Abstract
Purpose of review
We aimed to systematically evaluate the content validity of patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) specifically developed to measure (aspects of) health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in people with type 2 diabetes. A systematic review was performed in PubMed and Embase of PROMs measuring perceived symptoms, physical function, mental function, social function/participation, and general health perceptions, and that were validated to at least some extent. Content validity (relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility) was evaluated using COSMIN methodology.
Recent findings
We identified 54 (different versions of) PROMs, containing 150 subscales. We found evidence for sufficient content validity for only 41/150 (27%) (subscales of) PROMs. The quality of evidence was generally very low. We found 66 out of 150 (44%) (subscales of) PROMs with evidence for either insufficient relevance, insufficient comprehensiveness, or insufficient comprehensibility. For measuring diabetes-specific symptoms, physical function, mental function, social function/participation, and general health perceptions, we identified one to 11 (subscales of) PROMs with sufficient content validity, although quality of the evidence was generally low. For measuring depressive symptoms, no PROM with sufficient content validity was identified.
Summary
For each aspect of HRQL, we found at least one PROM with sufficient content validity, except for depressive symptoms. The quality of the evidence was mostly very low.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s11892-022-01482-z.
Keywords: Patient-reported outcomes, Questionnaire, Validity, Diabetes, Systematic review, Quality of life
Introduction
In recent years, the use of patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) in routine diabetes care has significantly increased. PROMs are questionnaires completed by patients that measure perceived symptoms and the impact of symptoms on physical function, mental function, social function, and general health perceptions (often referred to as (aspects of) health-related quality of life (HRQOL)). PROMs have the potential to harness the voice of patients. They provide clinically important and complementary predictive information regarding effects of interventions, risk of hospitalization, and medication needs, can help clinicians with treatment decision support and monitoring, and help prioritize the use of healthcare resources for optimal public health benefit [1].
Many different PROMs are used in care and research in people with type 2 diabetes, yet no consensus exists regarding which PROMs to use in research or clinical practice. In our recent systematic review, we identified 108 unique PROMs for measuring HRQOL in people with type 2 diabetes, addressing a variety of constructs [2]. The harmonization of PROMs for use in diabetes care and research has been challenged by a lack of conceptual clarity and consensus regarding the core domains and constructs to be measured such as “diabetes-related quality of life” [1]. This heterogeneity hampers the usefulness of PROMs to inform value-based health care and is a serious threat to comparative effectiveness research, despite recent initiatives such as from the International Consortium for Health Outcomes Measurements (ICHOM) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA) to standardized PRO measurements [3, 4].
A good-quality PROM is developed in collaboration with patients to ensure that it measures what is most important to patients. Furthermore, the PROM should have good measurement properties, which means it is valid (it measures what aims to measure), reliable (it gives the same scores on repeated measurements in stable patients), and responsive (it is able to measure change in the PRO over time) (Appendix 1) [5].
A key part of validity is content validity, which is considered the most important measurement property, referring to the relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility of a PROM (Table 1) [5–8]. Relevance means that all questions (also called items) of a PROM measure things that are relevant for the outcome (also called construct), which the PROM aims to measure. It also means that the PROM does not measure things that are not related to the outcome of interest. For example, if a PROM aims to measure “physical function”, the questions should ask about the capability to perform, or perceived limitations in, relevant activities. The PROM should not include questions about other constructs, such as pain or fatigue. Comprehensiveness means that the PROM should measure all important aspects of the construct of interest; no key aspects should be missing. Furthermore, comprehensibility means that the questions are understood by people who complete them as intended. To be able to test whether a PROM has good content validity, the PROM should have a clear definition of the construct that it aims to measure. If a PROM does not have good content validity, wrong conclusions may be drawn when using that PROM [6].
Table 1.
Criteria for good content validity [6]
| Relevance | |
| 1 | Are the included items relevant for the construct of interest? |
| 2 | Are the included items relevant for the target population of interest? |
| 3 | Are the included items relevant for the context of use of interest? |
| 4 | Are the response options appropriate? |
| 5 | Is the recall period appropriate? |
| Comprehensiveness | |
| 6 | Are all key concepts included? |
| Comprehensibility | |
| 7 | Are the PROM instructions understood by the population of interest as intended? |
| 8 | Are the PROM items and response options understood by the population of interest as intended? |
| 9 | Are the PROM items appropriately worded? |
| 10 | Do the response options match the question? |
High-quality systematic reviews are needed that evaluate and compare the measurement properties of PROMs to select the best PROMs for research or care. At least 16 systematic reviews of PROMs have been published in the field of diabetes [9–24]. However, only seven reviews evaluated content validity of the included PROMs to some extent [10, 12, 13, 18–20, 22]. Five of these reviews did not provide a comprehensive overview of content validity but only evaluated whether people with diabetes were involved in the PROM development [10, 13, 18–20]. One review did not take the quality of the PROM development into account, and results for relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility were not presented separately, which limits its usefulness for identifying gaps and further development of the PROMs [22]. One review evaluated relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility separately, but this was only done for PROMs relevant to differentiate effects of oral hypoglycaemic agents [12].
The aim of the present study was to systematically evaluate the content validity of PROMs, which have specifically been developed to measure (aspects of) HRQOL in people with type 2 diabetes. We included PROMs that measured perceived symptoms, physical function, mental function, social function/participation, and general health perceptions and which were validated to at least some extent. We aim to provide evidence-based recommendations for the most suitable PROMs for use as outcome measures in research and clinical practice.
Methods
Design
We performed a systematic review using the Consensus-based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN) methodology for systematic reviews of PROMs [25] and for assessing content validity [6]. This review was part of a larger project that aimed to identify all PROMs measuring (aspects of) HRQOL used in the field of type 2 diabetes [2]. The protocol was registered in the PROSPERO database: CRD42017071012.
Literature Search
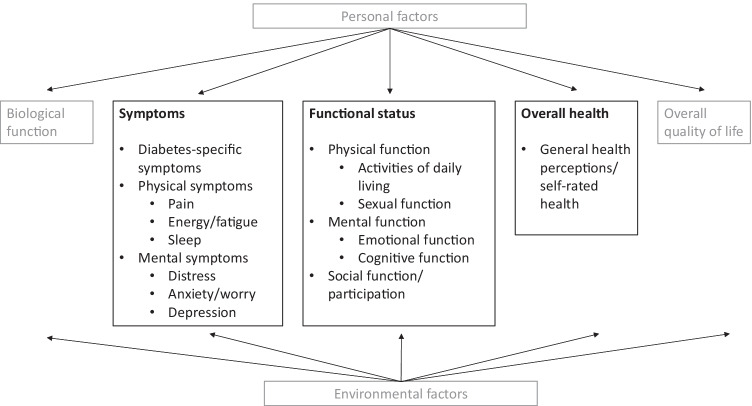
The full literature search and data extraction process are described elsewhere [2]. The exact search strategy can be found in Appendix 2. In brief, we searched the databases PubMed and Embase from inception till April 29, 2019. Inclusion criteria for this content validity review were, first, the PROM measures perceived symptoms, physical function, mental function, social function/participation, or general health perceptions (Fig. 1). Second, the PROM was developed specifically for people with type 2 diabetes or for all people with diabetes if at least 50% of the study population consisted of people with type 2 diabetes. Third, the PROM is useful for evaluative purposes (e.g. monitor change over time). Fourth, the aim of the study was the development of a PROM or an evaluation of content validity. Fifth, we also included studies reporting on a pilot study after translation of a PROM because such studies provide evidence for comprehensibility of the PROM. Sixth, we only included full-text papers, in English or Dutch, because detailed understanding of methods used in papers was required and the authors are not proficient in other languages. We excluded PROMs measuring overall quality of life (QOL) and PROMs that were primarily developed for diagnostic, screening, or prognostic purposes.
Fig. 1.
Model of health outcomes based on Wilson and Cleary [72]
Each abstract or full-text paper was independently reviewed by two reviewers from the review team. If reviewers disagreed, they discussed the abstract or paper until consensus was reached or a third author with experience in systematic reviews of PROMs made the final decision. References of the included articles were checked by one reviewer to search for additional potentially relevant studies. If information on PROM development was lacking in a paper, we searched Google (manuals or websites) and the PROQOLID database for additional resources.
