Abstract
Viruses are cellular parasites. The linkage between viral and host functions makes the study of a viral life cycle an important key to cellular functions. A deeper understanding of many aspects of viral life cycles has emerged from coordinated molecular and structural studies carried out with a wide range of viral pathogens. Structural studies of viruses by means of cryo-electron microscopy and three-dimensional image reconstruction methods have grown explosively in the last decade. Here we review the use of cryo-electron microscopy for the determination of the structures of a number of icosahedral viruses. These studies span more than 20 virus families. Representative examples illustrate the use of moderate- to low-resolution (7- to 35-Å) structural analyses to illuminate functional aspects of viral life cycles including host recognition, viral attachment, entry, genome release, viral transcription, translation, proassembly, maturation, release, and transmission, as well as mechanisms of host defense. The success of cryo-electron microscopy in combination with three-dimensional image reconstruction for icosahedral viruses provides a firm foundation for future explorations of more-complex viral pathogens, including the vast number that are nonspherical or nonsymmetrical.
INTRODUCTION
EM (abbreviations are listed at the end of this section) has long been a primary tool for classifying viruses and exploring their structures. The last decade has also seen a burst of activity in the use of EM for the elucidation of virus structures. This has resulted from two advances in technique. Firstly, cryo-EM has allowed the preservation of fragile specimens in the EM (1, 109). Secondly, the development of efficient algorithms for processing micrographs to produce 3D structures of icosahedral particles has allowed this higher-quality data to be used (9, 14, 42, 80, 86, 89, 91, 93, 130, 133, 210). These two developments have made 3D structural information accessible for a broad range of viruses at the same time that high-resolution X-ray diffraction studies have revealed atomic detail about a more limited range. These two approaches are complementary and together are bringing a new excitement to the field of virus structure.
The most widely used approach for the reconstruction of icosahedral structures begins with the method of common lines, which was developed by Crowther in the early 1970s (86, 89). The original application of the method relied upon estimating the orientation of each particle by eye and then using the symmetry relationships which are present in the projection of any icosahedral object to refine these orientations. The data from the resulting set of views are then combined to produce a 3D reconstruction by means of the projection theorem (43). Several 3D structures of negatively stained viruses were solved, and these results helped clarify the principles of quasi-equivalence that were being explored at the time (88, 89, 94, 95, 119, 120, 170, 216). The use of data from negatively stained specimens limited the efficacy of the method. The distortions of the structure caused by drying, flattening, nonuniform staining, and radiation damage resulted in a loss of the icosahedral symmetry upon which the reconstruction method depended. The applicability of the method was further constrained because many interesting structures such as enveloped viruses were destroyed by interaction with the stain. Finally, even ideal conditions of negative staining revealed only the distribution of the heavy metal stain embedding the specimen rather than the density of the specimen itself. The development of cryo-EM changed this situation (1). By maintaining a layer of vitrified water around the specimen, relying on defocus rather than heavy metal stains to generate contrast, and performing microscopy under low-dose conditions at near-liquid-nitrogen temperatures, this method was able to produce data of unprecedented quality. In particular, the distortions and artifacts which had limited the use of 3D reconstruction of icosahedral particles previously were eliminated in data collected by cryo-EM. The limitation then became the processing of the data. Relatively few characteristic views were recognizable by eye because a cryo-electron micrograph shows the entire density of the particle in projection. This was not the case for negatively stained samples, where uneven staining and the fact that only the outline of the specimen is observed resulted in a simpler image. Cryo-electron micrographs revealed higher-resolution data, but they did so with relatively low contrast (1). This further complicated the task of recognizing and refining views. A reformulation of the common lines method was necessary to allow this to be done reliably and automatically for these noisy, low-contrast, and complex images. The past decade has seen the successful development of such methods (9, 14, 42, 80, 93, 130, 133, 210), a resulting flowering of the use of the approach, and an explosion in the number and quality of the results (see Table 1).
TABLE 1.
3D reconstructions of spherical virusesa
| Virus family, subfamily (genus), species | Host | NA | Lattice symmetry | Size (Å) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenoviridae | |||||
| Ad2 | V | dD | T = 25 | 884–1,114 | 70, 296, 298 |
| Ad5 | V | dD | T = 25 | 884–1,114 | 328 |
| Ad5 (without fiber) | V | dD | T = 25 | 884–914 | 328 |
| Ad12 | V | dD | T = 25 | 884–1,114 | 70 |
| Ad2-Fab DAV-1 complex | V | dD | T = 25 | 884–1,114 | 297 |
| Ad2-αvβ5 complex | V | dD | T = 25 | 884–1,238 | 70 |
| Ad12-αvβ5 complex | V | dD | T = 25 | 884–1,204 | 70 |
| Ad3 penton dodecahedron | V | — | T = 1 | 400 | 267 |
| Ad3 penton dodecahedron (without fiber) | V | — | T = 1 | 280 | 267 |
| Birnaviridae | |||||
| (Avibirnavirus) | |||||
| IBDV | V | dR | T = 13d | 700 | 40 |
| Bromoviridae | |||||
| (Alphamovirus) | |||||
| Alfalfa mosaic virus capsid | Pl | — | T = 1 | 210 | 191 |
| (Bromovirus) | |||||
| CCMV | Pl | sR | T = 3 | 284 | 234, 290, 358 |
| CCMV capsid | Pl | — | T = 3 | 284 | 123 |
| CCMV RNA1 virion | Pl | sR | T = 3 | 284 | 123 |
| CCMV RNA2 virion | Pl | sR | T = 3 | 284 | 123 |
| CCMV (swollen-mixed) | Pl | sR | T = 3 | 310 | 290, 292 |
| CCMV expressed | Pl | sR | T = 3 | 284 | 358 |
| (Cucumovirus) | |||||
| Cucumber mosaic virus | Pl | sR | T = 3 | 280 | 343 |
| Caliciviridae | |||||
| Calicivirus | V | sR | T = 3 | 405 | 244 |
| Norwalk virus | V | — | T = 3 | 380 | 246 |
| Rabbit hemorrhagic disease VLP-MAb-E3 complex | V | — | T = 3 | >580 | 305 |
| Comoviridae | |||||
| (Comovirus) | |||||
| CPMV mixed | Pl | sR | P = 3 | 250–312 | 240, 336 |
| CPMV-T (top component) | Pl | — | P = 3 | 250–312 | 10, 62 |
| CPMV-M (middle component) | Pl | sR | P = 3 | 250–312 | 10 |
| CPMV-Bu (bottom component-upper) | Pl | sR | P = 3 | 250–312 | 10 |
| CPMV-M–Fab 5B2 complex | Pl | sR | P = 3 | 250–410 | 240, 336 |
| CPMV-M–Fab 10B7 complex | Pl | sR | P = 3 | 250–410 | 240 |
| CPMV-M–IgG 10B7 complex | Pl | sR | P = 3 | 250–>410 | 240 |
| CPSMV (severe strain) | Pl | sR | P = 3 | 250–312 | 234 |
| (Nepovirus) | |||||
| Tobacco ringspot virus, expressed | Pl | — | P = 3 | 300 | 279 |
| Cystoviridae | |||||
| φ6 nucleocapsid | B | dD | T = 13 | 580 | 48 |
| φ6 core | B | dD | T = 1 | 500–580 | 48 |
| φ6 procapsid | B | dD | T = 1 | 460 | 48 |
| φ6 P1 | B | — | T = 1 | 460 | 48 |
| φ6 P1P4 | B | — | T = 1 | 460 | 48 |
| Hepadnaviridae | |||||
| (Orthohepadnavirus) | |||||
| HepBc (human liver) (nHBc) | V | ? | T = 4 | 340 | 184 |
| HBc full length (flHBc) | V | sR | T = 3 & 4 | 300, 340 | 184 |
| HBc expressed (HBcAg) | V | sR | T = 3 & 4 | 320, 360 | 93 |
| HBcAg empty capsid | V | — | T = 3 & 4 | 320, 360 | 93 |
| HBcAg empty capsid-Fab 312 complex | V | — | T = 4 | 455 | 78 |
| HBc expressed, truncated (149-aa) empty capsid (HBcAgΔ) | V | — | T = 3 & 4 | 320, 360 | 41, 42, 80, 93, 184 |
| HBcAgΔ + decapeptide | V | — | T = 3 & 4 | 320, 360 | 41 |
| HBc expressed, truncated (147-aa) empty capsid (HBc Cp147) | V | — | T = 3 & 4 | 318, 350 | 365 |
| HBc Cp147 empty capsids | V | — | T = 4 | 350 | 364 |
| HBc Cp183 capsids | V | sR | T = 4 | 350 | 364 |
| HBc Cp*150 labeled with dodecagold | V | — | T = 4 | 350 | 364 |
| Hbc Cpe (N-terminal extension) | V | — | T = 3 & 4 | 290, 330 | 79 |
| (Avihepadnavirus) | |||||
| Duck hepatitis B expressed capsid | V | sR | T = 3 & 4 | 300, 340 | 184 |
| Herpesviridae | |||||
| Alphaherpesvirinae (Simplexvirus) | |||||
| HSV-1 | V | dD | ∼2,000 | 359 | |
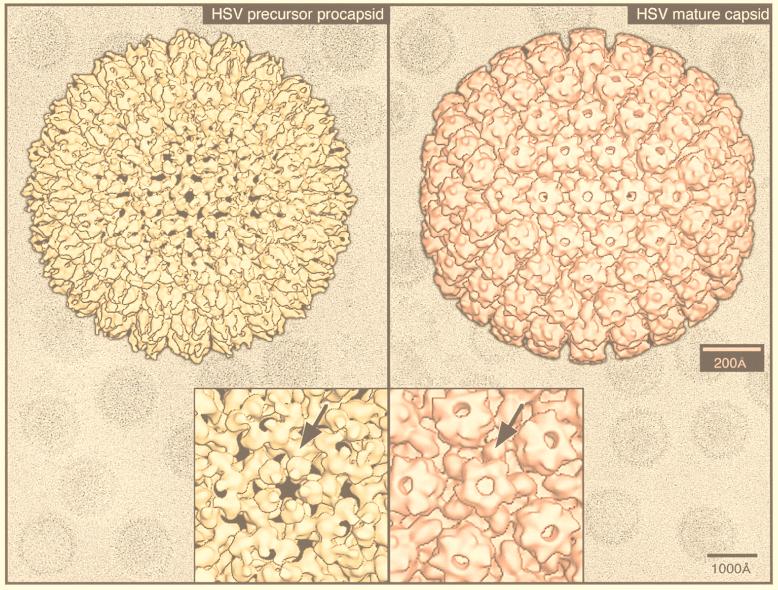
| HSV-1 A capsid | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 35, 269, 363 |
| HSV-1 B capsid (HSV-1 B) | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 83, 224, 313, 361, 362 |
| HSV-1 B + 2.0 M GuHCl (G2.0 capsid) | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 38, 224, 291 |
| G2.5 capsid | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 224 |
| G2.0 capsid + VP26 | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 38 |
| G2.0 capsid-MAb 6F10 complex | V | — | T = 16 | ∼1,380 | 291 |
| HSV-1 B-MAb 8F5 complex | V | — | T = 16 | ∼1,400 | 313 |
| HSV-1 B-MAb 6F10 complex | V | — | T = 16 | ∼1,300 | 311 |
| HSV-1 C capsid | V | dD | T = 16 | 1,250 | 35, 83, 269 |
| HSV-1 expressed capsid | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 312 |
| HSV-1 expressed (VP26−) capsid | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 312, 348, 362 |
| HSV-1 expressed (VP26−) capsid + VP26 | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 348 |
| HSV-1 procapsid-MAb 6F10 complex | V | — | T = 16 | 1,320 | 311 |
| Alphaherpesvirinae (Varicellovirus) | |||||
| Equineherpesvirus type 1 light capsid | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 17, 18 |
| Equineherpesvirus type 1 intermediate capsid | V | — | T = 16 | 1,250 | 17, 18 |
| Betaherpesvirinae (Cytomegalovirus) | |||||
| Human herpesvirus 5 B capsid | V | — | T = 16 | ∼1,300 | 49 |
| Unassigned virus in the family | |||||
| Channel catfish herpesvirus | V | — | T = 16 | 1,167 | 37 |
| Microviridae | |||||
| (Microvirus) | |||||
| φX174 114S virion | B | sD | T = 1 | 260–335 | 26, 166, 231 |
| φX174 108S procapsid | B | — | T = 1 | 363 | 166 |
| φX174 132S provirion | B | sD | T = 1 | 363 | 166 |
| (Spiromicrovirus) | |||||
| Spiroplasma phage 4 | B | sD | T = 1 | 270–360 | 68, 69 |
| Myoviridae | |||||
| Enterobacteria phage P2 | B | dD | T = 7 | 600 | 101 |
| Enterobacteria phage P4 | B | dD | T = 4 | 450 | 101 |
| Enterobacteria phage P4 Sid | B | dD | T = 4 | 450 | 213 |
| Enterobacteria phage P4 Psu | B | dD | T = 4 | 450 | 99 |
| Nodaviridae | |||||
| FHV | I | sR | T = 3 | 330 | 11, 66 |
| Papovaviridae | |||||
| (Polyomavirus) | |||||
| Polyomavirus | V | dD | T = 7d | 495 | 26, 30 |
| SV40 | V | dD | T = 7d | 495 | 14, 15 |
| (Papillomavirus) | |||||
| HPV-1 | V | dD | T = 7d | 600 | 19, 29 |
| HPV-1 expressed L1 capsid | V | — | T = 7d | 600 | 146 |
| HPV-1 expressed L1-L2 capsid | V | — | T = 7d | 600 | 146 |
| BPV-1 | V | dD | T = 7d | 600 | 19, 26, 314 |
| BPV-1–MAb 9 complex | V | dD | T = 7d | 710 | 36 |
| BPV-1–MAb 5B6 complex | V | dD | T = 7d | 650 | 36 |
| Cottontail rabbit papillomavirus type 1 | V | dD | T = 7d | 630 | 29 |
| Parvoviridae | |||||
| Parvovirinae (Parvovirus) | |||||
| Aleutian mink disease virus | V | sD | T = 1 | 285 | 214, 232 |
| Canine parvovirus-Fab complex | V | sD | T = 1 | 255–425 | 344 |
| Parvovirinae (Erythrovirus) | |||||
| Human parvovirus B19 VLP (B19) | V | — | T = 1 | 260 | 67 |
| B19 VLP-globoside complex | V | — | T = 1 | 260 | 67 |
| Densovirinae (Densovirus) | |||||
| Galleria mellonella densovirus | I | sD | T = 1 | 260 | 277 |
| Phycodnaviridae | |||||
| Paramecium bursaria Chlorella virus 1 | A | dD | T = 169 | 1,900 | 351 |
| Picornaviridae | |||||
| (Rhinovirus) | |||||
| HRV2 | V | sR | P = 3 | 300 | 156 |
| HRV14 | V | sR | P = 3 | 300 | 27, 284, 292 |
| HRV16 | V | sR | P = 3 | 300 | 9, 27 |
| HRV2-MAb 8F5 complex | V | sR | P = 3 | >440 | 156 |
| HRV2-Fab 3B10 complex | V | sR | P = 3 | >440 | 161 |
| HRV14-Fab 1-IA complex | V | sR | P = 3 | 440 | 58 |
| HRV14-Fab 12-IA complex | V | sR | P = 3 | 440 | 58 |
| HRV14-Fab 17-IA complex | V | sR | P = 3 | 440 | 205, 235, 289 |
| HRV14-IgG 17-IA complex | V | sR | P = 3 | >440 | 288 |
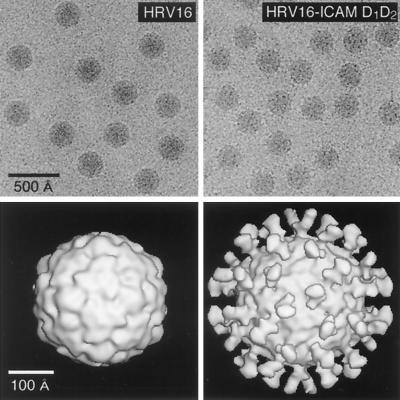
| HRV14-D1D2ICAM-1 complex | V | sR | P = 3 | 410 | 259 |
| HRV16-D1D2ICAM-1 complex | V | sR | P = 3 | 410 | 25, 233, 235, 261 |
| (Aphthovirus) | |||||
| FMDV-C–Fab SD6 complex | V | sR | P = 3 | 450 | 162 |
| Podoviridae | |||||
| T7-like phages | |||||
| Bacillus phage φ29 (φ29) isometric | B | — | T = 3 | 455 | 300 |
| φ29 fiberless isometric | B | — | T = 3 | 425 | 300 |
| Enterobacteria phage P22 head | B | dD | T = 7 | 630 | 245 |
| P22 procapsid | B | — | T = 7 | 612 | 245, 308 |
| P22 procapsid (minus scaffold) | B | — | T = 4 | 480 | 309 |
| P22 procapsid (minus scaffold) | B | — | T = 7 | 612 | 309 |
| P22 procapsid mutant 8tsL177I | B | — | T = 7 | 612 | 308 |
| Reoviridae | |||||
| (Aquareovirus) | |||||
| Aquareovirus | V | dR | T = 13l | 800 | 272 |
| Aquareovirus empty capsid | V | — | T = 13l | 800 | 272 |
| (Cypovirus) | |||||
| BmCPV-1 | I | dR | T = 1 | 600–800 | 356 |
| BmCPV-1 capsid | I | — | T = 1 | 600–800 | 356 |
| (Orbivirus) | |||||
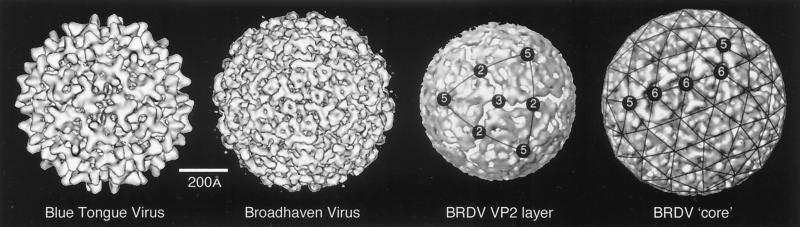
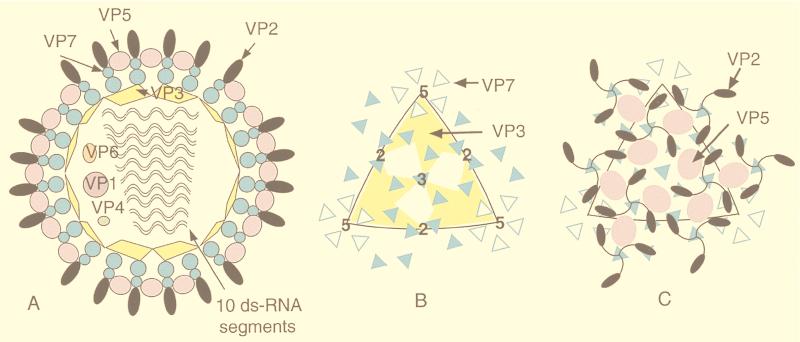
| BTV-10 | V | dR | T = 13l | 900 | 158, 332 |
| BTV-10 expressed, VLP | V | — | T = 13l | 860 | 159, 332 |
| BTV-10 core | V | dR | T = 13l | 690 | 145, 241, 332 |
| BTV-10 expressed, core-like particle | V | — | T = 13l | 690 | 157, 332 |
| BRDV | V | dR | T = 13l | 790 | 268 |
| (Orthoreovirus) | |||||
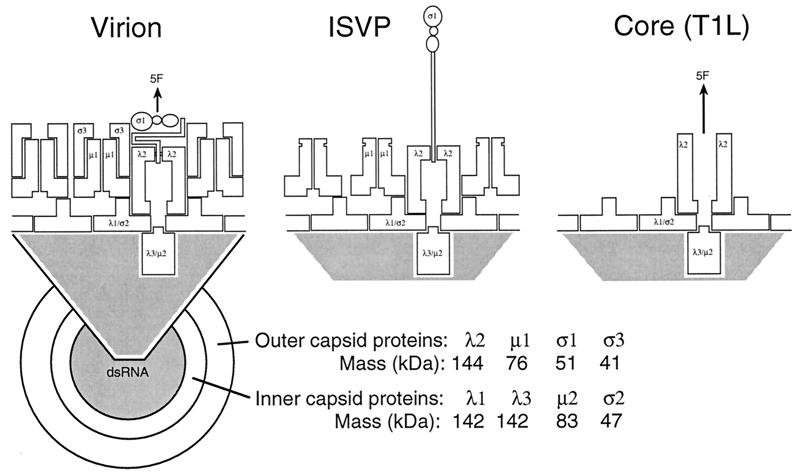
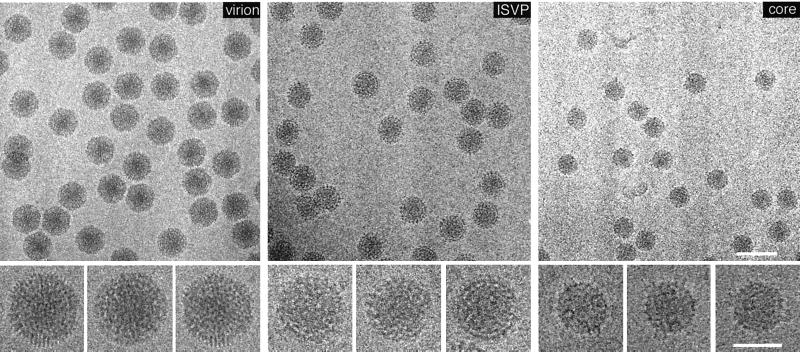
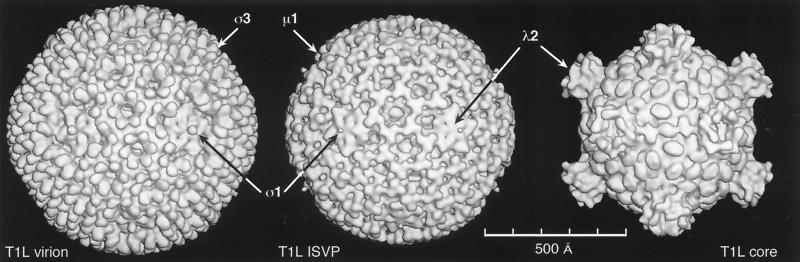
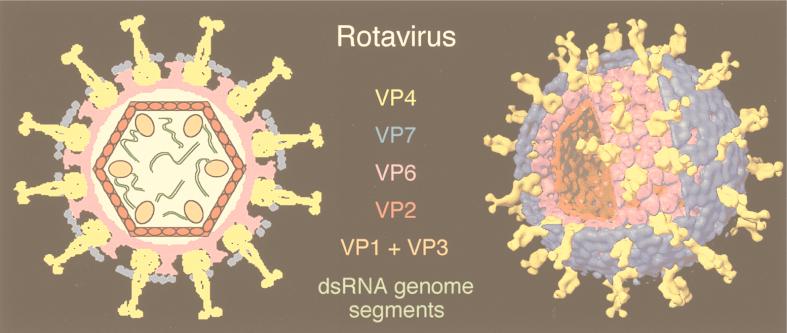
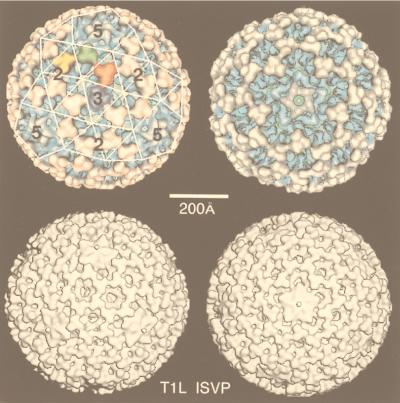
| T1L reovirus virion | V | dR | T = 13l | 850 | 108, 292 |
| T1L reovirus ISVP | V | dR | T = 13l | 800 | 108, 292 |
| T1L reovirus core | V | dR | T = 1 | 600–800 | 108, 292 |
| T1L reovirus empty virion | V | — | T = 13l | 850 | 107 |
| T1L reovirus empty ISVP | V | — | T = 13l | 800 | 107 |
| T1L reovirus empty core | V | — | T = 1 | 600–800 | 107 |
| Type 2 (Jones) reovirus virion | V | dR | T = 13l | 850 | 217 |
| T3D reovirus virion | V | dR | T = 13l | 850 | 217 |
| T3D reovirus core | V | dR | T = 1 | 600–800 | 209 |
| T3D reovirus empty core | V | — | T = 1 | 600–800 | 217 |
| T3D-Δλ2 | V | dR | T = 1 | 600–800 | 209 |
| Recoated core | V | dR | T = 1 | 850 | 57 |
| Recoated ISVP | V | dR | T = 1 | 850 | 171 |
| (Phytoreovirus) | |||||
| Rice dwarf virus | Pl | dR | T = 13l | 700 | 207 |
| (Rotavirus) | |||||
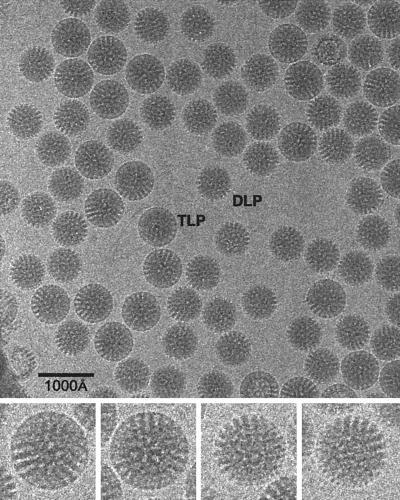
| Rhesus rotavirus | V | dR | T = 13l | 750–>950 | 353 |
| Simian rotavirus (SA11-4F) TLP | V | dR | T = 13l | 765–>950 | 248, 249, 271, 352 |
| Simian rotavirus (SA11-R004) TLP | V | dR | T = 13l | 765 | 271 |
| SA11/Vp4− | V | dR | T = 13l | 750 | 352 |
| SA11/VP4-Fab complex | V | dR | T = 13l | 765–1,000 | 242 |
| SA11-4F DLP | V | dR | T = 13l | 700 | 193, 195, 247, 249 |
| SA11-4F DLP transcribing mRNA | V | dR | T = 13l | 700 | 193 |
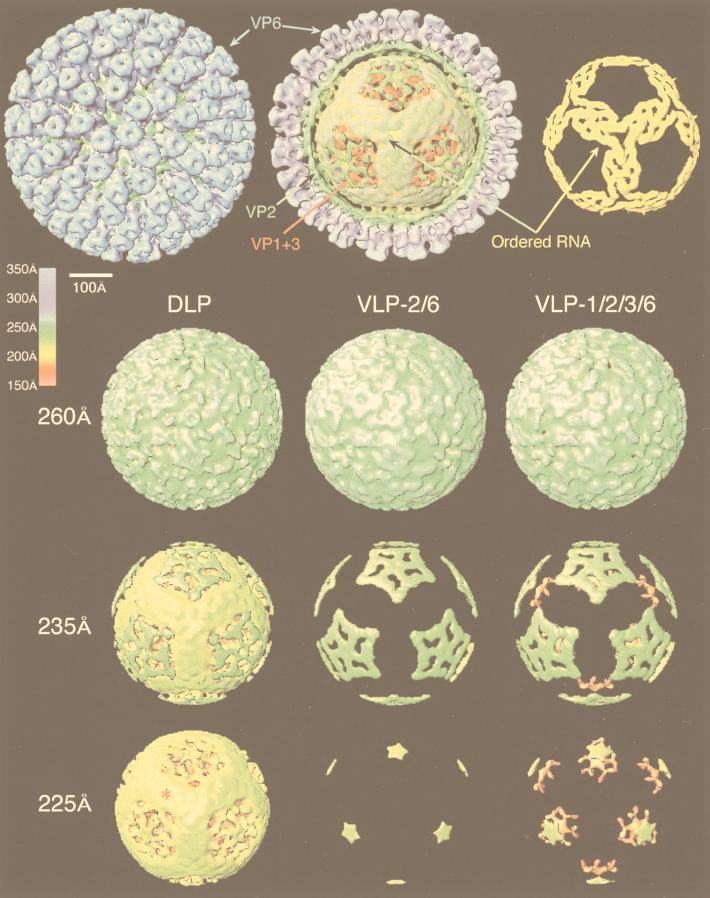
| SA11-4F 2-VLP | V | — | T = 1 | 525 | 247 |
| SA11-4F 2/6-VLP | V | — | T = 13l | 700 | 195, 247 |
| SA11-4F Δ2/6-VLP | V | — | T = 13l | 700 | 195 |
| SA11-4F 1/2/3/6-VLP | V | — | T = 13l | 700 | 247 |
| Siphoviridae | |||||
| (λ-like phages) | |||||
| Coliphage λ | B | dD | T = 7 | 630 | 100 |
| Coliphage λ prohead | B | dD | T = 7 | 540 | 100 |
| Coliphage λ gpD− | B | dD | T = 7 | 630 | 100 |
| Lambdoid phage HK97 prohead I | B | — | T = 7 | 470 | 81 |
| Lambdoid phage HK97 prohead II | B | — | T = 7 | 470 | 81 |
| Lambdoid phage HK97 head I | B | dD | T = 7 | 550 | 81 |
| Lambdoid phage HK97 head II | B | dD | T = 7 | 550 | 81 |
| Tectiviridae | |||||
| PRD1 | B | dD | T = 25 | 740 | 50 |
| PRD1 sus1 | B | — | T = 25 | 740 | 50 |
| PRD1 P3 shell | B | — | T = 25 | 740 | 50 |
| Tetraviridae | |||||
| Nudaurelia capensis β virus | I | sR | T = 4 | 397 | 229, 230 |
| Nudaurelia capensis ω virus | I | sR | T = 4 | 410 | 177 |
| Togaviridae | |||||
| (Alphavirus) | |||||
| Aura virus | V | sR | T = 4 | 708 | 357 |
| RRV | V | sR | T = 4 | 700 | 64, 286 |
| RRV-Fab complex | V | sR | T = 4 | 810 | 286 |
| SNV | V | sR | T = 4 | 700 | 130, 237, 238, 286 |
| SNV TRSB-N (noninfectious mutant) | V | sR | T = 4 | 700 | 238 |
| SNV TRSB-NE2G216 (infectious mutant) | V | sR | T = 4 | 700 | 238 |
| SNV core | V | sR | T = 4 | 400 | 131 |
| SNV-Fab complex | V | sR | T = 4 | 810 | 286 |
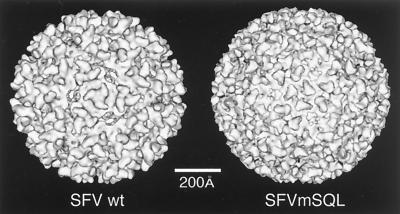
| SFV | V | sR | T = 4 | 700 | 132, 186, 327 |
| SFVmSQL mutant | V | sR | T = 4 | 700 | 118, 186 |
| SFV detergent E1 depleted | V | sR | T = 4 | 680 | 325 |
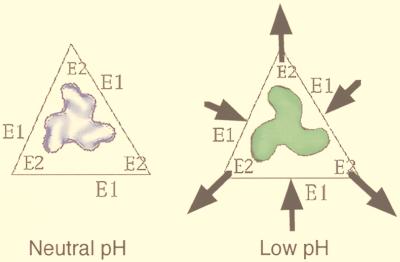
| SFV low pH (50-ms form) | V | sR | T = 4 | 700 | 132 |
| Tombusviridae | |||||
| Tomato bushy stunt virus | Pl | sR | T = 3 | 326 | |
| Totiviridae | |||||
| (Totivirus) | |||||
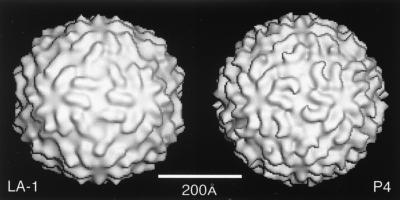
| L-A (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | F | dR | T = 1 | 430 | 55, 63 |
| L-A empty capsid | F | — | T = 1 | 430 | 55, 63 |
| P4 (Ustilago maydis) | F | dR | T = 1 | 430 | 63 |
| No family or subfamily name | |||||
| (Caulimovirus) | |||||
| CaMV cabbage | Pl | dD | T = 7 | 538 | 65 |
| CaMV turnip (CM1841) | Pl | dD | T = 7 | 538 | 65 |
| (Tymovirus) | |||||
| TYMV | Pl | sR | T = 3 | 300 | 39 |
| TYMV empty capsid | Pl | — | T = 3 | 300 | 39 |
| Other particles | |||||
| Yeast retrotransposon Ty1 VLP | F | sR | T = 3 & 4 | 166, 191 | 236 |
Abbreviations: NA, nucleic acid genome; V, vertebrate; Pl, plant; B, bacteria; I, invertebrate; A, algae; F, fungi; dD, dsDNA; —, none; dR, dsRNA; sR, ssRNA; ?, unknown; sD, ssDNA; T, triangulation number; P, pseudotriangulation number.
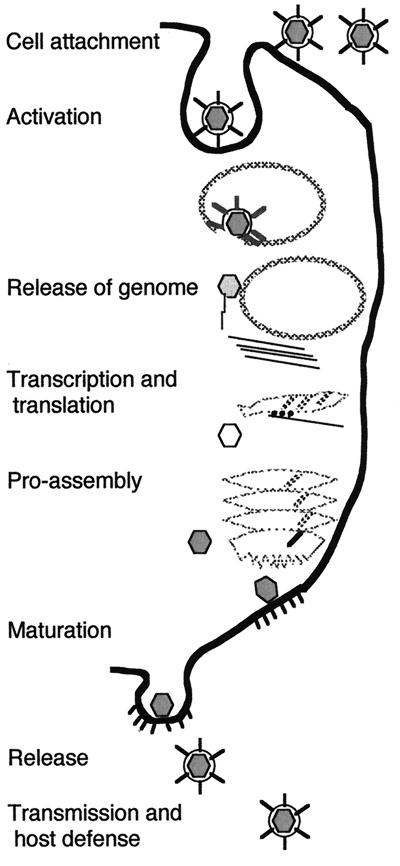
The value of the results produced by 3D reconstruction of viruses from cryo-EM must be considered in terms of its contribution to our understanding of viral structural biology. The morphology of the virus is only the first result gleaned from viewing a 3D reconstruction (Fig. 1). For a highly symmetric particle such as a virus, morphology reveals not only the shape of the virion but also the organization and shape of the components. As discussed below, the combination of an understanding of icosahedral symmetry with even a low-resolution density map can often allow one to infer the stoichiometry of the polypeptides comprising the virion. At a somewhat higher resolution (20 to 30 Å), one can visualize systematic changes in subunit conformation that allow the formation of the capsid. This may reveal fundamental relationships among the structures of members of a viral family such as the papovaviruses (14, 15, 19) or unexpected relationships such as that between a bacteriophage and the reoviruses (48). Interactions between the components of the virus which provide a glimpse into the process of virus assembly (e.g., see references 48, 101, 108, 130, 131, 245, 249, and 353) may also be revealed and generate ideas which can be tested by observations of intermediates in the assembly process (48, 100, 166, 213, 245, 294, 311). Together, the information provided by these methods is generating a deeper understanding of capsid assembly (294).
