Abstract
Helicobacter pylori virulence is associated with the presence of the cag pathogenicity island (PAI). The cag PAI is involved in the ability to induce interleukin-8 (IL-8) secretion by human cells, which is implicated in the inflammatory response of the gastric mucosa to H. pylori infection. The aim of this study was to determine whether the genetic structure of the cag PAI is conserved and whether it is linked to IL-8 induction ability. Detection of specific markers (cagA, picB, cag13-cag14, virD4, and IS605) by PCR and dot blot hybridization and long-distance PCR determination of the presence of cagI, cagII, and the middle region of the cag PAI were performed on 153 strains isolated from adults suffering from ulcers (n = 79) or gastritis (n = 74). IL-8 induction ability was evaluated by coculture of the strains with HEp-2 cells. Eighty-three strains (54.3%) had an entire cag PAI, 12 strains (7.8%) had the cag PAI split in two, 49 strains (32%) had no cag PAI, and 9 strains exhibited other structural combinations. The presence of an entire cag PAI was statistically correlated with the presence of IS605 (P = 0.006) and the ability to induce IL-8 secretion but not with clinical presentation of the infection. The structure of the cag PAI appears to be rather conserved and is related to the proinflammatory power of a strain. The existence of strains inducing IL-8 secretion regardless of the cag PAI structure suggests that this region is not the only requirement for IL-8 secretion.
Helicobacter pylori is recognized as the causative agent of gastritis and ulcer disease and is also a major risk factor for gastric cancer or mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (5, 12, 13, 21). The pathogenesis of the diseases associated with H. pylori is not yet fully understood, although several hypotheses have been proposed (3). The polymorphism of the clinical manifestations associated with H. pylori infection is potentially due to differences in virulence among individual H. pylori strains (3, 6, 7, 16, 29). Nevertheless, there are no reliable virulence markers that can be used to predict the severity of the disease associated with H. pylori infection.
One of the most studied putative virulence factors is the CagA protein, encoded by the cagA gene (9, 27). This gene is reported to be present in 60 to 70% of European isolates (9, 27), and the presence of cagA is statistically associated with duodenal ulceration, gastric mucosal atrophy, and gastric cancer (6, 9, 29). The cagA gene is one of the 31 genes of a pathogenicity island (PAI) called the cag PAI (7). The presence of cagA is considered a marker of presence of the cag PAI (1, 7).
The cag PAI is a 40-kb locus inserted in the chromosomal glutamate racemase gene (7). Its G+C content (35%) differs from the G+C content of the rest of the genome (39%), suggesting that it was acquired from another organism by horizontal transfer (1, 2, 7, 26). Several studies have revealed that the cag PAI can be found either as a single uninterrupted unit, split into two regions (cagI and cagII) either by an insertion sequence called IS605 or by a large piece of chromosomal DNA, or partially deleted (7, 9, 15, 20).
It has been shown that the cag PAI is involved in the induction of interleukin-8 (IL-8) secretion by human cells colonized by H. pylori. This property may be related to the proinflammatory power of a strain and thus to its virulence. Indeed, strains inducing IL-8 secretion have been associated with the presence of the cagA gene and with severe diseases (11, 23), although this has been contested recently (15, 20). Knockout of most of the genes of this region (except cagA and cagN) resulted in a decrease or a suppression of the IL-8 induction ability of a strain (1, 7, 10, 23, 28). The mechanism of IL-8 induction is not yet understood. However, some genes of the cag PAI are homologous to genes of a type IV secretion pathway, suggesting that this region encodes a secretion system involved in the export of virulence determinants (7, 8, 28).
Because the cag PAI has a variable genetic structure and because this structure may influence the IL-8 induction ability of the strain, we aimed to determine the cag PAI structure for a substantial number of French strains in order to learn whether the structure of this region is conserved and whether certain cag PAI structures are specifically associated with the ability to induce IL-8 secretion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients.
