Abstract
Reading and writing are crucial life skills but roughly one in ten children are affected by dyslexia, which can persist into adulthood. Family studies of dyslexia suggest heritability up to 70%, yet few convincing genetic markers have been found. Here we performed a genome-wide association study of 51,800 adults self-reporting a dyslexia diagnosis and 1,087,070 controls and identified 42 independent genome-wide significant loci: 15 in genes linked to cognitive ability/educational attainment, and 27 new and potentially more specific to dyslexia. We validated 23 loci (13 new) in independent cohorts of Chinese and European ancestry. Genetic etiology of dyslexia was similar between sexes, and genetic covariance with many traits was found, including ambidexterity, but not neuroanatomical measures of language-related circuitry. Dyslexia polygenic scores explained up to 6% of variance in reading traits, and might in future contribute to earlier identification and remediation of dyslexia.
Subject terms: Psychiatric disorders, Genome-wide association studies, Psychology
Genome-wide analysis of self-reported dyslexia identifies 42 associated loci, including 27 not previously associated with cognitive traits. Dyslexia shows genetic correlation with ambidexterity but not neuroanatomical measures of language-related circuitry.
Main
The ability to read is crucial for success at school and access to employment, information and health and social services, and is related to attained socioeconomic status1. Dyslexia is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by severe reading difficulties, present in 5–17.5% of the population, depending on diagnostic criteria2,3. It often involves impaired phonological processing (the decoding of sound units, or phonemes, within words) and frequently co-occurs with psychiatric and other developmental disorders4, especially attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)5,6 and speech and language disorders7,8. Dyslexia may represent the low extreme of a continuum of reading ability, a complex multifactorial trait with heritability estimates ranging from 40% to 80%9,10. Identifying genetic risk factors not only aids increased understanding of the biological mechanisms, but may also expand diagnostic capabilities, facilitating earlier identification of individuals prone to dyslexia and co-occurring disorders for specific support.
Previous genome-wide investigations of dyslexia have been limited to linkage analyses of affected families11 or modest (n < 2,300 cases) association studies of diagnosed children and adolescents12. Candidate genes from linkage studies show inconsistent replication, and genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have not found significant associations, although LOC388780 and VEPH1 were supported in gene-based tests12. Larger cohorts are vital for increasing sensitivity to detect new genetic associations of small effect. Here, we present the largest dyslexia GWAS to date, with 51,800 adults self-reporting a dyslexia diagnosis and 1,087,070 controls, all of whom are research participants with the personal genetics company 23andMe, Inc. We validate our association discoveries in independent cohorts, provide functional annotations of significant variants (mainly single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)) and potential causal genes, and estimates of SNP-based heritability. Lastly, we investigate genetic correlations with reading and related skills, health, socioeconomic, and psychiatric measures, and evaluate the evidence for previously implicated dyslexia candidate genes in our well-powered results.
Results
Genome-wide associations
The full dataset included 51,800 (21,513 males, 30,287 females) participants responding ‘yes’ to the question ‘Have you been diagnosed with dyslexia?’ (cases) and 1,087,070 (446,054 males, 641,016 females) participants responding ‘no’ (controls). Participants were aged 18 years or over (mean ages of cases and controls were 49.6 years (s.d. 16.2) and 51.7 years (s.d. 16.6), respectively). We identified 42 independent genome-wide significant associated loci (P < 5 × 10−8) and 64 loci with suggestive significance (P < 1 × 10−6) (Fig. 1 and Supplementary Table 1). Genomic inflation was moderate (λGC = 1.18) and consistent with polygenicity (see Q–Q plot, Extended Data Fig. 1). We also performed sex-specific GWAS and age-specific GWAS (younger or older than 55 years) because dyslexia prevalence was higher in our younger (5.34% in 20- to 30-year-olds) than older (3.23% in 80- to 90-year-olds) participants. These subsample analyses showed high consistency with the main GWAS (of the full sample). Genetic correlation estimated by linkage disequilibrium (LD) score regression (LDSC) was 0.91 (95% confidence intervals (CI): 0.86–0.96; P = 8.26 × 10−253) in males and females, and 0.97 (95% CI: 0.91–1.02; P = 2.32 × 10−268) between younger and older adults.
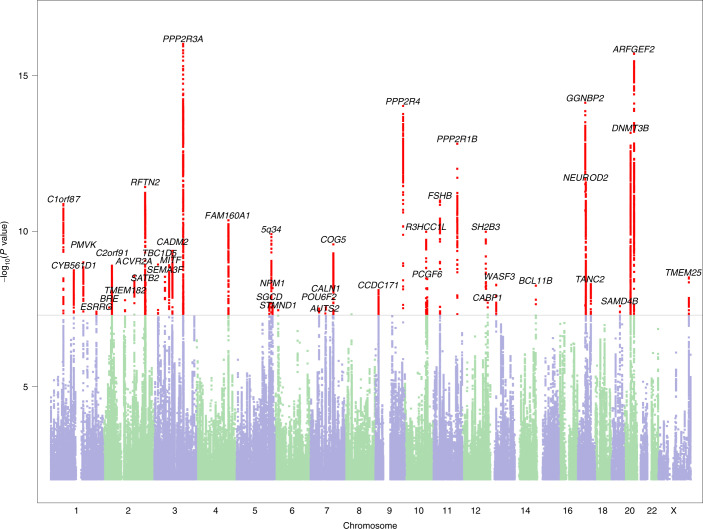
Fig. 1. Manhattan plot of the genome-wide association analysis of dyslexia.
The y axis represents the −log10 P value for association of SNPs with self-reported dyslexia diagnosis from 51,800 individuals and 1,087,070 controls. The threshold for genome-wide significance (P < 5 × 10−8) is represented by a horizontal grey line. Genome-wide significant variants in the 42 genome-wide significant loci are red. Variants located within a distance of <250 kb of each other are considered as one locus.
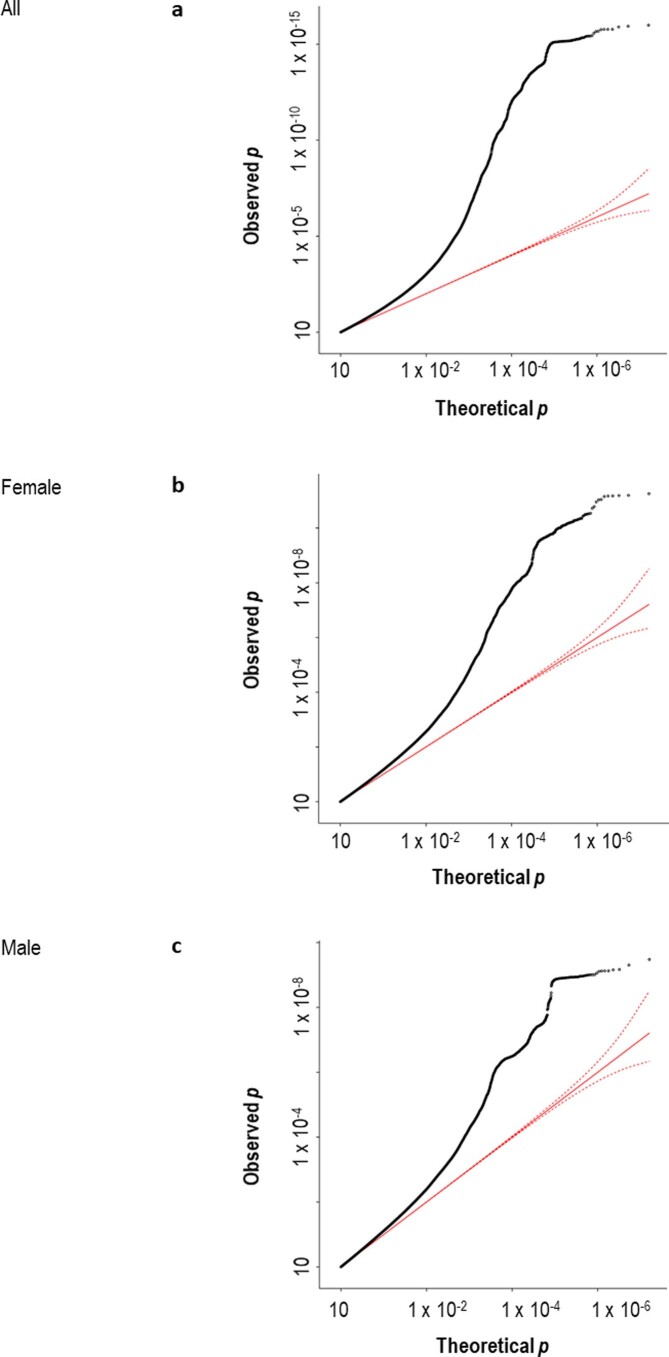
Extended Data Fig. 1. QQ plot of dyslexia GWAS results.
a-c, Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots of observed versus expected P values for associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms with self-reported dyslexia diagnosis in a genome-wide association analysis for all participants (n = 51,800 cases, 1,087,070 controls) (a), female participants (n = 30,287 cases, 641,016 controls) (b), and male participants (n = 21,513 cases, 446,054 controls) (c). The solid red line represents the distribution of P values under the null hypothesis, and the dashed red line represent 95% confidence intervals. The black circles represent the observed distribution of P values.
Of the 17 genome-wide significant variants in the female GWAS (Extended Data Fig. 2), all but four (rs61190714, rs4387605, rs12031924 and rs57892111) were significant in the main GWAS and, of these four, three were in LD with an SNP that approached significance (P < 3.3 × 10−7 or smaller) in the main analysis. Intergenic SNP rs57892111 (located between TFAP2B and PKHD1 on chromosome 6p) was not among the significant or suggestive SNPs of the main analysis, and so may represent a female-specific variant. There is no evidence from existing GWAS that this SNP is associated with any other human trait. Of the six genome-wide significant variants in the male GWAS (Extended Data Fig. 3), all were significant in the main GWAS.
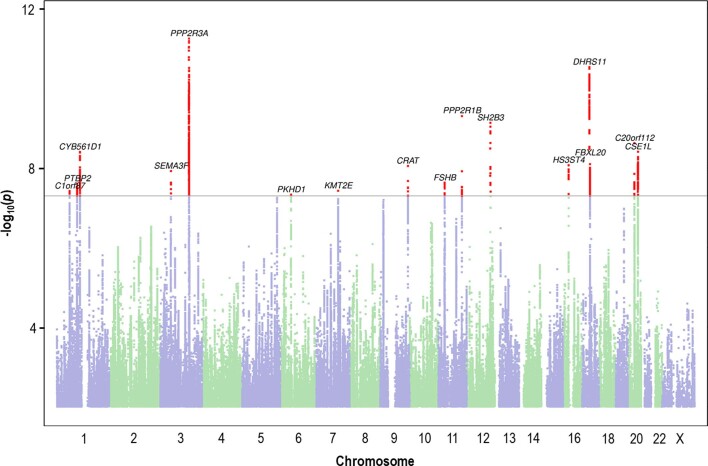
Extended Data Fig. 2. Manhattan plot of dyslexia GWAS results for females.