Data Extraction
Data extraction on PROM characteristics was performed in the larger review [2]. For this content validity review, characteristics of the study populations included in the PROM development and content validity studies, i.e. age, sex, disease characteristics, setting, country, and language version of the PROM, were extracted by one reviewer.
Evaluation of Content Validity
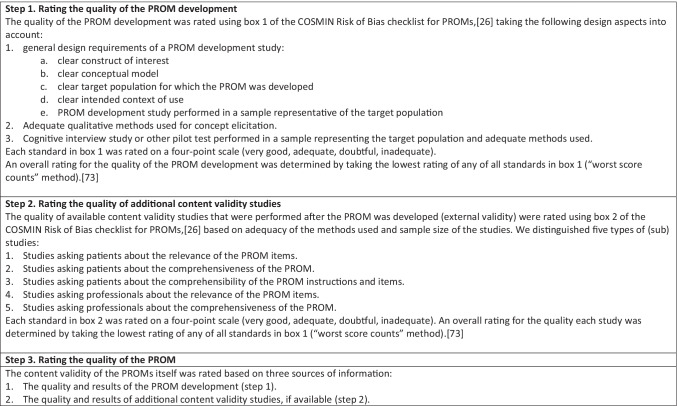
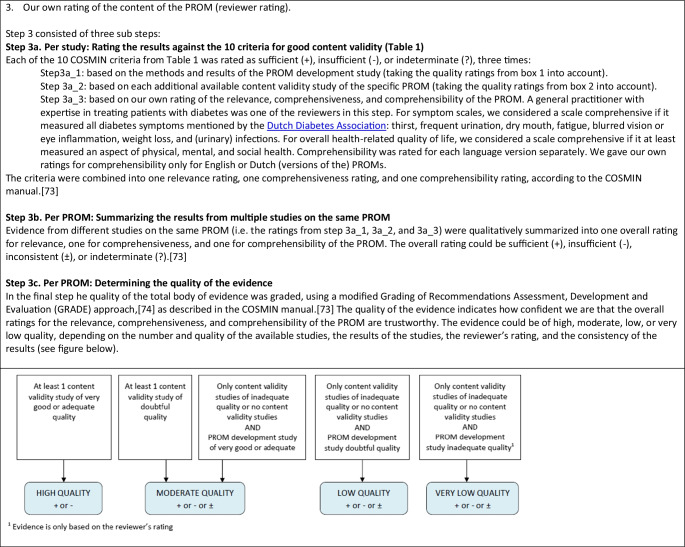
We assessed the content validity of the PROMs in three steps, described in detail in Table 2. In step 1, we evaluated the quality of the development study of the PROM, using box 1 of the COSMIN Risk of Bias checklist for PROMs [26]. In step 2, we evaluated the quality of available content validity studies, which were performed after the PROM was developed (external validity), using box 2 of the COSMIN Risk of Bias checklist for PROMs. In step 3, we evaluated the relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility of the PROMs itself, using the criteria described in Table 1, based on the methods and results of the available PROM development, additional content validity studies if available, and our own rating of the content of the PROM. This was done first per study (step 3a), and subsequently, all available evidence on the relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility of a specific PROM was summarized and rated as sufficient ( +), insufficient ( −), inconsistent ( ±), or indeterminate (?) (step 3b). Finally, each rating of the content validity per PROM was accompanied by a grade for the quality of the evidence (high, moderate, low, very low), using a modified GRADE approach [27], indicating how confident we are that the ratings are trustworthy (for example, the quality of the evidence was rated higher if the studies were of high-quality or if there was evidence from multiple studies) (step 3c).
Table 2.
Methodology for assessing content validity [6]
For multidimensional PROMs, i.e. PROMs that contain multiple subscales, we evaluated each subscale separately. We classified the PROM (subscales) according to our conceptual model (Fig. 1) and rated the relevance and comprehensiveness for measuring the specific concept that the PROM (subscale) was classified into. All ratings in all steps were performed by two reviewers independently. When assessing the quality of the included studies (step 1 and 2) at least one reviewer had expertise in PROM development and evaluation. When assessing the quality of the PROMs (step 3) both reviewers had expertise in PROM development and evaluation. When giving our own ratings of the content of the PROM (step 3a_3) one reviewer had expertise in PROM development and validation, and one reviewer was a clinician with experience in treating people with diabetes. Differences were discussed until consensus was reached.
Results
Literature Search
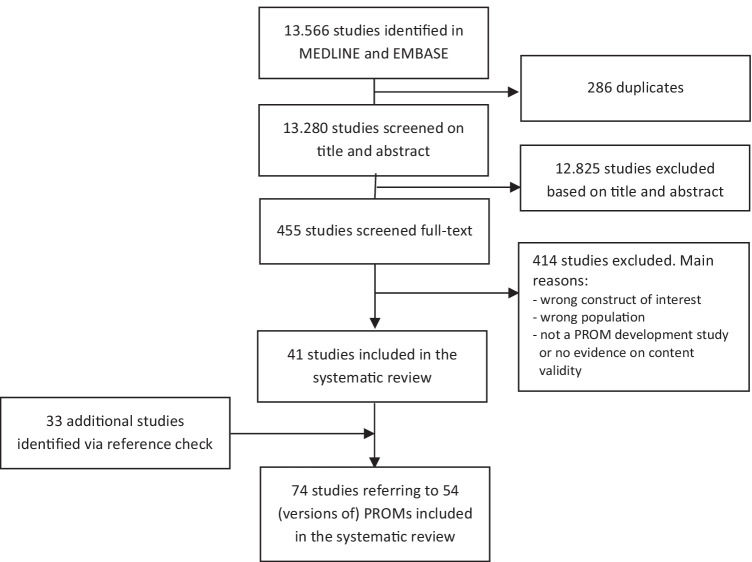
A flow chart of the abstract and article selection is presented in Fig. 2. A total of 13.280 unique abstracts were found, of which 41 articles were included: 23 articles on PROM development and 19 on content validity. Based on reference checking, 24 additional articles on PROM development were identified and nine on content validity, leading to a total of 74 included articles; 46 articles on PROM development, and 28 on content validity.
Fig. 2.
Flow chart of the search strategy
PROMs
In total, 54 (different versions of) PROMs were included, containing a total of 150 subscales related to (aspects of) HRQL (full names of the PROMs are listed in Appendix 3). We found 23 (subscales of) PROMs measuring diabetes-specific symptoms, six (subscales of) PROMs measuring energy/fatigue, 32 (subscales of) PROMs measuring distress, 21 (subscales of) PROMs measuring anxiety, three (subscales of) PROMs measuring depressive symptoms, ten (subscales of) PROMs measuring physical function, two PROM subscales measuring sexual function, 11 (subscales of) PROMs measuring emotional function, 24 (subscales of) PROMs measuring social function, and 22 (subscales of) PROMs measuring overall self-rated health. The number of items varied from 1 to 38 per subscale, most scales contained less than 10 items.
Step 1: Quality of PROM Development Studies
Details of the populations involved in the PROM development studies are provided in Appendix 4. All ratings of the quality of the PROM development are provided in Appendix 5. For only 24 of 54 (versions of) PROMs (44%), a clear definition of the construct to be measured was provided. Only 27 out of 54 PROMs (50%) were developed with input from people with type 2 diabetes. Twenty-six (48%) PROMs were pilot tested. The total PROM development was rated as inadequate for 46 out of 54 (85%) PROMs and doubtful for seven PROMs (the DD Core [28], DFS [29], DFS-SF [30], DSSI [31], IWADL [32], PRO-DM-Thai [33], and QOLID [34]) (full names and details of the PROMs can be found in Appendix 3). Only one PROM, the Diabetes Questionnaire [35], received an adequate rating for the PROM development.
Step 2: Quality of Content Validity Studies
Details of the populations involved in the content validity studies are provided in Appendix 6. All ratings of the quality of the content validity studies can be found in Appendix 7. Twenty-five studies evaluated at least one aspect of content validity (mostly comprehensibility) of 14 PROMs. Most studies were of doubtful quality.
