Abstract
Tissues and organs are composed of distinct cell types that must operate in concert to perform physiological functions. Efforts to create high-dimensional biomarker catalogs of these cells have been largely based on single-cell sequencing approaches, which lack the spatial context required to understand critical cellular communication and correlated structural organization. To probe in situ biology with sufficient depth, several multiplexed protein imaging methods have been recently developed. Though these technologies differ in strategy and mode of immunolabeling and detection tags, they commonly utilize antibodies directed against protein biomarkers to provide detailed spatial and functional maps of complex tissues. As these promising antibody-based multiplexing approaches become more widely adopted, new frameworks and considerations are critical for training future users, generating molecular tools, validating antibody panels, and harmonizing datasets. In this Perspective, we provide essential resources, key considerations for obtaining robust and reproducible imaging data, and specialized knowledge from domain experts and technology developers.
Mammalian tissues comprise a diverse array of cells that possess unique functional attributes and activation states. Many existing methods—immunohistochemistry (IHC)1, immunofluorescence (IF)2, transcriptomics3, mass spectrometry4–6, and cytometry7,8—capture this heterogeneity and complexity by studying tissues and organ systems at single-cell resolution. All of these approaches represent a trade-off between spatial information and coverage depth. Flow- or droplet-based single-cell methods, such as multiparameter flow and mass cytometry7,8, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq)9, and cellular indexing of transcriptomes and epitopes by sequencing (CITE-seq)10 can define unique cell subsets with incredible granularity. These technologies have greatly expanded our understanding of cell types and states and offer new ways for multiparametric stratification of samples or patients while identifying potential targets for clinical research. However, they typically require tissue dissociation and do not provide a spatial context for cell-to-cell interactions present in normal tissues and altered in disease11–13. Furthermore, these methods fail to retrieve all cell types owing to a combination of factors including, but not limited to, differences in dissociation procedures for individual cell types within a tissue, cell loss during sorting, and low sampling owing to cost or sequencing depth14. While recent imaging- or sequencing-based methods probe the spatial transcriptome at single-cell resolution15,16, in situ protein detection overwhelmingly relies on antibodies. Hence antibodies have been at the core of several new multiplexing approaches that allow detection of spatial cellular organization and composition of tissues at the protein level17,18 (Supplementary Table 1).
These multiplexed imaging technologies enable detailed interrogation and characterization of cell types of interest—lymphocytes, stromal cells, structural markers—in human tissues beyond the spectral limitations of conventional fluorescence microscopy (typically <5 targets). As the number of protein biomarkers detected via multiplexing increases (typically >10–50 parameters) (Fig. 1a), the assays become increasingly more complex. Therefore, additional effort is required for multiplexed panel design, antibody validation, and careful data acquisition to avoid artifacts while maintaining reproducibility. Future analyses will require robust workflows that yield high-quality images and the computational tools needed to optimally mine these data. Here, we provide a summary of several multiplexed antibody-based imaging approaches and outline strategies for sample and custom reagent preparation, rigorous antibody validation, and multiplex panel building. We then discuss unique challenges surrounding the processing, analysis, and storage of imaging data. Finally, we share a perspective on the future of the field that highlights the utility of these methods and provides practical guidelines for widespread adoption for the methods discussed here.
Fig. 1 |. obtaining high-content imaging data using a wide range of multiplexed antibody-based imaging platforms.
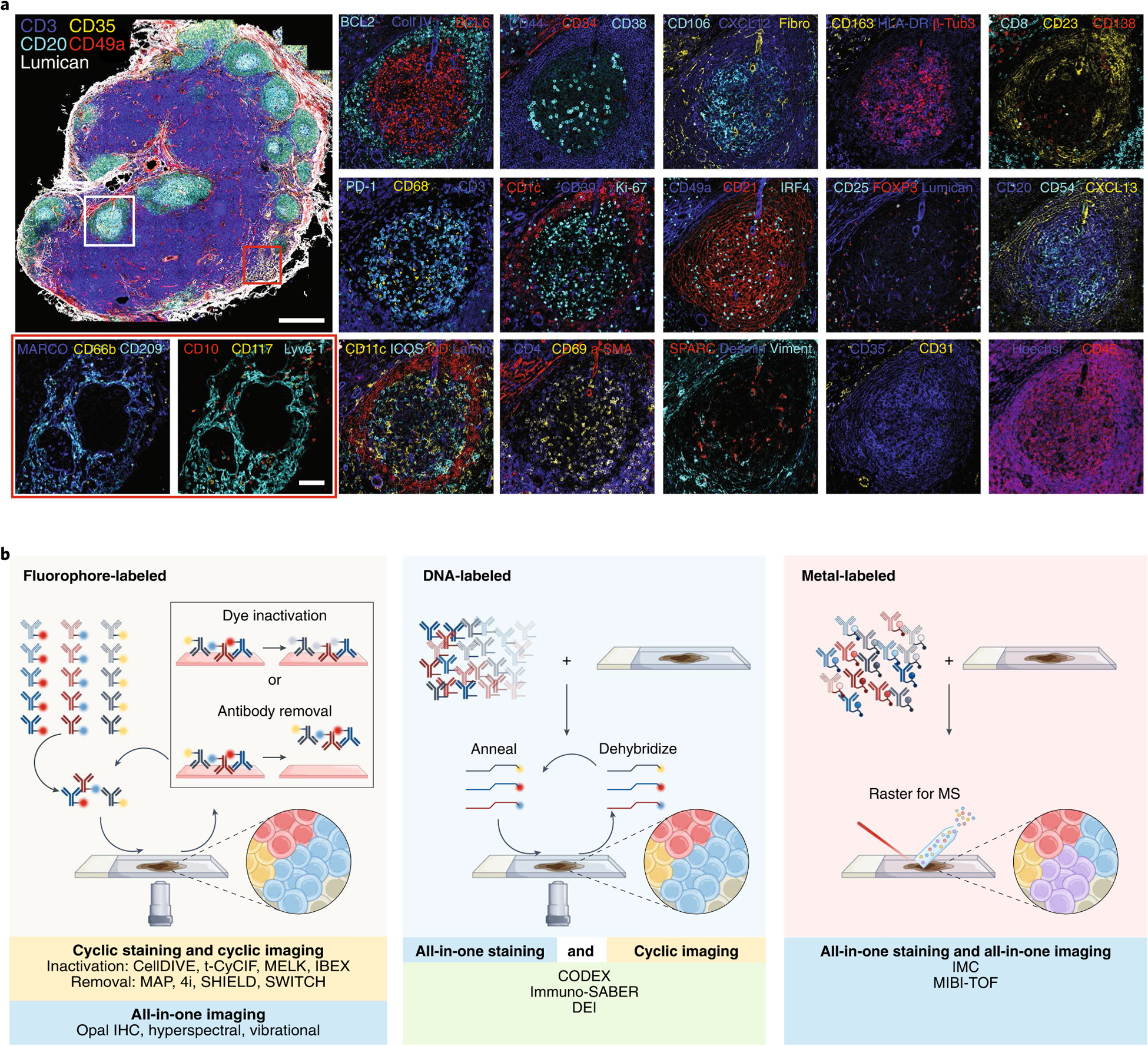
a, Fifty-plex confocal images of a human mesenteric lymph node obtained by the IBEX method. Two to four marker overlays for two regions (germinal center, white rectangle and medullary cords, red rectangle) are shown in higher zoom. Scale bars, 500 and 100 μm, for the overview and zoom-in images, respectively. β-Tubulin 3 (β-Tub3), collagen IV (Coll IV), fibronectin (Fibro), laminin (Lamin), and vimentin (Viment) (original lymph node dataset from Radtke et al.21). b, Graphical representation of the main approaches for multiplexed antibody-based imaging. Antibodies are commonly labeled with metals, fluorophores, or DNA oligonucleotides for complementary binding of fluorescently tagged DNA probes.
Multiplexed antibody-based imaging methods
Multiplexed antibody-based imaging methods can be classified on the basis of the mode of antibody tagging (such as metal tag, fluorophore, DNA oligonucleotide barcode, or enzyme) and detection modality (for example mass spectrometry, spectroscopy, fluorescence, or chromogen deposition), with each approach providing distinct advantages and disadvantages (Supplementary Table 1 and Fig. 1b). Detailed descriptions of these methodologies have been discussed elsewhere11,19,20, thus we focus on the practical aspects of highly multiplexed imaging experiments. Of these antibody-based imaging modalities, fluorescence-based multiplexed imaging is the most established given the wide availability of reagents and imaging systems (Fig. 1b). Typically, fluorescence experiments are limited to visualizing 4–7 antigens within a single imaging cycle owing to spectral overlap of selected fluorophores and availability of labeled commercial antibodies. Hyperspectral methods enable data collection beyond this limit, achieving single-pass multiplexed imaging of up to 21 channels by utilizing fluorophores with diverse excitation and emission spectra, advanced instruments, and methods that enable compensation for spectral overlap14 (Supplementary Table 1).