The y-axis represents the -log10 P value for association of single nucleotide polymorphisms with self-reported dyslexia diagnosis from 30,287 female individuals and 641,016 female controls. The threshold for genome-wide significance (P < 5 × 10−8) is represented by a horizontal grey line. Genome-wide significant variants in the 17 genome-wide significant loci are red. Variants located within a distance of 250 kb of each other are considered as one locus.
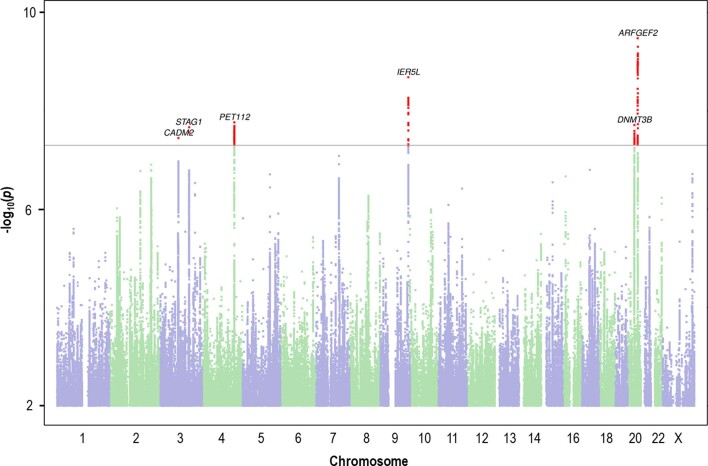
Extended Data Fig. 3. Manhattan plot of dyslexia GWAS results for males.
The y-axis represents the -log10 P value for association of single nucleotide polymorphisms with self-reported dyslexia diagnosis from 21,513 male individuals and 446,054 male controls. The threshold for genome-wide significance (P < 5 × 10−8) is represented by a horizontal grey line. Genome-wide significant variants in the 6 genome-wide significant loci are red. Variants located within a distance of 250 kb of each other are considered as one locus.
In the main GWAS, all significant variants were autosomal, except rs5904158 at Xq27.3 (for regional association plots, see Supplementary Fig. 1). A total of 17 index variants were in high LD with published (genome-wide significant) associated SNPs in the NHGRI GWAS Catalog13 (15 were associated with cognitive/educational traits; Supplementary Tables 1 and 2). Thus, a total of 27 associated loci showed no evidence of published genome-wide associations with traits expected to overlap with dyslexia (for example, educational attainment, cognitive ability) and were considered new (Table 1).
Table 1.
New SNP associations with dyslexia, including gene-based results, eQTL status, expression in brain and validation in three independent cohorts (GenLang Consortium, CRS and NeuroDys)
| Cytoband | SNP | Effect allele | Frequency | Odds Ratio | GWAS P | Gene(s) | Most probable gene | Validation cohort (P uncorrected for multiple testing) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr1q21.3 | rs4845687 | A | 0.56 | 1.044 | 1.1 × 10−9 | KCNN3, PMVK | PMVKab | GenLang (0.02) |
| chr2q22.3 | rs497418 | A | 0.38 | 1.043 | 3.0 × 10−9 | ACVR2A | AC062032.1c | GenLang (0.009) |
| chr2q33.1 | rs72916919 | G | 0.51 | 1.049 | 4.1 × 10−12 | RFTN2 | MARS2a | NeuroDys (0.02), GenLang (0.02) |
| chr3p12.1 | rs10511073 | A | 0.37 | 1.046 | 4.6 × 10−10 | CADM2 | CADM2a | GenLang (0.02) |
| chr3q22.3 | rs13082684 | A | 0.24 | 1.069 | 1.0 × 10−16 | PPP2R3A | PPP2R3A (intron)a | GenLang (0.0004); not in CRS |
| chr6p22.3 | rs2876430 | T | 0.34 | 1.041 | 3.7 × 10−8 | ATXN1, STMND1 | STMND1 | GenLang (0.04) |
| chr7p14.1 | rs62453457 | G | 0.48 | 1.039 | 3.3 × 10−8 | POU6F2 | POU6F2 | CRS (0.04) |
| chr7q11.22 | rs3735260 | G | 0.08 | 1.075 | 4.7 × 10−8 | AUTS2 | AUTS2 | GenLang (0.02) |
| chr7q11.22 | rs77059784 | G | 0.97 | 1.123 | 3.0 × 10−8 | CALN1 | CALN1 | GenLang (0.02); not in CRS |
| chr9q34.11 | rs9696811 | C | 0.69 | 1.069 | 1.1 × 10−16 | PPP2R3A | AL158151.4abc | GenLang (0.03) |
| chr11q23.1 | rs138127836 | A | 0.65 | 1.056 | 1.7 × 10−13 | PPP2R1B | PPP2R1B (intron)ab | GenLang (0.02) |
| chr17q23.3 | rs72841395c | C | 0.77 | 1.049 | 5.4 × 10−9 | TANC2 | TANC2a | GenLang (0.005) |
| chrXq27.3 | rs5904158 | GTA | 0.65 | 1.037 | 3.3 × 10−8 | TMEM257, CXorf51Bb | AL109653.3c | GenLang (0.02); not in NeuroDys/CRS |
| chr2q12.1 | rs367982014 | CAAT | 0.29 | 1.045 | 1.8 × 10−8 | TMEM182 | MFSD9a | Not available |
| chr3p24.3 | rs373178590 | G | 0.51 | 1.046 | 1.3 × 10−9 | TBC1D5 | TBC1D5 (intron)a | Not available |
| chr10q24.33 | rs34732054 | C | 0.57 | 1.045 | 3.7 × 10−9 | PCGF6 | USMG5a | Not available |
| chr13q12.13 | rs375018025 | CA | 0.57 | 1.044 | 5.6 × 10−9 | CDK8, WASF3 | WASF3 | Not available |
| chr1p32.1 | rs12737449 | G | 0.85 | 1.070 | 1.4 × 10−11 | C1orf87 | C1orf87 (missense)a | Not significant |
| chr2p23.2 | rs1969131 | T | 0.17 | 1.053 | 3.0 × 10−8 | BABAM2 | BABAM2 | Not significant |
| chr3q26.33 | rs7625418 | C | 0.21 | 1.056 | 4.3 × 10−9 | PEX5L, TTC14 | TTC14a | Not significant |
| chr3p13 | rs13097431 | G | 0.58 | 1.044 | 1.3 × 10−9 | MITF | MITFa | Not significant |
| chr5q33.3 | rs867009 | G | 0.36 | 1.041 | 2.3 × 10−9 | SGCD | SGCDa | Not significant |
| chr9p22.3 | rs3122702 | T | 0.5 | 1.041 | 8.3 × 10−9 | CCDC171 | CCDC171ab | Not significant |
| chr10q24.2 | rs10786387 | C | 0.68 | 1.049 | 1.1 × 10−10 | CRTAC1, R3HCC1L | R3HCC1La | Not significant |
| chr11p14.1 | rs676217 | G | 0.37 | 1.050 | 1.1 × 10−11 | KCNA4, FSHB | ARL14EPab | Not significant |
| chr19q13.2 | rs60963584 | A | 0.89 | 1.065 | 2.7 × 10−8 | GMFG, SAMD4B | SAMD4Ba | Not significant |
| chr20q11.21 | rs4911257 | C | 0.39 | 1.055 | 7.5 × 10−14 | DNMT3B | DNMT3B (intron)ab | Not significant |
Statistics for each variant are from the 23andMe GWAS (see Supplementary Table 1 for all 42 significant variants). Genes that are significant in gene-based tests are set in bold. Multi-allelic effect alleles represent insertions. The most probable gene is that most likely to be causal based on genetic and functional genomic data tied to the tag SNP (https://platform.opentargets.org/).
aeQTL.
beQTL linked to brain expression.
cNot available in gene-based results.
Of 38 associated loci (the 4 remaining were tagged by indels unavailable in validation cohorts), 3 (rs13082684, rs34349354 and rs11393101) were significant at a Bonferroni-corrected level (P < 0.05/38) in the GenLang consortium GWAS meta-analysis of reading (n = 33,959) and spelling (n = 18,514) ability14. At P < 0.05, 18 were associated in GenLang, 3 in the NeuroDys case-control GWAS12 (n = 2,274 cases), and 5 in the Chinese Reading Study (CRS) of reading accuracy and fluency (n = 2,270; Supplementary Note) (Table 1 and Supplementary Tables 3–6).
Gene-based tests identified 173 significantly associated genes (Supplementary Table 7) but no significantly enriched biological pathways (Supplementary Table 8). We estimated the LDSC liability-scale SNP-based heritability of dyslexia to be h2SNP = 0.152 (standard error = 0.006) using the 23andMe sample prevalence of 5%, and h2SNP = 0.189 (standard error = 0.008) using a 10% prevalence of dyslexia, which is more typical of the general population2,3.
Fine-mapping and functional annotations
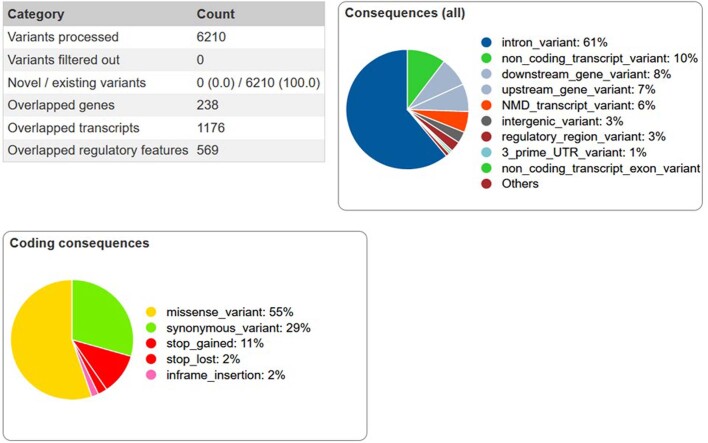
Within the credible variant set (Supplementary Table 1), missense variants were the most common (55%) of the coding variants; Extended Data Figure 4 summarizes all predicted variant effects. Predicted deleterious variants by SIFT (Sorting Intolerant From Tolerant) score were identified in R3HCC1L, SH2B3, CCDC171, C1orf87, LOXL4, DLAT, ALG9 and SORT1. Within the credible variant set, no genes were especially intolerant to functional variation (smallest LoFtool (Loss-of-Function) percentile was 0.39). For the 42 associated loci, the most probable gene targets of each were estimated by the Overall V2G (Variant-to-Gene) score from OpenTargets (Supplementary Table 9). Two index variants (missense variant rs12737449 (C1orf87) and rs3735260 (AUTS2)) could be causal because they had combined annotation dependent depletion (CADD) scores suggestive of deleteriousness to gene function according to Kircher et al.15 (Supplementary Table 10). The AUTS2 variant RegulomeDB rank of 2b indicated a regulatory role; its chromatin state supported location at an active transcription start site16,17.
