Abstract
A stressor-related disorder wherein traumatic experience precipitates protracted disruptions to mood and cognition, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is associated with wide-ranging abnormalities across the body. While various methods have investigated these deviations, only proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS) enables noninvasive measurement of small-molecule metabolites in the living human. 1H MRS has correspondingly been employed to test hypotheses about the composition and function of multiple brain regions putatively involved in PTSD. Here we systematically review methodological considerations and reported findings, both positive and negative, of the current 1H-MRS literature in PTSD (N = 32 studies) to communicate the brain regional metabolite alterations heretofore observed, providing random-effects model meta-analyses for those most extensively studied. Our review suggests significant PTSD-associated decreases in N-acetyl aspartate in bilateral hippocampus and anterior cingulate cortex with less evident effect in other metabolites and regions. Model heterogeneities diverged widely by analysis (I2 < 0.01% to 90.1%) and suggested regional dependence on quantification reference (creatine or otherwise). While observed variabilities in methods and reported findings suggest that 1H-MRS explorations of PTSD could benefit from methodological standardization, informing this standardization by quantitative assessment of the existing literature is currently hampered by its small size and limited scope.
Keywords: post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS), systematic review, meta-analysis, diagnostic biomarker, hippocampus, anterior cingulate cortex
Introduction
In post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), one or more exposures to a strong stressor precedes chronic disruption to sensory, emotional, and cognitive function. As currently defined in the DSM-V, PTSD takes on four clusters of symptoms that persist for at least one month following either direct or extensive indirect exposure to a traumatic event, including “actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence”: intrusive memories, dreams, sensory flashbacks, or triggered associations to psychological distress or physiological reactivity; avoidance of internal or external reminders of the trauma; negatively altered cognition and mood; and significantly altered arousal and reactivity.1
A 2017 survey over 24 countries reported trauma exposure in 70.4% of respondents, with conditional PTSD risk from 0.1% to 19.0%, depending on trauma type.2 Because trauma exposure thus does not necessitate PTSD development, a persistent question in especially post-trauma case-control analyses thereof is the degree to which group differences reflect PTSD predisposition as opposed to downstream effects of either the trauma itself or the ensuing illness. Studies involving both trauma-exposed individuals with PTSD and their genetically identical trauma-unmatched twins have been useful in unraveling these distinctions in putative causality.3 For example, hippocampal volume reductions observed in PTSD patients have also been seen in their trauma-unexposed twins, suggesting that a smaller hippocampus may predispose one to develop PTSD post-trauma.4,5 On the other hand, reduced extinction learning retention relative to trauma-exposed controls has been observed in PTSD patients but not their trauma-unmatched twins, suggesting that this factor does not reflect a genetically determined illness predisposition.6 In the absence of identical twin cohorts, some studies also attempt to separate the influences of trauma itself from those of either predisposition to or downstream effect of PTSD by distinguishing between trauma-unmatched and trauma-exposed controls. Of course, predispositions to and effects of trauma and/or PTSD are not necessarily mutually exclusive phenomena.3 For example, though reduced hippocampal volume may be a PTSD risk factor,4,5 even trauma-exposed individuals who did not develop PTSD have exhibited reduced hippocampal volumes relative to trauma-unmatched controls, suggesting an additional role for trauma itself in this phenotype.7
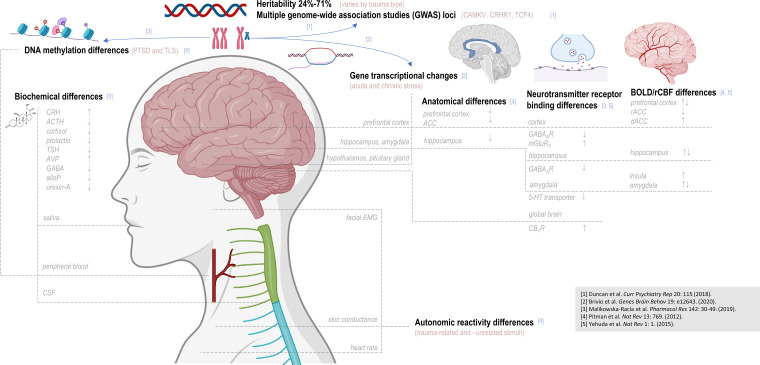
Whether cause and/or effect of illness, multitudinous differences from the molecular to the behavioral have been observed between PTSD patients and various controls (Figure 1). The following introduction is intended only as a brief integrative summary of PTSD's biological context, and the reader is referred elsewhere for comprehensive reviews of PTSD8 and its genetic associations,9 transcriptionally visible sex differences,10 interaction with brain development,11 pharmacologically manipulable manifestations,12 functional correlates in the brain,13 and biological studies in both human and animal models.3
Twin studies support PTSD heritability estimates ranging from 24% to 71% depending on cohort, with women suggesting higher heritability than men, and on trauma type, with PTSD following interpersonal trauma demonstrating higher heritability than that after accidents or natural disasters.9 Multiple disease-associated loci encompass both intergenic and potentially protein-coding sequences, supporting a polygenic origin for predisposition9 possibly modulated by developmental environment.14 PTSD-associated abnormalities in gene expression15,16 as well as methylation17,18 have also been observed.
Phenotypically, individuals with PTSD have demonstrated differential reactivity to both trauma-related and unrelated stimuli,3 including enhanced heart rate, skin conductance,19,20 ocular electromyographic responses,19 diastolic blood pressure, self-reported subjective distress,20 and cortical event-related potentials21 relative to various controls.
PTSD-associated changes in arousal state may also manifest in assorted endocrine abnormalities, including smaller pituitary gland volume;22 reduced plasma cortisol, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone,23 and GABA12 but higher cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cortisol;24 higher lymphocytic glucocorticoid receptor density;3,25 higher baseline plasma corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH);26 lower baseline plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) but increased ACTH following cognitive stress27 and reduced ACTH following dexamethasone injection;12,28 heightened ACTH release in a patient subset following exposure to opioid receptor antagonist naloxone, thought to disinhibit hypothalamic CRH from facilitating ACTH secretion;29 lower baseline plasma30 and CSF31 neuropeptide Y (NPY), a putative sympathetic nervous system modulator and endogenous anxiolytic; blunted plasma NPY30 and orbitofrontal and prefrontal cortex glucose metabolism rate response to α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist yohimbine;32 decreased plasma and CSF hypothalamic neuropeptide orexin-A;12,33 higher metabolic androgen precursor and GABAA receptor (GABAAR) antagonist dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA);3 reduced CSF GABAAR modulators allopregnanolone and pregnanolone in women;34 increased arginine vasopressin (AVP), a hormone possibly potentiating ACTH release, in men;35 and higher whole-brain cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1R) density.36 While different patient subsets may manifest abnormality in disparate neurotransmitter systems,37 many of these measures, including plasma cortisol,23 baseline plasma NPY,30 lymphocytic glucocorticoid receptor density,3,25 and CSF orexin-A,12,33 have correlated with PTSD symptom severity.
PTSD-associated aberrations in autonomic homeostasis are further accompanied by observations of anatomical, functional, and metabolic abnormalities in multiple brain regions, including those targeted by the in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) experiments forming the basis of the following review: frontal cortex including anterior cingulate cortex, basal ganglia, occipital cortex, parietal cortex and posterior cingulate gyrus, insula, temporal cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala (Supplementary Information).
Despite the unequivocal involvement of manifold biological systems in PTSD predisposition and/or evolution, still no definitive biomarker, MR-visible or otherwise, exists for its diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment monitoring. One result thereof is continued diagnostic uncertainty: Since PTSD entered the American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) third edition in 1980,38 the definitions surrounding qualifying traumas and symptoms have changed, most notably between the DSM-IV and DSM-V, resulting in diagnostic discrepancies in as many as 30% of patients in at least one analysis.8,39 Another consequence is limited pharmacotherapeutic options: Only two medications, sertraline and paroxetine, both selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are currently FDA-approved for the condition,12 though research continues on other candidates, including SSRI fluoxetine; serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) venlafaxine; dopamine and serotonin antagonist risperidone; multimodal norepinephrine modulator quetiapine; GABA and glutamate modulator topiramate;40 glutamate modulators lamotrigine and riluzole; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist ketamine; and NMDAR agonist D-cycloserine.41
Especially while rodent models of PTSD exhibit limited correspondence to human illness as defined by the DSM-V, particularly in female rodents42 despite the greater published prevalence of PTSD in women than men,43,44 as well as to specialized human prefrontal brain regions implicated in the disease,3 currently the only means of directly and noninvasively investigating the metabolic manifestation of PTSD is 1H MRS. The present study therefore serves as an update and extension to two previously published surveys of the 1H-MRS literature in PTSD, including a 2010 meta-analysis of findings in hippocampus and anterior cingulate cortex45 as well as a 2019 systematic review without meta-analysis of 24 research reports published between 1998 and 2017.46 The present report includes a systematic review of all metabolite comparisons with control and correlations published in located investigations on PTSD, as well as meta-analyses in all regions and metabolites involving at least four reported case-control comparisons therein.
Special attention is accorded in this review to study design decisions including participant sex, age, and comorbidity, as well as other methodological details like scanner field strength, voxel placement, and metabolite focus. Alongside age, sex appears to be an especially important mediator of PTSD development following trauma exposure and is therefore a salient consideration for investigations into possible mechanisms thereof. Lifetime prevalence of PTSD may be twice as high in women as men,42,43 potentially due to greater lifetime exposure to trauma, though disputed;47 greater exposure to trauma types, like sexual violence, disproportionately likely to precede PSTD development;2,9,48 and/or differential rates of conversion from trauma exposure to PSTD even once trauma frequency and type are controlled.8,49
Comorbidities, including to mood disorders and substance use, are also important to consider in PTSD research. The prevalence of, for example, major depressive disorder (MDD) in PTSD patients may be as high as 50%.50 These and other comorbidities may influence putative disease findings: While increased plasma cortisol has generally not been observed in PTSD, for example, this may not apply to individuals with comorbid MDD;3 inversely, reductions in anterior cingulate cortex 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) binding in PTSD patients relative to trauma-unmatched controls may reflect depression.51 Similarly, comorbidities like alcohol abuse52 and borderline personality disorder53 have, like PTSD, themselves been associated with reduced hippocampal volume,54 with variable confound by the former on the latter.3,55
With such methodological features under explicit consideration, the following review attempts to systematically investigate and report the current state of knowledge regarding 1H-MRS-visible in vivo brain metabolic abnormalities associated with a diagnosis of post-traumatic stress disorder.
