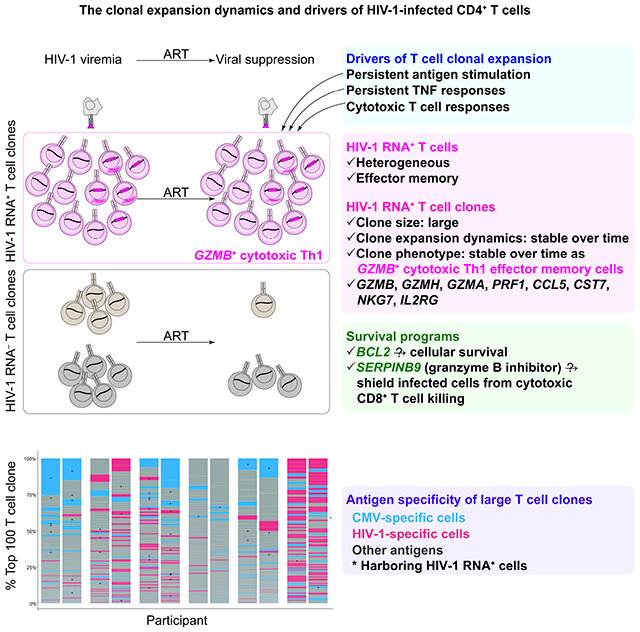
Summary
Understanding the drivers and markers of clonally expanding HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells is essential for HIV-1 eradication. We used single-cell ECCITE-seq, which captures surface protein expression, cellular transcriptome, HIV-1 RNA, and TCR sequences within the same single cell to track clonal expansion dynamics in longitudinally archived samples from six HIV-1-infected individuals (during viremia and after suppressive antiretroviral therapy) and two uninfected individuals, in unstimulated conditions and after CMV and HIV-1 antigen stimulation. Despite antiretroviral therapy, persistent antigen and TNF responses shaped T cell clonal expansion. HIV-1 resided in Th1 polarized, antigen-responding T cells expressing BCL2 and SERPINB9 that may resist cell death. HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones were larger in clone size, established during viremia, persistent after viral suppression, and enriched in GZMB+ cytotoxic effector memory Th1 cells. Targeting HIV-1-infected cytotoxic CD4+ T cells and drivers of clonal expansion provides another direction for HIV-1 eradication.
Keywords: HIV-1 persistence, clonal expansion, cytotoxic CD4+ T lymphocytes, single-cell RNA-seq, T cell expansion dynamics, HIV-1-induced immune dysfunction, antigen stimulation, TNF response, Bcl-2 family anti-apoptotic genes, HIV-1 latent reservoir
Graphical Abstract
eTOC blurb
Using single-cell ECCITE-seq, Collora et al. profiled 267 HIV-1 RNA+ cells and 68 expanded HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones from 215,458 CD4+ T cells. HIV-1 resides in GZMB+ cytotoxic Th1 effector memory CD4+ T cell clones that are large and persistent. HIV-1-infected cytotoxic CD4+ T cells may evade cytotoxic CD8+ T cell killing through Seprin B9 degradation of granzyme B.
Despite effective antiretroviral therapy (ART), the HIV-1 latent reservoir (Chun et al., 1997; Finzi et al., 1997; Wong et al., 1997) persists lifelong (Crooks et al., 2015; Siliciano et al., 2003). More than 50% of the HIV-1 latent reservoir is maintained by clonal expansion of infected cells (Bui et al., 2017; Hosmane et al., 2017; Lorenzi et al., 2016). Clonally expanding HIV-1-infected cells are established during acute viremia (Coffin et al., 2019) and persist under long-term suppressive ART (Maldarelli et al., 2014; Wagner et al., 2014). The clonal expansion of HIV-1-infected cells is a major barrier to cure. Understanding the drivers and markers of clonally expanding HIV-1-infected cells is essential for HIV-1 eradication.
The clonal expansion of HIV-1-infected cells is driven by antigen stimulation, homeostatic proliferation (Chomont et al., 2009), and HIV-1-driven cancer gene expression (Liu et al., 2020; Maldarelli et al., 2014; Wagner et al., 2014). Upon cognate antigen stimulation, T cells can proliferate into a T cell clone of many cells that share the same T cell receptor (TCR) sequence and antigen specificity. HIV-1 can reside in cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific (Mendoza et al., 2020; Simonetti et al., 2021), HIV-1-specific (Douek et al., 2002; Mendoza et al., 2020; Simonetti et al., 2021), and cancer-specific CD4+ T cells (Simonetti et al., 2016) that are clonally expanding. Presumably, antigen stimulation and cytokines that drive the proliferation of a T cell clone would also drive the proliferation of HIV-1-infected cells within this T cell clone. Unlike homeostatic proliferation which does not induce HIV-1 reactivation (Bosque et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2018), antigen stimulation can induce HIV-1 reactivation and viral protein expression from the clonally expanding HIV-1-infected cells and cause persistent low-level viremia despite ART (Bailey et al., 2006; Halvas et al., 2020). However, upon antigen stimulation, cells harboring inducible HIV-1 should presumably die of viral cytopathic effects or T cell activation. It remains unknown why HIV-1-infected cells can resist cell death upon reactivation and persist over time.
Antigen-specific CD4+ T cells are susceptible to HIV-1 infection (Douek et al., 2002; Mendoza et al., 2020; Simonetti et al., 2021). Among antigen-specific CD4+ T cells, cytotoxic CD4+ T cells are key effectors in cancer (Malandro et al., 2016; Oh et al., 2020) and viral infections, such as influenza (Brown et al., 2012), CMV (van Leeuwen et al., 2004), and SARS-CoV-2 infections (Meckiff et al., 2020). In HIV-1-infected individuals, cytotoxic CD4+ T cells are substantially expanded during HIV-1 infection (Appay et al., 2002) and CMV infection (Zaunders et al., 2004). Cytotoxic CD4+ T cells have a high proliferative capacity and exhibit polyfunctional cytotoxic responses through release of cytolytic granules [such as granzyme B (GZMB), granzyme K (GZMK), granzyme H (GZMH), and perforin (PRF1)] and expression of Th1 cytokines [interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-2, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)](Appay et al., 2002). Unlike cytotoxic CD8+ T cells which can control HIV-1 infection, the role of cytotoxic CD4+ T cells in HIV-1 infection remains unclear.
ART suppresses HIV-1 plasma viral load to clinically undetectable levels. However, ART neither kills infected cells nor inhibits HIV-1 viral protein production from existing infected cells. Therefore, HIV-1-infected cells can continue to produce viral antigens (Halvas et al., 2020; Pollack et al., 2017) and induce immune activation and exhaustion (Bengsch et al., 2018; Pollack et al., 2017). Early ART initiated within 6 months of infection, as opposed to delayed ART initiated after 6 months of infection, substantially reduces chronic immune activation (Jain et al., 2013). Given that people treated with immediate ART have a shorter duration of HIV-1 viremia, shorter duration of overt HIV-1 antigen exposure, and lower levels of immune activation (Jain et al., 2013), comparing immune responses in people treated with short versus long duration of viremia may help to understand HIV-1-specific immune response under different magnitude of HIV-1 antigen stimulation in vivo.
Several challenges prevent mechanistic understanding of HIV-1 persistence in people with HIV-1. First, intact inducible HIV-1-infected cells in ART-treated individuals are extremely rare, accounting for <0.001% of CD4+ T cells in the peripheral blood (Bruner et al., 2016; Bruner et al., 2019; Ho et al., 2013). Second, there are no known cellular markers that can exclusively differentiate HIV-1-infected cells from uninfected cells, given the heterogeneity (Neidleman et al., 2020) in polarization (Lee et al., 2017), activation state (Lee et al., 2019), memory differentiation (Gantner et al., 2020; Hiener et al., 2017; Venanzi Rullo et al., 2020), and immune exhaustion states (Fromentin et al., 2016). Third, while HIV-1-infected cells can be isolated using viral markers such as HIV-1 RNA expression (Liu et al., 2020) or Env protein expression (Cohn et al., 2018), these methods require ex vivo activation and thus cannot depict the in vivo status of infected cells. Advancements in single-cell technologies enable high-dimensional immune profiling to dissect the heterogeneous states of immune cells, capture rare cells, map T cell clonality, and identify upstream drivers of immune dysregulation (Hoang et al.; Kazer et al., 2020; Nguyen et al., 2019; Shalek et al., 2013; Wilk et al., 2020; Yost et al., 2019). Further, computational techniques including supervised and unsupervised machine learning, network analysis, and statistical methodologies enable confident identification of higher-fidelity predictors of different cellular states from the sparse and highly complex single-cell multi-modal data (Hu et al., 2016; Langfelder and Horvath, 2008; Pappalardo et al., 2020; Park et al., 2020; Stuart et al., 2019; Torang et al., 2019). Single-cell genome-wide transcriptome profiling can resolve the heterogeneity of immune cells, identify the rare HIV-1-infected cells, and discover mechanisms of HIV-1 persistence.
We hypothesize that HIV-1 persists by residing in CD4+ T cells that are proliferative, resistant to cell death, and persistent over time. We reasoned that immune drivers that determine the proliferation of T cell clones will also drive the proliferation of HIV-1-infected cells within these T cell clones. Here we use a single-cell multiomic approach to track CD4+ T cell immune responses during acute HIV-1 infection and after viral suppression, both in unstimulated in vivo states and after ex vivo antigen stimulation. We examined the transcriptional landscape, immune regulators, and T cell clonal expansion dynamics of T cell clones and HIV-1 RNA+ cells. We identified HIV-1-induced immune dysfunction, CD4+ T cell responses to antigen stimulation, drivers of the clonal expansion of HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones, and the survival programs that prevent cell death upon HIV-1 reactivation and T cell activation.
Results
Single-cell ECCITE-seq captures immune phenotype, HIV-1 RNA expression, and T cell clonality in the same single cell
To understand the impact of HIV-1 infection on CD4+ T cell immune responses, T cell clonal expansion dynamics, and HIV-1 persistence, we examined the transcriptome, surface protein expression, T cell clonality, and HIV-1 expression in total CD4+ T cells from six HIV-1-infected individuals at the single cell level. We used single-cell ECCITE-seq, which captures surface protein expression, cellular transcriptome, HIV-1 RNA, and TCR sequence within the same single cell, allowing clonal expansion dynamics tracking in longitudinally archived samples. We used longitudinally archived blood samples from the Sabes study (Lama et al., 2018; Lama et al., 2020), a prospective study that tested HIV-1 status monthly to identify early infection. We profiled paired CD4+ T cells at two time points, during viremia (<60 days within estimated date of detectable infection (EDDI) and after viral suppression (one year of suppressive ART, with >6 months of undetectable viral load), in six HIV-1-infected individuals (Figure 1A, Table S1, Figure S1). CD4+ T cells from two uninfected individuals served as controls. Notably, the uninfected individuals were recruited based on availability and matched with sex but not age or ethnicity. Our data would need to be cautiously interpretated as age and ethnicity may affect the immune profiles (Barreiro and Quintana-Murci, 2010; King Thomas et al., 2019).
Figure 1. Paired CD4+ T cell profiling during viremia and after viral suppression by single-cell multiomic ECCITE-seq reveals persistent TNF responses despite suppressive ART.
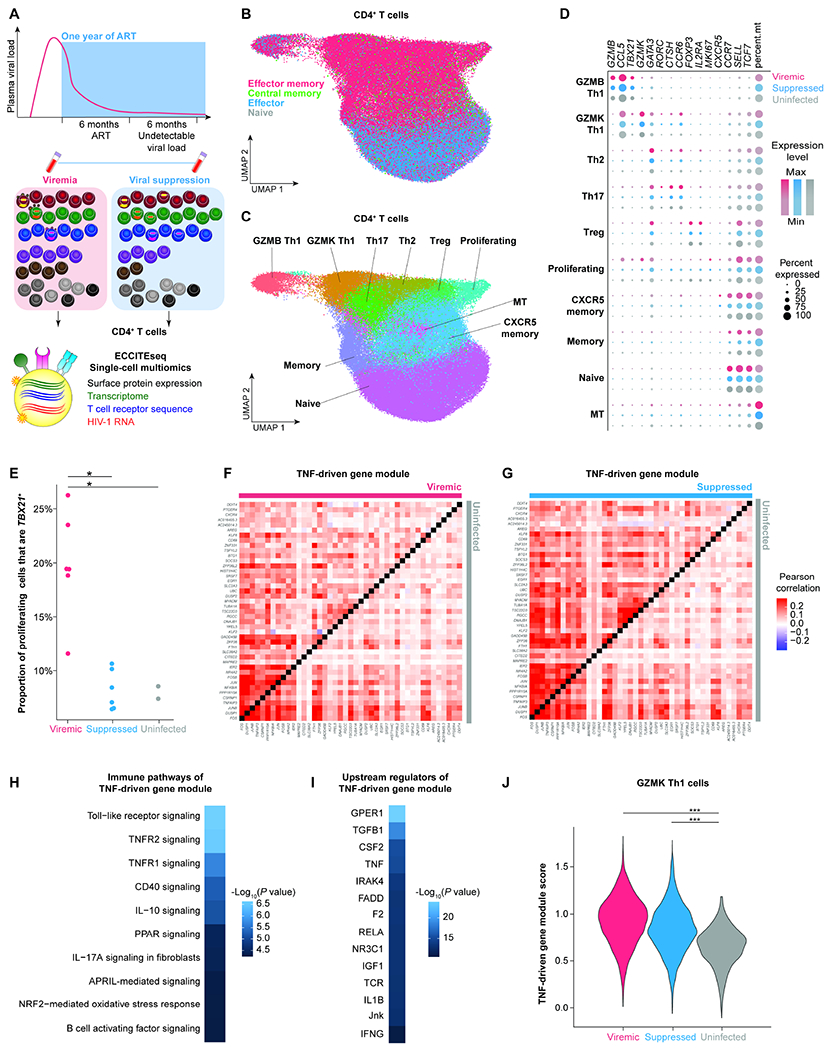
A, Study design. Participants enrolled in the Sabes study were prospectively tested monthly for HIV-1 infection using HIV-1 antibody detection, antigen detection, and viral RNA quantification. We profiled paired CD4+ T cells during acute viremia (<60 days after estimated date of detectable infection) and after one year of suppressive ART (with documented undetectable viral load 6 months prior to the viral suppression time point) from six HIV-1-infected individuals enrolled in Sabes and subsequently followed in the Merlin study. CD4+ T cells from two sex-matched uninfected individuals were used as controls. B, UMAP plot of memory phenotypes of cells (n = 52,473, 36,806, and 33,406 cells in the viremic, virally suppressed, and uninfected conditions, respectively) defined by surface CD45RA and CCR7 expression. C, UMAP of 10 clusters of CD4+ T cells defined by transcriptome. D, Dot plot depicting key cluster marker expression in viremic, suppressed, and uninfected conditions. E, The proportion of proliferating cells expressing TBX21, the key transcription factor for Th1 polarization. P values were determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test. F and G, Pearson’s correlation coefficient heatmaps of TNF-driven gene expression module of viremia versus uninfected conditions (F) and suppressed versus uninfected conditions (G). H and I, Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) heatmaps of enriched immune pathways (H) and predicted upstream regulators (I) of the TNF-driven gene expression module. P values were defined by Fisher’s exact test. J, Module score of TNF-driven gene expression module in viremia, viral suppression, and uninfected conditions in the Th1 polarized GZMK cluster. P values were determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test comparing HIV-1-infected conditions and uninfected conditions. *, P <0.05; ***, P <0.0001. P values were corrected for multiple comparisons using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure. See also Figure S1, Figure S2, Figure S3, Table S1, and Table S2.
We profiled 89,279 CD4+ T cells from six infected individuals, including 52,473 during viremia and 36,806 after viral suppression, and compared them to 33,406 cells from two uninfected individuals. Batch effects were removed using fastMNN (Haghverdi et al., 2018)(Figure 1A, Figure S2). Cells were clustered and visualized based on their transcriptome profile using Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction (UMAP)(Becht et al., 2018). For each sample, we identified a median of 7,447 cells, with a median of 1,346 genes, and 4,138 unique molecular identifiers (UMI) in each cell (Table S2).
We determined the memory phenotype of each cell based on their surface CD45RA and CCR7 protein expression and identified naive, central memory, effector memory, and effector CD4+ T cells (Figure 1B). Surface protein expression was determined as positive by >90th percentile of the expression level of isotype barcoded antibody controls. Based on cellular transcriptome and surface marker expression, we defined ten clusters including two of cytotoxic Th1 cells (GZMB Th1 and GZMK Th1), Th2, Th17, Treg, proliferating, two memory of cells, naive, and a high mitochondrial gene expression (MT)(Figure 1C, 1D, Figure S2, Table S2). In the proliferating cell cluster, there were more cells expressing the Th1 polarization transcription factor TBX21 than in suppressed and uninfected conditions, suggesting that proliferation of Th1 cells was most prominent during viremia (Figure 1E).
