Mitotic entry is regulated by the activity of cyclin B1-CDK1 complexes. In this study, Dantas et al. show that actomyosin-dependent nuclear tension during prophase regulates cyclin B1 nuclear translocation and has implications for chromosome segregation efficiency.
Abstract
As cells prepare to divide, they must ensure that enough space is available to assemble the mitotic machinery without perturbing tissue homeostasis. To do so, cells undergo a series of biochemical reactions regulated by cyclin B1-CDK1 that trigger cytoskeletal reorganization and ensure the coordination of cytoplasmic and nuclear events. Along with the biochemical events that control mitotic entry, mechanical forces have recently emerged as important players in cell-cycle regulation. However, the exact link between mechanical forces and the biochemical pathways that control mitotic progression remains unknown. Here, we identify a tension-dependent signal on the nucleus that sets the time for nuclear envelope permeabilization (NEP) and mitotic entry. This signal relies on actomyosin contractility, which unfolds the nucleus during the G2-M transition, activating the stretch-sensitive cPLA2 on the nuclear envelope and regulating the nuclear translocation of cyclin B1. Our data demonstrate how nuclear tension during the G2-M transition contributes to timely and efficient mitotic spindle assembly and prevents chromosomal instability.
Introduction
Cell-cycle progression is regulated by cyclins and their associated kinases. One such complex, composed of cyclin B1-CDK1, is responsible for regulating entry into mitosis. The biochemical mechanisms that regulate mitotic entry have been extensively studied in the past (for review, see Lindqvist et al. [2009]). For most of the cell cycle, the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex is inactive, due to low cyclin B1 expression levels and its mainly cytoplasmic localization (Hagting et al., 1998; Toyoshima et al., 1998). As cells transit from S to G2, cyclin B1 expression gradually increases (Akopyan et al., 2014; Feringa et al., 2016; Pines and Hunter, 1989). This results in cyclin B1 binding to CDK1. This cyclin B1-CDK1 complex is kept in an inactive state due to Myt1- and Wee1-mediated phosphorylations of CDK1 on residues T14 and Y15 (Lindqvist et al., 2009). Through the action of Cdc25 phosphatases, these inhibitory phosphorylations are removed, leading to complex activation. The active cyclin B1-CDK1 complex then stimulates its own nuclear import (Gavet and Pines, 2010) through the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs), resulting in chromosome condensation (Abe et al., 2011) and nuclear envelope permeabilization (NEP; Dantas et al., 2021). Consequently, the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex has been proposed to effectively synchronize cytoplasmic and nuclear events (Gavet and Pines, 2010), crucial for mitotic entry and efficient spindle assembly.
The influence of mechanical forces on the cell cycle and some of its key regulators has received considerable attention over the last few years (Huang et al., 1998; Klein et al., 2009; Lancaster et al., 2013; Benham-Pyle et al., 2015; Gudipaty et al., 2017; Uroz et al., 2018; Aureille et al., 2019). Experiments performed in isolated cells and epithelial layers have demonstrated that mechanical forces can stimulate the G1-S transition (Huang et al., 1998; Benham-Pyle et al., 2015; Uroz et al., 2018; Vianay et al., 2018; Aureille et al., 2019) by controlling specific transcriptional programs (Huang et al., 1998; Benham-Pyle et al., 2015; Aureille et al., 2019). This is likely due to forces imposed on the nucleus (Lombardi and Lammerding, 2011; Arsenovic et al., 2016) that induce its flattening (Elosegui-Artola et al., 2017; Aureille et al., 2019; Lomakin et al., 2020), facilitating the nuclear accumulation of transcription factors (TFs; Elosegui-Artola et al., 2017; Jacchetti et al., 2021), changing the organization of both chromatin (Nava et al., 2020) and the nuclear envelope (NE; Swift et al., 2013) or altering cell contractility (Lomakin et al., 2020; Venturini et al., 2020).
Evidence for mechanical regulation during other cell-cycle phases is more limited. Recently, mechanical stretching was proposed to trigger the G2-M transition by activating Piezo 1 (Gudipaty et al., 2017). Moreover, we and others have shown that cell traction forces decrease during the G2-M transition (Uroz et al., 2018; Vianay et al., 2018; Nunes et al., 2020), to allow mitotic cell rounding and efficient cell division (Lancaster et al., 2013; Nunes et al., 2020). Although these findings highlight the interplay between physical forces and cell proliferation, it remains unknown whether the main biochemical events that occur during the G2-M transition are sensitive to mechanical cues. Importantly, whether the spatial and temporal behavior of the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex responds to mechanical forces and contributes to ensure timely and efficient cell division remains unknown. Here, we investigate whether and how cyclin B1 responds to physical forces during the G2-M transition. We show that nuclear deformation triggers a contractility-mediated mechanism that facilitates the translocation of cyclin B1 to the nucleus, setting the timing of mitotic entry.
Results
Cellular confinement facilitates cyclin B1 nuclear translocation
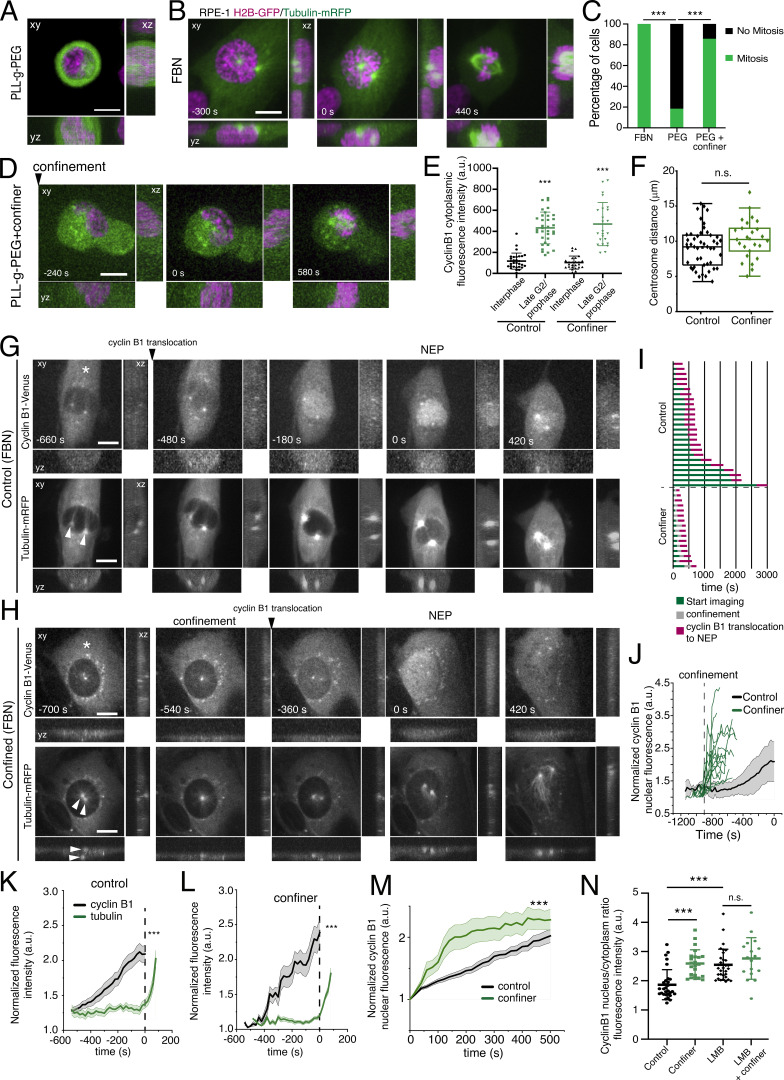
We started by investigating whether the G2-M transition is sensitive to the degree of cell adhesion. We seeded RPE-1 cells expressing H2B-GFP/tubulin-RFP in non-adherent, hydrophobic conditions (PLL-g-PEG). These cells were trypsinized, placed on a pLL-g-PEG-coated 35 mm2 dish and immediately placed on the microscope for high spatiotemporal resolution imaging. We selected individual cells that were in late G2/early prophase, based on the presence of separated centrosomes and condensed chromosomes, and determined their capacity to enter mitosis. During a period of at least 3 h of imaging, these cells failed to enter mitosis (Fig. 1, A and C; n = 11), confirming that mitotic entry requires cell adhesion. Inversely, adherent cells seeded on fibronectin (FBN), readily entered mitosis (Fig. 1, B and C; n = 23), within the same time frame. We then tested whether mechanically stimulating cells in non-adherent conditions was sufficient to induce mitotic entry. For this purpose, we used a dynamic cell confinement device (Le Berre et al., 2014), which gives us temporal control over the process. Confinement was achieved by imposing on cells a fixed height of 8 μm with a rigid polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-coated glass slide (Fig. S1 A). Upon acute confinement, the cells that were seeded on PLL-g-PEG regained the ability to enter mitosis (Fig. 1, A–D; n = 12; ***, P < 0.001), indicating that mechanical confinement is sufficient to overcome the lack of cell adhesion. Under confinement conditions, these cells entered mitosis within ∼260 ± 129 s (mean ± SD) after stimulation, ruling out that this event was due to increased cyclin B1 transcription, as previously described (Gudipaty et al., 2017). One alternative hypothesis is that physical confinement accelerates mitotic entry by inducing a premature transport of cyclin B1 to the nucleus, as previously proposed for YAP or MyoD (Elosegui-Artola et al., 2017; Jacchetti et al., 2021). To confirm this is the case, we monitored the dynamics of nuclear accumulation of endogenous cyclin B1 tagged with Venus in RPE-1 cells (Collin et al., 2013). We specifically selected cells in late G2/early prophase, based on the presence of high cytoplasmic levels of cyclin B1 (Fig. 1 E; ***, P < 0.001), the absence of nuclear cyclin B1, and the separation of centrosomes (Fig. 1 F), all of which were previously determined as reliable markers for this cell-cycle stage (Akopyan et al., 2014; Feringa et al., 2016). We then measured nuclear cyclin B1 translocation in normal and confined conditions (Fig. 1, G–I). Next, we normalized our measurements to the lowest fluorescence intensity levels of nuclear cyclin B1 (corresponding to a value of 1) and quantified its increase as cyclin B1 translocated into the nucleus, up until the moment of tubulin nuclear entry, which is defined as time 0. This last event marks the loss of the nuclear barrier function, which is defined as NEP. By analyzing the patterns of nuclear cyclin B1 translocation, we determined that, in comparison with unmanipulated cells, mechanical stimulation triggered a fast nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1 (Fig. 1, J–M; ***, P < 0.001), as well as an increased nuclear-to-cytoplasmic (N/C) cyclin B1 ratio just prior to NEP (Fig. 1 N; ***, P < 0.001). This change in the N/C ratio strengthens the hypothesis that cyclin B1 translocation is a mechanosensitive event. Indeed, recent evidence has shown that the transport of high-molecular weight proteins (>40 kD) across the NPCs is sensitive to mechanical stimulation, with a preference for increased nuclear import, which is reflected in elevated N/C ratios (Andreu et al., 2022). However, we cannot rule out that confinement could act on other aspects of the nucleocytoplasmic transport, such as the rate of export. Indeed, we observed that following treatment with leptomycin B (LMB), which prevents the nuclear export of cyclin B1 (Yang et al., 1998; Yang et al., 2001), the difference in the N/C ratio is lost, when comparing confined and non-confined cells (Fig. 1 N; n.s., not significant).
Figure 1.
Cell confinement alters the nuclear translocation of cyclin B1. (A) RPE-1 cell expressing H2B-GFP/tubulin-mRFP seeded on PLL-g-PEG coated substrate (non-adherent conditions). Scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. (B) RPE-1 cell expressing H2B-GFP/tubulin-mRFP dividing on a FBN-coated substrate. Time is in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with a 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to NEP. (C) Percentage of cells that enter mitosis when seeded in non-adherent conditions with (n = 25) and without (n = 23; ***, P < 0.001; Z score-test) confinement and comparing to cells seeded in FBN without confinement (n = 23; ***, P < 0.001; Z score-test) (D) RPE-1 cell expressing H2B-GFP and tubulin-mRFP dividing on a PLL-g-PEG substrate (non-adherent conditions) under confinement. Time is in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with a 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to NEP. As explained in the text, upon mechanical stimulation cells enter mitosis within 260 ± 129 s. (E) Quantification of cyclin B1–Venus fluorescence intensity in interphase cells when compared to cells in late G2/prophase (***, P < 0.001; Mann–Whitney rank sum test), for control (n = 43) and confined (n = 25) conditions. Note how cells in late G2/early prophase show elevated levels of cyclin B2 in the cytoplasm. (F) Quantification of centrosome distance in control (n = 34) and confined (n = 25) cells with elevated cytoplasmic levels of cyclin B1 (n.s., not significant). (G) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus (top) and tubulin-mRFP (bottom) dividing on an FBN-coated substrate. Time is in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with a 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to NEP. (H) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus (top) and tubulin-mRFP (bottom) dividing on an FBN-coated substrate under confinement. Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to NEP. Note the elevated levels of cytoplasmic cyclin B1–Venus (asterisks) and already separated centrosomes (white arrowheads). In the confined cell, centrosomes are separated vertically, on opposite sides of the nucleus. (I) Quantification of the time required for cyclin B1 nuclear accumulation and tubulin nuclear translocation in control (n = 28) versus confined (n = 18) conditions. (J) Normalized cyclin B1 fluorescence accumulation, inside the nucleus, over-time in control, non-confined cells (black; n = 26) and individual tracks for confined cells (green; n = 19; ***, P < 0.001). Cyclin B1–Venus signal is aligned relative to NEP, which corresponds to time 0. Confined cells are aligned to the moment of confinement, represented by the vertical dashed line. Note that the green lines have a shorter span, due to the faster NEP. (K and L) Correlation between the nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1 (black) and tubulin entry in the nucleus (green) over time in control cells (K; ***, P < 0.001, paired t test) and confined cells (L; ***, P < 0.001, paired t test). Note that tubulin is excluded from the nucleus until the moment of NEP in both conditions, which corresponds to time 0. (M) Correlation between cyclin B1–Venus nuclear fluorescence accumulation for control (black) and confined cells (green; ***, P < 0.001; Wilcoxon signed rank test). For this panel, cyclin B1 fluorescence values were aligned relative to the lowest intensity value inside the nucleus, which correspond to time zero. (N) N/C fluorescence intensity ratio measured immediately before NEP (***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant; Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA on Ranks). Note that confinement increases cyclin B1 N/C ratio, indicative of a mechanosensitive nuclear import. For E, F, and N, the box size represents 75% of the population and the line inside the box represents the median of the sample. The size of the bars (whiskers) represents the maximum (in the upper quartile) and the minimum (in the lower quartile) values. For J–M, the lines correspond to the average value and the shaded area corresponds to SEM. All experiments were replicated at least three times and n represents the number of cells analyzed.