Methods
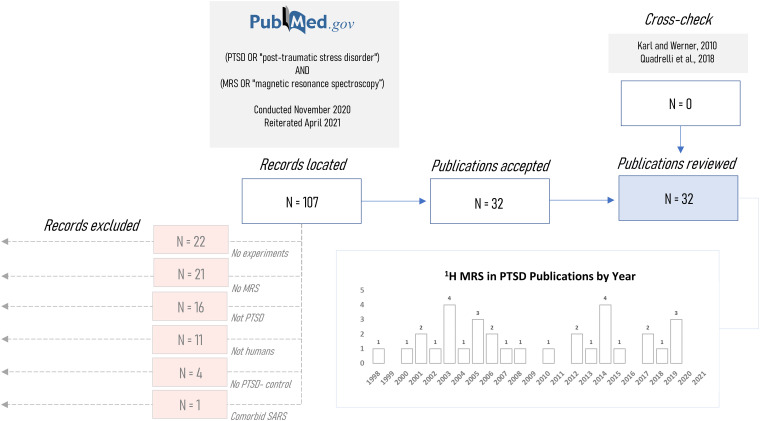
Literature review was conducted in November 2020 and updated in April 2021 according to search terms described previously,46 including all combinations of “post-traumatic stress disorder” or “PTSD” with “magnetic resonance spectroscopy” or “MRS” on PubMed®. This search yielded thirty-two unique publications that applied magnetic resonance spectroscopy to at least one individual reported to have post-traumatic stress disorder; this set was manually cross-checked with the previously mentioned 2019 systematic literature review46 and 2010 meta-analysis45 to ensure that it encompassed all studies included in these two latter reports. Studies were manually excluded if they did not report experiments (N = 22), did not use MR spectroscopy (N = 21) or examine PTSD patients (N = 16), humans (N = 11), or include a matched non-PTSD control group (N = 4), or if they involved a non-psychiatric comorbidity (N = 1) (Figure 2). One exception to these exclusion criteria was a case study included for examination of methodological variables.56 Review protocols were not registered in any database for public availability.
Figure 2.
Records processing pipeline for systematic review of published proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) investigations of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Initial records (N = 107) were located via designated search terms on PubMed based on Quadrelli et al46 following which abstracts were screened for exclusion on the basis of not being a human 1H-MRS case study of PTSD or comparative analysis with at least one healthy non-PTSD control. Remaining studies (N = 32) were cross-checked against an older systematic review46 and meta-analysis45 to confirm inclusion of all relevant studies in the present investigation. SARS: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome.
Figure 1.
Post-traumatic stress disorder has been associated with observed disparities from control over multiple biological levels of detail. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) has been associated with allelic variations at multiple genetic loci; DNA methylation patterns and gene transcription patterns have also been reported to differ with PTSD status and/or stress exposure. Disparate levels of multiple hormones and other biochemicals have been observed in saliva, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and differences in autonomic reactivity to either trauma-related or -unrelated stimuli have been suggested via measures of electromyography (EMG), skin conductance, and heart rate. Brain regions additionally examined by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS), such as the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala, have demonstrated abnormalities in volume, neurotransmitter receptor binding, and patterns of blood oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) contrast in PTSD. In assessing these reported differences, as in 1H-MRS findings, it should be noted that depending on study design, biological differences observed between PTSD patients and control may elucidate predisposition to develop PTSD, effect of trauma exposure or PTSD pathology, or all of the above. TLS: total life stress; CRH: corticotrophin-releasing hormone; ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone; TSH: thyroid-stimulating hormone; AVP: arginine vasopressin; AlloP: allopregnanolone; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; EMG: electromyogram; rCBF: regional cerebral blood flow; ACC: anterior cingulate cortex; 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin); CB1R: cannabinoid receptor type 1; rACC: rostral anterior cingulate cortex; dACC: dorsal anterior cingulate cortex. This figure was created with BioRender.com.
Data review was conducted manually by a single investigator. For completeness all reported significant and null findings in metabolite comparisons with control are described; for simplicity only significant correlations are reported. Total N-acetyl aspartate, total creatine, and total choline are named by single metabolites for simplicity.
Random-effects meta-analysis57 for the influence of PTSD on regional metabolite concentration was conducted for all metabolites and brain regions exhibiting at least four published comparisons against either trauma-exposed or trauma-unmatched groups, with or without comorbidities. When PTSD groups were compared with both trauma-unmatched and trauma-exposed controls in the same study, only comparisons with trauma-exposed controls were included for meta-analysis. When PTSD groups with and without additional comorbidities (eg, alcohol use disorder) were compared against distinct matched controls, both comparisons were included in meta-analysis. All statistics were conducted in R version 4 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Results
Methodological Overview
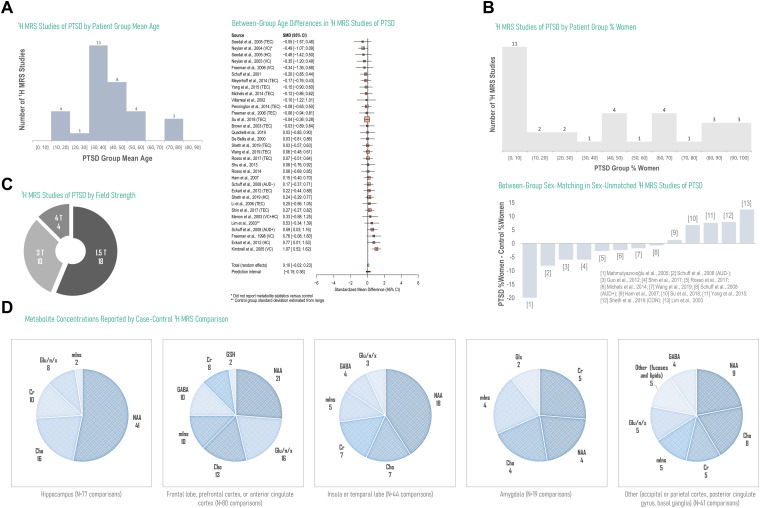
N = 33 PTSD versus control comparisons from N = 28 studies were assessed for average age of the PTSD group as well as age-matching between PTSD and control. Three studies did not provide patient group age means58–60 and one was a case study with no control;56 these were excluded from age analysis. PTSD group average ages most frequently represented the 30 to 40 year range and demonstrated a marginal trend to increase relative to control (random-effects model standardized mean difference 0.10 ± 0.062, P = .10) (Figure 3A; Supplementary Tables 1 and 2). While N = 10 studies not including the case study on a single male patient56 included all-male PTSD cohorts, N = 3 studies included all-female PTSD cohorts, with a median 2% decrease in control versus PTSD percent women among those N = 13 studies that did not exhibit sex-matched groups (Figure 3B; Supplementary Tables 3 and 4). N = 4 of 32 studies acquired data at 4 Tesla field strength, while none had been conducted at 7 Tesla or above (Figure 3C; Supplementary Table 5). N-acetyl aspartate (N = 93), choline (N = 48), and creatine (N = 35) comprised the majority of metabolite concentrations reported, particularly in non-cortical voxels, with fewer comparisons involving glutamate and/or glutamine (N = 34), myoinositol (N = 26), GABA (N = 18), glutathione (N = 2), or other resonances including fucoses and lipids (N = 5) (Figure 3D).
Figure 3.
Overview of current literature on 1H MRS in PTSD by study design, hardware, and reported significant or null findings by metabolite and brain region. Currently published reports on 1H MRS in PTSD cover a broad range of patient ages, with a smaller relative number of investigations into pediatric or geriatric participants, and generally demonstrate small disparities in age between groups under study for analyses reporting experimental group ages (random-effects standardized mean difference SMD 0.10, 95% confidence interval CI −0.02-0.23, P = .08; N = 33 comparisons from 28 studies) (A). The number of 1H-MRS analyses examining male-only participants is higher than the reverse, with an additional skew toward more male-saturated control groups in the few studies that demonstrated uneven between-group sex-matching (B). The majority of existing 1H-MRS investigations of PTSD have been conducted at 1.5 and 3T, field strengths that do not typically enable the straightforward separation of signals from neurotransmitter glutamate from those of its metabolic byproduct glutamine (C). Especially in hippocampus, for which voxel placement and size may contribute to challenging spectral quantification of lower-SNR metabolites, the 1H-MRS literature on PTSD is currently dominated by N-acetyl aspartate (NAA), free cholines (Cho), and creatine (Cr), with fewer investigations on neurotransmitters glutamate (Glu) and GABA or endogenous antioxidant glutathione (GSH) despite putative roles in excitatory/inhibitory balance and oxidative stress potentially important to regional anatomical and functional alterations previously observed in PTSD (D). D based on data reported in Tables 3, 5, and 6; see Supplementary Information for data tables underlying A-C. Gln: glutamine; Glx: glutamate + glutamine. TEC: trauma-exposed control; HC: healthy control; VC: veteran control; AUD: alcohol use disorder.
Explicitly reported consideration of comorbidities was also evaluated, including exclusion or other controls for comorbid psychiatric conditions (Table 1) and past or current use of alcohol, nicotine, or other substances (Table 2) in participants with PTSD.
Table 1.
1H MRS in PTSD Study Design Consideration of Psychiatric Comorbidities.
| Study Design Consideration | N | Citations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No exclusion from PTSD group due to non-substance-related psychiatric condition other than dementia | 8 | 60–67 | |
| No reported evaluation for psychiatric comorbidity | 3 | 60,65,67 | |
| PTSD participants reported current or past mood or anxiety disorders | 3 | 61,62,66 | |
| PTSD participants no difference from control in depression or overall psychopathology | 1 | 64 | |
| PTSD participants trend to greater depression symptoms but not state-trait anxiety than control | 1 | 63 | |
| Exclusion from PTSD group due to ≥1 past and/or current non-substance-related psychiatric condition other than dementia | 24 | 54,56,58,59,68–87 | |
| Schizophrenia, schizoaffective, bipolar, and/or psychotic disorder | 11 | 59,68,70–72,76,77,79–82 | |
| Psychiatric disorder including major depression | 5 | 58,78,84,85,87 | |
| Axis 1 disorder including major depression | 3 | 56,74,75 | |
| Psychiatric disorder excluding major depression | 2 | 54,83 | |
| Axis 1 disorder excluding major depression | 2 | 73,86 | |
| Autism | 2 | 69,70 | |
| Suicidal intention | 2 | 76,77 | |
| Anorexia | 1 | 70 | |
| Antisocial or borderline personality disorder | 1 | 75 | |
| Documented past and/or current comorbidities in PTSD group | 18 | 56,59,61,62,66,69–71,73,75–80,82,83,87 | |
| Major depression | 13 | 61,62,66,70,71,73,75,78–80,82,83,87 | |
| PTSD higher depression scores than control | 4 | 66,69,76,77 | |
| PTSD higher anxiety scores than control | 3 | 69,76,77 | |
| Panic disorder | 5 | 61,62,66,75,78 | |
| Generalized anxiety disorder | 2 | 61,75 | |
| Social phobia | 2 | 61,75 | |
| Somatoform disorder | 1 | 75 | |
| Oppositional defiant disorder | 1 | 70 | |
| Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) | 1 | 70 | |
| Borderline personality disorder | 1 | 59 | |
| Dysthymia | 1 | 61 | |
| Specific phobia | 1 | 61 | |
| Depersonalization disorder | 1 | 61 | |
| Separation anxiety disorder | 1 | 56 | |
1H MRS: proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy; PTSD: post-traumatic stress disorder.
Table 2.
