Abstract
Although several meta-analyses have revealed the beneficial effects of dietary fiber intake on human health, some have reported inconsistent findings. The purpose of this work was to perform an umbrella meta-analysis to evaluate the relevant evidence and elucidate the effect of dietary fiber intake on glycemic control, lipid profiles, systematic inflammation, and blood pressure. Eligible studies were searched in several electronic databases, including Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library, up to March 2022. A total of 52 meta-analyses involving 47,197 subjects were identified to assess the pooled effect size. Overall, higher dietary fiber intake was significantly associated with reductions in parameters involving glycemic control, including fasting plasma glucose (ES = −0.55, 95% CI: −0.73, −0.38, P < 0.001), fasting plasma insulin (ES = −1.22, 95% CI: −1.63, −0.82, P < 0.001), homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (ES = −0.43, 95% CI: −0.60, −0.27, P < 0.001), and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (ES = −0.38, 95% CI: −0.50, −0.26, P < 0.001). In terms of lipid profiles, higher dietary fiber intake was associated with significant reductions in the serum level of total cholesterol (ES = −0.28, 95% CI: −0.39, −0.16, P < 0.001) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (ES = −0.25, 95% CI: −0.34, −0.16, P < 0.001), but not triglycerides (ES = −0.001, 95% CI: −0.006, 0.004, P = 0.759) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (ES = −0.002, 95% CI: −0.004, 0.000, P = 0.087). Higher dietary fiber intake was also significantly associated with improved tumor necrosis factor-alpha serum levels (ES = −0.78, 95% CI: −1.39, −0.16, P = 0.013), while no significant effect was observed for C-reactive protein (ES = −0.14, 95% CI: −0.33, 0.05, P = 0.156). Finally, blood pressure was also significantly improved following higher dietary fiber intake (systolic blood pressure: ES = −1.72, 95% CI: −2.13, −1.30, P < 0.001; diastolic blood pressure: ES = −0.67, 95% CI: −0.96, −0.37, P < 0.001). Subgroup analysis revealed that the study population and type of dietary fiber could be partial sources of heterogeneity. In conclusion, the present umbrella meta-analysis provides evidence for the role of dietary fiber supplementation in the improvement of established cardiovascular risk factors.
Keywords: umbrella meta-analysis, dietary fiber, glycolipid metabolism, inflammation, blood pressure
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), which represent a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels, including coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, rheumatic heart disease, and other conditions, are the leading cause of death globally (1). It was estimated that, in 2017, 55 million people died worldwide, of which about 18 million deaths were attributable to CVDs (2, 3). Similarly, a report on disease burden in China during 1990–2017 pointed out that stroke and ischemic heart disease were the major causes of all-age disability-adjusted life years in 2017; in addition, a report on cardiovascular health and disease burden in China (2020) also revealed that CVDs accounted for the majority of all deaths, by 46.66 and 43.81% in rural and urban areas, respectively (4, 5). Thus, global strategies aimed at reducing the morbidity and mortality of these diseases are urgently required.
Despite the existence of non-variable risk factors for CVDs, such as age, gender, and family history, shifts in some variable risk factors, including sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, and physical inactivity, are much more important; among these, a healthy diet may be the most effective method with the lowest cost and could be regarded as a primary target for CVDs prevention (6). Dietary fiber is defined as a group of carbohydrates with three or more monomeric units that are resistant to digestion and absorption in the human small intestine but confer health benefits to the host (7). Several clinical studies have shown that patients at risk of CVDs can benefit from dietary fiber intake. For example, Xu et al. found that oat β-glucan led to significant reductions in serum total cholesterol by −8.41% and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol by −13.93% in individuals with hypercholesterolemia (8). Indeed, a previous review revealed the crucial role of dietary fiber consumption in the prevention and treatment of CVDs (9). Moreover, epidemiological studies have indicated an inverse relationship between dietary fiber intake and the risk of CVDs, such as ischemic heart disease (10) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (11). Evidence from another meta-analysis also suggested that every additional 7 g/d of total fiber intake could lower the risk of CVDs by 9% (12). However, other meta-analyses have indicated that dietary fiber intake may not cause significant improvements in CVDs risk factors, including blood glucose and inflammatory markers (13, 14). Since the strength, precision, and influence of potential bias in these studies, as well as the quality of existing meta-analyses still have not been clarified, it is necessary to address the broader scope of benefits related to dietary fiber intake and CVDs risk factors.
Umbrella meta-analysis is a synthesis method developed to evaluate the pooled effects of existing published meta-analyses and the quality and strength of the presented evidence. For example, Veronese et al. reported an umbrella meta-analysis of observational studies on the summarized associations of dietary fiber intake and various health outcomes (15). However, the pooled evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) exploring the effects of dietary fiber intake on cardiovascular risk markers (blood glucose/lipids, blood pressure, and inflammation) remains under investigation. The aim of the present work was to collect relevant evidence and perform an assessment, the results of which could provide robust evidence for the role of dietary fiber in patients at risk for CVDs.
Methods
Umbrella reviews can provide a broad understanding of a given topic for decision makers (16). The current umbrella review of meta-analyses was conducted in accordance with the guidance outlined in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention (17).
Literature search
Two authors (LF and SQ) independently searched the four databases (Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library) from inception to March 2022 for meta-analyses that explored the effects of dietary fiber intake on cardiovascular risk markers (blood glucose/lipids, blood pressure, or inflammation) using the following search strategy: (dietary fiber or fiber or fiber or whole grain or whole wheat or cereals or wheat bran or bran or barley or oat or beta-glucans or glucans or cellulose or pectin or resistant starch or secale cereale or rye or ryes or spelt or triticum or rice or rices or oryza sativa or fructooligosaccharides or inulin) AND (blood glucose or blood sugar or fasting plasma glucose or FPG or glycated hemoglobin A or glycated hemoglobin or HbA1c or insulin or homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance or HOMA-IR or cholesterol or lipids or total cholesterol or TC or triglyceride or TG or high density lipoprotein cholesterol or HDL-C or low density lipoprotein cholesterol or LDL-C or blood pressure or hypertension or systolic blood pressure or SBP or diastolic blood pressure or DBP or inflammatory or tumor necrosis factor-alpha or TNF-α or C-reactive protein or CRP) AND (systematic review or review, systematic or meta-analysis). We also performed a manual review of the references from eligible meta-analyses so that any relevant studies were not missed (Supplementary Files; Supplementary Table S1 presents the detailed search strategy and the results from all four databases). Table 1 shows the participants, interventions, comparators, and outcomes (PICO) criteria that were defined for the present umbrella review.
Table 1.
PICO criteria for the present umbrella meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
| Items | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Participants | Subjects who were treated with dietary fiber |
| Intervention | Dietary fiber or other conditions* |
| Comparator | Placebo or control group or low dietary fiber intake |
| Outcomes | Parameters involved with blood glucose or blood lipids or blood pressure or inflammatory factors |
*Other conditions including resistant starch, cereal β-glucan, guar gum, inulin-type fructan, psyllium, glucomannan and brown rice.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Relevant trials with the following characteristics were included: (1) meta-analysis of RCTs that explored the effects of dietary fiber intake on cardiovascular risk factors (blood glucose/lipids, blood pressure, and inflammatory factors) and reported the effect sizes (ESs) and corresponding confidence intervals (CIs) and (2) RCTs comparing any proper control groups (placebo, control group, or diet with low dietary fiber).
We excluded studies that (1) involved animal research; (2) were in vitro or ex vivo studies; (2) were only a systematic review without a meta-analysis; and (3) were a meta-analysis of observation studies on self-reported dietary fiber intake.
Data extraction
Two independent authors (QZ and GZ) screened the potential studies on the basis of the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Any disagreement was resolved either by consultation together or a third author (MT). For each eligible study, information regarding first author's name; published year (country); sample size (the number of involved subjects); the type, dosage, and duration of interventions; and outcomes assessed were extracted. In addition, the pooled ESs and corresponding CIs for the influence of dietary fiber intake on cardiovascular risk factors were also extracted.
Quality assessment
The AMSTAR 2 questionnaire was employed to evaluate the quality of each eligible meta-analysis and served as a reliable and valid tool for assessing the quality of systematic reviews and meta-analyses; it consisted of 16 items scored as High, Moderate, Low, or Critical low of overall confidence (18). When a study had one or no non-critical weaknesses, it was considered as a high-quality meta-analysis. Furthermore, we also evaluated the certainty of the evidence and the strength of recommendation with the GRADE (grading of recommendations, assessment, development, and evaluation) tool (19).
Data synthesis and statistics
We used the ESs and their corresponding CIs extracted from each eligible meta-analysis to obtain the overall pooled effect sizes. Heterogeneity between studies was calculated using the I2 statistic and Cochrane's Q-test. We considered an I2 value > 50% or a P-value from the Q-test of <0.1 as indicators of substantial heterogeneity, in which case the random-effect model was applied; otherwise, a fixed effect model was used (20). To further explore the sources of heterogeneity, a subgroup analysis including study population, sample size, and other characteristics was performed. Publication bias was measured using funnel plots and Egger's regression test, in which a P-value of <0.1 was considered significant (21, 22). In addition, we employed “trim and fill” analysis to simulate a new model without publication bias and calculated a new effect size with the insertion of new fictitious studies. Finally, we used the leave-one-out method for sensitivity analysis to measure the impact of each study on the overall results. The statistical analysis was performed using the Comprehensive Meta Analysis software version 3.0 with a level of significance of 5%.
Results
Study selection
Of the 3,699 publications initially found in our searches, we identified 75 articles for further assessment after removing duplicates and irrelevant records. After reading the full text of the remaining articles, a total of 52 meta-analyses were finally selected for the current umbrella meta-analysis; 23 articles were excluded for the following reasons: (1) abstracts or letters to editors (n = 7); (2) systematic reviews without meta-analysis (n = 4); (3) results confounded by non-dietary fiber (n = 9); and (4) outcomes were not interested (n = 3) (Figure 1). The studies of the excluded meta-analyses are listed in Supplementary Table S2 in the Supplementary Files.
Figure 1.
The flow diagram for present umbrella meta-analysis.
Characteristics of included meta-analyses
The characteristics of the included meta-analyses are depicted in Table 2. Briefly, the 52 eligible meta-analyses involved a total of 47,197 participants, including patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), dyslipidemia, hypertension, obesity (or who were overweight), metabolic syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD); women with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy; and healthy subjects. The dietary fibers included resistant starch, β-glucans, glucomannan, guar gum, inulin-type fructans, inulin-type carbohydrates, psyllium, and brown rice. The dosages and durations of dietary fiber intervention ranged from 3 g/day to 30 g/day (except for one study, which used guar gum at 15 mg/day, and another study that used brown rice at 225 g/d), and 4 to 13 weeks, respectively. Twenty-two meta-analyses were performed in China (23, 25–27, 29–31, 35–37, 42, 43, 45, 49, 51, 53–56, 69–71), six in Iran (24, 32–34, 38, 40), four in the UK (13, 39, 41, 57), one in Australia (14), eight in Canada (44, 46, 47, 50, 52, 58, 62, 72), five in the USA (48, 60, 65, 67, 68), one in Brazil (59), one in Ireland (61), one in South Africa (63), one in Italy (64), one in the Netherlands (66), and one in Malaysia (28).
Table 2.
Characteristics of included 50 trials for present umbrella meta-analysis.
