted at the binding energies of 794.61, 792.84, 778.99, and 777.15 eV. The peaks located at 792.84 and 777.15 eV correspond to the spin orbits of Ba 3d3/2 and Ba 3d5/2 respectively, demonstrating the generation of BaONCs on the TNS surface. The other two shoulder peaks (794.61 and 778.99 eV) are identified as Ba–O bond formation between the Ba in the BaONCs and the O in the TNS33,34. The concentration of Ba is determined to be 0.75 wt.% and 0.26 at.% by using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy (Supplementary Fig. 10). To investigate the underlying growth pattern and mechanism of BaONCs, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) measurements were conducted for the pristine TNS before and after light irradiation (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 11). The intensified signal for lone-pair electrons after light irradiation discloses that the oxygen vacancies in TNS can be constructed via light irradiation, which agrees with the reported results35–37. Furthermore, it is confirmed by density function theory (DFT, Fig. 2c) calculations that the construction of BaONCs at the defective site of TNS is more energy-favorable (−0.69 eV) than that of pristine TNS (−0.36 V). A uniform pattern for the deposition of other alkaline-earth MONCs on TNS is confirmed (Supplementary Figs. 12–15), which indicates that the subnanometric MONCs can be precisely immobilized at the light-induced vacancy sites on TNS with this general method. Since the number of lone-pair electrons is limited at the vacancy sites, the cluster size is restricted at the subnanometric region, which hampers their excessive agglomeration and growth, thus achieving operando construction of subnanometric MONCs at the defective sites of TNS.
Fig. 2. Chemical composition and electronic structure.
a Ba 3d X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra of BaONCs-TNS. b Room temperature solid electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) results of TNS before and after irradiation for 30 min. c Calculated binding energy of BaONCs deposited at pristine and deficient TNS surfaces respectively. d Time-resolved fluorescence emission decay spectra. Inset: UV–vis diffuse reflection spectra (DRS) results. e Calculated planer average potential energy profile using Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) + U correction. Inset: calculated charge difference distribution at the BaONCs/TNS interface, in which charge accumulation is marked in blue and charge depletion is marked in yellow. The isosurfaces were set to 0.005 eV Å−3.
Next, the optical and electronic properties of the as-prepared subnanometric MONCs-TNS composites were surveyed. Steady and time-resolved photoluminescence spectra (Fig. 2d and Supplementary Figs. 16 and 17) show that the charge separation capacity of TNS is observably enhanced after the operando construction of MONCs. The prolonged carriers’ lifetime is beneficial for the participation of photoinduced electrons to catalyze the NO3–NH4+ photosynthesis reaction. Besides, the red shift of the light absorption range (Fig. 2d inset and Supplementary Fig. 18) implies that the light capture and utilization ability is facilitated via the deposition of MONCs. Then the Mott-Schottky spectra and UV–vis diffuse reflection spectra (DRS) were combined to determine the band structures of TNS and BaONCs-TNS (Supplementary Fig. 19). It is noted that the conduction band position of BaONCs-TNS is elevated than that of the pristine TNS, which could enhance the reduction capacity for the elevated NO3−RR performance. Molecular-level insights into the charge transfer patterns at MONCs/TNS interface were further revealed by DFT calculations (Fig. 2e and Supplementary Figs. 20–22). As supported by both standard Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) functional and PBE + U correction calculations for the planar average potential energy profile, a distinct energy gap is generated between the BaONCs and TNS surface, which facilitates directional electron migration from the BaONCs to TNS. It is also confirmed by the charge difference distribution (Fig. 2e inset) that intense charge clouds accumulate at the BaONCs/TNS interface, building a unique electronic channel to promote charge transfer. Due to the superior photochemical properties contributed by the operando construction of the MONCs-TNS composite, the elevated catalytic performance of the NO3−RR for NH4+ photosynthesis is expected.
NO3− to NH4+ photosynthesis performance
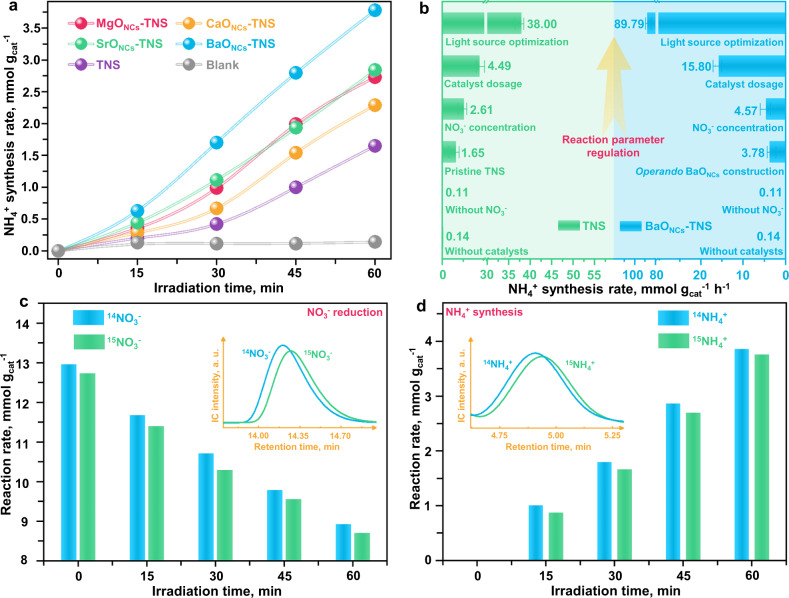
The evaluation of the NO3−RR for NH4+ photosynthesis was first conducted in 100 mL of KNO3 solution (20 mg/L of NO3−) containing 5.0% ethylene glycol (EG) as the hole sacrificial agent under full-spectrum illumination. Briefly, 5.0 mg of pristine TNS is applied as the catalyst support, in which 50.0 mg/L alkaline-earth ions are injected. As depicted in Fig. 3a, the pristine TNS exhibits nice catalytic activity (1.65 mmol gcat−1 h−1). The oxygen vacancies (OVs) in TNS are identified as the active sites due to the observable OVs construction via light irradiation (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 11). Most importantly, the operando construction of MONCs (illustrated in Fig. 1f) and enhancement of the NH4+ photosynthesis rate are simultaneously accomplished with the reaction on stream. Since the construction of MONCs and NH4+ synthesis proceed at the same time, the NH4+ synthesis rate by MONCs is elevated and the gradual increase of the slope for NH4+ generation is reasonable. The NH4+ synthesis rate is increased from 1.65 mmol gcat−1 h−1 with pristine TNS to 3.78 mmol gcat−1 h−1 with BaONCs-TNS, which demonstrates the significant advantage of subnanometric MONCs as cocatalyst. The apparent quantum efficiency (Supplementary Note 1) for these as-prepared samples is also enhanced in the order of TNS (1.86%) < CaONCs-TNS (2.59%) < MgONCs-TNS (3.09%) < SrONCs-TNS (3.22%) < BaONCs-TNS (3.46%). In addition, the controlled experiment is conducted by adding KCl into the catalysis system of pristine TNS without other cations or anions (Supplementary Fig. 23), which excludes the potential involvement of Cl− from the source of alkaline earth source (MCl2·xH2O). It is observed that the NO3−RR to ammonia efficiency is not promoted by the addition of Cl−, which identifies that the enhanced activity is contributed by the construction of MONCs-TNS. Since the operando production of MONCs on TNS is preferable to achieve at the OVs sites (Fig. 2c and Supplementary Figs. 12–15), the active sites in MONCs-TNS are regarded as the MONCs@OVs interfaces. Besides, to further unveil the activity origin of MONCs-TNS, we conduct an additional control experiment by replacing the TNS substrate with inert SiO2 nanoparticles (Supplementary Fig. 24). It is observed that no NH4+ can be detected during the simultaneous construction of MONCs-SiO2 and NO3−RR. Hence, it is clarified that the enhanced NH4+ synthesis efficiency gives credit to the construction of MONCs-TNS composites.