1H MRS in PTSD Study Design Consideration of Comorbid Alcohol, Nicotine, or other Substance Use.
| Study Design Consideration | N | Citations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol use disorder, dependence, or abuse | |||
| Exclusion from PTSD group for lifetime history of alcohol use disorder, dependence, or abuse | 5 | 54,58,65,66,75 | |
| Exclusion from PTSD group for current, recent, or chronic but not lifetime history of alcohol use disorder, dependence, or abuse | 17 | 59,60,68,71–74,76–78,80,81,83–87 | |
| Surveyed and compared alcohol use severity between PTSD and control | 1 | 64 | |
| Reported current heavy drinking among PTSD participants | 1 | 67 | |
| Reported consideration of general substance but not specifically alcohol abuse | 6 | 56,62,69,70,79,82 | |
| Did not report explicit consideration of alcohol or general substance abuse | 2 | 61,63 | |
| Nicotine, tobacco, or smoking | |||
| Exclusion criteria from PTSD group pertaining to nicotine, tobacco, or smoking | 3 | 62,73,82 | |
| Reported but did not control for nicotine, tobacco, or smoking | 4 | 64,67,75,77 | |
| Statistically considered effect of nicotine, tobacco, or smoking on metabolites | 2 | 61,76 | |
| Reported consideration of general substance use but not specifically nicotine, tobacco, or smoking | 20 | 54,56,58,70,8059,60,68,69,71,72,74,78,79,81,83–87 | |
| Did not report consideration of nicotine, tobacco, or smoking or general substance use | 3 | 63,65,66 | |
| General drug or substance use | |||
| Exclusion from PTSD group for lifetime history of drug or substance use, abuse, or dependence | 3 | 54,75,79 | |
| Exclusion from PTSD group for current, recent, or chronic but not necessarily lifetime history of drug or substance use, abuse, or dependence | 19 | 59,60,62,67,68,71,72,74,76–78,80–87 | |
| Exclusion from PTSD group for psychotropic drugs or medication but not substance abuse | 5 | 56,58,69,70,73 | |
| No exclusion for substance abuse but confirmed group similarity in drug abuse histories | 1 | 64 | |
| Did not report consideration of drug or substance use, abuse, or dependence | 4 | 61,63,65,66 | |
1H MRS: proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy; PTSD: post-traumatic stress disorder.
Frontal Cortex (Non-ACC)
In humans the frontal cortex comprises the six cortical layers of the brain's frontal lobe and is thought to be involved in numerous executive processes integrating and mediating activity in other brain regions. Prefrontal cortex (PFC) regions in particular have been implicated in PTSD for their connections with the hippocampus and amygdala that together regulate fear learning and memory,13 and it has been hypothesized that glutamatergic excitotoxicity in this area may play a role in PTSD pathogenesis.61
Complementarily to a number of non-1H-MRS findings in the frontal cortex, in PTSD multiple examinations of non-anterior cingulate prefrontal cortex N-acetyl aspartate : creatine (NAA/Cr),61,68 choline : creatine (Cho/Cr),68 glutamate : glutamine (Glu/Gln),61 GABA/Cr,61 and glutathione : creatine (GSH/Cr)61 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 3 and 4; see Supplementary Information for a detailed textual summary of findings).
Figure 4.
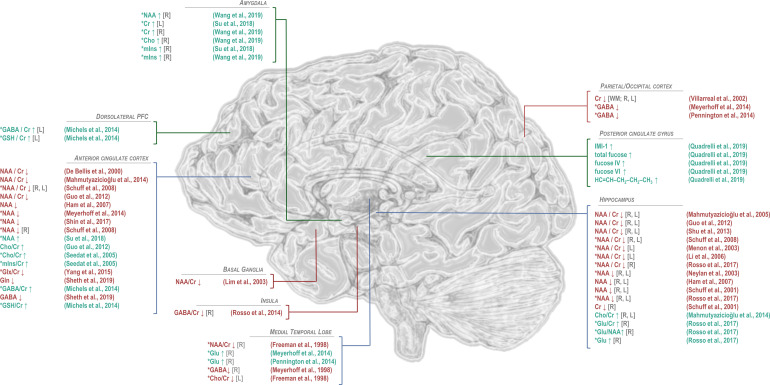
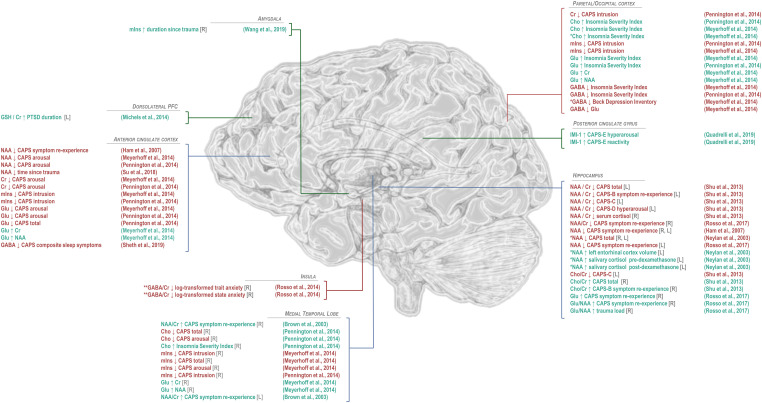
Findings of significant difference from control in 1H-MRS-visible brain metabolites for patients with post-traumatic stress disorder. General decreases in N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) in PTSD relative to trauma-exposed or -unmatched control groups have been observed predominantly in anterior cingulate cortex and hippocampus, while NAA increases in the amygdala have also been reported by one study. Differences from control in choline (Cho), when observed, have tended to be positive, also in anterior cingulate cortex and hippocampus, while decreases in choline have been observed in the medial temporal lobe. Regional effects of PTSD on common quantification reference metabolite creatine (Cr) have varied by region, with decreases reported in hippocampus and occipital cortex and increases in amygdala. Myoinositol (mIns) has been reported to increase in both anterior cingulate cortex and amygdala. Only a few studies have examined excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate to show increases in medial temporal lobe and hippocampus but decreases in both glutamate + glutamine (Glx) and glutamine (Gln) in anterior cingulate cortex. Reported alterations in GABA have similarly varied by region, with decreases reported in insula, medial temporal lobe, and parieto-occipital cortex; increases in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; and mixed findings in anterior cingulate cortex. Only two published findings have been reported for glutathione (GSH), both increases, in dorsolateral prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortices. Studies of additional metabolites, such as sugars and lipids measurable by 2D J-resolved proton spectroscopy reported in Quadrelli et al,79 have been limited. *PTSD versus control groups that included trauma-exposed and/or military veteran individuals. GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; Glu: glutamate; IMI-1: imidazole from histamine, histidine, and homocarnosine.
Table 3.
Controlled In Vivo 1H-MRS Findings for PTSD in Frontal Cortex and Basal Ganglia Metabolites.
| Metabolite | Region | Control | PTSD - control | Citation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal cortex (non-ACC) | |||||
| NAA/Cr | Frontal periventricular white matter | HC | -- | 68 | |
| NAA/Cr | Left dorsolateral PFC | TEC | -- | 61 | |
| Cho/Cr | Frontal periventricular white matter | HC | -- | 68 | |
| Glu/Gln | Left dorsolateral PFC | TEC | -- | 61 | |
| GABA/Cr | Left dorsolateral PFC | TEC | ↑ | 61 | |
| GSH/Cr | Left dorsolateral PFC | TEC | ↑ | 61 | |
| Frontal cortex (ACC) | |||||
| NAA/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | ↓ | 70 | |
| NAA/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | ↓ | 58 | |
| NAA/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | ↓ | 60 | |
| NAA/Cr | Right anterior cingulate cortex | TEC + AUD + VCb | ↓ | 71 | |
| NAA/Cr | Left anterior cingulate cortex | TEC + AUD + VCb | ↓ | 71 | |
| NAA/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 62 | |
| NAA/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 61 | |
| NAA/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 72 | |
| NAA/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 73 | |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | ↑ | 74 | |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | ↓ | 75 | |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | ↓ | 76 | |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | ↓ | 63 | |
| NAA | Right anterior cingulate cortex | TEC + AUD + VCb | ↓ | 71 | |
| NAA | Left anterior cingulate cortex | TEC + AUD + VCb | ↓a | 71 | |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | ↓a | 77 | |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 69 | |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 | |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 69 | |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 75 | |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 77 | |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 74 | |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 76 | |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 63 | |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 | |
| Cho/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | ↑ | 58 | |
| Cho/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | ↑ | 72 | |
| Cho/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 70 | |
| Cho/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 60 | |
| Cho/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 73 | |
| Cho | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 75 | |
| Cho | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 69 | |
| Cho | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 77 | |
| Cho | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| Cho | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 76 | |
| Cho | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 74 | |
| Cho | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD + AUD | ↑ | 77 | |
| mIns/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | ↑ | 72 | |
| mIns/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 73 | |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 69 | |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 75 | |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 74 | |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 77 | |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 76 | |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 63 | |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD + AUD | ↑ | 77 | |
| Glx/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | ↓ | 73 | |
| Glx | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 74 | |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 69 | |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 77 | |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 76 | |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 63 | |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD + AUD | ↑ | 77 | |
| Gln | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | ↓ | 69 | |
| Gln | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| Glu/GABA | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | ↑a | 69 | |
| Glu/GABA | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| Glu/Gln | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 69 | |
| Glu/Gln | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 61 | |
| Glu/Gln | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| GABA/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | ↑ | 61 | |
| GABA/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 62 | |
| GABA | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | ↓ | 69 | |
| GABA | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 77 | |
| GABA | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 76 | |
| GABA | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| GABA | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD + AUD | ↓ | 77 | |
| GABA/Gln | Anterior cingulate cortex | HC | -- | 69 | |
| GABA/Gln | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | -- | 69 | |
| GSH/Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | TEC | ↑ | 61 | |
| Basal ganglia | |||||
| NAA/Cr | Left basal ganglia | HC | ↓ | 68 | |
| Cho/Cr | Left basal ganglia | HC | -- | 68 | |
Reported as marginally significant trend.
PTSD group also involved AUD + participants.
1H MRS: proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy; PTSD: post-traumatic stress disorder; PFC: prefrontal cortex; ACC: anterior cingulate cortex; HC: trauma-unmatched control; TEC: trauma-exposed control; VC: veteran control; AUD: alcohol use disorder: NAA: N-acetyl aspartate; Cr: creatine; Cho: choline; mIns: myoinositol; Glx: glutamate + glutamine; Glu: glutamate; Gln: glutamine; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; GSH: glutathione.
Table 4.
Correlations with In Vivo 1H-MRS-Visible Frontal, Occipital, and Parietal Cortex Metabolites Reported in PTSD.
| Metabolite | Region | Group | Variable | Correlation | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal cortex (non-ACC) | |||||
| GSH/Cr | Left dorsolateral PFC | PTSD | PTSD duration | ↑ | 61 |
| Frontal cortex (ACC) | |||||
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↓ | 75 |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS arousal score | ↓ | 76 |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS arousal score | ↓ | 77 |
| NAA | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | Time since trauma | ↓ | 74 |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS arousal score | ↓ | 76 |
| Cr | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS arousal score | ↓ | 77 |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS intrusion score | ↓ | 76 |
| mIns | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS intrusion score | ↓ | 77 |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS arousal score | ↓ | 76 |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS arousal score | ↓ | 77 |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | CAPS total score | ↓ | 77 |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | Anterior cingulate cortex Cr | ↑ | 76 |
| Glu | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | Anterior cingulate cortex NAA | ↑ | 76 |
| GABA | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | Insomnia Severity Index | ↓a | 76 |
| GABA | Anterior cingulate cortex | PTSD | Composite CAPS sleep measure | ↓ | 69 |
| Occipital cortex | |||||
| Cr | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | CAPS intrusion score | ↓ | 77 |
| Cho | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | Insomnia Severity Index | ↑ | 77 |
| Cho | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | Insomnia Severity Index | ↑ | 76 |
| Cho | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD + TEC | Insomnia Severity Index | ↑ | 76 |
| mIns | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | CAPS intrusion score | ↓ | 76 |
| mIns | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | CAPS intrusion score | ↓ | 77 |
| Glu | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | Insomnia Severity Index | ↑ | 76 |
| Glu | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | Insomnia Severity Index | ↑ | 77 |
| Glu | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | Parieto-occipital cortex Cr | ↑ | 76 |
| Glu | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | Parieto-occipital cortex NAA | ↑ | 76 |
| GABA | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | Insomnia Severity Index | ↓ | 76 |
| GABA | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | Insomnia Severity Index | ↓ | 77 |
| GABA | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD + TEC | Beck Depression Inventory score | ↓ | 76 |
| GABA | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD | Parieto-occipital cortex glutamate | ↓ | 76 |
| Parietal cortex | |||||
| IMI-1 | Posterior cingulate gyrus | PTSD | CAPS-E hyperarousal score | ↑ | 79 |
| IMI-1 | Posterior cingulate gyrus | PTSD | CAPS-E reactivity score | ↑ | 79 |
Reported as marginally significant trend.