Biopsy specimens were sampled from 153 consecutive H. pylori-infected adults from a group of patients who had undergone upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in the Gastroenterology Department of Poitiers University Hospital (Poitiers, France) because of dyspeptic complaints. None of the patients was receiving antisecretory or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The patient population consisted of 107 males (aged 17 to 95 years; mean age, 48.2 years), and 46 females (aged 22 to 86 years; mean age, 57.6 years). The presence of an ulcer was based on endoscopic examination of the stomach and duodenum. Each patient's history was investigated for an earlier diagnosis of peptic ulcer. If the patient's documented history or endoscopic examination revealed peptic ulcer disease, the patient was considered to have an ulcer. Otherwise, he or she was considered to have dyspepsia or gastritis only. Patients were assigned to four groups: duodenal ulcer (n = 47), gastric ulcer (n = 22), both duodenal and gastric ulcers (n = 10), and nonulcer dyspepsia or chronic gastritis (n = 74).
H. pylori strains and culture conditions.
Gastroduodenal biopsy specimens were sent to the laboratory in 1 ml of transport medium. The specimens were ground, spread on Columbia agar plates containing 5% horse blood (BioMerieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France), and incubated under microaerobic conditions at 37°C for 2 to 5 days. Bacteria were identified as H. pylori by standard criteria, and the strains were stored at −80°C in 10% glycerol broth. These were referred to as stock cultures. Three reference strains were used as controls: strains ATCC 26695, J99, and Tx30a.
DNA isolation.
DNA was isolated from the cultured bacteria by harvesting cells from a plate and resuspending them in 500 μl of TE (10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA [pH 8.0]). Bacteria were lysed by addition of 50 μl of a 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate solution and 1.25 μl of a 20-mg/ml proteinase K solution (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). The mixture was incubated for 1 h at 37°C. Proteins were precipitated by 500 μl of phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (Eurobio, Les Ullis, France). After centrifugation, the supernatant was removed and DNA was precipitated twice with absolute ethanol at −20°C and washed with 75% ethanol at −20°C (Merck). After centrifugation, the pellet was dried and resuspended in 200 μl of deionized water containing 50 μg of RNase (Merck)/ml. The mixture was incubated for 1 h at 60°C, and the DNA extracts were stored at −20°C.
PCR-based typing and long-distance PCR.
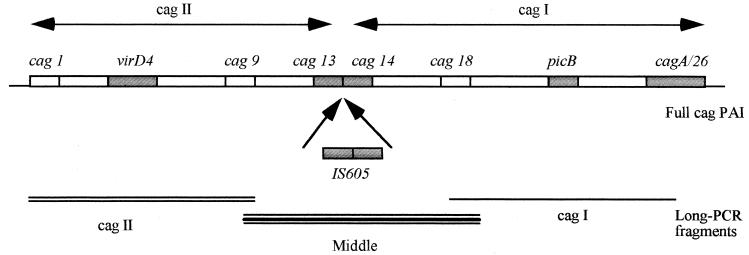
PCRs were performed in a volume of 100 μl using rTaq polymerase (Pharmacia Biotech, Orsay, France). The conditions used were those recommended by the manufacturer. The primers used to detect the presence of cagA, picB, virD4, cag13-cag14, IS605, and the cag-empty site are listed in Table 1. PCR amplification was performed under the usual conditions. For the long-distance PCR investigation, the primers used (Table 1) were designed so that the amplified products covered the entire cag PAI: from cag1 to cag9, from cag9 to cag18, and from cag18 to cag26 (see Fig. 1). The long-distance PCR amplification was performed with the Long-PCR kit (Perkin-Elmer), as recommended by the supplier. PCR products were visualized by electrophoresis on 1.8% agarose gels (Eurobio) after 20 to 30 min of migration at 150 V.
TABLE 1.
