Abstract
Background
Myocardial infarction (MI) remains the leading cause of death and disability among cardiovascular diseases worldwide. Studies show that elevated low-density lipid protein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels confer the highest absolute risk of MI, and Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is implicated in regulating levels of triglycerides (TGs), cholesterol, and LDL-C. Our study aimed to evaluate the association between APOE polymorphism and MI, and to provide evidence for the etiology of MI.
Methods
Case–control studies on the association between APOE polymorphisms and the risk of myocardial infarction were included by searching PubMed, Web of Science, and CNKI, and this meta-analysis was written in accordance with PRISMA guideline statement. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using either random-effects or fixed-effects models by R software.
Results
A total of 33 eligible articles involving 13,706 cases and 14,817 controls were finally selected. The pooled analysis based on the total eligible articles showed that the risk of MI was associated with ApoE epsilon 2 and epsilon 4 alleles. The results showed that patients with MI had a low frequency of the ε2 allele (OR 0.74, 95% CI 0.64–0.86) and a high frequency of the ε4 allele (OR 1.24, 95% CI 1.09–1.42).
Conclusions
APOE ε2-involved genotypes may be protective factors for MI; in contrast, ε4-involved genotypes (ε4/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3, and ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3) may be risk factors for MI.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12872-022-02566-0.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein E polymorphism, Myocardial infarction, Meta-analysis
Introduction
Myocardial infarction (MI) remains the leading cause of death and disability among cardiovascular diseases worldwide [1]. Blood lipid abnormalities are implicated in MI: elevated low-density lipid protein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels confer the highest absolute risk of MI [2]. Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is implicated in regulating levels of triglycerides (TGs), cholesterol, and LDL-C [3]. Myocardial infarction is usually due to thrombotic occlusion of a coronary vessel caused by the rupture of a vulnerable plaque [4]. Ischemia induces severe ion disturbance in the myocardium [4]. Vulnerable plaques tend to have 30 − 50% stenosis, thin fibrous caps and contain more inflammatory cells such as lipid-laden macrophages [5]. Infiltrated phagocytes clear dead cells and matrix debris, activate anti-inflammatory pathways, and inhibit cytokine and chemokine signaling [4]. Activation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system and release of transforming growth factor-beta promotes the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts [4].
Epidemiological findings show that the impact of myocardial infarction on global health is significant, with more than one-third of deaths in developed countries [5]. Today, NSTEMI (non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction) accounts for 60–75% of all myocardial infarctions. In addition, both in-hospital and 1-year mortality from STEMI (ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction) has declined over the past two decades (5–6% and 7–18%, respectively) [5]. The prevalence of MINOCA (myocardial infarction with no obstructive coronary atherosclerosis) was 6% (95% CI 5–7%), the median age of patients was 55 years (95% CI 51–59 years), and 40% were female. The 12-month mortality in MINOCA patients was 4.7% (95% CI 2.6–6.9%) [6]. The Framingham Heart Study’s 10- year follow-up data revealed that the incidence of MI was 12.9, 38.2, and 71.2 per 1000 in men and 2.2, 5.2, and 13.0 per 1000 in women in the age groups of 30–34, 35–44, and 45–54 years, respectively[7].
The study showed that, regardless of age, more women than men died within one year of the first acute myocardial infarction (AMI) (26% of women and 19% of men respectively) and more women than men died within 5 years of the first AMI (47% of women and 36% of men). At 5 and 10 years after AMI, women had a higher unadjusted mortality rate compared to men and had a 30% readmission rate within 30 days of the first hospitalization, partly due to differences in age, MI risk factors, clinical presentation, and treatment. Women also have a higher prevalence of heart failure and diabetes mellitus (DM) compared to men[8]. A meta-analysis has also shown that myocardial infarction is associated with genotype[9].
The exon 4 of APOE has two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (rs7412 and rs429358). The two SNPs are used to define the three major alleles of APOE (ε2, ε3, and ε4). Allele ε3 possesses cytosines in the amino-acid-coding positions corresponding to rs7412 and rs429358, conferring APOE3 with arginine at residue 158 and cysteine on residue 112 [10]. ε2 arises from substitution rs7412C>T, and rs429358C>T results in ε4. Thus, APOE2 carries cysteine at residue 158 and 112, and APOE4 carries arginine on both positions [11]. Because allele ε3 is the most common in populations, this allele is used as “wild-type”. ε2 and ε4 are used as variants of APOE alleles [12]. The six APOE haplotypes (ε2/ε2, ε2/ε3, ε2/ε4, ε3/ε3, ε3/ε4, and ε4/ε4) are formed by combinations of these three alleles [13].
Associations of APOE polymorphism and MI risks have been investigated extensively [14–17]. In 2014, Xu H. et al. performed a meta-analysis, finding that the frequency of MI increases for ε4ε4 vs. ε3ε3 (OR 1.59, 95% CI 1.15–2.19, P = 0.005); whereas, no significant association exists in ε2ε2 vs. ε3ε3 (OR 0.73, 95% CI 0.40–1.32, P = 0.29) [18]. In contrast, a meta-analysis issued in 2015 revealed that, for ε2ε2 vs. ε3ε3, a decreased frequency of MI exists (OR 0.40, 95% CI 0.20–0.83, P = 0.00), except in Caucasian and Asian populations, and no significant association exists in ε4ε4 vs. ε3ε3 (OR 1.34, 95% CI 0.91–1.98, P = 0.186) in these populations [19].
Possible reasons for the above results are: (1) they had different inclusion and exclusion criteria: Xu H. et al.'s study in 2014 did not consider cancer risk, but such studies were included in the 2015 article, further led to a large difference in the number of articles finally included in the study between the two: in 2014 (n = 33); in 2015 (n = 22); (2) the results of 2015 divided the ethnic group into three subgroups and found that Caucasians and Asians have different gene expression frequencies compared to other ethnic groups. But 2014 results only compared two subgroups of Caucasians and Asians. Thus, we conducted an up-to-date meta-analysis to resolve these conflicting results.
Materials and methods
Search strategy
According to the PRISMA guideline, we searched all articles published before May 1, 2021, from both English databases (PubMed, and Web of Science database) and Chinese databases (CNKI database) using the combination of keywords (“Apolipoprotein E” OR “ApoE” OR “APOE” AND “myocardial infarction” OR “MI” AND “polymorphism” OR “polymorphisms” OR “variants” OR “variant”). In addition, we searched related articles that had not been included in the initial search using Google (www.google.com).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Articles were included for further selection if they fulfilled the inclusion criteria: (1) articles issued in English or Chinese were performed under either hospital-based or population-based design; (2) evaluation of the association between APOE polymorphisms and MI was involved and the data can be extracted in articles; and (3) odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were evaluated or sufficient data were suggested to assess associations. Articles were removed according to the exclusion criteria: (1) non-English or non-Chinese articles; (2) abstracts, conference records, systematic reviews or meta-analysis, and articles without case–control studies; (3) articles with insufficient data to calculate the ORs and 95% CIs; (4) the data originated from the online dataset; (5) articles lacking usable data on genotypes or allele frequencies; and “star”, which was delimited in the 2.3 section judged (6) low-quality articles.
