Abstract
We previously demonstrated that Npy1rrfb mice, which carry the conditional inactivation of the Npy1r gene in forebrain principal neurons, display a sexually dimorphic phenotype, with male mice showing metabolic, hormonal and behavioral effects and females being only marginally affected. Moreover, exposure of Npy1rrfb male mice to a high-fat diet (HFD) increased body weight growth, adipose tissue, blood glucose levels and caloric intake compared to Npy1r2lox male controls. We used conditional knockout Npy1rrfb and Npy1r2lox control mice to examine whether forebrain disruption of the Npy1r gene affects susceptibility to obesity and associated disorders of cycling and ovariectomized (ovx) female mice in a standard diet (SD) regimen or exposed to an HFD for 3 months. The conditional deletion of the Npy1r gene increased body weight and subcutaneous white adipose tissue weight in both SD- and HFD-fed ovx females but not in cycling females. Moreover, compared with ovx control females on the same diet regimen, Npy1rrfb females displayed increased microglia number and activation, increased expression of Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-immunoreactivity (IR) and decreased expression of proopiomelanocortin-IR in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARC). These results suggest that in the ARC NPY-Y1R reduces the susceptibility to obesity of female mice with low levels of gonadal hormones and that this effect may be mediated via NPY-Y1R ability to protect the brain against neuroinflammation.
Keywords: obesity, high-fat diet, ovariectomy, hypothalamic Y1R receptors, neuroinflammation
1. Introduction
The incidence of metabolic disorders including obesity in women is lower than in men; however, prevalence of these disorders increases dramatically after menopause and is associated with an increased risk of inflammatory disorders (including type II diabetes, cardiovascular diseases) [1,2,3]. Considering the well described anti-inflammatory role of estrogens [4], it is conceivable that there is a role for this hormone in these dysmetabolic disorders.
A sexually dimorphic vulnerability to obesity is generally observed in mammals. For instance, in rodents exposed to a high-fat diet (HFD), females are generally more resistant to HFD-induced obesity than males [5,6,7,8]. Most interestingly, in male mice HFD-induced obesity is associated with hypothalamic microglial activation [9,10], while this is not observed in females that do not show the HFD-induced accumulation of reactive, pro-inflammatory microglia in the hypothalamus [11,12]. This suggests an involvement of the hypothalamus in the differential susceptibility to HFD-induced obesity of males and females.
Estradiol plays a leading role in the regulation of energy homeostasis in female mammals, and declining levels of estradiol in ovariectomized (ovx) rodents and postmenopausal women are associated with body weight increase and fat redistribution [2,13,14,15]. Moreover, estradiol has a protective effect against the development of diet-induced microgliosis in the hypothalamic nuclei involved in the control of food intake [5,10,11]. Several studies have demonstrated that, at the hypothalamic level, estrogens inhibit food intake and adipocyte activity by decreasing the excitability of the neuropeptide Y (NPY)/Agouti-related protein (AgRP) neurons in the arcuate (ARC) [15,16,17], which project to other nuclei of the circuit controlling food intake, including the paraventricular (PVN), ventromedial (VMH) and dorsomedial (DMH) nuclei [18]. Estrogens modulate NPY expression and Npy1r gene activity [15,19] and regulate Y1 (Y1R) expression during the estrous cycle [20] or after exposure to different diets [21], thus playing a role in the changes in feeding behavior characteristic of the estrous cycle. NPY is identified as the most potent orexigenic peptide that responds to peripheral orexigenic and anorexigenic signals such as ghrelin, leptin and insulin to regulate feeding [22,23,24,25]. Acute administration of NPY increases food intake and induces hyperinsulinemia [26], whereas its chronic administration produces hyperphagia and obesity and decreases thermogenesis [27]. Dysfunctions of the NPY system have been observed in diseases such as obesity, type II diabetes and metabolic syndrome [28,29,30]. NPY interacts with a family of G-protein coupled receptors, the most well-known being the Y1, the Y5 and the presynaptic Y2 receptors [31,32,33].
Several studies demonstrated that the NPY-Y1R system is sexually dimorphic and sensitive to gonadal steroids [16,17,32,34]. Sex-specific differences in NPY and Y1R expression in the hypothalamic system controlling food intake have been found by our and others’ laboratories [35,36,37,38,39]. Conditional knock-out mice (Npy1rrfb mice), carrying the deletion of the Npy1r gene in in forebrain principal neurons starting from a juvenile age [40,41], show a sexually dimorphic phenotype, revealing the existence of NPY-Y1R neuronal pathways involved in sex-biased differences of metabolic functions [42]. Indeed, Npy1rrfb male mice exhibited hyperactivation of the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis, reduced body weight growth, after-fasting refeeding, white adipose tissue (WAT) and plasma leptin levels compared with their Npy1r2lox control littermates. Conversely, mutant female mice appeared to be resilient to the effects of Npy1r gene inactivation on hormone and metabolic functions [42]. Interestingly, Npy1r mRNA expression was reduced in the ARC and in the PVN of female, but not male mice. In addition, Npy1rrfb male mice fed with an HFD display increased body weight, visceral adipose tissue and blood glucose levels, and food and calories intake as compared to control Npy1r2lox mice, suggesting that, in male mice, inactivation of the Npy1r gene increases susceptibility to diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance, which may be indexes of metabolic syndrome [43].
To better understand the role of gonadal hormones–NPY system interaction and hypothalamic microglia activity in the sex-specific susceptibility to obesity and associated disorders, in the present study we investigated the effect of the conditional inactivation of the Npy1r gene in the forebrain of sham (correctly cycling) and ovariectomized (ovx) female mice fed with a standard diet (SD) or with an HFD.
2. Results
Table 1 summarizes the ANOVA analysis of the results.
Table 1.
Statistical analysis.
| Measures | Female Mice | ANOVA | Variables | Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight | Cycling | 2-way RM |
Diet: F(1,101) = 80.54, p = 0.000 | Days–diet: F(11,1111) = 22.06, p = 0.000 |
| ovx | 2-way RM |
Genotype: F(1,96) = 13.99 p = 0.000 Diet: F(1,96) = 91.04, p = 0.000 |
Days–diet–genotype: F(11,1056) = 4.41; p = 0.000 Days–genotype: F(11,1056) = 7.35 p = 0.000 Days–diet: F(11,1056) = 107.36, p = 0.000 |
|
| Subcutaneous WAT | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Genotype: F(1,94) = 12.71, p = 0.001 Diet: F(1,94) = 279.77; p = 0.000 ovx: F(1,94) = 283.34; p = 0.000 |
Genotype–ovx: F(1,94) = 5.47; p = 0.022 ovx–diet: F(1,94) = 17.43; p = 0.000 |
| Visceral WAT |
Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,94) = 185.31; p = 0.000 ovx: F(1,94) = 116.32; p = 0.000 |
Genotype–diet: F(1,94) = 5.43; p = 0.022 |
| Gonadic WAT | cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,94) = 232.01; p = 0.000 ovx: F(1,94) = 33.14; p = 0.000 |
Diet–ovx: F(1,94) = 26.18; p = 0.000 |