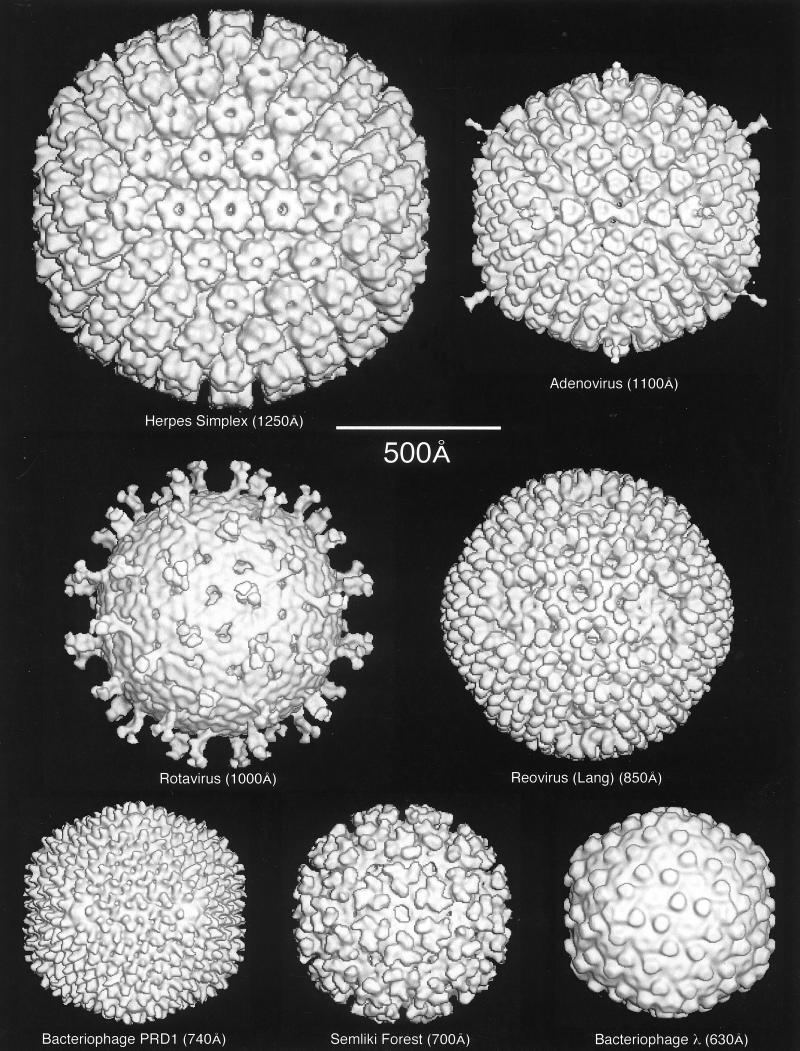
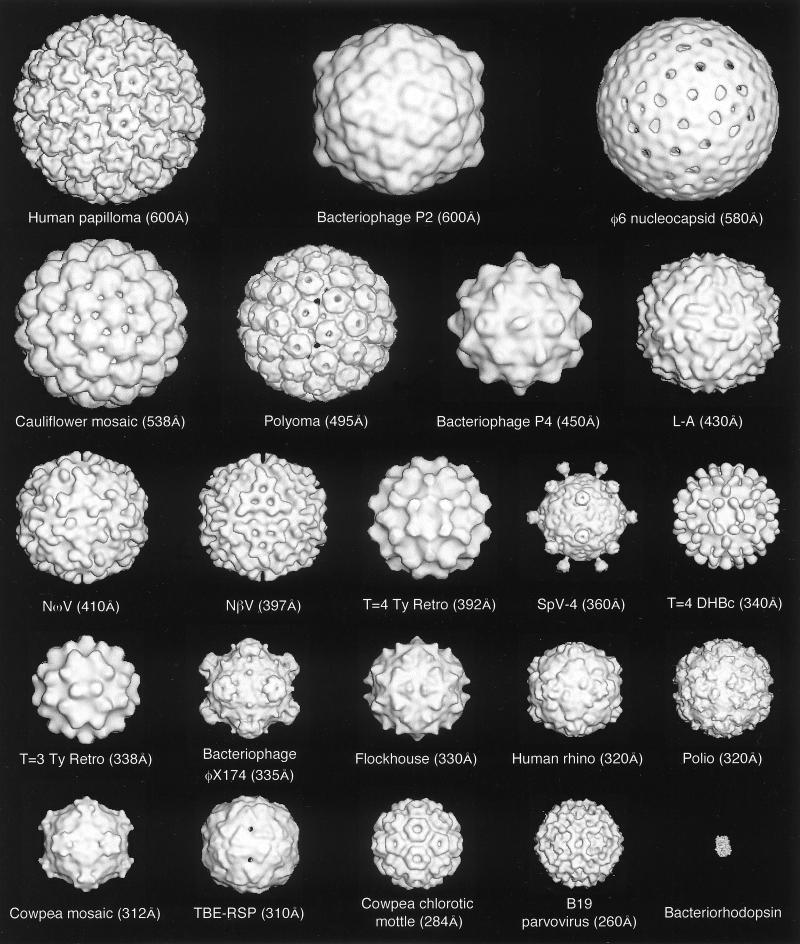
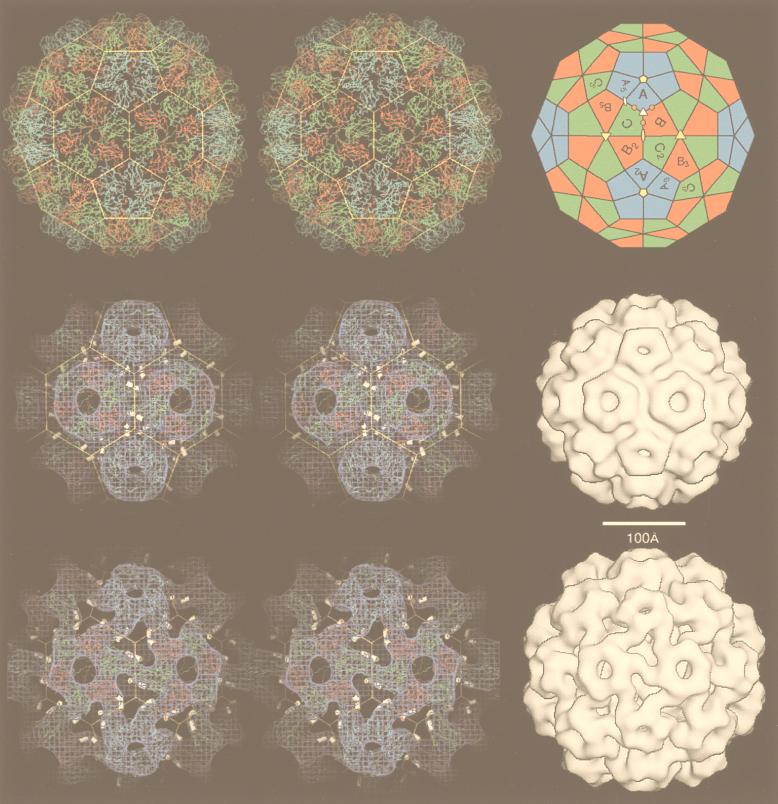
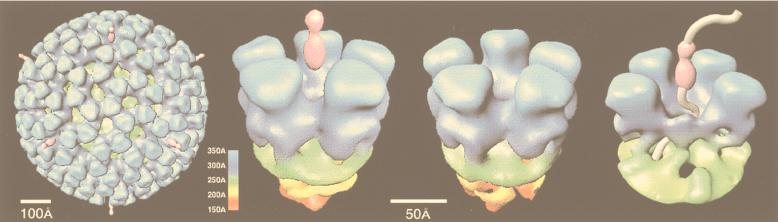
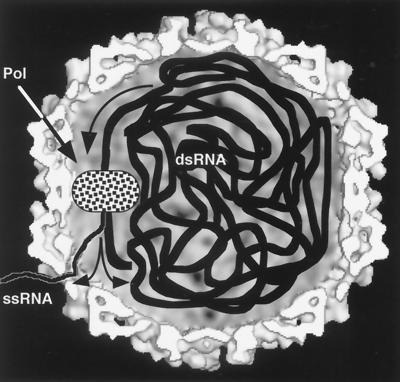
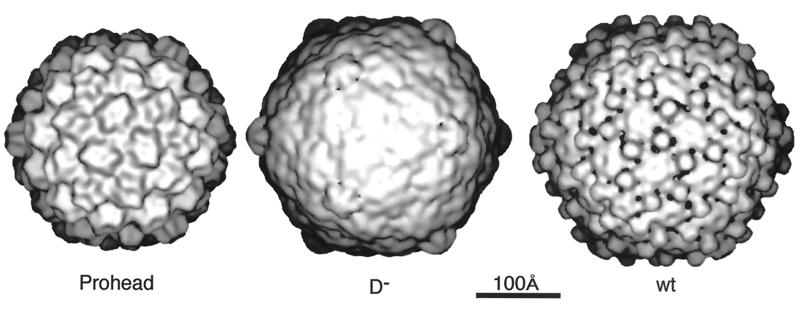
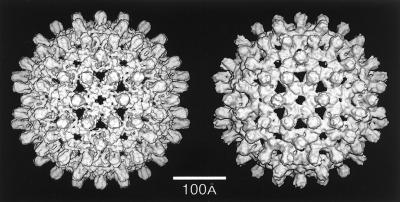
FIG. 1.
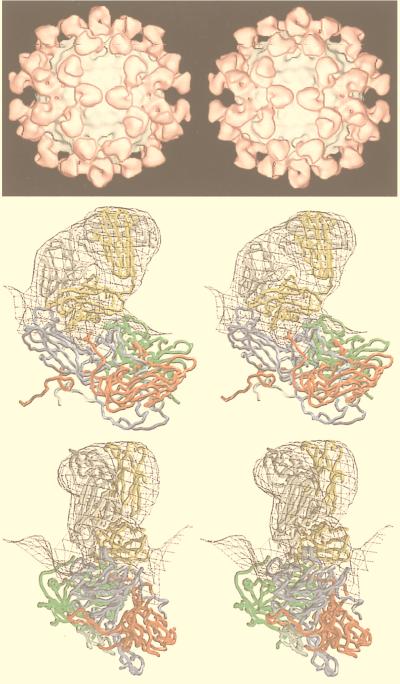
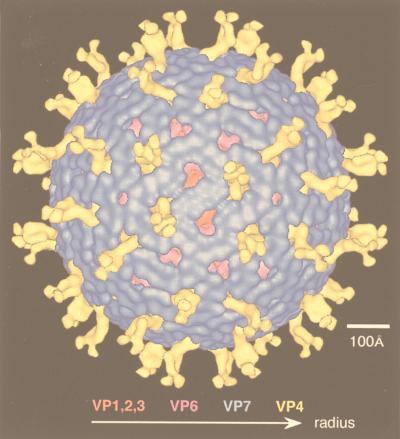
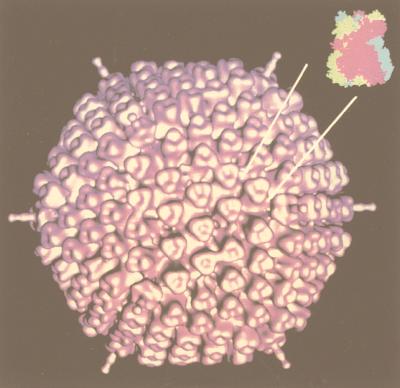
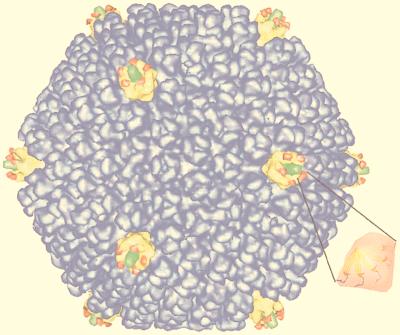
Gallery of representative icosahedral viruses studied by us using cryo-EM and 3D image reconstruction methods. The monomer of bacteriorhodopsin, a 26-kDa membrane protein which contains seven α helices oriented perpendicular to the membrane plane, is shown for comparison at the lower right of the right-hand page (extracellular surface faces upward). All shaded-surface virus structures are viewed along a twofold axis of symmetry. Table 1 presents more-detailed information about these and other 3D reconstructions of icosahedral viruses. TBE, tick-borne encephalitis recombinant subviral particle; Nωv, Nudaurelia capensis ω virus; Nβv, Nudaurelia capensis β virus; Ty Retro, yeast retrotransposon Ty1 VLP; SpV4, Spiroplasma virus type 4; DHBc, duck hepatitis B capsid; B19, human parvovirus B19.
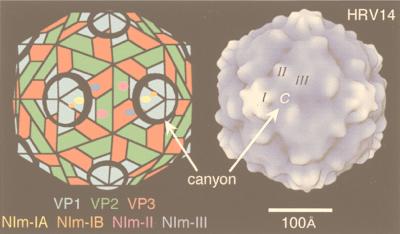
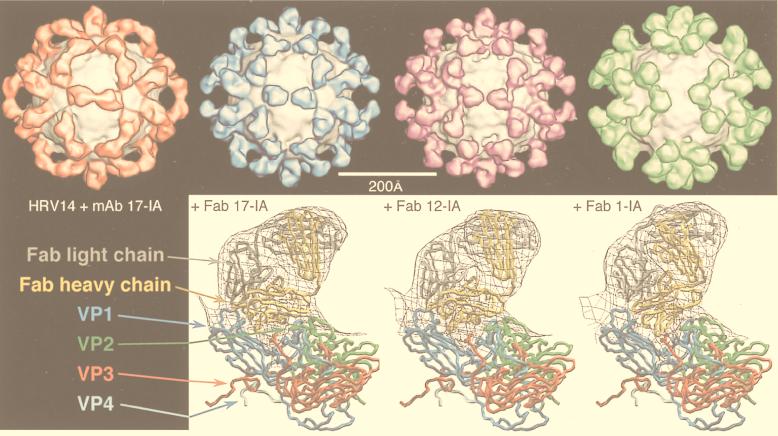
An important tool that provides a link between the reconstruction and the biochemistry and that facilitates its interpretation is the use of specific labels. Antibodies are an important example of such labels that have been used to identify components in a reconstruction (e.g., see references 242, 286, and 313). Localization of antibody binding sites also gives important functional information concerning the mechanism of neutralization (285, 287–289, 297) and receptor binding (242, 286). The conclusions reached in these studies can be supported by difference imaging, which takes advantage of the tools of expression and reconstitution to create particles of defined composition (312, 362, 365). The resolution of antibody labeling techniques is higher than expected from the resolution of the reconstruction because the complex can be modeled by fitting in the known structure of an Fab (73, 156, 161, 162, 235, 240, 243, 288, 289, 297, 336, 337). The promise of higher-resolution localization is realized in recent papers in which a combination of site-directed mutagenesis and undecagold labeling has been used to localize a particular residue with high precision in HepBc (364) and in which antibody Fab labeling has been used to localize the six-residue putative immunodominant loop of HepBc (78). Finally, the use of peptide-based difference mapping has been successfully exploited in the hepatitis virus system to locate the N terminus of HepBc (79) and to locate the binding site of peptides that block hepatitis virion assembly (41).
An increasingly important approach in structural biology is that of “divide and conquer” (16). Complex biological systems which are intractable when studied by a single technique yield to a combined approach. The structures of a number of isolated viral capsid proteins have been solved to high resolution by X-ray diffraction (e.g., see references 74, 254, 255, 324, and 347). Image reconstruction from electron micrographs cannot equal the resolution attained by X-ray diffraction (yet see references 42 and 80), but it provides a context for diffraction results by being able to orient the atomic structure of the subunit into the complex 3D structure of the virion (64, 145, 162, 166, 233, 261). Finally, cryo-EM followed by image reconstruction can be performed with heterogeneous populations of particles. This allows one to explore biochemical treatments which have known effects on virus composition or infectivity but which do not cause a transition of the entire population of particles to a defined state (132, 325). The ability to accommodate flexibility makes cryo-EM and 3D image reconstruction (cryoreconstruction) an ideal tool for exploring changes in virus structure.
This review focuses on the results of 3D reconstruction of icosahedrally symmetric viruses from cryo-electron micrographs. We begin with a brief introduction to the standard terminology so that the reader will share our language for describing the icosahedral structures presented. We then discuss the preparation and microscopy of vitrified specimens and describe 3D reconstruction by the common lines technique as it has been recently implemented for viral structures. More-detailed discussions of the processing methods have been presented elsewhere (9, 133, 210). We then address the question of interpretation of the reconstruction, describing the tools and pointing out some of the pitfalls to be avoided. We continue with a description of some of the portions of virus life cycles illustrated by these results. This section owes much to our colleagues who have very generously allowed us to present their work here. Their willingness to share results and ideas has made the development of this field rapid and enjoyable. We conclude with a comprehensive list of relevant details and literature citations for the bulk of image reconstruction work on icosahedral viruses and a brief discussion of the prospects for extending the technique to higher resolution and the examination of more-complex viral and nonviral systems.
Abbreviations used.
3D, three-dimensional; aa, amino acid(s); Ad, adenovirus; BmCPV-1, Bombyx mori cypovirus 1; BPV-1, bovine papillomavirus serotype 1; BRDV, Broadhaven diseaese virus; BTV, bluetongue virus; CaMV, cauliflower mosaic virus; CCMV, cowpea chlorotic mottle virus; CPMV, cowpea mosaic virus; cryo-EM, cryo-electron microscopy or cryo-electron microscope; cryoreconstruction, cryo-EM and 3D image reconstruction; CTF, contrast transfer function; DLP, double-layered particle; dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; EM, electron microscopy or electron microscope; FEG, field emission gun; FHV, flock house virus; FMDV, foot-and-mouth disease virus; FSC, Fourier shell correlation; HepBc, hepatitis B virus capsid; HK97, bacteriophage Hong Kong 97; HPV-1, human papillomavirus serotype 1; HRV2, HRV14, and HRV16, human rhinovirus serotypes 2, 14, and 16, respectively; HSV-1, herpes simplex virus serotype 1; IBDV, infectious bursal disease virus; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IgG, immunoglobulin G; ISVP, intermediate subviral particle; MAb, monoclonal antibody; NC, nucleocapsid; NIm, neutralizing immunogenic; RDV, rice dwarf virus; RGD, arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide; RRV, Ross River virus; SFV, Semliki Forest virus; SNV, Sindbis virus; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA; SV40, simian virus 40; T1L, type 1 Lang; T3D, type 3 Dearing; TLP, triple-layered particle; TYMV, turnip yellow mosaic virus; VLP, virus-like particle; wt, wild type.
THE LANGUAGE OF ICOSAHEDRAL SYMMETRY
Throughout this review, icosahedral structures are described in language which assumes their regularity and symmetry. This description is based on the theory of quasi-equivalence introduced by Caspar and Klug (53). There are several excellent reviews of icosahedral organization and its expression at the atomic level as determined by X-ray diffraction techniques (148, 149, 176, 202, 260). We will not enter into such a detailed discussion of these results but rather confine ourselves to their description and relevance for the interpretation of 3D reconstructions.
The basic problem addressed by Caspar and Klug (53) in their elegant paper was the understanding of virus structure as the consequence of the self-directed interaction of a large number of chemically identical units. Self-assembly requires specificity of bonding between the units of the structure. One way to accomplish this is to allow all subunits to form identical bonds with their neighbors. A crystal of water or sucrose is formed in this way, as are protein assemblies such as the octahedral assembly of pyruvate dehydrogenase (98). Since a virus structure is optimized for the propagation of its genome, it is advantageous to make a large shell with a small amount of information devoted to structural components. One can imagine that a virus with octahedral symmetry could enclose its genome only if it were formed from very large subunits. This would require that it devote a large fraction of its genome to coding for these structural proteins. Forming a shell from a larger number of small, identically bonded subunits would provide a more parsimonious solution both to the problem of encapsidating a large amount of genetic information and to that of self-assembly.
The Icosahedron
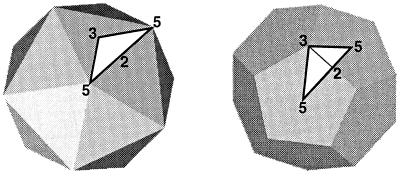
An icosahedron (Fig. 2, left) is an isometric structure with 12 pentagonal vertices and 20 triangular faces. Any icosahedron has a defined set of exact symmetry elements: 6 fivefold axes through the 12 vertices, 10 threefold axes through the 20 triangular faces, and 15 twofold axes through the edges. The related structure, the pentagonal dodecahedron (Fig. 2, right), shares the same symmetry elements but has a complementary morphology: 6 fivefold axes through the pentagonal faces, 10 threefold axes through the vertices, and 15 twofold axes through the edges. Both of these ideal geometric structures have icosahedral symmetry, as do spherical viruses, whose shapes lie between these two extremes.
FIG. 2.
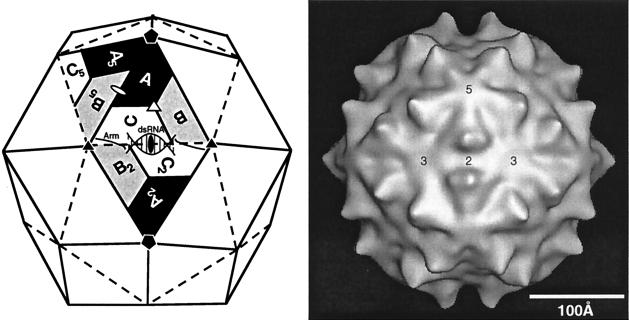
An icosahedron (left) and dodecahedron (right) with symmetry axes and the asymmetric unit used by microscopists. The numbers (2, 3, and 5) indicate the positions of some of the symmetry axes. The white triangle defines the asymmetric unit which is bounded by the lines joining adjacent fivefold and threefold positions.
The positions of the symmetry elements are the landmarks used to describe any icosahedral structure. Application of the icosahedral symmetry elements to a subunit which does not lie on a symmetry axis causes it to be repeated 60 times in the complete structure. This means that the complete structure can be generated by taking 1/60th, called the asymmetric unit, and operating on it with the symmetry elements. The choice of the unit cell is arbitrary. In icosahedral reconstruction, the asymmetric unit is usually defined as being the wedge-shaped volume which extends from the icosahedron’s center along edges formed by a threefold axis and two adjacent fivefold axes (14, 130, 133). In most high-resolution X-ray structures of viruses, the conventional asymmetric unit is bounded by a fivefold axis and two adjacent threefold axes (350). Another way of understanding the effect of the symmetry elements which is particularly appropriate to image reconstruction is to realize that a single, nonaxial view of an icosahedral object is equivalent to 59 other views generated by the symmetry axes.
The simplest icosahedral structure is one in which 60 identical subunits interact identically. Caspar and Klug (53) pointed out that, when more than 60 subunits interact to form a closed shell, as appeared to be true for many spherical viruses, all subunits cannot have identical environments. This lack of equivalence between the subunits reopened the question of self-assembly of the subunits. Quasi-equivalence is a solution to this problem (53). Their hypothesis was that shells with more than 60 subunits would be formed from chemically identical subunits with slight but regular changes in the bonding. Hence, a virus comprising 180 subunits would contain three types of bonding and three distinct environments for the subunits. The three types of subunits would no longer be equivalent but rather quasi-equivalent because their environments were similar but not identical.
Triangulation Numbers
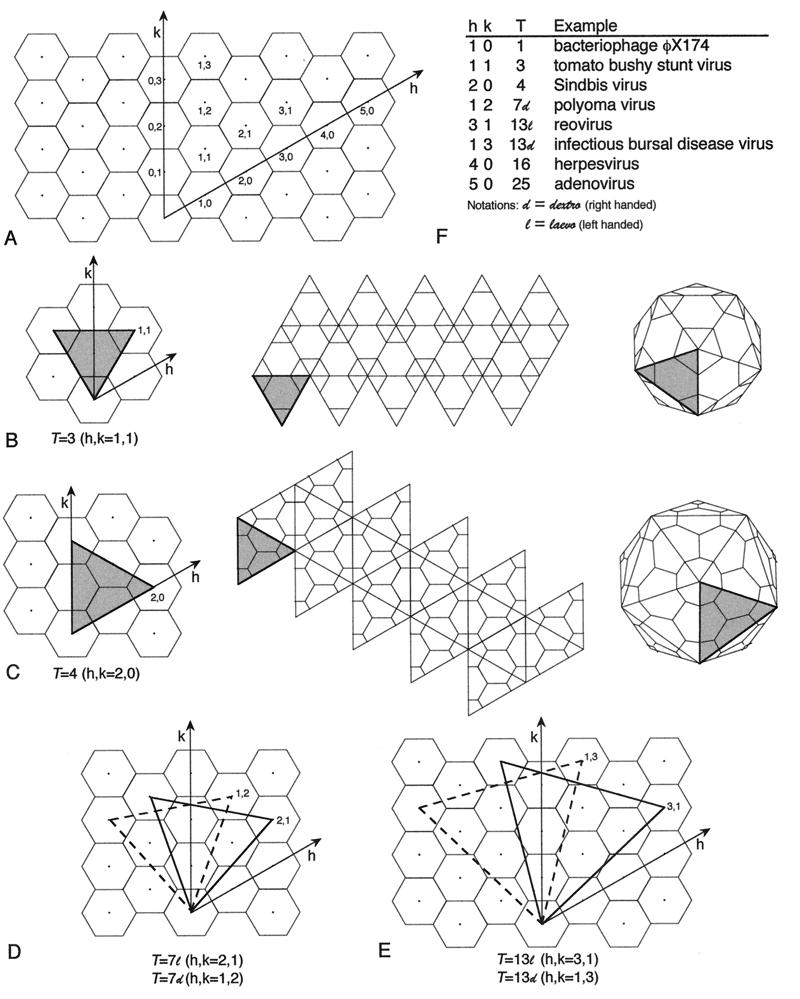
Triangulation number is a geometric and abstract concept that does not necessarily correspond to the structural components of an individual virus. It refers to the organization of the geometric figure (Fig. 2). One can visualize the formation of an isometric shell by beginning with a flat, hexagonal net. In the original net, all internal bonds are identical in environment. To curve the net and generate a closed structure, one converts some of the hexagons to pentagons. This concept of quasiequivalence can be naturally expressed by the triangulation number for an ideal icosahedron. This can be seen from a consideration of the building of larger icosahedra from a hexagonal net (Fig. 3). The simplest icosahedron has only equivalent units: all bonds are identical and all vertices have identical bonding. The larger icosahedra have hexagons between the pentagons and can be visualized as replacing the original triangular faces with larger ones formed from equilateral triangles. The number of triangles replacing the original one is the triangulation number. More precisely, the triangulation number is given by the following relationship, T = h2 + hk + k2, where h and k are positive integers which define the position of the fivefold vertex on the original hexagonal net. The different triangulation numbers have very different organizations of bonding (Fig. 4).
FIG. 3.
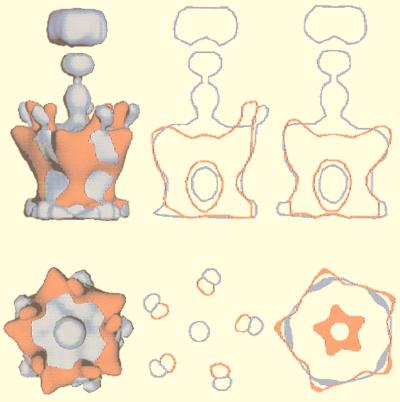
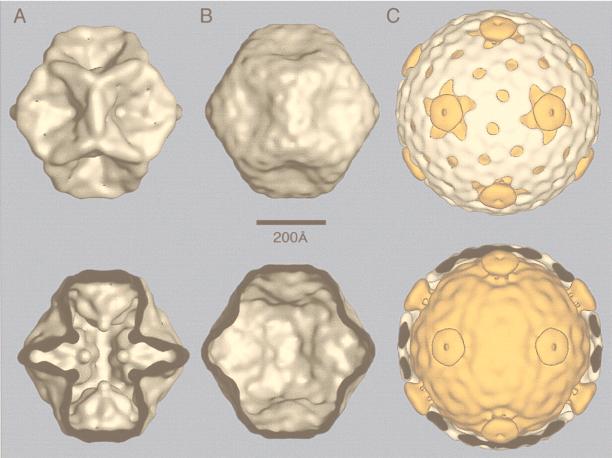
Geometric principles of constructing icosahedral lattices of defined T (triangulation) number. (A) An array of hexamers, represented as a flat sheet of hexagons, is the basis for generating icosahedra (178). A closed icosahedral shell that conforms to the principles of quasi-equivalent symmetry contains 60T subunits organized as hexamer and pentamer units (53). Hexamers are initially considered planar (hexagons in the flat sheet), and pentamers are considered convex and introduce curvature in the sheet of hexamers when they are inserted in place of specific hexamers. A closed shell is generated by inserting 12 pentamers at appropriate positions in the hexamer net as specified by (h,k) lattice points that mark the centers of the original hexagons in the sheet. The model of a particular quasi-equivalent lattice is constructed as follows. Generate one face of an icosahedron by defining an equilateral triangle in the net. The first side of the triangle is a line connecting the origin point of the net (h,k = 0,0) to any (h,k) point. This process will lead to a lattice of T number given by the relation T=h2 + hk + k2. The remaining two sides of the triangle are formed by connecting the (h,k) point to the appropriate points needed to form an equilateral triangle, as illustrated for the nonenantiomeric T=3 (B) and T=4 (C) lattices and the enantiomeric T=7l,d (D) and T=13l,d (E) lattices. A planar sheet of 20 such triangles is formed, and the sheet is then folded up to form a closed icosahedron as depicted for T=3 and T=4 lattices (B and C). In this way, each of the hexamers at the (h,k) lattice points that define the corners of the triangles are replaced by pentamers and each triangular face contains 3T subunits. (F) Examples of viruses with different T-lattice symmetries. Not all viruses conform to the simple rules of quasi-symmetry as stated above. For example, all T=7 papovaviruses such as polyomavirus have capsids built of 360 subunits arranged as 72 pentameric capsomers (29, 252, 293). A further useful relation is that the number of capsomers is given by 10T+2. Adapted from reference 178 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
FIG. 4.
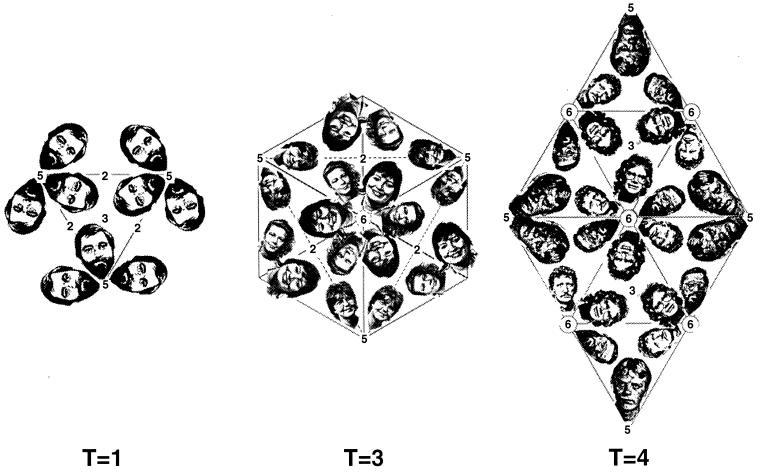
The environments of subunits in three different triangulation numbers shown by an arrangement of the heads of the members of one of our groups. Only a single environment is required in the T=1 arrangement, while three and four environments are present in T=3 and T=4, respectively. Notice that a larger head (subunit) is necessary to fill the same-sized asymmetric unit for the lower triangulation numbers. The positions of the icosahedral twofold (2), fivefold (5), and threefold (3) and the quasi-sixfold (6) axes are indicated.
The remnants of the hexagons, now rendered nonequivalent by their construction into an icosahedron, remain hexavalent and are seen as the positions of local or quasi-sixfold axes in the larger icosahedra. In general, the nonfivefold lattice points of the icosahedral net must correspond to the positions of hexavalent structural units. These positions often correspond to the positions of capsomers, which are apparent structural units on the surface of some viruses.
The number of different environments occupied by a subunit increases as the triangulation number increases. The original theory of quasi-equivalence stipulated that the number of different environments should equal the triangulation number; therefore, a T=4 virus would have four different subunit environments and 60T or 240 subunits (120, 130, 230). The correspondence between T number and the number of different subunit environments is not always strictly maintained. In agreement with the theory of quasi-equivalence, a T=1 (h=1,k=0) icosahedral virus such as satellite tobacco necrosis virus has only one type of environment for its subunit and a total of 60 subunits (203). Similarly, the T=3 (h=1,k=1) tomato bushy stunt virus has three separate environments for a total of 180 subunits (150). In contrast to this, the T=7 papovaviruses are composed of 72 pentamers and have six subunit environments and yet only 360 subunits (h=1,k=2 for the T=7dextro or right-handed organization as in SV40) (4, 201). The same arrangement is seen in three papillomaviruses (29, 188). However, not all T=7 viruses violate quasi-equivalence, since bacteriophage P2 (101) and CaMV (65) also display triangulation number T=7 but have 12 pentameric and 60 hexameric capsomers for a total of 420 subunits with seven distinct environments. When the correspondence is direct, determination of the triangulation number provides a count of the number of subunits; otherwise, it remains a descriptive tool. The nominal “T=2” arrangement of the fungal virus capsids (63) and the intermediates of the dsRNA viruses φ6 and BTV (48, 144) can be viewed as a T=1 arrangement of pairs of chemically identical subunits.
Cryo-EM in combination with image reconstruction provides a direct, objective way to determine triangulation numbers of spherical viruses and also allows direct determination of the number of subunits in the virion when individual units are resolved. For example, the trimeric nature of the capsomers that lie on the T=25 net of adenovirus is apparent in the reconstruction (296), and the number of subunits and their environments are clearly identified. Reconstructions also provide information concerning the alteration of subunit conformations and their interactions in the structure. In adenovirus, these changes appear to occur at the sites of interaction with the minor structural proteins of the virus (135, 296, 298) and so provide a view of the quasi-equivalence in practice.
Classically, the projected images of negatively stained viruses have been used for the determination of triangulation numbers (53). Two approaches have been employed. The first is the inference of capsomer positions and their placement on an icosahedral net, often by comparison with a model of the triangulated structure (121, 188, 189). This method is not only technically difficult but fraught with difficulties due to the vagaries of negative staining and the mental gymnastics associated with inferring a 3D structure from two-dimensional views of particles of unknown relative orientation. It has, however, produced the correct triangulation number when applied carefully to structures that respond well to negative staining (188). The second approach is to combine an estimate of the subunit size with the radius of the virus to infer the number of subunits and a triangulation number (i.e., 60 [T=1], 180 [T=3], 240 [T=4], … ). This approach is very straightforward, but it often produces the wrong answer. Microscopists who are tempted to utilize this second method should realize that their conclusions may be challenged by the more objective 3D reconstruction methods described here. Naturally, either method depends upon but does not validate the assumption of icosahedral symmetry (134).
PREPARATION OF VITRIFIED VIRUS SAMPLES
The methods of preparing viruses and many other types of biological macromolecules for cryo-EM studies are well established (1, 71, 109, 218). A vitrified specimen of a spherical virus is typically prepared in the following way (Fig. 5). A 2- to 5-μl aliquot of a purified, 0.05- to 5-mg/ml suspension of virus is applied to an EM grid coated with a holey carbon support film. The grid is secured with a pair of forceps in a guillotine-like device and suspended over a bath of cryogen slush (usually ethane or propane) maintained near its freezing point by a reservoir of liquid nitrogen. The grid is then blotted nearly dry by pressing a piece of filter paper directly against it, the guillotine is released, and the grid is rapidly plunged into the cryogen.
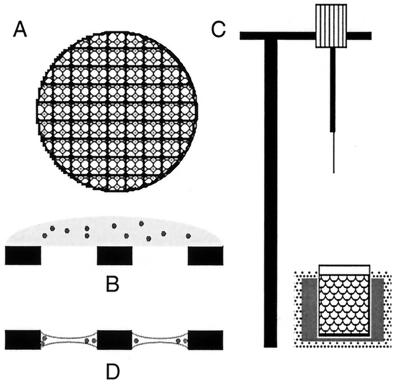
FIG. 5.