Data extraction and quality assessment
All included articles were identified by two investigators (Jikang Shi and Zhuoshuai Liang). If the two investigators could not agree on an included article, the third investigator (Lingfeng Pan) settled in conformity finally. We collected the following data (first author's name, publication year, ethnicity, distribution of genotypes and alleles in MI cases and controls, sample sizes of MI cases and controls, and evidence of conforming to the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) among controls). The other information was extracted, such as sex and the last name of the first author. We evaluated the quality of the included articles using the Newcastle–Ottawa scale (NOS). It allocated a score of one point when an included article met a condition; otherwise, no point (0 scores) was allocated. Furthermore, for each included article, the sum of all points (total Quality Score) represented the quality of this article [20]. Low-quality articles were also excluded to avoid selection bias.
Statistical analysis
The association of APOE polymorphisms and myocardial infarction was analyzed using R Studio (Version 1.1.383) (RStudio, Inc., MA, USA). We designated the ε3 allele and ε3/ε3 as the reference and collected the ORs and 95% CIs for evaluating the prognostic value of APOE polymorphisms. The pooled ORs and 95%CIs were estimated in the seven types (ε2/ε2 vs. ε3/ε3, ε2/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3, ε2/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3, ε4ε3 vs. ε3/ε3, ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3, ε2 allele vs. ε3 allele, and ε4 allele vs. ε3 allele).
Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) for each included article among control groups was evaluated using the Chi-square test of goodness, and HWE was rejected if P < 0.05. ORs and 95% CIs were used to assess the strength of association between APOE polymorphisms and MI risks. Heterogeneity sources were investigated based on the HWE test (Yes or No), score (< 6 or ≥ 6), and subgroup analysis for ethnicity (Asian or Other). Both Chi-square test-based Q-statistic and I2-statistic were utilized to evaluate heterogeneity. We carried out the comparisons of APOE genotypes, as genotypes can represent the combined effect of alleles. For heterogeneity between studies given by I2 > 50%, random-effect models were applied; otherwise, if I2 < 50%, fixed-effect models were used [21]. Furthermore, sensitivity analysis was used to assess the stability of articles. The publication bias of this meta-analysis was analyzed using funnel plot and Begg's test [22].
Trial sequential analysis (TSA)
Traditional meta-analysis is criticized because the data of articles are inevitably clinically diverse among patients, such as ethnicities and diseases states. Systematic bias and random errors result in false-positive results (type I errors) or overestimated treatment effects that may also be obtained by Meta-analyses. Because of neglecting heterogeneity, simply pooling the results is inappropriate [23].
Trial sequential analysis (TSA) provides the required sample size (RIS), analyzing monitoring boundaries of trial sequential if articles do not reach the RIS [24]. The horizontal ordinate is the sample size, and the vertical ordinate is the Z-curve score of the effect. The Z-curve in the upper half of the vertical ordinate indicates a protective effect. Rather, that in the lower half of the vertical ordinate indicates risk effect. The fewer participants and events are, the more restrictive the monitoring boundaries are needed. Furthermore, a much less P-value is required to obtain statistical significance [22]. TSA software (TSA, version 0.9.5.5; Copenhagen Trial Unit, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016) was used in this Meta-analysis. We set type I error as 5% and type II error as 20% [23]; thus, the statistical power was 80% (power = 1–20%). The relative risk reduction (RRR) was defined as 20%.
Results
Characteristics of studies
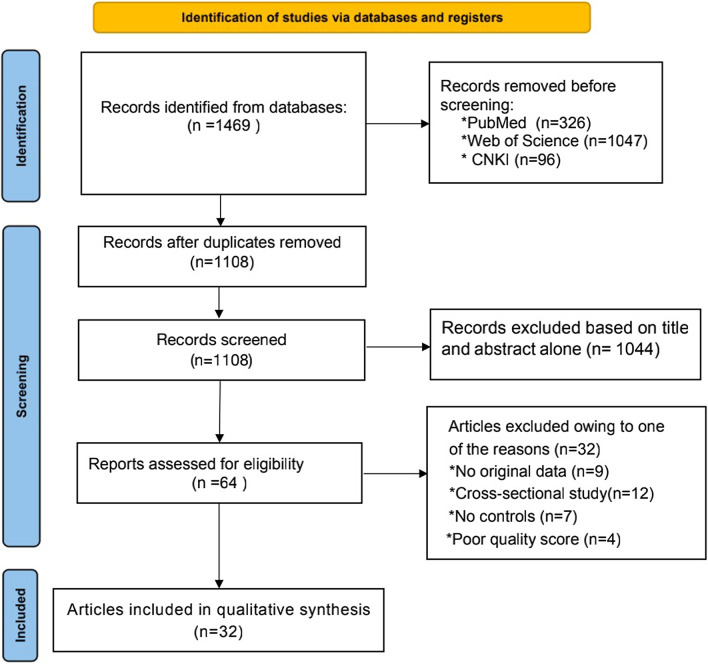
We scrutinized 1469 articles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, finally selecting 32 articles investigated in this meta-analysis [16, 25–51]. The selected 32 articles provided 13,706 cases with MI and 14,817 controls. (Fig. 1; Table 1).
Fig. 1.
Flow chart of the process for literature identification and selection
Table 1.