TNF responses persist despite ART and shape Th1 responses
To understand how HIV-1-induced immune dysfunction shapes the CD4+ T cell immune responses, we identified co-regulated genes that could distinguish the immune responses between viremia, viral suppression, and uninfected conditions using de novo gene set identification. Using weighted gene correlation network analysis (WGCNA)(Langfelder and Horvath, 2008), we identified nine consensus sets (modules) of genes that could distinguish gene expression differences between viremia, viral suppression, and uninfected conditions. We found that a proliferation module (Figure S2G–S2L), a GZMB-Treg module (Figure S2M–S2R), and a TNF signaling module (Figure 1F–1J) that distinguished viremia, viral suppression, and uninfected conditions (Figure S2). The proliferation module and GZMB-Treg module increased gene expression during viremia but returned to normal levels after viral suppression (Figure S2), reflecting the peak of host immune responses to acute viral infection. We found that the TNF signaling module was induced during viremia (Figure 1F) and persisted despite viral suppression (Figure 1G). Using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA), we found that genes in the TNF signaling module were enriched for pathways for signaling via TNF receptors, toll-like receptor, and CD40 (Figure 1H). The upstream drivers of the TNF signaling module included TGFβ, TNF, T cell activation, IL-1β, and IFNγ (Figure 1I). When we examined the TNF signaling module score, the aggregate normalized expression levels of these genes, we found that TNF signaling gene expression in GZMK Th1 was significantly higher during viremia and remained elevated after viral suppression relative to uninfected individuals (Figure 1J).
We next examined the impact of immediate versus deferred ART on immune responses (Figure S3). We found that immediate versus deferred ART did not change memory cell phenotypes (Figure S3A) or T cell polarization (Figure S3B). Th1 proliferation were not significantly different after immediate versus deferred ART (Figure S3C). We identified a TNF-driven gene module that was expressed at significantly higher levels in the deferred ART group than the immediate ART group (Figure S3D–S3F), particularly in the Th2 and CXCR5 memory cell populations but not in the GZMK Th1 population (Figure S3G–S3O). Our results suggest ART can reduce but cannot fully block HIV-1-induced immune activation. Cytokines such as TNF and TGFβ continue to shape Th1 responses despite suppressive ART.
The clonal expansion dynamics of cytotoxic Th1 CD4+ T cells are shaped by antigen and TNF responses
We then investigated how cytokine responses impacted T cell clonal expansion dynamics during HIV-1 infection. Inflammatory cytokines impact clonal expansion and differentiation of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells (Pape et al., 1997). T cell clones can be identified based on their shared TCR sequences: cells having identical TCR sequences presumably originate from the same T cell that proliferated into a T cell clone in response to the same antigen stimulation (Figure 2A). We profiled the TCR repertoire using bulk TCR sequencing in addition to single-cell TCR sequences captured in ECCITE-seq to determine T cell clone size with greater precision. In all, we profiled 1,118,713 TCR sequences (median of 57,778 TCR sequences per sample per time point) and identified 8,268 single cells in T cell clones (median of 575 cells per sample per time point).
Figure 2. T cell clone size is determined by antigen response, TNF signaling, and Th1 cytotoxic response.
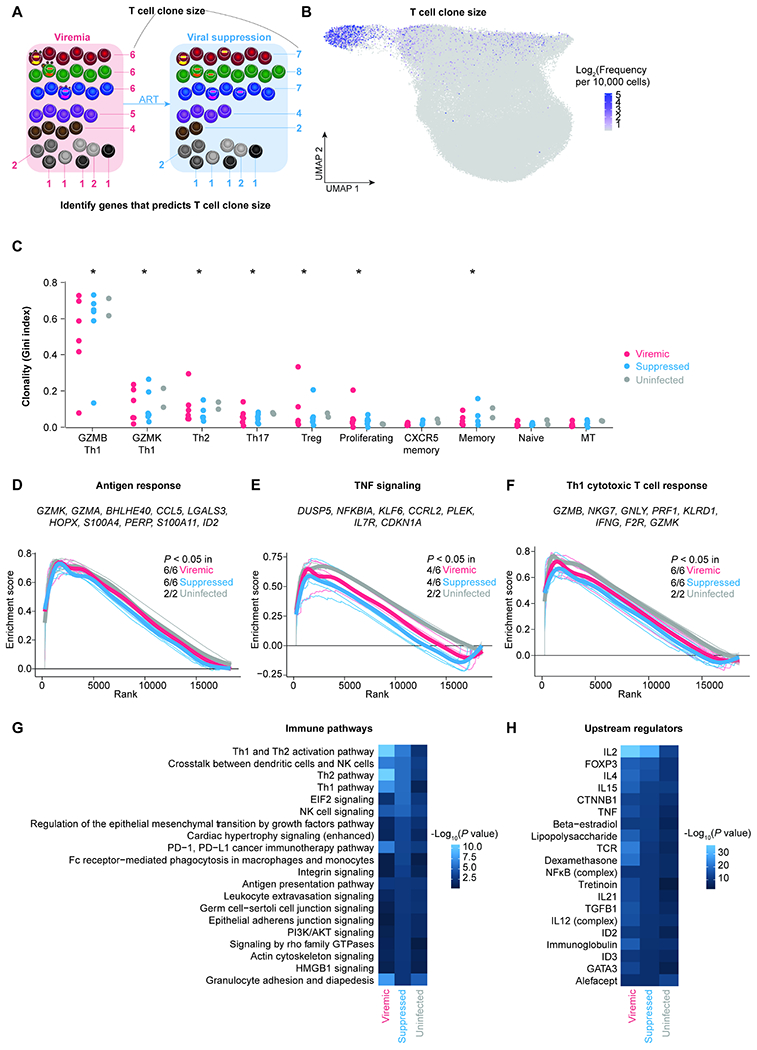
A, T cells sharing the same TCR in the same individual are identified as a T cell clone. T cell clone size is the frequency of T cells sharing the same TCR sequence out of all cells with detected TCR sequences. By calculating the correlation between T cell clone size and gene expression levels in individual cells, we can identify the determinants of T cell clone size. B, UMAP plot indicating the log2 bulk clone size of each cell based on TCRβ nucleotide CDR3 junction sequence per 10,000 CD4+ T cells. C, The level of clonality (as measured by Gini index) in each cluster in viremic, suppressed, and uninfected conditions. P values were determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test comparing each cluster to naive cells. D–F, To identify pathways correlating with T cell clone size, we first ranked genes based on their correlation with clones size and then used Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). We identified pathways including Goldrath antigen response (D), Hallmark TNF signaling via NFκB (E), and Bosco Th1 cytotoxic module (F). Representative leading-edge genes (the top genes enriched in each pathway) were shown in each panel. Thick lines indicate the mean enrichment score for each condition and thin lines indicate the enrichment score for each individual. G–H, Genes that were predictive of T cell clone size across cells in each condition were identified by elastic net regression. These genes were then examined by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to determine the immune pathways (G) and upstream regulators (H). P values were defined by Fisher’s exact test. P values were corrected for multiple comparisons using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure. *, P < 0.05. See also Figure S3 and Table S3.
We found that the most clonal clusters, as measured by the Gini index (Gillet et al., 2011), were proliferating cells and polarized effector memory cells, including GZMB Th1, GZMK Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg clusters (Figure 2B). These T cell clusters were significantly more clonal than naive cells (Figure 2C). Among them, the most clonal T cell cluster was the GZMB Th1 cells (Figure 2C).
To identify cellular transcriptional programs that correlate with T cell clone size, we ranked genes based on their correlation with T cell clone size in each participant at each time point, from most correlated with a large clone size to the most correlated with a small clone size. From this ranking, we identified the immune pathways correlated with T cell clone size using gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA, Table S3). We identified three pathways that are positively associated with T cell clone size: antigen responses (Figure 2D), TNF signaling (Figure 2E), and Th1 cytotoxic responses (Figure 2F). Of note, these pathways were not different between immediate versus deferred ART (Figure S3K–M). Our finding suggests that despite suppressive ART, antigen responses and TNF signaling continue to shape T cell clonal size.
To identify genes that predict T cell clone size, we used elastic net regression (Zhou, 2005) to analyze gene expression level and T cell clone size across participants in each condition. Elastic net regression is a machine learning method that weights each gene according to how efficiently it predicts clone size and eliminates genes that are weakly or not predictive of clone size. We identified 444, 672, and 283 genes that predicted T cell clone size in viremic, suppressed, and uninfected conditions, respectively. We found that genes involving Th1, Th2, and crosstalk with dendritic cells and NK cells predicted T cell clone size in HIV-1-infected individuals, both during viremia and after viral suppression (Figure 2G). Using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis, we found that the expression of these genes was driven by T cell polarization molecules (such as IL2, IL4, TNF, TGF, and IL21), T cell activation, and homeostatic cytokines (Figure 2H). Overall, we found that T cell polarization and activation predicted T cell clonality both in HIV-1-infected and in uninfected individuals. However, T cell polarization and cytokine signaling had substantially higher impacts on T cell clonal expansion during HIV-1 infection (Figure 2G).
TCR repertoire mapping revealed distinct transcriptome programs of CMV-specific versus HIV-1-specific cells in unstimulated states
We wanted to examine whether HIV-1-induced antigen responses and TNF signaling during viremia and after viral suppression changed the HIV-1 and CMV antigen responses. We identified antigen-specific cells using the activation induced marker (AIM) assay (Dan et al., 2016; Morou et al., 2019). We used flow cytometry to sort CD69 and CD154 double positive CD4+ T cells as CMV-specific or HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cells after 9 hours of antigen stimulation (Figure 3A, Figure S4A). Memory cells (CD45RO+) that were double negative for CD69 and CD154 were sorted for comparison. We profiled CD4+ T cells from the same six HIV-1 infected individuals during viremia and suppression using blood samples from the same time point. Using ECCITE-seq, we examined a total of 78,193 CD4+ T cells, with 6,091 from CMV-specific cells, 12,183 from HIV-1-specific cells, and 59,919 from memory cells. The frequency of CMV-specific and HIV-1-specific cells (Figure S4B) was not significantly different between conditions and was comparable to the frequency in previous reports (Morou et al., 2019; Simonetti et al., 2020). We used fastMNN to correct for batch effects (Figure S1). Antigen stimulated cells were mainly effector memory CD4+ T cells (Figure 3B). We identified 15 clusters based on transcriptome differences (Figure 3C, Figure S2, Figure S4C).
Figure 3. TCR repertoire mappings revealed the different transcriptome program of CMV-specific versus HIV-1-specific cells in unstimulated states.
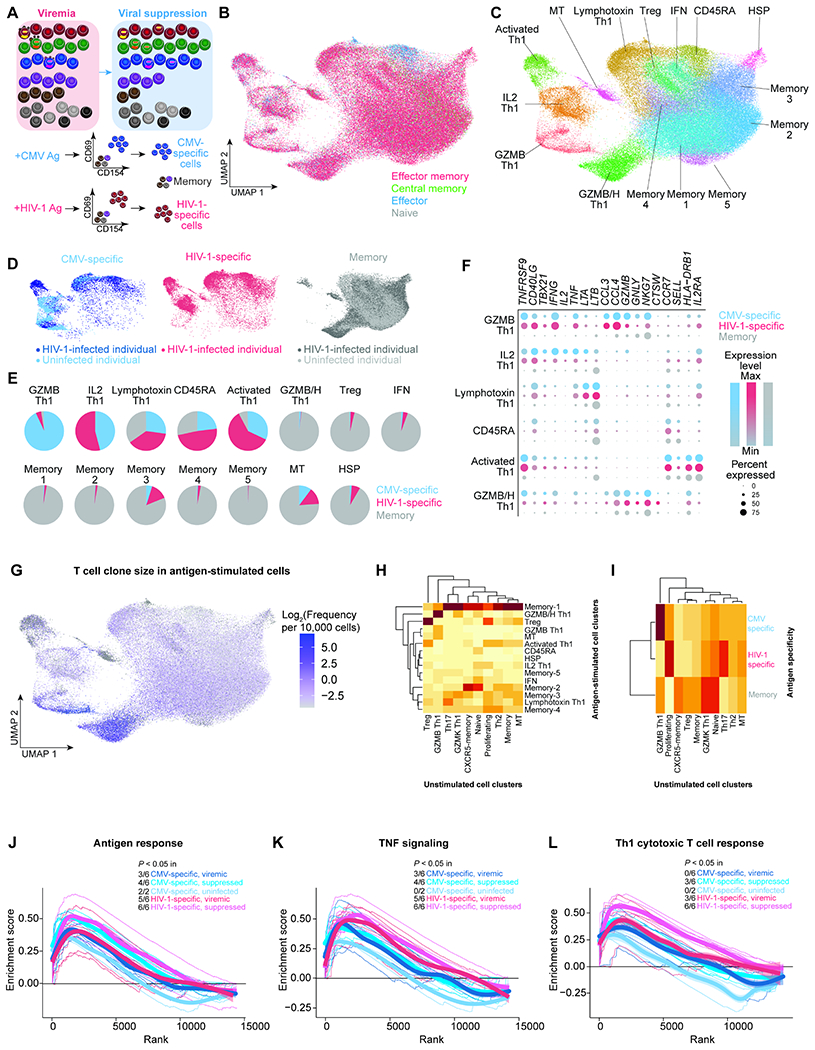
A, CMV-specific and HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cells were identified as cells expressing activation inducible markers (AIM)(CD69 and CD154) after 9 hours of antigen stimulation in the presence of autologous CD8-depleted PBMC. CMV-specific cells, HIV-1-specific cells, and CD45RO+ memory cells were sorted by flow cytometry for single-cell ECCITE-seq. B, UMAP plot of memory phenotypes of cells (n =3 3,805, 44,388, and 14,580 cells in the viremic (from 6 individuals), viral suppression (from 6 individuals), and uninfected conditions (from two individuals), respectively) defined by surface CD45RA and CCR7 expression. These samples came from the same infected study participants and same timepoints as profiled in the unstimulated conditions. CD45RA and CCR7 positivity was determined by barcoded surface protein staining. C, UMAP plot of 15 transcriptionally defined clusters identified in the viremic, virally suppressed, and uninfected conditions. D, UMAP plots of cells split across CMV-specific (n = 6,091), HIV-1-specific (n = 12,183), and sorted memory cell populations (n = 59,919). E, Proportion of each cluster grouped by antigen specificity, with 5 clusters predominantly antigen responsive. F, Dot plot of key effector gene expression across antigen-specific conditions in antigen-specific clusters. G, UMAP plot indicating the T cell clone size of each cell based on TCRβ nucleotide CDR3 junction sequence per 10,000 CD4+ T cells. H, Heatmap indicating the proportion of TCR sequence overlap between unstimulated and stimulated conditions. The majority of unstimulated cells were neither CMV-specific nor HIV-1-specific cells. I, Heatmap indicating the proportion of TCR sequence overlap between unstimulated CD4+ T cells and antigen-specific CD4+ T cells. J–L, Genes ranked by correlation with T cell clone size were analyzed by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) to determine whether the gene expression profile is enriched in specific immune pathways, such as Goldrath antigen response (J), Hallmark TNF signaling via NFκB (K), and Bosco Th1 cytotoxic module (L). Representative leading-edge genes are shown in each panel. Thick lines indicate the mean enrichment score for each condition and think lines indicate the enrichment score for each individual. See also Figure S3, Figure S4.
While not mutually exclusive, antigen-specific cells clustered distinctly from memory cells (Figure 3D). Antigen-specific cells were over-represented in 5 clusters: GZMB Th1, IL2 Th1, activated Th1, lymphotoxin Th1, and CD45RA clusters (Figure 3E). In particular, the GZMB Th1 cells were mainly comprised of CMV-specific cells, while few HIV-1-specific cells were polarized into the GZMB Th1 phenotype. Although both CMV-specific and HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cells were activated upon antigen stimulation, fewer HIV-1-specific cells upregulated Th1 and cytotoxic effector molecules (such as IL2, TNF, IFNG, LTA, LTB, GZMB, and GNLY) in the polarized Th1 clusters GZMB Th1 and IL2 Th1 (Figure 3F). This suggests that Th1 polarized HIV-1-specific cells have less robust cytotoxic T cell responses compared with CMV-specific CD4+ T cells. We found that the GZMB Th1 cells (mostly CMV-specific CD4+ T cells) and the GZMB/H Th1 cells (mostly memory cells) were the most clonal cells both during viremia and after viral suppression (Figure 3G).
By identifying the TCR sequence of antigen-specific cells and tracking back to CD4+ T cells having the same TCR sequence in unstimulated conditions (T cell repertoire overlap), we identified the unstimulated states of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells. We found that GZMB/H cells during antigen stimulation, which were mainly memory cells not responding to CMV and HIV-1 antigen stimulation, were GZMB Th1 cells in the unstimulated condition (Figure 3H). CMV-specific cells, mainly GZMB Th1 cells during antigen stimulation, were also GZMB Th1 cells in the unstimulated condition (Figure 3I). These cells had the highest T cell clonality. This suggests that CMV-specific cells and a subset of memory cells (with unknown antigen specificity) are polarized as GZMB Th1 cells in large clones both in unstimulated and stimulated conditions. In contrast, few HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cells polarized as GZMB Th1 cells – HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cells were mainly Th17 and proliferating T cells in unstimulated conditions (Figure 3I) and were less clonal (Figure 2C). Our results suggests that different antigen stimulation triggers different T cell polarization and proliferation.
