Abstract
Objectives
Use of illicit substances during sex (chemsex) may increase transmission of HIV and other STIs. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is highly effective at preventing HIV transmission, providing an important prevention tool for those who practise chemsex. However, it does not prevent acquisition of other STIs. We aim to examine the impact of chemsex on STI incidence among gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (gbMSM), and transgender women using PrEP in Montréal, Canada.
Methods
We linked baseline sociodemographic and behavioural data with follow-up STI testing from 2013 to 2020 among PrEP users in the l’Actuel PrEP Cohort (Canada). Focusing on the 24 months following PrEP initiation, we estimated the effect of chemsex reported at baseline on cumulative incidence of gonorrhoea and chlamydia using Kaplan-Meier curves and survival analyses. We investigated the role of polysubstance use and effect modification by sociodemographic factors.
Results
There were 2086 clients (2079 cisgender gbMSM, 3 transgender gbMSM, 4 transgender women) who initiated PrEP, contributing 1477 years of follow-up. There were no incident HIV infections among clients on PrEP. Controlling for sociodemographic confounders, clients reporting chemsex at baseline had a 32% higher hazard of gonorrhoea/chlamydia diagnosis (adjusted HR=1.32; 95% CI: 1.10 to 1.57), equivalent to a risk increase of 8.9 percentage points (95% CI: 8.5 to 9.4) at 12 months. The effect was greater for clients who reported polysubstance use (adjusted HR=1.51; 95% CI: 1.21 to 1.89). The strength of the effect of chemsex on STI incidence varied by age, education and income.
Conclusion
Among PrEP users, chemsex at baseline was linked to increased incidence of gonorrhoea and chlamydia. This effect was stronger for people reporting multiple chemsex substances. The high STI incidence among gbMSM who report chemsex highlights the importance of PrEP for this population and the need for integrated services that address the complexities of sexualised substance use.
Keywords: pre-exposure prophylaxis, neisseria gonorrhoeae, chalmydia trachomatis, hepatitis C
Introduction
In the past two decades, the incidence of STIs has risen globally, and gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (gbMSM) continue to bear a disproportionate burden of disease.1 In Canada, incidence rates for gonorrhoea and chlamydia have steadily risen since the 1990s, especially among men.2 Rising STI incidence among gbMSM represents a public health priority due to the link between STIs and increased HIV-acquisition risk and the threat of antibiotic-resistant STIs undermining available treatment options.3 4
Recently, there has been increased attention towards the role of chemsex and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in STI transmission among gbMSM. Chemsex is a form of sexualised drug use and is defined as the intentional use of illicit substances during sex to enhance pleasure. While the definition varies, these substances often include gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB), mephedrone and crystal meth.5 6 Men often report increased pleasure, intimacy and a heightened sense of confidence as motivations for chemsex.7 8 Within the context of STI transmission, chemsex has been associated with condomless anal sex and increased number of partners—behaviours associated with transmission of HIV and other STIs.9–12 It has also been associated with higher prevalence of self-reported and diagnosed STIs.13–15 Due to the demonstrated HIV-acquisition risk associated with chemsex, recent methamphetamine use was included in the HIV Incidence Risk Index for MSM screening index for PrEP, and chemsex was included as an eligibility criteria for PrEP in Québec’s provincial guidelines.16 17
PrEP is a highly effective biomedical HIV-prevention method for populations at ongoing HIV-acquisition risk. Oral PrEP taken daily or intermittently (event-driven regimen) has been partially reimbursable with public funds in Québec since 2013 and was approved by Health Canada in 2016.16 18–20 Since PrEP prevents HIV acquisition, but not other STIs, concerns have been raised about potential increases in STI incidence following PrEP initiation.21–23 However, these increases cannot be directly attributed to changes in behaviours, as higher STI incidence among PrEP users may be due to secular trends and regular STI screening during PrEP follow-up.24 25 PrEP offers an opportunity to develop comprehensive HIV prevention programmes that address STIs via regular screening and treatment.3 Such programmes could include, or link to, services for chemsex and other forms of substance use, given that few interventions are available for gbMSM who practise chemsex.26–28
This study aims to examine the effect of chemsex on gonorrhoea and chlamydia incidence among gbMSM and transgender women using PrEP. Leveraging 7 years of longitudinal data from the l’Actuel PrEP Cohort (2013–2020) in Montréal (Canada), we (1) estimated the impact of chemsex at baseline on STI incidence in the first 2 years following PrEP initiation and (2) investigated whether this effect varies by number and type of chemsex substances reported and if selected sociodemographic characteristics are effect modifiers.
Methods
Study setting
Clinique médicale l’Actuel (l’Actuel) is a large sexual health clinic in Montréal that serves a population consisting mostly of gbMSM and where the l’Actuel PrEP Cohort in 2013. A detailed cohort description and study protocols can be found elsewhere.29–31 Briefly, clients interested in PrEP have a baseline consultation with a nurse and doctor to discuss PrEP needs and assess eligibility. During the consultation, clients complete a questionnaire on their sociodemographic profile, sexual health and substance use. Clients who receive a PrEP prescription have a first follow-up visit after 1 month and regular quarterly follow-ups thereafter. Follow-up visits consist of prescription renewal, STI screening, and a questionnaire on PrEP adherence, side effects, and sexual behaviours. Clients may also use the clinic’s STI testing services outside of scheduled follow-up visits (eg, if they experience symptoms or are notified by a partner).
Study population
This study includes all adult (≥18 years) gbMSM and transgender women who provided written informed consent, were HIV seronegative at baseline, consulted for PrEP at l’Actuel between 1 January 2013 and 31 May 2020, and came to at least one follow-up visit within the 180 days following their initial consultation. We defined gbMSM as cisgender or transgender men who either (a) identified as homosexual, bisexual or another sexuality which would include attraction to men (eg, pansexual, queer) or (b) reported having sex with a man in the past 12 months (P12M). All clients who self-identified as transgender women were included. Transgender women were included in the study because Canadian PrEP guidelines recommend the same eligibility criteria for gbMSM and transgender women, hence, in this sample, their sexual behaviors may be comparable to those of gbMSM.32 The database includes follow-up visits up to 30 June 2020, allowing a 1-month lag between the baseline visit and the first follow-up.