Primers used to study the cag PAI structure
| Amplified area (reference) | Primer names | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| cagA (27) | F1 | GATAACAGCCAAGCTTTTGAGG |
| B1 | CTGCAAAAGATTGTTTGGCAGA | |
| picB | picB/AF | GGCTTTATCAAAGAATGGAGCGAGCG |
| picB/AR | TACTCAATAGCTCTTCTATGAGC | |
| picB/BF | GTGGAGGCTCTAAAGAGCAGGGC | |
| picB/BR | TGACATACTCCCCACCCATTGCG | |
| cag13-cag14 | cag13F | CAATAGTGGGAGCTTAGTGCC |
| cag14R | GCGATTGGTGGCTACTTATCGC | |
| virD4 | virD4AF | TTTATGATGATAATCGATCGCC |
| virD4AR | GAACGCCTGCCCTGCGTAAGCG | |
| virD4BF | TTTCATAGGTTCTATGGCAAGCGGG | |
| virD4BR | TTAGCGCCATTCCTACCATAACC | |
| cag empty site (19) | Luni1 | ACATTTTGGCTAAATAAACGCTG |
| 5280 | GGTTGCACGCATTTTCCCTTAATC | |
| IS605 TnpA | 605AF | CGCCTTGATCGTTTCAGGATTAGC |
| 605AR | CAACCAACCGAAGCAAGCATAATC | |
| IS605 TnpB | 605BF | GGCTGTTCTAGGGTCGTGTATAAC |
| 605BR | CAAGCTAGATGATGCAATCTAGCTACC | |
| Full IS605 (18) | ORF18F | CGCCTTGATCGTTTCAGGATTAGC |
| ORF19R | CAAGCTAGATGCAATCTAGCTACC | |
| cagII | cag1F | TGTTGTGTCTTGAGCGGTGC |
| cag9R | GGCGATGGTCTCTTTTATCGCC | |
| Middle zone | cag9F | GGCGATAAAAGAGACCATCGCC |
| cag18R2 | GCTGAGCAATGCGGAATAT | |
| cagI | cag18F2 | ATATTCCGCATTGTTGCTCAGC |
| cag26R | GCTTGCCTGTTATCCCTATCG |
FIG. 1.
Area amplified by long-distance PCR. Boxes, genes, detected by PCR and dot blot analysis.
Determination of cagA, picB, virD4, and cag13-cag14 status by dot blot hybridization.
To test the sensitivity and the specificity of PCR with primers specific for cagA, picB, virD4, and cag13-cag14, the 153 strains were analyzed by dot blotting using a method previously described (4). Briefly, cagA, picB, virD4, and cag13-cag14 probes were generated by PCR from chromosomal DNA of H. pylori ATCC 26695 using primers F1 and B1 for cagA, primers 544BF and 544BR for picB, primers 524AF and 524AR for virD4, and primers cag13F and cag14R for cag13-cag14. DNA from the 153 H. pylori strains was filtered through a 0.45-μm-pore-size nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad, Ivry sur Sein, France) using a 96-well dot blot apparatus filtration system. DNA probes, labeled by random priming, were incubated with the membrane, and autoradiography was performed with X-ray film (Kodak).
IL-8 induction by H. pylori strains.
The IL-8 induction ability of H. pylori was investigated on HEp-2 cells as previously described (4). Briefly, we cocultured HEp-2 cells for 24 h with an H. pylori suspension containing 5 × 108 bacteria/ml. Negative and positive controls were included. The medium was removed, and the IL-8 produced in the supernatant was evaluated by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using the specific ELISA kit provided by Diaclone (Besançon, France) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Statistical method.
Analysis of data was performed by using the chi-square test with Yates' correction. Probability levels (P) of <0.05% were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Statuses of the strains with regard to various genes of the cag PAI.
The presence of the cagA, picB, virD4, and cag13-cag14 genes and of IS605 was determined by PCR and dot blot hybridization. Those genes were choosen because they are well distributed over the cag PAI. Strains were considered negative for a gene if they tested negative by both PCR and dot blot hybridization. All the other strains were considered positive. The correlation between results obtained for the various genes by PCR and by dot blot hybridization ranged from 95 to 100%. The statuses of the 153 strains with regard to the cagA, picB, virD4, and cag13-cag14 genes and IS605 are shown in Table 2. None of these five genes correlated with the clinical manifestations of the infection.
TABLE 2.
Statuses of 153 strains with regard to various genes and fragments of the cag PAI
| Structure of cag PAI | No. (%) of strains | No. of strains from patients with:
|
No. of strains with the indicated geneb
|
No. of strains with the indicated regionc
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUDa | Ulcer | virD4 | cag13–cag14 | picB | cagA | IS605 | cagII | Middle | cagI | ||
| Uninterrupted | 83 (54.3) | 40 | 43 | 81 | 70 | 82 | 82 | 22 | 64 | 78 | 53 |
| No cag PAI | 49 (32) | 8 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Split in two | 12 (7.8) | 23 | 26 | 12 | 0 | 12 | 11 | 6 | 9 | 0 | 8 |
| Otherd | 9 (5.9) | 3 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
NUD, nonulcer dyspepsia.