Extended Data Fig. 4. Variant effect predictor summary for the credible set of variants significantly associated with dyslexia.
Summary information is output from the online variant effect predictor in ENSEMBL (release 104). All our variants were present in the 1000 Genomes reference panel so are considered existing, and no pre-filtering (for example, on MAF; consequence type) was done.
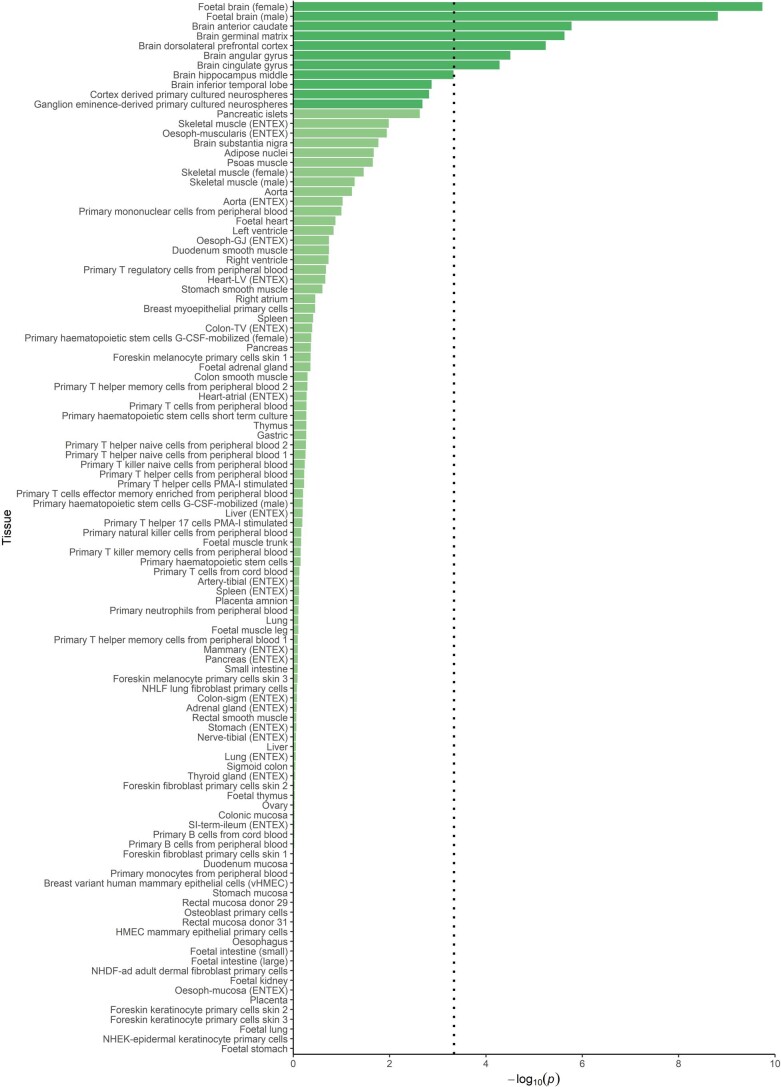
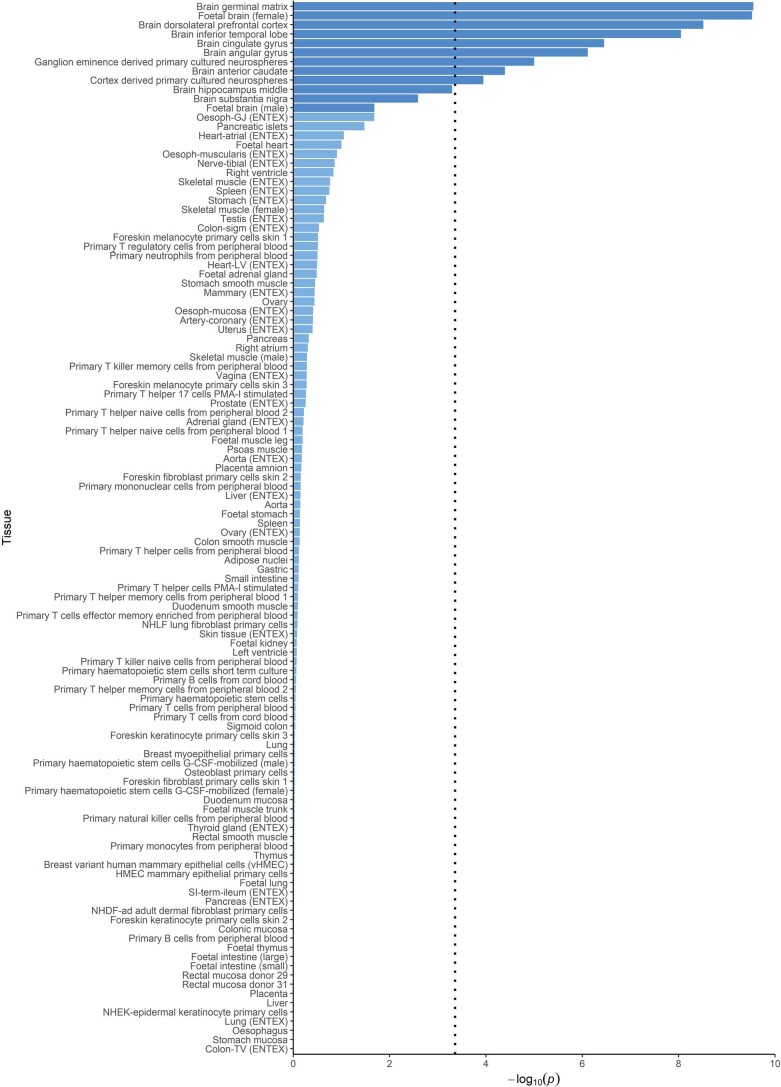
Of the 173 significant genes from genome-wide gene-based tests in MAGMA (see Supplementary Table 11 for their functions), 129 could be functionally annotated (Supplementary Table 12). Protein-coding and noncoding sequences are actively conserved in approximately three-quarters of these genes, 63% are more intolerant to variation than average and 33% are intolerant to loss-of-function mutations. Gene property analysis for general tissues and 13 brain tissues confirmed the importance of the brain and specific brain regions (Supplementary Tables 13 and 14). Levels of brain expression for 125 of the 173 significant genes from gene-based tests could be mapped in FUMA and are shown in Supplementary Table 15. A total of 20 genes showed high general brain expression levels and, of these, 3 (PPP1R1B, NPM1 and WASF3) were located near significant SNP associations. Of the 12 brain regions assessed, gene expression was generally highest in the cerebellar hemisphere, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex, consistent with the results of gene property analysis.
Partitioned heritability
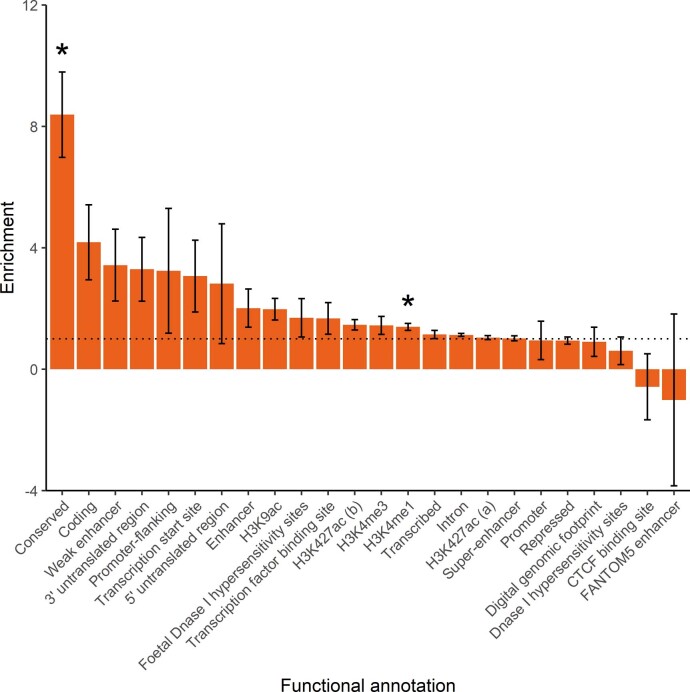
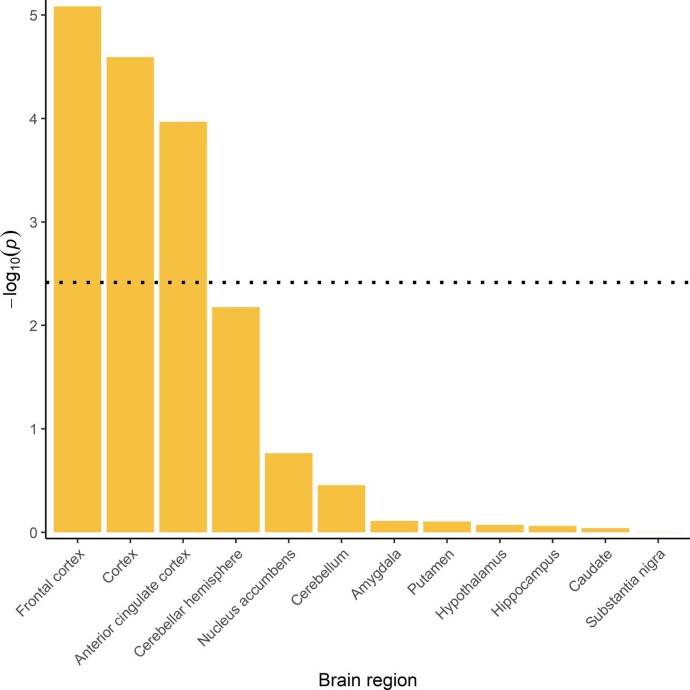
SNP-based heritability of dyslexia partitioned by functional annotation showed significant enrichment for conserved regions and H3K4me1 clusters (Supplementary Table 16 and Extended Data Fig. 5). There was enrichment in genes expressed in the frontal cortex, cortex and anterior cingulate cortex (P < 4.17 × 10−3) (Supplementary Table 17 and Extended Data Fig. 6), but not for brain cell type (Supplementary Table 18 and Extended Data Fig. 7). Enrichment was seen in enhancer and promoter regions, identified by the presence of H3K4me1 and H3K4me3 chromatin marks, respectively, in multiple central nervous system (CNS) tissues (Supplementary Tables 19 and 20 and Extended Data Figs. 8 and 9). Reading, an offshoot of spoken language, is a uniquely human trait, but there was no enrichment for a range of annotations related to human evolution spanning the last 30 million to 50,000 years18 (Supplementary Table 21).
Extended Data Fig. 5. Enrichment estimates for major functional annotations.
The 24 major functional annotations were defined by Finucane et al.39. Enrichment is the proportion of h2/proportion of SNPs. The horizontal dotted line indicates no enrichment (where proportion of h2/proportion of SNPs = 1). Error bars represent standard errors of the enrichment estimates. Asterisks indicate enrichment estimates are significant based on a Bonferroni-derived P value of < 2.08 × 10−3 (for 24 tests). Exact values of enrichment statistic, standard error, and P value can be found in Supplementary Table 16.
