Abstract
Brain ischemia affects all ages, from neonates to the elderly population, and is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity. Multiple preclinical rodent models involving different ages have been developed to investigate the effect of ischemia during different times of key brain maturation events. Traditional models of developmental brain ischemia have focused on rodents at postnatal day 7–10, though emerging models in juvenile rodents (postnatal days 17–25) indicate that there may be fundamental differences in neuronal injury and functional outcomes following focal or global cerebral ischemia at different developmental ages, as well as in adults. Here, we consider the timing of injury in terms of excitation/inhibition balance, oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, blood brain barrier integrity, and white matter injury. Finally, we review translational strategies to improve function after ischemic brain injury, including new ideas regarding neurorestoration, or neural repair strategies that restore plasticity, at delayed time points after ischemia.
Keywords: Juvenile, global cerebral ischemia, pediatric stroke, neonatal ischemia, neurodevelopment, neurorestoration
In Pediatrics, there is a saying that “children are not small adults,” highlighting differences in physiology across development. Likewise, it is increasingly clear that global and focal cerebral ischemia do not necessarily result in similar outcomes across the lifespan, nor do outcomes occur as the result of analogous mechanisms. Here, we review outcomes and mechanisms of global cerebral ischemia (e.g., cardiac arrest) and focal cerebral ischemia (e.g., stroke) in the developing brain, focusing on neonatal and juvenile time points. We highlight the enhanced recovery potential of the developing brain, compared to the mature brain, following cerebral ischemia.
Global cerebral ischemia (GCI) in children, resulting from the lack of perfusion due to asystole, often related to asphyxia, results in hypoxemia, hypercapnia, acidosis, and hypotension, ultimately leading to cardiopulmonary collapse. 1 It is estimated that 12,000 children per year suffer unexpected cardiac arrest (CA) in the United States, 1 though the incidence is markedly skewed toward infants, defined as children less than 12 months old, (73 per 100,000) compared to older children (4–6 per 100,000). 1 Survival to discharge for children suffering out of hospital CA is between 8 and 9%, whereas in-hospital CA survival is between 22 and 27%. 2 Survival is age-dependent, favoring neonates (birth to 30 days old) and infants (30 days to 12 months old) over older children. 2 A great deal of research has focused on improving rates of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), which has improved survival rates. However, therapeutic options to improve neurologic outcomes remain limited. To date, therapeutic hypothermia is the only therapy effective in improving survival and neurologic outcome and has become the standard of care in adults and neonates less than 6 hours old.3,4 However, recent studies of hypothermia in children after CA show little effect on outcome. 5
Among survivors of GCI, brain injury often leads to significant neurologic dysfunction, 6 including impaired memory and executive cognitive function.2,7,8 The sequelae may result in a lifetime of dependency for all aspects of care. 6 Brain injury is typically bilateral and likely preferentially affects different regions and cell-types depending on vulnerability at the time of insult. Most of our understanding of the pathophysiology of GCI comes from adult animal models and neonatal hypoxia-ischemia models, which in turn have created a void in therapies for childhood GCI. Emerging clinical evidence has emphasized the importance of considering the juvenile GCI population independently from other age groups, rather than treating them as small adults or large neonates.
In contrast to GCI, pediatric arterial ischemic stroke (AIS) results in focal or multi-focal cerebral ischemia without concurrent systemic hypercapnia and acidosis. Pediatric AIS is stratified into neonatal and childhood (occurring between 30 days and 18 years of life). The incidence for all pediatric AIS is approximately 1.6–4.6 per 100,000.9,10 As in GCI, the incidence is higher at very young age, primarily due to a particularly high incidence in neonates (24.6/100,000 in neonates vs 5.11/100,000 in older children).9,11 Incidence is lowest in children aged 1–9 years, with a subsequent increase in adolescents aged 10–18. 10 Stroke treatment in adults has focused on early recognition of symptoms and thrombolysis to restore blood flow, either through administering systemic tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), mechanical thrombectomy, or both 12 within a few hours of symptom onset.
In general, acute intervention is not possible following most pediatric AIS. Diagnosis of pediatric AIS is often delayed, 13 with the median time to diagnosis, after symptom onset, over 24 hours in children and 87 hours in neonates, 13 well beyond the safe window for acute thrombolysis or thrombectomy. While tPA has been used to treat acute pediatric AIS, and is generally considered safe, the only prospective trial to study its use in children was terminated early due to poor enrollment.14–16 Retrospective studies suggest that mechanical thrombectomy is also safe and effective, and prospective studies are ongoing.17,18 Further, the etiology of pediatric AIS is different compared to adults. In neonates, most AIS are idiopathic, but are thought to be placental-fetal thromboembolic events around the time of delivery, 19 though angiography rarely identifies persistent thrombus within cerebral vasculature. 20 In contrast, focal arteriopathies are the most common cause of pediatric AIS. 21 The majority of focal arteriopathies include sub-types, such as inflammatory arteriopathies or arterial dissection, in which the safety and efficacy of thrombolysis or thrombectomy is not established. 22 The consequence of delayed diagnosis, lack of acute treatments and differing etiology between adult and pediatric stroke is that there is no reliable therapy for most children who suffer stroke.
Survival from pediatric AIS is very high, with a stroke-related mortality rate of only 2.5–5%. 11 Between 30% and 60% of children have long-term neurologic impairment after stroke, and therefore a significant number of patients live with life-long neurologic sequelae. The developmental stage at which focal stroke occurs has a significant impact on the likelihood of specific long-term impairments. Approximately one third of neonatal stroke survivors have hemiparesis long-term, while over half of infants and children have hemiparesis after AIS.23,24 Conversely, up to half of neonates have long-term language deficits after stroke, though these only occur in 21% of older children.23,24 Generally, most children with stroke have long-term cognitive deficits, but children with neonatal stroke perform relatively poorly on cognitive assessments compared to children who suffered stroke beyond the neonatal period. 25 However, it is generally accepted that the neonatal brain has an enhanced potential for neural plasticity and reorganization 26 that is not generally experienced in adults, highlighting the importance of studying stroke in specific age-appropriate animal models.
The remainder of this review focuses on rodent models of cerebral ischemia in the developing brain to better understand the differences and similarities between the mechanisms of ischemic brain injury across brain development. One cannot assume that the same mechanisms are involved in ischemic injury of the mature brain compared to the developing brain. We emphasize critical periods of ischemic vulnerability in the developing brain that should be considered in pre-clinical translational models.
The developing brain and ischemic injury
An important consideration in studying injury in the developing brain is the maturational state of the brain, cells, and receptors at the time of injury. Patterns of injury in humans depend on the age at which the injury occurs. Susceptibility to ischemic brain injury during development in rodents is also dependent on age, likely attributed to the stage of maturation and regional vulnerability. 27 Across mammalian species, synapses are established prenatally, but undergo a critical period of proliferation after birth (synaptogenesis), 28 followed by a pruning phase extending into juvenile time periods. 28 Juveniles continue to add and retract synaptic connections, followed by a decrease in synaptic turnover as development turns toward adulthood. 29 The timing of synaptogenesis is region specific and likely provides a basis for the sequence of behavioral development during maturation. 30 Similarly, in rodents, the key period of synaptogenesis occurs in the first three weeks of postnatal development, generally peaking in the second week, 27 though the timing of synapse maturation varies among different regions of the developing brain, 31 and even within dendrites themselves. 32 Activity-dependent pruning follows proliferation of synapses to refine network circuitry, allowing for more efficient processing in the adult brain. Therefore, ischemic injury during active synaptogenesis or pruning may lead to different long-term consequences.
Brain development begins during early fetal stages and continues into the second decade of life in humans. 27 Development of the rodent brain begins in the early embryonic stages and continues through the first 3–4 postnatal weeks. 27 Though somewhat controversial, it is believed that the developing brain recovers better than the mature brain from ischemia.26,33 While there is limited evidence from juvenile ischemia models that younger brains do recover differently than adults, we have recently reported that juvenile mice exhibit recovery of hippocampal plasticity and memory function.34,35
In addition to synaptogenesis, neurotransmitter changes throughout development are likely to be important when considering age of injury. Neuronal activity is critical for synaptogenesis, and the relative (im)balance of excitation and inhibition in neuronal networks of the developing brain plays a role 36 (discussed below). Selecting an age-appropriate rodent model based on biochemical, neuroanatomical and channel physiology optimizes translational potential. The following discussion reflects recent and ongoing research in rodent models that provide a greater understanding of how developmental factors alter ischemic vulnerability and the potential for age- and injury-appropriate therapy following ischemia in the developing brain.
A universal model?
Most data regarding developmental aspects of early life ischemic brain injury have been extrapolated from model of permanent carotid ligation followed by hypoxemia. Since 1981, the Rice-Vannucci model of neonatal hypoxia/ischemia (H-I) 37 and has been widely used in the study of mechanisms and potential therapies for neonatal brain ischemia. The model was originally performed by ligating the carotid artery in postnatal day (PND) 7 rat pups, followed by exposure to 8% oxygen for 3.5 hours and has since been adapted to include older rodents (up to PND12) and mice. 38 The seminal publication observed ipsilateral brain injury 50 hours after the insult, 37 though others have observed injury at earlier time points. 39 This model has provided the translational foundation for many important mechanisms and therapies in human neonatal ischemic injury, most notable of which is therapeutic hypothermia.4,40 In addition, multiple therapies such as erythropoietin, 41 xenon, 42 melatonin, 41 stem cells 43 and others have used this model to begin investigation for adjunctive therapies. 41
The Rice-Vannucci model has been used to model early life global hypoxic ischemic injury (i.e., hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy) and stroke.44–48 Despite the many scientific and therapeutic gains from this model, it is not strictly an approximation of either global brain ischemia or focal ischemic brain injury, but rather has features of both. Without downplaying the important translational impact of the Rice-Vannucci model, we believe it important to mention a few aspects of the Rice-Vannucci model that do not model the conditions experiences in either global cerebral ischemia or focal stroke. Foremost among the differences of the Rice-Vannucci model regarding GCI is the lack of systemic ischemia that occurs during GCI. Most discussions on global ischemia in young rodents focus on cerebral injury, though there is clear evidence from human and adult rodent studies that visceral organ damage from systemic ischemia and reperfusion are important considerations in pathophysiology and treatment.49,50 Further, AIS results in confluent injury in an arterial distribution, with a relatively well-defined ischemic core and penumbra, 51 a pattern that is produced by reperfusion through a previously occluded artery whereas the Rice-Vannucci model produces patchy cell death primarily in cortex and hippocampus 37 which is not entirely analogous to AIS. We contend that the next generation of ischemia researchers should build on the successes of this model in using new, emerging models of cerebral ischemia (reviewed below) to augment the important knowledge gained thus far.
