Abstract
Type A γ-aminobutyric acid receptors (GABAARs) represent a family of pentameric GABA-gated Cl-/HCO3- ion channels which mediate inhibitory transmission in the central nervous system. Cell surface expression of GABAARs, a prerequisite for their function, is dependent on the appropriate assembly of the receptor subunits and their transient interactions with molecular chaperones within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus. Here, we describe a highly conserved amino acid sequence within the extracellular N-terminal domain of the receptor subunits adjoining the first transmembrane domain as a region important for GABAAR processing within the ER. Modifications of this region in the α1, β3, and γ2 subunits using insertion or site-directed mutagenesis impaired GABAAR trafficking to the cell surface in heterologous cell systems although they had no effect on the subunit assembly. We found that mutated receptors accumulated in the ER where they were shown to associate with chaperones calnexin, BiP, and Grp94. However, their surface expression was increased when ER-associated degradation or proteosome function was inhibited, while modulation of ER calcium stores had little effect. When compared to the wt, mutated receptors showed decreased interaction with calnexin, similar binding to BiP, and increased association with Grp94. Structural modeling of calnexin interaction with the wt or mutated GABAAR revealed that disruption in structure caused by mutations in the conserved region adjoining the first transmembrane domain may impair calnexin binding. Thus, this previously uncharacterized region plays an important role in intracellular processing of GABAARs at least in part by stabilizing their interaction with calnexin.
Keywords: GABA receptor, intracellular trafficking, endoplasmic reticulum, homology modeling, N-linked glycosylation, molecular chaperone, mutagenesis, protein-protein interaction, calnexin
Abbreviations: AP, alkaline phosphatase; EerI, Eeyarestatin I; Endo H, endoglycosidase H; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ERAD, ER-associated protein degradation; GABAAR, γ-aminobutyric acid receptor; Grp94, glucose-regulated protein 94; HBSS, Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; LAMP1, Lysosomal-Associated Membrane Protein 1; N-ECD, N-terminal extracellular domain; PDI, Protein Disulfide Isomerase; PFA, paraformaldehyde; PNGase F, peptide-N-glycosidase F; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site; TM, transmembrane; VPM, verapamil
Type A γ-aminobutyric acid receptors (GABAAR) are members of a large family of Cys-loop receptors, pentameric ligand-gated ion channels that mediate fast synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. GABAARs are inhibitory GABA-gated Cl/HCO3 ion channels expressed by the vast majority of neurones in the adult brain to coordinate the activity and counterbalance the excess excitation. As such, they have a pivotal role in the normal brain function as well as in various neurological and psychiatric diseases (1, 2, 3, 4).
GABAARs are functionally and pharmacologically diverse heteropentameric assemblies of subunits which have multiple isoforms and are classified as follows: α(1–6), β(1–3), γ(1–3), δ, ε, π, and θ (5), with a common transmembrane topology comprising a large N-terminal extracellular domain (N-ECD), four transmembrane domains (TMs), a major intracellular domain between TMs 3 and 4, and a short C-terminal extracellular domain (6). However, the most common in the brain are GABAARs composed of two α1, two β2, and a γ2 subunit (5).
The β-subunits play a role in subcellular localization of GABAARs to axons, dendrites or soma, and insertion into the plasma membrane (7, 8), while the presence of the γ2 or δ subunit determines their targeting to inhibitory synapses or extrasynaptic locations, respectively (3). Different isoforms of the α subunits however appear to be expressed more selectively at specific types of inhibitory synapses (9, 10, 11).
In order to reach the neuronal cell surface, which is a prerequisite for their function, GABAARs undergo a complex process of assembly from the newly synthesized subunits and posttranslational processing in the endoplasmic reticulum (12, 13). This includes precise coordination of protein–protein interactions between GABAARs and numerous resident proteins, including molecular chaperones which control for the correct folding, glycosylation, maturation and forward trafficking, as well as degradation of misfolded receptors. Our understanding of these processes has been drawn largely from the studies of GABAARs mutations associated with epileptic disorders, many of which impair the ER processing leading to reduced cell surface levels of fully functional receptors (14). At the subunit level, these mutations are grouped within the N-ECD and TMs (15), indicating that these domains are critical for GABAAR interactions with ER chaperones, including the BiP-quality control mechanism as well as the proteins operating within the glycosylation-dependent calnexin/calreticulin cycle. BiP (Grp78) is the most abundant member of the ER-resident heat shock chaperones that interacts with the hydrophobic parts of proteins, including some of the mutants of GABAARs (16), which become exposed due to irregular folding. BiP, assisted by several cofactors, can prevent aggregation of misfolded proteins and facilitate their folding, but, if unsuccessful, it can also initiate the unfolded protein response and ER-associated protein degradation (ERAD) (17). The newly synthesized and Asparagine N-glycosylated GABAARs are also subjected to calnexin/calreticulin binding cycle in the ER as the main quality control step. The glycosylation state changes from tri- to monoglucosylated glycans before GABAARs are processed by calnexin/calreticulin and other ER chaperones until correctly folded and trafficked to the Golgi, where they acquire the final glycosylation state with seven N-linked glycans in N-ECDs of the α1(murine N137/human N138), β3 (N105, N174), and γ2 subunits (murine N246/human N247) of the GABAAR heteropentamer (6, 18).
A number of epilepsy-linked mutations in GABAAR subunits have been shown to reduce their entry into this cycle (14, 19) and instead cause their targeting to ERAD pathway, where misfolded receptors interact with the glucose-regulated protein 94 (Grp94), an ER-specific Hsp90, and osteosarcoma amplified 9 protein to be subsequently ubiquitinated by Hrd1, translocated to the cytosol, and degraded by proteosome (20). However, several pharmacological chaperones have recently been shown to facilitate forward trafficking of GABAAR mutants likely by stabilizing the natively folded receptors allowing them to be transported from the ER to Golgi (16, 21, 22, 23, 24). The entry into the calnexin/calreticulin cycle thus represents a critical step for the forward trafficking of GABAARs yet how these interactions are regulated in addition to N-linked oligosaccharide recognition remains unknown. In this study, we have uncovered a highly conserved region in the N-terminal extracellular domains of GABAAR subunits close to the TM1 region which plays a role in positioning of the calnexin lectin domain close to the N-linked oligosaccharide group, thus facilitating the binding of calnexin to GABAARs.
Results
A conserved region in the N-ECD of GABAAR subunits adjacent to TM1 is important for cell surface expression
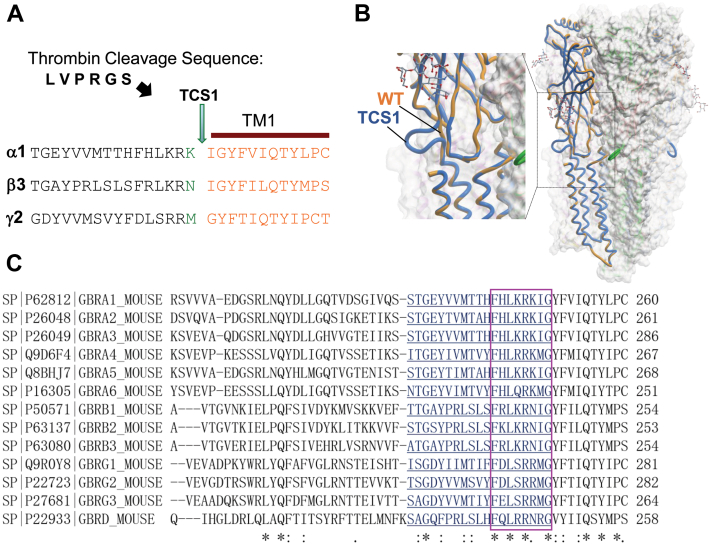
The N-ECDs of GABAARs are highly conserved, structurally complex, and essential for GABA-dependent activation, as well as allosteric modulation of these receptors by various clinically important compounds such as benzodiazepines (6). They also participate in the formation of GABAergic synapses by facilitating synaptic adhesion (25). The aim of our study was to develop an approach which would allow purification of the heteropentameric N-ECDs of GABAARs from the fully assembled and posttranslationally modified receptor pools expressed at the surface of heterologous cells in culture. To achieve this, we used extension overlap mutagenesis to insert a canonical cleavage site for the protease thrombin (LVPRGS) at the end of the N-ECDs of GABAAR α1, β3, and γ2 subunits at the position K248/I249, N242/I243, and M271/G272, respectively (Fig. 1A), taking into consideration the TM1 starting residue for each subunit as shown previously (26). Mutated GABAAR subunits were thus termed Thrombin Cleavage Site (TCS) 1 mutants. This region was selected because it retains a loose structure (Fig. 1B; (18)) with no specific function or interaction reported so far. Importantly, this region faces the outer surface of the receptor pentamer (Fig. 1B), which suggests that it would be easily accessible for thrombin cleavage. This region, however, contains several highly conserved amino acid residues in all main GABAAR subunits (Fig. 1C).
Figure 1.
Structural analysis of the conserved region in the N-terminal extracellular domain of GABAAR subunits adjacent to the TM1. A, insertion site for the thrombin cleavage sequence (LVPRGS; TCS1) in the α1, β3, and γ2 subunits. B, structural modeling of the TCS1-GABAAR α1/β3(blue)/γ2 heteropentamer superimposed on the wt-GABAAR α1/β3(orange)/heteropentamer, which illustrates that inserted TCS sequence forms a loop at the outer surface of the complex which is exposed to the external environment and accessible to thrombin cleavage. C, sequence alignment of the region adjacent to the TM1 of the main GABAAR subunits (∗ fully conserved residue: residue with strongly similar properties-scoring > 0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix. Residue with weakly similar properties-scoring = < 0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix). GABAAR, γ-aminobutyric acid receptor; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site; TM, transmembrane domain.
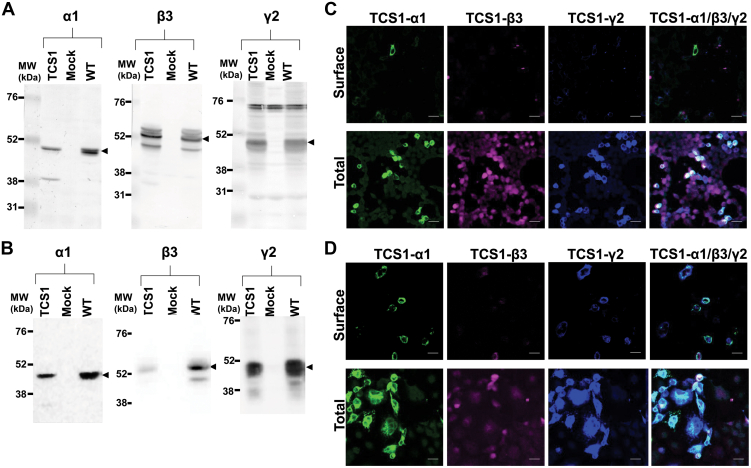
Following transient transfection of TCS1-α1, -β3, and -γ2 mutants into HEK293 cells (Fig. 2, A and C) or COS-7 cells (Fig. 2, B and D), immunoblotting analysis of protein lysates confirmed their expression at the MW similar to that of the wt subunits (Fig. 2, A and B). Further analysis of these mutants using immunocytochemistry with antibodies specific for the extracellular epitopes of the receptor subunits demonstrated that mutated subunits were not expressed at the surface of either HEK293 or COS7 cells, although they were abundantly expressed intracellularly in both cell types (Fig. 2, C and D). Although unexpected, these results indicated that insertion mutagenesis in this region impairs cell surface trafficking of GABAARs, guiding us to further explore the underlying mechanism and its functional implications.