The steps in a typical preparation of a specimen for cryo-EM are shown. A holey carbon film (A) is prepared by the evaporation of carbon onto a grid bearing a holey plastic film and the removal of the plastic by exposure of the grid to the fumes of ethyl acetate. This film contains holes with diameters between 1 and 5 μm. The specimen is applied to the film at concentrations between 50 μg/ml and 5 mg/ml (B). The grid may then be floated on a drop of water or low-ionic-strength buffer to remove excess salt. The grid is then placed in a pair of forceps which are locked into a guillotine-like device (C) and blotted with filter paper to produce a very thin aqueous film (1,000 to 2,000 Å) across the holes of the grid (D). Immediately after blotting (and before the aqueous film has had time to dry), the plunger is released to allow the forceps to drop into a bath of ethane slush held in a container of liquid nitrogen. The efficient cooling afforded by the ethane slush causes vitrification of the sample. It is then either stored under liquid nitrogen or placed in a liquid-nitrogen-cooled specimen holder for viewing in the microscope.
Vitrification of the water rather than crystallization (i.e., ice formation) occurs if the sample is thin enough (∼0.2 μm or less), so that cooling occurs very rapidly. Estimates vary, but there is agreement that the rate of cooling exceeds 104 °C/s (see discussion in reference 31). An efficient cryogen such as propane or ethane slush rather than liquid nitrogen must be used because the Leidenfrost effect (the creation of gas upon contact with the specimen) would otherwise slow heat transfer so that crystalline ice would be formed (110).
The concentration of the sample is critical and is usually higher than that needed for negative staining. Application of the sample to a continuous carbon film followed by a brief period of absorption (1 to 2 s) before negative staining can be used to determine the appropriate range of concentration. Prolonged absorption before staining will concentrate the sample on the grid so that it appears more concentrated than it will by cryo-EM.
The thickness of the water layer primarily depends on blotting time, wetting properties of the support, and the humidity near the sample. Excessive drying rapidly thins the specimen, often causes particles to migrate toward the periphery of the holes in the substrate, and can lead to drastically increased solute concentrations as well as dehydration, all of which alters the specimen’s environment and perhaps structure (211, 212, 330). Alternatively, inadequate drying leaves a sample in which particles are superimposed or embedded in a water layer that is too thick for the electron beam to penetrate. Some workers prepare their samples in cold rooms (174) or in 37°C rooms at 100% humidity (211, 212) to avoid the effects of drying on sensitive specimens. However, the use of humidity-controlled glove boxes (174), double-blotting techniques (310, 334), or a simple temperature-controlled mist device (75) may preserve the state of the specimen with less stress on the investigator.
All subsequent steps, including the recording of images in the microscope, are carried out with the sample below −160°C to avoid the devitrification which occurs at ∼−140°C (113, 198, 200). These include transfer of the grid from the cryogen into liquid nitrogen (where it may be stored indefinitely) and then into a cooled cryospecimen holder which is rapidly (and carefully) inserted into the EM. All of the transfer steps must be performed rapidly to avoid warming of the specimen and contamination by the condensation of water vapor. Such condensation can be minimized by continuously bathing the cold sample in dry nitrogen gas during transfer to the microscope vacuum, which is an option on some cryotransfer systems. Excess water vapor that gets into the microscope severely overloads the high-vacuum system and reduces its useful lifetime. This has become increasingly critical with the use of sensitive FEG sources. The beginner should become comfortable with all steps of transfer with cryoholder and specimen at room temperature before preparing a vitrified specimen.
As with other techniques in microscopy, various alternative procedures have been developed for each of the steps described above. Usually the specimen is prepared on a holey carbon film, which sometimes is glow discharged to enhance the spreading of the specimen. Alternatively, continuous carbon films, carbon-coated plastic films, or even bare grids (1) have been successfully used as supports for different viruses. The age of the carbon film often determines the quality of the specimen spreading: old support films can be recarboned to produce usable grids (335a). Sometimes, specimens prepared on holey films do not appear in the holes because they strongly adhere to the support film. If this occurs, the properties of the support must be altered. If hydrophobic support films are required, grids may be glow discharged in an atmosphere of amyl amine (112). However, support films that are too hydrophobic usually exhibit regions of thin “ice” surrounded by very thick “ice.” An alternative is to apply a dilute solution of lipids (0.1% [wt/vol] phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine in H2O) to the grid before the specimen. This results in a vitrified layer of water sandwiched between lipid monolayers (325). A number of different techniques and apparatuses that are capable of producing uniformly thin, vitrified samples have been developed. These procedures include the double blot (310), carbon sandwich (302, 303), jet spray (111, 114), pressurized liquid nitrogen (109), and many others.
Another concern of the microscopist is that many aqueous samples of biological specimens contain high concentrations of buffer salts (>100 mM) or solutes such as glycerol (5 to 10%). Their presence can lead to phase separation upon cooling and diminish the contrast in the image. This alteration of the specimen environment can lead to structural changes. Such solutes may sometimes be removed without disrupting the virus on the grid by floating the grid on a drop of distilled water or an appropriate, low-concentration buffer for a fraction of a minute, in much the same way as is common with the preparation of negatively stained samples. This washing technique works even when holey carbon films are used, since it appears that the sample adheres to the air-water interface (325). A somewhat more concentrated sample (3 to 5×) should be used when this washing approach is employed.
Success in obtaining a vitrified sample suitable for cryo-EM thus depends on many factors, the most important of which are dictated by the properties of the virus (pI, enveloped or not, etc.), solution (pH, ionic strength, etc.), and support film and certainly the experience (and persistence) of the microscopist. A number of studies have demonstrated that the dimensions and integrity of most viruses and other fragile macromolecular assemblies are well preserved by cryopreparation techniques (1, 26, 130, 211, 228). This provides strong evidence that the specimens are fully embedded in a vitreous layer; those that are not become distorted and compressed (197).
CRYO-EM OF VIRUSES
The main differences between conventional transmission EM and cryo-EM of biological specimens arise from the requirements to keep the specimen below the devitrification temperature, to minimize contamination and electron dose, and to enhance the inherently low contrast in unstained specimens. These requirements place additional demands on the microscope and microscopist.
Aqueous specimens examined by cryo-EM must be maintained at or below the devitrification temperature (∼−140°C) to prevent conversion of water in the sample to a crystalline state. A number of different designs for liquid nitrogen-cooled, cryospecimen holders have been described elsewhere (105, 109, 151, 152, 155, 301). Side-entry cryoholders have improved enormously over the past few years, but they remain less stable than conventional, room temperature holders.
Cryoholders are subject to greater instabilities due to the temperature gradient between the microscope at room temperature and the specimen and as a result of boiling of the coolant which transmits vibrations to the specimen. Current stage designs have minimized these problems with a satisfying improvement in resolution. Nevertheless, the maximum instrumental resolving power of most modern microscopes (∼0.7 to 2 Å) cannot yet be achieved with currently available cold holders which promise stability in the 2- to 4-Å range. The development of a microscope which incorporates a liquid-helium-cooled, specimen stage and a superconducting objective lens has provided a means to achieve even better resolving power (127, 128, 196, 354, 355), as has the development of practical top- and side-entry stages for liquid helium work. These stages have shown their worth in the increased resolution obtained with crystalline specimens (52, 153, 154, 190) and should provide similar advantages for single particle specimens such as viruses.
Even when the specimen holder is rapidly transferred to the microscope, water vapor is carried in by the rod of the holder. The low temperature of the specimen unfortunately makes it an efficient sink for contaminants. The consequent high rate of specimen contamination forces the cryomicroscopist to work quickly or use an auxiliary anticontamination device. Several devices such as the blade-type anticontaminators, which closely sandwich the specimen, have been constructed and are commercially available (113, 164, 173). These devices significantly reduce the level of contamination so that cryo-EM can now routinely be carried out for a period of several hours with an individual specimen grid. One drawback to the use of the auxiliary anticontaminator is that it often restricts the range of tilt normally allowed on a goniometer stage. Fortunately, this does not pose severe constraints in most work with icosahedral viruses because they tend to be randomly oriented in the vitreous sample layer, and it is usually not necessary to record different views by tilting in order to obtain 3D information. When virions show a strong preference for one or a few orientations as occurs with reovirus and adenovirus due to their surface projections, a tilt of 10°, which can be accommodated by the anticontaminator, is usually enough to give an adequate sampling of orientations (108, 296). Should higher tilts be necessary, the anticontaminator can be retracted after about an hour when most of the water vapor from the specimen holder has been trapped. The structure of adenovirus was determined to 35-Å resolution by combining images of 29 particles (296). The fibers which project from the fivefold axes cause the virus to tend to lie in orientations which are away from the surface of the water layer. This orientation preference was overcome by tilting the stage by 10° during microscopy. This was sufficient in combination with the rotational disorder of the virions in the water layer to allow the collection of a complete data set (296).
Search for Suitable Specimen Areas
After allowing some time (>15 min) for the specimen stage to stabilize after insertion into the microscope, the EM grid is searched at very low magnification (<×2,000 to ×3,000) and at a very low irradiation level (<0.05 e−/Å2/s) to locate a suitable specimen area for photography. At low magnification it is possible to assess the relative thickness of the vitrified sample (Fig. 6). The switch from high- to low-magnification operation is conveniently selected in many microscopes by the push of a single button. Some cryomicroscopists prefer to view the “false,” low-magnification image that is formed by highly defocusing the pattern formed in diffraction mode. The advantages of this technique are that the “diffraction” image exhibits very high contrast, and realignment of the microscope is usually not required. Many newer microscopes have a three-state system which allows switching among low magnification for searching, high magnification for focusing, and intermediate magnification for recording images. Areas on the grid that appear black are too thick for the electron beam to penetrate; areas that appear bright are likely to be dry. Sometimes, regions of the specimen appear to be vitrified but are actually dehydrated regions in which the buffer salt has crystallized and appears like an “ice” layer. Truly vitrified specimens of optimal thickness are usually characterized by a cloudy appearance. One can verify the vitrified nature of a particular specimen area at high magnification by the occurrence of bubbling at the sites of particles within the area during the first few seconds of irradiation.
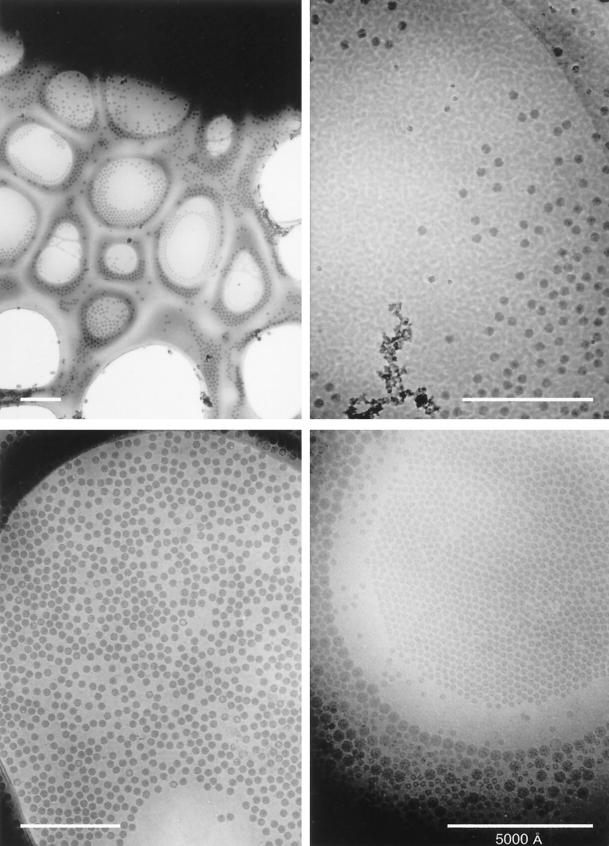
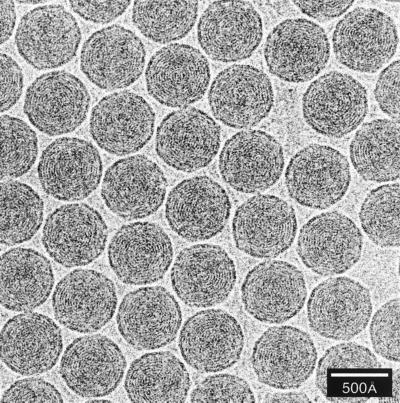
FIG. 6.
Low-magnification views of vitrified samples of icosahedral viruses, including Nudaurelia capensis β virus (upper left and upper right), SV40 (lower left), and a mixture of polyomavirus and bromegrass mosaic virus (lower right). The grid square with the N. capensis β virus specimen (upper left) is a particularly poor candidate for cryo-EM, but it nicely exhibits a complete spectrum of ice thicknesses, from much too thick at the top (black region) to completely absent at the bottom (holes with no specimen). Only a few holes in the carbon film at the border of the very thick ice have a suitable thickness and distribution of virus particles. The strongly mottled appearance of the N. capensis β virus sample (top right) is caused by ice contamination that quickly builds up on specimens if a blade-type anticontaminator is not used during microscopy. The SV40 sample is a nearly perfect monodispersed distribution of particles in a uniform layer of ice. The bare circular region presumably resulted when surface tension effects in the thinning water layer excluded the ∼500-Å-diameter particles just before vitrification occurred. The mixed polyomavirus and bromegrass mosaic virus sample shows a graded change in specimen thickness, from a thin region near the center of the hole where the small (∼300-Å-diameter) bromegrass mosaic virus particles congregate in a single layer to progressively thicker regions marked by a ring of 500-Å-diameter polyomaviruses surrounded by more polyomaviruses and multiple layers of bromegrass mosaic virus. All magnification bars represent 5,000 Å.
Because most viruses smaller than ∼1,000 Å are difficult to see directly at very low magnification, a convenient way to assess the particle concentration is to view one area (grid square) at a higher magnification and at a higher level of defocus, thereby sacrificing that specimen region. One then assumes that the particle concentration remains relatively constant in other areas of the grid for vitrified samples of similar thickness. The use of a video-rate TV camera system (e.g., see reference 104) provides a very effective means for scanning cryospecimens at a very low magnification and dose and simultaneously allows the user to easily assess particle distributions for viruses as small as 300 Å in diameter. Alternatively, a charge-coupled device camera can be used to visualize particles at higher magnification (232) and to check imaging conditions by performing a Fourier transform online.
Imaging Conditions
Once a suitable specimen area is selected at low magnification, the image is switched to high magnification for focusing and astigmatism correction. These adjustments are typically made 2 to 10 μm away from the area to be photographed and are often more easily performed at a magnification (>×100,000) much higher than that used for photography (×25,000 to 50,000). Several factors dictate the choice of operating conditions (magnification, defocus level, accelerating voltage, beam coherence, electron dose, etc.): the most significant ones are the overall dimension (diameter) of the virus studied, the anticipated resolution of the images, and the requirements of the image processing needed to compute a 3D reconstruction to the desired resolution. For example, for an expected resolution of 20 to 30 Å, images are typically recorded at ×25,000 to 50,000 magnification with an electron dose of between 5 and 20 e−/Å2. This produces a micrograph with sufficient optical density (0.2 to 1.0) for subsequent image processing steps (see “Image analysis and 3D reconstruction”).
Radiation Damage
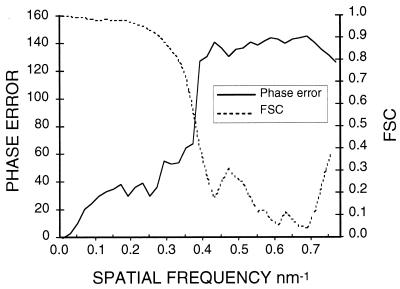
Unstained, vitrified biological specimens are very sensitive to the effects of electron irradiation (Fig. 7). At −170°C, features in the 20- to 40-Å resolution range are unaffected by a total electron dose of ∼10 to 20 e−/Å2, a value similar to that found for negatively stained specimens (7, 318) but 5 to 10 times greater than that for unstained specimens at room temperature (317). Thus, microscopy must be performed in a way which minimizes exposure of the specimen to the electron beam. This requires the use of minimal irradiation procedures (e.g., see references 8, 317, and 345) which act to limit specimen exposure to the minimum necessary to record a micrograph with sufficient optical density and signal. Most modern microscopes offer some convenient mode of low-dose operation. Dose levels may be measured directly by the use of a Faraday cage (215, 316) or they may be estimated from the standard microscope exposure meter after calibration. This latter procedure is done by measuring the optical densities on an EM film of known sensitivity which has been exposed for different times and developed under carefully controlled conditions (e.g., see reference 8). A careful study of the effect of radiation damage on the cryoreconstruction of the HSV-1 capsid showed that the reconstructions of particles which had received 30 to 40 e−/Å2 had recognizable but blurred features compared to particles which had received a more standard 7 to 10 e−/Å2 (84). The high-resolution reconstructions of HepBc which yielded resolutions of better than 10 Å used single images taken at 10 to 16 e−/Å2 or pairs of images taken at 7 to 10 e−/Å2 each (42, 80).
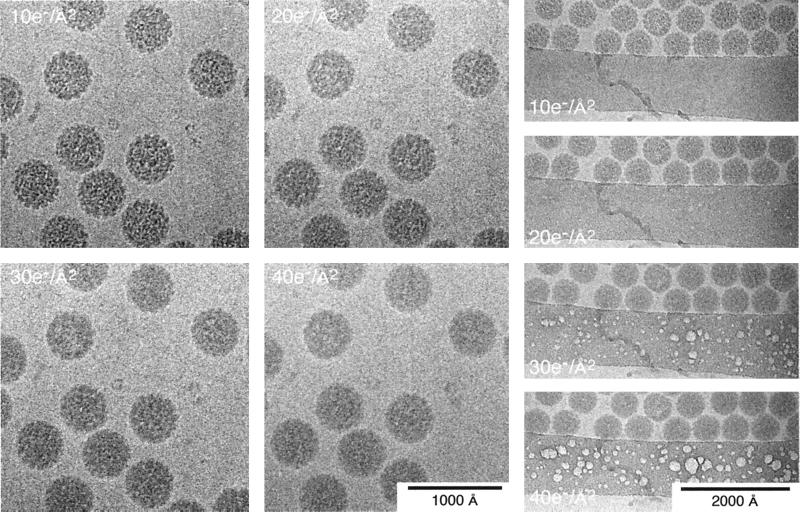
FIG. 7.
Radiation damage in vitrified SV40 samples. Fine structural details are progressively lost in the SV40 particles as the electron dose increases from 10 to 40 e−/Å2 (left series). The most prominent damage first appears as bubbling that occurs in the ice over the carbon support film (right series). Bubbling also occurs within particles suspended over the holes of the support film but usually only after doses of about 50 e−/Å2 or more (data not shown).
Contrast Enhancement
The image is carefully focused to optimally enhance phase contrast as discussed below. Because of the intrinsic low contrast in images of unstained specimens, it is not possible to focus accurately by observing specimen details directly as is routinely done with negatively stained specimens. Instead, a number of methods are used to set the desired focus level. First, focusing must be performed on an area (preferably on the tilt axis) that is adjacent to the one that will be photographed in order to minimize the electron dose to the specimen. Focusing is then done by observing the Fresnel fringes that appear at the edges of holes in the carbon film, the dry carbon “grain,” or the Fresnel fringes that appear around bubbles of volatile molecules which form during specimen irradiation.
The relationship between the electron image of the specimen and the specimen itself is, unfortunately, not straightforward. This relationship is described by the contrast transfer function, or CTF, which involves both phase- and amplitude-contrast components. These are characteristic of the particular microscope used, the specimen, and the conditions of imaging. The contrast-enhancing effect of the CTF arises from the spherical aberration present in all electromagnetic lenses and varies as a function of the objective lens focal setting and accelerating voltage (Fig. 8). The function includes both a phase-contrast and an amplitude-contrast component:
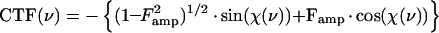 |
where χ(v) = π · λ · v2(Δf − 0.5 · Cs · λ2 · ν2), v is the spatial frequency, (per angstrom), Famp is the fraction amplitude contrast, λ is the electron wavelength (angstroms), where 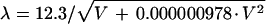 (0.042 Å for 80-kV electrons and 0.02527 Å for 200-kV electrons), V is the voltage (volts), Δf is the underfocus (micrometers), and Cs is the spherical aberration of the objective lens of the microscope in millimeters. The CTF is usually attenuated by an envelope function which depends upon the coherence of the beam, drift, and other factors (116, 329, 331). Thus, at any particular defocus setting of the objective lens, phase contrast in the electron image is positive and maximal at only a few specific spatial frequencies; at all other frequencies, contrast is either lower than expected, completely absent, or opposite (inverted or reversed) from what it should be. This allows the microscopist to selectively accentuate image details of a particular size much as an optical-phase microscope accentuates some features at the expense of others. This discussion ignores the effects of inelastic scattering, which can be severe for vitrified samples embedded in thick layers of water (192, 283). Inelastic scattering effects can be modeled by including an envelope function which imposes an exponential decay in the transfer function similar to that resulting from the lack of coherence in the beam (124). The effect is dramatically revealed in thick regions of the specimen; images of particles in these areas appear unsharp due to significant chromatic aberration effects.
(0.042 Å for 80-kV electrons and 0.02527 Å for 200-kV electrons), V is the voltage (volts), Δf is the underfocus (micrometers), and Cs is the spherical aberration of the objective lens of the microscope in millimeters. The CTF is usually attenuated by an envelope function which depends upon the coherence of the beam, drift, and other factors (116, 329, 331). Thus, at any particular defocus setting of the objective lens, phase contrast in the electron image is positive and maximal at only a few specific spatial frequencies; at all other frequencies, contrast is either lower than expected, completely absent, or opposite (inverted or reversed) from what it should be. This allows the microscopist to selectively accentuate image details of a particular size much as an optical-phase microscope accentuates some features at the expense of others. This discussion ignores the effects of inelastic scattering, which can be severe for vitrified samples embedded in thick layers of water (192, 283). Inelastic scattering effects can be modeled by including an envelope function which imposes an exponential decay in the transfer function similar to that resulting from the lack of coherence in the beam (124). The effect is dramatically revealed in thick regions of the specimen; images of particles in these areas appear unsharp due to significant chromatic aberration effects.
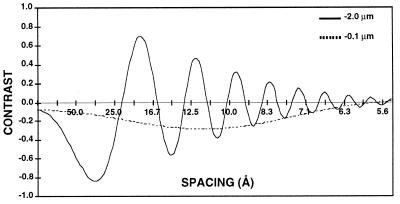
FIG. 8.
The CTF for a Philips CM200 FEG at 200 kV is plotted as a function of resolution in angstroms for an underfocus of 2 μm and an underfocus of 1,000 Å and a magnification of ×36,000. The decrease in the amplitude of the function with increased resolution reflects the measured attenuation due to the lack of coherence in the source, specimen movement, and other optical effects. The value of −0.1 at the origin is the amplitude contrast portion of the function.
In practice, cryomicroscopists typically underfocus images by 8,000 to 20,000 Å (0.8 to 2 μm) to enhance specimen features in the 20- to 40-Å size range (Fig. 9). This amount of defocus is quite foreign to conventional biological microscopists who are used to imaging shadowed or stained specimens much closer to focus (3,000- to 5,000-Å underfocus). Sometimes it is advantageous to record two or more images at different focal settings to selectively enhance different features of the cryospecimen. For example, the overall organization of the glycoprotein spikes in the enveloped SFV is best enhanced at an ∼3-μm or larger underfocus (Fig. 9), whereas the lipid bilayer is best visualized in images recorded much closer to focus (<1.5 μm). Images from a focal series can also be combined to compute 3D reconstructions as described in “Image analysis and 3D reconstruction” or can be useful for analyzing very noisy data (e.g., see reference 65).
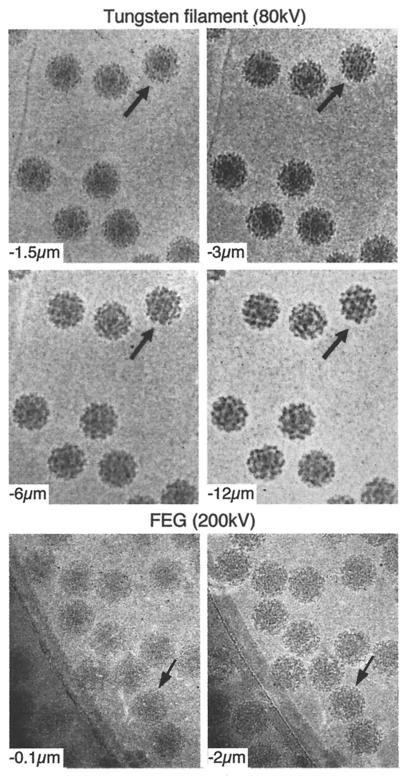
FIG. 9.
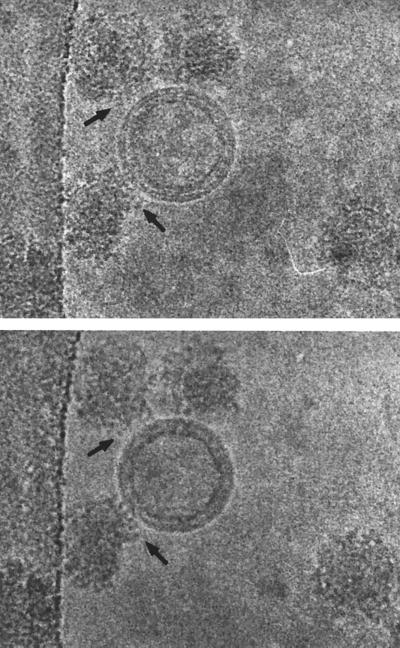
The effect of defocus is shown for cryo-EM of SFV. The top four images show a defocus series taken on a Philips 400 microscope with a tungsten filament at 80 kV for illumination and underfocus values of 1.5, 3, 6, and 12 μm. Notice that the overall contrast is lower in the closer-to-focus image; however, the very fine details, such as the membrane, are recorded. The further-from-focus images do not show these details but do show better contrast for the large features of the specimen such as the spikes and the outline of the particle. This reflects the fact that there is high attenuation of the transfer function with a tungsten filament and hence only the information in the first peak of the CTF is transmitted efficiently. The bottom two panels show cryo-electron micrographs of the same sample taken on a Philips CM200 FEG under the same defocus conditions for which the CTF is plotted in Fig. 8. Both images show fine details because the illumination from a field emission source is more coherent than the tungsten filament and hence a larger range in resolution is transmitted. Images at different defocus must still be combined because information is lost at the transfer function nodes and attenuated near them. Identical particles in each of the focal series are indicated (arrows).
The first work on cryo-EM studies of viruses was performed with conventional transmission EMs operated at accelerating voltages of 80 or 100 kV. Recent experience shows that the use of FEG illumination is an enormous advantage for cryo-EM (72, 210). The major source of contrast in an electron micrograph of an unstained specimen is phase contrast. The higher coherence of a FEG source makes the phase contrast in the image much stronger. Practically, focusing and aberration correction become much simpler, and the coherence-dominated falloff of intensity with resolution is greatly reduced. The drive toward higher resolution has required the correction of the contrast transfer effects in the data. This is best done by combining images at different defocus levels (see below). This can be done much more reliably with FEG data because a greater number of Thon rings are visible in optical or computed diffraction patterns of images (116, 304). Higher-voltage instruments are also being employed. The potential advantages of the use of much higher voltages include potentially higher resolution and beam penetration and reduced problems with specimen charging. Higher voltage is particularly important for obtaining higher resolution for larger viruses (>1,000-Å diameter) (360) due to the curvature of the Ewald sphere at lower voltages (210). Finally, several groups have used spot scan imaging for the collection of virus data. This method was originally developed for two-dimensional crystalline specimens, for which it has been shown to decrease the apparent beam-induced drift seen in conventional flood illumination (102, 103). Although a carefully controlled study has not yet been published, several groups have used spot scan images for reconstructions (214, 234, 306, 358, 361–363).
IMAGE ANALYSIS AND 3D RECONSTRUCTION
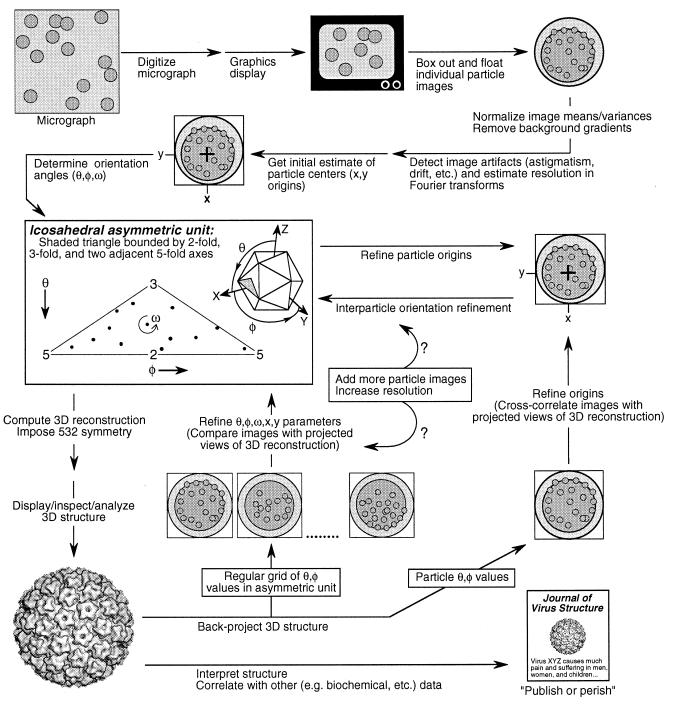
The icosahedral image reconstruction method produces a 3D structure by interpreting the separate images of different particles as distinct views of the same structure. Once the cryo-electron micrographs are obtained, the determination of the structure requires three fundamental steps: (i) determining an initial orientation and center for each particle, (ii) refining these parameters by comparison of common data among different views, and (iii) combining the data from a sufficient number of unique views with their relative orientations to produce the final 3D structure (Fig. 10). This section gives an overview of the processing methods and factors that affect the quality of the reconstruction; the details of this procedure are discussed more extensively elsewhere (9, 133, 210). The methods are implemented in a number of continually evolving software packages (9, 92, 93, 194) which are available from the individual authors. One hallmark of the field is the willingness to share code and ideas among different groups, and consequently the different packages use similar approaches. They all had their origin in the original implementation of common lines (86).
FIG. 10.
Schematic diagram of the 3D image reconstruction process from digitization of the micrograph to the dissemination of the structural results. Though some steps such as the boxing out of individual particle images lend themselves to automation (e.g., see references 33 and 306), many steps including the determination of particle origins and orientations must be repeated and involve some trial-and-error decision making (e.g., to determine which data should or should not be included). The scheme depicted here, which uses both cross-common lines (133) and model-based (9) approaches to determine and refine particle origin and orientation parameters, is but one of many suitable schemes.
Other reconstruction methods have been used for cryo-electron micrographs of icosahedral particles, including the ROSE (reconstruction by optimized series expansion) method (326, 327), the COMET (constrained maximum entropy tomography) method (282), and angular reconstitution (297) as implemented in the IMAGIC software package (322). In the latter two papers, the reconstruction was performed by using orientations derived from the common lines approach (282, 297).
Determination of Particle Orientation and Origin
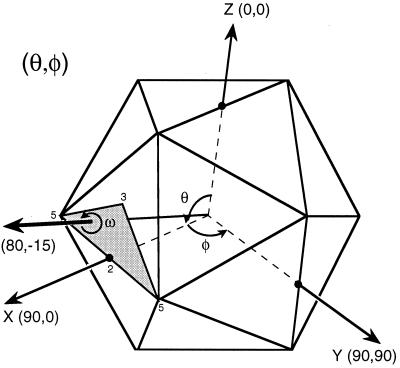
The bulk of the work in the reconstruction process rests in the determination and refinement of the orientations and origins of the views. Five parameters must be determined for each particle (Fig. 11): θ, the inclination of the view vector from a selected twofold axis (typically the z axis); φ, the azimuthal angle relative to the line connecting the adjacent fivefold axes; ω, the rotation of the projected view relative to the x axis in the scanned image; and x and y, the coordinates of the center of symmetry of the particle where all the symmetry axes cross. Icosahedral symmetry allows one to refer any view to one in the asymmetric unit. Hence, the unique views comprise a spherical triangle bounded by neighboring fivefold axes (θ = 90.0°, φ = ±31.72°) and an adjacent threefold axis (θ = 69.09°, φ = 0.0°). Typically, the view parameters must be determined to within about 1° for a low-resolution reconstruction and about 0.25° for a high-resolution reconstruction. This is possible because the projected image of a large object such as a virus changes dramatically with changes in its orientation (Fig. 12).
FIG. 11.
Definition of particle view orientation angles. By convention (189), θ, φ, and ω angles define the orientation in which each icosahedral particle is viewed. The standard setting of the icosahedron places three mutually perpendicular twofold axes of the icosahedron coincident with the x, y, and z axes of a Cartesian coordinate system. The direction of the view vector (thick arrow) is given by θ and φ (the view direction 80°,−15° is illustrated in this diagram), where θ is the angle of the vector projected onto the xz plane measured positive from the z axis, and φ is the angle of the vector projected onto the xy plane measured positive from the x axis. The rotational orientation of the icosahedron about the vector is given by the angle ω. Because the symmetry of an icosahedron makes it 60-fold redundant, any view vector can be referenced to a single asymmetric unit (shaded region), which is a spherical triangle bounded by neighboring fivefold axes (θ = 90.0°, φ = ±31.72°) and an adjacent threefold axis (θ = 69.09°, φ = 0.0°).
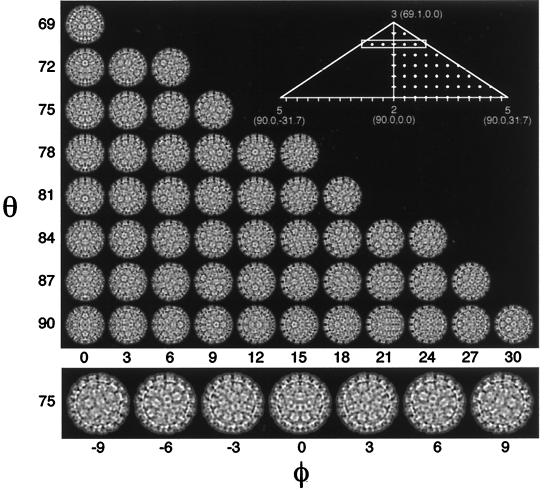
FIG. 12.
Change in projected structure with change in view orientation. (Upper panel) Images of a 3D reconstruction of BPV (19), projected on a regular grid at 3° intervals of θ and φ (ω always = 0°) within a half of the icosahedral asymmetric unit (represented by dots in the right half of the inset). This gallery demonstrates how small changes in viewing angle can produce dramatic differences in the projected views of a 600-Å-diameter particle. The magnitude of these differences is correlated with the change in view direction and with the size of the particle. Hence, a 3° change in view direction leads to more-pronounced differences in projection images for a larger particle (>600 Å) or less-pronounced differences for smaller particles (<600 Å). (Lower panel [corresponds to boxed region of inset]). Demonstration that projected views at θ,φ and θ,−φ are enantiomers related by a vertical line of mirror symmetry. Note that when φ = 0°, the particle itself is mirror symmetric about a central vertical line (true for all images in leftmost column of upper panel). All equatorial views give rise to mirror-symmetric images. An icosahedron has 15 equators, each of which encircles the icosahedron along a direction that follows adjacent symmetry axes. For example, the equator in the xy plane (θ always = 90°; φ varies between −180° and +180°) crosses, in order, the following symmetry axes: two-, five-, three-, two-, three-, five-, two-, five-, three-, two-, three-, and fivefold. Any view corresponding to a combination of θ and φ which lies on this equator will be a mirror-symmetric image with the mirror line parallel to the equator. For example, the bottom row of projected images in the upper panel (which represent some of the views along the xy equator) all exhibit horizontal lines of mirror symmetry. Projection views along strict symmetry axes are additionally unique because they exhibit n mirror lines, where n (= 2, 3, or 5) is the symmetry of the axis in view.