Even higher-dimensional datasets can be obtained through an iterative, multistep process (or cycle) that includes (Fig. 1b) (1) immunolabeling with fluorescent or oligonucleotide-barcoded antibodies, (2) direct image acquisition (fluorescent antibody-stained material), or reaction with fluorescent complementary oligonucleotides for a subset of the tagged antibodies, followed by image acquisition, and (3) fluorophore inactivation or removal of antibodies or hybridized oligonucleotide probes. This process circumvents spectral overlap by removing fluorescent signals after each cycle. Using iterative staining, imaging, and bleaching/antibody-removal methods, such as tissue-based cyclic immunofluorescence (t-CyCIF), iterative indirect immunofluorescence imaging (4i), iterative bleaching extends multiplexity (IBEX), multiepitope-ligand cartography (MELC), and multiplexed immunofluorescence (MxIF, Cell DIVE), it is possible to detect >60 targets in the same tissue section using off-the-shelf antibodies with fluorescent secondaries or fluorescently conjugated primaries21–28. Critical considerations for the implementation of such methods are the extended experimental time due to lengthy antibody incubation steps, potential for epitope loss, tissue degradation, and incomplete fluorophore inactivation over successive cycles. For these reasons, it is important to include appropriate controls as outlined here and described previously22–24,29.
Alternative methods that rely on DNA-barcoding of antibodies, such as DNA exchange imaging (DEI)30, immunostaining with signal amplification by exchange reaction (immuno-SABER)31, and co-detection by indexing (CODEX)12,32,33, allow one-step immunostaining and fast sequential barcode readout through rapid binding/unbinding of fluorescent oligonucleotides. Although these methods can detect a high number of target molecules in a wide range of tissues, their utility is limited in samples in which harsh fixation has reduced epitope retention or tissues with high autofluorescence. Amplification methods such as Immuno-SABER31, immunosignal hybridization chain reaction34,35, and enzymatic (for example horseradish peroxidase36) or tyramide signal amplification (TSA)1 approaches can be used to improve signal-to-noise while increasing the detection of low-abundance epitopes. Until recently, TSA methods such as Opal IHC1 have been restricted to the simultaneous detection of 6–8 markers11 as tyramide-linked fluorophores remain bound to the tissue despite rounds of antibody removal and amplification. Nonetheless, it has recently been shown that the fluorophore limitations of Opal IHC could be extended using lithium borohydride to eliminate signal from several Opal dyes, providing a means for the capture of highly multiplexed images in heavily fixed tissues21.
An alternative to fluorescence-based approaches is mass spectrometry (MS)-based methods that incorporate ionizable metal mass tags (Fig. 1b). These technologies enable visualization of >40 biomarkers in a tissue section using a single master mix of metal-conjugated primary antibodies and do not require antibody staining/removal cycles. The two most common technologies are multiplex ion beam imaging (MIBI)37 and imaging mass cytometry (IMC)38, which differ by the use of an ion beam or laser, respectively, for tag ionization. The major benefit of these MS-based technologies is the ability to detect and resolve dozens of metal-isotope-labeled antibodies simultaneously, aptly named ‘all in one’. The metal ion barcodes possess low background signal by circumventing autofluorescence and incorporating high instrumental mass-resolving power. Unlike other multiplexed approaches, samples must be vacuum stable, and antibody labels cannot be amplified. However, the limit of detection of MS systems is on the order of attomoles. The availability of bovine serum albumin (BSA)-free antibody formulations is a limitation shared with other imaging workflows requiring custom reagent creation, for example chelation or fluorophore conjugation. An additional potential barrier associated with expanding metal-tagged antibody panels is access to sufficient amounts of isotopically pure lanthanide metals. While image acquisition occurs in one cycle, it can be slow when considering large fields of view (~200 px/s or 1 mm2/2 h)39. Finally, to date, the instruments are less operationally stable than conventional fluorescence microscopes and require more specialized staff and environments for effective use.
Other spectroscopy methods that also employ all-in-one data collection include multiplexed vibrational imaging40 using techniques such as stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) or surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Instead of mass barcodes, these methods utilize the enhanced vibrational signatures of fluorophores and specialized modifiers at different wavelengths for multiplexing over 20 targets. Sample preparation for spectroscopic multiplexed imaging is similar to that for fluorescence microscopy and can be performed on various tissue preparations without a vacuum system.
Beyond investigating tissues in two dimensions (2D), recent advances in sample preparation and imaging have enabled exploration of entire tissue volumes (three dimensions, 3D) to allow a deeper understanding of total organ architecture while permitting detailed characterizations of rare cells that are frequently undersampled in thin (5–10 μm) tissue sections41. For instance, chemical clearing methods can be applied to transform intact tissues and organs into robust, transparent samples for future antibody staining and imaging. Importantly, clearing methods must preserve the spatial distribution of proteins and nucleic acids while remaining permeable to fluorescent probes. Several tissue-clearing options can be used, such as: clear lipid-exchanged anatomically rigid imaging/immunostaining-compatible tissue hydrogel (CLARITY), clearing-enhanced 3D (Ce3D), system-wide control of interaction time and kinetics of chemicals (SWITCH), magnified analysis of proteome (MAP), stabilization under harsh conditions via intramolecular epoxide linkages to prevent degradation (SHIELD), entangled link-augmented stretchable tissue-hydrogel (ELAST), and protein retention expansion microscopy (pro-ExM)42–48. After clearing, tissues have been reported to be amenable to antibody staining and subsequent probe removal using either heat, detergents42,44–46, oligo-probe dehybridization, or fluorochrome reduction. This allows the potential for higher multiplexed 3D imaging. Owing to the volume of tissue being analyzed, staining and imaging steps are significantly longer than in conventional histology, although the use of electrophoresis-accelerated antibody transport49,50 and light-sheet microscopy enables whole murine organs to be stained in a day and imaged within hours. Together, these approaches enable rapid and multiplexed 3D interrogation of intact tissues, providing system-scale structural and molecular information.
Initial experimental considerations
When selecting a multiplexed antibody-based workflow to adopt or implement, we suggest following the mantra: ‘begin with the end in mind’. The number of samples, whether multiplexed imaging will be a core focus of the outlined work, available budget, and analytical support are key considerations when choosing an approach for spatial profiling of tissues (Fig. 2a). As discussed above, each multiplexed imaging method has distinct advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, questions about final data requirements, available samples and format, and existing infrastructure must guide the choice of multiplexed imaging method (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Table 1). Similarly, the first and most essential step of creating a multiplexed imaging panel is to determine the scientific questions to be addressed. As all multiplexed imaging modalities share the process of creating and validating multiplexed antibody panels, we focus the majority of our recommendations on creating a validated panel of 10–60 antibodies (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2 |. Considerations for the choice and implementation of multiplexed antibody-based imaging technologies into existing workflows.