By PCR and dot blot hybridization.
By long-distance PCR.
One strain had the middle region and cagII, two strains had the middle region and cagI, one strain had cagII only, one strain had cagI only, one strain had the middle region only, and three strains had cagA only.
The presence of the cag PAI (cag PAI status) was systematically investigated by PCR using primers directed to the regions flanking the cag PAI. Therefore, if a full or partial cag PAI was present, the PCR could not be completed because of the size of the fragment to be amplified. If the cag PAI was absent, an amplification product of 500 bp was obtained. In this study we amplified the 500-bp fragment for 49 of 153 strains (32%), suggesting that these 49 strains did not have a cag PAI. Most, if not all, of these 49 strains were negative for the cagA, picB, virD4, and cag13-cag14 genes and for IS605 (49, 47, 49, 49, and 44 strains, respectively, were negative for the genes indicated) as determined by PCR and dot blot hybridization, confirming the absence of the cag PAI.
Structure of the cag PAI as determined by long-distance PCR.
The structure of the cag PAI was investigated using long-distance PCR. Primers were selected so that the amplified products covered the whole cag PAI (Fig. 1). The presence of the cagI part of the cag PAI was determined using primers specific to the cag18 and cag26 genes, that of cagII was determined using primers specific to the cag1 and cag9 genes, and that of the middle region of the cag PAI, where the separation mediated by IS605 is thought to occur, was detected using primers specific to the cag9 and cag18 genes. The prevalence of each of these fragments is shown in Table 2.
To establish the structure of the cag PAI, we hypothesized that the strains possessed the cagII part of the cag PAI when they were positive for virD4 or by long-distance PCR with primers cag1F and cag9R. They were considered positive for the middle region of the cag PAI when they were positive for cag13-cag14 or by long-distance PCR with primers cag9F and cag18R2. They were considered positive for the cagI part of the cag PAI when they possessed cagA and picB, or if they were positive by long-distance PCR with primers cag18F2 and cag26R. All the strains bearing at least one of these three fragments had positive cag PAI statuses (see above). Strains were considered negative for the portion studied when they were negative with by PCR, dot blot hybridization, and long-distance PCR.
Under these conditions three main cag PAI structures were observed: an uninterrupted cag PAI, no cag PAI, and a cag PAI split in two (Table 2). Nine strains did not fall into any of these three major groups: one strain had the middle region and cagII, two strains had the middle region and cagI, one strain had cagII only, one strain had cagI only, one strain had the middle region only, and three strains had the cagA gene only.
Of the 153 strains, 33 (21.6%) possessed an IS605. The distribution of IS605-positive strains over the different cag PAI structure groups is shown in Table 2. The presence of IS605 was statistically associated with the presence of an integral cag PAI, either uninterrupted or split in two (P = 0.0065).
Correlation between the cag PAI and IL-8 induction.
The ability of H. pylori to induce IL-8 secretion by eucaryotic cells was investigated by using 138 of the 153 isolates. A cutoff value of 71 pg/ml was established using the Tx30a reference strain, which is known as a non-IL-8 inducer (4). Among the 138 strains tested, 81 (58.7%) induced IL-8 secretion by the HEp-2 cells (from 71 to 4,071 pg/ml) while 57 (41.3%) induced no or low IL-8 secretion (from 0 to 71 pg/ml). The ability of a given strain to induce IL-8 secretion correlated with the structure of the cag PAI (Table 3). Strains possessing the entire cag PAI (either uninterrupted or split in two) induced IL-8 secretion significantly more often than strains with no cag PAI. However, no statistical difference with regard to IL-8 induction ability was observed between strains possessing an uninterupted cag PAI and strains with a cag PAI split in two. Neither the IL-8 induction ability nor the cag PAI structure was correlated with the clinical manifestations of the infection (Table 2).
TABLE 3.
