ABSTRACT
Wood-decaying fungi of the class Agaricomycetes (phylum Basidiomycota) are saprotrophs that break down lignocellulose and play an important role in nutrient recycling. They secrete a wide range of extracellular plant cell wall degrading enzymes that break down cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, the main building blocks of plant biomass. Although the production of these enzymes is regulated mainly at the transcriptional level, no activating regulators have been identified in any wood-decaying fungus in the class Agaricomycetes. We studied the regulation of cellulase expression in the wood-decaying fungus Schizophyllum commune. Comparative genomics and transcriptomics on two wild isolates revealed a Zn2Cys6-type transcription factor gene (roc1) that was highly upregulated during growth on cellulose, compared to glucose. It is only conserved in the class Agaricomycetes. A roc1 knockout strain showed an inability to grow on medium with cellulose as sole carbon source, and growth on cellobiose and xylan (other components of wood) was inhibited. Growth on non-wood-related carbon sources was not inhibited. Cellulase gene expression and enzyme activity were reduced in the Δroc1 strain. ChIP-Seq identified 1474 binding sites of the Roc1 transcription factor. Promoters of genes involved in lignocellulose degradation were enriched with these binding sites, especially those of LPMO (lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase) CAZymes, indicating that Roc1 directly regulates these genes. A conserved motif was identified as the binding site of Roc1, which was confirmed by a functional promoter analysis. Together, Roc1 is a key regulator of cellulose degradation and the first identified in wood-decaying fungi in the phylum Basidiomycota.
KEYWORDS: ChIP-Seq, comparative genomics, comparative transcriptomics, fungi, gene regulation, lignocellulose degradation
INTRODUCTION
Plants store a considerable amount of energy in lignocellulose, and for that reason wood has been used as a fuel since prehistoric times. Wood is recalcitrant to decay by most organisms, but fungi have evolved ways to degrade part of the lignocellulose into its monomeric constituents. Most wood decay fungi belong to the phylum Basidiomycota, or, more specifically, the class Agaricomycetes. Phylogenetically these are distantly related to the fungi in the phylum Ascomycota such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Neurospora crassa. The last common ancestor of ascomycete and basidiomycete fungi is estimated to have lived over 600 million years ago (1). Although the Ascomycota harbor potent lignocellulose-degrading fungi, the strongest wood-decaying fungi are found in the Basidiomycota.
Lignocellulose consists of a wide range of components, including cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, and the aromatic polymer lignin (2, 3). These polymers are found in the plant cell wall (4). Fungi can generally easily absorb glucose and other monomers from the growth medium, but lignocellulose requires extensive extracellular enzymatic degradation before the breakdown product can be transported into the cells and metabolized. Wood-degrading fungi have evolved a broad range of hydrolytic enzymes that break down the various components of lignocellulose, including cellulases, hemicellulases, pectinases and oxidative enzymes. Collectively, these plant cell wall degrading enzymes are known as carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) and are classified into families of Glycoside Hydrolases (GHs), Glycosyl Transferases (GTs), Polysaccharide Lyases (PLs), Carbohydrate Esterases (CEs), and Auxiliary Activities (AAs) (5, 6). A typical genome of a wood-degrading fungus encodes hundreds of CAZymes (7–9).
Basidiomycete wood decayers can be broadly divided into white rot fungi, which degrade all components of the plant cell wall, and brown rot fungi, which depolymerize cellulose, but leave lignin largely unmodified. However, fungi that show (genotypic and phenotypic) characteristics of both white rot and brown rot fungi have also been identified (7). Neither white rot fungi nor brown rot fungi form monophyletic groups, and the brown rot lifestyle has evolved several times from white rot fungi (1, 7, 10).
Genes that encode CAZymes are generally strictly regulated at the transcriptional level, since their production is energetically expensive and not always needed. The primary mechanism of regulation is carbon catabolite repression (CCR). CCR represses the production of ligninolytic enzymes in the presence of an easily metabolizable carbon source, such as glucose, and ensures that the organism pursues the most energy-efficient mode of growth by ideal resource utilization. CCR is regulated by a highly conserved zinc-finger transcription factor (CreA/Cre1/Cre-1) (11–13), which functions as a strong inhibitor of gene expression in the presence of simple sugars and has been described in several ascomycetes. The gene is conserved in basidiomycetes (13) and it indeed plays the same role in the mushroom-forming white rot Pleurotus ostreatus (14).
A wide range of transcription factors act downstream of CCR (i.e., in the absence of simple sugars). Generally, these transcription factors activate gene expression of CAZymes involved in the breakdown of specific polysaccharides. Examples include xlnR, CLR-1, CLR-2 and ACE1. In Aspergillus (15) and Trichoderma (16) the transcription factor xlnR regulates (hemi)cellulose degrading enzymes and it has an ortholog in almost all filamentous ascomycetes (17). In N. crassa the transcription factors CLR-1 and CLR-2 induce the expression of cellulolytic, but not the hemicellulolytic enzymes (18). In contrast to the aforementioned regulators, ACE1 is a repressor of cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzyme production in Trichoderma reesei (19). It is important to note that these regulators have only been identified in ascomycete fungi, and that there are no orthologs in basidiomycete fungi (13). To date, no regulators have been identified in the wood-degrading basidiomycetes that positively regulate CAZymes. In general, very little is known about the regulatory mechanisms involved in plant biomass degradation in the basidiomycetes.
Schizophyllum commune is a model system for mushroom-forming fungi in the class Agaricomycetes. Several molecular tools have been developed for this organism, including an efficient gene deletion protocol (20, 21) and a ChIP-Seq protocol for Histone H3 to study the epigenetic landscape (22). S. commune has a wide geographical distribution and is generally found as white fruiting bodies growing on wood. Its mode of wood decay is atypical, since it is not easily classified as either white rot or brown rot (7, 9, 23). S. commune lacks lignin-degrading peroxidases, limiting its ability to degrade lignin (24). Still, S. commune degrades all wood components, although during growth on aspen (Populus) it leaves the pectin-rich middle lamella of the plant cell wall mostly intact (23).
Here, we describe the identification of a regulator of cellulase expression (Roc1) by comparative genomics and comparative transcriptomics. A roc1 deletion strain was unable to efficiently utilize cellulose as a carbon source, and growth was inhibited on other components of wood and its breakdown products (hemicellulose and cellobiose). Moreover, with ChIP-Seq we identified the binding sites of this transcription factor, which were enriched near CAZymes involved in cellulose degradation. This is the first positive regulator of cellulase expression identified in basidiomycetes.
RESULTS
Comparison of growth profile of three strains of S. commune on various carbon sources.
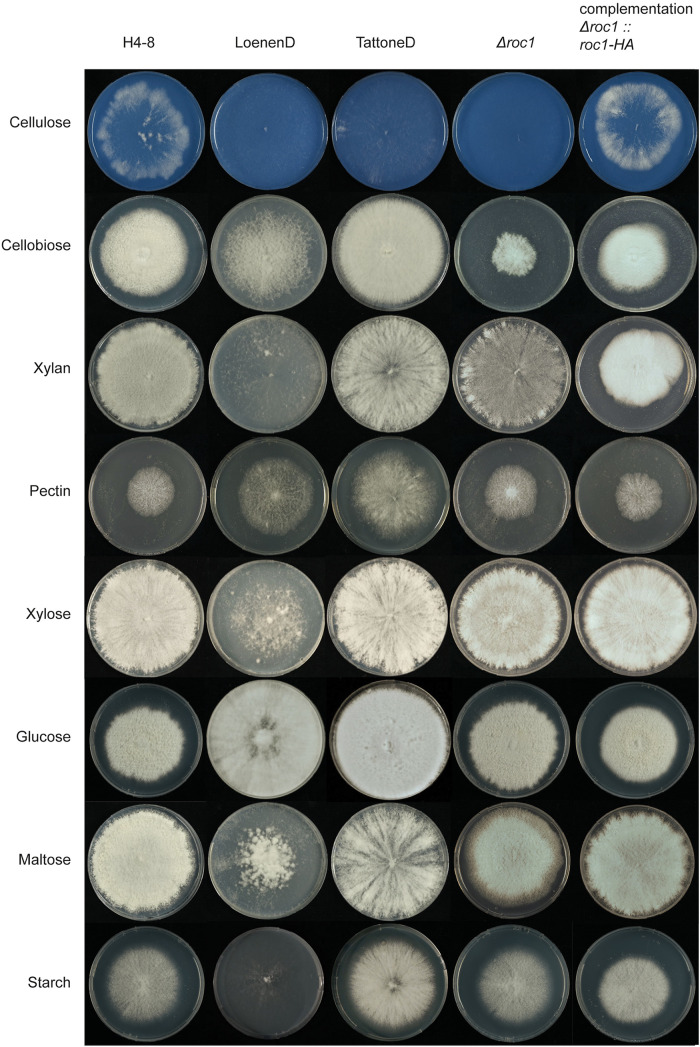
The growth profile of Schizophyllum commune was determined on carbon sources associated with wood (including cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin) and other carbon sources (including glucose, maltose, and starch) (Fig. 1). The reference strain H4-8 was compared to strains LoenenD and TattoneD. The latter two are haploid (monokaryotic) strains that were obtained (by protoplasting) from the dikaryotic wild isolate strains collected in Loenen aan de Vecht (Netherlands) and Tattone (Corsica, France). Strain LoenenD displayed reduced growth on maltose, starch, xylose, xylan and cellulose, but improved growth on pectin and cellobiose compared to H4-8 (Fig. 1). In contrast, the growth profile of strain TattoneD was more similar to that of strain H4-8, with the notable exceptions of cellulose (TattoneD grew slower than H4-8) and pectin (TattoneD grew faster than H4-8). Together, there is considerable phenotypic diversity between the various strains of S. commune.
FIG 1.
Growth phenotype of S. commune strains on various carbon sources. Reference strain H4-8 and wild isolate strains LoenenD and TattoneD displayed high phenotypic plasticity regarding growth on these carbon sources. Strain LoenenD showed reduced growth on maltose, starch, xylose, xylan, and cellulose (Avicel), but improved growth on pectin and cellobiose compared to the reference strain H4-8. In contrast, the growth profile of strain TattoneD was more similar to that of strain H4-8, with the notable exceptions of cellulose (TattoneD grew slower than H4-8) and pectin (TattoneD grew faster than H4-8). Deletion strain Δroc1 showed strongly reduced growth on cellulose and cellobiose, compared to its parent strain H4-8. This phenotype was rescued when the deletion was complemented. All strains were grown from a point inoculum for 7 days (glucose) and 11 days (other carbon sources) at 30°C. The cellulose medium was stained blue with Remazol Brilliant Blue R to enhance the visibility of the white mycelium on the white cellulose medium (the dye did not affect growth; data not shown).
Genome sequences of three strains of S. commune.
The genome sequence and annotation of strain H4-8 were previously published (version Schco1 [24]) and we here report an updated version (Schco3). The improvements in this updated assembly and annotation are reported in Text S1. Moreover, we sequenced strains TattoneD and LoenenD and generated draft assemblies and annotations (Table S1). Although both are more fragmented than the assembly of reference strain H4-8, the corresponding sets of gene predictions are similarly complete, as determined by BUSCO. Illumina-sequenced genomes are generally more fragmented than Sanger-sequenced genomes, especially regarding repeat-rich regions (25). This is reflected in the lower percentages of repetitive content for strains TattoneD and LoenenD, compared to H4-8. Importantly, the coding content of the assemblies are in a similar range, indicating that the set of gene predictions is reliable.