TNF responses and cytotoxic T cell responses shape the clonal expansion of HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cells after viral suppression
We examined the genes of which the expression levels correlate with T cell clone size in the antigen-stimulated cells. We found that antigen responses, TNF signaling, and cytotoxic T cell responses determine T cell clone size (Figure 3J–3L, Figure S3J–S3O) as observed in the unstimulated condition (Figure 2D–2F). However, these responses varied depending on the antigen and the participant: (Figure 3J–3L). Overall, we found that while antigen stimulation remains the major determinant of T cell clone size, T cell clonal expansion of HIV-1-specific cells is significantly affected by TNF signaling and cytotoxic T cell responses, particularly after viral suppression.
Prolonged viremia decreases GZMB Th1 effector cells
Comparing HIV-1-specific immune responses in individuals having shorter duration of viremia (in the immediate ART cohort, receiving ART in 30.3 days on average) versus longer duration of viremia (in the deferred ART cohort, receiving ART in 197.3 days on average, Figure S1, Table S1) allows us to examine the impact of HIV-1 antigen stimulation on HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cells in vivo. Previous reports have shown that HIV-1-specific T cells display a different phenotype based on the time of ART initiation (Ndhlovu et al., 2019). We found that in HIV-1-spcific CD4+ T cells, deferred ART decreased the proportion of GZMB/H Th1 cells (Figure S4C) and effector cells (Figure S4D). When we examined whether the gene expression profiles were different in each cluster between immediate versus deferred ART (Figure S4E–S4J), we found that in people receiving deferred ART, lymphotoxin Th1 cells had significantly lower levels of IFNG and GZMB expression (Figure S4G). Overall, prolonged viremia impairs HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cells function by decreasing GZMB effector cell proportion and Th1 effector function.
HIV-1 RNA+ cells are heterogeneous
We next wanted to examine the differences between HIV-1 RNA+ cells and HIV-1 RNA− cells (Figure 4A). We mapped single-cell transcriptome reads to autologous HIV-1 proviral sequences and HXB2 reference. Mapping the transcriptome to autologous HIV-1 sequences increased mapping rate by approximately 20% and increased spliced HIV-1 RNA capture (Figure S5). Due to the 5’-biased RNA capture by ECCITE-seq, most HIV-1 RNA captured were near the 5’ LTR. We identified spliced HIV-1 RNA, mostly spliced from the major splice donor site. To guard against potential sequencing artifacts generated by index hopping, HIV-1 RNA+ cells were defined by the presence of HIV-1 RNA having at least 2 UMIs (representing two unique reverse transcription events in the same single cell) or at least 4 reads of a single UMI. This threshold yielded no HIV-1 RNA+ cells in samples from uninfected individuals. In unstimulated and virally suppressed conditions, HIV-1 RNA+ cells indicated latency reversal in vivo. In the antigen-stimulated conditions, HIV-1 RNA+ cells indicated HIV-1 latency reversal ex vivo. Of note, we found that the normalized expression levels of HIV-1 RNA in viremic, suppressed, unstimulated, and stimulated conditions were not significantly different (Figure S5C–D), suggesting comparable levels of HIV-1 RNA transcriptional burst during in vivo and ex vivo latency reversal. Of note, HIV-1-infected cells that remained latent or had transcriptional defects might not be captured because of the lack of detectable HIV-1 RNA expression.
Figure 4. The heterogeneous transcriptional landscape of HIV-1 RNA+ cells demonstrated antigen responses, cytokine responses, and anti-apoptotic programs.
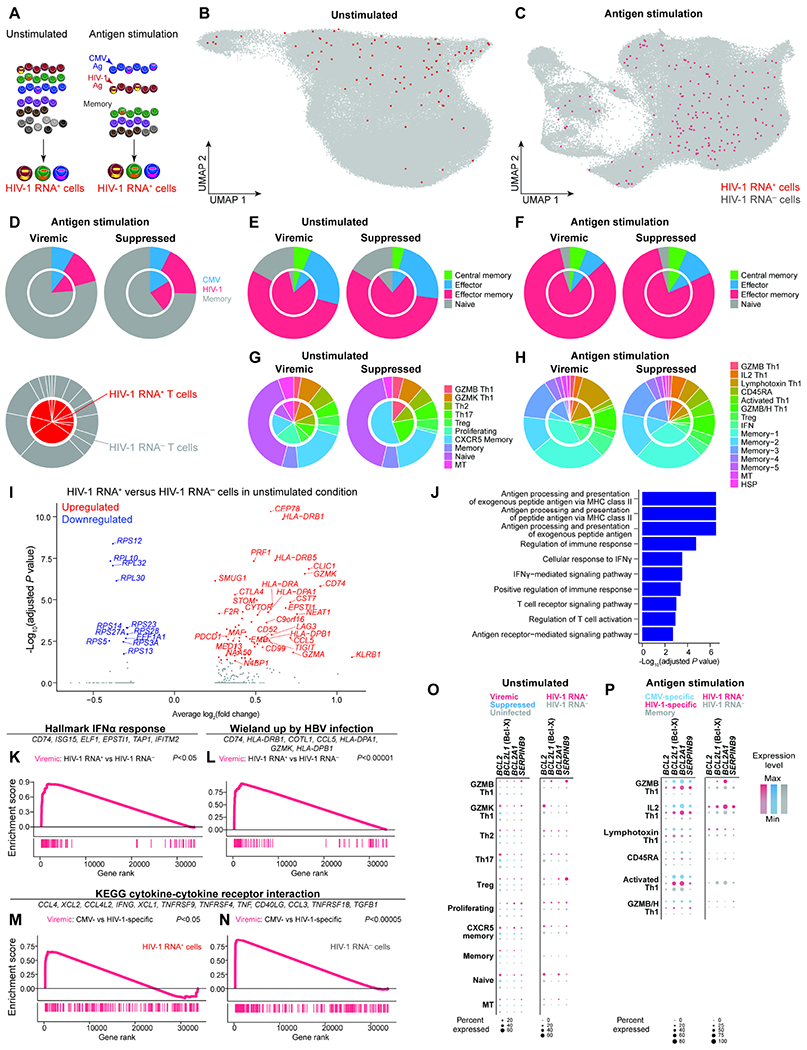
A, Cells expressing HIV-1 RNA were identified by mapping reads to autologous HIV-1 sequences in addition to HXB2 reference sequence in unstimulated conditions and stimulated conditions (including CMV-specific, and HIV-specific, and memory cells). HIV-1 RNA+ cells were defined by having at least 2 HIV-1-related UMI or at least 4 reads of a single UMI to guard against index hopping and sequencing artifacts. B–C, UMAP plots showing HIV-1 RNA+ cells in unstimulated (B), antigen-specific, and memory cells (C). D–H, Pie charts indicating the distribution of antigen specificity (D), memory phenotype in unstimulated (E) and in antigen stimulated conditions (F), transcriptionally defined clusters in unstimulated conditions (G) and in antigen stimulated conditions (H). The inner chart represents HIV-1 RNA+ cells and the outer chart represents HIV-1 RNA− cells. I, Volcano plot indicating differentially expressed genes between HIV-1 RNA+ and HIV-1 RNA− cells in the unstimulated condition during viremia. J, Gene ontology enrichment of immune pathways from upregulated genes. K–N, GSEA plots indicating the enrichment of gene sets in specific immune pathways, including IFNα response (K), viral response (L), cytokine and cytokine receptor interaction (M–N). Representative leading-edge genes are shown in each panel. O–P, Dot plots showing expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family genes BCL2 (encoding Bcl-2), BCL2L1 (encoding Bcl-xL), and BCL2A1 in unstimulated (O) and antigen stimulated conditions (P). See also Figure S5, Figure S6, and Table S3.
In the unstimulated samples, we identified 90 HIV-1 RNA+ cells, including 81 from the viremic time point and 9 from the suppressed time point (Figure 4B). In the antigen-stimulated conditions, we identified 177 HIV-1 RNA+ cells, including 134 during viremia and 43 during suppression (Figure 4C). Among them, 21 were CMV-specific cells, 28 were HIV-1-specific cells, and 128 were memory cells (Figure 4D). The majority of HIV-1 RNA+ cells resided in memory cells, likely because more memory cells were profiled than antigen-specific cells. These memory cells would likely respond to antigens other than CMV and HIV-1. Despite transcriptome and clonal expansion differences in CMV-specific and HIV-1-specific cells, there was no enrichment or proportional differences of HIV-1-RNA+ cells in CMV-specific or HIV-1-specific cells (Wilcoxon rank-sum test).
When we examined the distribution of HIV-1 RNA+ cells in memory cell subsets, we found that HIV-1 RNA+ cells were enriched in effector memory in unstimulated viremic (P < 2.2 x 10−16, Fisher’s exact test) conditions Figure 4E) but not in stimulated conditions (Figure 4F), generally consistent with previous studies of HIV-1 enrichment in effector memory cells (Cole et al., 2021; Duette et al., 2022; Hiener et al., 2017). When we examined the distribution of HIV-1 RNA+ cells in transcriptome defined clusters, HI V-1 RNA+ cells were identified from 9 out 10 different clusters in the unstimulated condition, highlighting the heterogeneity of HIV-1 RNA+ cells in vivo. By comparing the proportion of HIV-1 RNA+ cells and HIV-1 RNA− cells in these clusters, we found that there was enrichment of HIV-1 RNA+ cells during viremia in GZMK Th1 (P = 0.049) and proliferating cells (P = 0.00000001) and dis-enrichment of HIV-1 RNA+ cells in naive cells (P = 0.00006) and non-polarized memory cells (P = 0.02) in the unstimulated condition (Figure 4G). In antigen-stimulated conditions, HIV-1 RNA+ cells were identified from 14 out of 15 different clusters. We found that there was no enrichment of HIV-1 RNA+ cells in specific clusters and there was dis-enrichment of HIV-1 RNA+ cells in non-polarized IFN (P = 0.009) and memory-1 (P = 0.0001) clusters (Figure 4H). Due to their limited number, we avoided statistical analysis of HIV-1 RNA+ cells during viral suppression. Overall, we found that HIV-1 RNA+ cells were heterogeneous.
Antigen, IFN, and cytotoxic T cell response shapes the transcriptional landscape of HIV-1 RNA+ cells during viremia
We compared the transcriptional landscape of HIV-1 RNA+ cells versus HIV-1 RNA− cells only during viremia, as the 9 cells captured during viral suppression were too few for robust analysis. We found that HIV-1 RNA+ cells upregulated cytotoxicity genes (GZMK, GZMA, PRF1, CEP78, CCL5), MHC II genes (HLA-DRB1, HLA-DPB1, CD74), and exhaustion markers (PDCD1, TIGIT, LAG3, CTLA4)(Figure 4I, Table S3). These genes were enriched in antigen presentation and IFNγ responses (Figure 4J), reflecting antiviral responses during viremia.
To compare the transcriptional landscape of HIV-1 RNA+ cells versus HIV-1 RNA− cells across different conditions we ranked genes using expression fold change and conducted gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) on predefined gene expression signatures. First, when we compared HIV-1 RNA+ cells versus HIV-1 RNA− cells in unstimulated conditions during viremia, we found that HIV-1 RNA+ cells upregulated IFNα response (Figure 4K) and viral infection response genes (Figure 4L) (P < 0.05), reflecting innate immune responses to acute viral infections. When we compared CMV-specific cells versus HIV-1-specific cells during viremia, we found that CMV-specific cells upregulated cytokine and cytokine receptor genes, both in HIV-1 RNA+ cells (Figure 4M) and HIV-1 RNA− cells (Figure 4N). This suggests that CMV-specific cells have more robust cytokine responses upon antigen stimulation compared with HIV-1-specific cells.
GZMB Th1 cells express genes encoding anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL and cytotoxic CD8+ T cell resistant gene Serpin B9
We wanted to understand why HIV-1 RNA+ cells survived despite HIV-1 expression and antigen stimulation. We examined the expression levels of Bcl-2 family proteins (Ren et al., 2020), particularly the anti-apoptotic BCL2 (encoding Bcl-2), BCL2L1 (encoding Bcl-xL), and BCL2A1 (an NF-κB target gene upregulated by TNF that promotes cell survival (Vogler, 2012)). In unstimulated CD4+ T cells, we found that BCL2 expression was not significantly different between CD4+ T cells from viremic, suppressed, and uninfected individuals (Figure 4O). When we examined HIV-1 RNA+ cells in the unstimulated condition, BCL2L1 (Bcl-xL) expression in Th1 polarized clusters (GZMB Th1, Th2, Th17, and proliferating cells) trended higher in HIV-1 RNA+ cells than in HIV-1 RNA− cells, although this did not reach statistical significance (Figure 4O, Wilcoxon rank-sum test). Upon antigen stimulation, antigen responding cells expressed BCL2, BCL2L1, and BCL2A1 in Th1 polarized clusters (GZMB Th1, IL2 Th1, and Lymphotoxin Th1)(Figure 4P). When we examined HIV-1 RNA+ cells in the stimulated condition, BCL2L1 and BCL2A1 expression was comparable with that in HIV-1 RNA− cells.
In addition to Bcl2-family genes, we examined SERPINB9 gene expression. Granzyme secreting immune effectors such as cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and natural killer cells express serpin protease inhibitor 9 (Serpin B9) to protect themselves from self-inflicted granule-mediated apoptosis (Bird et al., 1998; Stout-Delgado et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2006). We reasoned that Serpin B9 expression in cytotoxic CD4+ T cells, while protecting themselves from their own granzyme B-mediated killing, can also make HIV-1-infected cells resistant to cytotoxic CD8+ T cell killing (proposed by R. Brad Jones in personal communications). We found that SERPINB9 expression was higher in HIV-1 RNA+ GZMB Th1 cells in the unstimulated condition, although this trend did not reach statistical significance (Figure 4O). We also found SERPINB9 expression in GZMB Th1 cells was higher in CMV-specific cells and HIV-1-specific cells than memory cells, but this trend did not reach statistical significance (Figure 4P). Our finding suggests a reason why HIV-1 RNA+ cells may resist cytotoxic CD8+ T cell killing by residing in cytotoxic CD4+ T cells which naturally resist granzyme B-mediated killing through Serpin B9 expression. Given the low number of cells examined, further studies involving more single cell analyses and in vitro testing are still required.
The majority of HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones are GZMB effector memory Th1 cells with unknown antigen specificity but robust antigen responses
We next examined the immune phenotype of T cell clones harboring HIV-1 RNA+ cells (termed HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones) versus T cell clones not harboring HIV-1 RNA+ cells (termed HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones). Of note, in a HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clone, only a subset of cells are HIV-1 infected, while the remaining are uninfected. These are T cells responding to the same antigen (having the same TCR sequence), with one or a few of these T cells within the clone having detectable HIV-1 RNA+. Unlike the heterogeneity of HIV-1 RNA+ T cells, HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones were enriched in specific clusters, mainly GZMB Th1 cells in unstimulated samples (Figure 5B) and in GZMB/H Th1 cells in the antigen-stimulated condition (Figure 5C). When we examined the antigen specificity of the largest 100 T cell clones in each individual, we found that CMV-specific and HIV-specific T cell clones are frequently captured in these 100 largest clones (Figure 5D). We found that significantly more HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones are memory T cells that did not respond to CMV and HIV-1 antigen stimulation (Fisher’s exact test, P<0.001, both viremia and viral suppression), and there was no enrichment of HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones in CMV or HIV-1-specific cells (Figure 5E). When we examined the memory cell phenotype, we found that more HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones were in enriched in effector memory cells relative to HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones in unstimulated (P<0.001, both viremia and viral suppression) but not stimulated conditions (Figure 5F–5G). When we examined the transcriptome-defined cell clusters, we found that cells in HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones were enriched in the GZMB Th1 cluster in unstimulated conditions (Figure 5H, P<0.001, both viremia and viral suppression) and the GZMB/H Th1 cluster in stimulated conditions (Figure 5I, P<0.001, both viremia and viral suppression). We found that within single T cell clones, there were limited transcriptional, cluster, or memory phenotype differences between viremia and after viral suppression (Table S4, Figure S6A–F). Our results indicate that HIV-1 takes the advantage of the immune system by infecting and persisting in GZMB+ effector memory T cell clones that are hardwired with strong antigen responses and robust clonal expansion capacity.
Figure 5. HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones are enriched in effector memory and GZMB+ Th1 cells.