Step 3: Quality of the PROMs
We were not able to give a reviewer rating for the quality of five PROMs (diabetes-39 short form 22 items [36], HSM [37], IRD-QOL [38], LQD [39], and QSD [40]), since we did not acquire full-text copies for them even after contacting a large number of authors that used them or developed them (Appendix 3).
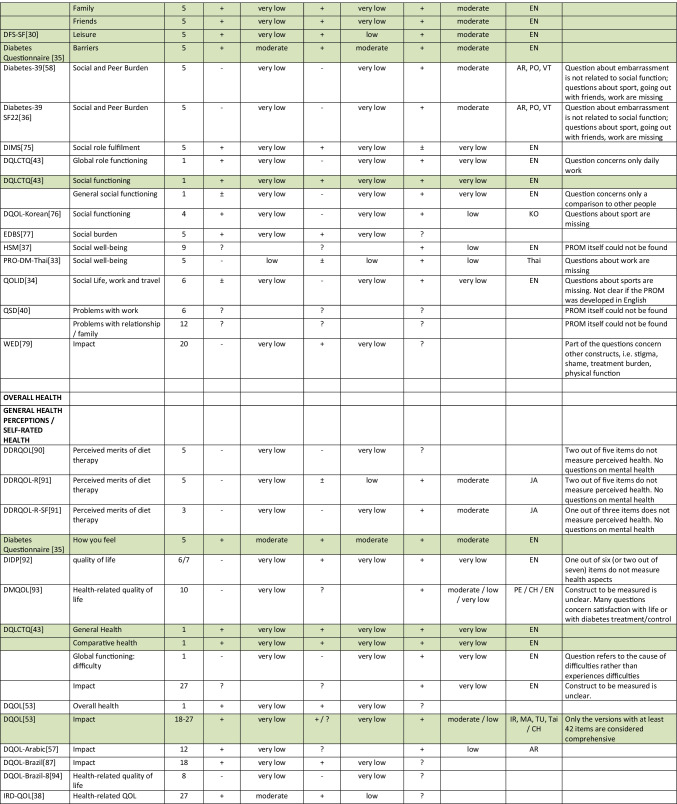
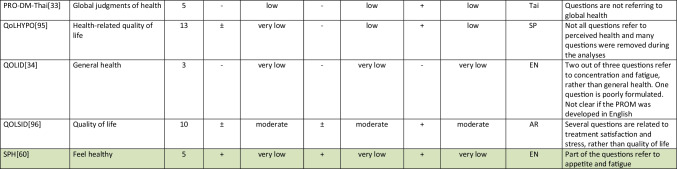
Summarizing all evidence per PROM (subscale), only 41 out of 150 PROM subscales (27%) were rated as having sufficient relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility. PROMs with sufficient content validity are presented in green in Table 3. We found 66 out of 150 PROM subscales (44%) with evidence for insufficient relevance, comprehensiveness, or comprehensibility. The quality of the evidence was mostly low to very low for all PROMs. For each aspect of HRQL (Fig. 1), we identified one to three (subscales of) PROMs with sufficient relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility, except for depressive symptoms, for which we found no PROM (subscale) with sufficient content validity. Below, we summarize per aspect of HRQL which (subscales of) PROMs were rated to have the best content validity. We also summarize the quality of the evidence, indicating how confident we are that the ratings are trustworthy.
Table 3.
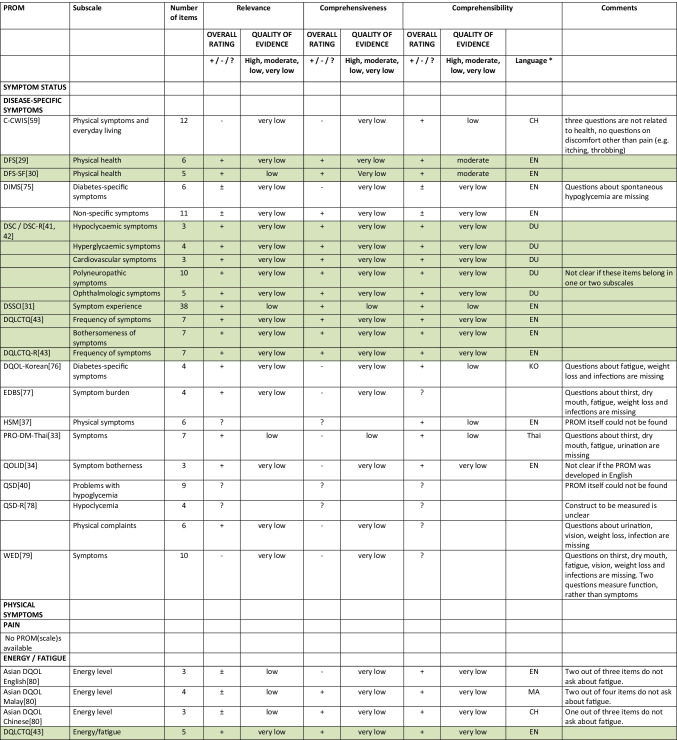
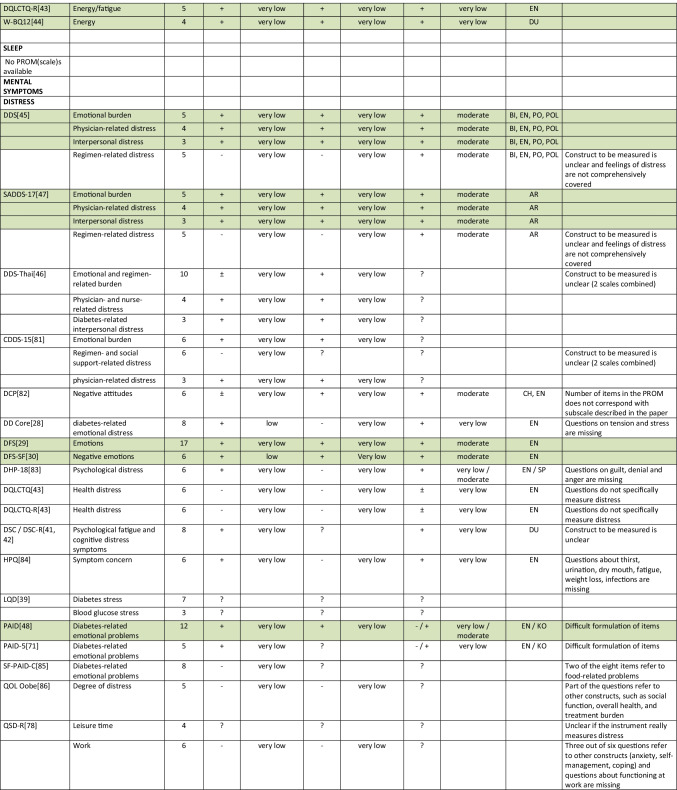
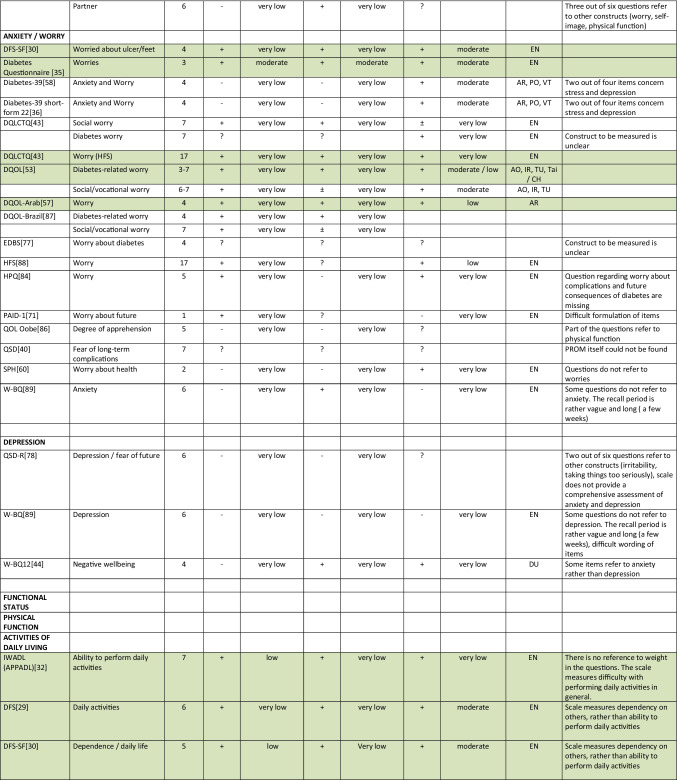
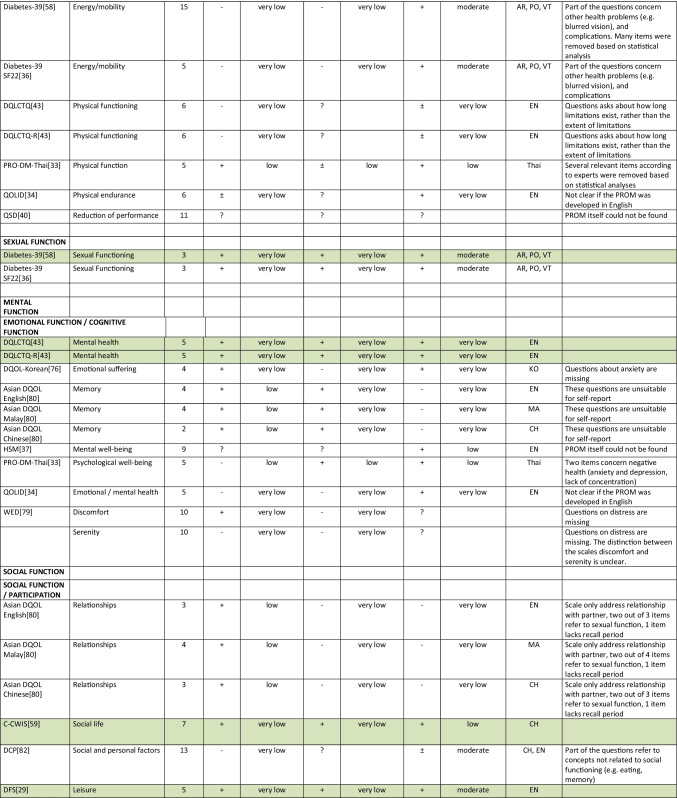
Content validity (relevance, comprehensiveness, comprehensibility) of disease-specific patient-reported health outcome measures developed for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (PROMs with positive ratings for content validity are presented in green)
*Language in which comprehensibility was rated. AR, Arabic; BI, Bahasa Indonesia; CH, Chinese; DA, Danish; DU, Dutch; EN, English; IR, Iranian; JA, Japanese; KO, Korean; MA, Malay; PE, Persian; PO, Portuguese; POL, Polish; SP, Spanish; Tai, Taiwanese; Thai, Thai; TU, Turkish; VT, Vietnamese
For measuring diabetes-specific symptoms, we found sufficient content validity (relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility) of the DSSCI [31], five subscales of the DSC/DSC-R [41, 42], and two subscales of the DQLCTQ/ DQLCTQ-R [43], but the quality of the evidence was low to very low. For measuring diabetes foot ulcer-specific symptoms, we found sufficient content validity for one subscale of the DFS/DFS-SF, with very low-to-moderate evidence [29, 30].
For measuring energy/fatigue, we found sufficient content validity of the DQLCTQ/DQLCTQ-R subscale energy/fatigue [43] and the W-BQ12 subscale energy [44], with very low-quality evidence.
For measuring distress, we found sufficient content validity of the DD Core [28], three subscales of the DDS [45, 46], three subscales of the SADDS-17 [47], one subscale of the DFS [29], one of the DFS-SF [30], and the PAID [48]. The quality of the evidence was very low to low for relevance and comprehensiveness and very low to moderate for comprehensibility across languages.
For measuring anxiety, we found sufficient content validity of the worry subscale of the Diabetes Questionnaire [35], based on moderate quality evidence, and sufficient content validity of the DFS-SF [30], DQLCTQ [43], DQOL [49–56], and DQOL-Arab [57], based on very low to low-quality evidence.
For measuring physical function, we found sufficient content validity of the IWADL [32], DFS [29], and DFS-SF [30], but based on low to very low-quality evidence, with the exception of moderate quality evidence for the comprehensibility of the DFS/DFS-SF.
For measuring sexual function,we found sufficient content validity of the Diabetes-39 [58]. The quality of the evidence was very low for relevance and comprehensiveness and moderate for comprehensibility.
For measuring emotional function, we found sufficient content validity of the mental health subscale of the DQLCTQ/DQLCT-R [43], with very low-quality evidence.
For measuring social function, we found sufficient content validity of the social life subscale or the C-CWIS [59], the barriers subscale of the Diabetes Questionnaire[35], four subscales of the DFS/DFS-SF [29, 30], and a single item of the DQLCTQ [43]. The quality of the evidence was moderate for the Diabetes Questionnaire, very low to moderate for the DFS/DFS-SF, very low to low for the C-CWIS, and very low for the DQLCTQ.