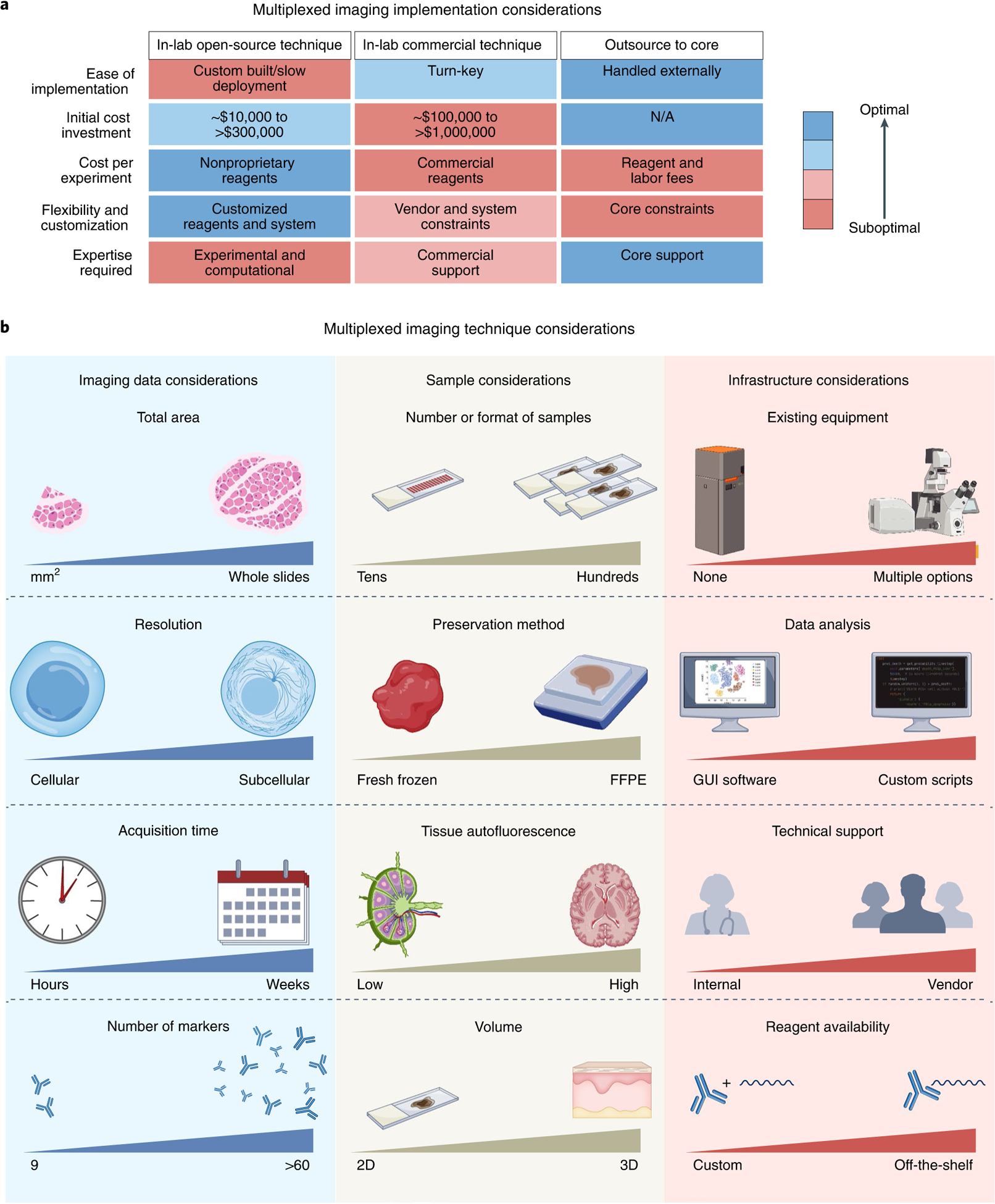
a, Open-source, commercial, and core facility options can be separated by advantages and disadvantages related to ease of implementation, initial cost investment, cost per experiment, flexibility and customization, and the required expertise. b, Several factors govern which method to implement: imaging data requirements (area of tissue needed to be imaged per sample, resolution of final images, time required for imaging each sample, number of markers), sample requirements (number and format of samples, preservation method used for samples, tissue autofluorescence, and whether 2D or 3D volume data are needed), and infrastructure requirements (where existing equipment can be leveraged, level of bioinformatics needed for analysis, technical support, and whether reagents can be purchased or must be customized). Comparisons between different multiplexed imaging techniques are summarized in Supplementary Table 1 and have been described in greater detail in other reviews11,19,20.
Fig. 3 |. Phases of panel development and validation for multiplexed antibody-based imaging assays.
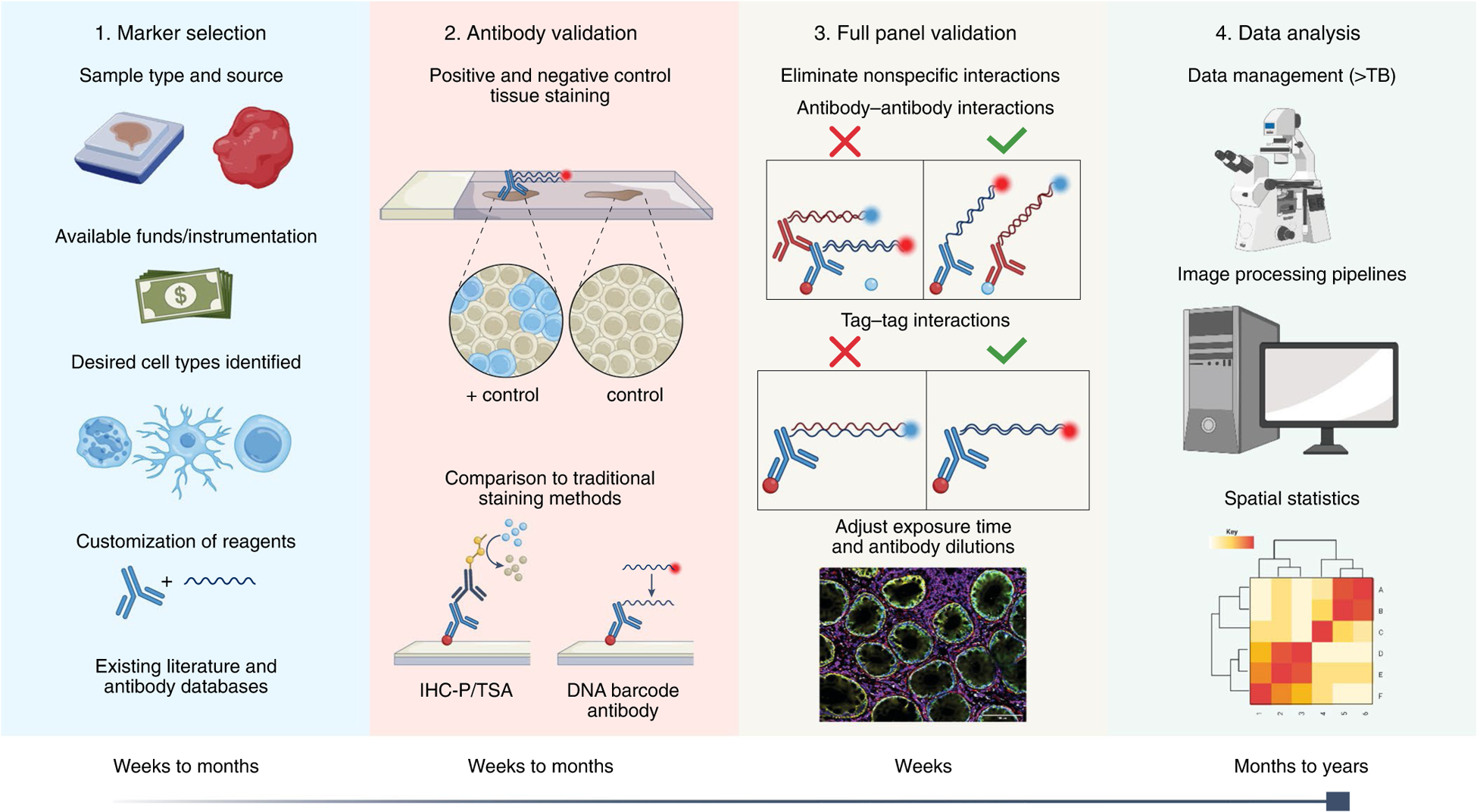
Graphical representation of assay development. In Step 1, markers are selected on the basis of the indicated criteria. Some multiplexing methods require custom reagents (that is, directly conjugated primary antibodies); see Fig. 4 for more details. In Step 2, antibodies are validated individually to verify target specificity. In Step 3, the full panel is validated to ensure that inclusion of additional antibodies does not affect target specificity. In Step 4, data are collected and analyzed.
Tissue handling.
The multiplexed antibody-based imaging methods described here are compatible with a wide range of tissue and sample preparations including fresh frozen (FF), formalin-fixed, or formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE, Fig. 3). When deciding on a sample preparation method, one should consider the preservation of tissue architecture, long-term storage conditions, epitope accessibility, and ease of multiplex tissue imaging. To this end, FFPE workflows preserve overall tissue architecture and cellular morphology better than do most FF methods19,36. Additionally, most clinical or archival tissues are stored as FFPE blocks due to enhanced preservation and compatibility with room-temperature storage. However, FFPE preservation renders many target epitopes inaccessible, increases autofluorescence due to formalin fixation20,51, and frequently requires antigen retrieval52,53. In contrast to single-marker IF/IHC, antigen-retrieval conditions suitable for one epitope may be incompatible with another epitope, requiring different antigen-retrieval methods for distinct molecules, making multiplex panel development increasingly challenging. In contrast, FF tissues overcome the need for antigen retrieval but instead require immediate snap freezing and ultralow temperature storage (<−80 °C) for best tissue preservation54,55. Lastly, a tissue-preservation method employing 1% paraformaldehyde and a detergent has been shown to preserve tissue architecture, minimize tissue autofluorescence by lysing red blood cells, and enable immunolabeling with a large range of antibodies without the need for antigen retrieval in a variety of human and mouse tissues21,56.
Costs.
An overlooked consideration when designing highly multiplexed imaging experiments is the overall cost and time investment, including that for reagents, antibodies, training, panel optimization, image acquisition, and data analysis (Fig. 3). Ultimately, the cost per unique data point and power of contextual multiplexed data can be useful metrics when rationalizing the increased costs described below. For example, whereas a single-plex experiment can cost a few hundred US dollars, a 50-plex panel could cost many thousands of US dollars for an identical number of tissue samples. Several factors contribute to the substantial increase in time and cost of the panel, including the complexity of the panel (for example number of antibodies, specimen type, sample preparation steps), stability of target epitopes over multiple cycles (if applicable), antibody compatibility and performance under unified immunolabeling conditions, and iterative panel design and adjustment for optimal results. Moreover, identifying and obtaining candidate antibodies can take days to weeks and may additionally require modification of primary antibodies with direct tags. In particular, in situ validation can consume weeks or even months for complex panels applied to a new tissue type where each antibody needs to be validated first in single-plex experiments and then assessed for performance within the entire panel. Not all antibody clones are likely to work across all multiplexed technologies, and each multiplexing technology requires sample-specific antibody titration. MS-based platforms are even more expensive, requiring specialized imaging instrumentation and expensive labeling reagents. Beyond raw materials, training requirements vary widely across different assays and methodologies and can dramatically increase costs. More time is invested in panel development in fluorescence-based approaches than in MS-based approaches because of the cyclic nature of these methods. However, as multiplexed methodologies are commercialized and adopted by core facilities, the time, training, and optimization costs will ultimately decrease.