|
First author, year (Country) |
No. of primary studies | No. of participants in meta-analysis | Type of Interventions |
Dosage (median) |
Health status of Participant | Outcomes evaluated | Duration (median) | Quality assessment scale (evidence) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wei et al. (23) (China) |
16 | 739 | Resistant starch | 7–45 g/d (NR) |
Healthy and patients with other metabolic diseases | TNF-α; CRP |
2 weeks to 3 months (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Mirzababaei et al. (24) (Iran) | 6 | 124 | Glucomannan | 3–15 g/d (4.8 g) |
Patients with obesity, T2DM, schizophrenia and dyslipidemia | FPG | 4–12 weeks (8 weeks) | Cochrane (moderate) |
| Xu et al. (8) (China) |
21 | 1,140 | Oat and barley β-glucan | 1.45–11.2 g/d (5.0 g) | Mildly hypercholesterolaemic individuals | TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C | 3–12 weeks (6 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Xiong et al. (25) (China) | 19 | 503 | Resistant starch | 5–66 g/d (21.5 g) |
Overweight, high risk of developing diabetes, diabetes | FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 2–12 weeks (6 weeks) | Jadad (moderate) |
| Xie et al. (26) (China) | 29 | 1,517 | Soluble dietary fiber | 1–20 g/d (10 g) |
T2DM | FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 3–12 weeks (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Wang et al. (27) (China) | 17 | 494 | Guar gum | 5–29 mg/d (15 mg) |
Diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, healthy people | TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C | 3 weeks to 6 months (12 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Rahim et al. (28) (Malaysia) |
7 | 417 | Brown rice | NR | T2DM and pre-diabetic | FPG, HbA1c, HDL-C, LDL-C, SBP, DBP | 6–16 weeks (12 weeks) | GRADE pro guideline development tool (moderate) |
| Ojo et al. (13) (UK) |
11 | 721 | Dietary fiber | NR | T2DM | TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C, TNF-α, CRP | 3–52 weeks (12 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Mao et al. (29) (China) | 22 | 911 | Dietary fiber | 3.1–28 g/d (10 g) |
T2DM | FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 4–12 weeks (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Lu et al. (30) (China) |
16 | 706 | Resistant starch | 6–27 g/d (11.75 g) |
T2DM. end stage renal disease, chronic kidney disease, people with potential health risk, healthy people | TNF-α; CRP |
4–12 weeks (8 weeks) | Jadad (moderate) |
| Li et al. (31) (China) |
33 | 1,047 | Inulin-type fructan | 3–30 g/d (11 g) |
Overweight and obese, prediabetes and diabetes, hyperlipidemia, healthy people | FPG, FPI, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TG | 2–18 weeks (6 weeks) | The Heyland Methodologic Quality Score (moderate) |
| Li et al. (31) (China) | 11 | 479 | Guar gum | 5–30 g/d (15 g) |
T2DM | TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C | 4 weeks to 6 months (12 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Haghighatdoost et al. (32) (Iran) | 8 | 308 | Resistant starch type 2 | 10–45 g/d (20 g) |
Patients with renal disease, diabetes, prediabetes, high risk of T2DM, obese and overweight | CRP, TNF-α |
4–12 weeks (8 weeks) | Delphi checklist (high-quality) |
| Golzarand et al. (33) (Iran) | 13 | 924 | Brown rice | 50–450 g/d (225 g) |
MetS, overweight, T2DM, hypercholesterolemia, impaired glucose tolerance | TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 4–104 weeks (10 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Faghihimani et al. (34) (Iran) | 6 | 233 | Inulin type-carbohydrates | 10–15 g/d (10) |
T2DM, obese patients, Women with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy | SBP, DBP | 3–8.5 weeks (6.5 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Zhang et al. (35) (China) | 9 | 661 | Inulin | 8.4–10 g/d (10 g) |
T2DM | FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 6–12 weeks (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Xiao et al. (36) (China) | 8 | 395 | Psyllium | 3.4–15 g/d (9 g) |
Diabetic patients | TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, FPG, HbA1c | 8–20 weeks (12 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Wang et al. (37) (China) | 15 | 772 | Resistant starch | 4.5–50 g/d (21 g) |
Persons diagnosed with T2DM and those at risk | FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 2–48 weeks (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Vahdat et al. (38) (Iran) | 13 | 672 | Resistant starch | 10–45 g/d (17 g) |
Healthy and patients with metabolic diseases | CRP, TNF-α |
4–14 weeks (8 weeks) | Jadad Scale, and the Downs Black assessment tools (moderate) |
| Ojo et al. (39) (UK) |
9 | 540 | Dietary fiber | NR | T2DM | FPG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 3–52 weeks (12 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Halajzadeh et al. (40) (Iran) | 19 | 1,014 | Resistant starch | 4.5–50 g/d (20 g) |
Patients with metabolic syndrome and related disorders | FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, TC, TG, HDL-c, LDL-c, CRP, TNF-α | 21 days to 12 months (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Clark et al. (41) (UK) | 11 | 592 | Psyllium | 3.7–15 g/d (10.5 g) |
T2DM, hyperlipidemia, hypertension | SBP, DBP | 4 weeks to 6 months (8 weeks) | Jadad (high-quality) |
| Wang et al. (42) (China) | 13 | 428 | Resistant starch | 10–45 g/d (30 g) |
Overweight or obese adults | FPG, FPI, HOMA-IR, TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-c, HbA1c | 2–12 weeks (4 weeks) | Effect public health practice project (high quality) |
| Wang et al. (42) (China) | 33 | 1,346 | Inulin-type fructans | 5.5–30 g/d (10 g) |
Healthy, overweight and obesity, prediabetes and type 2 diabetes populations, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis patients | FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 20–252 days (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Snelson et al. (14) (Australia) | 20 | 670 | Resistant starch type 2 | 8–66 g/d (29 g) |
Healthy, overweight/obese, MetS, prediabetes or T2DM | FPG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TG | 1–12 weeks (5.5 weeks) | Cochrane (moderate) |
| Rao et al. (43) (China) | 11 | 634 | Inulin-Type Carbohydrates | 2.7–10 g/d (10 g) |
T2DM | FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 6–12 weeks (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Jovanovski et al. (44) (Canada) | 27 | 1,394 | Viscous fiber | 2.55–21.0 g/d (13.1 g) | T2DM | FPG, FPI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR | 3–52 weeks (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Gao et al. (45) (China) | 14 | 515 | Resistant starch | 6.51–40 g/d (18.5g) | Patients with T2DM and simple obesity | FPG, FPI, HOMA-IR | 4–52 weeks (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Khan et al. (46) (Canada) | 22 | 1,430 | Viscous soluble fiber | 1.45–30 g/d (8.7 g) |
Overweight | SBP, DBP | 4–24 weeks (7 weeks) | Cochrane (moderate) |
| Jovanovski et al. (47) (Canada) | 28 | 1,924 | Psyllium | 7–15 g/d (10.2 g) |
Individuals with hyperlipidemia, healthy individuals, diabetes, MS | LDL-C | 3–52 weeks (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Thompson et al. (48) (USA) | 12 | 609 | Isolated soluble fiber | 3–30 g/d (8.75 g) |
Adults with overweight and obesity | FPG, FPI, HOMA-IR | 2–17 weeks (12 weeks) | The Heyland Methodologic Quality Score, and Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Liu et al. (49) (China) | 20 | 607 | Inulin-type fructans | 7.4–30 g/d (10.6 g) |
Healthy, dyslipidemia, overweight or obese, T2DM | FPG, FPI, HDL-C, LDL-C, TC, TG | 20 days to 6 months (6 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Hoang et al. (50) (Canada) | 12 | 370 | Konjac glucomannan | 2.0–15.1 g/d (3.3 g) |
hypercholesterolemic individuals, overweight/obese, insulin-resistant, healthy, others | LDL-C | 3–12 weeks (6 weeks) | The Heyland Methodologic Quality Score, and Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Shen et al. (51) (China) | 4 | 350 | Oat β-glucan | 2.5–3.5 g/d (3 g) |
T2DM | FPG, FPI, HbA1c | 3–8 weeks (4 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Ho et al. (52) (Canada) | 14 | 615 | Barley β-glucan | 1.5–12 g/d (6.5 g) |
Hypercholesterolemic individuals, others | LDL-C | 3–12 weeks (4 weeks) | The Heyland Methodologic Quality Score, and Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Ho et al. (52) (Canada) | 56 | 3,974 | Oat β-glucan | 0.9–10.3 g/d (3.5g) |
Slightly overweight, overweight/obese, hypercholesterolemic individuals | LDL-C | 3–12 weeks (6 weeks) | The Heyland Methodologic Quality Score, and Cochrane (high-quality) |
| He et al. (53) (China) | 18 | 1,024 | Oat β-glucan | 3–10 g/d (5 g) |
T2DM, moderate hyperlipidaemic subjects, overweight | FPG, FPI | 4 weeks to 3 months (8 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Zou et al. (54) (China) | 12 | 603 | Oat and barley β-glucan | 2.8–8.1 g/d (4.5 g) |
Mild or mild to moderate hyperlipidemia | FPG, FPI | 4–12 weeks (5.5 weeks) | Jadad, and Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Zhu et al. (55) (China) | 17 | 916 | Oat and barley β-glucan | 2.8–10.3 g/d (5 g) |
Hypercholesterolemic subjects | TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, FPG | 4–12 weeks (7 weeks) | Jadad, and Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Jiao et al. (56) (China) | 14 | 728 | Dietary fiber | 1.0–17.8 g/d (8 g) |
Overweight and obese adults | CRP | 3–16 weeks (12 weeks) | Jadad (moderate) |
| Evans et al. (57) (UK) | 28 | 1,690 | Dietary fiber | (6 g/d) | Healthy, mild hypertension, overweight or obese | SBP, DBP | 6 weeks to 14 months (12 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Whitehead et al. (58) (Canada) | 28 | 2,519 | Oat β-glucan | 3.0–12.4 g/d (5 g) |
Healthy, hypercholesterolemia, T2DM | TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C | 2–12 weeks (5.5 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Silva et al. (59) (Brazil) | 11 | 605 | Dietary fiber | 3.5–16.5 g/d (15 g) |
T2DM | FPG, HbA1c | 8–24 weeks (12 weeks) | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Post et al. (60) (USA) | 13 | 400 | Dietary fiber | 4–40 g/d (18.3 g) |
T2DM | FPG, HbA1c | NR | Cochrane (high-quality) |
| Tiwari et al. (61) (Ireland) | 30 | 1,250 | Oat and barley β-glucan | 2–14 g/d (4.5 g) |
Healthy, cholesterolemic individuals, diabetic and non-diabetic | TC, HDL-c, LDL-c | 3–12 weeks (5 weeks) | NR |
| AbuMweis et al. (62) (Canada) | 11 | 591 | barley β-glucan | 3–12 g/d (5 g) |
Healthy but not after myocardial infarction | TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C | 4–12 weeks (5 weeks) | A custom-built tool in collaboration with Health Canada (NR) |
| Sood et al. (63) (South Africa) | 14 | 531 | Glucomannan | 1.2–15.1 g/d (3.4 g) |
MS, T2DM, impaired glucose tolerance, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, obesity | TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, FPG, SBP, DBP | 3–16 weeks (5.5 weeks) | NR |
| Brighenti et al. (64) (Italy) | 15 | 290 | Inulin-type fructans | 4–32 g/d (14.2 g) |
Dyslipidemia, T2DM, NAFLD, healthy | TG | 21–64 days (4 weeks) | NR |
| Whelton et al. (65) (USA) | 25 | 1,477 | Dietary fiber | 3.8–125 g/d (10.7 g) | NR | SBP, DBP | 2–26 weeks (8 weeks) | NR |
| Streppel et al. (66) (Netherlands) | 24 | 1,404 | Dietary fiber | 3.5–42.6 g/d (7 g) |
People with/without hypertension | SBP, BP | 2–24 weeks (8 weeks) | Quantified by scoring of blinding toward the type of treatment (low-quality) |
| Brown et al. (67) (USA) | 67 | 2,990 | Dietary fiber | (9.5 g/d) | Healthy, hyperlipidemic, diabetic | TC, LDL-C, TG, HDL-C | 7 weeks | NR |
| Olson et al. (68) (USA) | 12 | 404 | Psyllium-enriched cereal | 3.0–12 g/d (9.9 g) |
Hypercholesterolemic adults | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C | 14–56 days (6 weeks) | NR |
FPG, fasting plasma glucose; FPI, fasting plasma insulin; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, High density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; CRP, C-reactive protein; SBP, Systolic blood pressure; DBP, Diastolic blood pressure; NR, not reported; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; MS, metabolic syndrome; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; GRADE, grading of recommendations, assessment, development, and evaluation.
Risk of bias and quality evaluation
Most of the meta-analyses employed the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool to assess the quality of individual meta-analyses (73); in addition, Jadad scores (74), Heyland Methodologic Quality Score (75), the Delphi checklist (76), the GRADE pro-guideline development tool (19), and the Downs Black assessment tools (77) were also applied in some of the meta-analyses. The results showed that of the 52 meta-analyses, 35 used high-quality studies, nine used studies with moderate quality, seven did not report the quality of the included studies, and one used low-quality studies (shown in Supplementary Files, Supplementary Table S3).
The results of the AMSTAR 2 scale indicated that the present umbrella meta-analysis included 30 meta-analyses with moderate overall confidence, nine meta-analyses with high overall confidence, and eight and five with low and critically low overall confidence, respectively (Table 3). In summary, we concluded that the current umbrella meta-analysis could provide an accurate summary of the results based on the available studies that were included in the review. The results of the GRADE working group classification can be seen in Supplementary Files, Supplementary Table S4.
Table 3.
Subgroup analysis of dietary fiber intake in glycaemic control.