Common Lines and Cross-Common Lines Methods
When a symmetry axis is along the direction of view or projection, the image obeys the symmetry of the axis. An axis which is not along the direction of view gives rise to common lines in the transform of the projection. Application of the symmetry operation to the transform of the projection yields a second, identical plane which intersects the first along a line. Application of the inverse of the symmetry element to the original transform generates a third, identical plane with a second line of intersection. These lines in the original transform are designated “common lines” since they are common to the original and symmetry-related planes. The values of the transform in the original plane along them must be identical since they are related by symmetry operations on the original plane (89, 133). Each pair of a symmetry element with its inverse gives rise to such a pair of common lines which lie to either side of the projection of the symmetry axis.
The 60 symmetry elements of the 532 point group symmetry of an icosahedral particle generate 37 pairs of common lines in the Fourier transform of an image of its projection. These 37 pairs include two pairs from each of the 6 fivefold axes, one pair from each of the 10 threefold axes, and one pair from each of the 15 twofold axes. Sixty pairs of common lines exist between the transforms of any two projected particle views. The positions of these lines, along which the values of the transform should be identical for objects with perfect icosahedral symmetry, are determined solely by the direction of the view. The orientation angles corresponding to an observed view can be found by stepping θ and φ through the asymmetric unit and selecting the values which give the lowest sum of residuals over all 37 pairs of common lines in the transform of the projection (86, 89, 91, 133). These are the view angles for which the observed view most closely matches that of an ideal icosahedron. The agreement of the phases along the 60 symmetry-related lines between pairs of images, which is called the cross-common lines residual, provides a measure of the agreement between the transforms of different projections and, hence, allows screening for consistency in the data set as well as the refinement of the orientations (14, 93, 130, 133).
Resolution Limits
The resolution of the reconstruction, by this or any other technique, is always limited by the worst steps in the entire process, from specimen preparation through imaging, densitometry, view parameter determination, and final calculation of the map (Fig. 10). For example, if the specimen was destroyed by the beam prior to imaging, nothing can be done to retrieve the information that was lost. Thus, it is important to design the steps of the processing to preserve the information in the images and not to expect to recapture information lost by a previous step.
Selection and Digitization of Micrographs
A prelude to the computer processing of images is the selection of micrographs and screening of them by eye (and sometimes by optical diffraction if there is enough carbon substrate in the image to give a strong transfer function pattern) to identify those of high quality which have the appropriate defocus (see above) and minimal astigmatism and image blurring owing to specimen movements (drift, vibration, etc.). The particle concentration should be high enough that a single scanned image will yield an adequate number of views but not so high that images of individual particles overlap. In this context, it is important to remember that the image of a particle includes the Fresnel rings at the periphery which arise from the CTF of the microscope. The effects of the CTF are most prominent where there are large differences in specimen density such as at the interface between the virus and the surrounding solvent. The resolutions at which the CTF has its first maximum and minimum should be noted, as these provide landmarks for use of the data in the reconstruction (Fig. 8).
Careful inspection of the cryo-EM images sometimes allows characteristic views to be recognized and also provides a sense of the heterogeneity of the preparation. If a large fraction of the particles appear to have adopted a preferred orientation, additional images should be recorded to expand the range of particle orientations. If necessary, a broader range of particle orientations can always be obtained by tilting the specimen holder by a small angle (∼10 to 20°) (108, 296). Although the bulk of the effort in icosahedral reconstruction is spent on computation, most workers have had the humbling experience of realizing that an extra few minutes spent at this screening stage could have avoided hours of frustrating computational work.
The digitization of the micrographs should be optimized to capture the information in the images. The Shannon sampling theorem (270) states that one should scan the micrograph at a step size which is at least twice as fine as the resolution desired. In practice, most workers err a bit on the side of caution, and images which are intended to carry 25-Å information are usually scanned at about 5- to 8-Å spacing (i.e., one-fifth to one-third of the desired resolution). Cryo-electron micrographs usually have a very limited dynamic range (i.e., low contrast), so the scanner should be adjusted to optimally capture this range without truncation or compression of the density values. We have used an Optronics C4100 rotating drum scanner at a 25- or 12.5-μm step size; a Perkin-Elmer Micro-D flatbed scanner with a step size between 25 and 10 μm; or a Zeiss Phodis flatbed scanner at step sizes of 7, 14, or 21 μm to scan images taken at magnifications between 20,000 and 50,000.
Processing the Digitized Micrograph
The common lines algorithm utilizes the Fourier transform of the image. The next steps (boxing, masking, background correction, and floating) are designed to minimize artifacts in the calculated transform. Ideally, the density array to be transformed should be a power of two in dimension and contain only the particle of interest, centered in the array and embedded within a background which is a smooth density of local average value equal to zero. After the scanned image is displayed on an appropriate graphics device, individual particle images are centered by eye within a box of the appropriate size and the box is extracted into a separate file that is stored on disk.
Almost all cryo-electron micrographs exhibit a varying thickness of the water layer in the specimen by having a nonuniform background. Corrections for this varying background are made by fitting a least-squares plane to the average background value and subtracting it from the entire image. A mask is then generated to screen out other particles and debris within the box. The mask must be large enough to include all of the particle’s features including the Fresnel defocus rings which surround the particle. The particle is then centered more accurately by use of cross correlation with a version of the same image rotated by 180° or with a low-pass filtered disk of the particle’s diameter or with an azimuthally averaged radial profile of the particle (e.g., see references 228 and 296). The boxed image is then embedded in a larger square array of pixels and Fast Fourier transformed. A typical example is that of SFV with a scanned diameter of 700 Å (or 62 pixels in a 25-μm scan of a ×22,000 micrograph) (325). SFV was extracted in a 100- by 100-pixel box, masked within a circular window of radius 40 pixels to exclude other particles, centered by cross correlation with a low-pass, Fourier-filtered (0.1 pixel−1) disk of 62 pixels in diameter, and finally placed in a 512- by 512-pixel box for transformation. Representative transforms should always be examined to check that the process has not resulted in the production of artifacts such as streaks or rings in the transform, as these will overpower the information from the particle and lead to erroneous refinement of the θ, φ, ω, x, and y particle parameters.
The selection of large numbers of particles has been made easier by the availability of a number of automated and semiautomated programs for selecting and preprocessing images. These include PTOOLS (306) and EMMA (33) as well as the more general-purpose packages SPIDER (126), IMAGIC (322), and the MRC image processing package (92).
Refinement of Particle Parameters and Calculation of 3D Reconstruction
Once Fourier transforms of properly selected, centered, and boxed images have been generated, a series of programs are used to determine the center and orientation of each view by minimizing the common lines residuals. After the best θ, φ, and ω parameters are found for the initial x,y center as described above, the center is recalculated to give the best common lines residual for that orientation. This center is then used to calculate a new orientation. This process is followed for 20 or more particles. Owing to the low signal-to-noise ratio in the images and systematic variation in common lines degeneracy, only a small fraction of the particles typically yield reliable orientations. A detailed description of the identification of these views and the explanation for the degeneracy in the common lines are presented in two recent reviews (9, 133). The identification of this apparently reliable subset is followed by comparison of the transforms by means of the cross-common lines residuals, allowing the refinement of particle orientations and origins against each other. Once a small, refined data set is available, a low-resolution 3D reconstruction is calculated from the available data set. If the reconstruction shows “reasonable” features such as continuity and yields projections which correspond with the original images, the set can be used as the basis for addition of further particle images. The additional data are refined against the original set until enough views have been collected to define the reconstruction to the desired resolution (9, 133). Modifications to the original common lines algorithms have recently been designed to improve and automate the orientation estimation search procedure and thereby enhance the potential resolution of computed reconstructions (307).
Model-Based Refinement
Once an initial reconstruction has been produced, it can be used to help with the orientation identification and refinement process. Two model-based methods are in widespread use. One uses a small set of projections (typically 6 to 10) to generate a fixed set of transforms for the calculation of cross-common lines residuals with the individual image transforms (93). The other calculates the complete set of projections for the asymmetric unit and then compares these with the images by using a polar Fourier transform method (9). This method has been further extended to help in the analysis of particles that prove particularly difficult to refine (54). Both methods allow rapid determination of image orientations for large numbers of images and give equivalent results (210). Their use has had a dramatic effect on the quality of reconstructions because they make it practical to combine hundreds (80) or even thousands (42) of images and to achieve an increased signal-to-noise ratio in the final reconstruction. A further advantage of model-based refinement is that it allows the determination of the relative scale of images in the data set. Magnification varies between and within images (3), and its correction is important for extracting the highest resolution from the data (210).
CTF Correction
The CTF that enables the visualization of unstained specimens must be compensated in the reconstruction in order to achieve a reliable representation of the structure. The transfer function reverses, removes, and attenuates data in resolution ranges in the image transform (Fig. 8). The problem can be minimized by working at a resolution limit lower than the first zero of the transfer function since no phase reversal occurs in this range. For typical imaging conditions, this limits the reconstruction to worse than 20-Å resolution.
Higher resolution requires more careful treatment. Careful determination of the transfer function allows correction of the phases by multiplying the appropriate regions of the transform by −1.0. The transfer function is usually determined by locating its zeros as the points of minimum contrast in the average power spectrum of the image. This procedure is much more reliable when FEG or high-voltage data is used so that multiple zeros can be seen in the power spectrum. Often, it is helpful to include the edge of a hole in the image since the greater scattering from the support film makes visualization of the transfer function easier. One can correct the transfer function approximately by dividing by it (called Wiener filtering), but this ignores the fact that data are removed in the regions near the zeros. It is necessary to use multiple images with complementary defocuses to fill in these missing data (210). Two fundamentally different approaches have been used. The first generates a transfer function-weighted sum of the images of each particle taken at different defocuses so that a single corrected image is passed to the reconstruction programs (80, 314). The second generates a separate reconstruction from each image and then calculates a combined, corrected reconstruction as a sum of the reconstructions weighted by the CTF (40, 42). Both methods have been used successfully to achieve high-resolution reconstructions.
An alternative approach to filling in the missing data is to take advantage of information which is not affected by the imaging process of the microscope to correct the reconstruction. The transfer function for an image which has no astigmatism is radially symmetric. Hence, knowledge of the radial density distribution, for example, from a low-angle X-ray pattern (130), or accurate knowledge of the structure of a component can be used to calculate the appropriate correction to the image data. The availability of X-ray structures for the adenovirus hexon (298), the protein shell of CPMV (10, 62), and the HRV (62, 233, 235) has allowed very accurate difference imaging to be performed after CTF correction.
Almost-Icosahedral Objects
A number of the reconstructions which are presented in “Virus life cycles in three dimensions” are of objects which do not actually have complete icosahedral symmetry. The phages P2, P4 (101), and λ (100) have a tail on one of their 12 fivefold vertices. The fiber of Ad2 (but not Ad3) has a bend which causes it to break icosahedral symmetry. The fibers of both viruses are trimeric and hence can never obey the fivefold symmetry required at an icosahedral fivefold vertex (239, 323). The effect of these departures from icosahedral symmetry is twofold. Firstly, they make it more difficult to orient the object. Usually, the nonicosahedral portion must be masked away to obtain reliable orientations (100, 101). Secondly, the nonicosahedral structure is smeared by the icosahedral averaging which takes place during reconstruction. Hence, we will never be able to use icosahedral reconstruction to visualize the trimeric structure of the adenovirus fiber (even in type 3 where it is shorter and straighter than in type 2) or to see the details of the site of tail interaction with bacteriophage capsids (100, 101).
Reliability of Reconstruction
The quality of the final reconstruction is, as described above, limited by the combined effects of the worst steps in the reconstruction process. The number of views needed to define the reconstruction to an isotropic resolution, d, depends on the distribution of views within the asymmetric unit and the diameter, D, of the particle. For evenly spaced views, the relation (πD)/(60d) gives a lower estimate of the number of views required (91). A more precise answer is found by examining the eigenvalue spectrum for the determination of the coefficients of the expansion functions used to calculate the reconstruction (91). If all eigenvalues are one or greater, the reconstruction is well determined and the data from separate views will be averaged to improve the signal-to-noise ratio in the reconstruction. If eigenvalues are less than one, the corresponding expansion functions are ill determined and the reconstruction will contain artifacts due to undersampling of data. In practice, cryo-EM data are very noisy, and therefore enough data should be combined to yield an average eigenvalue significantly greater than 10 and no eigenvalues less than 1.0. For adenovirus (D = 1,100 Å), more than 20 views were used to achieve a resolution of 35 Å with an acceptable signal-to-noise ratio (296), although the lower-limit formula cited above would indicate that fewer than four views could be used to compute the 3D map to that resolution.
A first step toward the interpretation of a reconstruction is the definition of its absolute scale. This is not always straightforward, since magnetic lens hysteresis as well as changes in the height of the specimen in the objective lens causes small changes in magnification. One way to determine the absolute scale is comparison with a reconstruction of a standard virus whose precise dimensions have been determined from X-ray diffraction (26, 30). Direct comparison in three dimensions is much more precise than attempting a similar comparison with the images, particularly for a virion whose aspect changes with orientation.
Some authors refer to the symmetry of the reconstruction as part of the proof of its validity. Such analyses should be viewed with caution. The Fourier-Bessel expansion method constrains the reconstruction to have D5 point group symmetry (91). This imposes one fivefold axis and the five twofold axes in the plane perpendicular to the fivefold axis on the density map. Agreement between the separate views, and hence quality of the reconstruction, is reflected in the additional symmetry, i.e., the nonimposed threefold symmetry found in a truly icosahedral object. The agreement is also reflected by the phase residual calculated from the cross-common lines between images, the cross-common lines phase residual. The average phase error should be less than 90° for all data out to the resolution limit imposed on the reconstruction. This is a different criterion than that typically used for work with crystalline specimens. However, it has been demonstrated to be an appropriate one both theoretically and by comparison with X-ray data (296).
A more robust assessment of the reliability of the 3D density map is to compare independent reconstructions of the virus from the same or similar samples, from the same micrograph, or from different micrographs recorded under similar conditions of microscopy (19, 101, 251, 295).
The different resolution criteria in common use include weighted phase difference residuals (251), Fourier shell correlation (FSC) (321), and R-factorAB (349). The formulas that define each of these criteria are as follows:
Phase residual
 |
FSC
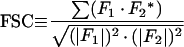 |
R-factorAB
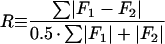 |
where F1 and F2 are the structure factors for the two maps, |F1| and |F2| are the structure amplitudes, F2* is the complex conjugate of F2, and the sums are taken separately over all structure factors within a given spherical resolution shell.
All three resolution criteria are computed for a series of concentric shells in the 3D transform and plotted as a function of spatial frequency (Fig. 13). The resolution limit normally defined by the phase residual is taken as the spatial frequency at which the residual exceeds 45°. For the FSC, the limit is considered to occur when the value falls below twice the value expected for noise with Gaussian correlation, which occurs at  , where N is the number of Fourier terms included. In tests with icosahedral data, the cross-common lines phase residual often serves as a more-stringent criterion for resolution than the FSC, although all criteria show a sharp change indicating a lack of correlation between independent reconstructions at roughly the same resolution (210).
, where N is the number of Fourier terms included. In tests with icosahedral data, the cross-common lines phase residual often serves as a more-stringent criterion for resolution than the FSC, although all criteria show a sharp change indicating a lack of correlation between independent reconstructions at roughly the same resolution (210).
FIG. 13.
Measures of the resolution of a reconstruction of SFV with 80 particle images. The plot shows both the phase error (left scale) and the FSC (right scale) against the spatial frequency in inverse nanometers. The resolution of the reconstruction is approximately 27 Å as shown by the position at which the FSC crosses 0.5 and the phase error becomes greater than 45°. Notice that the two measures of resolution yield almost identical results.
Difference maps computed between independent and properly normalized reconstructions also give a measure of data reliability, because, ideally, the magnitude of the differences should be no larger than the noise level in the reconstructions. If the average fluctuation in the normalized difference map exceeds the noise level by more than 1 standard deviation, then the differences may be attributable to real differences between the maps. Such tests of reliability are therefore quite useful for establishing confidence in differences that are seen.
Information from biochemical data or complementary structural techniques such as X-ray diffraction can help support the reliability of the reconstruction. Obviously, the interpretation of the results is very much case dependent, as is their presentation. The least-squares fitting of the D5 expansion, which is used to represent the data averages, can lead to different ratios of signal to noise in different regions of the map for small numbers of particles (90) or when a preferential orientation of the particles in the water layer leads to an uneven distribution of orientation angles in the data used for reconstruction (108, 296). For this reason, the variation between data sets of the individual features in the map should be examined, particularly for those near symmetry axes.
It is possible in this age of computer graphics to make a result of any quality appear impressive. A publication of a reconstruction should be accompanied by all of the following to allow the reader to assess its validity: (i) magnification, beam dose, defocus, and relevant CTF extrema (these define the limits of resolution in the original data); (ii) step size for digitization and a description of any computational enhancement of the data such as contrast stretching, noise removal, median, or Fourier filtering (these define the reliability of transfer of data from micrographs to the reconstruction programs); (iii) description of the eigenvalue spectrum as a function of resolution (this defines the completeness of the data and acts as a control for the effects of preferential orientation); (iv) cross-common lines residual as a function of resolution or correlation coefficient as a function of resolution for the final data set (this shows the degree of agreement between data and its reproducibility); and (v) comparison of independent reconstructions by FSC, R factor, or variance map (this is the most widely accepted method of assessing the actual resolution of the final density map).
The success of the combination of icosahedral reconstruction and cryo-EM should not make us forget that the method is still relatively new. Its acceptance to date has been a consequence of the careful and conservative approach that has been used in interpreting and presenting results. As the method becomes more widespread, it is necessary to be even more careful that the limits of the reliability of the results are clearly defined not only for the users of the method but for our colleagues who rely upon our results for their own work.
NOT JUST A PRETTY PICTURE
Once a reconstruction is complete and judged to be reliable by the criteria described above, the enjoyment of interpreting and building upon the structure begins.
Visualization and Representation
Computer graphics make it easy to present a colored surface or volume representation of the reconstruction which will illustrate its features. A number of computer graphics packages are available for this purpose, including AVS, for which a number of nice user-written modules (273) are available for the presentation of biological macromolecular structure. The choice of the density (contour) level at which to represent a reconstruction is not always straightforward. Often people represent a structure at 1.5 or 2 standard deviations above the background to provide a somewhat objective presentation. Alternatively, they present the structure at a volume which they believe is appropriate to the molecular mass. This can be difficult because the volume is very sensitive to small changes in contour level, which in turn is sensitive to scaling and CTF correction. Experience in a number of systems indicates that the simple calculation of the molecular mass from the volume of the reconstruction rarely matches the expected value. This remains true for very highly refined reconstructions derived from large data sets. There are a number of potential explanations for this phenomenon. Limited resolution (85) will tend to cause the apparent volume to appear larger than the expected one. Typically, one derives the volume from the mass of the protein and ignores (with good reason, because we do not really know how to model them) the contributions of carbohydrate, lipid, or tightly bound nucleic acid. Further, there is the issue of disorder. Portions of a structure which are visible at low resolution may be too mobile to be visible at higher resolution. Taken together, these factors mitigate against placing enormous emphasis on the precise value of the volume derived from a reconstruction. As a guide, workers typically need to contour at about 120% of the expected volume in order to obtain a surface that makes biological sense. Roughly speaking, a structure with a volume near this level is reasonable; drawing conclusions based on volume fluctuations of 20% is not.
One of the difficult tasks facing the presenter of a reconstruction is conveying the same sense of the structure which has been gleaned from hours of examining it to other biologists who have less experience in interpreting such data. Stereo images (50, 205) are one way of conveying the 3D nature of the results. They are best for showing small portions of a structure. One needs to remember that roughly 15% of the readers (and seemingly 97% of referees) will not be able to visualize an image in stereo, so that an alternative presentation should be present. The use of different colors for chemically distinct components (64, 145, 243, 294, 352, 353), cut-open views (10, 132), radially cut surfaces (14, 15, 20), icosahedrally cut surfaces (40), and polar sections (132) helps to convey the structural details, but they should always be carefully described to allow the reader to distinguish representation from result. Another very useful technique is radial depth cueing (141, 264, 292), which conveys an immediate, and often quantitative, view of the radial placement of details in a map (145). Animation provides an alternative approach to enhance the viewer’s perception of the 3D structure (106).
Reliability Of Difference Imaging (A Cautionary Note)
Difference imaging is one of the most powerful tools in the arsenal of the structural biologist. It has been used widely and successfully in many systems. One of the great advantages of cryo-EM over classical, negative-stain microscopy is that it allows reliable difference imaging (10, 17, 18, 38, 156, 162, 193, 240, 242, 243, 247, 267, 286, 297, 298, 308, 325, 352, 361, 362, 364). Many difference imaging results have been confirmed by biochemical and immunological means. Despite their potential, difference images must be calculated carefully to guarantee a reliable interpretation. The two maps whose difference is sought should be calculated to the same resolution and scaled in such a way that the differences are minimized. Propagation of error will guarantee that a difference image is always noisier than either of the two original images, and it is the noise in the difference map which determines the significance of features in it. Even if your understanding of the biology indicates that the only important difference is at a particular position, an understanding of statistics should inform your interpretation. One should always test to see whether a difference of a similar size can be found between independent reconstructions of the same structure before placing much weight on the result. Furthermore, one should always be very cautious about differences at symmetry axes, or equivalently at low radius, because noise tends to be higher at these locations. Finally, it is important to remember the caveats about the accuracy of molecular volume mentioned above, since a difference image is inherently more noisy and more sensitive to scaling errors.
Modeling and Comparison with X-Ray Structures
The combination of X-ray and cryo-EM is particularly powerful (16). The ability to fit an X-ray model into the reconstructed density allows the definition of the position of the model with greater precision than the resolution of the cryo-EM map. There is no commonly agreed method that has been used for the fitting. Indeed, the same group will use different approaches to different systems. All approaches have the same general outline.
Firstly, the absolute magnification of the reconstruction must be established. The absolute magnification of an EM varies with the conditions of imaging and can vary from image to image. An error of a few percent completely destroys any possibility of a reliable fit. Workers check the scale by comparing the EM map with clear features in the X-ray structure of an individual component (298, 299), by using radial density profile information derived from scattering experiments (64), or by using the X-ray structure of an entire viral shell when this is available (156, 162, 166, 240, 290). When a single component is used to define the scale, it is necessary to recheck the scaling after the proper position and orientation of that component have been identified.
Secondly, the variation in density through the reconstruction must be matched to that in the X-ray structure. In the case of the fitting of the hexon to adenovirus, this was done by convolving the X-ray structure with the transfer function for the EM reconstruction (298). Although the original reconstruction (296) had been calculated by combining images at different defocus values, only the high-resolution data were used for the comparison with the X-ray data to avoid having to deconvolve each defocus separately. The effect of the imaging conditions was simulated by using a CTF of the form employed by reference 185 with both phase and amplitude components as well as attenuation:
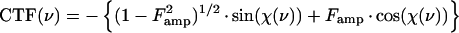 |
where δ is a decay factor which expresses the decrease in amplitude as a function of resolution due to the incoherence of the beam as well as the imprecision in aligning the images for the reconstruction. The defocus and decay values were fit empirically by convolving the X-ray map with the CTF and applying a Fermi filter to smoothly eliminate information beyond the resolution of the reconstruction (298, 299). Alternatively, when the extra density in the EM map can be cleanly masked away, the relative densities of the X-ray structure and the masked reconstruction can be adjusted by comparing the Fourier transforms of the projections of the two maps by using the smoothed ratio of the radially averaged amplitude to rescale the EM map (156, 162). Alternatively, one can simply normalize the EM map so that it is all positive and has the same range of density values as the corresponding X-ray map (166, 208, 344). An alternative, maximum-entropy approach (282) has been used for the treatment of CTF effects and has been shown to improve the correspondence with the X-ray structure for the adenovirus hexon by using the orientations and data from the original work (296, 298).
Thirdly, an interactive fit is made between the EM density and the X-ray structure by using a map-fitting program such as O (180) (Fig. 14). At this point, a subjective estimate of the quality of the fit is made. An important criterion for the quality of the fit is whether the hand of the structure can be identified. The EM density is generated from projected views of the structure, and although a relative hand is imposed during the refinement, the absolute hand must be determined from other data such as shadowing or comparison of the orientations of tilted images (28) of the same particle. The match with the X-ray data (for which the hand is known from the secondary structure and residue geometry) serves as an unambiguous determination of hand. Usually, both the correct hand and the wrong one are monitored through the rest of the analysis, and the difference between them is used as a criterion for the reliability of the data (205, 344). At this stage, one also needs to decide whether the X-ray structure should be fit as a single rigid body (298) or as two or more domains (145, 162, 166).
FIG. 14.
Atomic modeling of a 3D reconstruction of a virus-Fab complex shown in stereo. (Top) Reconstructed map of HRV14 (in white) complexed with Fab fragments from neutralizing MAb 17-IA (pink). (Middle and bottom) Orthogonal views of the atomic model of Fab 17-IA (light chain in grey; heavy chain in dark yellow) and the atomic model of HRV14 (VP1 to VP4 in blue, green, red, and cyan, respectively) fitted into the cryo-EM density envelope (wire mesh). The “hand-in-glove” fit of the atomic models into the cryo-EM envelope demonstrates that, at least in this example, the interacting surfaces can be defined to within a few angstroms (58, 285). See Fig. 55 for comparison.
Fourthly, the quality and uniqueness of the fit are assessed. This can be done simply by calculating an R factor between the two maps. A mask must be applied before calculation to remove the density which is not part of the structure being fit by the X-ray data (64, 205, 298). The uniqueness of the fit is then tested by rotating and shifting the X-ray structure in the EM density and monitoring the change in the R factor (58, 205).
Finally, an objective method of fitting is used to refine and check the uniqueness of the result of the interactive fitting. This refinement is performed either in reciprocal space or in real space. Reciprocal space refinement is usually performed with the program X-PLOR (47) after tailoring of the two maps to avoid ripple and edge effects due to masking and differences in contrast (145, 156, 162, 344). Some of the corrections compensate for the microscope imaging process, but others, such as the inclusion of a high-temperature factor (145, 298), correct for limitations in the reconstruction process such as alignment accuracy. Real space refinement has been performed with different procedures and programs by each group. The measure of the quality of fit is critical to the results. In the fit of SNV capsid protein to the RRV structure, the fitting was begun by superimposing the centers of mass of the capsid proteins on the centers of the capsid features in the map (64). The positions were refined by allowing a six-dimensional rotational and translational search to optimize the R factor between the two structures. The top 100 fits (which were reduced to 10 unique ones) were distinguished by two further criteria: the number of atoms placed in negative density (−den) and the number of atoms in steric collision between monomers (nclash). The product of these (−den∗nclash) appeared to be the most sensitive test. Reassurringly, the best fit was obtained with the hand of the EM map which was shown to be correct by tilting experiments (64). A different real space method, implemented in the program GAP (145), which used a method of steepest-ascent optimization of the correlation coefficient between the two densities was employed for the fitting of VP7 into the BTV core. The scaling of the density maps was first optimized by tests with X-PLOR. The X-ray map was then filtered by using a mask which included all density within 10 Å of an atom. This mask, which includes a solvent contribution, was used to ensure that the shape of the structure rather than its internal features was used for fitting. The comparison between the results of real space fitting and those of reciprocal space fitting is informative. Reciprocal space fitting usually is not constrained to avoid interpenetration of the densities, an issue which is easy to address in real space fitting. When the two approaches yield different solutions, the possibility of a change in the X-ray structure upon binding should be considered.
Phasing of X-Ray Data with EM Data
The use of EM data in combination with X-ray data is not limited to cases in which the high-resolution structure from X-ray diffraction is used to enhance the interpretation of a reconstruction. In several cases the EM map was used to help solve the phase problem in the solution of the X-ray structure of the virus. The great advantage of this approach is that it avoids the classical use of heavy atom derivatives which produce only small changes in the scattering of a large object such as a virus and introduce problems of nonisomorphism. The first such example was the solution of CCMV, where the cryoreconstruction was used as a model for phasing the X-ray data (290). The atomic coordinates of southern bean mosaic virus were placed into the density of the cryoreconstruction. A rotation function calculated to 15 Å was used to orient the model with respect to the crystallogrpahic data. This oriented model was then used to calculate phases which were extended to 4 Å by the use of phase extension and noncrystallographic symmetry. This 4 Å envelope was then used to construct a polyalanine model which provided phases to 3.5 Å. In the solution of the core of BTV, the EM map (241) was used to position the X-ray-derived structure of the VP7 protein so that an atomic model could be generated (145), which was then used to calculate initial phases for the X-ray data for the whole core. The cryo-EM-derived map of HRV14 in complex with neutralizing Fab 17-IA (205) was used in the solution of the X-ray structure of the same complex. The structures of the isolated Fab and the uncomplexed virus had been solved previously. The cryo-EM map was used to position these components and provide a phasing model for the X-ray data (285). Interestingly, the solution of the X-ray structure showed an unprecented conformational change in the binding site region of the Fab which allowed a closer approach of the Fab into the receptor binding canyon than had been inferred from the EM data (205, 285).
VIRUS LIFE CYCLES IN THREE DIMENSIONS
Shared Features of Virus Life Cycles
A virus is a parasite of its host. As a result, a virus’s life cycle is inextricably tied to that of the host cell. Despite this dependence, all viruses share a number of essential tasks which they must accomplish for survival (Fig. 15). A successful virus must be able to find and recognize a cell in which it can replicate, release its genome into the cell, generate new viral components by transcription and translation, and assemble these components into precursors that mature into a stable progeny virion which is released from the host cell and transmitted to encounter a new host. Each of these tasks involves interactions between components in the context of the whole virion. Visualization of such interacting components is a job ideally suited to cryo-EM. Different viruses accomplish these tasks in different ways as a result of adaptation to different cellular environments. We will describe the results of cryo-EM and image reconstruction which illustrate the structural response of different viruses to these common tasks. Visualization of these structural solutions enhances our understanding of the deeper biology underlying them. One unexpected commonplace of structural virology is the relatedness of structures which accomplish these tasks in different hosts. The observation that structural similarity is found in the absence of detectable sequence homology indicates that it reflects fundamental features of the tasks. Several examples will make this general description of common tasks more concrete.
FIG. 15.
The common tasks faced by all viruses as exemplified by the replication of SFV, an enveloped virus, in a mammalian cell. The virus first binds to a cell surface receptor (Cell attachment). Entry ensues by receptor-mediated endocytosis, and the capsid-bearing genome is released into the cytoplasm via membrane fusion mediated by the low pH of the endosome (Release of genome). The capsid and envelope proteins are synthesized, and the spike is assembled in the secretory pathway as a heterodimer comprising the precursor of E2 (p62) and the fusion sequence-bearing protein E1. The capsid incorporates the genomic RNA in the cytoplasm (Pro-assembly). The envelope protein complex is processed in the late secretory pathway to yield the fusion active complex of E1, E2, and E3 (Maturation). The mature spike assembles into small patches on the plasma membrane which are complementary to the arrangement of capsid proteins, and the budding particle forms and is released from the cell (Release). Propagation of the infection involves evading the host immune system and, in some cases, replication in a second host, such as a mosquito for the arbovirus SFV (Transmission and host defense).
Many of the best-studied icosahedral viruses which replicate in animal cells enter by means of receptor-mediated endocytosis.
An alphavirus, such as SFV, is a relatively simple example of an enveloped virus. This positive-strand RNA virus comprises a nucleocapsid made of 240 copies of the C protein, which is surrounded by a lipid envelope in which 240 copies of each of two transmembrane glycoproteins, E1 and E2, and an extrinsic membrane protein, E3, are located. SFV, binds to a cell surface receptor by means of its envelope glycoproteins and is then recruited to a coated pit and endocytosed (Fig. 15). In the low pH of the endosome, the envelope proteins undergo a low-pH-mediated conformational change which results in the fusion of the viral envelop with the endosomal membrane. The binding to the cell surface receptor (cell attachment, Fig. 15) and the irreversible low-pH-mediated conformational change (activation, Fig. 15), which occurs after endocytosis, are the two aspects of cell recognition. Both are mediated by the envelope proteins. Fusion requires not only low pH but also the presence of cholesterol and sphingomyelin in the target membrane. The joining of the membranes allows release of the nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm, where the genome is transcribed to produce new copies of the genome and the mRNAs for the structural and nonstructural proteins. Copies of the genome are encapsidated by the C protein in the cytoplasm (proassembly, Fig. 15). The envelope proteins are synthesized by membrane-bound polysomes and translocated into the endoplasmic reticulum, where they oligomerize to form the spike complex. E2 and E3 are initially synthesized as a precursor, p62, which is cleaved by a host protease during the transport of the spike complex through the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane. This cleavage of the precursor p62 (proassembly, Fig. 15) renders the spike pH sensitive and is a necessary stage in the production of an infectious virion. Budding occurs when the assembled nucleocapsid is enveloped at the plasma membrane as a result of its interaction with the spike complexes (assembly and release, Fig. 15). The released virion then proceeds to infect other host cells. SFV is transmitted in the wild by means of a mosquito vector which is protected from the deleterious effects of infection by the lack of cholesterol in the insect.
Many of the details of the life cycle which were described above are unique to alphaviruses. Despite this specificity, analogous stages exist in the life cycles of other viruses. Rotavirus, for example, enters by the receptor-mediated endocytosis and utilizes the secretory pathway for assembly as does SFV. It buds, however, into the endoplasmic reticulum and loses its membrane after budding. Loss of the membrane and other modifications are necessary maturation steps which are required for the initial budded virus to become an infectious virion. Transport of the virion through the secretory pathway terminates in its secretion from the cell. A nonmembranous virus, such as rotavirus, does fuse with the endosome. However, binding of rotavirus to the cell surface receptor and exposure to the environment of the endosome cause dramatic conformational changes in the virion. Picornaviruses, for example, undergo a conformational change upon binding to the appropriate cell surface receptor, which results in their becoming much more hydrophobic. The altered capsid is more open, as seen by its inability to protect the RNA from nuclease digestion, which may facilitate the release of genome into the cytoplasm. Assembly of the structural proteins around the genomic RNA generates a protease active site which causes cleavage of the polyprotein product to generate the mature, infectious virion. Picornaviruses are typical of many other nonenveloped viruses in being released from the cell by lysis rather than by budding.
Cell Attachment
The first step in a productive viral infection is the binding of the virus to the correct host. Viruses recognize target cells by binding to specific receptor molecules at the cell surface. Binding involves specific interaction between a viral protein or glycoprotein and the receptor. Successful attachment usually ensues upon binding to one or more identical receptor molecules. Some viruses, like adenovirus (165), utilize at least two different receptors to achieve attachment. Abortive infection occurs if attachment does not lead to the subsequent activation step that triggers entry of the viral genome into the cell.
Viral receptor binding sites are typically comprised of highly conserved amino acid residues (257, 258), a requirement that appears to guarantee survival of the virus. Early crystallographic studies of picornaviruses indicated that these and other viruses may shield their receptor binding sites in cavities or surface depressions (“canyons”) that are inaccessible to antibody molecules and would therefore provide viruses a selective advantage (258). Subsequent studies of other viruses have shown that receptor binding sites also occur in highly exposed regions of the viral surface, indicating that evolution of virus-receptor and virus-antibody interactions may be subject to independent constraints (76).
Detailed understanding of virus-receptor interactions ultimately requires structural analysis at high resolution. The first direct structural evidence for the nature of receptor interactions with complete virus capsids was accomplished by means of cryoreconstruction analyses and atomic modeling of two virus-receptor complexes: HRV16 complexed with the cellular receptor ICAM-1 (233) and the human parvovirus B19 complexed with the receptor globoside (67). The receptor molecule in each of these studies was shown to bind to a cavity or depression in the viral surface. A brief description of the HRV study illustrates the use of cryo-EM methods to examine virus-receptor interactions.
HRV16-ICAM complex.