Target selection.
Additionally, it is critical to consider downstream analytical requirements: image registration (for example nuclear labels such as DAPI or Hoechst 33342)57–59, cellular segmentation (for example robust nuclear and membrane stains)12, and unsupervised clustering (for example phenotyping discrete populations using a combination of markers)52,60–62. By considering these requirements, putative markers are suggested to be ranked and categorized as ‘essential’ or ‘desired’, greatly expediting overall panel development. This information, along with the budget and approximate timeline, will determine the number of markers to be included in a multiplexed imaging panel.
Marker selection can be guided by expert knowledge, existing literature, orthogonal datasets, and/or online resources (Supplementary Table 2). After establishing a target list of molecules, evaluating and purchasing appropriate antibodies is the next step. In recent years, multiple antibody search engines have been generated, offering intuitive user interfaces that curate antibody clones by citations or artificial-intelligence-based approaches (Supplementary Table 3). In addition to identifying highly cited antibody clones, these platforms allow investigators to query many relevant search fields, such as tissue and cell type, application, company, and host species, while often providing reference images. Notably, these databases do not provide details on performance related to multiplexed imaging, such as epitope stability, steric hindrance, and compatibility with other antibodies. For these reasons, we provide a list of antibody clones previously validated for FF, formalin-fixed, and/or FFPE prepared mouse and human tissues using high-content imaging methods (Supplementary Dataset). Additionally, a recent report outlining tissue-specific panels for highly multiplexed imaging of diverse human tissues is available56. These resources serve as a starting point for creating custom panels and can be tailored to the multiplexed imaging method and question(s) of interest.
For laboratories interested in routine multiplexed imaging, we recommend creating base panels with well-established antibodies that can be expanded as needed. Such an approach reduces the time and capital associated with antibody validation. Moreover, recombinant monoclonal or multiclonal antibodies with appropriate quality-control measures offer the least lot-to-lot variation, making them preferable for highly multiplexed panel development. Beyond that, preference is given to rigorously quality controlled hybridoma-derived monoclonal antibodies and, lastly, to polyclonal antibodies. Applications and sample-specific testing of each vendor lot is recommended to ensure reproducibility across experiments regardless of antibody type.
Creating custom reagents
Many low-plex IHC and IF methods utilize primary antibody detection via a secondary antibody (indirect detection) to enable signal amplification. While convenient, these indirect labeling approaches often cannot be employed to obtain highly multiplexed datasets owing to significant overlap between the primary antibody host species and isotype. Consequently, it is often necessary to modify primary antibodies with functional groups that enable detection (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Table 1). Ultimately, reagent preparation strategies are driven by the cost, availability of materials, technical capabilities, scale, and intended experimental design.
Fig. 4 |. Process of conjugating antibodies with modifiers for multiplexing.
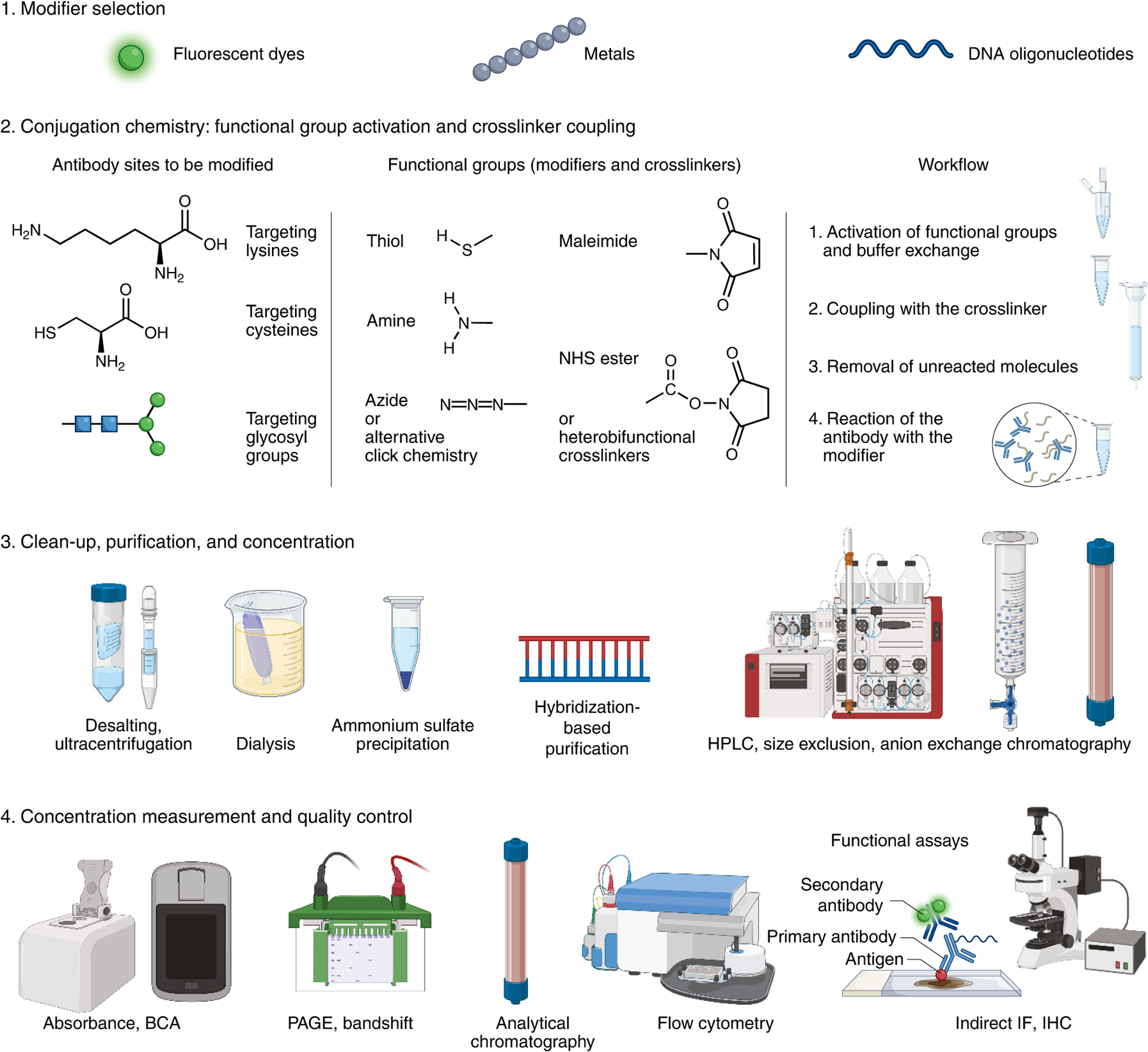
Following the selection of labeling chemistry and crosslinker, the workflow typically consists of these steps: (1) activation of modifier groups (for example reducing of thiol groups) and buffer exchange, (2) reaction with the crosslinker, (3) removal of the excess crosslinker, and (4) reaction of the antibody with the modifier. Since the reaction typically includes an excess of the modifier, the unreacted molecules are optionally removed from the mixture using buffer exchange, gel filtration, or sequence-directed pull-downs in the case of oligonucleotide barcode modifiers. Further purification can be performed by ion exchange or size-exclusion chromatography to remove the aggregated or degraded molecules, leftover modifiers, and under- or overconjugated antibodies. While purified reagents often improve quality and performance, purification may substantially reduce conjugated antibody yield, making it impractical or costly for small-scale preparations. The final product and its purity can be validated by a band shift on SDS–PAGE gels, where both the antibody and the modifier can be observed (for example using Coomassie, fluorescence, Sybr stains, or silver stain). The resulting antibody concentration can be determined using bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA) or spectrophotometry (for example, NanoDrop), although crosslinkers may interfere with these absorbance measurements and corrections need to be made accordingly. Crucially, the final product should be revalidated for the general target binding specificity (for example by flow cytometry) and for the assay of interest by functional comparison to the unconjugated antibody using direct detection or secondary antibody detection.
Numerous conjugation methods are used for antibody labeling, each having distinct advantages and disadvantages as well as several tunable variables including, but not limited, to: crosslinker chemistry, crosslinker concentration, pH, modifier concentration, reaction buffer, and purification strategy. Factors like degree of labeling and conjugate purity/homogeneity might vary depending on the method and adjustable variables63. Frequently, conjugation chemistries target lysine, cysteine, or glycan residues of the antibody (Fig. 4), though there are other site-directed approaches that target the amino terminus63, defined lysine groups64,65, or the fragment crystallizable (Fc) region of antibodies66. Furthermore, some noncovalent approaches rely on premixing of secondary affinity reagents (for example antigen-binding fragment (Fab) domains, nanobodies or protein A/G) for multiplexing67,68.