| Leptin | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,117) = 107.80, p = 0.000 ovx: F(1,117) = 120.41, p = 0.000 |
|
| Spontaneous locomotor activity | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,82) = 16.58; p = 0.000 ovx: F(1,82) = 41.42; p = 0.000 |
Genotype–ovx–diet: F(1,82) = 5.19; p = 0.025 ovx–diet: F(1,82) = 7.7905; p = 0.007 |
| Cumulative energy intake | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,24) = 52.50, p = 0.000 | |
| 9-day energy intake | Cycling and ovx | 3-way RM |
Diet: F(1,240) = 52.50, p = 0.000 | |
| GTT | Cycling and ovx | 3-way RM |
Diet: F(1,112) = 25.62; p = 0.000 ovx: F(1,112) = 10.62; p = 0.002 |
Diet–hours: F(3,336) = 7.46; p = 0.000 |
| GTT AUC | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,112) = 26.38; p = 0.000 ovx: F(1,112) = 9.06; p = 0.003 |
|
| ITT | Cycling and ovx | 3-way RM |
Diet: F(1,80) = 9.74; p = 0.003 | Diet–hours: F(3,240) = 6.08; p = 0.001 |
| ITT AUC | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,80) = 10.21; p = 0.002 | |
| PTT | Cycling and ovx | 3-way RM |
Diet: F(1,85) = 19.04; p = 0.000 | Diet–ovx: F(1,85) = 5.12; p = 0.026 |
| PTT AUC | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,85) = 19.23; p = 0.000 | |
| Heart rate | Cycling and ovx |
3-way | ovx: F(1,80) = 15.39; p = 0.000 | |
| ARC AgRP-IR | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,62) = 31.34, p = 0.000 ovx: F(1,62) = 21.1, p = 0.000 |
Genotype–diet: F(1,62) = 7.80, p = 0.007 |
| PVN AgRP-IR | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Genotype: F(1,57) = 4.54, p = 0.037 Diet: F(1,57) = 12.13, p = 0.001 ovx: F(1,57) = 14.24, p = 0.000 |
|
| ARC NPY-IR | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Genotype: F(1,45) = 5.11, p = 0.029 ovx: F(1,45) = 4.82, p = 0.033 |
Genotype–ovariectomy: F(1,45) = 4.35, p = 0.043 ovx–diet: F(1,45) = 5.38, p = 0.025 |
| ARC NPY-IR | ovx | 2-way | Genotype: F(1,21) = 10.44, p = 0.004 Diet: F(1,21) = 6.11, p = 0.022 |
|
| ARC POMC-IR | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Genotype: F(1,68) = 15.00; p = 0.000 | Genotype–ovx: F(1,68) = 6.86; p = 0.011 Diet–ovx: F(1,68) = 5.44; p = 0.023 |
| PVN POMC-IR | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Diet: F(1,61) = 4.04; p = 0.049 ovx: F(1,61) = 10.48; p = 0.002 |
|
| Microglia cb/c | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Genotype: F(1,32) = 5.95; p = 0.021 Diet: F(1,32) = 5.98; p = 0.020 ovx: F(1,32) = 36.01; p = 0.000 |
Genotype–ovx: F(1,32) = 6.35; p = 0.017 Diet–ovx: F(1,32) = 4.80; p = 0.036 |
| Microglia number | Cycling and ovx | 3-way | Genotype: F(1,32) = 5.91; p = 0.021 ovx: F(1,32) = 44.80; p = 0.000 |
Genotype–ovx: F(1,32) = 4.61; p = 0.039 Diet–ovx: F(1,32) = 4.27; p = 0.047 |
| Microglia cb/c | ovx | 2-way | Genotype: F(1,15) = 7.23, p = 0.017 Diet: F(1,15) = 6.32, p = 0.024 |
|
| Microglia number | ovx | 2-way | Genotype: F(1,15) = 8.80, p = 0.010 Diet: F(1,15) = 4.83, p = 0.044 |
2.1. Conditional Inactivation of the Npy1r Gene Is Associated with Increased Body and Fat Weight in Ovariectomized, but Not in Cycling Female Mice
2.1.1. Body Weight
After the beginning of the comparison of SD and HFD effects (day 60) in female mice, periodic measurement of body weight did not show significant differences between cycling Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb female mice, independently of the diet regimen (Figure 1A). This was not the case in ovx mice, where the conditional ablation of the Npy1r gene induced a growth in body weight that in time became significantly more pronounced in the Npy1rrfb mice. Furthermore, mutant mice appeared to be also more susceptible to the effect of the HFD, with a generalized trend to an increased weight growth which was significant towards the middle of the treatment (Figure 1B). The lack of significant differences after the 60th day of the diet regimen (postnatal day 120, P120) between HFD-fed ovx Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb females was attributed to the presence of a ceiling effect.
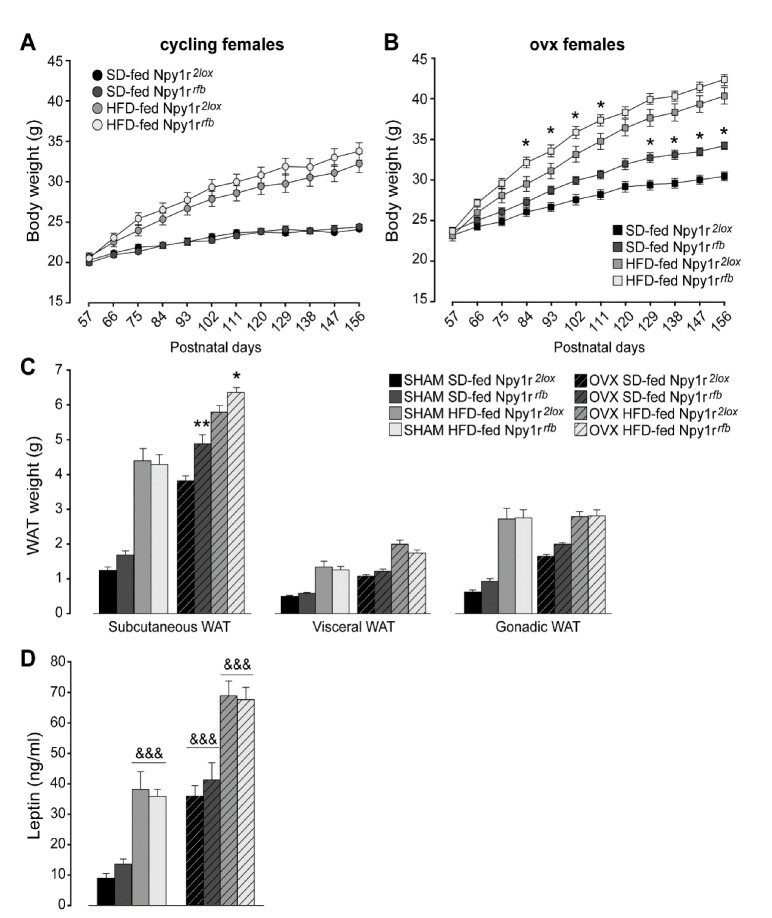
Figure 1.
Body weight of standard diet (SD)- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed cycling (A) and ovx (B) Npy1r2lox control and Npy1rrfb knockout female mice. No significant differences in body weight growth were observed between cycling Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb female mice during postnatal days (P) 57–156, independently of diet regimen. SD- and HFD-fed ovx Npy1rrfb females displayed a significantly greater body weight compared with their control littermates on the same diet regimen. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 17–26 from 6 litters. * p < 0.05 versus the corresponding control females. (C) Adiposity of standard diet (SD)- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox control and Npy1rrfb knockout female mice. Significantly larger depots of subcutaneous fat were observed in ovx Npy1rrfb females compared with their control littermates on the same diet regimen. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 10–15 from 3 litters. ** p < 0.01 and * p < 0.05 versus SD-fed and HFD-fed ovx Npy1r2lox female mice, respectively. (D) Leptin plasma levels of standard diet (SD)- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox control and Npy1rrfb knockout female mice. Both ovariectomy and HFD increased leptin plasma levels of female mice. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 10–15 from 3 litters. &&& p < 0.001.
These observations suggested that gonadal hormones were able to functionally mask the lack of Y1R activity in glutamatergic neurons, thus maintaining a balanced body weight in the SD and a physiological response to the HFD.
2.1.2. White Adipose Tissue (WAT) Weight
Overall, the HFD and ovariectomy significantly increased subcutaneous, visceral and gonadic WAT weight (Figure 1C). Similar to what was observed with regard to body weight, both SD- and HFD-fed ovx Npy1rrfb females displayed greater subcutaneous WAT weight compared with ovx control female mice on the same diet regimen (Figure 1C). No significant differences in visceral and gonadic WAT weight were observed between cycling or ovx Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb female mice, independently of the diet regimen (Figure 1C).
2.1.3. Leptin Plasma Levels
Both the HFD and ovariectomy significantly increased leptin plasma levels (Figure 1D). Neither cycling nor ovx Npy1rrfb females showed differences in leptin plasma levels compared with their control littermates on the same diet regimen (Figure 1D). These results suggest that an altered peripheral regulation of leptin release in the absence of gonadal hormones might determine the lack of enhanced leptin levels despite the increase of WAT weight in ovx Npy1rfb mice.
2.2. Npy1r Gene Inactivation Decreased Locomotor Activity but Failed to Affect the Food Intake of SD- and HFD-Fed Cycling and Ovariectomized Female Mice
2.2.1. Spontaneous Locomotor Activity
Overall, the HFD and ovariectomy decreased spontaneous locomotor activity in all experimental groups (Figure 2A). Npy1r gene inactivation further decreased spontaneous locomotor activity in HFD-fed cycling females and in SD-fed ovx females (Figure 2A). To test the relationship between body weight and locomotor activity, we used a regression analysis with locomotor activity as the dependent variable and body weight as the predictor. Body weight statistically predicted locomotor activity (b = −929.52, t(86) = −7.74, p < 0.001) and explained 64% of the variance in locomotor activity (R2 = 0.64, F(1,86) = 60.20, p < 0.001) (Figure 2B).