Figure 2.
TCS1-GABAARs expressed in heterologous cell lines fail to reach the cell surface. Expression of cotransfected TCS1-α1, TCS1-β3, and TCS1-γ2 subunits in (A) HEK293 cells and (B) COS7 cell, as detected by immunoblotting of total protein lysates (100 μg/lane) with the subunit-specific antibodies, followed by alkaline phosphatase–conjugated secondary antibodies. Arrowheads point to the immunoreactive bands of the expected MW (n = 3 independent biological replicates). Low level of cell surface expression of cotransfected TCS1-α1 (green), TCS1-β3 (purple), and TCS1-γ2 (blue) subunits in (C) HEK293 cells and (D) COS7 cell, as detected by fluorescent immunolabelling with the subunit-specific primary antibodies, followed by host species-specific secondary antibodies conjugated with Alexa488, Alexa555, and Alexa647, respectively. High levels of expressed subunits were detected intracellularly (total) when plasma membrane was permeabilized before the addition of the primary antibodies. Representative images of n = 3 independent biological replicates. The scale bar represents 25 μm. TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site mutant.
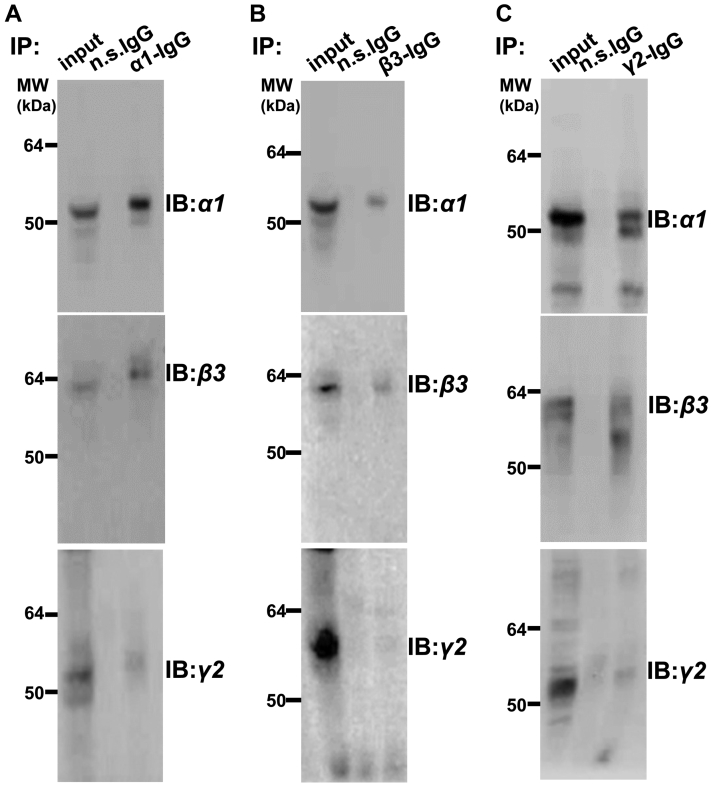
Given that efficient targeting of the newly synthesized GABAAR subunits to the cell surface is dependent on their correct assembly (7), we first tested if TCS1 mutant subunits are assembled with each other in the ER. In these experiments, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with TCS1-α1, -β3, and -γ2 subunit cDNA and their lysates were incubated with either α1-, β3-, or γ2-specific antibodies, followed by analysis of coimmunoprecipitated complexes using SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with specific antibodies. The results show that in their respective precipitated complexes, TCS1-α1 (Fig. 3A), TCS1-β3 (Fig. 3B), or TCS1-γ2 (Fig. 3C) were accompanied by the other two remaining subunits, indicating that the assembly of mutated subunits into heteropentameric receptors in the ER was not impaired. Thus, TCS mutants were able to form receptor complexes in the ER, but their targeting to the cell surface was inhibited.
Figure 3.
TCS1-α1, -β3, and -γ2 subunits coassemble when expressed in HEK293 cells.A and B, TCS1-α1, myc tagged TCS1-β3, and TCS1-γ2 subunits, or C, TCS1-α1, TCS1-β3, and myc tagged TCS1-γ2 subunits were transfected into HEK293 cells, and 24 h later, coimmunoprecipitation was carried out using (A) α1-C-terminal-specific antibody, or (B and C) myc antibody, followed by immunoblotting with the α1-, β3-, or γ2-specific primary antibodies and HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies. In all three cases, the immunoprecipitated subunit was detected in association with the other two subunits indicating that three subunits coassemble. Input contained 10% of the lysate used for immunoprecipitation. The representative examples of n = 2 independent biological replicates. HRP, horseradish peroxidase; n.s. IgG, non-specific IgG control; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site mutant.
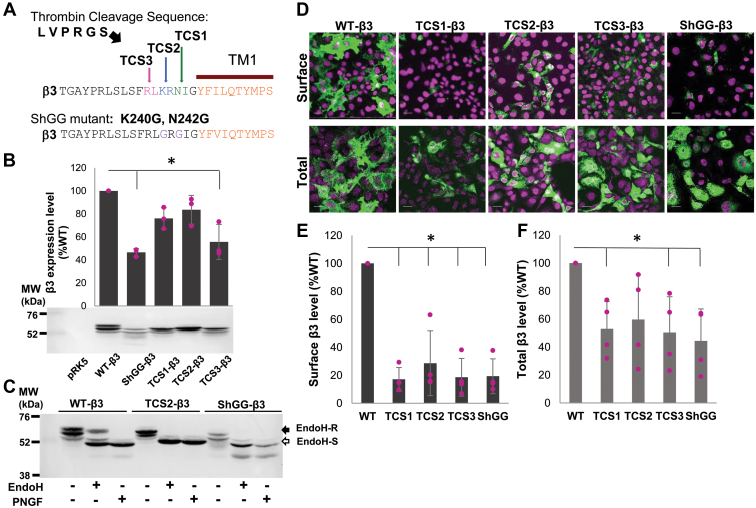
To test if altering the site of insertion could impact on processing of the mutated receptors and increase their cell surface expression, we have introduced thrombin sequence at the position (K240/R241) in TCS2 and (R238/L239) in TCS3 mutants of the β3 subunit (Fig. 4A). We have also altered the existing sequence in this region of the β3 subunit using site-directed mutagenesis to replace K with G at position 240 and N with G at position 242 to mimic the minimum consensus sequence for thrombin cleavage (Gly-Arg-Gly-X; (27)) in the mutant termed ShGG-β3 (Fig. 4A).
Figure 4.
TCS2, TCS3, and ShGG mutants of the β3 subunit are expressed intracellularly in COS7 cells but show low level of expression at the cell surface.A, TCS2- and TCS3-β3 mutants incorporate the thrombin cleavage sequence between K240/R241 and R238/L239, respectively. ShGG-β3 mutant contains an engineered minimum thrombin cleavage sequence with K240G and N242G point mutations generated by site-directed mutagenesis. B, expression of myc-tagged wt, ShGG, and TCS (1–3) mutants of the β3 subunit in COS7 cells analyzed by immunoblotting using a myc tag-specific primary antibody, followed by alkaline phosphatase–conjugated secondary antibody and quantification using ImageJ. Bar graph represents expression of individual mutants as % of the wt β3 set as 100%, with ShGG and TCS3 mutants showing statistically significant decrease in expression as indicated by a star (mean ± SD; n = 3 independent biological replicates; p = 0.00088, p = 0.0028, respectively; One-Way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test). C, detection by immunoblotting of Endo H–resistant (Endo H-R, post ER glycoforms that traffic to the Golgi compartment) and Endo H–sensitive (Endo H-S, glycoforms retained in the ER) pools of the wt-, TCS2-, and ShGG-β3 subunits in lysates of COS7 cells. The peptide-N-glycosidase F (PNGase F) enzyme selectively removes all the N-linked glycans from proteins and serves as control for unglycosylated β3 subunit (n = 3 independent biological replicates). D, high level of surface expression of the wt β3 subunit in contrast to a very low level of surface expression of TCS (1–3) and ShGG mutants of the β3 subunit in COS7 cells, analyzed by immunocytochemistry using myc primary antibody, followed by Alexa488-conjugated secondary antibody. The nuclei were labeled with To-Pro (purple). High levels of all expressed β3 subunits were detected intracellularly (total) when plasma membrane was permeabilized before the addition of the primary antibody (n = 3 independent biological replicates); the scale bar represents 25 μm. E, quantitative analysis of surface expression of the wt versus TCS (1–3) and ShGG mutants of the β3 subunit in COS7 cells using ELISA with a myc tag-specific primary antibody, followed by HRP-conjugated secondary antibody. Expression of mutants is shown as % expression of the wt β3 subunit set as 100% (mean ± SD). Cell surface expression level of each mutant is significantly lower than the cell surface expression level of the wt-β3 subunit as indicated by star (TCS1: p = 0.01; TCS2: p = 0.019; TCS3: p = 0.01; ShGG: p = 0.01; One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test; n = 4 independent biological replicates). F, quantitative analysis of total expression of the wt versus TCS (1–3) and ShGG mutants of the β3 subunit in COS7 cells using ELISA with a myc-tag specific primary antibody, followed by HRP-conjugated secondary antibody. Expression of mutants is shown as % expression of the wt β3 subunit set as 100% (mean ± SD). Only total expression level of TCS2 was not significantly lower than the total expression of the wt β3 subunit while other mutants were significantly lower in their expression as indicated by star (TCS1: p = 0.019; TCS3: p = 0.022; ShGG: p = 0.005; One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test; n = 4 independent biological replicates). ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site mutant.