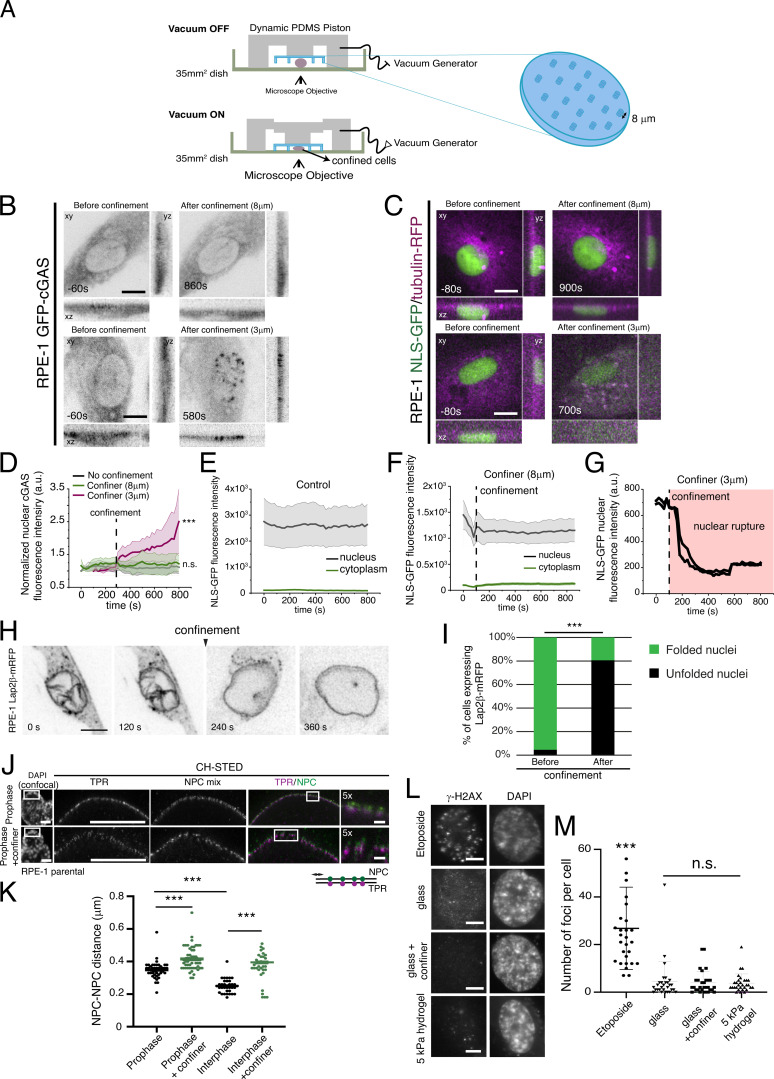
Figure S1.
Characterization of NE integrity following confinement. (A) Schematic representation of the dynamic confiner used to perform the experiments. (B) RPE-1 cell expressing GFP-cGAS before (left) and after (right) mechanical confinement (n = 20 for controls and n = 10 for confiner). In the upper panel, cells were subjected to 8 μm height confinement and no association of GFP-cGAS was visible. The bottom panel shows a cell which was confined to a height of 3 μm, causing NE rupture and GFP-cGAS association with DNA was visible. (C) RPE-1 cell expressing NLS-GFP/tubulin-mRFP imaged before and after mechanical confinement (n = 15 for controls and n = 15 for confiner). Note how confining cells to a height of 8 μm (top) does not induce NLS-GFP leakage into the cytoplasm. In the bottom panel, by confining cells to a height of 3 μm we cause NE rupture, as seen by the leakage of NLS-GFP into the cytoplasm. (D) Normalized GFP-cGAS nuclear fluorescence intensity over time for control, non-confined cells (black; n = 20), cells confined to 8 μm (green; n = 13; n.s., not significant) and cells confined with 3 μm height (magenta; n = 5; ***, P < 0.001; one-way repeated measure ANOVA). Note the increase in GFP-cGAS intensity with a confinement of 3 μm. Time 0 corresponds to the first frame of the video. (E–G) NLS-GFP fluorescence intensity in the nucleus (black) and in the cytoplasm (green) in control, non-confined cells (E), cells confined to 8 μm height (F), and cells confined to 3 μm height (G). In G, we show the individual lines for the two cells that we managed to film under these conditions. Note how a 3 μm confinement induces leakage of NLS-GFP from the nucleus. (H) Representative images of an RPE-1 cell expressing Lap2β-mRFP under confinement. Note that upon confinement the NE unfolds. Time frame is in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with a 20-s interval. (I) Quantification of the percentage of cells expressing Lap2β-mRFP with folded versus unfolded nuclei, before and after confinement. The percentage of cells with unfolded nuclei significantly increases after confinement (n = 46; ***, P < 0.001; Z-score test). (J) Representative images of prophase nuclei of parental RPE-1 cells stained with TPR (magenta) and an NPC mix (green) in control, non-confined conditions (top; n = 44) and under confined conditions (bottom; n = 55), acquired with CH-STED. Scale bar corresponds to 10 μm in the left and middle panels. Scale bar on insets corresponds to 2 μm. (K) Distance between neighboring nuclear pores (NPC-NPC distance) in control, non-confined (black) and confined conditions (green) for prophase and interphase cells (n = 34 for non-confined and n = 33 for confined; ***, P < 0.001). Measurements were done using a custom MATLAB algorithm, as described in the Materials and methods section. (L) Representative immunofluorescence images of parental RPE-1 prophase cells treated with Etoposide (positive control), cells seeded on glass, seeded on glass and under confinement, or cells seeded on a 5 kPa hydrogel, stained for histone γ-H2AX and DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. Note how etoposide generates a significant number of γ-H2AX-positive foci. (M) Quantification of the number of γ-H2AX foci per cell for the different treatments/seeding conditions (***, P < 0.001). Note that confining cells or seeding them on a 5 kPa hydrogel does not induce the appearance of γ-H2AX-positive foci. Pairwise comparisons were done using a two-sided t test when the samples had normal distribution. Otherwise, the comparison was performed using a rank sum test. For D–F, the lines correspond to the average value and the shaded area corresponds to SEM. In all cases, n represents the number of cells analyzed.
Next, to assess the kinetics of translocation, we aligned cyclin B1 fluorescence levels to the lowest value for both experimental groups (Fig. 1 M) and performed an exponential fitting. We determined the translocation to occur within 478 ± 102 s, with a half-time of 331 s for unmanipulated cells. Strikingly, in confined cells, translocation occurred within 101 ± 12 s, with a half-time of 70 s, which resulted in a faster mitotic entry (Fig. 1, J–L). This was not due to a rupture of the nucleus, as we could not detect any obvious association of GFP-cGAS with DNA (Fig. S1, B and D) or leakage of NLS-GFP into the cytoplasm (Fig. S1, C, E, and F), when cells were confined to a height of 8 μm, which we routinely used for our experimental setup. However, confining cells to a height of 3 μm did increase association of cGAS with DNA (Fig. S1, B and D) and resulted in NLS-GFP leakage into the cytoplasm (Fig. S1, C and G). These results, together with the observed delay between cyclin B1 accumulation and tubulin translocation to the nucleus (Fig. 1, K and L), strongly suggest that the nuclear barrier function remains intact after an 8 μm confinement. Instead, as previously reported (Lomakin et al., 2020), confinement promoted an unfolding of the NE which could be readily observed (Fig. S1, H and I; ***, P < 0.001) and resulted in an increase in the distance between neighboring NPCs (Fig. S1, J and K; ***, P < 0.001), when compared to unconfined cells. Importantly, this unfolding was also observed in unmanipulated cells as they progress from interphase to prophase (Fig. S1 K; ***, P < 0.001). Because DNA damage can affect nuclear cyclin B1 accumulation (Toyoshima et al., 1998), we measured the levels of histone γ-H2AX, to determine if our experimental setup could be inducing DNA damage, thus affecting cyclin B1 nuclear accumulation. We did not observe significant changes in the levels of γ-H2AX foci (Fig. S1, L and M; ***, P < 0.001), suggesting that this process is independent of DNA damage.
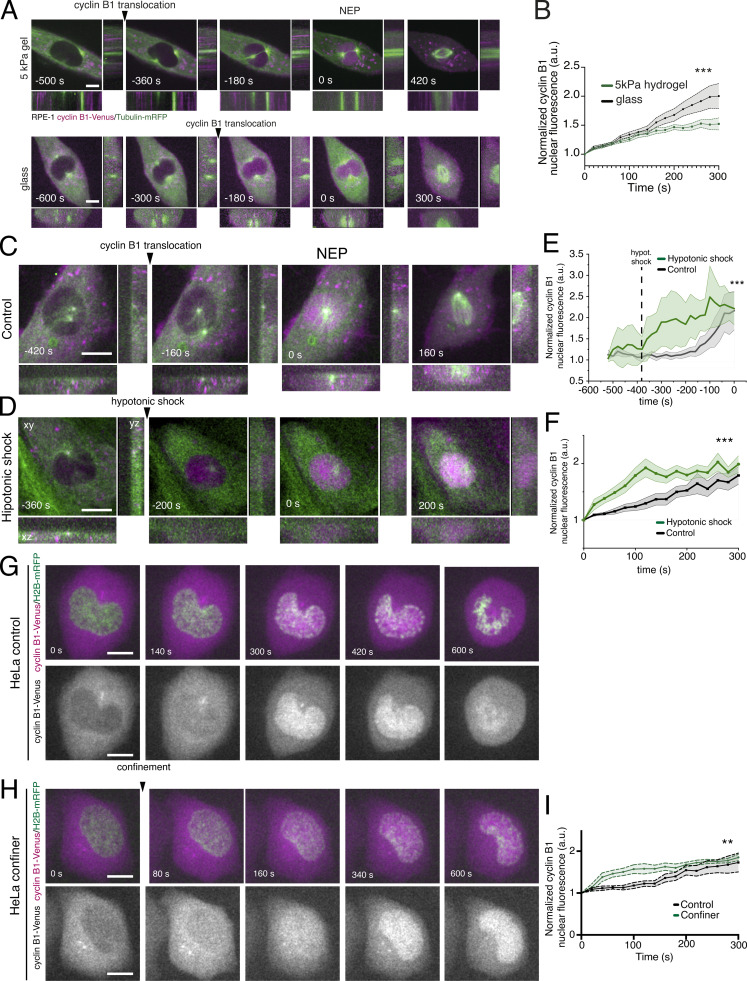
Our data suggest that the mechanical environment might affect cyclin B1 nucleoplasmic translocation. To test this, we seeded cells on a soft hydrogel (5 kPa) or on a rigid glass, inducing low or high cellular tension, respectively. As predicted, cells on glass were more efficient in cyclin B1 nuclear shuttling, than cells on a soft gel (Fig. S2, A and B; ***, P < 0.001). This mechanical stimulation of cyclin B1 translocation was further confirmed by treating RPE-1 cells with a hypotonic shock (Fig. S2, C and D), known to induce cell and nuclear membrane tension (Bakkenist and Kastan, 2003; Kumar et al., 2014), without generating apparent DNA damage (Bakkenist and Kastan, 2003). As expected, the hypotonic shock induced a faster translocation of cyclin B1 into the nucleus, when compared to controls (Fig. S2, C–F; ***, P < 0.001). Confinement of HeLa cells yielded similar faster translocation of cyclin B1 into the nucleus (Fig. S2, G–I; **, P < 0.01), suggesting a conservation of this mechanism. Nevertheless, it should be noted that our confinement setup does not allow distinction between cytoplasmic and nuclear compression and, therefore, we cannot rule out that confinement may trigger additional cytoplasmic mechanosensitive pathways that could contribute to the G2/M transition.
Figure S2.
Cyclin B1 translocation is sensitive to different stimuli. (A) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on a 5 kPa hydrogel (top; n = 16) or on glass (bottom; n = 17). Time is in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to NEP. (B) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for cells seeded on glass (black) or on a 5 kPa hydrogel (green; ***, P < 0.001; paired t test). Quantifications of cyclin B1 fluorescence were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that value (which we defined as time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. Note how seeding cells on a softer substrate (5 kPa gel) delays the accumulation of cyclin B1 inside the nucleus. (C and D) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate under control conditions (C) or subjected to a hypotonic shock (D). Time frame is in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with a 20-s interval and time 0 corresponds to NEP. (E) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence accumulation inside the nucleus, over time for control cells (black; n = 10) and cells subjected to a hypotonic shock (green; n = 19; ***, P < 0.001). Cyclin B1–Venus signal is aligned relative to NEP, which corresponds to time 0. The dashed line corresponds to the moment of the hypotonic shock. (F) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for control cells (black) and cells treated with a hypotonic shock (green; ***, P < 0.001). Quantifications of cyclin B1 fluorescence were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that value (which we defined as time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. (G and H) HeLa cells expressing cyclin B1–Venus/H2B-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate in non-confined (G) and confined (H) conditions. Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to the first imaged frame. The lower panels in G and H show the nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1 in the corresponding cell. (I) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for control (black; n = 6) and confined cells (green; n = 6; **, P < 0.01). Quantifications of cyclin B1 fluorescence were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that value (which we defined as time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. Statistical analysis of cyclin B1 accumulation was performed for the entire time course using an ANOVA repeated measures test when samples had a normal distribution. Otherwise, analysis was done using a repeated measures ANOVA on Ranks. For B, E, F, and I, the lines correspond to the average value and the shaded area corresponds to SEM. In all cases, n represents the number of cells analyzed.