Exposure and outcome definitions
Chemsex was defined as reporting sexual relations under the effect of cocaine, ecstasy, GHB, crystal meth, ketamine or crack at least once in the P12M at baseline. Other substances reported (ie, alcohol, cannabis, poppers, opioids and heroin) were not classified as chemsex. This definition is consistent with previous studies in Montréal and elsewhere.5 8 33 We defined polysubstance use as reporting two or more chemsex substances, similarly to previous studies,34–36 with the caveat that the questionnaire did not ask if substances were taken together.
For gonorrhoea and chlamydia incidence and prevalence, we defined STI diagnosis as a positive nucleic acid amplification test for anal and oral swabs, or urine samples. For seroprevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, we defined history of infection as a positive antibody test. We defined incident HCV infections as a first HCV-antibody positive test (seroconversion). We did not investigate syphilis diagnoses since this would have required additional clinical data that were not readily available retrospectively.
Statistical analyses
We present descriptive statistics based on the baseline questionnaire.29 For baseline prevalence of gonorrhoea and chlamydia, and HCV seroprevalence, we linked data for tests performed at baseline or up to 2 months prior.
We conducted survival analysis to estimate the impact of chemsex at baseline on cumulative incidence, focusing on the 2 years following PrEP initiation and using all tests performed after PrEP initiation. Follow-up started at the baseline consultation and clients were censored at (1) their last follow-up visit, (2) the last visit prior to a temporary PrEP discontinuation (gap in follow-up of >180 days) or (3) after 2 years of follow-up. We considered three event dates: date of first diagnosis for either gonorrhoea or chlamydia (primary outcome), date of first gonorrhoea diagnosis and date of first chlamydia diagnosis. Additional sensitivity analyses stratified each STI by sample type (ie, urethral, throat and rectal).
We used Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves and Cox proportional hazards regression to compare cumulative STI incidence between the chemsex and the no-chemsex groups. We fit univariate models and multivariable models adjusted for age, education, income, PrEP regimen and year of baseline consultation. We addressed missing data for education and income using multiple imputations, pooling estimates from 12 imputations using Rubin’s rules.37 38 We estimated the absolute risk difference at 12 months as recommended by Austin39 and computed CIs using a multiple imputation-bootstrap procedure40 (online supplemental methods present details on imputation procedure and risk difference estimation).
sextrans-2021-055215supp001.pdf (4.3MB, pdf)
To investigate the role of polysubstance use, we estimated KM curves and fit regression models using the chemsex variable trichotomised in mutually exclusive categories: no chemsex (reference), chemsex (one substance) and polysubstance use. We performed similar analyses for each substance, stratifying the chemsex variable into clients who reported one specific substance, those who reported any of the other five and those not reporting any chemsex.
To investigate effect modification, we fit regression models with product terms between chemsex and either age, income or education.41 To avoid small sample sizes, age and income were regrouped into three categories each and education was dichotomised (post-secondary vs not).
Analyses were performed with R V.3.6.2,42 using the packages survival and survminer 43 44 for survival analysis and the mice package for multiple imputation.45
Results
Of 3394 clients who consulted for PrEP at l’Actuel between January 2013 and May 2020, 382 (11%) did not consent and 89 (3%) did not meet the inclusion criteria. Of 2923 included clients who consulted for PrEP, 677 (20%) did not return for follow-up and 160 (5%) initiated PrEP more than 180 days after their baseline consultation, leaving 2086 clients in the analytical sample (online supplemental figure 1).
Of 2086 clients with at least one follow-up visit, 2079 were cisgender gbMSM, 3 were transgender gbMSM and 4 were transgender women. One in four PrEP users (24%) reported chemsex at baseline. Participants contributed 1477 person-years of follow-up, with similar median follow-up time between groups: 6.5 months in the chemsex group vs 5.8 months in the no-chemsex group (table 1). The time between follow-ups and time between STI tests were similar between groups (online supplemental figure 2).
Table 1.