Statistics of the assemblies and gene predictions of strains H4-8, TattoneD and LoenenD. For strain H4-8 an updated assembly and annotation were generated (version Schco3). Strains TattoneD and LoenenD were newly sequenced for this study. Download Table S1, XLSX file, 0.01 MB (11.7KB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Supplemental materials and methods and supplementary results. Download Text S1, DOCX file, 0.2 MB (223.5KB, docx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
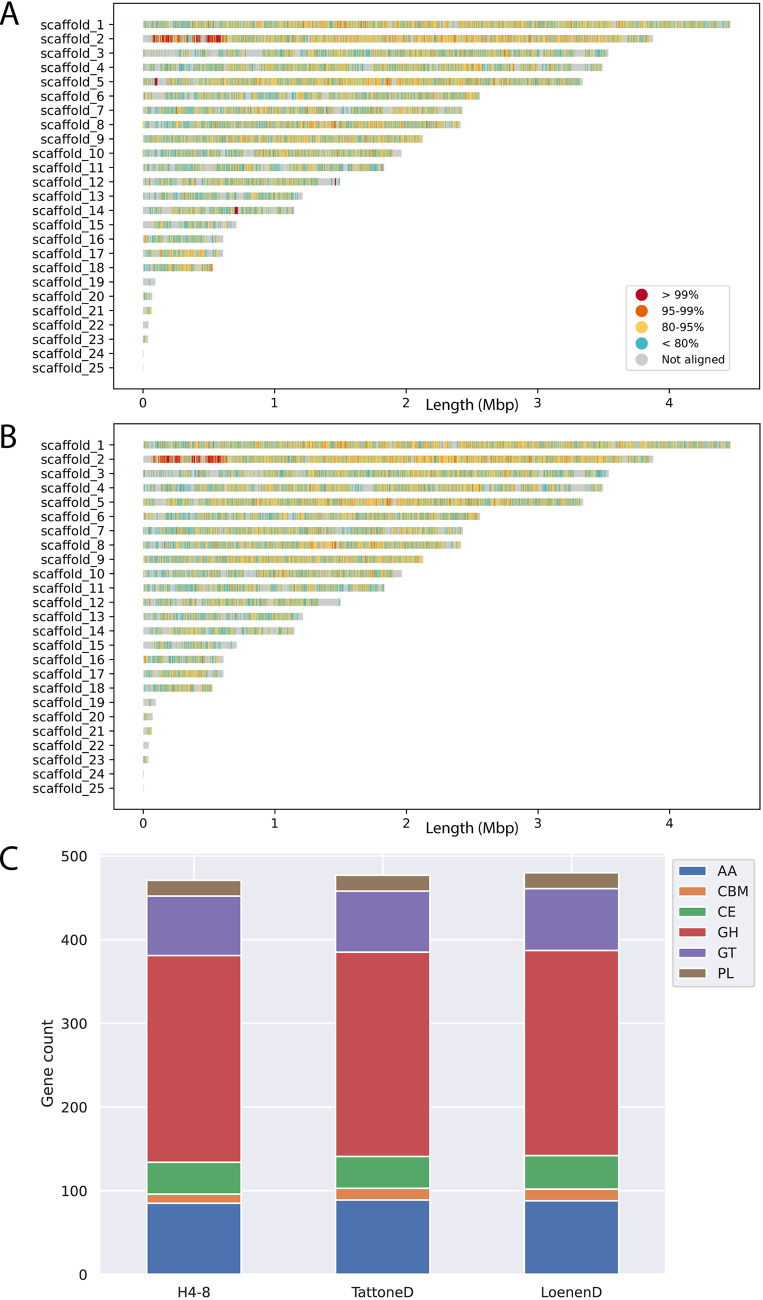
The three strains displayed a high degree of sequence diversity at the level of the genome (Fig. 2A and B). Large parts of the genome display less than 95% similarity (over a 1 kb sliding window). In some cases (e.g., scaffolds 12, 15 and 19) the (sub)telomeric regions of strain H4-8 are not found in strains TattoneD or LoenenD. Despite this high degree of sequence diversity among the three strains, the majority of genes are conserved between the strains (Fig. S1). The set of predicted carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) is remarkably similar between the strains (Fig. 2C). Therefore, the difference in growth profile on the various carbon sources cannot be easily explained by the CAZyme gene counts.
FIG 2.
Conservation between the reference assembly of strain H4-8 and the assemblies of strains (A) TattoneD and (B) LoenenD. Even though these are strains of the same species, their assemblies display a high degree of variation. (C). The number of predicted genes involved with plant cell wall degradation is very similar between the strains. These CAZymes are classified in subfamilies. GH: Glycoside Hydrolases; GT: Glycosyl Transferases; PL: Polysaccharide Lyases; CE: Carbohydrate Esterases; AA: Auxiliary Activities; CBM: carbohydrate-binding modules.
The number of predicted genes per strain and their conservation. The conservation was determined with Orthofinder. Genes in an orthogroup that had members from all three strains were labeled as ‘core’, genes in orthogroups that had members from two strains were labeled as ‘two strains’, and the remaining genes were labeled as ‘strain-specific’. Download FIG S1, TIF file, 0.8 MB (799.5KB, tif) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Comparative transcriptomics reveals conserved expression responses to lignocellulosic carbon sources.
We performed a comparative transcriptomics analysis to determine whether, despite the high level of phenotypic and sequence diversity, there is a conserved expression response to lignocellulosic carbon sources. Strains H4-8 and TattoneD were pregrown on minimal medium with glucose as carbon source and after 3 days the colonies were transferred to medium containing either glucose, cellulose (Avicel), or wood. After 3 days of exposure to this carbon source the colonies were harvested, RNA was isolated, and RNA-Seq was performed (Table S2). A gene was considered differentially expressed if its expression changed at least 4-fold and this change was statistically significant.
Expression values of genes (in RPKM) and enrichment of functional annotation terms in sets of differentially expressed genes. Download Table S2, XLSX file, 8.87 MB (8.9MB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Glucose does not require extracellular breakdown by CAZymes, in contrast to the polymeric compounds cellulose and wood. Therefore, the most relevant differences in expression profiles were expected between samples grown on glucose and either cellulose or wood. Indeed, 166 and 210 genes of strains H4-8 and TattoneD were upregulated when grown on cellulose compared to glucose, respectively. Similarly, 468 and 500 genes of these strains were upregulated on wood, respectively (Table S2).
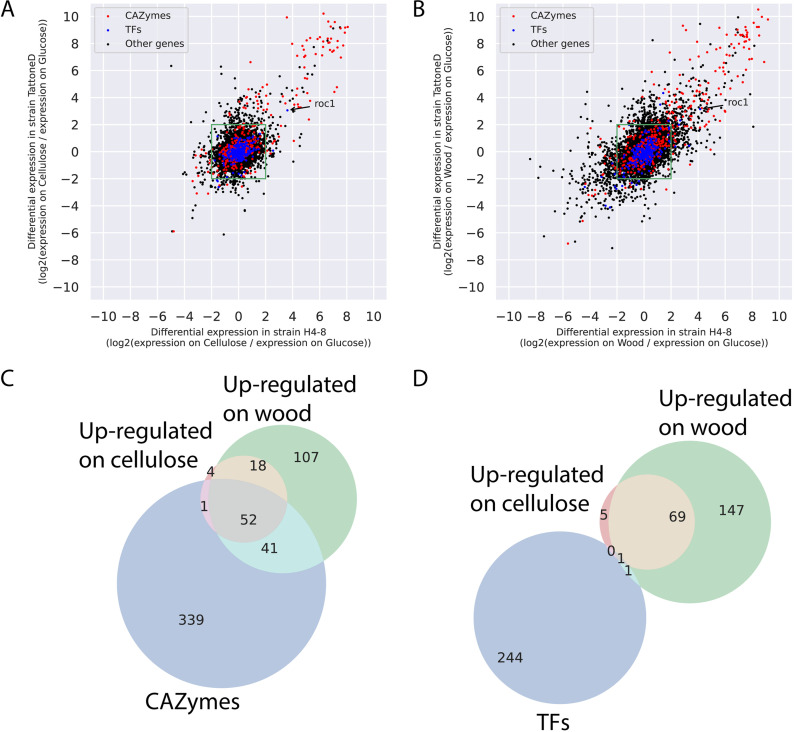
Next, we performed a comparative transcriptomics analysis on the two strains on various carbon sources, in an effort to identify conserved responses. Orthologs were identified between the two strains and their regulation profile was compared (Fig. 3). Again, we focused the analysis on expression on cellulose compared to glucose (Fig. 3A) and on wood compared to glucose (Fig. 3B). Orthologs in the upper right corner of Fig. 3A and B displayed a conserved expression profile on the corresponding carbon sources and many of those are predicted CAZymes. The orthologs annotated as CAZymes showed a more conserved response between the strains (Pearson correlation of 0.88 and 0.88, on cellulose and wood, respectively) than for the full set of genes (Pearson correlation of 0.54 and 0.66, on cellulose and wood, respectively). The expression profile of transcription factors was less conserved between the strains than the CAZymes (Pearson correlation of 0.5 and 0.7, on cellulose and wood, respectively). In fact, only one transcription factor displayed a conserved expression profile in both strains on cellulose and wood.
FIG 3.
Comparative transcriptomics in strains H4-8 and TattoneD. (A) Expression of orthologs in the two strains when grown on cellulose, compared to glucose. Orthologs in the green box are not differentially expressed in either strain. Orthologs in the top right quadrant are upregulated on cellulose in both strains, indicating that they show a conserved response. Many of these orthologs are CAZymes, and only one ortholog is a transcription factor (roc1). In general, the response of CAZymes is more conserved than that of other genes. (B) As in (A), but expression on wood compared to glucose. (C) VENN diagram of orthologs that are annotated as a CAZyme (blue circle), are upregulated on cellulose in both strains (compared to on glucose; red circle), or are upregulated on wood in both strains (compared to on glucose; green circle). Orthologs that are upregulated on cellulose in both strains are largely a subset of orthologs upregulated on wood. Moreover, a considerable number of the upregulated orthologs are annotated as CAZyme. (D) As in (C), but for orthologs annotated as transcription factors (blue circle). Only one transcription factor (roc1) was upregulated in both strains on both cellulose and wood.
Orthologs that are upregulated on complex carbon sources in one strain, but not in the other strain, (i.e., the dots above and to the right of the green square in Fig. 3A and B) do not show a conserved expression response. Therefore, those genes may explain part of the difference in phenotype displayed by these strains on complex carbon sources. Furthermore, orthologs that are upregulated in both strains during growth on cellulose or wood but that do not have a CAZyme annotation (i.e., the black dots in the upper right corners of Fig. 3A and B) may represent novel CAZymes, or other genes involved in growth on complex carbon sources.