Specific models of global cerebral ischemia in the developing brain
Contemporary models of GCI consist of asphyxial cardiac arrest (CA; performed by paralysis and ventilator discontinuation; PND17) 52 or CA induced by intravenous potassium chloride (PND21-25) 53 (Table 1). The juvenile CA models mimic the systemic hypoxemia, acidosis and hypoperfusion that occurs in the setting of complete cardiopulmonary collapse52,53 and important insights have been gained in regard to cerebral blood flow,54,55 brain tissue oxygenation, 56 and synaptic plasticity 57 in the juvenile brain during and after GCI. Neuronal sensitivity to GCI is influenced by the age of the animal, where adult mice have more neuronal death than juvenile animals for the same amount of ischemic time. 53 In a direct comparison of juvenile and adult hippocampal histology, there was less neuronal death in PND21–25 mice after 6 minutes of cardiac arrest compared to adult mice, however this difference in vulnerability was lost following 8 minutes of CA. 53 Similarly, juvenile mice exhibited undetectable injury in the thalamus following 8 min CA, in contrast to small, but evident thalamic injury in adults. 53 The mechanisms of these differences remain unclear and warrant further study.
Table 1.
Models of global cerebral ischemia in developing brain.
| Human pathological condition | Animal used and age or weight of the animal | Type of lesion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global cerebral ischemia | Rat 60–70 g | Bilateral internal carotid ligation | Gong et al.177 |
| Global ischemia | Rat P7 | KCl – cardiac arrest | Dijkhuizen, et al.178 |
| Rat P16–18 | Asphyxial CA/CPR | Fink, et al.52 | |
| Mouse P21–25 | KCl-induced CA/CPR | Deng, et al.53 |
P: postnatal day; KCl: potassium chloride; CA/CPR: cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Specific models of focal ischemia in the developing brain
The primary rodent model of arterial ischemic stroke has been the filament model of reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion (rMCAO). 58 In rMCAO, a nylon filament is advanced through the external carotid artery and into the internal carotid artery to the bifurcation of the middle cerebral artery. The filament is left in place for some time, and then removed to provide reperfusion. The rMCAO model provides a more accurate approximation of human arterial ischemic stroke, in which there is occlusion of arterial blood flow and reperfusion. One of the most important findings of studies using MCA occlusion-reperfusion models was that of a stroke “penumbra”; ischemic brain tissue that is salvageable if reperfusion is established within a critical time frame. 59 The discovery of penumbral tissue has focused clinical stroke treatment on re-establishing perfusion as quickly as possible, leading to development of medical recanalization during stroke (thrombolysis with tPA and mechanical thrombectomy).60,61
Despite the contributions that the rMCAO model has made to the adult stroke field, the technical difficulty of performing rMCAO prevented initial use in younger animals (Table 2). The rMCAO model was first adapted to PND14-15 spontaneously hypertensive rats by Ashwal et al., 62 followed by PND7 rats by Derugin et al., 63 Woo et al., 64 and Renolleau et al. 65 The rMCAO model has since been adapted to juvenile (PND20-25) mice,35,66,67 allowing comparison in injury and recovery mechanisms across development. Other methods of focal stroke in developing animals have included permanent occlusion of the proximal MCA, 68 and permanent distal MCA occlusion through electrocauterization with transient bilateral CCA occlusion. 69 Neither of these models include reperfusion through the occluded vessel. The importance of vascular reperfusion in studying mechanisms of injury in juvenile stroke is highlighted by the finding that caspases, key components to apoptosis, are activated after reperfusion compared to permanent occlusion in the young brain. 51
Table 2.
Models of focal ischemia in the developing brain.
| Model | Age | Description | Lesion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent MCA Occlusion | P7 rats | Permanent insertion of nylon filament via the CCA to the origin of the MCA | Cortical and subcortical ischemia involving the majority of ipsilateral hemisphere. | Wen et al.68 |
| Permanent MCA electrocauterization | P7 rats | Distal MCA electrocauterization with 50 minutes bilateral CCA occlusion. | Ischemia in cingulum cortex and adjacent external capsule. | Villapol et al.69 |
| Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion | P14–15 ratP7 ratP10 ratP20–25 mouse | Introduction of nylon filament via the ECA or ICA to occlude the origin of the MCA. The filament is removed after 45–90 minutes of occlusion, resulting in reperfusion. | Ischemic core and penumbra in the MCA territory (lateral striatum +/−cortex) | Ashwal et al.62Renolleau et al.65Derugin et al.63Gonzalez et al.179Woo et al.64Rodgers et al.153Faustino et al.67 |
| Photothrombotic stroke | P7 mice | IP Rose Bengal injection followed by exposure of surface cerebral vessels to a cold light source. | Focal ischemia in cortex. | Maxwel et al.71 |
| L-NIO | P20–25 mice | Stereotaxic injection of a potent endothelial nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. | Small focal area of ischemia at the injection site. | Dingman et al.74 |
CCA: common carotid artery; ECA: external carotid artery; ICA: internal carotid artery; MCA: middle cerebral artery; L-NIO: N5-(1-iminoethyhl)-L-ornithine (L-NIO); P: postnatal day; IP: Intraperitoneal.
Other models of stroke include photothrombosis70,71 or direct injection of the vasoconstrictors N5-(1-iminoethyhl)-L-ornithine (L-NIO) 72 or endothelin-1. 73 In photothrombotic stroke, the photoactive dye Rose Bengal, is systemically injected, followed by exposure of surface cerebral arteries to a cold light source, causing intravascular endothelial damage and subsequent arterial thrombosis. 70 L-NIO is a potent endothelial nitric oxide synthase inhibitor that causes focal ischemia within a small area around injection site.72,74 Endothelin-1 is a potent vasoconstrictor which leads to vasoconstriction and downstream ischemia. When the effect of the vasoconstrictor subsides, perfusion is re-established, thus allowing for a transient focal ischemia model. 73 The advantage of these models is that they are minimally invasive models of focal ischemia, making them appealing in developing rodents. The limitation to the photothrombotic and vasoconstrictor models is that it is not clear what timeframe reperfusion might occur.
Age-dependent differences in mechanisms of neuronal death
Excitation-Inhibition (Im)balance
Early in postnatal development, the mammalian brain is considered relatively more excitable in the first 7–10 days than it is later in life. This is due in large part to 1.) AMPA receptor subunit differences allowing for increased intracellular Ca2+ concentrations and 2.) excitatory GABA physiology. These changes in excitation-inhibition balance, compared to the mature brain, create age-specific targets that may affect outcomes following ischemic brain injury. This imbalance comes into play when considering excitotoxicity, which has emerged as a key mediator of brain injury after ischemia in adult and neonatal animal models.75–77 The excitotoxicity hypothesis suggests that injury is triggered by glutamate. 78 Glutamate is the primary excitatory amino acid transmitter in the central nervous system and is required for rapid synaptic transmission, as well as playing important roles in neuronal growth and axon guidance.75,76 Under ischemic conditions, glutamate accumulates, stimulating pathologic increases in sodium and calcium fluxes through glutamate receptors, thereby injuring the cell. 78 Much work has been done to understand the mechanisms and consequences of excitotoxicity, though efforts to translate these findings to improved patient outcome have yet to be achieved. 79
Glutamate receptors in the developing brain
Excitotoxicity during ischemia in the developing brain is impacted by the development of neuronal circuits, as well as the expression of specific glutamate receptor subtypes, which is a dynamic process. 29 The predominant glutamate receptors are N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors. Each of these receptors are made of subunits whose expression changes through development and is reviewed elsewhere. 32 NMDA receptors are multimeric glutamate receptors and are central in excitotoxicity due to the receptor’s high permeability to Ca2+ ions. Perhaps underappreciated is that functional activity of NMDA receptors may be enhanced in the young rodent brain compared to adults, 75 making them promising targets in the developing brain. AMPA receptors are also multimeric glutamate receptors that are important in synaptic physiology and pathophysiology. When stimulated by excessive release of glutamate, the activation of AMPA receptors triggers NMDA-receptor driven excitotoxicity. One subtype of AMPA receptors are Ca2+-permeable if lacking GluA2 subunits. 80 GluA2-containing AMPA receptors with age,32,80 with a switch to predominantly Ca2+-impermeable AMPA receptors in the 2nd to 3rd postnatal week in rodents. 81 This developmental switch potentially exposes developing neurons to higher Ca2+ burdens during ischemia than in the adult brain. While there are relatively few synapses in white matter, excitotoxicity has been shown to play an important role in the pathogenesis of white matter injury in the immature brain. 82 Thus, an environment exists where developing brain tissue may be more vulnerable to injury than adult brains and highlights potential age-specific glutamate receptor-mediated therapeutic targets for ischemic brain injury.
GABA receptors in the developing brain
There has been substantial interest in GABA receptor physiology during development regarding excitation-inhibition balance. GABA is among the primary inhibitory neurotransmitters in the mature central nervous system and primarily acts by binding to chloride (Cl–)-permeable GABAA receptors. 83 Neuronal Cl– is primarily regulated by two cation-chloride co-transporters (CCC), NKCC1 and KCC2, whose relative expression patterns change through development. 84 In the mature brain, KCC2 is the primary CCC and promotes Cl– extrusion from neurons so that when GABAA receptors are stimulated, Cl– is transported into neurons and the cells are hyperpolarized and activity is reduced (inhibited). 83 NKCC1 is the predominant CCC in immature neurons and transports Cl– into neurons, thereby producing relatively high intracellular Cl– concentrations in developing neurons. 85 When GABAA receptors are activated under these conditions, Cl– exits the neuron and the cell becomes depolarized, thus GABA is excitatory.84–86 The relative developmental shift in NKCC1 and KCC2 appears to occur around the end of the first to second postnatal weeks in rodents and the early in the first year in humans.36,84,85 Therefore, it is predicted that activating GABA receptors is protective in adults, while GABA receptor inhibitors would provide protection in the immature brain.
Contemporary models of ischemia in juvenile rodents have not yet investigated how the dynamic changes in glutamate receptor composition or evolving GABAA receptor physiology influences vulnerability to injury after global or focal ischemia. NMDA receptor function in hippocampus appears to be intact in surviving neurons after juvenile GCI, 57 but beyond that, little is known. One could speculate that many of the same mechanisms of excitotoxicity are involved in ischemic brain injury at this age. A reasonable hypothesis would propose that relative imbalance in excitation and inhibition in the developing brain may contribute to increased susceptibility of the juvenile brain to injury following global ischemia compared to adults. Work to test this hypothesis in juvenile ischemic brain injury is just underway.