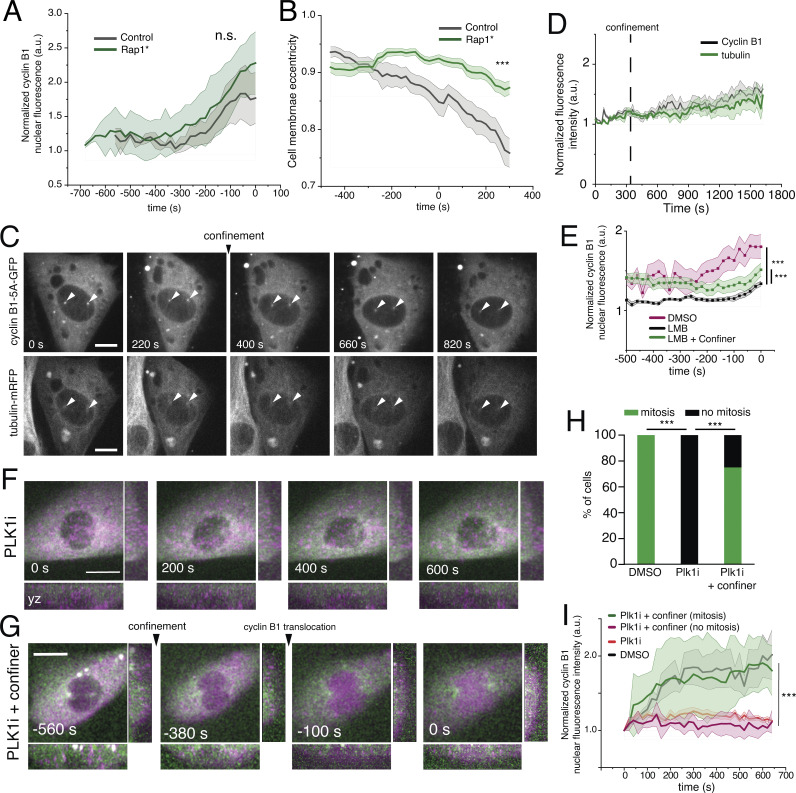
During mitotic entry, cells reorganize their cytoskeleton and round up (Maddox and Burridge, 2003), decreasing the traction forces exerted by cells on the extracellular environment (Nunes et al., 2020). To test whether the process of cell rounding interferes with cyclin B1 translocation, we expressed a mutant form of the GTPase Rap1 (Rap1Q63E, hereafter named Rap1*), which effectively blocks focal adhesion disassembly and prevents cell rounding. Expression of Rap1* did not alter cyclin B1 translocation, even though cell rounding was efficiently blocked, as measured by cell membrane eccentricity (Nunes et al., 2020; Fig. S3, A and B; ***, P < 0.001). Although we cannot completely rule out that cells with different rounding properties could exhibit changes in cyclin B1 translocation kinetics, our data are indicative that this process seems to be independent of cell rounding.
Figure S3.
Effect of cell rounding and Plk1 inhibition on cyclin B1 translocation. (A) Normalized cyclin B1 fluorescence accumulation, inside the nucleus, overtime in control cells (black; n = 10) nd in RPE-1 cells expressing the Rap1* (green; n = 19; n.s., not significant). Cyclin B1–Venus signal is aligned relative to NEP, which corresponds to time 0. (B) Cell membrane eccentricity in control cells (black) and cells expressing Rap1* (green; ***, P < 0.001). (C) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1-5A-GFP (top) and tubulin-mRFP (bottom) seeded on an FBN-coated substrate and under confinement (n = 19). Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to the first imaged frame. White arrowheads indicate separated centrosomes, which help identify cells in late G2/early prophase. (D) Normalized nuclear fluorescence intensity of cyclin B1-5A-GFP (black) and tubulin (green) over time. Quantifications of cyclin B1-5A-GFP fluorescence were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that value (which we defined as time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. The vertical dashed line corresponds to the moment of confinement. (E) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence accumulation inside the nucleus, over time for cells treated with LMB without (black; n = 19; ***, P < 0.001) or with confinement (green; n = 16; ***, P < 0.001). Cyclin B1–Venus signal is aligned relative to NEP, which corresponds to time 0. Note how cells treated with LMB have a delayed nuclear translocation of cyclin B1, even with confinement. (F and G) RPE-1 cells expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP seeded on an FBN-coated substrate, treated with Plk1 inhibitor (Plk1i) without (F; n = 25) or with (G; n = 12) confinement. Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval and time 0 corresponds to NEP. (H) Percentage of cells treated with Plk1i without or with mechanical confinement that enter mitosis, when compared to cells treated with DMSO (***, P < 0.001). (I) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for cells treated with DMSO (black), Plk1i (red), and confined cells treated with Plk1i that either enter (green) or fail to enter (magenta) mitosis (***, P < 0.001). Quantifications of cyclin B1 fluorescence were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that value (which we defined as time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. Statistical analysis of cyclin B1 accumulation was performed for the entire time course using an ANOVA repeated measures test when samples had a normal distribution. Otherwise, analysis was done using a repeated measures ANOVA on Ranks. For A, B, D, E, and I, the lines correspond to the average value and the shaded area corresponds to SEM. In all cases, n represents the number of cells analyzed.
Confinement-induced translocation of cyclin B1 relies on its transport mechanisms
Next, we set out to determine how this confinement-induced cyclin B1 translocation depended on the classical cyclin B1 import pathway. Because translocation in unconfined situations relies on cyclin B1-CDK1 activation (Gavet and Pines, 2010), we imaged cells treated with the CDK1 inhibitor RO-3306, with or without confinement (CDK1i; Fig. 2, A–C). As expected, CDK1 inhibition effectively blocked cyclin B1 translocation to the nucleus (Fig. 2, B and F). Interestingly, confinement was sufficient to overcome the inhibition of CDK1 and force translocation of cyclin B1 to the nucleus (Fig. 2, C and F; ***, P < 0.001). However, these cells failed to enter mitosis, as NEP was blocked by CDK1 inhibition (Heald and McKeon, 1990; Peter et al., 1990). This observation further strengthens the idea that confinement per se does not affect the nucleus barrier function. Accumulation of cyclin B1 relies on a balance between its nuclear import and export. Export is regulated by cyclin B1 binding to the exportin Crm1 (Yang et al., 2001), whereas import is dependent on binding to importin β (Moore et al., 1999) and is greatly enhanced by phosphorylation of cyclin B1 on its CRS sequence (Li et al., 1997; Hagting et al., 1999). We started by treating cells with importazole, to inhibit importin β function. This treatment efficiently blocked cyclin B1 nuclear translocation, even in confinement conditions (Fig. 2, D and G), indicating that the accelerated translocation of cyclin B1 to the nucleus cannot be explained by an increased diffusive shuttling alone, but by an active process, dependent on importin β. A similar block in cyclin B1 translocation was observed when cells expressing a mutant form of cyclin B1 with its five CRS phosphorylation sites mutated to alanines (cyclin B1-5A-GFP; Hagting et al., 1999), were subjected to confinement (Fig. S3, C and D). On the other hand, when nuclear export was inhibited by treatment with LMB, we observed significant decrease in the nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1 when compared to controls (Fig. 2, E and H; and Fig. S3 E), in accordance with previous reports (Santos et al., 2012). This effect was only partially rescued by confinement (Fig. 2 H; ***, P < 0.001). In addition to the mechanisms described above, Plk1 activity has also been recently proposed to regulate mitotic entry and cyclin B1-CDK1 activity (Gheghiani et al., 2017). To determine if confinement-induced translocation was dependent on Plk1 activity, we treated RPE-1 cells with 200 nM of the Plk1 inhibitor BI2536 for 2 h (Plk1i), a dose previously reported to block mitotic entry (Gheghiani et al., 2017). Accordingly, this treatment prevented cells from accumulating cyclin B1 in the nucleus and entering mitosis (Fig. S3, F–I). Strikingly, confining Plk1i cells was sufficient to rescue the accumulation of cyclin B1 and allow mitotic entry (Fig. S3, F–I; ***, P < 0.001). It should be noted that confined, Plk1i-treated cells that failed to enter mitosis also did not accumulate cyclin B1 in the nucleus (Fig. S3, H and I). Overall, our data strongly suggest that a mechanical signal acts in parallel with the biochemical pathways to help regulate the timing of cyclin B1 nuclear accumulation and control mitotic entry, in a process that requires phosphorylation of cyclin B1 in the CRS and binding to importin β.
Figure 2.
Characterization of confinement-induced cyclin B1 translocation. (A) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP, dividing on a FBN-coated substrate (n = 15). Right panels highlight cyclin B1 and tubulin accumulation at the nucleus. Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to NEP. (B) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP seeded on an FBN-coated substrate, treated with a CDK1 inhibitor (CDK1i; n = 23). Right panels highlight the lack of cyclin B1 and tubulin accumulation inside the nucleus even after a prolonged time, which reflect an inability to undergo NEP. Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval and time 0 corresponds to the first frame. (C) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP seeded on a FBN-coated substrate, treated with CDK1i and under confinement (n = 17). Right panel shows confinement-induced nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1 and the lack of nuclear tubulin accumulation. This demonstrates the ability of confinement to induce cyclin B1 translocation in the absence of CDK1 activity, without inducing mitotic entry. Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to the first frame. (D) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP seeded on a FBN-coated substrate, treated with importazole and under confinement (n = 18). Right panel highlights the absence of nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1 and tubulin. Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval and time 0 corresponds to the first frame. Note that cyclin B1 translocation and NEP require importin activity even under confinement. (E) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP seeded on an FBN-coated substrate, treated with Leptomycin B1 (LMB; n = 19). Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval and time 0 corresponds to NEP. Right panels highlight the nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1 and tubulin. (F) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time in control, DMSO-treated cells without (magenta; n = 15) and with mechanical confinement (gray; n = 30; ***, P < 0.001), cells treated with CDK1i (black; n = 23) and cells treated with CDK1i and subjected to confinement (green; n = 17; ***, P < 0.001). Values were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that (time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. (G) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time, in DMSO-treated cells without (magenta; n = 17; ***, P < 0.001) and with confinement (gray; n = 30; ***, P < 0.001), treated with importazole (black; n = 27), and treated with importazole and under confinement (green; n = 18; n.s.). Values were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that (time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. (H) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time in control DMSO treated cells without confinement (magenta; n = 17; ***, P < 0.001) and with mechanical confinement (gray: n = 30; ***, P < 0.001), cells treated with Leptomycin B1 (LMB; black; n = 19) and cells treated with LMB under confinement (green; n = 16). Values were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that (time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. Note that the DMSO and DMSO + confiner groups are the same for F–H. Statistical analysis of cyclin B1 accumulation was performed for the entire time course using an ANOVA repeated measures test when samples had a normal distribution. Otherwise, analysis was done using a repeated measures ANOVA on Ranks. For F–H, the lines correspond to the average value and the shaded area corresponds to SEM. All experiments were replicated at least three times and n represents the number of cells analyzed.
Cyclin B1 translocation requires actomyosin activity
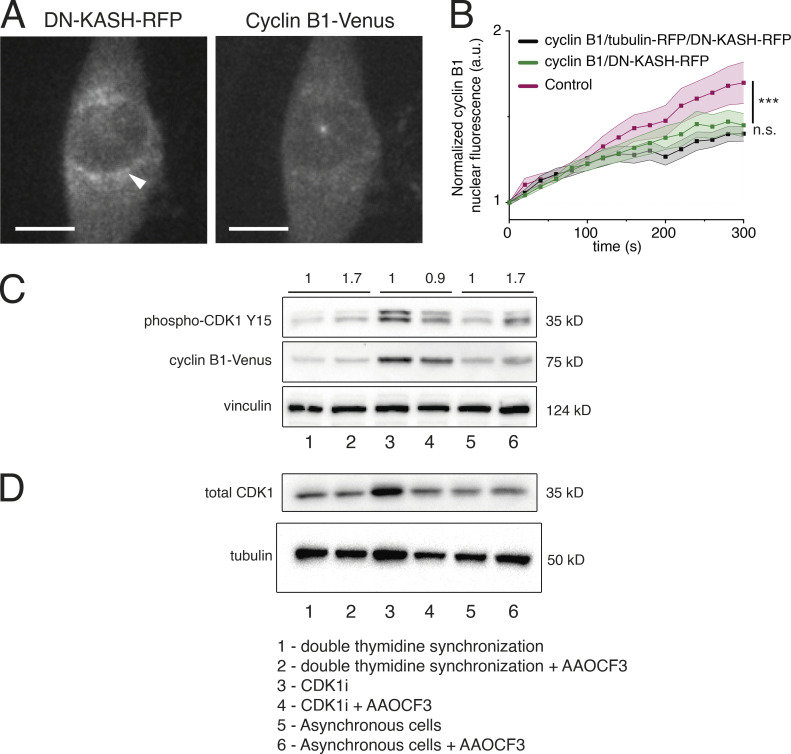
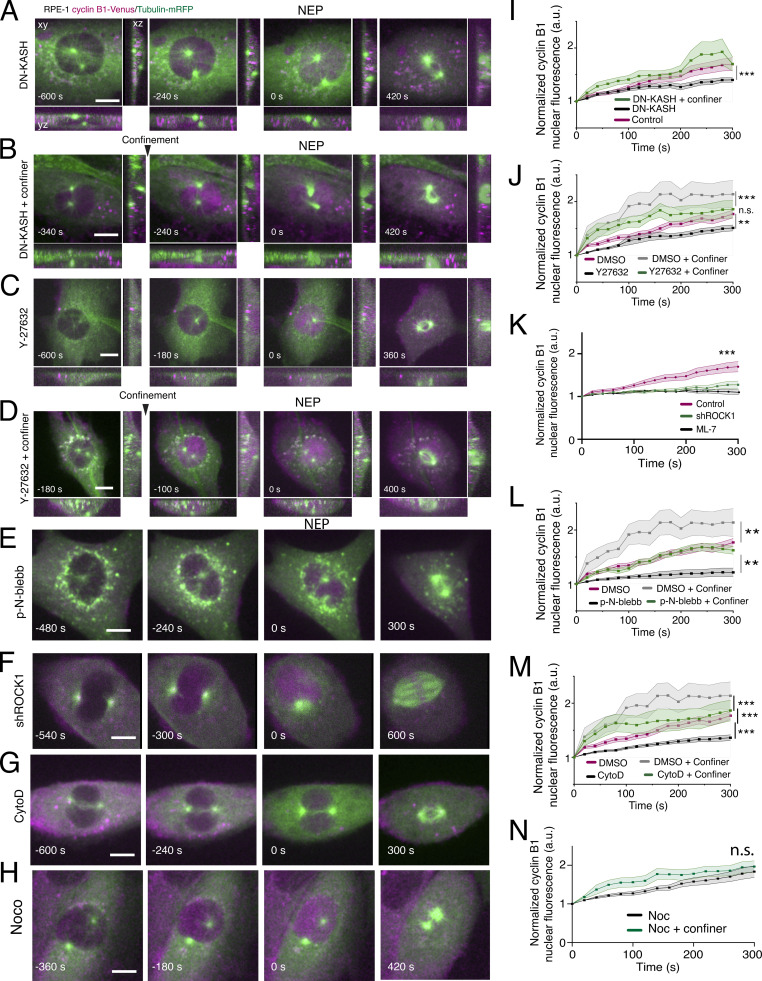
We then sought to identify potential mechanosensing mechanisms involved in the transport of cyclin B1 to the nucleus. Mechanical forces generated by the cytoskeleton are transmitted to the nucleus through the linker of cytoskeleton and nucleoskeleton (LINC) complex (Lombardi and Lammerding, 2011). To address how force transmission might affect cyclin B1 nuclear translocation, we exogenously expressed a dominant-negative form of nesprin tagged with RFP (DN-KASH-RFP) that prevents its binding to SUN proteins and blocks force propagation (Lombardi and Lammerding, 2011). This was performed in two parallel experiments: firstly, we expressed DN-KASH-RFP in the RPE-1 cyclin B1–Venus cell line. This allowed us to specifically select cells that were expressing the KASH construct (Fig. S4 A) and measure cyclin B1 translocation (Fig. S4 B). Secondly, we expressed the same construct in the RPE-1 cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-RFP that was used in our previous experiments, so that we could directly compare the effects on cyclin B1 translocation. Importantly, expressing DN-KASH-RFP in either cell line yielded similar results regarding cyclin B1 translocation (Fig. S4 B; ***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant), with a significant delay in cyclin B1 nuclear accumulation (Fig. 3, A and I; ***, P < 0.001). These results demonstrate that the effect of confinement was mediated by force transmission to the nucleus. Similarly, we also observed delays in cyclin B1 translocation following inhibition of ROCK with Y-27632 (Fig. 3, C and J; **, P < 0.01), depletion of ROCK1 with shRNA (Fig. 3, F and K; ***, P < 0.001), myosin II inhibition with para-nitro-blebbistatin (p-N-blebb; Fig. 3, E and L; **, P < 0.01), inhibition of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) with ML-7 (Fig. 3 K), and actin depolymerization with cytochalasin D (CytoD; Fig. 3, G and M; ***, P < 0.001). Conversely, microtubule depolymerization with nocodazole did not affect cyclin B1 translocation (Noc; Fig. 3 H; n.s., not significant). Importantly, confinement was able to fully rescue cyclin B1 accumulation that was lost upon expression of DN-KASH (Fig. 3, B and I; ***, P < 0.001) or treatment with Y27632 (Fig. 3, D and J), and partially rescued accumulation following actin (Fig. 3, G and M; ***, P < 0.001) or myosin (Fig. 3, E and L; **, P < 0.01) inhibitions. Overall, these experiments identify actomyosin-dependent force transmission to the nucleus as important players in facilitating cyclin B1 nuclear translocation.