Sociodemographic characteristics, sexual behaviours, STI history and prevalent STIs for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) users in the l’Actuel PrEP Cohort (2013–2020)
| Reported chemsex | No chemsex reported | Total | ||||
| Total | 507 | 1579 | 2086 | |||
| Median follow-up time (months) | 6.5 | 5.8 | 5.9 | |||
| Total follow-up time (person-years) | 370 | 1107 | 1477 | |||
| Age (median, IQR) | 33 | (28–43) | 36 | (29–46) | 36 | (29–45) |
| Gender identity (n, %) | ||||||
| Cis men | 503 | 99.2% | 1576 | 99.8% | 2079 | 99.7% |
| Trans men | 1 | 0.2% | 2 | 0.1% | 3 | 0.1% |
| Trans women | 3 | 0.6% | 1 | 0.1% | 4 | 0.2% |
| Sexual orientation (n, %) | ||||||
| Homosexual | 483 | 95.3% | 1482 | 93.9% | 1965 | 94.2% |
| Bisexual | 21 | 4.1% | 92 | 5.8% | 113 | 5.4% |
| Heterosexual | 2 | 0.4% | 3 | 0.2% | 5 | 0.2% |
| Other | 0 | 0.0% | 1 | 0.1% | 1 | 0.1% |
| Missing | 1 | 0.2% | 1 | 0.1% | 2 | 0.1% |
| Education (n, %) | ||||||
| Primary | 5 | 1.0% | 9 | 0.6% | 14 | 0.7% |
| Secondary | 70 | 13.8% | 145 | 9.2% | 215 | 10.3% |
| CEGEP | 113 | 22.3% | 203 | 12.9% | 316 | 15.2% |
| University | 255 | 50.3% | 800 | 50.7% | 1055 | 50.6% |
| Missing | 64 | 12.6% | 422 | 26.7% | 486 | 23.3% |
| Annual income (n, %) | ||||||
| ≤$C10 000 | 30 | 5.9% | 89 | 5.6% | 119 | 5.7% |
| $C10 001–$$C20 000 | 47 | 9.3% | 115 | 7.3% | 162 | 7.8% |
| $C20 001–$C35 000 | 73 | 14.4% | 141 | 8.9% | 214 | 10.3% |
| $C35 001–$C55 000 | 120 | 23.7% | 298 | 18.9% | 418 | 20.0% |
| $C55 001–$C75 000 | 96 | 18.9% | 231 | 14.6% | 327 | 15.7% |
| ≥$C75 000 | 100 | 19.7% | 368 | 23.3% | 468 | 22.4% |
| Missing | 41 | 8.1% | 337 | 21.3% | 378 | 18.1% |
| Intravenous drug use in P12M (n, %) | ||||||
| Yes | 5 | 1.0% | 7 | 0.4% | 12 | 0.6% |
| Missing | 131 | 25.8% | 539 | 34.1% | 670 | 32.1% |
| Year of baseline consultation (n, %) | ||||||
| 2013 | 8 | 1.6% | 16 | 1.0% | 24 | 1.2% |
| 2014 | 29 | 5.7% | 49 | 3.1% | 78 | 3.7% |
| 2015 | 119 | 23.5% | 254 | 16.1% | 373 | 17.9% |
| 2016 | 146 | 28.8% | 332 | 21.0% | 478 | 22.9% |
| 2017 | 102 | 20.1% | 311 | 19.7% | 413 | 19.8% |
| 2018 | 69 | 13.6% | 307 | 19.4% | 376 | 18.0% |
| 2019 | 28 | 5.5% | 250 | 15.8% | 278 | 13.3% |
| 2020 | 6 | 1.2% | 60 | 3.8% | 66 | 3.2% |
| Number of regular partners in P12M | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 2 | (1–3) | 2 | (1–3) | 2 | (1–3) |
| Missing (n, %) | 78 | 15.4% | 422 | 26.7% | 500 | 24.0% |
| Number of occasional partners in P12M | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 15 | (6–30) | 10 | (5–20) | 10 | (5–20) |
| Missing (n, %) | 57 | 11.2% | 403 | 25.5% | 460 | 22.1% |
| Condom use in P12M (insertive anal sex) (n, %)* | ||||||
| 0%–25% | 90 | 21.0% | 162 | 13.8% | 252 | 15.7% |
| >25%–50% | 75 | 17.5% | 143 | 12.2% | 218 | 13.6% |
| >50%–75% | 47 | 11.0% | 80 | 6.8% | 127 | 7.9% |
| >75%–100% | 176 | 41.0% | 594 | 50.6% | 770 | 48.1% |
| Missing | 41 | 9.6% | 194 | 16.5% | 235 | 14.7% |
| Condom use in P12M (receptive anal sex) (n, %)* | ||||||
| 0%–25% | 64 | 15.3% | 97 | 9.1% | 161 | 10.8% |
| >25%–50% | 43 | 10.3% | 86 | 8.1% | 129 | 8.7% |
| >50%–75% | 37 | 8.8% | 55 | 5.2% | 92 | 6.2% |
| >75%–100% | 121 | 28.9% | 459 | 43.1% | 580 | 39.1% |
| Missing | 154 | 36.8% | 368 | 34.6% | 522 | 35.2% |
| Previous PEP use (n, %) | ||||||
| Yes | 193 | 38.1% | 497 | 31.5% | 690 | 33.1% |
| Missing | 26 | 5.1% | 285 | 18.% | 311 | 14.9% |
| Self-reported STI history, ever (n, %) | ||||||
| Gonorrhoea | 291 | 57.4% | 617 | 39.1% | 908 | 43.5% |
| Chlamydia | 249 | 49.1% | 486 | 30.8% | 735 | 35.2% |
| Syphilis | 117 | 23.1% | 240 | 15.2% | 357 | 17.1% |
| Hepatitis C virus | 6 | 1.2% | 10 | 0.6% | 16 | 0.8% |
| Missing | 17 | 3.4% | 170 | 10.8% | 187 | 9.0% |
| Prevalent STI diagnoses—NAAT (n, %) | ||||||
| Gonorrhoea | 78 | 15.4% | 140 | 8.8% | 218 | 10.4% |
| Chlamydia | 44 | 8.7% | 116 | 7.3% | 160 | 7.7% |
| Missing | 36 | 7.1% | 141 | 8.9% | 177 | 8.5% |
| Seroprevalence (n, %) | ||||||
| Hepatitis C virus | 2 | 0.4% | 2 | 0.1% | 4 | 0.2% |
| Missing | 73 | 14.4% | 310 | 19.7% | 383 | 18.4% |
Created by the authors.
CEGEP is Québec’s system of post-secondary education which offers pre-university and professional degrees.
*For condom use variables, the denominator was only clients who reported either insertive or receptive anal sex, hence the numbers here may not add up to the total in the first row.
CEGEP, Collège d'enseignement général et professionnel; NAAT, nucleic acid amplification test; PEP, post-exposure prophylaxis; P12M, past 12 months.
Compared with clients who did not report chemsex, PrEP users who reported chemsex (P12M) at baseline reported more occasional partners (median=15 vs median=10 in P12M), lower levels of condom use and a higher proportion of previous post-exposure prophylaxis use (38% vs 32%) (table 1).