In summary, data suggests that excitation-inhibition imbalance plays a significant role in ischemic brain injury across models and ages. While there are physiologic differences in GABA and glutamate mechanics in the developing brain compared to adult brains, focusing on excitotoxicity may not be of high yield in seeking age- or disease-specific translational therapeutic strategies. However, this may be advantageous, as the relative similarity among the different age groups and ischemic models is likely to yield translatable approaches to most ischemic brain injury should there be promising pre-clinical discoveries.
Oxidative stress
Mechanisms related to oxidative stress are well described in response to cerebral ischemia in both developing and mature brains. Differential expression of proteins related to oxidative stress across development suggest that there is an age-related difference in vulnerability. Oxidative stress occurs during reperfusion, causing tissue injury through multiple processes, including overproduction of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species. Extensive research has focused on the role of mitochondria, which have severely impaired function during ischemia, and the return of oxygen supply during reperfusion resulting in ‘leaky’ mitochondria, leading to the production of oxygen radicals. 76 Reactive oxygen species (ROS) lead to lipid peroxidation, breakdown of the blood-brain barrier, and DNA fragmentation, causing cell injury and enhancing mechanisms of apoptosis. 87 Much of what we know regarding oxidative stress has been derived from adult ischemia models and has been reviewed in detail elsewhere. 87 Relevant to the current review, emerging data indicate increased sensitivity to oxidative stress in the developing brain.88,89
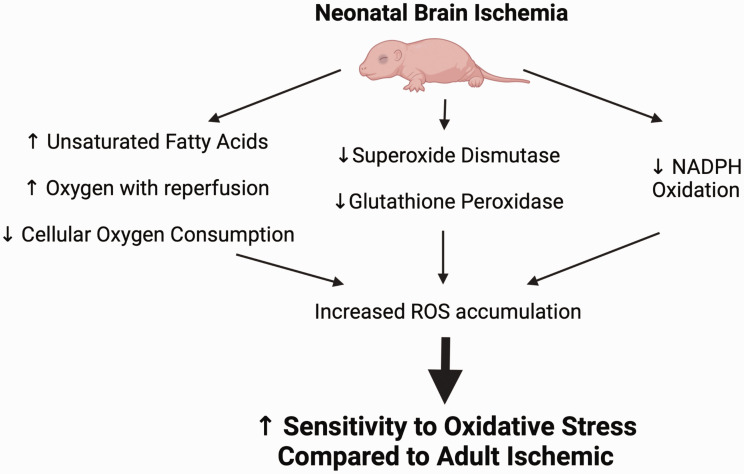
The neonatal brain may be at increased risk of oxidative injury due to high concentrations of unsaturated fatty acids, excessive oxygen content of arterial blood during a hyperoxygenated reperfusion phase 90 coupled with decreased cellular oxygen consumption,90,91 ultimately resulting in higher levels of ROS92,93 (Figure 1). Superoxide dismutase is among a group of metalloenzymes that attenuate ROS formation that has been found to be overexpressed following adult cerebral ischemia. 92 In the immature brain, there is a developmental lag in the expression of superoxide dismutase 94 and low activity of H2O2-utilizing enzymes glutathione peroxidase and catalase. Further, inhibition of NADPH oxidase did not reduce brain injury following hypoxia-ischemia in PND9 mice or ibotenate-induced excitotoxic injury in PND5 mice, 95 suggesting that NADPH oxidase may not play a role in the pathogenesis of neonatal brain injury like has been suggested in adult ischemic brain injury. Figure 1 provides a summary of these mechanisms which are likely sources of ROS accumulation contributing to susceptibility of the developing brain following ischemia.92,93
Figure 1.
Mechanisms leading to increased sensitivity to oxidative stress in the neonatal brain following cerebral ischemia. The neonatal brain may be at increased risk of oxidative injury due to high concentrations of unsaturated fatty acids, hyperoxygenation with reperfusion and decreased cellular oxygen consumption (leading to increased oxygen ions), as well as a developmental lag in the expression of superoxide dismutase and low expression and activity of H2O2-utilizing enzymes glutathione peroxidase and NADPH oxidase. These developmental changes lead to increased ROS accumulation and make the neonatal brain vulnerable to oxidative injury after cerebral ischemia.
Due in large part to the importance of oxidative stress during and after ischemia, targeted approaches attenuating reactive oxygen damage are needed.76,89 In the neonatal brain, novel uses of erythropoietin and melatonin target these mechanisms. 41 In adult and juvenile models of global and focal cerebral ischemia, downstream mediators of oxidative stress such as inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) or transient receptor potential melastatin-2 (TRPM2) channels have emerged as possible targets,96–99 and PARP-1 gene disruption may even provide some protection in male neonatal mice after hypoxic-ischemic injury. 100
Inflammation
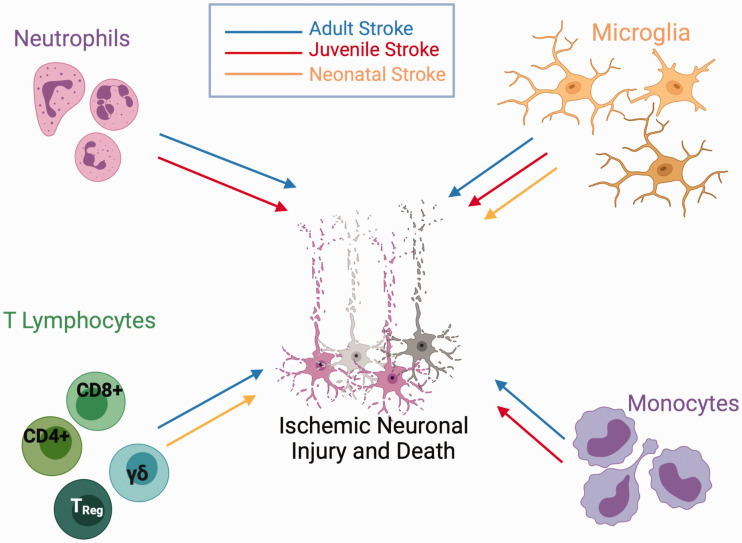
It is well documented that cerebral ischemia triggers robust local and systemic inflammatory responses, particularly following reperfusion.49,101 There are gaps in the literature as to which inflammatory mechanisms are engaged at different ages. There is evidence that infiltrating leukocytes, cytokines, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) fuel the innate and adaptive immune system in the brain and periphery, across ages. 101 The inflammatory cascade exacerbates ongoing secondary injury such as blood-brain barrier damage, edema, oxidative stress, and direct neuronal cell death.101,102 Following cerebral ischemia, inflammatory events directly contribute to evolving pathology and long-term neurological outcomes. However, the relative contribution of different immune components is dependent on the age at the time of injury and the type of insult. Figure 2 shows that neutrophils, infiltrating leukocytes, microglial activation and monocyte invasion are influenced differently after focal ischemia at different ages (adult stroke in blue, juvenile stroke in red, neonatal stroke in orange). Evidence exists to support a role for all these inflammatory pathways in adult stroke, but in neonatal stroke, only microglial activation is well supported in the literature (though a lack of evidence may only indicate that these mechanisms have not yet been explored). Differentiating the roles of immune cells across development following GCI has not been well described. We discuss these aspects below, highlighting differences in immune responses to ischemia across ages.
Figure 2.
Relative age-related role of inflammatory components following stroke. Following stroke in the adult brain (blue line), infiltration of neutrophils, lymphocytes, microglia and monocytes contribute to neuronal injury and death. Many of these same factors contribute to neuronal injury in the juvenile brain (red line), though infiltration of T lymphocytes has not been established. Following neonatal stroke (orange line), resident microglial activation contributes to ischemic neuronal injury and death, but infiltration of neutrophils and monocytes are not involved in the pathogenic cascade. γδT-cells contribute to acute neuronal cell death following neonatal H-I, whereas CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells contribute to chronic inflammatory changes in the neonatal brain following ischemia.
Neutrophils
Resident and infiltrating immune cells play an important role after cerebral ischemia across models and ages.103–105 In adult stroke neutrophils infiltrate the injured cortical tissue within the first 12 hours of reperfusion,106,107 although more recent studies suggest these neutrophils may not leave the perivascular spaces. 108 Neutrophils similarly accumulate in neonatal H-I 109 and juvenile stroke. 67 Neutrophils are thought to exacerbate ischemic injury in these models by accumulating in capillaries and reducing blood flow, 110 impairing blood-brain-barrier integrity through release of matrix metallopeptidases (MMPs) and myeloperoxidases (MPOs), 111 and injuring endothelium and neurons through production of cytokines and ROS. 112 Similar roles of neutrophils have been reported following adult GCI using permanent carotid occlusion, 113 suggesting that there may be converging mechanisms following adult brain ischemia.
A role for neutrophils in injury has emerged in the developing brain. Neutrophils have long been known to accumulate in neonatal H-I 109 and recent evidence suggests that the same occurs following juvenile stroke. 67 Surprisingly, neutrophils do not infiltrate after focal neonatal stroke, despite a rapid accumulation of the neutrophil chemoattractant CINC-1 in ischemic brain. 106
Adaptive immune response
There is abundant evidence that infiltrating lymphocytes contribute to neuronal injury in neonatal H-I, 114 adult stroke 115 and adult GCI. 116 In adult models of focal stroke and GCI, data strongly suggest that CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory T-cells are responsible for injury exacerbation. Depletion of these cell types reduces injury severity and promotes neurogenesis.116–118 Following neonatal H-I, infiltration of CD4+ cells can be detected in the hypoxic-ischemic hemisphere within the first week after insult and recruitment of CD8+ T-cells peaks up to 2 weeks after neonatal H-I 114 and have been conjectured to contribute to chronic inflammation following neonatal ischemic brain injury. To this point, a role for these cells is less clear in acute phases, though γδT-cells (the first T-cell subtype to arise during ontogeny) have been identified as soon as 6 hours after neonatal H-I brain injury. 119 Importantly, depletion of γδT-cells led to reduced brain injury. 119 Given the strength of data implicating infiltrating cellular immunity in neuronal injury, experiments should be performed in juvenile and neonatal stroke to further characterize the response of this important facet of injury and leading to translationally relevant discoveries.