Conjugation chemistries.
Lysine-directed conjugations69 are typically preferred for conventional dyes and oligonucleotide barcodes because they are quick, cost effective, controllable, and scalable. A typical IgG has over 40 solvent-exposed lysines, and the extent of conjugation on these residues enables adjustment of the antibody to modifier ratio. While optimizable, the labeling is not site-specific and can result in heterogeneous conjugation and crossreactivity with non-lysine amino acid residues. If critical lysines are in the antibody active site, the modification can reduce epitope binding activity. These factors can make probe standardization and validation more difficult, although recent publications have described site-specific lysine modification, which may address some of these issues64,65.
Alternatively, cysteine-directed conjugations70 are also fast, cost effective, scalable, and preferred for the addition of metal tags and oligonucleotide barcodes. While cysteine-based conjugation has been shown to generate more homogeneous and reproducible outcomes, there are only 12 available cysteine sites on a typical IgG. In addition to a lower degree of labeling, the proximity of cysteine residues may result in dyes conjugating near one another, which tends to reduce fluorescence due to quenching. Furthermore, the antibody must be mildly reduced with dithiothreitol or 2-carboxyethyl phosphine (tris) prior to conjugation with maleimide-fluorophore/chelator or crosslinkers, which can impact the antibody structure and affinity.
Often, glycan-directed approaches are preferred for small-scale conjugations, when other protocols fail, or when conjugating oligonucleotide barcodes. On average, an IgG contains two glycan sites on the heavy chain. Because of this, glycan-directed conjugations are site-specific, require less optimization of the antibody to modifier ratio, are more reproducible, and avoid binding site inactivation. Unfortunately, the protocol is typically longer and requires enzymatic reactions, which are more costly and difficult to scale.
Standard commercial antibody formulations may not be directly compatible with conjugation chemistries since they often contain sodium azide, bovine serum albumin (BSA), glycerol, and/or cryoprotectants. To facilitate conjugation, we recommend purchasing antibodies in simple buffers such as PBS or performing affinity purification. Further, stocks should be maintained in PBS or borate buffered saline. As each conjugation results in antibody loss, starting with 50–100 μg of the purified antibody is recommended to yield an appreciable amount of product. Although conjugation procedures and methods significantly vary, we visually summarize common approaches (Fig. 4).
Conjugation considerations.
Ultimately, the generation and validation of custom antibody reagents is a major bottleneck for developing multiplexed antibody-based imaging panels. Extended experimental planning and validation of conjugated antibodies associated with multiplexed experiments increases the cost and effort compared to their single-plex counterparts. Custom conjugation also introduces additional batch-to-batch variations, especially for the small-scale preparations done in academic research groups. While commercial custom conjugation services and ready-made conjugation kits make it easier to modify antibodies for custom panels, a wider selection of off-the-shelf primary antibodies conjugated with standard sets of dyes, metals, and oligonucleotide barcode libraries will facilitate their greater adoption. Additionally, antibody performance is frequently affected by the choice of metal tag, fluorophore, or oligonucleotide barcode to which it is conjugated (Supplementary Fig. 1). For this reason, antibodies that target low-abundance epitopes should be conjugated to bright fluorophores that do not overlap with native autofluorescence. Similarly, metal groups and oligonucleotide sequence combinations that have been previously validated for the tissue type are preferred. After custom conjugations, the functionality of the final antibody–conjugate should be confirmed by comparison to the unconjugated version and reassessed with the target assay (Fig. 4). Modified antibodies may also require alterations in tissue blocking and antibody incubation conditions for optimal performance.
Multiplexed antibody panel design and development
Antibody validation.
Antibodies must be validated for each workflow as antibody performance depends on tissue type, preservation method, antigen retrieval conditions, final antibody concentration, incubation buffers, and detection method (Fig. 3). While best practices for antibody validation have been described by Uhlen et al.71, and have been extensively covered before29,71,72, for multiplexed antibody-based tissue imaging, we recommend considering: (1) tissue and subcellular location of an antibody target, (2) positive and negative tissue controls, (3) native tissue autofluorescence and other types of background, (4) marker compatibility (for example no crossreactivity or steric hindrance between antibodies), (5) confirming antibody specificity through single-plex IF or IHC experiments73, and (6) signal-to-noise, particularly for experiments that cannot be amplified (Supplementary Fig. 1). In addition to the antibody-specific search engines discussed here (Supplementary Table 3), regularly updated databases (Supplementary Table 2) can aid in establishing the location and relative abundance of a marker. Using this information, one can validate antibodies using appropriate tissues with well-documented expression of targeted molecules. Additionally, knockout or knockdown cell lines74,75, or tissues with distinct spatial expression patterns of targets, can be used to further validate the specificity of an antibody71,76. Finally, pathologists can provide invaluable input into the specificity of antibody staining, particularly in the case of rare clinical samples or atypical markers, where artifactual staining may be more difficult to discern. While we provide an overview of antibody validation for multiplexing here, earlier resources provide a more in-depth and focused discussion of the antibody validation process20,24,29. To increase reproducibility and confidence in the results, we recommend including metadata on antibody validation with published work (Supplementary Table 4).
An additional consideration affecting antibody performance is native tissue autofluorescence, which can vary widely with tissue type, disease state, sample preparation, and fixation method20,51. Autofluorescence can significantly impact the visualization of markers, particularly if these markers are not paired with fluorophores or spectral channels that have higher signal yields. Thus, even if an antibody is validated for its target specificity, its effective use will depend on the anticipated signal in each tissue as compared with tissue autofluorescence, particularly if the label cannot be amplified. Although there is no standard protocol for controlling autofluorescence, we provide strategies for minimizing signal from commonly encountered endogenous fluorophores as a resource to the field (Supplementary Table 5).
Full-panel validation.
Many of the multiplexed imaging methods discussed here employ high numbers of antibodies incubated simultaneously or iteratively11,12,21–25,37,38. Therefore, once the desired marker list is established and antibody specificity validation is complete, it is necessary to validate the full panel, as there may be crossreactivity between antibodies or spectral overlap from reporters or barcodes within the panel that need to be adjusted (Fig. 3). When antigen retrieval is required for any of the antibodies in a multiplex panel, the same method of antigen retrieval must work for all antibodies in the panel. Thus it is crucial to compare specificity of an antibody within a multiplexed panel to its performance within a single-plex experiment. If an antibody does not perform similarly to this single-plex experiment, further adjustments may be needed (for example optimization of the staining or conjugation conditions, or alternative clones).
Finally, we recommend titrating antibodies over their dynamic range to determine the best signal-to-noise ratio while limiting spectral overlap11. Initial antibody validation and multiplexed panel design can be performed in control tissues that are prepared in the same manner as the experimental tissues. The use of control tissue allows precious samples to be reserved for final image collection using the fully validated panel of antibodies. Cell or tissue microarrays (TMAs) are particularly useful for a quantitative assessment of the optimal antibody titrations on the same slide72,77. TMAs, especially multi-organ TMAs, are also recommended for validation of the antibody specificity across multiple tissues in a single staining round. Recently, TMAs were used to validate IMC antibodies and predict biomarkers relevant to disease outcome using AQUA78,79, a software that uses molecularly defined compartments to automatically measure signal intensity with subcellular resolution. For cyclic methods, it is necessary to verify that tissue morphology and target epitopes remain intact during each stain/bleach cycle or the antibody-removal steps. Verification methods have been detailed elsewhere and include (1) comparing antibody performance in single-plex (serial) and cyclic (iterative) imaging experiments21, (2) varying the order of antibody addition (first cycle versus the fourth cycle), and (3) reimaging the same target across multiple cycles24. If loss of antibody immunogenicity is observed, we recommend placing the affected antibody earlier within the cycle order, substituting with a different clone, or optimizing the cycling conditions such that low-intensity antibodies proceed high-intensity antibodies.
Reproducibility and data analysis
One of the greatest challenges facing any scientific method involves reproducibility and rigor of the published conclusions80, particularly for antibody-based approaches that are prone to variable results in the absence of tightly controlled experiments81. Owing to the complexity surrounding multiplexed antibody-based experiments, we encourage the inclusion of detailed validation data in published work or for these data to be deposited as part of publicly available datasets. By mandating and standardizing these processes, we can facilitate appropriate data publishing and use practices, which will undoubtedly improve the experimental rigor and reproducibility. Sharing data on effective antibodies collectively saves an enormous amount of time and resources, but requires extensive, multipronged validation and stable antibody production. We believe that commercial products play a major role in the future adoption and high-fidelity use of multiplexed methods. Access to application-specific vendor validation and quality-control data with detailed information (for example optimal concentration, tested antigen-retrieval protocols, buffer conditions, stability/storage conditions, RRID/clone information), production of monoclonal antibodies with known sequences/epitopes, broader antibody tag options, and flexible formulations (for example conjugation compatible buffers, lyophilized products) will greatly support the field. Publicly available data repositories, such as the HuBMAP data portal82, HTAN data portal83, The Human Protein Atlas17, The Cancer Imaging Archive84, and The Image Data Resource85, can be leveraged as early domains for sharing and assessing data.