Fig. 3. Catalytic performance of NH3 photosynthesis on alkaline-earth oxide clusters.
a Catalytic efficiency tests showing the enhancement of operando construction of alkaline-earth oxide clusters on TNS surfaces. b Reaction parameter regulation for optimized NH4+ photosynthesis rates on TNS and BaONCs-TNS respectively. c, d Quantitative isotope-labeled 15NO3− study verifying the fed NO3− as the source for the prodcuced NH3. Inset: raw ion chromatography (IC) spectra for 14NO3−/15NO3− reduction (c) and 14NH4+/15NH4+ generation (d) respectively. The y-axis of c, d depict the reaction rates for NO3− reduction and NH4+ production respectively. The inset images are the raw IC data for 14NO3−/15NO3− (c) and 14NH4+/15NH4+ (d) respectively. The error bar was drawn based on the calculated standard error of two parallel tests.
Because the catalytic efficiency is directly related to reaction parameters, the reaction parameters are comprehensively optimized to further promote catalytic performance (Fig. 3b), including the NO3− concentration, catalyst dose, and light source. It is observed that the increase in NO3− concentration (100.0 mg/L) is beneficial for accelerating the reaction kinetics of NO3−RR (Supplementary Fig. 25). The saddle point of the catalyst dose is located at 1.0 mg to accomplish the optimal unit activity (Supplementary Fig. 26). Besides, since NO3− could be preactivated by UV light, which tailors the coordination environment of the stable NO3− and drives it into some active intermediates such as monodentate NO3−, –NO2 and NO2− (Supplementary Fig. 27), the utilization of different light sources was tested. Notably, the optimal NH4+ photosynthesis rate is 38.00 mmol gcat−1 h−1 with pristine TNS after regulating the reaction parameters (Supplementary Fig. 28). Moreover, an accelerated rate for NH4+ photosynthesis is accomplished on BaONCs-TNS (89.79 mmol gcat−1 h−1) with the reaction parameters of 100 mg L−1 of NO3−, 1.0 mg of BaONCs-TNS catalyst, and UV light irradiation. It is worth mentioning that the introduction of UV light not only increases the energy density but also realizes the preactivation of NO3−, which exceeds that of the full-spectrum (15.80 mmol gcat−1 h−1) and simulated solar light (3.07 mmol gcat−1 h−1). Then, as shown in the XRF results (Supplementary Fig. 10), 0.75 wt.% of Ba element is detected in the BaONCs-TNS composite. Hence, the rate (per Ba metal) is calculated to be 11.97 mol gBa−1 h−1. The optimal rate catalyzed by BaONCs-TNS manifests advances in comparison with that of the other ammonia synthesis by using alkaline-earth-containing catalysts (Supplementary Table 1).
To exclude the potential contribution of contaminative N-containing species, blank control experiments were subsequently performed (Supplementary Fig. 29) under the same testing procedure as that without catalysts and NO3−; these experiments confirm that almost no NH4+ is produced. Most importantly, a quantitative isotope measurement was executed to test the N source for generating NH4+ by combining IC and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technologies (Fig. 3c, d and Supplementary Figs. 30–32). K14NO3 and K15NO3 solutions are used as N sources. Within 60 min of reaction, 15NH4+ is observably detected when 15NO3− is employed. In addition, comparable rates for 14NO3−/15NO3− reduction (Fig. 3c) and 14NH4+/15NH4+ production (Fig. 3d) are identified, confirming that the produced ammonia is directly derived from the nitrate feedstock, thus, the contribution of contaminative N-containing species to ammonia can be neglected.