Next, we focused on the orthologs that displayed a conserved expression response (i.e., in both strains) to complex carbon sources compared to growth on glucose (Fig. 3C and D). Orthologs that were upregulated on cellulose in both strains were largely a subset of the orthologs that were upregulated on wood, and a considerable number of those were CAZymes (Fig. 3C). This indicates that the expression program that is activated during growth on cellulose is also activated during growth on wood. Functional annotations that were enriched in genes that were upregulated on cellulose included CAZymes of the AA9, CE1, GH5, and GH10 families (Text S1 and Table S2). The genes that were upregulated on wood (compared to glucose) but not on cellulose, may be involved in the degradation or detoxification of the complex set of polymers and other compounds present in wood. Functional annotations that were enriched in this set included CAZymes of the GH43, GH3, GH18, and AA9 families (Text S1 and Table S2).
Transcription factors, on the other hand, were not found to a large extent in the conserved changes in gene expression (Fig. 3D). In fact, only one transcription factor was upregulated on both cellulose and on wood (compared to on glucose) in both strain H4-8 and TattoneD (protein ID Schco3|2615561 and Schco_TatD_1|232687; Fig. 3A, B and D). In strain H4-8 the expression is upregulated 13-fold and 18-fold on cellulose and wood, respectively, compared to glucose (Table S2). We hypothesized that this transcription factor (from here on named Roc1 for ‘regulator of cellulases’) is involved in the regulation of gene expression during growth on lignocellulose.
Regulator Roc1 is only conserved in the class Agaricomycetes.
Roc1 is classified as a putative transcription factor based on the presence of a Zn2Cys6 DNA binding domain and a fungal-specific transcription factor domain (Pfam domains PF00172 and PF04082, respectively). These domains are frequently found together, and in most fungi this is the most common family of transcription factors (13) with many (distant and functionally unrelated) members across the fungal kingdom. Examples include GAL4 in S. cerevisiae (26) and XlnR in Aspergillus niger (27). The reference genome of S. commune (strain H4-8) encodes 41 members of this transcription factor family.
The genomes of 140 fungi from across the fungal tree were analyzed for orthologs of Roc1 (Table S3). Since the fungal-specific Zn2Cys6 transcription factor family is large, numerous homologs of Roc1 are found in each genome. We distinguished between homologs and orthologs using a gene tree-based approach, combined with the location of conserved domains (Fig. S2A). Roc1 orthologs were only found in members of the class Agaricomycetes in the phylum Basidiomycota (Fig. S2B). These orthologs clustered closely together in the gene tree (having short branch lengths) and were highly conserved across the length of the protein (Fig. S2A). The Roc1 orthologs of Agaricus bisporus and Dichomitus squalens displayed a similar expression profile on lignocellulose (Text S1) (28, 29).
(A) Gene tree of Roc1 orthologs and more distant homologs. The locations of the PFAM domains PF00172 (Zn2Cys6 binuclear cluster domain) and PF04082 (Fungal specific transcription factor domain) are indicated in blue and green, respectively. The location of a conserved Roc1 HMM domain is indicated in red. A protein is indicated as a Roc1 ortholog if the blue, green, and red domains are present, whereas other proteins in this tree are considered more distant homologs. Branch lengths between the Roc1 orthologs are generally considerably shorter than the branch lengths between the more distant homologs. Roc1 orthologs are only found in Agaricomycetes. The first part of the protein IDs represents a species code (see Table S3 for the full species name). (B) Species tree of 140 fungal species. The species with a putative Roc1 ortholog are indicated in green. Roc1 is only conserved in the Agaricomycetes. See Table S3 and (A) for the protein IDs of the Roc1 orthologs. Download FIG S2, PDF file, 0.5 MB (481.5KB, pdf) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
The genomes of species used in this study and their Roc1 orthologs. The previously published genome and genes were obtained from the indicated publications. The indicated phylogeny is based on the NCBI taxonomy database. Download Table S3, XLSX file, 0.02 MB (25.6KB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
A Δroc1 strain is incapable of efficiently utilizing cellulose as a carbon source.
A Δroc1 strain was generated in strain H4-8 using our previously published CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing protocol (20) by replacing 2759 bp (which includes the roc1 coding sequence) with a nourseothricin resistance cassette. Growth of Δroc1 on cellulose (Avicel) was strongly reduced compared to the reference (Fig. 1). Only a very thin mycelium was observed, and no aerial hyphae were formed. Moreover, growth on cellobiose and xylan was reduced, although to a lesser extent than on cellulose. Both these carbon sources are found in lignocellulose. In contrast, Δroc1 displays no phenotype when grown on glucose, maltose, starch, pectin, and xylose compared to the reference H4-8 (Fig. 1). The wild type phenotype was largely rescued when the Δroc1 strain was complemented with the roc1 coding sequence under the control of its own promoter (Fig. 1), confirming that the phenotype was caused by the deletion of roc1. The coding sequence included a C-terminal hemagglutinin tag, allowing us to use the complementation strain for ChIP-Seq with a commercially available anti-HA antibody (see below).
Total cellulase enzyme activity in the growth medium is strongly reduced in Δroc1.
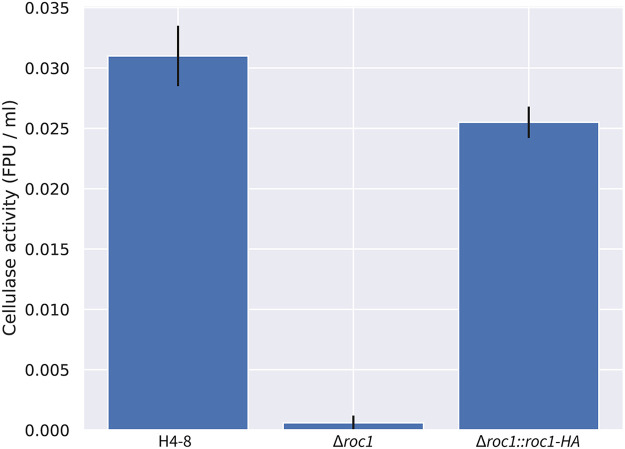
We assessed whether the strongly reduced growth of the Δroc1 strain on cellulose coincided with reduced cellulase enzyme activity in the growth medium. Biomass was pregrown in liquid minimal medium with glucose, washed and subsequently used to inoculate liquid shaking cultures containing cellulose as carbon source. After 6 days, the cellulase activity in the growth medium was determined (Fig. 4). Compared to the reference strain H4-8, the Δroc1 strain had strongly reduced cellulase activity in the growth medium. Moreover, this phenotype was rescued in the complemented Δroc1 strain. The lack of growth of Δroc1 on cellulose (Fig. 1) can be explained by the low cellulase activity in this strain, since these cellulases are required to break down cellulose. Furthermore, it suggests that Roc1 regulates the expression of cellulose-degrading genes.
FIG 4.
Total cellulase activity of S. commune strains in cellulose liquid shaking cultures. There is almost no activity in the Δroc1 strain compared to the reference H4-8. This phenotype is largely rescued upon complementation of the gene. All cultures were pregrown on glucose medium to ensure that sufficient biomass was present, transferred to cellulose medium, and grown for 6 additional days.
Expression of several CAZyme families is no longer upregulated on cellulose in Δroc1.
We performed an RNA-Seq analysis on wild type (reference strain H4-8) and the Δroc1 strain in order to identify the genes that are no longer upregulated in Δroc1 during growth on cellulose (Table S2). The strains were precultured on medium that contained glucose as sole carbon source. After 3 days, the mycelium was transferred to medium that contained either glucose or cellulose as sole carbon source and cultured for an additional 3 days. A total of 194 genes were upregulated during growth on cellulose (compared to glucose) in the wild type and not in Δroc1. These genes may therefore be regulated by Roc1, either directly or indirectly. Several CAZyme families are enriched in this set of 194 genes, of which the most striking was the lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs), also annotated as CAZyme family AA9 (auxiliary activity 9) (Table S2). This family was previously shown to disrupt cellulose fibers and enhance cellulose degradation by glucanases (30). Of the 22 predicted LPMO genes encoded in the genome, 14 were upregulated on cellulose in the wild type, and 12 of those were no longer upregulated on cellulose in Δroc1. Moreover, all five genes encoding a protein with a cellulose-binding PFAM domain were upregulated in the wild type, but no longer in Δroc1. The families GH43, GH5 and GH3 were also enriched. These glycoside hydrolase families comprise a diverse group of enzyme activities, several of which are involved in (hemi)cellulose degradation. GH43 includes members with β-d-xylosidase activity (involved in hemicellulose degradation), GH3 includes members with reported β-glucosidase (involved in cellulose degradation) and xylan 1,4-β-xylosidase (involved in hemicellulose degradation), while GH5 includes members with reported endo-β-1,4-glucanase (involved in cellulose degradation) (5, 6, 31–33). Combined, these activities may explain why the Δroc1 strain can no longer utilize cellulose as a carbon source and displays slower growth on hemicellulose.
ChIP-Seq reveals binding sites of Roc1 in promoters of cellulases.
Transcription factors may regulate the expression of genes in a direct (e.g., by binding to their promoter) or indirect manner (e.g., by regulating other transcription factors that in turn directly regulate these genes). A ChIP-Seq analysis was performed to identify the binding sites of Roc1 in the genome, allowing us to determine whether Roc1 directly binds the promoters of cellulase genes. The Roc1 transcription factor was tagged with a hemagglutinin (HA) epitope tag and expressed in the deletion strain (resulting in strain Δroc1:: roc1-HA), allowing the ChIP-Seq to be performed using commercially available antibodies against the HA-tag (Fig. S3). Since this tagged version can complement the phenotype of the roc1 deletion (Fig. 1 and 4), it can be concluded that the HA-tag does not interfere with the function of Roc1.
Western Blot confirms the expression of the HA-tagged Roc1 protein in Δroc1 of S. commune. The wild type (i.e., reference strain H4-8) and Δroc1::roc1-HA (i.e., the deletion strain complemented with the gene encoding the HA-tagged Roc1) were grown on cellulose or glucose. The predicted size of the HA-tagged Roc1 protein is 78.9 kDa. A band of this size is visible in the complemented deletion strain when grown on cellulose, but not when grown on glucose (the height of the band is indicated with a red arrow). As expected, this band is not found in the wild-type strain under either condition. Download FIG S3, TIF file, 1.2 MB (1.2MB, tif) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
The strains H4-8 and Δroc1:: roc1-HA were grown on medium containing cellulose, and the chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) procedure was performed to isolate the DNA to which Roc1 binds. This DNA was subsequently purified and sequenced using Illumina technology. The resulting sequence reads were aligned to the assembly of strain H4-8 and peaks were identified, which may be considered binding sites of Roc1. A total of 1474 binding sites of Roc1 were identified during growth on cellulose, which were associated with 1125 unique genes (Table S4), while 305 peaks could not be associated with a gene. CAZyme genes as a group were not enriched among those genes (P > 0.05), but, in contrast, specific CAZyme families were strongly enriched (Table S4), as well as genes that were no longer upregulated on cellulose in Δroc1 (Fig. 5A). Especially for the latter group of genes, it suggests that Roc1 functions as an activator by directly binding to their promoter. Roc1 does not appear to play a large role as a repressor of gene expression under the tested conditions, since only a single gene (Schco3|2481653, a predicted sugar transporter) was both associated with a ChIP-Seq peak and downregulated in the wild-type strain on cellulose compared to all other conditions (Tables S4 and S5).