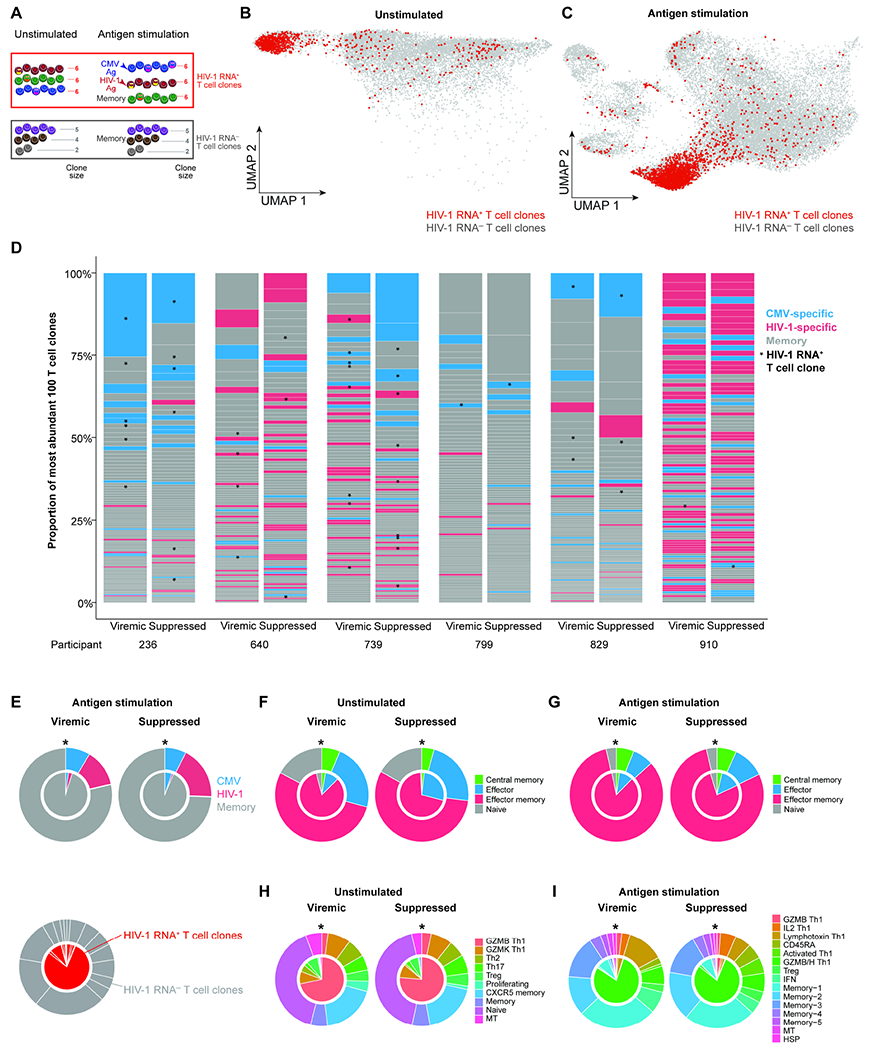
A, T cell clones were defined by at least two cells sharing the same TCR sequence. HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones were defined by T cell clones having at least one HIV-1 RNA+ cells. HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones were defined by T cell clones not having any HIV-1 RNA+ cells. B–C, UMAP plots indicating HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clone in unstimulated (B) and antigen stimulated conditions (C). D, The largest 100 T cell clones, as measured by bulk TCR sequencing in each participant at each time point. * in D, HIV-1 RNA+ clones. E–I, Pie charts indicating the distribution of antigen specificity (E), memory phenotype in unstimulated (F) and in antigen stimulated conditions (G) transcriptionally defined clusters in unstimulated conditions (H) and in antigen stimulated conditions (I). * in E–I, P < 0.05, Fisher’s exact test. See also Table S4, Figure S5 and Figure S6.
HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones are larger in clone size, stable, and persist over time, mainly GZMB+ Th1
We examined the T cell clone size and clonal expansion dynamics of HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones over time, during viremia and after viral suppression. We found that HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones were significantly larger in clone size than HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones both during viremia and after viral suppression, in unstimulated CD4+ T cells (Figure 6A) and after antigen stimulation in CMV-specific cells (Figure 6B), HIV-1-specific cells (Figure 6C), and memory cells (Figure 6D). The enrichment of HIV-1 in larger T cell clones may be because larger T cell clones are more likely to be infected or detected by chance. To test this possibility, we conducted a permutation-based approach. We found that in HIV-1 and CMV-specific T cell clones, both during viremia and viral suppression (Figure S6G–N), the permutation test did not reach statistical significance. This result suggests that HIV-1-specific or CMV-specific T cell clones were larger in size and therefore more likely to harbor HIV-1 RNA+ cells by chance. After viral suppression, these large HIV-1-specific or CMV-specific T cell clones were maintained at larger clone size due to chronic antigen stimulation or robust proliferation. In contrast, in memory cells and in unstimulated conditions, HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones were larger than HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones (significantly larger than all 10,000 permutations, Wilcoxon rank-sum test). This result suggests that HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones (with unknown antigen specificity) have preferential survival or proliferation over HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones.
Figure 6. HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones are large and persistent in GZMB and GZMB/H Th1 cells.
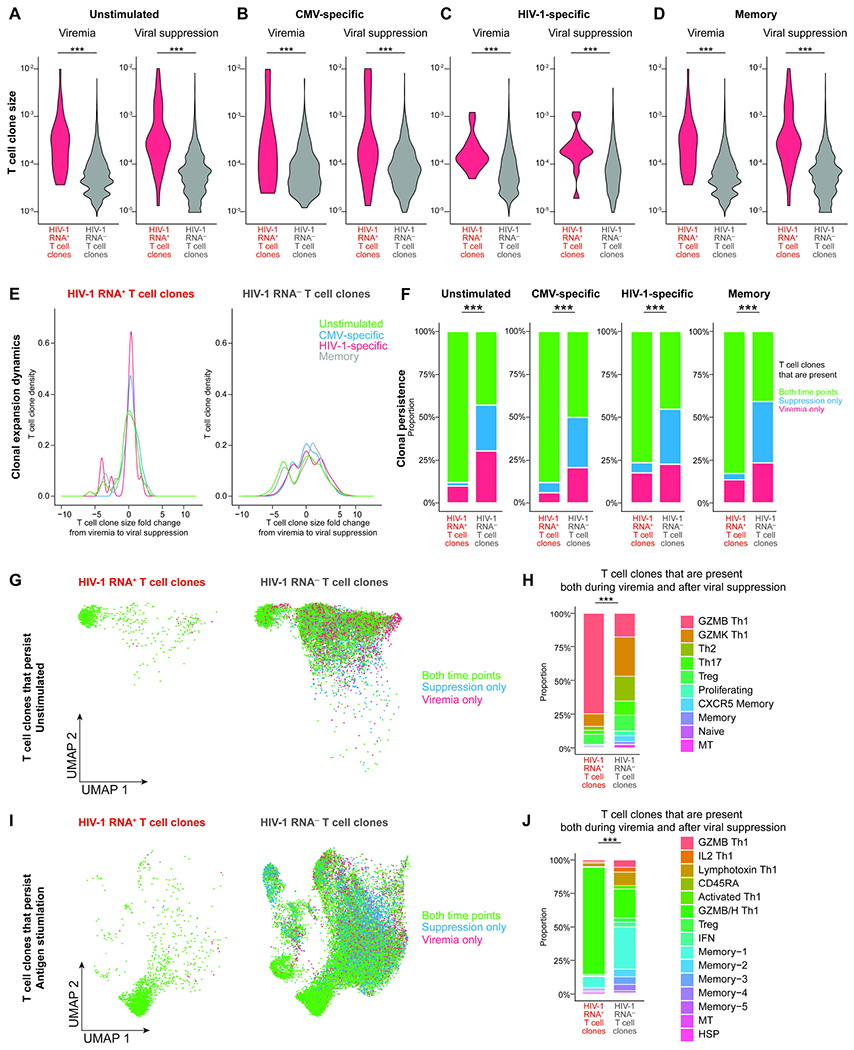
A–D, T cell clone size, as measured by the frequency of T cells sharing the same TCR sequence, in unstimulated (A) and antigen stimulated conditions in CMV-specific (B), HIV-1-specific (C), and memory cells (D). P values were determined by the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. E, T cell clonal expansion dynamics, as measured by the fold change of T cell clone size from viremia to viral suppression. F, T cell clonal persistence, as measured by the proportion of T cell clones that can be captured both during viremia and after viral suppression versus those that can be captured at one time point. G and I, UMAP plots showing T cell clones that persisted both during viremia and after viral suppression in unstimulated (G) and antigen-stimulated conditions (L). H and J, the proportion of transcriptionally defined T cell clusters in T cell clones that persisted both during viremia and after viral suppression in unstimulated (H) and antigen-stimulated (J) conditions. In F, H, and J, P values were determined by Fisher’s exact test. ***, P <0.001. See also Figure S6.
We next examined T cell clonal expansion dynamics by measuring the fold change of T cell clone size between viremia and viral suppression. We found that the majority of HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones remained at the same clone size between viremia and viral suppression, particularly HIV-1-specific cells and CMV-specific cells (Figure 6E). HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones had a greater diversity of fold changes in T cell clone size (Figure 6E). To measure T cell clone persistence, we counted T cell clones that were captured both during viremia and after viral suppression versus those that were captured at only one timepoint. We found that HIV-1 RNA+ clones were more persistent in both unstimulated and stimulated conditions in CMV-specific cells, HIV-1-specific cells, and memory cells (Figure 6F). When we examined the immune phenotype of T cell clones that persisted over time, we found that they were GZMB Th1 cells in the unstimulated condition (Figure 6G, 6H) and GZMB/H Th1 cells in the antigen stimulated condition (Figure 6I, 6J). Overall, we found that HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones are larger in clone size, stable, and persistent over time.
HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones upregulate cytotoxic T cell genes
We next wanted to identify transcriptional differences between HIV-1 RNA+ versus HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones. Using GSEA, we found that HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones upregulated cytotoxic T cell genes (such as GZMB, GZMH, GZMA, PFN1, CCL5, CST7, NKG7) and IL2RG (Figure 7A, 7B). To identify predictors that can differentiate HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones from HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones, we used the machine learning tool single-cell identity definition using random forests and recursive feature elimination (scRFE) to identify a subset of genes that were necessary and sufficient to differentiate HIV-1 RNA+ from HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones. We completed scRFE with 10,000 replicates and selected the top 200 genes which maximized model specificity and sensitivity (Figure S7A–C, Table S4). These 200 genes included both differentially expressed genes and nondifferentially expressed genes, highlighting this model’s ability to identify key genes that define populations beyond simple differential gene expression (Figure 7C). Upregulated genes identified by scRFE were enriched for pathways related to IFN responses, viral infection, IL12 signaling, and T cell signaling (Figure 7D).
Figure 7. HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones are enriched in effector memory CD4+ T cells and express cytotoxic T cell genes.
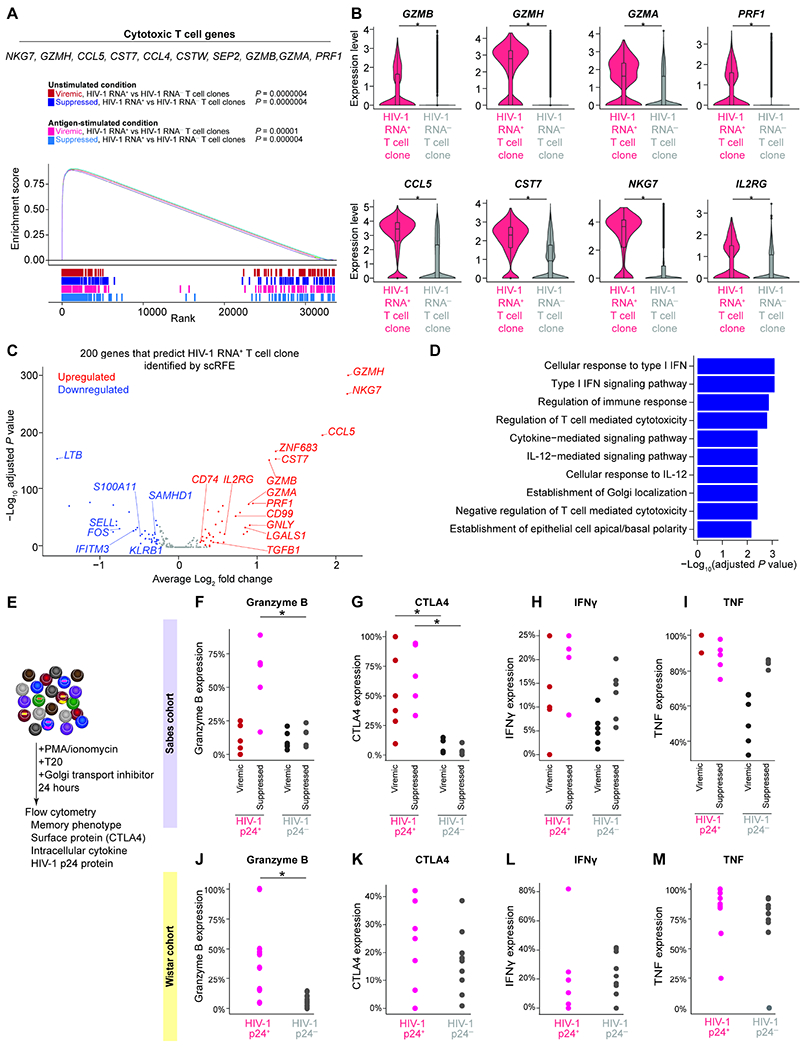
A, GSEA plot and example leading-edge genes (the top genes enriched in this pathway) showing enrichment of gene expression in T cell activation genes (GSE45739 unstimulated versus anti-CD3/CD28 stimulated CD4 T cell upregulated) in HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones. B, Expression level of cytotoxic T cell response genes. P values were derived from Wilcoxon rank-sum test. C, The 200 genes necessary and sufficient to differentiate HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clone from HIV-1 RNA−T cell clone were identified using single-cell identity definition using random forests and recursive feature elimination (scRFE). The volcano plot showed differential expression of the 200 scRFE defined genes. P values were derived from Wilcoxon rank-sum test. D, Enriched immune pathways of upregulated genes among the 200 genes necessary and sufficient to differentiate HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clone from HIV-1 RNA−T cell clones. P values were calculated by Fisher’s exact test. E, To validate whether the enrichment of HIV-1 RNA+ cells in GZMB+, CTLA4+, and effector memory populations at the protein level, we stimulated CD4+ T cells with PMA and ionomycin in the presence of ART (T20) and Golgi transport inhibitors for 24 hours. We then measured HIV-1 p24 protein expression, memory markers, granzyme B, CTLA4, IFNγ, and TNF protein expression in the Sabes cohort (F–I) and the Wistar cohort (J–M). Study participants in these two cohorts were significantly different in the duration of viral suppression, age, ethnicity, and geographic locations. P values were derived from Wilcoxon rank-sum test. *, P <0.05; ***, P <0.001. See also Figure S7 and Table S4.
A significantly higher proportion of HIV-1 p24 effector memory CD4+ T cells are granzyme B positive
To validate our findings, we tested whether granzyme B+ effector memory cells were enriched for HIV-1-infected cells. Using flow cytometry, we examined granzyme B protein expression in HIV-1-infected cells that expressed p24 protein upon PMA/ionomycin activation (Figure 7E, Figure S7C). We first used CD4+ T cells from the Sabes cohort during viremia and after viral suppression. We found that in effector memory cells, HIV-1 p24+ cells are granzyme B+ particularly during viral suppression (Figure 7F). CTLA4, a cellular marker known to enrich for HIV-1 RNA+ cells (Figure 4I)(McGary et al., 2017), was enriched in HIV-1 p24+ cells in the Sabes cohort, both during viremia and viral suppression (Figure 7G). We examined other Th1 effector proteins such as IFNγ and TNF expression to examine whether HIV-1 p24+ cells were simply enriched in polarized Th1 cells. We found that IFNγ and TNF expressing cells were not enriched in HIV-1 p24+ cells (Figure 7H, 7I).
To examine whether the enrichment of HIV-1 p24+ cells in granzyme B+ population is generalizable to other infected individuals, we recruited study participants from a separate cohort from the Wistar Institute. Study participants recruited at the Wistar cohort had a longer duration of undetectable viral load (mean 75 months in the Wistar cohort versus 8 months in the Sabes cohort, P = 0.006, two-tailed Student’s t-test), different ages (mean 44.1 years versus 24.5 years, P = 0.0004), different ethnicity (non-Hispanic versus Hispanic) from different geographic locations (Philadelphia versus Lima). We found that granzyme B+ effector memory T cells were enriched in HIV-1 p24+ cells compared with HIV-1 p24− cells (Figure 7J), while CTLA4, IFNγ, and TNF expression were not significantly enriched in HIV-1 p24+ cells (Figure 7K, 7L, 7M). Overall, we found that GZMB+ cytotoxic effector memory CD4+ T cells were enriched for inducible HIV-1-infected cells.
