Abstract
Potassium (K+) channels are highly regulated membrane proteins that control the potassium ion flux and respond to different cellular stimuli. These ion channels are grouped into three major families, Kv (voltage-gated K+ channel), Kir (inwardly rectifying K+ channel) and K2P (two-pore K+ channels), according to the structure, to mediate the K+ currents. In cancer, alterations in K+ channel function can promote the acquisition of the so-called hallmarks of cancer – cell proliferation, resistance to apoptosis, metabolic changes, angiogenesis, and migratory capabilities – emerging as targets for the development of new therapeutic drugs. In this review, we focus our attention on the different K+ channels associated with the most relevant and prevalent cancer types. We summarize our knowledge about the potassium channels structure and function, their cancer dysregulated expression and discuss the K+ channels modulator and the strategies for designing new drugs.
Keywords: K+ channels, potassium channel blockers, K+ channels expression, cancer
Introduction
Potassium Channels Structure and Function
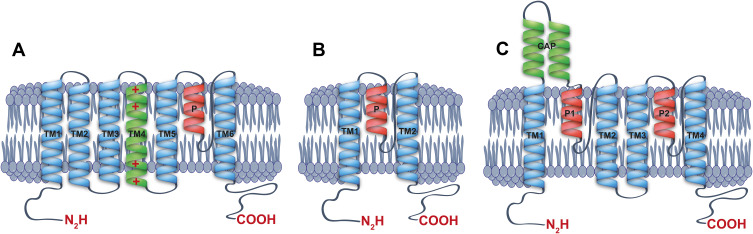
K+ channels are membrane proteins that facilitate the selective potassium ion flow under an electrochemical gradient. Besides the voltage-dependent gating, K+ channels are activated by several intracellular and extracellular stimuli,1–3 including extracellular and intracellular pH, kinases, SUMOylation, G protein-coupled receptors, stretch, and lipid regulation among others.1,2,4 These channels can be grouped into three major families according to their subunit structure: the Kv (voltage-gated K+ channel), Kir (inwardly rectifying K+ channel), and K2P (two-pore K+ channels)1,2,4 (see Figure 1A–C). K+ channels need four pore-forming domains, which together, generate a functional and selective ion pathway. Thus, the Kv and Kir channels need four subunits to form a functional pore in a tetramer architecture.2,4 On the other hand, the K2P family forms a functional channel in a dimer architecture (see Figure 1C).1,5 For each K+ channel, subunit is also clearly identifiable in this pore-forming P domain, characterized by the amino-acid signature GYG that confers the high selectivity to K+ ions observed in potassium channels.6 The Kv channels present a topology model with six transmembrane domains (TM1-6) and one pore-forming domain (P) (Figure 1A). This Kv family represents the most numerous K+ channel group, with 40 genes encoding for K+ subunits in humans. The transmembrane domain (TM4) into Kv channels present positive charged amino acids (Arg and Lys) which act as voltage sensors generating the channel opening in response to changes in voltages7,8 (Figure 1A).
Figure 1.
Schematic structure of potassium channels. Lateral view of monomers of a (A) voltage-gated potassium channel (Kv), (B) inward rectifier potassium channel (Kir) and (C) two-pore domain potassium channel (K2P), showing the transmembrane segments, the cap and their corresponding pore-forming loops (P-loops).
For the Kir channel family, each subunit has one P domain and two transmembrane domains (Figure 1B), and this family is integrated by 15 different genes grouped into 7 subfamilies (Kir1.x to Kir7.x), identified in mammals.2–4 Kir potassium channels present a gating governed by a voltage-dependent blocked process by Mg2+ and polyamines.3,4 Moreover, the gating voltage-dependence for Kir channels defines their characteristic K+ inward rectification (movement into the cell).3,4
K2P family has a two-pore forming domain and four transmembrane domains, whose subunits assemble as dimers (Figure 1C). Fifteen different genes found in mammals encode these family subunits and are grouped into 6 subfamilies according to their homology and functional properties.1,5,9,10 The K2P channels are voltage-independent and highly modulated channels, playing key roles in the maintenance of the resting membrane potential in the cells. These channels are recognized as the leak or background potassium channels.1,5
Potassium Channels in Cancer
Cancer condition is a major non-infectious public health problem and affects millions of people worldwide. Cancer is also the second most common cause of death after cardiovascular disease, with 10.0 million deaths (9.9 million excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer) in 2020,11 with estimated 28.4 million cases in 2040, a 47% rise from 2020.11 The Americas’ accounts 20.9% of cancer incidence and 14.2% of mortality worldwide,11 and for Latin America and the Caribbean region, it has been estimated that 1.7 million cancer cases will be diagnosed by 2030, whereas more than one million of the cases will die per year.12 Currently, more than 100 types of cancer have been identified, being breast (24.5%), colorectal (9.4%), lung (8.4%), cervix (6.5%), and thyroid (4.9%) most frequent types of cancer in women.11 Meanwhile, lung cancer (14.3%), prostate (14.1%), colorectal (10.6%), stomach (7.1%) and liver (6.3%) are the most common type of cancers among men.11
In recent years, ion channels, and particularly potassium (K+) channels, have emerged as relevant molecular targets for the development of cancer treatments.13–16 The association between potassium (K+) channels and cancer disease is mainly due to the participation of those proteins in the cancer progression mechanisms.13,16–18 Potassium channels are complex proteins that form selective pores for K+ conduction in biological membranes, which are critical in K+ homeostasis, cell volume regulation, setting of resting membrane potentials, the neurotransmitters release, and regulating the excitability of neurons and muscle tissue.1,2,19
For instance, overexpression of different potassium channels, such as Kv, Ca2+-activated (KCa), ether go-go human (hEag), ATP-sensitive (KATP), and K2P has been reported in prostate cancer cells, colon, lung, breast, and other organs.20 It has been hypothesized that there is a relationship between K+ channel overexpression and the generation and growth of malignant tumors,14,17,18,21 being involved in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation.14,18,21 Studies performed with pharmacological drugs that specifically block K+ channels have shown antitumor effects by inhibiting tumor growth directly or enhancing the effectiveness of chemotherapeutics or cytotoxic drugs as a combined therapeutical strategy.18,22 On the other hand, several studies have exhibited the impact of Kv channels (Eag1, HERG, and Kv1.3), Kir (Kir3.1), and Ca2+-activated potassium channels (KCa1.1 and KCa3.1) in cancer cell proliferation and their association with tumorigenesis process in patients and animal models.17,18,21–23
A relatively minor amount of research has focused on the relationship between K2P channels and cancer.18,24 Those studies suggested that TASK-3 is involved in tumor formation in several types of human cancer.14,18,24,25 Moreover, other investigations showed that breast cancer cells’ metastatic properties depend on TASK-3 expression levels.20
By contrast, the Kir channels have been related to different cancer conditions, such as lung, gastric, prostate, stomach, breast, and choroid plexus.26–32
Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels Involved in Cancer
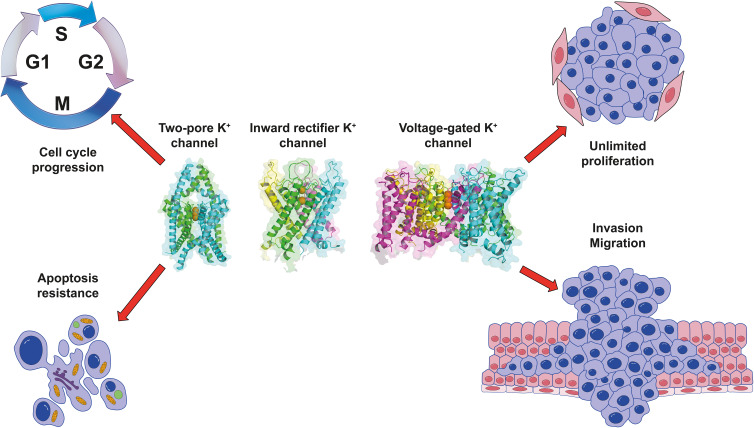
The Kv channel is the most numerous K+ channel family, playing relevant functions in various cellular and physiological processes.2 Additionally, these channels have been implicated in cancer hallmarks, such as cell proliferation, cancer progression, and migration14,15,33–35 (Figure 2 and Table 1).
Figure 2.
Roles of K+ channels in cancer hallmarks. Cellular processes associated with changes in expression and increased activity of the two-pore domain K+ channel (K2P), the inward rectifier K+ channel (Kir), and the voltage-gated K+ channel (Kv) in cancer. K+ channels structure in ribbon representation were generated with the PDB 6RV2, 7s5z and 7wf4.