FIG 5.
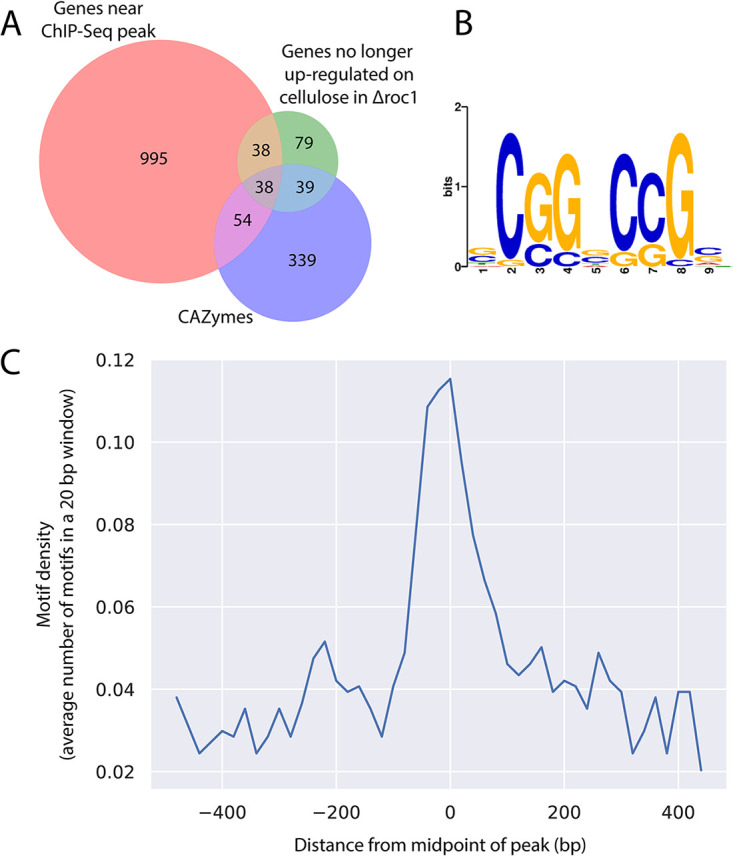
(A) Venn diagram depicting the overlap between the sets of genes that are associated with a Roc1 binding site (red circle), CAZymes (blue circle), and genes that are no longer upregulated in Δroc1 on cellulose (compared to glucose; green circle). (B) Conserved motif identified in the binding sites of Roc1. (C) The binding site in (B) is enriched in the center of the ChIP-Seq peaks.
Locations of the peaks identified in the ChIP-Seq analysis. These peaks can be regarded as Roc1 binding sites. The genes associated with these peaks, as well as information about their annotation and expression profile are indicated. Moreover, the enrichment of functional annotation terms among genes associated with a Roc1 binding site is indicated. Download Table S4, XLSX file, 1.2 MB (1.3MB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Primers used in this study. Download Table S5, XLSX file, 0.01 MB (10.8KB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
A notable family of genes with binding sites of Roc1 are the lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs), which were also shown by RNA-Seq to be regulated by Roc1 (see above). Of the 22 LPMO genes encoded in the genome, 13 were associated with a Roc1 binding site. Moreover, 11 of these 13 were no longer upregulated during growth on cellulose in Δroc1 (as determined by RNA-Seq). This indicates that Roc1 directly binds to the promoters of these genes during growth on cellulose, activating their expression. The GH3 and GH5 CAZyme families were also overrepresented among the genes with a Roc1 binding site (Table S4) and were also shown to be regulated by Roc1 based on the RNA-Seq data. In contrast, none of the genes in the GH43 family that were regulated by Roc1 according to the RNA-Seq data (see above) were associated with a ChIP-Seq peak. This suggests that Roc1 does not bind their promoters directly and may therefore regulate these genes indirectly. Furthermore, gene roc1 itself is also associated with a Roc1 binding site (Table S4). This indicates that Roc1 regulates its own expression, perhaps in a positive feedback loop.
Conserved motif in the Roc1 ChIP-Seq peaks.
The peaks identified in the ChIP-Seq analysis were analyzed to identify a conserved motif that represents the binding site of Roc1. The GC content of the 500 bp sequence around the top of each Roc1 peak was determined (Fig. S4A). There was a marked increase in GC content near the middle of the peaks, which indicates that the Roc1 binding site is GC-rich. Based on the GC curve, we further limited the search to 200 bp around the top of each Roc1 peak. The sequences were analyzed with STREME, which attempts to find conserved motifs that are overrepresented in the peak sequences, compared to a representative negative set (i.e., other genomic sequences). This led to the identification of a motif (Fig. 5B) that was present in 989 of the 1427 peaks and significantly enriched compared to the negative-control sequences (P = 2.8·10−8 in a Fisher exact test). Furthermore, this motif was found most frequently in the center of the identified peak (Fig. 5C), as would be expected for the binding site.
(A) GC content along the length of the 1427 ChIP-Seq peaks. Around the midpoint of the peaks there is an increase of the GC content, which indicates that the Roc1 binding motif is GC-rich. (B) Fluorescence of dTomato driven by the 700 bp promoter of lpmA. When grown on glucose, no fluorescence is observed. In contract, when grown on cellulose strong fluorescence is observed, in concordance with the expression profile of lpmA. When grown on a mix of glucose and cellulose, no fluorescence is observed, indicating the carbon catabolite repression overrules the induction by cellulose. In the reference strain H4-8, no fluorescence is observed under any condition. (C) Alignment of the orthologs of lpmA in S. commune strains H4-8, TattoneD and LoenenD. The genomic sequence includes the gene (with introns) and the promoter (approximately 325 bp upstream of the start codon). The putative Roc1 binding site (pink) is conserved in each of these strains, despite the 12% sequence diversity in the promoter part of the alignment (40 of 330 positions in the alignment display differences between the strains). The TATA box (black), start codon (green) and stop codon (red) are indicated. Download FIG S4, JPG file, 2.3 MB (2.4MB, jpg) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Functional promoter analysis of a CAZyme of the AA9 family reveals the Roc1 binding site.
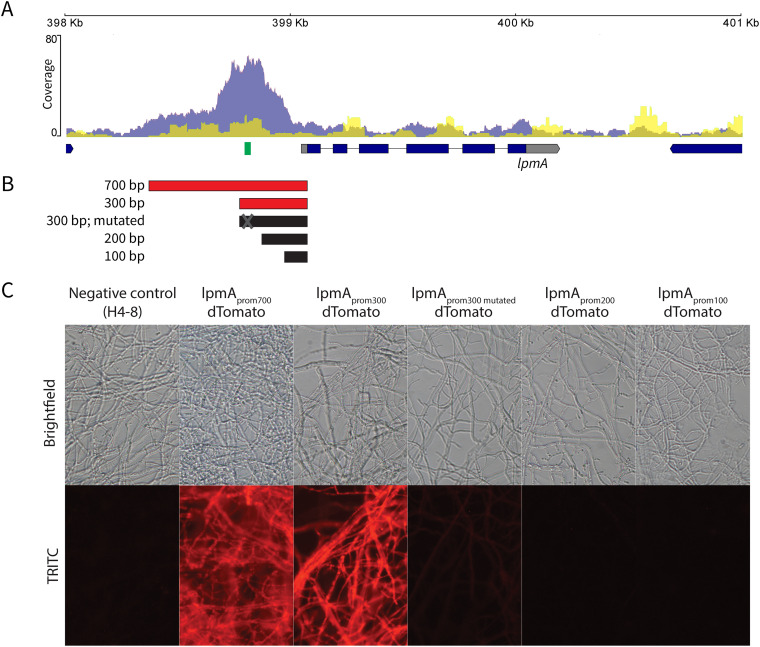
Twelve of the 22 members of the lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase family (LPMOs; CAZyme family AA9) were no longer upregulated in Δroc1 during growth on cellulose (compared to glucose). Moreover, Roc1 had direct binding sites in the promoters of 12 of the 22 LPMO genes, as determined by ChIP-Seq. The overlap between these two data sets was nine LPMO genes, which shows the strong correlation between the RNA-Seq and ChIP-Seq data sets for this gene family. One of these genes, lpmA (protein ID 1190128), was strongly upregulated on cellulose and wood, compared to growth on glucose (246 and 206-fold, respectively; Table S2). The peak from the Roc1 ChIP-Seq was located upstream of the translation start site (Fig. 6A).
FIG 6.
Functional promoter analysis of the lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase lpmA gene (protein ID 1190128). (A)ChIP-Seq read coverage curve in the locus of lpmA. The blue curve represents the coverage of the Roc1 ChIP-Seq reads, while the yellow curve represents the negative control. There is a peak in the promoter region upstream of the lpmA coding sequence. The location of the conserved motif (representing the Roc1 binding site; Fig. 5B) is indicated in green. (B) Five regions in the promoter of lpmA (5′ of the coding sequence) were tested for their ability to drive expression and fluorescence of dTomato. Active promoter fragments are indicated in red, and inactive promoter fragments in black. (C) Reporter strains with the dTomato gene under the control of the promoters in (B), grown on cellulose. The 700 and 300 bp promoters can drive dTomato expression and fluorescence, but the 200 and 100 bp promoters cannot. The 300 bp promoter in which the Roc1 binding motif had been mutated was not able to drive dTomato expression and fluorescence to the same extent, since only weak fluorescence is observed. When grown on glucose, no fluorescence was observed in any of these strains (Fig. S4B).
We performed a functional promoter analysis to further investigate the expression dynamics and to locate the transcription factor binding sites. The promoter of lpmA was used to drive expression of the red fluorescent reporter protein dTomato (Fig. 6B). The 700 bp promoter (i.e., the 700 bp upstream of the predicted translation start site) could drive expression of dTomato when growing on cellulose, resulting in red fluorescent mycelium (strain lpmAprom700-dTomato; Fig. 6C). No fluorescence was observed when grown on glucose or a combination of glucose and cellulose (Fig. S4B). Next, we produced similar reporter constructs with promoter lengths of 300, 200 and 100 bp. The promoter of 300 bp could still drive dTomato expression on cellulose, but, in contrast, the promoters of 200 bp and 100 bp could not (Fig. 6B and C). This indicates that the region between 300 and 200 bp upstream of the translation start site contains an important regulatory element. This region corresponds with the peak in the ChIP-Seq data and therefore a binding site of Roc1. Moreover, the conserved motif (Fig. 5B) is located in this region (Fig. 6A). In fact, the summit of the ChIP-Seq peak is located in the conserved motif. This motif is also conserved in the promoters of the lpmA orthologs in TattoneD and LoenenD, despite a 12% sequence diversity in the rest of the putative promoter (Fig. S4C). Removal of the motif from the 300 bp promoter of lpmA by site-directed mutagenesis resulted in a strong decrease in the ability of the promoter to drive dTomato expression (Fig. 6C), since only weak fluorescence is observed. This confirms that the motif is indeed the binding site of Roc1 and that this binding site is required for correct promoter activity.