| Fasting plasma glucose | Fasting plasma insulin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of studies |
ES (95% CI) |
Heterogeneity | No. of studies | ES (95% CI) | Heterogeneity | |||
| P | P | |||||||
| Country | ||||||||
| China | 16 | −0.69 (−0.92, −0.45) |
98.20 | <0.001 | 14 | −1.202 (−1.615, −0.789) |
56.36 | 0.005 |
| Iran | 3 | −0.66 (−3.41, 2.09) |
87.44 | <0.001 | 2 | −1.172 (−2.491, 0.147) |
68.96 | 0.073 |
| USA | 2 | −0.48 (−1.15, 0.18) |
90.54 | 0.001 | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Other | 6 | −0.26 (−0.61, 0.09) |
75.32 | 0.001 | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Study population | ||||||||
| Diabetics | 14 | −1.52 (−2.08, −0.97) |
98.46 | <0.001 | 9 | −1.619 (−2.492, −0.746) |
68.01 | 0.002 |
| Dyslipidemia | 2 | −0.04 (−0.09, 0.01) |
0 | 0.587 | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MS | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Other | 10 | −0.13 (−0. 21, −0.05) |
62.55 | 0.004 | 7 | −0.980 (−1.439, −0.522) |
46.17 | 0.084 |
| Type of effect size | ||||||||
| WMD | 13 | −0.17 (−0.28, −0.06) |
80.90 | <0.001 | 9 | −1.303 (−1.616, −0.991) |
38.04 | 0.115 |
| SMD | 2 | −0.42 (−0.70, −0.13) |
71.58 | 0.061 | 3 | −0.588 (−0.835, −0.341) |
0 | 0.397 |
| MD | 12 | −1.20 (−1.64, −0.77) |
98.63 | <0.001 | 6 | −1.947 (−2.917, −0.976) |
43.95 | 0.112 |
| Type of intervention | ||||||||
| RS | 6 | −0.094 (−0.185, −0.004) |
61.68 | 0.023 | 5 | −1.618 (−2.503, −0.732) |
69.02 | 0.012 |
| β-glucan | 4 | −0.056 (−0.102, −0.011) |
49.62 | 0.114 | 3 | 0.186 (−2.303, 2.675) |
34.19 | 0.219 |
| ITF | 5 | −2.807 (−3.741, −1.874) |
99.48 | <0.001 | 5 | −1.277 (−1.672, −0.881) |
0 | 0.811 |
| Others | 12 | −0.499 (−0.831, −0.168) |
83.54 | <0.001 | 5 | −0.961 (−1.872, −0.051) |
69.94 | 0.010 |
| Sample size | ||||||||
| n <300 | 5 | −0.628 (−1.181, −0.076) |
73.66 | 0.004 | 5 | −1.701 (−2.766, −0.636) |
50.27 | 0.09 |
| 300 ≤ n <600 | 13 | −0.89 (−1.23, −0.54) |
98.48 | <0.001 | 9 | −1.293 (−1.934, −0.651) |
54.96 | 0.023 |
| n ≥ 600 | 9 | −0.26 (−0.41, −0.13) |
86.34 | <0.001 | 4 | −1.094 (−1.689, −0.500) |
74.70 | 0.008 |
| Dosage | ||||||||
| n <5 | 6 | −0.103 (−0.212, 0.006) |
64.92 | 0.014 | 3 | −0.186 (−2.306, 2.675) |
34.19 | 0.219 |
| 5 ≤ n <10 | 7 | −2.843 (−3.843, −1.843) |
99.23 | <0.001 | 6 | −1.257 (−2.048, −0.465) |
68.50 | 0.007 |
| n ≥ 10 | 12 | −0.161 (−0.256, −0.067) |
74.06 | <0.001 | 8 | −1.448 (−2.029, −0.867) |
56.31 | 0.025 |
| Duration | ||||||||
| n <7 | 8 | −0.086 (−0.140, −0.032) |
52.86 | 0.038 | 6 | −0.902 (−1.218, −0.586) |
0 | 0.457 |
| 7 ≤ n <11 | 13 | −1.363 (−1.856, −0.869) |
98.55 | <0.001 | 11 | −1.452 (−2.037, −0.867) |
67.78 | 0.001 |
| n ≥ 12 | 5 | −0.175 (−0.598, 0.249) |
797.52 | 0.001 | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| HOMA-IR | HbA1c | |||||||
| Country | ||||||||
| China | 9 | −0.490 (−0.611, −0.369) |
21.31 | 0.254 | 10 | −0.442 (−0.627, −0.258) |
91.51 | <0.001 |
| Iran | 2 | −0.174 (−0.375, 0.027) |
0 | 0.451 | 2 | −0.293 (−0.910, 0.324) |
85.60 | 0.008 |
| USA | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Other | 3 | −0.245 (−0.844, 0.354) |
67.05 | 0.048 | 5 | −0.289 (−0.447, −0.130) |
56.37 | 0.057 |
| Study population | ||||||||
| Diabetics | 9 | −0.522 (−0.774, 0.270) |
54.78 | 0.024 | 13 | −0.393 (−0.535, −0.251) |
89.31 | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 0 | ~ | ~ | ~ | 0 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MS | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Other | 5 | −0.348 (−0.610, −0.086) |
56.80 | 0.055 | 4 | −0.297 (−0.447, −0.146) |
32.17 | 0.219 |
| Type of effect size | ||||||||
| WMD | 6 | −0.345 (−0.463, −0.228) |
51.25 | 0.068 | 8 | −0.361 (−0.549, −0.173) |
88.13 | <0.001 |
| SMD | 3 | −0.618 (−0.874, −0.362) |
0 | 0.829 | 2 | −0.596 (−0.779, −0.412) |
43.81 | 0.182 |
| MD | 6 | −0.458 (−0.899, −0.017) |
63.33 | 0.018 | 8 | −0.345 (−0.489, −0.202) |
71.82 | 0.001 |
| Type of intervention | ||||||||
| RS | 6 | −0.311 (−0.450, −0.173) |
0 | 0.827 | 5 | −0.225 (−0.384, −0.065) |
81.69 | <0.001 |
| β-glucan | 0 | ~ | ~ | ~ | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ITF | 3 | −0.648 (−0.882, −0.415) |
0 | 0.446 | 3 | −0.589 (−0.730, −0.448) |
38.07 | 0.199 |
| Others | 6 | −0.507 (−0.928, −0.086) |
72.86 | 0.002 | 9 | −0.408 (−0.587, −0.229) |
77.90 | <0.001 |
| Sample size | ||||||||
| n <300 | 6 | −0.347 (−0.506, −0.189) |
48.15 | 0.086 | 6 | −0.388 (−0.649, −0.128) |
89.89 | <0.001 |
| 300 ≤ n <600 | 5 | −0.353 (−0.567, −0.139) |
41.90 | 0.142 | 7 | −0.312 (−0.466, −0.157) |
80.40 | <0.001 |
| n ≥ 600 | 4 | −0.483 (−0.820, −0.147) |
74.96 | 0.007 | 5 | −0.493 (−0.726, −0.260) |
62.83 | 0.029 |
| Dosage | ||||||||
| n <5 | 0 | ~ | ~ | ~ | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| 5 ≤ n <10 | 6 | −0.653 (−0.829, −0.477) |
0 | 0.510 | 6 | −0.631 (−0.740, −0.521) |
8.87 | 0.359 |
| n ≥ 10 | 7 | −0.324 (−0.462, −0.186) |
1.02 | 0.416 | 8 | −0.304 (−0.456, −0.151) |
82.34 | <0.001 |
| Duration | ||||||||
| n <7 | 3 | −0.298 (−0.451, −0.144) |
0 | 0.398 | 4 | −0.196 (−0.380, −0.013) |
73.43 | 0.010 |
| 7 ≤ n <11 | 10 | −0.540 (−0.760, −0.320) |
54.06 | 0.021 | 9 | −0.474 (−0.682, −0.266) |
85.80 | <0.001 |
| n ≥12 | 2 | −0.374 (−1.762, −1.013) |
64.43 | 0.094 | 4 | −0.379 (−0.645, −0.113) |
79.96 | 0.002 |
ES, effect size; MS, metabolic syndrome; RS, resistant starch; ITF, inulin-type fructans; WMD, weight mean difference; SMD, standardized mean difference; MD, mean difference.
Effects of dietary fiber intake on glycemic control
Fasting plasma glucose
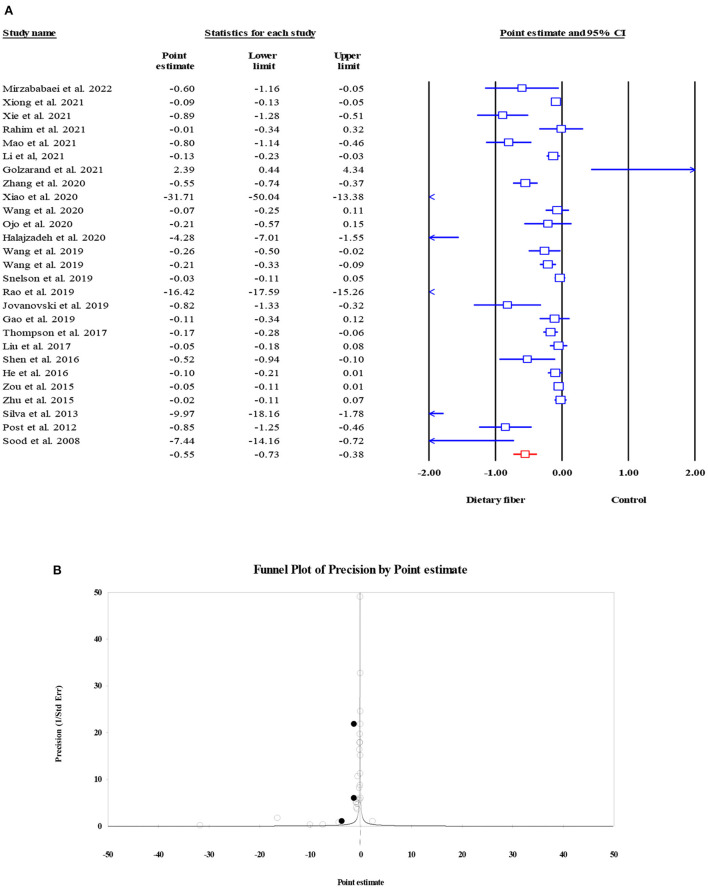
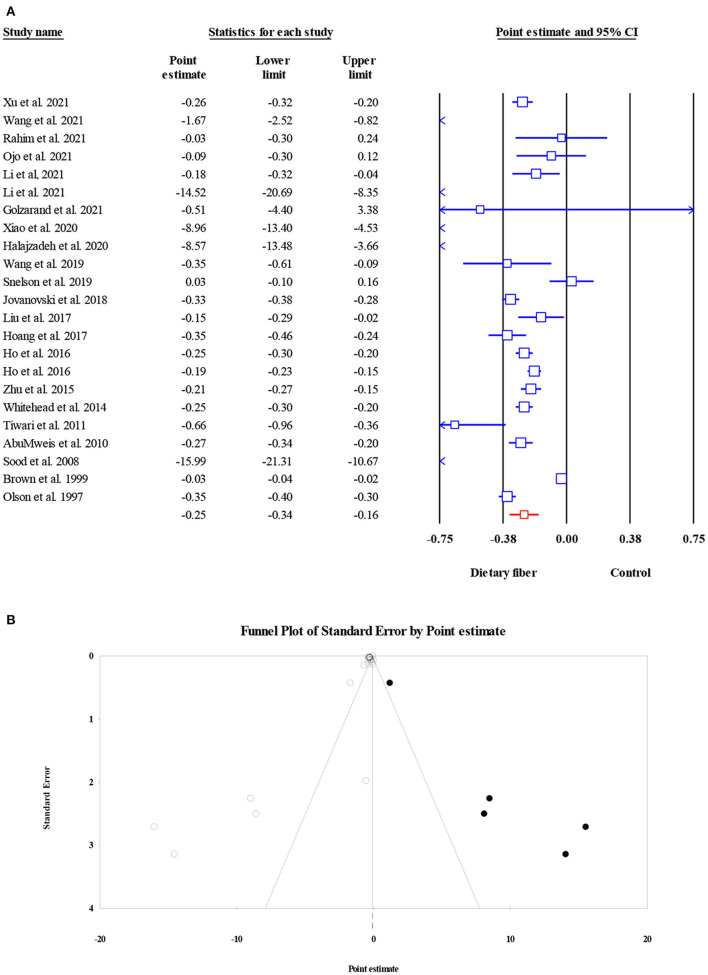
Overall, 27 meta-analyses with a total sample size of 15,464 participants showed that dietary fiber interventions resulted in a significant reduction in FPG (ES = −0.55, 95% CI: −0.73, −0.38, P < 0.001; Figure 2A). However, we observed considerable heterogeneity between these studies (I2 = 97.08, P < 0.001). A subgroup analysis by the type of intervention presented a moderate decrease in heterogeneity. On the other hand, the asymmetric distribution of the funnel plot showed the presence of publication bias (Egger's regression test P = 0.01). However, the “trim and fill” analysis with three imputed studies suggested that the effects of dietary fiber on FPG were still significant (ES = −0.72, 95% CI: −0.93, −0.52, P = 0.001; Figure 2B).
Figure 2.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on FPG (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for FPG (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
Fasting plasma insulin
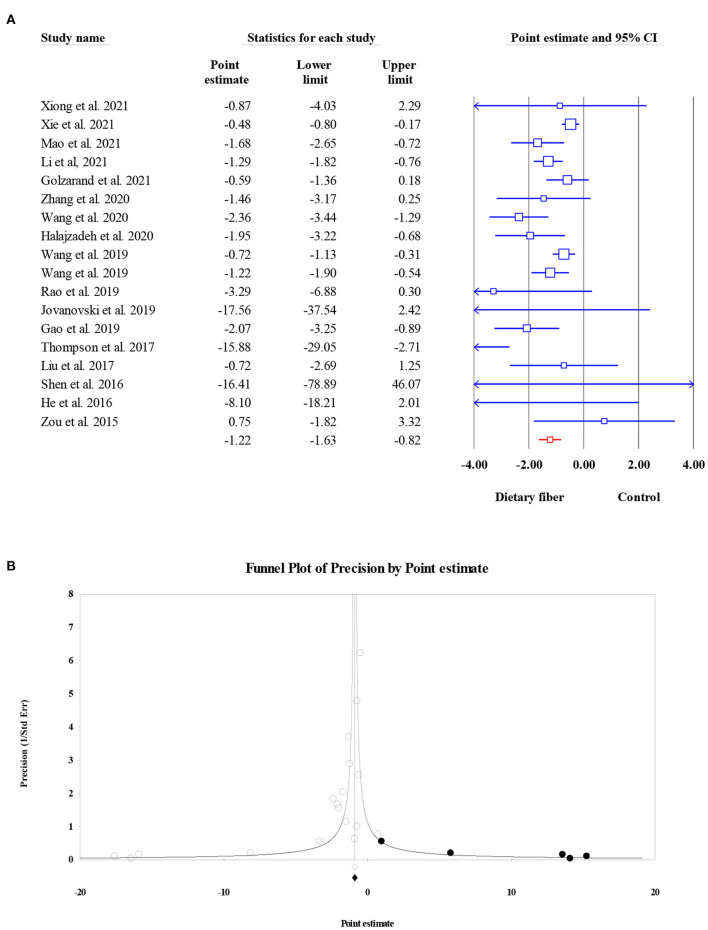
The pooled effect of dietary fiber intake on FPI was obtained from 18 meta-analyses with 7,808 subjects; it indicated a notable decrease in FPI in subjects who supplemented dietary fiber compared to those in the control group, although this finding was accompanied by significant heterogeneity (ES = −1.22, 95% CI: −1.63, −0.82, P < 0.001; I2 = 58.21, P = 0.001; Figure 3A). When a subgroup analysis by the type of effect size was carried out, the between-study heterogeneity became non-significant. Despite the presence of the small-study effect (Egger's regression test P = 0.003), the “trim and fill” analysis with five imputed studies suggested that FPI remained unchanged with dietary fiber intake (ES = −1.17, 95% CI: −1.60, −0.75, P < 0.001; Figure 3B).