Table 1.
Potassium Channels Associated with Cancer
| Protein (Gene) | Cancer Hallmark | Tumor or Cancer Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kv1.1 (KCNA1) | Cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion | Cervical cancer, medulloblastoma | [38,39] |
| Kv1.3 (KCNA3) | Cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration | Breast, lung, colon, prostate, pancreas, smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, and lymph node cancers, glioblastoma and melanoma | [40–47] |
| Kv1.4 (KCNA4) | Cell proliferation and cell cycle | Neuroblastoma cells | [52] |
| Kv1.5 (KCNA5) | Cell proliferation and apoptosis | Glioma, astrocytomas, gastric cancer cells, human non-Hodgkin lymphomas, smooth muscle tumors | [40,48–50] |
| Kv2.1 (KCNB1) | Cell cycle progression and migration | Prostate cancer cells, neuroblastoma cells | [51,52] |
| Kv3.1 (KCNC1) | Proliferation, migration and invasion | Lung and breast cancer cells] | [55] |
| Kv3.4 (KCNC4) | Proliferation, migration and invasion | Oral squamous cell carcinoma, head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, lung and breast cancer models | [53–55] |
| Kv4.1 (KCND1) | Cell cycle progression | Breast cancer and gastric cancer cells | [56,57] |
| Kv4.2 (KCND2) | Cell proliferation and cell cycle | Neuroblastoma cells | [52] |
| Kv7.1 (KCNQ1) | Cell proliferation | Colon cancer cells, neuroblastoma cells | [52,58,59] |
| Kv9.3 (KCNS3) | Cell proliferation | Colon carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma and cervical adenocarcinoma cells | [60,61] |
| Kv11.1 (KCNH2) | Cell cycle, apoptosis, migration and cell proliferation | Leukemia, ovarian, lung, pancreatic, colorectal and breast cancer cells | [74,79–81] |
| KCa1.1 (KCNMA1) | Cell proliferation and migration | Prostate, glia, breast, pancreas, and endometrium cancer cells | [82–87] |
| KCa2.3 (KCNN3) | Migration | Melanoma cells | [96] |
| Kir2.1 (KCNJ2) | Cell proliferation, invasion, cell cycle and apoptosis | Small-cell lung cancer and gastric cancer | [28,97] |
| Kir2.2 (KCNJ12) | Cell proliferation and cell cycle | Small-cell lung cancer, prostate, stomach, and breast | [31,98,99] |
| Kir3.1 (KCNJ3) | Cell proliferation and invasion | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, breast carcinomas, and non-small cell lung cancers | [26,100–102] |
| Kir3.4 (KCNJ5) | Cell proliferation | Adrenal aldosterone-producing adenomas | [29,103] |
| Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) | Cell proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis | Brain tumors, astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas | [32,104] |
| Kir6.1 (KCNJ8) | Cell proliferation, invasion, apoptosis and cell cycle | Leiomyoma cells, breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) and hepatocellular carcinoma | [30,105,106] |
| Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) | Cell proliferation, invasion, apoptosis and cell cycle | Leiomyoma cells, breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231), hepatocellular carcinoma, cervical cancer and glioma cells | [30,105–108] |
| Kir7.1 (KCNJ13) | Cell proliferation | Choroid plexus tumors | [27,109–111] |
| TASK-1 (KCNK3) | Cell proliferation, invasion and apoptosis | Medulloblastoma, Ehrlich ascites tumor cells, osteosarcoma, non-small cell lung cancers and adenomas adrenals | [121–123,125] |
| TASK-2 (KCNK5) | Cell proliferation, invasion and apoptosis | Breast cancer, and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | [126–128] |
| TASK-3 (KCNK9) | Cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis and cell cycle | Melanoma, ovarian carcinoma, breast tumors, colorectal cancers, lung and gastric cancer | [24,117,129–132,135,139,140] |
| TREK-1 (KCNK2) | Cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle | Prostate cancer, osteosarcoma and ovarian cancer | [116,118,141,142,182] |
| TREK-2 (KCNK10) | Cell proliferation and cell cycle | Bladder cancer cells | [119] |
| TWIK-1 (KCNK1) | Cell proliferation | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | [115] |
| TWIK-2 (KCNK6) | Cell proliferation, invasion and migration | Breast cancer | [120] |
The Kv1.1 (KCNA1) channel is relevant for potassium transport in the central nervous system and kidney.36,37 Moreover, it is overexpressed in cervical cancer tissues and medulloblastoma.38,39 Additionally, the Kv1.1 depletion suppressed growth, proliferation, migration and invasion of HeLa cells.38
Kv1.3 channels also have been reported as overexpressed in the breast, lung, colon, prostate, pancreas, smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, and lymph node of some types of cancers.40–44 However, its relevance as a therapeutic target has been evidenced in glioblastoma, melanoma, and pancreatic adenocarcinoma models,45–47 where Kv1.3 suppression induces apoptosis.
Another related channel is Kv1.5. This channel shows a correlated expression pattern with glioma entities and malignancy grades, with a high expression in astrocytomas, moderate in oligodendrogliomas, and low in glioblastomas.48 For the Kv1.5 channel, an overexpression was detected in some gastric cancer cell lines.49 Furthermore, Kv1.5 plays a role in the activation and proliferation of cells in the immune system, is remodeled during carcinogenesis, and has shown an abundance that inversely correlates with clinical aggressiveness in human non-Hodgkin lymphomas.50 In the same way that Kv1.3, this channel is overexpressed in human smooth muscle tumors.40 Kv1.5 has been involved in tumor cell proliferation of gastric cancer cells, where this channel is overexpressed.49
The expression of the Kv2.1 channel recently was reported to be higher in the metastatic prostate cancer cells (PC3), and their blockade with stromatoxin-1 or siRNA significantly inhibits the migration of malignant prostate cancer cells.51 This channel as Kv1.4, Kv4.2, Kv7.1 and large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel (BKCa) also showed a high expression in the CD133+ subpopulation of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.52
Increased levels of Kv3.4 channel expression were identified in OSCC (oral squamous cell carcinoma).53 In addition, the expression and clinical significance of this channel in the development and progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas was reported.54 The Kv3.4 and Kv3.1 are known as oxygen sensors, and their function in hypoxia has been well investigated.55 These channels, Kv3.1 and Kv3.4, are tumor hypoxia-related channels involved in cancer cell migration and invasion in A549 and MDA-MB-231 cells (lung and breast cancer models, respectively).55
Another set of experiments showed a varied expression of Kv4.1 mRNA depending on the tumor stage in human breast cancer tissues.56 Recent studies have demonstrated that Kv4.1 channels are expressed in the human gastric cancer cell lines.57 Moreover, the suppression of Kv4.1 induces a G1-S transition blockade affecting the cell cycle progression.57
Interestingly, together with the expression profile of Kv7.1 in neuroblastoma cells,52 this channel was also found to be up-regulated in human colonic cancer cells.58 Conversely, Kv7.1 and Kv7.5 expression in vascular cancers was reported to be down-regulated.59 In this case, the proposed role of Kv7 channels is related to cell proliferation rather than controlling vascular tone.59
A particular case is a Kv9.3 channel, an electronically silent subunit, which forms heterotetramers with Kv2.160. The Kv2.1/Kv9.3 heterotetramers are overexpressed in colon carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, and cervical adenocarcinoma cells.60,61 Moreover, the knockdown of Kv9.3 inhibits proliferation in colon carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma models.60
The Ether à go-go (Eag (hERG); Kv10.1) K+ channel expression is typically restricted to the adult brain and the heart, but it has been detected in several cancer cell lines and tumor tissues from patients,62,63 showing it to influence cell proliferation. This channel is overexpressed in 71% of tumors and cancer cell models of neuroblast, glial, liver, lung, breast, ovary, cervix, prostate, gastrointestinal tract, myeloid leukemia, and retinoblastoma.34,63–68 The Kv10.1 channel suppression generates apoptosis, inhibition of cell proliferation, and decrease in cancer cell migration.63,69–72 Additionally, the inhibition of Kv10.1 channels sensitizes the mitochondria of tumor cells to antimetabolic treatments, improving the efficacy of the metabolic inhibitors.73
Kv11.1 is overexpressed in leukemia, ovarian, lung, pancreatic, colorectal, and breast cancer cells, among others.74–79 The Kv11.1 channels have a key role in the cell cycle, acting as regulators for apoptosis and cell proliferation in cancer cells.74,79–81 However, blockers of Kv11.1 channels also retard the cardiac repolarization.80
Another subgroup of potassium channels involved in cancer corresponds to the calcium-activated potassium channels. These channels are activated by rise in cytosolic calcium ions, allowing the K+ ion to flow under an electrochemical gradient. As a member of this subgroup, the KCa1.1 channel is overexpressed in prostate, glia, breast, pancreas, and endometrium cancer cell types.82–86 KCa1.1 channel regulates the proliferation and migration of prostate cancer condition.83 In breast cancer, KCa1.1 channel overexpression has been associated with advanced tumor stage, cell proliferation, and poor prognosis.87
On the other side, the KCa3.1 (intermediate conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel) is overexpressed in 32% of glioma patients and correlates with poor patient survival.88 In addition, these channels are overexpressed in breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, leukemia, renal and hepatocellular carcinoma.89–94 The inhibition of KCa3.1 channel activity reduces the cancer cell motility, proliferation and induces apoptosis.91,94,95
A less associated channel to a cancer condition corresponds to KCa2.3 (SK3), with a report of overexpression in melanoma cell lines, and their knockdown led to plasma membrane depolarization and decreased cell motility.96
Inward Rectifying Potassium Channels in Cancer
The Kir channel family is integrated by 15 different genes grouped into seven subfamilies. Among these channels, different subunits have been associated with cancer conditions (Kir2.1, 2.2, 3.1, 3.4, 4.1, 6.1, 6.2)26,27,29–32,94 (Figure 2 and Table 1).