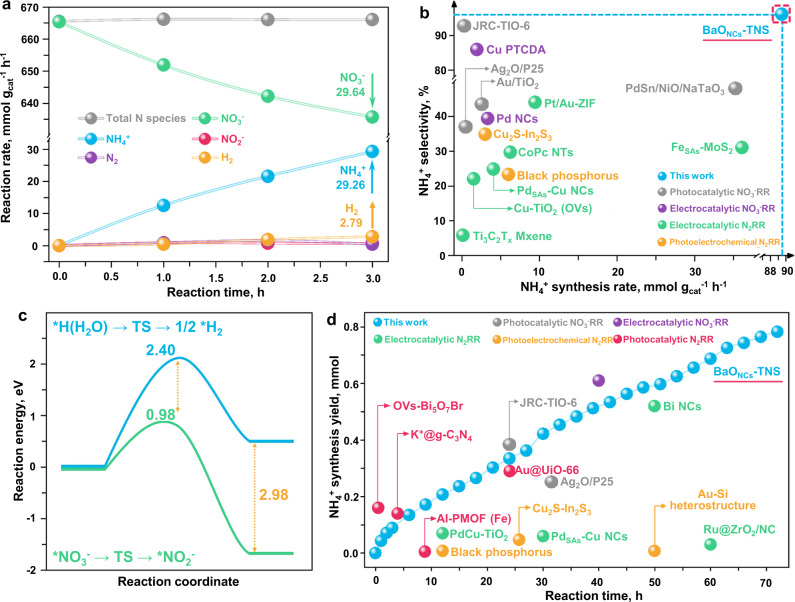
We further investigated the selectivity of the NO3−RR for NH4+ photosynthesis on BaONCs-TNS (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Figs. 33 and 34). After 3 h’ irradiation, 29.64 mmol gcat−1 NO3− is reduced to generate 29.26 mmol gcat−1 NH4+. Besides, the amount of total N species remains stable in the reaction mixture throughout the entire reaction, which implies that the five-electron transfer for partial reduction of NO3− to N2 is effectively impeded.In addition, generated H2 is detected (Supplementary Fig. 35) since water splitting is the primary side reaction in our reaction system. Trace amounts (2.79 mmol gcat−1 for 3 h) of H2 are produced. By comparing the eight-electron NO3−RR and two-electron water splitting reaction, the selectivity for NH4+ photosynthesis is determined to reach as high as 97.67%. The NH4+ synthesis rate and selectivity of the NO3−RR on BaONCs-TNS are superior among the routes under ambient conditions, exceeding that of the other photocatalytic NO3−RR works and even some leading electrocatalytic NO3−RR work (Fig. 4b and Supplementary Table 2). Not surprisingly, the results of this work also exhibit advances in comparison with those of N2RR routes at ambient conditions, including electrocatalytic, photocatalytic, and photoelectrochemical methods. Subsequently, the reaction activation energy of NO3−-NH4+ synthesis and water splitting for H2 production was calculated (Fig. 4c and Supplementary Fig. 36). A distinct activation energy decrease of 1.42 eV is noted for the NO3−RR compared with that of the water splitting reaction, which can enable efficient inhibition of electron consumption for the side reaction.
Fig. 4. Selectivity and long-term stability tests.
a NH4+ selectivity test from NO3−RR versus the other potential products. The related stand curves were provided in Supplementary Figs. 37–39. b Comparison of NH4+ production rate and selectivity with different ammonia synthesis routes under ambient conditions11,16,24,59–69. c Calculated activation energy for NO3−RR for NH4+ synthesis and water splitting for H2 generation. d Long-term stability of BaONCs-TNS and comparison of total NH4+ yield with different NH4+ synthesis routes11,16,25,42,59,68–75. The detailed comparison lists of b and d are provided in Supplementary Table 2.
Despite the ultra-high NH4+ photosynthesis rate and selectivity, the total NH4+ yield is a pivotal benchmark to evaluate the performance of ammonia synthesis catalysts and routes; notably, this benchmark is usually overlooked. Hence, long-term tests were performed to determine the accumulation of NH4+ (Fig. 4d). It is noted that a small amount of deactivation is observed in the first 3 h, which may be caused by the competing reduction reaction of Ba2+ and NO3−. After the BaONCs are stably formed on TNS, the significant stable production of NH4+ on the BaONCs-TNS composite is realized. As a result, a total NH4+ yield of 0.78 mmol is reached within 72 h. Moreover, the catalyst structure is well maintained after the long-term tests (Supplementary Figs. 40–43). By comparing the NH4+ synthesis efficiency between the NO3−RR for NH4+ photosynthesis and recently reported state-of-the-art routes (Supplementary Table 2), the NH4+ synthesis rate, selectivity, long-term stability and total NH4+ yield in this work all demonstrate advances in comparison with those of other ammonia synthesis routes under ambient conditions, including electrocatalytic, photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical methods. In addition, in the area of the NO3−RR for NH4+ synthesis, the yield of photosynthesis in this work (0.51 mmol within 40 h) is comparable to that of some leading work using electricity as the catalytic driving force (0.61 mmol within 40 h)11. Since the density of energy input for photosynthesis is lower than that of electrocatalysis, the current photosynthesis performance of the NO3−RR for NH4+ is very competitive.
Comprehensive understanding of the reaction mechanism
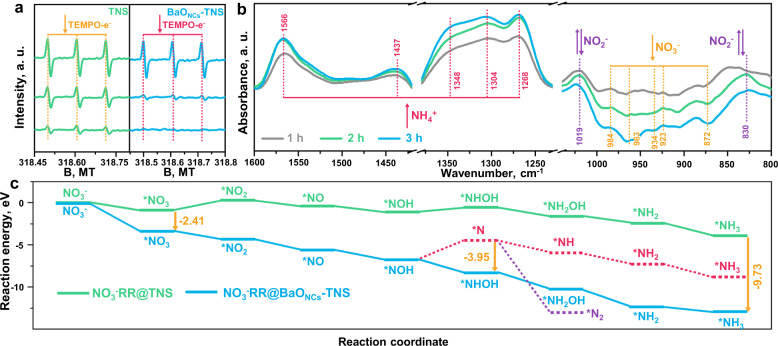
To further verify the active radicals responsible for the superior NO3−RR on the BaONCs-TNS composite, we applied the liquid-state EPR technology using 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy (TEMPO) as the trapping reagent (Fig. 5a). The signals of TEMPO decrease rapidly on BaONCs-TNS compared with the TEMPO signals on pristine TNS under light irradiation; this result indicates that more photoexcited electrons are generated and consumed on BaONCs-TNS. The incorporation of H+ and TEMPO-e− is significantly strengthened via the operando construction of subnanometric BaONCs, generating abundant active protons (H*) to catalyze the NO3−RR for NH4+ photosynthesis. In addition, enhanced •OH, •O2− and 1O2 production is also observed on BaONCs-TNS (Supplementary Fig. 44). These reactive oxygen species (ROS) are beneficial for the photocatalytic oxidation of EG, which facilitates hole consumption and charge separation.
Fig. 5. Molecular-level reaction mechanism of NO3−RR for NH3 photosynthesis.
a EPR spectra for 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy (TEMPO)-e− showing the reactive species. b In situ diffused reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) revealing the principal reactants and products within the NO3−RR on BaONCs-TNS. c Gibbs free-energy diagram of the reaction coordinates. Steps marked red and purple are the potential side reactions of NO3−RR on BaONCs-TNS.