Chemsex is associated with higher baseline proportion of self-reported STI history and prevalent STI diagnosis
At baseline, the chemsex group had a higher proportion of self-reported history of infection with gonorrhoea (57% vs 39%), chlamydia (49% vs 31%) and syphilis (23% vs 15%) as compared with clients who did not report chemsex. Baseline STI prevalence was higher in the chemsex group. Clients who reported chemsex at baseline had a higher prevalence of active gonorrhoea and chlamydia infection compared with the no-chemsex group (15% vs 9% and 9% vs 7%, respectively; table 1). One HCV seroconversion occurred during the study period (in the chemsex group), corresponding to a cumulative incidence proportion of 0.2% (1 of 432) over 2 years.
Chemsex at baseline leads to higher incidence of gonorrhoea and chlamydia
Median time to first diagnosis of gonorrhoea or chlamydia was shorter in the chemsex group (10.7 months; 95% CI: 9.4 to 14.0) compared with the no-chemsex group (16.4 months; 95% CI: 15.1 to 18.3) (figure 1A). This translated to a crude HR of 1.40 (95% CI: 1.18 to 1.67). The impact of chemsex on STI incidence remained after controlling for sociodemographic confounders: the adjusted HR for the effect of chemsex on STI incidence was 1.32 (95% CI: 1.10 to 1.57) (table 2; see also online supplemental table 1). This is equivalent to a marginal risk increase of 8.9 percentage points (95% CI: 8.5 to 9.4) 12 months after PrEP initiation.
Figure 1.
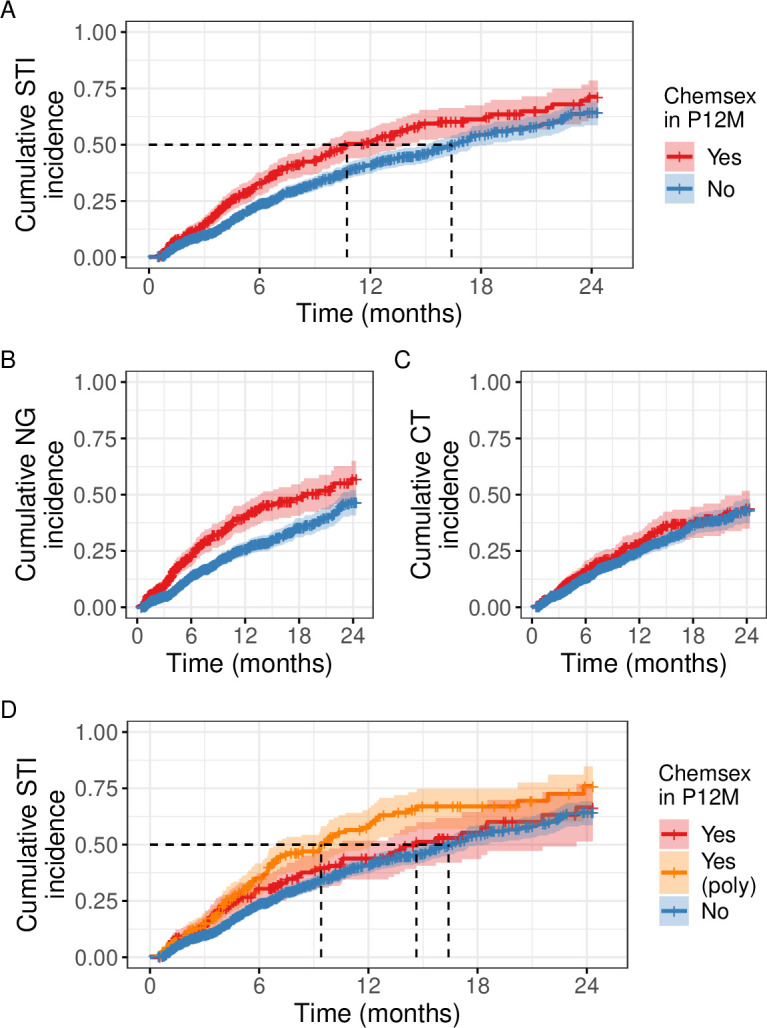
Cumulative STI incidence among pre-exposure prophylaxis users in the l’Actuel PrEP Cohort (2013–2020). (A) Gonorrhoea or chlamydia, any site. (B) Gonorrhoea, any site. (C) Chlamydia, any site. (D) Gonorrhoea or chlamydia, any site, chemsex stratified by polysubstance use (≥2 chemsex substances) or not (1 substance). The 95% CIs are shown as a shaded region, dotted lines show median time to first diagnosis. CT, Chlamydia trachomatis; NG, Neisseria gonorrhoeae; P12M: past 12 months. Created by the authors.
Table 2.
Effect of chemsex at baseline on time to first STI diagnosis among pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) users in the l’Actuel PrEP Cohort (2013–2020)
| Outcome | # of events | Crude models | Adjusted models |
| HR | HR | ||
| Model with chemsex only | |||
| Gonorrhoea or chlamydia | 614 | 1.40 (1.18 to 1.67) | 1.32 (1.10 to 1.57) |
| Gonorrhoea | 410 | 1.70 (1.38 to 2.08) | 1.59 (1.28 to 1.97) |
| Chlamydia | 369 | 1.15 (0.92 to 1.45) | 1.07 (0.84 to 1.36) |
| Model with chemsex and polysubstance use | |||
| Gonorrhoea or chlamydia | 614 | ||
| No chemsex | Reference | – | |
| Chemsex | 1.20 (0.94 to 1.53) | 1.12 (0.87 to 1.43) | |
| Polysubstance use | 1.61 (1.30 to 1.99) | 1.51 (1.21 to 1.89) | |
Created by the authors.
Models adjusted for age, education, income, PrEP regimen at baseline and year of entry into the cohort (all categorical).
Results were qualitatively identical when the models were restricted to cisgender gbMSM (online supplemental table 3).
gbMSM, gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men.