Kir2.1 (KCNJ2) is overexpressed in 44.23% of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) tissues, and it correlates with the clinical stage and chemotherapy response in SCLC patients. Additionally, the Kir2.1 knockdown in H69AR and H446AR cells inhibited cell growth and was sensitized to chemotherapeutic drugs by increasing cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.28 Kir2.1 channel also promotes the invasion and metastasis of human gastric cancer by enhancing MEKK2-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 signaling by interaction with Stk38.97
Similarly, Kir2.2 is found in human SCLC cells.31 Kir2.2 knockdown induced growth arrest and senescence by a mechanism involving reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation in cell lines derived from tissues of the prostate, stomach, and breast.98 Kir2.2 plays a role as an unconventional activator of RelA and increases the expression level of NF-κB targets, including cyclin D1, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)9, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)99 in cancer cells.
Another inward potassium channel associated with cancer is the Kir3.1 which is found within lymphocytes and in resected human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), overexpressed in 80% of tumor specimens. However, no associations were found between metastasis and Kir3.1 expression.26 On the other hand, the gene encoding the Kir3.1 channel was found to be aberrantly overexpressed in invasive breast carcinomas.100 In addition, the Kir3.1 overexpression correlates with lymph node metastasis, and this overexpression is greater in tumors with more than one positive lymph node.100
Kir3.1 gene overexpression is detected in tissue specimens from patients with non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs).101 In addition, the expression of Kir3.1 has been shown in tissue samples from approximately 40% of primary human breast cancers and in breast cancer cell lines.102
Also, the inwardly rectifying K+ channel Kir3.4 (KCNJ5 gene) (or GIRK4 channel) have been identified in adrenal aldosterone-producing adenomas (APAs), where several ion channel gain-of-function mutants are associated with the APA condition.29,103
In human brain tumors (low- and high-grade astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas), mislocalization (redistribution) of the Kir4.1 channel has been reported and suggests a compromised buffering capacity of glial tumor cells.32 Furthermore, in human astrocytic tumors, Kir4.1 channel expression markedly increases with the pathologic grade of cancer104 and suggests that Kir4.1 activation could promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in the tumors.104
The subunits of ATP-sensitive Kir potassium channels (Kir6.1, Kir6.2) are highly expressed in leiomyoma cells.30 The estrogen-induced proliferation of the leiomyoma cells is inhibited by treatment with glibenclamide (KATP-channel inhibitor).30 These two channels are expressed in MDA-MB-231 cancer cells, and the cytostatic effect of glibenclamide is mediated through KATP channels (Kir6.1 and 6.2), associated with the inhibition of the G1-S phase progression.105 In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the KCNJ11 (Kir6.2) gene was identified as a key dysregulated K+ channel and is associated with a poor prognosis in HCC patients.106 In agreement, the knockdown of Kir6.2 inhibited cell proliferation, promoted cell apoptosis, and reduced cell invasive capacity.106 The Kir6.2 overexpression was observed in cervical cancer cell lines and cervical tumor tissues.107 In particular, the increased Kir6.2 channel expression was observed in high-grade, poorly differentiated and invasive human cervical cancer biopsies.107 Moreover, an inhibitory effect of glibenclamide on the proliferation of cervical cancer cell lines is associated with Kir6.2 channel.107
Kir6.2 channel activity plays a critical role in the proliferation of glioma cells where the expression is greatly increased.108 Moreover, the treatment with tolbutamide (a Kir6.2 inhibitor) suppressed the proliferation of glioma cells and blocked the cell cycle.108 The Kir6.2 knockdown obtained a similar result in glioma cell proliferation.108
Finally, a less studied channel corresponds to Kir7.1 (KCNJ13) with a high expression linked to choroid plexus epithelium or choroid plexus tumors (CPTs)27,109,110 and it has been considered a sensitive and specific diagnostic marker for choroid plexus tumors.27,109,111
Two-Pore Domain Potassium Channels in Cancer
The two-pore domain K+ channels (K2P), encoded by the KCNK genes, are a family of fifteen members that form the leak or background channels.1,5,9 K2P channels display K+ outward rectifying currents, constitutively open, that control the neuronal excitability. Thus, activation of K2P channels stabilizes the cell membrane potential below the firing threshold, whereas the K2P channels inhibition facilitates membrane depolarization and cell excitability.
The K2P family can be divided into six subfamilies based on structural and functional properties.1,5,9 Regarding protein structure, each K2P channel subunit has four transmembrane domains (TM1-TM4) and two pore-forming domains (P1 and P2) (Figure 1C). Moreover, two subunits are required to form a functional channel.112,113 K2P channels display an exclusive extracellular cap domain formed by the extracellular loop that connects the first transmembrane domain and the first pore-forming sequence (TM1-P1 loop) (Figure 1C). The extracellular cap covers the upper selectivity filter (SF) pore,114 and this structure is responsible for the poor sensitivity of K2P channels to classical K+ channel blockers.114
From the K2P family, seven members are confirmed to be involved in cancer (TASK-1, TASK-2, TASK-3, TREK-1, TREK-2, TWIK-1, and TWIK-2)15,115–120 (Figure 2 and Table 1). Among these, TASK-1 (K2P3, encoded by KCNK3 gene) has been detected in medulloblastoma and Ehrlich ascites tumor cells.121,122 Also, in MG63 osteosarcoma cells, the overexpression of TASK-1 was reported.118 Additionally, TASK-1 is overexpressed in a subset of non-small cell lung cancers, promoting proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis. TASK-1 knockdown enhances apoptosis and reduces the proliferation of lung cancer cell-line A549.123 In these cells, A549, the overexpression of TASK-1 promoted epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), a pivotal event in lung cancer cell invasion and metastasis.124 Moreover, the expression of TASK-1 has been associated with aldosterone production in both aldosterone-producing adenomas and normal adrenals.125
The second K2P channel associated with cancer is TASK-2 (K2P5; encoded by KCNK5 gene), a member of the TALK subfamily. TASK-2 plays a role in the proliferation of estrogen α receptor positive breast cancer cells being highly upregulated in response to 17β-estradiol (E2) in MCF-7 and T47D breast cancer cell lines.126,127 In these cells, the knockdown of the TASK-2 channel reduces the estrogen-induced proliferation of breast cancer cells.127 Also, the overexpression of TASK-2 has found in HPAF cells, a human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell line, but the role in cancer progression has not been further studied.128
Among the K2P channels, the most studied in cancer correspond to TASK-3 (TWIK-related acid-sensitive K+ channel 3). This channel has been shown to localize in both the plasma membrane and mitochondrial inner membrane.117 The TASK-3 channel overexpression occurs in several types of cancer, such as melanoma, ovarian carcinoma, and breast cancer.24,117,129–132
Also, TASK-3 (KCNK9, located in chromosomal region 8q24.3) gene expression is enhanced by 10–44% in human breast tumors and 35% in lung tumors.24 Additionally, overexpression of KCNK9 has been reported in over 90% of ovarian tumors.130 In most cases studied, TASK-3 is associated with the acquisition of malignant characteristics, including hypoxia resistance or serum deprivation conditions.24,25 Consistently, a monoclonal antibody (Y4) against the cap domain of TASK-3 inhibits the growth of human lung cancer xenografts and breast cancer metastasis in mice.133 Further studies showed that TASK-3 gene knockdown in breast cancer cells is associated with an induction of cellular senescence and cell cycle arrest.132 Furthermore, TASK-3 is overexpressed in colorectal cancers and gastric cancers.134–136 In gastric adenocarcinoma cells, the TASK-3 gene knockdown causes changes in migration and reduces cell proliferation and viability by increasing apoptosis without ffecting cell cycle checkpoints.136
TASK-3 is highly expressed in melanoma,117,129,137 being identified in the inner mitochondrial membrane of melanocytes, WM35 and B16F10, and keratinocytes.117,129,137,138 In WM35 and A2058, human melanoma cells, the knockdown of TASK-3 resulted in compromised mitochondrial function, mitochondrial membrane depolarization, and reduced cell survival inducing apoptosis.139,140