HRVs comprise more than 100 serotypes and are the major cause of the common cold. The icosahedral virus (∼300-Å diameter) consists of 60 copies each of four proteins (VP1 to VP4) and a single copy of a positive-sense, ssRNA genome (Fig. 16). A 20-Å-deep and 12- to 15-Å-wide surface depression (canyon) encircles each of the 12 fivefold vertices and lies approximately halfway between the fivefold and three fold icosahedral axes.
FIG. 16.
Schematic diagram (left) and cryoreconstruction (right in radially depth-cued representation) of HRV14. The outer capsids of the more than 100 serotypes of HRV (family Picornaviridae) all contain 60 copies each of three viral proteins, VP1, VP2, and VP3. Four classes of neutralizing antibodies have been genetically mapped to viral epitopes on these surface proteins (274). NIm-IA and NIm-IB map to VP1, and NIm-II and NIm-III map to VP2 and VP3, respectively. The canyon, a prominent surface depression that completely surrounds each of the 12 fivefold vertices of the HRV capsid, was first recognized in the crystal structure analysis of HRV14 and hypothesized to be an important site of cellular recognition (258).
Structural, mutational, and drug binding studies motivated the hypothesis (260) that this canyon acted as the binding and recognition site of ICAM-1, the cellular receptor for the major group of rhinoviruses (142). ICAM-1 serves as a ligand for the lymphocyte, function-associated, antigen 1 adhesion receptor and for leukocyte adhesion during inflammation. The extracellular portion of ICAM-1 consists of five immunoglobulin-like domains (142). The N-terminal portion of ICAM-1 was believed to be narrow enough to dock into the canyon and bind to viral residues on the canyon floor (258). Indeed, cryo-EM images of the major group rhinovirus, HRV16, complexed with the amino-terminal, two-domain fragment (D1D2) of ICAM-1 and a subsequent 3D reconstruction at 25-Å resolution and atomic modeling supported this hypothesis (233) (Fig. 17). The reconstruction of the HRV16-D1D2 complex shows the virion fully saturated with D1D2 molecules (∼60 copies/virion), which are ∼75 Å long and bilobed as expected for the two-domain ICAM-1 fragment. The D1D2-virus footprint (interaction surface) was centered over the canyon, as predicted. Initial modeling of the D1D2-virus interactions, based on the crystal structure of CD4 (the receptor for human immunodeficiency virus homologous to ICAM-1 [263, 338]), indicated that D1D2 contacts both rims of the canyon (233). More-precise modeling of the interacting surfaces has recently been performed, now that the high-resolution crystal structure analysis of D1D2 is available (25). A more recent, unpublished analysis of a complex of HRV14 and D1D2 shows essentially identical results. X-ray crystallographic work on an HRV-Fab complex showed that large portions of the antibody and ICAM-1 footprints overlap, thereby indicating that conserved, receptor binding residues are accessible to at least some antibodies (285) (see “Host defense”).
FIG. 17.
Cryoreconstruction study of native HRV16 (left) and an HRV16-D1D2 complex (right). (Top) Small fields of view showing vitrified samples of native HRV16 and HRV16 complexed with the D1D2 fragment of the cellular receptor ICAM-1. (Bottom) Isosurface representations of the HRV16 and HRV16-D1D2 reconstructions. The two-domain D1D2 structure binds radially to the HRV16 surface at the canyons that surround the star-shaped VP1 pentamers as predicted elsewhere (258).
Other cryo-EM studies concerning receptor-virus interaction.
Indirect evidence about receptor binding to viruses has been obtained by means of cryoreconstruction studies of reoviruses, alphaviruses, adenoviruses, and the picornavirus FMDV. For example, the structure of VP4, the 88-kDa receptor recognition protein of rotavirus, has been the subject of several studies owing to its central importance to the rotavirus life cycle (242, 249, 271, 352, 353). VP4 manifests hemagglutinin activity and is a neutralization antigen as well as a determinant of virulence. It also mediates cell penetration and is susceptible to cleavage by trypsin, which enhances viral infectivity. VP4 has a role in the maturation of progeny virions through its interactions with VP6 and VP7 viral structural proteins (see above references for extensive citations concerning these functions). These studies showed that 60 dimers of VP4 (“spikes”) extend ∼100 Å above the viral capsid surface in a uniform arrangement that appears to facilitate binding interactions with cellular receptors (Fig. 18). The distal ends of the spikes are believed to contain the receptor binding sites, since neutralizing antibodies that bind near the distal ends inhibit viral penetration (242).
FIG. 18.
Cryoreconstruction of simian rotavirus (352). The prominent, dimeric VP4 spikes (yellow) project ∼110 Å radially outward from the viral surface in a manner that may facilitate binding to cellular receptors. VP7 (blue), the major outer capsid protein and an antigenic determinant, forms a smooth outer shell with 132 channels, through which the second major capsid protein, VP6 (pink), and the core proteins, VP1 to VP3 (red; individual proteins could not be distinguished in this reconstruction), are accessible. Twelve (type I) channels occur at the fivefold axes, 60 (type II) are partially occluded by the VP4 subunits, and 60 (type III) have the rather prominent crescent-shaped openings. Figure courtesy of M. A. Yeager.
Cryo-EM and 3D reconstruction have become a valuable tool for identifying and examining viral epitopes (see “Host defense”). This strategy has also helped identify putative receptor binding sites on the E2 glycoproteins of two alphaviruses, SNV and RRV (286), and facilitated examinations of highly mobile, RGD antigenic loops on Ad2 and Ad12 (70, 297) and FMDV (162), which contain integrin receptor binding sites.
Activation
Virus structure is a compromise between stability and instability. Viruses must be stable enough to survive the extracellular environment but be sufficiently labile to release their genome into a susceptible cells. In this context, the initial interaction of the virus with the host cell can do more than simply cause its localization there by binding. It may also alter the virion structure to ease the release of the genome. Clearly, such a destabilization must be precisely regulated so that it occurs only when the virus has actually reached a cellular location for which exposure of the genome is useful. We will describe some of the results of cryoreconstruction concerning activation in a mammalian enveloped virus family and in the nonenveloped adenovirus.
Enveloped virus entry.
SFV, SNV, and RRV are three alphaviruses which have been subjects of extensive work with cryo-EM (64, 130–132, 186, 237, 238, 286, 325, 327) as well as cell biology and biochemistry (reviewed in reference 187), making this family the best characterized of the icosahedral, enveloped viruses. The life cycle for each follows the general scheme described above for SFV (“Shared features of virus life cycles”). Activation in these viruses refers to the process of pH-mediated fusion. This process is selective in the sense that the mature virus will encounter low pH only after endocytosis by the host cell. The combination of cryo-EM and biochemistry has been able to shed new light on the process by which the virion is activated for fusion by low-pH exposure. An alternative model for alphavirus infection (reviewed in reference 46) invokes disulfide shuffling without the requirement for endocytosis or low pH; however, we will adhere to the low-pH–endocytosis paradigm in this review.
The virus contains two transmembrane spike proteins. Several lines of evidence (reviewed in reference 187) show that E1 bears an amphipathic fusion sequence which is believed to be inserted into the target membrane during the fusion process. E2 has been shown by antibody binding studies to contain the receptor binding activity (described in reference 286). 3D image reconstructions of SFV, RRV, and SNV have all been performed from cryo-electron micrographs to better than 30-Å resolution (64, 132, 238, 286), and all yield a consistent view of the structure.
The envelope proteins of the virion are arranged as 80 trimers in a T=4 arrangement (Fig. 19), and these spikes have an unexpectedly complex organization (Fig. 20). The projecting, triangular portion of the spike extends roughly 100 Å from the membrane and splits into three pairs of distal lobes at the vertices of the triangle. Within the spike, a large cavity opens toward the membrane so that the center of the spike is hollow. The base of the spike is edged by flat sheets, or skirts, which connect the spikes into an almost continuous layer outside the membrane. This layer is broken only by a relatively large hole on the icosahedral twofold position and a smaller one at the fivefold position. The spikes are connected to the capsid by the paired transmembrane regions of E1 and E2 which enter the membrane at the vertices of the spike (64, 132). Hence, the positions of the spikes are stabilized by the lateral interactions between spikes at the virion surface as well as the transmembrane interactions with the capsid. Complementing the biochemical work on alphavirus fusion requires establishing the relationship between the structural features seen in image reconstructions and the subunits. Each spike must contain three copies of each of the spike polypeptides. Difference imaging between SFV and SNV, which loses E3 (325), indicates that E3 occupies a distal position. Determining the locations of the other two spike proteins required the development of a selective extraction method for these transmembrane glycoproteins. Use of octyl-β-d-glucopyranoside with low ionic strength and neutral pH extracted E1 preferentially from the spike on the threefold axis, confirming the weaker interaction at this site as expected from the larger adjacent holes in the protein layer above the membrane (Fig. 20). This preferential extraction indicates that E1 fills in the sides (325) and that E2 stretches from the center to the vertex of the triangle. The difference imaging result must be viewed with some caution, because the detergent-treated particle is less well ordered than the intact virus, as one would expect if the edges of a hollow spike were removed (64, 132). Nevertheless, a seam between the two lobes at the vertices of the spike matches the position of the predicted interface (325), and antibody labeling in both SNV and RRV shows that a common E2 epitope, which is near the receptor binding sites, is in the distal portion of the region assigned to E2 (286).
FIG. 19.
A cutaway representation of the 22-Å-resolution reconstruction of SFV (132) revealing the organization of this enveloped virus. The outer surface (blue) of this T=4 virus is studded with 80 trimeric spikes, each comprising three copies of the transmembrane glycoproteins E1 and E2 and the extrinsic membrane protein E3. The spikes are connected above the surface of the membrane by a protein skirt which is penetrated by holes at the two- and fivefold positions. The two leaflets of the lipid bilayer are seen below the skirt. The capsid protein (gold) forms a T=4 array of hexamers and pentamers which surrounds the RNA. The capsid is complementary to the spikes and connected to them by transmembrane regions which are shown in red.
FIG. 20.
An exploded view of the SFV structure (132) around a single spike showing the modular nature of the virion structure. The projecting regions of the spikes are shown in blue. The skirt of protein which connects the spikes is shown in yellow. The cavity at the center of the spike is indicated by an arrow. The outer and inner leaflets of the bilayer and the transmembrane regions which span them are shown in red. The portion of the capsid which interacts with these transmembrane regions is shown in green. Adapted from reference 132 with the permission of the publisher.
An open pore, rather than a cavity, is seen in reconstructions of wt and mutant SNV (238). This difference does not reflect the freezing of the sample in phosphate buffer as was mistakenly suggested by one of us (118). The preparation of SNV used (5, 6, 253) does not employ phosphate buffer for storage; the origin of this difference must lie elsewhere (238). Despite this difference, there is agreement that the subunits alternate around the periphery of the alphavirus spike and that E2 contributes to the spike vertex (118, 132, 238, 286, 325).
The assignment of subunits to structural features allows one to monitor possible changes in subunit localization during low-pH exposure. This visualization is made more difficult by the fact that treatment with low pH for a few seconds caused exposure of the fusion sequence and aggregation and disordering of the virions. To avoid both of these phenomena, which destroy the icosahedral symmetry necessary for reconstruction, one needs to work at very early times (<50 ms) after low-pH treatment. This was accomplished by using a spray device which allows the examination of samples exposed to low pH for times between 5 and 100 ms prior to vitrification (132). Comparison of the reconstruction of the 50-ms-treated particles with that of the untreated particles (Fig. 21) shows that the regions assigned to E1 and E2 swivel around each other. E1 moves centrifugally as E2 moves distally. The cavity in the center of the spike is replaced by a homotrimer of E1, while the contacts to the membrane remain unchanged. This result provides a structural explanation for the control of E1 fusion activity by E2. The E2 subunits separate the E1’s prior to the low-pH-initiated change and hence inhibit the formation of the homotrimer which biochemical studies (333) have shown is formed during the fusion process. The later stages of the fusion process can be visualized with cryo-EM (Fig. 22), which provides some information on the geometry of the fusion complex (129). These stages cannot be analyzed by icosahedral reconstruction; contact with the target vesicle causes loss of icosahedral symmetry because the interaction sites varies from the unperturbed remainder of the virion.
FIG. 21.
The conformational change which occurs within the first 50 ms of exposure to low pH is shown for a single SFV spike. Initially, the fusion sequence-bearing E1 protein which forms the edge of the spike alternates with the receptor binding E2 protein which forms the vertices around the cavity in the center. The triggering of the conformational change by low pH leads to the movement of the E2 domains away from the center and the formation of an E1 homotrimer in the center of the spike. The transmembrane regions and the skirt appear undisturbed at this stage of the conformational change. Adapted from reference 132 with the permission of the publisher.
FIG. 22.
Images of SFV contacting a target vesicle in the process of fusion. A defocus pair of images (nominally −1,000 Å and −4 μm) allows the visualization of the leaflets of the target vesicle as well as the nature of the contact on the side of the virion. The contact appears to be formed by several spikes acting in concert which would then cooperate in the forming of a fusion pore.
Nonenveloped virus entry.
Adenovirus is a nonenveloped virus with apparent T=25 icosahedral (Fig. 23) symmetry. Cryo-EM and image reconstruction (296, 298) were used together with the high-resolution X-ray diffraction structure (255) of the major capsid protein (hexon) to identify the positions of all of the polypeptides by difference imaging. Many of these minor proteins appear to stabilize the complex structure of this large virus (see “T=25 structures: divide and conquer”). Hexon (polypeptide II) and the two proteins which comprise the fivefold vertex, penton base (polypeptide III) and the fiber (polypeptide IV), are known to have functions in the entry of the virion. Adenovirus utilizes at least two receptors to enter the cell (165, 340, 341). Entry is initiated by the attachment of the fiber to the primary cell surface receptor. For example, the fibers from Ad2 and Ad5 bind to CAR (coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor), which is a 46-kDa protein expressed on the surface of many cells, and the Ad2 fiber also binds to major histocompatibility class I antigens (see reference 328 and references cited therein). The second receptor, a cellular ανβ integrin, binds to the penton base through its RGD sequence and triggers internalization by clathrin-coated vesicles (341) but not virus attachment. This second receptor must fulfill an activation function as shown by the fact that interaction with this receptor potentiates permeabilization of the endosome by the particle (340). Cryoreconstructions have provided a wealth of information which enhances our understanding of activation during the entry process.
FIG. 23.
A surface representation of a cryoreconstruction of Ad2 shows the T=25 arrangement of the trimeric hexon protein (inset). Two proteins form the fivefold vertex. Five copies of polypeptide III form the penton base, and three copies of polypeptide IV form the trimeric fiber. The fiber has an ∼45° bend one-third of the way along its length, and hence only the proximal third is seen since the rest lacks full icosahedral symmetry. Reproduced from reference 298 with the permission of the publisher.
The original cryoreconstruction work produced a map of Ad2 at 35-Å resolution (296, 298) which was compared to the X-ray map after applying an empirically determined CTF and a Fermi filter to smoothly eliminate information beyond the resolution of the reconstruction (296, 298). A single, small difference density between the X-ray and EM maps, which corresponded to the position of a 19-residue segment of polypeptide chain that was too mobile to be fit in the original X-ray model, demonstrated the reliability of the difference imaging technique. The positions of the nonhexon proteins were identified along with the regions of the hexon sequence which interact with these proteins, including the site of interaction with the penton base. Residues 146 through 161, an unusual sequence of 16 consecutive acidic residues, form part of the contact with the penton base (298). At pH 5.5, this region would be negatively charged, leading to an electrostatic repulsion, and this would force the conformational change and expel the penton base from the capsid. The stretch of acidic residues is absent in the sequences of hexons from Ad40 and Ad41, which cause enteric dysentery, but these residues are present in Ad2 and Ad5, which cause respiratory infection. This may indicate that the enteric adenoviruses have adapted to resist exposure to low pH and use a different activation trigger upon entering the cell.
Cell biological studies of entry suggest that integrin binding to the RGD sequence of penton base causes a conformational change (340). A cryo-EM study of a dodecahedral assembly of Ad3 pentons provided a clear image of a conformational switch of this structure (267). The majority of the features of the penton base seen in the dodecahedron matched those of the Ad2 reconstruction. The full length of the fiber was not visualized in the Ad2 reconstruction because it is bent and hence blurred by icosahedral averaging (296). However, the shorter, straight Ad3 fiber can be visualized along its entire length (267). Comparison of reconstructions of dodecamers with and without the fiber shows that a small region of density at the edge of the base switches orientation (Fig. 24) between the two structures. The location of the RGD sequence at precisely this position was established by difference imaging with a higher-resolution reconstruction of Ad2 which had bound a MAb to that sequence (Fig. 25) (297). A reconstruction of dodecahedra with bound integrin (266) demonstrated that this was indeed the binding site and that integrin binding appears to require a conformational change of the same nature as that which occurs during fiber removal.
FIG. 24.
The change in the adenovirus penton base upon the removal of the fiber is shown by a comparison of cryoreconstructions of the dodecahedral structure formed by expressed Ad3 pentons. The structure of the dodecamer with the fiber attached is shown in blue for comparison with the fiberless structure shown in red. The top row shows a surface view (left) and sections through the surface for the two structures viewed from the side. The center of the virion would be toward the bottom of the page. The bottom row shows a surface view from the outside of the structure (left) and sections through the protrusions at the edge of the base and through the widest portion of the base. Reproduced from reference 267 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
FIG. 25.
The position and proposed structure of the RGD epitope on the surface of Ad2. The position of the epitope was established by Fab labeling. The structure was modeled from the sequence and shown to match the density seen at the appropriate position. Adapted from reference 297 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Many other examples of activation exist. Picornaviruses bind to cell surface receptors and then undergo a transition to a more hydrophobic 120S (for HRV) or 135S (for poliovirus, see reference 96) particle which is capable of releasing its RNA into the cell, albeit at low efficiency. Bacteriophages such as φX174 undergo transition to an eclipsed state which precedes the release of genome into the cell. Many of these activated states are short-lived and the intermediates are fragile. The use of cryo-EM is difficult for such systems, though it represents the most reasonable way of obtaining information about the activation process.
Release of Genome
Viruses employ a few basic strategies to deliver their genetic payload into susceptible host cells to permit viral replication. The genome may enter the host cytoplasm through the cell membrane(s) directly, for example, by an injection mechanism as occurs with many bacteriophages. Alternatively, viruses can enter cells intact or as subviral particles via translocation or endocytosis (nonenveloped viruses) or by fusion (enveloped viruses), and the genome is then released into the bulk cytoplasm (e.g., after pH-mediated disruption in an endosomal vesicle) or into the nucleus at nuclear pores (e.g., herpesviruses and adenoviruses). The segmented dsRNA genomes of reoviruses are a notable exception to the general rule because they remain packaged inside “core” particles that carry the enzymatic machinery required to synthesize nascent mRNA for production of progeny virus. This unique characteristic makes the reoviruses and other dsRNA viruses excellent systems for studying transcription by cryo-EM techniques (see “Transcription and translation”).
Release of the genome from any virus is an asymmetric process. Thus, genome release from icosahedral viruses induces functionally important asymmetry in the form of large conformational changes. As valuable as icosahedral image reconstruction methods may be, they are ill suited for producing detailed structural pictures of asymmetric particles. The use of single-particle reconstruction methods (e.g., see reference 125) is likely to yield more-detailed analysis of such structures. Despite the disadvantages, image reconstruction studies of a few icosahedral viruses have provided new insights and hypotheses regarding the processes of genome release.
Model of genome release in FHV.
Coordinated cryo-EM and X-ray crystallographic studies of FHV have provided information about genome organization (see “Genome organization”) and also have led to a hypothesis concerning genome release in this insect virus (66). FHV (Nodaviridae family) has a T=3 capsid consisting of 180 copies of a single, 44-kDa protein (407 aa) which encapsidates an ssRNA genome (three genes on two RNA molecules) (Fig. 26). The capsid proteins undergo a postassembly cleavage required for infectivity. This cleavage produces 180 γ peptides (C-terminal 44 aa) on the interior of the virus. Crystallographic analysis of FHV virions (122) showed that 16 residues at the N terminus of each peptide form an amphipathic α helix and that these γ helices lie in dramatically different environments owing to quasi-equivalent interactions among the β peptides (N-terminal 363 aa). A cryoreconstruction of virions at 22-Å resolution (66) revealed the organization of the bulk RNA that was invisible in the 3.0-Å crystal structure (122) and also showed density completely consistent with the highly ordered duplex RNA that was seen in contact with the inner capsid wall at the icosahedral twofold axes in the X-ray structure (Fig. 27).
FIG. 26.
Schematic diagram (left) and cryoreconstruction (right) of the ssRNA insect virus FHV (family Nodaviridae). The capsid of FHV consists of 180 copies of a single subunit arranged with T=3 icosahedral symmetry. Each icosahedral asymmetric unit consists of three quasi-equivalent subunits, labeled A, B, and C. A and B are related by a quasi-twofold axis (open ellipse). The positions of a peptide arm and a portion of the RNA genome that adopts a highly ordered, double-stranded loop are also indicated in the diagram. The isosurface rendering of the image reconstruction shows prominent peaks on the viral surface at local threefold positions (open triangle in diagram). Positions of four icosahedral symmetry axes (2, 5, and 3) are marked on the reconstruction. Adapted from reference 66 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
FIG. 27.
Positions of γ helices in FHV. (Top) Cutaway view of FHV with density derived from cryo-EM in blue and density derived from a difference map (cryoreconstruction minus X-ray structure of capsid only) in red. The cylinders represent the three types of γ helices, with γA in blue, γB in orange, and γC in green. Asterisks mark the helices shown in the middle panel. (Middle) Close-up view of two pairs of γ helices that are in close association with the bulk RNA (red mesh) and ordered RNA (space-filling model). (Bottom) Side view of region near the icosahedral fivefold axis (vertical white line) showing the bundle of γA helices and A subunits (one in a green-, yellow-, and red-ribbon representation and the others in thin-yellow-line Cα backbone traces) fit into the EM envelope (blue mesh). The ellipsoidal difference density (red contours) is situated on the fivefold axis in a position consistent with unmodeled density from the X-ray map (white contours). Adapted from reference 66 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
The cryo-EM map made it possible to model the interactions of the capsid proteins with the viral genome in greater detail than was possible from the X-ray structure alone. Excellent fidelity between corresponding regions of the cryoreconstruction and the X-ray structure provided a firm basis for the structural interpretations. The reconstruction showed that the three types of γ helices (γA, γB, and γC, corresponding to chemically identical products generated from the uncleaved A, B, and C coat protein subunits, respectively) interact differently with the viral RNA (Fig. 27), and these differences suggested a possible mechanism of cell attachment and genome release. The γA helices, which lie beneath the A subunits, form a radially oriented, pentameric bundle that has a hydrophobic surface and a hydrophilic core. The bundle lies suspended above the RNA and is stabilized by interactions among the hydrophilic surfaces of the helices. The γC helices form hydrophilic contacts with the ordered duplex RNA and with the γB helices in pairs about the icosahedral threefold axes (Fig. 27), whereas the γB helices contact only the bulk RNA. Because the relative positions of the γ peptides change dramatically near the symmetry axes as a consequence of the presence or absence of RNA interactions, the roles of the peptides appear to be dictated by differences in the quasi-equivalent environments. Kinetic studies, consistent with this model, showed that 120 subunits cleave at a higher rate than the remaining 60 subunits (137).
These and other supporting data (e.g., the presence of a picornavirus-like “pocket” factor beneath the fivefold axes but not at the threefold axes) led to a model for FHV attachment, entry, and release of the genome that is, in part, analogous to poliovirus (see references 66, 175, and references therein) (Fig. 28). In this model, FHV binds to a receptor and then contacts the cell membrane at a fivefold vertex where there is an exposed methionine residue on each A subunit. These methionines are buried in the quasi-equivalent B and C subunits at the icosahedral threefold (quasi-sixfold) axes. The membrane or receptor contact, or both, may trigger release of the pocket factor which then destabilizes the intersubunit contacts along the pentamer axis, thereby exposing an γA-helix bundle. This allows its insertion into the membrane via hydrophobic portions of the γA helices while the RNA is dragged into the cell via the C-terminal ends of the γ peptides. Indeed, recent evidence shows membrane activity for the γ peptide (172). The model is consistent with the γA helices having minimal interaction with the RNA so that release of the helix bundle along the fivefold axis is facilitated. This also explains the requirement for the coat protein cleavage reaction. RNA translocation across the endosomal membrane is thought to arise from a process of cotranslational disassembly similar to that which occurs in RNA plant viruses where RNA is translated into protein if the ribosome binding site is exposed to the cytosol (175). When FHV is heated (mimicking studies of poliovirus release from its receptor [44]), particles remain essentially intact, but a distinct, single “puff” of density appears associated with most particles (Fig. 9 of reference 66). Each puff may be a single bundle of γA peptides associated with RNA. This would be consistent with the proposed model and possibly indicates that release of a puff may lead to a configurational relaxation of the virus structure such that further puffs cannot be released. Alternatively, a specific RNA sequence may prime one pentamer site for release upon perturbation of the particle by destabilizing the pentamer with which it is associated.
FIG. 28.
Hypothetical entry pathway for FHV. (Top) Fivefold view of FHV cryoreconstruction. The pink circle marks the fivefold axis, and the two sets of blue, red, and green dots identify the exposed loops of the A, B, and C capsid subunits, respectively, at two of the five quasi-threefold positions on the viral surface adjacent to the marked fivefold axis. The arrow shows the view direction (perpendicular to fivefold axis) in the middle and bottom panels. (Middle) Initial interaction of six methionine residues (not depicted) at the tips of the loops in the A (blue), B (red), and C (green) capsid subunits with a bilayer membrane (grey balls). The bundle of γA peptides (pink) and the RNA genome are poised just inside the viral surface at the fivefold axis. (Bottom) Capsid subunits rotate toward the membrane, allowing the γA peptides to be inserted into the membrane and form a channel for release of the viral genome into the host cell. Middle and bottom panels courtesy of T. J. Smith.
Other cryo-EM studies concerning genome release.
Environmentally induced particle expansion is believed to be a common mechanism for achieving disassembly of plant viruses in vivo. CCMV, a T=3, ssRNA plant virus, swells by 10% when metal ions are removed and the pH is raised to 7.0. Cryo-EM analysis of native and swollen CCMV particles along with X-ray crystallographic analysis of the native virion and atomic modeling of the swollen particle revealed that the coat subunits undergo a 29-Å radial expansion as a result of electrostatic repulsion of carboxylate groups (290) (Fig. 29). Preservation of RNA-protein contacts as well as intersubunit contacts (interwoven C termini) keeps particles from completely disassembling. Upon swelling, the hexamers and pentamers remain essentially intact but move to a higher radius (along quasi-sixfold and fivefold axes, respectively). They thereby separate from each other at the threefold axes, creating holes ∼20 Å in diameter. These holes form large conduits for the radially expanded RNA genome which lies below the openings to them. The extent to which the observed swollen CCMV structure represents an in vivo particle state that is competent to release the genome for replication and translation is unknown. However, the viral RNA can act as a template for protein synthesis and as a substrate for RNase in the swollen particle (21, 45). Also, it is notable that the conditions that promote expansion (high pH, low Ca2+) are characteristic of intracellular conditions, whereas the conditions that promote the compact state of the virion (low pH, high Ca2+) are characteristic of extracellular sites in plants. Finally, an earlier crystallographic study of tomato bushy stunt virus, another T=3 plant virus, demonstrated that the capsid of this virus also undergoes an expansion that leads to opening of holes in similar sites (256).
FIG. 29.
Structures of native and swollen forms of CCMV determined by X-ray crystallography and cryoreconstruction (290). (Top left pair) Stereo view along twofold direction of the native CCMV protein shell rendered as a Cα tracing with the A, B, and C subunits colored blue, red, and green, respectively. The yellow cage depicts the edges of a truncated icosahedron. (Top right) Truncated icosahedral model of CCMV in the same view orientation and color coding as the stereo Cα model. Yellow symbols mark the locations of the strict two-, three-, and fivefold icosahedral symmetry axes, and white symbols mark the positions of quasi-two- and threefold axes. The central triangle of chemically identical A, B, and C subunits defines the asymmetric unit of the icosahedral structure. The subunits are colored differently to reflect the fact that they occupy slightly different geometric (and chemical) environments. Polygons with subscripts are related to A, B, and C by icosahedral symmetry (e.g., C and C2 are related by a strict twofold rotation and A and A5 are related by a strict fivefold rotation). The A, B, and C subunits of the asymmetric unit are related by a quasi- or local threefold axis (white triangle; vertices of yellow cage in stereo view to left). The three orange dots mark the putative calcium binding positions in one asymmetric unit of CCMV (290). (Middle row) CCMV capsid at pH 4.5. At the left is a magnified, stereo view of the native, 3.2-Å-resolution CCMV X-ray Cα model fit into the 23-Å-resolution cryoreconstruction envelope (blue mesh). The yellow, truncated icosahedral cage is the same as that depicted in the top row. Calcium ions (180/capsid) are bound between capsomers by residues associated with the helices (white cylinders) which appear as three pairs positioned around each quasi-threefold axis. An isosurface view of the cryoreconstruction is shown at the right (same size as models in the top row). (Bottom row) Same views as in middle row but for the swollen CCMV capsid at pH 7.5 in the absence of metal ions. The atomic models of the native capsid subunits were translated and rotated as rigid bodies to fit the 28-Å-resolution cryoreconstruction in the stereo view. Adapted from reference 290 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Transcription and Translation
Transcription and translation are critical steps in a viral infection cycle. This molecular biology typically involves asymmetric interactions among small numbers of macromolecules and does not occur in larger, symmetrical particles. These events are thus difficult or impossible to study with icosahedral image reconstruction methods, though much structural insight has been obtained from the recent flood of high-resolution X-ray crystallographic and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of key proteins and protein-nucleic acid complexes. Nonetheless, cryoreconstruction studies of reoviruses and other dsRNA viruses have provided preliminary clues about how the viral transcription may occur within particles.
The family Reoviridae includes moderately large (700- to 900-Å), nonenveloped, T=13 icosahedral viruses with a complex, multilayered protein structure which encapsidates 10 to 12 segments of dsRNA (225). The strategies for infection and replication are similar for all Reoviridae viruses, and all viruses contain the enzymes required for transcription of the dsRNA.
Early cryoreconstruction work on the rotaviruses, orbiviruses, and orthoreoviruses led to a consensus hypothesis that large channels in these structures might serve as pathways for importing metabolites required for viral RNA transcription and also for exporting newly synthesized mRNA molecules used in subsequent viral replication (108, 157, 158, 241, 249, 353). A similar conclusion has been proposed for an aquareovirus (272) and also for dsRNA fungal viruses L-A and P4, which have much smaller (10- to 15-Å) holes (55, 63). Cryoreconstruction methods were recently used to visualize mRNA release from actively transcribing rotavirus particles (193). This study showed that nascent mRNA transcripts generated within the rotavirus core by endogenous transcriptase complexes are translocated through the intact capsid through a system of channels at the icosahedral fivefold axes (Fig. 30). Acridine orange, an ssRNA intercalating agent, was used to enhance the visibility of the exiting mRNA in the cryo-EM specimens. As expected, the particles remain structurally intact during transcription, which can continue indefinitely.
FIG. 30.
Transcribing rotavirus DLP. (Left) Cryoreconstruction at a 25-Å resolution of the actively transcribing rotavirus DLP, viewed along a threefold axis and rendered with radial depth cueing (color bar gives corresponding radii for various colors). The pink “bowling pins” represent discernible portions of newly transcribed mRNA molecules as they exit the channels along the virus fivefold axes, each of which is bounded by five trimers of VP6 (blue). The two middle images compare close-up views of transcribing (left) and nontranscribing (right; at ∼28-Å resolution) DLPs. The rightmost image, in which one of the five VP6 trimers that surround the type I channel has been removed for clarity, depicts a hypothetical path (grey tube) that the mRNA transcript may take as it passes through the VP2 (green) and VP6 (blue) layers of the inner capsid. Adapted from reference 193 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Additional information about transcription in dsRNA viruses has been obtained in cryoreconstruction studies of rotavirus (195, 247), orthoreovirus (107, 209), cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (356), bacteriophage φ6 (48), and the fungal viruses L-A and P4 (55, 63). A common goal in these studies has been to probe the structure of the transcriptase complex in each virus. A noteworthy structural feature that appears to be unique to dsRNA viruses is that the fungal viruses and the cores of the other viruses all contain 120 copies of at least one protein subunit. This unique stoichiometry and the associated molecular architecture appear to be favored for the construction of specialized intracellular compartments for transcription and replication that protect the dsRNA genomes from host cell enzymes and may also serve to retain them in the cytoplasm.
In rotavirus, the viral dsRNA forms a dodecahedral structure in which the RNA interacts closely with 12 enzyme complexes located at the icosahedral fivefold axes. This arrangement is proposed to be conducive for an orchestrated movement of the RNA relative to the complex during transcription (247). Similar internal structures have been observed in orthoreovirus (107) and in the insect reovirus cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (356).
Heat and chymotrypsin treatment of reovirus core particles cleaves the 144-kDa λ2 protein, which carries the guanylyltransferase activity (adds 5′ caps to reovirus mRNAs), leaving a 120-kDa N-terminal fragment associated with the cores (209). Reconstruction of these modified cores revealed the loss of a distinctive outer region of λ2. Because these particles were shown to retain all activities required to transcribe and cap reovirus mRNAs, the missing portion of λ2 is dispensable for these functions.
Cryo-EM studies of the enveloped bacteriophage φ6 revealed an outer, T=13 layer of protein P8 and a core consisting of four proteins (P1, P2, P4, and P7). P1 is present in 120 copies (48). The core, which has a structure strikingly similar to that seen in reovirus (108), acts as the RNA packaging and polymerase complex. Expressed core proteins assemble into replication-competent procapsids. Comparison of several procapsid-related particles (expressed and assembled in Escherichia coli) with virion-isolated nucleocapsids and cores suggested that the maturation process involves extensive structural rearrangements that produce expansion. The movements are coordinated with the packaging of the viral RNA and with the RNA polymerization reactions leading to virion assembly (48).
The L-A virus of yeast has a capsid consisting of 120 copies of Gag protein (76 kDa), of which approximately two contain the Pol moiety and in which the proteins are arranged as 60 asymmetric dimers (55, 63). A model of how RNA transcription occurs in L-A was formulated on the basis of a cryoreconstruction at 16-Å resolution (55). The capsid wall is perforated by 10- to 15-Å-diameter holes which function as a molecular sieve by allowing exit of nascent mRNA and influx of metabolites while retaining and protecting the dsRNA from degradative enzymes (Fig. 31).
FIG. 31.
Model of transcription in L-A virus (55). Approximately two copies of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (Pol; shown with an arbitrary shape) are present in each virion. Each Pol, which is covalently attached to one of the 120 Gag subunits that comprise the icosahedral capsid of L-A virus, presumably lies at the inner surface of the capsid close to the dsRNA substrate. In this diagram of the hypothetical transcription pathway, as the genome is processed by Pol, the ssRNA transcripts are extruded through small openings in the capsid. Adapted from reference 55 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Proassembly and Maturation
Harried parents on Christmas Eve (and others of us who never read manufacturers’ instructions) cling to the belief that assembly proceeds through a series of stages which increasingly resemble the desired final product. Virus assembly rarely follows such an intuitively obvious path. Although the paradigm for understanding virus structures was based on the requirement for self-assembly (53), many virus capsids utilize chaperones and/or scaffolding proteins to ensure that the task of assembly is completed correctly and efficiently. All of the well-studied cases of assembly pathways include intermediate structures which need to undergo substantial conformational changes to reach the final state. Many of these states have been characterized by cryoreconstruction in combination with in vitro assembly and mutagenesis experiments. The results inform a more realistic view of general capsid assembly pathways (294).
Common features of capsid maturation in dsDNA viruses: from λ to HSV-1.