Extended Data Fig. 6. Heritability of dyslexia partitioned by brain tissue gene expression.
The -log10 P value of the enrichment estimates for heritability of dyslexia for genes expressed in 12 brain regions. The horizontal dotted line indicates significance after Bonferroni correction for 12 tests (P < 4.17 × 10−3).
Extended Data Fig. 7. Heritability of dyslexia partitioned by brain cell type.
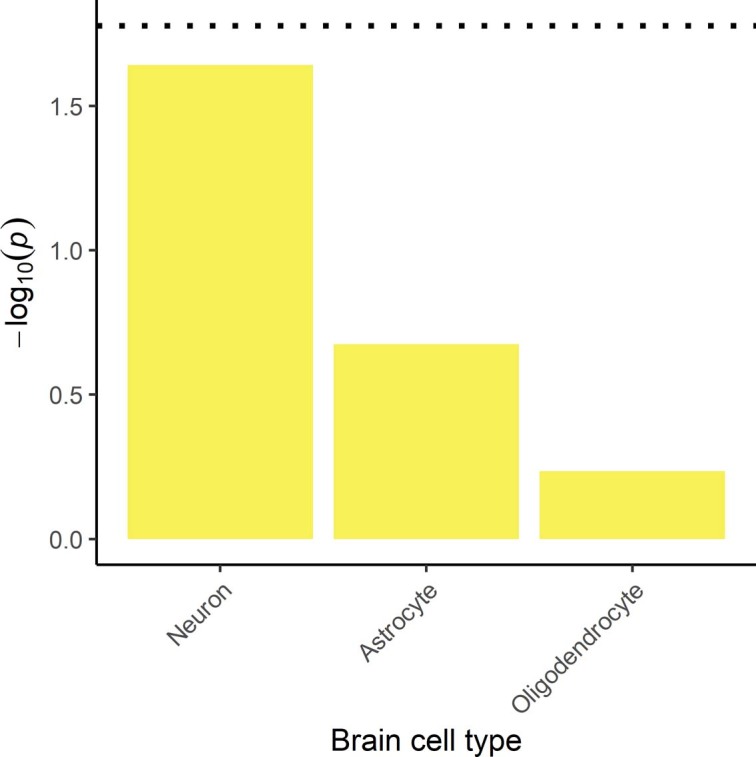
The -log10 P value of the enrichment estimates for heritability of dyslexia for brain cell types. The horizontal dotted line indicates significance after Bonferroni correction for three tests (P < 1.67 × 10−2).
Extended Data Fig. 8. Heritability of dyslexia partitioned by cell-type specific H3K4me1.
The -log10 P value of the enrichment estimates for heritability of dyslexia for variants located within H3K4me1 peaks of different tissues. Central nervous systems tissues are represented in dark green and other tissues are represented in light green. The vertical dotted line indicates significance after Bonferroni correction for 114 tests (P < 4.39 × 10−4).
Extended Data Fig. 9. Heritability of dyslexia partitioned by cell-type specific H3K4me3.
The -log10 P value of the enrichment estimates for heritability of dyslexia for variants located within H3K4me3 peaks of different tissues. Central nervous systems tissues are represented in dark blue and other tissues are represented in light blue. The vertical dotted line indicates significance after Bonferroni correction for 114 tests (P < 4.39 × 10−4).
Genetic correlations and LDSC
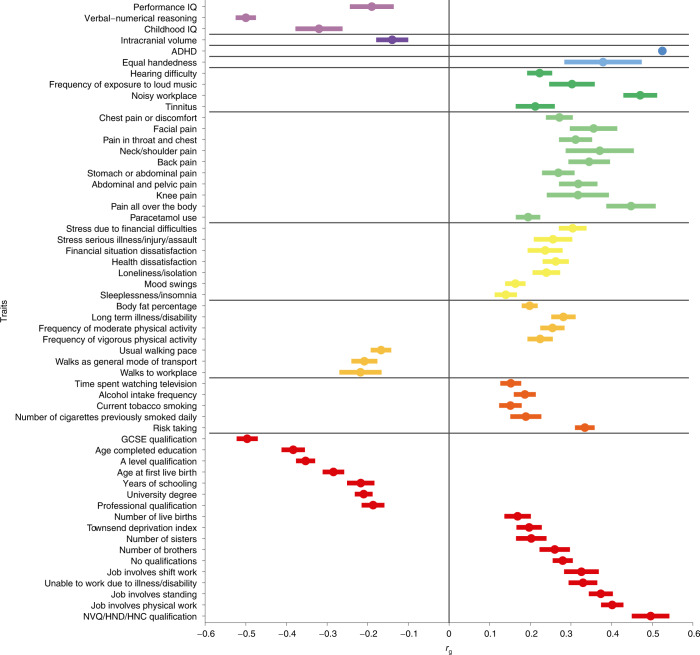
Genetic correlations were estimated for 98 traits (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Table 22), including reading and spelling measures, from GenLang (Fig. 3), and brain subcortical structure volumes, total cortical surface area and thickness from the Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA) consortium. A total of 63 traits showed genetic correlations with dyslexia at the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold (P < 0.05/98; Fig. 2). Genetic correlations (rg) with quantitative reading and spelling measures ranged from −0.70 to −0.75 (lowest 95% CI of −0.60, highest 95% CI of −0.86), and were −0.62 (95% CI: −0.50, −0.74) and −0.45 (95% CI: −0.26, −0.64) with phoneme awareness and nonword repetition measures, respectively. The childhood/adolescent performance (nonverbal) intelligence quotient (IQ) rg was lower (−0.19; 95% CI: −0.08, −0.30) than that for adult verbal-numerical reasoning19 (−0.50; 95% CI: −0.45, −0.55) but similar to that for childhood IQ20 (−0.32; 95% CIs: −0.21, −0.43) and educational attainment21 (−0.22; 95% CI: −0.15, −0.29). Traits showing positive rg included jobs involving heavy manual work21 (0.40; (95% CI: 0.34, 0.45)), work-related/vocational qualifications21 (0.50; 95% CI: 0.41, 0.59), ADHD22 (0.53; 95% CI: 0.29, 0.77), equal use of right and left hands21 (0.38; 95% CI: 0.19, 0.57) and pain measures21 (average = 0.31; 95% CI: 0.21, 0.41). Of the 11 ENIGMA measures tested, only intracranial volume was significantly correlated with dyslexia (rg = −0.14; 95% CI: −0.06, −0.22). Targeted investigation of 80 structural neuroimaging measures from UK Biobank, including surface-based morphometry and diffusion-weighted imaging for brain circuitry linked to language, were nonsignificant at a Bonferroni-corrected significance level for number of independent traits. Phenotype independence was estimated by spectral decomposition of the phenotypic correlation matrix implied by the bivariate LDSC intercept from GWAS summary statistics of these traits, using the PhenoSpD toolkit23 (Supplementary Table 23).
Fig. 2. Genetic correlations of dyslexia with other phenotypes.
Significant (P < 5 × 10−4) genetic correlations (rg) between self-reported dyslexia diagnosis from 23andMe and other phenotypes from the LD Hub database and Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics Through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA). We tested 98 traits but present only those that were significant after Bonferroni correction. Center points represent genetic correlations, and error bars represent standard errors around the estimate; exact values can be found in Supplementary Table 22. The vertical line indicates a genetic correlation of zero, and the horizontal lines divide groups of related traits. GCSE, General Certificate of Secondary Education; HNC, Higher National Certificate; HND, Higher National Diploma; NVQ, National Vocational Qualification.
Fig. 3. Genetic correlations between dyslexia and measures of reading, language and nonverbal IQ.
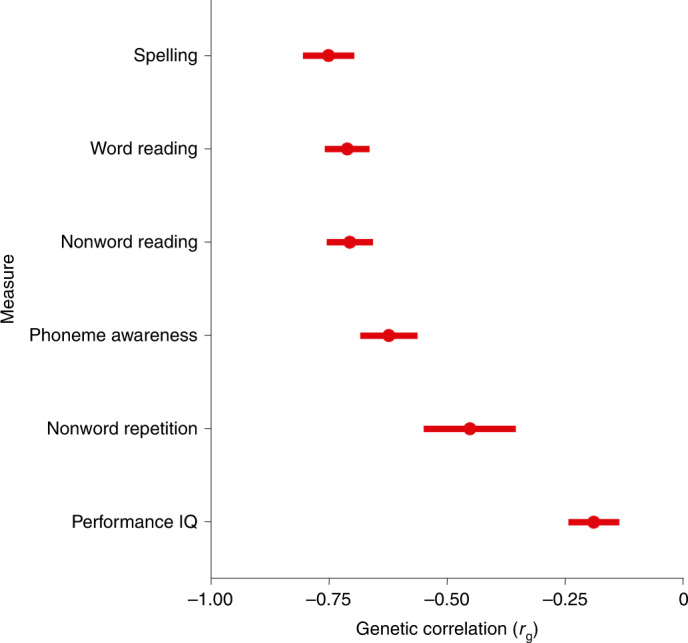
Genetic correlations (rg) between self-reported dyslexia diagnosis from 23andMe and measures of reading, language and performance (nonverbal) IQ in the GenLang consortium. Center points represent genetic correlations estimated in LDSC, and error bars represent standard errors around the estimate; exact values can be found in Supplementary Table 22.
Polygenic score analyses
Dyslexia polygenic scores (PGS) based on the 23andMe dyslexia GWAS were computed in four independent cohorts and, overall, higher PGS were associated with lower reading and spelling accuracy (Supplementary Table 24). In two Australian population-based samples (1,647 adolescents, 1,163 adults), the dyslexia PGS explained up to 3.6% of variance in the reading and spelling measures, being most predictive of lower performance on tests of nonword reading, an index of phonological decoding. Dyslexia PGS did not correlate with scores on tests of nonword repetition (considered a marker of phonological short-term memory). In developmental cohorts enriched for reading difficulties, the dyslexia PGS explained 3.7% (UKdys; n = 930) and 5.6% (CLDRC; n = 717) of variance in word recognition tests.
Analyses of dyslexia associations from the literature
Of 75 previously reported dyslexia associations, none showed genome-wide significance in our analyses (Supplementary Table 25). Of these targeted variants, 19 (in ATP2C2, CMIP, CNTNAP2, DCDC2, DIP2A, DYX1C1, FOXP2, KIAA0319L and PCNT) showed association surviving Bonferroni correction that accounted for LD (P < 0.05/68.7). In gene-based tests of 14 candidate genes from the literature24,25, association at a Bonferroni level (P < 0.05/14) was seen for KIAA0319L (P = 1.84 × 10−4) and ROBO1 (P = 1.53 × 10−3) (Supplementary Table 26). The CNTNAP2 association approached corrected replication-level significance (P = 0.004). Targeted gene set analysis of three pathways previously implicated in dyslexia (Supplementary Table 27) showed replication-level support (P = 2.00 × 10−3) for the axon guidance pathway (comprising 216 genes).