Figure 3.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on FPI (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for FPI (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance
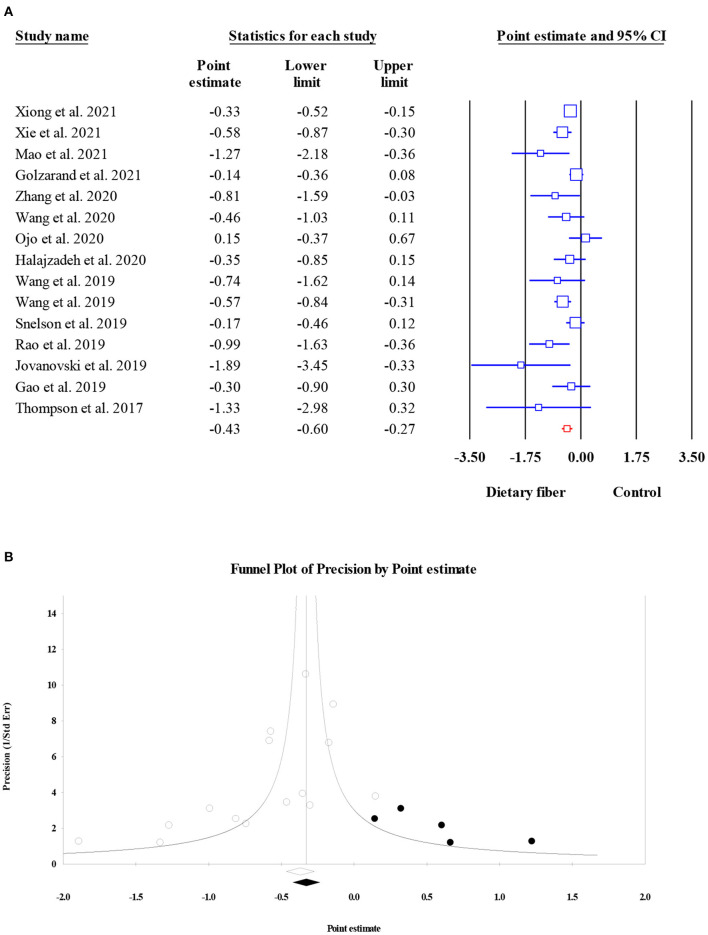
Data on the effects of dietary fiber intake on HOMA-IR were recorded from 6,236 participants based on 15 meta-analyses. We found a significant reduction in HOMA-IR following the intake of dietary fiber (ES = −0.43, 95% CI: −0.60, −0.27, P < 0.001; Figure 4A) as well as significant heterogeneity (I2 = 51.31, P = 0.011). The heterogeneity decreased when focusing on subgroup analyses by the type of intervention, sample size, and dosage. Similarly, the visual inspection of the funnel plot showed an asymmetric distribution (Egger's regression test P = 0.036), while the further “trim and fill” analysis with five imputed studies showed that the conclusion observed for HOMA-IR was reliable (ES = −0.33, 95% CI: −0.51, −0.16, P < 0.001; Figure 4B).
Figure 4.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on HOMA-IR (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for HOMA-IR (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
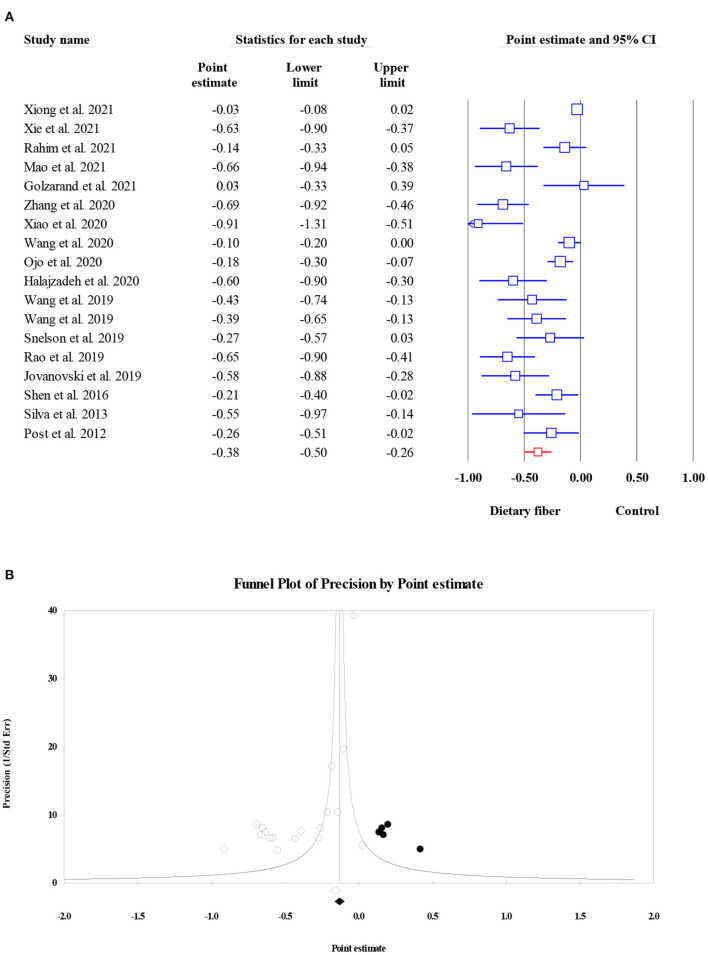
Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
Overall, HbA1c concentration was assessed as an outcome measure in 8,966 participants from 18 meta-analyses. The current umbrella meta-analysis provided evidence for the positive effect of dietary fiber intake on HbA1c levels (ES = −0.38, 95% CI: −0.50, −0.26, P < 0.001; Figure 5A), but with a high level of heterogeneity (I2 = 86.80, P < 0.001). A subgroup analysis by the type of intervention showed a mild decrease in between-study heterogeneity. The exploration of publication bias using funnel plots and egger's regression test showed evidence of the small-study effect in the present umbrella meta-analysis (P < 0.001). However, the results from the “trim and fill” analysis with five imputed studies showed that the overall effects were not significantly confounded by the bias (ES = −0.26, 95% CI: −0.37, −0.15, P < 0.001; Figure 5B).
Figure 5.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on HbA1c (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for HbA1c (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
Effects of dietary fiber intake on lipid profiles
Total cholesterol
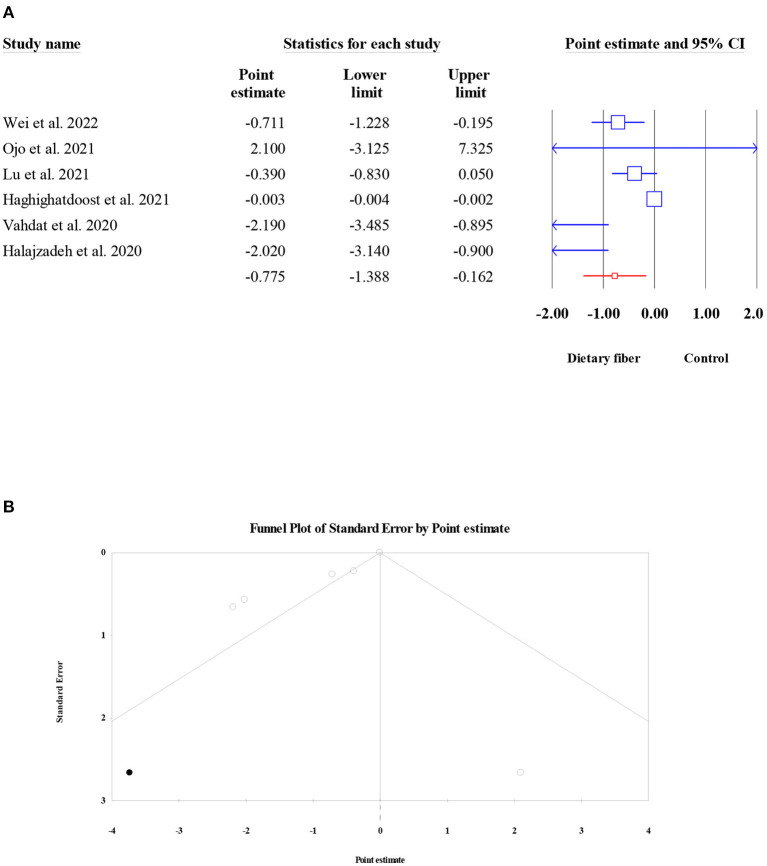
As shown in Figure 6, dietary fiber intake significantly decreased the serum TC level in the pooled results of 18 meta-analyses (15,529 participants) (ES = −0.28, 95% CI: −0.39, −0.16, P < 0.001; Figure 6A). The amount of heterogeneity was high (I2 = 96.09, P < 0.001), and the type of intervention was recognized as a potential source of this heterogeneity. Significant small-study effects were observed when conducting Egger's regression test (P < 0.001). Consequently, the “trim and fill” analysis was performed with five imputed studies, and the results showed that the corrected ES was still significant (ES = −0.26, 95% CI: −0.39, −0.13, P < 0.001; Figure 6B).
Figure 6.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on TC (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for TC (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
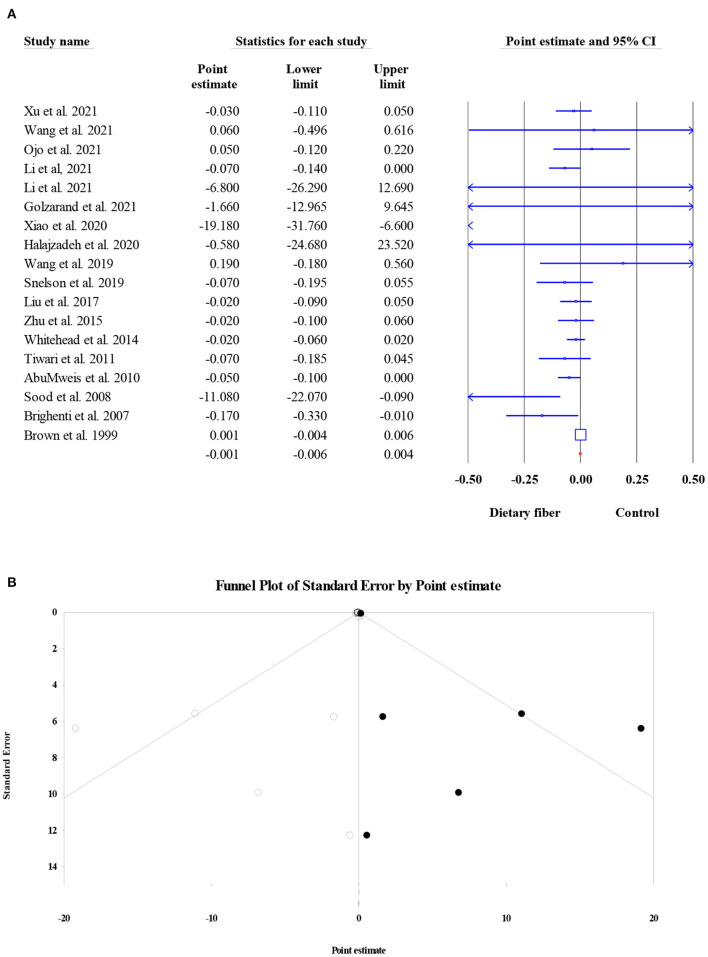
Triglycerides
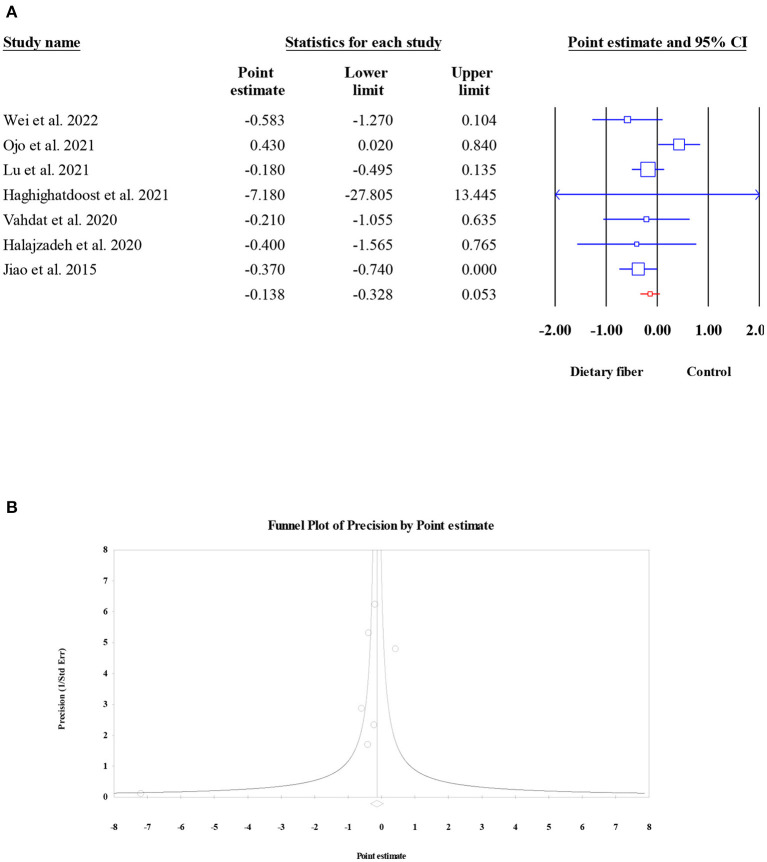
Overall, 18 meta-analyses involving 14,493 subjects investigated the effect of dietary fiber intake on TG level, and the pooled ES was not significant when compared with control group (ES = −0.001, 95% CI: −0.006, 0.004, P = 0.759; Figure 7A). In addition, the heterogeneity between studies was moderate (I2 = 46.10, P = 0.017). Factors such as the type of effect size, type of intervention, and dosage may have been possible sources of heterogeneity. The results of Egger's regression test showed the presence of publication bias (P = 0.003). Therefore, a “trim and fill” analysis was conducted with six imputed studies, and the results remained non-significant even after the amendment of the small-study effect (ES = 0.000, 95% CI: −0.005, 0.004, P < 0.001; Figure 7B).