Main characteristics of the included studies
| Study | Year | Country | Ethnicity | Sample size | Quality | HWE | ApoE ε2 (n) | ApoE ε3 (n) | ApoE ε4 (n) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Control | Score | Y/N | Case | Control | Case | Control | Case | Control | ||||
| Cumming et al | 1984 | Scotland | Scottish | 239 | 239 | 7 | Y (P = 0.57) | 28 | 39 | 351 | 367 | 99 | 70 |
| Yamamura et al | 1984 | Germany | Caucasian | 523 | 1031 | 6 | N (P < 0.01) | 93 | 379 | 826 | 1594 | 127 | 09 |
| Utermann et al | 1984 | Japan | Japanese | 523 | 1031 | 5 | N (P = 0.01) | 93 | 379 | 826 | 1594 | 127 | 309 |
| Lenzen et al | 1986 | Germany | Caucasian | 570 | 624 | 8 | Y (P = 0.16) | 63 | 99 | 907 | 978 | 170 | 171 |
| Luc et al | 1994 | Belfast | Caucasian | 183 | 176 | 7 | Y (P = 0.57) | 25 | 36 | 270 | 266 | 71 | 50 |
| Luc et al | 1994 | Lille | Caucasian | 64 | 150 | 7 | Y (P = 0.98) | 6 | 33 | 105 | 223 | 17 | 44 |
| Luc et al | 1994 | Strasbourg | Caucasian | 187 | 172 | 7 | Y (P = 0.51) | 27 | 29 | 288 | 274 | 59 | 41 |
| Luc et al | 1994 | Toulouse | Caucasian | 140 | 182 | 7 | Y (P = 0.84) | 16 | 20 | 228 | 311 | 36 | 33 |
| Joven et al | 1998 | Spain | Caucasian | 250 | 250 | 6 | Y (P = 0.19) | 39 | 25 | 397 | 438 | 64 | 37 |
| Nakai et al | 1998 | Japan | Japanese | 254 | 422 | 6 | Y (P = 0.29) | 12 | 20 | 418 | 744 | 66 | 80 |
| Batalla et al | 2000 | Spain | Spainish | 220 | 200 | 8 | Y (P = 0.89) | 10 | 19 | 389 | 348 | 41 | 33 |
| Zhao et al | 2000 | Liaoning | Asian | 50 | 49 | 7 | Y (P = 0.76) | 4 | 5 | 90 | 90 | 6 | 3 |
| Raslová et al | 2001 | Slovak | Caucasian | 71 | 71 | 6 | Y (P = 0.30) | 12 | 7 | 111 | 114 | 13 | 17 |
| Wang et al | 2001 | Xinjiang | Asian | 54 | 106 | 6 | Y (P = 0.58) | 3 | 15 | 82 | 174 | 23 | 23 |
| Gong et al | 2001 | Guangdong | Asian | 108 | 115 | 7 | Y (P = 0.47) | 14 | 16 | 170 | 196 | 32 | 18 |
| Bai et al | 2001 | Liaoning | Asian | 47 | 113 | 6 | Y (P = 0.36) | 4 | 11 | 90 | 200 | 6 | 9 |
| Kolovou et al | 2002 | Greece, | Greek | 267 | 240 | 7 | Y (P = 0.72) | 39 | 39 | 412 | 392 | 83 | 49 |
| Mamotte et al | 2002 | Australia | Caucasian | 359 | 639 | 6 | Y (P = 1.54) | 39 | 92 | 554 | 983 | 125 | 203 |
| Kumar et al | 2003 | North India | Indian | 35 | 45 | 5 | N (P = 0.03) | 7 | 13 | 36 | 73 | 27 | 4 |
| Li et al | 2003 | Nantong | Asian | 67 | 152 | 5 | Y (P = 0.10) | 16 | 26 | 98 | 253 | 22 | 25 |
| Chen et al | 2003 | Liaoning | Asian | 50 | 110 | 5 | Y (P = 0.09) | 4 | 11 | 90 | 92 | 6 | 3 |
| Keavney et al | 2004 | UK | Caucasian | 4484 | 5757 | 6 | N (P < 0.01) | 440 | 686 | 6778 | 8830 | 1206 | 1376 |
| Ranjith et al | 2004 | Indian | African | 195 | 300 | 6 | N (P < 0.01) | 10 | 27 | 330 | 517 | 50 | 56 |
| Aasvee et al | 2006 | estonia | Caucasian | 71 | 85 | 8 | Y (P = 0.98) | 7 | 18 | 110 | 133 | 23 | 21 |
| Baum et al | 2006 | Hongkong | chinese | 231 | 311 | 6 | Y (P = 0.81) | 17 | 70 | 387 | 505 | 58 | 47 |
| Koch et al | 2008 | Germany | Caucasian | 3657 | 1211 | 6 | Y (P = 0.72) | 517 | 201 | 5769 | 1899 | 1028 | 322 |
| Viitanen et al | 2011 | Finland | Caucasian | 118 | 110 | 5 | Y (P = 0.98) | 7 | 10 | 171 | 175 | 58 | 35 |
| Onrat et al | 2012 | Turkey | Turkish | 100 | 36 | 6 | Y (P = 0.55) | 12 | 4 | 172 | 62 | 16 | 6 |
| Tanguturi et al | 2013 | India | Indian | 202 | 210 | 8 | Y (P = 0.18) | 12 | 17 | 329 | 371 | 63 | 32 |
| Kukava et al | 2017 | Russia | Russians | 405 | 198 | 7 | Y (P = 0.50) | 68 | 32 | 698 | 326 | 44 | 38 |
| Gupta et al | 2018 | India | Indian | 168 | 89 | 6 | Y (P = 0.54) | 18 | 4 | 302 | 165 | 16 | 9 |
| Hu et al | 2020 | Jiangxi | Asian | 53 | 632 | 7 | N (P = 0.02) | 128 | 28 | 1055 | 83 | 81 | 23 |
Quantitative synthesis
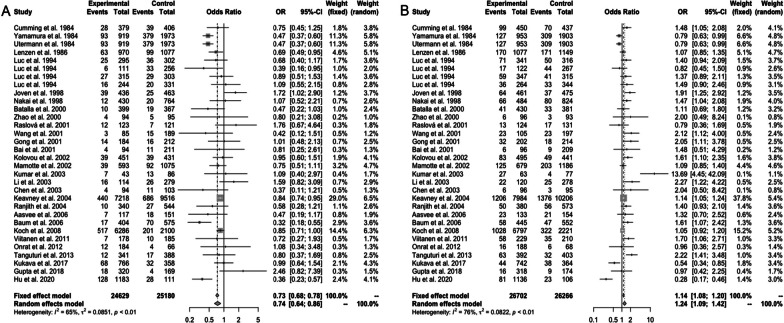
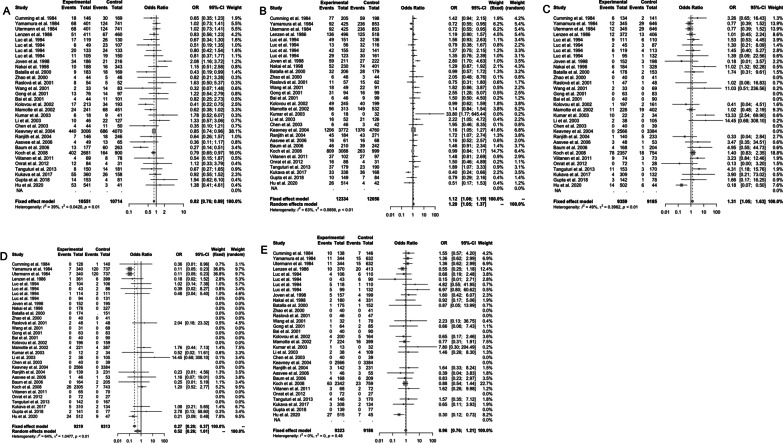
In the pooled analysis, the significant heterogeneity between APOE polymorphism and MI risks was found in ε2 vs. ε3 (I2 = 65%, P < 0.01) and ε4 vs. ε3 (I2 = 76%, P < 0.01). The random-effects model revealed that patients with MI had a low frequency of the ε2 (OR 0.74, 95% CI 0.64–0.86, P < 0.01) (Fig. 2A) and a high frequency of the ε4 (OR 1.24, 95% CI 1.09–1.42, P < 0.01) (Fig. 2B); the pooled OR of ε2/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3 was 0.82 (95% CI 0.76–0.89, P = 0.01) (Fig. 3A); the pooled OR of ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 was OR 1.20 (95% CI 1.05–1.37, P < 0.01) (Fig. 3B); and the pooled OR of ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 was OR = 1.31 (95% CI 1.05–1.63, P < 0.01) (Fig. 3C). However, compared with ε3/ε3, ε2/ε2 (Fig. 3D) and ε2/ε4 (Fig. 3E) might not influence MI risks (for ε2/ε2, OR 0.52, 95% CI 0.26–1.01, P < 0.01) (for ε2/ε4, OR 0.96, 95% CI 0.76–1.21, P = 0.48).