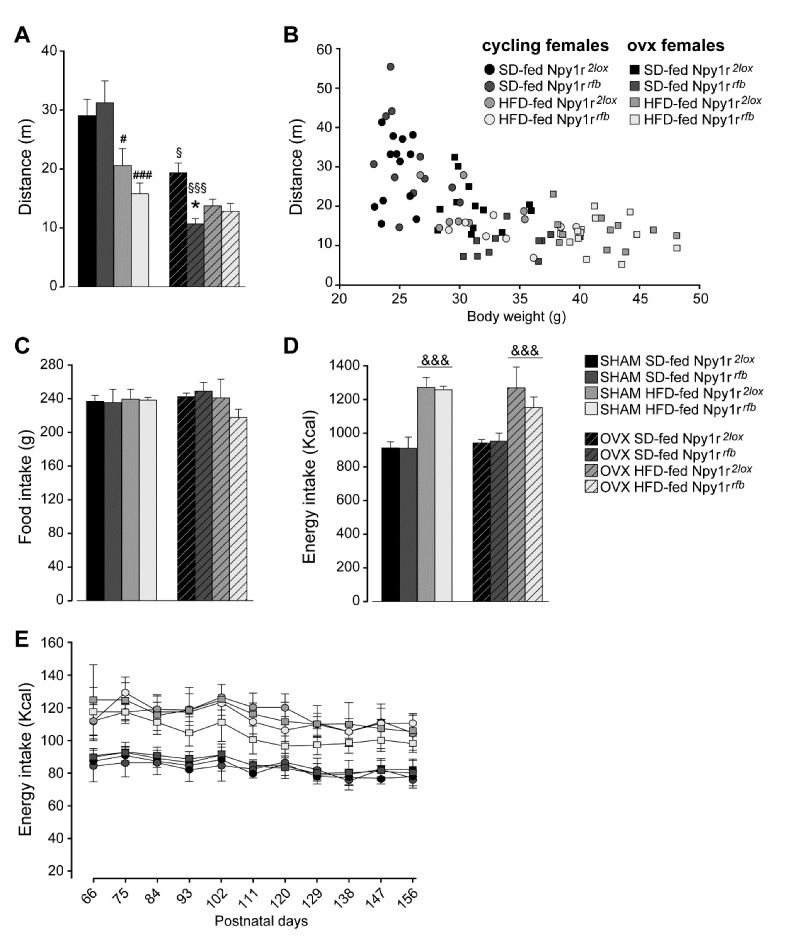
Figure 2.
(A) Spontaneous locomotor activity of standard diet (SD)- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox control and Npy1rrfb knockout female mice. Both HFD and ovariectomy significantly decreased locomotor activity (distance traveled, cm) of Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb female mice. HFD-fed cycling and SD-fed ovx Npy1rrfb females showed significantly lower locomotor activity compared with their corresponding controls. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 8–12 from 2 litters. # p < 0.05 versus SD-fed cycling controls; ### p < 0.001 versus SD-fed cycling Npy1rrfb female mice; § p < 0.05 versus SD-fed cycling controls; §§§ versus SD-fed cycling Npy1rrfb female mice; * p < 0.05 versus SD-fed ovx controls. (B) Correlation between locomotor activity and body weight of 156 days old SD- and HFD-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb female mice. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 6 from 3 litters. Food and energy intake of standard diet (SD)- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox control and Npy1rrfb knockout female mice (C–E). (C) No significant differences of cumulative food intake (g) were observed among the different experimental groups. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 4 from 3 litters. (D) HFD increased cumulative energy intake (Kcal) of cycling and ovx female mice, independently of the genotype. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 6 from 3 litters. &&& p < 0.001 versus SD-females. (E) Nine-day cumulative energy intake (kcal) of SD- and HFD-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox control and Npy1rrfb knockout female mice during the metabolic challenge procedure (P66–156). Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 6 from 3 litters.
2.2.2. Daily Food Intake
Analysis of the average cumulative amount of chow eaten showed that female mice of the different experimental groups consumed the same total amount of food over the entire length of the experiment, independently of the genotype (Figure 2C). Accordingly, the cumulative energy intake of HFD-fed cycling and ovx females was significantly higher than that measured in the corresponding controls on the SD regimen (Figure 2D). These data are confirmed by the analysis of energy intake every 9 days in the eight groups of mice. Both cycling and ovx control and conditional mutant mice increased energy intake when fed with HFD and no differences were observed during the length of the experiment (Figure 2E).
These results suggest that a reduced locomotor activity rather than an increased caloric intake might contribute to determine the obesity-like phenotype of Npy1rrfb conditional mutants in the absence of gonadal hormones.
2.3. Npy1r Gene Inactivation Failed to Affect Glucose Homeostasis and Metabolism, Heart Rate and Blood Pressure of SD- and HFD-Fed Cycling and Ovariectomized Female Mice
2.3.1. Glucose Homeostasis and Metabolism
Glucose tolerance tests (GTT, to assess glucose clearance from the blood) and insulin tolerance tests (ITT, to assess insulin resistance) were performed as measures of glucose homeostasis.
Three-way ANOVA analysis for repeated measures of glucose concentrations during GTT revealed that the HFD and ovariectomy decreased glucose tolerance during GTT (Figure 3A). Moreover, both ovariectomy and diet significantly increased the area under the curve (AUC) (Figure 3B).
Figure 3.
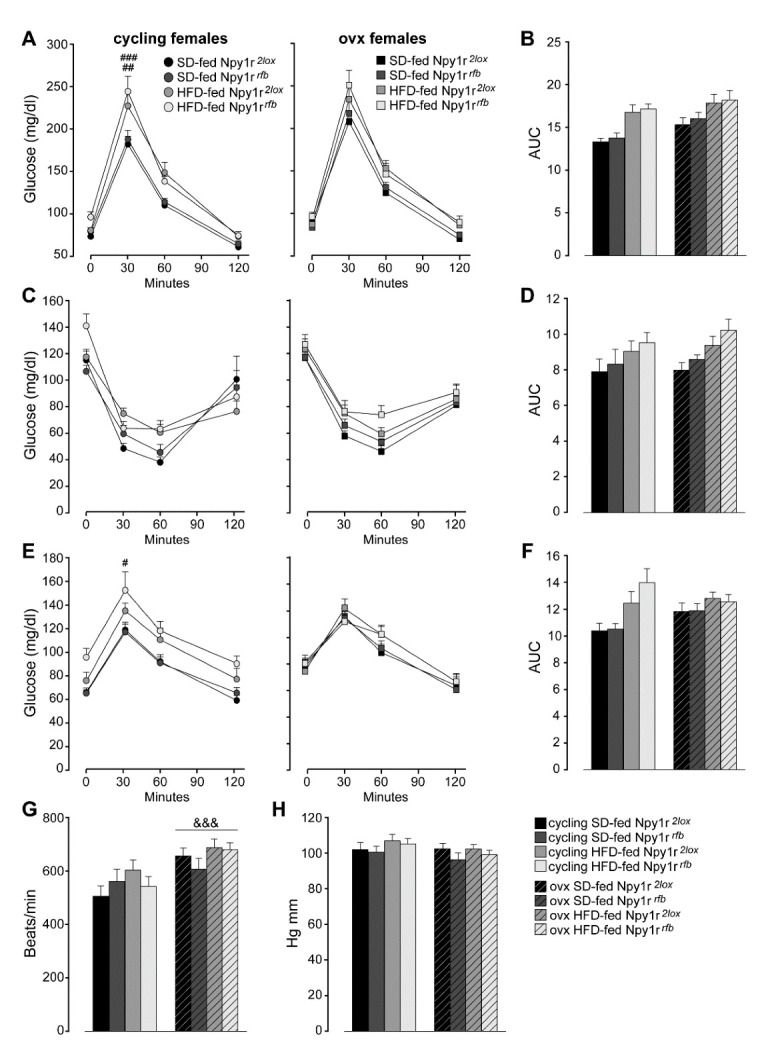
Glucose homeostasis and metabolism of standard diet (SD)- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox control and Npy1rrfb knockout female mice (A–F). (A) Glucose tolerance tests and (B) area under the curve (AUC) of SD- and HFD-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb females. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 11–20 from 3 litters. ## p < 0.01 HFD-fed versus SD-fed cycling controls; ### p < 0.001 HFD-fed versus SD-fed cycling Npy1r2lox female mice. (C) Insulin tolerance test and (D) area under the curve (AUC) of SD- and HFD-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb females. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 7–15 from 2 litters. (E) Pyruvate tolerance test and (F) area under the curve (AUC) of SD- and HFD-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb females. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 7–16 from 2 litters. # p < 0.05 HFD-fed versus SD-fed cycling Npy1rrfb females. (G) Heart rate and (H) blood pressure of standard diet (SD)- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox control and Npy1rrfb knockout female mice. &&& p < 0.001 versus cycling females.
