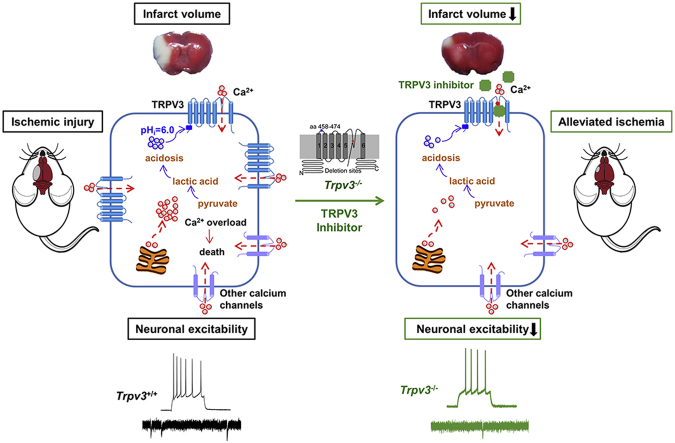
Abstract
Ischemic brain stroke is pathologically characterized by tissue acidosis, sustained calcium entry and progressive cell death. Previous studies focusing on antagonizing N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors have failed to translate any clinical benefits, suggesting a non-NMDA mechanism involved in the sustained injury after stroke. Here, we report that inhibition of intracellular proton-sensitive Ca2+-permeable transient receptor potential vanilloid 3 (TRPV3) channel protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. TRPV3 expression is upregulated in mice subjected to cerebral I/R injury. Silencing of TRPV3 reduces intrinsic neuronal excitability, excitatory synaptic transmissions, and also attenuates cerebral I/R injury in mouse model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). Conversely, overexpressing or re-expressing TRPV3 increases neuronal excitability, excitatory synaptic transmissions and aggravates cerebral I/R injury. Furthermore, specific inhibition of TRPV3 by natural forsythoside B decreases neural excitability and attenuates cerebral I/R injury. Taken together, our findings for the first time reveal a causative role of neuronal TRPV3 channel in progressive cell death after stroke, and blocking overactive TRPV3 channel may provide therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury.
KEY WORDS: TRPV3, Ca2+ influx, Acidosis, Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, Excitotoxicity, Neural excitability, Forsythoside B, tMACO, OGD, TRP
Graphical abstract
1. Introduction
As a result from an interruption of blood supply, ischemic brain injury is characterized by histopathological acidosis of brain tissues1,2. Oxygen and glucose deprivation necessitates a switch from aerobic metabolism to anaerobic glycolysis, which leads to the generation of lactic acid and intracellular protons3,4. Accumulation of lactic acid as a byproduct of glycolysis and protons produced by adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis causes a typical fall of intracellular pH between 6.5 and 6.0 in the ischemic area of the brain5, 6, 7. Consequently, tissue acidosis aggravates ischemic brain injury partly through acid-sensing ion channels8, 9, 10 and Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 111,12.
Despite the progress made in prevention, treatment for ischemic brain stroke still remains a major global challenge. The NMDA-based neuronal excitotoxicity theory is based on the observations that occurrence of cerebral ischemic injury causes the release of neuronal excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate that activates ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) and leads to an overload of Ca2+ influx, ultimately further aggravating ischemic injury and neuronal apoptosis and necrosis13, 14, 15, 16. Over the past three decades, all NMDA receptor antagonists, however, have been unable to translate any clinical benefits for stroke treatment due to poor clinical outcomes or severe adverse reactions17, 18, 19, 20, thus suggesting that glutamate-independent mechanisms for calcium overload during ischemia may be involved in the neuronal death after stroke21, 22, 23.
We have previously demonstrated that the warm-temperature sensitive and Ca2+-permeable cation transient receptor potential vanilloid 3 (TRPV3) channel is activated by intracellular protons with half-maximal activation (pH0.5) at pH 6.124. The proton-mediated activation of TRPV3 causes an overload of Ca2+ influx, leading to cell death24. TRPV3 is highly expressed in the brain, spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia (DRG)25, 26, 27. We therefore hypothesized that brain tissue acidosis during cerebral ischemia may trigger excessive activation of TRPV3 channels through intracellular rise of protons, which further causes intracellular Ca2+ overload and progressive cell death after ischemic injury.
To test this hypothesis, we investigated the role of intracellular proton-activated Ca2+-permeable TRPV3 channel in the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. We observed an upregulation of TRPV3 expression in mouse brain subjected to I/R injury. Overexpressing or re-expressing TRPV3 increases neuronal firing and aggravates cerebral I/R injury. Silencing or pharmacological inhibition of TRPV3 suppresses neural excitability and also protects against cerebral I/R injury. Our findings reveal a non-NMDA-mediated neural excitotoxicity involving overactive TRPV3 in the progression of ischemic injury, and that blocking overactive proton-sensitive and Ca2+-permeable TRPV3 channel may provide a potential therapy to promote recovery from ischemic brain stroke.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Chemicals
Forsythoside B (FB, molecular weight 756.7, 99% purity) was purchased from Shanghai Tongtian Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Antioxidant edaravone or redicava (Simcere) was used as a positive control for ischemia experiments. N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist d-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (AP5, 50 μmol/L), α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate (AMPA)/kainate glutamate receptor antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX, 10 μmol/L) were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich. Neurobiotin tracer N-(2-aminoethyl) biotinamide hydrochloride (Vector Laboratories), Alexa Fluor 488 or 647-conjugated streptavidin (Molecular Probes), sodium channel blocker tetrodotoxin (TTX, 500 nmol/L, Baomanbio), γ-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) receptor antagonist bicuculline (10 μmol/L, Abcam), and GABAB receptor antagonist CGP55845 (2 μmol/L, Abcam) were prepared before use, and the purity of each standard compound is no less than 98% by high-performance liquid chromatography analysis. FB and edaravone used in behavioral experiments were diluted in sterile normal saline for intravenous injection.
2.2. Animals
Male adult C57BL/6J mice (10 ± 2 weeks) and KM mice (10 ± 2 weeks) of SPF grade were purchased from Charles River Laboratories (Beijing, China; permit No. SCXK 2012-0001). All animals were kept on a 12 h:12 h light–dark cycle with free access to food and water. Animals were handled in strict accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the Principles for the Utilization and Care of Vertebrate Animals. All animal protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Peking University (Beijing, China) or Qingdao University (Qingdao, China) and efforts were made to minimize animal suffering and the number of animals used. In vivo experiments were blind to viral or drug treatment conditions during transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) and behavioral testing. C57BL/6J mice were used to generate the model of tMCAO to detect changes of TRPV3 protein and mRNA levels, etc., and KM mice were used to evaluate the neuroprotection of FB in ischemia injury.
Trpv3-deficient mice (Allele Symbol: Trpv3tm1Apat, 10 ± 2 weeks) as kind gifts from Dr. Yong Yang were originally produced in the laboratory of Dr. Ardem Patapoutian28 and bred in our animal facility. The mouse genotype was determined using PCR analysis. Briefly, genomic DNA was extracted from 0.2 cm tail snips using the alkali extraction method29. A PCR reaction was then performed using Ex Taq polymerase (TaKaRa) and the following primers:
primer 1, 5′-GTAGAGTCAGGGCCCTCAGAGGAGCC-3′;
primer 2, 5′-CTAATGTTGCAGGTACTGTGTCGCCCC-3′;
primer 3, 5′-GTGGGCTCTATGGCTTCTGAGGCGG-3′.
The PCR reaction consisted of an initial 2 min at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 59 °C, and 40 s at 72 °C. After the last cycle, the reaction was kept at 72 °C for 5 min and then held at 4 °C. A 304 bp band was observed for mice containing the wild-type (WT) allele, whereas a 182 bp band was seen for mice containing the mutant allele and heterozygotes contained both alleles. Male homozygotes Trpv3−/− mice (10 ± 2 weeks) and WT were used to generate ischemia injury.
2.3. Generation of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) in mice
Mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium (60 mg/kg). After sterilizing with 75% alcohol, mouse scalp was cut and skull was exposed. A probe was connected to the left skull by biomedical glue to monitor relative local cerebral blood flow (LCBF) with laser Doppler measurement (Perimed). Transient focal cerebral ischemia was induced by tMCAO surgery30. Briefly, a 6-0 nylon monofilament suture blunted at the tip and coated with silicone was introduced ∼0.8 mm into the internal carotid artery via the external carotid artery, to occlude the origin of the left middle cerebral artery (MCA) in the circle of Willis. The LCBF dropped and maintained below 20% of the baseline, indicating a success of ischemia during the surgery31. After 1.5 h, reperfusion via MCA, with recovery of over 80% of the baseline, was allowed by monofilament removal. Body temperature was monitored and maintained at 37 ± 0.5 °C by a heating operation table during the surgery and the reperfusion. For sham operations, the filament is inserted to occlude MCA before withdrawn immediately to allow instant reperfusion. The subsequent operation is identical to animals undergoing cerebral ischemia.
2.4. Neurologic deficit scoring
Neurologic deficit scores were evaluated at 24 h of reperfusion according to Longa's five-point scale method32. In detail, 0, no neurologic deficit; 1, a mild focal neurologic deficit: failure to extend left forepaw fully; 2, a moderate focal neurologic deficit: circling to the left; 3, a severe focal deficit: falling to the left; 4, mice did not walk spontaneously and had a depressed level of consciousness.
An expanded seven-point scale is used for evaluation of transgenic mice30 on Days 1, 3 and 5. That is, 0: normal; 1: failure to extend left forepaw fully; 2: mild circling behavior with or without inconsistent rotation when picked up by the tail, <50% attempts to rotate to the contralateral side; 3: mild consistent circling, >50% attempts to rotate to the contralateral side; 4: consistent strong and immediate circling, the mouse holds a rotation position for more than 1–2 s, with its nose almost reaching its tail; 5: severe rotation progressing into barreling, loss of walking or righting reflex; 6: comatose or moribund. The observer was blind to animal treatment, and one mouse obtaining no less than 2 scores is counted as a valid model.
2.5. Infarct volume measurement
Infarct volume was determined 24 h after reperfusion. Mice were perfused with saline to remove blood in brain tissue under anesthetizing. The brains were quickly removed, sectioned coronally into 6 slices at ∼1-mm thickness and stained by immersion in the vital dye 1% 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium hydrochloride (TTC, Amresco, w/v) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at 37 °C each side for 10 min33,34, followed by immersion-fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde. Then TTC-stained sections were photographed and the extents of the normal and infarcted areas were analyzed using Adobe Photoshop CC and determined by the indirect method, which corrects for edema33,35. The percentage of the corrected infarct volume was calculated by dividing the infarct volume by the total contralateral hemispheric volume to compensate for the effect of brain edema36.
2.6. Measurement of brain water content
Brain water content was determined according to the wet-dry methods37. In brief, brains were immediately weighed to obtain wet weight (W1), then dried in an oven at 120 °C for 8 h and weighed again to obtain the dry weight (W2). Brain water content was calculated as Eq. (1):
| Brain water content (%) = (W1–W2)/W1 × 100 | (1) |
2.7. Oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) in primary culture of mouse cortical neurons
Cortical neurons were removed from newborn mice (< 24 h) and dissociated by 0.25% trypsinization38. Cells were suspended in high-glucose DMEM (Gibco) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), and plated on poly-d-lysine hydrobromide (Sigma–Aldrich) coated culture plates or 15 mm confocal culture dish at a density of about 1.2 × 105 cells/cm2 for different experiments. After 4–6 h seeding, the medium was changed to phenol red-free neurobasal A medium (Gibco) supplemented with 2% B27 (Gibco), containing 0.5 mmol/L GlutaMAX-I, 0.5% penicillin–streptomycin, then one-half medium was refreshed every three days. At the 3rd day, to suppress the proliferation of glial cells, cytarabine (2.5 μg/mL) was added. Cells were maintained at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 95% air and 5% CO2 and used for in vitro experiments after 7–9 days.