Moreover, an in situ diffused reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) technique was introduced to dynamically detect the primary reaction process of the NO3−RR. As shown in Fig. 4b, the characteristic peaks regarding adsorbed NO3− are clearly identified at 872, 923, 934, 969, and 984 cm−1 38,39. It is noted that the intensity of NO3− gradually weakens with prolonged irradiation time, which confirms the consumption and reduction of NO3−. As the NO3−RR proceeds, the IR signals of the intermediate NO2− are observed at 830 and 1019 cm−1 40,41 and increase within the first two hours. After that, a decrease in the NO2− signals are noted (blue line in Fig. 4b), which illustrates that more NO2− has been consumed than generated. Most importantly, the continuous production of NH4+ is verified (1268, 1304, 1348, 1437, and 1566 cm−1)42–44. These results clarify that the NO3−RR route for NH4+ photosynthesis is feasible, in which NO2− is identified as the principal intermediate product. Based on the in situ DRIFTS detection, the primary reaction pathways of the NO3−RR for NH4+ photosynthesis are summarized (Note 1).
Note 1 Primary reaction pathways of NO3− reduction for NH4+ photosynthesis
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 6 |
| 7 |
| 8 |
The activation and reduction of NO3− on the catalyst surface were subsequently revealed by DFT calculations to support the experimental results. As depicted in Supplementary Fig. 45, the adsorption energy and received electrons of NO3− at the BaONCs/TNS interface is observably elevated compared with that of pristine TNS, which could promote the NO3− reduction process. Furthermore, the Gibbs free-energy diagrams (ΔG) were obtained to verify the effect of subnanometric BaONCs construction on the reaction energy and pathways (Fig. 5c). Referring to the experimental results, we first compared the eight-electron transfer reaction for the synthesis of NO3−–NH3 on pristine TNS (green line in Fig. 5c and Supplementary Fig. 46) and BaONCs-TNS (blue line and Supplementary Fig. 47). It is clearly revealed that facile NO3− dissociation (*NO3–*NO2) can be accomplished on BaONCs-TNS with an observable decrease in energy compared to that of pristine TNS, which is the dominant reason for the elevated NO3−RR performance on BaONCs-TNS. As the NO3−RR proceeds, a total energy decrease of 9.73 eV is noted for efficient NH3 synthesis. Two primary competing reaction pathways regarding N2 and NH4+ production were compared (Supplementary Note 2 and 3). A lower ΔG is required for *NOH-*NHOH (−1.63 eV) reduction than for *NOH-*N (+2.31 eV) reduction (red line in Fig. 5c and Supplementary Fig. 48). Since *N generation is prevented, N2 production (purple line in Fig. 5c and Supplementary Fig. 49) is not an optional process on BaONCs-TNS. Besides, the lower activation energy for NO3− dissociation (0.98 eV, Fig. 4c) is identified in comparison with that of the water splitting reaction (2.40 eV). Hence, among the three potential products in these reaction pathways (NH4+, N2 and H2), the highly selective eight-electron reduction of NO3− for NH4+ photosynthesis is achieved via the assistance of MONCs.
Practical applications of NO3−RR in simulated wastewater
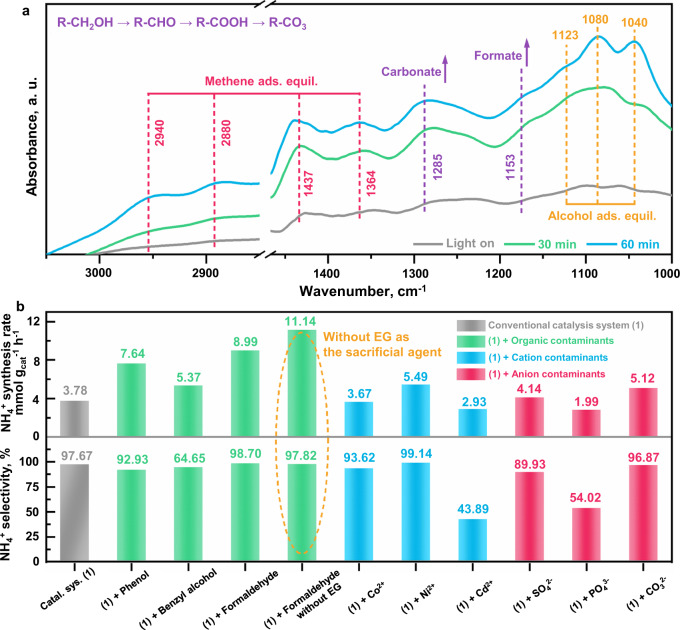
The practical application of the as-proposed NO3−RR for ammonia photosynthesis route was developed. Since the organic matter of EG is applied in the catalysis system (Catal. Sys.) as the hole sacrificial agent, the conversion pathways of EG are investigated via the in situ DRIFTS technology (Fig. 6a). It is observed that the dynamic adsorption equilibrium (Ads. Equil.) of EG is gradually formed based on the detection of methane (2940, 2880, 1437, and 1364 cm−1)45,46 and alcohol (1123, 1080, and 1040 cm−1)45,47 species. Then the generation and accumulation of formate (1153 cm−1)48 and carbonate (1285 cm−1)46,47 are observed, which can be attributed to the primary products for EG oxidation. Hence, it is concluded that the reactions of EG oxidation and NO3− reduction proceed simultaneously, in which the hole consumption by EG oxidation could in turn accelerate the NO3−RR to promote ammonia synthesis.
Fig. 6. Practical application of NO3−RR to NH4+ route in simulated wastewater.
a In situ DRIFTS for ethylene glycol (EG, hole sacrificial agent) oxidation during the NO3−RR. b Ammonia synthesis rates and selectivity evaluation by adding different types of simulated wastewater into the catalysis system (Catal. Sys.), including the organic matter (phenol, benzyl alcohol and formaldehyde), cation (Co2+, Ni2+ and Cd2+) and anion (SO42−, PO43− and CO32−) contaminants correspondingly. As for the condition of formaldehyde, the catalytic tests were conducted with and without EG respectively.