Discussion
In the largest GWAS of dyslexia to date (>50,000 self-reported diagnoses), we identified 42 significant independent loci. Of these, 27 represent new associations that have not been uncovered in GWAS of related cognitive traits; 12 of the new associations were validated in the GenLang consortium GWAS meta-analysis of reading/spelling in English and other European languages14, and 1 in a Chinese language cohort. Of the significant SNPs, 36% overlapped with variants from general cognitive ability GWAS, consistent with twin studies that find that genetic variation in reading disability is explained by general and reading-specific cognitive ability10. Similar to other complex traits, and consistent with high polygenicity, each significant locus showed small effects (odds ratios (ORs) ranging from 1.04 to 1.12). Our estimated SNP-based heritability of 19% (assuming a 10% dyslexia population prevalence) was equal to that reported in a smaller GWAS12, but lower than heritability estimates from twin studies (40–80%)26,27. This difference may be due partly to effects of rare and structural variants28, which have been implicated in reading and related traits29,30.
Whereas AUTS2 has been implicated in autism31, intellectual disability32 and dyslexia33, the variant we uncovered (rs3735260) represents the strongest AUTS2 SNP association with a neurodevelopmental trait to date. Amongst our findings were other known neurodevelopmental genes, such as TANC2 (implicated in language delay and intellectual disability34,35) and, especially, GGNBP2 (linked to neurodevelopmental delay36 and autism37) with variant rs34349354 supported in all our validation cohorts. However, rs34349354 is also associated with cognitive performance38, and based on expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) evidence is more likely linked to ZNHIT3, colocalizing with molecular QTLs (opentargets.org). Notably, none of the more established candidate genes for dyslexia approached genome-wide significance in our results.
Like other human complex traits, partitioning of SNP-based heritability revealed enrichment in conserved regions39. We further observed enrichment in the histone mark H3K4me1 (which has also been reported for ASD40), and at H3K4me1 and H3K4me3 clusters in the CNS (marking enhancers and promoters, respectively). Since reading/writing systems are built on our capacities for spoken language, it is plausible that evolutionary changes on the human lineage helped shape the underlying genetic architecture41. However, we did not find enrichment of significant associations for curated annotations spanning different periods of hominin prehistory.
Our self-reported dyslexia diagnosis binary trait showed strong negative genetic correlations with quantitative reading and spelling measures, supporting the validity of this measure in the 23andMe cohort, and suggesting that reading skills and disorder are not qualitatively distinct. The positive genetic correlation between hearing difficulties and dyslexia is consistent with genetic correlations reported for childhood reading skill42, suggesting that hearing problems at an early age could affect acquisition of phonological processing skills.
Dyslexia showed moderately negative genetic correlations with adult verbal-numerical reasoning, but there was a lack of a strong genetic correlation of dyslexia with (nonverbal) performance IQ. This would be consistent with phenotypic observations that individuals with dyslexia are disadvantaged on verbal IQ tests43. Educational attainment correlations were also not strong, which might reflect school adjustments and other support that counteract disadvantage in academic learning.
There was little evidence of common genetic variation in dyslexia being related to interindividual differences in subcortical volumes, or structural connectivity and morphometry for brain regions implicated in language processing in adults. Thus, the phenotypic correlations previously reported between dyslexia and aspects of neuroanatomy may in large part reflect environmental shaping of the brain, perhaps through the process of reading itself44. Left-handedness and ambidexterity show small genetic overlap with each other45 yet are both phenotypically linked to neurodevelopmental disorders/cognitive abilities46,47. We report a significant genetic correlation between dyslexia and self-reported equal hand use, but not left-handedness, supporting theories linking ambidexterity and dyslexia48.
Dyslexia and ADHD5,6 often co-occur (24% reporting ADHD in our cases versus 9% in controls), and we show a moderate genetic correlation between the two, potentially reflecting shared endophenotypes like deficits in working memory and attention49. Although we did not find significant genetic correlations between dyslexia and ASD, the GWAS for the latter encompassed diverse neurodevelopmental phenotypes, including subgroups with varying educational attainment and IQ40. Genetic correlations with pain-related traits suggest that individuals with dyslexia may have a lower threshold for pain perception. Links between pain and other neurodevelopmental disorders have been reported50,51.
Dyslexia polygenic scores were correlated with lower achievement on reading and spelling tests in population-based and reading-disorder enriched samples, especially for nonword reading, a measure of phonological decoding that is typically impaired in dyslexia. Polygenic scores could become a valuable tool to help identify children with a propensity for dyslexia, enabling learning support before development of reading skills. However, a limitation of our study is the potential for collider bias arising from sample selection (that is, people without dyslexia and from higher socioeconomic positions), which we were unable to quantify; thus, care should be taken in future research when using polygenic scores based on many variants52.
In summary, we report 42 new independent genome-wide significant loci associated with dyslexia, 27 of which have not been associated with cognitive-educational traits and should be prioritized for follow up as dyslexia candidates. Functional annotation of the variants highlights the importance of conserved and enhancer regions of the genome for this trait. Dyslexia shows positive genetic correlations with ADHD, vocational qualifications, physical occupations, ambidexterity and pain perception, and negative correlations with academic qualifications and cognitive ability; family-based methods are needed to dissociate pleiotropic and causal effects.
Methods
GWAS participants
Participants were drawn from the customer base of 23andMe, Inc., a consumer genetics company. Participants provided informed consent and participated in the research online, under a protocol approved by the external AAHRPP-accredited IRB, Ethical and Independent Review Services (www.eandireview.com). They included 51,800 (21,513 male, 30,287 female) participants who responded ‘yes’ to the question ‘Have you been diagnosed with dyslexia?’ (cases) and 1,087,070 (446,054 male, 641,016 female) participants who responded ‘no’ (controls). Age ranged from 18 to 110 years, with the prevalence of dyslexia higher for younger participants (5.34% in those aged 20–30 years) than older participants (3.23% in those aged 80–90 years). The negative linear relationship between dyslexia prevalence and participant age was expected given that screening for specific learning difficulties has only become commonplace in more recent decades. Moreover, this aligns with findings from the subsample (4.3%) of participants who reported age of diagnosis: younger participants were diagnosed at an earlier age (for example, 9.7 years (±4.7) for 20- to 30-year-olds) than older participants (for example, 22.4 years (±17.8) for 80- to 90-year-olds). The prevalence of dyslexia in our sample was similar for women (4.51%) and men (4.6%), although the slightly higher prevalence in males in this very large sample was statistically significant (P < 8.7 × 10−6). Such a prevalence lies at the lower end of the range typically reported in the US population3 and might represent the more severe cases of dyslexia given that a formal diagnosis was required; additionally, people with dyslexia might opt out of survey research that requires reading, further restricting the sample range.
Genotyping and imputation
DNA was extracted from saliva samples and genotyped on one of five genotyping platforms by the National Genetics Institute (NGI). In the present analysis, only participants with European ancestry were included. Details about the genotyping arrays, quality control of samples and ancestry derivation can be found in Fontanillas et al.53 and the Supplementary Note. Phased genotypes were imputed to a combined reference panel of the 1000 Genomes Phase 3 haplotypes (May 2015) and the UK10K imputation reference panel using Minimac3 (see Das et al.54).
Association analysis
Association analysis was performed on genotyped and imputed SNP dosage data using logistic regression and assuming an additive model of allelic effects. For X-chromosome analysis, male genotypes were treated as homozygous diploid. Covariates included age, age squared, gender, the first five ancestry principal components and genotype platform. SNP significance was evaluated by a likelihood ratio test, and genome-wide significance was determined as P < 5 × 10−8 (suggestive significance level as P < 1 × 10−6). Only reliably imputed SNPs (r2 > 0.80) and those with minor allele frequency (MAF) > 0.01 are presented (n = 7,995,923). We define associated regions by first identifying all variants with P < 5 × 10−8, then grouping these variants into regions separated by gaps of at least 250 kb. Index variants are the variants with smallest P value within each associated region. We use the same approach for regions with suggestive associations, but by first identifying all variants with P < 10−5. Subsidiary genome-wide association analysis of separate male (n = 21,513 cases, 446,054 controls) and female (n = 30,287 cases, 641,016 controls) groups, and younger (below 55 years; n = 30,763 cases, 582,276 controls) and older (55 and above; n = 21,037 cases, 504,794 controls) groups was performed. The latter was to check whether reliability of diagnosis (assumed to be higher in the younger sample whose recall of diagnosis should be better and who would have been exposed to greater levels of dyslexia screening) affected the GWAS signal.
We also looked to independently validate our genome-wide significant variants within (1) a published GWAS meta-analysis of 2,274 dyslexia cases from nine European countries representing six different languages (NeuroDys) by Gialluisi et al.55; (2) a population sample (Chinese Reading Study; CRS) of children measured on quantitative traits of reading accuracy and reading fluency (n = 2,270; described in the Supplementary Note), and; (3) within the GenLang quantitative trait GWAS meta-analysis of word reading (up to n = 33,959) and spelling (up to n = 18,514) skills measured in cohorts of children and adolescents from Europe, the United States and Australia, and representing seven European languages, of which English was the most common14.
Genomic control
Top SNPs are reported from the more conservative GWAS results adjusted for genomic control (Fig. 1, Extended Data Figs. 1–4, and Supplementary Tables 1, 2, 9 and 10), whereas downstream analyses (including gene-set analysis, enrichment and heritability partitioning, genetic correlations, polygenic prediction, candidate gene replication) are based on GWAS results without genomic control.
Gene-based analyses
The GWAS results were used to calculate gene-based P values for association with dyslexia by performing the gene analysis in MAGMA v.1.08 (ref. 56) through the FUMA interface57 using standard settings. In total, 19,039 genes were tested, and P values were judged based on a Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold of P < 2.63 × 10−6. We also performed gene set analyses for association of biological pathways (all available gene ontology (GO) terms and curated gene sets from the Molecular Signatures Database (MsigDB)58,59) with dyslexia in MAGMA through the FUMA interface. The total number of pathways tested was 15,486, and P values were judged based on a Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold of P < 3.23 × 10−6.
Biological annotations
Genome-wide significant variants and nearby gene(s) were annotated using external reference data and evaluated for functional or regulatory impact. A 99% credible set of potentially causal variants for SNPs in significant regions was based on approximate Bayes factor (ABFs)60 assuming a prior variance of 0.1, and using the method of Maller et al.61 to define these sets. Variant effect prediction of these was done in ENSEMBL (release 104)62. For genome-wide significant variants, we considered: gene context (whether a variant is intergenic or located within a specific functional region within a gene locus); deleteriousness (Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion (CADD) score); functionality (RegulomeDB (RDB) category); chromatin state (minimum and common 15-core chromatin state); and SNP-trait associations reported in the NHGRI GWAS Catalog13.