OGD model was carried out as described previously39. The original media were removed, the cells were washed with 37 °C glucose-free and phenol red-free DMEM twice and treated with 10 mmol/L of sodium dithionite (Na2S2O4, a deoxygenated reagent) in glucose-free and phenol red-free DMEM. A duration of 30 or 20 min later, the media were removed, the cells were washed with 37 °C neurobasal A medium twice, and returned to their original culture condition and maintained for 24 h until the assay of cell injury. FB (0.1, 1, and 10 μmol/L) and edaravone (10 μmol/L) were added to culture medium 30 min before exposed to OGD and maintained for 24 h after reoxygenation.
2.8. Cell viability and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assays
A cell counting kit-8 assay (CCK-8, Dojindo) was used to estimate cell viability. Briefly, a highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt, WST-8, is reduced by dehydrogenase activities in cells to give a yellow-color formazan dye, which is soluble in the tissue culture media. The amount of the formazan dye, generated by the activity of dehydrogenases in cells, is directly proportional to the number of living cells. CCK-8 reagents (10%) were added into wells, and the absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader at 2 h after CCK-8 addition. At least three wells were measured for cell viability in each group40.
The release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) into the culture medium was measured using LDH assay reagent (Promega) following the instructions of the kit menu. Briefly, the supernatant medium (50 μL) was transferred to 96-well plates, mixed with 50 μL of reaction solution in kits and incubated for 30 min at room temperature. Stop solution in kits was then added and the optical density was measured at 490 nm.
2.9. Stereotactic injection and histological examinations
Viral AAV2 constructs of mTRPV3 with enhanced green fluorescent protein (mTRPV3-EGFP) and control-EGFP carrying human synapsin (hSyn) promoter for neuron-specific expression were designed and packed by Shanghai Hanbio Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). For viral injection, mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium (60 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection, i.p.) and placed in a stereotaxic apparatus (RWD). Mice were bilaterally injected with AAV virus (∼1012 infections units per mL) into the cortex (coordinates from bregma: +0.5 mm anterior/posterior, ±2.0 mm medial/lateral, −1.8 mm dorsal/ventral, 2 μL per point) and the striatum (coordinates from bregma: +0.5 mm anterior/posterior, ±2.0 mm medial/lateral, −3.5 mm dorsal/ventral, 2 μL per point) at a slow rate (∼100–150 nL/min). The injection needle was slowly withdrawn 5 min after the virus infusion. For the left tMCAO surgery, viruses were injected in the left cortex and striatum. tMCAO experiments or electrophysiological recordings were performed at least 30 days after viral injection.
After 30 days of viral injection, mice were deeply anesthetized and perfused with normal saline followed by 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS. Brains were post-fixed overnight in the same 4% paraformaldehyde solution and dehydrated by immersion in 20% and 30% sucrose in PBS, each for 1 day. Frozen brains were sectioned at 20 μm with a cryostat (Leica) in the coronal plane. Brain slices from mice injected with AAV viruses were directly examined under a fluorescent microscope.
2.10. Immunostaining and confocal microscopy
HEK 293T cells were transfected with mouse-TRPV3-EGFP plasmid using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer's instructions and were maintained at 37 °C under 5% CO2 in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. HEK 293T cells expressing TRPV3 and mouse cortical neurons in a 15 mm confocal culture dish were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at 4 °C after removal of culture medium. The cells were added with 0.3% Triton X-100 (Amresco) in PBS for 15 min and blocked by 10% sheep serum in 0.01 mol/L PBS for 1 h at room temperature before incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C. The rabbit monoclonal NeuN antibody (1:1000; Abcam), mouse monoclonal TRPV3 antibody (1:1000; Abcam). The immunoreactivity was visualized with Alexa Fluor 488- or 594-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:200; ZSGB-BIO). Immunocytochemistry was used for visualization of TRPV3 proteins in cells using a confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems).
2.11. RNA isolation, reverse transcription, qPCR analysis
After MCAO surgery at 6, 12, and 24 h, mouse brains were divided into ischemia part and contralateral part for extraction of RNAs. Total RNAs were extracted with TRIzol reagent (Sigma) from mouse cerebral tissues according to the manufacturer's instructions. RNA (4 μg) was subjected to reverse transcription using a GoScript Reverse Transcription System (Promega), and resulting cDNAs were subjected to quantitative PCR analysis using the GoTaq qPCR master mix (Promega) and specific primers in a 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). PCR primer sequences were as follows:
mouse Trpv3 forward 5′-ACAGGTTCATCAACGCTGAGT-3′;
mouse Trpv3 reverse 5′-CACCCGCTGCTATAAGCACT-3′;
mouse Actb forward 5′-GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG-3′;
mouse Actb reverse 5′-CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT-3′;
mGapdh-forward 5′-GTCTTCACCACCATGGAGA-3′;
mGapdh-reverse 5′-AAGCAGTTGGTGGTGCAG-3′.
Gapdh levels, Actb levels and Trpv3 mRNA expression in contralateral cortex were used as an endogenous control for normalization using the ΔΔCt method41. In brief, test (T): ΔCtT = [CtT (target gene)–CtT (internal control)]–[CtT (contralateral target gene)–CtT (contralateral internal control)]; Sham control (C): ΔCtC = [CtC (target gene)–CtC (internal control)]–[CtC (contralateral target gene)–CtC (contralateral internal control)]; ΔΔCt = ΔCtT–ΔCtC; Amount of the target = 2–ΔΔCt.
2.12. Western blot
Brain regions from the right and left hemispheres corresponding to the ischemic core, penumbra and contralateral cerebral were dissected42,43. Briefly, a midline between the two hemispheres was identified before a longitudinal cut (from top to bottom) approximately 2 mm from the midline through each hemisphere. A transverse diagonal cut was made at approximately “10 o'clock” position to separate the penumbra (adjacent cortex) from the core (i.e., striatum and overlying cortex). We made minor modifications for estimates of core and penumbra based on our earlier investigations by TTC staining. Proteins were extracted from cerebral regions in cold RIPA Lysis Buffer containing 2% Cocktail (Roche). Protein samples were loaded on 8% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis before transferred using gel electrophoresis to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore). After 5% milk blocking, PVDF membranes were incubated with mouse monoclonal TRPV3 antibody or mouse β-actin antibody (1:5000, Abcam) at 4 °C overnight. The membranes were then incubated with their corresponding secondary horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibodies and detected using an ECL Western blotting detection system (Millipore). The immunoreactive bands were scanned by Tanon 5200 instrument (Tanon), captured by the Tanon MP system (Tanon) and quantitatively analyzed by densitometry with Tanon GIS software (Tanon) or ImageJ software. For increase of low TRPV3 protein signal in Western blot assay, a reagent called “SuperSignal Western blot enhancer (Thermo Fisher)” was used. TRPV3 proteins were used as positive controls (TRPV3 protein expression on HEK293 cell line or on mouse skin) and molecular weight of 91 kDa was checked to make sure the TRPV3 protein band site.
2.13. Acute brain slice preparations and electrophysiological whole-cell recordings
Mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium (60 mg/kg) and decapitated before brains were dissected into ice-cold slice solution containing the following (in mmol/L): 110 choline chloride, 2.5 KCl, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 25 NaHCO3, 0.5 CaCl2, 7 MgCl2, 25 glucose, 0.6 ascorbic acid, 3.1 pyruvic acid (bubbled with 95% O2 and 5% CO2, pH 7.4). Acute horizontal [for patch recordings of medial entorhinal cortex (mEC) layer II stellate neurons] or coronal slices [for patch recordings of striatal medium spiny neuron (MSNs)] at 300-μm thickness were cut on a vibratome before transferred to artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) containing (in mmol/L): 125 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 2.0 CaCl2, 2.0 MgCl2, 25 NaHCO3, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 10 glucose (bubbled with 95% O2 and 5% CO2, pH 7.4). Brain slices were incubated at 37 °C for 20–30 min and stored at room temperature before use.
All somatic whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were performed in identified mEC layer II stellate neurons or striatal MSNs. The selection criteria for stellate cells were based on their morphological characteristics44 (i.e., large cell body presenting polygon or rhombus) and firing properties and shape of APs (i.e., upon subthreshold depolarization and prominent membrane potential sags induced by both hyperpolarizing and depolarizing current injection at the somata). The selection criteria for MSNs were based on morphological characteristics with a large cell body presenting polygon or rhombus and numerous dendritic spines and their much lower resting membrane potential (RMP, about −80 mV)45.
For whole-cell current-clamp recordings, the internal solution contained (in mmol/L): 118 KMeSO4, 15 KCl, 2 MgCl2, 0.2 EGTA, 10 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), 4 Na2ATP, 0.3 Tris-GTP, 14 Tris-phosphocreatine, adjusted to pH 7.3 with KOH. AP5 (NMDA receptor antagonist, 50 μmol/L), CNQX (AMPA/kainate glutamate receptor antagonist, 10 μmol/L) were applied to block excitatory synaptic transmission, bicuculline (GABAA receptor antagonist, 10 μmol/L) and CGP55845 [selective γ-aminobutyric acid B (GABAB) receptor antagonist, 2 μmol/L] were applied to block inhibitory synaptic transmission.
The input resistance (IR) was calculated with Eq. (2):
| Input resistance = (Vbaseline–Vsteady-state) × 10 (MΩ) | (2) |
where Vbaseline is the resting membrane potential or −70 mV (for stellate cells) or −80 mV (for MSNs) and Vsteady-state is the voltage recorded at 0–10 ms before the end of −100 pA stimulus.
For whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs), the internal solution contained (in mmol/L): 122 CsCl, 1 CaCl2, 5 MgCl2, 10 EGTA, 10 HEPES, 4 Na2ATP, 0.3 Tris-GTP, 14 Tris-phosphocreatine, adjusted to pH 7.3 with CsOH. TTX (sodium channel blocker, 0.5 μmol/L), AP5 (NMDA receptor antagonist, 50 μmol/L), CNQX (AMPA/kainate glutamate receptor antagonist, 10 μmol/L) for block of excitatory synaptic transmission. For recordings of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs), the internal solution contained (in mmol/L): 118 KMeSO4, 15 KCl, 2 MgCl2, 0.2 EGTA, 10 HEPES, 4 Na2ATP, 0.3 Tris-GTP, 14 Tris-phosphocreatinin, adjusted to pH 7.3 with KOH. TTX (sodium channel blocker, 0.5 μmol/L), bicuculline (GABAA receptor antagonist, 10 μmol/L) and CGP55845 (selective GABAB receptor antagonist, 2 μmol/L) were applied to block inhibitory synaptic transmission. Only a single neuron was recorded in each slice.
Thick-wall borosilicate pipettes were used with open-tip resistance of 4–6 MΩ. All recordings were started at least 10 min after breakthrough for internal solution exchange equilibrium using a MultiClamp 700B amplifier (Molecular Device). Data were acquired with a sampling rate at 33 kHz with a Digidata 1440A digitizer (Molecular Devices) before filtered at 2 kHz and analyzed using pCLAMP 10.6 software. Slices were maintained under continuous perfusion of artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) at 36.5–37.5 °C with a 2–3 mL/min flow. In the whole-cell configuration, the series resistance (Rs) was 15–30 MΩ, and recordings with unstable Rs or a change of Rs > 20% were aborted.