Infiltrating monocyte and resident microglial response
The role of microglia and infiltrating monocyte-derived macrophages after ischemia has long been a focus of stroke research in adults (for review see 120 ) and is particularly complex. The relative contribution of invading monocytes (derived from bone marrow and infiltrate the brain parenchyma in response to cytokine and chemokine engagement as a result of brain ischemia 120 ) versus resident microglia (derived from the yolk sac in early development, colonizing the central nervous system in fetal life, ready to be “activated” by different combinations of cytokines and chemokines 120 ) across ages likely has implications for potential therapies. Microglia have long been thought to contribute to injury extension, particularly in the penumbra after AIS, primarily through the production of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Selective pharmacologic inhibition of iNOS reduces injury in adult animals after stroke, but not in neonatal animals. 121 More recent data suggest that the microglial milieu is more diverse, and some microglia may be important for moderating injury extent. In adult and neonatal animals after focal stroke, selectively ablating proliferating resident microglia exacerbates injury size.122,123 Interestingly, while these developmental stages share a protective phenotype for resident microglia, the mechanism of protection varies across ages. In adults, microglia appear to provide trophic support for the brain, through producing factors such as IGF-1. 122 Data has emerged showing both a beneficial and detrimental role for recruited (infiltrating) macrophages following adult stroke. New molecular markers have facilitated the study of infiltrating macrophages and ongoing work shows there may be promise in targeting circulating macrophages to enhance stroke recovery, although this work is ongoing.
In contrast, depletion of resident microglia prior to neonatal stroke resulted in increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, larger infarct size, and induced micro-hemorrhages and increased blood brain barrier permeability,106,123 suggesting that microglia play an important role in vascular integrity and in modulating the immune response in the developing brain. The lack of monocyte infiltration after focal neonatal stroke is despite robust increases in chemoattractant cytokines in injured brain and plasma.124,125 Therefore, therapeutic approaches to enhance microglial support of post-ischemic brain will likely differ in the neonatal vs adult brains.
Cytokines and chemokines in the developing brain
Cytokines and chemokines are important in peripheral-cerebral immune signaling after ischemia.103,105,126 In a juvenile GCI model, microglial activation and cytokine production are increased following ischemia. 127 Specifically, chemokines such as macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α), regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted (RANTES), growth-related oncogene (GRO-KC) and the cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) are increased after juvenile GCI, compared to controls. Administration of minocycline, known to attenuate microglial activation and proinflammatory cytokine production, reduced the increases in MIP-1α and RANTES induced by juvenile GCI, 127 thereby reducing neuronal death.
After neonatal rMCAO, several cytokines, including interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1 (CINC-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), increase rapidly in the plasma and injured brain. 124 Minocycline administration attenuates the systemic inflammatory response after neonatal stroke, though cytokine production and microglial activation in the brain are not reduced, and neither is injury size. 125 The study of cytokines in brain injury following ischemia in the neonatal brain is still in its infancy and more studies need to be performed to better elucidate the effects of the cytokine response following cerebral ischemia in the immature brain and whether alterations in ischemic vulnerability and recovery potential can be modified in developing brain.
In summary, the data show that there is a robust and detrimental inflammatory response in adult models of brain ischemia, both global and focal. However, a full picture of the inflammatory response is less clear in various models of brain ischemia in the developing brain. For example, relatively little has been studied regarding varying inflammatory responses following juvenile GCI or neonatal stroke. While Figure 2 summarizes data regarding the inflammatory response following stroke at various ages, it also shows that several holes remain to be filled in an age- and disease-specific way. Indeed, the model suggests that not every pathway is involved in each of the models. Therefore, we cannot conclude that the developing brain has a similar response that of the mature brain, and in some cases the responses appear to be oppositional. We strongly advocate those mechanisms involving inflammation need to be better elucidated to improve the efforts of producing age- and disease-specific translational strategies to improve the outcomes of patients.
Blood brain barrier (BBB)
BBB in adult ischemia
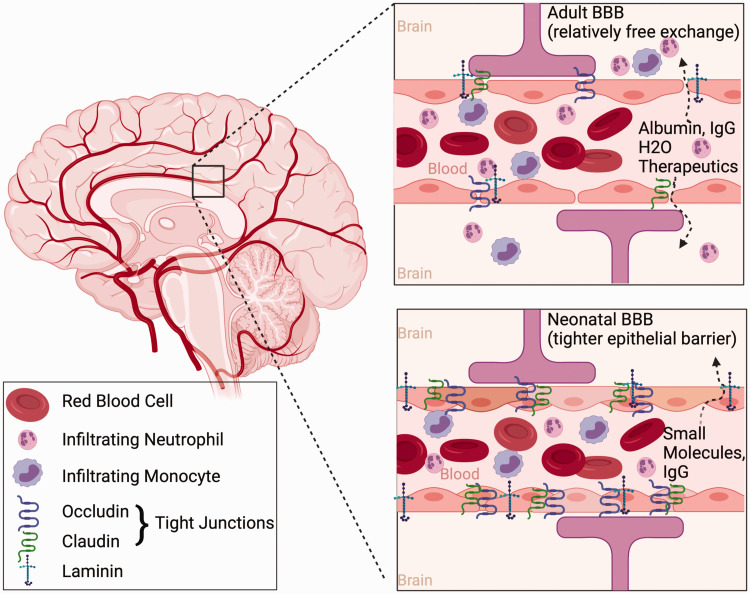
Relevant to peripheral factors reaching the brain, including immune cells and pharmacologic agents administered to outcomes, is the extent to which the BBB is compromised after ischemia and if these mechanisms differ across ages. The BBB is a complex barrier between the vasculature and central nervous system and has been shown to be a key factor in the pathogenesis of injury and efficacy of pharmacologic therapies after focal cerebral ischemia. 128 Following stroke in adults, increased BBB permeability leads to water crossing the BBB resulting in cerebral edema and its deleterious consequences. BBB permeability after adult GCI appears to be more variable, and depends on factors such as insult duration, insult type, and temperature.129,130 Indeed Figure 3 indicates BBB permeability following adult cerebral ischemia leads to relatively free exchange of proteins and water resulting in increased edema and peripheral inflammatory infiltration but may also provide an opportunity to deliver therapeutics to the injured brain parenchyma following ischemia.
Figure 3.
Age-related differences in the blood brain barrier (BBB). Compared to the compromised BBB after ischemia in the adult brain, the BBB in the neonate is less permeable (varying by BBB permeability assay, see text for more detail) following ischemia. This is likely due to the relative increase in tight junction and basal lamina proteins occludin, claudin, and laminin in the neonatal brain. The result is increased infiltration of inflammatory cells, large proteins, and edema in the adult brain, whereas only small molecules such as sucrose cross the BBB into the neonatal brain. This likely has implications for the available delivery of therapeutics into the neonatal brain via the vasculature following cerebral ischemia.
BBB in neonatal ischemia
Following neonatal rMCAO, the BBB is less compromised, compared to adult rats, evidenced by limited extravasation of Evan’s blue dye, albumin, and dextran 24 hours after MCAO. 131 Wang and colleagues observed compromised BBB 3 days after neonatal rMCAO in spontaneously hypertensive rats. 132 While not directly compared to adults, BBB compromise appears modest relative to adult reports. Decreased permeability of the BBB is explained in part due to increased expression of collagen-IV and laminin, as well as the tight junction proteins claudin-5 and occludin in the postnatal brain (Figure 3). 131 These proteins are critical in the endothelial-endothelial junction seal and the expression of these proteins was better preserved following neonatal stroke compared to adult. It has further been shown that, at chronic time-points (14 days) after neonatal rMCAO, there is decreased expression of endothelial barrier antigen in the injured hemisphere, 133 suggesting that decreased BBB integrity may be a delayed event after neonatal stroke. In contrast, following H-I models in neonatal mice, data suggests a rapid and transient opening of the BBB, illustrated by increased permeability to sucrose up to 24 hours after hypoxia-ischemia and resolving by 3 days. 130 Inulin permeability following H-I was not different than control at any time point, 130 suggesting that the opening in the BBB limits the size of molecules that transmigrate. This decreased BBB penetration will need to be considered in future translational therapeutic studies.
BBB in juvenile ischemia
The juvenile rodent appears to be different concerning the response to BBB opening after global ischemia. Following juvenile GCI, the BBB was not permeable to the contrast agent gadoteridol at 3 hours after GCI, 134 or small and large molecular weight tracers during the first 24 hours after GCI. 129 There was a small increase in cerebral water three hours after GCI, though there was a lack of appreciable gain in percent brain water at 24 hours after GCI. 129 This increase in cerebral water content, despite the lack of evidence for BBB disruption, could represent some degree of edema or ion imbalance secondary to energy failure. 135 Therefore, the response of the BBB after juvenile GCI has some similarities to adult and neonatal models, but the pathologic phenotype has some aspects that are unique to this age group.
In summary, the functional role of the BBB changes with maturation, in that the physical barrier in the developing brain limits the passage of larger molecules like proteins, but not smaller molecules such as sucrose. 136 Decreased compromise in very young brains may restrict edema and infiltration of inflammatory cells while also limiting the opportunity for vascular delivery of larger therapeutic molecules to the injured brain. This contrasts with the abundance of research that has been done in the adult brain showing that the integrity of the BBB is altered (for review, see 136 ) As pharmacologic agents are advanced, adequate delivery strategies will need to be imagined in the developing brain where the less-compromised BBB decreases permeability to large molecules.
White matter injury and repair
The impact of ischemia on white matter injury (WMI) in the preterm brain has been extensively studied, whereas WMI in rodent models of focal or global ischemia at term equivalent and older is less described. This is despite evidence that WMI in global and focal ischemia occurs across the lifespan, and in clinical studies measures of WMI are predictors of long-term outcome.137–142
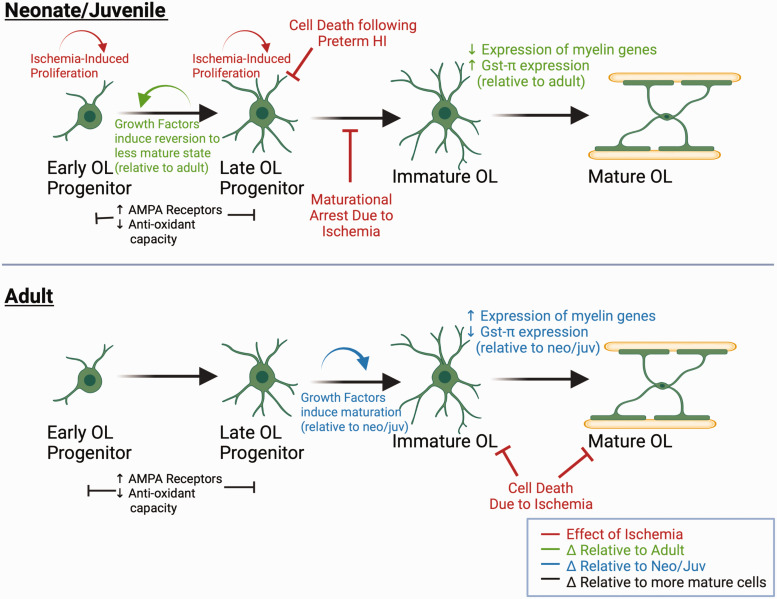
Studies using the Rice-Vannucci model established the importance of timing and developmental stage to WMI. Late oligodendrocyte (OL) progenitors, as opposed to early progenitors or more mature oligodendrocytes, are the subtype most vulnerable to cell death after hemispheric hypoxia-ischemia. 143 Importantly, these late progenitors predominate white matter at preterm equivalent age (PND2 in rodents), but not closer to term equivalent (PND7), 143 resulting in age-dependent oligodendrocyte progenitor vulnerability. There are numerous injurious mechanisms to OL progenitors after H-I, including excitotoxicity, cytokine production by reactive microglia and astrocytes, and oxidative stress (for review, see46,144) Oligodendrocyte susceptibility to ROS exemplifies age-dependent differences in injury response. In the developing brain, oligodendrocyte progenitors cells are much more sensitive to oxidative stress compared to mature oligodendrocytes (Figure 4), due to reduced expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase and glutathione-S-transferase.145,146 Further, oligodendrocyte progenitors have increased expression of AMPA receptors, increasing their susceptibility to AMPA-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS generation. 146 Therefore, it seems logical that rodents at term-equivalent (p10) and older would be less susceptible to overall oligodendrocyte loss because progenitors are not the predominant oligodendrocyte cell type. However, we previously found that mature oligodendrocytes have different antioxidant capacities depending on the age of the animal. Striatal WM is markedly preserved one week after rMCAO in juvenile mice compared to adult mice, which appears to be due to increased expression of GSTπ in mature oligodendrocytes in younger animals 66 (Figure 4). In sum, oligodendrocyte vulnerability is related to the makeup of sub-populations of the OL lineage, and antioxidant properties of oligodendrocytes throughout development.