The new mutants of the β3 subunit were expressed in COS7 cells and detected at the MW similar to that of the wt-β3 subunit in immunoblotting experiments (Fig. 4B). However, quantification of their expression revealed that ShGG and TCS3 were expressed at significantly lower levels of 46.6 ± 3.3 % and 55.7 ± 15.1 % of the wt-β3 expression, respectively (mean ± SD; n = 3 independent biological replicates; p < 0.05; One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test; Fig. 4B and Table S1). The expression levels of TCS1 and TCS2 were similar to the wt-β3 subunit with 76.1 ± 9.2 % and 83.6 ± 12.5 % of the wt-β3 expression, respectively (mean ± SD; n = 3 independent biological replicates; Fig. 4B and Table S1). To assess the intracellular processing of these mutants, we incubated cell lysates with endoglycosidase H (Endo H) or peptide-N-glycosidase F enzymes, followed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting to detect various glycosylated forms. The two enzymes have different specificity, such that Endo H selectively cleaves after asparaginyl-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in the N-linked glycans while PNGase selectively cleaves between the innermost N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and asparagine residue in N-linked glycoproteins yielding the unglycosylated forms. After Endo H digestion, proteins running at a molecular weight similar to the unglycosylated (PGNase processed) forms represent the Endo H–sensitive protein pools, while the higher molecular weight forms represent glycosylated pools resistant to Endo H which have been processed in the Golgi after leaving the ER. While the wt-β3 subunit contained both Endo H–sensitive and Endo H–resistant forms, with Endo H–sensitive form showing 27.1 ± 1.4 % (mean ± SD; n = 3 independent biological replicates) of total β3 immunoreactivity, TCS2-β3 and ShGG-β3 mutants only contained the Endo H–sensitive forms (Fig. 4C; Endo H-S and Endo H-R), suggesting that their exit from the ER was impaired.
When transfected into COS7 cells, these mutants showed limited expression at the cell surface in comparison with the wt-β3 subunit, which was successfully targeted to the cell surface as shown previously (Fig. 4D, surface; (8, 28)), However, they were expressed intracellularly in abundance (Fig. 4D, total).
The surface expression of TCS1-, TCS2-, TCS3-, and ShGG-β3 mutants was quantitatively assessed and compared to that of the wt-β3 subunit using cell surface ELISA (29). As shown in the Figure 4E, these mutants showed a low level of cell surface expression, with TCS1 showing 17.1 ± 8.5 %, TCS2 28.6 ± 23.1 %, TCS3 18.6 ± 13.5 %, and ShGG 19.3 ± 12.4 % of the wt-β3 surface expression (mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Table S2), although they were detected intracellularly in abundance, with TCS1 showing 53.1 ± 19.5%, TCS2 59.7 ± 31.9 %, TCS3 50.4 ± 25.6 %, and ShGG 44.3 ± 22.9 % of the wt-β3 expression (mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Fig. 4F and Table S2). The low level of surface expression of TCS and ShGG mutants was deemed insufficient for attempting to proceed with the thrombin cleavage and purification of N-terminal domains, as originally planned.
Thus, modifications of the highly conserved region at the end of the extracellular N-ECD of GABAAR α1, β3, and γ2 subunits do not appear to impair their assembly but, nevertheless, result in significant reduction in cell surface expression of these receptors. These findings suggest that this region may be important for various molecular interactions in the ER that facilitate forward trafficking of GABAAR to the cell surface.
TCS and ShGG mutants accumulate in the ER
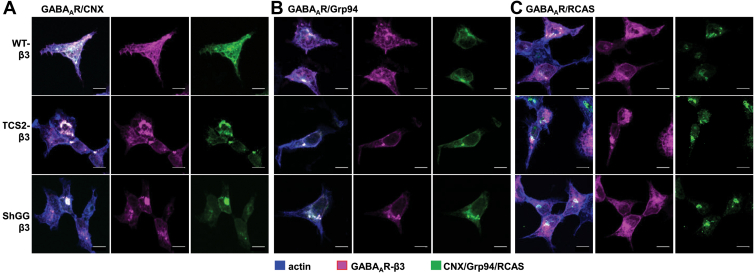
To characterize further the intracellular localization of TCS2-β3 and ShGG-β3 mutants, we have carried out immunocytochemical analysis using a β3-specific antibody in combination with antibodies specific for calnexin or Grp94, as ER markers, or Receptor-binding Cancer Antigen expressed on SiSo cells (RCAS1), as a Golgi marker (Fig. 5). The wt-β3 subunit, expressed in control samples, showed expression at the cell surface, as well as intracellularly in the ER and Golgi, where it was partially colocalized with calnexin (Fig. 5A; upper panel), Grp94 (Fig. 5B; upper panel), and RCAS1 (Fig. 5C, upper panel). In contrast, labeled TCS2-β3 and ShGG-β3 were predominantly detected intracellularly in the ER showing a high degree of colocalization with calnexin and Grp94 (Fig. 5, A and B, middle and lower panels) and less colocalization with the Golgi marker RCAS1 (Fig. 5C, middle and lower panels) and, as expected, low level, if any, at the cell surface (Fig. 5, A–C, middle and lower panels). The intracellular localization of TCS mutants was further characterized by subcellular fractionation using discontinuous sucrose gradients and immunoblotting (Fig. S1). GABAARs composed of the wt-α1/β3/γ2 subunits were predominantly detected in the membrane Fraction 3 collected at the interface between 500 mM and 1 M sucrose in lysates of cultured cortical neurones and HEK293 cells (Fig. S1, A and B) where Grp94, calnexin, Protein Disulfide Isomerase (PDI), RCAS1, and Lysosomal-Associated Membrane Protein 1 (LAMP1) were also detected in abundance, indicating that this fraction is enriched in ER and Golgi membranes. In contrast, GABAARs composed of TCS2-α1/β3/γ2 subunits were predominantly detected in the membrane Fraction 4 collected at the interface between 1 M and 1.3 M sucrose, in which Grp94, calnexin, PDI, and LAMP1 could also be detected, but not RCAS1 (Fig. S1C). Collectively, these experiments demonstrate that TCS mutants of GABAARs accumulate in the ER.
Figure 5.
TCS2 and ShGG mutants of the β3 subunit accumulate in the ER and colocalize with calnexin and Grp94.A–C, fluorescent immunolabelling of the wt (upper panels), TCS2 (middle panels), and ShGG (lower panels) β3 subunit (myc-tagged; purple) and calnexin (CNX; green) in (A), Grp94 (green) in (B), or RCAS (green) in (C), and actin (blue) in HEK293 cells. Representative images of n = 3 independent biological replicates. The scale bar represents 10 μm. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site mutant.
Pharmacological modulation of ER function has little effect on cell surface expression of TCS2 mutants
Cell surface expression of newly formed GABAARs is a tightly controlled process which can be upregulated in several ways, including modulation of ER function (21), inhibition of receptor degradation by the proteosome (30), or GABA-mediated chaperoning (31). To test if regulation of any of these processes using well-established pharmacological approaches could increase targeting of TCS mutants to the cell surface, we have carried out cell surface ELISA with COS7 cells transiently expressing the wt or TCS2 mutants of the α1/β3-Myc/γ2 GABAAR subunits.
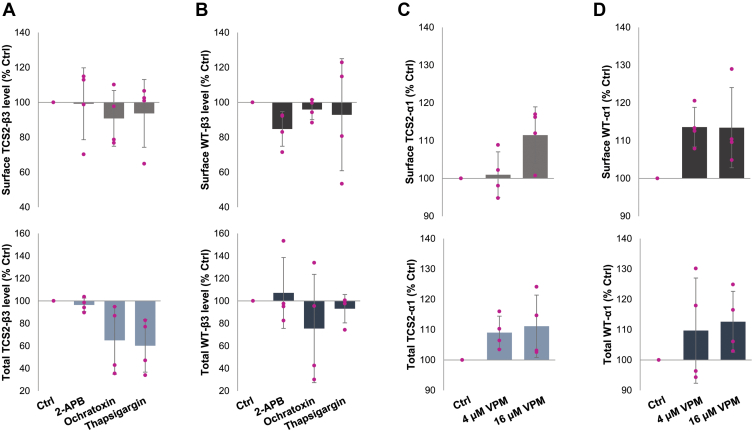
Following transfection, cells were incubated with 2-APB (100 μM), an IP3-receptor antagonist, Ochratoxin A (10 μM), a SERCA ATPase stimulator, or Thapsigargin (10 μM), a SERCA ATPase inhibitor, for 4 h, fixed and subjected to cell surface ELISA using a Myc tag-specific antibody. These treatments caused no significant change in cell surface levels of TCS2 mutant in comparison with the control DMSO treatment (2-APB: 99.2 ± 20.6 %, Ochratoxin A: 90.9 ± 16.0 %, Thapsigargin: 93.7 ± 19.3 % of control DMSO; all mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Figure 6A, upper graph; Table S3). These treatments also had no significant effect on cell surface expression of the wt-GABAARs (2APB: 84.8 ± 9.9 %; Ochratoxin A: 95.9 ± 5.9 %, Thapsigargin: 92.9 ± 32.1 % control DMSO; all mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Figure 6B, upper graph; Table S3). Total levels of expression of TCS2-mutant showed no change with 2-APB (96.5 ± 6.1 %; mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Figure 6A, lower graph; Table S3) but a significant decrease with Ochratoxin and Thapsigargin (Ochratoxin: 65.1 ± 30.1 %; Thapsigargin: 60.2 ± 23.5 % control DMSO; both mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; p < 0.05; One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey test; Figure 6A, lower graph; Table S3). Total levels of expression of the wt GABAAR were unchanged following these treatments (2-APB: 107.1 ± 31.5 %, Ochratoxin: 75.5 ± 48.2 %, Thapsigargin: 93.1 ± 12.6 % control DMSO; all mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Figure 6B, lower graph; Table S3). Furthermore, we have tested the effects of prolonged 24-h incubation with GABA (100 μM) on cell surface expression of TCS2 or wt GABAARs. Surface levels were also quantified using cell surface ELISA showing that surface expression of TCS2 mutant or wt GABAAR remained unchanged (TCS2: 90.7 ± 10.3 % control; wt:107.1 ± 8.6 % control DMSO; mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Fig. S2, A and B; upper graphs; Table S7). Total expression was also unchanged, with TCS2 mutants showing 82.6 ± 13.6 % control and wt receptor showing 104.7 ± 15.9 % control (mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Fig. S2, A and B, lower graphs; Table S7).
Figure 6.
Cell surface expression of TCS2 mutant or the wt GABAARs cannot be increased by pharmacological modulation of ER function.A and B, COS-7 cells were transfected with (A), TCS2-α1/myc-β3/γ2 cDNAs or (B), wt-α1/myc-β3/γ2 for 24 h, treated with DMSO (Ctrl), 100 μM 2-APB, 10 μM Ochratoxin, or 10 μM Thapsigargin for 2 h, washed and fixed using PFA/sucrose buffer. Surface (upper graphs) and total (lower graphs) levels of GABAA receptors were measured by ELISA using a myc tag-specific antibody followed by HRP-conjugated secondary antibody. Expression level of receptors is shown as % expression of the DMSO control set as 100% (mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates, with individual data points shown as pink dots). Total expression levels of TCS2 mutants were significantly decreased following the treatments with Ochratoxin (p = 0.003) and Thapsigargin (p = 0.0007), One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey Test. C and D, COS-7 cells were transfected with (C), TCS2 myc-α1/β3/γ2 cDNAs or (D), wt myc-α1/β3/γ2 for 24 h, treated with DMSO (Ctrl), 4 μM, and 16 μM Verapamil (VPM) for 24 h, washed and fixed using PFA/sucrose buffer. Surface (upper graphs) and total (lower graphs) levels of GABAA receptors were measured by ELISA as above. Expression level of receptors is shown as % expression of the DMSO control set as 100% (mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; individual data points shown as pink dots). ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; PFA, paraformaldehyde; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site mutant.