For each variant, the most probable gene target was identified using the Open Target Genetics portal63, which draws on evidence from QTL and chromatin interaction experiments, functional predictions and distance from a gene’s transcription start site. For genome-wide significant genes, we considered: loss-of-function intolerance (probability of loss-of-function Intolerance (pLI) score); variation intolerance (residual variation intolerance score, RVIS); variation intolerance in noncoding regions (noncoding RVIS, ncRVIS); evolutionary constraint of noncoding regions (noncoding genomic evolutionary rate profiling (ncGERP) score); evolutionary constraint of protein-coding regions (protein-coding genomic evolutionary rate profiling (pcGERP) score); deleteriousness across noncoding regions (noncoding CADD (ncCADD) score); combined functionality of variants in noncoding regions (noncoding genome-wide annotation of variants (ncGWAVA) score); and expression in 12 brain tissues (amygdala, anterior cingulate cortex, caudate basal ganglia, cerebellar hemisphere, cerebellum, cortex, frontal cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, nucleus accumbens basal ganglia, putamen basal ganglia and substantia nigra). All annotations were obtained through FUMA57 except RVIS, ncGERP, pcGERP, ncCADD and ncGWAVA, which were taken from Petrovski et al.64. Details of each annotation including original sources are in the Supplementary Note.
Partitioned heritability
We partitioned SNP heritability of dyslexia using stratified LDSC, as described by Finucane et al.39, to determine whether SNPs that share the greatest proportion of the heritability are also clustered in specific functional categories in the genome. Overall, we performed 266 different tests, which would give a very conservative Bonferroni-corrected significance level of 1.88 × 10−4, but because there will be overlap among annotation groups, we also report corrections to significance within different classes of annotation, each of which we now describe. Partitioning was performed for the 24 main functional annotations defined by Finucane et al.39. LD scores, regression weights and allele frequencies are from European ancestry samples and were retrieved from https://alkesgroup.broadinstitute.org/LDSCORE. Heritability estimates were considered statistically significant if the P value surpassed an α level of 2.08 × 10−3, derived by Bonferroni correction based on 24 tests.
We also estimated the enrichment for heritability of dyslexia for tissue-specific annotations, while controlling for the annotations in the baseline model, including gene expression in three brain cell types, gene expression in 12 brain regions, and chromatin marks H3K4me1 and H3K4me3 in multiple tissues (108 and 114, respectively) since these marks are enriched at enhancers65 and promoters66, respectively. Enrichment is the proportion of SNP heritability divided by the proportion of SNPs. For the brain cell types, we estimated enrichment for heritability of dyslexia for genes expressed in neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes using data from Cahoy et al.67. Enrichments were considered statistically significant if the P value surpassed an α level of 0.017, derived by Bonferroni correction based on three tests. The gene expression data used to estimate the enrichment of heritability in genes expressed in certain brain regions was from the GTEx database68, and the Bonferroni-derived α level for enrichment was 4.17 × 10−3 (based on 12 tests). Chromatin annotations include data from the Roadmap Epigenomics consortium17 and EN-TEx69,70. For H3K4me1, the Bonferroni-derived α level for enrichment was 4.63 × 10−4 (based on 108 tests) and, for H3K4me3, the Bonferroni-derived α level for enrichment was 4.39 × 10−4 (based on 114 tests).
Evolutionary annotations
Although reading and writing is a human cultural invention, it builds on fundamental pathways involved in language processing. Therefore, we investigated whether annotations related to human evolution were significantly enriched for heritability of dyslexia by applying an evolutionary analysis pipeline adapted from Tilot et al.18. These analyses capture a range of periods in an evolutionary timeframe on the lineage that led to humans, from approximately 30 million years ago to 50,000 years ago.
Enrichment of heritability was estimated in adult brain human gained enhancers (HGEs)71, fetal brain HGEs72, ancient selective sweep regions73, Neanderthal-introgressed SNPs74 and Neanderthal-depleted regions75 (see Supplementary Note for a description of each annotation); and controlled for using the baselineLD v.2 model from Gazal et al.76. Heritability enrichment in human adult and fetal HGEs were additionally controlled for adult and fetal brain active regulatory elements from the Roadmap Epigenomics resource17. Active regulatory elements were defined using chromHMM16. Enrichment P values were judged by an α level of 10−2, derived by Bonferroni correction based on five tests.
Genetic correlations
Genetic correlations within the 23andMe GWAS of dyslexia
Genetic correlation between self-reported dyslexia diagnosis in males and females, and between younger (<55 years old) and older (≥55 years old) adults was calculated using LDSC77,78.
Genetic correlations of dyslexia with other traits
We present the pairwise genetic correlation of dyslexia with 98 traits. Summary statistics for most of these traits are publicly available through LD Hub77–79—a centralized database and web interface that automates the LDSC regression analysis pipeline. A selection of brain magnetic resonance imaging measures obtained from the ENIGMA-3 consortium80–83, and measures of reading and spelling accuracy, and performance IQ from the GenLang Consortium14 were analyzed locally using LDSC. Word reading accuracy in GenLang was measured by the number of correct words read aloud from a list in a time restricted or unrestricted fashion. Examples of tools that include this measure are Test of Word Reading Efficiency (TOWRE), the British Ability Scales (BAS) and the Wide Range Achievement Test (WRAT). Spelling accuracy in GenLang was measured by the number of words correctly spelled orally or in writing. The words were dictated as single words or in a sentence. Examples of tools that include this measure are the BAS, WRAT and Wechsler Objective Reading Dimensions (WORD). Performance IQ in GenLang was based on subtests of IQ tests that did not depend on verbal cues, as included for example in the BAS and Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC). Trait descriptions and summary statistic sources are in Supplementary Table 22. Bonferroni correction for multiple testing derived an adjusted critical P value of 5.1 × 10−4 from 98 independent tests.
Genetic correlations were further estimated in a targeted analysis of structural brain magnetic resonance imaging measures from UK Biobank, which were more comprehensive than those currently available from ENIGMA, along with further advantages such as hemisphere-specific data and greater homogeneity in cohort and scanning procedures. GWAS summary statistics from brain imaging-derived phenotypes for 33,000 participants were downloaded from the Oxford Brain Imaging Genetics Server84. Structural brain imaging traits encompassed both diffusion tensor imaging and surface-based morphometric phenotypes85 where selected tracts or regions of interest had a known link to language. For diffusion tensor imaging, fractional anisotropy values derived from both tract-based-spatial statistics and probabilistic tractography were used for available tracts spanning the extended language network86. For surface-based morphometric (cortical volume, surface area and thickness) GWAS, summary statistics for regions of interest derived from the Desikan-Killiany atlas (white surface) were used, again selected for their relevance in language processing, based on previous literature87–90. To correct for multiple testing, phenotypic correlations between the UK Biobank imaging indices were derived and analyzed by PhenoSpD23 to obtain the number of independent variables (36.08) to use for Bonferroni correction (adjusted critical P value of 1.39 × 10−3).
Polygenic score analyses
Dyslexia polygenic scores were based on increasingly larger numbers of SNPs corresponding to their association P values from the 23andMe GWAS (P < 5 × 10−8, P < 1 × 10−5, P < 0.001, P < 0.01, P < 0.05, P < 0.1, P < 0.5, 1). They were calculated in four independent cohorts. Two were general population cohorts from Australia: n = 1,640 (772 families) adolescents/young adults (Brisbane adolescents)91; n = 1,165 (966 families) older adults (Brisbane adults)25. The other two were family-based samples selected for dyslexia: one from the United Kingdom (UKdys), n = 930 (595 families); the other from the United States (Colorado Learning Disabilities Research Center, CLDRC), n = 717 (336 families)92. In the Australian samples, polygenic scores were calculated on 1000 Genomes Phase 3 (v.20101123) imputed genetic data using PLINK93. Only reliably imputed SNPs (R2 > 0.80) and those with a minor allele frequency >0.01 were included, and the default clumping procedure was used where index SNPs formed a clump with other SNPs in LD (R2 > 0.1) and within a 250 kb distance. In the UKdys and CLDRC samples, polygenic scores were calculated on Haplotype Reference Consortium imputed genetic data using PRSice94, with the same imputation quality and MAF exclusions for the base (23andMe GWAS) sample, and clumping parameters.
Polygenic scores were then used as predictors in linear models of quantitative trait outcomes (Australia: word, nonword (phonetic), irregular word (lexical) reading and spelling tests from an extended version of the Components of Reading Examination95, and two nonword repetition tests which are sensitive to developmental language disorders—Dollaghan and Campbell96, Gathercole and Baddeley97; UKdys and CLDRC: word recognition). All quantitative traits were preadjusted for sex, age and ancestry principal components (10 principal components in UKdys and CLDR; 20 principal components in Australian samples). Further adjustments were made for imputation run (separate runs for different genotyping arrays) in the Australian samples, and for nonverbal IQ in all samples (except for the Australian adults), and for hearing difficulties in the Australian older adults. Because the cohorts included related family members (twins or siblings), linear mixed models (lme) were specified in RStudio98, with family membership modeled as a random effect and the dyslexia polygenic score as a fixed effect. Where monozygotic twins were present, their trait scores were averaged and they were used as a single case.
Evaluation of candidates from previous literature
We used the results of the 23andMe dyslexia GWAS to assess variants, genes and biological pathways previously associated with or implicated in dyslexia and/or variation in reading and spelling ability in past association studies, linkage analyses and other studies.
Previously reported variants
We assessed 75 previously reported variants within our summary statistics, adopting a replication/validation significance threshold of P < 7.28 × 10−4, derived by Bonferroni correction based on 68.7 independent tests derived through matrix spectral decomposition, taking into account LD (see Doust et al.25 for details on how these variants were selected). The sources for each variant are provided in Supplementary Table 26.
Dyslexia candidate genes
We evaluated gene-based results from MAGMA v.1.08 (ref. 56) for overrepresentation of genome-wide significant variants from the 23andMe dyslexia GWAS within the loci of 14 candidate genes from earlier literature: CMIP, CNTNAP2, CYP19A1, DCDC2, DIP2A, DYX1C1, GCFC2, KIAA0319, KIAA0319L, MRPL19, PCNT, PRMT2, S100B and ROBO1. The rationale for this selection is detailed by Luciano et al.24 and Doust et al.5. The critical P value, based on Bonferroni correction for 14 tests, was 3.57 × 10−3.
Candidate dyslexia gene sets
We performed a gene set analysis in MAGMA to test for overrepresentation of genome-wide significant variants within (1) a set of transcriptional targets of FOXP2, a highly conserved transcription factor linked to speech and language impairment99; and (2) two biological pathways previously suggested to play a role in dyslexia susceptibility100,101—axon guidance (GO:0007411: ‘chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site’; 216 genes) and neuron migration (GO:0001764: ‘movement of an immature neuron from germinal zones to specific positions where they will reside as they mature’; 145 genes). An adjusted critical P value of 0.017 was derived using Bonferroni correction based on three independent tests.