Another K2P channel related to cancer is TREK-1 (K2P2, encoded by KCNK2). This channel has been shown to play a pro-proliferative role in the human prostate cancer cell-line PC3.116 In MG63 osteosarcoma cells, overexpression of TREK-1 was reported118 and it is correlated with the proliferation of the osteoblast cells.141 TREK-1 is also overexpressed in prostate cancer tissues142 and epithelial ovarian cancer.130 For TREK-1 channel, the exact role of cancer development is still unclear. However, TREK-1 overexpression is associated with a poor prognosis for patients with prostate cancer.142 In prostate cancer, inhibition or knockdown of TREK-1 inhibits proliferation by inducing cell cycle arrest at the G1/S checkpoint.142 On the other side, the treatment with TREK-1-blocking agents, such as curcumin, has shown reduced ovarian cancer cells proliferation and increased late apoptosis processes.130
Among the TREK subfamily, the TREK-2 channel (K2P10, encoded by KCNK10) was present in bladder cancer cell lines and contributed to cell cycle-dependent growth.119 The sixth K2P channel involved in cancer is TWIK-1 (K2P1, encoded by KCNK1). The TWIK-1 was detected as an upregulated channel in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) compared to normal tissue.115 Recently, TWIK-2 (K2P6, encoded by KCNK6 gene) was reported as a significantly overexpressed channel in breast cancer.120 Moreover, the overexpression of TWIK-2 increases the capacity of proliferation, invasion, and migration of breast cancer cells.120
Strategies for Designing New K+ Channels Blockers
The rational design and development of selective blockers is a dynamic field of study that includes diverse methods such as high-throughput screening, bioengineering techniques, and chemical modification, among others.143,144 Fortunately, we count on several software and computational tools that allow us to explore innovative approaches based on the molecular interaction of potassium channels structural data from the ligands and molecules, and the physicochemical and pharmacological properties of K+ channels interacting with drugs.
Some computational tools used for the rational design of specific modulators (blockers and activators) examine the three-dimensional structure of the target (K+ channels, in this case), previously solved by X-ray crystallography, cryoelectron microscopy145 or comparative modeling. Following this, it is necessary to study the binding sites and affinity of the ligand.143 This approach has been particularly helpful for the identification of ligands, targeting membrane proteins.146,147
Additionally, the multidisciplinary work among different areas, such as biochemistry, bioinformatics, bioengineering, medical chemistry, genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, has contributed to the development of new computational tools for the rational design of ion channel modulators.143 Thus, the combinatory strategy including docking, virtual screening, de novo drug design, molecular simulations and the experimental validation by electrophysiological measures have allowed the development and a successful search for small modulators.146,147 For the K+ channels, a three-dimensional structure of representative K+ subunits (Kv, K2P, and Kir) has been reported, providing insights into how these channels can be used to design specific modulators for cancer treatment.
Moreover, ion channels with limited background expression in normal tissues and strong overexpression in tumors due to their cell-surface accessibility constitute a preferential target for the development of antibody-based therapies.148–152 Antibodies recognizing ion channels represent a strategy effective in modulation of ion channel activity. The mechanisms of action include direct block of ion permeation pathway, modulation of ion channel gating, and internalization and degradation upon surface clustering.152–154 For example, systemic administration of specific mouse monoclonal antibodies generated in the human channel K2P9 (KCNK9) using its M1P1 loop fused into the Fc domain of IgG2a, effectively inhibits the growth of human lung cancer xenografts and murine breast cancer metastasis in mice.133 In addition, a specific monoclonal antibody which inhibits the function of highly oncogenic Kv10.1 potassium channel can effectively restrict cancer cell proliferation and reduce tumor growth in animal models with no significant side effects.155 However, currently, only one polyclonal antibody (BIL010t; Biosceptre) targeting a non-functional form of P2X7 (nfP2X7) has reached the level of clinical trials for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma.156,157
Other developing innovative strategies consist of the rational design of specific short peptides (less than 50 amino acid residues), which have acquired widespread interest as tools to address challenging protein−protein interactions (PPIs).158,159 These short peptides can form complexes, and structures, mimicking critical motifs of proteins,160 which allow them to inhibit PPIs or functional activities with high specificity and affinity, emerging as a promising alternative to small molecules and biopharmaceuticals (>5000 Da). Furthermore, short peptides are easy to produce and modify161 and present low off-target side-effects given their higher specificity and reduced immunogenicity.161 All those attractive features make short peptides exceptional candidates to serve as therapeutics, even more considering that more than 100 peptide-based drugs are available in the market for AIDS, Cancer, and other medical conditions.162,163 Some examples of therapeutic drug-based peptides include oxytocin (8 aa), calcitonin (32 aa), teriparatide (34 aa), Fuzeon (36 aa, antiretroviral), corticotropin-releasing hormone (41 aa), and growth-hormone-releasing hormone (44 aa).159
Additionally, animal venoms are a natural and affluent source of peptides.164–166 These peptide sources (from different animals such as cone snails, scorpions, sea anemones, snakes, spiders, among others) have been widely used as a starting point to develop toxin-based drugs, and some of them have currently reached clinical trials.165 Captopril was the first toxin-based drug approved for humans (1981). It is a nonapeptide that acts by blocking the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity inhibiting the production of angiotensin II and was developed from Bothrops jararaca snake venom.167 Captopril is currently suitable and widely used for hypertension treatment.168 Among the different approved toxin-based drugs marketed, the ziconotide is obtained from cone snails, exenatide and lixisenatide are obtained from lizards. Bivalirudin and desirudin from leeches and Batroxobin and cobratide are purified from snake venoms.165 Desirudin, on the other hand, is a recombinant peptide derivated from snake. Other drugs (bivalirudin, enalapril, eptifibatide, exenatide, tirofiban, and ziconotide) are synthetic molecules from the same source.165
Currently, a large number of ionic channel blocking peptides (for Ca2+, K+ and Na+ channels) have been reported and obtained from different origin.166,169–173 For instance, some peptides with antitumor effect are κ-hefutoxin 1 and analogues, APETx4, purpurealidin analogs, KAaH1 and KAaH2 among others.174–177
There is no doubt that the specific short peptide blockers can inhibit the functional activity of K+ channels and show an antitumor effect, impacting the hallmark of cancer and representing a novel strategy for the rational design of new cancer drugs.
Conclusion
Compelling evidence indicates that the upregulation of the majority of K+ channels is associated with current cancer hallmarks (Figure 2 and Table 1). Thus, these channels have emerged as alternatives to develop new cancer treatments. K+ channel subunits are diverse and highly regulated proteins that respond to different stimuli. In different cancer conditions, where K+ channels are overexpressed, K+ channel blockers have been shown to reduce the tumorigenic properties and reverse the cancer progression in cell lines and animal models. However, K+ channels are critical regulators in several cellular and physiological processes; therefore, the search for selective K+ channel blockers becomes restrictive in developing future cancer treatments. Fortunately, the 3D structure of representative K+ channels178–180 opens new possibilities for the rational design of highly selective K+ modulators.
The research for these highly selective potassium channel blockers must also include natural products (eg, plant extracts), bioinformatics search using the database (eg, Zinc181), venoms peptides, and the design of cyclic peptides (CPs) as modulators of protein–protein interactions. Indeed, there is no doubt that rational design, search, and development might increase the therapeutic arsenal of drugs against cancer conditions associated with K+ channels. Nevertheless, the design, search, and development of selective K+ channel blockers remains a challenge that must be addressed in a multidisciplinary manner, including chemistry, bioinformatics, bioengineering, and biophysics groups.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by Fondecyt 1191133 to WG and LZ, FIC-R BIP 40.027.577-0 “Portafolio de servicios para la caracterización de blancos terapéuticos para el tratamiento de cáncer y enfermedades crónicas no transmisibles” to WG and LZ. C.V. acknowledges the financial support of the National Fund for Science & Technology Development – FONDECYT 1201147 and the BASAL Grant AFB180001 (CEDENNA) from the National Research and Development Agency (ANID), Government of Chile.