In a separate set of experiments, we have assessed whether 24-h treatments with Verapamil (VPM; 4 μM and 16 μM), a L-type Ca2+ blocker which leads to a decrease in ER Ca2+ efflux and depletion (32) can regulate targeting to the cell surface using cell surface ELISA with COS7 cells transiently expressing the wt or TCS2 mutants of α1-Myc/β3/γ2 GABAAR subunits. However, cell surface levels of TCS2 mutant as well as the wt GABAARs remained unchanged following these treatments (TCS2 at 4 μM: 100.9 ± 6.1 %, TCS2 at 16 μM: 111.5 ± 7.5 %, WT at 4 μM: 113.6 ± 5.2 %, WT at 16 μM: 113.4 ± 10.6 % control DMSO; all mean ± SD: n = 4 independent biological replicates; Figure 6, C and D, upper graph; Table S4). No significant change was detected in total levels of expression of either TCS2 mutant (at 4 μM: 109.1 ± 5.4 %, at 16 μM: 111.1 ± 10.3 % control DMSO; mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Figure 6C, lower graph; Table S4) or wt-GABAAR (at 4 μM: 109.7 ± 17.3 %, at 16 μM: 112.6 ± 10.1 % control DMSO; mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; Figure 6D, lower graph; Table S4). Thus, inhibition or stimulation of ER-dependent intracellular Ca2+ release, or pharmacological chaperoning mediated by GABA, have no effect on processing or forward trafficking of TCS mutants once they are synthesized and assembled in the ER.
Inhibition of proteolysis increases cell surface and total expression of TCS2- and wt-GABAARs
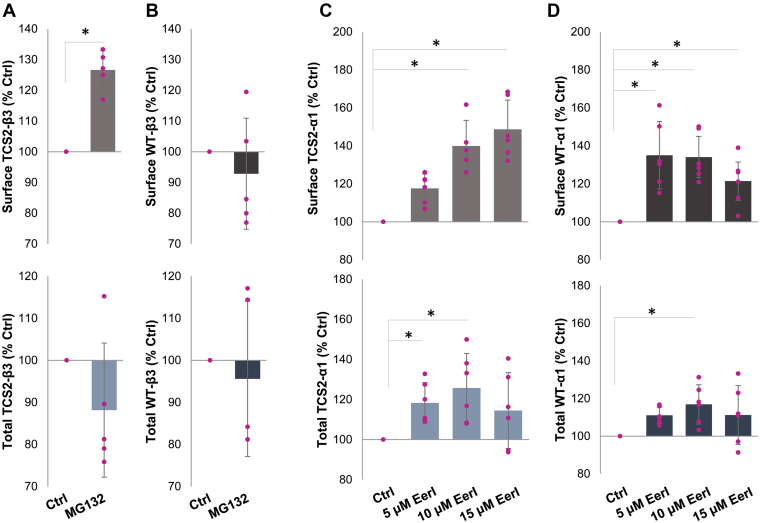
We have also tested the effects of MG-132 (10 μM), a proteosome inhibitor, on cell surface expression of TCS2- and wt-GABAARs in COS7 cells transiently expressing the α1/β3-Myc/γ2 subunits. Surface levels of TCS2 mutant were increased after 5-h incubation with MG-132 (126.6 ± 6.3 % of control DMSO; mean ± SD; n = 5 independent biological replicates; p < 0.05, t test; Figure 7A, upper graph; Table S5), while surface expression of the wt receptor remained unchanged (92.8 ± 18.1 % control DMSO; mean ± SD; n = 5 independent biological replicates; Figure 7B, upper graph; Table S5). The total expression level remained unchanged with the MG-132 treatments for TCS2 mutant (88.2 ± 15.9 % control DMSO; mean ± SD; n = 5 independent biological replicates; Figure. 7A, lower graph; Table S5) and wt receptor (95.6 ± 18.5 % control DMSO; mean ± SD; n = 5 independent biological replicates; Figure. 7B, lower graph; Table S5).
Figure 7.
Cell surface expression of TCS2 mutant and wt GABAARs can be increased by inhibition of ERAD.A and B, COS-7 cells were transfected with (A), TCS2-α1/myc-β3/γ2 cDNAs or (B), wt-α1/myc-β3/γ2 for 24 h, treated with DMSO (Ctrl) or 10 μM MG-132 for 5 h, washed and fixed using PFA/sucrose buffer. Surface (upper graphs) and total (lower graphs) levels of GABAA receptors were measured by ELISA using a myc tag-specific antibody followed by HRP-conjugated secondary antibody. Expression level of receptors is shown as % expression of the DMSO control set as 100% (mean ± SD; n = 5 independent biological replicates; with individual data points shown as pink dots). A statistically significant increase in TCS2 surface expression was indicated by star (p = 0.04; t test). C and D, COS-7 cells were transfected with (C), TCS2 myc-α1/β3/γ2 cDNAs or (D), wt myc-α1/β3/γ2 for 24 h, treated with DMSO (Ctrl) or 5, 10, or 15 μM Eerl for 6 h, washed and fixed using PFA/sucrose buffer. Surface (upper graphs) and total (lower graphs) levels of GABAA receptors were measured by ELISA as above. Expression level of receptors is shown as % expression of the DMSO control set as 100% (mean ± SD; n = 6 independent biological replicates; individual data points shown as pink dots). A statistically significant increase in surface and total expression of TCS2 (5 μM: p = 0.056; 10 μM: 0.00002; 15 μM: p = 0.00002) and wt (5 μM: p = 0.00001; 10 μM: 0.00002; 15 μM: p = 0.026; One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test) receptors is indicated by a start. EerI, Eeyarestatin I; ERAD, ER-associated protein degradation; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; PFA, paraformaldehyde; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site mutant.
In a separate set of experiments, we have assessed whether treatments with increasing concentration of Eeyarestatin I (Eerl; 5, 10, and 15 μM), a potent inhibitor of ERAD, can increase targeting of TCS2- or wt-GABAARs to the cells surface of COS7 cells transiently expressing α1-myc/β3/γ2 subunits. Eerl at 10 μM and 15 μM significantly increased the cell surface expression of TCS2 mutant (139.9 ± 13.5 % control DMSO and 148.7 ± 15.4 % control DMSO, respectively; n = 6 independent biological replicates; p < 0.05 One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test; Figure 7C, upper graph; Table S6). The cell surface expression of the wt GABAARs was increased by all three concentrations tested (5 μM: 135 ± 17.5 %, 10 μM: 134.1 ± 12.5 %, 15 μM: 121.4 ± 12.5 % control DMSO; all mean ± SD; n = 6 independent biological replicates; p < 0.05 One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test; Figure 7D, upper graph; Table S6). Total expression of TCS2 mutant was significantly increased by 5 μM and 10 μM Eerl (118.3 ± 10.1 %, 125.7 ± 17.2 % control DMSO, respectively; mean ± SD; n = 6 independent biological replicates; p < 0.05 One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test; Figure 7C, lower graph; Table S6). Total expression of the wt GABAARs was significantly increased by 10 μM Eerl (116.9 ± 10.4 % control DMSO; mean ± SD; n = 6 independent biological replicates; p < 0.05 One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test; Figure 7D, lower graph; Table S6). These data indicate that inhibition of ERAD or proteosome leads to increased levels of cell surface and total expression of TCS2- and wt-GABAARs.
Forward trafficking of TCS mutants is impaired due to reduced interaction with calnexin
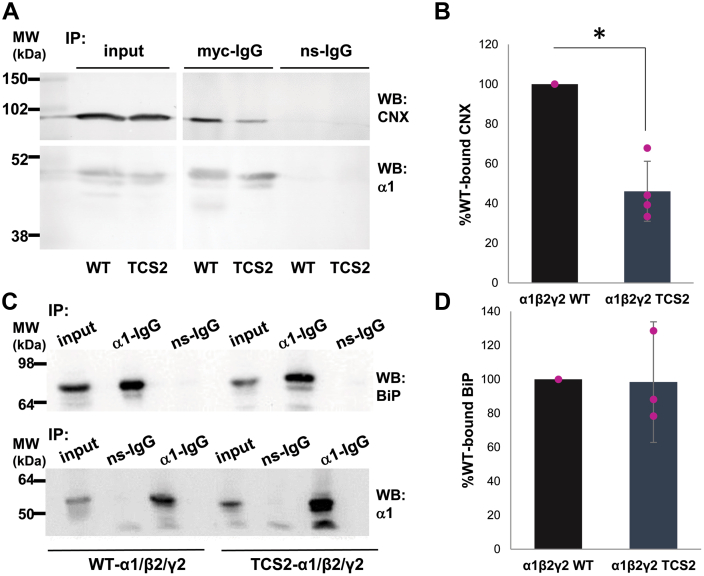
Forward trafficking of GABAARs from ER to Golgi is dependent on their complex protein–protein interactions with the ER chaperons, calnexin, BiP, or Grp94. To test which of these interactions may be critical for trafficking of TCS mutants, we have carried out coimmunoprecipitation experiments from lysates of HEK293 cells transiently transfected with either wt-α1/β3/γ2-GABAAR subunits or TCS2-α1/β3/γ2 subunit mutants. Precipitated GABAAR complexes were subjected to SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies specific for calnexin, BiP, or Grp94. We have observed a statistically significant reduction in the amount of calnexin coimmunoprecipitated with TCS2 mutants to 46.1 ± 15.1 % of the amount detected in association with the wt-GABAARs (mean ± SD; n = 4 independent biological replicates; p < 0.05, t test; Figure 8, A, upper panel, and B; Table S9). In contrast, there was no difference in the amount of BiP coimmunoprecipitated with TCS2 mutants when compared to the wt-GABAARs (98.4 ± 35.5 %; mean ± SD; n = 3 independent biological replicates; Figure 8, C, upper panels, and D; Table S9). In control blots, the amount of precipitated GABAARs was similar in both conditions (Fig. 8, A and C, lower panels).
Figure 8.