In addition, both cycling and ovx HFD-fed mice showed delayed glucose clearance in response to exogenous insulin during ITT (Figure 3C). HFD also increased the AUC (Figure 3D).
To further explore the impact of ovariectomy and an HFD on liver glucose metabolism in control and mutant female mice, we examined pyruvate incorporation into glucose via gluconeogenesis in a pyruvate tolerance test (PTT). As shown in Figure 3E, the HFD increased glucose concentrations during PTT in cycling but not in ovx mice. Moreover, HFD-fed cycling females showed a significant increase of the AUC (Figure 3F).
Neither cycling nor ovx Npy1rrfb females showed differences in GTT, ITT and PTT compared with their control littermates on the same diet regimen (Figure 3A–F).
Taken together, these results show an increased adiposity without significant changes in glucose homeostasis and metabolism in ovx Npy1rrfb females and suggest a specific role of Y1R in the regulation of fat accumulation in the absence of gonadal hormones.
2.3.2. Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
A significant increase of heart rate was observed in ovx females, independently of genotype and diet regimen (Figure 3G). No difference in blood pressure was observed among mice groups (Figure 3H).
2.4. Effects of Npy1r Inactivation on the Expression of Neuropeptides Implicated in the Control of Energy Metabolism in the ARC and PVN of SD- and HFD-Fed Cycling and Ovariectomized Female Mice
2.4.1. AgRP
Overall, both ovx and HFD-fed mice showed a significant decrease of AgRP expression in the ARC compared with cycling and SD-fed females, respectively (Figure 4A). Conditional inactivation of the Npy1r gene induced a significant decrease of AgRP-IR in the ARC of SD-fed cycling females compared to their control littermates. A decrease of AgRP-IR was also observed in SD-fed ovx Npy1rrfb females, although it was not significant (Figure 4A,C).
Figure 4.
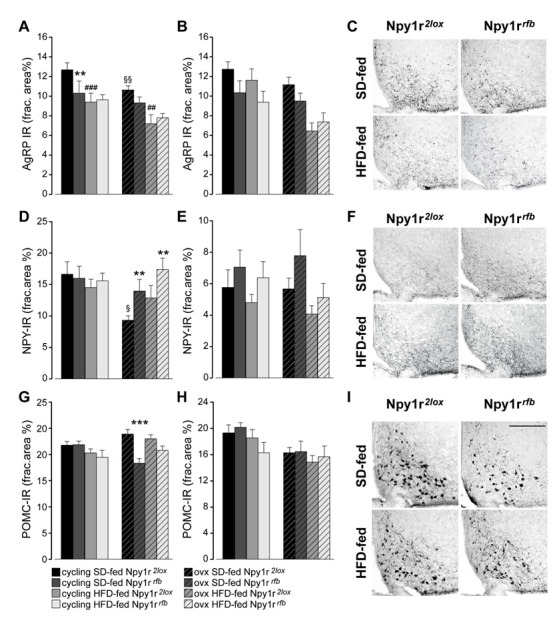
Expression of neuropeptides in the ARC and PVN of standard diet (SD)- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox control and Npy1rrfb knockout female mice. Agouti-related protein immunoreactivity (AgRP-IR) in the ARC (A) and in the PVN (B) of SD- and HFD-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb females. HFD and ovx significantly decreased AgRP expression in the ARC of female mice. SD-fed cycling Npy1rrfb conditional mutants showed a significant decrease of AgRP-IR in the ARC compared to SD-fed cycling control females. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 8–9 (ARC) and n = 7–10 (PVN) from 2 litters. ** p < 0.01 and ### p < 0.001 versus SD-fed cycling Npy1r2lox females; §§ p < 0.01 versus SD-fed cycling Npy1r2lox; mice; ## p < 0.01 versus SD-fed ovx Npy1r2lox female mice. (C) Representative images of the ARC of ovx females expressing AgRP-IR immunoreactivity (scale bar: 150 μm). Neuropeptide Y immunoreactivity (NPY-IR) in the ARC (D) and in the PVN (E) of SD- and HFD-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb females. A significant decrease of NPY-IR was observed in the ARC of ovx Npy1r2lox mice compared with cycling Npy1r2lox mice. A significant increase of NPY-IR was observed in the ARC of ovariectomized Npy1rrfb mice compared with their control littermates on the same diet regimen. § p < 0.05 versus cycling Npy1r2lox females on the same diet regimen. ** p < 0.01 versus ovx Npy1r2lox on the same diet regimen. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 5–8 from 2 litters. (F) Representative images of the ARC of ovx females expressing NPY-IR immunoreactivity (scale bar: 150 μm). Proopiomelanocortin immunoreactivity (POMC-IR) in the ARC (G) and in the PVN (H) of SD- and HFD-fed cycling and ovx Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb females. A significant decrease of POMC-IR was observed in the ARC of SD-fed ovx Npy1rrfb mice compared with SD-fed ovx Npy1r2lox mice. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 7–11 from 2 litters. *** p < 0.001 versus SD-fed ovx Npy1r2lox mice. (I) Representative images of the ARC of ovx females expressing POMC-IR (scale bar: 150 μm).
A similar pattern of AgRP expression was observed in the PVN. The overall analysis revealed a significant effect of ovariectomy, diet and genotype (Figure 4B).
2.4.2. NPY
As shown in Figure 4D, SD-fed ovx Npy1r2lox females displayed a significant decrease of NPY expression compared with SD-fed cycling control females. In ovx females, the inactivation of the Npy1r gene significantly increased NPY-IR in the ARC of Npy1rrfb mice compared with Npy1r2lox mice on the same diet regimen (Figure 4D,F). No significant differences in NPY expression were observed among the experimental groups in the PVN (Figure 4E).
2.4.3. Proopiomelanocortin (POMC)
As shown in Figure 4G,I, a significant decrease of POMC-IR was observed in the ARC of SD-fed ovx Npy1rrfb females compared with their corresponding controls. In the PVN, both ovariectomy and diet significantly decreased POMC-IR, independently of the genotype (Figure 4H).
2.5. Npy1r Gene Inactivation Is Associated with Increased Microglial Number and Activation in the Arcuate Nucleus of Ovariectomized, but Not Cycling Female Mice
The total cell body size divided by the total cell size (cb/c) was used as measure of microglial activation. The genotype did not affect microglial activation (Figure 5A) and the number of microglia (Figure 5C) in cycling animals. The Npy1r gene deletion clearly affected the microglia state of activity after ovariectomy as both the morphology (Figure 5B) and number of microglia cells (Figure 5D) were increased in animals fed by the SD and even more in animals subjected to the HFD (Figure 5E,F).
Figure 5.