Figure 7.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on TG (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for TG (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
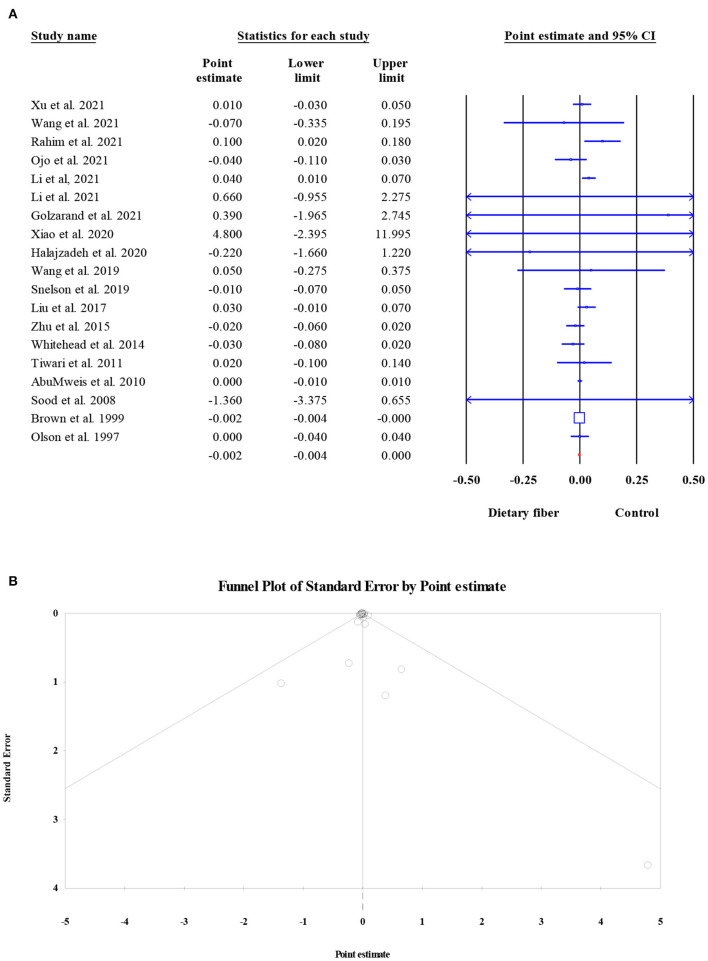
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
The effects of dietary fiber intake on serum HDL-C concentration were evaluated in 13,913 participants from 19 meta-analyses. The combined ES demonstrated that dietary fiber had no significant effect on the HDL-C level (ES = −0.002, 95% CI: −0.004, 0.000, P = 0.087; Figure 8A). In addition, there was no obvious between-study heterogeneity (I2 = 26.85, P = 0.136) or small-study effect (Egger's regression test P = 0.296, Figure 8B).
Figure 8.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on HDL-C (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for HDL-C (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
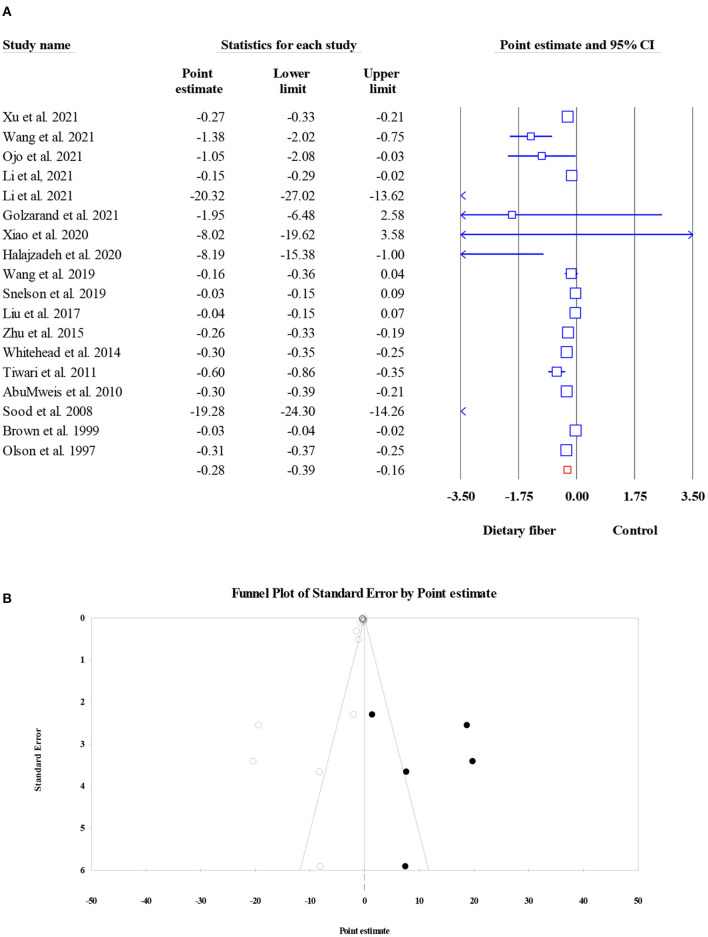
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
Twenty-three meta-analyses involving 21,887 participants reported the effect of dietary fiber intake on serum LDL-C level, and the pooled ES suggested a significant decrease in LDL-C (ES = −0.25, 95% CI: −0.34, −0.16, P < 0.001; Figure 9A). There was significant heterogeneity between studies (I2 = 96.59, P < 0.001), which was reduced with a subgroup analysis by the type of intervention. Notably, a significant small-study effect was observed when performing Egger's regression test (P < 0.001). The results of the “trim and fill” analysis with five imputed studies showed a robust effect after considering the publication bias (ES = −0.23, 95% CI: −0.32, 0.14, P < 0.001; Figure 9B).
Figure 9.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on LDL-C (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for LDL-C (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
Effects of dietary fiber intake on inflammatory factors and blood pressure
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
There were six meta-analyses involving 1,647 subjects that presented the pooled effect of dietary fiber intake on the levels of TNF-α. A significant reduction in TNF-α was noted after the intake of dietary fiber (ES = −0.78, 95% CI: −1.39, −0.16, P = 0.013; Figure 10A). The heterogeneity between studies was high (I2 = 85.39, P < 0.001), and there was a moderate small-study effect (Egger's regression test P = 0.056). However, further “trim and fill” analysis with one imputed study indicated that the corrected ES for the effect of dietary fiber on TNF-α remained the same (ES = −0.78, 95% CI: −1.39, −0.16, P = 0.013; Figure 10B).
Figure 10.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on TNF-α (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for TNF-α (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
C-reactive protein
The pooled effect of dietary fiber intake on the serum levels of CRP was examined in seven meta-analyses (2,780 participants). Overall, the present umbrella meta-analysis showed that compared to the control group, dietary fiber intake did not lead to a significant decrease in serum CRP concentration (ES = −0.14, 95% CI: −0.33, 0.05, P = 0.156; Figure 11A). In addition, no obvious between-study heterogeneity (I2 = 46.59, P = 0.081) or publication bias (Egger's regression test P = 0.532; Figure 11B) were observed.
Figure 11.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on CRP (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for CRP (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
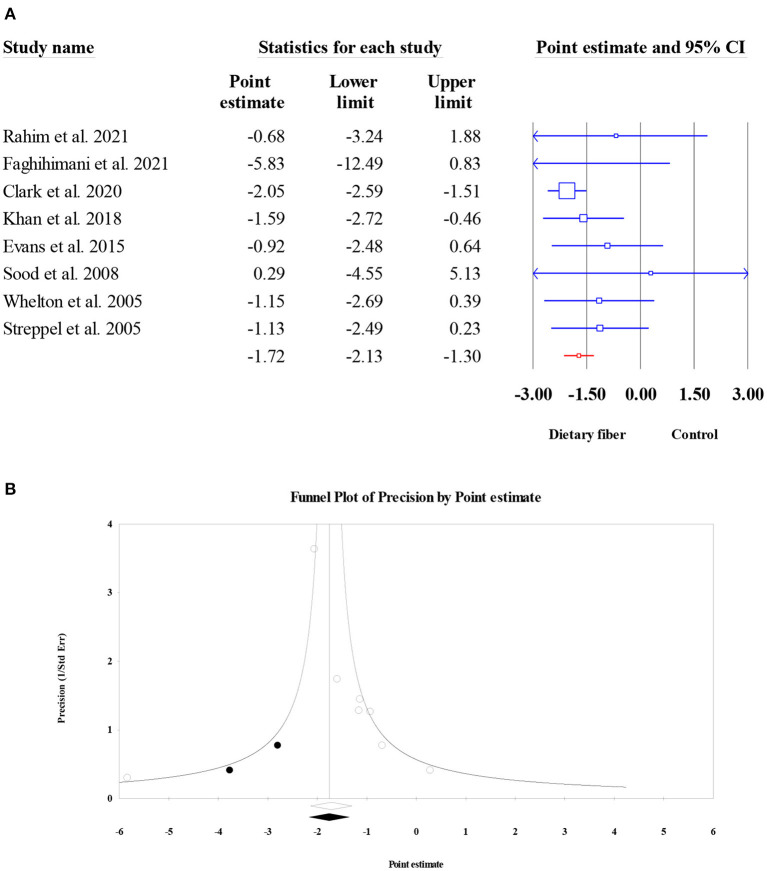
Systolic blood pressure
The effect of dietary fiber intake on SBP was assessed in eight meta-analyses (6,827 subjects). The results revealed a significant reduction in SBP after dietary fiber intake (ES = −1.72, 95% CI: −2.13, −1.30, P < 0.001; Figure 12A) and no heterogeneity (I2 = 0, P = 0.480). However, the visual inspection of the funnel plot indicated an asymmetric distribution (Egger's regression test P = 0.040). Therefore, we conducted a “trim and fill” analysis with two imputed studies, and the corrected result showed that the beneficial effect of dietary fiber on SBP was stable (ES = −1.76, 95% CI: −2.17, −1.35, P < 0.001; Figure 12B).
Figure 12.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on SBP (A), assessment of publication bias and “trim and fill” analysis for SBP (B); *Each black circle represents one imputed study.
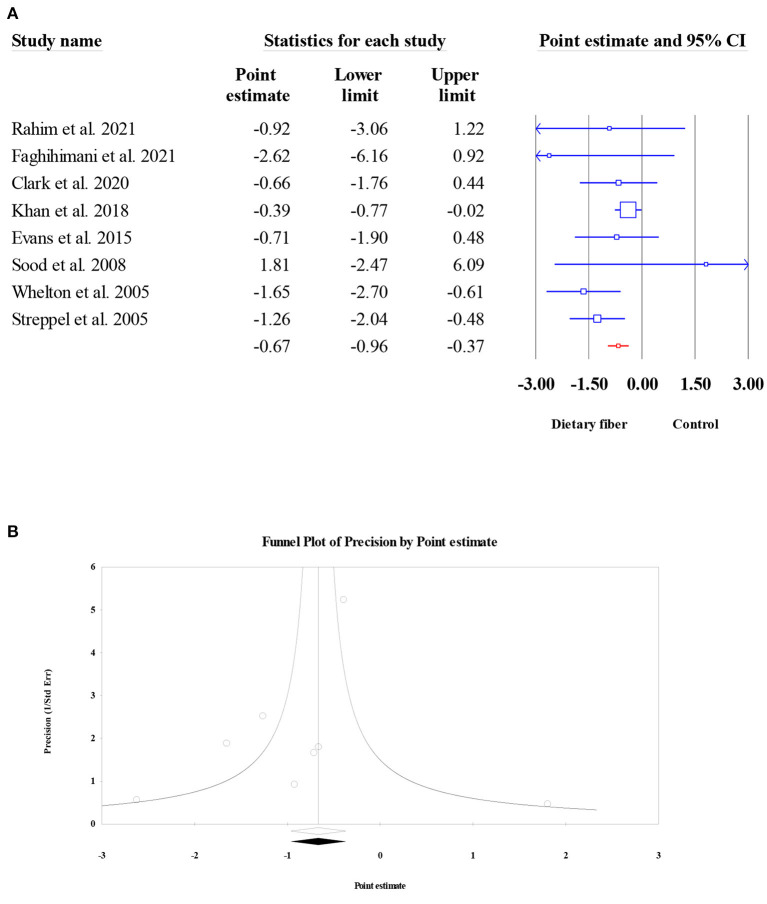
Diastolic blood pressure
Similar to SBP, a total of eight meta-analyses involving 6,827 participants were evaluated to obtain the pooled ES for dietary fiber intake on DBP. The results presented an obvious decrease in DBP following dietary fiber intake (ES = −0.67, 95% CI: −0.96, −0.37, P < 0.001; Figure 13A). Moderate between-study heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 31.62, P = 0.176). In addition, no evidence of publication bias was found (Egger's regression test P = 0.346; Figure 13B).
Figure 13.
Forest plot of the effect of dietary fiber intake on DBP (A), assessment of publication bias for DBP (B).
Sensitivity analysis
A sensitivity analysis, which is carried out by sequentially removing each eligible meta-analysis and then repeating the umbrella meta-analysis, was also applied to assess the effect of single meta-analysis on the overall ESs. The results showed that the overall ESs did not change by excluding any individual meta-analysis (data are not shown).
Subgroup analysis of dietary fiber intake on glucose metabolism
We also conducted subgroup analyses on studies that used dietary fiber for the four glycemic parameters stratified based on seven specific factors, including country, study population, type of effect size, type of intervention, sample size, dosage, and duration. It seemed that the beneficial effects of dietary fiber on glycemic control were more pronounced in patients with diabetes than in the rest of the population (Table 3). In addition, the type of dietary fiber may have caused different effects on glucose metabolism, where inulin-type fructans supplementation obviously presented more reductions in indicators involved with glucose control than resistant starch and β-glucan (Table 3) as well as lower heterogeneity. In terms of sample size, the subgroup analysis suggested that meta-analyses with a sample size of > 600 led to the largest decline in HOMA-IR and HbA1c. However, we did not find a positive association between a higher dosage of dietary fiber intake or a longer duration of dietary fiber intervention and a greater decrease in glucose parameters; moreover, the between-study heterogeneity did not present a significant decrease, indicating that dosage and duration may not have been the sources of heterogeneity.
Subgroup analysis of dietary fiber intake on lipid profiles
Similar to the subgroup analysis above, we also performed a subgroup analysis of the effect of dietary fiber on lipid profiles. Firstly, we noted that the effect of dietary fiber intake on serum TC became non-significant in patients with diabetes, which was contradictory to patients with dyslipidemia (Table 4). Next, a subgroup analysis based on the type of intervention showed that resistant starch and β-glucan possessed a greater efficacy in lowering serum TC and LDL-C concentration than inulin-type fructans; furthermore, it seemed that β-glucan could lead to a mild but significant decrease in serum TG level (Table 4). Finally, we failed to find any evidence recognizing dosage and duration as sources of heterogeneity (Table 4).