In STI-specific analyses, there was a clear separation of the cumulative incidence curve for the chemsex group for gonorrhoea but not chlamydia (figure 1B, C). The adjusted HRs for the effect of chemsex on STI incidence were 1.59 (95% CI: 1.28 to 1.97) for gonorrhoea and 1.07 (95% CI: 0.84 to 1.36) for chlamydia (table 2). The magnitude of the impact of chemsex on gonorrhoea incidence was similar across infection sites. In contrast, the adjusted HR for chlamydia was 1.21 (95% CI: 0.93 to 1.57) for rectal and throat infections, and 0.99 (95% CI: 0.64 to 1.51) for urethral infections (online supplemental table 2).
Polysubstance use and certain substances have a stronger effect on STI incidence
When chemsex was stratified according to polysubstance use, the median time to first STI diagnosis was 9.4 months (95% CI: 7.0 to 12.1) in the chemsex polysubstance use group, 14.6 months (95% CI: 10.5 to 23.4) in the single-substance chemsex group and 16.4 months (95% CI 15.1 to 18.3) in the no-chemsex group (figure 1D). Compared with no indication of chemsex at baseline, the adjusted HR for single-substance chemsex was 1.12 (95% CI: 0.87 to 1.43) and 1.51 (95% CI: 1.21 to 1.89) for polysubstance use (table 2).
In our analyses considering each chemsex substance separately, GHB, crystal meth and crack were associated with a shorter median time to first STI diagnosis. In contrast, stratifying chemsex by cocaine or ecstasy did not substantially change the median time (online supplemental figure 3).
Age, education and income are effect modifiers of the chemsex–STI relationship
The effect of chemsex at baseline on STI incidence varied by age: the HRs were 1.71 (95% CI: 1.36 to 2.15) among PrEP users aged 18–35 years, 0.77 (95% CI: 0.55 to 1.07) among those aged 36–50 years and 1.53 (95% CI: 0.90 to 2.60) among those >50 years old. When including a chemsex-education product term, the effect of chemsex was greater among clients with secondary education or less (HR=1.61; 95% CI: 0.98 to 2.64) than among clients with post-secondary education (HR=1.27; 95% CI: 1.04 to 1.55). For income, the magnitude of the effect of chemsex decreased among higher-income clients: the HRs were 1.71 (95% CI: 1.23 to 2.36) for clients reporting income of ≤$C35 000, 1.25 (95% CI: 0.96 to 1.63) for clients reporting $C35 001–75 000 and 1.05 (95% CI: 0.72 to 1.54) for clients reporting income of >$C75 000 (table 3).
Table 3.
Modification of the effect of chemsex at baseline on time to first STI diagnosis among pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) users by age, education or income
| No chemsex reported | Chemsex reported | HR (95% CI) for chemsex within strata | |||
| n | HR | n | HR | ||
| Effect modification by age | |||||
| 18–35 | 750 | 1.57 (1.17 to 2.10) | 290 | 2.69 (1.96 to 3.68) | 1.71 (1.36 to 2.15) |
| 36–50 | 575 | 1.30 (0.97 to 1.74) | 164 | 1.00 (0.67 to 1.48) | 0.77 (0.55 to 1.07) |
| >50 | 254 | 1.00 (ref.) |
53 | 1.53 (0.90 to 2.60) |
1.53 (0.90 to 2.60) |
| Effect modification by education | |||||
| Secondary or under | 230 | 1.00 (ref.) | 87 | 1.61 (0.98 to 2.64) | 1.61 (0.98 to 2.64) |
| Post-secondary | 1349 | 1.16 (0.81 to 1.65) | 420 | 1.47 (1.03 to 2.11) | 1.27 (1.04 to 1.55) |
| Effect modification by income ($C) | |||||
| ≤35 000 | 449 | 1.00 (ref.) | 162 | 1.71 (1.23 to 2.36) | 1.71 (1.23 to 2.36) |
| 35 001–75 000 | 668 | 1.01 (0.76 to 1.34) | 238 | 1.26 (0.92 to 1.71) | 1.25 (0.96 to 1.63) |
| >75 000 | 462 | 1.18 (0.88 to 1.57) | 107 | 1.24 (0.82 to 1.86) | 1.05 (0.72 to 1.54) |
Created by the authors.
Models adjusted for age, education, income, PrEP regimen at baseline and year of entry into the cohort (all categorical).
For education and income, the group size n in each cell is the average group size from the imputed datasets.
Discussion
Among gbMSM using PrEP, chemsex is linked to increased STI incidence, highlighting unmet prevention needs arising from the substance use and STI syndemic.46 47 We found that participants using PrEP were 32% (95% CI: 10% to 57%) more likely to be diagnosed with gonorrhoea or chlamydia if they reported chemsex at baseline, relative to those who did not report chemsex. This was equivalent to a 1-year increase of 8.9 percentage points (95% CI: 8.5 to 9.4) in STI risk. This effect was heterogeneous, however, and polysubstance use had a stronger effect on STI incidence. Despite the high STI incidence, there were no incident HIV infections in this cohort, demonstrating that PrEP is meeting a harm-reduction need for gbMSM, including those who practise chemsex.
Using baseline data, we observed higher prevalence of gonorrhoea (15% vs 9%) and chlamydia (9% vs 7%) infection among PrEP users who reported chemsex. These results are consistent with previous cross-sectional studies that showed an association with self-reported and lab-confirmed STI diagnosis among gbMSM.11 14 15 In longitudinal analyses, chemsex at baseline led to higher cumulative incidence of gonorrhoea and chlamydia. Analyses stratified by infection site showed that chemsex at baseline was strongly linked with gonorrhoea incidence regardless of infection site. In contrast, the results suggest a potential effect on chlamydia infection at the rectum or throat and no effect on urethral infection. The stronger impact of chemsex on gonorrhoea incidence and the difference for chlamydia by anatomical site could be due to differences in transmission efficiencies. For example, transmission from the throat to the urethra or rectum during oral sex or anal play may be more likely for gonorrhoea than chlamydia.48 49
People who engage in chemsex may use different substances which may have different impacts on STI acquisition risk. We found that clients reporting substances commonly associated with chemsex culture—crystal meth and GHB—had shorter median time to STI diagnosis. In contrast, substances with more diverse uses (cocaine and ecstasy) did not show this trend.5 6 50 Reporting sex while under the influence of cocaine or ecstasy may reflect a combination of chemsex and substance use prior to a sexual encounter (eg, while at a bar or club). A previous study in Montréal found that sexualised substance use with crystal meth or GHB had stronger association with condomless anal sex than cocaine or ecstasy.9 In contrast, a study in the Netherlands found similar magnitude of effect for GHB, ecstasy and cocaine, a difference that could potentially be attributed to different patterns of substance use in this country.35 Additionally, some authors have argued that sexualised use of crystal meth and GHB may be linked to higher risk of harm due to their stronger effects and less documented history of use.5 28 Taken together, this evidence highlights the importance of considering the complexities of chemsex when developing harm-reduction interventions.