For cell labeling, the internal solution either for whole-cell current-clamp recordings or for voltage-clamp recordings contained 0.1%–0.2% (w/v) neurobiotin tracer. At the end of electrophysiological recordings (∼30 min), slices were stored in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight at 4 °C before processed with streptavidin conjugated to Alexa 488 (1:500; Invitrogen) or Alexa 594 (1:500; Invitrogen) for neurobiotin visualization46.
2.14. Imaging and Sholl analysis
Neurobiotin labeled neurons in brain slices were imaged using a laser scanning confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems) with 63 × oil-immersion objectives for stellate neurons or MSNs and 40 × oil-immersion objectives for cortical layer V pyramidal neurons. For measurement of total dendritic branch length, 3D Z-stacks were reconstructed from ∼40 to 250 sequential scans at low zoom (1024 × 1024 μm) at 1-μm steps. The concentric sphere method of Sholl47 was used to analyze dendritic complexity. Briefly, concentric circles at 20 μm intervals were drawn around the somata and the number of dendrites crossing each circle was counted manually from the two-dimensional display. Dendritic spine images were captured with 63 × oil-immersion objectives at 0.3-μm steps before further 6 × high zoom amplification. Spine density was sampled in second-to fourth-order branches. The dendrite derived directly from the soma is the first-order branch or primary dendrite. The daughter branches arising from the first-order branch are second-order branches, and so on. Results were expressed in terms of spine density/10 μm.
2.15. Multi-electrode array (MEA) recordings of primary cortical neurons
Cortical neurons from newborn C57BL/6J mice (< 24 h) were acutely dissociated and suspended in NbActiv4 (Brain Bits) medium. Approximately ∼7 × 104 neurons in 8 μL medium were seeded on 12-well MEA plates (Axion Biosystems) coated with poly-d-lysine (40 μg/mL)/laminin (20 μg/mL). The cells were incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 for 1 h. NbActiv4 media (0.4 mL per well) were added to the cells. On the 3rd day, cytarabine (2.5 μg/mL) was added to suppress the proliferation of glial cells by mitotic inhibition for up to seven days48. Cells were maintained at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator, and culture medium was changed every 3 days by replacing approximately 2/3 of the medium.
Neurons were in fresh culture medium for 1 h before recorded in a 12-well plate consisting of a total of 768 electrodes. Recordings were carried out 30 min before and 60 min after FB (100 μmol/L in neuronal medium) application using an MEA system (Axion Biosystems). For each experiment, at least 7–13 wells (with 448–832 available electrodes for recording) were used to assess neuronal excitability. A spike detection criterion of > 6 standard deviations above background signals were used to separate monophasic or biphasic action potential spikes from noise. Active electrodes were defined as 1 spike over a 200 s analysis period49. Firing frequencies were averaged among all active electrodes from wells. MEA data were analyzed using Axion Integrated Studio AxIS2.1 (Axion Biosystems) and NeuroExplorer (Nex Technologies). The recording files were divided into every 5-min. The average response for each 5-min was calculated, and the lowest value was selected for analysis. The neuronal and network activities were assessed by criteria such as spike frequency, burst frequency, network burst frequency and synchrony index. A minimum of 5 spontaneous spikes with a maximum inter-spike interval of 0.1 s was defined as a burst, as previously reported50, and a minimum of 10 spontaneous spikes with a maximum inter-spike interval of 0.1 s and a minimum of 25% active electrodes were as a network burst. Specifically, the network burst was manually verified by a single-blind method.
2.16. Statistical analysis
Unless otherwise noted, all data were expressed as the means ± standard error of mean (SEM), statistical significance was determined using unpaired Student's t-test for the comparison between two groups. Two-way ANOVA was used for the comparison between multiple groups. Each “n” indicates an independent experiment, and P < 0.05 was statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Upregulation of TRPV3 channel expression in mouse model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
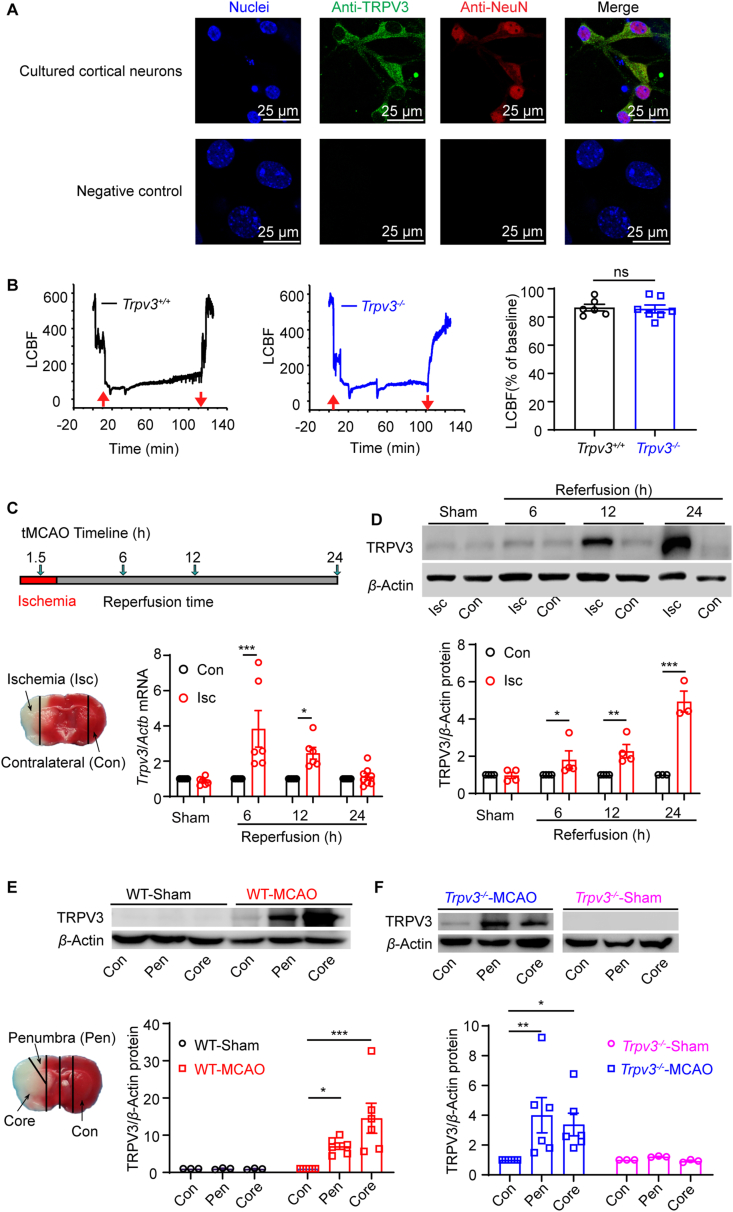
To recapitulate the cerebral expression of TRPV325,26,51, 52, 53, we started examining TRPV3 channel proteins in mouse cerebral neurons using immunohistochemistry. As shown in Fig. 1A, TRPV3 channel proteins (green) were robustly expressed in cultured mouse cortical neurons (red) as detected by TRPV3 specific monoclonal antibodies that were also used for detection of mTRPV3 proteins expressed in HEK 293 cells in immunofluoresscence assay (Supporting Information Fig. S1A), confirming the neuronal expression of TRPV3 channel proteins.
Figure 1.
Upregulation of TRPV3 channel expressions induced by cerebral ischemic–reperfusion injury in mice. (A) Upper panels, immunohistochemical co-staining of TRPV3 protein (green) and NeuN biomarker (red) in cultured mouse primary cortical neurons were observed using confocal microscopy with 4 repeats. Bottom panels, secondary antibodies were used alone without primary antibodies as a negative control. Nuclei are stained by DAPI (blue). (B) Measurement of ipsilateral local cerebral blood flow (LCBF) by laser Doppler flowmetry in Trpv3+/+ mouse (left panel) and Trpv3−/− mouse (middle panel) subjected to 1.5 h ischemia/24 h reperfusion (I/R) injury induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) surgery. Up- and down-arrows (red) indicate the insertion and withdrawal of the filament, respectively. In right panel, the statistics of declined LCBF of baseline. ns, no significance. (C) Top panel, a timeline for generation of tMCAO in mice subjected to 1.5 h ischemia (I) before 6, 12 or 24 h reperfusion (R) injury. Bottom left panel, representative image of ischemic (Isc) and contralateral (Con) regions at 24 h reperfusion, and upregulation of Trpv3 mRNA levels in ischemia region at 6 and 12 h reperfusion after 1.5 h ischemia using quantitative real-time PCR assay (bottom right panel) using the two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak's test from GraphPad 8. (D) Time-dependent increase of TRPV3 protein expressions in the ischemia area at 6, 12, and 24 h of reperfusion after 1.5 h ischemia (top panel) and their analysis for TRPV3 protein expression (bottom panel) using the two-way ANOVA followed by Uncorrected Fisher's LSD from GraphPad 8. (E) Top panel, Western blot analysis for upregulation of TRPV3 protein expressions in ischemia penumbra and core regions in Trpv3+/+ mice. Bottom left panel, a representative image of ischemic core, penumbra (Pen) and contralateral (Con) regions at 24 h of reperfusion and their analysis for TRPV3 expression (bottom panel) using the two-way ANOVA followed by Uncorrected Fisher's LSD from GraphPad 8. (F) Upregulation of TRPV3 protein expressions in ischemia penumbra and core regions in Trpv3−/− mice subjected to tMCAO injury and their analysis of TRPV3 expression using the two-way ANOVA followed by Uncorrected Fisher's LSD from GraphPad 8. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n represents the number of mice. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Also see Supporting Information Fig. S1A for antibody specificity; Fig. S1B for upregulations of Trpv3 mRNA levels after tMCAO injury.
To examine TRPV3 expression after ischemia, we established the mouse model of ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) under the monitoring of local cerebral blood flow (LCBF) by laser Doppler flowmetry during surgery with 80% decline of LCBF over baseline in either WT Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− (pore-deleted mutant) mice (Fig. 1B). The Trpv3 mRNA level was increased in the ischemic regions at 6 and 12 h after 1.5 h-tMCAO injury (Fig. 1C and Fig. S1B). TRPV3 protein expressions were also increased by 1.8-fold at 6 h, 2.3-fold at 12 h and 4.9-fold at 24 h (Fig. 1D) or 7.1-fold in the penumbra and 14.5-fold in the ischemic core as compared with the contralateral regions at 24 h reperfusion (Fig. 1E). Cerebral I/R injury also resulted in an upregulation of truncated TRPV3 proteins in the ischemic core and penumbra in Trpv3−/− brain (Fig. 1F), consistent with the observations from WT mice (Fig. 1E). These results indicate a time-dependent upregulation of TRPV3 induced by cerebral I/R injury, suggesting a role of TRPV3 channel in progressive neuronal death after ischemic stroke.