Table 4.
Subgroup analysis of dietary fiber intake in lipides profiles.
| Total cholesterol | Triglyceride | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of studies |
ES (95% CI) |
Heterogeneity | No. of studies | ES (95% CI) | Heterogeneity | |||
| P | P | |||||||
| Country | ||||||||
| China | 8 | −0.254 (−0.418, −0.089) |
89.16 | <0.001 | 8 | −0.034 (−0.071, 0.003) |
42.51 | 0.095 |
| Canada | 2 | −0.300 (−0.344, −0.256) |
0 | 0.999 | 2 | −0.032 (−0.063, 0.000) |
0 | 0.358 |
| USA | 2 | −0.168 (−0.443, 0.106) |
98.77 | <0.001 | 1 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Other | 6 | −1.329 (−2.297, −0.361) |
93.75 | <0.001 | 7 | −0.069 (−0.153, −0.015) |
18.34 | 0.290 |
| Study population | ||||||||
| Diabetics | 3 | −9.630 (−23.499, 4.238) |
93.80 | <0.001 | 3 | −7.743 (−21.351, 5.865) |
78.83 | 0.009 |
| Dyslipidemia | 3 | −0.282 (−0.318, −0.246) |
0 | 0.504 | 2 | −0.025 (−0.082, 0.032) |
0 | 0.862 |
| Other | 12 | −0.254 (−0.399, −0.110) |
95.42 | <0.001 | 13 | −0.001 (−0.006, 0.004) |
43.02 | 0.049 |
| Type of effect size | ||||||||
| WMD | 7 | −0.909 (−1.601, −0.216) |
93.95 | <0.001 | 7 | −0.056 (−0.214, 0.101) |
56.62 | 0.032 |
| SMD | 3 | −0.628 (−1.146, −0.110) |
88.43 | <0.001 | 4 | −0.083 (−0.172, 0.007) |
15.03 | 0.317 |
| MD | 8 | −0.196 (−0.325, −0.067) |
97.21 | <0.001 | 7 | 0.000 (−0.005, 0.005) |
14.84 | 0.317 |
| Type of intervention | ||||||||
| RS | 3 | −0.100 (−0.358, 0.159) |
67.437 | 0.046 | 3 | −0.043 (−0.162, 0.075) |
0 | 0.426 |
| β-glucan | 5 | −0.288 (−0.320, −0.257) |
42.86 | 0.136 | 5 | −0.032 (−0.059, −0.006) |
0 | 0.853 |
| ITF | 2 | −0.084 (−0.169, 0.001) |
34.76 | 0.216 | 3 | −0.056 (−0.103, −0.009) |
35.89 | 0.210 |
| Others | 8 | −0.622 (−0.977, −0.267) |
96.44 | <0.001 | 7 | 0.015 (−0.210, 0.239) |
56.36 | 0.033 |
| Sample size | ||||||||
| n <500 | 7 | −0.449 (−0.701, −0.197) |
88.28 | <0.001 | 6 | −0.026 (−0.173, 0.122) |
64.63 | 0.015 |
| 500 ≤ n <1,000 | 6 | −0.230 (−0.576, 0.116) |
93.59 | <0.001 | 8 | −0.028 (−0.070, 0.013) |
0 | 0.560 |
| n ≥ 1,000 | 5 | −0.248 (−0.416, −0.081) |
97.81 | <0.001 | 4 | −0.020 (−0.051, 0.012) |
52.93 | 0.095 |
| Dosage | ||||||||
| n <5 | 7 | −0.382 (−0.524, −0.241) |
91.81 | <0.001 | 7 | −0.032 (−0.059, −0.006) |
0 | 0.501 |
| 5 ≤ n <10 | 3 | −0.173 (−0.448, 0.103) |
97.60 | <0.001 | 2 | −8.52 (−27.19, 10.16) |
88.80 | 0.003 |
| n ≥10 | 6 | −0.130 (−0.378, 0.117) |
88.32 | <0.001 | 7 | −0.054 (−0.098, −0.010) |
0 | 0.503 |
| Duration | ||||||||
| n <6 | 6 | −0.304 (−0.522, −0.086) |
93.74 | <0.001 | 7 | −0.039 (−0.068, −0.011) |
36.79 | 0.148 |
| 6 ≤ n <12 | 7 | −0.181 (−0.316, −0.046) |
96.68 | <0.001 | 6 | 0.000 (−0.005, 0.005) |
1.43 | 0.407 |
| n ≥ 12 | 5 | −3.643 (−6.231, −1.056) |
87.65 | <0.001 | 5 | −0.027 (−0.759, 0.705) |
58.06 | 0.049 |
| High density lipoprotein cholesterol | Low density lipoprotein cholesterol | |||||||
| Country | ||||||||
| China | 9 | 0.019 (0.001, 0.037) |
10.05 | 0.351 | 8 | −0.282 (−0.433, −0.131) |
86.16 | <0.001 |
| Canada | 2 | −0.001 (−0.011, 0.009) |
24.80 | 0.249 | 6 | −0.266 (−0.314, −0.218) |
77.15 | 0.001 |
| USA | 2 | −0.002 (−0.004, 0.000) |
0 | 0.922 | 2 | −0.189 (−0.503, 0.125) |
99.34 | <0.001 |
| Other | 6 | 0.008 (−0.029, 0.046) |
45.31 | 0.104 | 7 | −0.378 (−0.846, 0.090) |
90.50 | <0.001 |
| Study population | ||||||||
| Diabetics | 4 | 0.035 (−0.104, 0.175) |
66.51 | 0.03 | 4 | −0.774 (−1.734, 0.186) |
91.78 | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 3 | −0.003 (−0.026, 0.020) |
0 | 0.571 | 4 | −0.269 (−0.329, −0.209) |
79.08 | 0.002 |
| Other | 12 | −0.002 (−0.004, 0.000) |
20.02 | 0.247 | 15 | −0.260 (−0.366, −0.153) |
96.40 | <0.001 |
| Type of effect size | ||||||||
| WMD | 7 | 0.029 (0.005, 0.053) |
0 | 0.459 | 7 | −0.898 (−1.532, −0.264) |
92.60 | <0.001 |
| SMD | 3 | 0.009 (−0.094, 0.113) |
0 | 0.805 | 3 | −0.727 (−1.213, −0.240) |
78.85 | 0.009 |
| MD | 9 | −0.002 (−0.004, 0.000) |
33.56 | 0.149 | 13 | −0.199 (−0.289, −0.109) |
97.58 | <0.001 |
| Type of intervention | ||||||||
| RS | 3 | −0.008 (−0.067, 0.051) |
0 | 0.900 | 3 | −0.274 (−0.870, 0.322) |
88.97 | <0.001 |
| β-glucan | 5 | −0.001 (−0.011, 0.008) |
0 | 0.627 | 7 | −0.242 (−0.279, −0.205) |
61.35 | 0.017 |
| ITF | 2 | 0.036 (0.012, 0.060) |
0 | 0.695 | 2 | −0.164 (−0.262, −0.067) |
0 | 0.762 |
| Others | 9 | −0.002 (−0.004, 0.000) |
32.47 | 0.158 | 11 | −0.316 (−0.510, −0.122) |
97.41 | <0.001 |
| Sample size | ||||||||
| n <500 | 9 | 0.001 (−0.009, 0.010) |
31.62 | 0.165 | 11 | −0.299 (−0.476, −0.123) |
91.41 | <0.001 |
| 500 ≤ n <1,000 | 5 | 0.002 (−0.023, 0.028) |
0 | 0.494 | 6 | −0.209 (−0.292, −0.126) |
64.03 | 0.016 |
| n ≥ 1,000 | 5 | 0.007 (−0.015, 0.029) |
56.42 | 0.057 | 6 | −0.254 (−0.386, −0.121) |
98.34 | <0.001 |
| Dosage | ||||||||
| n <5 | 7 | −0.002 (−0.011, 0.008) |
0 | 0.596 | 9 | −0.289 (−0.370, −0.207) |
87.51 | <0.001 |
| 5 ≤ n <10 | 3 | −0.002 (−0.004, 0.000) |
0 | 0.423 | 4 | −0.231 (−0.456, −0.006) |
98.70 | <0.001 |
| n ≥10 | 6 | 0.030 (−0.008, 0.052) |
0 | 0.723 | 7 | −0.223 (−0.432, −0.015) |
90.38 | <0.001 |
| Duration | ||||||||
| n <6 | 6 | −0.001 (−0.011, 0.008) |
0 | 0.642 | 8 | −0.276 (−0.385, −0.166) |
88.83 | <0.001 |
| 6 ≤ n <12 | 7 | −0.002 (−0.004, 0.000) |
46.17 | 0.084 | 9 | −0.218 (−0.335, −0.101) |
97.98 | <0.001 |
| n ≥ 12 | 6 | 0.018 (−0.033, 0.070) |
47.35 | 0.091 | 6 | −1.062 (−1.930, −0.195) |
89.88 | <0.001 |
ES, effect size; MS, metabolic syndrome; RS, resistant starch; ITF, inulin-type fructans; WMD, weight mean difference; SMD, standardized mean difference; MD, mean difference.
Since the number of meta-analyses reporting the effect of dietary fiber intake on systematic inflammation and blood pressure is scarce, we did not think it was necessary to perform further subgroup analyses.
Discussion
Despite the critical role of dietary fiber intake in the management of CVDs, a consistent conclusion between studies has yet to be reached. Our purpose in this work was to provide a systematic overview of the current evidence and evaluate the methodological quality of this evidence, which could be expected to be used as dietary advice in patients at risk for CVDs. The present umbrella meta-analysis, which consisted of 52 meta-analyses involving 47,197 participants, demonstrated that compared to the control group, dietary fiber intake conferred a favorable effect on glucose metabolism, improving lipid profiles (TC and LDL-C), ameliorating inflammation factors (TNF-α), and controlling blood pressure, indicating a strong protection effect against cardiovascular-related diseases.
Historical evidence has indicated a negative relationship between dietary fiber intake and the risk of diabetes mellitus (15). In the present umbrella meta-analysis, we found that dietary fiber intake could significantly reduce the plasma concentrations of biomarkers involved in blood glucose metabolism, including FPG and HbA1c, which showed some consistency with another umbrella review and meta-analysis conducted by Xu et al., who found similar pronounced decreases in plasma FPG and HbA1c in a high microbiota-accessible carbohydrates intervention group (78). Mechanistic studies have suggested that on the one hand, dietary fiber intervention could increase the viscosity of intestinal content, which acts as a barrier to the absorption of glucose and the postprandial gastric emptying rate (79); on the other hand, some types of dietary fiber can increase the concentration of serum glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), an enteroendocrine-derived peptide secreted in response to nutrient ingestion that plays a crucial role in antidiabetic action (80, 81). Indeed, one clinical trial found that intervention with GLP-1 for 6 weeks led to a significant improvement in blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients (82). Although the present results regarding blood glucose were in agreement with those of most of previous studies, we noted that, in the subgroup analysis, it seemed that patients with dyslipidemia did not obtain the beneficial effects of dietary fiber intake. We speculated that the difference in dietary background may have caused some bias, since a direct association between improvements in diet quality and improvements in blood glucose control was still under debate (83). Based on the evidence that insulin resistance is a determining factor in the pathophysiology of T2DM (84), our umbrella meta-analysis suggests that dietary fiber intake effectively regulates insulin sensitivity by decreasing the concentration of FPI and index of HOMA-IR. Moreover, a meta-analysis performed by Reynolds et al. also supported the improved effects of high-fiber diets on insulin sensitivity (85). Emerging evidence has shown that dietary fiber can be fermented by gut microbiota to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and eventually, humans, especially patients with T2DM, can benefit from the increased level of SCFAs (86). Furthermore, one mechanistic study indicated that the increased processes of glucose oxidation and insulin clearance, as well as the decreased process of fatty acid release, were the two key actions of SCFA in improvements of insulin sensitivity (87). Consistent with clinical controlled trials, the beneficial effects of dietary fiber intervention on plasma insulin and circulating SCFA have also been observed by researchers (88, 89). However, it should be noted that β-glucan failed to confer a beneficial effect on the improvement of FPI when we performed a subgroup analysis by the type of intervention; the results were consistent with several published meta-analyses (51, 90) but contradictory to the meta-analysis conducted by Bao et al. (91). Since meta-analyses evaluating β-glucan for glycemic control were scarce in the current umbrella meta-analysis, we should explain this result with caution.
Regarding the effect of dietary fiber intake on serum lipid profiles, most of our results concurred with the report from a recent meta-analysis, which showed that fiber-fortified food consumption could significantly reduce the levels of serum TC, TG, and LDL-C, while no significant effect was observed in serum HDL-C concentration (92). However, in contrast, we only found a significant decrease in the subgroup analysis based on β-glucan intervention in the serum TG level, but not in overall pooled ESs. Since the cholesterol-lowering effect was highly correlated with the viscosity of the gel-forming fiber, nonviscous soluble and insoluble fibers might exert different health benefits (93). It is well established that dyslipidemia is a key contributor to the development of CVDs (94), while previous evidence has suggested that the abnormality of serum lipids could be improved by dietary fiber via different kinds of mechanisms. Firstly, the dietary fiber-induced high-viscosity microenvironment within the small intestine could prevent the absorption of dietary cholesterol as well as promote the excretion of bile acids (synthesized by endogenous cholesterol) from stool (95). Similarly, clinical trials and reviews have proposed that dietary fiber intake could stimulate an increase in the abundance of probiotics, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium; these gut microbiota are known to contain bile acid hydrolase-positive species, which can accelerate the excretion of unconjugated bile acids via deconjugation action (96, 97). Lastly, dietary fiber-fermented SCFA, particularly propionate, could reduce plasma cholesterol by suppressing the activity of 3-hydroxy 3-methylglutaryl co-enzyme A reductase (HMG-Co AR), which serves as a rate limiting enzyme during endogenous cholesterol biosynthesis (98). In vitro studies have also shown that some types of dietary fiber (β-glucan) can act as inhibitors of HMG-Co AR, leading to impairment in endogenous cholesterol biosynthesis (99, 100), which may also partly explain the effect observed in the subgroup where β-glucan intake presented a more pronounced improvement in TC and LDL-C levels than other types of dietary fiber.