Another large source of variability comes from how and to what extent the raw imaging data are processed. To facilitate this discussion, we propose using predefined data states that can describe any multiplexed imaging set (Supplementary Table 6). Many of these processing and segmentation analyses can be performed using a combination of commercial, freeware, and lab-built software packages. Some of the most widely used software packages include Zen (commercial and freeware, Zeiss), ImageJ (open source)86, ASHLAR (open source)87, cytokit (open source)88, CellProfiler (open source)89, CellPose (open source)90, NAPARI (open source), CODEX Processing and inForm/MAV (commercial, Akoya Biosciences), HALO (commercial, Indica Labs), QUPath (open source)91, DeepCell (open source)92, ilastik (open source)93, Visiopharm TissueAlign/TMA (commercial, Visiopharm), histoCAT (open source)94, MCMICRO (open source)95, Squidpy (open source)96, CytoMAP (open source)97, and many others98–100. Alternative, segmentation-free approaches have also been developed for quantitative analysis of imaging data using pixel-based assignment of subcellular features22,78,79 as well as classification of irregularly shaped myoepithelial cells101.
Multiplexed tissue-imaging experiments typically result in sizable files owing to multiple imaging cycles for large regions of interest scanned with tiling and z-stacks. To account for this, workstations or computer servers with extensive memory, high processing speeds, efficient graphic cards, integrated storage, and multicore processors are required for handling these large datasets. Generally, processing pipelines work down the data state levels and are, principally, an accumulation of different software packages that transform the raw data into processed and segmented data. Of note, cell type or functional unit annotations typically require incorporating the opinion of a field expert (for example a pathologist or tissue biologist) which limits the speed, and sometimes the accuracy, of the assignment, as such tasks cannot be easily automated.
Future directions and challenges
Despite the efforts required for more complicated experimental design and thorough validation, multiplexed imaging experiments are important, and often the only way to visualize diverse cell types and physiological states within complex biological systems in situ102. For instance, the most recent advances in multiplexed imaging technologies allow over 60 antigens to be stained within a single tissue section; an order of magnitude higher than single-pass experiments performed on the best microscopy systems. Most mammalian systems contain hundreds of different cell types that serve essential functions and are subject to regulation by their spatial position and neighbors. Importantly, disease formation, progression, and treatment response may be governed by unique cellular associations within tissues101. All of these factors necessitate highly multiplexed microscopy approaches to understand the complexity of healthy and diseased tissues. In a recent example, >50 proteins were visualized to reveal how distinct cellular neighborhoods orchestrate the spatial organization of the immune tumor microenvironment and contribute to colorectal cancer outcome32.
Extending capabilities and reach.
Antibodies have long formed the backbone of in situ protein detection, yet they are imperfect tools that require careful characterization and empirical optimization, which makes multiplexed implementation tedious. They are large molecules whose diffusion, target access and binding are highly sensitive to sample preparation conditions, and critical biochemical characterization information, such as antibody protein sequence, stability, exact epitopes, or binding kinetics, is rarely available. Widespread availability of recombinant antibodies, a bigger selection of nanobodies, and alternative probes like aptamers and engineered binders103 have the potential to make multiplexed antibody panel creation more efficient and lower cost in the future. Also adoption of multiplexable signal amplification methods (as described above) and brighter nano-emitters as alternatives to commonly used organic dyes would improve the detection sensitivity of multiplex experiments.
Further improvements are expected to include improved reproducibility, automated end-to-end workflows, a higher number of markers per experiment, larger imageable areas, and inspiration from outside the field of multiplexed imaging. Of note, a recent study incorporated principles from astronomy to aid in the collection of high-quality datasets from a six-plex TSA-based imaging assay of human melanoma samples. The resulting workflow, AstroPath, offers guidelines for operator-independent field selection and solutions for commonly encountered problems in multispectral imaging including image processing artifacts, improper image segmentation and classification, and batch-effects due to variation in marker intensities104. Importantly, these principles are scalable to the high-content imaging assays described here. Another exciting area of development involves computational/automated segmentation of multiplexed images for specific cell types and subtypes to enable tissue-wide assessment of cellular populations. To this end, the HuBMAP consortium82 has invested significant resources to compare existing cell-segmentation algorithms for their ability to segment membrane and nuclei across multiplexed imaging platforms and defined data-processing pipelines. In contrast to the many methods described for cellular segmentation, our ability to segment bulk functional units, such as glomeruli within the kidney or ventricles in the heart, are not as advanced. While individual cells are functionally important, their active coordination within anatomical structures is critical for overall organ function. Multiplexed microscopy approaches are key for advancing this field, as several markers are often needed to define a structure completely, and automation enables bulk tissues to be analyzed quickly. Finally, effective implementation of these analytical methods in thicker volumes will greatly advance organ-level studies.
Dealing with data: standardization, reproducibility, and storage challenges.
While the increased parameter depth is crucial for understanding complex mammalian systems, each cycle or protein biomarker provides additional data, often leading to terabytes of raw microscopy images. As such, there are considerable challenges associated with transferring, storing, and sharing raw data. These datasets present challenges, as multiplexed experiments often require proprietary software, and scale with the number of cycles, markers, and samples captured. The sheer size of datasets alone presents unique challenges for storage and handling. For instance, the raw data for a 10-cycle CODEX experiment (200 tiles, 11 z-stacks, ×20 objective) is >1.5 TB (150 GB/cycle of 3 probes and DAPI). Many databases or data banks will not store data of this size without considerable cost to the authors or journal, discouraging open data sharing. Processing steps such as compression, extended depth of field, and overlap cropping will reduce the file size considerably (~290 GB using the above example), but this involves altering the image, preventing others from reprocessing the original data with improved algorithms and software. Moreover, data analysis and processing steps should be transparent, such that analysis-specific metadata or processing standards are reported to enhance the reproducibility and reliability of the final dataset in line with FAIR data reporting standards105. The HTAN consortium has recently provided detailed guidelines and references for components and a structured database for recording of multiplex tissue-imaging metadata106. Datasets are most valuable if available in an open or nonproprietary format, such as OME-tiff or BDV, which enables free access to datasets in standardized formats107. As an alternative, long-term storage or archiving solutions (cheap but slow) can be utilized for raw data (state 0), whereas higher-level data states are maintained on more accessible storage solutions (more expensive but easier to access (Supplementary Table 6)).
Challenges in managing these large datasets are further compounded by the different approaches and tools used to acquire and process the data. Remedying this requires standardized, nonproprietary formats and common infrastructures for sharing and depositing data. We see value in adopting the open science culture and nationally or internationally funded and managed large data repository structures, such as the HuBMAP data portal and the Cancer Imaging Archive84. This endeavor surely requires a consorted effort from all stakeholders including funding bodies, publishers, method developers, biotechnology companies that commercialize these methods into hardware, software, and chemical products, and the scientists who utilize these resources.
From multiplexed imaging to sequencing.
As multiplexed imaging approaches are integrated with orthogonal modalities such as flow cytometry, CITE-seq, mass spectrometry, transcriptomics, and spectroscopy, it is crucial to bring the resulting data closer to established ‘-omics’ practices. Incorporating the multiplexed antibody recommendations discussed here will improve the characterization of cell types and potentially lead to the discovery of cell (sub)types. In addition to independent validation of new discoveries, such multimodal analysis will enable simultaneous measurement of gene expression and protein products for individual cell types and allow a better understanding of the physiological functions and interacting partners of cells in complex tissues108. In addition to the multiplexed imaging methods covered here, new techniques such as DBit-Seq109 and Digital Spatial Profiling52 offer a spatially defined collection of nucleotide barcodes and enable multiplexed protein detection using sequencing platforms. The best practices described here are also largely applicable to these hybrid methods, although distinct considerations may apply for subcellular sampling and sequencing-based detection of targets.
Conclusion
Here, we have provided an overview for multiplexed antibody-based imaging, collated key resources, and outlined considerations for planning and executing multiplexed protein detection experiments which can provide the highly resolved spatial context that is much needed to create true cell and tissue atlases. Furthermore, these approaches offer direct insights for cell–cell interactions, signaling events, subcellular localizations or translational modifications of proteins, and can complement other bulk assays or single-cell omics analyses of dissociated tissues. By following the suggestions presented here and in cited resources, we aim to empower other investigators to obtain high-quality imaging data using state-of-the-art multiplexed methods. We believe that this primer will facilitate important contributions to biomedical research, and that the emerging findings will be of great impact to the larger scientific community.
Ethics declaration.