DISCUSSION
Fungal deconstruction of lignocellulose in the plant cell requires the complex orchestration of a broad set of enzymes, and the expression of these enzymes is generally tailored to the type of polymers in the substrate by transcription factors. Several such transcriptional regulators have been identified in the phylum Ascomycota, but to date not in the phylum Basidiomycota. These phyla diverged over 600 million years ago (1). Here, we identified the transcription factor Roc1 as a regulator of cellulase expression in the wood-decaying mushroom Schizophyllum commune. A roc1 deletion strain cannot efficiently utilize cellulose (and, to a lesser extent, hemicellulose) as a carbon source. Moreover, ChIP-Seq revealed that Roc1 binds the promoters of various types of cellulase genes (including several lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases) while growing on cellulose, indicating that Roc1 directly regulates those genes. Furthermore, Roc1 activates its own expression, likely in a positive feedback loop.
S. commune is a highly polymorphic basidiomycete, both phenotypically and genetically. Strains H4-8, TattoneD and LoenenD varied considerably in their growth profiles, and showed a high variation in their genomes. This extraordinary genetic diversity was previously shown for other strains of S. commune as well (34). Despite the high level of sequence variation between the strains, the number of CAZyme genes was remarkably similar. Therefore, it is challenging to link the phenotypical differences in growth profiles to a signature in the genome. However, the comparative transcriptomics approach allowed us to detect conserved responses in the expression profile, despite the high strain diversity. Although there is considerable variation between how the strains change their expression profile to the various carbon sources, the expression profile of CAZymes is more conserved. LPMOs (AA9), CE1, GH5, GH10, GH43 and GH3 are enriched among the genes that are upregulated on cellulose or wood, indicating their importance in lignocellulose degradation. Furthermore, although the response of transcription factors was generally less conserved than the response of CAZymes, we identified a single transcription factor gene (roc1) that was consistently upregulated under these conditions in both strains.
Cellulose, cellobiose, and xylan are major constituents of lignocellulose in wood. Cellulose is a polysaccharide of β-1,4-linked glucose residues. Cellobiose is a dimer of β-1,4-linked glucose residues and is an intermediate breakdown product of cellulose during enzymatic digestion. Xylan is a group of hemicelluloses consisting of a backbone of β-1,4-linked xylose residues. The observation that growth of Δroc1 on these carbon sources is specifically affected, but not on other carbon sources, is a strong indication that Roc1 regulates the process of lignocellulose degradation. Growth on pectin, another constituent of lignocellulose in wood, is not negatively affected in Δroc1. This indicates that Roc1 is likely not directly involved in pectinase expression. This is further supported by the observation that (direct and indirect) targets of Roc1 predominantly included CAZymes involved in cellulose and hemicellulose degradation, but not pectin degradation.
It was previously shown that transcription factors involved in the regulation of polysaccharide degradation are generally poorly conserved between ascomycetes and basidiomycetes (13), and this is also the case for Roc1. Even within the basidiomycetes, Roc1 is only conserved in the class Agaricomycetes, which contains some of the most potent wood-degrading organisms. Indeed, the majority of fungi in this class are wood-degrading (8), although it also includes mycorrhizal and plant-pathogenic fungi (some of which have a partially saprotrophic lifestyle). This correlation between lifestyle (lignocellulose-degrading) and the presence of a Roc1 ortholog suggests that the function of Roc1 may be conserved in other members of the Agaricomycetes as well. Ectomycorrhizal fungi in the Agaricomycetes have lost most of their ability to degrade lignocellulose, which is also reflected in a strongly reduced set of CAZymes (35). Nevertheless, most have retained at least one gene encoding an LPMO, which suggests that Roc1 may still be involved in the regulation of cellulase degradation in this set of fungi. For example, Laccaria bicolor encodes 10 and Amanita muscaria encodes 2 predicted LPMO genes (35, 36). The Roc1 orthologs of A. bisporus and D. squalens displayed a similar expression profile on lignocellulose as in S. commune, further suggesting a conserved role (Text S1) (28, 29).
Regulators of cellulases were previously identified in the distantly related ascomycete N. crassa (18). It is important to note that these transcription factors (CLR-1 and CLR-2) are not orthologous to Roc1 of S. commune, nor are these two genes conserved in S. commune. Remarkably, however, the consensus binding motifs of CLR-1 (CGG-N5-CCG-N-CGG) and Roc1 (CGG-N-CCG) show a large degree of similarity. It is tempting to speculate that this is an example of convergent evolution, or that the binding motif predates either Roc1 or CLR-1. In the latter case, one transcription factor could have taken over the role of the other in an ancestor of ascomycetes and basidiomycetes. It should be noted, however, that Roc1 and CLR-1 are both transcription factors of the Zn2Cys6 zinc finger family. The binding motifs of regulators of this family frequently contain a CCG triplet (37, 38), as is also the case for Gal4 of S. cerevisiae (26). The Roc1 consensus binding motif does not match with the GC box promoter element (39), which represents a binding site of C2H2 zinc finger family transcription factor. We cannot exclude that the binding site of Roc1 is more complex than the consensus motif CGG-N-CCG, and further study may reveal additional base pairs that contribute to efficient binding of Roc1 and subsequent activation of transcription. We could not identify additional (nearby) binding sites that may be required for potential cofactors to bind in concert with Roc1.
While Roc1 ChIP-Seq revealed an enrichment of binding sites near lignocellulolytic CAZymes, the majority of putative binding sites were not in the promoter region of CAZymes or even genes that were affected in expression in the Δroc1 strain (Fig. 5A). This suggests that binding of Roc1 does not always affect gene expression in an apparent way. However, binding of Roc1 to these sites may affect expression of genes that are located considerably more distant, due to the 3D architecture of the genome. A similar number of ChIP-Seq peaks has previously been reported for the Zn2Cys6 transcription factor PRO1 in Sordaria macrospora (40), while fewer peaks were reported for other Zn2Cys6 transcription factors, including AflR in Aspergillus flavus (41), CrzA in Aspergillus fumigatus (42) and FgHtf1 in Fusarium graminearum (43). Since the consensus sequence of the binding motif is rather short, it seems likely that spurious binding of Roc1 may occur and that not every occurrence of the motif results in a change of gene expression after binding by Roc1.
It is currently unknown how Roc1 fits into the wider carbohydrate-degrading regulatory network, which includes the carbon catabolite repressor CreA. The self-regulation of Roc1 (by directly binding its own promoter) likely leads to high expression during growth on cellulose, but it is unknown if CreA directly inhibits expression of roc1 in the presence of glucose. Furthermore, inhibition of CAZyme expression by CreA may overrule induction by Roc1. It is tempting to speculate that overexpression of roc1 will induce cellulase production during growth on non-inducing conditions, although it seems likely that carbon-catabolite repression (in the presence of glucose) overrides induction by Roc1.
This is the first report of ChIP-Seq with a specific transcription factor in a mushroom-forming fungus. It is a crucial step to mapping the regulatory networks of transcription factors in this group of fungi, since direct interactions between transcription factors and promoters can now be revealed in vivo. This will also be useful for studying the direct targets of the transcription factors involved in mushroom development (22, 24, 44, 45) and other processes in this important group of fungi.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains, media composition, and culture conditions.
The reference strains used in this study were Schizophyllum commune H4-8 (matA43matB41; FGSC 9210) and the compatible isogenic strain H4-8b (matA41matB43) (24). Strain Δku80 was derived from H4-8 and was used for gene deletion (21). The dikaryotic strains S. commune Tattone and S. commune Loenen were collected in Tattone (Corsica, France) and Loenen aan de Vecht (The Netherlands), respectively. The monokaryotic strains S. commune TattoneD and S. commune LoenenD were isolated from these strains by protoplasting. Protoplasting was performed using a Trichoderma harzianum Horst lytic enzyme mix as described previously (46).
The strains were grown at 30°C on a medium comprising per L: 22 g glucose monohydrate, 1.32 g (NH4)2SO4, 0.5 g MgSO4·7H2O, 0.12 g thiamin, 1 g K2HPO4, 0.46 g KH2PO4, 5 mg FeCl3.6H2O, trace elements and with or without 1.5% agar (47). For cultures with other carbon sources, glucose was replaced with 1% (wt/vol) Avicel (cellulose), 1% (wt/vol) glucose + 1% (wt/vol) Avicel, 1% (wt/vol) cellobiose, 1% (wt/vol) xylan from corncob, 1% (wt/vol) pectin from apple, 1% (wt/vol) starch from potato, 2.2% (wt/vol) xylose, 2.2% (wt/vol) maltose monohydrate. To improve the visualization of the fungal colonies growing on Avicel, the medium was supplemented with 20 μg μL−1 Remazol Brilliant Blue R. Liquid cultures were grown in Erlenmeyer flasks at 30°C with shaking at 200 rpm. For selection on nourseothricin (Bio-Connect, Netherlands), phleomycin (Bio-Connect, Netherlands) or hygromycin (Bio-Connect, Netherlands), the medium was supplemented with 15 μg mL−1, 25 μg mL−1 and 20 μg mL−1 antibiotic, respectively.
Genome sequencing, assembly, and annotation.
The genome assembly version Schco1 of S. commune H4-8 (24) was improved as described in Text S1, resulting in version Schco3. The genomes of S. commune TattoneD and LoenenD were sequenced using 270 bp insert standard fragment Illumina libraries in 2 × 150 format. The resulting reads were filtered for artifact and process contamination and were subsequently assembled with Velvet (48). The resulting assembly was used to create in silico long mate-pair library with insert 3000 ± 300 bp, which was then assembled together with the original Illumina library with AllPathsLG release version R42328 (49).
The genomes were annotated using the JGI Annotation Pipeline (50, 51), which combines several gene prediction and annotation methods, and integrates the annotated genome into the web-based fungal resource MycoCosm (51). Functional annotation of the assembly and predicted genes is described in Text S1. RNA-Seq data (see below) was used during gene prediction for strains H4-8 and TattoneD, but not for LoenenD.
The assemblies of strains TattoneD and LoenenD were aligned to the assembly of H4-8 using PROmer version 3, which is part of the MUMmer package (52). The setting “mum” was used. Next, a sliding window approach (1 kbp window with 100 bp step size) was taken to determine the percentage of identity across the assemblies of the strains.
Comparative transcriptomics during growth on various carbon sources.
Cultures of strain H4-8 and TattoneD were pregrown on a Whatman Cyclopore polycarbonate (PC) membrane on top of minimal medium containing glucose at 30°C in the dark. After 3 days, the PC membranes containing the cultures were carefully transferred to fresh plates containing solid minimal medium with either glucose, cellulose (Avicel) or birchwood (ground to a particle size of 1 to 3 mm) as sole carbon source. After 3 days, the cultures were harvested, lyophilized, powdered in liquid nitrogen, and RNA was extracted using the Zymo Direct-zol RNA MiniPrep kit. All conditions were analyzed with biological triplicates. RNA-Seq was performed on the Illumina HiSeq-2000 platform (see Text S1 for details on sequencing and analysis). The resulting sequence reads were aligned to their respective genome assemblies, S. commune H4-8 (version Schco3) or S. commune TattoneD (version Schco_TatD_1), using the aligner Hisat version 2.1.0 (53) and differential expression was analyzed with Cuffdiff version 2.2.1, which is part of the Cufflinks package (54). In addition to the cutoff used by Cuffdiff to identify differentially expressed genes, we applied an additional filter of at least a 4-fold change in expression value, as well as at least one condition with an expression value of at least 10 RPKM. Overrepresentation and under-representation of functional annotation terms in sets of differentially expressed genes were calculated using the Fisher Exact test. The Benjamini-Hochberg correction was used to correct for multiple testing and as a cutoff for significance we used a corrected P value of 0.05.