TCS2 insertion causes a reduction in GABAAR binding to calnexin while their interaction with BiP remains unaffected.A, HEK293 cells were transfected with myc-tagged wt-α1/β2/γ2 or myc-tagged TCS2-α1/β2/γ2 cDNAs for 24 h, lysed, and incubated with a myc-tag specific antibody (two replicates) or α1-C-terminal–specific antibody (two replicates) to immunoprecipitate GABAAR complexes. Proteins were resolved using SDS/PAGE and the presence of calnexin (CNX; upper panel) was detected by immunoblotting with a specific primary antibody followed by an alkaline phosphatase– (two independent biological replicates) or HRP-conjugated (two independent biological replicates) secondary antibody. In control blots (lower panel), the presence of α1 subunit was confirmed using the myc-specific antibody (two independent biological replicates) or α1-N-terminal–specific antibody (two independent biological replicates). B, quantification using ImageJ revealed a significant decrease in CNX binding to TCS2 expressed in all four replicates. The graph shows binding of CNX to TCS2 expressed as % binding to the wt receptor set as 100% (p = 0.022; t test). C, HEK293 cells were transfected with myc-tagged wt-α1/β2/γ2 or myc-tagged TCS2-α1/β2/γ2 cDNAs for 24 h, lysed and incubated with an α1-C-terminal–specific antibody to immunoprecipitate GABAAR complexes. Proteins were resolved using SDS/PAGE and the presence of BiP (upper panel) was detected by immunoblotting with a specific primary antibody followed by an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody. In control blots (lower panel), the presence of α1 subunit was confirmed using the α1-N-terminal–specific antibody. D, quantification using ImageJ of BiP binding to TCS2 expressed as % binding to the wt receptor set as 100% (p = 0.68; t test; n = 3 independent biological replicates). GABAAR, γ-aminobutyric acid receptor; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site mutant.
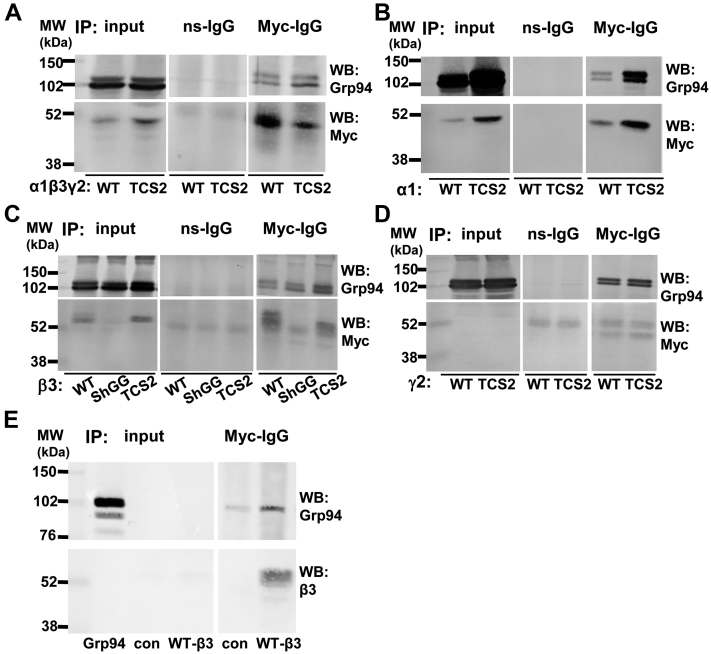
Interestingly, we have detected an apparent increase in binding of TCS2-α1/β3/γ2 receptors to Grp94 when compared to the wt-α1/β3/γ2-GABAARs in the presence of MG-132 (Fig. 9A, upper panel). An increase in association with Grp94 was also detected when TCS2-α1, -β3, or -γ2 subunit was expressed alone, as well as when ShGG-β3 subunit was expressed, and compared to the wt subunit (Fig. 9, B–D, upper panels). This likely represents a direct association between GABAAR subunits and Grp94, given that Grp94, when translated in vitro, was also able to bind to GABAAR β3 subunit (Fig. 9E, upper panel). The amount of precipitated GABAARs was detected in control blots (Fig. 9, A–E, lower panels). However, pharmacological inhibition of Grp94 by PU-WS13 (10 μM; (33)) had little effect on surface or total expression level of either the wt-GABAARs or TCS2-GABAARs (Fig. S3 and Table S8).
Figure 9.
TCS2-GABAARs, individual TCS2-mutants of α1, β3, and γ2 or ShGG mutant of β3 subunit all show increased binding to Grp94.A, HEK293 cells were transfected with the myc-tagged wt-α1/β3/γ2 or myc-tagged TCS2-α1/β3/γ2 cDNAs and HA-tagged Grp94 cDNA for 24 h. DSP cross-linking was applied before cell lysis. A myc tag-specific antibody was used to immunoprecipitate GABAAR complexes which were resolved by SDS/PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with an HA tag-specific antibody to detect Grp94 (upper panel). The presence of GABAARs was confirmed by immunoblotting with a myc tag-specific antibody (lower panel; n = 2 independent biological replicates). B, coimmunoprecipitation of the wt-α1 and TCS2-α1 subunit with Grp94 (n = 2 independent biological replicates). C, coimmunoprecipitation of the wt-β3, ShGG-β3, and TCS2-β3 subunit with Grp94 (n = 2 independent biological replicates). D, coimmunoprecipitation of wt-γ2 and TCS2-γ2 subunit with Grp94 (n = 2 independent biological replicates). E, direct binding of the in vitro translated Grp94 to the wt-β3 subunit immunoprecipitated from HEK293 cell lysates (n = 2 independent biological replicates). GABAAR, γ-aminobutyric acid receptor; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site mutant.
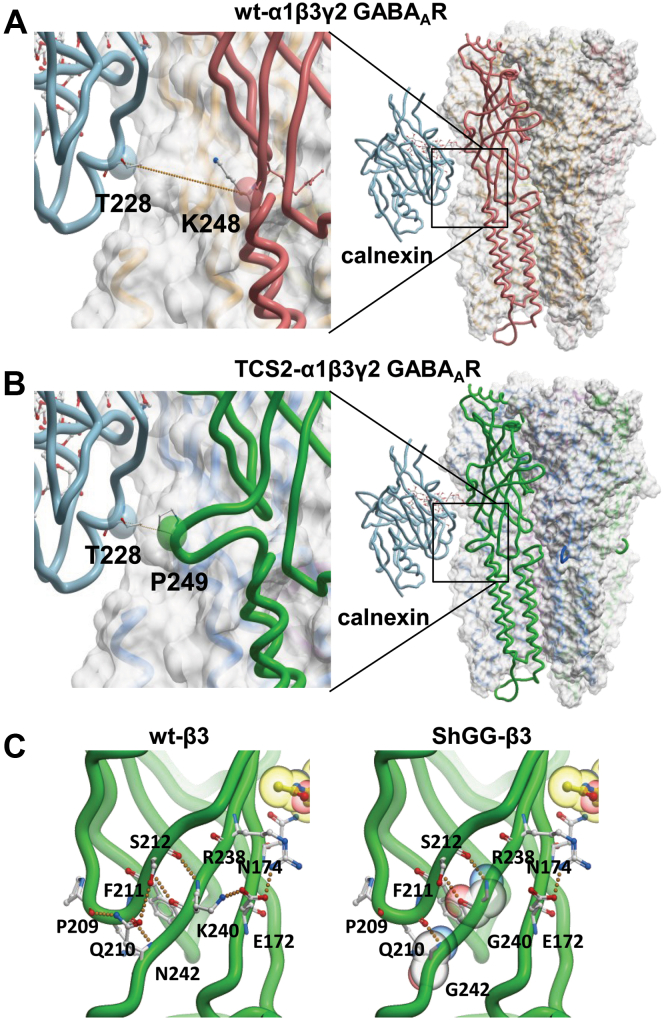
To investigate further how TCS mutants interact with calnexin, we have modeled GABAARs with glycans and studied interactions with calnexin. We first generated a model of heteropentameric GABAARs incorporating TCS2-α1/β3/γ2-GABAARs using coordinates of the wt-α1/β3/γ2-GABAARs structure (PDB 6HUG (18); using Modeller (see methods for details). Glc1-Man9-GlcNAc2 glycan was then added to this structure using GLYCAM Glycoprotein Builder at residue N174 of the β3 subunit. Human calnexin was modeled using coordinates of the canine calnexin structure as template (PDB 1JHN, (34); Fig. S5). Since there is no structure available of calnexin in complex with a glycan, we used a highly conserved homolog calreticulin in complex with Glc1-Man3 tetrasaccharide (PDB 3O0W, (35)) to identify how glycans and calnexin interact (Fig. S6). Glc1-Man3 tetrasaccharide, from the calreticulin structure, was superimposed onto the GLYCAM-modeled glycan in the α1/β3/γ2 heteropentamer using Molsoft ICM software (Fig. S7). After superimposition, the coordinates of calnexin were extracted and positioned relative to the α1/β3/γ2 heteropentamer. Calnexin–wt-GABAAR complex and calnexin–TCS2–GABAAR complex are illustrated in Figure 10, A and B, respectively. In the calnexin–wt GABAAR complex, calnexin bound to the N174-linked glycan in the β3 subunit is in a proximity to the conserved N-ECD region adjoining the TM1 of the neighboring α1 subunit, with the distance between two closest α carbons (calnexin T228 and α1 subunit residue K248) of 14.5 Å (Fig. 10A, orange dotted line in the left panel). In the calnexin–TCS2–GABAAR complex due to insertion of TCS sequence, calnexin bound to the N174-linked glycan in the β3 subunit is even closer to this region, with a significantly shorter distance between two closest α carbons (calnexin T228 and α1 subunit residue P249) of 7.16 Å (Fig. 10B, orange dotted line in the left panel). This suggests that insertion of TCS may interfere with the calnexin binding to N-linked glycan at position N174 in the β3 subunit due to the bulge in structure generated in the mutated adjacent α1 subunit causing structural hindrance.
Figure 10.
Modeling by homology indicates that TCS2 and ShGG mutations may block CNX binding.A, structure of the wt-α1(pink)/β3(orange)/γ2(yellow) heteropentamer in complex with CNX (light blue). The distance (orange dotted line) between two closest α carbons (CNX: T228 and GABAAR α1 subunit: K248) is 14.5 Å as shown in the close-up on the left. B, structure of TCS2- α1(green)/β3(blue)/γ2(purple) heteropentamer in complex with CNX (light blue). The distance (orange dotted line) between two closest α carbons (CNX: T228 and TCS2-GABAAR α1 subunit: P249) is 7.16 Å as shown in the close-up on the left. C, K240 and N242 of the β3 subunit (green) make hydrogen bonds (orange dotted lines in the left panel) with backbone atoms of residues P209, Q210, F211, and S212 located on β9 strand. The lysyl side chain of K240 forms a part of the K240-E172-N174 triad. The K240G mutation disrupts hydrogen bonds between K240 and E172 (left panel). The N242G mutation would result in the loss of hydrogen bond interactions between N242 and P209 or S212. GABAAR, γ-aminobutyric acid receptor; TCS, Thrombin Cleavage Site mutant.