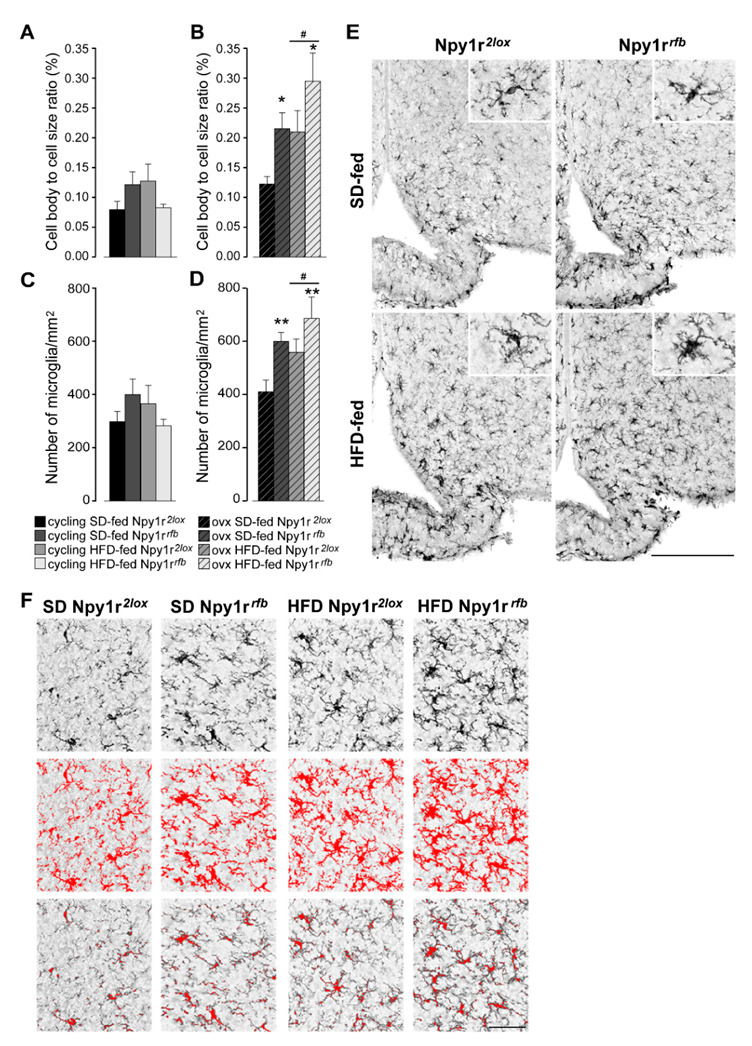
Effect of HFD and Npy1r gene deletion on microglial activation and microglia number. The cell body to cell size ratio (cb/c) of microglia (A,B) and the number of microglia/mm2 (C,D). HFD significantly increased cb/c (B) and microglia number (D) in the ARC of ovx females. Conditional inactivation of Npy1r gene increased cb/c (B) and microglia number (D) in the ARC of SD- and HFD-fed ovx mice. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 4–6 from 2 litters. # p < 0.05 versus SD-fed ovx females. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 versus Npy1r2lox ovx females on the same diet regimen. (E) Representative images of the ARC of ovx females expressing ionized calcium-binding adaptor protein-1 (IBA-1) immunoreactivity (scale bar: 150 μm). (F) Image analysis used to quantify the morphological characteristics of microglia in Iba-1 staining in ovx females. Upper panels: the unprocessed pictures. Middle panels: pixels darker than the background are traced (red) to determine the total cell size of microglia. Lower panels: pixel-clusters that are above an applied staining threshold and size-filter are traced (red) to determine the total cell body size of all microglia, as well as the number of microglia.
These data pointed to a direct relationship of microglia activity in the ARC with the effects of ovariectomy and diet on body weight.
3. Discussion
In this study we investigated the role of Y1R on vulnerability to diet-induced obesity and associated disorders of cycling and ovx female mice. To this aim, we used a conditional knockout mouse model in which the postnatal inactivation of the Npy1r gene in glutamate-containing neurons differentially affects male and female phenotypes, with Npy1rrfb male mice showing metabolic, hormonal and behavioral effects and Npy1rrfb females being only marginally affected [42,43].
Here, we demonstrated that the conditional deletion of the Npy1r gene did not affect body weight and WAT weight in HFD-fed cycling female mice, thus confirming sex-related effects of NPY-Y1R functions. However, a clear effect of the conditional deletion of the Npy1r gene was observed after ablation of the ovaries; indeed, in ovx mice we observed the mutants showing an increased body and WAT weight in mice fed with an SD and such an effect was enhanced by the HFD regimen. These findings suggest that Y1R might interact with gonadal hormones in counteracting the development of obesity. The ARC neuroinflammatory response observed in the conditional Npy1rrfb females after ovariectomy further supports a central role of gonadal hormones in the maintenance of a homeostatic control.
However, as suggested by the data on systemic leptin levels, the peripheral impact of the cross-talk mechanisms linking Y1R to gonadal hormones could be not always detectable. In fact, the HFD-induced increase in WAT weight was associated with increased leptin circulating levels and the conditional deletion of the Npy1r gene in cycling females did not affect either WAT weight or leptin release, thus confirming that the increase in leptin concentration is in proportion to the size of white fat depots [44]. Leptin synthesis is known to also be modulated by sex hormones, specifically suppressed by testosterone and increased by estrogen and progesterone [45]. Here, despite a further increase in WAT weight recorded in Npy1rrfb ovx female, no significant changes in level of this adipokine was detected, thus indicating a prevalence of sex-related control of leptin secretion, at least in our experimental conditions. On the other hand, we cannot exclude the involvement of other adipokines or gastric hormones, such as ghrelin, that induces adiposity independently of the orexigenic effect [46].
In cycling females, HFD exposure increased energy intake, body weight growth, subcutaneous WAT, plasma leptin levels and decreased glucose tolerance in both control and conditional mutant females. These metabolic alterations were associated with a concomitant decrease of locomotor activity with no changes in feeding behavior. Moreover, HFD exposure decreased AgRP-IR in the ARC of Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb cycling females, a decrease that was also observed in SD-fed Npy1rrfb mutants, as previously reported [42]. These results are in agreement with previous studies showing that ARC AgRP neurons are very sensitive to peripheral metabolic signals [47,48,49,50] and suggest that the decreased AgRP expression in the ARC may be a consequence of the increase of WAT mass and plasma leptin levels. Conversely, no significant differences were observed in NPY expression in the ARC of HFD-fed Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb cycling females compared with cycling females on the SD regimen. The different response to the HFD of AgRP- and NPY-IR in cycling females could be explained by the observation that, in the ARC, leptin receptors are expressed in a small population of NPY neurons and that the NPY neurons expressing leptin receptors do not co-express AgRP [23,25].
The most significant finding of this study was the observation that both SD- and HFD-fed ovx Npy1rrfb females showed a significant increase of body weight growth and WAT weight that is associated with microglia activation and proliferation in the ARC.
A number of studies have shown that exposure to HFD promotes microgliosis and increases the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines mostly in the ARC [9,10,51,52], which contains both anorexigenic and orexigenic neurons involved in the neural control of energy homeostasis.
This rapid HFD-induced pro-inflammatory response precedes the HFD-induced weight gain, suggesting that neuroimmune response in the ARC might play a causal role in the pathophysiology of obesity [51]. Previous studies demonstrated that sex differences in microglial activation in the brain nuclei involved in the modulation of energy homeostasis and estradiol have protective effects against HFD-induced microgliosis in the hypothalamus [11,12,53]. Accordingly, here we report that the HFD increased microglial number and activation in the ARC of ovx, but not of cycling Npy1rrfb females, thus pointing to a role of NPY in the sex-specific control of energy homeostasis.
Emerging evidence has indicated that NPY acts as a critical link between the nervous system and immune system and demonstrated that NPY directly modulates immune cells by acting on NPY receptors [54]. Microglia expresses Y1R and NPY, acting through Y1R, and significantly inhibits microglial activation, phagocytosis and cytokine secretion [55,56,57,58]. In Npy1rrfb mice, the conditional inactivation of the Npy1r gene is driven by the alpha-CaMKII promoter, which is expressed specifically in forebrain glutamate positive cells [41]. Given that microglia express alpha-CamKII [59,60], we hypothesize that, in the absence of the inhibitory role of gonadal hormones on neuroinflammation, the conditional deletion of the Npy1r gene in microglia results in the activation and proliferation of microglia and, in turn, in the obesity observed in SD- and HFD-fed Npy1rrfb ovx females. In the present study, we did not carry out hormone replacement; thus, our experimental design does not allow the specific impact of each ovarian steroid on body weight increase and microglia activation on ovx females to be defined. However, estradiol emerged as a leading candidate since progesterone replacement does nor revert ovariectomy-induced obesity [61] and progesterone receptors are not expressed in microglia in adult mice [62] (Figure 6).
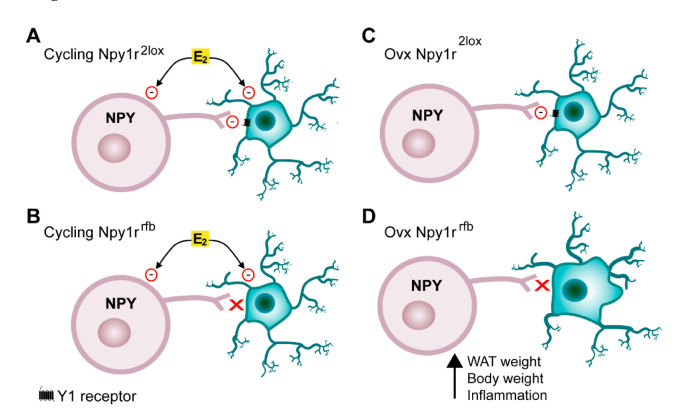
Figure 6.
Interactions between estradiol and the NPY-Y1 receptor system in the ARC. (A) Estrogens (E2) directly inhibit NPY neurons. Microglia activation and proliferation is increased by HFD and inhibited by E2 and the NPY-Y1 receptor system. (B) In cycling females, the HFD-induced microglia activation is inhibited by E2 also in the absence of Y1 receptors on microglia. (C) In ovx Npy1r2lox females, NPY inhibits microglia through activation of Y1 receptors. (D) In Npy1rrfb ovx females, on both SD and HFD regimen, the deletion of Y1 receptors in microglia increases microglia activation and, in turn, body and WAT weight.