Bacteriophage λ is one of the most widely used phages in molecular biology. The virion comprises a nearly icosahedral, isometric head that encapsidates 47 kbp of dsDNA and to which a helical tail is attached. The head contains 405 copies of the two major capsid proteins, gpD and gpE, clustered on a T=7laevo lattice as shown by conventional EM (51, 221, 265, 346). Protein gpE (38.2 kDa) is clustered as hexamers and pentamers, and gpD (11.6 kDa) is clustered as trimers (167, 183). Morphogenesis of λ proceeds via the assembly of the prohead, an empty precursor capsid, which is subsequently filled with DNA. An initiator complex, which eventually gives rise to the portal vertex, begins prohead assembly and nucleates the polymerization of gpE to complete the procapsid shell. The packaging of DNA through the portal vertex is accompanied by a transition of the capsid to the expanded form which is stabilized by the addition of polypeptide gpD. Mutant virions which lack gpD can be propagated when stabilized by the presence of a high concentration of Mg2+. Mutations in the terminase, which recognizes and cleaves the λ DNA and packages it into the procapsid (220), produce proheads that also lack gpD and can be isolated.
Cryo-EM and icosahedral reconstruction of these three particle states revealed changes in capsomer organization in the λ capsid (100). The wt λ structure was compared to that of a gpD− mutant to reveal the location of gpD on the surface (Fig. 32). The reconstructions showed that hexamers in the mature capsid have a flat, cartwheel-like structure, whereas trimers appear as prominent, thimble-shaped structures that protrude from the capsid surface. The thimble and the hub of the cartwheel appear as continuous densities in which subunits cannot be distinguished. The spokes of the cartwheel radiate from the central hub with a right-handed skew and make a bend before entering the trivalent thimbles. Spoke geometry varies with environment, suggesting that it is here where alterations accommodate the varying quasi-equivalent contacts required by the T=7l symmetry. The identity of the thimbles as the site of gpD was confirmed by the reconstruction of the gpD− mutant, which was otherwise indistinguishable from wt. The absence of the thimbles allows one to see the details of the trivalent contact of the spokes which form an annulus between the capsomers (Fig. 32).
FIG. 32.
The structural transitions in the bacteriophage λ capsid during maturation. The capsid has T=7l icosahedral symmetry and is formed of hexamers of protein gpE. The prohead reconstruction shows the capsid prior to the packaging of DNA and the accompanying expansion. Notice that the gpE hexamers are skewed in this form of the capsid. Genome packaging in the wt virion leads to a much smoother surface in which the individual hexamers have expanded. Expansion is also accompanied by the addition of protein gpD, which helps to stabilize the capsid structure. gpD is bound at the local threefold positions of the T=7 lattice as shown by the comparison of the wt reconstruction with that of a mutant (D−) which lacks gpD. Adapted from reference 100 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
The λ prohead is smaller than the other structures (outside radii: λ prohead, 270 Å, versus 315 Å for the wt and gpD− λ virions), but its shell is the thickest (69 versus ∼40Å). Comparison with the mature capsid shows their shared T=7 arrangement (Fig. 32). The hexameric capsomers of the prohead are elongated and distorted structures compared to the symmetric rings in wt λ. The subunits appear peanut shaped in the prohead and are positioned perpendicular to the capsid surface, accounting for its greater thickness. A portion of each subunit extends toward the center of the virion where it broadens into a bulb and forms the trivalent contacts of adjacent subunits. There are also extensive divalent contacts between adjacent hexamers. The conformation of the gpE subunits in the prohead is similar in different environments; however, the intersubunit contacts are nonequivalent between hexamers and within the hexamer. Although gpD is required for the formation of filled particles, its external location makes a direct interaction with the DNA unlikely. Virions which lack gpD are very sensitive to the removal of Mg2+. In the prohead, this position is the site of additional divalent ion binding. In the mature capsid, the same site is occupied by gpD. Only with this extra degree of stabilization can the capsid accommodate the strain of packaging a full head of DNA. An alternative (or additional) function for gpD would be to close the trivalent site to keep DNA from leaking from the filled virion, as has been suggested for the Psu protein of P4 (99, 101, 169).
The features seen in λ are also found in a number of other systems. Bacteriophage HK97 has a thickened, procapsid shell with split, asymmetric hexavalent capsomers that mature into a larger, smooth-surfaced capsid with sixfold symmetric capsomers (Fig. 33) (82) upon packaging of DNA. Bacteriophage P22 (245, 250, 308, 309) and the animal virus HSV-1 (311) undergo similar changes in capsomer structure (Fig. 34). Thus, systems as disparate as bacteriophages and enveloped animal viruses all proceed to generate a stable capsid structure by proceeding through a smaller, thicker-walled, less angular precursor which contains asymmetric hexamers.
FIG. 33.
Procapsid maturation in bacteriophage HK97 (81). Shown are isosurface views along the twofold direction of cryoreconstructions of the T=7 HK97 precursor (left) and mature (right) capsids. HK97 capsid proteins (42 kDa) aggregate into pentamers and hexamers and form a prohead, but without scaffold proteins as often occurs in other viruses. A viral protease is incorporated into the prohead upon completion of assembly, and when activated, it cleaves the 11-kDa amino-terminal domain from the inner surface of the capsid protein. This reaction triggers transformation of the prohead into the expanded, mature capsid, in which adjacent subunits become covalently cross-linked. The hexamers undergo a dramatic change from their asymmetric, sheared state to a more symmetrical structure in the mature capsid. Adapted from reference 294 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
FIG. 34.
Procapsid maturation in HSV-1 (311, 312). Shown are isosurface views along a twofold direction of cryoreconstructions of the T=16 HSV-1 precursor procapsid at 28-Å resolution (left), mature capsid at 25-Å resolution (right), close-up views of each capsid along a fivefold axis (insets). The color images are overlaid on the unprocessed cryo-EM images of the corresponding vitrified specimens. Comparison of the two structures reveals the substantial changes that occur in the hexons (hexameric capsomers), which are distorted and nonsymmetric in the procapsid but become symmetric in the mature capsid. HSV-1 capsids contain three major proteins: VP5 (150 kDa; 960 copies), VP19c (50 kDa; ∼320 copies), and VP23 (34 kDa; ∼640 copies). The 320 “triplexes” (arrows in insets), which occupy local threefold axes of symmetry, consist of two copies each of VP23 and one copy of VP19c. The horns of density at the tips of the hexons, but not pentons, in the mature capsids are monomers of VP26 (12 kDa), an additional viral protein that is dispensable for capsid assembly but which binds to the capsid if present. Adapted from reference 294 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Assembly proteins.
Chaperones were first identified by their effects on the assembly of phage λ in E. coli. Cryoreconstruction has provided direct views of these proteins in action. Traditionally, scaffolding proteins are described as sitting within the procapsid and being ejected upon the entry of the genome. This indeed appears to be true for P22 (308, 309) and HSV (311), where interior scaffolding protein density has been visualized. Unfortunately, much of the scaffolding protein density is not arranged with icosahedral symmetry (Fig. 35) and hence is not seen in its entirety. In contrast, bacteriophages P4 and φX174 do have icosahedrally arranged scaffolding proteins on the outside of the virions (99, 169). The scaffolding protein density is seen in positions which constrain the geometry of the capsomers and define the procapsid diameter (Fig. 36).
FIG. 35.
The position of the scaffolding protein in the procapsid of the bacteriophage P22 scaffolding mutant is shown in outer surface and cut-open views of the reconstruction. (A) Outer surface of the structure; the density attributed to the internal scaffolding protein is colored white whereas that of the coat protein is colored yellow. One copy of each of the seven quasi-equivalent coat proteins is highlighted in a different color. (B) Cut-open view shows the distribution of the scaffolding protein (white) which extends to a radius of 206 Å within the outer layer (yellow). Adapted from reference 308 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
FIG. 36.
The role of the capsid-size-determining protein in the bacteriophage P2-P4 system is shown by a series of surface views of reconstructions. Bacteriophage P2 forms a T=7 particle of 600 Å in diameter (A) which packages its 33-kb genome efficiently. Bacteriophage P4 uses the proteins of P2 to form a 450-Å T=4 shell (B) which can package its smaller 11-kb genome but excludes the larger P2 one. The change in capsid size is controlled by the P4 gpSid protein. Reconstruction of a recombinant particle which resembles the 390-Å P4 procapsid (C) and the procapsid bearing a full complement of gpSid (D) shows that the size determination protein forms a 400-Å dodecahedral shell on the outside of the procapsid. Expansion after packaging brings the mature P4 to its final 450-Å diameter. Adapted from references 101 and 213 with the permission of the author and the publishers.
An enveloped bacteriophage, PRD1, provides an interesting counterpoint to the capsid expansion seen in other viral systems. Here the membrane may serve the role of the scaffold. The procapsid form of PRD1 is visualized by using a packaging mutant, sus1, and is indistinguishable in size from the mature virion (Fig. 37). A structural change between the two forms is revealed by examination of the interior density, since the transmembrane projections beneath the outer protein shell are markedly better ordered in the mature, DNA-filled virion (50).
FIG. 37.
The structure of the membrane-containing bacteriophage PRD1 is shown by three surface representations of PRD1 particles. The wt phage and a mutant phage which does not package the genomic DNA show that the T=25-like exterior is not changed by the packaging. The structures within the interior membrane of the virus increase in order after packaging. The structure of the P3 protein shell shows the organization of the major capsid protein and the removal of the fivefold vertex structures. The similarity to adenovirus (Fig. 23) is striking; both are T=25-like arrangements in which trimeric proteins fill hexavalent sites and have a separate protein complex that forms the vertex at the fivefold position and which also includes a trimeric protein. Adapted from reference 50 with the permission of the publisher.
A different type of maturation is that of viral envelope proteins during their transport through the secretory pathway. The viral envelope proteins will eventually function as the mediators of viral fusion on the surface of the virion. During transport to the cell surface, the spike complex must pass through the low pH of the trans-Golgi complex on its way through the secretory pathway. Since the conformational change which mediates fusion is irreversible for many viruses, some mechanism must protect the spike from this premature exposure to an acid environment. In the alphaviruses, this protection is afforded by the timing of the activating cleavage of the precursor p62 to E2 and E3. Prior to p62 cleavage, the spike complex is relatively insensitive to low pH; after cleavage, exposure to low pH causes irreversible conformational change. The development of a system for the expression of mutant SFV (204) allowed the examination of the effect of the activating cleavage of p62 on the spike structure. Expression of the SQL mutant, in which the normal processing was abolished by mutation of the cleavage site, led to production of a virion which was not capable of fusion. The SQL virion has the same T=4 arrangement of spikes as the wt SFV, but the extramembranous portion of the spike is separated into three distinct domains (Fig. 38) (186), leaving a hole on the quasi-threefold axis (118). Comparison of the SQL spike structure with that of the SFV structure shows that the mass corresponding to E1 has been displaced from its relatively central position to a distal one (186, 325). Hence, the cleavage necessary for activation of the spike causes a movement of E1 toward the center of the trimer to form the compact structure with the central cavity that plays such an important role in the low-pH-initiated conformational changes. E1 trimer formation would be inhibited in the SQL virion by the association of E1 with the distal end of p62. This separation provides a plausible explanation for the mechanism of fusion inhibition in the precursor. Presumably, similar large conformational changes could accompany the maturation of other, enveloped virus fusion proteins; however, a comparison of mature SNV and uncleaved mutant (238) does not reveal the same dramatic structural change as visualized in SFV.
FIG. 38.
Comparison of the structure of the wt mature SFV with that of the SFVmSQL mutant shows the effect of cleavage of the spike protein precursor (p62) on the spike structure. The spike coalesces from an open structure with separated E1E2 heterodimers to a closed structure containing a cavity at its center. The modular nature of the structure is reflected in the observation that the capsid, transmembrane regions, and spike skirts are unchanged by the cleavage. Adapted from reference 118 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Features of mature structures: quasi-equivalence in practice.
We have focused on the dynamic features of virus life cycles throughout most of this review. In this section, we examine the results of maturation and the architecture of the mature virion. Understanding the concept of triangulation number is a basis for a theoretical appreciation of the roles of quasiequivalence and nonequivalence in viral assemblies. An intuitive feeling for the richness in expression of these concepts is gained only by considering specific examples. There are fundamental aspects buried in this variety. We begin with the dsRNA viruses which have little sequence homology but yet exhibit recurring structural features. We then look at the way in which capsid assembly is controlled to alter size and, in some cases, the biology of the assembly. This section concludes with a discussion of the exceptions to the rule, viruses so large that quasiequivalence could never provide a basis for their formation.
(i) dsRNA viruses.
The dsRNA viruses have been intensely studied because of their medical and economic significance and because they make excellent model systems for examining all of the stages of viral pathogenesis. They range in size from ∼400 to 1,000 Å in diameter. They vary in complexity from the one-segment genome fungal viruses to the 12-segmented coltiviruses. Most have multilayered protein shells comprising multiple copies of up to eight different structural proteins. In addition, these viruses are able to actively transcribe mRNA, generally as subviral particles (virions in the case of fungal viruses). These properties have made dsRNA viruses ideal subjects for cryoreconstruction studies. Indeed, the number of cryo-EM studies of dsRNA viruses is quite daunting, and a detailed description and comparison of them are beyond the scope of this review. The bulk of cryo-EM work has involved various members of the family Reoviridae, though intriguing corollaries with the mammalian dsRNA viruses have emerged in recent studies of fungal viruses and an enveloped bacteriophage. Here, we briefly introduce and highlight structural characterizations by cryoreconstruction of four groups of reoviruses (orthoreoviruses, rotaviruses, orbiviruses, and aquareoviruses), a birnavirus, two fungal viruses, and the enveloped bacteriophage φ6. Viral transcription and genome organization are treated in “Transcription and translation” and “Genome organization.”
(a) Reoviridae.
The family Reoviridae includes moderately large (700- to 900-Å), nonenveloped, icosahedral viruses that have a complex, multilayered protein structure that encapsidates 10 to 12 segments of dsRNA (225). Five genera infect vertebrates including humans (orthoreovirus, rotavirus, coltivirus, and orbivirus) and fish (aquareovirus), whereas other genera infect plants (phytoreovirus, fijivirus, and oryzavirus) and insects (cypovirus). The strategies for infection and replication are similar for all Reoviridae viruses, and all viruses contain the enzymes required for transcription of the dsRNA.
(b) Reoviridae: Orthoreovirus genus.
Mammalian reoviruses, the prototype viruses of the genus Orthoreovirus, have two proteinaceous shells that encapsidate the genome (Fig. 39). The 10 genome segments encode eight structural and three nonstructural proteins. Four proteins, ς1 (51 kDa), ς3 (41 kDa), μ1 (76 kDa), and λ2 (144 kDa), comprise the outer capsid, whereas ς2 (47 kDa), μ2 (83 kDa), λ1 (142 kDa), and λ3 (142 kDa) comprise the bulk of the core (225). Although not a human pathogen, reovirus has been a model system for studying viral pathogenesis. Partial proteolysis of intact virions removes ς3 and probably leads to the unfolding of ς1, the cell attachment protein (136). The resulting ISVPs are infectious, and cleavage of μ1 appears to facilitate cell penetration (226). Continued proteolysis converts ISVPs to cores with the loss of μ1 and ς1 (179), and λ2 undergoes a dramatic change in conformation to form the core spikes.
FIG. 39.
Schematic diagrams of the compositions and structures of orthoreovirus virions, ISVPs, and cores. The structures of virions and ISVPs appear very similar for all serotypes studied, but the λ2 spike of the serotype 1 Lang (T1L) core adopts a more open conformation than the cores of other serotypes, such as T3D (reovirus serotype 3, Dearing). The virion has a triple-layered structure, depicted as three concentric circles at the lower left. Outer and inner capsids, each comprised of multiple copies of four different proteins, encapsidate a central core that contains the segmented dsRNA genome. Adapted from reference 225 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Virions of several strains of reovirus and related subviral particles have been examined by cryo-EM techniques to elicit detailed structural information about capsid and genome organization during the early and late stages of reovirus infection (108, 209, 217, 335). Virions (∼850-Å diameter), ISVPs (∼800 Å), and cores (∼600 Å) are easily distinguished by size and surface features (Fig. 40). Images of virions show short (∼80-Å), finger-like projections at the periphery, and some particles exhibit a profile which is clearly noncircular (Fig. 40). Images of ISVPs show coarse, knob-like bumps and short, villus-like projections at the particle periphery (Fig. 40). A fraction of the ISVPs also have filamentous projections that extend up to 400 Å beyond the outer surface. Cores have large protrusions that extend beyond the main particle periphery (Fig. 40). Virions and ISVPs often assume preferred orientations in vitrified samples, presumably due to specific interactions made by extended ς1 fibers with the air-water interface in samples prepared for quick freezing. Hence, it was necessary to record images of these particles with the microscope stage tilted up to 10° to obtain a satisfactory distribution of unique projected images for 3D studies of T1L reovirus particles (108, 335).
FIG. 40.
Cryo-EM of orthoreovirus T1L virions, ISVPs, and cores. Magnified views of three representative particles of each type are shown below. Bars represent 1,000 Å (low-magnification views) and 500 Å (higher-magnification views).
3D reconstructions of several vitrified reovirus particles have been reported (108, 209, 217). Virions and ISVPs both have “subunits” that form an incomplete, T=13l icosahedral lattice (Fig. 41). The structure of the T1L virion is essentially identical to that of two other virion serotypes, T2D (type 2, Jones) and T3D (type 3, Dearing) (217). The external surface of the virion has 600 finger-like projections attributed to protein subunits (ς3) which surround 60 channels and the 12, large cavities at the icosahedral vertices (Fig. 41). The external surface of the ISVP consists of 200 trimeric “subunits” (μ1) and a star-shaped mass of density (λ2) at the base of each shallow cavity similar to that in the virions (Fig. 41). ISVPs also have a density feature (ς1) that extends above the surface along each fivefold axis. The core consists of 12 turret-like “spikes” (λ2, the guanylyltransferase) at the vertices and 150 ellipsoidal nodules (ς2 and λ1; both bind dsRNA) on the surface (Fig. 41). The minor proteins (12 copies each of μ2 and λ3, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase) appear to be located inside the core and extend beneath the spikes at the fivefold vertices (107) in a manner similar to that found for the transcriptase complex of rotavirus (247). Features of the core shell appear very similar in reconstructions of serotype 1 virions, ISVPs, and cores (see Fig. 6 in reference 108). The correlation of specific density features with the various structural components as suggested here is based in part on biochemical characterizations (see reference 225 and references therein) and in part on interpretation of difference maps computed between various particle types (108, 209). The 3D reconstruction studies reveal a myriad number of protein subunit interactions that characterize each particle form and which presumably are required to coordinate the morphogenesis of a series of metastable structures. The recent application of “recoating genetics,” in which reovirus ISVPs or cores are incubated with expressed outer capsid proteins in an in vitro assembly system to produce virion-like particles, has provided a powerful tool to examine the roles of specific proteins in viral morphogenesis and infection (57, 171).
FIG. 41.
Isosurface views in the twofold orientation of the cryoreconstructions of the orthoreovirus T1L virion, ISVP, and core. These reconstructions were computed from images like those depicted in Fig. 40. The T1L virion is characterized by 600 finger-like projections (ς3 protein) and 12 depressions with flower-shaped features (λ2 protein) at the fivefold vertices and a knob of density (ascribed to the ς1 protein) on the fivefold axis. The T1L ISVP has similar flower-like features centered on the icosahedral vertex positions and 200 trimeric structures (μ1 protein) distributed over the capsid surface. The ς1 protein adopts a more extended conformation in the ISVP, though this is not apparent at the high contour level at which the isosurfaces are rendered (see Fig. 4 of reference 108). The λ2 spikes (open, turret-like structures) are the most prominent feature of the T1L core. The composition of the knob-like features on the surface of the core is still undetermined (possibly a combination of λ1 and ς2 proteins), but the components of the viral RNA polymerase (λ3 and μ2 proteins) have been located inside the core shell and hence are not visible in this view (107).
(c) Reoviridae: Rotavirus genus.
Rotavirus is the primary cause of infant gastroenteritis in numerous mammals and is the major cause of human infant mortality in developing countries (117). The rotavirus genome contains 11 dsRNA segments which encode six structural and five nonstructural proteins. The majority of the virion protein mass (VP4, 87 kDa; VP6, 45 kDa; VP7, 37 kDa) forms two T=13l capsid shells, whereas the remaining proteins (VP1, 125 kDa; VP2, 102 kDa; VP3, 98 kDa) are associated with the core (Fig. 42). VP6 and VP7 form two concentric capsid shells, with VP7 comprising the outermost layer. The viral cell attachment protein and hemagglutinin, VP4, interacts with both VP7 and VP6 (see below and “Cell attachment”). Proteolysis of VP4 (producing VP5* and VP8*) appears to play a central role both in viral entry into the cell (181) and in the enhancement of viral infectivity (206).
FIG. 42.
Organization and structure of rotavirus. A schematic diagram (left) and 3D reconstruction (right) illustrate the multilayered rotavirus structure and the disposition of its major components. The dsRNA genome and viral RNA polymerase (VP1 and VP3) are encapsidated by a core shell composed of VP2. This core is surrounded by two concentric shells of protein which include 260 trimeric-shaped columns of density (VP6) on the inside and 260 trimers of VP7 on the outside. VP7 forms a relatively smooth outer surface with 132 channels through which VP6 and VP2 are accessible (shown more clearly in Fig. 18). Sixty dimeric spikes (VP4), which contain the receptor recognition domain, project ∼110 Å radially outward from the viral surface and ∼90 Å beneath the surface and are in close contact with both VP7 and VP6 (352). Adapted from references 117 and 352 with the permission of the authors and the publishers.
A large number of naturally occurring as well as expressed, reassortant, and modified rotavirus particles have been examined by cryoreconstruction methods (193, 195, 242, 247, 249, 271, 352, 353). These studies, in conjunction with numerous biochemical characterizations and excluded volume estimates, have allowed the assignment of most of the viral proteins to specific structural features in the 3D reconstructions.
Images show virions with a smooth outer edge (765-Å diameter) and a characteristic spoked-wheel appearance (Fig. 43). Cryo-EM images recorded at 2- to 3-μm underfocus (data not shown) show spikes that project radially at least 100 Å from the smooth surface. Double-shelled particles (DLP = core plus VP6) have a bristly outer surface and are ∼705 Å in diameter (Fig. 43). The VP4 spikes in virions are dimers that extend ∼110 Å above the VP7 shell and ∼90 Å deep into the virion where a hexameric base makes extensive interactions with VP6 (242, 271, 352) (Fig. 42). A total of 132 aqueous channels penetrate the VP6-VP7 layers, and these provide likely pathways for the diffusion of ions and small regulatory molecules to the transcriptionally active core (249, 353). VP7 and VP6 are each organized as 260 trimers with T=13l symmetry in the respective layers (e.g., see reference 352).
FIG. 43.
Cryo-electron micrograph of a rotavirus sample containing both double-layered and triple-layered particles. The larger TLPs have a characteristic smooth circular profile whereas the smaller DLPs have a bristly outer profile. Magnified views of two TLPs (left) and two DLPs (right) are shown in the insets at the bottom.
Recent studies of genome-deficient particles assembled from expressed proteins have helped identify the locations of the core proteins (247). Reconstructions of DLPs which contain dsRNA and of several VLPs that lack one or more protein components (2-VLP, 2/6-VLP, and 1,2,3,6-VLP) demonstrate that 120 subunits of VP2 form a relatively smooth, contiguous layer (radii of 230 to 260 Å) that interacts with an outer layer of VP6 (260 to 350 Å) (Fig. 44). A small portion of VP2 forms a pentagonal structure that extends further inward at the fivefold axes, whereas VP1 and VP3 are attached to the inside tip of VP2 and form a flower-shaped structure that extends to a radius of 160 Å. The structures of the 2/6-VLP and a VLP with the amino terminus of VP2 deleted (Δ2/6-VLP) were compared by difference image analysis (195). The N termini of the VP2 subunits, which possess nonspecific ssRNA and dsRNA binding activity and are essential for incorporating VP1 (polymerase) and VP3 (guanylyltransferase) into cores, were shown to be located near the icosahedral vertices inside the core.
FIG. 44.
Organization of rotavirus DLPs as visualized in radial-depth-cued surface representations, viewed along a threefold direction. (Top) DLP cryoreconstruction at a nominal resolution of 19 Å, depicted to show an exterior view of the entire particle (left), the internal organization in a cutaway view (middle), and the dodecahedral shell of ordered RNA (right), which represents ∼25% of the total genome. The disposition of VP6 (blue) and VP2 (green) layers and the VP1-plus-VP3 RNA polymerase complex (red) and the ordered RNA (greyish green and yellow in the middle and yellow on the right) are denoted by arrows. (Bottom three rows) Radial cutaway views compare the internal features of the DLP (left column) and recombinant baculovirus-expressed VLPs composed of VP2 and VP6 (VLP-2/6 [middle column]) and of VP1, VP2, VP3, and VP6 (VLP-1/2/3/6 [right column]). The radial cutaways from cryoreconstructions computed to 23-Å resolution include only densities from radii of 160 out to 260 Å (top row), 235 Å (middle row), and 225 Å (bottom row). Features between radii 260 and 350 Å are invariant in these structures. RNA density (yellow) appears in the DLP at a radius of ∼230 Å where corresponding regions of the VLPs are empty. The VP2 protrudes inward at the fivefold vertices from the main core shell to a radius of ∼220 Å. A flower-shaped density, attributed to VP1 and VP3, attaches to the tips of VP2 at the fivefold axes in VLP-1/2/3/6, and similar density occurs in the DLP. Adapted from reference 247 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
(d) Reoviridae: Orbivirus genus.
The Orbivirus genus is divided into 14 distinct serogroups (262) (Fig. 45). Orbiviruses, unlike reoviruses and rotaviruses, are transmitted between vertebrate hosts by arthropods and replicate in both vertebrates and arthropods. They cause diseases of economic importance in many livestock, though they are not considered to be important human pathogens. The orbiviruses are double-shelled structures with 10 segments of dsRNA that encode seven structural and four nonstructural proteins. BTV, the prototype and most-studied orbivirus, has an outer capsid composed of two proteins (VP2, 111 kDa; VP5, 59 kDa) and a core with five proteins, two of which are major components (VP3, 103 kDa; VP7, 38.5 kDa) and the remaining three of which are minor components (VP1, 150 kDa; VP4, 76 kDa; VP6, 36 kDa).
FIG. 45.
Comparison of the structures of BTV and BRDV reveals the common features of orbivirus structures. The views of the outer surface along the twofold axis show that these two viruses have a similar organization but quite different elaborations of the structure. The structure of the triskelion on the threefold axis (VP2 in BTV and VP4 in BRDV) shows this clearly. The core structure of BRDV is shown in a surface view masked at 250 Å to show the VP2 layer. The crystal structure of the BTV core (144) shows that this layer is composed of 60 pairs of nonequivalent copies of the major core structural protein which is described as a “T=2” structure. The T=13l arrangement of the VP7 trimers is shown in a surface representation of the structure masked at a radius of 290 Å. Adapted from reference 268 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Several cryoreconstruction studies have been performed with BTV virions (158), cores (145, 241), tubes (160), and expressed, reassembled VLPs (157, 159). BTV cores appear quite similar to rotavirus DLPs, having a bristly surface and a 690-Å diameter (Fig. 45). The T=13l surface lattice is composed of 260 knob-like trimers of VP7, which span radii from 260 to 345 Å, and 132 solvent channels (Fig. 45). The VP7 layer surrounds a smooth, “T=2” layer of 120 paired VP3 molecules (radii, 230 to 260 Å) (143, 145). A pseudoatomic model of the outer layer of the BTV core (145), based on the crystal structure of VP7 (143), showed that the two-domain VP7 subunits form a rather precise T=13l icosahedral lattice in accordance with the postulates of quasi-equivalence (53). The model predicts that the β-barrel domains of VP7 face the outer layer of mature virions and that the lower, α-helical domains face the VP3 layer, which is postulated to function like a scaffold to determine particle size and form a smooth surface upon which VP7 trimers can associate (145). The recent determination of the crystal structure of the BTV core at ∼3.5 Å resolution has confirmed and extended these predictions and has revealed that the ∼1,000 component proteins self-assemble by making use of classical as well as geometric quasi-equivalent contacts (144).
The outer shell of BTV is intriguing in that it fits onto the underlying T=13l VP7 lattice and forms a relatively continuous shell around the core but is not itself a T=13l lattice (Fig. 46). The outer shell (∼900-Å diameter) consists of 60 sail-shaped spikes (VP2, the viral hemagglutinin) that sit above 180 of the VP7 trimers (contacting all but 20 of the VP7 trimers) and 120 globular regions (VP5) that sit on top of all 120 hexameric rings of VP7 trimers (332). VP2 and VP5 appear to be required to maintain the 60 VP7 trimers at the fivefold axes (159). Cryo-EM analysis of Broadhaven virus showed an outer capsid structure similar to that of BTV and established that the BTV VP5 protein is organized as 120 trimers (268).
FIG. 46.
The arrangement of proteins in BTV is shown in a series of schematic diagrams. (A) Placement of the individual structural proteins in the multilayered virion. (B) Arrangement of the proteins in the core in which the T=13 VP7 layer sits atop the “T=2” VP2 shell which surrounds the 10 segments of dsRNA. (C) The outer surface of VP2 sits atop the VP5 layer which mediates its interaction with the VP7 layers. Adapted from reference 332 with the permission of the authors and the publisher.
(e) Reoviridae: Aquareovirus genus.
Aquareoviruses, like other reoviruses, have a T=13l outer shell and a T=2 core. They are stable at pH 3 and are resistant to ether. They infect a variety of bony fish and crustaceans. The 11-segment genome codes for seven structural proteins (VP1 to VP7) and five nonstructural proteins. Though the stoichiometry and distribution of the structural proteins are unknown at this time, a recent cryo-EM structure determination of striped bass aquareovirus at 23-Å resolution displays a structure with an outer shell (∼800-Å diameter) containing 600 trimeric morphological subunits that surround an inner shell of ∼600 Å in diameter consisting of 120 subunits arranged as described previously (272) (Fig. 47). This 120-subunit stoichiometry and arrangement in the core shell appear to be a fundamentally important structural requirement of transcriptionally active dsRNA-containing particles. The same stoichiometry and organization have been found in or suggested for rotavirus (195, 247), reovirus (209), BTV (145), two fungal viruses (63), and bacteriophage φ6 (48). Another set of proteins cluster at the fivefold axes and form continuous density that spans both capsid layers.
FIG. 47.
Comparison of aquareovirus (top) to orthoreovirus T1L ISVP (bottom). Shown are isosurface views of aquareovirus (in color and in perspective) and T1L ISVP (black and white) in threefold (left) and fivefold (right) view orientations. The threefold view of aquareovirus shows the incomplete T=13l surface lattice (white overlay) and the axes of icosahedral symmetry labeled. The distribution and orientations of the 200 trimeric morphological units are essentially identical in the two particles. The flower-like structures on the fivefold vertices are distinct (e.g., in aquareovirus there is an axial channel). Differences in the relative sizes of features in the two structures are mainly attributed to aquareovirus being viewed in perspective whereas T1L ISVP is not. Aquareovirus images are adapted from reference 272 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
A noteworthy feature of the aquareovirus structure is that it is strikingly similar to reovirus ISVPs (108), with the pattern of 600 trimers in aquareovirus (ascribed to VP7, 35 kDa) appearing quite similar to the arrangement of μ1 trimers in ISVPs (Fig. 47). Also, both virus samples adopt preferred fivefold orientations in cryo-EM preparations, which is uncommon for most cryo-EM specimens of icosahedral viruses. In ISVPs, the ς1 protein (located at the fivefold axes) adopts an extended conformation which presumably induces preferential orientation of particles in thin, aqueous samples prepared for cryomicroscopy (108).
(f) Reoviridae: Cypovirus genus.
A significant pathogen of arthropods is a reovirus commonly referred to as cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus. Infectious particles occur inside characteristic crystalline inclusion bodies (called polyhedra) composed of viral proteins (222). Insects become infected when they ingest polyhedra contained on contaminated food. The high pH of the insect gut dissolves the polyhedra and releases virus particles. These then infect the epithelial cells that line the gut wall, where they replicate in the cytoplasm.
Recent cryoreconstruction studies of full and empty particles of BmCPV-1 have provided a detailed look at the organization of this reovirus (356). BmCPV-1 consists of a 10-segmented dsRNA genome, five structural proteins, and a single-shelled capsid. The single-shelled capsid appears to be unique among reoviruses. This contrasts with the typical double-layered (e.g., RDV) or triple-layered (e.g., orthoreovirus, rotavirus, and BTV) shells characteristic of most reoviruses. However, BmCPV-1 appears both morphologically and functionally similar to the transcriptionally active cores of many reoviruses and, like these other reoviruses, has an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase that can make mRNA transcripts. Cryoreconstructions of BmCPV-1 virions and capsids at 17- and 25-Å resolution, respectively, revealed a T=1 icosahedral shell whose outer surface displays 12 prominent spikes, each with a turret-like structure similar to that seen in orthoreoviruses (e.g., see references 108 and 217) and also like that of the dsRNA bacteriophage φ6 (48). Examination of empty BmCPV-1 capsids also revealed 12 mushroom-shaped densities attributed to the transcription enzyme complexes, again of size and morphology similar to those of complexes observed in orthoreovirus (107) and in rotavirus (247). The dsRNA in BmCPV-1 is organized into a series of compact concentric shells, about 25 Å apart, as also occurs in orthoreovirus (108).
(g) Reoviridae: Pytoreovirus genus.
RDV, which replicates in both insects and graminaceous plants, is transmitted only by insects (e.g., leafhoppers). The widespread infection of rice plants in Southeast Asia causes severe reduction in crop production and hence poses a major economic threat to people in this region. The structure of the 700-Å-diameter RDV capsid was recently solved to 25-Å resolution by use of cryoreconstruction methods (207). The results revealed an outer T=13l capsid, composed of 260 trimers of the 48-kDa P8 viral protein and an inner T=1 shell composed of 60 dimers of the 114-kDa P3 protein. Atomic models of the VP7 trimer of BTV in the two crystal conformations REF and HEX (23, 143) were docked into the outer capsid density of the RDV cryoreconstruction and revealed a better fit of the HEX structure. This and a sequence comparison between the RDV and BTV P8 and VP7 proteins, respectively, led to a proposal that P8 may have an upper domain with a β-sandwich motif and a lower domain of α helices (207).
Animal and plant reoviruses presumably enter cells via different mechanisms owing to variations in host selectivity as manifested in cell receptors and in the differences of the outer capsid proteins among other factors. The extensive analysis of a wide variety of reoviruses by cryoreconstruction studies as briefly highlighted in the sections above, in combination with molecular studies and the prospects of more-detailed crystallographic investigations, should provide a deeper understanding of the complexities inherent in virus-host interactions.
(h) Birnaviridae.
The family Birnaviridae includes nonenveloped, icosahedral viruses that have a worldwide geographic distribution and are characterized by having a two-segment dsRNA genome. IBDV, an important pathogen of young chickens, has a genome that codes for four structural proteins. These include two major components, VP2 (40 kDa; carries major neutralizing epitopes) and VP3 (32 kDa; contains a very basic C-terminal region believed to interact with the viral RNA), and two minor components, VP4 (28 kDa) and VP1 (90 kDa; the viral RNA polymerase) (222).
The cryo-EM structure of IBDV, at 18-Å resolution, revealed an icosahedral capsid (700-Å maximum diameter) of 90 Å in thickness with 780 subunits, clustered as 260 trimers, arranged in a T=13d lattice (40). Small holes occur at each of the fivefold and local sixfold axes. The inner wall of the capsid has 200 Y-shaped trimer units that project toward the center of the virus from a continuous shell. The 60 positions closest to the fivefold axes in this region are occupied by material that makes a rim around a pentagonal cavity. The model proposed for the organization of IBDV predicts 780 copies of VP2, 600 copies of VP3, and 60 copies of VP4. Though no sequence homologies were detected among the trimer-forming proteins of rotavirus, BTV, and reovirus (40), a striking similarity exists between the shape and disposition of the VP3 trimers in IBDV and those of μ1 in reovirus ISVPs (108).