Human tissues in Fig. 1 and Supplementary Fig. 1 were obtained by following a NIH Institutional Review Board (IRB)-approved protocol (13-C-0076) at the time of risk-reducing surgery performed as a consequence of germline genetic mutation(s). All tissue procured was grossly normal, as determined by the operative surgeon, and histopathologically normal, as determined by a board-certified pathologist.
Reporting Summary.
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for engaging and thoughtful discussions from the Affinity Reagent Imaging and Validation Working Group, HuBMAP Consortium. The authors would like to acknowledge funding from the following sources: NIH U54 DK120058, NIH U54 EY032442, NIH R01 AI145992, NIH R01 AI138581 (R. M. C. and J. M. S.), NIH T32ES007028 (E. K. N), NIH U54 HG010426-01 (M. P. S. and G. P. N.), NIH UG3 HL145600-01, NIH UH3 CA246633-01 (R. M. A), NIH UH3 CA246635-01 (N. L. K.), Swedish Research Council 2018-06461 (E. L.), Erling Persson Family Foundation (E. L.), Wallenberg Foundation (E. L.), NIH UH3 CA246594-01 (A. S. and E. M.), NIH T32CA196585 and ACS PF-20-032-01-CSM (J. W. H.), and NIH UH3 CA255133-03 (S.K.S.) and European Molecular Biology Laboratory (S. K. S.). This work was supported, in part, by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, NIAID and NCI. We thank J. Hernandez and J. Davis (National Cancer Institute, NIH) for providing de-identified human tissues featured in this work, and K. Prummel (EMBL) for comments on the manuscript. Figures were made using the tools on Biorender.com.
Footnotes
Competing interests
A. E. W. is an employee and shareholder of Abcam plc. J. F. is an employee of Cell Signaling Technologies. J. C. is an employee and shareholder of BioLegend. J. H. is an employee of Bio-Techne. E. S. is an employee of Thermo Scientific. E. M. and A. S. are current or past employees of GE Research. K. C. is an inventor for patent applications covering some technologies described in this paper and a cofounder of LifeCanvas Technologies. G. P. N. is inventor on a US patent, covering some technologies described in this paper, has equity in and/or is a member of the scientific advisory board of Akoya Biosciences. S. K. S. is an inventor for patent applications related to some of the methods described here.
Supplementary information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01316-y.
References
- 1.Stack EC, Wang C, Roman KA & Hoyt CC Multiplexed immunohistochemistry, imaging, and quantitation: A review, with an assessment of Tyramide signal amplification, multispectral imaging and multiplex analysis. Methods 70, 46–58 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thul PJ et al. A subcellular map of the human proteome. Science 356, eaal3321 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gawad C, Koh W & Quake SR Single-cell genome sequencing: current state of the science. Nat. Rev. Genet 17, 175–188 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Massonnet P & Heeren RMA A concise tutorial review of TOF-SIMS based molecular and cellular imaging. J. Anal. Spectrom 34, 2217–2228 (2019). [Google Scholar]
- 5.Neumann EK, Do TD, Comi TJ & Sweedler JV Exploring the fundamental structures of life: non-targeted, chemical analysis of single cells and subcellular structures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 58, 9348–9364 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhang L & Vertes A Single-cell mass spectrometry approaches to explore cellular heterogeneity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 57, 4466–4477 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Porwit A & Béné MC Multiparameter flow cytometry applications in the diagnosis of mixed phenotype acute leukemia. Cytom. Part B: Clin. Cytom 96, 183–194 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bandura DR et al. Mass cytometry: technique for real time single cell multitarget immunoassay based on inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem 81, 6813–6822 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kolodziejczyk AA, Kim JK, Svensson V, Marioni JC & Teichmann SA The technology and biology of single-cell RNA sequencing. Mol. cell 58, 610–620 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stoeckius M et al. Simultaneous epitope and transcriptome measurement in single cells. Nat. Methods 14, 865–868 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Taube JM et al. The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer statement on best practices for multiplex immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF) staining and validation. J. Immunother. Cancer 8, e000155 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Goltsev Y et al. Deep profiling of mouse splenic architecture with CODEX multiplexed imaging. Cell 174, 968–981.e915 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.van den Brink SC et al. Single-cell sequencing reveals dissociation-induced gene expression in tissue subpopulations. Nat. Methods 14, 935–936 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gerner MY, Kastenmuller W, Ifrim I, Kabat J & Germain RN Histo-cytometry: a method for highly multiplex quantitative tissue imaging analysis applied to dendritic cell subset microanatomy in lymph nodes. Immunity 37, 364–376 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Asp M, Bergenstråhle J & Lundeberg J Spatially resolved transcriptomes—next generation tools for tissue exploration. BioEssays 42, 1900221 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Marx V Method of the year: spatially resolved transcriptomics. Nat. Methods 18, 9–14 (2021). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Uhlén M et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 347, 1260419 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Uhlen M et al. A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science 357, eaan2507 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tan WCC et al. Overview of multiplex immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence techniques in the era of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun. 40, 135–153 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bodenmiller B Multiplexed epitope-based tissue imaging for discovery and healthcare applications. Cell Syst. 2, 225–238 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Radtke AJ et al. IBEX: a versatile multiplex optical imaging approach for deep phenotyping and spatial analysis of cells in complex tissues. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci 117, 33455–33465 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gut G, Herrmann MD & Pelkmans L Multiplexed protein maps link subcellular organization to cellular states. Science 361, eaar7042 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lin J-R, Fallahi-Sichani M & Sorger PK Highly multiplexed imaging of single cells using a high-throughput cyclic immunofluorescence method. Nat. Commun 6, 8390 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lin J-R et al. Highly multiplexed immunofluorescence imaging of human tissues and tumors using t-CyCIF and conventional optical microscopes. eLife 7, e31657 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gerdes MJ et al. Highly multiplexed single-cell analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded cancer tissue. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 11982–11987 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schubert W et al. Analyzing proteome topology and function by automated multidimensional fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Biotechnol 24, 1270–1278 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wählby C, Erlandsson F, Bengtsson E & Zetterberg A Sequential immunofluorescence staining and image analysis for detection of large numbers of antigens in individual cell nuclei. Cytometry 47, 32–41 (2002). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zrazhevskiy P & Gao X Quantum dot imaging platform for single-cell molecular profiling. Nat. Commun 4, 1–12 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Du Z et al. Qualifying antibodies for image-based immune profiling and multiplexed tissue imaging. Nat. Protoc 14, 2900–2930 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang Y et al. Rapid sequential in situ multiplexing with DNA exchange imaging in neuronal cells and tissues. Nano Lett. 17, 6131–6139 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Saka SK et al. Immuno-SABER enables highly multiplexed and amplified protein imaging in tissues. Nat. Biotechnol 37, 1080–1090 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schürch CM et al. Coordinated cellular neighborhoods orchestrate antitumoral immunity at the colorectal cancer invasive front. Cell 182, 1341–1359.e1319 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Neumann EK et al. Highly multiplexed immunofluorescence of the human kidney using co-detection by indexing. Kidney Int. 10.1016/j.kint.2021.08.033 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lin R et al. A hybridization-chain-reaction-based method for amplifying immunosignals. Nat. Methods 15, 275–278 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang Y et al. Multiplexed in situ protein imaging using DNA-barcoded antibodies with extended hybridization chain reactions. Preprint at bioRxiv 10.1101/274456 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tsujikawa T et al. Quantitative multiplex immunohistochemistry reveals myeloid-inflamed tumor-immune complexity associated with poor prognosis. Cell Rep. 19, 203–217 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Angelo M et al. Multiplexed ion beam imaging of human breast tumors. Nat. Med 20, 436–442 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Giesen C et al. Highly multiplexed imaging of tumor tissues with subcellular resolution by mass cytometry. Nat. Methods 11, 417–422 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chang Q et al. Imaging mass cytometry. Cytom. Part A 91, 160–169 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wei L et al. Super-multiplex vibrational imaging. Nature 544, 465–470 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wong HS et al. A local regulatory T cell feedback circuit maintains immune homeostasis by pruning self-activated T cells. Cell, 3981–3997 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chung K et al. Structural and molecular interrogation of intact biological systems. Nature 497, 332–337 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Li W, Germain RN & Gerner MY Multiplex, quantitative cellular analysis in large tissue volumes with clearing-enhanced 3D microscopy (Ce3D). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, E7321–E7330 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Murray E et al. Simple, scalable proteomic imaging for high-dimensional profiling of intact systems. Cell 163, 1500–1514 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ku T et al. Multiplexed and scalable super-resolution imaging of three-dimensional protein localization in size-adjustable tissues. Nat. Biotechnol 34, 973–981 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Park Y-G et al. Protection of tissue physicochemical properties using polyfunctional crosslinkers. Nat. Biotechnol 37, 73–83 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tillberg PW et al. Protein-retention expansion microscopy of cells and tissues labeled using standard fluorescent proteins and antibodies. Nat. Biotechnol 34, 987–992 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhang J et al. Evaluation of the tumor-targeting efficiency and intratumor heterogeneity of anticancer drugs using quantitative mass spectrometry imaging. Theranostics 10, 2621–2630 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yun DH et al. Ultrafast immunostaining of organ-scale tissues for scalable proteomic phenotyping. Preprint at bioRxiv 10.1101/660373 (2019). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kim S-Y et al. Stochastic electrotransport selectively enhances the transport of highly electromobile molecules. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, E6274–E6283 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Davis AS et al. Characterizing and diminishing autofluorescence in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human respiratory tissue. J. Histochemistry Cytochemistry 62, 405–423 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Merritt CR et al. Multiplex digital spatial profiling of proteins and RNA in fixed tissue. Nat. Biotechnol 38, 586–599 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Shi S-R, Shi Y & Taylor CR Antigen retrieval immunohistochemistry: review and future prospects in research and diagnosis over two decades. J. Histochem. Cytochem 59, 13–32 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Shi S-R et al. Evaluation of the value of frozen tissue section used as ‘gold standard’ for immunohistochemistry. Am. J. Clin. Pathol 129, 358–366 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Neumann EK, Comi TJ, Rubakhin SS & Sweedler JV Lipid heterogeneity between astrocytes and neurons revealed by single-cell MALDI-MS combined with immunocytochemical classification. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 58, 5910–5914 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Radtke AJ et al. IBEX: an iterative immunolabeling and chemical bleaching method for high-content imaging of diverse tissues. Nat. Protoc 10.1038/s41596-021-00644-9(2021). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Muzzey D & Oudenaarden AV Quantitative time-lapse fluorescence microscopy in single cells. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol 25, 301–327 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Santi PA Light sheet fluorescence microscopy: a review. J. Histochem. Cytochem 59, 129–138 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Leung BO & Chou KC Review of super-resolution fluorescence microscopy for biology. Appl. Spectrosc 65, 967–980 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Shakya R, Nguyen TH, Waterhouse N & Khanna R Immune contexture analysis in immuno-oncology: applications and challenges of multiplex fluorescent immunohistochemistry. Clin. Transl. Immunol 9, e1183 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Samusik N, Good Z, Spitzer MH, Davis KL & Nolan GP Automated mapping of phenotype space with single-cell data. Nat. Methods 13, 493–496 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Brummelman J et al. Development, application and computational analysis of high-dimensional fluorescent antibody panels for single-cell flow cytometry. Nat. Protoc 14, 1946–1969 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Szabó Á et al. The effect of fluorophore conjugation on antibody affinity and the photophysical properties of dyes. Biophys. J 114, 688–700 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Adusumalli SR et al. Chemoselective and site-selective lysine-directed lysine modification enables single-site labeling of native proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 59, 10332–10336 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Matos MJ et al. Chemo-and regioselective lysine modification on native proteins. JACS 140, 4004–4017 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Cremers GAO, Rosier BJHM, Riera Brillas R, Albertazzi L & de Greef TFA Efficient small-scale conjugation of DNA to primary antibodies for multiplexed cellular targeting. Bioconjug Chem. 30, 2384–2392 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sograte-Idrissi S et al. Circumvention of common labelling artefacts using secondary nanobodies. Nanoscale 12, 10226–10239 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rajagopalan A et al. SeqStain is an efficient method for multiplexed, spatialomic profiling of human and murine tissues. Cell Rep. Methods 1, 100006 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Brun M-P & Gauzy-Lazo L in Antibody–Drug Conjugates 173–187 (Springer, 2013). [Google Scholar]
- 70.Datta-Mannan A et al. The properties of cysteine-conjugated antibody–drug conjugates are impacted by the IgG subclass. AAPS J. 20, 103 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Uhlen M et al. A proposal for validation of antibodies. Nat. Methods 13, 823–827 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Bordeaux J et al. Antibody validation. BioTechniques 48, 197–209 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Pagès F et al. International validation of the consensus Immunoscore for the classification of colon cancer: a prognostic and accuracy study. Lancet 391, 2128–2139 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Stadler C et al. Systematic validation of antibody binding and protein subcellular localization using siRNA and confocal microscopy. J. Proteom 75, 2236–2251 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Giuliano CJ, Lin A, Girish V & Sheltzer JM Generating single cell-derived knockout clones in mammalian cells with CRISPR/Cas9. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol 128, e100 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Hewitt SM, Baskin DG, Frevert CW, Stahl WL & Rosa-Molinar E Controls for immunohistochemistry: The Histochemical Society’s standards of practice for validation of immunohistochemical assays. J. Histochem. Cytochem 62, 693–697 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gustavson MD, Rimm DL & Dolled-Filhart M Tissue microarrays: leaping the gap between research and clinical adoption. Personalized Med. 10, 441–451 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Camp RL, Chung GG & Rimm DL Automated subcellular localization and quantification of protein expression in tissue microarrays. Nat. Med 8, 1323–1328 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Martinez-Morilla S et al. Biomarker discovery in patients with immunotherapy-treated melanoma with imaging mass cytometry. Clin. Cancer Res 27, 1987–1996 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Baker M 1,500 scientists lift the lid on reproducibility. Nature 533, 452 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Jarvis MF & Williams M Irreproducibility in preclinical biomedical research: perceptions, uncertainties, and knowledge gaps. Trends Pharmacol. Sci 37, 290–302 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Snyder MP et al. The human body at cellular resolution: the NIH Human Biomolecular Atlas Program. Nature 574, 187–192 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Rozenblatt-Rosen O et al. The human tumor atlas network: charting tumor transitions across space and time at single-cell resolution. Cell 181, 236–249 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Clark K et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): maintaining and operating a public information repository. J. Digit. Imaging 26, 1045–1057 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Williams E et al. Image Data Resource: a bioimage data integration and publication platform. Nat. Methods 14, 775–781 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Schneider CA, Rasband WS & Eliceiri KW NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 671–675 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Rashid R et al. Highly multiplexed immunofluorescence images and single-cell data of immune markers in tonsil and lung cancer. Sci. Data 6, 323 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Czech E, Aksoy BA, Aksoy P & Hammerbacher J Cytokit: a single-cell analysis toolkit for high dimensional fluorescent microscopy imaging. BMC Bioinf. 20, 448 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.McQuin C et al. CellProfiler 3.0: next-generation image processing for biology. PLoS Biol. 16, e2005970 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Stringer C, Wang T, Michaelos M & Pachitariu M Cellpose: a generalist algorithm for cellular segmentation. Nat. Methods 18, 100–106 (2021). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bankhead P et al. QuPath: open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep 7, 16878 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Bannon D et al. DeepCell Kiosk: scaling deep learning-enabled cellular image analysis with Kubernetes. Nat. Methods 18, 43–45 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Sommer C, Straehle C, Koethe U & Hamprecht FA in 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro. 230–233 (IEEE, 2011). [Google Scholar]
- 94.Schapiro D et al. histoCAT: analysis of cell phenotypes and interactions in multiplex image cytometry data. Nat. Methods 14, 873–876 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Schapiro D et al. MCMICRO: A scalable, modular image-processing pipeline for multiplexed tissue imaging. Preprint at bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.03.15.435473 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Palla G et al. Squidpy: a scalable framework for spatial single cell analysis. Preprint at bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.02.19.431994 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Stoltzfus CR et al. CytoMAP: a spatial analysis toolbox reveals features of myeloid cell organization in lymphoid tissues. Cell Rep. 31, 107523 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Paintdakhi A et al. Oufti: an integrated software package for high-accuracy, high-throughput quantitative microscopy analysis. Mol. Microbiol 99, 767–777 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Sage D et al. DeconvolutionLab2: an open-source software for deconvolution microscopy. Methods 115, 28–41 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kulikov V et al. DoGNet: a deep architecture for synapse detection in multiplexed fluorescence images. PLoS Comput. Biol 15, e1007012 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Risom T et al. Transition to invasive breast cancer is associated with progressive changes in the structure and composition of tumor stroma. Preprint at bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.01.05.425362 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Kramer BA & Pelkmans L Cellular state determines the multimodal signaling response of single cells. Preprint at bioRxiv 10.1101/2019.12.18.880930 (2019). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Yu X, Yang Y-P, Dikici E, Deo SK & Daunert S Beyond antibodies as binding partners: the role of antibody mimetics in bioanalysis. Annu Rev. Anal. Chem 10, 293–320 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Berry S et al. Analysis of multispectral imaging with the AstroPath platform informs efficacy of PD-1 blockade. Science 372, eaba2609 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Wilkinson MD et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci. Data 3, 160018 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Schapiro D et al. MITI Minimum Information guidelines for highly multiplexed tissue images. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.09499 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 107.Moore J et al. OME-NGFF: scalable format strategies for interoperable bioimaging data. Preprint at bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.03.31.437929 (2021). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Nirmal AJ et al. The spatial landscape of progression and immunoediting in primary melanoma at single cell resolution. Preprint at bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.05.23.445310 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Liu Y et al. High-spatial-resolution multi-omics sequencing via deterministic barcoding in tissue. Cell 183, 1665–1681(2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