3.2. Attenuation of ischemic injury in Trpv3−/− mice
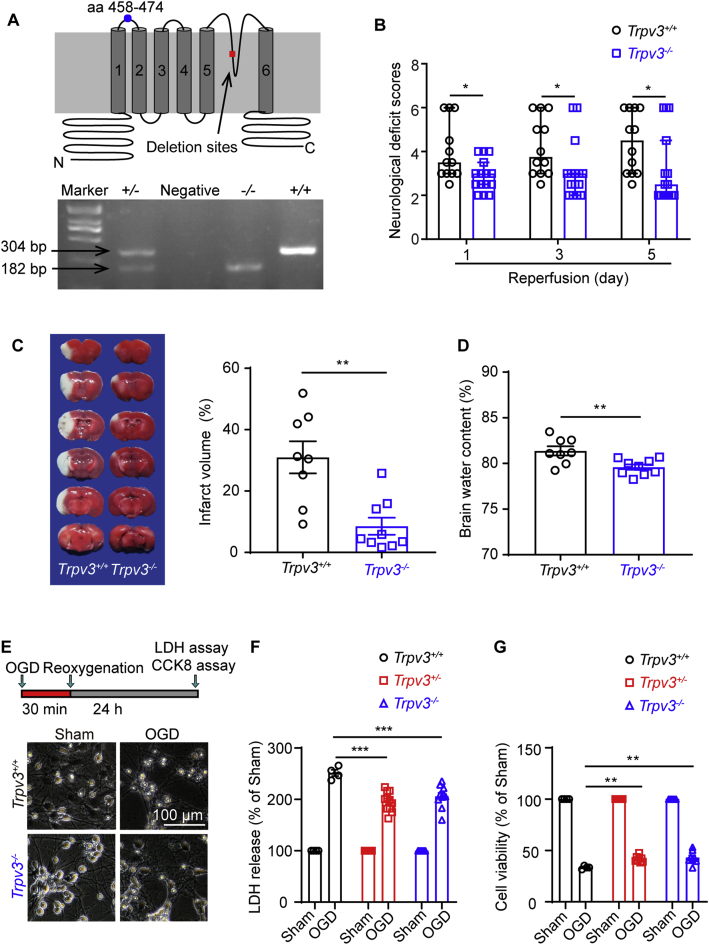
To examine the functional role of TRPV3 in ischemic injury, we utilized Trpv3 null (Trpv3−/−) mice in which the 13 and 14 exons of Trpv3 gene encoding the pore region were genetically deleted by expressing the targeted knockout construct28. Homozygous Trpv3−/− mice expressed a low level of truncated TRPV3 transcripts without pore region detected by TRPV3 monoclonal antibody recognizing the antigen of residues 458–474 between S1 to S2 transmembrane domain (Fig. 2A). Neurological scoring revealed that Trpv3–/– mice exhibited a significant reduction of neurological deficit scores on Day 1, 3 and 5 after tMCAO (Fig. 2B). The brain infarct volume (8.7± 2.6%) was significantly reduced in Trpv3–/– mice as compared with Trpv3+/+ mice (31 ± 4.9%, Fig. 2C), and the cerebral edema in Trpv3–/– mice was also significantly attenuated with brain water content at 79.6 ± 0.3%, as compared with 81.4 ± 0.5% in Trpv3+/+ mice (Fig. 2D). These in vivo results demonstrated that Trpv3 deficiency could protect against ischemic injury.
Figure 2.
Silencing of TRPV3 attenuates ischemic brain injury. (A) Top panel, a schematic TRPV3 topology illustrating the deletion of exons 13 and 14 that encoding the putative pore region and adjacent transmembrane segments five and six. And the region of residues 458–474 between S1 to S2 transmembrane domain recognized by the monoclonal TRPV3 antibody (ab94582). Bottom panel, the PCR genotyping for confirmation of Trpv3−/− with detected cDNA band at 182 bp, Trpv3+/+ with 304 bp, and Trpv3+/− mice carrying the two bands. (B) Attenuation of neurological deficit scores at time points of day 1, 3 and 5 after 1.5 h tMCAO injury in Trpv3−/− mice. Two-tailed nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. Data are shown as the median with 95% CI, and n indicates the number of mice. ∗P < 0.05. (C) Representative TTC-stained brain slices at 24 h after reperfusion from Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− mice. The white regions indicate the infarct size, and the red regions indicate the viable tissues. Reduction of infarction volume in Trpv3−/− mice subjected to cerebral I/R (1.5 h/24 h) injury. (D) A decrease of brain water content in Trpv3−/− mice subjected to cerebral I/R (1.5 h/24 h) injury. (E) Top panel, a schematic drawing for primary mouse cortical neurons subjected to 30 min oxygen-glucose deprivation and 24 h reoxygenation (OGD/R) injury. The representative images for morphological changes of Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− neurons subjected to OGD/R injury (bottom panel). Scale bar, 100 μm. The statistics of the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release (F) in LDH assay and cell viability (G) by cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) assay of primary cortical neurons subjected to OGD/R injury from Trpv3+/+, Trpv3+/− and Trpv3−/− mice. Data are expressed as means ± SEM, n indicates the number of mice. Two-way ANOVA was used and followed by Dunnett's test from GraphPad 8. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001.
As prolonged oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) can also cause neurotoxicity, we further tested the effect of TRPV3 silencing on cortical neurons subjected to OGD insult for 30 min and reoxygenation for 24 h. As shown in Fig. 2E–G, increase of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release and reduction of cell viability were observed in three different types of neurons subjected to OGD/R damage. In contrast to Trpv3+/+ neurons, these detrimental effects were significantly reduced in Trpv3+/− and Trpv3−/− neurons, further demonstrating that suppressing TRPV3 channel function attenuated OGD-induced neurotoxicity.
3.3. Reduction of neuronal excitability and excitatory transmissions of striatal medium spiny neurons and cortical stellate neurons by Trpv3 silencing
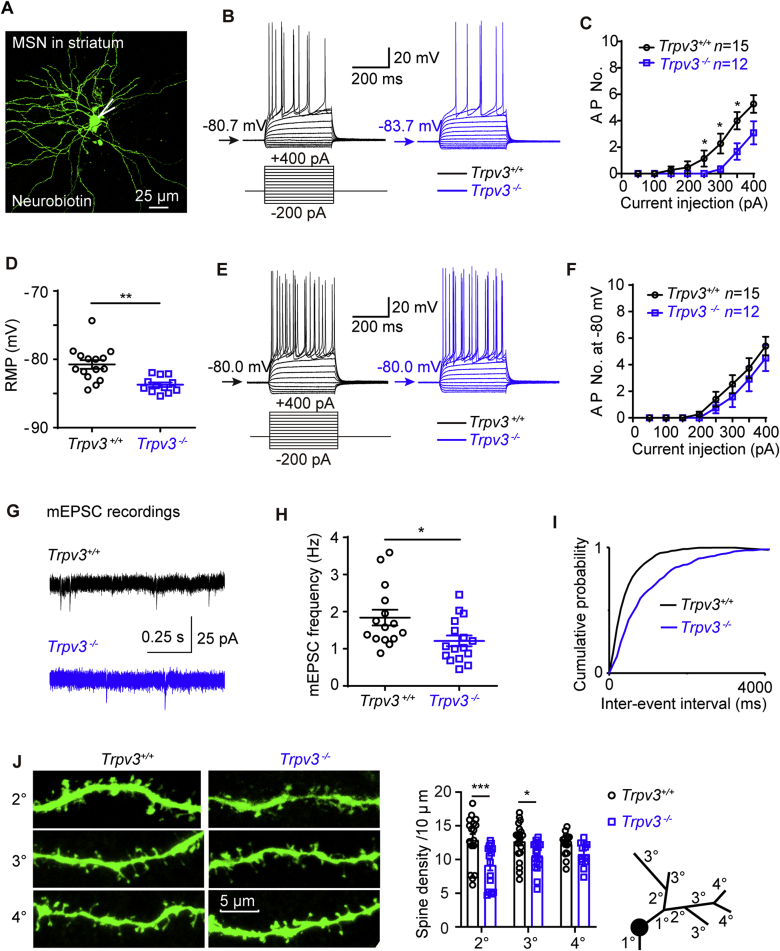
As cortical neurons surrounding acute ischemic infarcts undergo repetitive spontaneous depolarizations54, we reasoned that silencing of TRPV3 might affect neuronal excitability. To test this notion, we carried out brain-slice recordings of principal medium spiny neurons (MSNs, Fig. 3A) from the striatum which is vulnerable to hypoxia and ischemia55. In response to a family of 400 ms current steps, MSNs from Trpv3−/− mice fired significantly fewer action potentials (APs, Fig. 3B and C), and exhibited hyperpolarized resting membrane potential (RMP, Fig. 3D and Supporting Information Table S1). To exclude the influence of voltage-gated ion channels, we held neurons at the membrane potential of −80 mV and recorded APs that showed no significant difference between Trpv3−/− and Trpv3+/+ neurons (Fig. 3E and F), demonstrating that Trpv3−/− MSNs were less excitable due to their hyperpolarized RMP.
Figure 3.
Reduction of neural excitability in Trpv3−/− striatal medium spiny neurons. (A) Morphology of a typical mouse medium spiny neuron (MSN) in the striatum labeled with neurobiotin. (B) Representative traces for neuronal firings by whole-cell current-clamp recordings of the MSN at resting membrane potential (RMP) from Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− mice. (C) The summary of action potential numbers (AP No.) at RMP. AP No. of each current step was analyzed by two-tailed nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. (D) The summary of RMP values. (E) Representative traces for neuronal firings of MSNs at −80 mV from Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− mice. (F) The summary of AP No. at −80 mV. AP No. of each current step was analyzed by two-tailed nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. (G) Representative traces for mEPSCs in striatal MSNs from Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− mice by whole-cell voltage clamp recordings. (H) The frequency of mEPSCs and associated cumulative probability (I). (J) Left panel, representative images showing the morphology of the spines in striatal MSNs from Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− mice. The summary of dendrite spine density (middle panel) and a schematic drawing of dendrite branch classifications (right panel). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n represents the number of neurons patched. Two-way ANOVA was used and followed by Holm–Sidak's test from GraphPad 8. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Also see Fig. S2 for no obvious morphological changes of complex dendritic trees in Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− neurons; Fig. S3 for reduced neural excitability of cortical stellate neurons from Trpv3−/− mice and Table S1 for electrophysiological parameters on medium spiny neurons (MSNs) and layer II principal stellate neurons from medial entorhinal cortex (mEC) from Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− mice and Table S2 for mEPSCs and mIPSCs parameters of mouse striatal MSNs or mEC layer II stellate neurons.
To further explore the impact of Trpv3 null on synaptic transmissions, we recorded miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) and miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) from MSNs of brain slices using voltage-clamp recordings. As shown in Fig. 3G–I and Supporting Information Table S2, the mEPSC frequency of Trpv3−/− neurons was decreased with its cumulative probability moving towards a longer inter-event interval. While the mIPSC frequency was not changed between Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− MSNs, which means the Trpv3 null decreased the excitatory but not the inhibitory synaptic transmissions. Sholl analysis of dendritic trees further showed no observable differences in dendritic trees of MSNs in the striatum (as well as other principal neurons including stellate neurons in mEC layer II and pyramidal neurons in cortical layer V) between Trpv3+/+ and Trpv3−/− neurons (Supporting Information Fig. S2), suggesting that Trpv3 null had little influence on neural development. The dendrite spine density of Trpv3−/− MSNs in striatum was decreased across classifications (2° and 3°, Fig. 3J), consistent with the reduced mEPSC frequency.