1H MRS: proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy; PTSD: post-traumatic stress disorder; ACC: anterior cingulate cortex; TEC: trauma-exposed control; NAA: N-acetyl aspartate; Cr: creatine; Cho: choline; mIns: myoinositol; Glu: glutamate; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; CAPS: clinician-administered PTSD scale; IMI-1: imidazole from histamine, histidine, and homocarnosine.
Anterior Cingulate Cortex
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) overlaps with portions of both ventromedial and dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, both of which have demonstrated structural and functional abnormality in PTSD.13 It is thought that with roles in fear conditioning and extinction the dorsal ACC (dACC) in particular could contribute to PTSD vulnerability and/or pathogenesis,69 with local functional abnormalities possibly contributing to disruptions in the salience network leading to hypervigilance.88
In PTSD comparisons against control and/or correlation analyses of anterior cingulate NAA/Cr,58,60–62,70–73 NAA,63,69,71,74–77 creatine,63,69,74–77 Cho/Cr,58,60,69,70,72–77 myoinositol : creatine (mIns/Cr),63,69,72–77 (glutamate + glutamine) : creatine (Glx/Cr),73 Glx,63,69,74,76,77 glutamate,76,77 glutamine,69 Glu/Gln,61,69 GABA/Cr,61,62 GABA,69,76,77 GABA/Gln,69 and GSH/Cr61 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 3 and 4; Supplementary Information).
Figure 5.
Findings of significant correlation or regression coefficient between 1H-MRS-measured brain metabolites with each other or other measures in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Because proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) experiments measure multi-functional small molecules in large (>1 cm3) heterogeneous voxels containing many different types of tissue, cell, and associated functional circuitry, correlations between measured metabolite concentrations and anatomical or cognitive measures or clinically relevant variables like symptom reports are useful for interpreting other putative metabolite findings in 1H-MRS studies of disease. The majority of such reported correlations have pertained to clinician-administered PTSD scale (CAPS) indices like arousal, intrusion, symptom re-experience, or total score. Other correlates have included self-reported insomnia indices, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-measured brain region volumes, memory performance, and other metabolites, though the latter may also sometimes indicate relationships introduced by quantification method rather than findings of biological significance. *In combined PTSD and control groups including trauma-exposed and/or military veteran individuals; **In combined PTSD and trauma-unmatched control groups. NAA: N-acetyl aspartate; Cr: creatine; mIns: myoinositol; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; Glu: glutamate; GSH: glutathione; Cho: total choline; IMI-1: imidazole from histamine, histidine, and homocarnosine.
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia are a cluster of subcortical grey-matter nuclei comprising the striatum (caudate and putamen) and the globus pallidus.89
One previous proton spectroscopy study has targeted this region due to its proximity to the temporal lobes, also linked with a number of PTSD-associated metabolic abnormalities (below) while maintaining greater separation from the hippocampus enabling larger voxel size without partial-volume contamination from this other grey-matter region, as well as for its putative vulnerability to hypoxic damage and exposure to toxic metals.68 In this study findings against control from left basal ganglia NAA/Cr68 and Cho/Cr68 were reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 3 and 4; Supplementary Information).
Occipital Cortex
The occipital cortex is a large posterior cortical region thought to predominantly comprise circuitry responsible for visual processing. While PTSD-specific hypotheses regarding this brain area are sparse and it has therefore served as a control region for hypothesis-driven research,72,78 metabolite concentration abnormalities in parieto-occipital regions have been reported in anxiety and mood disorders, also impelling their targeted exploration in PTSD.76,77 In addition, the occipital cortex tends to lie close to radiofrequency receive coils and does not exhibit the steep transitions in magnetic susceptibility between tissue and air cavities that can influence data acquired from temporal and especially frontal regions, justifying its 1H-MRS examination for methodological convenience.
In PTSD comparative and/or correlation analyses of occipital or parieto-occipital cortex NAA/Cr,72 NAA,76–78 creatine,76–78 Cho/Cr,72 choline,76–78 mIns/Cr,72 myoinositol,76,77 glutamate,76,77 and GABA76,77 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 4 and 5; Supplementary Information).
Table 5.
Controlled In Vivo 1H-MRS Findings for PTSD in Occipital and Parietal Cortex Metabolites.
| Metabolite | Region | Control | PTSD - control | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occipital cortex | ||||
| NAA/Cr | Left occipital grey matter | TEC | -- | 72 |
| NAA | Left occipital white matter | HC | -- | 78 |
| NAA | Right occipital white matter | HC | -- | 78 |
| NAA | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| NAA | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 76 |
| NAA | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 |
| Cr | Left occipital white matter | HC | ↓ | 78 |
| Cr | Right occipital white matter | HC | ↓ | 78 |
| Cr | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| Cr | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 76 |
| Cr | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 |
| Cho/Cr | Left occipital grey matter | TEC | -- | 72 |
| Cho | Left occipital white matter | HC | -- | 78 |
| Cho | Right occipital white matter | HC | -- | 78 |
| Cho | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 76 |
| Cho | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| Cho | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 |
| mIns/Cr | Left occipital grey matter | TEC | -- | 72 |
| mIns | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| mIns | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 76 |
| mIns | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 |
| Glu | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| Glu | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | -- | 76 |
| Glu | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 |
| GABA | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | ↓ | 77 |
| GABA | Parieto-occipital cortex | TEC | ↓ | 76 |
| GABA | Parieto-occipital cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 |
| Parietal cortex | ||||
| NAA/Cr | Right parietal periventricular white matter | HC | -- | 68 |
| NAA | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | -- | 79 |
| Cho/Cr | Right parietal periventricular white matter | HC | -- | 68 |
| mIns | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | -- | 79 |
| Glu | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | -- | 79 |
| Gln | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | -- | 79 |
| GABA | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | -- | 79 |
| IMI-1 | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | ↑ | 79 |
| total fucose | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | ↑ | 79 |
| fucose IV | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | ↑ | 79 |
| fucose VI | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | ↑ | 79 |
| lipid HC = CH–CH2–CH2–CH3 | Posterior cingulate gyrus | HC | ↑ | 79 |
1H MRS: proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy; PTSD: post-traumatic stress disorder; HC: trauma-unmatched control; TEC: trauma-exposed control; AUD: alcohol use disorder: NAA: N-acetyl aspartate; Cr: creatine; Cho: choline; mIns: myoinositol; Glu: glutamate; Gln: glutamine; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; IMI-1: imidazole from histamine, histidine, and homocarnosine.
Parietal Cortex
The parietal cortex, posterior to the frontal lobe and superior to the occipital lobe, is a large area of associative cortex involved in somatosensory integration, motor planning, and attention, among other functions.90 While, like the occipital cortex, the parietal cortex has been implicated in a minimum of hypothesis-driven 1H-MRS research into PTSD, it has been involved in one study of regional periventricular white matter.68 It also envelops the posterior cingulate gyrus, the traditionally preferred target of 2D COrrelated SpectroscopY (COSY) for its proximity to the radiofrequency receive hardware employed.79
In PTSD comparative and/or correlation analyses of parietal cortex or posterior cingulate NAA/Cr,68 NAA,79 Cho/Cr,68 glutamate,79 glutamine,79 myoinositol,79 GABA,79 the imidazole moiety visible on histamine, histidine, and homocarnosine (IMI-1),79 fucosylated glycans (including t-fucose, fucose IV, and fucose VI),79 and lipid HC = CH–CH2–CH2–CH379 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 4 and 5; Supplementary Information).
Insula
The insula correspond to Brodmann Areas 13 through 16, each located deep in the bilateral Sylvian fissures beneath the corresponding opercula, and are connected with several brain regions demonstrating reported associations with PTSD, including the prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, and amygdala.91 They are also thought to be involved in emotional recall and have, among other regions, demonstrated regional cerebral blood flow signals correlating positively with severity of PTSD-associated flashbacks,92 justifying their exploration by 1H MRS.54
In PTSD comparative and/or correlation analyses of right insular NAA/Cr,54,62 NAA,54 creatine,54 and GABA/Cr,62 as well as left insular NAA/Cr,54 NAA,54 and creatine54 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 6 and 7; Supplementary Information).
Table 6.
Controlled In Vivo Proton 1H-MRS Findings for PTSD in Insular, Hippocampal, and Amygdalar Metabolites.