On the other hand, on the basis of previous studies [15,19,20], we cannot exclude that other cross-talk mechanisms between estrogen and NPY may exist in neurons and glia.
It is well known that hypothalamic inflammation reduces the responsiveness of POMC and NPY neurons in the ARC to the physiological actions of leptin and insulin and alters the normal activity of the orexigenic and anorexigenic peptides, thereby promoting energy imbalance and obesity [48]. Here we demonstrated that the inflammatory response and the metabolic alterations observed in Npy1rrfb ovx females are associated with an increased expression of NPY in the ARC. Moreover, a significant decrease of POMC-IR was observed in the ARC of ovx Npy1rrfb females in SD regimen. These findings are in line with previous studies showing that neuroinflammation is associated with an alteration of NPY and POMC neuron activity [50,63].
In conclusion, here we provide the first evidence that the NPY-Y1R transmission in the ARC plays a pivotal role in reducing susceptibility to obesity in female mice with low levels of ovarian hormones and that this protective effect may be mediated via NPY ability to protect the brain against neuroinflammation. These results may provide a better understanding of the causative mechanisms for the multimorbidities associated with females’ reproductive aging, including the metabolic syndrome, cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb B6129S (129/SvJ, C57BL/6N derived strain) female mice were generated as previously described [41]. Mice were housed in a temperature (22 ± 1 °C) and humidity (50 ± 10%) controlled room, in groups of 4–6 per cage, with ad libitum access to food and water. Nesting paper materials and cardboard houses were used for environmental enrichment and diurnal rhythm was maintained with a 12:12 h light–dark cycle (08:00 a.m.–08:00 p.m.).
Eight-week-old (P48) Npy1r2lox and Npy1rrfb female mice were sham operated (cycling) or ovx and maintained on an SD. Starting from postnatal day 60 (P60), ovx and cycling females were fed a hypercaloric HFD or maintained on an SD until the sacrifice.
All cycling females were in estrous cycle at euthanasia that was induced by anesthesia overdosing (ketamine and xylazine, Vetefarma, Cuneo, Italy) and cervical dislocation. Vaginal smears were performed at 9:00–10:00 a.m. Mice were euthanized at 5–5.5 months of age between 2:00 and 5:00 p.m.
All experiments were conducted in accordance with the European Community Council Directive of 24 November 1986 (86/EEC) and approved by the University of Turin Ethical Committee for animal research and by the Italian Ministry of Health (licenses no. 574/2016).
4.2. Body Weight and Food Intake Analysis
Mice body weight and food intake were measured twice a week from P60 to P156 with a digital scale accurate to 0.01 g, always from 10:00 a.m. to 11:00 a.m. Food intake was quantified by calculating the difference between pre- and post-weighed food. The amount of food consumed by the single cage was averaged by the number of mice and the number of days, then the Kcal consumed were calculated for each diet.
4.3. Diet Composition
The SD consisted of 4.3% fat, 67.3% carbohydrate and 19.2% protein with 10% Kcal derived from fat, 70% Kcal derived from carbohydrates and 20% Kcal derived from proteins (D12450B, Research Diets, NJ, USA). The HFD consisted of 35% fat, 26% carbohydrate and 26% protein with 60% of Kcal derived from fat, 20% Kcal from carbohydrates and 20% Kcal from proteins (D12492, Research Diets, NJ, USA). Free access to the diets was provided.
4.4. Spontaneous Locomotor Activity
Spontaneous locomotor activity in the home cage was performed on females in estrous cycle. Locomotor activity was continuously recorded for 3 h using an infrared video camera, starting at the onset of the dark phase (active period [42]). Mice were allowed to become accustomed to their clean home cage for 24 h before starting collection of the data. The total distance (meters) traveled by mice was recorded and data were analyzed automatically from the digitized images by using a computerized video tracking software (Ethovision XT 15 video track system; Noldus Information Technology, Wageningen, The Netherlands).
4.5. Glucose (GTT), Insulin (ITT) and Pyruvate (PTT) Tolerance Tests
GTT and PTT were performed following an overnight fasting (12 h), while for ITT mice were fasted for 5 h prior to the test. All tests were performed between 9:00 a.m. and 11:00 a.m. Blood glucose levels from tail bleeding were measured using a glucose meter FreeStyle Lite (Abbot, Alameda, CA, USA) at 0, 30, 60, 90 and 120 min after i.p. injection of a 1 g/kg d-glucose solution for GTT, a 0.5 g/kg insulin solution for ITT and a 1 g/kg pyruvate solution for PTT (Carlo Erba Reagent S.R.L., Milan, Italy). GTT, ITT and PTT were performed starting on P161 and one-week time was allowed for the mice to recover between tests.
4.6. Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
Blood pressure and heart rate were measured by tail cuff plethysmography by using a BP-2000 Series II Blood Pressure Analysis System, 2 channels mouse platform (Visitech Systems, Napa Pl, Apex, NC, USA) at P160 as previously described [64].
4.7. Tissue Collection and Analysis
Blood samples were collected from the atrium of anesthetized mice. EDTA (12.5 mM, Merck, Life Science, Milano, Italy) was added immediately to prevent clotting and plasma, obtained by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C, was stored at −80 °C until analysis. Levels of circulating leptin were measured in duplicate with a commercially available kit (Mouse leptin ELISA, Merck, Life Science, Milano, Italy). To avoid the inter-assay variability, all samples were run in a single assay. WAT (subcutaneous, visceral and gonadic) was collected and weighed, then frozen on dry ice for later analysis.
4.8. Histological Analysis
NPY, AgRP, POMC and ionized calcium-binding adaptor protein-1 (IBA-1) immunohistochemical analysis was performed on postfixed brains. Right after blood collection, mice brains were dissected and fixed for 24 h with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS. Free-floating cryostat brain coronal sections (30 μm) were immunostained and DAB-developed as previously described [42]. For each peptide analyzed, sections were incubated for 2 days with 1:4000 rabbit anti-POMC, 1:3000 rabbit anti-NPY, 1:2500 rabbit anti-AgRP (all three from Phoenix Europe GMBH, Karlsruhe, Germany) or 1:2000 rabbit-anti IBA-1 (Wako Chemicals—Richmond, VA, USA) primary antibody.
NPY, POMC and AgRP quantitative analysis was performed on three to five sections of ARC (between −1.58 and −1.82 mm relative to bregma) and PVNmp (−0.94 to −0.82 mm relative to bregma) from each animal by one operator blind to the genotype, treatment and diet. Brain slices images (2088 × 1550 pixels) were captured using the 10× objective of a Zeiss Axioplan microscope equipped with a digital camera (Leica DFC 320, Wetzlar, Germany). ImageJ software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA) was used to measure immunoreactivity through a threshold method and the number of positive pixels and the extension of area of interest were used to determine the fractional area covered by the specific signal.
4.9. Analysis of Microglial Activation
To quantify the number of microglial cells in the ARC and their suggestive activation state, 30 μm slices immunostained for IBA-1 were scanned at 20× magnification on a Zeiss Axioscan 7, High-performance Slide Scanner (Carl-Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) and three to five sections of ARC (between −1.58 and −1.82 mm relative to bregma) for each animal were analyzed using ImageJ software as described before [65]. The number of microglia were counted and corrected for the size of the area of interest. Cell body to total cell size ratio (cb/c) was determined and utilized as a measurement for morphological changes that suggest microglial activation.
To generate cb/c, the “Adjusted threshold” and “Analyze particles” functions of ImageJ software were applied to 8-bit images of ARC. The intensity threshold (default algorithm) and size filter were applied to measure the pixels from the cell body size and pixels from the total cell size (cell body + dendrites) as previously described [65,66]. Based on area coverage, the total microglial cell size and total microglial cell body size were determined. The total cell body size was divided by the total cell size to obtain the cb/c as a measure of microglial activation.