Discussion
HIV-1 persists in proliferating CD4+ T cells despite suppressive ART. To reach a cure, key questions need to be answered: which cell subsets harbor HIV-1, what drives the proliferation and persistence of HIV-1-infected cells, and how do HIV-1-infected cells resist cell death despite HIV-1 reactivation? By combining single-cell profiling methods, bioinformatic analysis, and machine learning algorithms on longitudinally collected blood samples from the prospective Sabes study, we tracked HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones from viremia to viral suppression. We found that antigen response and TNF response persisted despite suppressive ART, indicating ongoing antigen stimulation from existing HIV-1-infected cells and other co-infections as a cause of chronic immune activation. Antigen, TNF, and cytotoxic T cell responses determined T cell clone size. By comparing cells sharing the same TCR between unstimulated conditions and after antigen stimulation, we found that CMV-specific cells were primed as GZMB Th1 in unstimulated conditions, while HIV-1-specific cells were primed as Th17 and proliferating cells in unstimulated conditions. We identified HIV-1 RNA+ cells without ex vivo stimulation and found that HIV-1 RNA+ cells were heterogeneous, that no single marker could exclusively distinguish HIV-1 RNA+ cells from HIV-1 RNA− cells. By tracking T cell clonal expansion dynamics – namely T cell clone size, stability, persistence, and transcriptional phenotype – both in unstimulated conditions (reflecting the in vivo status of the cells) and after CMV and HIV-1 antigen stimulation (reflecting antigen responses), we found that HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones had unique signatures as cytotoxic effector memory CD4+ T cells expressing granzyme B). Using machine learning algorithms, we identified key genes that could distinguish HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones from HIV-1 RNA− T cell clones. By testing our transcriptome-based findings with protein-based validations using flow cytometry, both from the Sabes study and an independent Wistar cohort, we validated our result and confirmed that HIV-1-infected cells resided in granzyme B+ Th1 effector memory CD4+ T cells after suppressive ART. It is plausible that these cells resist cell death by Bcl-2 family gene expression and are shielded from cytotoxic CD8+ T cell killing because of Serpin B9 expression, but further studies are needed to test this possibility. Our study indicates that HIV-1 persists by residing in cells having robust antigen responses, proliferation potential, and long-term clonal stability. The maintenance of these HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones can be further fueled by HIV-1-induced chronic immune activation through TNF signaling.
The dose and duration of antigen stimulation determines the activation, proliferation capacity, and fate of T cells (Iezzi et al., 1998). We found that CMV-specific cells were highly polarized GZMB+ cytotoxic CD4+ T cells while HIV-1-specific cells, likely responding to heterogeneous HIV-1 antigen stimulation, were polarized into different effector phenotypes but were not able to polarize into GZMB+ cytotoxic T cells. Further, different memory T cells may have different proliferation rate: the estimated proliferation rate is highest in effector memory CD4+ T cells (0.042/day), followed by central memory CD4+ T cells (0.01/day) and naïve CD4+ T cells (0.004/day)(Macallan et al., 2019). Our finding suggests that by residing in T cells that have robust proliferative capacity, such as cytotoxic effector memory CD4+ T cells, the clonally expanding HIV-1-infected cells can be maintained by chronic antigen stimulation. Although CMV-specific and HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cells only account for a small proportion of antigen-specific cells, eliminating immune drivers of clonal expansion, such as by controlling CMV infection (Hunt et al., 2011), inhibiting HIV-1 expression (Yeh et al., 2020), and reducing TNF-induced chronic immune activation, may halt the clonal expansion of HIV-1-infected cells and accelerate HIV-1 eradication.
Limitations of the study
A major limitation of this study is that this method does not capture HIV-1 latently infected cells that do not express HIV-1 RNA. Methods that can capture HIV-1 DNA, HIV-1 RNA, and cellular transcriptome within the same cell are needed to examine the immune profile of the transcriptionally silent latently infected cells, which can potentially be achieved by advanced technologies. Still, recent studies have demonstrated that up to 30% of the HIV-1-infected cells actively express HIV-1 RNA and persist over time despite ART (Einkauf et al., 2022). The result highlights the importance of understanding both transcriptionally active and latent HIV-1-infected cells.
STAR Methods
RESOURCE AVAILABILITY
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the lead contact Ya-Chi Ho (ya-chi.ho@yale.edu).
Materials availability
This study did not generate new unique reagents.
Data and code availability
Single-cell RNA-seq, and bulk TCR sequencing data have been deposited at GEO and are publicly available. Accession numbers are listed in the key resources table. All original code has been deposited at Github and is publicly available. DOIs are listed in the key resources table. Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| CD8-BV510 clone SK1 | BioLegend | CAT# 344731 |
| CD14-BV510 clone M5E2 | BioLegend | CAT# 301841 |
| CD19-BV510 clone HIB19 | BioLegend | CAT# 302241 |
| CD56-BV510 clone 5.1H11 | BioLegend | CAT# 362533 |
| CD3-BV421 clone SK7 | BioLegend | CAT# 344833 |
| CD69-BV650 clone FN50 | BioLegend | CAT# 310933 |
| CD154-PE clone 24-31 | BioLegend | CAT# 310805 |
| CD45RO-APC/Fire750 clone UCHL1 | BioLegend | CAT# 304249 |
| TotalSeq-C IL7RA clone A019D5 | BioLegend | CAT# 351356 |
| TotalSeq-C CCR7 clone G043H7 | BioLegend | CAT# 353251 |
| TotalSeq-C CD25 clone BC96 | BioLegend | CAT# 302649 |
| TotalSeq-C CD27 clone O323 | BioLegend | CAT# 302853 |
| TotalSeq-C CD3 clone UCHT1 | BioLegend | CAT# 300479 |
| TotalSeq-C CD4 clone RPA-T4 | BioLegend | CAT# 300567 |
| TotalSeq-C CD8 clone RPA-T8 | BioLegend | CAT# 301071 |
| TotalSeq-C CD45RA clone HI100 | BioLegend | CAT# 304163 |
| TotalSeq-C CD45RO clone UCHL1 | BioLegend | CAT# 304259 |
| TotalSeq-C CD62L clone DREG-56 | BioLegend | CAT# 304851 |
| TotalSeq-C CD69 clone FN50 | BioLegend | CAT# 310951 |
| TotalSeq-C HLA-DR clone L243 | BioLegend | CAT# 307663 |
| TotalSeq-C CD47 clone CC2C6 | BioLegend | CAT# 323131 |
| TotalSeq-C CCR5 clone J418F1 | BioLegend | CAT# 359137 |
| TotalSeq-C CXCR3 clone G025H7 | BioLegend | CAT# 353747 |
| TotalSeq-C CCR6 clone G034E3 | BioLegend | CAT# 353440 |
| TotalSeq-C CCR4 clone L291H4 | BioLegend | CAT# 359425 |
| TotalSeq-C CXCR5 clone J252D4 | BioLegend | CAT# 356939 |
| TotalSeq-C CD40L clone 24-31 | BioLegend | CAT# 310849 |
| TotalSeq-C 4-1BB clone 4B4-1 | BioLegend | CAT# 309839 |
| TotalSeq-C OX40 clone ACT35 | BioLegend | CAT# 350035 |
| TotalSeq-C PD-1 clone EH12.2H7 | BioLegend | CAT# 329963 |
| TotalSeq-C CTLA-4 clone BNI3 | BioLegend | CAT# 369621 |
| TotalSeq-C TIGIT clone A15153G | BioLegend | CAT# 372729 |
| TotalSeq-C mouse IgG1 clone MOPC-21 | BioLegend | CAT# 400187 |
| TotalSeq-C mouse IgG2a clone MOPC-173 | BioLegend | CAT# 400293 |
| TotalSeq-C mouse IgG2b clone MPC-11 | BioLegend | CAT# 400381 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 1 | BioLegend | CAT# 394661 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 2 | BioLegend | CAT# 394663 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 3 | BioLegend | CAT# 394665 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 4 | BioLegend | CAT# 394667 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 5 | BioLegend | CAT# 394669 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 6 | BioLegend | CAT# 394671 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 7 | BioLegend | CAT# 394673 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 8 | BioLegend | CAT# 394675 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 9 | BioLegend | CAT# 394677 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 10 | BioLegend | CAT# 394679 |
| CD45RA-BUV737 clone HI100 | BD Biosciences | CAT# 612846 |
| CCR7-BUV395 clone 3D12 | BD Biosciences | CAT# 740267 |
| CTLA4-PE-Dazzel594 clone L3D10 | Bioledgend | CAT# 349921 |
| IFNG-BV711 clone 4S.B3 | BD Biosciences | CAT# 564793 |
| TNF-BV605 clone Mab11 | Biolegend | CAT# 502935 |
| p24-PE clone KC57 | Beckman Coulter | CAT# 6604667 |
| p24-APC clone 28B7 | Medimabs | CAT# MM-0289-APC |
| GZMB-AF700 GB11 | BD Biosciences | CAT# 561016 |
| Biological samples | ||
| Demographics of study participants, see Table S1 | This paper | N/A |
| Human serum | Sigma Aldrich | CAT# H4522-20ML |
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| Staphylococcal enterotoxin type B (SEB) toxin | List Biological Laboratories | CAT# 122 |
| HIV-1 group B Gag, Pol, Env, and Nef peptide pools | NIH HIV Reagent Program | CAT# 12425, 12438, 12540, 12545 |
| CMV lysate, strain AD-169 | ZeptoMetrix | CAT# 810003 |
| HCMV pp65 peptide pool | NIH HIV Reagent Program | CAT# 11549 |
| enfuvirtide | NIH HIV Reagent Program | CAT# 12732 |
| Ionomycin | Millipore | CAT# 407950-1MG |
| PMA | Millipore | CAT# 5.00582.0001 |
| Brefeldin A | Thermo Fisher Scientific | CAT# 00-4506-51 |
| Monensin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | CAT# 00-4505-51 |
| CD40 antibody | Miltenyi Biotech | CAT# 130-094-133 |
| Critical commercial assays | ||
| Chromium Next GEM Single Cell 5’ Library & Gel Bead Kit v1.1 | 10x Genomics | PN-1000165 |
| Chromium Single Cell V(D)J Enrichment Kit, Human T Cell | 10x Genomics | PN-1000005 |
| Chromium Single Cell 5’ Feature Barcode Library Kit | 10x Genomics | PN-1000080 |
| NEBNext Immune Sequencing Kit | New England Biolabs | CAT# E6320S |
| EasySep Direct Human CD4+ T cell kit | STEMCELL | 19662 |
| CD4 T cell isolation kit, human | Miltenyi Biotech | 130-096-533 |
| EasySep Dead Cell Removal (Annexin V) Kit | STEMCELL | 17899 |
| Dynabead CD8 | Thermo Fisher | 11147D |
| LIVE/DEAD Fixable Aqua Dead Cell Stain Kit | Thermo Fisher | L34957 |
| LIVE/DEAD Fixable Near-IR Dead Cell Stain Kit | Thermo Fisher | L10119 |
| Deposited data | ||
| ECCITE-seq unstimulated CD4+ T cells | This study | GSE187515 |
| ECCITE-seq stimulated CD4+ T cells | This study | GSE187515 |
| Bulk TCR repertoire profiling from HIV-1 infected and uninfected individuals | This study | GSE187515 |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| cellranger count version 3.0.2 | 10X Genomics | https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/software/downloads/3.0/ |
| cellranger vdj version 3.1 | 10X Genomics | https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/software/downloads/3.1/ |
| Seurat version 4.0.3 | Stuart et al. 2018 | https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/Seurat/index.html |
| batchelor version 1.6.3 | Haghverdi et al., 2018 | https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/batchelor.html |
| uwot version 0.1.10 | NA | https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/uwot/index.html |
| STAR version 2.5.3 | Dobin et al., 2012 | https://github.com/alexdobin/STAR |
| WGCNA version 1.70-3 | Langfelder and Horvath, 2008 | https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/WGCNA/index.html |
| pRESTO version 0.6.1 | Vander Heiden et al., 2014 | https://presto.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ |
| ChangeO version 1.0.0 | Gupta et al., 2015 | https://changeo.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ |
| scikit-learn version 0.23 | Pedregosa et al., 2011) | https://scikit-learn.org/stable/ |
| IPA summer 2021 release | Krämer et al., 2014 | https://digitalinsights.qiagen.com/products-overview/discovery-insights-portfolio/analysis-and-visualization/qiagen-ipa/ |
| scRFE, version 1.5.6 | Park et al., 2020) | https://github.com/czbiohub/scRFE |
| Imbalanced-learn version 0.7.0 | Lemaître et al., 2017 | https://imbalanced-learn.org/stable/ |
| fGSEA version 1.16.0 | Korotkevich et al., 2019) | http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/fgsea.html |
| R version 4.0.3 | R Core Team (2021) | https://www.r-project.org/ |
| CodonCode version 7 | CodonCode Corporation | https://www.codoncode.com/aligner/ |
| Analysis scripts | This paper | https://github.com/Ya-ChiHo/Collora-and-Liu-et-al-2022 |
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL AND SUBJECT DETAILS
Study participants
The demographics of the study participants are listed in Table S1. The Sabes and MERLIN studies were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and the non-government organization Asociación Civil Impacta Salud y Educación, Lima, Perú (Impacta) as well as by the ethics committee of Impacta and the Peruvian National Institute of Health. Specimen collection from Yale University and Wistar Institute was reviewed and approved by the IRB at Yale University and Wistar Institute, respectively. All participants provided written informed consent, including consent for storage and future use of specimens.
For paired blood samples during viremia and after viral suppression, participants were recruited under the Sabes study protocol and viably frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were obtained under the MERLIN study protocol (Lama et al., 2018; Lama et al., 2020). Briefly, uninfected study participants were prospectively tested monthly by third-generation HIV-1 antibody immunoassays. Seronegative samples were tested for HIV-1 RNA with pooled nucleic acid amplification (NAAT) tests. Participants with incident HIV-1 infection were rapidly linked to the next phase of the study. After specimen collection during viremia (viremic samples with a documented viral load), participants were randomly assigned to immediate and deferred ART initiation arms. In the immediate ART arm, participants initiated ART (either EFV/FTC/TDF or EGV/COBI/FTC/TDF) at the baseline visit (<2 months of estimated date of infection (Lama et al., 2020)). In the deferred ART arm, participants initiated ART 24 weeks after the baseline visit (6–8 months after estimated date of infection). After one year of suppressive ART (documented by a plasma viral load <200 copies/mL at 6 months prior to blood sampling), the virally suppressed specimens were taken. We obtained blood samples from 3 individuals from the immediate ART arm and three individuals from the deferred ART arm to ensure our results are generalizable to different treatment conditions.
For uninfected controls, two sex-matched HIV-1-uninfected individuals were recruited at Yale University. For flow cytometry validation studies, eight sex-matched HIV-1-infected individuals under long-term suppressive ART (mean 75 months, range 41–182 months) were recruited at Wistar institute.
METHOD DETAILS
Isolation of unstimulated and antigen-specific CD4+ T cells
For unstimulated CD4+ T cells, aliquots of 20 million PBMCs were thawed. Dead cells were removed by magnetic depletion (STEMCELL Technologies). CD4+ T cells were purified with magnetic negative selection (Miltenyi Biotec) and stained with Total-Seq C antibodies (BioLegend). Antigen-specific CD4+ T cells were isolated from cryopreserved PBMC following activation induced marker (AIM) protocols previously described (Morou et al., 2019). CD8+ T cells were depleted (using CD8 Dynabeads, Thermo Fisher) to prevent CD8 killing of HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells during activation. CD8-depleted PBMCs were aliquoted as 15 million cells per well in 24-well plates in RPMI media supplemented with 10% human serum (Sigma-Aldrich). Cells were rested at 37 °C incubator for 3h. 15 min before stimulation, 0.5 μg/ml CD40 antibody (Miltenyi Biotec) was added to reduce CD40L internalization. Cells were stimulated with an overlapping peptide pool corresponding to HIV-1 group B Gag, Pol, Env, and Nef (1 μg/ml per peptide, NIH HIV Reagent Program) for HIV-1 antigen stimulation. For CMV antigen stimulation, cells were stimulated with CMV lysate (1 μg/ml, ZeptoMetrix) and an overlapping peptide pool corresponding to HCMV pp65 (1 μg/ml per peptide, NIH HIV Reagent Program). 10 μM enfuvirtide (T20) was added to each well to prevent new infection events in vitro. For each assay, aliquots of PBMC were stimulated with DMSO as a negative control and with Staphylococcal enterotoxin type B (SEB) toxin (1 μg/ml, List Biological Laboratories) as a positive control. After 9 h stimulation, cells were stained for viability using LIVE/DEAD Fixable Aqua Dead Cell Stain Kit (Thermo Fisher) and a panel of antibodies against CD8 (BV510, BioLegend, clone SK1), CD14 (BV510, BioLegend, clone M5E2), CD19 (BV510, BioLegend, clone HIB19), CD56 (BV510, BioLegend, clone NCAM), CD3 (BV421, BioLegend, clone SK7), CD69 (BV650, BioLegend, clone FN50), CD154 (PE, BioLegend, clone 24-31), and CD45RO (APC/Fire750, BioLegend, clone UCHL1) in Brilliant Stain Buffer (BD Biosciences). CD69 and CD154 double positive CD4+ T cells were sorted by flow cytometry as antigen-specific cells. CD69 and CD154 double negative, CD45RO positive cells were sorted as memory CD4+ T cells that did not respond to HIV-1 or CMV antigen stimulations. All cells were sorted on a BD FACSAria Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences) into tubes containing RPMI media with 20% fetal bovine serum, 25 mM HEPES, 50 U/ml penicillin, and 50 μg/ml streptomycin (Thermo Fisher). Sorted cells were pelleted and stained with Total-Seq C antibodies (BioLegend).