Fig. 2.
Forest plot for the association between myocardial infarction risk and APOE ε2 allele vs. ε3 allele (A); forest plot for the association between myocardial infarction risk and APOE ε4 allele vs. ε3 allele (B)
Fig. 3.
Forest plot for association between APOE polymorphism and MI risks in genotypes: A ε2/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3; B ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3; C ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3; D ε2/ε2 vs. ε3/ε3; E ε2/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3
Subgroup analysis
To find the potential source of heterogeneity, we ran meta-regression analysis before subgroup analysis, The results show that HWE is a source of heterogeneity in ε4 vs. ε3(P = 0.019); in ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3, both HWE (P = 0.0025)and ethnicity (P = 0.0294)are sources of heterogeneity.
We performed subgroup analysis based on the HWE, finding that articles satisfying the HWE had significant heterogeneity. Furthermore, we found that low MI risks existed in carriers of the ε2 allele (OR 0.82, 95% CI 0.74–0.90, P = 0.01) and those of ε2/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 0.75, 95% CI 0.67–0.85, P < 0.01); in contrast, high MI risks existed in carriers of the ε4 allele (OR 1.34, 95% CI 1.18–1.52, P < 0.01) and those of ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 1.27, 95% CI 1.09–1.48, P < 0.01). In addition, articles not satisfying the HWE had significant heterogeneity (for ε2 allele, P < 0.01; for ε4 allele, P < 0.01; for ε2/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3, P = 0.04; for ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3, P < 0.01; and for ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3, P < 0.01). Moreover, we found that low MI risks existed in carriers of the ε2 allele (OR 0.56, 95% CI 0.40–0.79, P < 0.01), but there were no associations of MI risks with carriers of ε4 allele or with those of ε4-involved (ε2/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3, and ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3) genotypes.
We carried out subgroup analysis based on ethnicity, finding that articles involving Asians had significant heterogeneity. The ε2 allele was a protective factor for MI (P < 0.01, OR 0.70, 95% CI 0.50–0.98); in contrast, the ε4 allele (P < 0.01, OR 1.56, 95% CI 1.04–2.35) and ε4/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3 (P < 0.01, OR 1.44, 95% CI 1.03–2.01) were risk factors for MI. In addition, there were no significant associations of MI risks with carriers of ε2/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (P = 0.27), with those of ε2/ε2 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 0.38, 95% CI 0.12–1.20, P = 0.16), with those of ε2/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 0.85, 95% CI 0.68–1.03, P = 0.34), or with those of ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 2.90, 95% CI 0.91–9.23, P = 0.48). Furthermore, we found that articles involving other ethnicities had significant heterogeneity. The ε2 allele was a protective factor for MI (P < 0.01, OR 0.78, 95% CI 0.67–0.91); on the contrary, the ε4 allele was a risk factor for MI (P < 0.01, OR 1.16, 95% CI 1.04–1.30). There was no significant heterogeneity of MI risks with carriers of ε2/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3 (P = 0.09), with those of ε2/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (P = 0.55), or with those of ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (P = 0.71). There was no significant association of MI risks with carriers of ε2/ε2 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 0.59, 95% CI 0.26–1.36, P = 0.09) or with those of ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 1.13, 95% CI 0.97–1.31, P = 0.63).
We carried out subgroup analysis based on the score, finding that articles satisfying the high score had no heterogeneity of MI risks with carriers of the ε2 allele (P > 0.05) or with those of ε2-involved genotypes (all P > 0.05). There was no significant association of MI risks with carriers of ε4 vs. ε3 (P < 0.01, OR 1.17, 95% CI 0.90–1.53), with those of ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (P < 0.01, OR 1.16, 95% CI 0.91–1.47), or with those of ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (P = 0.03, OR 1.32, 95% CI 0.89–1.94). In addition, articles not satisfying the low score showed that all genotypes had significant heterogeneity (all P < 0.01). Low MI risks existed in carriers of the ε2 allele (P < 0.01, OR 0.78, 95% CI 0.63–0.97); in contrast, high MI risks existed in carriers of the ε4 allele (P < 0.01, OR 0.78, 95% CI 1.09–1.50) or in those of ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (P < 0.01, OR 1.22, 95% CI 1.03–1.45). There were no significant associations of MI risks with carriers of ε2/ε2 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 1.22, 95% CI 1.03–1.4, P > 0.05), with those of ε2/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 0.87, 95% CI 0.72–1.60, P > 0.05), or with those of ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (OR 1.53, 95% CI 0.91–2.59) (Table 2).
Table 2.
Subgroup analysis of associations of MI risks with APOE alleles or with genotypes
| Variable | Asian | Other | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | I2 (%) | OR (95%CI) | I2 (%) | |
| Alleles | ||||
| ε2 | 0.70 (0.50,0.98) | 66 | 0.78 (0.67,0.91) | 55 |
| ε4 | 1.56 (1.04,2.35) | 86 | 1.16 (1.04,1.30) | 57 |
| Genotypes | ||||
| ε2/ε2 | 0.38 (0.12,1.20) | 62 | 0.59 (0.26, 1.36) | 61 |
| ε2/ε3 | 0.85 (0.60, 1.22) | 50 | 0.82 (0.75, 0.90) | 32 |
| ε2/ε4 | 0.96 (0.61, 1.51) | 19 | 0.96 (0.74, 1.25) | 0 |
| ε3/ε4 | 1.44 (1.03, 2.01) | 64 | 1.13 (0.97, 1.31) | 64 |
| ε4/ε4 | 2.90 (0.91, 9.23) | 79 | 1.19 (0.92, 1.55) | 0 |
ε2/ε2, ε2/ε3, ε2/ε4, ε3/ε4 and ε4/ε4 were compared with ε3/ε3. ε2 and ε4 were compared with ε3
Sensitivity analysis
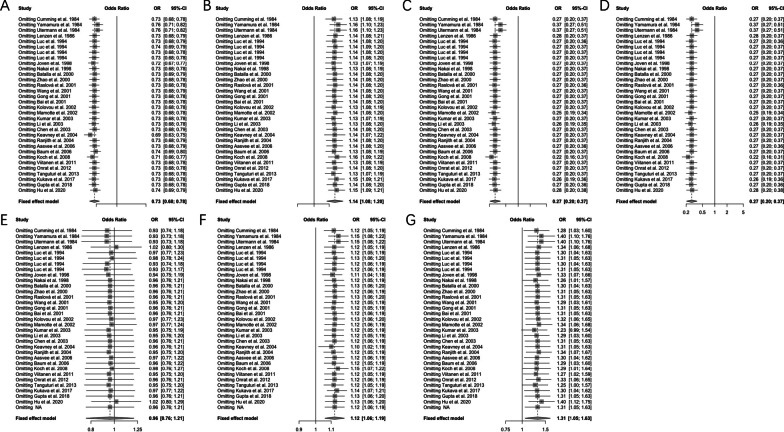
To clarify the sources of heterogeneity, sensitivity analyses were performed to assess the stability of the results and the source of the heterogeneity by omitting individual studies and to show the influence of the individual data on the total ORs. Results of sensitivity analysis on the ε2 allele (Fig. 4A), the ε4 allele (Fig. 4B), ε2/ε2 vs. ε3/ε3 (Fig. 4C), ε2/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3 (Fig. 4D), ε2/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (Fig. 4E), ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (Fig. 4F), and ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (Fig. 4G) were presented in Fig. 4. No individual article affected the corresponding pooled ORs and 95%CIs; therefore, the result of this meta-analysis was statistically robust (Tables 3, 4).