4.10. Statistical Analysis
A three-way ANOVA (genotype, diet and ovariectomy) for repeated measures (days and minutes, RM) was run to analyze body weight, calories intake and GTT, ITT and PTT during metabolic challenge. For mean body weight, this analysis was followed by a two-way ANOVA for repeated measures (genotype and diet as independent variables, days as repeated measures) independently performed on cycling and ovx females. A three-way ANOVA (genotype, diet and ovariectomy) was run to analyze WAT, plasma leptin levels, spontaneous locomotor activity, food and calories intake, AUC, heart beats, systolic pressure, AgRP-, NPY-, POMC-IR and IBA-1 IR. For microglia cb/c and microglia number, this analysis was followed by a 2-way ANOVA (genotype and diet as independent variables) independently performed on cycling and ovx females. The association between body weight and locomotor activity was analyzed by a regression analysis with locomotor activity as the dependent variable and body weight as the predictor. Data were analyzed by means of Statistica 10.0 (Stat-Soft, Tulsa, OK, USA). The significance level was set at p < 0.05. Post hoc tests were performed by the Newman–Keuls test. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM, and the level of statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Symbols used to indicate statistical significance are: & for the main factor effects of the ANOVA and * (genotype), # (diet) and § (ovariectomy) for the post hoc tests.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Davide Ponzi for the help provided with the statistical analysis and to Massimo Collino for the helpful discussion.
Abbreviations
AGRP (Agouti-related protein), alpha-CaMKII (alpha calmodulin kinase II), ARC (arcuate nucleus), AUC (area under the curve), CB/C (cell body size divided by the total cell size), GTT (glucose tolerance test), HFD (high-fat diet), HPA (hypothalamic pituitary axis), IBA-1 (ionized calcium-binding adaptor protein-1), IR (immunoreactivity), ITT (insulin tolerance test), NPY (neuropeptide Y), OVX (ovariectomized), P (postnatal day), POMC (proopiomelanocortin), PTT (pyruvate tolerance test), PVN (paraventricular nucleus), SD (standard diet), Y1R (Y1 receptors), WAT (white adipose tissue).
Author Contributions
C.E., P.P. and A.M. conceived, planned and supervised experiments and performed data analysis, interpretation, writing and editing of the manuscript; I.B. contributed to data analysis, interpretation, writing and editing of the manuscript; A.O. and A.L. administered treatments to and monitored animal groups and performed parameter measurement, tissue collection, histochemical analysis and data analysis; S.B., S.P., C.M. and S.D.T. contributed to experimental planning/data analysis and interpretation. All authors contributed to editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experiments were conducted in accordance with the European Community Council Directive of 24 November 1986 (86/EEC) and approved by the University of Turin Ethical Committee for animal research and by the Italian Ministry of Health (licenses no. 574/2016).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Cariplo Foundation (Grant 2013-0786 to CE).
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Santos Machado V.d.S., Ribeiro Valadares A.L., Costa-Paiva L.H., Osis M.J., Sousa M.H., Pinto-Neto A.M. Aging, obesity, and multimorbidity in women 50 years or older: A population-based study. Menopause. 2013;20:818. doi: 10.1097/GME.0b013e31827fdd8c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wildman R.P., Tepper P.G., Crawford S., Finchelstein J.S., Sutton-Tyrrell K., Thurston R.C., Santoro N., Sternfeld B., Greendale G.A. Do changes in sex steroid hormones precede or follow increases in body weight during the menopause transition? Results from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012;97:E1695–E704. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lizcano F., Guzmán G. Estrogen deficiency and the origin of obesity during menopause. BioMed Res. Int. 2014;2014:757461. doi: 10.1155/2014/757461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Della Torre S., Benedusi V., Fontana R., Maggi A. Energy metabolism and fertility—A balance preserved for female health. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014;10:13–23. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dorfman M.D., Krull J.E., Douglass J.D., Fasnacht R., Lara-Lince F., Meek T.H., Shi X., Damian V., Nguyen H.T., Matsen M.E., et al. Sex differences in microglial CX3CR1 signalling determine obesity susceptibility in mice. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:14556. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hong J., Stubbins R.E., Smith R.R., Harvey A.E., Núñez N.P. Differential susceptibility to obesity between male, female and ovariectomized female mice. Nutr. J. 2009;8:11. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-8-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lainez N.M., Jonak C.R., Nair M., Ethell I.M., Wilson E.H., Carson M.J., Coss D. Diet-induced obesity elicits macrophage infiltration and reduction in spine density in the hypothalami of male but not female mice. Front. Immunol. 2018;9:1992. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Underwood E.L., Thompson L.T. A high-fat diet causes impairment in hippocampal memory and sex-dependent alterations in peripheral metabolism. Neural Plast. 2016;2016:7385314. doi: 10.1155/2016/7385314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thaler J.P., Yi C.-X., Schur E.A., Guyenet S.J., Hwang B.H., Dietrich M., Zhao X., Sarruf D.A., Izgur V., Maravilla K.R., et al. Obesity is associated with hypothalamic injury in rodents and humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2012;122:153–162. doi: 10.1172/JCI59660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ullah R., Rauf N., Nabi G., Yi S., Yu-Dong Z., Fu J. Mechanistic insight into high-fat diet-induced metabolic inflammation in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. BioMed Pharmacother. 2021;142:112012. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Butler M.J., Perrini A.A., Eckel L.A. Estradiol treatment attenuates high fat diet-induced microgliosis in ovariectomized rats. Horm. Behav. 2020;120:104675. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Morselli E., Fuente-Martin E., Finan B., Kim M., Frank A., Garcia-Caceres C., Navas C.R., Gordillo R., Neinast M., Kalainayakan S.P., et al. Hypothalamic PGC-1α protects against high-fat diet exposure by regulating ERα. Cell Rep. 2014;9:633–645. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.09.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Asarian L., Geary N. Cyclic estradiol treatment normalizes body weight and restores physiological patterns of spontaneous feeding and sexual receptivity in ovariectomized rats. Horm. Behav. 2002;42:461–471. doi: 10.1006/hbeh.2002.1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Eckel L.A. The ovarian hormone estradiol plays a crucial role in the control of food intake in females. Physiol. Behav. 2011;104:517–524. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.04.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fontana R., Della Torre S., Meda C., Longo A., Eva C., Maggi A.C. Estrogen replacement therapy regulation of energy metabolism in female mouse hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 2014;155:2213–2221. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Eva C., Oberto A., Longo A., Palanza P., Bertocchi I. Sex differences in behavioral and metabolic effects of gene inactivation: The neuropeptide Y and Y receptors in the brain. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020;119:333–347. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Olofsson L.E., Pierce A.A., Xu A.W. Functional requirement of AgRP and NPY neurons in ovarian cycle-dependent regulation of food intake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:15932–15937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904747106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Valassi E., Scacchi M., Cavagnini F. Neuroendocrine control of food intake. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008;18:158–168. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2007.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Musso R., Maggi A., Eva C. 17β-Estradiol stimulates mouse neuropeptide Y-Y1 receptor gene transcription by binding to estrogen receptor alpha in neuroblastoma cells. Neuroendocrinology. 2000;72:360–367. doi: 10.1159/000054605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Martini M., Sica M., Gotti S., Eva C., Panzica G.C. Effects of estrous cycle and sex on the expression of neuropeptide Y Y1 receptor in discrete hypothalamic and limbic nuclei of transgenic mice. Peptides. 2011;32:1330–1334. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zammaretti F., Panzica G., Eva C. Sex-dependent regulation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y-Y1 receptor gene expression in moderate/high fat, high-energy diet-fed mice. Pt 2J. Physiol. 2007;583:445–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.133470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Beck B., Pourié G. Ghrelin, neuropeptide Y, and other feeding-regulatory peptides active in the hippocampus: Role in learning and memory. Nutr. Rev. 2013;71:541–561. doi: 10.1111/nure.12045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee N.J., Qi Y., Enriquez R.F., Clarke I., Ip C.K., Wee N., Baldock P.A., Herzog H. Energy partitioning between fat and bone mass is controlled via a hypothalamic leptin/NPY relay. Int. J. Obes. 2020;44:2149–2164. doi: 10.1038/s41366-020-0550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nguyen A.D., Mitchell N.F., Lin S., Macia L., Yulyaningsih E., Baldock P.A., Enriquez R.F., Zhang L., Shi Y.-C., Zolotukhin S., et al. Y1 and y5 receptors are both required for the regulation of food intake and energy homeostasis in mice. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e40191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhang L., Reed F., Herzog H. Leptin signalling on arcuate NPY neurones controls adiposity independent of energy balance or diet composition. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2020;32:e12898. doi: 10.1111/jne.12898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Stanley B.G., Leibowitz S.F. Neuropeptide Y injected in the paraventricular hypothalamus: A powerful stimulant of feeding behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1985;82:3940–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Stanley B.G., Kyrkouli S.E., Lampert S., Leibowitz S.F. Neuropeptide Y chronically injected into the hypothalamus: A powerful neurochemical inducer of hyperphagia and obesity. Peptides. 1986;7:1189–1192. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90149-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ding B., Kull B., Liu Z., Mottagui-Tabar S., Thonberg H., Gu H.F., Brookes A.J., Grundemar L., Karlsson C., Hamsten A., et al. Human neuropeptide Y signal peptide gain-of-function polymorphism is associated with increased body mass index: Possible mode of function. Regul. Pept. 2005;127:45–53. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2004.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nordman S., Ding B., Östenson C.-G., Kärvestedt L., Brismar K., Efendic S., Gu H. Leu7Pro polymorphism in the neuropeptide Y (NPY) gene is associated with impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes in Swedish men. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes. 2005;113:282–287. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-865650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ukkola O., Kesäniemi Y.A. Leu7Pro polymorphism of PreproNPY associated with an increased risk for type II diabetes in middle-aged subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007;61:1102–1105. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Eva C., Serra M., Mele P., Panzica G.C., Oberto A. Physiology and gene regulation of the brain NPY Y1 receptor. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2006;27:308–339. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2006.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lin S., Boey D., Herzog H. NPY and Y receptors: Lessons from transgenic and knockout models. Neuropeptides. 2004;38:189–200. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2004.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pedrazzini T., Seydoux J., Künstner P., Aubert J.-F., Grouzmann E., Beermann F., Brunner H.R. Cardiovascular response, feeding behavior and locomotor activity in mice lacking the NPY Y1 receptor. Nat. Med. 1998;4:722–726. doi: 10.1038/nm0698-722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Xu Y., Elmquist J.K., Fukuda M. Central nervous control of energy and glucose balance: Focus on the central melanocortin system. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011;1243:1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bo E., Farinetti A., Marraudino M., Sterchele D., Eva C., Gotti S., Panzica G. Adult exposure to tributyltin affects hypothalamic neuropeptide Y, Y1 receptor distribution, and circulating leptin in mice. Andrology. 2016;4:723–734. doi: 10.1111/andr.12222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Clegg D.J. Minireview: The year in review of estrogen regulation of metabolism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012;26:1957–1960. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Oberto A., Mele P., Zammaretti F., Panzica G.C., Eva C. Evidence of Altered Neuropeptide Y Content and Neuropeptide Y1 Receptor Gene Expression in the Hypothalamus of Pregnant Transgenic Mice. Endocrinology. 2003;144:4826–4830. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rugarn O., Hammar M., Theodorsson A., Theodorsson E., Stenfors C. Sex differences in neuropeptide distribution in the rat brain. Peptides. 1999;20:81–86. doi: 10.1016/S0196-9781(98)00139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zammaretti F., Panzica G., Eva C. Fasting, leptin treatment, and glucose administration differentially regulate Y1 receptor gene expression in the hypothalamus of transgenic mice. Endocrinology. 2001;142:3774–3782. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.9.8404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Statello R., Carnevali L., Paterlini S., Gioiosa L., Bertocchi I., Oberto A., Eva C., Palanza P., Sgoifo A. Reduced NPY Y1 receptor hippocampal expression and signs of decreased vagal modulation of heart rate in mice. Physiol. Behav. 2017;172:31–39. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bertocchi I., Oberto A., Longo A., Mele P., Sabetta M., Bartolomucci A., Palanza P., Sprengel R., Eva C. Regulatory functions of limbic Y1 receptors in body weight and anxiety uncovered by conditional knockout and maternal care. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:19395–19400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109468108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bertocchi I., Oberto A., Longo A., Palanza P., Eva C. Conditional inactivation of Npy1r gene in mice induces sex-related differences of metabolic and behavioral functions. Horm. Behav. 2020;125:104824. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Paterlini S., Panelli R., Gioiosa L., Parmigiani S., Franceschini P., Bertocchi I., Oberto A., Bartolomucci A., Eva C., Palanza P. Conditional inactivation of limbic neuropeptide y-1 receptors increases vulnerability to diet-induced obesity in male mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:8745. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Frederich R.C., Hamann A., Anderson S., Löllmann B., Lowell B.B., Flier J.S. Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: Evidence for diet-induced resistance to leptin action. Nat. Med. 1995;1:1311–1314. doi: 10.1038/nm1295-1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Di Carlo C., Tommaselli G.A., Nappi C. Effects of sex steroid hormones and menopause on serum leptin concentrations. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2002;16:479–491. doi: 10.1080/gye.16.6.479.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Perez-Tilve D., Heppner K., Kirchner H., Lockie S.H., Woods S.C., Smiley D.L., Tschöp M., Pfluger P. Ghrelin-induced adiposity is independent of orexigenic effects. FASEB J. 2011;25:2814–2822. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-183632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Baver S.B., Hope K., Guyot S., Bjørbaek C., Kaczorowski C., O’Connell K.M.S. Leptin modulates the intrinsic excitability of AgRP/NPY neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. J. Neurosci. 2014;34:5486–5496. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4861-12.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Benedusi V., Della Torre S., Mitro N., Caruso D., Oberto A., Tronel C., Meda C., Maggi A. Liver ERα regulates AgRP neuronal activity in the arcuate nucleus of female mice. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:1194. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01393-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Breen T.L., Conwell I.M., Wardlaw S.L. Effects of fasting, leptin, and insulin on AGRP and POMC peptide release in the hypothalamus. Brain Res. 2005;1032:141–148. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Varela L., Horvath T.L. Leptin and insulin pathways in POMC and AgRP neurons that modulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis. EMBO Rep. 2012;13:1079–1086. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Valdearcos M., Xu A.W., Koliwad S.K. Hypothalamic inflammation in the control of metabolic function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015;77:131–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021014-071656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ceasrine A.M., Bilbo S.D. Dietary fat: A potent microglial influencer. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022;33:196–205. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2021.12.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Azcoitia I., Barretoc G.E., Garcia-Segura L.M. Molecular mechanisms and cellular events involved in the neuroprotective actions of estradiol. Analysis of sex differences. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2019;55:100787. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2019.100787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Chen W-c Liu Y-b Liu W-f Zhou Y-y He H-f Lin S. Neuropeptide Y is an immunomodulatory factor: Direct and indirect. Front. Immunol. 2020;11:2624. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.580378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ferreira R., Xapelli S., Santos T., Silva A.P., Cristóvão A., Cortes L., Malva J.O. Neuropeptide Y modulation of interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-induced nitric oxide production in microglia. Int. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:41921–41934. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.164020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ferreira R., Santos T., Viegas M., Cortes L., Bernardino L., Vieira O.V., O Malva J. Neuropeptide Y inhibits interleukin-1β-induced phagocytosis by microglial cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011;8:169. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ferreira R., Santos T., Cortes L., Cochaud S., Agasse F., Silva A.P., Xapelli S., Malva J.O. Neuropeptide Y inhibits interleukin-1 beta-induced microglia motility. J. Neurochem. 2012;120:93–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Li Q., Dong C., Li W., Bu W., Wu J., Zhao W. Neuropeptide Y protects cerebral cortical neurons by regulating microglial immune function. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9:959. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.133140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhou K., Enkhjargal B., Xie Z., Sun C., Wu L., Malaguit J., Chen S., Tang J., Zhang J., Zhang J.H. Dihydrolipoic acid inhibits lysosomal rupture and NLRP3 through LAMP1/CaMKII/TAK1 pathways after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rat. Stroke. 2018;49:175–183. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang X., Connelly J., Levitan E.S., Sun D., Wang J.Q. Calcium/Calmodulin–Dependent Protein Kinase II in Cerebrovascular Diseases. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021;12:513–529. doi: 10.1007/s12975-021-00901-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Richard D. Effects of ovarian hormones on energy balance and brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1986;250:R245–R249. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.2.R245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Villa A., Vegeto E., Poletti A., Maggi A. Estrogens, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration. Endocr. Rev. 2016;37:372–402. doi: 10.1210/er.2016-1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cai D., Liu T. Hypothalamic inflammation: A double-edged sword to nutritional diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011;1243:E1–E39. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Nuzzo A.M., Moretti L., Mele P., Todros T., Eva C., Rolfo A. Effect of Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Conditioned Media on an LPS-Induced Mouse Model of Preeclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:167. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hovens I.B., Nyakas C., Schoemakern R.G. A novel method for evaluating microglial activation using ionized calcium-binding adaptor protein-1 staining: Cell body to cell size ratio. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2014;1:82–88. doi: 10.4103/2347-8659.139719. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gomes J.A., Silva J.F., Marçal A.P., Silva G., Gomes G.F., de Oliveira A.C., Soares V.L., Oliveira M., Ferreira A.V., Aguiar D.C. High-refined carbohydrate diet consumption induces neuroinflammation and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020;77:108317. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.