DNA-barcoded surface protein staining
CD4+ T cells from four participants (236, 829, 739, and 799) in unstimulated conditions and all participants in the antigen stimulated conditions were stained with a full panel of 24 surface protein markers [IL7RA (clone A019D5), CCR7 (clone G043H7), CD25 (clone BC96), CD27 (clone O323), CD3 (clone UCHT1), CD4 (clone RPA-T4), CD8 (clone RPA-T8), CD45RA (clone HI100), CD45RO (clone UCHL1), CD62L (clone DREG-56), CD69 (clone FN50), HLA-DR clone (L243), CD47 (clone CC2C6), CCR5 (clone J418F1), CXCR3 (clone G025H7), CCR6 (clone G034E3), CCR4 (clone L291H4), CXCR5 (clone J252D4), CD40L (clone 24-31), 4-1BB (clone 4B4-1), OX40 (clone ACT35), PD-1 (clone EH12.2H7), CTLA-4 (clone BNI3), and TIGIT (clone A15153G)] and three isotype control staining antibodies [mouse IgG1 (clone MOPC-21), mouse IgG2a (clone MOPC-173), and mouse IgG2b (clone MPC-11)]. CD4+ T cells from antigen stimulated conditions were additionally stained with anti-human Hashtag antibodies (BioLegend Total-seq C) for sample pooling. CD4+ T cells from four individuals (M2, M3, 640, and 910) in the unstimulated condition were stained with a panel of 13 antibodies [IL7RA (clone A019D5), CCR7 (clone G043H7), CD25 (clone BC96), CD27 (clone O323), CD3 (clone UCHT1), CD4 (clone RPA-T4), CD45RA (clone HI100), CD45RO (clone UCHL1), CD62L (clone DREG-56), CD69 (clone FN50), HLA-DR (clone L243), PD-1 (clone EH12.2H7), and TIGIT (clone A15153G)] and the same three isotype control staining antibodies [mouse IgG1 (clone MOPC-21), mouse IgG2a (clone MOPC-173), and mouse IgG2b (clone MPC-11)].
ECCITE-seq library preparation and sequencing
Cells were loaded into the 10x Genomics Chromium Controller with a target capture of 10,000 single cells per sample. Library preparation for the single cell immune profiling with feature barcoding were performed according to manufacturer instructions (10x document CG000186 Rev D). Briefly, polyadenylated mRNA was reverse transcribed using poly(dT) primers and captured by template switch oligos. DNA barcodes on the surface protein staining and hashing antibodies were captured by annealing the reverse complement template switch oligo to the template switch oligo. After cDNA amplification, high molecular weight DNA was isolated for separate T cell receptor (TCR) and transcriptome library preparation, while low molecular weight DNA was used for surface antibody barcode library preparation. Libraries were then sequenced on either HiSeq 4000 or NovaSeq 6000 in appropriate read configurations.
Bulk T cell receptor library preparation and sequencing
Total RNA from aliquots of ~2 million CD4+ T cells were used to capture a broader CD4+ TCR repertoire using NEBNext Immune Sequencing Kit (New England Biolabs) according to manufacturer’s instruction. Briefly, RNA underwent reverse transcription using a UMI-labeled oligonucleotide. cDNA was universally amplified and then enriched for TCRβ chain by targeted amplification. Resulting libraries were sequenced on a MiSeq in 2x300 bp read mode.
Autologous HIV-1 sequencing
RNA transcripts from ECCITE-seq were mapped to HIV-1 genome. To increase mapping efficiency, autologous HIV-1 RNA sequences were used for mapping in addition to the HXB2 reference sequence. Autologous HIV-1 sequences from study participants were identified from the supernatant of p24 positive viral outgrowth culture wells and from near-full length limiting-dilution PCR from DNA of CD4+ T cells (Ho et al., 2013). Sequences from both methods were assembled into contigs and aligned to HXB2 using CodonCode (version 7). Gaps were filled with HXB2 sequence.
Flow cytometric validation
Aliquots of 100 million (Sabes samples) or 200 million (Wistar samples) cryopreserved PBMC were thawed. CD4+ T cells were isolated by negative selection (Miltenyi Biotec). Cells were cultured for 24 h in 1 μg/mL PMA, 1 μM lonomycin, 30 U/mL IL-2 2, 3 μg/mL brefeldin A, and 2 μM monensin. 10 μM enfuvirtide (T20) was added to each well to prevent new infection events in vitro. Cells were then stained with viability dye (LIVE/DEAD Fixable Near-IR Dead cell stain kit, Thermo Fisher) and surface protein antibodies [CD45RA (BUV737, BD Biosciences, clone HI100), CCR7 (BUV395, BD Biosciences, clone 3D12), CTLA4 (PEDazzel594, BioLegend, clone L3D10] for 30 minutes at 4 °C in 1 mL with Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (BD Biosciences). Cells were washed twice with wash media and fixed in 1 mL of Foxp3 Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set (Thermo Fisher) for 45 minutes at room temperature according to manufacturer instructions. Cells were washed twice with permeabilization buffer and then stained with intracellular protein antibodies [IFNγ (BV711, BD Biosciences, clone 4S.B3), TNF (BV605, BioLegend, clone Mab11), p24 (PE, Beckman Coulter, clone KC57), p24 (APC, Medimabs, clone 28B7), granzyme B (AF700, BD Biosciences, GB11)] for 45 minutes at room temperature. Cells were washed twice with permeabilization buffer and resuspended in wash media for analysis using BD FACSAria. Flow cytometry results were analyzed using FlowJo (BD Biosciences, version 10.8.0).
Single-cell multi-omic analysis
Sequence alignment
Reads from gene expression and surface protein antibody barcode were aligned using cellranger count (10x Genomics, version 3.0.2). Reads from TCR sequencing were assembled and aligned using cellranger vdj (10x Genomics, version 3.1). Unfiltered count matrices and TCR assignments were output for downstream analysis.
Doublet discrimination
TCR sequences were used first to identify doublets as defined by >3 productive TCR chain contigs assigned to a single cell barcode. Cells identified as doublets were removed from count matrices.
Quality control
To prevent downstream identification of T cell variable gene fragments were removed from consideration for variable genes. Count matrices were then used to initialize Seurat Objects (Stuart et al., 2019), with TCR data added as metadata. Cells were filtered to remove cells with greater than 10% mitochondrial gene expression or fewer than 500 genes.
Hashing antibody demultiplexing
To separate individual samples from pooled antigen specific single cell libraries, we utilized the Seurat function HTODemux on each individual library. Hashing antibody-defined doublets and barcodes without hashing assignment were discarded.
Batch effect correction by integration
Following this rough filtering, for unstimulated data two rounds of integration were performed. In the first integration step, each sample was normalized using SCTransform and integrated using fastMNN (Haghverdi et al., 2018). We chose fastMNN (as opposed to reciprocal principal component analysis in Seurat3 (Stuart et al., 2019) or Harmony (Korsunsky et al., 2019)) because this integration method preserves the biological differences between sorted CD69+CD154+ cells versus CD69−CD154−cells without over integration. Twenty nearest neighbors in the mutual nearest neighbor space were identified and used to generate clusters with a resolution parameter of 0.4. Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) was used to visualize cells in a low dimensional space (version 3)(McInnes and Melville, 2018). Clusters without >50% CD3 barcoded surface antibody staining were discarded as non-T cells. Clusters with expression of CD8A, KLRC1, or KLRC3 in more than 20% of cells were discarded as CD8+ T cells or NKT cells. In the second integration step, the remaining cells were reintegrated using the same workflow without contaminating cells. Since the stimulated data was generated from sorted CD4+ T cell populations, only a single round of integration was required with the same parameters as above.
Surface protein expression analysis
Similar to flow cytometry-based antibody staining and measurement of surface protein expression, cells having higher normalized read counts of barcoded surface antibody staining, as measured by >90th percentile of the expression level of isotype barcoded antibody controls, were defined as positive for the respective surface protein expression.
Cell type identification
Following cluster identification in the mutual nearest neighbor space with a resolution parameter of 0.4, the single-cell transcriptional landscape was plotted by UMAP (Mclnnes and MeIville, 2018). Genes having >0.25 log2 fold change difference were used in conjunction with protein expression to annotate the CD4+ T cell immune phenotype of individual clusters. By examining the expression level of two surface protein expression in the same single cell, memory cell phenotype can be defined as naive (CD45RA+, CCR7+), central memory (CD45RA−, CCR7+), effector memory (CD45RA−, CCR7−), and effector (CD45RA+, CCR7−) CD4+ T cells.
HIV-1 RNA+ cell identification
Transcriptome reads were aligned to a compendium of autologous viruses using STAR (version 2.5.3)(Dobin et al., 2012). STAR was run in two passes, first to identify and annotate splice sites in the input HIV-1 genomes, and second to realign to the annotated genomes. No multiple mapping reads were discarded at this stage. Barcodes and UMIs were extracted from the associated reads and filtered in an R script to identify HIV-1 RNA+ cells. To guard against artifacts generated by potential index hopping, cells with a minimum of 2 HIV-1-related UMI or 4 reads of a single UMI were considered positive.
Gene expression module analysis and scoring
Gene expression modules were identified as previously described (Kazer et al., 2020). Briefly, objects were subset by cell types of interest, the first 3–10 principal components were used to identify the 50 most significant genes positively and negatively associated with those components (Kazer et al., 2020). The expression matrix of those identified genes was used as input for weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA, version 1.70-3)(Langfelder and Horvath, 2008). A soft power was selected per author’s recommendations where possible and reduced if fewer than 3 modules of a minimum size 10 were identified. Module significance was determined by bootstrapped sampling as previously described (Kazer et al., 2020) Modules were clustered using the R function hclust to merge similar modules with a cutoff of 2.2. Modules were scored as previously described (Tirosh et al., 2016) using the Seurat function AddModuleScore. Differences between groups were identified using Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
T cell clone analysis
Reads from bulk TCR sequencing were trimmed, merged, and assembled into consensus contigs based on UMI using pRESTO (version 0.6.1)(Vander Heiden et al., 2014). Resulting contigs were aligned to a database of IGMT TCR segment genes and annotated by ChangeO (version 1.0.0)(Gupta et al., 2015). TCRs were then filtered for productive contigs. Clones were defined based on the complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) nucleotide junction on TCRβ by individual. Bulk frequencies were quantified, normalized to the total captured TCRs, and used to annotate the size of single TCR clones. TCRs captured by 10x Genomics TCR sequencing in single cells but not in bulk sequencing were set to singleton frequency for each individual. Cells with >1 captured TCR from the same individuals at any time point were defined as clonal (from 595,014 unique TCRs 115,478 clones were identified in bulk. 15,004, 1,152, 1,394, and 9,285 of those clones had single cell RNA-seq derived transcriptomes in unstimulated, CMV-specific, HIV-1-specific, and sorted memory conditions respectively). Each clone was tested for significant changes between time points using Fisher’s exact test comparing viremia and suppression. Clones with at least one cell that was HIV-1 RNA+ were considered as HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clone.
Permutation testing of observed HIV-1 RNA+ clone size relative to overall clone size distribution.
To determine if the observed increased HIV-1 RNA+ clone size was due to the increased chance of observing an HIV-1 RNA+ cell in a large clone as opposed to an increased size intrinsic to HIV-1 RNA+ clones we implemented a permutation test. First, we determined the number of HIV-1 RNA+ cells in clones detected in a given group “HIV N”. We then subset all our observed cells to exclusively cells in clones (the same TCR sequence detected twice) “clonal pool”. We then randomly sampled “HIV N” cells from the “clonal pool” without replacement. Cells in both the HIV group and the sampled cells were collapsed into independent clones so that no clone frequency was counted multiple times. Finally, this subset of sampled clone frequency was compared to the observed HIV-1 RNA+ clone sizes using a one-tailed Wilcoxon Rank-sum to determine if HIV-1 RNA+ clones were larger than the sampled clone sizes. This procedure was completed 10,000 times for each comparison. We considered a given relationship significant if greater than 95% of permutation comparisons were significant.
Elastic net clonal regression
To identify gene expression profile that correlate with T cell clone size, we used elastic net, a regression method that utilizes Lasso feature elimination and the coefficient reduction of Ridge regression (Zhou, 2005). Data were split by condition. A matrix of the gene expression and clone sizes were output for from Seurat for elastic net regression in scikit-learn (Pedregosa et al., 2011) (version 0.23). Data were split 80-20 with genes serving as candidate predictive features and clone size as target data. A parameter search was used to identify and alpha value maximizing accuracy with the initial 80 split, yielding values ranging from 0.1 to 0.001. Optimal alphas were then averaged (resulting in 0.0285) and used to train final models. This resulted in accuracy scores between 0.54 and 0.83 (median 0.68) in the test set. Coefficients and gene names were output for further analysis using ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA)(Krämer et al., 2014).
Single-cell recursive feature elimination and random forest validation (scRFE)
To identify key features that differentiate clones containing an HIV-1 RNA+ cell and clones without an HIV-1 RNA+ cell, we employed single-cell identity definition using random forests and recursive feature elimination (scRFE, version 1.5.6)(Park et al., 2020) with a bootstrapping modification. Briefly, this method trained a binary random forest classifier between two groups. These groups were artificially set to be of equivalent size prior to model training. After each training, features were ranked by importance and the least important features were removed. After several iterations, a core set of markers was identified that is necessary and sufficient to differentiate the two groups. Due to the extreme imbalance of our dataset, we additionally performed 10,000 replicates of scRFE. Results of all replicates were then aggregated to select the 200 features consistently selected by scRFE. This process was completed independently for all cells, cells only from the viremic time point, and cells only from the suppressed time point. These 100 features identified from all cells were validated in a subsequent model on the whole dataset. First, data were split into training and test sets (80–20), then Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE (Chawla et al., 2002), Imbalanced-learn (Lemaître et al., 2017)) was used to generate artificial samples for the minority class in only the training dataset. A random forest classifier was then trained with default parameters except for a min_samples_leaf parameter of 16, oob_score set to true, and an nEstimators parameter of 100. Model performance was evaluated using the test set for both area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) and F1-score weighted towards recall.
Pathway enrichment analysis
Genes were ranked using average log fold change in gene expression comparisons between groups. Genes were ranked using Pearson correlations with clone size. The resulting gene ranks were used to run pre-ranked gene set enrichment analysis as implemented by fGSEA (version 1.16.0)(Korotkevich et al., 2019). Human gene sets H (“hallmark”), C2 (“curated”), C6 (“oncogenic”), and C7 (“immunologic”) were used, version 7.4 (Liberzon et al., 2011). Gene sets were considered significantly enriched with an adjusted P value less than 0.05. To identify gene ontology pathways with a specific set of genes, we utilized Enrichr (Chen et al., 2013).
To identify differentially expressed gene sets and the upstream regulators of the transcription profile, ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA, Summer 2021 release, Qiagen)(Krämer et al., 2014) was performed using gene expression log fold change cutoff of 0.25 or a non-zero coefficient where applicable. Analysis was performed with default settings.
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Unless otherwise noted, statistical analysis was performed using R (version 4.0.3). Multiple hypothesis correction was applied where applicable using the method described by Benjamini-Hochberg (Benjamini and Hochberg, 1995).
Supplementary Material
Table S2. Single-cell library characteristics, markers for transcriptome defined clusters, and N in each figure. Related to Figure 1–7.
Table S3. GSEA pathway list and differential expression for HIV+ cells. Related to Figure 2, Figure 3, and Figure 4.
Table S4. Within clone transcriptional differences and 200 genes that distinguish HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones from HIV-1 RNA− T cell clone. Related to Figure 5, Figure 6, and Figure 7.
Highlights.
Most HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones are large, stable, GZMB+ cytotoxic effector memory Th1s
Some HIV-1 RNA+ cells express SERPINB9 and may be shielded from CD8+ T cell killing
Antigen stimulation, TNF, and cytotoxic T cell responses determine T cell clone size
Early ART cannot fully reduce chronic immune activation, and TNF responses persist
Acknowledgements.
We thank all study participants. We thank Alex Shalek, Sam Kazer, Carly Ziegler, Joseph Craft, Steven Kleinstein, Roy Jiang, Nicolas Chomont, Pierre Gantner, Michael Betts, Vincent Wu, Dan Kaufmann, Elsa Brunet-Ratnasingham, and R. Brad Jones for their insightful suggestions. We thank Siavash Pasalar, Beth Peterson, and Kenneth Lynn for coordinating study participant recruitment. This work is supported by Yale Top Scholar, Rudolf J. Anderson Fellowship, NIH R01 AI141009, NIH R61/R33 DA047037, NIH R37 AI147868, NIH R01 DA051906, NIH R01AI145164, NIH UM1 DA051410, NIH U01 DA053628, NIH CHEETAH P50 AI150464, NIH REACH Martin Delaney Collaborator UM1 AI164565, NIH BEAT-HIV Martin Delaney Collaboratory UM1 AI126620, Gilead HIV Research Scholar, American Foundation for AIDS Research (amfAR 110029-67-RGRL)(Y.-C.H and D.D.), NIH R35 GM143072 (D.D.), the Robert I. Jacobs Fund of The Philadelphia Foundation (L.J.M.), Yale Gruber Fellowship (J.A.C.), NIH T32 AI055403 (J.A.C.), and a Yale Center for Genome Analysis-10X Genomics Pilot Award (R.L). The Sabes and MERLIN studies were supported by NIH R01 DA032106 and NIH R01 DA040532 (A.D.). We thank NIH HIV Reagent Program providing antigen peptides and enfuvirtide. We gratefully acknowledge ART drug donation from Merck & Co. and Gilead Sciences Inc for the Sabes and Merlin cohorts.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Competing interests. The authors declare no competing interests.