Finally, for measuring overall self-rated health, we found sufficient content validity of the how you feel subscale of the Diabetes Questionnaire[35], the impact subscale of the 42 + item versions of the DQOL [49–56], the subscale feel healthy of the SPH [60], and two items of the DQLCTQ that were developed to be used as single items [43]. The quality of the evidence was moderate for the Diabetes Questionnaire, very low to moderate for the DQOL, and very low for the SPH and DQLCTQ.
Discussion
We systematically evaluated the content validity of PROMs specifically developed to measure (aspects of) HRQOL in people with type 2 diabetes. We found evidence for sufficient content validity for only 41 out of the 150 (27%) included PROM subscales. For each aspect of HRQL, we identified one to 11 (subscales of) PROMs with sufficient content validity, except for depressive symptoms, for which we found no PROM (subscale) with sufficient content validity. However, the quality of evidence was generally low to very low. The highest quality evidence was found for the Diabetes Questionnaire subscales worries (measuring anxiety), barriers (measuring social function), and how you feel (measuring general health perceptions), for the DSSCI measuring symptom experience, and the IWADL measuring the ability to participate in daily activities.
Our results and conclusions differ from previous reviews [9–22] because these reviews did not provide a comprehensive overview of content validity, did not take the quality of the PROM development into account, or did not consider evidence for relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility separately. Striking is that some of the PROMs with the best evidence for content validity based on our review (Diabetes Questionnaire, DFS, and IWADL) were not included in the most recent review, by Wee et al. [22], indicating that their review was likely incomplete.
We found moderate evidence for the comprehensibility of many PROMs, indicating that the questions seem well understood by people with type 2 diabetes across different languages. However, the quality of the evidence for relevance and comprehensiveness of most PROMS was very low. More high-quality research is warranted to determine if these PROMS measure the most relevant aspects of HRQOL for people with type 2 diabetes.
The quality of the PROM development studies was considered inadequate for 85% of the included PROMs. Only half of the PROMs were developed with (some) input from people with type 2 diabetes. This is a major limitation because it is well-known that patients and healthcare professionals may have different opinions about important outcomes to measure. Also, many PROMs are modified versions of previously developed PROMs. Items were often removed based on statistical analyses without addressing the relevance of these items for people with type 2 diabetes. Also, the decision to add new items was often not discussed with people with type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, for more than half of the PROMs, it was unclearly described what the PROM (subscales) exactly aimed to measure. Undefined names are used, such as “physical health”, “emotional burden”, “dependence”, “impact”, or “how you feel”. The content of the (subscales of) PROMs is often very different (even though they claim to measure the same construct) and a rationale for the questions within scales is not provided. If what is being measured is unclear or not based on what is most relevant for the target population, this may affect other measurement properties, such as responsiveness. Furthermore, it will impede the identification of the best PROM for a specific context of use, it will hamper interpretation and comparison of PROM results in studies, and it will limit the usefulness of PROMs in clinical practice.
Another striking finding of this review is that many PROMs that claim to measure (aspects of) HRQOL measure in fact (partly) other things, such as contextual factors or patient experiences (Appendix 3). Examples of contextual factors are behaviour (diet adherence, self-management), attitudes, stigma, support, or financial worries [2]. These are important factors that influence HRQOL, but they are not aspects of HRQOL. Examples of patient experiences are treatment satisfaction, treatment burden or barriers, and doctor–patient relationship. These are patient experience measures (PREMs), not PROMs [61]. It should be noted, however, that many of the included PROMs were developed many years ago, when the methodology of PROM development and validation was not yet as strongly developed as it is today.