Author Contributions
All authors made a significant contribution to the work reported, whether that is in the conception, study design, execution, analysis and interpretation, or in all these areas; took part in drafting, revising or critically reviewing the article; gave final approval of the version to be published; have agreed on the journal to which the article has been submitted; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed in the funding section and report no conflicts of interest in relation to this work.
References
- 1.Goldstein SAN, Bockenhauer D, O’Kelly I, Zilberberg N. Potassium leak channels and the KCNK family of two-P-domain subunits. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2(3):175–184. doi: 10.1038/35058574 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.González C, Baez-Nieto D, Valencia I, et al. K+ channels: function-structural overview. Compr Physiol. 2012;2:2087–2149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hibino H, Inanobe A, Furutani K, et al. Inwardly rectifying potassium channels: their structure, function, and physiological roles. Physiol Rev. 2010;90(1):291–366. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cui M, Cantwell L, Zorn A, Logothetis DE. Kir channel molecular physiology, pharmacology, and therapeutic implications. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;267:277–356. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zúñiga L, Zúñiga R. Understanding the cap structure in K2P channels. Front Physiol. 2016;7:228. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhou Y, Morais-Cabral JH, Kaufman A, MacKinnon R. Chemistry of ion coordination and hydration revealed by a K+ channel-Fab complex at 2.0 Å resolution. Nature. 2001;414(6859):43–48. doi: 10.1038/35102009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bezanilla F. The voltage sensor in voltage-dependent ion channels. Physiol Rev. 2000;80(2):555–592. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2000.80.2.555 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jiang Y, Lee A, Chen J, et al. X-ray structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature. 2003;423(6935):33–41. doi: 10.1038/nature01580 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lotshaw DP. Biophysical, pharmacological, and functional characteristics of cloned and native mammalian two-pore domain K+ channels. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2007;47:209–256. doi: 10.1007/s12013-007-0007-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Enyedi P, Czirják G. Molecular background of leak K+ currents: two-pore domain potassium channels. Physiol Rev. 2010;90:559–605. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00029.2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Goss PE, Lee BL, Badovinac-Crnjevic T, et al. Planning cancer control in Latin America and the Caribbean. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(5):391–436. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70048-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bates E. Ion channels in development and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2015;31(1):231–247. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100814-125338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huang X, Jan LY. Targeting potassium channels in cancer. J Cell Biol. 2014;206(2):151–162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201404136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pardo LA, Stühmer W. The roles of K+ channels in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(1):39–48. doi: 10.1038/nrc3635 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Prevarskaya N, Skryma R, Shuba Y. Ion channels in cancer: are cancer hallmarks oncochannelopathies? Physiol Rev. 2018;98(2):559–621. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00044.2016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Ahidouch A. K+ channel expression in human breast cancer cells: involvement in cell cycle regulation and carcinogenesis. J Membr Biol. 2008;221(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/s00232-007-9080-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shen Z, Yang Q, You Q. Researches toward potassium channels on tumor progressions. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9(4):322–329. doi: 10.2174/156802609788317874 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lesage F, Lazdunski M. Molecular and functional properties of two-pore-domain potassium channels. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000;279:F793–F801. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.2000.279.5.F793 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee G-W, Park HS, Kim E-J, et al. Reduction of breast cancer cell migration via up-regulation of TASK-3 two-pore domain K+ channel. Acta Physiol. 2012;204:513–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02359.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kunzelmann K. Ion channels and cancer. J Membr Biol. 2005;205:159–173. doi: 10.1007/s00232-005-0781-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang Z. Roles of K+ channels in regulating tumour cell proliferation and apoptosis. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol. 2004;448:274–286. doi: 10.1007/s00424-004-1258-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Asher V, Sowter H, Shaw R, Bali A, Khan R. Eag and HERG potassium channels as novel therapeutic targets in cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 2010;8(1):113. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-8-113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mu D, Chen L, Zhang X, et al. Genomic amplification and oncogenic properties of the KCNK9 potassium channel gene. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:297–302. doi: 10.1016/S1535-6108(03)00054-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pei L, Wiser O, Slavin A, et al. Oncogenic potential of TASK3 (Kcnk9) depends on K+ channel function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:7803–7807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1232448100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brevet M, Fucks D, Chatelain D, et al. Deregulation of 2 potassium channels in pancreas adenocarcinomas: implication of KV1.3 gene promoter methylation. Pancreas. 2009;38(6):649–654. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181a56ebf [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hasselblatt M, Böhm C, Tatenhorst L, et al. Identification of novel diagnostic markers for choroid plexus tumors: a microarray-based approach. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30(1):66–74. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000176430.88702.e0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Liu H, Huang J, Peng J, et al. Upregulation of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir2.1 (KCNJ2) modulates multidrug resistance of small-cell lung cancer under the regulation of miR-7 and the Ras/MAPK pathway. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:59. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0298-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Murthy M, Azizan EA, Brown MJ, O’Shaughnessy KM. Characterization of a novel somatic KCNJ5 mutation delI157 in an aldosterone-producing adenoma. J Hypertens. 2012;30(9):1827–1833. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328356139f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Park S-H, Ramachandran S, Kwon S-H, et al. Upregulation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels for estrogen-mediated cell proliferation in human uterine leiomyoma cells. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2008;24(5):250–256. doi: 10.1080/09513590801893315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sakai H, Shimizu T, Hori K, et al. Molecular and pharmacological properties of inwardly rectifying K+ channels of human lung cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;435(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/S0014-2999(01)01567-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Warth A, Mittelbronn M, Wolburg H. Redistribution of the water channel protein aquaporin-4 and the K+ channel protein Kir4.1 differs in low- and high-grade human brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol. 2005;109(4):418–426. doi: 10.1007/s00401-005-0984-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wulff H, Castle NA. Therapeutic potential of KCa3.1 blockers: an overview of recent advances, and promising trends. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2010;3(3):385–396. doi: 10.1586/ecp.10.11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Ahidouch A, Pardo LA. Kv10.1 K+ channel: from physiology to cancer. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol. 2016;468(5):751–762. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1784-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chow LW, Cheng K-S, Wong K-L, Leung Y-M. Voltage-gated K+ channels promote BT-474 breast cancer cell migration. Chin J Cancer Res. 2018;30(6):613–622. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2018.06.06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Miceli F, Guerrini R, Nappi M, et al. Distinct epilepsy phenotypes and response to drugs in KCNA1 gain- and loss-of function variants. Epilepsia. 2022;63(1):e7–e14. doi: 10.1111/epi.17118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.van der Wijst J, Konrad M, Verkaart SA, et al. A de novo KCNA1 mutation in a patient with tetany and hypomagnesemia. Nephron. 2018;139:359–366. doi: 10.1159/000488954 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liu L, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Li C. Silencing of KCNA1 suppresses the cervical cancer development via mitochondria damage. Channels. 2019;13(1):321–330. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2019.1648627 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Taylor MD, Northcott PA, Korshunov A, et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;123(4):465–472. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0922-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bielanska J, Hernández-Losa J, Moline T, et al. Differential expression of Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 voltage-dependent K+ channels in human skeletal muscle sarcomas. Cancer Invest. 2012;30(3):203–208. doi: 10.3109/07357907.2012.654872 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bielanska J, Hernández-Losa J, Moline T, et al. Increased voltage-dependent K+ channel Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 expression correlates with leiomyosarcoma aggressiveness. Oncol Lett. 2012;4(2):227–230. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Comes N, Bielanska J, Vallejo-Gracia A, et al. The voltage-dependent K+ channels Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 in human cancer. Front Physiol. 2013;4:283. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00283 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Teisseyre A, Gąsiorowska J, Michalak K. Voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.3 Potentially new molecular target in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2015;24(3):517–524. doi: 10.17219/acem/22339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Teisseyre A, Palko-Labuz A, Sroda-Pomianek K, Michalak K. Voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 as a target in therapy of cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:933. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00933 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Leanza L, Romio M, Becker KA, et al. Direct pharmacological targeting of a mitochondrial ion channel selectively kills tumor cells in vivo. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(4):516–531. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Venturini E, Leanza L, Azzolini M, et al. Targeting the potassium channel Kv1.3 kills glioblastoma cells. Neurosignals. 2017;25(1):26–38. doi: 10.1159/000480643 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Checchetto V, Prosdocimi E, Leanza L. Mitochondrial Kv1.3: a new target in cancer biology? Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;53(S1):52–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Preußat K, Beetz C, Schrey M, et al. Expression of voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 in human gliomas. Neurosci Lett. 2003;346(1–2):33–36. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3940(03)00562-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lan M, Shi Y, Han Z, et al. Expression of delayed rectifier potassium channels and their possible roles in proliferation of human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005;4(12):1342–1347. doi: 10.4161/cbt.4.12.2175 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Vallejo-Gracia A, Bielanska J, Hernández-Losa J, et al. Emerging role for the voltage-dependent K+ channel Kv1.5 in B-lymphocyte physiology: expression associated with human lymphoma malignancy. J Leukoc Biol. 2013;94(4):779–789. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0213094 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Park HW, Song MS, Sim HJ, Ryu PD, Lee SY. The role of the voltage-gated potassium channel, Kv2.1 in prostate cancer cell migration. BMB Rep. 2021;54(2):130–135. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.2.210 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Park JH, Park SJ, Chung MK, et al. High expression of large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel in the CD133+ subpopulation of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;396(3):637–642. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.142 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chang K-W, Yuan T-C, Fang K-P, et al. The increase of voltage-gated potassium channel Kv3.4 mRNA expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 2003;32(10):606–611. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0714.2003.00197.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Menéndez ST, Rodrigo JP, Allonca E, et al. Expression and clinical significance of the Kv3.4 potassium channel subunit in the development and progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Pathol. 2010;221(4):402–410. doi: 10.1002/path.2722 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Song MS, Park SM, Park JS, et al. Kv3.1 and Kv3.4, are involved in cancer cell migration and invasion. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1061. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jang SH, Choi C, Hong S-G, et al. Silencing of Kv4.1 potassium channels inhibits cell proliferation of tumorigenic human mammary epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;384(2):180–186. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kim H-J, Jang SH, Jeong YA, et al. Involvement of Kv4.1 K+ channels in gastric cancer cell proliferation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(10):1754–1757. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1754 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Shimizu T, Fujii T, Takahashi Y, et al. Up-regulation of Kv7.1 channels in thromboxane A2-induced colonic cancer cell proliferation. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol. 2014;466(3):541–548. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1341-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Serrano-Novillo C, Oliveras A, Ferreres JC, Condom E, Felipe A. Remodeling of Kv7.1 and Kv7.5 expression in vascular tumors. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):6019. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lee J-H, Park J-W, Byun JK, et al. Silencing of voltage-gated potassium channel Kv9.3 inhibits proliferation in human colon and lung carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6:8132–8143. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3517 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Suzuki T, Takimoto K. Selective expression of HERG and Kv2 channels influences proliferation of uterine cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2004;25(1):153–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hemmerlein B, Weseloh RM. Mello de Queiroz F, et al. Overexpression of Eag1 potassium channels in clinical tumours. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:41. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-41 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cázares-Ordoñez V, Pardo LA. Kv10.1 potassium channel: from the brain to the tumors. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017;95(5):531–536. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2017-0062 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mello de Queiroz F, Suarez-Kurtz G, Stühmer W, Pardo LA. Ether à go-go potassium channel expression in soft tissue sarcoma patients. Mol Cancer. 2006;5(1):42. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-42 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Martínez R, Stühmer W, Martin S, et al. Analysis of the expression of Kv10.1 potassium channel in patients with brain metastases and glioblastoma multiforme: impact on survival. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:839. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1848-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wang X, Chen Y, Zhang Y, et al. Eag1 voltage-dependent potassium channels: structure, electrophysiological characteristics, and function in cancer. J Membr Biol. 2017;250(2):123–132. doi: 10.1007/s00232-016-9944-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Agarwal JR, Griesinger F, Stühmer W, Pardo LA. The potassium channel Ether à go-go is a novel prognostic factor with functional relevance in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Cancer. 2010;9(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Chávez-López MG, Zúñiga-García V, Castro-Magdonel BE, et al. Eag1 gene and protein expression in human retinoblastoma tumors and its regulation by pRb in HeLa cells. Genes. 2020;11(2):119. doi: 10.3390/genes11020119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hartung F, Stühmer W, Pardo LA. Tumor cell-selective apoptosis induction through targeting of KV10.1 via bifunctional TRAIL antibody. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:109. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Pardo LA, Gómez-Varela D, Major F, et al. Approaches targeting KV10.1 open a novel window for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(5):675–682. doi: 10.2174/092986712798992011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Sales TT, Resende FF, Chaves NL, et al. Suppression of the Eag1 potassium channel sensitizes glioblastoma cells to injury caused by temozolomide. Oncol Lett. 2016;12(4):2581–2589. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Valdés-Abadía B, Morán-Zendejas R, Rangel-Flores JM, Rodríguez-Menchaca AA. Chloroquine inhibits tumor-related Kv10.1channel and decreases migration of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;855:262–266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hernández-Reséndiz I, Pacheu-Grau D, Sánchez A, Pardo LA. Inhibition of Kv10.1 channels sensitizes mitochondria of cancer cells to antimetabolic agents. Cancers. 2020;12(4):920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Staudacher I, Jehle J, Staudacher K, et al. HERG K+ channel-dependent apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human glioblastoma cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Banderali U, Belke D, Singh A, et al. Curcumin blocks Kv11.1 (erg) potassium current and slows proliferation in the infant acute monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;28(6):1169–1180. doi: 10.1159/000335850 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Perez-Neut M, Rao VR, Gentile S. hERG1/Kv11.1 activation stimulates transcription of p21waf/cip in breast cancer cells via a calcineurin-dependent mechanism. Oncotarget. 2016;7(37):58893–58902. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3797 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lastraioli E, Romoli MR, Iorio J, et al. The hERG1 potassium channel behaves as prognostic factor in gastric dysplasia endoscopic samples. OncoTargets Ther. 2019;12:9377–9384. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S226257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Pillozzi S, D’Amico M, Bartoli G, et al. The combined activation of KCa3.1 and inhibition of Kv11.1/hERG1 currents contribute to overcome Cisplatin resistance in colorectal cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2018;118(2):200–212. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.He S, Moutaoufik MT, Islam S, et al. HERG channel and cancer: a mechanistic review of carcinogenic processes and therapeutic potential. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020;1873(2):188355. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Arcangeli A, Becchetti A. Novel perspectives in cancer therapy: targeting ion channels. Drug Resist Updat. 2015;21:11–19. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2015.06.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Jehle J, Schweizer PA, Katus HA, Thomas D. Novel roles for hERG K+ channels in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2011;2(8):e193. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.77 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Du C, Chen L, Zhang H, et al. Caveolin-1 limits the contribution of BKCa channel to MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(11):20706–20722. doi: 10.3390/ijms151120706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Du C, Zheng Z, Li D, et al. BKCa promotes growth and metastasis of prostate cancer through facilitating the coupling between αvβ3 integrin and FAK. Oncotarget. 2016;7(26):40174–40188. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Klumpp L, Sezgin EC, Eckert F, Huber SM. Ion channels in brain metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(9):1513. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091513 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Li N, Liu L, Li G, et al. The role of BKCa in endometrial cancer HEC-1-B cell proliferation and migration. Gene. 2018;655:42–47. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.02.055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Noda S, Chikazawa K, Suzuki Y, Imaizumi Y, Yamamura H. Involvement of the γ1 subunit of the large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel in the proliferation of human somatostatinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;525(4):1032–1037. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Oeggerli M, Tian Y, Ruiz C, et al. Role of KCNMA1 in breast cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041664 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Turner KL, Honasoge A, Robert SM, McFerrin MM, Sontheimer H. A proinvasive role for the Ca2+-activated K+ channel KCa3.1 in malignant glioma. Glia. 2014;62(6):971–981. doi: 10.1002/glia.22655 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Steudel FA, Mohr CJ, Stegen B, et al. SK4 channels modulate Ca2+ signalling and cell cycle progression in murine breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2017;11(9):1172–1188. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Glaser F, Hundehege P, Bulk E, et al. KCa channel blockers increase effectiveness of the EGF receptor TK inhibitor erlotinib in non-small cell lung cancer cells (A549). Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):18330. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97406-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Schmidt J, Friebel K, Schönherr R, Coppolino MG, Bosserhoff A-K. Migration-associated secretion of melanoma inhibitory activity at the cell rear is supported by KCa3.1 potassium channels. Cell Res. 2010;20:1224–1238. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.121 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Stoneking CJ, Shivakumar O, Thomas DN, Colledge WH, Mason MJ. Voltage dependence of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel KCa3.1 in human erythroleukemia cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013;304(9):C858–C872. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00368.2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Rabjerg M, Oliván-Viguera A, Hansen LK, et al. High expression of KCa3.1 in patients with clear cell renal carcinoma predicts high metastatic risk and poor survival. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0122992. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Liu Y, Zhao L, Ma W, et al. The blockage of KCa3.1 channel inhibited proliferation, migration and promoted apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Cancer. 2015;6(7):643–651. doi: 10.7150/jca.11913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ruggieri P, Mangino G, Fioretti B, et al. The inhibition of KCa3.1 channels activity reduces cell motility in glioblastoma derived cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47825. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047825 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Chantome A, Girault A, Potier M, et al. KCa2.3 channel-dependent hyperpolarization increases melanoma cell motility. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(20):3620–3630. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.07.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Ji C-D, Wang Y-X, Xiang D-F, et al. Kir2.1 interaction with Stk38 promotes invasion and metastasis of human gastric cancer by enhancing MEKK2–MEK1/2–ERK1/2 signaling. Cancer Res. 2018;78(11):3041–3053. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3776 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Lee I, Park C, Kang WK. Knockdown of inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir2.2 suppresses tumorigenesis by inducing reactive oxygen species–mediated cellular senescence. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(11):2951–2959. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Lee I, Lee S-J, Kang TM, Kang WK, Park C. Unconventional role of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir2.2 as a constitutive activator of RelA in cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73(3):1056–1062. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Stringer BK, Cooper AG, Shepard SB. Overexpression of the G-protein inwardly rectifying potassium channel 1 (GIRK1) in primary breast carcinomas correlates with axillary lymph node metastasis. Cancer Res. 2001;61(2):582–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Takanami I, Inoue Y, Gika M. G-protein inwardly rectifying potassium channel 1 (GIRK 1) gene expression correlates with tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2004;4(1):79. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-4-79 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Plummer HK, Yu Q, Cakir Y, Schuller HM. Expression of inwardly rectifying potassium channels (GIRKs) and beta-adrenergic regulation of breast cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer. 2004;4(1):93. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-4-93 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Scholl UI, Lifton RP. New insights into aldosterone-producing adenomas and hereditary aldosteronism: mutations in the K+ channel KCNJ5. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013;22(2):141–147. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32835cecf8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Tan G, Sun SQ, Yuan DL. Expression of Kir 4.1 in human astrocytic tumors: correlation with pathologic grade. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367(4):743–747. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Núñez M, Medina V, Cricco G, et al. Glibenclamide inhibits cell growth by inducing G0/G1 arrest in the human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;14(1):6. doi: 10.1186/2050-6511-14-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Zhang K, Mu L, Ding M-C, et al. NFκB mediated elevation of KCNJ11 promotes tumor progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through interaction of lactate dehydrogenase A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495(1):246–253. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Vázquez-Sánchez AY, Hinojosa LM, Parraguirre-Martínez S, et al. Expression of KATP channels in human cervical cancer: potential tools for diagnosis and therapy. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(5):6302–6308. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8165 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Huang L, Li B, Li W, Guo H, Zou F. ATP-sensitive potassium channels control glioma cells proliferation by regulating ERK activity. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(5):737–744. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Schittenhelm J, Nagel C, Meyermann R, Beschorner R. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors may show morphological and immunohistochemical features seen in choroid plexus tumors. Neuropathology. 2011;31(5):461–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2010.01189.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Japp AS, Klein-Hitpass L, Denkhaus D, Pietsch T. OTX2 defines a subgroup of atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors with close relationship to choroid plexus tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2017;76(1):32–38. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlw101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Katoh M, Sawamura Y, Tanaka S, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of cerebral intraparenchymal choroid plexus tumor: case report. J Neurol Surg a Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2019;80(1):53–57. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1615284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Brohawn SG, Del Mármol J, MacKinnon R. Crystal structure of the human K2P TRAAK, a lipid- and mechano-sensitive K+ ion channel. Science. 2012;335(6067):436–441. doi: 10.1126/science.1213808 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Miller AN, Long SB. Crystal structure of the human two pore domain potassium channel K2P1. Science. 2012;335(6067):432–436. doi: 10.1126/science.1213274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Concha G, Bustos D, Zúñiga R, Catalán M, Zúñiga L. The insensitivity of TASK-3 K2P channels to external tetraethylammonium (TEA) partially depends on the cap structure. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2437. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082437 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Williams S, Bateman A, O’Kelly I. Altered expression of two-pore domain potassium (K2P) channels in cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8:e74589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Voloshyna I, Besana A, Castillo M, et al. TREK-1 is a novel molecular target in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68(4):1197–1203. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Pocsai K, Kosztka L, Bakondi G, et al. Melanoma cells exhibit strong intracellular TASK-3-specific immunopositivity in both tissue sections and cell culture. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63(19–20):2364–2376. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6166-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Li X, Dong X, Zheng S, Xiao J. Expression and localization of TASK-1, −2 and −3 channels in MG63 human osteoblast-like cells. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(3):865–869. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.1088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Park K-S, Han MH, Jang HK, et al. The TREK2 channel is involved in the proliferation of 253J cell, a human bladder carcinoma cell. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;17(6):511–516. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.6.511 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Hou X, Tang L, Li X, et al. Potassium channel protein KCNK6 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:616784. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.616784 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Ernest NJ, Logsdon NJ, McFerrin MB, Sontheimer H, Spiller SE. Biophysical properties of human medulloblastoma cells. J Membr Biol. 2010;237(2–3):59–69. doi: 10.1007/s00232-010-9306-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Hougaard C, Jørgensen F, Hoffmann E. Modulation of the volume-sensitive K+ current in Ehrlich ascites tumour cells by pH. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol. 2001;442(4):622–633. doi: 10.1007/s004240100585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Leithner K, Hirschmugl B, Li Y, et al. TASK-1 regulates apoptosis and proliferation in a subset of non-small cell lung cancers. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0157453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157453 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Wang X-G, Yuan N-X, Li X-P, Chen -F-F. TASK-1 induces gefitinib resistance by promoting cancer initiating cell formation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(1):365–370. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Nogueira EF, Gerry D, Mantero F, Mariniello B, Rainey WE. The role of TASK1 in aldosterone production and its expression in normal adrenal and aldosterone-producing adenomas. Clin Endocrinol. 2010;73(1):22–29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Williams C, Edvardsson K, Lewandowski SA, Ström A, Gustafsson J-Å. A genome-wide study of the repressive effects of estrogen receptor beta on estrogen receptor alpha signaling in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2008;27(7):1019–1032. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210712 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Alvarez-Baron CP, Jonsson P, Thomas C, Dryer SE, Williams C. The two-pore domain potassium channel KCNK5: induction by estrogen receptor α and role in proliferation of breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25(8):1326–1336. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-0045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Fong P, Argent BE, Guggino WB, Gray MA. Characterization of vectorial chloride transport pathways in the human pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma cell line HPAF. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;285(2):C433–C445. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00509.2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Rusznák Z, Bakondi G, Kosztka L, et al. Mitochondrial expression of the two-pore domain TASK-3 channels in malignantly transformed and non-malignant human cells. Virchows Arch. 2008;452(4):415–426. doi: 10.1007/s00428-007-0545-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Innamaa A, Jackson L, Asher V, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of the oncogenic K2P potassium channel KCNK9 (TASK-3) in ovarian carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:1401–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Patel AJ, Lazdunski M. The 2P-domain K+ channels: role in apoptosis and tumorigenesis. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol. 2004;448:261–273. doi: 10.1007/s00424-004-1255-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Zúñiga R, Valenzuela C, Concha G, Brown N, Zúñiga L. TASK-3 downregulation triggers cellular senescence and growth inhibition in breast cancer cell lines. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1033. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Sun H, Luo L, Lal B, et al. A monoclonal antibody against KCNK9 K+ channel extracellular domain inhibits tumour growth and metastasis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10339. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Kovács I, Pocsai K, Czifra G, et al. TASK-3 immunoreactivity shows differential distribution in the human gastrointestinal tract. Virchows Arch. 2005;446(4):402–410. doi: 10.1007/s00428-005-1205-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Kim CJ, Cho YG, Jeong SW, et al. Altered expression of KCNK9 in colorectal cancers. APMIS. 2004;112(9):588–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2004.apm1120905.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Cikutović-Molina R, Herrada AA, González W, Brown N, Zúñiga L. TASK-3 gene knockdown dampens invasion and migration and promotes apoptosis in KATO III and MKN-45 human gastric adenocarcinoma cell lines. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6077. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236077 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Toczylowska-Maminska R, Olszewska A, Laskowski M, et al. Potassium channel in the mitochondria of human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(3):764–772. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.422 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Checchetto V, Leanza L, De Stefani D, et al. Mitochondrial K+ channels and their implications for disease mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;227:107874. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107874 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Kosztka L, Rusznák Z, Nagy D, et al. Inhibition of TASK-3 (KCNK9) channel biosynthesis changes cell morphology and decreases both DNA content and mitochondrial function of melanoma cells maintained in cell culture. Melanoma Res. 2011;21(4):308–322. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e3283462713 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Nagy D, Gönczi M, Dienes B, et al. Silencing the KCNK9 potassium channel (TASK-3) gene disturbs mitochondrial function, causes mitochondrial depolarization, and induces apoptosis of human melanoma cells. Arch Dermatol Res. 2014;306(10):885–902. doi: 10.1007/s00403-014-1511-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Hughes S, Magnay J, Foreman M, et al. Expression of the mechanosensitive 2PK+ channel TREK-1 in human osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(3):738–748. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20536 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Zhang G-M, Wan F-N, Qin X-J, et al. Prognostic significance of the TREK-1 K2P potassium channels in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(21):18460–18468. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3782 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Ramírez D. Computational methods applied to rational drug design. Open Med Chem J. 2016;10:7–20. doi: 10.2174/1874104501610010007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Bedoya M, Rinné S, Kiper AK, et al. TASK channels pharmacology: new challenges in drug design. J Med Chem. 2019;62(22):10044–10058. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Ye D, Wang J, Yu K, et al. Current strategies for the discovery of K+ channel modulators. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9(4):348–361. doi: 10.2174/156802609788317865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Ramírez D, Concha G, Arévalo B, et al. Discovery of novel TASK-3 channel blockers using a pharmacophore-based virtual screening. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(16):4014. doi: 10.3390/ijms20164014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Toplak Ž, Hendrickx LA, Gubič Š, et al. 3D pharmacophore-based discovery of novel KV10.1 inhibitors with antiproliferative activity. Cancers. 2021;13(6):1244. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061244 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Stortelers C, Pinto-Espinoza C, Van Hoorick D, Koch-Nolte F. Modulating ion channel function with antibodies and nanobodies. Curr Opin Immunol. 2018;52:18–26. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2018.02.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Haustrate A, Hantute-Ghesquier A, Prevarskaya N, Lehen’kyi V. Monoclonal antibodies targeting ion channels and their therapeutic potential. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:606. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00606 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Hernandez-Resendiz I, Hartung F, Pardo LA. Antibodies targeting KV potassium channels: a promising treatment for cancer. Bioelectricity. 2019;1(3):180–187. doi: 10.1089/bioe.2019.0022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Hutchings CJ, Colussi P, Clark TG. Ion channels as therapeutic antibody targets. mAbs. 2019;11(2):265–296. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1548232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Wulff H, Christophersen P, Colussi P, Chandy KG, Yarov-Yarovoy V. Antibodies and venom peptides: new modalities for ion channels. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019;18(5):339–357. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0013-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sun H, Li M. Antibody therapeutics targeting ion channels: are we there yet? Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(2):199–204. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Douthwaite JA, Finch DK, Mustelin T, Wilkinson TC. Development of therapeutic antibodies to G protein-coupled receptors and ion channels: opportunities, challenges and their therapeutic potential in respiratory diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;169:113–123. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.04.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Gómez-Varela D, Zwick-Wallasch E, Knötgen H, et al. Monoclonal antibody blockade of the human Eag1 potassium channel function exerts antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 2007;67(15):7343–7349. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0107 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Gilbert SM, Oliphant CJ, Hassan S, et al. ATP in the tumour microenvironment drives expression of nfP2X7, a key mediator of cancer cell survival. Oncogene. 2019;38(2):194–208. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0426-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Gilbert SM, Gidley-Baird A, Glazer S, et al. A Phase I clinical trial demonstrates that nfP2X7-targeted antibodies provide a novel, safe and tolerable topical therapy for basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177(1):117–124. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15364 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Nevola L, Giralt E. Modulating protein-protein interactions: the potential of peptides. Chem Commun. 2015;51(16):3302–3315. doi: 10.1039/C4CC08565E [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Craik DJ, Fairlie DP, Liras S, Price D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2013;81(1):136–147. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Pelay-Gimeno M, Glas A, Koch O, Grossmann TN. Structure-based design of inhibitors of protein–protein interactions: mimicking peptide binding epitopes. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2015;54(31):8896–8927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Fosgerau K, Hoffmann T. Peptide therapeutics: current status and future directions. Drug Discov Today. 2015;20(1):122–128. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2014.10.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Naider F, Anglister J. Peptides in the treatment of AIDS. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009;19(4):473–482. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.07.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Schneider JA, Craven TW, Kasper AC, et al. Design of peptoid-peptide macrocycles to inhibit the β-catenin TCF interaction in prostate cancer. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4396. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06845-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Herzig V, Cristofori-Armstrong B, Israel MR, et al. Animal toxins — nature’s evolutionary-refined toolkit for basic research and drug discovery. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;181:114096. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Bordon KC, Cologna CT, Fornari-Baldo EC, et al. From animal poisons and venoms to medicines: achievements, challenges and perspectives in drug discovery. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1132. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Díaz-García A, Varela D. Voltage-gated K+/Na+ channels and scorpion venom toxins in cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:913. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Ferreira SH, Greene LJ, Alabaster VA, Bakhle YS, Vane JR. Activity of various fractions of bradykinin potentiating factor against angiotensin I converting enzyme. Nature. 1970;225(5230):379–380. doi: 10.1038/225379a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Weber MA, Schiffrin EL, White WB, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypertension in the community. J Clin Hypertens. 2014;16(1):14–26. doi: 10.1111/jch.12237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Olivera BM, Miljanich GP, Ramachandran J, Adams ME. Calcium channel diversity and neurotransmitter release: the ω-conotoxins and ω-agatoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63(1):823–867. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.King GF, Escoubas P, Nicholson GM. Peptide toxins that selectively target insect NaV and CaV channels. Channels. 2008;2(2):100–116. doi: 10.4161/chan.2.2.6022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Kalia J, Milescu M, Salvatierra J, et al. From foe to friend: using animal toxins to investigate ion channel function. J Mol Biol. 2015;427(1):158–175. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.07.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Doupnik CA. Venom-derived peptides inhibiting Kir channels: past, present, and future. Neuropharmacology. 2017;127:161–172. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Chow CY, Absalom N, Biggs K, King GF, Ma L. Venom-derived modulators of epilepsy-related ion channels. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;181:114043. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Moreels L, Peigneur S, Galan DT, et al. APETx4, a novel sea anemone toxin and a modulator of the cancer-relevant potassium channel KV10.1. Mar Drugs. 2017;15(9):287. doi: 10.3390/md15090287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Moreels L, Peigneur S, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Expanding the pharmacological profile of κ-hefutoxin 1 and analogues: a focus on the inhibitory effect on the oncogenic channel KV10.1. Peptides. 2017;98:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2016.08.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Moreels L, Bhat C, Voráčová M, et al. Synthesis of novel purpurealidin analogs and evaluation of their effect on the cancer-relevant potassium channel KV10.1. PLoS One. 2017;12(12):e0188811. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188811 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Aissaoui D, Mlayah-Bellalouna S, Jebali J, et al. Functional role of Kv1.1 and Kv1.3 channels in the neoplastic progression steps of three cancer cell lines, elucidated by scorpion peptides. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;111:1146–1155. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.144 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Rödström KE, Kiper AK, Zhang W, et al. A lower X-gate in TASK channels traps inhibitors within the vestibule. Nature. 2020;582:443–447. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2250-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Tyagi A, Ahmed T, Jian S, et al. Rearrangement of a unique Kv1.3 selectivity filter conformation upon binding of a drug. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022;119(5):e2113536119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113536119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Zhao C, MacKinnon R. Molecular structure of an open human KATP channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118(48):e2112267118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2112267118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK. ZINC − a free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J Chem Inf Model. 2005;45(1):177–182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Innamaa A, Jackson L, Asher V, et al. Expression and effects of modulation of the K2P potassium channels TREK-1 (KCNK2) and TREK-2 (KCNK10) in the normal human ovary and epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2013;15:910–918. doi: 10.1007/s12094-013-1022-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]