Inclusion and diversity. One or more of the authors of this paper self-identified as living with a disability. One or more of the authors of this paper self-identified as an under-represented minority. One or more of the authors of this paper received support from a program designed to increase minority presentation in science.
References
- Appay V, Zaunders JJ, Papagno L, Sutton J, Jaramillo A, Waters A, Easterbrook P, Grey P, Smith D, McMichael AJ, et al. (2002). Characterization of CD4(+) CTLs ex vivo. J Immunol 168, 5954–5958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey JR, Sedaghat AR, Kieffer T, Brennan T, Lee PK, Wind-Rotolo M, Haggerty CM, Kamireddi AR, Liu Y, Lee J, et al. (2006). Residual human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viremia in some patients on Antiretroviral therapy is dominated by a small number of invariant clones rarely found in circulating CD4(+) T cells. Journal of Virology 80, 6441–6457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barreiro LB, and Quintana-Murci L (2010). From evolutionary genetics to human immunology: how selection shapes host defence genes. Nat Rev Genet 11, 17–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becht E, McInnes L, Healy J, Dutertre C-A, Kwok IWH, Ng LG, Ginhoux F, and Newell EW (2018). Dimensionality reduction for visualizing single-cell data using UMAP. Nature Biotechnology 37, 38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengsch B, Ohtani T, Khan O, Setty M, Manne S, O’Brien S, Gherardini PF, Herati RS, Huang AC, Chang K-M, et al. (2018). Epigenomic-Guided Mass Cytometry Profiling Reveals Disease-Specific Features of Exhausted CD8 T Cells. Immunity 48, 1029–1045.e1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini Y, and Hochberg Y (1995). Controlling the False Discovery Rate - a Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B-Statistical Methodology 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Bird CH, Sutton VR, Sun J, Hirst CE, Novak A, Kumar S, Trapani JA, and Bird PI (1998). Selective regulation of apoptosis: the cytotoxic lymphocyte serpin proteinase inhibitor 9 protects against granzyme B-mediated apoptosis without perturbing the Fas cell death pathway. Mol Cell Biol 18, 6387–6398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosque A, Famiglietti M, Weyrich AS, Goulston C, and Planelles V (2011). Homeostatic proliferation fails to efficiently reactivate HIV-1 latently infected central memory CD4+ T cells. PLoS Pathog 7, e1002288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown DM, Lee S, Garcia-Hernandez Mde L, and Swain SL (2012). Multifunctional CD4 cells expressing gamma interferon and perforin mediate protection against lethal influenza virus infection. J Virol 86, 6792–6803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruner KM, Murray AJ, Pollack RA, Soliman MG, Laskey SB, Capoferri AA, Lai J, Strain MC, Lada SM, Hoh R, et al. (2016). Defective proviruses rapidly accumulate during acute HIV-1 infection. Nat Med 22, 1043–1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruner KM, Wang Z, Simonetti FR, Bender AM, Kwon KJ, Sengupta S, Fray EJ, Beg SA, Antar AAR, Jenike KM, et al. (2019). A quantitative approach for measuring the reservoir of latent HIV-1 proviruses. Nature 566, 120–125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bui JK, Sobolewski MD, Keele BF, Spindler J, Musick A, Wiegand A, Luke BT, Shao W, Hughes SH, Coffin JM, et al. (2017). Proviruses with identical sequences comprise a large fraction of the replication-competent HIV reservoir. PLoS Pathog 13, e1006283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, and Kegelmeyer WP (2002). SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique. Journal of Artificial Intellegence Research 16, 341–378. [Google Scholar]
- Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z, Meirelles GV, Clark NR, and Ma’ayan A (2013). Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinformatics 14, 128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomont N, El-Far M, Ancuta P, Trautmann L, Procopio FA, Yassine-Diab B, Boucher G, Boulassel MR, Ghattas G, Brenchley JM, et al. (2009). HIV reservoir size and persistence are driven by T cell survival and homeostatic proliferation. Nat Med 15, 893–900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun TW, Stuyver L, Mizell SB, Ehler LA, Mican JA, Baseler M, Lloyd AL, Nowak MA, and Fauci AS (1997). Presence of an inducible HIV-1 latent reservoir during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94, 13193–13197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin JM, Wells DW, Zerbato JM, Kuruc JD, Guo S, Luke BT, Eron JJ, Bale M, Spindler J, Simonetti FR, et al. (2019). Clones of infected cells arise early in HIV-infected individuals. JCI Insight 4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn LB, da Silva IT, Valieris R, Huang AS, Lorenzi JCC, Cohen YZ, Pai JA, Butler AL, Caskey M, Jankovic M, et al. (2018). Clonal CD4(+) T cells in the HIV-1 latent reservoir display a distinct gene profile upon reactivation. Nat Med 24, 604–609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B, Lambrechts L, Gantner P, Noppe Y, Bonine N, Witkowski W, Chen L, Palmer S, Mullins JI, Chomont N, et al. (2021). In-depth single-cell analysis of translation-competent HIV-1 reservoirs identifies cellular sources of plasma viremia. Nature Communications 12, 3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooks AM, Bateson R, Cope AB, Dahl NP, Griggs MK, Kuruc JD, Gay CL, Eron JJ, Margolis DM, Bosch RJ, et al. (2015). Precise Quantitation of the Latent HIV-1 Reservoir: Implications for Eradication Strategies. J Infect Dis 212, 1361–1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan JM, Lindestam Arlehamn CS, Weiskopf D, da Silva Antunes R, Havenar-Daughton C, Reiss SM, Brigger M, Bothwell M, Sette A, and Crotty S (2016). A Cytokine-Independent Approach To Identify Antigen-Specific Human Germinal Center T Follicular Helper Cells and Rare Antigen-Specific CD4+ T Cells in Blood. J Immunol 197, 983–993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, and Gingeras TR (2012). STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29, 15–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douek DC, Brenchley JM, Betts MR, Ambrozak DR, Hill BJ, Okamoto Y, Casazza JP, Kuruppu J, Kunstman K, Wolinsky S, et al. (2002). HIV preferentially infects HIV-specific CD4+ T cells. Nature 417, 95–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duette G, Hiener B, Morgan H, Mazur FG, Mathivanan V, Horsburgh BA, Fisher K, Tong O, Lee E, Ahn H, et al. (2022). The HIV-1 proviral landscape reveals Nef contributes to HIV-1 persistence in effector memory CD4+ T-cells. J Clin Invest. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einkauf KB, Osborn MR, Gao C, Sun W, Sun X, Lian X, Parsons EM, Gladkov GT, Seiger KW, Blackmer JE, et al. (2022). Parallel analysis of transcription, integration, and sequence of single HIV-1 proviruses. Cell 185, 266–282.e215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finzi D, Hermankova M, Pierson T, Carruth LM, Buck C, Chaisson RE, Quinn TC, Chadwick K, Margolick J, Brookmeyer R, et al. (1997). Identification of a reservoir for HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science 278, 1295–1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromentin R, Bakeman W, Lawani MB, Khoury G, Hartogensis W, DaFonseca S, Killian M, Epling L, Hoh R, Sinclair E, et al. (2016). CD4+ T Cells Expressing PD-1, TIGIT and LAG-3 Contribute to HIV Persistence during ART. PLoS Pathog 12, e1005761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantner P, Pagliuzza A, Pardons M, Ramgopal M, Routy J-P, Fromentin R, and Chomont N (2020). Single-cell TCR sequencing reveals phenotypically diverse clonally expanded cells harboring inducible HIV proviruses during ART. Nature Communications 11, 4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillet NA, Malani N, Melamed A, Gormley N, Carter R, Bentley D, Berry C, Bushman FD, Taylor GP, and Bangham CR (2011). The host genomic environment of the provirus determines the abundance of HTLV-1-infected T-cell clones. Blood 117, 3113–3122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta NT, Vander Heiden JA, Uduman M, Gadala-Maria D, Yaari G, and Kleinstein SH (2015). Change-O: a toolkit for analyzing large-scale B cell immunoglobulin repertoire sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31, 3356–3358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haghverdi L, Lun ATL, Morgan MD, and Marioni JC (2018). Batch effects in single-cell RNA-sequencing data are corrected by matching mutual nearest neighbors. Nat Biotechnol 36, 421–427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvas EK, Joseph KW, Brandt LD, Guo S, Sobolewski MD, Jacobs JL, Tumiotto C, Bui JK, Cyktor JC, Keele BF, et al. (2020). HIV-1 viremia not suppressible by antiretroviral therapy can originate from large T cell clones producing infectious virus. J Clin Invest 130, 5847–5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiener B, Horsburgh BA, Eden JS, Barton K, Schlub TE, Lee E, von Stockenstrom S, Odevall L, Milush JM, Liegler T, et al. (2017). Identification of Genetically Intact HIV-1 Proviruses in Specific CD4(+) T Cells from Effectively Treated Participants. Cell Rep 21, 813–822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho YC, Shan L, Hosmane NN, Wang J, Laskey SB, Rosenbloom DI, Lai J, Blankson JN, Siliciano JD, and Siliciano RF (2013). Replication-competent noninduced proviruses in the latent reservoir increase barrier to HIV-1 cure. Cell 155, 540–551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang TN, Pino M, Boddapati AK, Viox EG, Starke CE, Upadhyay AA, Gumber S, Nekorchuk M, Busman-Sahay K, Strongin Z, et al. Baricitinib treatment resolves lower-airway macrophage inflammation and neutrophil recruitment in SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus macaques. Cell. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosmane NN, Kwon KJ, Bruner KM, Capoferri AA, Beg S, Rosenbloom DI, Keele BF, Ho YC, Siliciano JD, and Siliciano RF (2017). Proliferation of latently infected CD4(+) T cells carrying replication-competent HIV-1: Potential role in latent reservoir dynamics. J Exp Med 214, 959–972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y, Hase T, Li HP, Prabhakar S, Kitano H, Ng SK, Ghosh S, and Wee LJ (2016). A machine learning approach for the identification of key markers involved in brain development from single-cell transcriptomic data. BMC Genomics 17, 1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt PW, Martin JN, Sinclair E, Epling L, Teague J, Jacobson MA, Tracy RP, Corey L, and Deeks SG (2011). Valganciclovir reduces T cell activation in HIV-infected individuals with incomplete CD4+ T cell recovery on antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis 203, 1474–1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iezzi G, Karjalainen K, and Lanzavecchia A (1998). The duration of antigenic stimulation determines the fate of naive and effector T cells. Immunity 8, 89–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain V, Hartogensis W, Bacchetti P, Hunt PW, Hatano H, Sinclair E, Epling L, Lee TH, Busch MP, McCune JM, et al. (2013). Antiretroviral Therapy Initiated Within 6 Months of HIV Infection Is Associated With Lower T-Cell Activation and Smaller HIV Reservoir Size. Journal of Infectious Diseases 208, 1202–1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazer SW, Aicher TP, Muema DM, Carroll SL, Ordovas-Montanes J, Miao VN, Tu AA, Ziegler CGK, Nyquist SK, Wong EB, et al. (2020). Integrated single-cell analysis of multicellular immune dynamics during hyperacute HIV-1 infection. Nat Med 26, 511–518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King Thomas J, Mir H, Kapur N, and Singh S (2019). Racial Differences in Immunological Landscape Modifiers Contributing to Disparity in Prostate Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korotkevich G, Sukhov V, and Sergushichev A (2019). Fast gene set enrichment analysis. bioRxiv, 060012. [Google Scholar]
- Korsunsky I, Millard N, Fan J, Slowikowski K, Zhang F, Wei K, Baglaenko Y, Brenner M, Loh P.-r., and Raychaudhuri S (2019). Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nature Methods 16, 1289–1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A, Green J, Pollard J Jr., and Tugendreich S (2014). Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 30, 523–530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lama JR, Brezak A, Dobbins JG, Sanchez H, Cabello R, Rios J, Bain C, Ulrich A, De la Grecca R, Sanchez J, et al. (2018). Design Strategy of the Sabes Study: Diagnosis and Treatment of Early HIV Infection Among Men Who Have Sex With Men and Transgender Women in Lima, Peru, 2013-2017. Am J Epidemiol 187, 1577–1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lama JR, Ignacio RAB, Alfaro R, Rios J, Cartagena JG, Valdez R, Bain C, Barbarán KS, Villaran MV, Pilcher CD, et al. (2020). Clinical and Immunologic Outcomes after Immediate or Deferred Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation during Primary HIV Infection: The Sabes Randomized Clinical Study. Clin Infect Dis. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langfelder P, and Horvath S (2008). WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 9, 559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E, Bacchetti P, Milush J, Shao W, Boritz E, Douek D, Fromentin R, Liegler T, Hoh R, Deeks SG, et al. (2019). Memory CD4 + T-Cells Expressing HLA-DR Contribute to HIV Persistence During Prolonged Antiretroviral Therapy. Front Microbiol 10, 2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee GQ, Orlova-Fink N, Einkauf K, Chowdhury FZ, Sun X, Harrington S, Kuo HH, Hua S, Chen HR, Ouyang Z, et al. (2017). Clonal expansion of genome-intact HIV-1 in functionally polarized Th1 CD4+ T cells. J Clin Invest 127, 2689–2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaître G, Nogueira F, and Aridas CK (2017). Imbalanced-learn: A Python Toolbox to Tackle the Curse of Imbalanced Datasets in Machine Learning. Journal of Machine Learning Research 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liberzon A, Subramanian A, Pinchback R, Thorvaldsdottir H, Tamayo P, and Mesirov JP (2011). Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 27, 1739–1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu R, Yeh YJ, Varabyou A, Collora JA, Sherrill-Mix S, Talbot CC Jr., Mehta S, Albrecht K, Hao H, Zhang H, et al. (2020). Single-cell transcriptional landscapes reveal HIV-1-driven aberrant host gene transcription as a potential therapeutic target. Sci Transl Med 12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzi JC, Cohen YZ, Cohn LB, Kreider EF, Barton JP, Learn GH, Oliveira T, Lavine CL, Horwitz JA, Settler A, et al. (2016). Paired quantitative and qualitative assessment of the replication-competent HIV-1 reservoir and comparison with integrated proviral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113, E7908–E7916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macallan DC, Busch R, and Asquith B (2019). Current estimates of T cell kinetics in humans. Current Opinion in Systems Biology 18, 77–86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malandro N, Budhu S, Kuhn, Nicholas F, Liu C, Murphy, Judith T, Cortez C, Zhong H, Yang X, Rizzuto G, Altan-Bonnet G, et al. (2016). Clonal Abundance of Tumor-Specific CD4+ T Cells Potentiates Efficacy and Alters Susceptibility to Exhaustion. Immunity 44, 179–193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldarelli F, Wu X, Su L, Simonetti FR, Shao W, Hill S, Spindler J, Ferris AL, Mellors JW, Kearney MF, et al. (2014). HIV latency. Specific HIV integration sites are linked to clonal expansion and persistence of infected cells. Science 345, 179–183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGary CS, Deleage C, Harper J, Micci L, Ribeiro SP, Paganini S, Kuri-Cervantes L, Benne C, Ryan ES, Balderas R, et al. (2017). CTLA-4(+)PD-1(−) Memory CD4(+) T Cells Critically Contribute to Viral Persistence in Antiretroviral Therapy-Suppressed, SIV-Infected Rhesus Macaques. Immunity 47, 776–788.e775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnes LH,J, and Melville J (2018). UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction. arXivLabs, arXiv:1802.03426. [Google Scholar]