(i) Fungal viruses.
The family Totiviridae includes RNA viruses of simple eukaryotes (342). These viruses have a genome that is a single segment of dsRNA encapsidated in an icosahedral shell and that encodes a major coat protein and an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. L-A virus, the most-studied member of the group, has a 76-kDa Gag coat protein and an estimated one or two copies per particle of a minor 180-kDa Gag-Pol fusion protein. Cryoreconstruction studies of two totiviruses, L-A of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and P4 of Ustilago maydis, showed that both viruses have similar 430-Å-diameter structures (Fig. 48), consisting of 120 subunits arranged as 60 asymmetric dimers in a T=1 lattice and with 60 small holes (10- to 15-Å diameter) that extend through the capsid wall (55, 63). The two subunits in each dimer occupy nonequivalent bonding environments. The holes act as molecular sieves, being large enough to allow influx of metabolites needed for RNA synthesis and replication and for exit of new transcripts but small enough to shield the genome from degradative enzymes (Fig. 31).
FIG. 48.
Reconstructions of two fungal viruses, L-A (left) and P4 (right), as viewed along an axis of twofold symmetry. The two viruses exhibit very similar features with 120 morphological units packed on a T=1 lattice (63). The capsids consist of 12 pentons, each of which has 10 elongated and curved subunits arranged in two sets of five. An inner ring of five subunits is encircled by an outer ring of five subunits that are offset like fish scales from the inner ring. Despite occupying nonequivalent packing environments, the inner and outer ring subunits are similar in appearance. The known capsid stoichiometry indicates that each subunit is a monomer of the Gag protein (55, 63). The images are rendered at an isosurface threshold too low to reveal the small channels that penetrate the capsid wall and are presumed to be exit portals through which nascent mRNA transcripts can pass (see Fig. 31).
Part of the interest in these viruses stems from the desire to understand the basis for this unusual arrangement of subunits, which is characteristic of all dsRNA viruses whose structures have been examined. In all known examples, the 120-subunit motif appears essential to the maintenance of a particle structure that must function as a biosynthetic compartment capable of carrying out synthesis of nascent mRNA in host cells while protecting the dsRNA from host enzymes. Fungal viruses are particularly attractive model systems because they are perhaps the simplest such transcriptionally active particles.
(j) Bacteriophage φ6.
φ6 is an enveloped dsRNA phage of the plant pathovar Pseudomonas syringae. Virions consist of four concentric structures: an outer lipid bilayer, a lysozyme layer, a nucleocapsid (NC), and a polymerase complex (core) which encapsidates a three-segment genome of dsRNA (Fig. 49). The outer lipid bilayer contains five proteins, two of which form a spike complex which mediates binding to the pilus of the host. Virus fuses with the outer bacterial membrane, releasing the NC and phage lysozyme into the periplasmic space which interacts with the inner bacterial membrane, resulting in penetration of the NC into the cytoplasm. NC contains the RNA polymerase complex (P1, 85 kDa; P2, 75 kDa; P4, 35 kDa; P7, 17 kDa) which is covered by a layer of a single protein (P8, 16 kDa) (219, 278, 319, 320). Loss of P8 activates the polymerase complex which initiates transcription and replication of the three-segment genome.
FIG. 49.
Stages of the bacteriophage φ6 life cycle. The virus enters the bacterium by attaching to a pilus (A) and crossing the outer membrane (B), digesting the proteoglycan layer with a viral lysozyme, and then crossing the inner membrane (C) to deposit the nucleocapsid in the cytoplasm (D). Plus RNA strands are synthesized and lead to the production of proteins P1, P2, P4, and P7 (E), which assemble to form the prohead (F). The prohead packages a single copy of each of the three plus strands, which leads to expansion and minus-strand synthesis (G). Later events in the transcription cycle lead to the production of protein P8, which attaches to the expanded prohead to form the nucleocapsid (H). This is followed by envelopment (I) and lysis (J).
Phage assembly proceeds via a pathway which roughly reverses the steps of dissociation during entry. The RNA polymerase complex is assembled first into an elaborated dodecahedral cage. One copy of each of three genome segments is then packaged, and the cage is closed by addition of P8 to form a 580-Å-diameter NC. Interaction of the filled NC with the phage lysozyme and the inner bacterial membrane leads to envelopment of the phage, which remains in the cytoplasm until the cell lyses (219, 319). Several features of the φ6 life cycle are reminiscent of mammalian dsRNA viruses, as are some of the structures of the φ6 subassemblies.
Cryoreconstructions of several assemblies isolated from mature virions as well as several particles assembled from expressed proteins, including a polymerase-competent one, have been determined (48). Subcomplex particles with a variety of protein compositions (P1247, P14, P124, P127, etc.) can be generated by the expression of the cDNA for P1 in the presence of the cDNAs of the other proteins (139, 140, 227). Reconstructions were made of NC (P12478+RNA), core (P1247+RNA), procapsid (P1247), P14, and P1 particles. The outer layer of the NC is quite similar to that of the spikeless rotavirus (352); it has 132 holes, and calculations indicate that 600 dimers of P8 are arranged in a T=13 lattice (48) (Fig. 50). Cores isolated from virions display a 500-Å-diameter spherical shell from which 12 turrets with axial holes project ∼40 Å above the surface at the fivefold axes (Fig. 50). Comparison of the NC and core reconstructions reveals that the ring of density surrounding each fivefold axis in the NC is contributed by the turret of the core.
FIG. 50.
The internal structures of bacteriophage φ6 are shown in surface views of the exterior and cut-open reconstructions of the polymerase complex (proteins P1, P2, P4, and P7) in its unexpanded (A) and expanded (B) forms as well as the nucleocapsid (C). The expansion of the polymerase complex allows the attachment of protein P8 (white in panel C) to form the T=13 shell of the nucleocapsid. The major structural protein of the polymerase complex (P1) forms a T=2-like shell similar to that of BTV. The remaining proteins contribute to the turret structure which extends from the vertex of the polymerase complex and projects through the holes of the T=13 shell of the nucleocapsid. Recent work (97) shows that this structure does not have the fivefold symmetry imposed by the icosahedral reconstruction and hence is blurred in the average shown. Adapted from reference 48 with the permission of the publisher.
The structure of the polymerase complex has several unexpected features. The shell of the complex is a dodecahedron containing 120 copies of P1 in a “T=2”-like arrangement. The turrets or satellites are positioned on its fivefold axes. This 120-subunit organization is the same arrangement seen in the fungal viruses (63) and in several of the Reoviridae cores (145, 195, 209, 247). The major component of the turret is a hexamer of protein P4, the packaging nucleoside triphosphatase, so that the polymerase complex has a symmetry mismatch at each vertex (97). This mismatch may function in the RNA packaging process in a way similar to the symmetry mismatch of the portal vertex in dsDNA phages (24). The core undergoes an expansion upon packaging of RNA which may signal the end of minus-strand packaging and the beginning of the plus-strand synthesis and the later events of the life cycle. The similarity of the φ6 and reovirus (108) core structures is striking.
Reconstructions of the procapsid, P1247, P124, P14, and P127 particles reveal an identical (460-Å-diameter), dodecahedral cage (Fig. 50). Small differences correspond to the presence of P2, reflecting its low copy number (219), whereas the absence of P4 caused complete loss of the projecting turret structure. Subunit boundaries consistent with a “T=2” arrangement are consistent with the 120 copies of P1 estimated from the volume.
The striking, higher-order, structural features shared between φ6 and the other dsRNA viruses suggest either that similarities in replication strategies have resulted in a similar structural solution or that all dsRNA viruses have a common ancestor.
(ii) Modulation of T number. (a) Bacteriophage P2 and the assembly parasite P4.
The P2-P4 system represents an opportunity to use cryo-EM to study the mechanism by which a capsid protein can be directed to form two different-sized shells (for a review, see reference 32). This addresses a common problem in phage assembly. In phages such as λ, the information which controls the size of the capsid appears to reside in the capsid proteins themselves. Mutations in the major λ capsid protein alone can result in variations of the assembled capsid size (115). In others, such as P22 (182), the presence of a scaffolding protein is necessary to ensure the final correct capsid size.
The P2 capsid is normally ∼600 Å in diameter. When a P2-infected cell is superinfected with P4, the capsids produced are only 450 Å in diameter (Fig. 36). P4 does not code for its own major capsid protein but takes control of the P2 gene products and uses them to assemble the smaller capsid (280, 281). The smaller capsid that forms in the presence of P4 infection is one-third the volume of the normal P2 capsid. As a result, it is too small to encapsidate the P2 genome (33 kb for P2 versus 11.6 kb for P4 [32, 147]), and so, only capsids filled with P4 genomes are produced by the infected cells. This hijacking of the structural proteins of P2 to assemble capsids which can contain only P4 genomes casts P4 in the role of an assembly parasite of P2.
The change in capsid size, or morphopoietic transition, depends on the 27-kDa P4-encoded protein, Sid (for “size determining” [275]). The target of Sid action is presumably gpN, the major capsid protein, since mutations in gpN (sir mutations for “Sid resistant”) render it impervious to the effect of Sid. The Sid protein appears to act at the procapsid stage and is not found in high amounts in the mature virion (22). Another protein, gpO, is believed to function as a scaffolding protein in both P2 and P4 assembly (2, 138). The final player in the assembly story is the 21-kDa nonessential protein, Psu, which is found only in P4 and makes the smaller capsid more thermostable (169).
The P2 and P4 reconstructions (Fig. 36) showed that the capsid of P2 has T=7 symmetry whereas P4 has T=4 symmetry (101). The major capsid protein was observed to form pentamers and hexamers in both structures. P2, like CaMV (65) and HK97 (81), is an example of true T=7 symmetry, unlike that observed in the all-pentamer papovaviruses (12, 13, 19, 29, 252). Hence, the morphopoietic mechanism in the P2-P4 system can be reduced to the mechanism of determining the triangulation number of the assembled capsids. For capsids which follow the rules of quasi-equivalence (53), the transition between T=7 and T=4 can be accomplished by a restriction in the flexibility of the capsid protein so that it adopts the four conformations required for T=4 rather than the seven required for T=7.
The major capsid protein, gpN, displays a clear two-domain structure with one domain forming the hexamer or pentamer capsomers and the other forming the extended arms of the trimeric connections between capsomers. The angle of the lower-density hinge region between these is equally great in the two capsids, which indicates that a difference in the flexibility of the hinge region does not cause the difference in size. In contrast, the hexamers vary greatly between the two structures. The angle across the hexamer is sharper in P4 (110° versus 135° in P2), and as a result, the hole in the capsomer is noticeably larger. Hence, although the hinge plays an important role in allowing gpN to take on the range of conformations required for T=7 capsomers, the origin of the size change lies in a more fundamental reorganization of the capsomer structure itself.
The easiest interpretation of the available evidence is that the sir mutations in gpN affect the binding of Sid to gpN. Sid, which binds only transiently to the capsid, probably acts in concert with the scaffolding protein, gpO, to force the capsid to adopt a smaller conformation by altering the angle across the hexamer. This is seen directly in reconstructions of P4 procapsids (Fig. 36) which show the Sid protein as a brace crossing between fivefold positions and fixing the size of the hexamer (213). The simple P4 capsid is not as thermostable as the full-sized P2 capsid. Additional stability is provided by the presence of the Psu protein (168, 169). Difference imaging (99) showed the position of the Psu protein as a bridge spanning (Fig. 36) and presumably stabilizing the conformation imposed by Sid in concert with gpO during assembly.
A different implementation of the control of size in icosahedral capsids is shown in the work on the dsRNA phage P22. T=4 and T=7 shells are produced by this P22 by a very different mechanism from that just described for the P2-P4 system. The capsomers in the two shells are very similar in size and shape (308), consistent with a different mechanism of size control.
(b) Size control in hepatitis B virus.
Size control in the P2-P4 system allows the parasitic P4 capsids to exclude the full-length P2 genome. In contrast, the importance of dimorphism in the HepBc is obscure. Hepatitis B virus consists of an inner nucleopcapsid or core surrounded by a viral envelope containing virus envelope glycoproteins. Cores can be formed either by expression in E. coli or by reassembly after purification, urea treatment, and refolding. When a full-length capsid protein is used, the resulting cores are a mixture of small and large shells which correspond to T=3 and T=4, respectively (93). Capsids isolated from infected human liver tissues show that same dimorphism, although the ratio is skewed heavily toward the larger T=4 form (13:1) (184). Careful analysis of the effect of mutations showed that truncation of the carboxy-terminal tail caused loss of nucleic acid packaging and an increase in the fraction of T=3 reassembled cores (365). Only 5% of cores, which extended to residue 149, formed T=3 shells, whereas 85% of shells truncated to 140 residues were reassembled as T=3 structures. Truncated sequences shorter than 138 residues did not assemble at all. The results with cores isolated directly after expression show a similar trend, although there is greater variability (184). Recently, cryoreconstruction has achieved unprecedented resolution for the cores formed from the 149-residue protein (42, 80). Reconstructions at 7.4-Å (42) and 9-Å (80) resolution (Fig. 51) have demonstrated that the bulk of the assembly domain of HepBc protein is a four-helix bundle. This result opened the way toward understanding the mechanism of size determination. Undecagold maleamide labeling of Cys-150 (364) demonstrated that this residue lies at the crowded dimer interface inside the core shell. Hence, the C termini of adjacent subunits crowd each other around the fivefold vertices and, to a lesser degree, quasi-sixfold vertices. The larger fraction of dimers in quasi-sixfold positions would explain the preference of longer-tailed variants for the T=4 structure.
FIG. 51.
Cryoreconstructions of the T=4 HepBc computed to 7.4-Å (42) and 9-Å (80) resolution (left and right, respectively). Both reconstructions revealed details of the tertiary structure of the capsid protein. In particular, dimer clustering of two core protein subunits produces the prominent surface spikes, which consist of four long α helices arranged in a radial bundle. A series of subsequent labeling studies have further defined details of the HepBc structure at similar resolutions (41, 78, 79, 364). Adapted from references 42 and 80 with the permission of the authors and the publisher.
(iii) Big viruses.
The hypothesis of quasi-equivalence (53) suggested that regular but small changes in the binding between subunits would solve the problem of self-assembly of virions containing more than 60 subunits. Such a scheme of regular alteration of binding patterns of chemically identical subunits is compelling for low triangulation numbers but becomes less and less tenable for larger ones. How can a virus with T=25 symmetry and hence 25 separate potential sets of binding interactions complete its assembly in an efficient and rapid manner? The issue is even more extreme for the 1,900-Å-diameter algal virus Paramecium bursaria Chlorella virus type 1 with triangulation number T=169 (351). The classical answer to this paradox is that assembly of large and complex viruses utilizes scaffolding and accessory proteins to guide the decisions which the capsid protein must make during its complicated assembly. The details of such a solution have been revealed for several systems by cryo-EM and image reconstruction.
(a) T=25 structures: divide and conquer.
Adenovirus can be viewed as an assembly of a set of relatively inflexible bricks (hexons) into a complex structure by the application of the appropriate cement in the form of a series of accessory proteins. The hexon itself assembles as an extremely stable trimer which forms all of the hexa-coordinated capsomers on the virion. The fivefold positions are formed by a separate protein, penton base. Hence, the intimidating task of assembling the 1,500 subunits of a true T=25 structure is reduced to the much simpler one of modulating the 240 hexon trimers which sit in four distinct environments on the surface of the virion. The analysis of the structure by cryoreconstruction is made much simpler because the structure of the hexon trimer is known to high resolution from X-ray crystallography (255). Further, the stoichiometry of all of the components of the virion has been established by careful quantitation (323). Together, these two results allow the use of difference imaging to assign locations to the minor proteins of the capsid and to localize the hexon sequences which form contacts in the structure.
Difference imaging was used to identify the nonhexon components (Fig. 52) and showed their role in the stabilization of the virion. The penton structures were described above (“Activation”). Polypeptide IX was identified as existing as trimers that sit atop the hexon interfaces for those hexons that form the center of a facet. This is consistent with their role in stabilizing the “groups of nine” hexons which can be isolated as a relatively stabile unit. The other accessory proteins interact at other sites. Polypeptide IIIa links separate facets together across the edge of the virion. Polypeptide VI sites within the virion and links the peripentonal hexons of adjacent facets. Although its mechanism is not clear, it appears that each type of hexon interact only with a single type of accessory protein. Hence, the 240 copies of the hexon do not adopt markedly different conformations on the surface but rather bind to one of a set of accessory proteins to define their mode of interaction.
FIG. 52.
The positions of the proteins of adenovirus are shown by difference imaging with an atomic model based on the high-resolution structure of the adenovirus hexon protein (blue in panels A and B). An external view of the virion along the twofold axis (A) shows the position of the trimers of polypeptide IX which link the group of nine hexons in a single facet and polypeptide IIIa which links adjacent facets. The penton base I is represented in yellow with the fiber being shown in green. The view from the interior of the virion shows polypeptide IIIa, which passes through the layer of hexons, and of polypeptide VI hexamers near the penton base. These positions are shown schematically in panel C, where the triangular top and hexagonal base of hexon and the pentagonal penton base are shown in white. The polypeptide IX trimers are shown as black triangles. The polypeptide VI hexamers are shown as black circles, and the hexon layer spanning polypeptide IIIa is shown as filled black bars. The fit between the hexon density seen in the high-resolution structure and that in the reconstruction is shown for the region surrounding the penton base in panel D. Adapted from reference 298 with the permission of the publisher.
A different way of solving the problem of generating a T=25 structure can be found in PRD1 (50). Here the major capsid protein, P3, forms stable trimers at all hexavalent positions in a way similar to that of adenovirus. The organization of the trimers occurs on a membrane of defined diameter (Fig. 37) which appears to act as an assembly template.
(b) A T=16 structure: organizing 960 identical subunits.
The capsid of HSV-1 has T=16 symmetry and differs from adenovirus in that both its five-coordinated and six-coordinated capsomers are made from the same protein, VP5. In contrast to adenovirus, VP5 does not form stable hexamers and pentamers which would simplify the assembly problem. Image reconstruction (17, 18, 34, 223, 224, 269, 363) confirms that the pentavalent and hexavalent capsomers are indeed pentamers and hexamers (Fig. 34). Reconstructions also show that nodules of density, called triplexes, are at all of the local threefold axes of symmetry. The T=16 symmetry and the presence of triplex nodules have also been demonstrated for other members of the herpesvirus family, such as channel catfish herpesvirus (37) and human cytomegalovirus (49). In HSV-1, a further protein, VP26, has been shown to be localized to the tops of the hexavalent capsomers. VP26 is not present on the pentavalent ones (38, 312, 313, 348, 362). HSV appears to make use of a scaffolding protein which organizes a procapsid. Assembly of the procapsid requires three components: the major capsid protein (VP5), the triplex proteins (VP19c and VP23), and a scaffolding protein (VP22a and/or pre-VP21). In vitro assembly experiments show that VP5, the triplex proteins, and the scaffolding protein form a complex which can pack to define the procapsid size. Examination of procapsid structures (311, 359) suggests that the majority of the scaffold protein is not icosahedrally arranged but may act as a loose micelle on whose surface VP5 can move and interact with the triplex proteins to define the interactions between capsomers (Fig. 34) which survive into the mature virion. A recent examination of whole virions (average diameter, ∼2,000 Å) has revealed the presence of extensive interactions between the tegument and the icosahedrally ordered capsid (359).
(iv) Genome organization.
Viruses package all types of genomes (single-stranded DNA, dsDNA, ssRNA, and dsRNA), and some nucleic acids are packaged with additional components such as host-encoded histones which, together with the dsDNA viral genome, form nucleosomes that are arranged in the viral minichromosomes of papovaviruses. In addition, both linear and circular forms of genomes are found packaged in virions.
The one-dimensional nature of the genetic code means that all virus nucleocapsids, even those with icosahedral shells, must be asymmetric particles. That is, the genome can never strictly adopt the higher symmetry, if it exists, of the encapsidating shell. However, numerous X-ray crystallographic studies of icosahedral viruses have demonstrated the existence of portions of the packaged genome that are able to adopt a highly ordered structure inside the virus (e.g., see references 59–61, 122, 315, 339). Such organization is typically a consequence of nonspecific interactions that the nucleic acid molecules make with the inside surface of the regularly arranged protein capsid.
There are also now several cryo-EM studies of viruses in which the packaged genome has been shown to adopt various levels of higher organization. For example, the dsDNA of many bacteriophages and animal viruses is densely packed inside the viral capsids in a liquid crystalline arrangement, and projected views of individual virus particles display “fingerprint” features with fine striations and punctate arrays (Fig. 53). Such features, typically with spacings of about 25 to 30 Å, have been imaged in bacteriophages T4 and λ (199) and T7 (56) and also in HSV (35, 359). A similar fingerprint pattern has been observed in images of the dsRNA viruses orthoreovirus (108) and cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (356). The dsRNA genome of the fungal L-A virus exhibits punctate and/or swirl motifs with spacings between strands in the range of 41 to 46 Å; thus, it is less densely packed than the genomes in all these other viruses (55).
FIG. 53.
Cryo-electron micrograph of a densely packed monolayer of bacteriophage T7 heads recorded at 2.5-μm defocus (56). The particles exhibit characteristic fingerprint patterns with 25-Å spacings associated with closely packed strands of dsDNA. The pattern motifs vary according to the viewing direction, with concentric rings revealed in axial views and punctate arrays revealed in side views. In the particular double mutant sample shown here, the T7 heads adopt a preferred axial orientation. Modeling analysis of these and other images established that the T7 chromosome is spooled around an axis in approximately six coaxial shells in quasi-crystalline packing (56). Adapted from reference 56 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Most icosahedral image reconstruction studies yield 3D density maps constrained to have either 52 symmetry (86) or the full 532 icosahedral symmetry (130). Hence, density corresponding to the packaged genome will also have this symmetry enforced on it. If the nucleic acid organization is truly random, then the 3D map will show a rather featureless ball of mass with lower average density than that found in the ordered capsid shell. This effect was found for the chromatin core in the cryoreconstructions of several papovaviruses including SV40 (14), BPV-1, and HPV-1 (19). Similarly, the dsDNA in two strains of CaMV was found confined within two concentric layers in association with portions of the viral capsid protein (65).
For viruses in which some of the genome may be ordered by association with the protein capsid, 3D reconstruction analysis may reveal density features that can be ascribed to nucleic acid structure. Partially ordered genomes, typically in a layer in close proximity to the inner capsid wall, have been detected with cryoreconstruction methods in many viruses such as the middle and bottom components of cowpea mosaic virus (10), calicivirus (244), FHV (66), native and swollen forms of CCMV (290), rotavirus (247), TYMV (39), and aquareovirus (272). Difference map analysis is often helpful in ascribing genome density (10, 39, 66, 247).
Genome organization is important for viral functions. For example, in rotavirus and presumably in most dsRNA viruses, the complementary organization of both the dsRNA and the transcriptase complex near each fivefold axis inside the inner capsid shell is thought to move RNA through the complex during transcription (247). In two studies of ssRNA viruses, one with the plant virus CCMV (290) and the other with the insect virus FHV (66), high-resolution information available from X-ray crystallography made it possible to ascribe density with high confidence to regions of ordered nucleic acid in the 3D cryoreconstructions. The overall excellent agreement between corresponding portions of the cryo-EM-derived and X-ray structures made it possible to interpret cryo-EM data for the swollen form of CCMV, for which no X-ray structure was available (290), and to understand aspects of the maturation of FHV (66).
For CCMV, an atomic model of the swollen particle was built by individually fitting the A, B, and C subunits from the X-ray structure of the native virus into the cryo-EM density map (Fig. 29) (290). Careful examination of the structural changes that had to be introduced to convert from the native to the expanded state made it possible to define the nature of many protein-protein and protein-RNA interactions and to better understand the stabilizing interactions that affect both assembly and disassembly of CCMV. Ordered RNA in swollen CCMV clusters beneath the quasi-threefold axes, where protein-protein interactions formerly occurred in native virus but became absent in the swollen particles. In this position, the RNA has a clear path to the outside of the particle, which could explain why RNA in swollen CCMV can act as a template for protein synthesis and as a substrate for RNase (21, 45). In addition, the pseudoatomic model of the swollen CCMV shows that important dimer and β-hexamer subunit interactions are retained and also that RNA-protein interactions stabilize the expanded state.
For FHV, the X-ray structure determination revealed regions of highly ordered, duplex RNA, accounting for ∼20% of the total genome, in contact with the inner capsid wall at the icosahedral twofold axes (Fig. 54) (122). This was also seen with high fidelity in the 22-Å-resolution cryoreconstruction (66). This, along with several other examples of excellent agreement between the two maps, gave added confidence that density in a difference map was correctly assigned to the bulk RNA (invisible in the X-ray map). The cryo-EM map made it possible to model the interactions of the capsid proteins with the viral genome in greater detail than was possible from the X-ray structure alone. The γB and γC helices directly contact the bulk RNA over their lengths with the region in each of these helices that lies close to the cleavage site and also lies adjacent to the RNA. However, only the C terminus of each γA helix contacts the bulk RNA, and the cleavage site for each A subunit is 35 Å away from the bulk RNA. These observations are completely consistent with kinetic results in which 120 subunits are cleaved at a much higher rate than the remaining 60 subunits (137). Additional aspects of the different interactions between γ peptides and the genomic RNA are also consistent with the proposed scheme concerning how viral entry and genome release might occur (see “Release of genome”).
FIG. 54.
Ordered duplex RNA in FHV as viewed from the side toward the C-C intersubunit contact (see Fig. 26). (Top) Thin (∼20-Å) cross-sectional view of FHV cryo reconstruction (blue mesh) superimposed on the FHV X-ray Cα backbone model (yellow), the contoured difference density map (red mesh; cryo-EM density map minus X-ray capsid structure only), and the locally ordered RNA (space-filling representation). The vertical white line is a twofold axis. The other lines mark the locations of two adjacent fivefold axes. (Bottom) Same view as above with ribbon representations of two complete B (red) and C (green) capsid subunits in close association with the dsRNA (space-filling model) and the peptide arm. Adapted from reference 66 with the permission of the author and the publisher.
Release of Progeny Virus
Viruses which assemble in the cytoplasm are released when the cytopathic effects of infection cause cell lysis. Viruses which assemble on the membranes of the secretory pathway and then bud into the luminal space have a further set of interactions to consider as a portion of their assembly. In essence, these viruses effect their release by enveloping themselves in a portion of the cellular membrane.
Virus budding in animal cells must overcome two further problems beyond the ones of assembly that occur in nonenveloped viruses. Firstly, budding must be constrained to the appropriate membrane of the many that exist in an animal cell. Budding of an alphavirus into the lysosomes would not be an effective strategy for propagation. Secondly, the budding must incorporate the viral envelope proteins and exclude the host proteins. Even at very late stages of infection, viral envelope proteins represent around 1% of the cellular membrane proteins, and so the incorporation must have great selectivity. The solutions to these two problems must lie in the interaction of the viral envelope proteins and the internal proteins of the virion. The presence (or their lack) of sorting signals on a viral glycoprotein can cause it to be directed to a particular cellular membrane (276). The first problem then reduces to one of constraining virus budding to compartments in which the envelope proteins exceed a critical threshold concentration. The availability of structures from cryoreconstruction of several alphaviruses provides an opportunity to examine the interactions of the envelope proteins and of the spikes for clues to the control of budding.
Examination of the alphavirus structures shows that four types of independently modulable interactions need to be considered for the spike proteins. First is the interaction between the E1 and E2 proteins within the heterodimer. This interaction is first formed in the endoplasmic reticulum (Fig. 38) and remains the most important one until the precursor p62 is cleaved in the formation of the compact spike complex (118, 186). This interaction is lost completely after exposure to low pH (Fig. 21) (132). The second is the interaction of the heterodimers in forming the spike trimer which is initiated by p62 cleavage and replaced by the formation of the E1 trimer after low-pH treatment. The third is the lateral interaction of spikes via their skirts (64, 132). Finally, the spikes interact with the nucleocapsid via their transmembrane regions (64). These last two interactions are not affected by cleavage of p62 nor changed during the early times after low pH (118, 132).
The independence of these interactions suggests a way in which virion assembly can be dependent on a critical concentration of envelope proteins and exclude the host proteins which fill the membrane from which it buds. The capsid binding sites are complementary to the arrangement of spikes on the surface. Although the spike protein/capsid protein ratio is 1:1, the three heterodimers of a spike always interact with three separate nucleocapsid capsomers. Binding needs to be cooperative as a result. The envelope proteins can pack on the surface of the membrane to form hexagonal arrays which exclude host membrane proteins by means of their lateral interactions. The skirts extending between spikes would allow relatively little space for other membrane proteins. The hexagonal packing produces a relatively flat region of envelope proteins which would be stabilized by the binding of the complementary capsid. Reorganization of the spikes must occur upon introduction of the fivefold positions. This allows the interaction of spikes which are partially bound by capsid hexamers to completely bind their third cytoplasmic domain to the capsid pentamer. The use of cryoreconstruction not only has defined the broad outlines of this scheme but, by fitting the high-resolution structure of the capsid protein into the nucleocapsid density (64), also has begun to define potential atomic interactions which accomplish the individual steps.
Virus Transmission and Host Defense
Virus transmission.
Little is known from cryoreconstruction studies concerning the structural basis of transmission. The limited clues that we have thus far suggest that virion structure is adapted to the requirements of transmission. For example, the alphaviruses use an arthropod host as a vector to transmit viruses between mammalian hosts. The evidence suggests a feature of the virion structure which may be important for adaptation to this task, i.e., for replication in two hosts. In mammalian cells, alphavirus budding occurs at the plasma membrane. In insect cells, virus buds into the early compartments of the secretory pathway (reviewed in reference 187). Hence, budding in insect cells occurs before the cleavage of the spike precursor, which activates the spike complex for fusion after endocytosis in the mammalian cell. Because this is such a major functional change, it is likely to be accompanied by a major structural change that might be incompatible with budding. The structure of the SFVmSQL mutant indicates that an answer to this question lies in the unchanged spike-spike interactions mediated by the spike skirt in the uncleaved virus (118). Hence, the alteration in the projecting regions of the spike by cleavage, interactions between the spikes, and interactions between the spikes and the capsid, which are important for budding, remain unaffected. This property would allow the virion to bud efficiently in the early secretory pathway in the insect cell, prior to cleavage, as well as at the plasma membrane in the mammalian cell after cleavage of the precursor in the late Golgi phase.
Host defense.
The immune system in vertebrates provides a first line of defense by which infectious agents like viruses are detected and neutralized. Though several theories have been proposed to explain how neutralization occurs, the mechanisms by which it occurs are not well understood. Neutralization may involve antibody-induced structural changes in the virus, or antibodies may interfere with virus-receptor interactions by competing for common binding sites or by steric hindrance. Alternatively, antibodies may prevent viral uncoating, by aggregation (intercapsid cross-linking) or by stabilizing the virus capsid with bivalent (intracapsid) cross-linking. A given host probably employs different mechanisms for different viruses. The antibody-mediated response to an infectious challenge must act in synergy with other defense mechanisms such as opsonization (antibody-mediated phagocytosis).
Cryoreconstruction methods have proved to be extremely effective tools for examining fundamental structural aspects of viral neutralization in several different viral systems. This is true partly because these methods provide a rapid means to visualize directly virus-antibody complexes, which are typically too large (≫400-Å diameter) to be routinely studied by high-resolution methods such as X-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In addition, if high-resolution structures of the virus and antibody Fab molecules (or closely related ones) are known, a pseudoatomic model of the virus-antibody complex can be produced by docking the atomic structures together with the cryo-EM density map as a guide (163).
The first study that established the feasibility and power of the cryo-EM approach in examining virus-antibody complexes involved a mapping of the neutralization sites on the VP4 viral hemagglutinin of rotavirus with MAb Fab labels (242). Subsequent mapping of epitope sites and examination of various aspects of viral neutralization have been performed with picornaviruses including several HRVs (156, 161, 205, 235, 285, 287–289) and FMDV (162), HSV (291, 313), CPMV (240, 336), canine parvovirus (344), SNV and RRV (286), adenovirus (297), BPV (36), and calicivirus (305). The studies of HRV neutralization illustrate how cryo-EM techniques can be used to examine virus-antibody interactions.
Antibody neutralization of HRVs.
The structure of HRV has already been introduced (“Cell attachment” and Fig. 16). Based on sequence analysis of escape mutants, four areas on the surface of the virion were identified as NIm sites (for a review, see reference 260). The three major classes identify epitopes in the VP1 (NIm-IA and NIm-IB), VP2 (NIm-II), and VP3 (NIm-III) viral coat subunits. These epitopes lie either on the “north” (NIm-I) or “south” canyon rims (NIm-II and NIm-III) where the fivefold vertex points north.
Several HRV14 complexes with IgGs or Fab fragments have been studied with cryoreconstruction techniques (Fig. 55). These include HRV14 complexed with two Fab fragments (Fab 17-IA and Fab 12-IA) from a strongly neutralizing, weakly aggregating MAb (58, 289), with an Fab fragment (Fab 1-IA) of a weakly neutralizing, strongly aggregating MAb (58), and with a whole IgG (MAb 17-IA) (288). In all complexes, the Fab or MAb molecules appear to fully saturate the HRV virions (60 Fab fragments per virion or 30 MAbs per virion), though the Fc portion of the MAb is not seen. Each Fab molecule appears as a 75-Å-long, bilobed structure with the variable domain in contact with the viral surface and the constant domain at high radius. The central depression in each Fab corresponds to the switch region between the constant and variable domains.
FIG. 55.
Complexes between HRV14 and NIm-IA neutralizing MAbs (58). (Top) Isosurface representations, all viewed along a twofold axis of symmetry, of cryoreconstructions of HRV14 complexed with a neutralizing MAb (MAb 17-IA in red) and with Fab fragments from strongly neutralizing MAbs 17-IA (blue) and 12-IA (purple) and weakly neutralizing MAb 1-IA (green). (Bottom) Pseudoatomic fitting of different Fab models into the cryo-EM density envelopes of the HRV-Fab complexes (wire mesh) illustrates in side views the close interactions that each Fab makes with the HRV structure. Fab 17 and Fab 12 bind in essentially identical, tangential orientations to the viral surface, which favors bidentate binding over icosahedral twofold axes. Fab 1 binds in a more radial orientation that makes bidentate binding unlikely. All three Fabs contact a significant portion of the viral canyon and directly overlap much of the ICAM-1 receptor binding site.
The striking fidelity of the cryoreconstruction for comparison with the X-ray results enabled molecular docking which defined the viral epitopes and antibody footprints. The atomic structures of HRV14 (258), Fab 17-IA (205), and Fab 1-IA (58) were used to model the different antibody-virus complexes. These studies led to several results and conclusions. (i) Each Fab footprint covers ∼500 Å2 of the viral surface and appears to straddle the viral canyon, touching both north and south rims of the canyon, and to block (overlap) the site of cellular receptor attachment (233, 287–289) as predicted previously (77, 258). (ii) MAb 17-IA and MAb 12-IA bind bivalently across icosahedral twofold axes, whereas MAb 1-IA binds monovalently (288). (iii) MAb 17-IA blocks attachment of HRV14 to HeLa cells (289). (iv) The elbow angle in MAb 17-IA increases by 15 to 18° compared to that in Fab 17-IA, indicating that flexibility in the elbow accommodates bivalent attachment (288). (v) The Fc region cannot be seen in the reconstruction of the HRV14–MAb 17-IA complex (the MAbs are visible in cryo-EM images and are biochemically intact), indicating that the MAb hinge region is highly flexible (288). This interpretation is consistent with recent studies of MAb binding to HRV2 (156) and to calicivirus (305). (vi) The epitope-paratope interface includes complementary charged residues important for antibody recognition (205, 289), which is consistent with studies that show a high frequency of charge changes in escape mutants (274). (vii) No gross conformational changes occur in HRV14 upon binding of Fab (289) or MAb (288). (viii) The atomic model fitting to a cryoreconstruction at ∼25-Å-resolution is accurate to ∼4 to 5 Å (205, 288, 289).