We also recorded layer II principal stellate neurons from the medial entorhinal cortex (mEC) that provides the main excitatory inputs to the hippocampus56 (Supporting Information Fig. S3A). Current-clamp recordings of cortical neurons in Trpv3−/− brain slices revealed less firing of APs with lower RMP and smaller input resistance (IR, Fig. S3B–S3E), indicating that cortical stellate Trpv3−/− neurons were less excitable. The mEPSC frequency of Trpv3−/− stellate neurons was also decreased with a longer inter-event interval cumulative probability (Fig. S3F–S3H). And the dendrite spine density was also reduced across classifications (2°, 3° and 4°, Fig. S3I), consistent with the results from Trpv3−/− MSNs. Other kinetic parameters of mEPSCs and all kinetic parameters of mIPSC of stellate neurons or MSNs were not significantly different between the two groups (Table S2). These results demonstrate that Trpv3 null striatal MSNs or cortical stellate neurons exhibited a reduction of both intrinsic neuronal excitability and excitatory transmissions.
3.4. Overexpressing TRPV3 increases neural excitability and aggravates ischemic injury
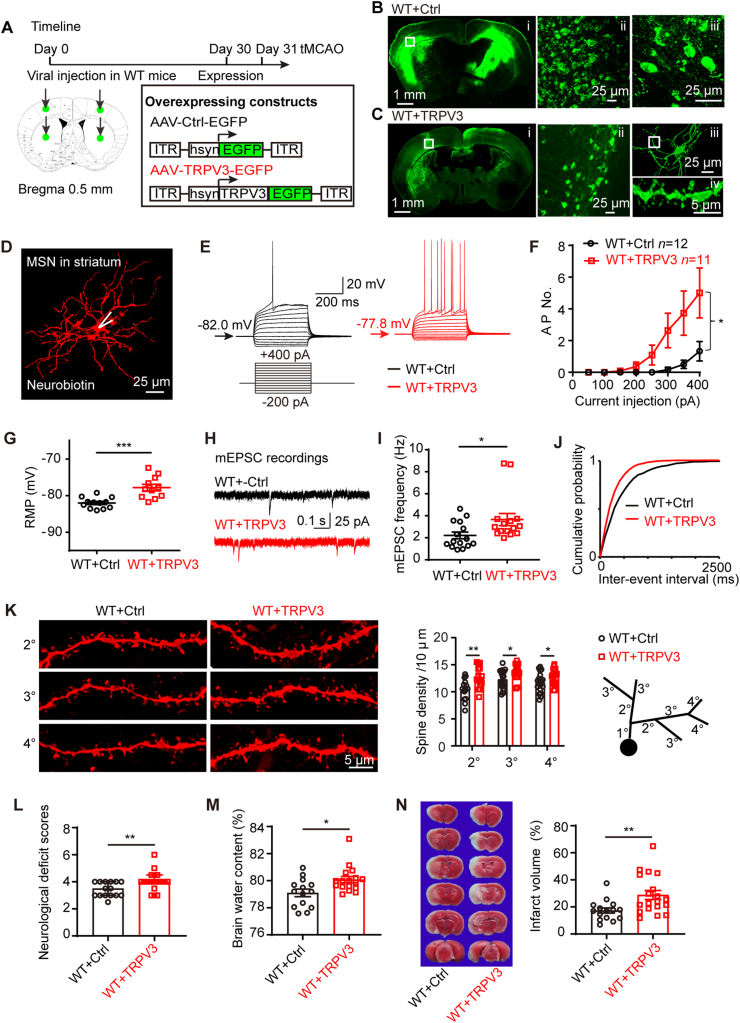
Earlier data show that silencing of TRPV3 reduced ischemic injury and neural excitability, we wondered if overexpressing TRPV3 could lead to an opposite effect. To examine the impact of TRPV3 overexpression on neural excitability, we carried out bilateral intracerebral injections of adeno-associated virus (AAV) constructs of control-EGFP (AAV-Ctrl-EGFP) or TRPV3-EGFP (AAV-TRPV3-EGFP) into mouse cortical and striatal regions (Fig. 4A). Both Ctrl-EGFP and TRPV3-EGFP proteins were robustly expressed in both cortex and striatum 30 days post-injection (Fig. 4Bi and Ci). Fluorescence imaging reveals that the control-EGFP proteins only were expressed in neuronal somata (Fig. 4Bii and 4Biii), whereas TRPV3-EGFP proteins were expressed in neuronal somata, dendrites and dendritic spines (Fig. 4Cii, 4Ciii and 4Civ). TRPV3 channel overexpression in the mouse cortex or striatum was further confirmed by Western blot and real-time PCR analysis (Supporting Information Fig. S4A–S4F). Current-clamp recordings of striatal MSNs overexpressing TRPV3 channels exhibited more firing of APs with depolarized RMP (Fig. 4D–G and Supporting Information Table S3), demonstrating that MSNs overexpressing TRPV3 were hyperexcitable.
Figure 4.
Overexpressing TRPV3 increases neural excitability and aggravates cerebral I/R injury. (A) Experimental timeline for viral injection on Day 0 and detection expression of AAV constructs at day 30 and executing tMCAO model on Day 31, and illustration of bilateral viral injecting sites in mouse cortex and striatum. Schematic drawing of AAV constructs for a control (AAV-Ctrl-EGFP) and overexpression of TRPV3-EGFP (AAV-TRPV3-EGFP). ITR, inverted terminal repeats; hsyn, human synapsin promoter; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein. (B) Representative fluorescent images of coronal mouse brain slice from WT mice injected with control virus after 30 days (Bi, WT + Ctrl) and control-EGFP proteins expressed in neuronal somata (Bii and Biii). The amplifications are from the sensory cortical regions indicated by white square frame. (C) Representative fluorescent coronal brain slice from WT mice injected with TRPV3 overexpressing virus. (Ci, WT + TRPV3) and TRPV3-EGFP proteins expressed in neuronal somata (Cii), dendrites (Ciii) and dendritic spines (Civ) from Ciii. (D) Morphology of a typical mouse MSN in striatum labeled with neurobiotin that we patched. (E) Representative traces for neuronal firings in striatal MSNs from WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 groups obtained at RMP by whole-cell current-clamp recordings. (F) Graph depicting the average AP No. at RMP. AP No. of each current step was analyzed by two-tailed nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. (G) The summary of RMP values. (H) Representative traces for mEPSC in striatal MSNs from WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 groups by whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings. (I) The frequency of mEPSC and associated cumulative probability (J). (K) Representative images showing the morphology of spines in striatal MSNs from WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 mice. The summary of spine density and a schematic drawing of a dendrite. Two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak's test. (L) Increase of neurological deficit scores, (M) brain water content (%) and (N) infarction volume (%) in TRPV3 overexpressing mice subjected to cerebral I/R (1.5/24 h) injury. Data for neurological deficit scores are shown as the median with 95% CI, and was analyzed two-tailed nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, n represents the number of neurons or the number of mice. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Also see Fig. S4 for efficiency of TRPV3 overexpression in mouse cortex and striatum; and Table S3 for electrophysiological parameters of mouse striatal MSNs between WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 groups; Table S4 for mEPSC parameters in mouse striatal MSNs between WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 groups.
Consistent with the observations of intrinsic hyperexcitability, overexpressing TRPV3 channels also resulted in an increased mEPSC frequency (Fig. 4H–J and Table S4), and upregulation of dendrite spine density (Fig. 4K) without significant changes of dendritic tree (Fig. S4G). In the cerebral I/R injury in vivo model, overexpressing TRPV3 exacerbated the neurological deficit scores, increased the brain water content and also the infarct size (Fig. 4L–N). These results indicate that overexpressing TRPV3 caused neural hyperexcitability and aggravated ischemic injury.
3.5. Re-expressing TRPV3 reverses neural excitability and neuroprotection against cerebral I/R injury
To further confirm the causative role of TRPV3 in the cerebral I/R injury, we re-expressed TRPV3 channels in Trpv3 null mice by intracerebral injections of AAV-TRPV3-EGFP or AAV-Ctrl-EGFP constructs into left cortical and striatal regions because we carried out the left MCAO model (Fig. 5A). Current-clamp recordings of MSNs from Trpv3 gene knock-in (Trpv3−/− + TRPV3) mice showed an increased firing, depolarized RMP and increased input resistance as compared with Trpv3 KO neurons transduced with AAV-Ctrl (Trpv3−/− + Ctrl) (Fig. 5B–F and Supporting Information Table S5), indicating that genetic rescue by re-expressing TRPV3 increased neuronal excitability of Trpv3 null neurons.
Figure 5.
Re-expressing TRPV3 reverses neural excitability and neuroprotection against cerebral I/R injury. (A) Experimental timelines for viral injections of AAV-Ctrl-EGFP and AAV-TRPV3-EGFP constructs into the left cortex and striatum in Trpv3 null mice on Day 0 (D0), and generation of tMCAO model on Day 31 (D31). (B) Morphology of a typical mouse MSN in striatum labeled with neurobiotin that we patched. (C) Representative traces obtained in striatal MSNs from Trpv3−/− + Ctrl and Trpv3−/− + TRPV3 mice obtained at RMP by whole-cell current-clamp recordings. (D) The summary of AP No. at RMP. AP No. of each current step was analyzed by two-tailed nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. (E) The statistics of RMP values and (F) input resistance (IR) values at RMP. (G) Representative traces of mEPSC in striatal MSNs from Trpv3−/− + Ctrl and Trpv3−/− + TRPV3 groups by whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings. (H) The frequency of mEPSC and associated cumulative probability (I). (J) Representative images showing the morphology of spines in MSNs from Trpv3−/− + Ctrl and Trpv3−/− + TRPV3 mice and the summary of spine density with a schematic of the dendrite. Exacerbation of neurological deficit scores (K) shown as the median with 95% CI and analyzed by Mann–Whitney test, brain water content (%) (L) and infarction volume (%) (M) in Trpv3−/− + TRPV3 mice subjected to cerebral I/R (1.5/24 h) injury. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n shows the number of neurons or the number of mice. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Also see Fig. S4H for unnoticeable change of the complex dendritic trees in Trpv3−/− + Ctrl and Trpv3−/− + TRPV3 neurons and Table S5 for electrophysiological parameters of mouse striatal MSNs between Trpv3−/− + Ctrl and Trpv3−/− + TRPV3; and Table S6 for mEPSC parameters of mouse striatal MSNs between Trpv3−/− + Ctrl and Trpv3−/−+ TRPV3 groups.
Re-expressing TRPV3 also resulted in an increased mEPSC frequency (Fig. 5G–I and Supporting Information Table S6) and augmented dendrite spine density (Fig. 5J) without dendritic tree change (Fig. S4H), demonstrating that re-expression of TRPV3 channels restored the decreased excitatory network excitability and dendrite spine density of Trpv3 null MSNs. In vivo evaluation further revealed that re-expressing TRPV3 also significantly exacerbated the neurological deficit, increased the brain water content and the infarct area (Fig. 5K–M), further confirming that re-expressing TRPV3 channels in Trpv3 null mouse brain reinstated the susceptibility to ischemic damage.