It is believed that the acceleration of arterial plaque formation and transformation into vulnerable plaques induced by chronic low-grade inflammation is one pathophysiology of atherosclerotic disease (101). Indeed, a previous study proposed that elevated levels of circulating inflammatory makers could be recognized as a strong predictor of CVDs (102). In our present umbrella meta-analysis, we found that dietary fiber intake resulted in a significant decrease in the serum TNF-α level, while its effect on serum CRP was not significant. One epidemiological study suggested that compared to a lower intervention of dietary fiber, women with a higher ingestion of dietary fiber had a lower level of plasma TNF-α-R2 (receptor 2 of TNF-α); however, but no significant association was observed between dietary fiber and CRP (103). However, a report from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2010 indicated that dietary fiber is negatively correlated with serum CRP level in adults in the US (104). The consideration of the baseline values of inflammatory biomarkers may also have important clinical implications in evaluating dietary fiber-mediated improvements in serum inflammatory biomarkers, which means that, if the baseline values of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the population are not high, a significant response to the dietary fiber intake may be difficult to observe. Several mechanisms have been proposed for the anti-inflammatory effects of dietary fiber. In their study on rodents, Yang et al. found that dietary fiber could alleviate inflammation by modulating the gut microbiota (increasing the abundance of Barnesiella and Lactobacillus) and inhibiting the expressions of proteins involved with the Toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappa B (TLR-4/NF-κB) signaling pathway (105). In addition, in an in vitro study, Hung et al. found that guar gum, a type of dietary fiber, could increase suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 expression through the TLR-2 and dectin-1 pathways, resulting in anti-inflammatory regulation in small intestinal cells (106). Currently, numerous studies have highlighted the roles of healthy diets in preventing chronic diseases (107, 108), the results of which also support our current results to some extent.
Hypertension, an asymptomatic clinical condition, is an important public health issue. Both observational studies and meta-analyses have demonstrated graded associations between higher SBP/DBP and increased CVDs risk (109, 110). The blood pressure results of the current study suggested that dietary fiber intake significantly reduced SBP and DBP, although the reductions may not have been large enough to clinical implications. These findings were in line with an animal study conducted by Marques et al., who found that a high-fiber diet could downregulate the early growth response protein 1, which serves as a master cardiovascular regulator that is involved in cardiac hypertrophy, cardiorenal fibrosis, and inflammation; the mechanism behind this may be attributed to the improved gut microbiota and its metabolites of acetate (a SCFA) (111). However, it should be noted that the effects of dietary fiber on blood pressure may vary with the types of dietary fiber, and β-glucan fiber may be the most effective dietary fiber for the regulation of blood pressure (57). Since the number of meta-analyses assessing the effect of dietary fiber on blood pressure was small, we did not explore a subgroup analysis based on the type of interventions, which should be addressed in future works.
There are some limitations to our study that should be noted. Firstly, dosage plays an important role in nutritional assessment, and we failed to provide evidence for a dose–response relationship between dietary fiber intake and improvements in cardiovascular risk factors. In addition, it seems that most of our funnel plots presented some asymmetries, indicating potential publication bias in the present umbrella meta-analysis; however, further “trim and fill” analysis delivered evidence for the robustness of the results. Finally, we did not register the protocol of this umbrella meta-analysis in the Cochrane Library or PROSPERO. On the other hand, our study is the first umbrella meta-analysis to systemically evaluate the relevant evidence and elucidate the efficacy of dietary fiber intake on cardiovascular risk factors. Additionally, we performed a subgroup analysis and assessment of the study population, type of intervention, dosage, and sample size, which could provide some strategies for precision nutrition.
Conclusion
The results of the current umbrella meta-analysis strongly support the beneficial effects of dietary fiber intake for the improvement cardiovascular risk factors. However, it should be noted that the health-promoting effects of dietary fiber intake may differ between populations with different metabolic diseases.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LF designed the study and wrote the paper. LF and SQ employed the searched strategies and reviewed the relevant trials. QZ and GZ are responsible for the data extraction. MT played a role as a consultant. GZ was responsible for the quality assessments for the studies and the corresponding author. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.972399/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1.World Health Organization. Health Topics of Cardiovascular Diseases. (2021). Available online at: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases#tab=tab_1
- 2.Stanaway JD, Afshin A, Gakidou E, Lim SS, Abate D, Abate KH, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1923–94. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019 update from the GBD 2019. Study J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 76:2982–3021. 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhou MG, Wang HD, Zeng XY, Yin P, Zhu J, Chen WQ, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2019) 394:1145–58. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.China TW. CotRoCHaDi. Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases Burden in China: an Updated Summary of 2020 (2021). [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yusuf S, Joseph P, Rangarajan S. Modifiable risk factors, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in 155 722 individuals from 21 high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries (PURE): a prospective cohort study (vol 395, pg 795, 2020). Lancet. (2020) 395:784. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32008-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Commission E. Dietary fiber. (2020). Available online at: https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/health-knowledge-gateway/promotion-prevention/nutrition/fibre
- 8.Xu DF, Wang SK, Feng MY, Shete V, Chu YF, Kamil A, et al. Serum metabolomics reveals underlying mechanisms of cholesterol-lowering effects of oat consumption: a randomized controlled trial in a mildly hypercholesterolemic population. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2021) 65:2001059. 10.1002/mnfr.202001059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Waddell IS, Orfila C. Dietary fiber in the prevention of obesity and obesity-related chronic diseases: from epidemiological evidence to potential molecular mechanisms. Crit Rev Food Sci. (2022) 5:1–16. 10.1080/10408398.2022.2061909 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Crowe FL, Key TJ, Appleby PN, Overvad K, Schmidt EB, Egeberg R, et al. Dietary fibre intake and ischaemic heart disease mortality: the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition-heart study. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2012) 66:950–6. 10.1038/ejcn.2012.51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cho SS, Qi L, Fahey GC, Klurfeld DM. Consumption of cereal fiber, mixtures of whole grains and bran, and whole grains and risk reduction in type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr. (2013) 98:594–619. 10.3945/ajcn.113.067629 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Threapleton DE, Greenwood DC, Evans CEL, Cleghorn CL, Nykjaer C, Woodhead C, et al. Dietary fibre intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ-Brit Med J. (2013) 347:f6879. 10.1136/bmj.f6879 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ojo O, Ojo OO, Zand N, Wang X. The effect of dietary fibre on gut microbiota, lipid profile, and inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1805. 10.3390/nu13061805 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Snelson M, Jong J, Manolas D, Kok S, Louise A, Stern R, et al. Metabolic effects of resistant starch type 2: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients. (2019) 11:1833. 10.3390/nu11081833 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Veronese N, Solmi M, Caruso MG, Giannelli G, Osella AR, Evangelou E, et al. Dietary fiber and health outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Am J Clin Nutr. (2018) 107:436–44. 10.1093/ajcn/nqx082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Aromataris E, Fernandez R, Godfrey CM, Holly C, Khalil H, Tungpunkom P. Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. Int J Evid Based Healthc. (2015) 13:132–40. 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nasser M. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Am J Public Health. (2020) 110:753–4. 10.2105/AJPH.2020.30560935352103 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. Bmj-Brit Med J. (2017) 358:j4008. 10.1136/bmj.j4008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol. (2011) 64:383–94. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Brit Med J. (2003) 327:557–60. 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sterne JAC, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JPA, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ-Brit Med J. (2011) 343:d4002. 10.1136/bmj.d4002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ-Brit Med J. (1997) 315:629–34. 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wei Y, Zhang X, Meng Y, Wang Q, Xu H, Chen L. The effects of resistant starch on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Cancer. (2022) 125:294–307. 10.1080/01635581.2021.2019284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mirzababaei A, Zandkarimi R, Moradi S, Rasaei N, Amini MR, Pourreza S, et al. The effect of Glucomannan on fasting and postprandial blood glucose in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Diabetes Metab Disord. (2022) 21:1055–63. 10.1007/s40200-022-00993-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xiong K, Wang J, Kang T, Xu F, Ma A. Effects of resistant starch on glycaemic control: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. (2021) 125:1260–9. 10.1017/S0007114520003700 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xie Y, Gou L, Peng M, Zheng J, Chen L. Effects of soluble fiber supplementation on glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:1800–10. 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang N, Pan D, Guo Z, Xiang X, Wang S, Zhu J, et al. Effects of guar gum on blood lipid levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized clinical trials. J Funct Foods. (2021) 85:104605. 10.1016/j.jff.2021.10460534607737 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rahim AFA, Norhayati MN, Zainudin AM. The effect of a brown-rice diets on glycemic control and metabolic parameters in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and controlled clinical trials. PeerJ. (2021) 9:11291. 10.7717/peerj.11291 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mao T, Huang F, Zhu X, Wei D, Chen L. Effects of dietary fiber on glycemic control and insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Funct Foods. (2021) 82:614–23. 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104500 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lu J, Ma B, Qiu X, Sun Z, Xiong K. Effects of resistant starch supplementation on oxidative stress and inflammation biomarkers: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2021) 30:614–23. 10.6133/apjcn.202112_30(4).0008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li L, Li P, Xu L. Assessing the effects of inulin-type fructan intake on body weight, blood glucose, and lipid profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 9:4598–616. 10.1002/fsn3.2403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Haghighatdoost F, Gholami A, Hariri M. Effect of resistant starch type 2 on inflammatory mediators: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Med. (2021) 56:102597. 10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102597 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Golzarand M, Toolabi K, Eskandari Delfan S, Mirmiran P. The effect of brown rice compared to white rice on adiposity indices, lipid profile, and glycemic markers: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 27:1–18. 10.1080/10408398.2021.1914541 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Faghihimani Z, Namazi N, Ghaffari S, Rezaei Kelishadi M, Sharifi S, Nattagh-Eshtivani E, et al. Effects of inulin type-carbohydrates on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Food Prop. (2021) 24:129–39. 10.1080/10942912.2020.1858863 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang W, Tang Y, Huang J, Yang Y, Yang Q, Hu H. Efficacy of inulin supplementation in improving insulin control, HbA1c and HOMA-IR in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2020) 66:176–83. 10.3164/jcbn.19-103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Xiao Z, Chen H, Zhang Y, Deng H, Wang K, Bhagavathula AS, et al. The effect of psyllium consumption on weight, body mass index, lipid profile, and glucose metabolism in diabetic patients: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytotherapy Research. (2020) 34:1237–47. 10.1002/ptr.6609 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang H, Qiu B, Xu T, Zong A, Liu L, Xiao J. Effects of resistant starch on the indicators of glucose regulation in persons diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and those at risk: a meta-analysis. J Food Process Preserv. (2020) 44:5101423. 10.1111/jfpp.14594 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vahdat M, Hosseini SA, Mohseni G, Heshmati J, Rahimlou M. Effects of resistant starch interventions on circulating inflammatory biomarkers: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition J. (2020) 19:33. 10.1186/s12937-020-00548-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ojo O, Feng Q-Q, Ojo OO, Wang X-H. The role of dietary fibre in modulating gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Nutrients. (2020) 12:3239. 10.3390/nu12113239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Halajzadeh J, Milajerdi A, Reiner Z, Amirani E, Kolahdooz F, Barekat M, et al. Effects of resistant starch on glycemic control, serum lipoproteins and systemic inflammation in patients with metabolic syndrome and related disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Crit Rev Food Sci. (2020) 60:3172–84. 10.1080/10408398.2019.1680950 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Clark CCT, Salek M, Aghabagheri E, Jafarnejad S. The effect of psyllium supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Korean J Intern Med. (2020) 35:1385–99. 10.3904/kjim.2019.049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang Y, Chen J, Song Y-H, Zhao R, Xia L, Chen Y, et al. Effects of the resistant starch on glucose, insulin, insulin resistance, and lipid parameters in overweight or obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Diabetes. (2019) 9:19. 10.1038/s41387-019-0086-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rao M, Gao C. Effect of inulin-type carbohydrates on insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Diabetes Res. (2019) 2019:5101423. 10.1155/2019/5101423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jovanovski E, Khayyat R, Zurbau A, Komishon A, Mazhar N, Sievenpiper JL, et al. Should viscous fiber supplements be considered in diabetes control? results from a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care. (2019) 42:755–66. 10.2337/dc18-1126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gao C, Rao M, Huang W, Wan Q, Yan P, Long Y, et al. Resistant starch ameliorated insulin resistant in patients of type 2 diabetes with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. (2019) 18:205. 10.1186/s12944-019-1127-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Khan K, Jovanovski E, Ho HVT, Marques ACR, Zurbau A, Mejia SB, et al. The effect of viscous soluble fiber on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2018) 28:3–13. 10.1016/j.numecd.2017.09.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Jovanovski E, Yashpal S, Komishon A, Zurbau A, Mejia SB, Ho HVT, et al. Effect of psyllium (Plantago ovata) fiber on LDL cholesterol and alternative lipid targets, non-HDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. (2018) 108:922–32. 10.1093/ajcn/nqy115 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Thompson SV, Hannon BA, An R, Holscher HD. Effects of isolated soluble fiber supplementation on body weight, glycemia, and insulinemia in adults with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. (2017) 106:1514–28. 10.3945/ajcn.117.163246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Liu F, Prabhakar M, Ju J, Long H, Zhou HW. Effect of inulin-type fructans on blood lipid profile and glucose level: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2017) 71:9–20. 