We also observed possible modification of the effect of chemsex on STI incidence by age, education and income. Qualitative evidence suggests that some gbMSM incorporate harm-reduction strategies in their chemsex practices, such as strict condom use, open discussion of HIV serostatus, and having established plans to address overdoses or loss of consciousness.10 51 It is possible that the stronger effect of chemsex among gbMSM aged 18–35 years and >50 years is due to age-dependent differences in the presence of such strategies and to different substance use patterns. Similarly, the smaller effect of chemsex on STI incidence for higher levels of income and post-secondary education may be due to differences in sexual mixing patterns and access to chemsex substances. This is in line with syndemic theory as applied to STIs and substance use among gbMSM,46 where health disparities are rooted in structural conditions such as social and economic marginalisation (reflected by lower education, income and access to prevention strategies).
Our results should be interpreted considering several limitations. First, despite adjusting for sociodemographic confounders, residual confounding of the chemsex–STI relationship cannot be ruled out. Second, the dynamic nature of PrEP use means that discontinuation is common, reducing lengths of follow-up. However, this type of attrition was non-differential between groups.31 Third, there were no questions on chemsex frequency and chemsex was only measured at the initial consultation. To alleviate this shortcoming, we restricted our follow-up to the first 2 years, since there is evidence of little within-person change in chemsex practices over this time frame.52 Fourth, it is possible some clients who practised chemsex did not report it due to perceived stigma. This misclassification would be non-differential with respect to STI outcome ascertainment, leading to a bias towards the null. Lastly, there were not enough transgender men and women in the study to perform stratified analyses for these individuals who might have different STI acquisition risks.
The strengths of our study include the use of prospectively collected, longitudinal clinical data spanning 7 years of follow-up from a large cohort, enabling more granular analyses of chemsex and exploratory effect-modification analyses. The STI data came from lab-confirmed diagnoses and were prospectively collected through regular screening, an important characteristic given that many STIs are asymptomatic.
Conclusions
Among gbMSM using PrEP, chemsex and polysubstance use led to increased incidence of gonorrhoea and chlamydia. The lack of incident HIV diagnoses among PrEP users suggests that PrEP is meeting a prevention need among people who practise chemsex. However, the prevalence of chemsex and high STI incidence in this population highlight the need for integrated services that address the intersection of sexualised substance use and sexual health. Future work should examine the role of specific substances and potential effect modification by age, education and income to tailor services to subpopulations with the greatest unmet prevention needs.
Key messages.
Chemsex at baseline is linked to 32% higher hazard of gonorrhoea or chlamydia diagnoses among gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (gbMSM) using pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in a large cohort in Montréal.
Despite high STI incidence, no HIV infections were observed among gbMSM using PrEP, demonstrating that PrEP is meeting a harm-reduction need.
The impact of chemsex on STI incidence is stronger among gbMSM reporting polysubstance use and those reporting specific chemsex substances.
Age, education and income are potentially modifying the effect of chemsex on STI incidence.
sextrans-2021-055215supp002.pdf (51.6KB, pdf)
sextrans-2021-055215supp003.pdf (183.8KB, pdf)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participants of the l’Actuel PrEP Cohort, as well as all the clinicians, nurses and research staff without whom this work would not have been possible.
Footnotes
Handling editor: Jonathan Ross
Contributors: JLFA, MM-G, DP, RT and ZRG conceptualised the study. JLFA planned the statistical analyses with input from MM-G, DP, ZRG and MB. CT, MV, LC and JS organised data collection and management. JLFA conducted the background literature review, formatted the databases and performed the analyses. JLFA drafted the manuscript and all authors revised it for important intellectual content. All authors have approved the final version of the article. MM-G acts as the guarantor for the overall content.
Funding: This work was funded by the Canadian Foundation for AIDS Research (CANFAR) and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR). JLFA received a Frederick Banting and Charles Best Canada Graduate Scholarship (Master’s) from CIHR. MM-G’s research programme is funded by a Tier II Canada Research Chair in Population Health Modelling.
Competing interests: MM-G reports an investigator-sponsored research grant from Gilead Sciences, and contractual arrangements from the Institut national de santé publique du Québec (INSPQ), the Institut d’excellence en santé et services sociaux (INESSS), the WHO, and the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), all outside of the submitted work. RT is a member of advisory boards for AbbVie, Gilead, Merck and ViiV; has received grants/honoraria from AbbVie, Gilead, Merck and ViiV; and has participated in clinical trials with AbbVie, Gilead, Merck, GSK/ViiV and Janssen.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Data availability statement
Data are available upon reasonable request.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not required.
Ethics approval
This study involves human participants and ethics approval was obtained through the Veritas Institutional Review Board, and the Institutional Review Board of McGill University (A12-E84-18A) approved the secondary data analyses presented in this paper. Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
References
- 1. Chow EPF, Grulich AE, Fairley CK. Epidemiology and prevention of sexually transmitted infections in men who have sex with men at risk of HIV. Lancet HIV 2019;6:e396–405. 10.1016/S2352-3018(19)30043-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Public Health Agency of Canada . Report on sexually transmitted infections in Canada, 2017. public health agency of Canada, 2019. Available: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/diseases-conditions/report-sexually-transmitted-infections-canada-2017.html [Accessed 13 Feb 2020].