3.6. Pharmacological inhibition of TRPV3 channel reduces neural excitability and alleviates cerebral I/R injury in mice
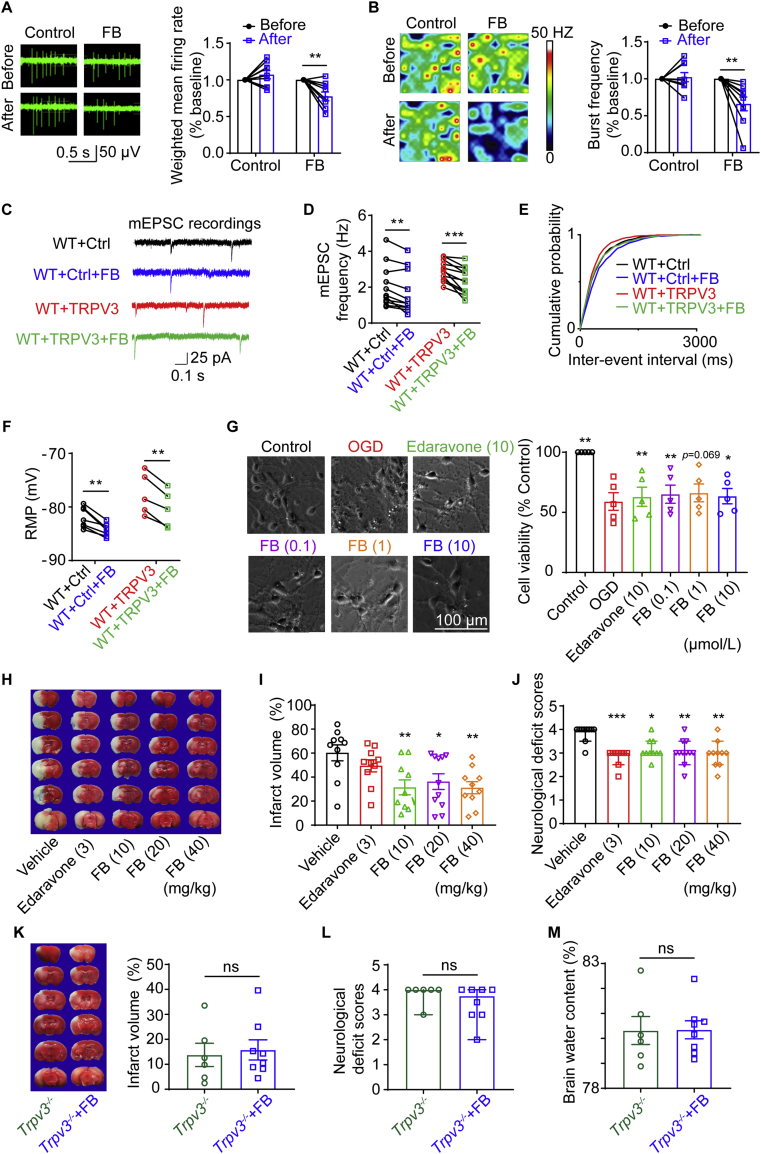
To examine the effect of pharmacological inhibition of TRPV3 on neural excitability, we recently identified a natural TRPV3 inhibitor forsythoside B from plant Lamiophlomis rotate that specifically inhibits TRPV3 current activated by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) at 50 μmol/L with an IC50 of 6.7 μmol/L without obvious inhibitory effects on other thermoTRP channels such as hTRPA1, hTRPV1 and hTRPV457. We recorded the electrophysiological signals of mouse primary cortical neurons in the presence of forsythoside B using the multi-electrode array (MEA) assay. Application of forsythoside B (100 μmol/L) resulted in a decrease of neuronal firing, burst frequency and synchrony index (Fig. 6A, B, and Supporting Information Fig. S5A–S5D). Brain slice recordings further confirmed that perfusion of forsythoside B (50 μmol/L) decreased the mEPSC frequency and the RMP in WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 transduced MSNs (Fig. 6C–F, Supporting Information Tables S7 and S8), meanwhile FB also decreased the mEPSC frequency in WT stellate neurons (Fig. S5E–S5H).
Figure 6.
Pharmacological inhibition of TRPV3 channel by natural compound forsythoside B reduces neural excitability and alleviates ischemia injury. (A) Raw traces from a single electrode recording of mouse primary cortical neurons in multi-electrode array (MEA) system. Cortical neurons produce fewer spikes after 100 μmol/L FB treating. (B) Heat-maps of representative MEA recordings from cortical neurons culture at 37 °C. Application of FB decreases bust frequency of cortical neurons. (n shows the number of wells, ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01 versus before group). (C) Representative traces for mEPSCs in striatal MSNs from before and after 50 μmol/L FB application in WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 groups by whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings. (D) The frequencies of mEPSC with associated cumulative probability (E) before and after 50 μmol/L FB application in WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 groups (∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001, paired student t-test). (F) Application of FB (50 μmol/L) induced hyperpolarized RMP of striatal MSNs from WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 groups. (G) The morphology of primary mouse cortical neurons under normal condition (Control) or subjected to OGD/R injury, or in the presence and absence of different concentrations of FB or edaravone. Scale bar = 100 μm. Summary of cell viability of primary mouse cortical neurons subject to OGD/R injury. n represents the number of independent experiments, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, versus OGD group, one-way ANOVA with the Geisser–Greenhouse correction followed by uncorrected Fisher's LSD test from GraphPad 8. (H) Representative images of TTC-stained mouse brain slices at 24 h after reperfusion. The white regions indicate the infarct size, and the red regions indicate the viable tissues. (I) Reduction of infarction volume (%) in mice subjected to cerebral I/R (1.5 h/24 h) injury by intravenous injection of FB (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) at the beginning of reperfusion. (J) Decreases of neurological deficit scores in mice subjected to cerebral I/R injury by intravenous injection of FB (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) or 3 mg/kg edaravone at the beginning of reperfusion. (K) Lack of neuroprotection by FB (10 mg/kg), neurological deficit scores (L) and brain water content (M) after I/R injury in Trpv3 null mice by intravenous injection at the beginning of reperfusion. n indicates the number of mice, ns, no significance, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 versus vehicle group. Data for infract volume were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test. Data for neurological deficit scores are shown as the median with 95% CI and analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's test from GraphPad 8. Other data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Also see Fig. S5 for pharmacological inhibition of TRPV3 channels by forsythoside B (FB) that reduces neural excitability, Fig. S6 for therapeutic time window of FB on the viability of primary mouse cortical neurons subjected to OGD/R injury and Table S7 for effects of FB (50 μmol/L) on electrophysiological parameters and Table S8 for effects of FB (50 μmol/L) on mEPSC parameters of mouse striatal MSNs from WT + Ctrl and WT + TRPV3 groups.
We also tested the effect of TRPV3 inhibition on primary cortical neurons in the presence of different concentrations of FB (0.1, 1, and 10 μmol/L) added to the culture medium 30 min before exposure to OGD for 20 min maintained for 24 h after reoxygenation. As shown in Fig. 6G, adding forsythoside B or antioxidant edaravone (10 μmol/L) as positive control significantly increased the number of viable cells subjected to OGD injury in CCK-8 assay as compared with OGD vehicle group, demonstrating the protective effect of TRPV3 inhibition on OGD-induced neuronal injury.
We next made intravenous injections of different concentrations of forsythoside B (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) or edaravone (3 mg/kg) at the beginning of reperfusion after mouse tMCAO for 1.5 h. Systematic administration of forsythoside B resulted in a significant reduction of infarct volumes and neurological scores after 24 h (Fig. 6H–J), but no additive effect on Trpv3 null mice (Fig. 6K–M). All these results indicate that pharmacological inhibition of TRPV3 reduced neural hyperexcitability and attenuated ischemic brain injury.
To determine the therapeutic time window of FB, we tested the time-dependent effect of FB on the viability of primary mouse cortical neurons subjected to OGD/R in CCK8 assay. As shown in Supporting Information Fig. S6, addition of FB (10 μmol/L) led to a significant alleviation of neuronal OGD/R injury at time points of 0.5 and 1 h, but not after 2 and 6 h after reoxygenation. These results suggest that inhibition of TRPV3 can alleviate neuronal cell death after an early onset of OGD injury.
4. Discussion
An excessive rise in intracellular Ca2+ during ischemia stroke has previously been shown to be attributed to the NMDA receptor mediated current and excitotoxicity58. However, blocking glutamate receptors has failed to translate any clinical benefits for the last three decades as the high glutamate concentration has a narrow window of only one hour post-stroke17, suggesting a sustained Ca2+ entry after ischemic injury is likely mediated by a non-NMDA mechanism.
In this study we attempted to identify and validate molecular targets underlying the sustained calcium entry that causes progressive brain cell death after stroke. Our rationale is based on the observations that ischemic stroke results in acute brain tissue acidosis due to elevated lactic acid in the affected area. Lactic acid, an alpha hydroxyl acid, is constantly produced from pyruvate by lactate dehydrogenase during normal metabolism; however, its production dramatically increases as ischemia suppresses oxygen-dependent acetyl CoA synthesis process. Although the acetyl CoA-based citric acid cycle is usually the main energy source for living tissues, the latest findings indicate that in mammalian brain lactate is preferentially metabolized59, 60, 61, 62. The resultant strenuous anaerobic process causes acute brain acidosis63. Lactic acid-induced acidosis occurring in well-oxygenated muscles during intense exercise can increase blood lactic acid concentration from 1 to 2 to over 20 mmol/L. In blood supply-deprived brain regions, lactic acid synthesis elevates while its removal is absent. Therefore, lactic acid accumulation can be even more severe. Indeed, upon ischemia onset, within minutes both extracellular and intracellular pH values of the affected region can drop below 6.5, and accumulation of CO2 following ischemic stroke also contributes to a local decrease in pH value64,65.
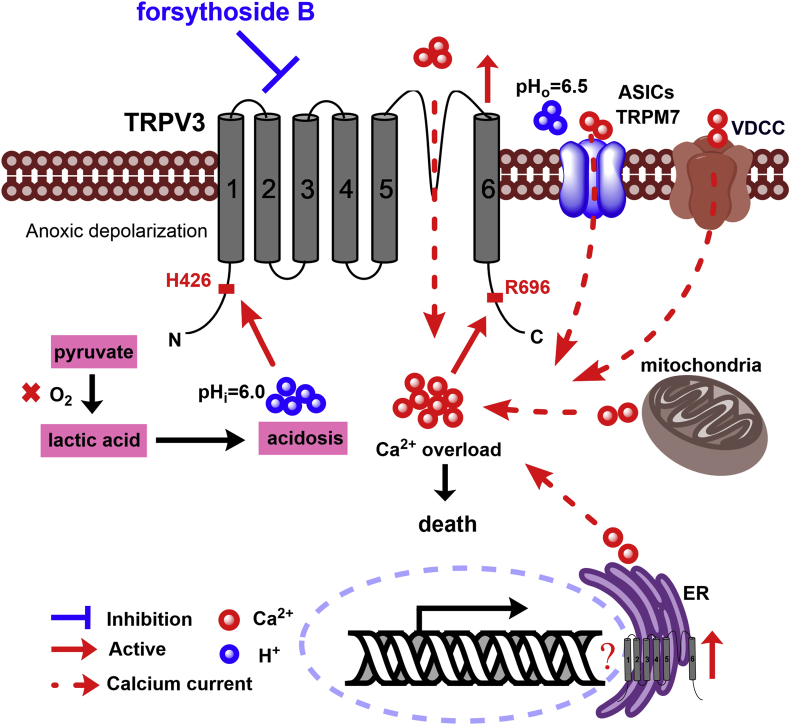
The warm-temperature activated Ca2+-permeable TRPV3 channel expressed in the brain can be directly activated by intracellular acidification24,66, suggesting that TRPV3 can be critical to induce cytotoxicity and cerebral tissue damage after ischemic stroke (Fig. 7). Genetic gain-of-functional mutations of TRPV3 lead to apoptosis of keratinocytes and skin diseases in patients with Olmsted syndrome67, although there is no clinical evidence yet for their susceptibility for ischemic stroke. In hippocampal neurons, TRPV3 has been indicated to contribute to ischemia-induced depolarization, intracellular Ca2+ accumulation and cell swelling52. When hippocampal slices are cooled slightly or when ruthenium red was applied to block TRPV3, these harmful cellular effects are sharply reduced52. Indeed, before TRPV3 and other heat-sensitive TRP channels were discovered, a number of independent studies show that mild hypothermia can protect CA1 neurons from damage caused by experimental ischemia68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74. These observations may help explain the beneficial effects of deliberate hypothermia treatment of patients with head injuries71,75. ThermoTRPV3 is broadly distributed in brain tissues53, and also is present throughout the cortex, thalamus, striatum and cerebellum25,26,51,52, among which its expression and function in hippocampal pyramidal neurons are studied25,26,51,76. Pyramidal neurons lacking thermoTRPV1 or TRPV4 are less excitable, with resting membrane potentials about 5 mV more negative than cells from WT mice77,78. Notably, ruthenium red, a TRPV channel blocker, hyperpolarizes the membrane of WT cells, further supporting that these TRPV channels are open at the resting membrane potential and contributing to depolarization of brain neurons52.