Correlations between the structure of the cag PAI and IL-8 induction ability
| Structure of cag PAI | No. of IL-8 inducers/ total no. of strains (%) | Avg (SD) IL-8 production (pg/ml) |
|---|---|---|
| Uninterrupted | 60/78 (76.9) | 454.1 (751.7) |
| No cag PAI | 8/40 (20) | 102 (280.5) |
| cag PAI split in two | 8/12 (66.6) | 632.9 (864.5) |
| Other combinations | 4/8 (55.5) | —a |
One strain had the middle region and cagII (IL-8 production, 10.8 pg/ml), two strains had the middle region and cagI, (137.8 pg/ml), one strain had cagII only (113.3 pg/ml), one strain had cagI only (25.2 pg/ml), one strain had the middle region only (250 pg/ml), and three strains had cagA only (70.45 pg/ml).
DISCUSSION
The outcome of H. pylori infection is likely to be determined by a combination of factors including the virulence of the infecting strain, the host response to the infection, and several environmental cofactors. Of these factors, the virulence markers of the infecting strains have been the most studied, although the roles of most of them are still under discussion and many of them remain unknown. Like others, we support the hypothesis that the inflammatory response of the gastric mucosa to H. pylori infection is key to understanding the mechanisms leading to the severe diseases associated with the infection (11, 14, 20). Any factor resulting in an increase in gastric inflammation may also increase the risk of severe outcomes, especially gastroduodenal ulcer and gastric adenocarcinoma. In this work, the proinflammatory power of a strain was evaluated by its ability to induce IL-8 secretion from HEp-2 cells. This method has been validated previously (4, 10) and assesses for the intrinsic virulence of the strain independently of the patient response.
Previous studies showed that the cag PAI was rather conserved and that a few markers could be used to described it (1, 15, 20). Therefore we used a simple and global technique to investigate the structure of the cag PAI: the whole cag PAI was covered by long-distance PCR using three sets of primers. We completed this study by amplifying genes belonging to the various parts of the cag PAI (virD4 for cagII, cag13-cag14 for the middle part, and picB and cagA for cagI). The structure of the cag PAI appeared to be conserved, as three major groups representing 94.1% of the strains studied were observed: an uninterrupted cag PAI, no cag PAI, and a cag PAI split in two. This is consistent with the findings of other studies which showed that the structure of the cag PAI was rather conserved; Censini et al. (7), Jenks et al. (15), and Maeda et al. (20) reported that only 5 to 10% of strains had partial deletions in the cag PAI. In our study, 21 strains (13.7%) presented partial deletions of the cag PAI. Therefore, we explored the mechanisms underlying cag PAI partial deletion by testing for the presence of the insertion sequence IS605. IS605 may be present anywhere in the H. pylori chromosome and is thought to be involved in rearranging the order of H. pylori genes (2, 26). It has been hypothesized that IS605 was acquired by H. pylori later in evolutionary time than the cag PAI and that it is a prerequisite for cag deletions (7). In our study 50% of the strains that had the cag PAI split in two possessed an IS605. Although the location of the IS605 was not determined, we can hypothesize that the separation of the two halves of the cag PAI could have been mediated by that transposase. On the other hand, the strains without an IS605 underwent other mechanisms to split their cag PAI. This is confirmed by the fact that none of the nine strains with partial deletions of cag PAI possessed an IS605. Maeda et al. (20) and Jenks et al. (15) also found that some strains with partial cag PAI deletions lacked IS605 and observed that some strains lacking the cag PAI possessed an IS605 (10% in our study). Although these findings do not disprove the original explanation of cag deletion, they suggest that deletion without IS605 may be possible. Further research is needed to clarify this.
From the different genes and parts of the cag PAI studied, the elements which appeared to be the best markers for the presence of the cag PAI were the picB and the virD4 genes. Those two genes were better predictors than the cagA gene (15, 20), although none of the markers studied could predict at 100% the presence of the cag PAI. Because the cag PAI may be partially deleted or diversely organized, it is likely that the presence of one or even several genes is not sufficient to assess the presence of this region.
As was previously found by different authors, the structure of the cag PAI was not correlated with the clinical manifestations of the disease (14, 15, 20, 24). Our results suggest that the ability to induce IL-8 secretion by HEp-2 cells depends on the presence of an entire cag PAI, either uninterrupted or split in two. Although the presence of a functional cag PAI increases the proinflammatory power of a strain, it may have no predictive value for the presence or the future development of a clinically significant outcome, as other factors influence the evolution of the disease (14). Nevertheless, it is likely that strains with functional cag PAIs are more often involved in severe outcomes.