We have also investigated how substitutions K240G and N242G substitutions in the conserved N-ECD region adjoining the TM1 of the wt-β3 subunit may affect calnexin binding. K240 and N242 residues are positioned at the C-terminal end of the β10 strand within this region where they make hydrogen bonds (Fig. 10C, orange dotted lines in the left panel) with backbone atoms of residues P209, Q210, F211, and S212 located on the β9 strand. This network of hydrogen bonds maintains the structural integrity of the local secondary structural elements. The lysyl side chain of K240 forms a part of the K240-E172-N174 triad. K240G mutation disrupts hydrogen bonds between K240 and E172 thereby reducing the stability of these interactions. The free energy change (ΔΔG) of this mutation is 1.64 kcal/mol, suggesting a destabilizing effect. The side chain of N242 forms two hydrogen bonds with the backbone of P209 and the hydroxyl group in the side chain of S212 on the β9 strand. The N242G mutation results in the loss of these hydrogen bond interactions (Fig. 10C, right panel). The ΔΔG for N242G mutation is 2.28 kcal/mol. Positive ΔΔG values for both K240G and N242G indicate that glycine is not tolerated at these two positions, suggesting that ShGG mutations will cause disruption of β sheet structure in this region. Furthermore, N174 glycosylated residue in the β3 subunit is located on β7 strand, which indicates that any localized structural destabilization may decrease calnexin binding to the N174-linked glycan.
Overall, these results indicate that TCS mutations of GABAAR subunits are likely to specifically effect interactions with calnexin, leading to accumulation of these mutants in the ER and increased association with Grp94 which accelerates their degradation by ERAD. Inhibition of ERAD facilitates trafficking of these mutants to the cell surface by prolonging their retention and processing in the ER.
Discussion
The N-ECDs of GABAAR subunits are essential for their assembly into functional heteropentamers and expression at the cell surface (7, 8). While the structure and function of many segments of these domains have been investigated in detail (6), the region located at the very end adjoining the TM1 has not been characterized to date. However, this region contains several highly conserved amino acid residues in all main GABAAR subunits, with R247 of the mouse α1 subunit also conserved in other Cys-loop receptor subunits, including glycine receptor subunits, 5HT3 receptor subunits, and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits. Other conserved residues in this region of GABAAR subunits, F243 and L245, are not fully conserved in other Cys-loop receptors. We present here experimental evidence for an important role of this region in the receptor processing in the ER and forward trafficking to the cell surface.
Initially, our aim was to develop a method which would allow purification of the N-terminal extracellular domains from the GABAARs expressed at the cell surface. Towards this aim, we have selected this end region of the N-ECDs of the GABAAR subunits as a point of insertion of the thrombin cleavage sequence which would allow proteolytic cleavage of fully assembled heteropentamers of N-ECDs by exogenously added thrombin in a cell culture system. However, not only insertion of the thrombin site into this region but also much smaller modifications of two existing amino acids (K240G and N242G) to mimic the minimum thrombin site significantly impaired forward trafficking of the mutated receptors but had no effect on subunit assembly. Instead, the mutants accumulated in the ER, indicating that structural changes in this conserved region may influence how GABAARs are processed by various ER protein quality control mechanisms. Indeed, our coimmunoprecipitation experiments have demonstrated that mutated receptors showed equal ability to interact with BiP, reduced binding to calnexin, and increased association with Grp94 when compared to the wt receptors, indicating that these mutations do not induce random unfolding but rather specific structural changes. In agreement with biochemical experiments, structural modeling indicates that mutations introduced specifically effect interactions with calnexin. Although calnexin binds directly to N-linked glycans, structural changes in the surrounding regions may influence how stable this interaction is and when it will occur during the processing (17). The proximity of the N174-linked glycan in the β3 subunit to the mutated region in the adjacent α1 subunit in the GABAAR heteropentamer suggests that calnexin binding to this glycan may be decreased due to steric hindrance. Furthermore, structural changes caused by point mutations in this region in the ShGG β3 subunit observed in our modeling studies are predicted to also influence how efficiently calnexin can bind to N174-linked glycan in the β3 homopentameric receptors.
It is also important to note that D219N substitution in the α1 subunit linked to familial idiopathic generalized epilepsy and febrile seizures (36) is also located near this conserved end region of the N-ECDs following GABAAR subunit assembly into heteropentamers (18). This mutation was also shown to impair ER processing of GABAARs and their interactions with calnexin and calreticulin. Moreover, prolonged treatments with VPM, an L-type Ca2+ channel blocker which leads to depletion of ER Ca2+ stores after long incubation, enhanced the interaction between this mutant and calnexin/calreticulin and facilitated the calnexin-assisted forward trafficking, without inhibiting degradation through ERAD (24). However, VPM treatments had little effect on ER processing and forward trafficking of TCS mutants in our study, which indicates that D219N substitution in the α1 subunit may cause specific structural changes different to those described based on structural modeling of TCS2 and ShGG mutants. Pharmacological treatments using other chemical inhibitors or activators of ER Ca2+ stores also had little effect on trafficking of TCS2 mutants to the cell surface.
ER accumulation of TCS and ShGG mutants is likely to lead to their increased association with Grp94, as shown in our biochemical experiments. However, this can only be observed in the presence of a potent proteosome inhibitor MG-132, which indicates that mutated receptors are rapidly targeted to ERAD by Grp94. The role of Grp94 in GABAAR processing in the ER and translocation to proteosome complex has been characterized previously in a study investigating another epilepsy-linked mutation in the α1 subunit, A332D (20).
Consistent with this, blocking translocation of TCS2 mutants from the ER to proteosome by Eerl or inhibiting proteosome function by MG-132 was shown to lead to an increase in cell surface expression of these mutants, as well as the wt receptors, possibly due to their prolonged retention and processing in the ER. We hypothesize based on our structural analysis that a combination of approaches to prevent rapid ERAD of TCS2 mutants and stabilize their interaction with calnexin lectin domain may prove efficient in facilitating their forward trafficking and increasing further their cell surface expression.
In conclusion, the conserved end region of the N-terminal extracellular domains of the GABAAR subunits plays an important role in ER processing and forward trafficking of these receptors at least in part by regulating their interaction with calnexin.
Experimental procedures
cDNA constructs
Mouse GABAA receptor subunit α1, β3, and γ2S cDNAs were cloned into the plasmid vector pRK5 (37). Myc tag (EQKLISEEDL) was inserted between the fourth and fifth residue of the mature α1, β3, or γ2S cDNA (7). Myc-tagged cDNAs were also cloned into pRK5 vector. HA-tagged Grp94 cDNA in pCMV3 vector was purchase from Sino Biological (HG16275-CY).
Overlap extension PCR
Thrombin cleavage sequence was inserted into GABAA receptor subunit DNA (α1, myc-tagged α1, β3, myc-tagged β3, γ2, and myc-tagged γ2) using overlap extension-PCR. The forward and reverse primers for TCS1-α1 were 5′-CTGGTACCCAGAGGATCCATTGGCTACTTTGTTATT-3′ and 5′-GGATCCTCTGGGTACCAGTTTTCTCTTCAAGTGGAA-3′. The forward and reverse primers for TCS2-α1 were 5′-CTGGTACCCAGAGGATCCAGAAAAATTGGCTACTTT-3′ and 5′-GGATCCTCTGGGTACCAGCTTCAAGTGGAAGTGAGT-3′. The forward and reverse primers for TCS1-β3 were 5′-CTGGTACCCAGAGGATCCATCGGGTACTTCATTCTT-3′ and 5′-GGATCCTCTGGGTACCAGATTTCTCTTCAACCGAAA-3′. The forward and reverse primers for TCS2-β3 were 5′-CTGGTACCCAGAGGATCCAGAAATATCGGGTACTTC-3′ and 5′-GGATCCTCTGGGTACCAGCTTCAACCGAAAACTCAA-3′. The forward and reverse primers for TCS3-β3 were 5′-CTGGTACCCAGAGGATCCTTGAAGAGAAATATCGGG-3′ and 5′-GGATCCTCTGGGTACCAGCCGAAAACTCAATCGAGG-3′. The forward and reverse primers for TCS1-γ2 were 5′-CTGGTACCCAGAGGATCCGGCTACTTCACCATCCAG-3′ and 5′-GGATCCTCTGGGTACCAGCATTCTTCTGCTCAGATC-3′. The forward and reverse primers for TCS2-γ2 were 5′-CTGGTACCCAGAGGATCCAGAAGAATGGGCTACTTC-3′ and 5′-GGATCCTCTGGGTACCAGGCTCAGATCGAAGTACAC-3′. All primers were synthesized by Eurofins. Forward primer (250 pmol), reverse primer (250 pmol), and GABAA receptor subunit DNA (100 ng) were mixed with 2× Phusion Master Mix (25 μl; F531S-Thermo Fisher). ddH2O was added into the mixture to 50 μl. PCR was run in a Thermo PX2 thermal cycler using the following setting: initial denaturation at 98 °C for 30 s; 35 cycles of 5 s at 98 °C, 30 s at 55 °C, and 32 s at 72 °C; and final extension at 72 °C for 7 min. PCR product was ran on agarose gel (1% agarose (BP1356-100-Fisher-Scientific) in 1× TAE (BP1332-1-Fisher-Scientific)), and DNA band was then purified using PCR purification kit (28104-Qiagen). DNA was fused into pRK5 vector by restriction cleavage (EcoRI/HindIII for α1, γ2, myc-tagged α1, or myc tagged γ2 subunit; ClaI/XbaI for β3 or myc-tagged β3 subunit) and ligation.
Site-directed mutagenesis
ShGG mutant of myc-tagged β3 subunit was produced using QuickChange Lightning site-directed mutagenesis kit (210518-Agilent). Forward and reverse primers were designed as 5′-CGACTTTCATTGAGTTTTCGGTTGGGGAGAGGTATCGGGTACTTCATTCTTCAGACG-3′ and 5′-CGTCTGAAGAATGAAGTACCCGATACCTCTCCCCAACCGAAAACTCAATGAAAGTCG-3′. Reaction buffer (10× , 5 μl), myc-tagged β3 DNA in pRK5 vector (25 ng), forward primer (125 ng), reverse primer (125 ng), dNTP mix (1 μl), QuickSolution reagent (1.5 μl), and ddH2O were mixed to a final volume of 50 μl. PCR was run using the following setting: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min; 18 cycles of 20 s at 95 °C, 10 s at 60 °C, and 6.5 min at 68 °C; and final extension at 68 °C for 5 min. PCR product was transformed into Escherichia coli to generate ShGG-β3 DNA for further research.
Cell culture and transfection
HEK293 cells and COS-7 cells were purchased from the ATCC and cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (11960-044-Gibco) with heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (10%; 10082-147-Gibco), L-glutamine (2 mM; 25030-024-Gibco), penicillin and streptomycin (100 units/ml and 100 μg/ml; 15140-148-Gibco) in 5% CO2 at 37 °C. When cell monolayer reached ∼80% confluency, HEK293 cells were passaged with versene (15040-033-Gibco), and COS-7 cells were passaged with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA (25200-056-Gibco).