Most importantly, it should be noted that abundant organic contaminants are distributed in many NO3−-containing emission conditions such as agricultural and chemical wastewater degradation and drinking water purification, in which the organic contaminants can be utilized as what is called the hole sacrificial agent. Based on this consideration, phenol, benzyl alcohol and formaldehyde were added into the catal. sys. as potential contaminants respectively (Fig. 6b and Supplementary Fig. 50a–f). It is found that the ammonia synthesis rates and selectivity are all retained, which indicates that the NO3−RR route is established in the simulated organic wastewater. Interestingly, the ammonia synthesis rates are increased in the order of conventional catal. sys. (3.78 mmol g−1 h−1) < benzyl alcohol (5.37 mmol g−1 h−1) < phenol (7.64 mmol g−1 h−1) < formaldehyde (8.99 mmol g−1 h−1). It is deduced that the hole consumption capacity of these organic contaminants is higher than that of EG, which leaves more electrons to catalyze the NO3−RR. Then, the corresponding test of formaldehyde was conducted without EG as the hole sacrificial agent (Fig. 6b and Supplementary Fig. 50g–h). It is observed that the ammonia synthesis rate is further elevated to 11.14 mmol g−1 h−1 with 97.82% of selectivity noted, which reveals that the formaldehyde can act as the “hole sacrificial agent” more efficiently than that of EG. Based on the organic contaminant investigation in the simulated wastewater, it is clarified that the NO3−RR route can be developed as a “sacrificial-agent-free” technology for the application of ammonia synthesis in wastewater coupled with the organic pollutants’ oxidation, which demonstrates scientific significance in both areas of environmental remediation and energy conversion. Besides, the addition of cation contaminants (Co2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+, Supplementary Fig. 51) and anion contaminants (SO42+, PO43− and CO32−, Supplementary Fig. 52) have also been considered, in which the catalytic efficiency is accomplished in general. Some discrepancy in the performance is noted among these ions, which could be raised by the complicated impact of added ions on the catal. sys. and requires further investigation in the future.
Discussion
In summary, a highly active and selective NO3−RR for NH4+ photosynthesis was achieved by operando construction of subnanometric MONCs on TNS. The dynamic evolution pattern, growth mechanism, and interfacial structure of MONCs were characterized and well-defined. A superior NH4+ photosynthesis rate, selectivity, long-term stability and total yield were achieved among the various NH4+ synthesis routes under ambient conditions. Then it was proposed that the unique electronic structure at the MONCs/TNS interface was mainly responsible for the enhanced NO3− dissociation and eight-electron reduction reaction. The practical application of NO3−RR route in simulated wastewater was developed, which demonstrated scientific significance in both areas of environmental remediation and energy conversion. The discovery of subnanometric MONCs for sustainable NO3−-NH4+ photosynthesis is inspiring and is of general knowledge, thereby providing numerous opportunities for research into cluster chemistry and artificial photosynthesis.
Methods
Chemicals
All chemicals were purchased without further treatment. The respective source and purity were listed in Supplementary Table 3.
Synthesis of TNS
The synthesis of TiO2 nanosheets (TNS) was conducted via slight modification of the reported work49,50. In a typical preparation procedure, 3 mL of HF solution was dropped slowly into 25 mL of Ti(OBu)4•(TBOT) under continuous magnetic stirring for 2 h until the solution formed into a gel-like solution. Then the mixture was transferred into a Teflon autoclave with a volume of 50 mL and then heated at 180 °C for 24 h. After naturally cooling down to room temperature, the powder was separated and collected by high-speed centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 5 min with distilled water (DI) and ethanol washing for at least 10 times respectively, which removes the residual organic matter and F−. At last, the obtained sample was dried at 80 °C overnight in the vacuum drying oven.
Construction of MONCs on TNS
Five milligrams of TNS powder was dispersed in 100 mL of reaction solution containing 10 mg/L of NO3−-N, 50 mg/L of alkaline earth chlorides (MgCl2, CaCl2, SrCl2, and BaCl2 respectively) and 10 mL EG. Then the mixture was transferred into a photocatalytic reactor (MC-GF250, Merry Change, China) and degassed for soluble air with high-purity Ar (99.999%) at 50 mL/min for 30 min under stirring. A 300 W Xe lamp (MC-X301B, Merry Change, China) was used at the light source. After 1 h’s irradiation with continuous Ar pumping and stirring, the obtained powder was collected by washing with ethanol and DI for three times respectively. With the irradiation on stream, the reaction mixture was extracted several times for the tests of MX+ concentration and operando evolution of MONCs on the substrate surface.
Catalyst characterization
The crystal information was examined by the X-ray diffraction (XRD, model D/max RA, Rigaku Co.) technology. The morphology was surveyed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, XL30 ESEM FEG), transmission electron microscopy (TEM, FEI Talos F200S). The operando evolution of MONCs was verified by quasi in situ high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM, JEOL JEM-ARM200F) with spherical aberration correction to investigate the morphology at the atomic scale. The chemical composition was tested via the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Thermo Scientific K-Alpha plus) with an Al Kα X-ray light source. The elemental component analysis was conducted by X-ray fluorescence (XRF, BRUKER, M4 TORNADO). The solid-state EPR (JES FA200) spectra were performed to identify the vacancy signals.
Optical and electronic property identification
The light absorption capacity was performed by a scanning UV–vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-2450) outfitted with an integrating sphere, using barium sulfate as the comparison sample. The Mott-Schottky spectra were conducted using catalysts/C, Ag/AgCl and Pt as working, reference and counter electrodes respectively on an electrochemical workstation (CHI-660E), and the results were recorded from −1.0 to 1.5 V at 1000 Hz without light irradiation. The steady photoluminescence (PL) spectra were investigated using a fluorescence spectrophotometer (Edinburgh Instruments FLSP-920). Time-resolved fluorescence emission decay spectra (PicoQuant Fluotime 300) were carried out to verify the carrier’s life time under light irradiation. The liquid-state EPR spectra of active radicals were obtained on a JES FA200 spectrometer to investigate the production of the ROS under light illumination. The 5, 5-Dimethyl-1-Pyrroline-N-Oxide (DMPO) was used as the trapping agent to confirm the involvement of DMPO-•OH and DMPO-•O2− respectively in aqueous methanol dispersion. 4-oxo-2, 2, 6, 6-Tetramethyl-1-Piperidinyloxy (TEMP) was applied to survey the TEMP-1O2 and TEMP-1-oxyl (TEMPO) was used to characterize the photo-induced electrons (TEMPO-e−).