We report here the induction of IL-8 secretion by strains negative for cag PAI and the existence of cag PAI-positive strains unable to induce IL-8 secretion. This indicates that the cag PAI, or at least part of it, is not the only element required for IL-8 induction. Yamaoka et al. (30) found that cag PAI-negative strains containing a functional HP0638 gene, encoding one of the 32 outer membrane proteins detected in the genome sequence (2, 26), produced more than threefold more IL-8 than cag-negative strains containing a nonfunctional HP0638 gene. They therefore hypothesized that HP0638 may be an important marker of the inflammatory power of a strain and designated the HP0638 gene as encoding an outer membrane inflammatory protein (oipA).
The precise functions of the cag PAI, involved in the inflammatory power of the strain, are still not identified, although several pathways are suspected. Odenbreit et al. (22) and Stein et al. (25) showed that cagA-positive strains translocated the bacterial protein CagA into gastric epithelial cells using a type IV secretion system encoded by the cag PAI. CagA was then phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by an as yet unidentified host cell kinase and induced changes in the tyrosine phosphorylation of distinct cellular proteins. Such modifications of host cell components by bacterial protein translocation add a new dimension to the understanding of chronic H. pylori infection with several yet unknown consequences. Keates et al. (17) showed that cag PAI-positive isolates were more potent than cag PAI-negative strains in inducing mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase phosphorylation and that some gene products of the cag PAI were required for maximal MAP kinase activation. They also demonstrated that the p38 and MEK-1 MAP kinase activities were required for IL-8 induction by H. pylori but did not appear to be essential for H. pylori-induced NF-κB activation. Since MAP kinases regulate cell proliferation, cell differentiation, programmed cell death, reactions to stress, and inflammatory responses, activation of gastric epithelial cell MAP kinases by H. pylori cag PAI-positive strains may be crucial in inducing gastroduodenal inflammation, ulceration, and neoplasia. Despite these interesting results, much remains to be learned about the role of the cag PAI in colonization by H. pylori, persistence of infection, and mechanisms of associated disease.
Using an original approach, we have described the global structure of the cag PAI for a substantial number of clinical H. pylori strains. As previously shown, we observed that cag PAIs belong to three major structural groups and that IS605 may play a role in determining the structural type. A few strains have cag PAIs with atypical structures. Such evaluation of the structure of the cag PAI may help to define the virulence of a given H. pylori strain but is not sufficient to predict the clinical outcome of the disease.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the University and the CHU of Poitiers, as well as the Fondation pour la Recherche Medical, for their financial support.
REFERENCES
- 1.Akopyants N, Clifton S, Kersulyte D, Crabtree J E, Youree B E, Reece C A, Bukanov N O, Drazek E S, Roe B A, Berg D. Analyses of the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori. Mol Microbiol. 1998;28:37–53. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alm A, Ling L-S, Moir D, King B, Brown E, Doig P, Smith D, et al. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature. 1999;397:176–180. doi: 10.1038/16495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Atherton J C. Helicobacter pylori virulence factors. Br Med Bull. 1998;54:105–120. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a011662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Audibert C, Janvier B, Grignon B, Salaün L, Burucoa C, Lecron J C, Fauchére J L. Correlation between IL-8 induction, cagA status and vacA genotypes in 153 French Helicobacter pylori isolates. Res Microbiol. 2000;151:191–200. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2508(00)00139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Blaser M J. Ecology of Helicobacter pylori in the human stomach. J Clin Investig. 1997;100:759–762. doi: 10.1172/JCI119588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Blaser M J, Perez-Perez G I, Kleanthous H, Cover T L, Peek M, Chyou P, Stemmermann G N, Nomura A. Infection with Helicobacter pylori strains possessing cagA is associated with an increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2111–2115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Censini S, Lange C, Xiang Z, Crabtree J, Ghiara P, Borodovsky M, Rappuoli R, Covacci A. cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:14648–14653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Covacci A, Telford J, Del Giudice G, Parsonnet J, Rappuoli R. Helicobacter pylori virulence and genetic geography. Science. 1999;284:1328–1333. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5418.1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Covacci A, Censini S, Bugnoli M, Petracca R, Burroni D, Machia G, Massone A, Papini E, Xiang Z, Figura N. Molecular characterization of the 128-kDa immunodominant antigen of Helicobacter pylori associated with cytotoxicity and duodenal ulcer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:5791–5795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Crabtree J, Covacci A, Farmery S, Xiang Z, Tompkins D, Perry S, Lindley L, Rappuoli R. Helicobacter pylori-induced interleukin-8 expression in gastric epithelial cells is associated with CagA positive phenotype. J Clin Pathol. 