- 3. Scott HM, Klausner JD. Sexually transmitted infections and pre-exposure prophylaxis: challenges and opportunities among men who have sex with men in the US. AIDS Res Ther 2016;13:5. 10.1186/s12981-016-0089-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Unemo M, Jensen JS. Antimicrobial-Resistant sexually transmitted infections: gonorrhoea and Mycoplasma genitalium. Nat Rev Urol 2017;14:139–52. 10.1038/nrurol.2016.268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Bourne A, Reid D, Hickson F. The Chemsex study: drug use in sexual settings among gay and bisexual men in Lambeth, Southwark and Lewisham. London: Sigma Research, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, 2014. https://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/id/eprint/2197245 [Google Scholar]
- 6. Stuart D. Chemsex: origins of the word, a history of the phenomenon and a respect to the culture. DAT 2019;19:3–10. 10.1108/DAT-10-2018-0058 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Flores-Aranda J, Goyette M, Aubut V, et al. Let’s talk about chemsex and pleasure: the missing link in chemsex services. DAT 2019;19:189–96. 10.1108/DAT-10-2018-0045 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Maxwell S, Shahmanesh M, Gafos M. Chemsex behaviours among men who have sex with men: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Drug Policy 2019;63:74–89. 10.1016/j.drugpo.2018.11.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Blais M, Otis J, Lambert G, et al. Consommation de substances en contexte sexuel chez des hommes gbHSH de Montréal : 2009-2016. Drogues, santé et société 2018;17:76. 10.7202/1062117ar [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Bourne A, Reid D, Hickson F, et al. Illicit drug use in sexual settings ('chemsex') and HIV/STI transmission risk behaviour among gay men in South London: findings from a qualitative study. Sex Transm Infect 2015;91:564–8. 10.1136/sextrans-2015-052052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Curtis TJ, Rodger AJ, Burns F, et al. Patterns of sexualised recreational drug use and its association with risk behaviours and sexual health outcomes in men who have sex with men in London, UK: a comparison of cross-sectional studies conducted in 2013 and 2016. Sex Transm Infect 2020;96:197–203. 10.1136/sextrans-2019-054139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hammoud MA, Vaccher S, Jin F, et al. The new MTV generation: using methamphetamine, Truvada™, and Viagra™ to enhance sex and stay safe. Int J Drug Policy 2018;55:197–204. 10.1016/j.drugpo.2018.02.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Guerra FM, Salway TJ, Beckett R, et al. Review of sexualized drug use associated with sexually transmitted and blood-borne infections in gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men. Drug Alcohol Depend 2020;216:108237. 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.108237 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Ottaway Z, Finnerty F, Amlani A, et al. Men who have sex with men diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection are significantly more likely to engage in sexualised drug use. Int J STD AIDS 2017;28:91–3. 10.1177/0956462416666753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Pufall EL, Kall M, Shahmanesh M, et al. Sexualized drug use ('chemsex') and high-risk sexual behaviours in HIV-positive men who have sex with men. HIV Med 2018;19:261–70. 10.1111/hiv.12574 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Direction générale de la santé publique . La prophylaxie préexposition au virus de l’immunodéficience humaine : Guide pour les professionnels de la santé du Québec. Ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux, 2019. Available: https://publications.msss.gouv.qc.ca/msss/document-000313/ [Accessed 21 Aug 2020].
- 17. Smith DK, Pals SL, Herbst JH, et al. Development of a clinical screening index predictive of incident HIV infection among men who have sex with men in the United States. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2012;60:421–7. 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318256b2f6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux . Direction générale de la santé publique. Avis intérimaire sur la prophylaxie préexposition au virus de l’immunodéficience humaine, 2013. Available: https://numerique.banq.qc.ca/patrimoine/details/52327/2303869 [Accessed 24 Mar 2021].
- 19. Health Canada . Regulatory Decision Summary - TRUVADA, 2016. Available: https://hpr-rps.hres.ca/reg-content/regulatory-decision-summary-detail.php?linkID=RDS00107 [Accessed 20 Feb 2021].