Figure S4.
Effect of cPLA2 inhibition on CDK1 and cyclin B1 levels. (A) Representative image of an RPE-1 cell expressing DN-KASH-RFP construct. Note the accumulation of KASH on the NE, which allowed us to specifically select cells that were expressing the construct. (B) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for control cells (magenta; n = 16; ***, P < 0.001), cells expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin m-RFP/DN-KASH-RFP (black; n = 20; n.s., not significant) and cells expressing cyclin B1–Venus/DN-KASH-RFP (green; n = 18). In all cases, n represents the number of cells analyzed. No difference was found between the two cell lines expressing the DN-KASH construct. Quantifications of cyclin B1 fluorescence were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that value (which we defined as time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. Lines represent average values and shaded areas correspond to SEM. Statistical significance was analyzed for the entire time course, using a repeated measures ANOVA on Ranks. (C) Western blot analysis of phospho-CDK1 (Y15), cyclin B1, and vinculin levels in thymidine synchronized cells without (1) or with (2) AAOCF3, cells treated with CDK1i without (3) or with (4) AAOCF3, and asynchronous cells without (5) or with (6) AAOCF3. Semi-quantitative analysis of phosphor-CDK1 (Y15) was performed by comparing the AAOCF3-treated cells with the corresponding controls. Fold variations relative to the respective controls are annotated above the blot. As can be seen, treatment with AAOCF3 increases the levels of phospho-CDK1 (Y15) both in synchronous and asynchronous populations. There is no variation in CDK1i-treated cells. (D) Western blot analysis of total CDK1 and tubulin levels in thymidine synchronized cells without (1) or with (2) AAOCF3, cells treated with CDK1i without (3) or with (4) AAOCF3, and asynchronous cells without (5) or with (6) AAOCF3. Treatment with AAOCF3 does not increase total CDK1 levels. These experiments were done in duplicate. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData FS4.
Figure 3.
Actomyosin contractility contributes to cyclin B1 translocation. (A) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate, expressing a DN-KASH-RFP mutant (n = 17). (B) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate, expressing a DN-KASH-RFP mutant and subjected to confinement (n = 17). (C) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate and treated with Y-27632 (n = 21). (D) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus and tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate, treated with Y-27632 and dividing under confinement (n = 19). Note that confinement overcomes the lack of ROCK activity and enhances cyclin B1 accumulation. (E) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate and treated p-Nitro-blebbistatin (p-N-blebb; n = 15). (F) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate and depleted for ROCK1 (shROCK1; n = 15). (G) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate and treated Cytochalasin D (CytoD; n = 26). (H) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate and treated Nocodazole (Noco; n = 20). For all images, time frame is in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with a 20-s interval and time 0 corresponds to NEP, as determined by tubulin accumulation in the nuclear space. (I) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for control cells (magenta; n = 22) and cells expressing the DN-KASH mutant without (black; n = 17; ***, P < 0.001) or with confinement (green; n = 17; ***, P < 0.001). (J) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time in cells treated with DMSO without (magenta; n = 14) and with mechanical confinement (gray; n = 30; ***, P < 0.001), non-confined cells treated with Y-27632 (black; n = 21; **, P < 0.01) and confined cells treated with Y-27632 (green; n = 19; n.s., not significant). (K) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for control cells (magenta; n = 22; ***, P < 0.001), cells expressing shROCK1 (green; n = 15) and cells treated with ML-7 (black; n = 12). (L) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for cells treated with DMSO without (magenta; n = 14) and with mechanical confinement (gray; n = 30; **, P < 0.01), non-confined cells treated with p-Nitro-blebbistatin (p-N-blebb; black; n = 15; P < 0.01) and confined cells treated with p-N-blebb (green; n = 18). (M) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for cells treated with DMSO without (magenta; n = 14) and with mechanical confinement (gray; n = 30; **, P < 0.01), non-confined cells treated with Cytochalasin D (CytoD; black; n = 26; ***, P < 0.001) and confined cells treated with CytoD (green; n = 18; ***, P < 0.001). (N) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for cells treated with Noco without (black; n = 20) or with confinement (green; n = 20; n.s., not significant). In I–N, quantifications of cyclin B1 fluorescence were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that value (which we defined as time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. Note that the confiner experimental group is the same for J, L, and M. Statistical analysis of cyclin B1 accumulation was performed for the entire time course using an ANOVA repeated measures test when samples had a normal distribution. Otherwise, analysis was done using a repeated measures ANOVA on Ranks. For I–N, the lines correspond to the average value and the shaded area corresponds to SEM. All experiments were replicated at least three times and n represents the number of cells analyzed.
Tension on the nuclear envelope regulates cyclin B1 nuclear translocation
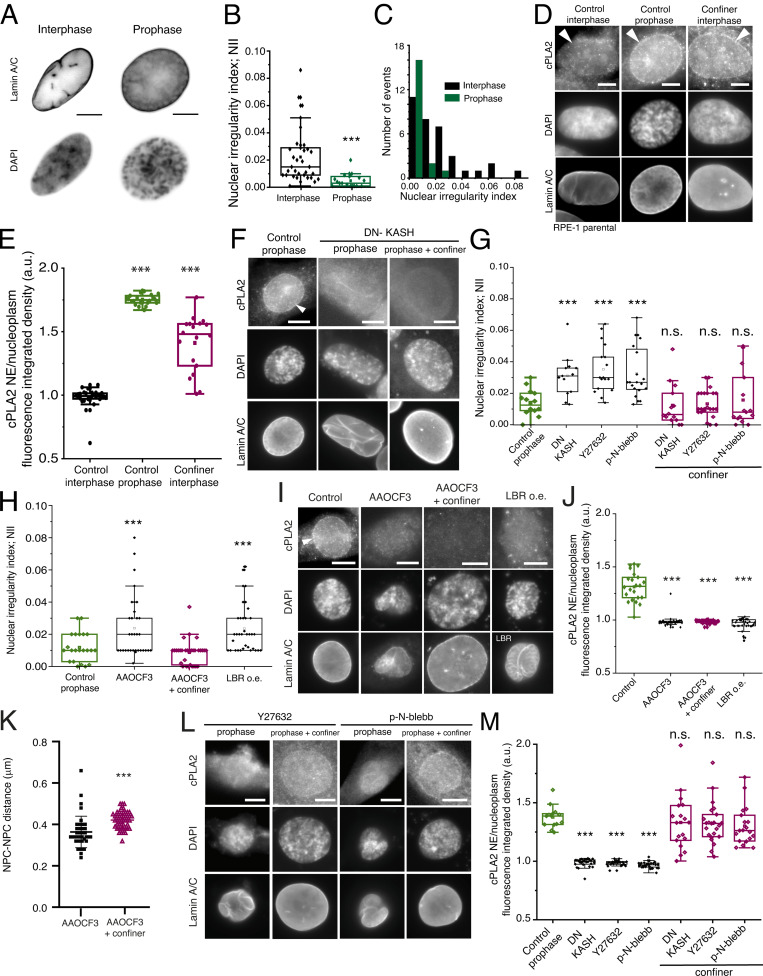
Our results indicate that during the G2-M transition, the NE unfolds an event that can be exacerbated by mechanical confinement (Fig. S1). Moreover, we showed that actomyosin contractility facilitates the translocation of cyclin B1 into the nucleus (Fig. 3). Since increased actomyosin contractility was recently shown to induce NE unfolding (Lomakin et al., 2020; Venturini et al., 2020), we tested whether such a mechanism also acted during the G2-M transition. To do so, we evaluated the nuclear irregularity index (NII) of interphase and prophase nuclei using fixed-cell analysis. This parameter was calculated as 1-solidity (solidity is defined as nucleus area/nucleus convex area). Our results confirm a decrease in NII in prophase cells, when compared to interphase, indicating an unfolding of the NE (Fig. 4, A–C; ***, P < 0.001). Nuclear unfolding was previously associated with increased nuclear tension (Enyedi et al., 2016), which triggers the recruitment and activation of the calcium-dependent, nucleoplasmic phospholipase cPLA2 to the NE. Active cPLA2 was proposed to stimulate actomyosin contractility, creating a positive feedback loop (Lomakin et al., 2020; Venturini et al., 2020). If indeed prophase nuclei are under increased tension, it is possible that cPLA2 is recruited to the NE at this stage. Accordingly, we found that cPLA2 is recruited to the NE during prophase, similarly to what happens in confined interphase cells (Lomakin et al., 2020; Venturini et al., 2020; white arrows, Fig. 4, D and E; ***, P < 0.001), suggestive of increased NE tension and cPLA2 activation at this stage. While our data show that NE unfolding during prophase can recruit cPLA2, it does not explain how the NE unfolds in the first place. To determine this, we analyzed the NII of cells expressing DN-KASH or treated with actomyosin inhibitors. All treatments led to an increase in NII, which was reverted upon confinement (Fig. 4, F and G; ***, P < 0.001). This confinement-generated decrease in NII likely reflects an unfolding of the NE, which is evident from the images of confined nuclei (Fig. 4, F and L) as well as the increased NPC-NPC distance (Fig. S1; ***, P < 0.001). Overall, this suggests that actomyosin activity transmits forces to the NE through the LINC complex, leading to nuclear unfolding. To further characterize the mechanism behind nuclear unfolding and cPLA2 recruitment, we then inhibited cPLA2 activity with AAOCF3 and analyzed the changes in NII. Indeed, interfering with cPLA2 activity significantly increased NII (Fig. 4 H; ***, P < 0.001), although to a lesser extent than actomyosin inhibition (0.024 ± 0.019 for AAOCF3, 0.035 ± 0.015 for Y27632; P = 0.007 and 0.033 ± 0.016 for p-N-blebb; P = 0.019). As expected, inhibition of cPLA2 also led to a decrease of its association with the NE, even after confinement (Fig. 4, I and J; ***, P < 0.001). Importantly, confinement was able to induce nuclear unfolding and increase NPC distance, even after cPLA2 inhibition (Fig. 4, I–K; ***, P < 0.001). It should be noted that AAOCF3 treatment alone does not decrease NPC distance below those observed for control cells (Fig. S1 K and Fig. 4 K; 0.350 ± 0.05 μm for controls vs. 0.364 ± 0.08 μm for AAOCF3-treated cells).
Figure 4.