| Metabolite | Region | Control | PTSD - control | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insula | ||||
| NAA/Cr | Right insula | HC | -- | 54 |
| NAA/Cr | Right insula | TEC | -- | 54 |
| NAA/Cr | Right insula | TEC | -- | 62 |
| NAA | Right insula | HC | -- | 54 |
| NAA | Right insula | TEC | -- | 54 |
| Cr | Right insula | HC | -- | 54 |
| Cr | Right insula | TEC | -- | 54 |
| GABA/Cr | Right insula | HC | ↓ | 62 |
| NAA/Cr | Left insula | HC | -- | 54 |
| NAA/Cr | Left insula | TEC | -- | 54 |
| NAA | Left insula | HC | -- | 54 |
| NAA | Left insula | TEC | -- | 54 |
| Cr | Left insula | HC | -- | 54 |
| Cr | Left insula | TEC | -- | 54 |
| Temporal lobe | ||||
| NAA/Cr | Right medial temporal lobe | VC | ↓ | 80 |
| NAA/Cr | Right medial temporal lobe | VC | -- | 64 |
| NAA/Cr | Right medial temporal lobe | TEC | -- | 65 |
| NAA | Right temporal cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| NAA | Right temporal cortex | TEC | -- | 76 |
| NAA | Right temporal cortex | PTSD + AUD | ↑ | 77 |
| Cr | Right temporal cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| Cr | Right temporal cortex | TEC | -- | 76 |
| Cr | Right temporal cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 |
| Cho/Cr | Right medial temporal lobe | VC | -- | 80 |
| Cho/Cr | Right medial temporal lobe | TEC | -- | 65 |
| Cho | Right temporal cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| Cho | Right temporal cortex | TEC | -- | 76 |
| Cho | Right temporal cortex | PTSD + AUD | ↑ | 77 |
| mIns/Cr | Right medial temporal lobe | TEC | -- | 65 |
| mIns | Right temporal cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| mIns | Right temporal cortex | TEC | -- | 76 |
| mIns | Right temporal cortex | PTSD + AUD | ↑a | 77 |
| Glu | Right temporal cortex | TEC | ↑ | 77 |
| Glu | Right temporal cortex | TEC | ↑ | 76 |
| Glu | Right temporal cortex | PTSD + AUD | ↑ | 77 |
| GABA | Right temporal cortex | TEC | ↓ | 76 |
| GABA | Right temporal cortex | TEC | -- | 77 |
| GABA | Right temporal cortex | PTSD + AUD | -- | 77 |
| NAA/Cr | Left medial temporal lobe | TEC | ↓a | 65 |
| NAA/Cr | Left medial temporal lobe | VC | -- | 80 |
| NAA/Cr | Left medial temporal lobe | VC | -- | 64 |
| Cho/Cr | Left medial temporal lobe | VC | ↓ | 80 |
| Cho/Cr | Left medial temporal lobe | TEC | -- | 65 |
| mIns/Cr | Left medial temporal lobe | TEC | -- | 65 |
| Hippocampus | ||||
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 58 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 60 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 81 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | TEC + AUD + VCb | ↓ | 71 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | TEC | ↓ | 82 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 54 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | VC | -- | 66 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | VC + HC | -- | 67 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | TEC | -- | 54 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | TEC | -- | 66 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | TEC | -- | 83 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 84 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 75 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | VC | ↓ | 85 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | TEC | ↓ | 82 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 78 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 54 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | TEC + AUD + VCb | -- | 71 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | TEC | -- | 54 |
| NAA/Cho | Right hippocampus | TEC | -- | 83 |
| Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 84 |
| Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 54 |
| Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 75 |
| Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 78 |
| Cr | Right hippocampus | TEC | -- | 54 |
| Cho/Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | ↑ | 60 |
| Cho/Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 58 |
| Cho/Cr | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 81 |
| Cho/Cr | Right hippocampus | VC | -- | 66 |
| Cho/Cr | Right hippocampus | TEC | -- | 66 |
| Cho | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 75 |
| Cho | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 84 |
| Cho | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 78 |
| mIns | Right hippocampus | HC | -- | 75 |
| Glu/Cr | Right hippocampus | TEC | ↑ | 82 |
| Glu/NAA | Right hippocampus | TEC | ↑ | 82 |
| Glu | Right hippocampus | TEC | ↑ | 82 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 58 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 60 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 81 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | TEC + AUD + VCb | ↓ | 71 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | VC + HC | ↓ | 67 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | TEC | ↓ | 83 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 54 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | VC | -- | 66 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 54 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 66 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 82 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | HC | ↓a | 78 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 84 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | HC | ↓ | 75 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | VC | ↓ | 85 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | TEC | ↓ | 82 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 54 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | TEC + AUD + VCb | -- | 71 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 54 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 63 |
| NAA/Cho | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 83 |
| Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | ↓a | 78 |
| Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 54 |
| Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 75 |
| Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 84 |
| Cr | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 54 |
| Cho/Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | ↑ | 60 |
| Cho/Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 58 |
| Cho/Cr | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 81 |
| Cho/Cr | Left hippocampus | VC | -- | 66 |
| Cho/Cr | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 66 |
| Cho | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 78 |
| Cho | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 84 |
| Cho | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 75 |
| mIns | Left hippocampus | HC | -- | 75 |
| Glx | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 63 |
| Glu/Cr | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 82 |
| Glu/NAA | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 82 |
| Glu | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 82 |
| Glu | Left hippocampus | TEC | -- | 63 |
| Amygdala | ||||
| NAA | Right amygdala | TEC | ↑ | 86 |
| NAA | Right amygdala | TEC | -- | 74 |
| Cr | Right amygdala | TEC | ↑ | 86 |
| Cr | Right amygdala | TEC | -- | 74 |
| Cho | Right amygdala | TEC | ↑ | 86 |
| Cho | Right amygdala | TEC | -- | 74 |
| mIns | Right amygdala | TEC | ↑ | 74 |
| mIns | Right amygdala | TEC | ↑ | 86 |
| Glx | Right amygdala | TEC | -- | 74 |
| NAA | Left amygdala | TEC | -- | 74 |
| NAA | Left amygdala | TEC | -- | 86 |
| Cr | Left amygdala | TEC | ↑ | 74 |
| Cr | Left amygdala | TEC | -- | 86 |
| Cr | Left amygdala | BPD | -- | 59 |
| Cho | Left amygdala | TEC | -- | 86 |
| Cho | Left amygdala | TEC | -- | 74 |
| mIns | Left amygdala | TEC | -- | 74 |
| mIns | Left amygdala | TEC | -- | 86 |
| Glx | Left amygdala | TEC | -- | 74 |
Reported as marginally significant trend.
PTSD group also involved AUD + participants.
1H MRS: proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy; PTSD: post-traumatic stress disorder; HC: trauma-unmatched control; TEC: trauma-exposed control; VC: veteran control; AUD: alcohol use disorder: NAA: N-acetyl aspartate; Cr: creatine; Cho: choline; mIns: myoinositol; Glx: glutamate + glutamine; Glu: glutamate; Gln: glutamine; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; BPD: borderline personality disorder.
Table 7.
Correlations with In Vivo 1H-MRS-Visible Insular, Hippocampal, and Amygdalar Metabolites Reported in PTSD.
| Metabolite | Region | Group | Variable | Correlation | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insula | |||||
| GABA/Cr | Right insula | PTSD + HC | Log-transformed trait anxiety | ↓ | 62 |
| GABA/Cr | Right insula | PTSD + HC | Log-transformed state anxiety | ↓ | 62 |
| Temporal lobe | |||||
| NAA/Cr | Right medial temporal lobe | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↑ | 65 |
| Cho | Right temporal cortex | PTSD | CAPS total score | ↓ | 77 |
| Cho | Right temporal cortex | PTSD | CAPS arousal score | ↓ | 77 |
| Cho | Right temporal cortex | PTSD | Insomnia Severity Index | ↑ | 77 |
| mIns | Right temporal cortex | PTSD | CAPS intrusion score | ↓ | 76 |
| mIns | Right temporal cortex | PTSD | CAPS total score | ↓ | 76 |
| mIns | Right temporal cortex | PTSD | CAPS arousal score | ↓ | 76 |
| Glu | Right temporal cortex | PTSD | Right temporal cortex Cr | ↑ | 76 |
| Glu | Right temporal cortex | PTSD | Right temporal cortex NAA | ↑ | 76 |
| NAA/Cr | Left medial temporal lobe | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↑ | 65 |
| Hippocampus | |||||
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | PTSD | Serum cortisol | ↓ | 81 |
| NAA/Cr | Right hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↓ | 82 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↓ | 75 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↓a | 82 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | PTSD + VC | CAPS total score | ↓ | 85 |
| NAA | Right hippocampus | PTSD + VC | Right entorhinal cortex volume | ↑a | 85 |
| Cho/Cr | Right hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS total score | ↑ | 81 |
| Cho/Cr | Right hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS-B symptom re-experience score | ↑ | 81 |
| Glu | Right hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↑ | 82 |
| Glu/NAA | Right hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↑ | 82 |
| Glu/NAA | Right hippocampus | PTSD | Trauma load | ↑ | 82 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS total score | ↓ | 81 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS-B symptom re-experience score | ↓ | 81 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS-C score | ↓ | 81 |
| NAA/Cr | Left hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS-D hyperarousal symptoms | ↓ | 81 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↓ | 75 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS symptom re-experience score | ↓ | 82 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | PTSD + VC | CAPS total score | ↓ | 85 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | PTSD + VC | Left entorhinal cortex volume | ↑ | 85 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | PTSD + VC | Pre-dexamethasone cortisol | ↑ | 85 |
| NAA | Left hippocampus | PTSD + VC | Post-dexamethasone cortisol | ↑ | 85 |
| Cho/Cr | Left hippocampus | PTSD | CAPS-C score | ↓ | 81 |
| Amygdala | |||||
| mIns | Right amygdala | Pediatric PTSD | Duration since trauma | ↑ | 86 |
| NAA | Left amygdala | Pediatric PTSD | Age | ↑a | 86 |
Reported as marginally significant trend.
1H MRS: Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy; PTSD: Post-traumatic stress disorder; HC: trauma-unmatched control; VC: veteran control; TEC: trauma-exposed control; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; NAA: N-acetyl aspartate; Cr: creatine; Cho: choline; mIns: myoinositol; Glu: glutamate; CAPS: clinician-administered PTSD scale.
Temporal Lobe (Right)
The temporal lobe is the seat of both the hippocampus and the amygdala, subcortical structures that have both demonstrated a number of structural and functional abnormalities in PTSD (Supplementary Information).
The subcortical hippocampus within the medial temporal lobe has generally been the target of proton spectroscopy voxels located in the temporal lobe, including within one group choosing the nomenclature “temporal cortex” instead.76,77 In PTSD comparative and/or correlation analyses of right temporal lobe NAA/Cr,64,65,80 NAA,76,77 creatine,76,77 Cho/Cr,65,80 choline,76,77 mIns/Cr,65 myoinositol,76,77 glutamate,76,77 and GABA76,77 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 6 and 7; Supplementary Information).
Temporal Lobe (Left)
In PTSD comparative and/or correlation analyses of left temporal lobe NAA/Cr,64,65,80 Cho/Cr,65,80 and mIns/Cr65 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 6 and 7; Supplementary Information).
Hippocampus (Right)
The hippocampus is a subcortical structure implicated in the encoding of spatial information as well as episodic memories.93
Complementary to a number of other non-1H-MRS investigations in this region, comparative and/or correlation 1H-MRS analyses of right hippocampal NAA/Cr,54,58,60,66,67,71,81–83 NAA,54,71,75,78,82,84,85 NAA/Cho,83 creatine,54,75,78,84 Cho/Cr,58,60,66,81 choline,75,78,84 myoinositol,75 Glu/Cr,82 Glu/NAA,82 and glutamate82 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 6 and 7; Supplementary Information).
Hippocampus (Left)
In PTSD comparative and/or correlation analyses of left hippocampal NAA/Cr,54,58,60,66,67,71,81–83 NAA,54,63,71,75,78,82,84,85 NAA/Cho,83 creatine,54,75,78,84 Cho/Cr,58,60,66,81 choline,75,78,84 myoinositol,75 Glx,63 Glu/Cr,82 Glu/NAA,82 and glutamate63,82 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 6 and 7; Supplementary Information).
Amygdala
The amygdala comprises two almond-shaped subcortical structures located in the bilateral medial temporal lobes and is implicated in the integration of sensory information, predicted threats, and ensuing emotional and behavioral responses. As such, the amygdalae exhibit connections with the hippocampus and multiple regions in the prefrontal cortex, with which they are thought to regulate the learning and memory of fear.13
Complementarily to numerous non-1H-MRS findings in PTSD, comparative and/or correlation analyses of amygdalar NAA,74,86 creatine,59,74,86 choline,74,86 myoinositol,74,86 and Glx74 have been reported (Figures 4 and 5; Tables 6 and 7; Supplementary Information).
Meta-Analysis of Anterior Cingulate Cortex and Bilateral Hippocampus Metabolite Findings
We conducted meta-analyses for all regions and metabolites for which at least four previously published comparisons with explicitly reported group statistics were present, which included NAA (seven), NAA/Cr (six), Glx or glutamate (four), creatine (four), myoinositol (four), and Cho/Cr (four) in the anterior cingulate cortex as well as NAA (seven, six) or NAA/Cr (seven, six) in the left and right hippocampus, respectively.