Fig. 4.
Forest plot of subgroup analysis of the association between APOE alleles/genotypes and myocardial infarction
Table 3.
Sensitivity analysis of associations between APOE alleles and MI risks
| Study | ε2 | ε4 |
|---|---|---|
| Cumming et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.13 (1.08, 1.19) |
| Yamamura et al | 0.76 (0.71, 0.82) | 1.16 (1.10, 1.23) |
| Utermann et al | 0.76 (0.71, 0.82) | 1.16 (1.10, 1.23) |
| Lenzen et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.79) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.21) |
| Luc et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.79) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Luc et al | 0.74 (0.69, 0.79) | 1.14 (1.09, 1.20) |
| Luc et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Luc et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Joven et al | 0.72 (0.67, 0.77) | 1.13 (1.07, 1.19) |
| Nakai et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.13 (1.08, 1.19) |
| Batalla et al | 0.73 (0.69, 0.79) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Zhao et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Raslová et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Wang et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.79) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Gong et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Bai et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Kolovou et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.13 (1.08, 1.19) |
| Mamotte et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Kumar et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.13 (1.07, 1.19) |
| Li et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.13 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Chen et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.79) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Keavney et al | 0.69 (0.63, 0.75) | 1.14 (1.07, 1.22) |
| Ranjith et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.79) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Aasvee et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.79) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Baum et al | 0.74 (0.69, 0.80) | 1.13 (1.08, 1.19) |
| Koch et al | 0.71 (0.66, 0.77) | 1.16 (1.09, 1.22) |
| Viitanen et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.13 (1.08, 1.19) |
| Onrat et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Tanguturi et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.13 (1.07, 1.19) |
| Kukava et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.15 (1.09, 1.21) |
| Gupta et al | 0.73 (0.68, 0.78) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.20) |
| Hu et al | 0.74 (0.69, 0.79) | 1.15 (1.09, 1.21) |
ε2 and ε4 were compared with ε3
Table 4.
Sensitivity analysis of associations between APOE genotypes and MI risks
| Study | ε2/ε2 | ε2/ε3 | ε2/ε4 | ε3/ε4 | ε4/ε4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cumming et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.93 (0.74, 1.18) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.28 (1.03, 1.60) |
| Yamamura et al | 0.37 (0.27, 0.51) | 0.37 (0.27, 0.51) | 0.93 (0.73, 1.18) | 1.15 (1.08, 1.22) | 1.40 (1.10, 1.76) |
| Utermann et al | 0.37 (0.27, 0.51) | 0.37 (0.27, 0.51) | 0.93 (0.73, 1.18) | 1.15 (1.08, 1.22) | 1.40 (1.10, 1.76) |
| Lenzen et al | 0.28 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.28 (0.20, 0.37) | 1.02 (0.80, 1.30) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.34 (1.06, 1.68) |
| Luc et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.36) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.36) | 0.97 (0.77, 1.23) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.30 (1.04, 1.63) |
| Luc et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.98 (0.78, 1.24) | 1.13 (1.06, 1.20) | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Luc et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.93 (0.74, 1.18) | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) | 1.30 (1.04, 1.63) |
| Luc et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.93 (0.73, 1.17) | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Joven et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.94 (0.75, 1.19) | 1.11 (1.04, 1.18) | 1.33 (1.07, 1.66) |
| Nakai et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.26 (1.01, 1.57) |
| Batalla et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.13 (1.06, 1.20) | 1.30 (1.04, 1.63) |
| Zhao et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Raslová et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.36) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.36) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.13 (1.06, 1.20) | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Wang et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.95 (0.76, 1.20) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.29 (1.03, 1.61) |
| Gong et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Bai et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Kolovou et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.97 (0.77, 1.23) | 1.13 (1.06, 1.20) | 1.32 (1.06, 1.65) |
| Mamotte et al | 0.25 (0.19, 0.34) | 0.25 (0.19, 0.34) | 0.97 (0.77, 1.24) | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) | 1.34 (1.06, 1.68) |
| Kumar et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.95 (0.75, 1.19) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.23 (0.99, 1.54) |
| Li et al | 0.26 (0.19, 0.35) | 0.26 (0.19, 0.35) | 0.95 (0.76, 1.20) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.29 (1.03, 1.60) |
| Chen et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Keavney et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.10 (1.02, 1.19) | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Ranjith et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.95 (0.75, 1.20) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.34 (1.07, 1.67) |
| Aasvee et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.36) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.36) | 0.97 (0.77, 1.22) | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) | 1.30 (1.04, 1.62) |
| Baum et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.22) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.29 (1.03, 1.60) |
| Koch et al | 0.22 (0.16, 0.31) | 0.22 (0.16, 0.31) | 0.98 (0.76, 1.27) | 1.15 (1.07, 1.22) | 1.29 (1.01, 1.64) |
| Viitanen et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.95 (0.75, 1.20) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.27 (1.02, 1.59) |
| Onrat et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) | 1.33 (1.06, 1.65) |
| Tanguturi et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.37) | 0.95 (0.75, 1.20) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.25 (1.00, 1.57) |
| Kukava et al | 0.26 (0.19, 0.36) | 0.26 (0.19, 0.36) | 0.97 (0.77, 1.22) | 1.14 (1.07, 1.21) | 1.30 (1.04, 1.62) |
| Gupta et al | 0.27 (0.20, 0.36) | 0.27 (0.20, 0.36) | 0.96 (0.76, 1.21) | 1.13 (1.06, 1.20) | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Hu et al | 0.28 (0.20, 0.38) | 0.28 (0.20, 0.38) | 1.02 (0.80, 1.29) | 1.13 (1.06, 1.20) | 1.40 (1.12, 1.75) |
ε2/ε2, ε2/ε3, ε2/ε4, ε3/ε4 and ε4/ε4 were compared with ε3/ε3
Publication bias
Funnel plots were performed to assess the publication bias and quantified by Begg’s test. The results showed that there was no significant publication bias in neither alleles nor genotypes (all P > 0.05) (Additional file 1: Figure S1).
TSA
For associations of MI risks with ε2 allele (Additional file 2: Figure S2A), with ε2/ε2 vs. ε3/ε3 (Additional file 2: Figure S2B), and with ε2/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3 (Additional file 2: Figure S2C), simple sizes reached RIS, and Z-curves crossed the trial sequential monitoring boundaries. For associations of MI risks with ε4 allele (Additional file 3: Figure S3A), with ε3/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (Additional file 3: Figure S3B), and with ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3 (Additional file 3: Figure S3C), simple sizes reached the RIS but Z-curves did not crosse the trial sequential monitoring boundaries. For associations of MI risks with ε2/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3, simple size neither reached the RIS nor Z-curves crosse the trial sequential monitoring boundaries (Additional file 4: Figure S4). Thus, the ε2 allele and ε2-involved genotypes were protective factors for MI; in contrast, the ε4 allele and ε4-involved genotypes (ε4/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3, and ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3) were risk factors for MI. There was no significant association between MI risks and genotype ε2/ε4.