- Meckiff BJ, Ramírez-Suástegui C, Fajardo V, Chee SJ, Kusnadi A, Simon H, Eschweiler S, Grifoni A, Pelosi E, Weiskopf D, et al. (2020). Imbalance of Regulatory and Cytotoxic SARS-CoV-2-Reactive CD4(+) T Cells in COVID-19. Cell 183, 1340–1353.e1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza P, Jackson JR, Oliveira TY, Gaebler C, Ramos V, Caskey M, Jankovic M, Nussenzweig MC, and Cohn LB (2020). Antigen-responsive CD4+ T cell clones contribute to the HIV-1 latent reservoir. J Exp Med 217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morou A, Brunet-Ratnasingham E, Dubé M, Charlebois R, Mercier E, Darko S, Brassard N, Nganou-Makamdop K, Arumugam S, Gendron-Lepage G, et al. (2019). Altered differentiation is central to HIV-specific CD4(+) T cell dysfunction in progressive disease. Nat Immunol 20, 1059–1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ndhlovu ZM, Kazer SW, Nkosi T, Ogunshola F, Muema DM, Anmole G, Swann SA, Moodley A, Dong K, Reddy T, et al. (2019). Augmentation of HIV-specific T cell function by immediate treatment of hyperacute HIV-1 infection. Sci Transl Med 11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidleman J, Luo X, Frouard J, Xie G, Hsiao F, Ma T, Morcilla V, Lee A, Telwatte S, Thomas R, et al. (2020). Phenotypic analysis of the unstimulated in vivo HIV CD4 T cell reservoir. Elife 9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen S, Deleage C, Darko S, Ransier A, Truong DP, Agarwal D, Japp AS, Wu VH, Kuri-Cervantes L, Abdel-Mohsen M, et al. (2019). Elite control of HIV is associated with distinct functional and transcriptional signatures in lymphoid tissue CD8(+) T cells. Sci Transl Med 11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh DY, Kwek SS, Raju SS, Li T, McCarthy E, Chow E, Aran D, Ilano A, Pai CS, Rancan C, et al. (2020). Intratumoral CD4(+) T Cells Mediate Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity in Human Bladder Cancer. Cell 181, 1612–1625.e1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape KA, Khoruts A, Mondino A, and Jenkins MK (1997). Inflammatory cytokines enhance the in vivo clonal expansion and differentiation of antigen-activated CD4+ T cells. The Journal of Immunology 159, 591–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappalardo JL, Zhang L, Pecsok MK, Perlman K, Zografou C, Raddassi K, Abulaban A, Krishnaswamy S, Antel J, van Dijk D, et al. (2020). Transcriptomic and clonal characterization of T cells in the human central nervous system. Sci Immunol 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M, Vorperian S, Wang S, and Pisco AO (2020). Single-cell identity definition using random forests and recursive feature elimination. bioRxiv, 2020.2008.2003.233650. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa FV,G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V, Vanderplas J, et al. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Pollack RA, Jones RB, Pertea M, Bruner KM, Martin AR, Thomas AS, Capoferri AA, Beg SA, Huang SH, Karandish S, et al. (2017). Defective HIV-1 Proviruses Are Expressed and Can Be Recognized by Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes, which Shape the Proviral Landscape. Cell Host Microbe 21, 494–506.e494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Y, Huang SH, Patel S, Alberto WDC, Magat D, Ahimovic D, Macedo AB, Durga R, Chan D, Zale E, et al. (2020). BCL-2 antagonism sensitizes cytotoxic T cell-resistant HIV reservoirs to elimination ex vivo. J Clin Invest 130, 2542–2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalek AK, Satija R, Adiconis X, Gertner RS, Gaublomme JT, Raychowdhury R, Schwartz S, Yosef N, Malboeuf C, Lu D, et al. (2013). Single-cell transcriptomics reveals bimodality in expression and splicing in immune cells. Nature 498, 236–240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano JD, Kajdas J, Finzi D, Quinn TC, Chadwick K, Margolick JB, Kovacs C, Gange SJ, and Siliciano RF (2003). Long-term follow-up studies confirm the stability of the latent reservoir for HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T cells. Nat Med 9, 727–728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonetti FR, Sobolewski MD, Fyne E, Shao W, Spindler J, Hattori J, Anderson EM, Watters SA, Hill S, Wu X, et al. (2016). Clonally expanded CD4+ T cells can produce infectious HIV-1 in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113, 1883–1888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonetti FR, Zhang H, Soroosh GP, Duan J, Rhodehouse K, Hill AL, Beg SA, McCormick K, Raymond HE, Nobles CL, et al. (2021). Antigen-driven clonal selection shapes the persistence of HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells in vivo. J Clin Invest 131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonetti FR, Zhang H, Soroosh H, Beg SA, Duan J, Rhodehouse K, Nobles CL, Lai JH,R, Deeks SG, Bushman FD, et al. (2020). Antigen-driven clonal selection shapes the fate of HIV-infected CD4+ T cells in vivo. In Conferences on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (Boston, MA, USA.). [Google Scholar]
- Stout-Delgado HW, Getachew Y, Rogers TE, Miller BC, and Thiele DL (2007). The role of serpinb9/serine protease inhibitor 6 in preventing granzyme B-dependent hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 46, 1530–1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart T, Butler A, Hoffman P, Hafemeister C, Papalexi E, Mauck WM 3rd, Hao Y, Stoeckius M, Smibert P, and Satija R (2019). Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 177, 1888–1902.e1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirosh I, Izar B, Prakadan SM, Wadsworth MH 2nd, Treacy D, Trombetta JJ, Rotem A, Rodman C, Lian C, Murphy G, et al. (2016). Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 352, 189–196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torang A, Gupta P, and Klinke DJ 2nd (2019). An elastic-net logistic regression approach to generate classifiers and gene signatures for types of immune cells and T helper cell subsets. BMC Bioinformatics 20, 433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen EM, Remmerswaal EB, Vossen MT, Rowshani AT, Wertheim-van Dillen PM, van Lier RA, and ten Berge IJ (2004). Emergence of a CD4+CD28− granzyme B+, cytomegalovirus-specific T cell subset after recovery of primary cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol 173, 1834–1841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Heiden JA, Yaari G, Uduman M, Stern JN, O’Connor KC, Hafler DA, Vigneault F, and Kleinstein SH (2014). pRESTO: a toolkit for processing high-throughput sequencing raw reads of lymphocyte receptor repertoires. Bioinformatics 30, 1930–1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venanzi Rullo E, Pinzone MR, Cannon L, Weissman S, Ceccarelli M, Zurakowski R, Nunnari G, and O’Doherty U (2020). Persistence of an intact HIV reservoir in phenotypically naive T cells. JCI Insight 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler M (2012). BCL2A1: the underdog in the BCL2 family. Cell Death Differ 19, 67–74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner TA, McLaughlin S, Garg K, Cheung CY, Larsen BB, Styrchak S, Huang HC, Edlefsen PT, Mullins JI, and Frenkel LM (2014). HIV latency. Proliferation of cells with HIV integrated into cancer genes contributes to persistent infection. Science (New York, NY) 345, 570–573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z, Gurule EE, Brennan TP, Gerold JM, Kwon KJ, Hosmane NN, Kumar MR, Beg SA, Capoferri AA, Ray SC, et al. (2018). Expanded cellular clones carrying replication-competent HIV-1 persist, wax, and wane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115, E2575–e2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk AJ, Rustagi A, Zhao NQ, Roque J, Martínez-Colón GJ, McKechnie JL, Ivison GT, Ranganath T, Vergara R, Hollis T, et al. (2020). A single-cell atlas of the peripheral immune response in patients with severe COVID-19. Nature Medicine 26, 1070–1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong JK, Hezareh M, Gunthard HF, Havlir DV, Ignacio CC, Spina CA, and Richman DD (1997). Recovery of replication-competent HIV despite prolonged suppression of plasma viremia. Science 278, 1291–1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh YJ, Jenike KM, Calvi RM, Chiarella J, Hoh R, Deeks SG, and Ho YC (2020). Filgotinib suppresses HIV-1-driven gene transcription by inhibiting HIV-1 splicing and T cell activation. J Clin Invest. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost KE, Satpathy AT, Wells DK, Qi Y, Wang C, Kageyama R, McNamara KL, Granja JM, Sarin KY, Brown RA, et al. (2019). Clonal replacement of tumor-specific T cells following PD-1 blockade. Nat Med 25, 1251–1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaunders JJ, Dyer WB, Wang B, Munier ML, Miranda-Saksena M, Newton R, Moore J, Mackay CR, Cooper DA, Saksena NK, et al. (2004). Identification of circulating antigen-specific CD4+ T lymphocytes with a CCR5+, cytotoxic phenotype in an HIV-1 long-term nonprogressor and in CMV infection. Blood 103, 2238–2247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M, Park S-M, Wang Y, Shah R, Liu N, Murmann AE, Wang C-R, Peter ME, and Ashton-Rickardt PG (2006). Serine Protease Inhibitor 6 Protects Cytotoxic T Cells from Self-Inflicted Injury by Ensuring the Integrity of Cytotoxic Granules. Immunity 24, 451–461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou HH, Trevor (2005). Regularization and variable selection via the Elastic Net. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Methodological) 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S2. Single-cell library characteristics, markers for transcriptome defined clusters, and N in each figure. Related to Figure 1–7.
Table S3. GSEA pathway list and differential expression for HIV+ cells. Related to Figure 2, Figure 3, and Figure 4.
Table S4. Within clone transcriptional differences and 200 genes that distinguish HIV-1 RNA+ T cell clones from HIV-1 RNA− T cell clone. Related to Figure 5, Figure 6, and Figure 7.
Data Availability Statement
Single-cell RNA-seq, and bulk TCR sequencing data have been deposited at GEO and are publicly available. Accession numbers are listed in the key resources table. All original code has been deposited at Github and is publicly available. DOIs are listed in the key resources table. Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| CD8-BV510 clone SK1 | BioLegend | CAT# 344731 |
| CD14-BV510 clone M5E2 | BioLegend | CAT# 301841 |
| CD19-BV510 clone HIB19 | BioLegend | CAT# 302241 |
| CD56-BV510 clone 5.1H11 | BioLegend | CAT# 362533 |
| CD3-BV421 clone SK7 | BioLegend | CAT# 344833 |
| CD69-BV650 clone FN50 | BioLegend | CAT# 310933 |
| CD154-PE clone 24-31 | BioLegend | CAT# 310805 |
| CD45RO-APC/Fire750 clone UCHL1 | BioLegend | CAT# 304249 |
| TotalSeq-C IL7RA clone A019D5 | BioLegend | CAT# 351356 |
| TotalSeq-C CCR7 clone G043H7 | BioLegend | CAT# 353251 |
| TotalSeq-C CD25 clone BC96 | BioLegend | CAT# 302649 |
| TotalSeq-C CD27 clone O323 | BioLegend | CAT# 302853 |
| TotalSeq-C CD3 clone UCHT1 | BioLegend | CAT# 300479 |
| TotalSeq-C CD4 clone RPA-T4 | BioLegend | CAT# 300567 |
| TotalSeq-C CD8 clone RPA-T8 | BioLegend | CAT# 301071 |
| TotalSeq-C CD45RA clone HI100 | BioLegend | CAT# 304163 |
| TotalSeq-C CD45RO clone UCHL1 | BioLegend | CAT# 304259 |
| TotalSeq-C CD62L clone DREG-56 | BioLegend | CAT# 304851 |
| TotalSeq-C CD69 clone FN50 | BioLegend | CAT# 310951 |
| TotalSeq-C HLA-DR clone L243 | BioLegend | CAT# 307663 |
| TotalSeq-C CD47 clone CC2C6 | BioLegend | CAT# 323131 |
| TotalSeq-C CCR5 clone J418F1 | BioLegend | CAT# 359137 |
| TotalSeq-C CXCR3 clone G025H7 | BioLegend | CAT# 353747 |
| TotalSeq-C CCR6 clone G034E3 | BioLegend | CAT# 353440 |
| TotalSeq-C CCR4 clone L291H4 | BioLegend | CAT# 359425 |
| TotalSeq-C CXCR5 clone J252D4 | BioLegend | CAT# 356939 |
| TotalSeq-C CD40L clone 24-31 | BioLegend | CAT# 310849 |
| TotalSeq-C 4-1BB clone 4B4-1 | BioLegend | CAT# 309839 |
| TotalSeq-C OX40 clone ACT35 | BioLegend | CAT# 350035 |
| TotalSeq-C PD-1 clone EH12.2H7 | BioLegend | CAT# 329963 |
| TotalSeq-C CTLA-4 clone BNI3 | BioLegend | CAT# 369621 |
| TotalSeq-C TIGIT clone A15153G | BioLegend | CAT# 372729 |
| TotalSeq-C mouse IgG1 clone MOPC-21 | BioLegend | CAT# 400187 |
| TotalSeq-C mouse IgG2a clone MOPC-173 | BioLegend | CAT# 400293 |
| TotalSeq-C mouse IgG2b clone MPC-11 | BioLegend | CAT# 400381 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 1 | BioLegend | CAT# 394661 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 2 | BioLegend | CAT# 394663 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 3 | BioLegend | CAT# 394665 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 4 | BioLegend | CAT# 394667 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 5 | BioLegend | CAT# 394669 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 6 | BioLegend | CAT# 394671 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 7 | BioLegend | CAT# 394673 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 8 | BioLegend | CAT# 394675 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 9 | BioLegend | CAT# 394677 |
| TotalSeq-C human hashing antibody 10 | BioLegend | CAT# 394679 |
| CD45RA-BUV737 clone HI100 | BD Biosciences | CAT# 612846 |
| CCR7-BUV395 clone 3D12 | BD Biosciences | CAT# 740267 |
| CTLA4-PE-Dazzel594 clone L3D10 | Bioledgend | CAT# 349921 |
| IFNG-BV711 clone 4S.B3 | BD Biosciences | CAT# 564793 |
| TNF-BV605 clone Mab11 | Biolegend | CAT# 502935 |
| p24-PE clone KC57 | Beckman Coulter | CAT# 6604667 |
| p24-APC clone 28B7 | Medimabs | CAT# MM-0289-APC |
| GZMB-AF700 GB11 | BD Biosciences | CAT# 561016 |
| Biological samples | ||
| Demographics of study participants, see Table S1 | This paper | N/A |
| Human serum | Sigma Aldrich | CAT# H4522-20ML |
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| Staphylococcal enterotoxin type B (SEB) toxin | List Biological Laboratories | CAT# 122 |
| HIV-1 group B Gag, Pol, Env, and Nef peptide pools | NIH HIV Reagent Program | CAT# 12425, 12438, 12540, 12545 |
| CMV lysate, strain AD-169 | ZeptoMetrix | CAT# 810003 |
| HCMV pp65 peptide pool | NIH HIV Reagent Program | CAT# 11549 |
| enfuvirtide | NIH HIV Reagent Program | CAT# 12732 |
| Ionomycin | Millipore | CAT# 407950-1MG |
| PMA | Millipore | CAT# 5.00582.0001 |
| Brefeldin A | Thermo Fisher Scientific | CAT# 00-4506-51 |
| Monensin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | CAT# 00-4505-51 |
| CD40 antibody | Miltenyi Biotech | CAT# 130-094-133 |
| Critical commercial assays | ||
| Chromium Next GEM Single Cell 5’ Library & Gel Bead Kit v1.1 | 10x Genomics | PN-1000165 |
| Chromium Single Cell V(D)J Enrichment Kit, Human T Cell | 10x Genomics | PN-1000005 |
| Chromium Single Cell 5’ Feature Barcode Library Kit | 10x Genomics | PN-1000080 |
| NEBNext Immune Sequencing Kit | New England Biolabs | CAT# E6320S |
| EasySep Direct Human CD4+ T cell kit | STEMCELL | 19662 |
| CD4 T cell isolation kit, human | Miltenyi Biotech | 130-096-533 |
| EasySep Dead Cell Removal (Annexin V) Kit | STEMCELL | 17899 |
| Dynabead CD8 | Thermo Fisher | 11147D |
| LIVE/DEAD Fixable Aqua Dead Cell Stain Kit | Thermo Fisher | L34957 |
| LIVE/DEAD Fixable Near-IR Dead Cell Stain Kit | Thermo Fisher | L10119 |
| Deposited data | ||
| ECCITE-seq unstimulated CD4+ T cells | This study | GSE187515 |
| ECCITE-seq stimulated CD4+ T cells | This study | GSE187515 |
| Bulk TCR repertoire profiling from HIV-1 infected and uninfected individuals | This study | GSE187515 |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| cellranger count version 3.0.2 | 10X Genomics | https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/software/downloads/3.0/ |
| cellranger vdj version 3.1 | 10X Genomics | https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/software/downloads/3.1/ |
| Seurat version 4.0.3 | Stuart et al. 2018 | https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/Seurat/index.html |
| batchelor version 1.6.3 | Haghverdi et al., 2018 | https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/batchelor.html |
| uwot version 0.1.10 | NA | https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/uwot/index.html |
| STAR version 2.5.3 | Dobin et al., 2012 | https://github.com/alexdobin/STAR |
| WGCNA version 1.70-3 | Langfelder and Horvath, 2008 | https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/WGCNA/index.html |
| pRESTO version 0.6.1 | Vander Heiden et al., 2014 | https://presto.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ |
| ChangeO version 1.0.0 | Gupta et al., 2015 | https://changeo.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ |
| scikit-learn version 0.23 | Pedregosa et al., 2011) | https://scikit-learn.org/stable/ |
| IPA summer 2021 release | Krämer et al., 2014 | https://digitalinsights.qiagen.com/products-overview/discovery-insights-portfolio/analysis-and-visualization/qiagen-ipa/ |
| scRFE, version 1.5.6 | Park et al., 2020) | https://github.com/czbiohub/scRFE |
| Imbalanced-learn version 0.7.0 | Lemaître et al., 2017 | https://imbalanced-learn.org/stable/ |
| fGSEA version 1.16.0 | Korotkevich et al., 2019) | http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/fgsea.html |
| R version 4.0.3 | R Core Team (2021) | https://www.r-project.org/ |
| CodonCode version 7 | CodonCode Corporation | https://www.codoncode.com/aligner/ |
| Analysis scripts | This paper | https://github.com/Ya-ChiHo/Collora-and-Liu-et-al-2022 |