To compare gene expression, we first identified orthologs between the two strains. Here, proteins are considered orthologs if they show strong homology (having a best bidirectional hit in a blastP analysis applying an E-value cutoff of 1e-10) and if they display syntenic gene order conservation (at least 1 of 4 neighbors should be shared between the strains).
The gene expression profiles were visualized with a heat map generated by the seaborn package for python (https://seaborn.pydata.org). The genes were clustered using the euclidean distance and average linkage methods. The values were scaled for each gene with a z-transformation, resulting in a z-score.
Conservation of Roc1 in the fungal kingdom.
The genome sequences and predicted genes/proteins of 140 previously published fungi were obtained from the publications listed in Table S3. Conserved protein domains were identified using PFAM version 32 (55). Roc1 is classified as a putative transcription factor based on the presence of a Zn2Cys6 DNA binding domain as well as a fungal specific transcription factor domain (Pfam domains PF00172 and PF04082, respectively). We took a multistep approach to more accurately identify putative Roc1 orthologs, resulting in a gene tree (Text S1). A phylogenetic tree of the 140 species (species tree) was reconstructed using 25 highly conserved proteins identified with BUSCO v2 (data set 'fungi_odb9') (56) (Text S1) and was rooted on 'early-diverging fungi' (i.e., non-Dikarya).
Deletion of gene roc1 in strain H4-8 and its complementation.
Gene roc1 (proteinID 2615561 in version Schco3 of the genome of S. commune) was deleted using our previously published protocol (20), which uses preassembled Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoproteins and a repair template to replace the target gene with a selectable marker (Text S1 and Table S5). The resulting Δroc1 deletion strain was complemented with a plasmid expressing a C-terminally hemagglutinin-tagged version of roc1 (Text S1). The resulting strain was named Δroc1:: roc1-HA. A Western blot was performed (Text S1) and this strain showed a 78 kDa band when grown on cellulose, which was absent in the wild type. This indicated that the Roc1 protein was correctly tagged with the HA-tag.
Cellulase activity assay.
The S. commune strains were precultured on a Poretics Polycarbonate Track Etched (PCTE) Membrane (GVS, Italy) placed on top of glucose medium for 5 days at 30°C. The mycelia of five cultures for each strain were macerated in 100 mL minimal medium with 1% cellulose (Avicel) for 1 min at low speed in a Waring Commercial Blender. The macerate was evenly distributed to 250 mL Erlenmeyers (20 mL each) containing 80 mL minimal medium with 1% cellulose (Avicel). Four Erlenmeyers for each strain were placed in an Innova incubator shaker for 10 days at 30°C with shaking at 200 rpm. Samples of the culture medium (1 mL) were collected after 6 days and centrifuged at 9400 g for 10 min. The supernatant was then used for the total cellulase enzyme activity measurement using the filter paper activity (FPase) assay (57). Total cellulase activity was determined by an enzymatic reaction employing circles with a diameter of 7.0 mm of Whatman No. 1 filter paper and 60 μL of supernatant. The reaction mixture was incubated at 50°C for 72 h. Next, 120 μL of dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) was added to the reaction, which was then heated at 95°C for 5 min. Finally, 100 μL of each sample was transferred to the wells of a flat-bottom plate and absorbance was read at 540 nm using a BioTek Synergy HTX Microplate Reader. One enzyme unit (FPU) was defined as the amount of enzyme capable of liberating 1 μmol of reducing sugar per minute (as determined by comparison to a glucose standard curve).
Transcriptomics on Δroc1 strain.
Gene expression was analyzed with RNA-Seq in the wild type (H4-8 reference strain) and the Δroc1 strain, in an effort to identify the genes that are regulated (directly or indirectly) by Roc1. The strains were precultured on a PCTE Membrane on top of solid minimal medium that contained glucose as sole carbon source at 30°C. After 3 days, the membranes were transferred to fresh minimal medium containing either glucose or cellulose. After an additional 3 days, the cultures were harvested and stored at −80°C until RNA isolation. The samples were homogenized by two metal beads in a Tissue Lyser II (Qiagen, Germany) at 25 Hz for 60 s. RNA was extracted with TRIzol (Thermofisher Scientific, USA) according to manufacturer’s specifications and subsequently treated with DNase I (Thermofisher Scientific, USA). After the DNase I treatment, the samples were cleaned up with the GeneJET RNA purification kit (Thermofisher Scientific, USA). Illumina libraries were generated for RNA-Seq and subsequently sequenced on the Illumina NextSeq 500 platform with unpaired high output of 75 bp by the Utrecht Sequencing Facility (USeq, www.useq.nl). The computational analysis was subsequently performed as described above.
ChIP-seq analysis.
Protein-DNA interaction and binding sites of Roc1 were surveyed by chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by next-generation sequencing (ChIP-Seq). The ChIP procedure was adapted from previous studies in human cell lines and Zymoseptoria tritici (58, 59) and our recently developed method for ChIP-Seq on Histone H3 (H3K4me2) in S. commune (22). We analyzed WT H4-8 and H4-8 Δroc1::roc1-HA, and two biological replicates were used for each of these conditions. Moreover, genomic DNA isolated from these strains was used as input control (also two biological replicates). The full methodology can be found in Text S1. Briefly, monokaryons of strains H4-8 or H4-8 Δroc1::roc1-HA were grown on medium with Avicel on Poretics™ Polycarbonate Track Etched (PCTE) Membrane (GVS, Italy). After 9 days 10 colonies were combined per biological replicate, and a ChIP analysis was performed. The resulting DNA samples were sequenced on an Illumina NextSeq 500 with paired-end mid output of 75 bp by the Utrecht Sequencing Facility (USeq, www.useq.nl). The resulting paired-end reads were aligned to the S. commune H4-8 reference genome (version Schco3) with bowtie2 (version 2.3.4.1) (60). ChIP-Seq peaks were identified in both WT H4-8 and H4-8 Δroc1::roc1-HA with the program macs2 (version 2.2.3) (61). To filter out any nonspecific binding, peaks identified in both the WT and Δroc1::roc1-HA strains were excluded from the analysis. Peaks that overlapped repetitive regions (including transposons) were removed. The peaks were associated with a gene if they were within 1000 bp of the predicted translation start site. The correlation between replicates was determined with the R package DiffBind (version 2.12.0).
Motif discovery.
STREME (which is part of the MEME Suite [62]) was used to identify conserved motifs in the ChIP-Seq peaks. STREME looks for ungapped motifs that are relatively enriched in a set of sequences compared to negative-control sequences. The 200 bp region around the center of the peak was analyzed for enriched motifs, with 10000 regions of the same length from across the genome as negative sequence set. The minimum motif length was set to 5 bp and the maximum motif length to 25 bp. The location of these motifs in the ChIP-Seq peaks was determined with FIMO (which is part of the MEME Suite [62]). The GC content along the ChIP-Seq peaks was determined with a sliding 25 bp window (step size 5 bp) and averaging the GC content for that window in all ChIP-Seq peaks. To plot the location of the conserved motifs, the peaks were first divided into bins of 20 bp. Next, the density of the motifs along the ChIP-Seq peaks was determined for each bin by dividing the number of motifs in that bin (in all ChIP-Seq peaks) by the total number of ChIP-Seq peaks.
Functional promoter analysis.
Several lengths (approximately 100 bp, 200 bp, 300 bp, and 700 bp) of the promoter (defined here as the region located 5′ of the predicted translation start site) of gene lpmA (proteinID 1190128) were analyzed for their ability to drive expression of the gene encoding the red fluorescent protein dTomato (Text S1 and Table S5). The promoters were amplified from H4-8 genomic DNA. The gene encoding the red fluorescent protein dTomato (63) was amplified from plasmid pRO151 (64). A motif in the 300 bp promoter was changed from CGGACCG to ATTAAAT by site directed mutagenesis. Protoplasts of strain H4-8b were transformed with these dTomato reporter constructs, as previously described (46). Nourseothricin-resistant transformants were selected for further analysis under the fluorescence microscope (Text S1).
Data availability.
All genome assemblies and annotations can be interactively accessed through the JGI fungal genome portal MycoCosm at http://mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov. The data are also deposited in DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the following accessions numbers ADMJ02000000 for S. commune H4-8 (version Schco3), JAIQYW010000000 for S. commune TattoneD (version Schco_TatD_1), and JAIQUK010000000 for S. commune LoenenD (version Schco_LoeD_1).
The RNA Sequencing reads have been deposited in the NCBI Short Read Archive under project IDs SRP048482 (strain H4-8 on various carbon sources) and SRP053470 (strain TattoneD on various carbon sources) and PRJNA828126 (wild type and Δroc1, grown on either glucose or cellulose). The ChIP-Seq reads have been deposited in the NCBI Short Read Archive under bioproject ID PRJNA726034.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work conducted by the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute, a DOE Office of Science User Facility, is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231. This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (grant agreement number 716132). We thank Utrecht Sequencing Facility for providing sequencing service and data for the ChIP-Seq analysis. Utrecht Sequencing Facility is subsidized by the University Medical Center Utrecht, Hubrecht Institute, Utrecht University and The Netherlands X-omics Initiative (NWO project 184.034.019). We thank Steven Ahrendt for technical assistance with data submission to GenBank.
Performed experiments and analyzed the data: I.M.M., P.J.V., I.D.V., B.B., A.C., C.D., H.L., A.L., H.P., M.B.P.S., M.T., A.T., J.S., J.G., L.G.G., R.A.O. Supervised/coordinated experiments: K.B., J.G., L.G.G., I.G.C., H.A.B.W., I.V.G., R.A.O. Wrote the manuscript: I.M.M., P.J.V., I.D.V., R.A.O. Provided funding: I.G.C., H.A.B.W., I.V.G., R.A.O. Conceived the project: R.A.O. Read and approved the manuscript: all authors.
We have no competing interests to report.
Contributor Information
Robin A. Ohm, Email: r.a.ohm@uu.nl.