The large number of available (versions of) PROMs (and subscales) and the variety in content being measured with these PROMs suggests lack of consensus on which aspects of HRQOL are most relevant to measure in people with type 2 diabetes and how to measure them. Recent initiatives towards standardization of outcomes may improve this situation. Harman et al. recently established international consensus among a large group of people with type 2 diabetes and healthcare providers on the most important outcomes to be measured in clinical trials in people with type 2 diabetes. They identified global quality of life and activities of daily living as two core patient-reported outcomes [62]. We did not include PROMs for measuring global quality of life in our review, but we found sufficient content validity of the IWADL[32] for measuring activities of daily living. A second initiative, the International Consortium for Health Outcomes Measurement (ICHOM), developed a standard set of outcomes to be measured in all type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients in clinical practice. They included psychological well-being, depression, and distress as core outcomes and recommend the WHO5, the PHQ9, and the PAID for measuring these outcomes, respectively [63]. The WHO5 and PHQ9 were not included in this review because they are not diabetes-specific. A recent review of the WHO5 concluded that this PROM has adequate validity [64]. It should be noted that the WHO5 is often used to measure depression but actually measures well-being. Another systematic review identified good measurement properties of the PHQ9, although evidence on the content validity for people with type 2 diabetes is lacking [13]. We found sufficient content validity for the PAID [48] to measure distress, although with very low evidence.
Unfortunately, these two sets do not contain the same outcomes, while there is no justification why the most important outcomes to measure in clinical trials would be different from those in clinical practice. Skovlund et al. reviewed recent evidence and key opportunities and challenges for the clinical use of PROMs to support person-centred diabetes care. They recommended most of the above mentioned outcomes (quality of life, self-reported health, depression, anxiety, and distress) to measure in routine diabetes care [1]. Finally, there is increasing evidence that across adults having different kind of diseases, the same patient-reported health outcomes are important, such as fatigue, sleep disturbances, anxiety, depression, physical function, and the ability to participate in social roles and activities [65–67]. All these studies provide important input for what to measure routinely in people with type 2 diabetes.
Recommendations for Further Research
This review shows the need for more high-quality content validity studies on diabetes-specific HRQL PROMs. Furthermore, the evidence on other measurement properties of those PROMs with sufficient content validity should be summarized in a next review, or evidence from previous reviews [9–21] should be updated. Wee et al. recently performed such a review [22], but their review was likely incomplete.
In addition, we recommend to consider the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) for future validation studies in people with type 2 diabetes [67]. PROMIS is a set of generic, high-quality, and efficient PROMs, based on modern psychometric methods (item response theory)[68] that measure relevant outcomes such as fatigue, sleep disturbances, anxiety, depression, physical function, and the ability to participate in social roles and activities. PROMIS measures have been extensively validated and are increasingly being used across different (patient) populations [69]. PROMIS measures are especially suitable for people with multiple medical conditions who would otherwise need to complete multiple PROMs for different health care providers. PROMIS measures are already used in routine care for people with diabetes [70] but as far as we know have not yet been validated in people with diabetes.
Recommendations for the Use of PROMs in Research and Clinical Practice
We recommend that researchers and clinicians first consider carefully which aspects of HRQOL are most relevant to measure in their specific context. We recommend to involve people with type 2 diabetes in this selection process. We also recommend to consider outcomes that have shown to be relevant for many (patient) populations, such as fatigue, sleep disturbances, anxiety, depression, physical function, and the ability to participate in social roles and activities. We recommend to use (subscales of) PROMs with sufficient content validity (presented in green in Table 3), such as the DSSCI for measuring disease-specific symptoms, the Diabetes Questionnaire subscales for measuring worries and general health perceptions, and the IWADL measuring the ability to participate in daily activities. As an alternative, high-quality generic PROMs, such as the WHO5, PHQ9, and PROMIS, may be considered. We recommend not to use the 61 PROM subscales identified in this review with evidence for either insufficient relevance, insufficient comprehensiveness, or insufficient comprehensibility.
Limitations
This review has some limitations. First, we identified PROMs based on screening studies on PROM development or content validity. However, additional (versions of) PROMs may have been developed, for example, based on factor analysis, published in papers on other measurement properties. Not all of these papers were identified through our screening approach which means that this review may not include all existing (versions of) PROMs. However, PROMs based on statistic methods only would not be rated as having sufficient content validity, so we are quite confident that we did not miss PROMs with good content validity.
Second, we could not rate five PROMs because we were unable to find full copies of the PROMs, it was not always possible to distinguish between different versions of a PROM, and it was sometimes difficult to distinguish PROM development studies from content validity studies. This, as well as poor reporting of development and validation studies, may have led to underestimation of some of our ratings. Third, we found many papers by reference checking, which may indicate lack of comprehensiveness of the original search strategy. However, we were not able to identify additional search terms that would have identified these papers. It is likely that papers were not included in the search due to poor reporting of content validity details in the abstracts.
The strengths of our review were the extensive search strategy, with more than 13,000 papers screened and extensive reference checking, and the detailed and transparent assessment of all aspects of content validity, using the consensus-based COSMIN methodology [6].
Conclusion
We found 54 (different versions of) PROMs, containing a total of 150 subscales measuring (aspects of) HRQL in people with type 2 diabetes. Only 41 of these 150 subscales (27%) were rated as having sufficient content validity. For each aspect of HRQL, we found one to 11 (subscales of) PROMs with sufficient relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility, except for depressive symptoms. The quality of the evidence was, however, mostly very low. In order to help clinicians and researchers to select those PROMs that are most suited for the intended purpose, future reviews should evaluate other measurement properties of those PROMs with sufficient content validity. Additionally, the use of generic PROMs in people with diabetes needs more study.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Wia Barkema, Lenka Groeneveld, Ilana Halperin, and Geetha Mukerji for their help with screening abstracts, rating papers, and finding copies of the PROMs.
Author Contribution
Caroline B. Terwee, Cecilia A. C. Prinsen, and Femke Rutters conceived the study; Caroline B. Terwee carried out the literature searches; Caroline B. Terwee, Petra J. M. Elders, Amber A. van der Heijden, Maartje de Wit, Joline W. J. Beulens, and Femke Rutters screened titles and abstracts; Caroline B. Terwee, Marlous Langendoen-Gort, Ellen B. M. Elsman, and Lidwine B. Mokkink extracted the data; Caroline B. Terwee, Ellen B. M. Elsman, Cecilia A. C. Prinsen, Amber A. van der Heijden, and Lidwine B. Mokkink assessed the study quality; Caroline B. Terwee, Petra J. M. Elders, Ellen B. M. Elsman, and Lidwine B. Mokkink performed the reviewer ratings of the PROMs; Caroline B. Terwee, Ellen B. M. Elsman, and Lidwine B. Mokkink assessed the summary and quality of the evidence; Caroline B. Terwee wrote the manuscript; Caroline B. Terwee, Petra J. M. Elders, Ellen B. M. Elsman, Amber A. van der Heijden, Maartje de Wit, Joline W. J. Beulens, Lidwine B. Mokkink, and Femke Rutters revised the manuscript.
Data Availability
All data extracted or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Declarations
Ethics Approval
As no original human data was included in the manuscript, no ethical approval has been obtained.
Competing Interests
M de Wit was co-author on one of the included PROM development papers [71]. She was not involved in any of the ratings of this paper.