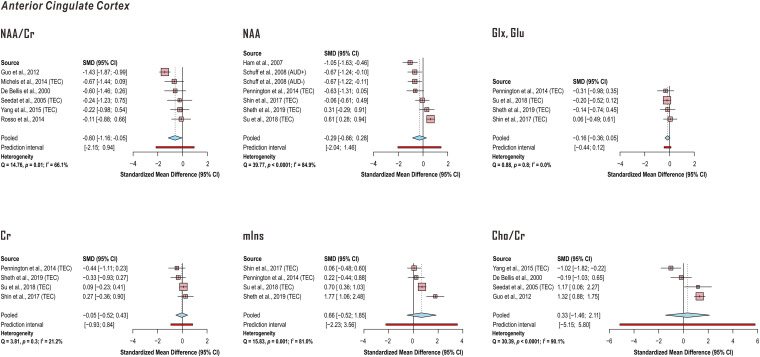
Random-effects models demonstrated significantly lower anterior cingulate cortex NAA in PTSD when referenced to creatine (k = 6 studies; pooled standardized mean difference −0.60, 95% confidence interval (CI) −1.16 to −0.05, P = .04) but not otherwise (k = 7 comparisons in 6 studies). No significant effect of PTSD was discerned for anterior cingulate cortex Glx or glutamate (k = 4 studies), creatine (k = 4 studies), myoinositol (k = 4 studies), or Cho/Cr (k = 4 studies). Between-study heterogeneities appeared to be higher for NAA (NAA/Cr Q = 14.76, P = .01, I2 = 66.1%; NAA Q = 39.77, P < .0001, I2 = 84.9%) reports than those for Glx or glutamate findings (Q = 0.88, P = .8, I2 < 0.01%) or creatine (Q = 3.81, P = .3, I2 = 21.2%) regardless of quantification reference. Because study pools from Meyerhoff et al76 and Pennington et al77 exhibited significant overlap, only values from Pennington et al77 were reported here (Figure 6; Supplementary Tables 6-11).
Figure 6.
Random-effects models of group difference between post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and control in proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS)-measured anterior cingulate cortex metabolite concentrations examined by four or more independent published investigations. Random-effects models across the listed studies demonstrated significantly lower anterior cingulate cortex N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) in PTSD when referenced to total creatine (Cr) (pooled standardized mean difference −0.60, 95% confidence interval CI −1.16 to −0.05, P = .04) but not otherwise. No significant effect of PTSD was discerned for anterior cingulate cortex glutamate (Glx, Glu), creatine (Cr), myoinositol (mIns), or creatine-referenced choline (Cho/Cr). Between-study heterogeneities were higher for NAA reports than those for glutamate or creatine findings regardless of quantification reference. Because study pools from Meyerhoff et al76 and Pennington et al77 exhibited overlap, only values Pennington et al77 were reported here. When PTSD groups were compared with both trauma-unmatched and trauma-exposed controls (TEC) in the same study, only comparisons with TEC were included in this analysis. Supporting group statistics reported in Supplementary Tables 6-11. AUD: alcohol use disorder.
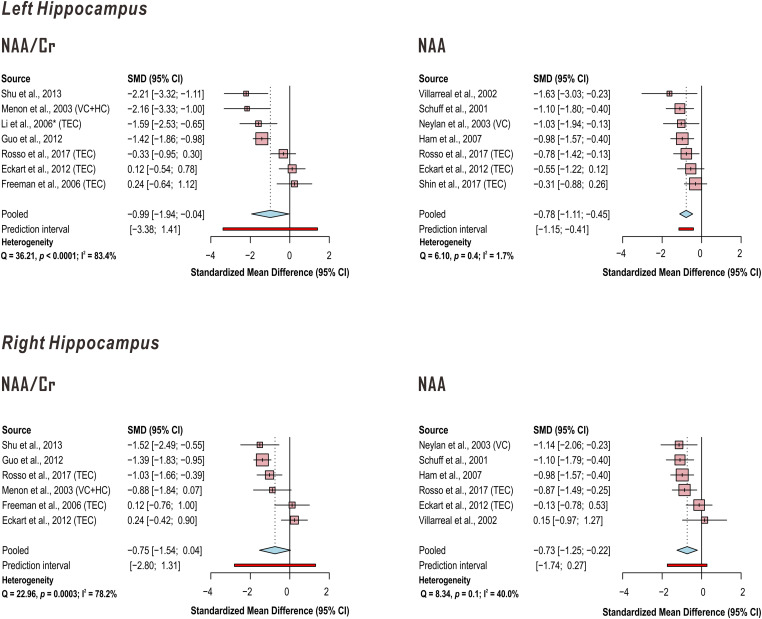
In addition, random-effects models demonstrated significantly lower left hippocampus N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) in PTSD when referenced to creatine (Cr) (k = 7 studies; pooled standardized mean difference −0.99, 95% CI −1.94 to −0.04, P = .04) with a marginally significant decrease on the right (k = 6 studies; pooled standardized mean difference −0.75, 95% CI −1.54 to 0.04, P = .06), while NAA referenced otherwise demonstrated significant effect for both left (k = 7 studies; pooled standardized mean difference −0.78, 95% CI −1.11 to −0.45, P = .001) and right (k = 6 studies; pooled standardized mean difference −0.73, 95% CI −1.25 to −0.22, P = .01) hippocampus. Between-study heterogeneities appeared to be higher for studies of hippocampal NAA when creatine was used as a reference (left hippocampus NAA/Cr Q = 36.21, P < .0001, I2 = 83.4%; right hippocampus NAA/Cr Q = 22.96, P = .0003, I2 = 78.2%) than when it was not (left hippocampus NAA Q = 6.10, P = .4, I2 = 1.7%; right hippocampus NAA Q = 8.34, P = .1, I2 = 40.0%) (Figure 7; Supplementary Tables 12-15).
Figure 7.
Random-effects models of group difference between PTSD and control in in proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS)-measured hippocampal metabolite concentrations examined by four or more independent published investigations. Random-effects models across the listed studies demonstrated significantly lower left and a trend to lower right hippocampus N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) in PTSD when referenced to creatine (Cr) (pooled standardized mean difference left −0.99, 95% CI −1.94 to −0.04, P=.04; right −0.75, 95% confidence interval CI −1.54 to 0.04, P=.06); NAA referenced otherwise demonstrates significant effect for left (pooled standardized mean difference −0.78, 95% CI −1.11 to −0.45, P=.001) and right (pooled standardized mean difference −0.73, 95% CI −1.25 to −0.22, P=.01) hippocampus. Between-study heterogeneities were higher for studies of hippocampal NAA when creatine was used as a reference than when it was not. When PTSD groups were compared with both trauma-unmatched and trauma-exposed controls (TEC) in the same study, only comparisons with TEC were included in this analysis. Supporting group statistics reported in Supplementary Tables 12-15. *Descriptive statistics estimated from Figure 2. VC: veteran control; HC: healthy control.
Discussion
Here we have reviewed the proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy literature targeted to comparisons of individuals with PTSD and either trauma-exposed or trauma-unmatched controls to find N = 32 publications, including 31 studies reporting group 1H-MRS data collection and one case report included for methodological considerations, fitting our inclusion criteria.
While the current 1H-MRS literature in PTSD exhibits better age-matching between experimental and control groups than the currently available 1H-MRS literature of at least one other disease,94 the distribution of ages previously studied is not uniform (Figure 3A) and the sex distribution is heavily skewed toward male participants (Figure 3B) despite a lifetime PTSD prevalence in women potentially double that of men.42,43 In addition, hardware fields employed by reviewed 1H-MRS analyses of PTSD do not exceed 4 Tesla (Figure 3C), which may contribute to the relative skew of reported metabolite comparisons toward traditionally high-SNR singlets like NAA, creatine, and choline (Figure 3D).
Meta-analyses for all regions and metabolites for which at least four previously published comparisons with control were present included NAA and NAA/Cr in anterior cingulate cortex and bilateral hippocampus as well as Glx or glutamate, creatine, myoinositol, and Cho/Cr in the anterior cingulate cortex; no other metabolites in any other region passed this k = 4 threshold of published studies.
As concluded for a recent similar review of the literature on multiple sclerosis,94 regional decreases in N-acetyl aspartate are potentially too nonspecific and insensitive to serve as a biomarker for PTSD vulnerability, development, or treatment response. Abnormal decreases in anterior cingulate NAA or NAA/Cr have also been reported by meta-analysis of studies on first-episode psychosis95 and autism spectrum disorders;96 reductions in hippocampal NAA or NAA/Cr have additionally been observed in meta-analyses on schizophrenia,95 fibromyalgia,97 obstructive sleep apnea,98 mild cognitive impairment,99 and Alzheimer's disease.100 The heavy focus of currently published 1H-MRS literature in PTSD on N-acetyl aspartate therefore in principle limits the application of its findings to the development of clinically useful 1H-MRS-based regional single-molecule biomarkers, calling for further targeted research into a more diverse range of metabolites measurable by the method, especially at higher field strengths and using acquisition, processing, and analysis pipelines that minimize both imprecision and inaccuracy in metabolite concentration estimates.
Meta-analysis demonstrated decreased anterior cingulate cortex NAA in PTSD only when referenced to creatine and decreased hippocampal NAA regardless of reference. These findings further support the conclusions of a previous systematic review observing consistent decreases in hippocampal and anterior cingulate cortex NAA across the 1H-MRS literature on PTSD.46 In particular, our anterior cingulate cortex results also extend previous meta-analytic findings of decreased anterior cingulate NAA/Cr in PTSD relative to healthy controls and update three previously reviewed comparisons from two studies71,75 underlying a significant effect of NAA in anterior cingulate cortex45 with four more63,69,74,77 that bring this metabolite result to non-significance. Similarly, reported reductions in left hippocampal NAA/Cr and NAA extend previously significant meta-analytic findings in both indices.45 Our finding of significant right hippocampal NAA decreases in PTSD repeats in a mixed-control cohort a previous meta-analytic result using trauma-exposed controls,45 while our own marginally significant random-effects model for right hippocampal NAA/Cr did not replicate a previous significant result, potentially because of our choice to exclude three previously incorporated studies that either did not report at least one group standard deviation or reported a voxel in the medial temporal lobe but not specifically the hippocampus.60,65,71
Conflicting meta-analytic results between NAA and NAA/Cr in anterior cingulate cortex and right hippocampus may be suggestive of systematic heterogeneities between studies choosing to employ either referencing technique, ie, groups choosing either creatine or non-creatine references may differ in other methodological details that themselves influence reported metabolite effect size. Indeed, very few groups included in our meta-analyses reported both values, making this a feasible explanation for the differences observed here. NAA results that differ by concentration reference may also suggest the disparate influence of the reference itself either as an unwanted source of error or, on the other hand, as more sensitive to actual biological differences among the participants of each study. It is important to note that these two directions of influence are not necessarily mutually exclusive and may lead to different outcomes in different brain regions, as we observed here for PTSD-associated reductions in anterior cingulate NAA that were definitively significant only when referenced to creatine but right hippocampus NAA significant only when not referenced to creatine. It is of potential note that increased cross-study heterogeneity was observed among reports of left and right hippocampal NAA/Cr relative to NAA, which, when combined with the lower number of included studies targeting right than left hippocampal NAA/Cr, may have contributed to the lack of significance in the former statistic, especially considering the previously mentioned published significant meta-analytic finding in the same region.45
Meta-analysis of anterior cingulate glutamate or Glx, not previously attempted by the above reference,45 demonstrated no significant effect of PTSD. So far only one significant effect of PTSD on anterior cingulate cortex glutamate or Glx, referenced to creatine, has been published,73 though significant negative correlations with clinician-administered PTSD scale (CAPS) arousal76,77 and total scores77 have been previously observed. In one model of PTSD pathogenesis, regional glutamate excitotoxicity can result from increases in the ratio of extrasynaptic to synaptic glutamate due to glutamate “spillover,” a consequence of inadequate astrocytic clearance of extrasynaptic glutamate, and attendant stimulation of presynaptic mGluR-2/3 inhibiting its further release at the synapse.41 It is important to note that while 1H MRS may provide clues regarding the biochemical composition over a whole voxel, eg, the possible cross-voxel density of metabolically healthy neurons75 or glial cells74 as inferred from N-acetyl aspartate and myoinositol or choline concentrations, respectively, the proposed mechanism of regional excitotoxic damage in PTSD does not necessitate cross-voxel changes in glutamate concentration large enough to be detected by 1H MRS. It remains therefore important to note that the mechanistic reasons behind disease-related metabolic abnormalities visible to 1H MRS are often themselves unknown, complicating the use of this method for conclusive hypothesis testing regarding pathophysiological mechanisms at the cellular or molecular scale.