Cells in T75 flasks were grown to reach 60 to 70% confluence before calcium phosphate transfection. Plasmid DNA (20 μg) was diluted with TE buffer containing Tris (1 mM, pH 8.0; T1503-Sigma-Aldrich) and EDTA (0.1 mM; EDS-100G-Sigma-Aldrich) to a final volume of 450 μl. Diluted DNA was mixed with 2.5 M CaCl2 (50 μl; 275844L-BDH), which was then added into 2× HBS (500 μl) containing Hepes (50 mM, pH 7.12; B2001-Melford), NaCl (280 mM; 10735921-Fisher-Scientific), and Na2HPO4 (1.1 mM; 103834G-BDH) dropwise. After 45 min incubation at room temperature, final mixture (1 ml) was dripped into one flask. Cells were incubated in 5% CO2 at 37 °C for 24 h.
Cells in 24-well plates were transfected with Effectene Transfection Reagent (301425-Qiagen) or Lipofectamine LTX Reagent (15338–030-Invitrogen). For 1-well Effectene transfection, DNA (200 ng) was diluted with EC buffer to a final volume of 60 μl and mixed with Enhancer (1.6 μl). After 5 min incubation at room temperature, DNA mixture was combined with Effectene (5 μl) and incubated for another 10 min at room temperature. Final mixture was diluted to 350 μl with culture medium, which was added into cell culture. Cells were incubated in 5% CO2 at 37 °C for 24 h.
For Lipofectamine LTX transfection in each well, DNA (500 ng) or Lipofectamine LTX reagent (1.25 μl) was diluted to 25 μl with Opti-MEM (31985-047-Gibco). Diluted DNA was combined with Plus reagent (0.5 μl) and mixed with diluted Lipofectamine. After 5 min incubation at room temperature, final mixture was added into cell culture. Cells were incubated in 5% CO2 at 37 °C for 24 h.
SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting
Each protein sample or protein marker (5 μl; RPN800E-Cytiva) was mixed with 5 × sample buffer (20 μl) containing Tris (312.5 mM, pH 8.0), sodium dodecyl sulfate (10%; L3771-Sigma), glycerol (50%; 56–81-5-VWR) and bromophenol blue (0.0125%; 32712-Riedel-de-Haën)), 1M DTT (10 μl; R0861-Thermo-Scientific) and lysis buffer to a final volume of 100 μl. After being heated at 90 °C for 10 min, protein samples were separated in SDS PAGE (10 % separation gel, 5% stacking gel) using a Hoefer SE 600 vertical gel unit containing SDS running buffer (Tris (25 mM, pH 8.3), glycine (192 mM; G7126-Sigma), and SDS (0.1 %)). Proteins in gels were transferred onto 0.2 μm nitrocellulose membranes (10600011-Amersham) with a Hoefer TE62 transfer unit containing transfer buffer (Tris (20 mM, pH 8.6), glycine (120 mM), and methanol (20%; 67-56-1-Sigma-Aldrich)) for 4 h with a constant current of 200 mA. Membranes were incubated with blocking solution (skimmed milk powder (1.5%; Marvel) in Tris-buffered saline-Tween 20 containing Tris (50 mM, pH 7.6), NaCl (200 mM), and Tween 20 (0.05%, 663684B-BDH)) for 30 min to block nonspecific binding. Membranes were incubated with primary antibody (rabbit anti-α1 antibody (2.6 μg/ml) (38), rabbit anti-β3 antibody (UCL 74; 1:200), rabbit anti-γ2 antibody (3.4 μg/ml) (39), mouse anti-c-myc antibody (2 μg/ml; 05-724-Millipore), rabbit anti-HA antibody (1 μg/ml; ab184643-Abcam), rabbit anti-Grp94 antibody (1 μg/ml; 36-2600-Invitrogen), rabbit anti-calnexin antibody (1 μg/ml; ab22595-Abcam), rabbit anti-PDI antibody (1:1000; 3501P-Cell-Signaling), rabbit anti-RCAS1 antibody (1:1000; 12290P-Cell-Signaling), rabbit anti-LAMP1 antibody (1:1000; 9091P-Cell-Signaling), or rabbit anti-BiP antibody (1 μg/ml; ab21685-Abcam)) in blocking solution for 2 h at room temperature. Membranes were rinsed twice and washed twice for 10 min with blocking solution. Secondary antibodies alkaline phosphatase (AP)–conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (0.5 μg/ml; A16099-Invitrogen), AP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (0.35 μg/ml; 115-055-174-Jackson-ImmunoResearch), or horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated mouse anti-rabbit IgG (0.4 μg/ml)) were applied in blocking solution for 1-h incubation at room temperature. Membranes were washed as above with blocking solution, TBS-T and TBS, respectively. For HRP-conjugated secondary antibody, bands were probed using West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate (34094-Thermo-Scientific). For AP-conjugated secondary antibody, after being rinsed with AP buffer containing Tris (100 mM, pH 9.5), NaCl (100 mM), and MgCl2 (10 mM; 101494V-BDH), membranes were incubated with 4-nitro blue tetrazolium chloride (0.66 mg/ml; 11383213001-Sigma-Aldrich) and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-phosphate (0.33 mg/ml; 11383221001-Sigma-Aldrich) in AP buffer. Membranes were rinsed with water to stop the reaction when protein bands were clearly visible.
Coimmunoprecipitation
For coimmunoprecipitation of calnexin and BiP with GABAARs, HEK293 cells were transfected with TCS2 or wt GABAAR subunit cDNAs for 24 h. Cells were scraped into the lysis buffer (2 ml) containing Tris (50 mM, pH 7.4), NaCl (150 mM), EGTA (1 mM, 03778-Fluka), MgCl2 (0.1 mM), Triton (1%; A16046-Alfa-Aesar), sodium deoxycholate (0.5%; D6750-Sigma-Aldrich), SDS (0.1%), PMSF (1 mM; P7626-Sigma), leupeptin (10 μg/ml; 4041-Peptide-Institute), antipain (10 μg/ml; 178220-Millipore), pepstatin (5 μg/ml; A2571-Apexbio), and chymostatin (5 μg/ml; 152845-MP-Biomeicals). Cells were homogenized with tight-fitting glass-glass homogenizer for 30 times and agitated for 1 h at 4 °C. Total cell lysates were centrifuged for 10 min at 16,000g and 4 °C to remove cell debris. Protein concentration was measured using BCA assay. Proteins (400 μg) from each group were precleared with protein G Sepharose beads (50 μl; NB-45-00037-5-Neo-Biotech) in lysis buffer (1:1) for 1 h at 4 °C. Beads were pelleted and removed by centrifugation (500g, 1 min at 4 °C). The precleared samples were incubated with mouse anti-myc antibody (5 μg) or nonimmune mouse IgG (5 μg) for 2 h at 4 °C with rotation and with protein G sepharose beads (50 μl) in lysis buffer (1:1) for 1 h at 4 °C with rotation. The beads were collected by centrifugation (500g, 1 min at 4 °C) and washed with lysis buffer for six times. The proteins binding on the beads were eluted by adding the mixture of 5× SDS sample buffer (20 μl), 1 M DTT (10 μl), and lysis buffer (70 μl).
For coimmunoprecipitation of Grp94 and GABAARs, HEK293 cells were transfected with myc-tagged TCS2 or wt GABAAR subunit cDNAs and HA-tagged Grp94 cDNA (Sino Biological) and incubated for 24 h. Cells were treated with MG-132 (10 μM; 474787-Millipore) for 2 h to inhibit proteasome and washed with chilled PBS (10010-015-Gibco). Cross-linking was applied using dithiobis (succinimidyl propionate) (5 ml; 1.5 mM; 22585-Thermo-Scientific) in PBS at 4 °C for 30 min. After cross-linking, the reaction was quenched by adding Tris (50 μl; 1 M, pH 7.5) and incubating at 4 °C for 10 min. Cells were lysed and processed further as described above.
Immunocytochemistry
HEK293 cells or COS-7 cells (50,000) were seeded and grown overnight on poly-L-lysine (0.1 mg/ml; P6282-Sigma) coated 13-mm glass coverslips in 24-well plates. Lipofectamine or Effectene was introduced to transfect cells with myc-tagged α1, β3, and γ2 DNA (500 ng) for 24 h. Cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde (4 %; 158127-Sigma-Aldrich)/sucrose (4 %) in PBS (PFA) for 10 min at room temperature. PBS was used to wash cells by rinsing twice and washing for 5 min 3 times. Cells were incubated with glycine (0.3 M) in PBS for 10 min at room temperature to block unreacted PFA, washed with PBS, and incubated with Triton X-100 (0.5%) in PBS to permeabilize the plasma membrane. Cells were incubated with bovine serum albumin (1%; BP9704-100-Fisher-Scientific) in PBS for 30 min at room temperature to block nonspecific binding of antibodies. Primary antibodies (anti-RCAS1 (1:200), anti-CNX (1 μg/ml), anti-α1 (2.6 μg/ml), anti-β2/3 (5 μg/ml; MAB341-Millipore), or anti-myc (2 μg/ml)) were incubated overnight at 4 °C. Cells were washed with PBS, incubated with 1% BSA/PBS to block nonspecific binding, followed by incubation with secondary antibodies and phalloidin for 1 h at room temperature. Cells were washed in PBS, and coverslips were mounted with Prolong antifade reagent (P36930-Invitrogen). Images were acquired with Zeiss LSM 710 confocal microscope.
Cell surface ELISA
COS-7 cells were seeded at 5 × 104 cells/well in 24-well plates coated with poly-D-lysine (0.1 mg/ml; P1149-Sigma) and incubated in 5% CO2 at 37 °C overnight. Cells were transfected with myc-α1, β3, and γ2 cDNA or α1, myc-β3, and γ2 cDNA (wt or mutated) using Lipofectamine LTX reagent. After transfection and treatment (if applicable), cells were washed twice with PBS and fixed for 10 min with 4% PFA/sucrose in PBS. Cells were rinsed twice with PBS and washed twice with Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS; 14185–052-Gibco) for 10 min. Nonspecific binding of primary antibodies was blocked by application of rabbit serum (10%)/BSA (1%) in HBSS for 30 min at room temperature. For total levels, cell membrane was permeabilized by addition of Triton X-100 (0.5%). Cells were incubated with mouse anti-myc antibody (2 μg/ml; M4439-Sigma) in BSA (1%)/HBSS at 4 °C overnight. Cells were washed with HBSS, blocked as above and incubated with HRP-conjugated rabbit anti-mouse IgG (0.4 μg/ml; 61-6520-Invitrogen) in BSA (1%)/HBSS for 2 h at room temperature. Cells were rinsed twice and washed twice for 20 min with HBSS. HRP-substrate 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (0.5 ml; T0440-Sigma) was applied to each well at 5-s intervals. Reaction was stopped by transferring reagent to 1.5 ml water. Absorbance was measured at 655 nm in a Beckman DU800 spectrophotometer.