Footnotes
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Diabetes Epidemiology
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Skovlund SE, Lichtenberg TH, Hessler D, Ejskjaer N. Can the routine use of patient-reported outcome measures improve the delivery of person-centered diabetes care? A review of recent developments and a case study. Curr DiabRep. 2019;19:84. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1190-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Langendoen-Gort M, Groeneveld L, Prinsen CAC, Beulens JW, Elders PJM, Halperin I, et al. Patient-reported outcome measures for assessing health-related quality of life in people with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 3.Young-Hyman D, de Groot M, Hill-Briggs F, Gonzalez JS, Hood K, Peyrot M. Psychosocial care for people with diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:2126–2140. doi: 10.2337/dc16-2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.ICHOM Diabetes in Adults Working Group. Type 1 and type 2
- 5.Mokkink LB, Terwee CB, Patrick DL, Alonso J, Stratford PW, Knol DL, et al. The COSMIN study reached international consensus on taxonomy, terminology, and definitions of measurement properties for health-related patient-reported outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. 2010;63:737–745. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Terwee CB, Prinsen CAC, Chiarotto A, Westerman MJ, Patrick DL, Alonso J, et al. COSMIN methodology for evaluating the content validity of patient-reported outcome measures: a Delphi study. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1159–1170. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-1829-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH). Guidance for Industry. Patient-Reported Outcome Measures: Use in Medical Product Development to Support Labeling Claims. 2009.
- 8.European Medical Agency. Reflection paper on the regulatory guidance for the use of health related quality of life (HRQL) measures in the evaluation of medicinal products. 2005.
- 9.El Achhab Y, Nejjari C, Chikri M, Lyoussi B. Disease-specific health-related quality of life instruments among adults diabetic: a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;80:171–84. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2007.12.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Garratt AM, Schmidt L, Fitzpatrick R. Patient-assessed health outcome measures for diabetes: a structured review. Diabet Med: J British Diabet Assoc. 2002;19:1–11. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Luscombe FA. Health-related quality of life measurement in type 2 diabetes. Value Health. 2000;3(Suppl 1):15–28. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-4733.2000.36032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Roborel de Climens A, Tunceli K, Arnould B, Germain N, Iglay K, Norquist J, et al. Review of patient-reported outcome instruments measuring health-related quality of life and satisfaction in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with oral therapy. Curr Med Res Opinion. 2015;31:643–65. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1020364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.van Dijk SEM, Adriaanse MC, van der Zwaan L, Bosmans JE, van Marwijk HWJ, van Tulder MW, et al. Measurement properties of depression questionnaires in patients with diabetes: a systematic review. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1415–1430. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-1782-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vieta A, Badia X, Sacristan JA. A systematic review of patient-reported and economic outcomes: value to stakeholders in the decision-making process in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther. 2011;33:1225–1245. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bottino LG, Madalosso MM, Garcia SP, Schaan BD, Teló GH. Diabetes-specific questionnaires validated in Brazilian Portuguese: a systematic review. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2020;64:111–120. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hogg FR, Peach G, Price P, Thompson MM, Hinchliffe RJ. Measures of health-related quality of life in diabetes-related foot disease: a systematic review. Diabetologia. 2012;55:552–565. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Levterova BA, Dimitrova DD, Levterov GE, Dragova EA. Instruments for disease-specific quality-of-life measurement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus–a systematic review. Folia Med. 2013;55:83–92. doi: 10.2478/folmed-2013-0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ortega-Avila AB, Cervera-Garvi P, Ramos-Petersen L, Chicharro-Luna E, Gijon-Nogueron G. Patient-reported outcome measures for patients with diabetes mellitus associated with foot and ankle pathologies: a systematic review. J Clin Med. 2019;8:46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Gibbons E, Fitzpatrick R. A structured review of patient-reported outcome measures for people with diabetes: an update 2009. Oxford: University of Oxford, Department of Public Health, Patient-reported Outcome Measurement Group; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee J, Lee EH, Kim CJ, Moon SH. Diabetes-related emotional distress instruments: a systematic review of measurement properties. Int J Nurs Stud. 2015;52:1868–1878. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2015.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen YT, Tan YZ, Cheen M, Wee HL. Patient-reported outcome measures in registry-based studies of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Curr DiabRep. 2019;19:135. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wee PJL, Kwan YH, Loh DHF, Phang JK, Puar TH, Østbye T, et al. Measurement properties of patient-reported outcome measures for diabetes: systematic review. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23:e25002. doi: 10.2196/25002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Martin-Delgado J, Guilabert M, Mira-Solves J. Patient-reported experience and outcome measures in people living with diabetes: a scoping review of instruments. Patient. 2021;14:759–773. doi: 10.1007/s40271-021-00526-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pérez-Panero AJ, Ruiz-Muñoz M, Fernández-Torres R, Formosa C, Gatt A, Gónzalez-Sánchez M. Diabetic foot disease: a systematic literature review of patient-reported outcome measures. Qual Life Res. 2021;30:3395–3405. doi: 10.1007/s11136-021-02892-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Prinsen CAC, Mokkink LB, Bouter LM, Alonso J, Patrick DL, de Vet HCW, et al. COSMIN guideline for systematic reviews of patient-reported outcome measures. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1147–1157. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-1798-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mokkink LB, de Vet HCW, Prinsen CAC, Patrick DL, Alonso J, Bouter LM, et al. COSMIN risk of bias checklist for systematic reviews of patient-reported outcome measures. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1171–1179. doi: 10.1007/s11136-017-1765-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64:383–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Polonsky WH, Fisher L, Hessler D, Desai U, King SB, Perez-Nieves M. Toward a more comprehensive understanding of the emotional side of type 2 diabetes: a re-envisioning of the assessment of diabetes distress. J Diabetes Complications. 2022;36:108103. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.108103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Abetz L, Sutton M, Brady L, McNulty P, Gagnon DD. The diabetic foot ulcer scale (DFS): a quality of life instrument for use in clinical trials. Practical Diabetes Int. 2002;19:167–175. doi: 10.1002/pdi.356. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bann CM, Fehnel SE, Gagnon DD. Development and validation of the diabetic foot ulcer scale-short form (DFS-SF) Pharmacoeconomics. 2003;21:1277–1290. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200321170-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Garcia AA. The diabetes symptom self-care inventory: development and psychometric testing with Mexican Americans. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2011;41:715–727. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2010.06.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hayes RP, Nelson DR, Meldahl ML, Curtis BH. Ability to perform daily physical activities in individuals with type 2 diabetes and moderate obesity: a preliminary validation of the Impact of Weight on Activities of Daily Living Questionnaire. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011;13:705–712. doi: 10.1089/dia.2011.0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chuayruang K, Sriratanaban J, Hiransuthikul N, Suwanwalaikorn S. Development of an instrument for patient-reported outcomes in Thai patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (PRO-DM-Thai) Asian Biomedicine. 2015;9:7–19. doi: 10.5372/1905-7415.0901.363. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nagpal J, Kumar A, Kakar S, Bhartia A. The development of 'quality of life instrument for Indian diabetes patients (QOLID): a validation and reliability study in middle and higher income groups. J Assoc Physicians India. 2010;58:295–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Svedbo Engstrom M, Leksell J, Johansson UB, Eeg-Olofsson K, Borg S, Palaszewski B, et al. A disease-specific questionnaire for measuring patient-reported outcomes and experiences in the Swedish National Diabetes Register: development and evaluation of content validity, face validity, and test-retest reliability. Patient Educ Couns. 2018;101:139–146. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2017.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Leite WL, Huang IC, Marcoulides GA. Item selection for the development of short forms of scales using an ant colony optimization algorithm. Multivar Behav Res. 2008;43:411–431. doi: 10.1080/00273170802285743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Elasy TA, Samuel-Hodge CD, DeVellis RF, Skelly AH, Ammerman AS, Keyserling TC. Development of a health status measure for older African-American women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000;23:325–329. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Alavi NM, Ghofranipour F, Ahmadi F, Emami A. Developing a culturally valid and reliable quality of life questionnaire for diabetes mellitus. East Mediterr Health J. 2007;13:177–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hirsch A, Bartholomae C, Volmer T. Dimensions of quality of life in people with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Qual Life Res. 2000;9:207–218. doi: 10.1023/A:1008959810698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Duran G, Herschbach P, Waadt S, Strian F, Zettler A. Assessing daily problems with diabetes: a subject-oriented approach to compliance. Psychol Rep. 1995;76:515–521. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1995.76.2.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Arbuckle RA, Humphrey L, Vardeva K, Arondekar B, Danten-Viala M, Scott JA, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the diabetes symptom checklist-revised (DSC-R)–a measure of symptom distress. Value Health. 2009;12:1168–1175. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2009.00571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Grootenhuis PA, Snoek FJ, Heine RJ, Bouter LM. Development of a type 2 diabetes symptom checklist: a measure of symptom severity. Diabet Med. 1994;11:253–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1994.tb00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shen W, Kotsanos JG, Huster WJ, Mathias SD, Andrejasich CM, Patrick DL. Development and validation of the diabetes quality of life clinical trial questionnaire. Med Care. 1999;37:AS45–66. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199904001-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pouwer F, Snoek FJ, van der Ploeg HM, Ader HJ, Heine RJ. The well-being questionnaire: evidence for a three-factor structure with 12 items (W-BQ12) Psychol Med. 2000;30:455–462. doi: 10.1017/S0033291700001719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Polonsky WH, Fisher L, Earles J, Dudl RJ, Lees J, Mullan J, et al. Assessing psychosocial distress in diabetes: development of the diabetes distress scale. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:626–631. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.3.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Thanakwang K, Thinganjana W, Konggumnerd R. Psychometric properties of the Thai version of the diabetes distress scale in diabetic seniors. Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9:1353–1361. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S67200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Batais MA, Alosaimi FD, AlYahya AA, Aloofi OA, Almashouq MK, Alshehri KS, et al. Translation, cultural adaptation, and evaluation of the psychometric properties of an Arabic diabetes distress scale: a cross sectional study from Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2021;42:509–516. doi: 10.15537/smj.2021.42.5.20200286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Polonsky WH, Anderson BJ, Lohrer PA, Welch G, Jacobson AM, Aponte JE, et al. Assessment of diabetes-related distress. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:754–760. doi: 10.2337/diacare.18.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bujang MA, Ismail M, Hatta N, Othman SH, Baharum N, Lazim SSM. Validation of the Malay version of diabetes quality of life (DQOL) questionnaire for adult population with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Malaysian J Med Sci: MJMS. 2017;24:86–96. doi: 10.21315/mjms2017.24.4.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cheng AY, Tsui EY, Hanley AJ, Zinman B. Developing a quality of life measure for Chinese patients with diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1999;46:259–267. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8227(99)00091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Cheng AY, Tsui EY, Hanley AJ, Zinman B. Cultural adaptation of the diabetes quality-of-life measure for Chinese patients. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:1216–1217. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.7.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hui LF, Yee-Tak Fong D, Yam M, Yuk IW. Translation and validation of the Chinese diabetic foot ulcer scale - short form. Patient. 2008;1:137–145. doi: 10.2165/01312067-200801020-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Jacobson A, Barvsky I, Cleary P, Rand L. Reliability and validity of a diabetes quality-of life measure for the diabetes control and complications trial (DCCT). The DCCT Research Group. Diabetes Care. 1988;11:725–32. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 54.Pakpour AH, Saffari M, Burri A. Translation and validation of an Iranian version of the diabetes quality of life measure. J Diabetes Investig. 2012;3:471–478. doi: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2012.00217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sato F, Mita T, Yamamoto R, Hirose T, Ito C, Tamura Y, et al. Reliability and validity of the Japanese version of the diabetes quality-of-life questionnaire for Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol Int. 2014;5:21–29. doi: 10.1007/s13340-013-0125-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yildirim A, Akinci F, Gozu H, Sargin H, Orbay E, Sargin M. Translation, cultural adaptation, cross-validation of the Turkish diabetes quality-of-life (DQOL) measure. Qual Life Res. 2007;16:873–879. doi: 10.1007/s11136-007-9172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Al-Qerem W, Al-Maayah B, Ling J. Developing and validating the Arabic version of the diabetes quality of life questionnaire. East Mediterr Health J. 2021;27:414–426. doi: 10.26719/emhj.20.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Boyer JG, Earp JA. The development of an instrument for assessing the quality of life of people with diabetes. Diabetes-39. Med Care. 1997;35:440–53. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199705000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Huang Y, Wu M, Xing P, Xie T, Cao Y, Qian P, et al. Translation and validation of the Chinese Cardiff wound impact schedule. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2014;13:5–11. doi: 10.1177/1534734614521233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Rao PR, Shobhana R, Lavanya A, Padma C, Vijay V, Ramachandran A. Development of a reliable and valid psychosocial measure of self-perception of health in type 2 diabetes. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005;53:689–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kingsley C, Patel S. Patient-reported outcome measures and patient reported experience measures. BJA Education. 2017;17:137–144. doi: 10.1093/bjaed/mkw060. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Harman NL, Wilding JPH, Curry D, Harris J, Logue J, Pemberton RJ, et al. Selecting Core Outcomes for randomised effectiveness trials in type 2 diabetes (SCORE-IT): a patient and healthcare professional consensus on a core outcome set for type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019;7:e000700. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-000700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Nano J, Carinci F, Okunade O, Whittaker S, Walbaum M, Barnard-Kelly K, et al. A standard set of person-centred outcomes for diabetes mellitus: results of an international and unified approach. Diabetic Med: J British Diabetic Assoc. 2020;37:2009–2018. doi: 10.1111/dme.14286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Topp CW, Østergaard SD, Søndergaard S, Bech P. The WHO-5 well-being index: a systematic review of the literature. Psychother Psychosom. 2015;84:167–176. doi: 10.1159/000376585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Terwee CB, Zuidgeest M, Vonkeman HE, Cella D, Haverman L, Roorda LD. Common patient-reported outcomes across ICHOM Standard Sets – the value of PROMIS. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2021;21:259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 66.Gangannagaripalli J, Albagli A, Myers SN, Whittaker S, Joseph A, Clarke A, et al. A standard set of value-based patient-centered outcomes and measures of overall health in adults. The Patient-Patient-Centered Outcomes Research. 2022;15(3):341–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 67.Cella D, Riley W, Stone A, Rothrock N, Reeve B, Yount S, et al. The patient-reported outcomes measurement information system (PROMIS) developed and tested its first wave of adult self-reported health outcome item banks: 2005–2008. J Clin Epidemiol. 2010;63:1179–1194. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cappelleri JC, Jason Lundy J, Hays RD. Overview of classical test theory and item response theory for the quantitative assessment of items in developing patient-reported outcomes measures. Clin Ther. 2014;36:648–662. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.http://www.healthmeasures.net/promis.
- 70.Scholle SH, Morton S, Homco J, Rodriguez K, Anderson D, Hahn E, et al. Implementation of the PROMIS-29 in routine care for people with diabetes: challenges and opportunities. J Ambul Care Manage. 2018;41:274–287. doi: 10.1097/JAC.0000000000000248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.McGuire BE, Morrison TG, Hermanns N, Skovlund S, Eldrup E, Gagliardino J, et al. Short-form measures of diabetes-related emotional distress: the problem areas in diabetes scale (PAID)-5 and PAID-1. Diabetologia. 2010;53:66–69. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1559-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wilson IB, Cleary PD. Linking clinical variables with health-related quality of life. A conceptual model of patient outcomes. JAMA. 1995;273:59–65. doi: 10.1001/jama.1995.03520250075037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Terwee CB, Prinsen CAC, Chiarotto A, de Vet HCW, Bouter LM, Alonso J, et al. COSMIN methodology for assessing the content validity of PROMs. User manual version 1.0. www.cosmin.nl.