Figure 4.
Age, cellular maturation, and ischemia-induced changes in oligodendrocytes. Both Panels: OPC’s have greater expression of AMPA GluR’s and decreased anti-oxidant proteins and enzymes compared to more mature oligodendrocytes. As oligodendrocytes mature, antioxidant capacity increases due to increased expression of glutathione pathway enzymes. However, there are age-related differences in oligodendrocytes at similar cellular maturational stages. FGF and IGF induce late OPCs from neonatal brains to revert to a less mature state and proliferate (top panel), while late OPCs from adult rodent brains are more likely to differentiate under the same conditions (bottom panel). Immature OL’s in juvenile mice express more GSTπ (top panel) relative to immature OL’s in adult mice (bottom panel). In response to ischemia, late OPCs are selectively vulnerable to cell death, there is rapid proliferation of less mature OPCs (top panel). However, there is maturational arrest of OPCs, limiting remyelination (top panel). In the adult brain, immature and mature OL’s are relatively more vulnerable to ischemia (bottom panel).
There are also age-dependent differences in intrinsic properties oligodendrocyte progenitors that likely influence white matter repair capability. It is now well established that oligodendrocyte progenitor cells persist in the brain through adulthood and are capable of proliferation, migration, and maturation in response to CNS injury. 147 Late OL-progenitors (O4+) isolated from neonatal vs adult animals and grown in vitro show very different responses to growth factors. In response to FGF and IGF, adult progenitors differentiate into mature O1+ cells, while neonatal progenitors revert to a less mature state (A2B5+) and proliferate 148 (Figure 4). Further, neonatal progenitors had increased expression of ribosomal genes and cell cycle associated genes such as Cdk4, Cyclin D1 and p53, while adult progenitors had much more expression of cells that regulate cell death, such as Bcl. 148 These in vitro findings parallel in vivo findings that OL-precursor cells have differing responses to ischemia depending on animal age. In the rMCAO stroke model and in LNIO-induced focal subcortical WM stroke, juvenile mice have OL-progenitor proliferation after ischemia compared to adult mice.66,74 However, newborn oligodendrocytes in juveniles fail to mature to myelinating cells, and there is a chronic loss of axonal transmission in WMI. 74 Together, ischemia affects different oligodendrocyte sub-populations in unique ways through developmental stages. Figure 4 summarizes the age-dependent vulnerability of OL-progenitors in response to brain ischemia among neonatal, juvenile, and adult animals. These data suggest that WM preservation/repair may be a viable therapeutic target at delayed timepoints after ischemic injury in the developing brain. This is relevant to neonatal and pediatric stroke, as a significant number of survivors experience decline in cognitive function during childhood. 149
New approaches to an old problem
It is clear that GCI in juvenile rodents causes delayed neuronal cell death in the cortex, hippocampus, thalamus and cerebellum,52,53,57 though the striatum may be spared. 53 Data related to mechanisms of brain injury after GCI in children remain limited. Currently, hypothermia is the only treatment available for improving brain recovery after GCI,3,4 though even hypothermia has come under recent scrutiny in children 5 and adult human studies. 150 While various adjunctive therapies are being investigated in neonatal cerebral ischemia, 41 the lack of therapeutics available to neonates and children following cerebral ischemia warrants innovative strategies to improve translational efficacy.
Stem cell therapy and neurogenesis
Neurogenesis capacity appears to decrease with age due to the production of negative regulators. 151 However, following developmental ischemia, neurogenesis capacity increases following neonatal H-I injury in rodents. 151 Indeed, stem cell treatment (SCT), particularly with the use of mesenchymal stem cells, has been proposed to increase the capacity for repair and regeneration following ischemia.151–153 SCT has been shown to offer some neuroprotection when applied early following neonatal H-I. In juvenile and adult mice following rMCAO, neurogenesis is robust and efficient in juveniles following stroke, but newborn cells in the adult mice failed to reach maturity.151,153 Moreover, motor recovery gained through endogenous neuronal replacement could be attenuated with irradiation and reversed in the juvenile mice. 153 The opportunity to advance the field of neuronal restoration through STC is exciting and should be studied in different ages and specific disease models.
Neurorestoration as alternative strategy to acute neuroprotection
As noted above, cognitive and motor impairments are common among patients of all ages after AIS or GCI.6–8 Unfortunately, very few preclinical trials aiming for neuroprotection have succeeded in translating to clinical success and, as such, some have commented on the need for alternative strategies.154,155 The cognitive decline and motor impairment in those who experience cerebral ischemia is due, in part, to neuronal cell death, though there is also an under-recognized contribution of altered physiology to the neurons that survive. Studying new therapeutic strategies that target restoration of impaired neuronal physiology (neurorestoration) is necessary. In this way, one could envision resetting the brain to a status conducive to acquiring new skills and memories. We posit that studying long term functional outcomes is a vital tool in understanding synaptic and functional recovery of surviving neurons after ischemia and may provide new therapeutic approaches.
We highlight here several studies focusing on neurorestoration, or neural repair strategies that restore plasticity. Intervening after cell death and focusing on repairing neural networks is a little used approach with a potentially large payoff. In preclinical studies, recovery has been assessed by examining different brain areas associated with sensory, motor, and memory to directly test neurorestoration. The antidepressant fluoxetine was among the first agents to be used to reopen critical periods of plasticity following visual cortex injury in adult brains, with potential mechanistic properties in reducing GABAergic signaling and well as increased BDNF expression. 156 More recently, use of ephrin-A5 antagonists, 157 GABAα5 inverse agonists, 158 histone deacetylase 5 inhibitors, 159 or C-C chemokine receptor 5 knockdown 160 at delayed time points after adult stroke augmented motor and cognitive recovery, opening the door to neurorestoration after ischemia.
Recent work has examined hippocampal synaptic plasticity that underlies cognitive dysfunction following ischemia. As the field continues to consider measures beyond neuroprotection and move towards toward functional outcomes, electrophysiologic and behavior paradigms that assess neuronal activity in the surviving neurons has yielded important information for neurorestorative targets. Synaptic plasticity is the leading model for the cellular changes that underlie learning and memory and has been extensively studied in the hippocampus. 161 It has also been a valuable physiologic process to better understand the complexities of synaptic function. One of the most established models of activity dependent synaptic plasticity is long-term potentiation (LTP), which is well correlated with learning and memory, as well as cognitive impairment after ischemia. 162 Studies using juvenile cerebral ischemia (both MCAO and GCI) have found impairments in long-term potentiation,34,35,57,99 Morris water maze testing,52,55 and contextual fear conditioning34,35,99 days to weeks after the ischemic event. In addition, increases in thalamocortical neuron spike probability were observed 6 weeks after juvenile cardiac arrest. 163 Compound action potentials have been measured in the corpus collosum at acute and chronic time points to identify differences in white matter responses to juvenile and adult stroke. 74 Together, electrophysiologic and behavioral outcomes can, and should, be used to devise new strategies that can potentially reverse detrimental changes in physiology after GCI at time points beyond those when neuronal death occurs. To emphasize these ideas, we highlight recent work describing neurorestorative strategies following cerebral ischemia.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in global cerebral ischemia
There has been much interest in neurotrophic factors as targets for improved recovery after ischemia,34,164 though the efficacy even in rodent models remains unclear. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has received much of this attention. BDNF has long been known to be a critical component of growth and differentiation of neurons in development as well as synaptic plasticity. 165 Intriguingly, the effect of BDNF after GCI may be age dependent. BDNF levels decrease in the hippocampus following GCI in juvenile mice, allowing for specific targeting of the neurotrophin receptor tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) to restore memory and synaptic plasticity. 34 However, similar decreases in hippocampal BDNF do not occur following GCI in adult animals, but rather BDNF exon I was elevated for 24 hours after adult GCI. 166 Studies of adult GCI suggest that acute BDNF infusion following injury did not result in improved functional outcome or survival. 167 Following neonatal stroke, BDNF expression is decreased 1 day, but not different at 7 days after stroke, 168 and juvenile stroke shows increase in BDNF at 7 or 14 days after stroke. 169 These paradoxical results following cerebral ischemia at different ages and in different models highlight that while the physiologic role of BDNF is well studied in the healthy mammalian brain, there remain many areas in BDNF research that are unexplored, particularly regarding age-related ischemic injury. We cannot assume that the lack of effect in the adult brain will be extended to the developing brain. Therefore, BDNF-augmenting therapy may work in some age-specific models and not others and requires special attention to study design.
Transient receptor potential M2 (TRPM2)
A role for TRPM2 channels in mediating neuronal injury following ischemia has been proposed for several years,170,171 including multiple studies in adult mice confirming a male-specific pattern of neuropathology following adult focal and juvenile ischemia.96,98,172 On the other end of the age spectrum, TRPM2 inhibition by AG490 or mice lacking TRPM2 expression resulted in decreased infarct volume in neonatal H-I models.173,174 Activation of TRPM2 channels has now been implicated in cellular and functional impairments following ischemic injury across the age spectrum, from neonates 173 to aged adults. 172 Following juvenile GCI, inhibition of TRPM2 indicates a complex pattern of involvement in prolonged functional dysfunction (LTP and memory behavior), but not acute cell death. 99 Further, adult GCI mice signal male specific neuroprotection after acute TRPM2 channel inhibition as well as persistent TRPM2 channel activity contributing to sustained synaptic dysfunction after GCI in both males and females. 98 The differences in neuroprotection between adults and juvenile mice following GCI, including lack of acute neuroprotection in juveniles, emphasize the need for age and injury specific models.