Ethical standards
Participants provided informed consent and participated in the research online, under a protocol approved by the external AAHRPP-accredited IRB, Ethical and Independent Review Services. Participants were included in the analysis on the basis of consent status as checked at the time data analyses were initiated.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Online content
Any methods, additional references, Nature Research reporting summaries, source data, extended data, supplementary information, acknowledgements, peer review information; details of author contributions and competing interests; and statements of data and code availability are available at 10.1038/s41588-022-01192-y.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Note and Fig. 1.
Supplementary Tables 1–27.
Acknowledgements
We thank the research participants and employees of 23andMe Inc, the GenLang Consortium, the Brisbane Adults Reading Study, and the CRS. E.E., G.A., B.M., B.S.P., C.F. and S.E.F. are supported by the Max Planck Society (Germany). The CRS was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61807023), Funds for Humanities and Social Sciences Research of the Ministry of Education (Grant No. 19YJC190023 and 17XJC190010) and General Project of Shaanxi Natural Science Basic Research Program (2018JQ8015) (Grant No. 2018JQ8015 and 2021JQ-309). S.P. is funded by the Royal Society. Acknowledgements for the GenLang Consortium appear in the Supplementary Note.
Extended data
Author contributions
M.L., S.E.F., T.C.B. and N.G.M. conceived the study, with M.L. overseeing general analysis and A.A. overseeing 23andMe analysis. C.D., P.F., E.E., G.A., S.D.G., Z.W., B.M. and M.L. performed statistical and/or downstream annotation analysis. R.E.M. advised C.D. on some analysis. C.D. drafted the manuscript, with sections contributed by P.F., E.E., G.A., Z.W. and M.L. B.S.P., C.F. and S.E.F. supervised the GenLang GWAS. J.Z. managed the Chinese Reading Study. S.P., J.B.T., A.P.M. and J.F.S. managed the UKDys study. J.R.G., R.K.O., E.G.W., J.C.D., B.F.P. and S.D.S. managed the CLDRC study. M.J.W., T.C.B. and N.G.M. managed the Australian adolescent twin studies. M.L., T.C.B., S.E.F. and N.G.M. managed the Australian adult reading study. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Genetics thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Data availability
The full summary statistics for each dyslexia GWAS presented in this paper will be made available through 23andMe website (https://research.23andme.com/dataset-access/) to qualified researchers under an agreement with 23andMe that protects the privacy of the 23andMe participants. The top 10,000 associated SNPs from the main GWAS can be downloaded from 10.7488/ds/3465.
Competing interests
P.F., A.A. and the 23andMe Research Team are employed by and hold stock or stock options in 23andMe, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Lists of authors and their affiliations appear at the end of the paper.
Change history
2/23/2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: 10.1038/s41588-023-01336-8
Contributor Information
Michelle Luciano, Email: michelle.luciano@ed.ac.uk.
23andMe Research Team:
Stella Aslibekyan, Adam Auton, Elizabeth Babalola, Robert K. Bell, Jessica Bielenberg, Katarzyna Bryc, Emily Bullis, Daniella Coker, Gabriel Cuellar Partida, Devika Dhamija, Sayantan Das, Sarah L. Elson, Teresa Filshtein, Kipper Fletez-Brant, Will Freyman, Pooja M. Gandhi, Karl Heilbron, Barry Hicks, David A. Hinds, Ethan M. Jewett, Yunxuan Jiang, Katelyn Kukar, Keng-Han Lin, Maya Lowe, Jey McCreight, Matthew H. McIntyre, Steven J. Micheletti, Meghan E. Moreno, Joanna L. Mountain, Priyanka Nandakumar, Elizabeth S. Noblin, Jared O’Connell, Aaron A. Petrakovitz, G. David Poznik, Morgan Schumacher, Anjali J. Shastri, Janie F. Shelton, Jingchunzi Shi, Suyash Shringarpure, Vinh Tran, Joyce Y. Tung, Xin Wang, Wei Wang, Catherine H. Weldon, Peter Wilton, Alejandro Hernandez, Corinna Wong, and Christophe Toukam Tchakouté
Quantitative Trait Working Group of the GenLang Consortium:
Filippo Abbondanza, Andrea G. Allegrini, Till F. M. Andlauer, Cathy L. Barr, Manon Bernard, Kirsten Blokland, Milene Bonte, Dorret I. Boomsma, Thomas Bourgeron, Daniel Brandeis, Manuel Carreiras, Fabiola Ceroni, Valéria Csépe, Philip S. Dale, Peter F. de Jong, Jean Francois Démonet, Eveline L. de Zeeuw, Yu Feng, Marie-Christine J. Franken, Margot Gerritse, Alessandro Gialluisi, Sharon L. Guger, Marianna E. Hayiou-Thomas, Juan Hernández-Cabrera, Jouke-Jan Hottenga, Charles Hulme, Philip R. Jansen, Juha Kere, Elizabeth N. Kerr, Tanner Koomar, Karin Landerl, Gabriel T. Leonard, Zhijie Liao, Maureen W. Lovett, Heikki Lyytinen, Angela Martinelli, Urs Maurer, Jacob J. Michaelson, Nazanin Mirza-Schreiber, Kristina Moll, Angela T. Morgan, Bertram Müller-Myhsok, Dianne F. Newbury, Markus M. Nöthen, Tomas Paus, Zdenka Pausova, Craig E. Pennell, Robert J. Plomin, Kaitlyn M. Price, Franck Ramus, Sheena Reilly, Louis Richer, Kaili Rimfeld, Gerd Schulte-Körne, Chin Yang Shapland, Nuala H. Simpson, Margaret J. Snowling, John F. Stein, Lisa J. Strug, Henning Tiemeier, J. Bruce Tomblin, Dongnhu T. Truong, Elsje van Bergen, Marc P. van der Schroeff, Marjolein Van Donkelaar, Ellen Verhoef, Carol A. Wang, Kate E. Watkins, Andrew J. O. Whitehouse, Karen G. Wigg, Margaret Wilkinson, and Gu Zhu
Extended data
is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41588-022-01192-y.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41588-022-01192-y.
References
- 1.Ritchie SJ, Bates TC. Enduring links from childhood mathematics and reading achievement to adult socioeconomic status. Psychol. Sci. 2013;24:1301–1308. doi: 10.1177/0956797612466268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shaywitz SE, Shaywitz BA, Fletcher JM, Escobar MD. Prevalence of reading disability in boys and girls: results of the Connecticut Longitudinal Study. JAMA. 1990;264:998–1002. doi: 10.1001/jama.1990.03450080084036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Katusic SK, Colligan RC, Barbaresi WJ, Schaid DJ, Jacobsen SJ. Incidence of reading disability in a population-based birth cohort, 1976–1982, Rochester, Minn. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2001;76:1081–1092. doi: 10.4065/76.11.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Carroll JM, Maughan B, Goodman R, Meltzer H. Literacy difficulties and psychiatric disorders: evidence for comorbidity. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 2005;46:524–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Margari L, et al. Neuropsychopathological comorbidities in learning disorders. BMC Neurol. 2013;13:198. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-13-198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Willcutt EG, Pennington BF, DeFries JC. Twin study of the etiology of comorbidity between reading disability and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000;96:293–301. doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(20000612)96:3<293::AID-AJMG12>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McArthur GM, Hogben JH, Edwards VT, Heath SM, Mengler ED. On the ‘specifics’ of specific reading disability and specific language impairment. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 2000;41:869–874. doi: 10.1111/1469-7610.00674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Catts HW, Fey ME, Tomblin JB, Zhang X. A longitudinal investigation of reading outcomes in children with language impairments. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2002;45:1142–1157. doi: 10.1044/1092-4388(2002/093). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bates TC, et al. Genetic and environmental bases of reading and spelling: a unified genetic dual route model. Read. Writ. 2007;20:147–171. doi: 10.1007/s11145-006-9022-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Haworth CMA, et al. Generalist genes and learning disabilities: a multivariate genetic analysis of low performance in reading, mathematics, language and general cognitive ability in a sample of 8000 12-year-old twins. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 2009;50:1318–1325. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fisher SE, DeFries JC. Developmental dyslexia: genetic dissection of a complex cognitive trait. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002;3:767–780. doi: 10.1038/nrn936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gialluisi A, et al. Genome-wide association study reveals new insights into the heritability and genetic correlates of developmental dyslexia. Mol. Psychiatry. 2021;26:3004–3017. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-00898-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Buniello A, et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS catalog of published genome-wide association studies, targeted arrays and summary statistics 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;47:D1005–D1012. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Eising E, et al. Genome-wide analyses of individual differences in quantitatively assessed reading- and language-related skills in up to 34,000 people. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2022;119:e2202764119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202764119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kircher M, et al. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014;46:310–315. doi: 10.1038/ng.2892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ernst J, Kellis M. ChromHMM: automating chromatin-state discovery and characterization. Nat. Methods. 2012;9:215–216. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kundaje A, et al. Integrative analysis of 111 reference human epigenomes. Nature. 2015;518:317–330. doi: 10.1038/nature14248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tilot AK, et al. The evolutionary history of common genetic variants influencing human cortical surface area. Cerebral Cortex. 2020;31:1873–1887. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sniekers S, et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis of 78,308 individuals identifies new loci and genes influencing human intelligence. Nat. Genet. 2017;49:1107–1112. doi: 10.1038/ng.3869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Benyamin B, et al. Childhood intelligence is heritable, highly polygenic and associated with FNBP1L. Mol. Psychiatry. 2014;19:253–258. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bycroft C, et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature. 2018;562:203–209. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0579-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Middeldorp CM, et al. A genome-wide association meta-analysis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in population-based pediatric cohorts. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 2016;55:896–905.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2016.05.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zheng J, et al. PhenoSpD: an integrated toolkit for phenotypic correlation estimation and multiple testing correction using GWAS summary statistics. Gigascience. 2018;7:giy090. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giy090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Luciano M, Gow AJ, Pattie A, Bates TC, Deary IJ. The influence of dyslexia candidate genes on reading skill in old age. Behav. Genet. 2018;48:351–360. doi: 10.1007/s10519-018-9913-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Doust C, et al. The association of dyslexia and developmental speech and language disorder candidate genes with reading and language abilities in adults. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2020;23:23–32. doi: 10.1017/thg.2020.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Davis CJ, Knopik VS, Olson RK, Wadsworth SJ, DeFries JC. Genetics and environmental influences on rapid naming and reading ability. Ann. Dyslexia. 2001;51:231–247. doi: 10.1007/s11881-001-0012-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gayán J, Olson RK. Genetic and environmental influences on orthographic and phonological skills in children with reading disabilities. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2001;20:483–507. doi: 10.1207/S15326942DN2002_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hannula-Jouppi K, et al. The axon guidance receptor gene ROBO1 is a candidate gene for developmental dyslexia. PLoS Genet. 2005;1:e50. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0010050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ganna A, et al. Ultra-rare disruptive and damaging mutations influence educational attainment in the general population. Nat. Neurosci. 2016;19:1563–1565. doi: 10.1038/nn.4404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gialluisi A, et al. Investigating the effects of copy number variants on reading and language performance. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2016;8:17–17. doi: 10.1186/s11689-016-9147-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Oksenberg N, Stevison L, Wall JD, Ahituv N. Function and regulation of AUTS2, a gene implicated in autism and human evolution. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003221. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Beunders G, et al. Two male adults with pathogenic AUTS2 variants, including a two-base pair deletion, further delineate the AUTS2 syndrome. Eur. J. Human Genet. 2015;23:803–807. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Girirajan S, et al. Relative burden of large CNVs on a range of neurodevelopmental phenotypes. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wessel K, et al. 17q23.2q23.3 de novo duplication in association with speech and language disorder, learning difficulties, incoordination, motor skill impairment, and behavioral disturbances: a case report. BMC Med. Genet. 2017;18:119. doi: 10.1186/s12881-017-0479-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Guo H, et al. Disruptive mutations in TANC2 define a neurodevelopmental syndrome associated with psychiatric disorders. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:4679. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12435-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pasmant E, et al. Characterization of a 7.6-Mb germline deletion encompassing the NF1 locus and about a hundred genes in an NF1 contiguous gene syndrome patient. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008;16:1459–1466. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2008.