Nuclear unfolding during prophase recruits cPLA2 to the NE. (A) Representative images of nuclei of interphase and prophase cells immunostained for Lamin A/C and DAPI. Please note the irregularities on the NE surface in interphase cells. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) Nuclear irregularity index (NII) in interphase (black; n = 34) versus mitotic cells (green; n = 20; ***, P < 0.001; rank sum test). (C) Distribution of NII values in interphase (black) and mitotic cells (green). (D) Representative immunofluorescence images of parental RPE-1, non-confined interphase cells (control interphase; n = 32), non-confined prophase cells (control prophase; n = 28), and confined interphase cells (interphase confiner; n = 19), stained for cPLA2, Lamin A/C, and DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. White arrowheads indicate the NE limit. (E) Quantification of the NE/nucleoplasm integrated fluorescence intensity for cPLA2 in control interphase cells (black), control prophase cells (green; ***, P < 0.001) and confined interphase cells (magenta; ***, P < 0.001). Comparison between experimental groups was performed using a one-way ANOVA test. (F) Representative immunofluorescence images of parental RPE-1 cells in non-confined prophase cells (control prophase; n = 14), prophase cells expressing the DN-KASH (n = 26) and prophase cells expressing DN-KASH under confinement (n = 27), stained with cPLA2, DAPI, and Lamin A/C. (G) NII in control, prophase cells (n = 15), prophase cells expressing DN-KASH without (n = 14) or with (n = 13) confinement, prophase cells treated with Y-27632 without (n = 17) or with (n = 23) confinement and cells treated p-Nitro-blebb without (n = 20) or with confinement (n = 16; ***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant). (H) NII in control prophase cells (green; n = 20), cells treated with AACOCF3 without (black; n = 30; ***, P < 0.001) or with confinement (magenta; n = 30; n.s.) and cells over-expressing LBR (LBR o.e.; black; n = 30; ***, P < 0.001). (I) Representative immunofluorescence images of parental RPE-1 cells in prophase, non-confined conditions, prophase cells treated with AACOCF3 without (n = 34) or with (n = 29) confinement and stained with cPLA2, DAPI, and Lamin A/C. The panel on the right corresponds to a representative image of cells stained with cPLA2 and DAPI and over-expressing LBR. As cam be seen both the treatment with AACOCF3 and over-expression of LBR increase NE folding during prophase. Scale bars, 10 μm. (J) Quantification of the NE/nucleoplasm integrated fluorescence intensity for cPLA2 in control, prophase cells (green; n = 20), AAOCF3-treated prophase without (black; n = 30; ***, P < 0.001) or with confinement (magenta; n = 30; ***, P < 0.001) and cells prophase over-expressing LBR (black; n = 30; ***, P < 0.001). Note how both the treatment with AACOCF3 and LBR over-expression impair the accumulation of cPLA2 at the NE during prophase. Comparison between experimental groups was performed using a one-way ANOVA when samples had a normal distribution. Otherwise, comparisons were done using a Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA on Ranks. (K) Quantification of the NPC-NPC distance in cells treated with AACOCF3 without (black; n = 41) and with mechanical confinement (magenta; n = 47; ***, P < 0.001). Note how confinement increases NPC-NPC distance even with cPLA2 inhibition. This measurement was done using the custom MATLAB algorithm, as described in the Materials and methods section. (L) Representative immunofluorescence images of parental RPE-1 cells in prophase treated with Y-27632 without (n = 17) or with (n = 23) confinement and cells treated with p-N-blebb without (n = 20) or with (n = 16) confinement. Cells were stained for cPLA2, DAPI, and Lamin A/C. Note how confinement restores the accumulation of cPLA2 on the NE, even with actomyosin inhibition. Scale bars, 10 μm. (M) Quantification of the NE/nucleoplasm integrated fluorescence intensity for cPLA2 in control prophase cells, prophase cells expressing DN-KASH (n = 26), treated with Y-27632 or treated with p-Nitro-blebb, without or with confinement (***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant). Note how interfering with the LINC complex or the actomyosin cytoskeleton prevents cPLA2 recruitment to the NE and is reverted by confinement. For B, E, G, H, J, K, and M, the box size represents 75% of the population and the line inside the box represents the median of the sample. The size of the bars (whiskers) represents the maximum (in the upper quartile) and the minimum (in the lower quartile) values. All experiments were replicated at least three times and n represents the number of cells analyzed.
So far, our results indicate that actomyosin activity leads to increased nuclear unfolding and cPLA2 NE recruitment. Whether this is reflective of increased nuclear tension, it remained unknown. For that purpose, we sought to interfere with nuclear tension, independently of actomyosin activity, by overexpressing lamin B receptor (LBR). Overexpression of LBR is known to cause NE folding (Gravemann et al., 2010), decrease nuclear tension, and significantly affect cytoplasmic calcium levels and production of arachidonic acid, key components of the cPLA2 signaling pathway (Lomakin et al., 2020). As expected, overexpression of LBR resulted in a significant increase in NII (Fig. 4, H and I; ***, P < 0.001) and a consequent decrease in the levels of cPLA2 on the NE (Fig. 4, I and J; ***, P < 0.001). Collectively, these data indicate that actomyosin contractility triggers NE unfolding and increased tension during prophase. This was further confirmed by blocking actomyosin activity or expressing DN-KASH, which significantly decreased cPLA2 accumulation on the NE (Fig. 4, F, L, and M; ***, P < 0.001), and could be rescued by confinement (Fig. 4, L and M; ***, P < 0.001). Taken together, this indicates that an intact connection between the cytoskeleton and nucleus is required to set off a tension-dependent signal that results in cPLA2 recruitment to the NE.
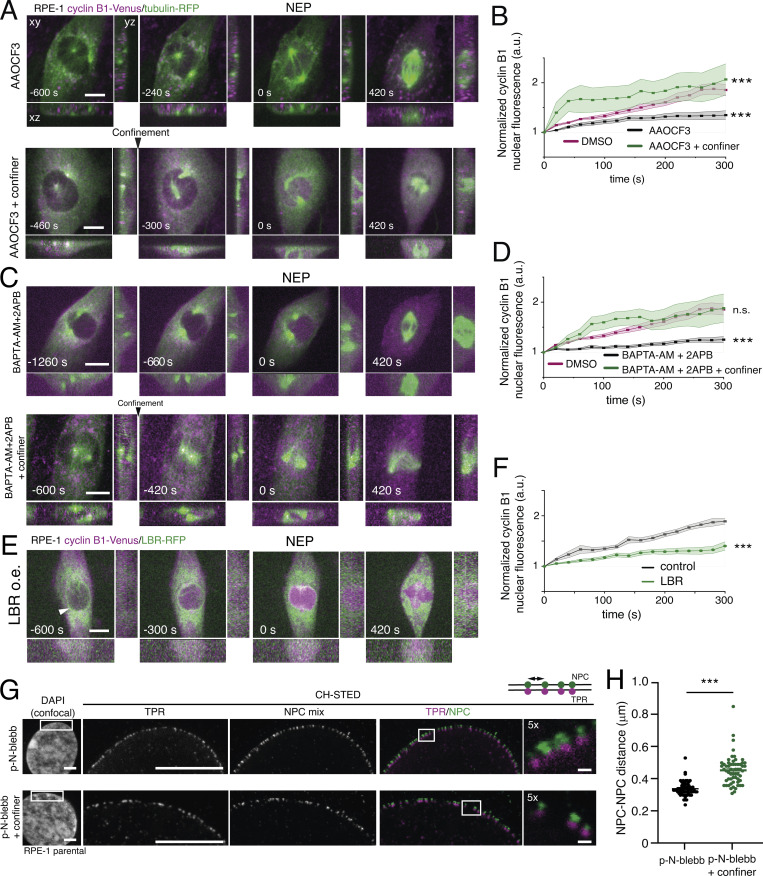
Overall, we concluded that an increase in actomyosin contractility during prophase is required to unfold the NE, increasing nuclear tension, and leading to cPLA2 recruitment. The question remains of the functional relevance of cPLA2 NE recruitment. If cPLA2 is functionally important to facilitate cyclin B1 translocation, inhibiting its activity should result in a delay in cyclin B1 nuclear accumulation. Indeed, inhibition of cPLA2 activity with AAOCF3 led to a significant decrease in cyclin B1 nucleoplasmic shuttling (Fig. 5, A and B; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). To further understand how cPLA2 interfered with cyclin B1 translocation, we analyzed the levels of CDK1 Y15 phosphorylation and cyclin B1, following cPLA2 inhibition. Phosphorylation of CDK1 on T14/Y15 is well known to prevent mitotic entry (Parker et al., 1992; Kornbluth et al., 1994; Mueller et al., 1995). We reasoned that if cPLA2 affected the pathway controlling CDK1 activation, we should see an increase in this inhibitory phosphorylation, following treatment with AAOCF3. Accordingly, treatment with AAOCF3 increased the levels of CDK1 Y15, when compared to controls for both synchronized (1 for controls vs. 1.7 for AAOCF3-treated cells) and asynchronous cells (1 for controls vs. 1.7 for AAOCF3-treated cells), but not for CDK1i cells (1 for CDK1i vs. 0.9 for CDK1i + AAOCF3), without affecting total CDK1 levels (Fig. S4 D). These results suggest that inhibition of cPLA2, through a yet unknown mechanism, delays activation of the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex, which could partly explain the delay in nuclear translocation of cyclin B1 observed upon treatment with AAOCF3 (Fig. 5, A and B).
Figure 5.
cPLA2 is required for cyclin B1 nuclear translocation. (A) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate treated with AACOCF3 in non-confined conditions (top; n = 12) and confined conditions (bottom; n = 15). Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval and time 0 corresponds to NEP. (B) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for cells treated with DMSO (magenta; n = 16; ***, P < 0.001) and the cPLA2 inhibitor (AACOCF3) in non-confined (black; n = 15) or confined (green; n = 12) conditions. (C) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate treated with BAPTA-AM + 2APB in non-confined (top; n = 17) or confined (bottom; n = 11) conditions. Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval, and time 0 corresponds to NEP. (D) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for cells treated with DMSO (magenta; n = 16) and cells treated with BAPTA-AM + 2APB in non-confined (black; n = 17) or confined (green; n = 11) conditions (***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant). Statistical analysis of cyclin B1 accumulation was performed for the entire time course using an ANOVA repeated measures test when samples had a normal distribution. Otherwise, analysis was done using a repeated measures ANOVA on Ranks. (E) RPE-1 cell expressing cyclin B1–Venus/LBR-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate (n = 30). Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 20-s interval and time 0 corresponds to NEP. White arrowhead indicates the presence of LBR on the NE. (F) Normalized nuclear cyclin B1 fluorescence over time for mock-transfected cells (black; n = 11) and cells with LBR-RFP overexpression (green; n = 16; ***, P < 0.001). Note how LBR over-expression delays the nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1. Statistical analysis of cyclin B1 accumulation was performed for the entire time course using an ANOVA repeated measures test when samples had a normal distribution. Otherwise, analysis was done using a repeated measures ANOVA on Ranks. In B, D, and F, quantifications of cyclin B1 fluorescence were normalized to the lowest fluorescence intensity inside the nucleus and aligned relative to that value (which we defined as time 0), to obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate. Note that the DMSO treated group is the same for B and D. (G) Representative images of parental RPE-1 cells stained for TPR (magenta) and an NPC mix (green) in non-confined (top panel; n = 62) and confined conditions (bottom panel; n = 59), after treatment with p-N-blebb, acquired with CH-STED. Scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Note in the inset how mechanical confinement increases NPC-NPC distances (scale bar on inset corresponds to 2 μm). (H) Distance between neighboring nuclear pore complexes (NPC-NPC distance) in cells treated with p-N-blebb without (black) or with confinement (green; ***, P < 0.001). This measurement was done using the custom MATLAB algorithm, as described in the Materials and methods section. For B, D, and F, the lines correspond to the average value and the shaded area corresponds to SEM. All experiments were replicated at least three times and n represents the number of cells analyzed.
Since the release of internal Ca2+ stores triggers cPLA2 NE recruitment and activation (Enyedi et al., 2016), we next decided to acutely interfere with the release of Ca2+ using BAPTA-AM + 2APB. Strikingly, this treatment also decreased cyclin B1 nuclear translocation (Fig. 5, C and D; ***, P < 0.001), as anticipated. While we cannot rule out that interfering with calcium release might affect other cellular processes, the use of BAPTA to disrupt internal calcium release during prophase has been previously described (Kao et al., 1990) and should not affect NEP at the concentrations used in our study. Moreover, we sought to minimize possible side effects by adding the drugs acutely in late G2. Similarly to the BAPTA treatment, decreasing nuclear stiffness by overexpression of LBR also significantly delayed cyclin B1 nuclear translocation (Fig. 5, E and F; ***, P < 0.001) and decreased cPLA2 loading on the NE (Fig. 4, I and J). Remarkably, confinement was able to stimulate cyclin B1 translocation, when cPLA2 activity or calcium release was inhibited (Fig. 5, A–D; ***, P < 0.001). This likely occurs due to confinement-induced unfolding of the NE (Fig. S1), that is sufficient to bypass the pharmacological inhibition of contractility and still induce an increase in NPC distance (Fig. 5, G and H; ***, P < 0.001). Together, these observations support a working model for the mechanical regulation of mitotic entry based on actomyosin activity, that triggers nuclear unfolding and increases tension on the nucleus, leading to cPLA2 activation. This facilitates cyclin B1 transport across the NPCs, increasing its nuclear accumulation.
Premature nuclear entry of cyclin B1 increases the frequency of mitotic errors
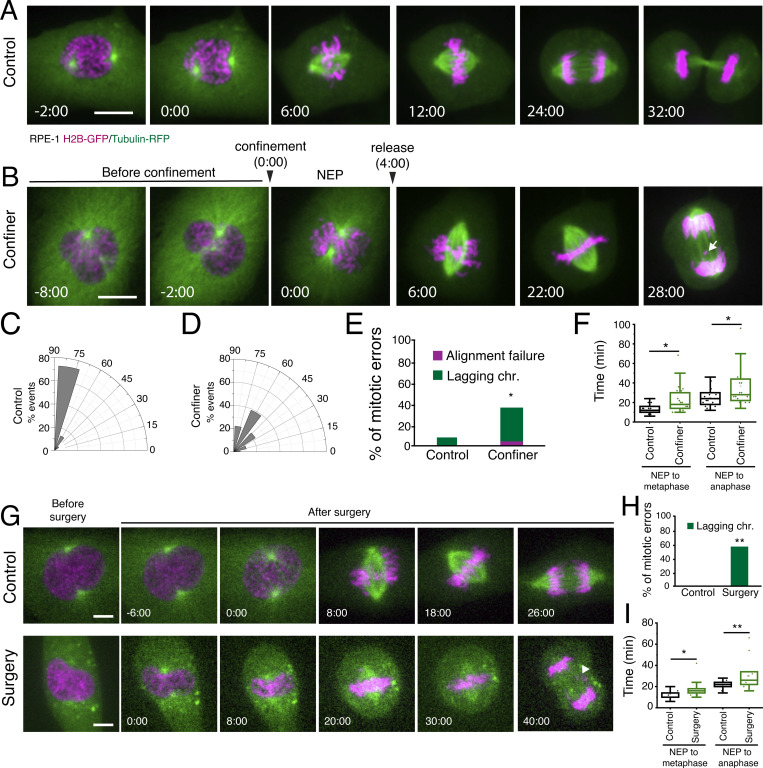
Nuclear translocation of cyclin B1 sets the time for the G2-M transition (Strauss et al., 2018) and is essential for preventing untimely mitotic entry, which results in chromosome segregation errors (Furuno et al., 1999). Similarly, confining cells throughout mitosis also contribute to the occurrence of segregation errors (Tse et al., 2012; Lancaster et al., 2013). Whether a short confinement during prophase only, which is sufficient to induce premature cyclin B1 translocation and NEP, results in chromosome segregation errors remains unknown. To test this, we subjected cells in prophase to a short confinement, which was released shortly after NEP (Fig. 6 A). This approach should induce mitotic entry, while still providing enough volume for the spindle to assemble unconstrained (Lancaster et al., 2013). Cells were then allowed to progress through mitosis unperturbed, so that we could determine mitotic timings, as well as the rate of chromosome missegregation. Notably, a significant proportion of cells that were subjected to short confinement entered mitosis with incomplete centrosome separation (Fig. 6, A–D). This condition has been shown, by us and others, to increase the frequency of mitotic errors, in particular the occurrence of lagging chromosomes (Silkworth et al., 2012; Nunes et al., 2020), by favoring the establishment of erroneous kinetochore-microtubule attachments. Importantly, our acute confinement resulted in increased chromosome segregation errors (Fig. 6 E; *, P < 0.05) and a slight mitotic delay (Fig. 6 F; 24 ± 7 min for controls vs. 36 ± 20 min for confined cells; *, P < 0.05), when compared to unconfined cells. We propose these mitotic errors are triggered by the acute confinement that accelerates NEP, before cells had time to organize a mitotic spindle. To test this, we decided to generate an artificial rupture of the NE with laser microsurgery (Schweizer et al., 2015), allowing cyclin B1 and tubulin to enter the nuclear space and anticipating mitotic entry (Fig. 6 G). Using this approach, we triggered immediate mitotic entry, which was sufficient to increase chromosome missegregation events (white arrowhead, Fig. 6, G and H; **, P = 0.02) and induce a slight mitotic delay (Fig. 6 I). Together, these experiments demonstrate that untimely mitotic entry through acute mechanical confinement during the G2-M transition can have deleterious downstream consequences for chromosome segregation.