Discussion
This meta-analysis, based on up-to-date data, further investigate the association between APOE polymorphism and MI risks, indicating that the ε2 allele and ε2-involved genotypes may be protective factors for MI; in contrast, the ε4 allele and ε4-involved genotypes (ε4/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3, and ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3) may be risk factors for MI.
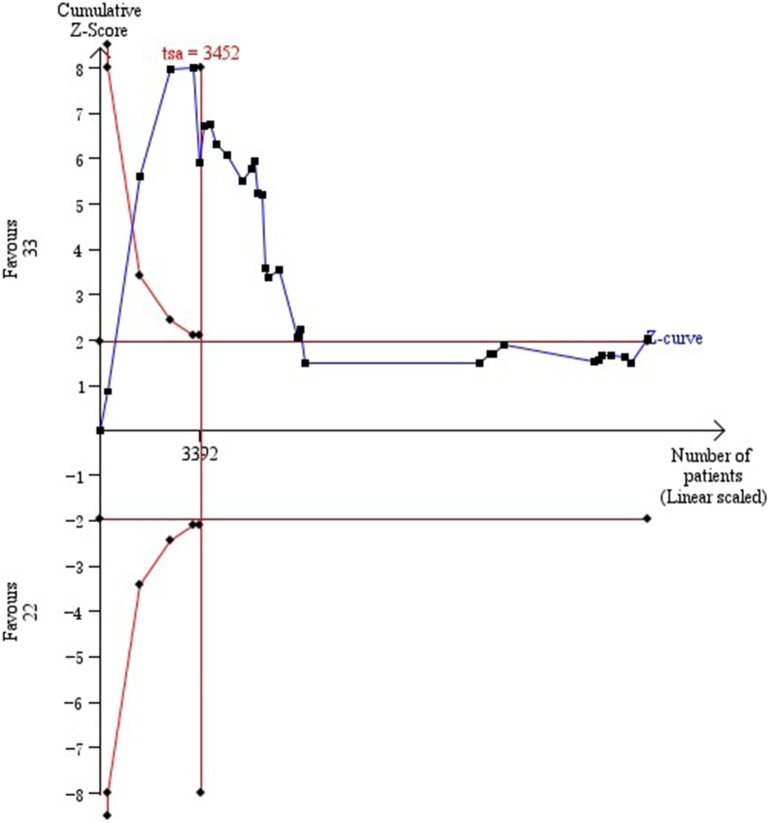
We found that the genotype ε2/ε2 is associated with MI risks. Of note, Qi et al. observed the genotype ε2/ε2 is not associated with MI risks [53]. Apart from methods that Qi et al. used [53], we adopted TSA additionally. Simple sizes reached RIS, and Z-curves crossed the trial sequential monitoring boundaries, documenting that the association of the genotype ε2/ε2 with MI risks is robust (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
Trial sequential analysis of the association between ApoE genotype ε2/ε2 vs. ε3/ε3 and myocardial infarction
Both the meta-analysis of Luc [29] and our meta-analysis identified that the ε2 allele and ε2-involved genotypes may be implicated in MI as protective factors; in contrast, the ε4 allele and ε4-involved genotypes (ε4/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3, and ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3) may be implicated in MI as risk factors. Luc et al. conducted their meta-analysis based on a multicenter population-based case–control study [29]. Population-based articles are more creditable than hospital-based articles and are less frequently performed in other meta-analyses. [18, 29, 40].
Wang et al. observed the genotype ε4/ε4 had no significant association with MI risks [18]. In addition, Kenji et al. and Prabhat et al. both observed the ε2 allele and ε2-involved genotype (ε2/ε2 and ε2/ε3) had no significant association with MI risks [31, 40]. Because we performed TSA, the disagreements may be because the false-negative error was existed in those studies [18, 31, 40]. In addition, Kenji et al. just enrolled Japanese patients [31] and the articles of Prabhat et al. investigated Indian individuals[40]. For these reasons, we performed subgroup analysis stratified by ethnicity, identifying that the association of MI risks with the APOE ε2 allele and with genotypes (ε2/ε2, ε2/ε3) is weaker in Asian than that in other ethnicities. Furthermore, we performed sensitivity analyses and TSA to obtain a reliable conclusion.
Our study has some limitations. First, despite subgroup analyses and regression, the main sources of heterogeneity remain difficult to identify. Second, our study focused on articles based on case–control design, merely providing the associations between APOE polymorphism and MI risks, rather than a causal relationship. Third, we did not retrieve other confounding factors, such as the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene, lifestyle, and gene–gene or gene-environment interactions, because the articles included in this meta-analysis did not provide any information about the other confounding factors.
Despite the limitations above, our study has some strengths. First, up-to-date articles were collected extensively, conferring our study more statistical power to draw valid conclusions on the associations between APOE polymorphism and MI risks. Second, the result of sensitivity analysis documented that our conclusions are stable and reliable. Third, in contrast to previous meta-analyses on the association between APOE gene polymorphism and MI risks, this is the first study to use TSA to further build reliable evidence to draw conclusions.
In conclusion, the ε2 allele and ε2-involved genotypes, as protective factors, have been implicated in MI. However, the ε4 allele and ε4-involved genotypes (ε4/ε3 vs. ε3/ε3, and ε4/ε4 vs. ε3/ε3) may perform as risk factors for MI.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Figure S1. Funnel plot of the association between APOE gene polymorphism and myocardial infarction. (A) ε2 allele; (B) ε4 allele; (C) ε2/ε2 genotype; (D) ε2/ε3 genotype; (E) ε2/ε4 genotype; (F) ε3/ε4 genotype; (G)ε4/ε4 genotype.
Additional file 2. Figure S2. Trial sequential analysis of the association between ApoE gene polymorphism and myocardial infarction. (A) ε2 allele; (B) ε2/ε2 genotype; (C) ε2/ε3 genotype.
Additional file 3. Figure S3. Trial sequential analysis of the association between ApoE gene polymorphism and myocardial infarction. (A) ε4 allele; (B) ε3/ε4 genotype; (C) ε4/ε4 genotype.
Additional file 4. Figure S4. Trial sequential analysis of the association between ε2/ε4 genotype and myocardial infarction.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participants of the study.