DFT calculation
The spin-polarized DFT calculations were operated with the “Vienna ab initio simulation package” (VASP 5.4), in which the PBE exchange-correlation functional was included51–53. The PBE + U correction (U = 4.0 eV) was implemented to account for the on-site charge interaction of the d electrons in Ti elements54, which improved the accuracy for the calculations of electron migration at the MONCs-TNS interfaces. The cut-off energy was set to 400 eV. K points in the Brillouin zone were set to 5 × 5 × 1 for both structural and electronic optimization. Geometry relaxation was achieved after the residual forces were smaller than 0.01 eV Å−1. The Gaussian smearing width was set to 0.2 eV. The initial calculation model of TNS contains 60 Ti atoms and 120 O atoms respectively (Supplementary Fig. 12a). The typical [001] facet is exposed for further calculations. The lattice parameters were set to 11 × 15 × 25 Å3, which contains a vacuum slab of 15 Å to impede the potential interaction between neighboring lattices. The initial calculation models of MgONCs, CaONCs, SrONCs and BaONCs were constructed with the cluster size of 0.73, 0.83, 0.89, and 0.96 nm respectively (Supplementary Fig. 12b–e)
The adsorption energy (Eads) for molecules was calculated as follows:
| 9 |
where Etot, Ecat., and Emol depicted the total energy of adsorption structure, catalyst support, and isolated molecule respectively.
The Gibbs free energy variation (ΔG)55,56 between the initial state (IS) and final state (FS) was determined with the following equation
| 10 |
where EFS and EIS referred to the DFT total energy for FS and IS correspondingly. ΔEZPE and ΔS denoted the variation of zero-point energy and entropy. The room temperature (T, 298.15 K) was applied.
The climbing image-nudged elastic band (CI-NEB)57,58 code was conducted to identify the reaction coordinates from IS to FS, which located the transition state (TS) with single imaginary frequency verification. The activation energy (Ea) and reaction energy (Er) were defined as follows
| 11 |
| 12 |
where EIS, ETS, and EFS were DFT calculated total energy of IS, TS, and FS respectively.
NO3−–NH4+ photosynthesis efficiency test
Photosynthesis tests were first conducted to determine the activity enhancement by operando MONCs construction. In a typical experimental procedure, 5 mg of TNS powder was dispersed in 100 mL of reaction solution containing 10 mg/L of NO3−-N, 50 mg/L of alkaline earth chlorides (MgCl2, CaCl2, SrCl2, and BaCl2 respectively) and 10 mL EG. Then the mixture was transferred into a photocatalytic reactor (MC-GF250, Merry Change, China) and degassed for soluble air with Ar at 50 mL/min for 30 min under stirring. A 300 W Xe lamp (MC-X301B, Merry Change, China) was used at the light source. After the photocatalysis reaction, the operando construction of MONCs on TNS is accomplished. The photocatalysts were collected and washed for further characterization. The blank control experiment was also performed, which excluded the catalysts and NO3−-N respectively. The consumed NO3− and produced NH4+ were both detected by ion chromatography (IC, Shimadzu IC-16 for NH4+ and Analysis Lab CS2000 for NO3− respectively). After that, the reaction parameter was comprehensively optimized to obtain the optimal NH4+ photosynthesis efficiency, which included NO3−-N concentration (from 10 to 500 mg/L), catalyst dosage (from 0.5 to 5 mg) and the irradiation source (UV, full spectrum and simulated solar light). The pH of this catalytic system remains at ca. 7.0 during the test since the KNO3 and EG consist of neutral solutions (Supplementary Fig. 53). The temperature is controlled at 25 °C by using the circulating chiller (Supplementary Fig. 54).
The quantitative 15N isotope tracing measurement was conducted, using 10 mg/L of K14NO3 and K15NO3 as the feedstock respectively, the produced 14NH4+ and 15NH4+ were quantified by IC. Then the 1H NMR (Bruker 400 M) was used to complement the IC results. As for the long-term stability test, the NO3−-N concentration was increased to 500 mg/L to guarantee sufficient feedstock. Meanwhile, the catalyst dosage was increased to 50 mg to elevate the total yield of NH4+. In order to investigate the NH4+ selectivity, the H2 was also detected during the NO3−RR, using gas chromatography (Kechuang GC 2002) with the thermal conductivity detector (TCD). The selectivity was calculated as follows
| 13 |
In situ DRIFTS investigation
In situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS, Bruker INVENIO R) was utilized to monitor the adsorbed species on the BaONCs-TNS surface within the reaction process, in which an in situ diffuse-reflectance cell (Harrick) and a reaction chamber (HVC) were equipped. Before measurement, the catalyst was mixed into 100 mg/L of NO3−-N solution by continuous stirring and then dried at 110 °C in a vacuum drying oven. The as-prepared sample was transferred in the reaction chamber and heated for 30 min at 110 °C to completely remove the adsorbed species on the surface. High-purity He (99.999%) was continuously pumped into the reaction system to maintain the inert atmosphere. A Xe lamp was used as the light source. The IR detection was conducted during the light irradiation.
Practical applications in simulated wastewater
Some potential contaminants were added into the catalysis system of BaONCs-TNS to evaluate the NO3−RR performance in simulated wastewater, including phenol, benzyl alcohol, and formaldehyde as organic matters, Co2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+ as cations, SO42−, PO43− and CO32− as anions respectively. CoCl2, NiCl2, and CdCl2 were used as the source of cations. K2SO4, K3PO4, and K2CO3 were used as the source of anions respectively. Based on the formaldehyde test, the EG is excluded from the reaction mixture for comparison. The concentration variation of SO42−, PO43−, and CO32− is determined by ion chromatograph (Shimadzu IC-16). An inductive coupled plasma emission spectrometer (Agilent ICPOES730) is applied to reveal the concentration of Co2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+. Phenol and benzyl alcohol were tested on the liquid chromatography (Shimadzu LC-20AT). In addition, we measured the concentration of formic acid as the oxidative product of formaldehyde by IC (Shimadzu IC-16).
Supplementary information
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National key R&D project of China (Grant No. 2020YFA0710000), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21822601, 22176029, and 22006009), Excellent Youth Foundation of Sichuan Scientific Committee Grant in China (No. 2021JDJQ0006), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (ZYGX2019Z021) and the 111 Project (B20030).
Author contributions
J.Y.L and F.D. conceived and designed the experiments. J.Y.L., R.M.C., and J.L.W carried out the materials fabrication, performance tests, characterizations, and calculations. Y.Z. and G.D.Y. helped analyzed the experimental data. J.Y.L. and F.D. wrote the paper, and all authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Bing-Jie Ni, X and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Data availability
All data generated in this study are provided in the Source Data files, in which the data presented in Figures from the Maintext and Supplementary Information are listed in the Excel files of Source Data 1 and Source Data 2 respectively.
Code availability
Only the commercial codes were used in this work (See references).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41467-022-28740-8.