Figure 6.
Premature mitotic entry potentiates chromosome segregation errors. (A and B) RPE-1 cell expressing H2B-GFP/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate without (A) or with (B) short-term confinement. Time frame in min:sec and scale bars correspond to 10 μm. Images were acquired with a 2-min interval and time 0 corresponds to NEP. White arrowhead in B is pointing to a lagging chromosome which is generated after a short confinement. (C and D) Centrosome positioning relative to the shortest nuclear axis at the moment of NEP in cells dividing without (C) or with (D) confinement. (E) Percentage of mitotic errors in control, non-confined cells (n = 26) and cells under a short period of confinement (n = 23; *, P < 0.05; Z-score test). (F) Mitotic timings (NEP-metaphase and NEP-anaphase) in control, non-confined cells (black) and cells under a short period of confinement (green; *, P < 0.05). (G) RPE-1 cells expressing H2B-GFP/tubulin-mRFP dividing on an FBN-coated substrate, with a mock laser microsurgery performed on the cytoplasm (top; n = 12), and NE rupture induced by laser microsurgery (bottom; n = 15). Time frame in seconds and scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. Images were acquired with 2-min interval, and time 0 corresponds to NEP. White arrowhead indicates the presence of lagging chromosomes. (H) Percentage of mitotic errors in control cells and cells where the NE was ruptured using laser microsurgery (**, P < 0.01). (I) Mitotic timings (NEP-metaphase and NEP-anaphase) in control cells (black) and cells where the NE was ruptured using laser microsurgery (green; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). Comparison between groups was performed using a two-sided t test when the sample had normal distribution. Otherwise, the comparison was performed using a rank sum test. For F and I, the box size represents 75% of the population and the line inside the box represents the median of the sample. The size of the bars (whiskers) represents the maximum (in the upper quartile) and the minimum (in the lower quartile) values. All experiments were replicated at least three times and n represents the number of cells analyzed.
Discussion
The biochemical regulation of the G2-M transition has been extensively studied (Pines and Hunter, 1989; Li et al., 1997; Hagting et al., 1998; Hagting et al., 1999; Toyoshima et al., 1998; Gavet and Pines, 2010). A master regulator of this transition is the complex composed of cyclin B1-CDK1, whose activity must be tightly regulated. During interphase, cyclin B1 is expressed at low levels and localizes mainly to the cytoplasm (Hagting et al., 1998; Toyoshima et al., 1998). As cells transit from S to G2, cyclin B1 levels progressively increase (Akopyan et al., 2014; Feringa et al., 2016; Pines and Hunter, 1989), leading to cyclin binding to CDK1 in late G2. Once this occurs, the complex is inactivated by Myt1- and Wee1-mediated phosphorylation of CDK1 on residues T14 and Y15 (Lindqvist, 2010). When these inhibitory phosphorylations are removed by Cdc25 phosphatases, the complex becomes activated, rapidly stimulating its own nuclear import (Gavet and Pines, 2010). In addition to the removal of inhibitory phosphorylations on CDK1, additional mechanisms ensure the nuclear translocation of cyclin B1. These involve phosphorylation of the CRS sequence in cyclin B1 (Li et al., 1997; Hagting et al., 1999) and binding to importin β in a Ran-independent manner (Moore et al., 1999; Takizawa et al., 1999). Once inside the nucleus, the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex then triggers NPC disassembly by phosphorylating nucleoporin Nup53 (Linder et al., 2017) and is involved in the phosphorylation and subsequent disassembly of the nuclear lamina (Heald and McKeon, 1990). This mechanism allows a fast redistribution of the cyclin B1–CDK1 complexes between the cytoplasm and the nucleus, ensuring the spatiotemporal coordination of all necessary steps leading up to mitotic entry.
So far, the contribution of mechanical forces for this essential step of the cell cycle was little explored. Recent evidence proposed that during the G2-M transition, mechanical stretch activated Piezo 1, ultimately leading to cyclin B1 transcription and consequent mitotic entry (Gudipaty et al., 2017). Here, we propose a nongenetic, mechanical pathway based on nuclear tension that acts during the G2-M transition, impacting cyclin B1 translocation and NEP. In agreement with this model, we showed that this process requires force transmission to the nucleus through the LINC complex (Fig. 3, A, B, and I). Interestingly, the LINC complex was previously proposed to play a role in early spindle assembly, by facilitating chromosome alignment in a myosin II-dependent manner (Booth et al., 2019) and assisting in centrosome positioning (Stiff et al., 2020). Our work now proposes an additional role for the LINC complex- and actomyosin activity in facilitating cyclin B1 translocation (Fig. 3). In addition, we also demonstrated that decreasing nuclear tension by overexpression of LBR significantly impaired nuclear cyclin B1 uptake. Taken together, these observations suggest that nuclear force transmission and sensing could be an important player for early mitotic events. One key aspect that remains to be determined is how these forces crosstalk with the biochemical pathways that control cyclin B1 translocation. Our data clearly show that both importin β (Fig. 2 G) and CRS phosphorylation (Fig. S3, C and D) are essential for force-mediated cyclin B1 translocation. Moreover, inhibition of cPLA2 increases the levels of inactive CDK1 (Fig. S3 L). Therefore, while forces seem to accelerate nuclear entry of cyclin B1, they cannot bypass the biochemical requirements for cyclin B1–CDK1 translocation. How and when physical forces might affect the biochemical pathways regulating the G2-M transition is an interesting question for future studies.
Physical forces acting on the nucleus can trigger NE unfolding and increase nuclear tension (Lomakin et al., 2020; Venturini et al., 2020). Here, we demonstrate that nuclear unfolding is a process that normally occurs in prophase cells (Figs. 4 and S1), similarly to previous observations in G2 cells (Lomakin et al., 2020). This unfolding increases cPLA2 recruitment to the NE (Fig. 4, D and E), indicative of cPLA2 activation (Enyedi et al., 2016; Lomakin et al., 2020; Venturini et al., 2020) and likely reflects higher nuclear tension during the G2-M transition. So how does this increased tension affect cyclin B1 transport? Recent work showed that imposing forces on the nucleus is sufficient to drive nuclear import (Andreu et al., 2022) and decrease the restriction to nuclear transport, due to NPC deformation (Elosegui-Artola et al., 2017). It is tempting to speculate that during the G2-M transition, this increased nuclear tension could be sufficient to deform the nucleus and NPCs, leading to faster cyclin B1 transport across the NE, as was proposed for YAP or MyoD (Elosegui-Artola et al., 2017; Jacchetti et al., 2021). In fact, a recent report showed that NPCs can deform in vivo, and facilitate transport across the NE (Zimmerli et al., 2021). Such a model, based on force-induced modifications in the stringency of NPCs could also explain how cyclin B1 enters the nucleus even when CDK1 is inhibited (Gavet and Pines, 2010) and why CDK1-inhibited cells show only partial rescue of nuclear cyclin B1 under confinement (Fig. 2 F). Overall, we propose this mechanical pathway cooperates with the classical cyclin B1 transport machinery to fine-tune NEP according to the cellular tension state, thus ensuring timely and accurate cell division.
Establishing mechanical forces as an important player in cyclin B1 nuclear translocation and mitotic entry raises the interesting possibility that the nucleus might act as a sensor (Lomakin et al., 2020; Venturini et al., 2020) for external forces, regulating cell-cycle progression and cell division to control tissue growth and avoid over-proliferation.
Materials and methods
Cell lines
Cell lines used were cultured in DMEM (Gibco, Life Technologies) supplemented with 10% FBS (Gibco, Life Technologies) and kept in culture in a 37°C humidified incubator with 5% CO2. RPE-1 parental, and RPE-1 cell lines expressing exogenous H2B-GFP and tubulin-mRFP were already available in our lab. The RPE-1 cell line expressing endogenously tagged cyclin B1–Venus was a gift from Jonathon Pines (Collin et al., 2013). The RPE-1 cell line expressing endogenous cyclin B1–Venus/tubulin-mRFP was generated in our lab by transduction with lentiviral vectors containing pRRL-mRFP-α-tubulin, as previously described (Nunes et al., 2020). In brief, HEK293T cells at a 50–70% confluence were co-transfected with lentiviral packaging vectors (16.6 μg of Pax2, 5.6 μg of pMD2, and 22.3 μg of LV-tubulin-mRFP), using 5 μl of Lipofectamin 2000 (Life Technologies). Approximately 4–5 d after the transduction, the virus-containing supernatant was collected, filtered, and stored at −80°C. The RPE-1 cyclin B1–Venus cells were infected with virus particles together with polybrene (1:1,000) in standard culture media for 24 h. Approximately 2–3 d after the infection, the cells expressing tubulin-mRFP were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS; FACS Aria II). To deplete ROCK1, a shRNAi-LV vector (kind gift from João Relvas, i3S, Porto, Portugal) was co-transfected using a lentiviral packaging vector, as explained above. The viral particles were then transduced in the RPE-1 Tub-mRFP cell line to generate stable cells depleted of ROCK1. The RPE-1 cell line expressing exougenous cGAS-GFP was a kind gift from Matthieu Piel (Institut Curie, Paris, France). The RPE-1 cell line expressing GFP-NLS/tubulin-mRFP was created by lentiviral transduction using a pCDH-NLS-copGFP-EF1-BlastiS plasmid (#132772; Addgene), as described above. The RPE-1 cell lines expressing exogenous LBR-mCherry and endogenous cyclin B1–Venus/LBR-mCherry were generated by lentiviral transfection as described above, with the plasmid pWPT LBR-mCherry (kind gift from Stephen Royle, Warwick Medical School, Warwick, UK).
Drug treatments
CDK1 inhibitor (RO-3306; sc-358700A; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used at a concentration of 9 μM for 16 h. Importazole (kind gift from Helder Maiato) was added to the cells at a final concentration of 40 μM 2 h before the experiment, ROCK inhibitor (Y-27632; cat. no. Y0503; Sigma-Aldrich) was used at 5 μM for 30 min. To interfere with cPLA2 activity, AACOCF3 was used at 20 μM (cat. no. 1462; TOCRIS) for 30 min. To block the release of calcium ions from internal cellular stores, BAPTA-AM and 2APB (ab120503 and ab120124, respectively; Abcam) were used at 10 μM for 15–30 min. Myosin activity was perturbed using p-nitro-blebbistatin at 50 μM for 30 min (cat. no. 1621326-32-6; MotorPharma). MLCK activity was blocked using ML-7 (I2764; Merck) at 50 μM for 30 min. To interfere with the actin cytoskeleton, we used cytochalasin D at 0.5 μM (TO-1233; Biogen Científica) for 30 min. To perturb microtubules, nocodazole (M1404; Merck) was used at 3.3 μM for 30 min. Plk1 inhibitor (BI2536; AXON 1129; Axon Med Chem) was used at 200 mM for 2 h. To induce DNA damage, cells were treated with 1 μM of Etoposide (S1225; Selleck Chemicals CO.) for 2 h before fixation. Cell synchronization was performed by incubating with 2 mM thymidine (T1895; Sigma-Aldrich) for 16 h, followed by a 10 h release. A second block was performed for another 16 h, followed by a 6–8 h release. Control cells were treated with either DMSO (D4540; Sigma-Aldrich) or mock transfected with Lipofectamin 2000 (cat. no. 11668019; Invitrogen), as explained in the text.
Hypotonic shock
To perform the hypotonic shock, RPE-1 cells expressing cyclin B1–Venus and tubulin-mRFP were seeded as described above. When cells were at the microscope, MiliQ water was added to the imaging medium (1:5 dilution).
Transfections
Cells were transfected with the plasmids encoding the DN-KASH or the Rap1Q63E (Rap1*) mutant using Lipofectamin 2000. Specifically, 5 μl of Lipofectamin 2000 and 0.5 μg of plasmid DNA were diluted separated and incubated in OPTIMEM (Alfagene) for 30 min. The mixture was then added to confluent cells cultured and incubated for 6 h in reduced serum medium (DMEM with 5% FBS). Cells were analyzed 48 h after transfection.
Time-lapse microscopy
Between 12 and 24 h before the experiments, 1.5 × 105 cells were seeded on fluorodishes (WPI) coated with FBN (25 μg/ml; F1141; Sigma-Aldrich). Shortly before each experiment, DMEM 10% FBS medium was changed to Leibovitz’s-L15 medium (Life Technologies), supplemented with 10% FBS and Antibiotic-Antimycotic 100X (AAS; Life Technologies). Live-cell imaging experiments were performed at 37°C, using temperature-controlled Nikon TE2000 microscopes equipped with a modified Yokogawa CSU-X1 spinning-disk head (Yokogawa Electric), an electron multiplying iXon + DU-897 EM-CCD camera (Andor) and a filter wheel. Three laser lines were used to excite 488, 561, and 647 nm, and all the experiments were done with an immersion oil, 60× 1.4NA Plan-Apo DIC objective (Nikon). Image acquisition was controlled by NIS Elements AR software. Images with 17–21 z-stacks (0.5 μm step) were collected with a 20 s interval.