Figure 7.
A proposed mechanism for a causative role of overactive intracellular proton-sensitive and Ca2+-permeable TRPV3 channels in brain ischemic injury. Upon cerebral ischemia injury occurs, quick energy depletion leads to metabolic acidosis resulted from metabolizing pyruvate into lactic acid through the anaerobic pathway. Accumulation of lactic acid1,88 results in intracellular rise of H+ that activates TRPV3 channels likely through binding to intracellular N-terminal H426 site for induction of calcium influx24. Intracellular calcium also actives TRPV3 channels through binding to R696 site89. Energy depletion induces anoxic depolarization that can activate some voltage-dependent calcium channels. In addition, the extracellular acidification (pHo = 6.5)90 can activate acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) and potentiate the activation of transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) channels for further Ca2+ toxicity23. All these cascade events including calcium releases from endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria cause intracellular calcium overload, thus leading to neuronal death. Conversely, pharmacological inhibition of overactive TRPV3 channels by forsythoside B reduces neuronal death and alleviates ischemic brain injury.
TRPV3 channel is activated by arachidonic acid metabolites such as epoxyeicosatrienoic acids that present in cerebral neurons79,80, and can be potentiated by free fatty acids81. The basal activity of TRPV3 makes neurons more susceptible to acidification attack because the channel can conduct H+ current to cause intracellular acidification. The high susceptibility of TRPV3 to a variety of physical and chemical stimuli makes it a very attractive target for clinical intervention under ischemia conditions. It has been reported that a natural incensole acetate, a Boswellia resin constituent, shows protective effects on cerebral ischemic injury82. The incensole acetate, as a non-specific TRPV3 agonist, activates TRPV3 expressed in HEK293 cells at high concentration of 200 μmol/L82, and also inhibits inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, IL-1β, TGF-β and NF-κB to reduce inflammation in cerebral ischemic injury83.
While most H+-activated receptors and channels in the brain can sense extracellular acidification, the warm-temperature sensitive and Ca2+-permeable TRPV3 is an only known member of TRPs activated by intracellular protons24. This distinct feature makes neuronal TRPV3 an interesting and attractive target for stroke pathology and recovery as well as potential intervention. In support of this view, a low extracellular pH level under aerobic conditions has little impact on intracellular calcium [Ca2+]i, whereas hypoxia significantly increases Ca2+ influx in neurons and decreases extracellular pH level84. These observations define TRPV3 as a unique brain pH-sensitive channel that mediates Ca2+ influx. As a non-selective cation channel, TRPV3 is featured of high PCa/PNa ratio of 3–1225,27. Importantly, TRPV3 does not desensitize, and instead, repetitive or prolonged stimulation causes strong potentiation of TRPV3 activation, making the Ca2+-carrying current larger over time85,86. In contrast, most ligand-gated ion channels, including NMDA receptors, can rapidly desensitize upon the persistent presence of ligand molecules, often at a time constant in the range of seconds to minutes.
5. Conclusions
We propose that overactive intracellular proton-sensitive and calcium-permeable TRPV3 plays a causative role in neuronal hyperexcitability and ischemia-induced sustained Ca2+ influx for cerebral injury after stroke (Fig. 7), a mechanism that is independent of NMDA-mediated excitotoxicity. Unlike most other neurological behavioral tests, the neurological deficit scores were determined by Longa's method32, which is positively related to neuronal death87, rather than directly to the neuronal excitabilities. Our data indicate that the over-expression of TRPV3 channels increases neuronal excitabilities, resulting in those neurons more vulnerable to excitatory toxicity or death due to ischemic injury and leading to more severe neurological deficit scores. In consideration of thermoTRPV3 as an attractive drug target with therapeutic potential, we further screened out and identified a natural compound forsythoside B that reduces neuronal hyperexcitability and alleviates ischemic injury. Therefore, pharmacological inhibition of overactive TRPV3 after ischemic injury may lead to an effective prevention and therapy for ischemic brain stroke.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants awarded to KeWei Wang from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81903734 and 81973299) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2018ZX09711001-004-006).
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
Supporting data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2022.01.001.
Author contributions
Xiaoling Chen designed and performed experiments of immunostaining, Western blot, MCAO model, OGD model, MEA recording, dendritic spine, and drafted the manuscript. Jingliang Zhang designed and performed brain slice electrophysiological recordings, and drafted the manuscript. KeWei Wang designed the study and finalized the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following is the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Rehncrona S. Brain acidosis. Ann Emerg Med. 1985;14:770–776. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(85)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Simon R., Xiong Z. Acidotoxicity in brain ischaemia. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:1356–1361. doi: 10.1042/BST0341356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Huang Y., McNamara J.O. Ischemic stroke: “acidotoxicity” is a perpetrator. Cell. 2004;118:665–666. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chu X.P., Xiong Z.G. Acid-sensing ion channels in pathological conditions. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:419–431. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4756-6_36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Siesjo B.K., Katsura K., Kristian T. Acidosis-related damage. Adv Neurol. 1996;71:209–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wang W.Z., Chu X.P., Li M.H., Seeds J., Simon R.P., Xiong Z.G. Modulation of acid-sensing ion channel currents, acid-induced increase of intracellular Ca2+, and acidosis-mediated neuronal injury by intracellular pH. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:29369–29378. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605122200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Guo Y., Zhou I.Y., Chan S.T., Wang Y., Mandeville E.T., Igarashi T., et al. pH-sensitive MRI demarcates graded tissue acidification during acute stroke—pH specificity enhancement with magnetization transfer and relaxation-normalized amide proton transfer (APT) MRI. Neuroimage. 2016;141:242–249. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xiong Z.G., Zhu X.M., Chu X.P., Minami M., Hey J., Wei W.L., et al. Neuroprotection in ischemia: blocking calcium-permeable acid-sensing ion channels. Cell. 2004;118:687–698. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xiong Z.G., Chu X.P., Simon R.P. Acid sensing ion channels—novel therapeutic targets for ischemic brain injury. Front Biosci. 2007;12:1376–1386. doi: 10.2741/2154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xiong Z.G., Pignataro G., Li M., Chang S.Y., Simon R.P. Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) as pharmacological targets for neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008;8:25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2007.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nakamura K., Kamouchi M., Arimura K., Nishimura A., Kuroda J., Ishitsuka K., et al. Extracellular acidification activates cAMP responsive element binding protein via Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1-mediated Ca2+ oscillation in central nervous system pericytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:2670–2677. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.254946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Begum G., Song S., Wang S., Zhao H., Bhuiyan M.I.H., Li E., et al. Selective knockout of astrocytic Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 reduces astrogliosis, BBB damage, infarction, and improves neurological function after ischemic stroke. Glia. 2018;66:126–144. doi: 10.1002/glia.23232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Choi D.W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous-system. Neuron. 1988;1:623–634. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Choi D.W. Calcium-mediated neurotoxicity—relationship to specific channel types and role in ischemic damage. Trends Neurosci. 1988;11:465–469. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee J.M., Zipfel G.J., Choi D.W. The changing landscape of ischaemic brain injury mechanisms. Nature. 1999;399:A7–A14. doi: 10.1038/399a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chamorro A., Dirnagl U., Urra X., Planas A.M. Neuroprotection in acute stroke: targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:869–881. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ikonomidou C., Turski L. Why did NMDA receptor antagonists fail clinical trials for stroke and traumatic brain injury?. Lancet Neurol. 2002;1:383–386. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(02)00164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Albensi B.C., Igoechi C., Janigro D., Ilkanich E. Why do many NMDA antagonists fail, while others are safe and effective at blocking excitotoxicity associated with dementia and acute injury?. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2004;19:269–274. doi: 10.1177/153331750401900502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.MacDonald J.F., Jackson M.F. Transient receptor potential channels of the melastatin family and ischemic responses of central neurons. Stroke. 2007;38:665–669. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000251671.77351.e2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lai T.W., Zhang S., Wang Y.T. Excitotoxicity and stroke: identifying novel targets for neuroprotection. Prog Neurobiol. 2014;115:157–188. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Simard J.M., Tarasov K.V., Gerzanich V. Non-selective cation channels, transient receptor potential channels and ischemic stroke. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1772:947–957. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2007.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang E., Liao P. Brain transient receptor potential channels and stroke. J Neurosci Res. 2015;93:1165–1183. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Leng T., Shi Y., Xiong Z.G., Sun D. Proton-sensitive cation channels and ion exchangers in ischemic brain injury: new therapeutic targets for stroke?. Prog Neurobiol. 2014;115:189–209. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.12.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cao X., Yang F., Zheng J., Wang K. Intracellular proton-mediated activation of TRPV3 channels accounts for the exfoliation effect of alpha-hydroxyl acids on keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:25905–25916. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.364869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xu H., Ramsey I.S., Kotecha S.A., Moran M.M., Chong J.A., Lawson D., et al. TRPV3 is a calcium-permeable temperature-sensitive cation channel. Nature. 2002;418:181–186. doi: 10.1038/nature00882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Smith G.D., Gunthorpe M.J., Kelsell R.E., Hayes P.D., Reilly P., Facer P., et al. TRPV3 is a temperature-sensitive vanilloid receptor-like protein. Nature. 2002;418:186–190. doi: 10.1038/nature00894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Peier A.M., Reeve A.J., Andersson D.A., Moqrich A., Earley T.J., Hergarden A.C., et al. A heat-sensitive TRP channel expressed in keratinocytes. Science. 2002;296:2046–2049. doi: 10.1126/science.1073140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Moqrich A., Hwang S.W., Earley T.J., Petrus M.J., Murray A.N., Spencer K.S., et al. Impaired thermosensation in mice lacking TRPV3, a heat and camphor sensor in the skin. Science. 2005;307:1468–1472. doi: 10.1126/science.1108609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schmitteckert E.M., Prokop C.M., Hedrich H.J. DNA detection in hair of transgenic mice—a simple technique minimizing the distress on the animals. Lab Anim. 1999;33:385–389. doi: 10.1258/002367799780487922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rousselet E., Kriz J., Seidah N.G. Mouse model of intraluminal MCAO: cerebral infarct evaluation by cresyl violet staining. J Vis Exp. 2012;69:4038. doi: 10.3791/4038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Liu F., McCullough L.D. The middle cerebral artery occlusion model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1135:81–93. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0320-7_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Longa E.Z., Weinstein P.R., Carlson S., Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20:84–91. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bu Q., Liu X., Zhu Y., Liu Y., Wang Y. w007B protects brain against ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats through inhibiting inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy. Brain Res. 2014;1558:100–108. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.02.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chiang T., Messing R.O., Chou W.H. Mouse model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Vis Exp. 2011;48:2761. doi: 10.3791/2761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jackman K., Kunz A., Iadecola C. Modeling focal cerebral ischemia in vivo. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;793:195–209. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-328-8_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yan H., Zhang X., Hu W., Ma J., Hou W., Zhang X., et al. Histamine H3 receptors aggravate cerebral ischaemic injury by histamine-independent mechanisms. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3334. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chao X., Zhou J., Chen T., Liu W., Dong W., Qu Y., et al. Neuroprotective effect of osthole against acute ischemic stroke on middle cerebral ischemia occlusion in rats. Brain Res. 2010;1363:206–211. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nunez J. Primary culture of hippocampal neurons from P0 newborn rats. J Vis Exp. 2008;19:895. doi: 10.3791/895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hu Z., Bian X., Liu X., Zhu Y., Zhang X., Chen S., et al. Honokiol protects brain against ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats through disrupting PSD95–nNOS interaction. Brain Res. 2013;1491:204–212. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Guan L., Song Y., Gao J., Gao J., Wang K. Inhibition of calcium-activated chloride channel ANO1 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of epithelium originated cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7:78619–78630. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Livak K.J., Schmittgen T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–ΔΔCT Method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ashwal S., Tone B., Tian H.R., Cole D.J., Pearce W.J. Core and penumbral nitric oxide synthase activity during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Stroke. 1998;29:1037–1046. discussion 47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Memezawa H., Minamisawa H., Smith M.L., Siesjo B.K. Ischemic penumbra in a model of reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Exp Brain Res. 1992;89:67–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00229002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Alessi C., Raspanti A., Magistretti J. Two distinct types of depolarizing afterpotentials are differentially expressed in stellate and pyramidal-like neurons of entorhinal-cortex layer II. Hippocampus. 2016;26:380–404. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Torres-Garcia M.E., Solis O., Patricio A., Rodriguez-Moreno A., Camacho-Abrego I., Limon I.D., et al. Dendritic morphology changes in neurons from the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and nucleus accumbens in rats after lesion of the thalamic reticular nucleus. Neuroscience. 2012;223:429–438. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.07.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zhang J., Chen X., Kårbø M., Zhao Y., An L., Wang R., et al. Anticonvulsant effect of dipropofol by enhancing native GABA currents in cortical neurons in mice. J Neurophysiol. 2018;120:1404–1414. doi: 10.1152/jn.00241.2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sholl D.A. Dendritic organization in the neurons of the visual and motor cortices of the cat. J Anat. 1953;87:387–406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schwieger J., Esser K.H., Lenarz T., Scheper V. Establishment of a long-term spiral ganglion neuron culture with reduced glial cell number: effects of AraC on cell composition and neurons. J Neurosci Methods. 2016;268:106–116. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yang Y., Adi T., Effraim P.R., Chen L., Dib-Hajj S.D., Waxman S.G. Reverse pharmacogenomics: carbamazepine normalizes activation and attenuates thermal hyperexcitability of sensory neurons due to Nav 1.7 mutation I234T. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175:2261–2271. doi: 10.1111/bph.13935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liu D.C., Seimetz J., Lee K.Y., Kalsotra A., Chung H.J., Lu H., et al. Mdm2 mediates FMRP- and Gp1 mGluR-dependent protein translation and neural network activity. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26:3895–3908. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kunert-Keil C., Bisping F., Krüger J., Brinkmeier H. Tissue-specific expression of TRP channel genes in the mouse and its variation in three different mouse strains. BMC Genom. 2006;7:1–14. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lipski J., Park T.I., Li D., Lee S.C., Trevarton A.J., Chung K.K., et al. Involvement of TRP-like channels in the acute ischemic response of hippocampal CA1 neurons in brain slices. Brain Res. 2006;1077:187–199. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Caterina M.J. Transient receptor potential ion channels as participants in thermosensation and thermoregulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292:R64–R76. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00446.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nedergaard M., Hansen A.J. Characterization of cortical depolarizations evoked in focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993;13:568–574. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Calabresi P., Pisani A., Mercuri N.B., Bernardi G. On the mechanisms underlying hypoxia-induced membrane depolarization in striatal neurons. Brain. 1995;118:1027–1038. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.4.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Steward O. Topographic organization of the projections from the entorhinal area to the hippocampal formation of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1976;167:285–314. doi: 10.1002/cne.901670303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang H., Sun X., Qi H., Ma Q., Zhou Q., Wang W., et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the temperature-sensitive and Ca2+-permeable transient receptor potential vanilloid TRPV3 channel by natural forsythoside B attenuates pruritus and cytotoxicity of keratinocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;368:21–31. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.254045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Tu W., Xu X., Peng L., Zhong X., Zhang W., Soundarapandian M.M., et al. DAPK1 interaction with NMDA receptor NR2B subunits mediates brain damage in stroke. Cell. 2010;140:222–234. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zilberter Y., Zilberter T., Bregestovski P. Neuronal activity in vitro and the in vivo reality: the role of energy homeostasis. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010;31:394–401. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2010.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gladden L.B. Lactate metabolism: a new paradigm for the third millennium. J Physiol. 2004;558:5–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.058701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pellerin L., Bouzier-Sore A.K., Aubert A., Serres S., Merle M., Costalat R., et al. Activity-dependent regulation of energy metabolism by astrocytes: an update. Glia. 2007;55:1251–1262. doi: 10.1002/glia.20528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Wyss M.T., Jolivet R., Buck A., Magistretti P.J., Weber B. In vivo evidence for lactate as a neuronal energy source. J Neurosci. 2011;31:7477–7485. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0415-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Siesjö B., Ekholm A., Katsura K., Theander S. Acid-base changes during complete brain ischemia. Stroke. 1990;21:III194–I199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lam T.I., Wise P.M., O'Donnell M.E. Cerebral microvascular endothelial cell Na/H exchange: evidence for the presence of NHE1 and NHE2 isoforms and regulation by arginine vasopressin. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;297:C278–C289. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00093.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Rehncrona S., Rosén I., Smith M.L. Effect of different degrees of brain ischemia and tissue lactic acidosis on the short-term recovery of neurophysiologic and metabolic variables. Exp Neurol. 1985;87:458–473. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(85)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gao L., Yang P., Qin P., Lu Y., Li X., Tian Q., et al. Selective potentiation of 2-APB-induced activation of TRPV1-3 channels by acid. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20791. doi: 10.1038/srep20791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lin Z., Chen Q., Lee M., Cao X., Zhang J., Ma D., et al. Exome sequencing reveals mutations in TRPV3 as a cause of Olmsted syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90:558–564. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.02.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Onitsuka M., Mihara S., Inokuchi H., Shigemori M., Higashi H. Mild hypothermia protects rat hippocampal CA1 neurons from irreversible membrane dysfunction induced by experimental ischemia. Neurosci Res. 1998;30:1–6. doi: 10.1016/s0168-0102(97)00110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Busto R., Dietrich W.D., Globus M.Y.T., Ginsberg M.D. Postischemic moderate hypothermia inhibits CA1 hippocampal ischemic neuronal injury. Neurosci Lett. 1989;101:299–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90549-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Busto R., Dietrich W.D., Globus M.Y.-T., Valdés I., Scheinberg P., Ginsberg M.D. Small differences in intraischemic brain temperature critically determine the extent of ischemic neuronal injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987;7:729–738. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Clifton G.L., Allen S., Barrodale P., Plenger P., Berry J., Koch S., et al. A phase II study of moderate hypothermia in severe brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 1993;10:263–271. doi: 10.1089/neu.1993.10.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Clifton G.L., Jiang J.Y., Lyeth B.G., Jenkins L.W., Hamm R.J., Hayes R.L. Marked protection by moderate hypothermia after experimental traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991;11:114–121. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Resnick D.K., Marion D.W., Darby J.M. The effect of hypothermia on the incidence of delayed traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 1994;34:252–256. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199402000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bramlett H.M., Green E.J., Dietrich W.D., Busto R., Globus M.Y.T., Ginsberg M.D. Posttraumatic brain hypothermia provides protection from sensorimotor and cognitive behavioral deficits. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:289–298. doi: 10.1089/neu.1995.12.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Mellergård P. Changes in human intracerebral temperature in response to different methods of brain cooling. Neurosurgery. 1992;31:671–677. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199210000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Mutai H., Heller S. Vertebrate and invertebrate TRPV-like mechanoreceptors. Cell Calcium. 2003;33:471–478. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4160(03)00062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Shibasaki K., Suzuki M., Mizuno A., Tominaga M. Effects of body temperature on neural activity in the hippocampus: regulation of resting membrane potentials by transient receptor potential vanilloid 4. J Neurosci. 2007;27:1566–1575. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4284-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Edwards J.G., Gibson H.E., Jensen T., Nugent F., Walther C., Blickenstaff J., et al. A novel non-CB1/TRPV1 endocannabinoid-mediated mechanism depresses excitatory synapses on hippocampal CA1 interneurons. Hippocampus. 2012;22:209–221. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Xu H., Delling M., Jun J.C., Clapham D.E. Oregano, thyme and clove-derived flavors and skin sensitizers activate specific TRP channels. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:628–635. doi: 10.1038/nn1692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Fernandes J., Lorenzo I.M., Andrade Y.N., Garcia-Elias A., Serra S.A., Fernandez-Fernandez J.M., et al. IP3 sensitizes TRPV4 channel to the mechano- and osmotransducing messenger 5′-6′-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid. J Gen Physiol. 2008;131:i2. doi: 10.1085/JGP1315OIA2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hu H.Z., Xiao R., Wang C., Gao N., Colton C.K., Wood J.D., et al. Potentiation of TRPV3 channel function by unsaturated fatty acids. J Cell Physiol. 2006;208:201–212. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Moussaieff A., Rimmerman N., Bregman T., Straiker A., Felder C.C., Shoham S., et al. Incensole acetate, an incense component, elicits psychoactivity by activating TRPV3 channels in the brain. FASEB J. 2008;22:3024–3034. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-101865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Moussaieff A., Yu J., Zhu H., Gattoni-Celli S., Shohami E., Kindy M.S. Protective effects of incensole acetate on cerebral ischemic injury. Brain Res. 2012;1443:89–97. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.O'Donnell B.R., Bickler P.E. Influence of pH on calcium influx during hypoxia in rat cortical brain slices. Stroke. 1994;25:171–177. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Chung M.K., Guler A.D., Caterina M.J. Biphasic currents evoked by chemical or thermal activation of the heat-gated ion channel, TRPV3. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:15928–15941. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500596200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Cheng W., Yang F., Liu S., Colton C.K., Wang C., Cui Y., et al. Heteromeric heat-sensitive transient receptor potential channels exhibit distinct temperature and chemical response. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:7279–7288. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.305045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Senda D.M., Franzin S., Mori M.A., de Oliveira R.M., Milani H. Acute, post-ischemic sensorimotor deficits correlate positively with infarct size but fail to predict its occurrence and magnitude after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2011;216:29–35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.06.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Siesjo B.K., Katsura K., Mellergard P., Ekholm A., Lundgren J., Smith M.L. Acidosis-related brain damage. Prog Brain Res. 1993;96:23–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Broad L.M., Mogg A.J., Eberle E., Tolley M., Li D.L., Knopp K.L. TRPV3 in drug development. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2016;9:55. doi: 10.3390/ph9030055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Nedergaard M., Kraig R.P., Tanabe J., Pulsinelli W.A. Dynamics of interstitial and intracellular ph in evolving brain infarct. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:R581–R588. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.260.3.R581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.