- 74.Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2008;336:924–926. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hammond GS, Aoki TT. Measurement of health status in diabetic patients Diabetes Impact Measurement Scales. Diabetes Care. 1992;15:469–477. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Lee EH, Lee YW, Lee KW, Kim DJ, Kim SK. Development and psychometric evaluation of a diabetes-specific quality-of-life (D-QOL) scale. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;95:76–84. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Araki A, Ito H. Development of elderly diabetes burden scale for elderly patients with diabetes mellitus. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2003;3:212–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-1586.2003.00084.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Herschbach P, Duran G, Waadt S, Zettler A, Amm C, Marten-Mittag B. Psychometric properties of the questionnaire on stress in patients with diabetes–revised (QSD-R) Health Psychol: Off J Division Health Psychol Am Psychol Assoc. 1997;16:171–174. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.16.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Mannucci E, Ricca V, Bardini G, Rotella CM. Well-being enquiry for diabetics: a new measure of diabetes-related quality of life. Diabetes Nutr Metab-Clin Exp. 1996;9:89–102. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Goh SG, Rusli BN, Khalid BA. Development and validation of the Asian diabetes quality of life (AsianDQOL) QUestionnaire. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;108:489–498. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ting RZ, Nan H, Yu MW, Kong AP, Ma RC, Wong RY, et al. Diabetes-related distress and physical and psychological health in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:1094–1096. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Fitzgerald JT, Davis WK, Connell CM, Hess GE, Funnell MM, Hiss RG. Development and validation of the diabetes care profile. Eval Health Prof. 1996;19:208–230. doi: 10.1177/016327879601900205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Meadows KA, Abrams C, Sandbaek A. Adaptation of the diabetes health profile (DHP-1) for use with patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus: psychometric evaluation and cross-cultural comparison. Diabet Med. 2000;17:572–580. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2000.00322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kawata AK, Wilson H, Ong SH, Kulich K, Coyne K. Development and psychometric evaluation of the hypoglycemia perspectives questionnaire in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Patient. 2016;9:395–407. doi: 10.1007/s40271-016-0163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Hsu HC, Chang YH, Lee PJ, Chen SY, Hsieh CH, Lee YJ, et al. Developing and psychometric testing of a short-form problem areas in diabetes scale in Chinese patients. J Nursing Res: JNR. 2013;21:212–218. doi: 10.1097/01.jnr.0000432048.31921.e2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Oobe M, Tanaka M, Fuchigami M, Sakata T. Preparation of a quality of life (QOL) questionnaire for patients with type II diabetes and prospects for its clinical application. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi. 2007;98:379–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Correr CJ, Pontarolo R, Melchiors AC, Rossignoli P, Fernandez-Llimos F. Radominski RB [Translation to Portuguese and validation of the diabetes quality of life measure (DQOL-Brazil)] Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2008;52:515–522. doi: 10.1590/S0004-27302008000300012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Cox DJ, Irvine A, Gonder-Frederick L, Nowacek G, Butterfield J. Fear of hypoglycemia: quantification, validation, and utilization. Diabetes Care. 1987;10:617–621. doi: 10.2337/diacare.10.5.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Bradley C, Lewis KS. Measures of psychological well-being and treatment satisfaction developed from the responses of people with tablet-treated diabetes. Diabet Med. 1990;7:445–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1990.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Sato E, Suzukamo Y, Miyashita M, Kazuma K. Development of a diabetes diet-related quality-of-life scale. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1271–1275. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.6.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Sato E, Ochiai R, Shibayama T, Nishigaki M, Abe Y, Sawa T, et al. Reliability and validity of revised and short form versions of diabetes diet-related quality of life scale. Diabetol Int. 2017;8:181–192. doi: 10.1007/s13340-016-0291-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Holmes-Truscott E, Skovlund SE, Hendrieckx C, Pouwer F, Peyrot M, Speight J. Assessing the perceived impact of diabetes on quality of life: psychometric validation of the DAWN2 impact of diabetes profile in the second diabetes MILES - Australia (MILES-2) survey. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;150:253–263. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lin CY, Lee TY, Sun ZJ, Yang YC, Wu JS, Ou HT. Development of diabetes-specific quality of life module to be in conjunction with the World Health Organization quality of life scale brief version (WHOQOL-BREF) Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017;15:167. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0744-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Brasil F, Brasil AM, e Souza RA, Pontarolo R, Correr CJ. Development of the Brazilian brief version of the diabetes quality of life measure (DQOL-Brazil-8) Rev Bras Epidemiol. 2015;18:943–52. doi: 10.1590/1980-5497201500040021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Orozco-Beltran D, Artola S, Jansa M, Lopez de la Torre-Casares M, Fuster E. Impact of hypoglycemic episodes on health-related quality of life of type-2 diabetes mellitus patients: development and validation of a specific QoLHYPO((c)) questionnaire. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2018;16:52. doi: 10.1186/s12955-018-0875-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Mikhael E, Hassali M, Hussain S, Shawky N. The development and validation of quality of life scale for Iraqi patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2020;12:262–268. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_190_19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Terwee CB, Jansma EP, Riphagen II, de Vet HC. Development of a methodological PubMed search filter for finding studies on measurement properties of measurement instruments. Qual Life Res. 2009;18:1115–1123. doi: 10.1007/s11136-009-9528-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Peyrot M, Burns KK, Davies M, Forbes A, Hermanns N, Holt R, et al. Diabetes attitudes wishes and needs 2 (DAWN2): a multinational, multi-stakeholder study of psychosocial issues in diabetes and person-centred diabetes care. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013;99:174–184. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2012.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Choe MA, Padilla GV, Chae YR, Kim S. Quality of life for patients with diabetes in Korea–I: the meaning of health-related quality of life. Int J Nurs Stud. 2001;38:673–682. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7489(00)00115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Li J, Li Z, Zhao W, Pan H, Halloran EJ. The reliability and validity of the diabetes care profile for Chinese populations. Eval Health Prof. 2015;38:200–218. doi: 10.1177/0163278714525628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Curcio R, Costa Alexandre NM, de Carvalho TH, Melo Lima MH. Translation and adaptation of the “Diabetes Distress Scale – DDS” in Brazilian culture. Acta Paul Enferm. 2012;25:762–767. doi: 10.1590/S0103-21002012005000025. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Farm BAS, Perwitasari DA, Thobari JA, Cao Q, Krabbe PFM, Postma MJ. Translation, revision, and validation of the diabetes distress scale for indonesian type 2 diabetic outpatients with various types of complications. Value Health Reg Issues. 2017;12:63–73. doi: 10.1016/j.vhri.2017.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Krzemińska S, Bąk E. Psychometric properties of the polish version of the diabetes distress scale (DDS) Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2021;14:1149–1156. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S320675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Benazizi I, Bernal-Soriano MC, Pardo Y, Ribera A, Peralta-Chiriboga A, Ferrer M, et al. Adaptation and psychometric validation of diabetes health profile (DHP-18) in patients with type 2 diabetes in Quito, Ecuador: a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021;19:189. doi: 10.1186/s12955-021-01818-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Khader YS, Bataineh S, Batayha W. The Arabic version of Diabetes-39: psychometric properties and validation. Chronic Illn. 2008;4:257–263. doi: 10.1177/1742395308100647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Nguyen TQ, Vo TQ, Nguyen GH, Nguyen TD. Assessment of health-related quality of life in patients with type II diabetes mellitus: a population-based study at a tertiary hospital. J Clin Diagn Res. 2018;12:LC44–LC51. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Queiroz FA, Pace AE, Santos CB. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the instrument Diabetes - 39 (D-39): Brazilian version for type 2 diabetes mellitus patients - stage 1. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2009;17:708–715. doi: 10.1590/S0104-11692009000500018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Li TC, Lin CC, Liu CS, Li CI, Lee YD. Validation of the Chinese version of the diabetes impact measurement scales amongst people suffering from diabetes. Qual Life Res. 2006;15:1613–1619. doi: 10.1007/s11136-006-0024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Saffari M, Lin CY, O’Garo K, Koenig HG, Sanaeinasab H, Pakpour AH. Psychometric properties of Persian diabetes-mellitus specific quality of life (DMQoL) questionnaire in a population-based sample of Iranians. Int J Diabetes Dev Countries. 2019;39:218–227. doi: 10.1007/s13410-018-0648-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Huang IC, Hwang CC, Wu MY, Lin W, Leite W, Wu AW. Diabetes-specific or generic measures for health-related quality of life? Evidence from psychometric validation of the D-39 and SF-36. Value Health. 2008;11:450–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Diriba DC, Leung DYP, Suen LKP. Cultural adaptation and psychometric properties of the diabetes quality of life scale in Afaan Oromoo among people living with type 2 diabetes in Ethiopia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:7435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 112.Lee EH, Lee YW, Lee KW, Kim YS, Nam MS. Measurement of diabetes-related emotional distress using the problem areas in diabetes scale: psychometric evaluations show that the short form is better than the full form. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014;12:142. doi: 10.1186/s12955-014-0142-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Chin YW, Lai PS, Chia YC. The validity and reliability of the English version of the diabetes distress scale for type 2 diabetes patients in Malaysia. BMC Fam Pract. 2017;18:25. doi: 10.1186/s12875-017-0601-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data extracted or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.