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Takata A, et al. Integrative analyses of de novo mutations provide deeper biological insights into autism spectrum disorder. Cell Reports. 2018;22:734–747. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lee JJ, et al. Gene discovery and polygenic prediction from a genome-wide association study of educational attainment in 1.1 million individuals. Nat. Genet. 2018;50:1112–1121. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0147-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Finucane HK, et al. Partitioning heritability by functional annotation using genome-wide association summary statistics. Nat. Genet. 2015;47:1228–1235. doi: 10.1038/ng.3404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Grove J, et al. Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019;51:431–444. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0344-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mozzi A, et al. The evolutionary history of genes involved in spoken and written language: beyond FOXP2. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:22157. doi: 10.1038/srep22157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schmitz J, Abbondanza F, Paracchini S. Genome-wide association study and polygenic risk score analysis for hearing measures in children. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2021;186:318–328. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vellutino F. Alternative conceptualizations of dyslexia: evidence in support of a verbal-deficit hypothesis. Harvard Educ. Rev. 2012;47:334–354. doi: 10.17763/haer.47.3.u117j10167686115. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dehaene S, Cohen L, Morais J, Kolinsky R. Illiterate to literate: behavioural and cerebral changes induced by reading acquisition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015;16:234–244. doi: 10.1038/nrn3924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cuellar-Partida G, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 48 common genetic variants associated with handedness. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2021;5:59–70. doi: 10.1038/s41562-020-00956-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Papadatou-Pastou M, et al. Human handedness: a meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2020;146:481–524. doi: 10.1037/bul0000229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Peters M, Reimers S, Manning JT. Hand preference for writing and associations with selected demographic and behavioral variables in 255,100 subjects: the BBC internet study. Brain Cogn. 2006;62:177–189. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2006.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Brandler WM, Paracchini S. The genetic relationship between handedness and neurodevelopmental disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2014;20:83–90. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Willcutt EG, Pennington BF, Olson RK, Chhabildas N, Hulslander J. Neuropsychological analyses of comorbidity between reading disability and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: in search of the common deficit. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2005;27:35–78. doi: 10.1207/s15326942dn2701_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gu X, et al. Heightened brain response to pain anticipation in high-functioning adults with autism spectrum disorder. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018;47:592–601. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Whitney DG, Shapiro DN. National prevalence of pain among children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. JAMA Pediatr. 2019;173:1203–1205. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.3826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Munafò MR, Tilling K, Taylor AE, Evans DM, Davey Smith G. Collider scope: when selection bias can substantially influence observed associations. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018;47:226–235. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyx206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Fontanillas P, et al. Disease risk scores for skin cancers. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:160. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20246-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Das S, et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016;48:1284–1287. doi: 10.1038/ng.3656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Gialluisi A, et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies new variants associated with a cognitive predictor of dyslexia. Transl. Psychiatry. 2019;9:77. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0402-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.de Leeuw CA, Mooij JM, Heskes T, Posthuma D. MAGMA: generalized gene-set analysis of GWAS data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015;11:e1004219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Watanabe K, Taskesen E, van Bochoven A, Posthuma D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:1826. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01261-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Subramanian A, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Liberzon A, et al. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:1739–1740. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wakefield J. A Bayesian measure of the probability of false discovery in genetic epidemiology studies. Am. J. Human Genet. 2007;81:208–227. doi: 10.1086/519024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Maller JB, et al. Bayesian refinement of association signals for 14 loci in 3 common diseases. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:1294–1301. doi: 10.1038/ng.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Howe KL, et al. Ensembl 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;49:D884–D891. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Carvalho-Silva D, et al. Open Targets Platform: new developments and updates two years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;47:D1056–D1065. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Petrovski S, et al. The intolerance of regulatory sequence to genetic variation predicts gene dosage sensitivity. PLoS Genet. 2015;11:e1005492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Rada-Iglesias A. Is H3K4me1 at enhancers correlative or causative? Nat. Genet. 2018;50:4–5. doi: 10.1038/s41588-017-0018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Heintzman ND, et al. Distinct and predictive chromatin signatures of transcriptional promoters and enhancers in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:311–318. doi: 10.1038/ng1966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Cahoy JD, et al. A transcriptome database for astrocytes, neurons, and oligodendrocytes: a new resource for understanding brain development and function. J. Neurosci. 2008;28:264. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4178-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.The GTEx Consortium. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science. 2015;348:648. doi: 10.1126/science.1262110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Finucane HK, et al. Heritability enrichment of specifically expressed genes identifies disease-relevant tissues and cell types. Nat. Genet. 2018;50:621–629. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0081-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Dunham I, et al. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature. 2012;489:57–74. doi: 10.1038/nature11247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Vermunt MW, et al. Epigenomic annotation of gene regulatory alterations during evolution of the primate brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2016;19:494–503. doi: 10.1038/nn.4229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Reilly SK, et al. Evolutionary genomics. Evolutionary changes in promoter and enhancer activity during human corticogenesis. Science. 2015;347:1155–1159. doi: 10.1126/science.1260943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Peyrégne S, Boyle MJ, Dannemann M, Prüfer K. Detecting ancient positive selection in humans using extended lineage sorting. Genome Res. 2017;27:1563–1572. doi: 10.1101/gr.219493.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Simonti CN, et al. The phenotypic legacy of admixture between modern humans and Neandertals. Science. 2016;351:737–741. doi: 10.1126/science.aad2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Vernot B, et al. Excavating Neandertal and Denisovan DNA from the genomes of Melanesian individuals. Science. 2016;352:235–239. doi: 10.1126/science.aad9416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Gazal S, et al. Linkage disequilibrium-dependent architecture of human complex traits shows action of negative selection. Nat. Genet. 2017;49:1421–1427. doi: 10.1038/ng.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bulik-Sullivan BK, et al. LD score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2015;47:291–295. doi: 10.1038/ng.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Bulik-Sullivan BK, et al. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat. Genet. 2015;47:1236–1241. doi: 10.1038/ng.3406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Zheng J, et al. LD Hub: a centralized database and web interface to perform LD score regression that maximizes the potential of summary level GWAS data for SNP heritability and genetic correlation analysis. Bioinformatics. 2016;33:272–279. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Grasby KL, et al. The genetic architecture of the human cerebral cortex. Science. 2020;367:eaay6690. doi: 10.1126/science.aay6690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Satizabal CL, et al. Genetic architecture of subcortical brain structures in 38,851 individuals. Nat. Genet. 2019;51:1624–1636. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0511-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Hibar DP, et al. Novel genetic loci associated with hippocampal volume. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:13624. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Adams HH, et al. Novel genetic loci underlying human intracranial volume identified through genome-wide association. Nat. Neurosci. 2016;19:1569–1582. doi: 10.1038/nn.4398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Smith SM, et al. An expanded set of genome-wide association studies of brain imaging phenotypes in UK Biobank. Nat. Neurosci. 2021;24:737–745. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00826-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Alfaro-Almagro F, et al. Image processing and Quality Control for the first 10,000 brain imaging datasets from UK Biobank. Neuroimage. 2018;166:400–424. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.10.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Forkel SJ, Catani M. The Oxford Handbook of Neurolinguistics: Diffusion Imaging Methods in Language Sciences. Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Price CJ. The anatomy of language: a review of 100 fMRI studies published in 2009. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010;1191:62–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Richardson FM, Price CJ. Structural MRI studies of language function in the undamaged brain. Brain Struct. Funct. 2009;213:511–523. doi: 10.1007/s00429-009-0211-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Perdue MV, Mednick J, Pugh KR, Landi N. Gray matter structure is associated with reading skill in typically developing young readers. Cereb. Cortex. 2020;30:5449–5459. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Roehrich-Gascon D, Small SL, Tremblay P. Structural correlates of spoken language abilities: a surface-based region-of interest morphometry study. Brain Lang. 2015;149:46–54. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2015.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Luciano M, et al. A genome-wide association study for reading and language abilities in two population cohorts. Genes Brain Behav. 2013;12:645–652. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Gialluisi A, et al. Genome-wide screening for DNA variants associated with reading and language traits. Genes Brain Behav. 2014;13:686–701. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Purcell S, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Human Genet. 2007;81:559–575. doi: 10.1086/519795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Euesden J, Lewis CM, O’Reilly PF. PRSice: polygenic risk score software. Bioinformatics. 2015;31:1466–1468. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Bates TC, et al. Behaviour genetic analyses of reading and spelling: a component processes approach. Aust. J. Psychol. 2004;56:115–126. doi: 10.1080/00049530410001734847. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Dollaghan C, Campbell TF. Nonword repetition and child language impairment. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1998;41:1136–1146. doi: 10.1044/jslhr.4105.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Gathercole SE, Willis CS, Baddeley AD, Emslie H. The Children’s Test of Nonword Repetition: a test of phonological working memory. Memory. 1994;2:103–127. doi: 10.1080/09658219408258940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. (Boston, MA, 2020).
- 99.Ayub Q, et al. FOXP2 Targets show evidence of positive selection in European populations. Am. J. Human Genet. 2013;92:696–706. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.03.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Poelmans G, Buitelaar JK, Pauls DL, Franke B. A theoretical molecular network for dyslexia: integrating available genetic findings. Mol. Psychiatry. 2011;16:365–382. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Guidi LG, et al. The neuronal migration hypothesis of dyslexia: a critical evaluation 30 years on. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018;48:3212–3233. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Note and Fig. 1.
Supplementary Tables 1–27.
Data Availability Statement
The full summary statistics for each dyslexia GWAS presented in this paper will be made available through 23andMe website (https://research.23andme.com/dataset-access/) to qualified researchers under an agreement with 23andMe that protects the privacy of the 23andMe participants. The top 10,000 associated SNPs from the main GWAS can be downloaded from 10.7488/ds/3465.