Western blotting
Cell extracts were collected after trypsinization and centrifuged at 1,200 rpm for 5 min, washed and resuspended in 30–50 μl of lysis buffer (20 nM HEPES/KOH, pH 7.9, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% NP40, 10% glycerol, and 1:50 protease inhibitor; 1:100 Phenylmethylsulfonul fluoride). The cells were then flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and kept on ice for 30 min. After centrifugation at 14,000 rpm for 8 min at 4°C, the supernatant was collected, and protein concentration determined using the Bradford protein assay (Bio-Rad). The proteins were run on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel (50 μg/lane for all blots) and transferred using a wet blot apparatus for 1.5 h at 70 V, with constant amperage. For detection of total CDK1, the proteins were run on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel (5 μg/lane) and transferred using the Trans-Blot Turbo Transfer System blot apparatus for 10 min. Later, the membranes were blocked with 5% milk in Tris-buffered saline (TBS) with 0.1% Tween-20 (TBS-T) for 1 h at room temperature (RT). The primary antibodies used were rabbit anti-vinculin (1:1,000, cat. no. 700062; Thermo Fisher Scientific), rat anti-tyrosinated α-tubulin (1:500, MCA77G; Bio-Rad), mouse anti-cyclin B1 (1: 1,000; cat. no. 4135; Cell Signaling Technology), mouse anti-p34/Cdc2 (B-6; 1:500; cat. no. sc-8395; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), and rabbit anti-phospho Cdc2 Tyr15 (1:1,000; cat. no. 4539T; Cell Signaling Technology). All primary antibodies were incubated overnight at 4°C with shaking. After three washes in TBS-T, the membranes were incubated with the secondary antibody for 1 h at RT. The secondary antibodies used was anti-rabbit-HRP at 1:5,000 (cat. no. 111-005-003; Jackson Immuno Research) or 1:2,500 when detecting total CDK1. After several washes with TBS-T, the detection was performed with Clarity Western ECL Substrate (cat. no. 1705060; Bio-Rad), using a Bio-Rad ChemiDoc XRS + imaging system.
Cell confinement setup
For dynamic confinement experiments, we adapted a cell confiner as previously described (Le Berre et al., 2014), using a custom-designed polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS, RTV615, GE) layout to fit a 35-mm fluorodish. A suction cup was custom-made with a 10/1 mixture (w/w PDMS A/crosslinker B), baked on an 80°C hot plate for 1 h and left to dry overnight before unmoulding. The confinement slide was polymerized on 10 mm round coverslips. These round coverslips were first treated with air plasma for 2 min (Zepto system, Diener Electronics) and incubated with a 0.3% Bind-Silane (M6514; Sigma-Aldrich)/5% acetic acid solution in ethanol. Then, the coverslips were rinsed with ethanol and left to dry. A gel with ∼15 kPa stiffness was prepared using an acrylamide (Bio-Rad)/bisacrylamide (Bio-Rad) mix. The mixture was added to the coverslips and allowed to polymerize. After polymerization, gels were hydrated with PBS and incubated with cell culture medium for at least 30 min. The confinement slide was then attached to the PDMS suction cup described above and connected to a vacuum generator apparatus (Elveflow).
For static confinement experiments, we used a commercially available 6-well confinement device (4DCell) with custom-designed confinement slides. The confinement slide was polymerized in PDMS on a round 10-mm standard microscope coverslip and designed with a regular holes array (diameter 449 μm, 1 mm spacing). Briefly, after activating the coverslip in a plasma chamber (Diener Electronics) for 2 min, this coverslip then was used to press a PDMS drop on top of the wafer, to obtain a thin layer. After baking at 95°C on a hot plate for 15 min, excess PDMS was removed. Isopropanol was used to peel off the glass slide with the PDMS pillars from the wafer. Microfabricated coverslips with confining pillars (8 μm height) were then attached to PDMS spacers that were stuck on a 6-well plate lid (4DCell).
CH-STED super-resolution microscopy
For CH-STED microscopy, cells were grown as described above. Parental RPE-1 cells were seeded in the day before the experiment in coverslips coated with FBN. After fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde in cytoskeleton buffer, the cells were extracted in PBS with 0.5% Triton-X100 (Sigma-Aldrich). The coverslips were incubated with the primary antibodies (rabbit anti-TPR, 1:100, NB100-2867; and mouse anti-NUPs, 1:100, 24609; Abcam) in blocking solution overnight at 4°C. After washing with PBS-0.1% Triton-X, the coverslips were incubated with a 1:100 dilution of secondary antibodies (Abberior anti-rabbit STAR 580, cat. no. 2-0012-005-8, and Abberior anti-mouse STAR 635P, cat. no. 2-0002-007-5) at RT for 1 h. Later, coverslips were washed in PBS with 0.1% Triton-X100 and sealed on a glass slide using mounting medium (20 nM Tris pH 8, 0.5 N-propyl gallate, and 90% glycerol).
The images were acquired with an Abberior Instruments “Expert Line” gated-STED coupled to a Nikon Ti microscope. For all the acquisitions, we used an oil-immersion, 60× 1.4NA Plan-Apo objective (Nikon, Lambda Series) and pinhole size of 0.8 Airy units. The CH-STED technique creates an orthogonal direction on the STED parametric space that enables the independent tuning of both resolution and contrast using only one depletion beam in a standard STED setup (circular polarization based).
Immunofluorescence
For the immunofluorescence experiments, cells were grown as previously described. RPE-1 parental cells were seeded in the day before the experiment in coverslips coated with FBN. After fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde in cytoskeleton buffer (274 mM NaCl, 2.2 mM Na2HPO4, 10 mM KCL, 0.8 mM KH2PO4, 4 mM EDTA, 4 mM MgCl2, and 10 mM glucose, pH 6.1), cells were extracted with PBS-0.5% Triton-X100 (Sigma-Aldrich) following three washes (5 min each) with PBS-0.1% Triton-X100 and a 30 min incubation in blocking solution (10% FBS in 10% Triton-X100 in PBS). The coverslips were incubated with the primary antibodies (rabbit anti-cPLA2, 1:100, #2832; Cell Signaling; mouse anti-LaminA/C, 1:500, ABCAM ab8994; rat anti-tyrosinated α-tubulin 1:500, MCA77G; Bio-Rad; mouse γ-H2AX, 1:2,000, 05-636; Milipore) in blocking solution for 1 h at RT. After washing with PBS-0.1%Tríton-X for 5 min, the coverslips were incubated with the secondary antibodies (AlexaFluor 488, 568 and 647, 1:2,000; Invitrogen) at RT for 1 h. Later, coverslips were washed, three times, in PBS with 0.1% Triton-X100 and once with PBS. Images were acquired using an AxioImager z1 with a 63×, Plan oil DIC objective lens, 1.4NA (from Carl Zeiss), coupled with a CCD camera (ORCA-R2; Hamamatsu Photonics) and the Zen software (Carl Zeiss).
Quantitative image analysis
For the quantifications of cyclin B1 levels, images were analyzed using ImageJ. A small square region of interest (ROI) was defined, and cyclin B1 fluorescence intensity measured, throughout time in the cell nucleus. The same ROI was used to measure the background outside the cell area. All fluorescence intensity values were then background-corrected and the values were normalized to the lowest nuclear cyclin B1 level. To obtain a measure of cyclin B1 translocation rate, cyclin B1 fluorescence values were aligned relative to the lowest value, which was defined as time zero. In alternative, normalized fluorescence intensity values were normalized to the time of NEP.
For quantification of cPLA2 fluorescence intensity on the NE, images were analyzed using ImageJ. A defined ROI was used to measure the fluorescence intensity values in five different regions outside the cells, which was then used to calculate the average background levels. Afterwards, a different ROI was used to measure fluorescence intensity in the nucleoplasm and at the NE. Images were background-subtracted and integrated fluorescence density was measured using the ImageJ Measure tool. cPLA2 enrichment at the NE was calculated by obtaining ratio between fluorescence in the NE and in nucleoplasm.
NII was used to estimate the overall folding of the nucleus. To do so, we first obtained 2D images of the medial section of the nucleus using an anti-Lamin A/C antibody. These images were processed to obtain the nuclear area and convex area using ImageJ. Nuclear solidity was then calculated as area/convex area. Nuclear Irregularity Index was defined as 1-nuclear solidity.
MATLAB custom algorithm for nuclear pore analysis
A computational algorithm was developed in MATLAB (v2018b; The MathWorks, Inc.) to quantify compression-induced topological changes in the nuclear pores, within the nuclear membrane. For the analyses performed in this study, we used a method focused on estimating changes on the average inter-distance between TPR and a mixture of proteins that compose the NPC, respectively, tagged with Abberior anti-rabbit STAR 580 and anti-mouse STAR 635P. Spatial periodicity on staining (either TPR or NPC) was estimated through a spatial Fast-Fourier Transform (FFT) operation on membrane cross-section images. As an alternative, and as validation, intensity profile autocorrelation was also used to assess the spatial periodicity. The entire length of the nuclear membrane was previously scanned to select only segments with low curvatures and the “Straighten” tool (Schindelin et al., 2012) was used prior to the FFT/autocorrelation operations.
MATLAB custom algorithm for centrosome tracking
To perform a detailed quantitative analysis of centrosome positioning and movement and cell rounding, we used a previously described, custom-designed MATLAB (v2018b; The MathWorks Inc) script (Nunes et al., 2020). The algorithm used as a specific workflow designed for centrosome tracking in a 3D space having in consideration a pixel size of 0.176 μm and a z-step of 0.5 μm. The nucleus shape was reconstructed using H2B-GFP as marker, and cell shape was reconstructed using tubulin-RFP as a marker. Using this tool, we were able to correlate the angle between the centrosomes and the nucleus, as well as cell rounding during mitotic entry.
Laser microsurgery
Laser microsurgery was performed with a doubled-frequency laser (FQ-500-532; Elforlight) coupled with an inverted microscope (TE2000U; Nikon), using a 100× 1.4NA, plan-apochromatic DIC objective lens and equipped with an iXonEM + EM-CD camera (Andor Technology). To induce a break on the NE, we used 8 consecutive pulses, with a pulse energy of 3–5 μJ and an interval of around 10 ns.
Statistical analysis
Three to six independent experiments were used for statistical analysis. When data are represented as box-whisker plots, the box size represents 75% of the population and the line inside the box represents the median of the sample. The size of the bars (whiskers) represents the maximum (in the upper quartile) and the minimum (in the lower quartile) values. Normality of the samples was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Statistical analysis for multiple group comparison was performed using a parametric one-way ANOVA when the samples had a normal distribution. Otherwise, multiple group comparison was performed using a nonparametric ANOVA (Kruskal–Wallis). Multiple comparisons were analyzed using either post-hoc Student-Newman-Keuls (parametric) or Dunn’s (nonparametric) tests. When only two experimental groups were compared, we used either a parametric two-sided t test or a nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. Comparison for multiple time-course datasets was carried out using an ANOVA Repeated Measures, when the samples had a normal distribution. Otherwise, group comparison was carried out using Repeated Measures ANOVA on Ranks. No power calculations were used. All statistical analyses were performed using SigmaStat 3.5 (Systat Software, Inc.).
Online supplemental material
Fig. S1 contains the schematics of the dynamic cell confiner device and shows data regarding the integrity of the NE following confinement. Fig. S1 also shows evidence of nuclear unfolding upon confinement using live-cell imaging and CH-STED super resolution. Fig. S2 shows that cyclin B1 translocation is sensitive to the stiffness of the external environment. Fig. S2 also shows that cyclin B1 translocation is sensitive to alternative mechanical stimulation such as a hypotonic shock and demonstrates that mechanical stimulation of cyclin B1 translocation is maintained in HeLa cells. Fig. S3 shows that cyclin B1 translocation is insensitive to mitotic cell rounding and that expression of cyclin B1-5A-GFP blocks cyclin B1 translocation even under confinement. Fig. S3 also shows the effects of Plk1 inhibition on cyclin B1 translocation. Fig. S4 shows expression of DN-KASH-RFP and compares cyclin B1 translocation in two different cell lines expressing DN-KASH-RFP. It also shows the increase in phospho-CDK1 (Y15) levels after AAOCF3 treatment.
Code availability
All custom-designed computational tools used in this manuscript are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Data availability
The data that support the findings included in this manuscript are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. All cell lines and reagents generated for this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Supplementary Material
is the source file for Fig. S4.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jonathon Pines (The Institute of Cancer Research, London, UK) for the gift of the RPE-1 cyclin B1–Venus and HeLa cyclin B1–Venus cell lines and the plasmid for expression of cyclin B1-5A-GFP. The authors thank Matthieu Piel for the RPE-1 cGAS-GFP cell line. The authors thank Stephen Royle for the plasmid pWPT LBR-mCherry. The authors thank Joana Lima for performing the western blot to detect CDK1 levels in Fig. S4. The authors thank Dr. Buzz Baum, Dr. Alexis Lomakin, and members of the Ferreira and Maiato labs for critical reading of the manuscript.
This work was funded by Portuguese funds through FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia/Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior in the framework of the project PTDC/BIA-CEL/6740/2020. M. Dantas is supported by grant PD/BD/135548/2018 from the BiotechHealth FCT-funded PhD program. Work in the Maiato lab is funded by the European Research Council (ERC) consolidator grant CODECHECK, under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (grant agreement 681443), Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia of Portugal (PTDC/MED-ONC/3479/2020), and the NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000051 project supported by NORTE 2020 under the PORTUGAL 2020 Partnership Agreement through the European Regional Development Fund.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author contributions: M. Dantas performed experimental work, analyzed data, prepared figures, and jointly wrote the manuscript. J.G. Ferreira provided the conceptual framework, analyzed data, prepared figures, secured funding, and jointly wrote the manuscript. H. Maiato provided access to essential equipment, reviewed, and edited the manuscript. A. Oliveira and P. Aguiar developed MATLAB computational tools, reviewed and edited the manuscript.