References
- 1.Rod TH, Logadottir A, Norskov JK. Ammonia synthesis at low temperatures. J. Chem. Phys. 2000;112:5343–5347. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen JG, et al. Beyond fossil fuel-driven nitrogen transformations. Science. 2018;360:eaar6611. doi: 10.1126/science.aar6611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ye TN, et al. Vacancy-enabled N2 activation for ammonia synthesis on an Ni-loaded catalyst. Nature. 2020;583:391–395. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2464-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Comer BM, et al. Prospects and challenges for solar fertilizers. Joule. 2019;3:1578–1605. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Qing G, et al. Recent advances and challenges of electrocatalytic N2 reduction to ammonia. Chem. Rev. 2020;120:5437–5516. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Guo J, Chen P. Interplay of alkali, transition metals, nitrogen, and hydrogen in ammonia synthesis and decomposition reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021;54:2434–2444. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lehnert N, Dong HT, Harland JB, Hunt AP, White CJ. Reversing nitrogen fixation. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018;2:278–289. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Minteer SD, Christopher P, Linic S. Recent developments in nitrogen reduction catalysts: a virtual issue. ACS Energy Lett. 2019;4:163–166. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang Y, Wang C, Li M, Yu Y, Zhang B. Nitrate electroreduction: mechanism insight, in situ characterization, performance evaluation, and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021;50:6720–6733. doi: 10.1039/d1cs00116g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li J, et al. Efficient ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate on strained ruthenium nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020;142:7036–7046. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c00418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen GF, et al. Electrochemical reduction of nitrate to ammonia via direct eight-electron transfer using a copper–molecular solid catalyst. Nat. Energy. 2020;5:605–613. [Google Scholar]
- 12.van Langevelde PH, Katsounaros I, Koper MTM. Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction for sustainable ammonia production. Joule. 2021;5:1–5. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wu ZY, et al. Electrochemical ammonia synthesis via nitrate reduction on Fe single atom catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:2870. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23115-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li L, et al. Efficient nitrogen fixation to ammonia through integration of plasma oxidation with electrocatalytic reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021;60:14131–14137. doi: 10.1002/anie.202104394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu Y, et al. Pothole-rich ultrathin WO3 nanosheets that trigger N identical with N bond activation of nitrogen for direct nitrate photosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019;58:731–735. doi: 10.1002/anie.201808177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hirakawa H, Hashimoto M, Shiraishi Y, Hirai T. Selective nitrate-to-ammonia transformation on surface defects of titanium dioxide photocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2017;7:3713–3720. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhang X, et al. Recent advances in non-noble metal electrocatalysts for nitrate reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;403:126269. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhou L, et al. Electron flow shifts from anode-respiration to nitrate reduction during electroactive biofilm thickening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020;54:9593–9600. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c01343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kani NC, et al. Solar-driven electrochemical synthesis of ammonia using nitrate with 11% solar-to-fuel efficiency at ambient conditions. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021;14:6349–6359. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gao Z, et al. Constructing well-defined and robust Th-MOF-supported single-site copper for production and storage of ammonia from electroreduction of nitrate. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021;7:1066–1072. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c00370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Smith KEC, Jeong Y. Passive sampling and dosing of aquatic organic contaminant mixtures for ecotoxicological analyses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021;55:9538–9547. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c08067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang Y, Zhou W, Jia R, Yu Y, Zhang B. Unveiling the activity origin of a copper-based electrocatalyst for selective nitrate reduction to ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020;59:5350–5354. doi: 10.1002/anie.201915992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li P, Jin Z, Fang Z, Yu G. A single-site iron catalyst with preoccupied active centers that achieves selective ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021;14:3522–3531. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lim J, et al. Structure sensitivity of Pd facets for enhanced electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia. ACS Catal. 2021;11:7568–7577. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hao Y-C, et al. Promoting nitrogen electroreduction to ammonia with bismuth nanocrystals and potassium cations in water. Nat. Catal. 2019;2:448–456. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xue X, et al. Review on photocatalytic and electrocatalytic artificial nitrogen fixation for ammonia synthesis at mild conditions: advances, challenges and perspectives. Nano Res. 2019;12:1229–1249. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jiang K, et al. Metal ion cycling of Cu foil for selective C–C coupling in electrochemical CO2 reduction. Nat. Catal. 2018;1:111–119. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Liu L, Corma A. Confining isolated atoms and clusters in crystalline porous materials for catalysis. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021;6:244–263. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Babucci M, Guntida A, Gates BC. Atomically dispersed metals on well-defined supports including zeolites and metal-organic frameworks: structure, bonding, reactivity, and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2020;120:11956–11985. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Corma A, et al. Exceptional oxidation activity with size-controlled supported gold clusters of low atomicity. Nat. Chem. 2013;5:775–781. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tyo EC, Vajda S. Catalysis by clusters with precise numbers of atoms. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015;10:577–588. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liu L, et al. Structural modulation and direct measurement of subnanometric bimetallic PtSn clusters confined in zeolites. Nat. Catal. 2020;3:628–638. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Craciun V, Singh RK. Characteristics of the surface layer of barium strontium titanate thin films deposited by laser ablation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000;76:1932–1934. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Miot C, Husson E, Proust C, Erre R, Coutures JP. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy characterization of barium titanate ceramics prepared by the citric route. Residual carbon study. J. Mater. Res. 2011;12:2388–2392. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang S, et al. Light-switchable oxygen vacancies in ultrafine Bi5O7Br nanotubes for boosting solar-driven nitrogen fixation in pure water. Adv. Mater. 2017;29:1701774. doi: 10.1002/adma.201701774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ricci D, Bano G, Pacchioni G, Illas F. Electronic structure of a neutral oxygen vacancy in SrTiO3. Pyhs. Rev. B. 2003;68:224105. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Qi Y, et al. Photoinduced defect engineering: enhanced photothermal catalytic performance of 2D black In2O3-x nanosheets with bifunctional oxygen vacancies. Adv. Mater. 2020;32:1903915. doi: 10.1002/adma.201903915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Li J, et al. The spatially oriented charge flow and photocatalysis mechanism on internal van der Waals heterostructures enhanced g-C3N4. ACS Catal. 2018;8:8376–8385. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hadjiivanov K, Knözinger H. Species formed after NO adsorption and NO+O2 co-adsorption on TiO2: an FTIR spectroscopic study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000;2:2803–2806. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kantcheva M. Identification, stability, and reactivity of NOx species adsorbed on titania-supported manganese catalysts. J. Catal. 2001;204:479–494. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hadjiivanov K, Avreyska V, Klissurski D, Marinova T. Surface species formed after NO adsorption and NO + O2 coadsorption on ZrO2 and sulfated ZrO2: an FTIR spectroscopic study. Langmuir. 2012;18:1619–1625. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li P, et al. Visible light-driven nitrogen fixation catalyzed by Bi5O7Br nanostructures: enhanced performance by oxygen vacancies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020;142:12430–12439. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c05097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Li H, Shang J, Ai Z, Zhang L. Efficient visible light nitrogen fixation with BiOBr nanosheets of oxygen vacancies on the exposed {001} facets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015;137:6393–6399. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b03105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhao Y, et al. Layered-double-hydroxide nanosheets as efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysts for dinitrogen fixation. Adv. Mater. 2017;29:1703828. doi: 10.1002/adma.201703828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pigos JM, Brooks CJ, Jacobs G, Davis BH. Low temperature water-gas shift: characterization of Pt-based ZrO2 catalyst promoted with Na discovered by combinatorial methods. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2007;319:47–57. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lukaski A. Photocatalytic oxidation of methyl formate on TiO2: a transient DRIFTS study. J. Catal. 2004;223:250–261. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gao H, Yan T. DFT and DRIFTS study on the vibrational spectra of formate species adsorbed on the Cu–Al2O3 catalyst. J. Mol. Struct. 2008;889:191–196. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Corral-Pérez JJ, Copéret C, Urakawa A. Lewis acidic supports promote the selective hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to methyl formate in the presence of methanol over Ag catalysts. J. Catal. 2019;380:153–160. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wan J, et al. Defect effects on TiO2 nanosheets: stabilizing single atomic site au and promoting catalytic properties. Adv. Mater. 2018;30:1705369. doi: 10.1002/adma.201705369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liu G, et al. Visible light responsive nitrogen doped anatase TiO2 sheets with dominant {001} facets derived from TiN. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:12868–12869. doi: 10.1021/ja903463q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B. 1996;54:11169–11186. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.54.11169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996;77:3865–3868. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comp. Mater. Sci. 1996;6:15–50. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.54.11169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Dudarev SL, Botton GA, Savrasov SY, Humphreys CJ, Sutton AP. Electron-energy-loss spectra and the structural stability of nickel oxide. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1998;57:1505–1509. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zuluaga S, Stolbov S. Factors controlling the energetics of the oxygen reduction reaction on the Pd-Co electro-catalysts: insight from first principles. J. Chem. Phys. 2011;135:134702. doi: 10.1063/1.3643714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Norskov JK, et al. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004;108:17886–17892. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Henkelman G. A climbing image nudged elastic band method for finding saddle points and minimum energy paths. J. Chem. Phys. 2000;113:9901–9904. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Henkelman G, Jónsson H. Improved tangent estimate in the nudged elastic band method for finding minimum energy paths and saddle points. J. Chem. Phys. 2000;113:9978–9985. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ren HT, Jia SY, Zou JJ, Wu SH, Han X. A facile preparation of Ag2O/P25 photocatalyst for selective reductionof nitrate. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2015;176-177:53–61. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Anderson JA. Simultaneous photocatalytic degradation of nitrate and oxalic acid over gold promoted titania. Catal. Today. 2012;181:171–176. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tong N, et al. PdSn/NiO/NaTaO3:La for photocatalytic ammonia synthesis by reduction of NO3− with formic acid in aqueous solution. J. Catal. 2018;361:303–312. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Luo YR, et al. Efficient electrocatalytic N2 fixation with MXene under ambient conditions. Joule. 2019;3:279–289. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wu T, et al. Identifying the origin of Ti(3+) activity toward enhanced electrocatalytic N2 reduction over TiO2 nanoparticles modulated by mixed-valent copper. Adv. Mater. 2020;32:2000299. doi: 10.1002/adma.202000299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Han LL, et al. Modulating single-atom palladium sites with copper for enhanced ambient ammonia electrosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021;60:345–350. doi: 10.1002/anie.202010159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ghorai UK, et al. Scalable production of cobalt phthalocyanine nanotubes: efficient and robust hollow electrocatalyst for ammonia synthesis at room temperature. ACS Nano. 2021;15:5230–5239. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c10596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Sim HYF, et al. ZIF-induced d-band modification in a bimetallic nanocatalyst: achieving over 44% efficiency in the ambient nitrogen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020;59:16997–17003. doi: 10.1002/anie.202006071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Su HY, et al. Single atoms of iron on MoS2 nanosheets for N2 electroreduction into ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020;59:20411–20416. doi: 10.1002/anie.202009217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Bi K, et al. Charge carrier dynamics investigation of Cu2S–In2S3 heterostructures for the conversion of dinitrogen to ammonia via photo-electrocatalytic reduction. J. mater. Chem. A. 2021;9:10497–10507. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Liu D, et al. Photoelectrochemical synthesis of ammonia with black phosphorus. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30:2002731. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zheng J, et al. Photoelectrochemical synthesis of ammonia on the aerophilic-hydrophilic heterostructure with 37.8% efficiency. Chem. 2019;5:617–633. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Chen C, et al. Coupling N2 and CO2 in H2O to synthesize urea under ambient conditions. Nat. Chem. 2020;12:717–724. doi: 10.1038/s41557-020-0481-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Tao H, et al. Nitrogen fixation by Ru single-atom electrocatalytic reduction. Chem. 2019;5:204–214. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wang W, et al. Potassium-ion-assisted regeneration of active cyano groups in carbon nitride nanoribbons: visible-light-driven photocatalytic nitrogen reduction. Angew. Chem. Int Ed. Engl. 2019;58:16644–16650. doi: 10.1002/anie.201908640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Shang S, et al. Atomically dispersed iron metal site in a porphyrin-based metal–organic framework for photocatalytic nitrogen fixation. ACS Nano. 2021;15:9670–9678. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c10947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Chen LW, et al. Metal-organic framework membranes encapsulating gold nanoparticles for direct plasmonic photocatalytic nitrogen fixation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021;143:5727–5736. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c13342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Data Availability Statement
All data generated in this study are provided in the Source Data files, in which the data presented in Figures from the Maintext and Supplementary Information are listed in the Excel files of Source Data 1 and Source Data 2 respectively.
Only the commercial codes were used in this work (See references).