- 20. Spinner CD, Boesecke C, Zink A, et al. Hiv pre-exposure prophylaxis (PreP): a review of current knowledge of oral systemic HIV PreP in humans. Infection 2016;44:151–8. 10.1007/s15010-015-0850-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Nguyen V-K, Greenwald ZR, Trottier H, et al. Incidence of sexually transmitted infections before and after preexposure prophylaxis for HIV. AIDS 2018;32:523–30. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Traeger MW, Cornelisse VJ, Asselin J, et al. Association of HIV preexposure prophylaxis with incidence of sexually transmitted infections among individuals at high risk of HIV infection. JAMA 2019;321:1380. 10.1001/jama.2019.2947 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Traeger MW, Schroeder SE, Wright EJ, et al. Effects of pre-exposure prophylaxis for the prevention of human immunodeficiency virus infection on sexual risk behavior in men who have sex with men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis 2018;67:676–86. 10.1093/cid/ciy182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Marcus JL, Katz KA, Krakower DS, et al. Risk Compensation and Clinical Decision Making - The Case of HIV Preexposure Prophylaxis. N Engl J Med 2019;380:510–2. 10.1056/NEJMp1810743 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Marcus JL, Volk JE, Snowden JM. Concerns about a study on sexually transmitted infections after initiation of HIV preexposure prophylaxis. AIDS 2018;32:955–6. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001769 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Flores-Aranda J, Goyette M, Larose-Osterrath C. Online intervention as strategy to reach men who have sex with other men and who use substances in a sexual context. development of the MONBUZZ.ca project. Front Psychiatry 2019;10:183. 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Stardust Z, Kolstee J, Joksic S, et al. A community-led, harm-reduction approach to chemsex: case study from Australia's largest gay City. Sex Health 2018;15:179. 10.1071/SH17145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Stuart D, Weymann J. ChemSex and care-planning: one year in practice. HIV Nursing 2015;15:24–8. [Google Scholar]
- 29. Greenwald ZR, Maheu-Giroux M, Szabo J, et al. Cohort profile: l'Actuel pre-exposure prophylaxis (PreP) cohort study in Montreal, Canada. BMJ Open 2019;9:e028768. 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028768 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Xia Y, Greenwald ZR, Milwid RM, et al. Pre-Exposure prophylaxis uptake among men who have sex with men who used nPEP: a longitudinal analysis of attendees at a large sexual health clinic in Montréal (Canada). J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2020;85:408–15. 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002472 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Flores Anato JL, Panagiotoglou D, Greenwald ZR, et al. Chemsex practices and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PreP) trajectories among individuals consulting for PreP at a large sexual health clinic in Montréal, Canada (2013-2020). Drug Alcohol Depend 2021;226:108875. 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.108875 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Tan DHS, Hull MW, Yoong D, et al. Canadian guideline on HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis and nonoccupational postexposure prophylaxis. CMAJ 2017;189:E1448–58. 10.1503/cmaj.170494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Messier-Peet M, Apelian H, Lambert G. Chemsex & Mental Health in gbMSM in Montreal: Results from Engage Cycle 1, 2018. Available: https://www.engage-men.ca/our-work/orals/ [Accessed 21 May 2020].
- 34. Daskalopoulou M, Rodger A, Phillips AN, et al. Recreational drug use, polydrug use, and sexual behaviour in HIV-diagnosed men who have sex with men in the UK: results from the cross-sectional ASTRA study. Lancet HIV 2014;1:e22–31. 10.1016/S2352-3018(14)70001-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Evers YJ, Van Liere GAFS, Hoebe CJPA, et al. Chemsex among men who have sex with men living outside major cities and associations with sexually transmitted infections: a cross-sectional study in the Netherlands. PLoS One 2019;14:e0216732. 10.1371/journal.pone.0216732 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Tomkins A, Ahmad S, Cannon L, et al. Prevalence of recreational drug use reported by men who have sex with men attending sexual health clinics in Manchester, UK. Int J STD AIDS 2018;29:350–6. 10.1177/0956462417725638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. van BS, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K. Mice: multivariate imputation by Chained equations in R. J Stat Softw 2011;45:1–67. [Google Scholar]
- 38. White IR, Royston P, Wood AM. Multiple imputation using chained equations: issues and guidance for practice. Stat Med 2011;30:377–99. 10.1002/sim.4067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Austin PC. Absolute risk reductions and numbers needed to treat can be obtained from adjusted survival models for time-to-event outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol 2010;63:46–55. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.03.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Schomaker M, Heumann C. Bootstrap inference when using multiple imputation. Stat Med 2018;37:2252–66. 10.1002/sim.7654 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Knol MJ, VanderWeele TJ. Recommendations for presenting analyses of effect modification and interaction. Int J Epidemiol 2012;41:514–20. 10.1093/ije/dyr218 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. R Core Team . R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: : R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2019. Available: https://www.R-project.org/ [Accessed 23 Dec 2020].
- 43. Kassambara A, Kosinski M, Biecek P. survminer: Drawing Survival Curves using “ggplot2.”, 2019. Available: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survminer [Accessed 23 Dec 2020].
- 44. Therneau TM. Survival: a package for survival analysis in R, 2019. Available: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival [Accessed 23 Dec 2020].
- 45. van BS, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K, Vink G. Mice: multivariate imputation by Chained equations, 2021. Available: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=mice [Accessed 16 Jun 2021].
- 46. Halkitis PN, Wolitski RJ, Millett GA. A holistic approach to addressing HIV infection disparities in gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men. Am Psychol 2013;68:261–73. 10.1037/a0032746 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Singer M, Bulled N, Ostrach B, et al. Syndemics and the biosocial conception of health. Lancet 2017;389:941–50. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30003-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Barbee LA, Khosropour CM, Dombrowski JC, et al. An estimate of the proportion of symptomatic gonococcal, chlamydial and non-gonococcal non-chlamydial urethritis attributable to oral sex among men who have sex with men: a case-control study. Sex Transm Infect 2016;92:155–60. 10.1136/sextrans-2015-052214 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Chow EP, Fairley CK. The role of saliva in gonorrhoea and Chlamydia transmission to extragenital sites among men who have sex with men: new insights into transmission. J Int AIDS Soc 2019;22 Suppl 6:e25354. 10.1002/jia2.25354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. W Hawkins B, Armstrong HL, Kesselring S, et al. Substance use as a mechanism for social inclusion among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men in Vancouver, Canada. Subst Use Misuse 2019;54:10.1080/10826084.2019.1621901:1945–55. 10.1080/10826084.2019.1621901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Santoro P, Rodríguez R, Morales P, et al. One “chemsex” or many? Types of chemsex sessions among gay and other men who have sex with men in Madrid, Spain: findings from a qualitative study. Int J Drug Policy 2020;82:10.1016/j.drugpo.2020.102790 10.1016/j.drugpo.2020.102790 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Sewell J, Cambiano V, Speakman A, et al. Changes in chemsex and sexual behaviour over time, among a cohort of MSM in London and Brighton: findings from the AURAH2 study. Int J Drug Policy 2019;68:10.1016/j.drugpo.2019.03.021:54–61. 10.1016/j.drugpo.2019.03.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
sextrans-2021-055215supp001.pdf (4.3MB, pdf)
sextrans-2021-055215supp002.pdf (51.6KB, pdf)
sextrans-2021-055215supp003.pdf (183.8KB, pdf)
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request.