Abbreviations
- APOE
Apolipoprotein E
- MI
Myocardial infarction
- LDL-C
Low-density lipid protein cholesterol
- TGs
Triglycerides
- SNPs
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- HWE
Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium
- NOS
Newcastle–Ottawa scale
- CI
Confidence interval
- TSA
Trial sequential analysis
- RIS
Required sample size
Authors' contributions
Conception and design: AYS, YC, and YCQ. Provision of study materials: AYS, JKS, ZSL, and LFP. Collection and assembly of data: AYS, JKS, and ZSL. Data analysis and interpretation: AYS, and JKS. Manuscript writing: AYS. Revised the language/article: All authors. Final approval of manuscript: All authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant Number: 81702606), Department of Science and Technology of Jilin Province (Grant Numbers: 20180414086GH and 20170520007JH), the Department of Health and Family Planning Commission of Jilin Province (Grant Number: 2017Q037), The Education Department of Jilin Province (Grant Number: JJKH20180238KJ), and the Bethune Plan (Grant Number: 2020B16).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Aiyu Shao and Jikang Shi contributed equally to this work
Contributor Information
Yi Cheng, Email: chengyi@jlu.edu.cn.
Yichun Qiao, Email: qiaoyichun@jlu.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Nazir S, Gadi I, Al-Dabet MM, Elwakiel A, Kohli S, Ghosh S, Manoharan J, Ranjan S, Bock F, Braun-Dullaeus RC, et al. Cytoprotective activated protein C averts Nlrp3 inflammasome-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury via mTORC1 inhibition. Blood. 2017;130(24):2664–2677. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-05-782102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mortensen MB, Nordestgaard BG. Elevated LDL cholesterol and increased risk of myocardial infarction and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in individuals aged 70–100 years: a contemporary primary prevention cohort. Lancet (London, England) 2020;396(10263):1644–1652. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cahua-Pablo G, Cruz M, Moral-Hernández OD, Leyva-Vázquez MA, Antúnez-Ortiz DL, Cahua-Pablo JA, Alarcón-Romero Ldel C, Ortuño-Pineda C, Moreno-Godínez ME, Hernández-Sotelo D, et al. Elevated levels of LDL-C are associated with ApoE4 but not with the rs688 polymorphism in the LDLR gene. Clin Appl Thrombosis/Hemostasis. 2016;22(5):465–470. doi: 10.1177/1076029614568714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Frangogiannis NG. Pathophysiology of myocardial infarction. Compr Physiol. 2015;5(4):1841–1875. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Reed GW, Rossi JE, Cannon CP. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 2017;389(10065):197–210. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30677-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pasupathy S, Air T, Dreyer RP, Tavella R, Beltrame JF. Systematic review of patients presenting with suspected myocardial infarction and nonobstructive coronary arteries. Circulation. 2015;131(10):861–870. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.011201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gulati R, Behfar A, Narula J, Kanwar A, Lerman A, Cooper L, Singh M. Acute myocardial infarction in young individuals. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(1):136–156. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mehta LS, Beckie TM, DeVon HA, Grines CL, Krumholz HM, Johnson MN, Lindley KJ, Vaccarino V, Wang TY, Watson KE, et al. Acute myocardial infarction in women: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133(9):916–947. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang Q, Zhou SB, Wang LJ, Lei MM, Wang Y, Miao C, Jin YZ. Seven functional polymorphisms in the CETP gene and myocardial infarction risk: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(2):e88118. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marais AD. Apolipoprotein E in lipoprotein metabolism, health, and cardiovascular disease. Pathology. 2019;51(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2018.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Huebbe P, Rimbach G. Evolution of human apolipoprotein E (APOE) isoforms: gene structure, protein function and interaction with dietary factors. Aging Res Rev. 2017;37:146–161. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2017.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lin YJ, Pan JL, Jiang MJ, Tan JH, Zhong W, Gong TK, Jin XC, Cai SH, Wu YJ. Apo E gene polymorphism affects the development of type 2 diabetic nephropathy in Asian populations, especially in East Asians: an updated meta-analysis. Medi Sci Monit: Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2014;20:1596–1603. doi: 10.12659/MSM.892111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Al-Asmary SM, Kadasah S, Arfin M, Tariq M, Al-Asmari A. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to schizophrenia among Saudis. Arch Med Sci: AMS. 2015;11(4):869–876. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2015.53308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chiodini BD, Franzosi MG, Barlera S, Signorini S, Lewis CM, D'Orazio A, Mocarelli P, Nicolis E, Marchioli R, Tognoni G. Apolipoprotein E polymorphisms influence effect of pravastatin on survival after myocardial infarction in a Mediterranean population: the GISSI-Prevenzione study. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(16):1977–1983. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Remmler C, Cascorbi I. Pharmacogenomics in acute coronary syndrome. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9(3):363–376. doi: 10.1517/14656566.9.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Baum L, Ng HK, Wong KS, Tomlinson B, Rainer TH, Chen X, Cheung WS, Tang J, Tam WW, Goggins W, et al. Associations of apolipoprotein E exon 4 and lipoprotein lipase S447X polymorphisms with acute ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2006;44(3):274–281. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2006.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Singh NK, Banerjee BD, Bala K. Mitrabasu, Dung Dung AA, Chhillar N: APOE and LRPAP1 gene polymorphism and risk of Parkinson's disease. Neurol Sci: Off J Ital Neurol Soc Ital Soc Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;35(7):1075–1081. doi: 10.1007/s10072-014-1651-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xu H, Li H, Liu J, Zhu D, Wang Z, Chen A, Zhao Q. Meta-analysis of apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism and susceptibility of myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(8):e104608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang YL, Sun LM, Zhang L, Xu HT, Dong Z, Wang LQ, Wang ML. Association between Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and myocardial infarction risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. FEBS Open Biol. 2015;5:852–858. doi: 10.1016/j.fob.2015.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 2003;327(7414):557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wetterslev J, Jakobsen JC, Gluud C. Trial Sequential Analysis in systematic reviews with meta-analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12874-017-0315-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Brok J, Thorlund K, Gluud C, Wetterslev J. Trial sequential analysis reveals insufficient information size and potentially false-positive results in many meta-analyses. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(8):763–769. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2007.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta-analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(1):64–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2007.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cumming AM, Robertson FW. Polymorphism at the apoprotein-E locus in relation to risk of coronary disease. Clin Genet. 1984;25(4):310–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Utermann G, Hardewig A, Zimmer F. Apolipoprotein E phenotypes in patients with myocardial infarction. Hum Genet. 1984;65(3):237–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00286509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yamamura T, Yamamoto A, Sumiyoshi T, Hiramori K, Nishida Y, Nambu S. New mutants of apolipoprotein E associated with atherosclerotic diseases but not to type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Investig. 1984;74(4):1229–1237. doi: 10.1172/JCI111532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lenzen HJ, Assmann G, Buchwalsky R, Schulte H. Association of apolipoprotein E polymorphism, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and coronary artery disease. Clin Chem. 1986;32(5):778–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Luc G, Bard JM, Arveiler D, Evans A, Cambou JP, Bingham A, Amouyel P, Schaffer P, Ruidavets JB, Cambien F, et al. Impact of apolipoprotein E polymorphism on lipoproteins and risk of myocardial infarction. The ECTIM Study. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis: J Vascul Biol. 1994;14(9):1412–1419. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.9.1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Joven J, Simó JM, Vilella E, Camps J, Masana L, de Febrer G, Camprubí M, Richart C, Bardaji A, Casao E, et al. Lipoprotein(a) and the significance of the association between platelet glycoprotein IIIa polymorphisms and the risk of premature myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1998;140(1):155–159. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(98)00076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nakai K, Fusazaki T, Zhang T, Shiroto T, Osawa M, Kamata J, Itoh M, Nakai K, Habano W, Kiuchi T, et al. Polymorphism of the apolipoprotein E and angiotensin I converting enzyme genes in Japanese patients with myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis. 1998;9(6):329–334. doi: 10.1097/00019501-199809060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Batalla A, Alvarez R, Reguero JR, Hevia S, Iglesias-Cubero G, Alvarez V, Cortina A, González P, Celada MM, Medina A et al: Synergistic effect between apolipoprotein E and angiotensinogen gene polymorphisms in the risk for early myocardial infarction. Clinical chemistry 2000, 46Meta-Analysis: Apolipoprotein E Genotypes and Risk for Coronary Heart Disease (12):1910–1915. [PubMed]
- 32.Mei Z. Analysis of blood lipid level and ApoE gene polymorphism in siblings with early myocardial infarction. Master. China Medical University; 2000.