This currently small literature limits the feasibility of further meta-analysis evaluating the use of 1H MRS as a source of biomarkers for PTSD risk, effect, or both via parsing effect sizes by control group type (trauma-exposed or trauma-unmatched), though such bifurcations have been previously reported.45 Even the most well studied metabolite (NAA) in the most widely studied regions (anterior cingulate cortex and left hippocampus) represents a maximum of four published analyses of either trauma-exposed or trauma-unmatched controls, each with group sizes well under N = 100.
In addition, psychiatric comorbidity may present a limiting factor for assigning specificity of reported metabolic changes to PTSD alone. For example, shared metabolic effects have been reported between PTSD and anxiety,101 or abnormalities reported in PTSD groups with comorbid depressive symptoms,51 the latter of which has a documented association with PTSD.50 Changes in brain morphology52,55 and neurometabolite concentrations have also been found with both acute102 and chronic103 alcohol use, as in tobacco or nicotine use,104 also possibly confounding putative findings attributed to PTSD status. As such, parsing the specific effects of PTSD on metabolite concentrations apart from those associated with comorbid conditions remains a significant challenge.
A few investigations reviewed here noted associations between certain comorbid symptom axes and the metabolites under study, eg, parieto-occipital GABA and depressive symptoms76 or right insula GABA/Cr and anxiety symptoms,62 or showed metabolite differences between PTSD patients with and without, for example, alcohol use disorder.77 Others statistically controlled their results for comorbidities like nicotine use to find no interactive effect.61,76 Despite such efforts, it is important to note the small number of participants within these studies and attendant limitations in statistical power and generalizability.
Taken together, our findings suggest a small (N = 32 studies) literature using 1H MRS to investigate PTSD that is well balanced in terms of participant ages but heavily skewed toward the male sex, lower field strengths, limited regional targets, and high-SNR metabolites. Regardless, a number of notable findings have been reported, including in brain areas like dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus previously shown to exhibit structural and/or functional abnormalities in PTSD relative to either trauma-unmatched or trauma-exposed controls (Figure 4, Tables 3, 5, and 6; Supplementary Information), as well as a number of significant correlations between metabolites in these regions and clinically relevant variables like CAPS scores or other measures of symptom experience (Figure 5, Tables 4 and 7; Supplementary Information). As such, the potential for 1H MRS to forge new ground in the understanding of PTSD, as well as play a role in the development of biomarkers for risk, diagnosis, and/or treatment monitoring, is not only as-yet largely untried but has also yielded meaningfully interpretable information where it has been, therefore remaining a useful piece of the puzzle behind the pathogenesis and evolution of this life-changing condition.
Supplemental Material
Supplemental material, sj-docx-1-css-10.1177_24705470221128004 for Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder—Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis by Kelley M. Swanberg, Leonardo Campos, Chadi G. Abdallah and Christoph Juchem in Chronic Stress
Footnotes
Author Contributions: KMS: Data review and analysis, manuscript drafting; LC: Data review, manuscript drafting; CGA: Manuscript editing; CJ: Manuscript editing.
CGA has served as a consultant and/or on advisory boards for Aptinyx, Genentech, Janssen, Psilocybin Labs, Lundbeck, Guidepoint, and FSV7, and as editor of Chronic Stress for Sage Publications, Inc. He also filed a patent for using mTORC1 inhibitors to augment the effects of antidepressants (Aug 20, 2018).
Ethical Approval: Not applicable, because this article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Funding: The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This work was supported by the Yale Center for Clinical Investigation.
Informed Consent: Not applicable, because this article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
ORCID iDs: Kelley M. Swanberg https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1254-190X
Chadi G. Abdallah https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5783-6181
Trial Registration: Not applicable, because this article does not contain any clinical trials.
Supplemental Material: Supplemental material for this article is available online.
References
- 1.American Psychiatric Association. DSM-5 Task Force. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:xliv, 947. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kessler RC, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Alonso J, et al. Trauma and PTSD in the WHO World Mental Health Surveys. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2017;8(suppl 5):1353383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pitman RK, Rasmusson AM, Koenen KC, et al. Biological studies of post-traumatic stress disorder. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(11):769–787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gilbertson MW, Shenton ME, Ciszewski A, et al. Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5(11):1242–1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Van Rooij SJ, Kennis M, Sjouwerman R, Van Den Heuvel MP, Kahn RS, Geuze E. Smaller hippocampal volume as a vulnerability factor for the persistence of post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychol Med. 2015;45(13):2737–2746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Milad MR, Orr SP, Lasko NB, Chang Y, Rauch SL, Pitman RK. Presence and acquired origin of reduced recall for fear extinction in PTSD: results of a twin study. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42(7):515–520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Woon FL, Sood S, Hedges DW. Hippocampal volume deficits associated with exposure to psychological trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder in adults: a meta-analysis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2010;34(7):1181–1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yehuda R, Hoge CW, McFarlane AC, et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1(1):15057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Duncan LE, Cooper BN, Shen H. Robust findings From 25 years of PTSD genetics research. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2018;20(12):115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brivio E, Lopez JP, Chen A. Sex differences: transcriptional signatures of stress exposure in male and female brains. Genes Brain Behav. 2020;19(3):e12643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cisler JM, Herringa RJ. Posttraumatic stress disorder and the developing adolescent brain. Biol Psychiatry. 2021;89(2):144–151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Malikowska-Racia N, Salat K. Recent advances in the neurobiology of posttraumatic stress disorder: a review of possible mechanisms underlying an effective pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Res. 2019;142:30–49. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.02.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Harnett NG, Goodman AM, Knight DC. PTSD-related neuroimaging abnormalities in brain function, structure, and biochemistry. Exp Neurol. 2020;330:113331. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nelson EC, Agrawal A, Pergadia ML, et al. Association of childhood trauma exposure and GABRA2 polymorphisms with risk of posttraumatic stress disorder in adults. Mol Psychiatry. 2009;14(3):234–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Segman RH, Shefi N, Goltser-Dubner T, Friedman N, Kaminski N, Shalev AY. Peripheral blood mononuclear cell gene expression profiles identify emergent post-traumatic stress disorder among trauma survivors. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10(5):500–513, 425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wuchty S, Myers AJ, Ramirez-Restrepo M, et al. Integration of peripheral transcriptomics, genomics, and interactomics following trauma identifies causal genes for symptoms of post-traumatic stress and major depression. Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Jul;26(7):3077-3092. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Smith AK, Ratanatharathorn A, Maihofer AX, et al. Epigenome-wide meta-analysis of PTSD across 10 military and civilian cohorts identifies methylation changes in AHRR. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):5965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Uddin M, Ratanatharathorn A, Armstrong D, et al. Epigenetic meta-analysis across three civilian cohorts identifies NRG1 and HGS as blood-based biomarkers for post-traumatic stress disorder. Epigenomics. 2018;10(12):1585–1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Orr SP, Metzger LJ, Lasko NB, et al. Physiologic responses to sudden, loud tones in monozygotic twins discordant for combat exposure: association with posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60(3):283–288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Keane TM, Kolb LC, Kaloupek DG, et al. Utility of psychophysiological measurement in the diagnosis of posttraumatic stress disorder: results from a Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1998;66(6):914–923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miller LN, Simmons JG, Whittle S, Forbes D, Felmingham K. The impact of posttraumatic stress disorder on event-related potentials in affective and non-affective paradigms: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;122:120–142. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.12.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Atmaca M, Ozer O, Korkmaz S, Taskent I, Yildirim H. Evidence for the changes of pituitary volumes in patients with post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2017;260:49–52. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2016.12.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Olff M, Guzelcan Y, De Vries GJ, Assies J, Gersons BP. HPA- and HPT-axis alterations in chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2006;31(10):1220–1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Baker DG, Ekhator NN, Kasckow JW, et al. Higher levels of basal serial CSF cortisol in combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(5):992–994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yehuda R, Lowy MT, Southwick SM, Shaffer D, Giller EL, Jr. Lymphocyte glucocorticoid receptor number in posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1991;148(4):499–504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.de Kloet CS, Vermetten E, Geuze E, et al. Elevated plasma corticotrophin-releasing hormone levels in veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Prog Brain Res. 2008;167:287–291. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)67025-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.de Kloet CS, Vermetten E, Rademaker AR, Geuze E, Westenberg HG. Neuroendocrine and immune responses to a cognitive stress challenge in veterans with and without PTSD. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2012;3. doi:10.3402/ejpt.v3i0.16206. Epub 2012 Jun 12. PMID: 22893842; PMCID: PMC3402140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Strohle A, Scheel M, Modell S, Holsboer F. Blunted ACTH response to dexamethasone suppression-CRH stimulation in posttraumatic stress disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42(14):1185–1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hockings GI, Grice JE, Ward WK, Walters MM, Jensen GR, Jackson RV. Hypersensitivity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis to naloxone in post-traumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 1993;33(8-9):585–593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rasmusson AM, Hauger RL, Morgan CA, Bremner JD, Charney DS, Southwick SM. Low baseline and yohimbine-stimulated plasma neuropeptide Y (NPY) levels in combat-related PTSD. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;47(6):526–539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sah R, Ekhator NN, Jefferson-Wilson L, Horn PS, Geracioti TD, Jr. Cerebrospinal fluid neuropeptide Y in combat veterans with and without posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014;40:277–283. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.10.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bremner JD, Innis RB, Ng CK, et al. Positron emission tomography measurement of cerebral metabolic correlates of yohimbine administration in combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54(3):246–254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Strawn JR, Pyne-Geithman GJ, Ekhator NN, et al. Low cerebrospinal fluid and plasma orexin-A (hypocretin-1) concentrations in combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2010;35(7):1001–1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rasmusson AM, Pinna G, Paliwal P, et al. Decreased cerebrospinal fluid allopregnanolone levels in women with posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;60(7):704–713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.De Kloet CS, Vermetten E, Geuze E, Wiegant VM, Westenberg HG. Elevated plasma arginine vasopressin levels in veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42(3):192–198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Neumeister A, Normandin MD, Pietrzak RH, et al. Elevated brain cannabinoid CB1 receptor availability in post-traumatic stress disorder: a positron emission tomography study. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(9):1034–1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Southwick SM, Krystal JH, Bremner JD, et al. Noradrenergic and serotonergic function in posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54(8):749–758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.American Psychiatric Association and Task Force on Nomenclature and Statistics. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3d ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1980:494. American Psychiatric Association. Committee on Nomenclature and Statistics. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hoge CW, Riviere LA, Wilk JE, Herrell RK, Weathers FW. The prevalence of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in US combat soldiers: a head-to-head comparison of DSM-5 versus DSM-IV-TR symptom criteria with the PTSD checklist. Lancet Psychiatry. 2014;1(4):269–277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.De Moraes Costa G, Zanatta FB, Ziegelmann PK, Soares Barros AJ, Mello CF. Pharmacological treatments for adults with post-traumatic stress disorder: a network meta-analysis of comparative efficacy and acceptability. J Psychiatr Res. 2020;130:412–420. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.07.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Averill LA, Purohit P, Averill CL, Boesl MA, Krystal JH, Abdallah CG. Glutamate dysregulation and glutamatergic therapeutics for PTSD: evidence from human studies. Neurosci Lett. 2017;649:147–155. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.11.064 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Perrin M, Vandeleur CL, Castelao E, et al. Determinants of the development of post-traumatic stress disorder, in the general population. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2014;49(3):447–457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Duckers MLA, Olff M. Does the vulnerability paradox in PTSD apply to women and men? An exploratory study. J Trauma Stress. 