1995;48:41–45. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Crabtree J, Wyatt J, Trejdosiewicz L, Peichl P, Nichols P, Ramsay N, Primrose J, Lindley I. IL-8 expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected, normal, and neoplastic gastroduodenal mucosa. J Clin Pathol. 1994;47:61–66. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eurogast Study Group. An international association between Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer. Lancet. 1993;341:359–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fischbach W, Tacke W, Greiner A, Konrad H, Müller-Hermelink H K. Regression of immunoproliferative small intestine disease after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1997;349:31–32. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)62165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Graham D, Yamaoka Y. Disease-specific Helicobacter pylori virulence factors: the unfulfilled promise. Helicobacter. 2000;5(Suppl. 1):3–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-5378.2000.0050s1003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jenks P, Megraud F, Labigne A. Clinical outcome after infection with Helicobacter pylori does not appear to be reliably predicted by the presence of any of the genes of the cag pathogenicity island. Gut. 1998;43:752–758. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.6.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jiang Q, Hiratsaka K, Taylor D. Variability of gene order in different Helicobacter pylori strains contributes to genome diversity. Mol Microbiol. 1996;20:833–842. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Keates S, Keates A, Warny M, Peek R, Murray P, Kelly C. Differential activation of mitogen-activated kinases in AGS gastric epithelial cells by cag+Helicobacter pylori. J Immunol. 1999;163:5552–5559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kersulyte D, Akopyants N, Clifton S, Roe B, Berg D. Novel sequence organization and insertion specificity of IS605 and IS606: chimaeric transposable elements of Helicobacter pylori. Gene. 1998;223:175–186. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kersulyte D, Chalkauskas H, Berg D. Emergence of recombinant strains of Helicobacter pylori during human infection. Mol Microbiol. 1999;31:31–43. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Maeda S, Yoshida H, Ikenoue T, Ogura K, Kanai F, Kato N, Shiratori Y, Omata M. Structure of cag pathogenicity island in Japanese Helicobacter pylori isolates. Gut. 1999;44:336–341. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Marshall B. Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983;983:1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Odenbreit S, Puls J, Sedlmaier B, Gerland E, Fischer W, Haas R. Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion. Science. 2000;287:1497–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5457.1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Peek R, Miller G, Tham K, Perez-Perez G, Zhao X, Atherton J, Blaser M. Heightened inflammatory response and cytokine expression in vivo to cagA+Helicobacter pylori strains. Lab Investig. 1995;71:760–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Slater E, Owen R, William M, Pounder R. Conservation of the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori: associations with vacuolating cytotoxin allele and IS605 diversity. Gastroenterology. 1999;117:1308–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stein M, Rappuoli R, Covacci A. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the Helicobacter pylori CagA antigen after cag-driven host cell translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:1263–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.3.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tomb J-F, White O, Kerlavage A, Clayton R, Sutton G, Fleischmann R, Ketchum K, Klenk H, et al. The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature. 1997;388:539–546. doi: 10.1038/41483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tummuru M, Cover T, Blaser M. Cloning and expression of a high-molecular-mass major antigen of Helicobacter pylori: evidence on linkage to cytotoxin production. Infect Immun. 1993;61:1799–1809. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1799-1809.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tummuru M, Sharma S, Blaser M. Helicobacter pylori picB, a homologue of the Bordetella pertussis toxin secretion protein, is required for induction of IL-8 in gastric epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:867–876. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.18050867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Warburton V, Everett S, Mapstone N, Axon A, Hawkey P, Dixon M. Clinical and histological association of cagA and vacA genotypes in Helicobacter pylori gastritis. J Clin Pathol. 1998;51:55–61. doi: 10.1136/jcp.51.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yamaoka Y, Kwon D, Graham D. A Mr 34,000 proinflammatory outer membrane protein (oipA) of Helicobacter pylori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:7533–7538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.130079797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]