- 33.Raslová K, Smolková B, Vohnout B, Gasparovic J, Frohlich JJ. Risk factors for atherosclerosis in survivors of myocardial infarction and their spouses: comparison to controls without personal and family history of atherosclerosis. Metab: Clin Exp. 2001;50(1):24–29. doi: 10.1053/meta.2001.19499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Guoquan W, Xinli W, Chunrong Y, Xuan L, Biyu X, Yujian Z. Analysis of the relationship between apoE gene polymorphism and life span and blood lipid in Uyghur population of Xinjiang. Chin J Gerontol. 2001;21(5):325–327. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wuxing G, Shu P, Jian P, Jun W. Correlation analysis of apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism with myocardial infarction and blood lipid in the elderly. Chin J Gerontol. 2001;01:49–50. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Xiaojuan B, Mei Z, Bo W, Ran G, Yan C, Yanyan Z, Ming Z, Yuxiang C. Analysis of ApoE gene polymorphism in patients with myocardial infarction and their siblings with dyslipidemia. Chin Med J. 2001;81(6):340–343. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kolovou G, Yiannakouris N, Hatzivassiliou M, Malakos J, Daskalova D, Hatzigeorgiou G, Cariolou MA, Cokkinos DV. Association of apolipoprotein E polymorphism with myocardial infarction in Greek patients with coronary artery disease. Curr Med Res Opin. 2002;18(3):118–124. doi: 10.1185/030079902125000444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mamotte CD, Burke V, Taylor RR, van Bockxmeer FM. Evidence of reduced coronary artery disease risk for apolipoprotein epsilon2/3 heterozygotes. Eur J Intern Med. 2002;13(4):250–255. doi: 10.1016/s0953-6205(02)00030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kumar P, Luthra K, Dwivedi M, Behl VK, Pandey RM, Misra A. Apolipoprotein E gene polymorphisms in patients with premature myocardial infarction: a case-controlled study in Asian Indians in North India. Ann Clin Biochem. 2003;40(Pt 4):382–387. doi: 10.1258/000456303766477020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Li S, Lei ZW, Chen ZL, Lin D, Ke XS, Zhong YM, Wu SF. Relationship between apoliporotein E and apoliporotein B polymorphisms in youths with coronary heart disease. Chin J Med Genet. 2003;20(3):241–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yan C, Ming Z, Yunjia L, Xiaojuan B, Lixia Z. Analysis of serum lipid levels and ApoE gene in patients with myocardial infarction and their siblings. Chin Lab Diagnost. 2003;7(4):316–319. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Keavney B, Palmer A, Parish S, Clark S, Youngman L, Danesh J, McKenzie C, Delépine M, Lathrop M, Peto R, et al. Lipid-related genes and myocardial infarction in 4685 cases and 3460 controls: discrepancies between genotype, blood lipid concentrations, and coronary disease risk. Int J Epidemiol. 2004;33(5):1002–1013. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyh275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ranjith N, Pegoraro RJ, Rom L, Rajput MC, Naidoo DP. Lp(a) and apoE polymorphisms in young South African Indians with myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc J S Afr. 2004;15(3):111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Aasvee K, Jauhiainen M, Kurvinen E, Tur I, Sundvall J, Roovere T, Baburin A. Determinants of risk factors of atherosclerosis in the postinfarction period: the Tallinn MI study. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2006;66(3):191–199. doi: 10.1080/00365510600564881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Koch W, Hoppmann P, Schömig A, Kastrati A. Apolipoprotein E gene epsilon2/epsilon3/epsilon4 polymorphism and myocardial infarction: a case-control study in a large population sample. Int J Cardiol. 2008;125(1):116–117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Shakhtshneider EV, Ragino YI, Chernjavski AM, Kulikov IV, Ivanova MV, Voevoda MI. Apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism in men with coronary atherosclerosis in Siberia. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2011;150(3):355–358. doi: 10.1007/s10517-011-1141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Onrat ST, Akci O, Söylemez Z, Onrat E, Avşar A. Prevalence of myocardial infarction polymorphisms in Afyonkarahisar, Western Turkey. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(9):9257–9264. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1799-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tanguturi P, Pullareddy B, Kumar PS, Murthy DK. Association between apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism and myocardial infarction. Biochem Genet. 2013;51(5–6):398–405. doi: 10.1007/s10528-013-9572-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kukava NG, Titov BV, Osmak GJ, Matveeva NA, Kulakova OG, Favorov AV, Shakhnovich RM, Ruda MY, Favorova OO. Multilocus analysis of genetic susceptibility to myocardial infarction in Russians: Replication Study. Acta Naturae. 2017;9(4):74–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gupta MD, Girish MP, Sarkar PG, Gupta A, Kategari A, Bansal A, Saijpaul R, Batra V, Rain M, Tyagi S, et al: Role of ApoE gene polymorphism and nonconventional biochemical risk factors among very young individuals (aged less than 35 years) presenting with acute myocardial infarction. Indian Heart J. 2018, 70 Suppl 3(Suppl 3): S146-S156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 51.Yao H: Association between apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism and myocardial infarction in hyperlipidemia patients. Anhui Med. 2020, 24(9).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Figure S1. Funnel plot of the association between APOE gene polymorphism and myocardial infarction. (A) ε2 allele; (B) ε4 allele; (C) ε2/ε2 genotype; (D) ε2/ε3 genotype; (E) ε2/ε4 genotype; (F) ε3/ε4 genotype; (G)ε4/ε4 genotype.
Additional file 2. Figure S2. Trial sequential analysis of the association between ApoE gene polymorphism and myocardial infarction. (A) ε2 allele; (B) ε2/ε2 genotype; (C) ε2/ε3 genotype.
Additional file 3. Figure S3. Trial sequential analysis of the association between ApoE gene polymorphism and myocardial infarction. (A) ε4 allele; (B) ε3/ε4 genotype; (C) ε4/ε4 genotype.
Additional file 4. Figure S4. Trial sequential analysis of the association between ε2/ε4 genotype and myocardial infarction.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.