2017;30(2):200–204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Verbitsky A, Dopfel D, Zhang N. Rodent models of post-traumatic stress disorder: behavioral assessment. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Karl A, Werner A. The use of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in PTSD research--meta-analyses of findings and methodological review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010;34(1):7–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Quadrelli S, Mountford C, Ramadan S. Systematic review of in-vivo neuro magnetic resonance spectroscopy for the assessment of posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2018;282:110–125. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2018.07.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tolin DF, Foa EB. Sex differences in trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder: a quantitative review of 25 years of research. Psychol Bull. 2006;132(6):959–992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cortina LM, Kubiak SP. Gender and posttraumatic stress: sexual violence as an explanation for women's increased risk. J Abnorm Psychol. 2006;115(4):753–759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Breslau N, Anthony JC. Gender differences in the sensitivity to posttraumatic stress disorder: an epidemiological study of urban young adults. J Abnorm Psychol. 2007;116(3):607–611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rytwinski NK, Scur MD, Feeny NC, Youngstrom EA. The co-occurrence of major depressive disorder among individuals with posttraumatic stress disorder: a meta-analysis. J Trauma Stress. 2013;26(3):299–309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Murrough JW, Czermak C, Henry S, et al. The effect of early trauma exposure on serotonin type 1B receptor expression revealed by reduced selective radioligand binding. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68(9):892–900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Agartz I, Momenan R, Rawlings RR, Kerich MJ, Hommer DW. Hippocampal volume in patients with alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999;56(4):356–363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Driessen M, Herrmann J, Stahl K, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging volumes of the hippocampus and the amygdala in women with borderline personality disorder and early traumatization. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57(12):1115–1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Eckart C, Kaufmann J, Kanowski M, et al. Magnetic resonance volumetry and spectroscopy of hippocampus and insula in relation to severe exposure of traumatic stress. Psychophysiology. 2012;49(2):261–270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Woodward SH, Kaloupek DG, Streeter CC, et al. Hippocampal volume, PTSD, and alcoholism in combat veterans. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(4):674–681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.De Bellis MD, Keshavan MS, Harenski KA. Anterior cingulate N-acetylaspartate/creatine ratios during clonidine treatment in a maltreated child with posttraumatic stress disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2001;11(3):311–316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Schwarzer G. Meta: an R package for meta-analysis. R News. 2007;7:40–45. https://cran.r-project.org/doc/Rnews/Rnews_2007-3.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Guo M, Chen F, Guo J-C, et al. Study of the hippocampus and the anterior cingulate gyrus by proton MR spectroscopy in patients with post–traumatic stress disorder. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012;5(2):162–164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hoerst M, Weber-Fahr W, Tunc-Skarka N, et al. Metabolic alterations in the amygdala in borderline personality disorder: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(5):399–405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mahmutyazicioglu K, Konuk N, Ozdemir H, Atasoy N, Atik L, Gundogdu S. Evaluation of the hippocampus and the anterior cingulate gyrus by proton MR spectroscopy in patients with post-traumatic stress disorder. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2005;11(3):125–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Michels L, Schulte-Vels T, Schick M, et al. Prefrontal GABA and glutathione imbalance in posttraumatic stress disorder: preliminary findings. Psychiatry Res. 2014;224(3):288–295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rosso IM, Weiner MR, Crowley DJ, Silveri MM, Rauch SL, Jensen JE. Insula and anterior cingulate GABA levels in posttraumatic stress disorder: preliminary findings using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Depress Anxiety. 2014;31(2):115–123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Shin JE, Choi CH, Lee JM, et al. Association between memory impairment and brain metabolite concentrations in North Korean refugees with posttraumatic stress disorder. PLoS One. 2017;12(12):e0188953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kimbrell T, Leulf C, Cardwell D, Komoroski RA, Freeman TW. Relationship of in vivo medial temporal lobe magnetic resonance spectroscopy to documented combat exposure in veterans with chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2005;140(1):91–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Brown S, Freeman T, Kimbrell T, Cardwell D, Komoroski R. In vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the medial temporal lobes of former prisoners of war with and without posttraumatic stress disorder. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003;15(3):367–370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Freeman T, Kimbrell T, Booe L, et al. Evidence of resilience: neuroimaging in former prisoners of war. Psychiatry Res. 2006;146(1):59–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Mohanakrishnan Menon P, Nasrallah HA, Lyons JA, Scott MF, Liberto V. Single-voxel proton MR spectroscopy of right versus left hippocampi in PTSD. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2003;123(2):101–108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Lim MK, Suh CH, Kim HJ, et al. Fire-related post-traumatic stress disorder: brain 1H-MR spectroscopic findings. Korean J Radiol. 2003;4(2):79–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Sheth C, Prescot AP, Legarreta M, Renshaw PF, McGlade E, Yurgelun-Todd D. Reduced gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) and glutamine in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) of veterans exposed to trauma. J Affect Disord. 2019;248:166–174. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.01.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.De Bellis MD, Keshavan MS, Spencer S, Hall J. N-Acetylaspartate concentration in the anterior cingulate of maltreated children and adolescents with PTSD. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157(7):1175–1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Schuff N, Neylan TC, Fox-Bosetti S, et al. Abnormal N-acetylaspartate in hippocampus and anterior cingulate in posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2008;162(2):147–157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Seedat S, Videen JS, Kennedy CM, Stein MB. Single voxel proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in women with and without intimate partner violence-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2005;139(3):249–258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Yang ZY, Quan H, Peng ZL, Zhong Y, Tan ZJ, Gong QY. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy revealed differences in the glutamate + glutamine/creatine ratio of the anterior cingulate cortex between healthy and pediatric post-traumatic stress disorder patients diagnosed after 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2015;69(12):782–790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Su X, Xia C, Wang W, et al. Abnormal metabolite concentrations and amygdala volume in patients with recent-onset posttraumatic stress disorder. J Affect Disord. 2018;241:539–545. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.08.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ham BJ, Chey J, Yoon SJ, et al. Decreased N-acetyl-aspartate levels in anterior cingulate and hippocampus in subjects with post-traumatic stress disorder: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25(1):324–329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Meyerhoff DJ, Mon A, Metzler T, Neylan TC. Cortical gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate in posttraumatic stress disorder and their relationships to self-reported sleep quality. Sleep. 2014;37(5):893–900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Pennington DL, Abe C, Batki SL, Meyerhoff DJ. A preliminary examination of cortical neurotransmitter levels associated with heavy drinking in posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2014;224(3):281–287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Villarreal G, Petropoulos H, Hamilton DA, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the hippocampus and occipital white matter in PTSD: preliminary results. Can J Psychiatry. 2002;47(7):666–670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Quadrelli S, Tosh N, Urquhart A, et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder affects fucose-alpha(1-2)-glycans in the human brain: preliminary findings of neuro deregulation using in vivo two-dimensional neuro MR spectroscopy. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Freeman TW, Cardwell D, Karson CN, Komoroski RA. In vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the medial temporal lobes of subjects with combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Magn Reson Med. 1998;40(1):66–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Shu XJ, Xue L, Liu W, et al. More vulnerability of left than right hippocampal damage in right-handed patients with post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2013;212(3):237–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Rosso IM, Crowley DJ, Silveri MM, Rauch SL, Jensen JE. Hippocampus glutamate and N-acetyl aspartate markers of excitotoxic neuronal compromise in posttraumatic stress disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017;42(8):1698–1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Li L, Chen S, Liu J, Zhang J, He Z, Lin X. Magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of deficits in hippocampal structure in fire victims with recent-onset posttraumatic stress disorder. Can J Psychiatry. 2006;51(7):431–437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Schuff N, Neylan TC, Lenoci MA, et al. Decreased hippocampal N-acetylaspartate in the absence of atrophy in posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;50(12):952–959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Neylan TC, Schuff N, Lenoci M, Yehuda R, Weiner MW, Marmar CR. Cortisol levels are positively correlated with hippocampal N-acetylaspartate. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54(10):1118–1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Wang W, Sun H, Su X, et al. Increased right amygdala metabolite concentrations in the absence of atrophy in children and adolescents with PTSD. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;28(6):807–817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Neylan TC, Lenoci M, Rothlind J, et al. Attention, learning, and memory in posttraumatic stress disorder. J Trauma Stress. 2004;17(1):41–46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Abdallah CG, Averill LA, Akiki TJ, et al. The neurobiology and pharmacotherapy of posttraumatic stress disorder. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019;59(1):171–189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Lanciego JL, Luquin N, Obeso JA. Functional neuroanatomy of the basal ganglia. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2(12):a009621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Behrmann M, Geng JJ, Shomstein S. Parietal cortex and attention. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004;14(2):212–217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Augustine JR. Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1996;22(3):229–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Osuch EA, Benson B, Geraci M, et al. Regional cerebral blood flow correlated with flashback intensity in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;50(4):246–253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Bird CM, Burgess N. The hippocampus and memory: insights from spatial processing. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9(3):182–194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Swanberg KM, Landheer K, Pitt D, Juchem C. Quantifying the metabolic signature of multiple sclerosis by in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: current challenges and future outlook in the translation From proton signal to diagnostic biomarker. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1173. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01173 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Whitehurst TS, Osugo M, Townsend L, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of N-acetyl aspartate in chronic schizophrenia, first episode of psychosis and high-risk of psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020;119:255–267. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.10.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ipser JC, Syal S, Bentley J, Adnams CM, Steyn B, Stein DJ. 1H-MRS In autism spectrum disorders: a systematic meta-analysis. Metab Brain Dis. 2012;27(3):275–287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Aoki Y, Inokuchi R, Suwa H. Reduced N-acetylaspartate in the hippocampus in patients with fibromyalgia: a meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2013;213(3):242–248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Xia Y, Fu Y, Xu H, Guan J, Yi H, Yin S. Changes in cerebral metabolites in obstructive sleep apnea: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):28712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Tumati S, Martens S, Aleman A. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in mild cognitive impairment: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013;37(10):2571–2586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Wang H, Tan L, Wang HF, et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in Alzheimer's disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;46(4):1049–1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Trousselard M, Lefebvre B, Caillet L, et al. Is plasma GABA level a biomarker of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) severity? A preliminary study. Psychiatry Res. 2016;241:273–279. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.05.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Monnig MA, Woods AJ, Walsh E, et al. Cerebral metabolites on the descending limb of acute alcohol: a preliminary 1H MRS study. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019;54(5):487–496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Zahr NM, Pfefferbaum A. Alcohol's effects on the brain: neuroimaging results in humans and animal models. Alcohol Res. 2017;38(2):183–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Domino EF. Tobacco smoking and MRI/MRS brain abnormalities compared to nonsmokers. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32(8):1778–1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental material, sj-docx-1-css-10.1177_24705470221128004 for Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder—Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis by Kelley M. Swanberg, Leonardo Campos, Chadi G. Abdallah and Christoph Juchem in Chronic Stress