Modeling of GABAARs in complex with calnexin
The wt mouse model of GABAA receptor α1/β3/γ2 heteropentamer was constructed by MODELLER v10.1 program (40) using the human α1/β3/γ2 heteropentamer crystal structure (PDB code 6HUG; (41)) as the template. The sequence of mouse α1/β3/γ2 subunit was obtained from UniProt database (UniProt ID P62812/P63080/P22723; Figs. S4A and S5A). This wt model was then used for the TCS2 α1/β3/γ2 heteropentamer model building by inserting TCS, LVPRGS, between K246 and R247 (α1), K240 and R241 (β3), or S268 and R269. Human calnexin (UniProt ID P27824) model was constructed through the same method using the dog calnexin crystal structure as the template (PDB code 1JHN; (34)). Modeling structures with lower discrete optimized protein energy (DOPE) scores from 50 generated structures were evaluated via Ramachandran plot (Figs. S4B and S5B) and Protein Structure Analysis (42, 43). For the highly flexible loop regions that did not pass the model evaluation, loop refinement was conducted in MODELLER v10.1 program. For the ShGG mutant, the ΔΔG free energy calculations were carried out using the Mutagenesis module implemented in the MolSoft ICM Software (44).
Glc1-Man9-GlcNAc2 glycan was added onto β3 subunit of GABAAR α1/β3/γ2 heteropentamer using the GLYCAM Glycoprotein Builder (https://glycam.org). The lectin domain of calreticulin was introduced to construct calnexin-GABAARα1/β3/γ2 heteropentamer complex. The crystal structure of calreticulin with Glc1-Man3 (PDB code 3O0W; (35)) revealed how the lectin domain of calreticulin, which is highly conserved with the lectin domain of calnexin, is bound with the glycan (45). The lectin domain of calreticulin was replaced by its highly conserved homolog the lectin domain of calnexin to build a complex of calnexin and Glc1-Man3 tetrasaccharide using Molsoft ICM software (44). Glc1-Man3 tetrasaccharide of the complex was superimposed with the glycan built on the α1/β3/γ2 heteropentamer to generate the model of calnexin binding to the receptor.
Data availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary information files and are available in Zenodo platform https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7111766.
Supporting information
This article contains supporting information.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Alex Thomson for her support, Dr Sarah Cousins for technical help, and Dr Anya Sihra-Jovanovic for proof reading the manuscript. This work was supported by the MRC UK project grant (G0800498) and The Wellcome Trust.
Author contributions
B. Y., C. H.-W., P. L., and Z. X. investigation; F. A. S., S. H., and J. N. J. supervision; F. A. S. and J. N. J. conceptualization; J. N. J. data curation; J. N. J. writing–original draft.
Edited by Roger Colbran
Supporting information
References
- 1.Sallard E., Letourneur D., Legendre P. Electrophysiology of ionotropic GABA receptors. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021;78:5341–5370. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03846-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chua H.C., Chebib M. GABAA receptors and the diversity in their structure and pharmacology. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017;79:1–34. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2017.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fritschy J.M., Panzanelli P. GABAA receptors and plasticity of inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014;39:1845–1865. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lorenz-Guertin J.M., Bambino M.J., Jacob T.C. gamma2 GABAAR trafficking and the consequences of human genetic variation. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:265. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sieghart W. Structure, pharmacology, and function of GABAA receptor subtypes. Adv. Pharmacol. 2006;54:231–263. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(06)54010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Scott S., Aricescu A.R. A structural perspective on GABAA receptor pharmacology. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019;54:189–197. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2019.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Connolly C.N., Krishek B.J., McDonald B.J., Smart T.G., Moss S.J. Assembly and cell surface expression of heteromeric and homomeric gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:89–96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Connolly C.N., Wooltorton J.R., Smart T.G., Moss S.J. Subcellular localization of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors is determined by receptor beta subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996;93:9899–9904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.18.9899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Klausberger T., Roberts J.D., Somogyi P. Cell type- and input-specific differences in the number and subtypes of synaptic GABA(A) receptors in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2002;22:2513–2521. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-07-02513.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mohler H. GABA(A) receptor diversity and pharmacology. Cell Tissue Res. 2006;326:505–516. doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Thomson A.M., Jovanovic J.N. Mechanisms underlying synapse-specific clustering of GABA(A) receptors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010;31:2193–2203. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mele M., Costa R.O., Duarte C.B. Alterations in GABAA-receptor trafficking and synaptic dysfunction in brain disorders. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:77. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lorenz-Guertin J.M., Jacob T.C. GABA type a receptor trafficking and the architecture of synaptic inhibition. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018;78:238–270. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Macdonald R.L., Kang J.Q., Gallagher M.J. Mutations in GABAA receptor subunits associated with genetic epilepsies. J. Physiol. 2010;588:1861–1869. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.186999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hernandez C.C., Macdonald R.L. A structural look at GABAA receptor mutations linked to epilepsy syndromes. Brain Res. 2019;1714:234–247. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fu Y.L., Han D.Y., Wang Y.J., Di X.J., Yu H.B., Mu T.W. Remodeling the endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis network restores proteostasis of pathogenic GABAA receptors. PLoS One. 2018;13 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Adams B.M., Canniff N.P., Guay K.P., Hebert D.N. The role of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones in protein folding and quality control. Prog. Mol. Subcell Biol. 2021;59:27–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-67696-4_3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Laverty D., Desai R., Uchanski T., Masiulis S., Stec W.J., Malinauskas T., et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human alpha1beta3gamma2 GABAA receptor in a lipid bilayer. Nature. 2019;565:516–520. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0833-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hirose S. Mutant GABA(A) receptor subunits in genetic (idiopathic) epilepsy. Prog. Brain Res. 2014;213:55–85. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63326-2.00003-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Di X.J., Wang Y.J., Han D.Y., Fu Y.L., Duerfeldt A.S., Blagg B.S., et al. Grp94 protein delivers gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors to Hrd1 protein-mediated endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016;291:9526–9539. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.705004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang Y.J., Di X.J., Mu T.W. Using pharmacological chaperones to restore proteostasis. Pharmacol. Res. 2014;83:3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Di X.J., Wang Y.J., Cotter E., Wang M., Whittsette A.L., Han D.Y., et al. Proteostasis regulators restore function of epilepsy-associated GABAA receptors. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021;28:46–59 e47. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Han D.Y., Di X.J., Fu Y.L., Mu T.W. Combining valosin-containing protein (VCP) inhibition and suberanilohydroxamic acid (SAHA) treatment additively enhances the folding, trafficking, and function of epilepsy-associated gamma-aminobutyric acid, type A (GABAA) receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2015;290:325–337. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.580324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Han D.Y., Guan B.J., Wang Y.J., Hatzoglou M., Mu T.W. L-Type calcium channel blockers enhance trafficking and function of epilepsy-associated alpha1(d219N) subunits of GABA(A) receptors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015;10:2135–2148. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Brown L.E., Nicholson M.W., Arama J.E., Mercer A., Thomson A.M., Jovanovic J.N. Gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor subunits play a direct structural role in synaptic contact formation via their N-terminal extracellular domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2016;291:13926–13942. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.714790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Laverty D., Desai R., Uchański T., Masiulis S., Stec W.J., Malinauskas T., et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human α1β3γ2 GABA A receptor in a lipid bilayer. Nature. 2019;565:516–520. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0833-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chang J.Y. Thrombin specificity. Requirement for apolar amino acids adjacent to the thrombin cleavage site of polypeptide substrate. Eur. J. Biochem. 1985;151:217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Taylor P.M., Thomas P., Gorrie G.H., Connolly C.N., Smart T.G., Moss S.J. Identification of amino acid residues within GABA(A) receptor beta subunits that mediate both homomeric and heteromeric receptor expression. J. Neurosci. 1999;19:6360–6371. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-15-06360.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nicholson M.W., Sweeney A., Pekle E., Alam S., Ali A.B., Duchen M., et al. Diazepam-induced loss of inhibitory synapses mediated by PLCdelta/Ca(2+)/calcineurin signalling downstream of GABAA receptors. Mol. Psych. 2018;23:1851–1867. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0100-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Saliba R.S., Pangalos M., Moss S.J. The ubiquitin-like protein Plic-1 enhances the membrane insertion of GABAA receptors by increasing their stability within the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:18538–18544. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802077200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang P., Eshaq R.S., Meshul C.K., Moore C., Hood R.L., Leidenheimer N.J. Neuronal gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) type A receptors undergo cognate ligand chaperoning in the endoplasmic reticulum by endogenous GABA. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:188. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ong D.S., Mu T.W., Palmer A.E., Kelly J.W. Endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ increases enhance mutant glucocerebrosidase proteostasis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010;6:424–432. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Patel P.D., Yan P., Seidler P.M., Patel H.J., Sun W., Yang C., et al. Paralog-selective Hsp90 inhibitors define tumor-specific regulation of HER2. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013;9:677–684. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schrag J.D., Bergeron J.J., Li Y., Borisova S., Hahn M., Thomas D.Y., et al. The Structure of calnexin, an ER chaperone involved in quality control of protein folding. Mol. Cell. 2001;8:633–644. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kozlov G., Pocanschi C.L., Rosenauer A., Bastos-Aristizabal S., Gorelik A., Williams D.B., et al. Structural basis of carbohydrate recognition by calreticulin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:38612–38620. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.168294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lachance-Touchette P., Brown P., Meloche C., Kinirons P., Lapointe L., Lacasse H., et al. Novel alpha1 and gamma2 GABAA receptor subunit mutations in families with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011;34:237–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Moss S.J., Ravindran A., Mei L., Wang J.B., Kofuji P., Huganir R.L., et al. Characterization of recombinant GABAA receptors produced in transfected cells from murine alpha 1, beta 1, and gamma 2 subunit cDNAs. Neurosci. Lett. 1991;123:265–268. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90947-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Duggan M.J., Stephenson F.A. Biochemical evidence for the existence of gamma-aminobutyrateA receptor iso-oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:3831–3835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Stephenson F.A., Duggan M.J., Pollard S. The gamma 2 subunit is an integral component of the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor but the alpha 1 polypeptide is the principal site of the agonist benzodiazepine photoaffinity labeling reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:21160–21165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Eswar N., Webb B., Marti-Renom M.A., Madhusudhan M.S., Eramian D., Shen M.Y., et al. Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2007 doi: 10.1002/0471140864.ps0209s50. Chapter 2, Unit 2 9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Masiulis S., Desai R., Uchanski T., Serna Martin I., Laverty D., Karia D., et al. GABAA receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacology. Nature. 2019;565:454–459. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0832-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Spencer R.K., Butterfoss G.L., Edison J.R., Eastwood J.R., Whitelam S., Kirshenbaum K., et al. Stereochemistry of polypeptoid chain configurations. Biopolymers. 2019;110 doi: 10.1002/bip.23266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wiederstein M., Sippl M.J. ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucl. Acids Res. 2007;35:W407–W410. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cardozo T., Totrov M., Abagyan R. Homology modeling by the ICM method. Proteins. 1995;23:403–414. doi: 10.1002/prot.340230314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kozlov G., Gehring K. Calnexin cycle - structural features of the ER chaperone system. FEBS J. 2020;287:4322–4340. doi: 10.1111/febs.15330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary information files and are available in Zenodo platform https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7111766.