B. Gillian Turgeon, Cornell University
REFERENCES
- 1.Floudas D, Binder M, Riley R, Barry K, Blanchette RA, Henrissat B, Martínez AT, Otillar R, Spatafora JW, Yadav JS, Aerts A, Benoit I, Boyd A, Carlson A, Copeland A, Coutinho PM, de Vries RP, Ferreira P, Findley K, Foster B, Gaskell J, Glotzer D, Górecki P, Heitman J, Hesse C, Hori C, Igarashi K, Jurgens JA, Kallen N, Kersten P, Kohler A, Kües U, Kumar TKA, Kuo A, LaButti K, Larrondo LF, Lindquist E, Ling A, Lombard V, Lucas S, Lundell T, Martin R, McLaughlin DJ, Morgenstern I, Morin E, Murat C, Nagy LG, Nolan M, Ohm RA, Patyshakuliyeva A, et al. 2012. The Paleozoic origin of enzymatic lignin decomposition reconstructed from 31 fungal genomes. Science 336:1715–1719. doi: 10.1126/science.1221748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pauly M, Keegstra K. 2010. Plant cell wall polymers as precursors for biofuels. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:304–311. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2009.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zoghlami A, Paës G. 2019. Lignocellulosic Biomass: understanding Recalcitrance and Predicting Hydrolysis. Front Chem 7:874. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Popper ZA, Michel G, Hervé C, Domozych DS, Willats WGT, Tuohy MG, Kloareg B, Stengel DB. 2011. Evolution and diversity of plant cell walls: from algae to flowering plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:567–590. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Levasseur A, Drula E, Lombard V, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B. 2013. Expansion of the enzymatic repertoire of the CAZy database to integrate auxiliary redox enzymes. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:41. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-6-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lombard V, Golaconda Ramulu H, Drula E, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B. 2014. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D490–D495. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Riley R, Salamov AA, Brown DW, Nagy LG, Floudas D, Held BW, Levasseur A, Lombard V, Morin E, Otillar R, Lindquist EA, Sun H, LaButti KM, Schmutz J, Jabbour D, Luo H, Baker SE, Pisabarro AG, Walton JD, Blanchette RA, Henrissat B, Martin F, Cullen D, Hibbett DS, Grigoriev IV. 2014. Extensive sampling of basidiomycete genomes demonstrates inadequacy of the white-rot/brown-rot paradigm for wood decay fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:9923–9928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1400592111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ohm RA, Riley R, Salamov A, Min B, Choi I-G, Grigoriev IV. 2014. Genomics of wood-degrading fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 72:82–90. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2014.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Almási É, Sahu N, Krizsán K, Bálint B, Kovács GM, Kiss B, Cseklye J, Drula E, Henrissat B, Nagy I, Chovatia M, Adam C, LaButti K, Lipzen A, Riley R, Grigoriev IV, Nagy LG. 2019. Comparative genomics reveals unique wood‐decay strategies and fruiting body development in the Schizophyllaceae. New Phytol 224:902–915. doi: 10.1111/nph.16032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang J, Silverstein KAT, Castaño JD, Figueroa M, Schilling JS. 2019. Gene regulation shifts shed light on fungal adaption in plant biomass decomposers. mBio 10:e02176-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02176-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Strauss J, Horvath HK, Abdallah BM, Kindermann J, Mach RL, Kubicek CP. 1999. The function of CreA, the carbon catabolite repressor of Aspergillus nidulans, is regulated at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional level. Mol Microbiol 32:169–178. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Portnoy T, Margeot A, Linke R, Atanasova L, Fekete E, Sándor E, Hartl L, Karaffa L, Druzhinina IS, Seiboth B, Le Crom S, Kubicek CP. 2011. The CRE1 carbon catabolite repressor of the fungus Trichoderma reesei: a master regulator of carbon assimilation. BMC Genomics 12:269. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Todd RB, Zhou M, Ohm RA, Leeggangers HA, Visser L, de Vries RP. 2014. Prevalence of transcription factors in ascomycete and basidiomycete fungi. BMC Genomics 15:214. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yoav S, Salame TM, Feldman D, Levinson D, Ioelovich M, Morag E, Yarden O, Bayer EA, Hadar Y. 2018. Effects of cre1 modification in the white-rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus PC9: altering substrate preference during biological pretreatment. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:212. doi: 10.1186/s13068-018-1209-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.van Peij NNME, Gielkens MMC, de Vries RP, Visser J, de Graaff LH. 1998. The transcriptional activator XlnR regulates both xylanolytic and endoglucanase gene expression in Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3615–3619. doi: 10.1128/AEM.64.10.3615-3619.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stricker AR, Grosstessner-Hain K, Würleitner E, Mach RL. 2006. Xyr1 (xylanase regulator 1) regulates both the hydrolytic enzyme system and -xylose metabolism in Hypocrea jecorina. Eukaryot Cell 5:2128–2137. doi: 10.1128/EC.00211-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Benocci T, Aguilar-Pontes MV, Zhou M, Seiboth B, de Vries RP. 2017. Regulators of plant biomass degradation in ascomycetous fungi. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:152. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0841-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Craig JP, Coradetti ST, Starr TL, Glass NL. 2015. Direct target network of the Neurospora crassa plant cell wall deconstruction regulators CLR-1, CLR-2, and XLR-1. mBio 6:e01452-15–e01415. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01452-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Aro N, Ilmén M, Saloheimo A, Penttilä M. 2003. ACEI of Trichoderma reesei is a repressor of cellulase and xylanase expression. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:56–65. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.1.56-65.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vonk PJ, Escobar N, Wösten HAB, Lugones LG, Ohm RA. 2019. High-throughput targeted gene deletion in the model mushroom Schizophyllum commune using pre-assembled Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Sci Rep 9:7632. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44133-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.de Jong JF, Ohm RA, de Bekker C, Wösten HAB, Lugones LG. 2010. Inactivation of ku80 in the mushroom-forming fungus Schizophyllum commune increases the relative incidence of homologous recombination. FEMS Microbiol Lett 310:91–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vonk PJ, Ohm RA. 2021. H3K4me2 ChIP-Seq reveals the epigenetic landscape during mushroom formation and novel developmental regulators of Schizophyllum commune. Sci Rep 11:8178. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87635-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Floudas D, Held BW, Riley R, Nagy LG, Koehler G, Ransdell AS, Younus H, Chow J, Chiniquy J, Lipzen A, Tritt A, Sun H, Haridas S, LaButti K, Ohm RA, Kües U, Blanchette RA, Grigoriev IV, Minto RE, Hibbett DS. 2015. Evolution of novel wood decay mechanisms in Agaricales revealed by the genome sequences of Fistulina hepatica and Cylindrobasidium torrendii. Fungal Genet Biol 76:78–92. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2015.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ohm RA, de Jong JF, Lugones LG, Aerts A, Kothe E, Stajich JE, de Vries RP, Record E, Levasseur A, Baker SE, Bartholomew KA, Coutinho PM, Erdmann S, Fowler TJ, Gathman AC, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Knabe N, Kües U, Lilly WW, Lindquist E, Lucas S, Magnuson JK, Piumi F, Raudaskoski M, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Schwarze FWMR, vanKuyk PA, Horton JS, Grigoriev IV, Wösten HAB. 2010. Genome sequence of the model mushroom Schizophyllum commune. Nat Biotechnol 28:957–963. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ohm RA, Feau N, Henrissat B, Schoch CL, Horwitz BA, Barry KW, Condon BJ, Copeland AC, Dhillon B, Glaser F, Hesse CN, Kosti I, LaButti K, Lindquist EA, Lucas S, Salamov AA, Bradshaw RE, Ciuffetti L, Hamelin RC, Kema GHJ, Lawrence C, Scott JA, Spatafora JW, Turgeon BG, de Wit PJGM, Zhong S, Goodwin SB, Grigoriev IV. 2012. diverse lifestyles and strategies of plant pathogenesis encoded in the genomes of eighteen dothideomycetes fungi. PLoS Pathog 8:e1003037. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Traven A, Jelicic B, Sopta M. 2006. Yeast Gal4: a transcriptional paradigm revisited. EMBO Rep 7:496–499. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.van Peij NNME, Visser J, de Graaff LH. 1998. Isolation and analysis of xln R, encoding a transcriptional activator co-ordinating xylanolytic expression in Aspergillus niger. Mol Microbiol 27:131–142. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Morin E, Kohler A, Baker AR, Foulongne-Oriol M, Lombard V, Nagy LG, Ohm RA, Patyshakuliyeva A, Brun A, Aerts AL, Bailey AM, Billette C, Coutinho PM, Deakin G, Doddapaneni H, Floudas D, Grimwood J, Hildén K, Kües U, Labutti KM, Lapidus A, Lindquist EA, Lucas SM, Murat C, Riley RW, Salamov AA, Schmutz J, Subramanian V, Wösten HAB, Xu J, Eastwood DC, Foster GD, Sonnenberg ASM, Cullen D, de Vries RP, Lundell T, Hibbett DS, Henrissat B, Burton KS, Kerrigan RW, Challen MP, Grigoriev IV, Martin F. 2012. Genome sequence of the button mushroom Agaricus bisporus reveals mechanisms governing adaptation to a humic-rich ecological niche. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:17501–17506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206847109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Daly P, Peng M, Falco M.d, Lipzen A, Wang M, Ng V, Grigoriev IV, Tsang A, Mäkelä MR, de Vries RP. 2019. Glucose-mediated repression of plant biomass utilization in the white-rot fungus Dichomitus squalens. Appl Environ Microbiol 85. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01828-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Villares A, Moreau C, Bennati-Granier C, Garajova S, Foucat L, Falourd X, Saake B, Berrin J-G, Cathala B. 2017. Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases disrupt the cellulose fibers structure. Sci Rep 7:40262. doi: 10.1038/srep40262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Henrissat B, Davies G. 1997. Structural and sequence-based classification of glycoside hydrolases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 7:637–644. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(97)80072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shallom D, Leon M, Bravman T, Ben-David A, Zaide G, Belakhov V, Shoham G, Schomburg D, Baasov T, Shoham Y. 2005. Biochemical characterization and identification of the catalytic residues of a family 43 beta-D-xylosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus T-6. Biochemistry 44:387–397. doi: 10.1021/bi048059w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.The CAZypedia Consortium. 2018. Ten years of CAZypedia: a living encyclopedia of carbohydrate-active enzymes. Glycobiology 28:3–8. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwx089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Baranova MA, Logacheva MD, Penin AA, Seplyarskiy VB, Safonova YY, Naumenko SA, Klepikova AV, Gerasimov ES, Bazykin GA, James TY, Kondrashov AS. 2015. Extraordinary genetic diversity in a wood decay mushroom. Mol Biol Evol 32:2775–2783. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kohler A, Kuo A, Nagy LG, Morin E, Barry KW, Buscot F, Canbäck B, Choi C, Cichocki N, Clum A, Colpaert J, Copeland A, Costa MD, Doré J, Floudas D, Gay G, Girlanda M, Henrissat B, Herrmann S, Hess J, Högberg N, Johansson T, Khouja H-R, LaButti K, Lahrmann U, Levasseur A, Lindquist EA, Lipzen A, Marmeisse R, Martino E, Murat C, Ngan CY, Nehls U, Plett JM, Pringle A, Ohm RA, Perotto S, Peter M, Riley R, Rineau F, Ruytinx J, Salamov A, Shah F, Sun H, Tarkka M, Tritt A, Veneault-Fourrey C, Zuccaro A, Tunlid A, Grigoriev IV, Mycorrhizal Genomics Initiative Consortium, et al. 2015. Convergent losses of decay mechanisms and rapid turnover of symbiosis genes in mycorrhizal mutualists. Nat Genet 47:410–415. doi: 10.1038/ng.3223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Martin F, Aerts A, Ahrén D, Brun A, Danchin EGJ, Duchaussoy F, Gibon J, Kohler A, Lindquist E, Pereda V, Salamov A, Shapiro HJ, Wuyts J, Blaudez D, Buée M, Brokstein P, Canbäck B, Cohen D, Courty PE, Coutinho PM, Delaruelle C, Detter JC, Deveau A, DiFazio S, Duplessis S, Fraissinet-Tachet L, Lucic E, Frey-Klett P, Fourrey C, Feussner I, Gay G, Grimwood J, Hoegger PJ, Jain P, Kilaru S, Labbé J, Lin YC, Legué V, Le Tacon F, Marmeisse R, Melayah D, Montanini B, Muratet M, Nehls U, Niculita-Hirzel H, Oudot-Le Secq MP, Peter M, Quesneville H, Rajashekar B, Reich M, et al. 2008. The genome of Laccaria bicolor provides insights into mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nature 452:88–92. doi: 10.1038/nature06556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Todd RB, Andrianopoulos A. 1997. Evolution of a fungal regulatory gene family: the Zn(II)2Cys6 binuclear cluster DNA binding motif. Fungal Genet Biol 21:388–405. doi: 10.1006/fgbi.1997.0993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fu YH, Feng B, Evans S, Marzluf GA. 1995. Sequence-specific DNA binding by NIT4, the pathway-specific regulatory protein that mediates nitrate induction in Neurospora. Mol Microbiol 15:935–942. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lundin M, Nehlin JO, Ronne H. 1994. Importance of a flanking AT-rich region in target site recognition by the GC box-binding zinc finger protein MIG1. Mol Cell Biol 14:1979–1985. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1979-1985.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Steffens EK, Becker K, Krevet S, Teichert I, Kück U. 2016. Transcription factor PRO1 targets genes encoding conserved components of fungal developmental signaling pathways. Mol Microbiol 102:792–809. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kong Q, Chang P-K, Li C, Hu Z, Zheng M, Sun Q, Shan S. 2020. Identification of AflR Binding Sites in the Genome of Aspergillus flavus by ChIP-Seq. JoF 6:52. doi: 10.3390/jof6020052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.de Castro PA, Chen C, de Almeida RSC, Freitas FZ, Bertolini MC, Morais ER, Brown NA, Ramalho LNZ, Hagiwara D, Mitchell TK, Goldman GH. 2014. ChIP-seq reveals a role for CrzA in the Aspergillus fumigatus high-osmolarity glycerol response (HOG) signalling pathway. Mol Microbiol 94:655–674. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fan G, Zheng H, Zhang K, Devi Ganeshan V, Opiyo SO, Liu D, Li M, Li G, Mitchell TK, Yun Y, Wang Z, Lu G. 2020. FgHtf1 regulates global gene expression towards aerial mycelium and conidiophore formation in the cereal fungal pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Appl Environ Microbiol 86:e03024-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03024-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ohm RA, de Jong JF, de Bekker C, Wösten HAB, Lugones LG. 2011. Transcription factor genes of Schizophyllum commune involved in regulation of mushroom formation. Mol Microbiol 81:1433–1445. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pelkmans JF, Patil MB, Gehrmann T, Reinders MJT, Wösten HAB, Lugones LG. 2017. Transcription factors of Schizophyllum commune involved in mushroom formation and modulation of vegetative growth. Sci Rep 7:1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00483-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.van Peer AF, de Bekker C, Vinck A, Wösten HAB, Lugones LG. 2009. Phleomycin increases transformation efficiency and promotes single integrations in Schizophyllum commune. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1243–1247. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02162-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Dons JJM, de Vries OMH, Wessels JGH. 1979. Characterization of the genome of the basidiomycete Schizophyllum commune. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 563:100–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90011-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zerbino DR, Birney E. 2008. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res 18:821–829. doi: 10.1101/gr.074492.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gnerre S, MacCallum I, Przybylski D, Ribeiro FJ, Burton JN, Walker BJ, Sharpe T, Hall G, Shea TP, Sykes S, Berlin AM, Aird D, Costello M, Daza R, Williams L, Nicol R, Gnirke A, Nusbaum C, Lander ES, Jaffe DB. 2011. High-quality draft assemblies of mammalian genomes from massively parallel sequence data. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:1513–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017351108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Grigoriev IV, Martinez DA, Salamov AA. 2006. Fungal genomic annotation, p 123–142. In Arora DK, Berka RM, Singh GB (ed), Applied Mycology and BioTechnology. Elsevier. doi: 10.1016/S1874-5334(06)80008-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Grigoriev IV, Nikitin R, Haridas S, Kuo A, Ohm R, Otillar R, Riley R, Salamov A, Zhao X, Korzeniewski F, Smirnova T, Nordberg H, Dubchak I, Shabalov I. 2014. MycoCosm portal: gearing up for 1000 fungal genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D699–D704. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kurtz S, Phillippy A, Delcher AL, Smoot M, Shumway M, Antonescu C, Salzberg SL. 2004. Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol 5:R12. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-2-r12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL. 2015. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods 12:357–360. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L. 2010. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol 28:511–515. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.El-Gebali S, Mistry J, Bateman A, Eddy SR, Luciani A, Potter SC, Qureshi M, Richardson LJ, Salazar GA, Smart A, Sonnhammer ELL, Hirsh L, Paladin L, Piovesan D, Tosatto SCE, Finn RD. 2019. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D427–D432. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva E.v, Zdobnov EM. 2015. BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 31:3210–3212. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Xiao Z, Storms R, Tsang A. 2004. Microplate-based filter paper assay to measure total cellulase activity. Biotechnol Bioeng 88:832–837. doi: 10.1002/bit.20286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Soyer JL, Möller M, Schotanus K, Connolly LR, Galazka JM, Freitag M, Stukenbrock EH. 2015. Chromatin analyses of Zymoseptoria tritici: methods for chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq). Fungal Genet Biol 79:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2015.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Johnson DS, Mortazavi A, Myers RM, Wold B. 2007. Genome-Wide Mapping of in Vivo Protein-DNA Interactions. Science 316:1497–1502. doi: 10.1126/science.1141319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Langmead B, Salzberg SL. 2012. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Feng J, Liu T, Qin B, Zhang Y, Liu XS. 2012. Identifying ChIP-seq enrichment using MACS. Nat Protoc 7:1728–1740. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS. 2009. MEME Suite: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W202–W208. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Shaner NC, Campbell RE, Steinbach PA, Giepmans BNG, Palmer AE, Tsien RY. 2004. Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 22:1567–1572. doi: 10.1038/nbt1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ohm RA, Aerts D, Wösten HAB, Lugones LG. 2013. The blue light receptor complex WC-1/2 of Schizophyllum commune is involved in mushroom formation and protection against phototoxicity. Environ Microbiol 15:943–955. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Statistics of the assemblies and gene predictions of strains H4-8, TattoneD and LoenenD. For strain H4-8 an updated assembly and annotation were generated (version Schco3). Strains TattoneD and LoenenD were newly sequenced for this study. Download Table S1, XLSX file, 0.01 MB (11.7KB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Supplemental materials and methods and supplementary results. Download Text S1, DOCX file, 0.2 MB (223.5KB, docx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
The number of predicted genes per strain and their conservation. The conservation was determined with Orthofinder. Genes in an orthogroup that had members from all three strains were labeled as ‘core’, genes in orthogroups that had members from two strains were labeled as ‘two strains’, and the remaining genes were labeled as ‘strain-specific’. Download FIG S1, TIF file, 0.8 MB (799.5KB, tif) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Expression values of genes (in RPKM) and enrichment of functional annotation terms in sets of differentially expressed genes. Download Table S2, XLSX file, 8.87 MB (8.9MB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
(A) Gene tree of Roc1 orthologs and more distant homologs. The locations of the PFAM domains PF00172 (Zn2Cys6 binuclear cluster domain) and PF04082 (Fungal specific transcription factor domain) are indicated in blue and green, respectively. The location of a conserved Roc1 HMM domain is indicated in red. A protein is indicated as a Roc1 ortholog if the blue, green, and red domains are present, whereas other proteins in this tree are considered more distant homologs. Branch lengths between the Roc1 orthologs are generally considerably shorter than the branch lengths between the more distant homologs. Roc1 orthologs are only found in Agaricomycetes. The first part of the protein IDs represents a species code (see Table S3 for the full species name). (B) Species tree of 140 fungal species. The species with a putative Roc1 ortholog are indicated in green. Roc1 is only conserved in the Agaricomycetes. See Table S3 and (A) for the protein IDs of the Roc1 orthologs. Download FIG S2, PDF file, 0.5 MB (481.5KB, pdf) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
The genomes of species used in this study and their Roc1 orthologs. The previously published genome and genes were obtained from the indicated publications. The indicated phylogeny is based on the NCBI taxonomy database. Download Table S3, XLSX file, 0.02 MB (25.6KB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Western Blot confirms the expression of the HA-tagged Roc1 protein in Δroc1 of S. commune. The wild type (i.e., reference strain H4-8) and Δroc1::roc1-HA (i.e., the deletion strain complemented with the gene encoding the HA-tagged Roc1) were grown on cellulose or glucose. The predicted size of the HA-tagged Roc1 protein is 78.9 kDa. A band of this size is visible in the complemented deletion strain when grown on cellulose, but not when grown on glucose (the height of the band is indicated with a red arrow). As expected, this band is not found in the wild-type strain under either condition. Download FIG S3, TIF file, 1.2 MB (1.2MB, tif) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Locations of the peaks identified in the ChIP-Seq analysis. These peaks can be regarded as Roc1 binding sites. The genes associated with these peaks, as well as information about their annotation and expression profile are indicated. Moreover, the enrichment of functional annotation terms among genes associated with a Roc1 binding site is indicated. Download Table S4, XLSX file, 1.2 MB (1.3MB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Primers used in this study. Download Table S5, XLSX file, 0.01 MB (10.8KB, xlsx) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
(A) GC content along the length of the 1427 ChIP-Seq peaks. Around the midpoint of the peaks there is an increase of the GC content, which indicates that the Roc1 binding motif is GC-rich. (B) Fluorescence of dTomato driven by the 700 bp promoter of lpmA. When grown on glucose, no fluorescence is observed. In contract, when grown on cellulose strong fluorescence is observed, in concordance with the expression profile of lpmA. When grown on a mix of glucose and cellulose, no fluorescence is observed, indicating the carbon catabolite repression overrules the induction by cellulose. In the reference strain H4-8, no fluorescence is observed under any condition. (C) Alignment of the orthologs of lpmA in S. commune strains H4-8, TattoneD and LoenenD. The genomic sequence includes the gene (with introns) and the promoter (approximately 325 bp upstream of the start codon). The putative Roc1 binding site (pink) is conserved in each of these strains, despite the 12% sequence diversity in the promoter part of the alignment (40 of 330 positions in the alignment display differences between the strains). The TATA box (black), start codon (green) and stop codon (red) are indicated. Download FIG S4, JPG file, 2.3 MB (2.4MB, jpg) .
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Data Availability Statement
All genome assemblies and annotations can be interactively accessed through the JGI fungal genome portal MycoCosm at http://mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov. The data are also deposited in DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the following accessions numbers ADMJ02000000 for S. commune H4-8 (version Schco3), JAIQYW010000000 for S. commune TattoneD (version Schco_TatD_1), and JAIQUK010000000 for S. commune LoenenD (version Schco_LoeD_1).
The RNA Sequencing reads have been deposited in the NCBI Short Read Archive under project IDs SRP048482 (strain H4-8 on various carbon sources) and SRP053470 (strain TattoneD on various carbon sources) and PRJNA828126 (wild type and Δroc1, grown on either glucose or cellulose). The ChIP-Seq reads have been deposited in the NCBI Short Read Archive under bioproject ID PRJNA726034.