10.1038/ejcn.2016.156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ho HVT, Jovanovski E, Zurbau A, Mejia SB, Sievenpiper JL, Au-Yeung F, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of the effect of konjac glucomannan, a viscous soluble fiber, on LDL cholesterol and the new lipid targets non-HDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B. Am J Clin Nutr. (2017) 105:1239–47. 10.3945/ajcn.116.142158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Shen XL, Zhao T, Zhou Y, Shi X, Zou Y, Zhao G. Effect of oat beta-glucan intake on glycaemic control and insulin sensitivity of diabetic patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients. (2016) 8:3239. 10.3390/nu8010039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ho HVT, Sievenpiper JL, Zurbau A, Mejia SB, Jovanovski E, Au-Yeung F, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of the effect of barley beta-glucan on LDL-C, non-HDL-C and apoB for cardiovascular disease risk reduction. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2016) 70:1239–45. 10.1038/ejcn.2016.89 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.He LX, Zhao J, Huang YS, Li Y. The difference between oats and beta-glucan extract intake in the management of HbA1c, fasting glucose and insulin sensitivity: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Funct. (2016) 7:1413–28. 10.1039/C5FO01364J [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zou Y, Liao D, Huang H, Li T, Chi H. A systematic review and meta-analysis of beta-glucan consumption on glycemic control in hypercholesterolemic individuals. Int J Food Sci Nutr. (2015) 66:355–62. 10.3109/09637486.2015.1034250 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhu X, Sun X, Wang M, Zhang C, Cao Y, Mo G, et al. Quantitative assessment of the effects of beta-glucan consumption on serum lipid profile and glucose level in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2015) 25:714–23. 10.1016/j.numecd.2015.04.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jiao J, Xu J-Y, Zhang W, Han S, Qin L-Q. Effect of dietary fiber on circulating C-reactive protein in overweight and obese adults: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Food Sci Nutr. (2015) 66:114–9. 10.3109/09637486.2014.959898 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Evans CEL, Greenwood DC, Threapleton DE, Cleghorn CL, Nykjaer C, Woodhead CE, et al. Effects of dietary fibre type on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of healthy individuals. J Hypertens. (2015) 33:897–911. 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Whitehead A, Beck EJ, Tosh S, Wolever TMS. Cholesterol-lowering effects of oat beta-glucan: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. (2014) 100:1413–21. 10.3945/ajcn.114.086108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Silva FM, Kramer CK, de Almeida JC, Steemburgo T, Gross JL, Azevedo MJ. Fiber intake and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev. (2013) 71:790–801. 10.1111/nure.12076 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Post RE, Mainous AG III, King DE, Simpson KN. Dietary fiber for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. J Am Board Fam Med. (2012) 25:16–23. 10.3122/jabfm.2012.01.110148 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tiwari U, Cummins E. Meta-analysis of the effect of β-glucan intake on blood cholesterol and glucose levels. Nutrition. (2011) 27:1008–16. 10.1016/j.nut.2010.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.AbuMweis SS, Jew S, Ames NP. Beta-glucan from barley and its lipid-lowering capacity: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2010) 64:1472–80. 10.1038/ejcn.2010.178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sood N, Baker WL, Coleman CI. Effect of glucomannan on plasma lipid and glucose concentrations, body weight, and blood pressure: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. (2008) 88:1167–75. 10.1093/ajcn/88.4.1167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Brighenti F. Dietary fructans and serum triacylglycerols: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Nutrition. (2007) 137(11 Suppl):2552s−6s. 10.1093/jn/137.11.2552S [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Whelton SP, Hyre AD, Pedersen B, Yi Y, Whelton PK, He J. Effect of dietary fiber intake on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled clinical trials. J Hypertens. (2005) 23:475–81. 10.1097/01.hjh.0000160199.51158.cf [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Streppel MT, Arends LR, van't Veer P, Grobbee DE, Geleijnse JM. Dietary fiber and blood pressure-a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. (2005) 165:150–6. 10.1001/archinte.165.2.150 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Brown L, Rosner B, Willett WW, Sacks FM. Cholesterol-lowering effects of dietary fiber: a meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. (1999) 69:30–42. 10.1093/ajcn/69.1.30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Olson BH, Anderson SM, Becker MP, Anderson JW, Hunninghake DB, Jenkins DJA, et al. Psyllium-enriched cereals lower blood total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, but not HDL cholesterol, in hypercholesterolemic adults: Results ef a meta-analysis. J Nutrition. (1997) 127:1973–80. 10.1093/jn/127.10.1973 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Xu D, Liu H, Yang C, Xia H, Pan D, Yang X, et al. Effects of different delivering matrices of beta-glucan on lipids in mildly hypercholesterolaemic individuals: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. (2021) 125:294–307. 10.1017/S0007114520001610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Li J, Chen R, Chen Y, Zhu D, Wu Z, Chen F, et al. The effect of guar gum consumption on the lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 1−10. 10.1080/10408398.2021.2001429 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wang L, Yang H, Huang H, Zhang C, Zuo HX, Xu P, et al. Inulin-type fructans supplementation improves glycemic control for the prediabetes and type 2 diabetes populations: results from a GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of 33 randomized controlled trials. J Transl Med. (2019) 17:410. 10.1186/s12967-019-02159-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ho HVT, Sievenpiper JL, Zurbau A, Mejia SB, Jovanovski E, Au-Yeung F, et al. The effect of oat-glucan on LDL-cholesterol, non-HDL-cholesterol and apoB for CVD risk reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised-controlled trials. Br J Nutr. (2016) 116:1369–82. 10.1017/S000711451600341X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The cochrane collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ-Brit Med J. (2011) 343:d5928. 10.1136/bmj.d5928 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Clark HD, Wells GA, Huet C, McAlister FA, Salmi LR, Fergusson D, et al. Assessing the quality of randomized trials: reliability of the Jadad scale. Control Clin Trials. (1999) 20:448–52. 10.1016/S0197-2456(99)00026-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Heyland DK, Novak F, Drover JW, Jain A, Su XY, Suchner U. Should immunonutrition become routine in critically ill patients? a systematic review of the evidence. JAMA. (2001) 286:944–53. 10.1001/jama.286.8.944 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Verhagen AP, de Vet HCW, de Bie RA, Kessels AGH, Boers M, Bouter LM, et al. The delphi list: a criteria list for quality assessment of randomized clinical trials for conducting systematic reviews developed by Delphi consensus. J Clin Epidemiol. (1998) 51:1235–41. 10.1016/S0895-4356(98)00131-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Downs SH, Black N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epidemiol Commun H. (1998) 52:377–84. 10.1136/jech.52.6.377 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Xu BC, Fu J, Qiao YX, Cao JP, Deehan EC, Li Z, et al. Higher intake of microbiota-accessible carbohydrates and improved cardiometabolic risk factors: a meta-analysis and umbrella review of dietary management in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. (2021) 113:1515–30. 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa435 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Muller M, Canfora EE, Blaak EE. Gastrointestinal transit time, glucose homeostasis and metabolic health: modulation by dietary fibers. Nutrients. (2018) 10:275. 10.3390/nu10030275 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Cani PD, Dewever C, Delzenne NM. Inulin-type fructans modulate gastrointestinal peptides involved in appetite regulation (glucagon-like peptide-1 and ghrelin) in rats. Br J Nutr. (2004) 92:521–6. 10.1079/BJN20041225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Cani PD, Knauf C, Iglesias MA, Drucker DJ, Delzenne NM, Burcelin R. Improvement of glucose tolerance and hepatic insulin sensitivity by oligofructose requires a functional glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. Diabetes. (2006) 55:1484–90. 10.2337/db05-1360 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Zander M, Madsbad S, Madsen JL, Holst JJ. Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide 1 on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: a parallel-group study. Lancet. (2002) 359:824–30. 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07952-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Krishnan S, Adams SH, Allen LH, Laugero KD, Newman JW, Stephensen CB, et al. A randomized controlled-feeding trial based on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans on cardiometabolic health indexes. Am J Clin Nutr. (2018) 108:266–78. 10.1093/ajcn/nqy113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Sacerdote A, Dave P, Lokshin V, Bahtiyar G. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, and vitamin D. Curr Diabetes Rep. (2019) 19:101. 10.1007/s11892-019-1201-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Reynolds AN, Akerman AP, Mann J. Dietary fibre and whole grains in diabetes management: systematic review and meta-analyses. Plos Med. (2020) 17:e1003053. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zhao LP, Zhang F, Ding XY, Wu GJ, Lam YY, Wang XJ, et al. Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes. Science. (2018) 359:1151–6. 10.1126/science.aao5774 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Canfora EE, Jocken JW, Blaak EE. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2015) 11:577–91. 10.1038/nrendo.2015.128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Chambers ES, Byrne CS, Morrison DJ, Murphy KG, Preston T, Tedford C, et al. Dietary supplementation with inulin-propionate ester or inulin improves insulin sensitivity in adults with overweight and obesity with distinct effects on the gut microbiota, plasma metabolome and systemic inflammatory responses: a randomised crossover trial. Gut. (2019) 68:1430–8. 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Xu DF, Feng MY, Chu YF, Wang SK, Shete V, Tuohy KM, et al. The prebiotic effects of oats on blood lipids, gut microbiota, and short-chain fatty acids in mildly hypercholesterolemic subjects compared with rice: a randomized, controlled trial. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:787797. 10.3389/fimmu.2021.787797 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Xu DF, Fu LM, Pan D, Lu YF, Yang C, Wang YY, et al. Role of whole grain consumption in glycaemic control of diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients. (2022) 14:109. 10.3390/nu14010109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bao L, Cai XX, Xu MH Li Y. Effect of oat intake on glycaemic control and insulin sensitivity: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. (2014) 112:457–66. 10.1017/S0007114514000889 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Lee DPS, Peng AW, Taniasuri F, Tan D, Kim JE. Impact of fiber-fortified food consumption on anthropometric measurements and cardiometabolic outcomes: a systematic review, meta-analyses, and meta-regressions of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci. (2022) 15:1–19. 10.1080/10408398.2022.2053658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.McRorie JW, McKeown NM. Understanding the physics of functional fibers in the gastrointestinal tract: an evidence-based approach to resolving enduring misconceptions about insoluble and soluble fiber. J Acad Nutr Diet. (2017) 117:251–64. 10.1016/j.jand.2016.09.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Zhao D, Liu J, Xie WX, Qi Y. Cardiovascular risk assessment: a global perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2015) 12:301–11. 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Gunness P, Gidley MJ. Mechanisms underlying the cholesterol-lowering properties of soluble dietary fibre polysaccharides. Food Funct. (2010) 1:149–55. 10.1039/c0fo00080a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Deehan EC, Duar RM, Armet AM, Perez-Munoz ME, Jin ML, Walter J. Modulation of the gastrointestinal microbiome with nondigestible fermentable carbohydrates to improve human health. Microbiol Spectr. (2017) 5:BAD-0019-2017. 10.1128/microbiolspec.BAD-0019-2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Jones BV, Begley M, Hill C, Gahan CGM, Marchesi JR. Functional and comparative metagenomic analysis of bile salt hydrolase activity in the human gut microbiome. P Natl Acad Sci USA. (2008) 105:13580–5. 10.1073/pnas.0804437105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Morrison DJ, Preston T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes. (2016) 7:189–200. 10.1080/19490976.2015.1134082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Morales D, Rutckeviski R, Villalva M, Abreu H, Soler-Rivas C, Santoyo S, et al. Isolation and comparison of alpha- and beta-D-glucans from shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes) with different biological activities. Carbohydr Polym. (2020) 229:115521. 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115521 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Morales D, Smiderle FR, Villalva M, Abreu H, Rico C, Santoyo S, et al. Testing the effect of combining innovative extraction technologies on the biological activities of obtained beta-glucan-enriched fractions from Lentinula edodes. J Funct Foods. (2019) 60:103446. 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103446 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease-Reply. New Engl J Med. (2005) 353:429–30. 10.1056/NEJM200507283530425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Venugopal SK, Devaraj S, Jialal I. Effect of C-reactive protein on vascular cells: evidence for a proinflammatory, proatherogenic role. Curr Opin Nephrol Hy. (2005) 14:33–7. 10.1097/00041552-200501000-00006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Ma YS, Hebert JR, Li WJ, Bertone-Johnson ER, Olendzki B, Pagoto SL, et al. Association between dietary fiber and markers of systemic inflammation in the Women's Health Initiative Observational Study. Nutrition. (2008) 24:941–9. 10.1016/j.nut.2008.04.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Grooms KN, Ommerborn MJ, Pham DQ, Djousse L, Clark CR. Dietary fiber intake and cardiometabolic risks among US adults, NHANES 1999–2010. Am J Med. (2013) 126:1059. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.07.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Yang LN, Lin Q, Han L, Wang ZY, Luo MS, Kang WR, et al. Soy hull dietary fiber alleviates inflammation in BALB/C mice by modulating the gut microbiota and suppressing the TLR-4/NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Food Funct. (2020) 11:5965–75. 10.1039/D0FO01102A [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Hung TV, Suzuki T. Guar gum fiber increases suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 expression via toll-like receptor 2 and dectin-1 pathways, regulating inflammatory response in small intestinal epithelial cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2017) 61. 10.1002/mnfr.201700048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Aleksandrova K, Koelman L, Rodrigues CE. Dietary patterns and biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation: a systematic review of observational and intervention studies. Redox Biol. (2021) 42. 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Barbaresko J, Koch M, Schulze MB, Nothlings U. Dietary pattern analysis and biomarkers of low-grade inflammation: a systematic literature review. Nutr Rev. (2013) 71:511–27. 10.1111/nure.12035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R, Collaboration PS. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. (2002) 360:1903–13. 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11911-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Rapsomaniki E, Timmis A, George J, Pujades-Rodriguez M, Shah AD, Denaxas S, et al. Blood pressure and incidence of twelve cardiovascular diseases: lifetime risks, healthy life-years lost, and age-specific associations in 125 million people. Lancet. (2014) 383:1899–911. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60685-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Marques FZ, Nelson E, Chu PY, Horlock D, Fiedler A, Ziemann M, et al. High-fiber diet and acetate supplementation change the gut microbiota and prevent the development of hypertension and heart failure in hypertensive mice. Circulation. (2017) 135:964. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024545 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.