References
- Abe, S., Nagasaka K., Hirayama Y., Kozuka-Hata H., Oyama M., Aoyagi Y., Obuse C., and Hirota T.. 2011. The initial phase of chromosome condensation requires Cdk1-mediated phosphorylation of the CAP-D3 subunit of condensin II. Genes Dev. 25:863–874. 10.1101/gad.2016411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akopyan, K., Silva Cascales H., Hukasova E., Saurin A.T., Mullers E., Jaiswal H., Hollman D.A.A., Kops G.J.P.L., Medema R.H., and Lindqvist A.. 2014. Assessing kinetics from fixed cells reveals activation of the mitotic entry network at the S/G2 transition. Mol. Cell. 53:843–853. 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.01.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreu, I., Granero-Moya I., Garcia-Manyes S., and Roca-Cusachs P.. 2022. Understanding the role of mechanics in nucleocytoplasmic transport. APL Bioeng. 6:020901. 10.1063/5.0076034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsenovic, P.T., Ramachandran I., Bathula K., Zhu R., Narang J.D., Noll N.A., Lemmon C.A., Gundersen G.G., and Conway D.E.. 2016. Nesprin-2G, a component of the nuclear LINC complex, is subject to myosin-dependent tension. Biophysical J. 110:34–43. 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.11.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aureille, J., Buffiere-Ribot V., Harvey B.E., Boyault C., Pernet L., Andersen T., Bacola G., Balland M., Fraboulet S., Van Landeghem L., and Guilluy C.. 2019. Nuclear envelope deformation controls cell cycle progression in response to mechanical force. EMBO Rep. 20:e48084. 10.15252/embr.201948084 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakkenist, C.J., and Kastan M.B.. 2003. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature. 421:499–506. 10.1038/nature01368 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham-Pyle, B.W., Pruitt B.L., and Nelson W.J.. 2015. Cell adhesion. Mechanical strain induces E-cadherin-dependent Yap1 and β-catenin activation to drive cell cycle entry. Science. 348:1024–1027. 10.1126/science.aaa4559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth, A.J., Yue Z., Eykelenboom J.K., Stiff T., Luxton G.G., Hochegger H., and Tanaka T.U.. 2019. Contractile acto-myosin network on nuclear envelope remnants positions human chromosomes for mitosis. eLife. 8:e46902. 10.7554/eLife.46902 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collin, P., Nashchekina O., Walker R., and Pines J.. 2013. The spindle assembly checkpoint works like a rheostat not a toggle-switch. Nat. Cell Biol. 15:1378–1385. 10.1038/ncb2855 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantas, M., Lima J.T., and Ferreira J.G.. 2021. Nucleus-cytoskeleton crosstalk during mitotic entry. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:649899. 10.3389/fcell.2021.649899 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elosegui-Artola, A., Andreu I., Beedle A.E.M., Lezamiz A., Uroz M., Kosmalska A.J., Oria R., Kechagia J.Z., Rico-Lastres P., Le Roux A.L., et al. 2017. Force triggers YAP nuclear entry by regulating transport across nuclear pores. Cell. 171:1397–1410.e14. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi, B., Jelcic M., and Niethammer P.. 2016. The cell nucleus serves as a mechanotransducer of tissue damage-induced inflammation. Cell. 165:1160–1170. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feringa, F.M., Krenning L., Koch A., van den Berg J., van den Broek B., Jalink K., and Medema R.H.. 2016. Hypersensitivity to DNA damage in antephase as a safeguard for genome stability. Nat. Commun. 7:12618. 10.1038/ncomms12618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuno, N., Elzen N.D., and Pines J.. 1999. Human cyclin A is required for mitosis until mid prophase. J. Cell Biol. 147:295–306. 10.1083/jcb.147.2.295 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavet, O., and Pines J.. 2010. Progressive activation of CyclinB1-Cdk1 Coordinates entry to mitosis. Dev. Cell. 18:533–543. 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.02.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheghiani, L., Loew D., Lombard B., Mansfeld J., and Gavet O.. 2017. PLK1 activation in late G2 sets up commitment to mitosis. Cell Rep. 19:2060–2073. 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravemann, S., Schnipper N., Meyer H., Vaya A., Nowaczyk M.J., Rajab A., Hofmann W.K., Salewsky B., Tonnies H., Neitzel H., et al. 2010. Dosage effect of zero to three functional LBR-genes in vivo and in vitro. Nucleus. 1:179–189. 10.4161/nucl.1.2.11113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudipaty, S.A., Lindblom J., Loftus P.D., Redd M.J., Edes K., Davey C.F., Krishnegowda V., and Rosenblatt J.. 2017. Mechanical stretch triggers rapid epithelial cell division through Piezo1. Nature. 543:118–121. 10.1038/nature21407 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagting, A., Karlsson C., Clute P., Jackman M., and Pines J.. 1998. MPF localization is controlled by nuclear export. EMBO J. 17:4127–4138. 10.1093/emboj/17.14.4127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagting, A., Jackman M., Simpson K., and Pines J.. 1999. Translocation of cyclin B1 to the nucleus at prophase requires a phosphorylation-dependent nuclear import signal. Curr. Biol. 9:680–689. 10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80308-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heald, R., and McKeon F.. 1990. Mutations of phosphorylation sites in lamin A that prevent nuclear lamina disassembly in mitosis. Cell. 61:579–589. 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90470-Y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S., Chen C.S., and Ingber D.E.. 1998. Control of cyclin D1, p27(Kip1), and cell cycle progression in human capillary endothelial cells by cell shape and cytoskeletal tension. Mol. Biol. Cell. 9:3179–3193. 10.1091/mbc.9.11.3179 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacchetti, E., Nasehi R., Boeri L., Parodi V., Negro A., Albani D., Osellame R., Cerullo G., Matas J.F.R., and Raimondi M.T.. 2021. The nuclear import of the transcription factor MyoD is reduced in mesenchymal stem cells grown in a 3D micro-engineered niche. Sci. Rep. 11:3021. 10.1038/s41598-021-81920-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao, J.P., Alderton J.M., Tsien R.Y., and Steinhardt R.A.. 1990. Active involvement of Ca2+ in mitotic progression of Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 111:183–196. 10.1083/jcb.111.1.183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein, E.A., Yin L., Kothapalli D., Castagnino P., Byfield F.J., Xu T., Levental I., Hawthorne E., Janmey P.A., and Assoian R.K.. 2009. Cell-cycle control by physiological matrix elasticity and in vivo tissue stiffening. Curr. Biol. 19:1511–1518. 10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.069 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth, S., Sebastian B., Hunter T., and Newport J.. 1994. Membrane localization of the kinase which phosphorylates p34(cdc2) on threonine 14. Mol. Biol. Cell. 5:273–282. 10.1091/mbc.5.3.273 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A., Mazzanti M., Mistrik M., Kosar M., Beznoussenko G.V., Mironov A.A., Garre M., Parazzoli D., Shivashankar G.V., Scita G., et al. 2014. ATR mediates a checkpoint at the nuclear envelope in response to mechanical stress. Cell. 158:633–646. 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, O.M., Le Berre M., Dimitracopoulos A., Bonazzi D., Zlotek-Zlotkiewicz E., Picone R., Duke T., Piel M., and Baum B.. 2013. Mitotic rounding alters cell geometry to ensure efficient bipolar spindle formation. Dev. Cell. 25:270–283. 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.03.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Berre, M., Zlotek-Zlotkiewicz E., Bonazzi D., Lautenschlaeger F., and Piel M.. 2014. Methods for two-dimensional cell confinement. Methods Cell Biol. 121:213–229. 10.1016/B978-0-12-800281-0.00014-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, J., Meyer A.N., and Donoghue D.J.. 1997. Nuclear localization of cyclin B1 mediates its biological activity and is regulated by phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94:502–507. 10.1073/pnas.94.2.502 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder, M.I., Kohler M., Boersema P., Weberruss M., Wandke C., Marino J., Ashiono C., Picotti P., Antonin W., and Kutay U.. 2017. 43. 141:156.e7. Mitotic disassembly of nuclear pore complexes involves CDK1- and PLK1-mediated phosphorylation of key interconnecting nucleoporins, Dev. Cell. 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.08.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist, A. 2010. Cyclin B-Cdk1 activates its own pump to get into the nucleus. J. Cell Biol. 189:197–199. 10.1083/jcb.201003032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist, A., Rodríguez-Bravo V., and Medema R.H.. 2009. The decision to enter mitosis: Feedback and redundancy in the mitotic entry network. J. Cell Biol. 185:193–202. 10.1083/jcb.200812045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomakin, A.J., Cattin C.J., Cuvelier D., Alraies Z., Molina M., Nader G.P.F., Srivastava N., Saez P.J., Garcia-Arcos J.M., Zhitnyak I.Y., et al. 2020. The nucleus acts as a ruler tailoring cell responses to spatial constraints. Science. 370:eaba2894. 10.1126/science.aba2894 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, M.L., and Lammerding J.. 2011. Keeping the LINC: The importance of nucleocytoskeletal coupling in intracellular force transmission and cellular function. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 39:1729–1734. 10.1042/BST20110686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox, A.S., and Burridge K.. 2003. RhoA is required for cortical retraction and rigidity during mitotic cell rounding. J. Cell Biol. 160:255–265. 10.1083/jcb.200207130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.D., Yang J., Truant R., and Kornbluth S.. 1999. Nuclear import of Cdk/cyclin complexes: Identification of distinct mechanisms for import of Cdk2/cyclin E and Cdc2/cyclin B1. J. Cell Biol. 144:213–224. 10.1083/jcb.144.2.213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, P.R., Coleman T.R., Kumagai A., and Dunphy W.G.. 1995. Myt1: A membrane-associated inhibitory kinase that phosphorylates Cdc2 on both threonine-14 and tyrosine-15. Science. 270:86–90. 10.1126/science.270.5233.86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nava, M.M., Miroshnikova Y.A., Biggs L.C., Whitefield D.B., Metge F., Boucas J., Vihinen H., Jokitalo E., Li X., Garcia Arcos J.M., et al. 2020. Heterochromatin-driven nuclear softening protects the genome against mechanical stress-induced damage. Cell. 181:800–817.e22. 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, V., Dantas M., Castro D., Vitiello E., Wang I., Carpi N., Balland M., Piel M., Aguiar P., Maiato H., and Ferreira J.G.. 2020. Centrosome–nuclear axis repositioning drives the assembly of a bipolar spindle scaffold to ensure mitotic fidelity. Mol. Biol. Cell. 31:1675–1690. 10.1091/mbc.e20-01-0047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker, L.L., Atherton-Fessler S., and Piwnica-Worms H.. 1992. p107wee1 is a dual-specificity kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2 on tyrosine 15. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89:2917–2921. 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2917 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter, M., Nakagawa J., Doree M., Labbe J.C., and Nigg E.A.. 1990. In vitro disassembly of the nuclear lamina and M phase-specific phosphorylation of lamins by cdc2 kinase. Cell. 61:591–602. 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90471-P [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines, J., and Hunter T.. 1989. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: Evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 58:833–846. 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos, S.D.M., Wollman R., Meyer T., and Ferrell J.E. Jr. 2012. Spatial positive feedback at the onset of mitosis. Cell. 149:1500–1513. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, J., Arganda-Carreras I., Frise E., Kaynig V., Longair M., Pietzsch T., Preibisch S., Rueden C., Saalfeld S., Schmid B., et al. 2012. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods. 9:676–682. 10.1038/nmeth.2019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer, N., Pawar N., Weiss M., and Maiato H.. 2015. An organelle-exclusion envelope assists mitosis and underlies distinct molecular crowding in the spindle region. J. Cell Biol. 210:695–704. 10.1083/jcb.201506107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silkworth, W.T., Nardi I.K., Paul R., Mogilner A., and Cimini D.. 2012. Timing of centrosome separation is important for accurate chromosome segregation. Mol. Biol. Cell. 23:401–411. 10.1091/mbc.E11-02-0095 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiff, T., Echegaray-Iturra F.R., Pink H.J., Herbert A., Reyes-Aldasoro C.C., and Hochegger H.. 2020. Prophase-specific perinuclear actin coordinates centrosome separation and positioning to ensure accurate chromosome segregation. Cell Rep. 31:107681. 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107681 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, B., Harrison A., Coelho P.A., Yata K., Zernicka-Goetz M., and Pines J.. 2018. Cyclin B1 is essential for mitosis in mouse embryos, and its nuclear export sets the time for mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 217:179–193. 10.1083/jcb.201612147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift, J., Ivanovska I.L., Buxboim A., Harada T., Dingal PCDP, Pinter J., Pajerowski J.D., Spinler K.R., Shin J.W., Tewari M., et al. 2013. Nuclear lamin-A scales with tissue stiffness and enhances matrix-directed differentiation. Science. 341:1240104. 10.1126/science.1240104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa, C.G., Weis K., and Morgan D.O.. 1999. Ran-independent nuclear import of cyclin B1-Cdc2 by importin beta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 96:7938–7943. 10.1073/pnas.96.14.7938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima, F., Moriguchi T., Wada A., Fukuda M., and Nishida E.. 1998. Nuclear export of cyclin B1 and its possible role in the DNA damage-induced G2 checkpoint. EMBO J. 17:2728–2735. 10.1093/emboj/17.10.2728 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse, H.T.K., Weaver W.M., and Carlo D.. 2012. Increased asymmetric and multi-daughter cell division in mechanically confined microenvironments. PLoS ONE. 7:e38986. 10.1371/journal.pone.0038986 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uroz, M., Wistorf S., Serra-Picamal X., Conte V., Sales-Pardo M., Roca-Cusachs P., Guimera R., and Trepat X.. 2018. Regulation of cell cycle progression by cell–cell and cell–matrix forces. Nat. Cell Biol. 20:646–654. 10.1038/s41556-018-0107-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venturini, V., Pezzano F., Catala Castro F., Hakkinen H.M., Jimenez-Delgado S., Colomer-Rosell M., Marro M., Tolosa-Ramon Q., Paz-Lopez S., Valverde M.A., et al. 2020. The nucleus measures shape changes for cellular proprioception to control dynamic cell behavior. Science. 370:eaba2644. 10.1126/science.aba2644 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vianay, B., Senger F., Alamos S., Anjur-Dietrich M., Bearce E., Cheeseman B., Lee L., and Thery M.. 2018. Variation in traction forces during cell cycle progression. Biol. Cell. 110:91–96. 10.1111/boc.201800006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.H., Whitmarsh A.J., Davis R.J., and Sharrocks A.D.. 1998. Differential targeting of MAP kinases to the ETS-domain transcription factor Elk-1. EMBO J. 17:1740–1749. 10.1093/emboj/17.6.1740 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J., Bogerd H.P., Wang P.J., Page D.C., and Cullen B.R.. 2001. Two closely related human nuclear export factors utilize entirely distinct export pathways. Mol. Cell. 8:397–406. 10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00303-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli, C.E., Allegretti M., Rantos V., Goetz S.K., Obarska-Kosinska A., Zagoriy I., Halavatyi A., Hummer G., Mahamid J., Kosinski J., and Beck M.. 2021. Nuclear pores dilate and constrict in cellulo. Science. 374:eabd9776. 10.1126/science.abd9776 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
is the source file for Fig. S4.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings included in this manuscript are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. All cell lines and reagents generated for this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.