Nogo-A in juvenile Middle cerebral artery occlusion
Recent studies investigated Nogo-A, an important neurite growth inhibitory factor 175 and negative regulator of structural plasticity in development 175 in juvenile rMCAO. Previous literature in adult synaptic plasticity has shown that Nogo-A restricts memory formation and hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) 176 via the interaction of the Nogo-66 domain of the Nogo Receptor 1 (NgR1). In juvenile stroke models, Nogo-A expression increased in hippocampal astrocytes leading to hippocampal dysfunction in juvenile, but not adult mice after stroke. 35 Treatment with the Nogo receptor antagonist NEP(1-40) reversed synaptic plasticity impairment in juveniles 7 days after rMCAO, but not in adults, 35 providing further support for age-specific modeling for discovery of therapeutic targets. Given the role of Nogo-A in the regulation of structural plasticity in the developing brain, it would be of great benefit to better understand how this signaling affects post-ischemic synaptic plasticity following neonatal stroke.
Given that numerous neuroprotection studies have not translated to clinical therapy (particularly in children), novel strategies are required. We postulate that focusing on enhancing the function of surviving neurons in the developing brain to restore brain function may be one such strategy. The fundamental principles included in the neurorestorative strategies described here rely on 1) intervention beyond the time for neuronal death, and 2) measuring cognitive and/or motor change at multiple brain levels, from molecules to synapses to functional connectivity. It is likely that neurorestorative interventions may be complex, requiring multiple interacting mechanisms, but identification of neural repair and plasticity recovery is likely the next strategy in treating cerebral ischemia in all ages.
Conclusion
Recently developed models of specific cerebral ischemia in young rodents have provided important insights for investigators regarding thoughtful modeling of brain ischemia across development and differences in outcome at different ages. Emerging themes suggest that developmental physiology and pathologic responses to ischemia during maturation may have subtle, yet potentially significant, impact on our understanding of ischemic brain injury and potential therapies. Data reviewed here suggest that many important mechanisms for brain injury seem be exacerbated in the developing brain. It is increasingly clear with better modeling, that the young brain has enhanced potential for recovery after focal and global cerebral ischemia. Together, the data strongly suggest that the availability of age- and disease-specific models provides a unique opportunity for the next generation of ischemia researchers to use these models to enhance translational potential. The models in the developing brain reviewed here hold the promise of providing novel translatable strategies to improve functional outcome for children that suffer cerebral ischemia.
Acknowledgements
Illustrations with BioRender.com.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
ORCID iD: Robert M Dietz https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1474-9106
References
- 1.Topjian AA, de Caen A, Wainwright MS, et al. Pediatric post-cardiac arrest care: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019; 140: e194–e233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Meaney PA, Nadkarni VM, Cook EF, et al. Higher survival rates among younger patients after pediatric intensive care unit cardiac arrests. Pediatrics 2006; 118: 2424–2433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Arrich J, Holzer M, Havel C, et al. Hypothermia for neuroprotection in adults after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Cochr Database Syst Rev 2012; 9: CD004128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jacobs SE, Berg M, Hunt R, et al. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochr Database Syst Rev 2013; 1: CD003311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Moler FW, Silverstein FS, Holubkov R, et al. Therapeutic hypothermia after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in children. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 1898–1908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Michiels EA, Dumas F, Quan L, et al. Long-term outcomes following pediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2013; 14: 755–760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.O'Reilly SM, Grubb NR, O'Carroll RE. In-hospital cardiac arrest leads to chronic memory impairment. Resuscitation 2003; 58: 73–79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nitta M, Iwami T, Kitamura T, et al. Age-specific differences in outcomes after out-of-hospital cardiac arrests. Pediatrics 2011; 128: e812-20–e820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Agrawal N, Johnston SC, Wu YW, et al. Imaging data reveal a higher pediatric stroke incidence than prior US estimates. Stroke 2009; 40: 3415–3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Oleske DM, Cheng X, Jeong A, et al. Pediatric acute ischemic stroke by age-group: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies and hospitalization records. Neuroepidemiology 2021; 55: 331–341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.deVeber GA, Kirton A, Booth FA, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of arterial ischemic stroke in children: the Canadian pediatric ischemic stroke registry. Pediatr Neurol 2017; 69: 58–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019; 50: e344–e418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Srinivasan J, Miller SP, Phan TG, et al. Delayed recognition of initial stroke in children: need for increased awareness. Pediatrics 2009; 124: e227-34–e234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Amlie-Lefond C, deVeber G, Chan AK, et al. Use of alteplase in childhood arterial ischaemic stroke: a multicentre, observational, cohort study. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8: 530–536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Amlie-Lefond C, Shaw DWW, Cooper A, et al. Risk of intracranial hemorrhage following intravenous tPA (tissue-type plasminogen activator) for acute stroke is low in children. Stroke 2020; 51: 542–548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rivkin MJ, deVeber G, Ichord RN, et al. Thrombolysis in pediatric stroke study. Stroke 2015; 46: 880–885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sporns PB, Kemmling A, Lee S, et al. A prospective multicenter registry on feasibility, safety, and outcome of endovascular recanalization in childhood stroke (save ChildS pro). Front Neurol 2021; 12: 736092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sporns PB, Sträter R, Minnerup J, et al. Feasibility, safety, and outcome of endovascular recanalization in childhood stroke: the save ChildS study. JAMA Neurol 2020; 77: 25–34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Biswas A, Mankad K, Shroff M, et al. Neuroimaging perspectives of perinatal arterial ischemic stroke. Pediatr Neurol 2020; 113: 56–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Siddiq I, Armstrong D, Surmava AM, et al. Utility of neurovascular imaging in acute neonatal arterial ischemic stroke. J Pediatr 2017; 188: 110–114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mackay MT, Wiznitzer M, Benedict SL, et al. Arterial ischemic stroke risk factors: the international pediatric stroke study. Ann Neurol 2011; 69: 130–140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wintermark M, Hills NK, deVeber GA, et al. Arteriopathy diagnosis in childhood arterial ischemic stroke: results of the vascular effects of infection in pediatric stroke study. Stroke 2014; 45: 3597–3605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chabrier S, Peyric E, Drutel L, et al. Multimodal outcome at 7 years of age after neonatal arterial ischemic stroke. J Pediatr 2016; 172: 156–161.e3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Goeggel Simonetti B, Cavelti A, Arnold M, et al. Long-term outcome after arterial ischemic stroke in children and young adults. Neurology 2015; 84: 1941–1947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Westmacott R, Askalan R, MacGregor D, et al. Cognitive outcome following unilateral arterial ischaemic stroke in childhood: effects of age at stroke and lesion location. Dev Med Child Neurol 2010; 52: 386–393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Laumann TO, Ortega M, Hoyt CR, et al. Brain network reorganisation in an adolescent after bilateral perinatal strokes. Lancet Neurol 2021; 20: 255–256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Semple BD, Blomgren K, Gimlin K, et al. Brain development in rodents and humans: Identifying benchmarks of maturation and vulnerability to injury across species. Prog Neurobiol 2013; 106-107: 1–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Huttenlocher PR. Synaptic density in human frontal cortex – developmental changes and effects of aging. Brain Res 1979; 163: 195–205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Heckman EL, Doe CQ. Establishment and maintenance of neural circuit architecture. J Neurosci 2021; 41: 1119–1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Herschkowitz N, Kagan J, Zilles K. Neurobiological bases of behavioral development in the first year. Neuropediatrics 1997; 28: 296–306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dehorter N, Vinay L, Hammond C, et al. Timing of developmental sequences in different brain structures: physiological and pathological implications. Eur J Neurosci 2012; 35: 1846–1856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lohmann C, Kessels HW. The developmental stages of synaptic plasticity. J Physiol: Physiol Soc 2014; 592: 13–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Anderson V, Spencer-Smith M, Wood A. Do children really recover better? Neurobehavioural plasticity after early brain insult. Brain 2011; 134: 2197–2221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dietz RM, Orfila JE, Rodgers KM, et al. Juvenile cerebral ischemia reveals age-dependent BDNF-TrkB signaling changes: novel mechanism of recovery and therapeutic intervention. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2018; 38: 2223–2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Orfila JE, Dietz RM, Rodgers KM, et al. Experimental pediatric stroke shows age-specific recovery of cognition and role of hippocampal Nogo-A receptor signaling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2020; 40: 588–599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rakhade SN, Jensen FE. Epileptogenesis in the immature brain: emerging mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurol 2009; 5: 380–391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rice JE, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 1981; 9: 131–141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Titomanlio L, Fernández-López D, Manganozzi L, et al. Pathophysiology and neuroprotection of global and focal perinatal brain injury: lessons from animal models. Pediatr Neurol 2015; 52: 566–584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang Y, Cheung PT, Shen GX. Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the neonatal rat model: relationship between lesion size at early MR imaging and irreversible infarction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006; 27: 51–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Drury PP, Gunn ER, Bennet L, et al. Mechanisms of hypothermic neuroprotection. Clin Perinatol 2014; 41: 161–175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.McAdams RM, Juul SE. Neonatal encephalopathy: update on therapeutic hypothermia and other novel therapeutics. Clin Perinatol 2016; 43: 485–500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hobbs C, Thoresen M, Tucker A, et al. Xenon and hypothermia combine additively, offering long-term functional and histopathologic neuroprotection after neonatal hypoxia/ischemia. Stroke 2008; 39: 1307–1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bennet L, Tan S, Van den Heuij L, et al. Cell therapy for neonatal hypoxia-ischemia and cerebral palsy. Ann Neurol 2012; 71: 589–600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Adams KV, Mahmud N, Green-Holland M, et al. Constraint-induced movement therapy promotes motor recovery after neonatal stroke in the absence of neural precursor activation. Eur J Neurosci 2021; 53: 1334–1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Charriaut-Marlangue C, Baud O. A model of perinatal ischemic stroke in the rat: 20 years already and what lessons? Front Neurol 2018; 9: 650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rumajogee P, Bregman T, Miller SP, et al. Rodent Hypoxia-Ischemia models for cerebral palsy research: a systematic review. Front Neurol 2016; 7: 57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ. Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: evolution of an animal model. Dev Neurosci 2005; 27: 81–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yager JY, Ashwal S. Animal models of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Pediatr Neurol 2009; 40: 156–167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Eltzschig HK, Eckle T. Ischemia and reperfusion – from mechanism to translation. Nat Med 2011; 17: 1391–1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hutchens MP, Traystman RJ, Fujiyoshi T, et al. Normothermic cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a mouse model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. JoVE 2011; [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Manabat C, Han BH, Wendland M, et al. Reperfusion differentially induces caspase-3 activation in ischemic core and penumbra after stroke in immature brain. Stroke 2003; 34: 207–213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Fink EL, Alexander H, Marco CD, et al. Experimental model of pediatric asphyxial cardiopulmonary arrest in rats. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2004; 5: 139–144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Deng G, Yonchek JC, Quillinan N, et al. A novel mouse model of pediatric cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation reveals age-dependent neuronal sensitivities to ischemic injury. J Neurosci Meth 2014; 222: 34–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Foley LM, Clark RS, Vazquez AL, et al. Enduring disturbances in regional cerebral blood flow and brain oxygenation at 24 h after asphyxial cardiac arrest in developing rats. Pediatr Res 2017; 81: 94–98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Manole MD, Kochanek PM, Foley LM, et al. Polynitroxyl albumin and albumin therapy after pediatric asphyxial cardiac arrest: effects on cerebral blood flow and neurologic outcome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2012; 32: 560–569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Manole MD, Kochanek PM, Bayir H, et al. Brain tissue oxygen monitoring identifies cortical hypoxia and thalamic hyperoxia after experimental cardiac arrest in rats. Pediatr Res 2014; 75: 295–301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Dietz RM, Deng G, Orfila JE, et al. Therapeutic hypothermia protects against ischemia-induced impairment of synaptic plasticity following juvenile cardiac arrest in sex-dependent manner. Neuroscience 2016; 325: 132–141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989; 20: 84–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Minematsu K, Li L, Sotak CH, et al. Reversible focal ischemic injury demonstrated by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in rats. Stroke 1992; 23: 1304–1310. discussion 10-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.National Institute of Neurological D, Stroke rt PASSG. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The New England Journal of Medicine 1995; 333: 1581–1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016; 387: 1723–1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ashwal S, Cole DJ, Osborne S, et al. A new model of neonatal stroke: reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat pup. Pediatr Neurol 1995; 12: 191–196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Derugin N, Ferriero DM, Vexler ZS. Neonatal reversible focal cerebral ischemia: a new model. Neurosci Res 1998; 32: 349–353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Woo MS, Wang X, Faustino JV, et al. Genetic deletion of CD36 enhances injury after acute neonatal stroke. Ann Neurol 2012; 72: 961–970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Renolleau S, Aggoun-Zouaoui D, Ben-Ari Y, et al. A model of transient unilateral focal ischemia with reperfusion in the P7 neonatal rat: morphological changes indicative of apoptosis. Stroke 1998; 29: 1454–1460; discussion 61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ahrendsen JT, Grewal HS, Hickey SP, et al. Juvenile striatal white matter is resistant to ischemia-induced damage. Glia 2016; 64: 1972–1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Faustino J, Chip S, Derugin N, et al. CX3CR1-CCR2-dependent monocyte-microglial signaling modulates neurovascular leakage and acute injury in a mouse model of childhood stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2019; 39: 1919–1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wen TC, Rogido M, Gressens P, et al. A reproducible experimental model of focal cerebral ischemia in the neonatal rat. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 2004; 13: 76–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Villapol S, Fau S, Renolleau S, et al. Melatonin promotes myelination by decreasing white matter inflammation after neonatal stroke. Pediatr Res 2011; 69: 51–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Busto R, et al. Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol 1985; 17: 497–504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Maxwell KA, Dyck RH. Induction of reproducible focal ischemic lesions in neonatal mice by photothrombosis. Dev Neurosci 2005; 27: 121–126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Van Slooten AR, Sun Y, Clarkson AN, et al. L-NIO as a novel mechanism for inducing focal cerebral ischemia in the adult rat brain. J Neurosci Methods 2015; 245: 44–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Roome RB, Bartlett RF, Jeffers M, et al. A reproducible endothelin-1 model of forelimb motor cortex stroke in the mouse. J Neurosci Methods 2014; 233: 34–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Dingman AL, Rodgers KM, Dietz RM, et al. Oligodendrocyte progenitor cell proliferation and fate after white matter stroke in juvenile and adult mice. Dev Neurosci 2019; 12: 1–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Johnston MV. Excitotoxicity in perinatal brain injury. Brain Pathol 2005; 15: 234–240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Quillinan N, Herson PS, Traystman RJ. Neuropathophysiology of brain injury. Anesthesiol Clin 2016; 34: 453–464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Szydlowska K, Tymianski M. Calcium, ischemia and excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 2010; 47: 122–129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Choi DW. Excitotoxicity: Still hammering the ischemic brain in 2020. Front Neurosci 2020; 14: 579953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Herson PS, Traystman RJ. Animal models of stroke: translational potential at present and in 2050. Future Neurol 2014; 9: 541–551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Weiss JH. Ca permeable AMPA channels in diseases of the nervous system. Front Mol Neurosci 2011; 4: 42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Kumar SS, Bacci A, Kharazia V, et al. A developmental switch of AMPA receptor subunits in neocortical pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 3005–3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Follett PL, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE. NBQX attenuates excitotoxic injury in developing white matter. J Neurosci 2000; 20: 9235–9241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Kaila K. Ionic basis of GABAA receptor channel function in the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 1994; 42: 489–537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Raimondo JV, Richards BA, Woodin MA. Neuronal chloride and excitability – the big impact of small changes. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2017; 43: 35–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Ito S. GABA and glycine in the developing brain. J Physiol Sci 2016; 66: 375–379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ben-Ari Y, Gaiarsa JL, Tyzio R, et al. GABA: a pioneer transmitter that excites immature neurons and generates primitive oscillations. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 1215–1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Chan PH. Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2001; 21: 2–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Odorcyk FK, Ribeiro RT, Roginski AC, et al. Differential age-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis induced by neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in the immature rat brain. Mol Neurobiol 2021; 58: 2297–2308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ikonomidou C, Kaindl AM. Neuronal death and oxidative stress in the developing brain. Antioxid Redox Signal 2011; 14: 1535–1550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Greisen G. Cerebral blood flow and oxygenation in infants after birth asphyxia. Clinically useful information? Early Hum Dev 2014; 90: 703–705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Liu P, Huang H, Rollins N, et al. Quantitative assessment of global cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) in neonates using MRI. NMR Biomed 2014; 27: 332–340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Vexler ZS, Yenari MA. Does inflammation after stroke affect the developing brain differently than adult brain? Dev Neurosci 2009; 31: 378–393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Dietz RM, Wright CJ. Oxidative stress diseases unique to the perinatal period: a window into the developing innate immune response. Am J Reprod Immunol 2018; 79: e12787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Folkerth RD, Haynes RL, Borenstein NS, et al. Developmental lag in superoxide dismutases relative to other antioxidant enzymes in premyelinated human telencephalic white matter. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2004; 63: 990–999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Doverhag C, Keller M, Karlsson A, et al. Pharmacological and genetic inhibition of NADPH oxidase does not reduce brain damage in different models of perinatal brain injury in newborn mice. Neurobiol Dis 2008; 31: 133–144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Nakayama S, Vest R, Traystman RJ, et al. Sexually dimorphic response of TRPM2 inhibition following cardiac arrest-induced global cerebral ischemia in mice. J Mol Neurosci 2013; 51: 92–98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Shimizu T, Macey TA, Quillinan N, et al. Androgen and PARP-1 regulation of TRPM2 channels after ischemic injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013; 33: 1549–1555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Dietz RM, Cruz-Torres I, Orfila JE, et al. Reversal of global Ischemia-Induced cognitive dysfunction by delayed inhibition of TRPM2 ion channels. Transl Stroke Res 2019; 11: 254–266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Dietz RM, Orfila JE, Chalmers N, et al. Functional restoration following global cerebral ischemia in juvenile mice following inhibition of transient receptor potential M2 (TRPM2) ion channels. Neural Plast 2021; 2021: 8774663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Hagberg H, Wilson MA, Matsushita H, et al. PARP-1 gene disruption in mice preferentially protects males from perinatal brain injury. J Neurochem 2004; 90: 1068–1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Shi K, Tian DC, Li ZG, et al. Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol 2019; 18: 1058–1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Li B, Concepcion K, Meng X, et al. Brain-immune interactions in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Prog Neurobiol 2017; 159: 50–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Anrather J, Iadecola C. Inflammation and stroke: an overview. Neurotherapeutics 2016; 13: 661–670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Hagberg H, Mallard C, Ferriero DM, et al. The role of inflammation in perinatal brain injury. Nat Rev Neurol 2015; 11: 192–208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Rayasam A, Fukuzaki Y, Vexler ZS. Microglia-leucocyte axis in cerebral ischaemia and inflammation in the developing brain. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2021; 233: e13674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Fernández-López D, Faustino J, Klibanov AL, et al. Microglial cells prevent hemorrhage in neonatal focal arterial stroke. J Neurosci 2016; 36: 2881–2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Stevens SL, Bao J, Hollis J, et al. The use of flow cytometry to evaluate temporal changes in inflammatory cells following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Brain Res 2002; 932: 110–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Enzmann G, Mysiorek C, Gorina R, et al. The neurovascular unit as a selective barrier to polymorphonuclear granulocyte (PMN) infiltration into the brain after ischemic injury. Acta Neuropathol 2013; 125: 395–412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Bona E, Andersson AL, Blomgren K, et al. Chemokine and inflammatory cell response to hypoxia-ischemia in immature rats. Pediatr Res 1999; 45: 500–509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.del Zoppo GJ, Schmid-Schönbein GW, Mori E, et al. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes occlude capillaries following middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion in baboons. Stroke 1991; 22: 1276–1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Rosell A, Cuadrado E, Ortega-Aznar A, et al. MMP-9-positive neutrophil infiltration is associated to blood-brain barrier breakdown and basal lamina type IV collagen degradation during hemorrhagic transformation after human ischemic stroke. Stroke 2008; 39: 1121–1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Garcia-Bonilla L, Moore JM, Racchumi G, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase in neutrophils and endothelium contributes to ischemic brain injury in mice. Ji 2014; 193: 2531–2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Chang CY, Kao TK, Chen WY, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine inhibits neutrophil activation following permanent cerebral ischemia in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2015; 463: 421–427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Winerdal M, Winerdal ME, Kinn J, et al. Long lasting local and systemic inflammation after cerebral hypoxic ischemia in newborn mice. PLoS One 2012; 7: e36422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Offner H, Subramanian S, Parker SM, et al. Experimental stroke induces massive, rapid activation of the peripheral immune system. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2006; 26: 654–665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Deng G, Carter J, Traystman RJ, et al. Pro-inflammatory T-lymphocytes rapidly infiltrate into the brain and contribute to neuronal injury following cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation. J Neuroimmunol 2014; 274: 132–140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Hum PD, Subramanian S, Parker SM, et al. T- and B-cell-deficient mice with experimental stroke have reduced lesion size and inflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007; 27: 1798–1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Kleinschnitz C, Kraft P, Dreykluft A, et al. Regulatory T cells are strong promoters of acute ischemic stroke in mice by inducing dysfunction of the cerebral microvasculature. Blood 2013; 121: 679–691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Albertsson AM, Zhang X, Vontell R, et al. Gammadelta T cells contribute to injury in the developing brain. Am J Pathol 2018; 188: 757–767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Benakis C, Garcia-Bonilla L, Iadecola C, et al. The role of microglia and myeloid immune cells in acute cerebral ischemia. Front Cell Neurosci 2014; 8: 461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Dingman A, Lee SY, Derugin N, et al. Aminoguanidine inhibits caspase-3 and calpain activation without affecting microglial activation following neonatal transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 2006; 96: 1467–1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Lalancette-Hébert M, Gowing G, Simard A, et al. Selective ablation of proliferating microglial cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 2596–2605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Faustino JV, Wang X, Johnson CE, et al. Microglial cells contribute to endogenous brain defenses after acute neonatal focal stroke. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 12992–13001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Denker SP, Ji S, Dingman A, et al. Macrophages are comprised of resident brain microglia not infiltrating peripheral monocytes acutely after neonatal stroke. J Neurochem 2007; 100: 893–904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Fox C, Dingman A, Derugin N, et al. Minocycline confers early but transient protection in the immature brain following focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2005; 25: 1138–1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Iadecola C, Buckwalter MS, Anrather J. Immune responses to stroke: mechanisms, modulation, and therapeutic potential. J Clin Invest 2020; 130: 2777–2788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Tang M, Alexander H, Clark RS, et al. Minocycline reduces neuronal death and attenuates microglial response after pediatric asphyxial cardiac arrest. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2010; 30: 119–129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Jiang X, Andjelkovic AV, Zhu L, et al. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and recovery after ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 2018; 163-164: 144–171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Tress EE, Clark RS, Foley LM, et al. Blood brain barrier is impermeable to solutes and permeable to water after experimental pediatric cardiac arrest. Neurosci Lett 2014; 578: 17–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Ek CJ, D'Angelo B, Baburamani AA, et al. Brain barrier properties and cerebral blood flow in neonatal mice exposed to cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2015; 35: 818–827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Fernandez-Lopez D, Faustino J, Daneman R, et al. Blood-brain barrier permeability is increased after acute adult stroke but not neonatal stroke in the rat. J Neurosci 2012; 32: 9588–9600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Wang R, Ashwal S, Tone B, et al. Albumin reduces blood-brain barrier permeability but does not alter infarct size in a rat model of neonatal stroke. Pediatr Res 2007; 62: 261–266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Fernández-López D, Faustino J, Derugin N, et al. Acute and chronic vascular responses to experimental focal arterial stroke in the neonate rat. Transl Stroke Res 2013; 4: 179–188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Manole MD, Foley LM, Hitchens TK, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of regional cerebral blood flow after asphyxial cardiac arrest in immature rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2009; 29: 197–205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Nag S, Manias JL, Stewart DJ. Pathology and new players in the pathogenesis of brain edema. Acta Neuropathol 2009; 118: 197–217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Neuwelt EA, Bauer B, Fahlke C, et al. Engaging neuroscience to advance translational research in brain barrier biology. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011; 12: 169–182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Massaro AN, Evangelou I, Fatemi A, et al. White matter tract integrity and developmental outcome in newborn infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia. Dev Med Child Neurol 2015; 57: 441–448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Ressel V, Berati D, Raselli C, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging markers reflect cognitive outcome after rehabilitation in children with acquired brain injury. Eur J Radiol 2020; 126: 108963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Ressel V, O'Gorman Tuura R, Scheer I, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging predicts motor outcome in children with acquired brain injury. Brain Imaging Behav 2017; 11: 1373–1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.van der Aa NE, Northington FJ, Stone BS, et al. Quantification of white matter injury following neonatal stroke with serial DTI. Pediatr Res 2013; 73: 756–762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Velly L, Perlbarg V, Boulier T, MRI-COMA Investigators et al. Use of brain diffusion tensor imaging for the prediction of long-term neurological outcomes in patients after cardiac arrest: a multicentre, international, prospective, observational, cohort study. Lancet Neurol 2018; 17: 317–326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Wang Y, Liu G, Hong D, et al. White matter injury in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 2016; 141: 45–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Back SA, Han BH, Luo NL, et al. Selective vulnerability of late oligodendrocyte progenitors to hypoxia-ischemia. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 455–463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Mifsud G, Zammit C, Muscat R, et al. Oligodendrocyte pathophysiology and treatment strategies in cerebral ischemia. CNS Neurosci Ther 2014; 20: 603–612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Back SA, Gan X, Li Y, et al. Maturation-dependent vulnerability of oligodendrocytes to oxidative stress-induced death caused by glutathione depletion. J Neurosci 1998; 18: 6241–6253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Spaas J, van Veggel L, Schepers M, et al. Oxidative stress and impaired oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation in neurological disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci 2021; 78: 4615–4637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Dimou L, Gallo V. NG2-glia and their functions in the Central nervous system. Glia 2015; 63: 1429–1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Lin G, Mela A, Guilfoyle EM, et al. Neonatal and adult O4(+) oligodendrocyte lineage cells display different growth factor responses and different gene expression patterns. J Neurosci Res 2009; 87: 3390–3402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Westmacott R, MacGregor D, Askalan R, et al. Late emergence of cognitive deficits after unilateral neonatal stroke. Stroke 2009; 40: 2012–2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Dankiewicz J, Cronberg T, Lilja G, et al. Hypothermia versus normothermia after out-of-Hospital cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med 2021; 384: 2283–2294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Donega V, van Velthoven CT, Nijboer CH, et al. The endogenous regenerative capacity of the damaged newborn brain: boosting neurogenesis with mesenchymal stem cell treatment. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013; 33: 625–634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Lippmann ES, Azarin SM, Kay JE, et al. Derivation of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 2012; 30: 783–791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Rodgers KM, Ahrendsen JT, Patsos OP, et al. Endogenous neuronal replacement in the juvenile brain following cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 2018; 380: 1–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Jolkkonen J, Kwakkel G. Translational hurdles in stroke recovery studies. Transl Stroke Res 2016; 7: 331–342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Ward NS, Carmichael ST. Blowing up neural repair for stroke recovery: Preclinical and clinical trial considerations. Stroke 2020; 51: 3169–3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Maya Vetencourt JF, Sale A, Viegi A, et al. The antidepressant fluoxetine restores plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Science 2008; 320: 385–388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Overman JJ, Clarkson AN, Wanner IB, et al. A role for ephrin-A5 in axonal sprouting, recovery, and activity-dependent plasticity after stroke. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012; 109: E2230–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Clarkson AN, Huang BS, Macisaac SE, et al. Reducing excessive GABA-mediated tonic inhibition promotes functional recovery after stroke. Nature 2010; 468: 305–309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Lin YH, Dong J, Tang Y, et al. Opening a new time window for treatment of stroke by targeting HDAC2. J Neurosci 2017; 37: 6712–6728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Joy MT, Ben Assayag E, Shabashov-Stone D, et al. CCR5 is a therapeutic target for recovery after stroke and traumatic brain injury. Cell 2019; 176: 1143–1157 e13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 1993; 361: 31–39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Escobar I, Xu J, Jackson CW, et al. Altered neural networks in the papez circuit: Implications for cognitive dysfunction after cerebral ischemia. J Alzheimers Dis 2019; 67: 425–446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Shoykhet M, Simons DJ, Alexander H, et al. Thalamocortical dysfunction and thalamic injury after asphyxial cardiac arrest in developing rats. J Neurosci 2012; 32: 4972–4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Beck T, Lindholm D, Castren E, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects against ischemic cell damage in rat hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1994; 14: 689–692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Minichiello L. TrkB signalling pathways in LTP and learning. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009; 10: 850–860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Vosler PS, Logue ES, Repine MJ, et al. Delayed hypothermia preferentially increases expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor exon III in rat hippocampus after asphyxial cardiac arrest. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2005; 135: 21–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Callaway CW, Ramos R, Logue ES, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor does not improve recovery after cardiac arrest in rats. Neurosci Lett 2008; 445: 103–107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Atif F, Yousuf S, Stein DG. Progesterone in the treatment of neonatal arterial ischemic stroke and acute seizures: role of BDNF/TrkB signaling. Neuropharmacology 2016; 107: 317–328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Cheng J, Shen W, Jin L, et al. Treadmill exercise promotes neurogenesis and myelin repair via upregulating wnt/betacatenin signaling pathways in the juvenile brain following focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Int J Mol Med 2020; 45: 1447–1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Rempe DA, Takano T, Nedergaard M. TR(I)Pping towards treatment for ischemia. Nat Neurosci 2009; 12: 1215–1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Aarts MM, Tymianski M. TRPMs and neuronal cell death. Pflugers Arch – Eur J Physiol 2005; 451: 243–249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Shimizu T, Dietz RM, Cruz-Torres I, et al. Extended therapeutic window of a novel peptide inhibitor of TRPM2 channels following focal cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 2016; 283: 151–156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Huang S, Turlova E, Li F, et al. Transient receptor potential melastatin 2 channels (TRPM2) mediate neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in mice. Exp Neurol 2017; 296: 32–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Li F, Wong R, Luo Z, et al. Neuroprotective effects of AG490 in neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol 2019; 56: 8109–8123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Schwab ME. Functions of nogo proteins and their receptors in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 2010; 11: 799–811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Delekate A, Zagrebelsky M, Kramer S, et al. NogoA restricts synaptic plasticity in the adult hippocampus on a fast time scale. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011; 108: 2569–2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Gong H, Shu L, Xu H, et al. Bilateral internal carotid arteries ligation temporary impairs brain vasculature in young rats. Auton Neurosci 2013; 173: 39–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Dijkhuizen RM, de Graaf RA, Tulleken KA, et al. Changes in the diffusion of water and intracellular metabolites after excitotoxic injury and global ischemia in neonatal rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1999; 19: 341–349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Gonzalez FF, McQuillen P, Mu D, et al. Erythropoietin enhances long-term neuroprotection and neurogenesis in neonatal stroke. Dev Neurosci 2007; 29: 321–330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]