The crystal structure of the HRV14–Fab 17-IA complex, recently solved to 4-Å-resolution by using the cryo-EM-derived pseudoatomic model of the complex for initial phasing (285), confirmed and extended most of the above conclusions and revealed several new facts about the interface. (i) the Fab 17-IA footprint covers ∼550 Å2 of the viral surface at the north wall and ∼300 Å2 of the south wall (where there is extensive overlap with the cellular receptor binding site). (ii) Fab 17-IA penetrates deep within the canyon in which the cellular receptor for HRV14 (ICAM-1) binds. This observation contradicts the prediction that the receptor binding site in the HRV canyon would be hidden from immune surveillance because antibodies were thought to be too large to fit inside the canyon and could only span it (258). (iii) The antibody paratope undergoes a large (∼5- to 6-Å) conformational change to accommodate the viral epitope while the viral epitope remains largely unchanged except for a few side chain movements that accommodate tighter fit of the antibody. (iv) The conserved framework region of Fab 17-IA makes extensive contact with the virus, unlike any other previously described antibody-antigen complex.
The correlative cryo-EM and X-ray crystallographic study of the HRV14–Fab 17-IA complex underscores an important lesson: modeling X-ray structures into cryo-EM density maps at moderate resolutions (20 to 30 Å) requires caution both in the modeling and in the ensuing interpretation of the pseudoatomic structure. A postmortem analysis indicated that the original fitting of the Fab 17-IA crystal structure into the HRV14–Fab 17-IA cryo-EM density map could have been improved and would have led to a closer fit to the actual structure solved to 4 Å. However, in the original study (289) there was no sound basis for predicting that the Fab structure would undergo large conformational changes upon binding to the virus surface and that, additionally, the virus surface would remain unchanged.
Recent combined cryo-EM and X-ray modeling studies of MAb binding to two other picornaviruses, HRV2 (156, 161) and FMDV (162), have provided additional information about the nature of antibody-virus interactions and neutralization. For HRV2, a minor group rhinovirus, it was found that a weakly neutralizing MAb can bind bivalently to the virus, and the antibody does so with a shorter spanning distance (60 Å) than was previously thought possible (156). This example showed that bivalent binding does not ensure strong neutralization. In FMDV, a strongly neutralizing MAb was found to bind monovalently to virus and to do so by interacting with a very small region of the virus capsid that is highly disordered in the native virus (the 27-residue GH loop of VP1 that contains the integrin receptor binding RGD sequence) (162). This and the HRV14–Fab crystal study show that the receptor binding sites need not be hidden from antibodies, because residues adjacent to but outside the receptor site can mutate and lead to production of viable virus that is able to escape detection by particular MAbs.
Antibody-mediated neutralization of human Ad2.
A recent cryo-EM and X-ray modeling study of the binding of Fab molecules to the highly mobile integrin binding sequence (RGD) on the penton base of Ad2 revealed a novel mechanism for evasion of antibody-mediated neutralization (297). The Fab fragment from a MAb that recognizes a nine-residue linear epitope, including the RGD motif, when bound to virus adopts a wide range of conformations. Hence, the epitope is quite flexible even with bound Fab. Careful inspection and interpretation of the image reconstruction provided a structural basis for explaining why Fabs but not IgGs inhibit virus infection. The position of Fab binding and the high mobility of the RGD loop as well as the smaller size of a Fab compared to MAb permit saturation of viral epitopes with Fabs but not IgGs. When only a few of the five potential RGD sites on each penton base have IgGs bound, the remaining sites remain accessible to cell integrins, but the bound IgGs and the adenovirus fiber cause steric hindrance and hence block further binding of IgGs.
SUMMARY OF 3D RECONSTRUCTIONS OF SPHERICAL VIRUSES
Published results obtained for structural studies of spherical viruses that have been examined with cryoreconstruction procedures are summarized in Table 1. The success and popularity of cryoreconstruction have guaranteed a wealth of new information about the structures and functions of many spherical viruses, and unfortunately, we are unable to highlight each of these. Consequently, Table 1 provides a more comprehensive, referenced catalog of the physical characteristics of viruses studied by these procedures by our laboratories and others.
FUTURE PROSPECTS
The power of cryoreconstruction procedures for studying icosahedral virus structure is evident. As illustrated in “Virus life cycles in three dimensions,” the coordinated application of complementary structural, biochemical, and molecular biology methods will continue to yield further insight into structure-function relationships in viruses. The progress in this field has been extremely rapid and shows no sign of abating. More than a hundred reconstructions have been published since R. A. Crowther’s insight (86–89, 91) into common lines produced the first in 1970. The quality and resolution of the reconstructions have continued to improve. For many of the better-established systems, the limits are computational and instrumental. The two reconstructions of HepBc which broke the 10-Å resolution barrier and allowed the first identification of a novel protein fold by cryo-EM and single-particle reconstruction are a landmark. They will not stand alone for very long. We are aware of other groups who have reached similar levels in their work on other viral systems. Improvements in microscopes and the increasing availability of computation resources will bring improved resolution in the near future. Work on the less well characterized systems is directed less at higher resolution than at specific biological questions. As the methods have become better understood and refined, workers have become more willing to attempt less homogeneous and stable samples. The past 10 years have seen this method pass from a difficult methodological challenge to a standard and reliable tool in the structural biologists’ repertoire.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This review is dedicated to R. Crowther, L. Amos, J. Finch, D. DeRosier, and A. Klug, who originally introduced us to the fascination of virus structure. T.S.B. is especially grateful to L. Amos for a patient introduction to the power and “joys” of computing; R. Henderson and N. Unwin for teaching the intricacies of low-dose microscopy of unstained and vitrified specimens; D. Eisenberg, F. Eiserling, and D. L. D. Caspar for their guidance and inspiration and for laying the “foundation”; and J. Johnson and M. Rossmann for their relentless enthusiasm. S.D.F. would like to thank R. Henderson for tempering his urge to compute first and think later, J. Dubochet for introducing him to cryo-EM, and S. Harrison and M. Rossmann for rekindling his interest in virus structure. We thank L. Amos for providing the original set of IBM FORTRAN icosahedral processing programs which formed the framework for the programs described here, M. Sturgeon and T. Smith for help in preparing many figures, and M. Sturgeon and C. Budreau for maintaining a bibliographic database. We gratefully acknowledge current and former members of our groups (T.S.B.: R. Ashmore, J. Bell, D. Belnap, M. Bernardon, V. Bowman, P. Chipman, R. Cheng, C. Contreras, N. Dilley, J. Drak, K. Dryden, E. Eltzroth, J. Folk, B. French, B. Fuller, W. Grochulski, H. Hinkel, C. Ho, V. Livingston, L. Mattern, M. McDonough, D. McKay, E. Meyer, C. Music, M. Sturgeon, S. Walker, G. Wang, W. Xu, X. Yan, W. Zhang, L. Zhu, and R. Zigon; S.D.F.: P. Buck, S. Butcher, M. Clarke, M. Cyrklaff, F. DeHaas, T. Dokland, I. Ferlenghi, B. Gowen, R. Heinkel, J. Kenney, E. Mancini, T. Ruttan, P. Stewart, D. Thomas, and C. Vénien-Bryan) as well as numerous colleagues who made the work described here possible through their enthusiasm, hard work, and patience. We gratefully acknowledge the help provided by colleagues in preparing many of the figures: D. Belnap (Fig. 10); V. Reddy (Fig. 26 and 54), J. Speir (Fig. 3 and 29), and T. Smith (Fig. 14, 16, and 55). Finally, we thank the two anonymous referees for their diligent critique of this “bible” and for graciously alerting us to several errors and inconsistencies in the text and the figures.
The work was supported by grants GM33050 and AI35212 from the National Institutes of Health (T.S.B.), DMB-8905062 and MCB-9206305 from the National Science Foundation (T.S.B.), a Lucille P. Markey Charitable Trust grant for the development of structural studies at Purdue, Human Frontiers Science Programme grant RG 509/96 (S.D.F.), and EU Biotechnology grant B104-CT97-2364 (S.D.F.).
REFERENCES
- 1.Adrian M, Dubochet J, Lepault J, McDowall A W. Cryo-electron microscopy of viruses. Nature (London) 1984;308:32–36. doi: 10.1038/308032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Agarwal M, Arthur M, Arbeit R D, Goldstein R. Regulation of icosahedral virion capsid size by the in vitro activity of a cloned gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:2428–2432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aldroubi U, Trus B L, Unser M, Booy F P, Steven A C. Magnification mismatches between micrographs: corrective procedures and implications for structural analysis. Ultramicroscopy. 1992;46:175–188. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90013-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Anderer F A, Schlumberger H D, Koch M A, Frank H, Eggers H J. Structure of simian virus 40. II. Symmetry and components of the virus particle. Virology. 1967;32:511–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Anthony R P, Brown D T. Protein-protein interactions in an alphavirus membrane. J Virol. 1991;65:1187–1194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1187-1194.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Anthony R P, Paredes A M, Brown D T. Disulphide bonds are essential for the stability of the Sindbis virus envelope. Virology. 1992;190:330–336. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91219-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Baker T S. Proceedings of the Ninth International Congress on Electron Microscopy, Toronto, Canada. Vol. 2. 1978. Preirradiation and minimum beam microscopy of periodic biological specimens; pp. 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Baker T S, Amos L A. Structure of the tubulin dimer in zinc-induced sheets. J Mol Biol. 1978;123:89–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90378-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Baker T S, Cheng R H. A model-based approach for determining orientations of biological macromolecules imaged by cryoelectron microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:120–130. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Baker T S, Cheng R H, Johnson J E, Olson N H, Wang G J, Schmidt T S. Organized packing of RNA inside viruses as revealed by cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis. Proc Electron Microsc Soc Am (Boston) 1992;50:454–455. . San Francisco Press, Inc., San Francisco, Calif. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Baker T S, Cheng R H, Reddy V S, Olson N H, Fisher A J, Johnson J E. International Congress on Electron Microscopy 13, Paris, France. 3A. 1994. Cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallographic studies of flock house virus, a T=3 icosahedral animal virus (invited) pp. 525–526. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Baker T S, Drak J, Bina M. Cryo-electron microscopy and image analysis of SV40. Electron Microsc Soc Am Proc. 1985;43:316–317. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Baker T S, Drak J, Bina M. The structure of SV40 virus by electron microscopy of unstained frozen hydrated suspensions and negatively stained crystalline arrays. Biophys J. 1985;47:50a. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Baker T S, Drak J, Bina M. Reconstruction of the three-dimensional structure of simian virus 40 and visualization of the chromatin core. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:422–426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Baker T S, Drak J, Bina M. The capsid of small papova viruses contains 72 pentameric capsomeres: direct evidence from cryo-electron microscopy of simian virus 40. Biophys J. 1989;55:243–253. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82799-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Baker T S, Johnson J E. Low resolution meets high: towards a resolution continuum from cells to atoms. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1996;6:585–594. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(96)80023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baker T S, Newcomb W W, Booy F P, Brown J C, Steven A C. Three-dimensional reconstructions of ‘light’ and ‘intermediate’ capsids of equine herpes virus. Electron Microsc Soc Am Proc. 1989;47:822–823. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baker T S, Newcomb W W, Booy F P, Brown J C, Steven A C. Three-dimensional structures of maturable and abortive capsids of equine herpesvirus 1 from cryoelectron microscopy. J Virol. 1990;64:563–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.563-573.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Baker T S, Newcomb W W, Olson N H, Cowsert L M, Olson C, Brown J C. Structures of bovine and human papilloma viruses: analysis by cryoelectron microscopy and three-dimensional image reconstruction. Biophys J. 1991;60:1445–1456. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82181-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Baker T S, Olson N H, Newcomb W W, Brown J C, Olson C. Electron microscopy of stained and unstained bovine papilloma virus: comparison with polyoma virus. Electron Microsc Soc Am Proc. 1989;47:820–821. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bancroft J B, Hills G J, Markham R. A study of the self-assembly process in a small spherical virus: formation of organized structures from protein subunits in vitro. Virology. 1967;31:354–379. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Barrett K J, Marsh M L, Calandar R. Interactions between a satellite bacteriophage and its helper. J Mol Biol. 1976;106:683–707. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Basak A K, Grimes J M, Gouet P, Roy P, Stuart D I. Structures of orbivirus VP7: implications for the role of this protein in the viral life cycle. Structure. 1997;5:871–883. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bazinet C, King J. The DNA translocating vertex of dsDNA bacteriophage. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:109–129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bella J, Kolatkar P R, Marlor C W, Greve J M, Rossmann M G. The structure of the two amino-terminal domains of human ICAM-1 suggests how it functions as a rhinovirus receptor and as an LFA-1 integrin ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:4140–4145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Belnap D M, Grochulski W D, Olson N H, Baker T S. Use of radial density plots to calibrate image magnification for frozen-hydrated specimens. Ultramicroscopy. 1993;48:347–358. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(93)90110-j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Belnap D M, Kumar A, Folk J T, Smith T J, Baker T S. Low-resolution density maps from atomic models: how stepping “back” can be a step “forward.”. J Struct Biol. 1999;125:166–175. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1999.4093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Belnap D M, Olson N H, Baker T S. A method for establishing the handedness of biological macromolecules. J Struct Biol. 1997;120:44–51. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1997.3896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Belnap D M, Olson N H, Cladel N M, Newcomb W W, Brown J C, Kreider J W, Christensen N D, Baker T S. Conserved features in papillomavirus and polyomavirus capsids. J Mol Biol. 1996;259:249–263. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Belnap D M, Olson N H, Grochulski W D, Baker T S. Proceedings of the Electron Microscopy Society of America. Vol. 50. San Francisco, Calif: San Francisco Press, Inc.; 1992. The use of radial density plots to calibrate images of frozen-hydrated specimens; pp. 998–999. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Berriman J, Unwin N. Analysis of transient structures by cryo-microscopy combined with rapid mixing of spray droplets. Ultramicroscopy. 1994;56:241–252. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(94)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bertani L E, Six E. The P2-like phages and their parasite P4. In: Calender R, editor. The bacteriophages. Vol. 2. New York, N.Y: Plenum Press; 1988. pp. 73–143. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Boier-Martin I M, Marinescu D C, Lynch R E, Baker T S. Identification of spherical virus particles in digitized images of entire electron micrographs. J Struct Biol. 1997;120:146–157. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1997.3901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Booy F P, Conway J F, Steven A C, Trus B L, Brown J C, Newcomb W W, Baker T S, Johnson C A. Herpesvirus capsid structure. Curr Biol. 1993;3:455. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Booy F P, Newcomb W W, Trus B L, Brown J C, Baker T S, Steven A C. Liquid-crystalline, phage-like packing of encapsidated DNA in herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1991;64:1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90324-r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Booy F P, Roden R B S, Greenstone H L, Schiller J T, Trus B L. Two antibodies that neutralize papillomavirus by different mechanisms show distinct binding patterns at 13 Å resolution. J Mol Biol. 1998;281:95–106. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Booy F P, Trus B L, Davison A J, Steven A C. The capsid architecture of channel catfish virus, an evolutionary distant herpesvirus, is largely conserved in the absence of discernable sequence homology with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1996;215:134–141. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Booy F P, Trus B L, Newcomb W W, Brown J C, Conway J F, Steven A C. Finding a needle in a haystack: detection of a small protein (the 12-kDa VP26) in a large complex (the 200-MDa capsid of the herpes simplex virus) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:5652–5656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Böttcher B, Crowther R A. Difference imaging reveals ordered regions of RNA in turnip yellow mosaic virus. Structure. 1996;4:387–394. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Böttcher B, Kiselev N A, Stel’mashchuk V Y, Perevozchikova N A, Borisov A V, Crowther R A. Three-dimensional structure of infectious bursal disease virus determined by electron cryomicroscopy. J Virol. 1997;71:325–330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.1.325-330.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Böttcher B, Tsuji N, Takahashi H, Dyson M R, Zhao S, Crowther R A, Murray K. Peptides that block hepatitis B virus assembly: analysis by cryomicroscopy, mutagenesis and transfection. EMBO J. 1998;17:6839–6845. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.23.6839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Böttcher B, Wynne S A, Crowther R A. Determination of the fold of the core protein of hepatitis B virus by electron microscopy. Nature. 1997;386:88–91. doi: 10.1038/386088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bragg W L. The determination of parameters in crystal structures by means of Fourier series. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A. 1929;123:537–559. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Breindl M. The structure of heated poliovirus particles. J Gen Virol. 1971;11:147–156. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-11-3-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Brisco M, Hull R, Wilson T M A. Swelling of isometric and of bacilliform plant virus nucleocapsids is required for virus-specific protein synthesis in vitro. Virology. 1986;148:210–217. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90416-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Brown D T, Edwards J. Structural changes in alphaviruses accompanying the process of membrane penetration. Semin Virol. 1992;3:519–527. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Brünger A T, Kuriyan J, Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987;235:458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Butcher S, Dokland T, Ojala P, Bamford D, Fuller S. Intermediates in the assembly pathway of the double stranded RNA virus φ6. EMBO J. 1997;16:4477–4487. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.14.4477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Butcher S J, Aitken J, Mitchell J, Gowen B, Dargan D J. Structure of the human cytomegalovirus B capsid by electron cryomicroscopy and image reconstruction. J Struct Biol. 1998;124:70–76. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1998.4055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Butcher S J, Bamford D H, Fuller S D. DNA packaging orders the membrane of bacteriophage PRD1. EMBO J. 1995;14:6078–6086. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Casjens S, Hendrix R W. Localization and amounts of the major structural proteins in bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1974;88:535–545. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90500-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Caspar D L D. Bacteriorhodopsin—at last! Nature (London) 1990;345:666–667. doi: 10.1038/345666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Caspar D L D, Klug A. Physical principles in the construction of regular viruses. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:1–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Castón J R, Belnap D M, Steven A C, Trus B L. A strategy for determining the orientations of refractory particles for reconstruction from cryo-electron micrographs with particular reference to round, smooth-surfaced, icosahedral viruses. J Struct Biol. 1999;125:209–215. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1999.4085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Caston J R, Trus B L, Booy F P, Wickner R B, Wall J S, Steven A C. Structure of L-A virus: a specialized compartment for the transcription and replication of double-stranded RNA. J Cell Biol. 1997;138:975–985. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.5.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cerritelli M E, Cheng N, Rosenberg A H, McPherson C, Booy F P, Steven A C. Encapsidated conformation of bacteriophage T7 DNA. Cell. 1997;91:271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chandran K, Walker S B, Chen Y, Contreras C M, Schiff L A, Baker T S, Nibert M L. In vitro recoating of reovirus cores with baculovirus-expressed outer-capsid proteins μ1 and ς3. J Virol. 1999;73:3941–3950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.5.3941-3950.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Che Z, Olson N H, Leippe D, Lee W-M, Mosser A G, Rueckert R R, Baker T S, Smith T J. Antibody-mediated neutralization of human rhinovirus 14 explored by means of cryoelectron microscopy and X-ray crystallography of virus-Fab complexes. J Virol. 1998;72:4610–4622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.6.4610-4622.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Chen Z, Stauffacher C, Schmidt T, Fisher A, Johnson J E. RNA packaging in bean pod mottle virus. In: Brinton M A, Heinz F X, editors. New aspects of positive-strand RNA viruses. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology; 1990. pp. 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chen Z, Stauffacher C V, Johnson J E. Capsid structure and RNA packaging in comoviruses. Semin Virol. 1990;1:453–466. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chen Z, Stauffacher C V, Li Y, Schmidt T, Bomu W, Kamer G, Shanks M, Lomonossoff G, Johnson J E. Protein-RNA interactions in an icosahedral virus at 3.0Å resolution. Science. 1989;245:154–159. doi: 10.1126/science.2749253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Cheng R H. Correlation of cryo-electron microscopic and X-ray data and compensation of the contrast transfer function. Proc Electron Microsc Soc Am (Boston) 1992;50:996–997. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cheng R H, Caston J R, Wang G-J, Gu F, Smith T J, Baker T S, Bozarth R F, Trus B L, Cheng N, Wickner R B, Steven A C. Fungal virus capsids, cytoplasmic compartments for the replication of double-stranded RNA, formed as icosahedral shells of asymmetric gag dimers. J Mol Biol. 1994;244:255–258. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Cheng R H, Kuhn R J, Olson N H, Rossmann M G, Choi H-K, Smith T J, Baker T S. Nucleocapsid and glycoprotein organization in an enveloped virus. Cell. 1995;80:621–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90516-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Cheng R H, Olson N H, Baker T S. Cauliflower mosaic virus, a 420 subunit (T=7), multi-layer structure. Virology. 1992;186:655–668. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90032-k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Cheng R H, Reddy V S, Olson N H, Fisher A J, Baker T S, Johnson J E. Functional implications of quasi-equivalence in a T=3 icosahedral animal virus established by cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. Structure. 1994;2:271–282. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00029-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Chipman P R, Agbandje-McKenna M, Kajigaya S, Brown K E, Young N S, Baker T S, Rossmann M G. Cryo-electron microscopy studies of empty capsids of human parvovirus B19 complexed with its cellular receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:7502–7506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Chipman P R, Agbandje-McKenna M, Renaudin J, Baker T S, McKenna R. Structural analysis of the spiroplasma virus, SpV4: implications for evolutionary variation to obtain host diversity among the Microviridae. Structure. 1998;6:135–145. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00016-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Chipman P R, McKenna R, Renaudin J, Baker T S. Cryo-electron microscopy of spiroplasma virus SpV4. Proc Microsc Microanal. 1997;3:87–88. . Springer-Verlag, New York, N.Y. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Chiu C Y, Mathias P, Nemerow G R, Stewart P L. Structure of adenovirus complexed with its internalization receptor, αvβ5 integrin. J Virol. 1999;73:6759–6768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.8.6759-6768.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Chiu W. Electron microscopy of frozen, hydrated biological specimens. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:237–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Chiu W, Schmid M F. Pushing back the limits of electron cryomicroscopy. Nat Struct Biol. 1997;4:331–333. doi: 10.1038/nsb0597-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Chiu W, Smith T J. Structural studies of virus-antibody complexes by electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1994;4:219–224. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Choi H-K, Tong L, Minor W, Dumas P, Boege U, Rossmann M G, Wengler G. Structure of Sindbis virus core protein reveals a chymotrypsin-like serine protease and the organization of the virion. Nature (London) 1991;354:37–43. doi: 10.1038/354037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Chrétien D, Metoz F, Verde F, Karsenti E. Lattice defects in microtubules: protofilament numbers vary within individual microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1992;117:1031–1040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Colman P M. Virus versus antibody. Structure. 1997;5:591–593. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Colonno R J, Callahan P L, Leippe D M, Rueckert R R, Tomassini J E. Inhibition of rhinovirus attachment by neutralizing monoclonal antibodies and their Fab fragments. J Virol. 1989;63:36–42. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.36-42.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Conway J F, Cheng N, Zlotnick A, Stahl S J, Wingfield P T, Belnap D M, Kanngiesser U, Noah M, Steven A C. Hepatitis B virus capsid: localization of the putative immunodominant loop (residues 78 to 83) on the capsid surface, and implications for the distinction between c and e-antigens. J Mol Biol. 1998;279:1111–1121. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Conway J F, Cheng N, Zlotnick A, Stahl S J, Wingfield P T, Steven A C. Localization of the N terminus of hepatitis B virus capsid protein by peptide-based difference mapping from cryoelectron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:14622–14627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.25.14622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Conway J F, Cheng N, Zlotnick A, Wingfield P T, Stahl S J, Steven A C. Visualization of a 4-helix bundle in the hepatitis B virus capsid by cryo-electron microscopy. Nature (London) 1997;386:91–94. doi: 10.1038/386091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Conway J F, Duda R L, Cheng N, Hendrix R W, Steven A C. Electron Microscopy Society of America. 1994. Bacteriophage HK97: structural transitions along the capsid assembly pathway; pp. 112–113. New Orleans, La. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Conway J F, Duda R L, Cheng N, Hendrix R W, Steven A C. Proteolytic and conformational control of virus capsid maturation: the bacteriophage HK97 system. J Mol Biol. 1995;253:86–99. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Conway J F, Trus B L, Booy F P, Newcomb W W, Brown J C, Steven A C. Effects of radiation damage on frozen hydrated capsids of HSV-1. Proc Electron Microsc Soc Am (Boston) 1992;50:532–533. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Conway J F, Trus B L, Booy F P, Newcomb W W, Brown J C, Steven A C. The effects of radiation damage on the structure of frozen hydrated HSV-1 capsids. J Struct Biol. 1993;111:222–233. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1993.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Conway J F, Trus B L, Booy F P, Newcomb W W, Brown J C, Steven A C. Visualization of three-dimensional density maps reconstructed from cryoelectron micrographs of viral capsids. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:200–208. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Crowther R A. Procedures for three-dimensional reconstruction of spherical viruses by Fourier synthesis from electron micrographs. Phil Trans R Soc Lond Ser B. 1971;261:221–230. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Crowther R A. Three-dimensional reconstruction and the architecture of spherical viruses. Endeavour. 1971;30:124–129. doi: 10.1016/0160-9327(71)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Crowther R A, Amos L A. Three-dimensional image reconstruction of some small spherical viruses. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:489–494. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Crowther R A, Amos L A, Finch J T, DeRosier D J, Klug A. Three dimensional reconstructions of spherical viruses by Fourier synthesis from electron micrographs. Nature (London) 1970;226:421–425. doi: 10.1038/226421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Crowther R A, Amos L A, Klug A. Fifth European Regional Conference on Electron Microscopy. 1972. Three dimensional image reconstruction using functional expansions; pp. 593–597. Manchester, United Kingdom. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Crowther R A, DeRosier D J, Klug A. The reconstruction of a three-dimensional structure from projections and its application to electron microscopy. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A. 1970;317:319–340. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1972.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Crowther R A, Henderson R, Smith J M. MRC image processing programs. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:9–16. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Crowther R A, Kiselev N A, Böttcher B, Berriman J A, Borisova G P, Ose V, Pumpens P. Three-dimensional structure of hepatitis B virus core particles determined by electron cryomicroscopy. Cell. 1994;77:943–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Crowther R A, Klug A. Three dimensional image reconstruction on an extended field—a fast, stable algorithm. Nature (London) 1974;251:490–492. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Crowther R A, Klug A. Structural analysis of macromolecular assemblies by image reconstruction from electron micrographs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:161–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Curry S, Chow M, Hogle J. The poliovirus 135S particle is infectious. J Virol. 1996;70:7125–7131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.10.7125-7131.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.de Haas F, Paatero A O, Mindich L, Bamford D H, Fuller S D. A symmetry mismatch at the site of RNA packaging in the polymerase complex of dsRNA bacteriophage φ6. J Mol Biol. 1999;294:357–372. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.DeRosier D J. Structure of a dehydrogenase enzyme complex by electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. Am Crystallogr Assoc Trans. 1973;9:1–9. [Google Scholar]
- 99.Dokland T, Isaksen M L, Fuller S D, Lindqvist B H. Capsid localization of the bacteriophage-P4 Psu protein. Virology. 1993;194:682–687. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Dokland T, Murialdo H. Structural transitions during maturation of bacteriophage lambda capsids. J Mol Biol. 1993;233:682–694. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Dokland T E, Lindqvist B H, Fuller S D. Image reconstruction from cryo-electron micrographs reveals the morphopoietic mechanism in the P2-P4 bacteriophage system. EMBO J. 1992;11:839–846. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05121.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Downing K H. Observations of restricted beam-induced specimen motion with small-spot illumination. Ultramicroscopy. 1988;24:387–398. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(88)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Downing K H. Spot-scan imaging in transmission electron microscopy. Science. 1991;251:53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.1846047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Downing K H. Progress in design and applications of CCD cameras for electron microscopy. Microsc Today. 1995;95:12. [Google Scholar]
- 105.Downing K H, Chiu W. Cold stage design for high resolution electron microscopy of biological materials. Electron Microsc Rev. 1990;3:213–226. doi: 10.1016/0892-0354(90)90002-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Dryden K A. Proceedings of the XIIth International Congress on Electron Microscopy, Seattle, Wash. Vol. 1. San Francisco, Calif: San Francisco Press, Inc.; 1990. A computer graphic method to enhance the display and interpretation of three-dimensional data; pp. 540–541. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Dryden K A, Farsetta D L, Wang G, Keegan J M, Fields B N, Baker T S, Nibert M L. Internal structures containing transcriptase-related proteins in top component particles of mammalian orthoreovirus. Virology. 1998;245:33–46. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Dryden K A, Wang G, Yeager M, Nibert M L, Coombs K M, Furlong D B, Fields B N, Baker T S. Early steps in reovirus infection are associated with dramatic changes in supramolecular structure and protein conformation: analysis of virions and subviral particles by cryoelectron microscopy and image reconstruction. J Cell Biol. 1993;122:1023–1041. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Dubochet J, Adrian M, Chang J-J, Homo J-C, Lepault J, McDowall A W, Schultz P. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified specimens. Q Rev Biophys. 1988;21:129–228. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Dubochet J, Adrian M, Lepault J, McDowall A W. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified biological specimens. Trends Biochem Sci. 1985;10:143–146. [Google Scholar]
- 111.Dubochet J, Chang J-J, Freeman R, Lepault J, McDowall A W. Frozen aqueous suspensions. Ultramicroscopy. 1982;10:55–62. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Dubochet J, Groom M, Müller-Neuteboom S. The mounting of macromolecules for electron microscopy with particular reference to surface phenomena and the treatment of support films by glow discharge. Adv Opt Electron Microsc. 1982;8:107–135. [Google Scholar]
- 113.Dubochet J, Lepault J, Freeman R, Berriman J A, Homo J-C. Electron microscopy of frozen water and aqueous solutions. J Microsc. 1982;128:219–237. [Google Scholar]
- 114.Dubochet J, McDowell A W. Vitrification of pure water for electron microscopy. J Microsc. 1981;124:RP3–RP4. [Google Scholar]
- 115.Earnshaw W, King J. Structure of phage P22 coat protein aggregates formed in the absence of the scaffolding protein. J Mol Biol. 1978;126:721–747. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Erickson H P, Klug A. Measurement and compensation of defocusing and aberrations by Fourier processing of micrographs. Phil Trans R Soc Lond Ser B. 1971;261:105–118. [Google Scholar]
- 117.Estes M K. Rotaviruses and their replication. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, et al., editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed. Vol. 2. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven; 1996. pp. 1627–1655. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Ferlenghi I, Gowen B, de Haas F, Mancini E J, Garoff H, Sjöberg M, Fuller S D. The first step: maturation of the Semliki Forest virus spike occurs through a dramatic localized conformational change. J Mol Biol. 1998;283:71–81. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Finch J T. The surface structure of polyoma. J Gen Virol. 1974;24:359–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-2-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Finch J T, Crowther R A, Hendry D A, Struthers J K. The structure of Nudaurelia capensis β virus: the first example of a capsid with icosahedral surface symmetry T=4. J Gen Virol. 1974;24:191–200. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Finch J T, Klug A. The structure of viruses of the papilloma-polyoma type. III. Structure of rabbit papilloma virus. J Mol Biol. 1965;13:1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Fisher A J, Johnson J E. Ordered duplex RNA controls capsid architecture in an icosahedral animal virus. Nature (London) 1993;361:176–179. doi: 10.1038/361176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Fox J M, Wang G, Speir J A, Olson N H, Johnson J E, Baker T S, Young M J. Comparison of the native CCMV virion with in vitro assembled CCMV virions by cryoelectron microscopy and image reconstruction. Virology. 1998;244:212–218. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Frank J. Three-dimensional electron microscopy of macromolecular assemblies. San Diego, Calif: Academic Press; 1996. pp. 1–342. [Google Scholar]
- 125.Frank J. The ribosome at higher resolution—the donut takes shape. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997;7:266–272. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(97)80035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Frank J, Radermacher M, Penczek P, Zhu J, Li Y, Ladjadj M, Leith A. SPIDER and WEB: processing and visualization of images in 3D electron microscopy and related fields. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:190–199. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Fujiyoshi Y. Proceedings of the XIIth International Congress on Electron Microscopy, Seattle, Wash. Vol. 1. San Francisco, Calif: San Francisco Press, Inc.; 1990. High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy of biological macromolecules; pp. 126–127. [Google Scholar]
- 128.Fujiyoshi Y, Mizusaki T, Morikawa K, Yamagishi H, Aoki Y, Kihara H, Harada Y. Development of a superfluid helium stage for high-resolution electron microscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 1991;38:241–251. [Google Scholar]
- 129.Fuller, S., M. Clarke, and B. Gowen. Unpublished data.
- 130.Fuller S D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by complementary interactions with a T=3 icosahedral capsid. Cell. 1987;48:923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Fuller S D, Argos P. Is Sindbis a simple picornavirus with an envelope? EMBO J. 1987;6:1099–1105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Fuller S D, Berriman J A, Butcher S J, Gowen B E. Low pH induces the swivelling of the glycoprotein heterodimers in the Semliki Forest virus spike complex. Cell. 1995;81:715–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90533-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Fuller S D, Butcher S J, Cheng R H, Baker T S. Three-dimensional reconstruction of icosahedral particles: the uncommon line. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:48–55. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Fuller S D, Wilk T, Gowen B E, Kräusslich H-G, Vogt V E. Cryo-electron microscopy reveals ordered domains within the immature HIV-1 particle. Curr Biol. 1997;7:729–738. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Furcinitti P S, van Oostrum J, Burnett R M. Adenovirus polypeptide IX revealed as capsid cement by difference images from electron microscopy and crystallography. EMBO J. 1991;12:3563–3570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Furlong D B, Nibert M L, Fields B N. Sigma 1 protein of mammalian reoviruses extends from the surface of viral particles. J Virol. 1988;62:246–256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.246-256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Gallagher T M, Rueckert R R. Assembly-dependent maturation cleavage in provirions of a small icosahedral insect ribovirus. J Virol. 1988;62:3399–3406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3399-3406.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Geisselsoder J, Chidambaram M, Goldstein R. Transcriptional control of capsid size in the P2:P4 bacteriophage system. J Mol Biol. 1978;126:447–456. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Gottlieb P, Strassman J, Bamford D, Mindich L. Production of a polyhedral particle in Escherichia coli from a cDNA copy of the large genome segment of φ6. J Virol. 1988;62:181–187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.181-187.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Gottlieb P, Strassman J, Qiao X Y, Frucht A, Mindich L. In vitro replication, packaging, and transcription of the segmented double-stranded RNA genome of bacteriophage φ6: studies with procapsids assembled from plasmid-encoded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1990;172:5774–5782. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5774-5782.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Grant R A, Cranic S, Hogle J M. Radial depth provides the cue. Curr Biol. 1992;2:86–87. [Google Scholar]
- 142.Greve J M, Davis G, Meyer A M, Forte C P, Yost S C, Marlor C W, Kamarck M D, McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989;56:839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Grimes J, Basak A K, Roy P, Stuart D. The crystal structure of bluetongue virus VP7. Nature (London) 1995;373:167–170. doi: 10.1038/373167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Grimes J M, Bourroughs J N, Gouet P, Diprose J M, Malby R, Ziéntara S, Mertens P P C, Stuart D I. The atomic structure of the bluetongue virus core. Nature (London) 1998;395:470–478. doi: 10.1038/26694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Grimes J M, Jakana J, Ghosh M, Basak A K, Roy P, Chiu W, Stuart D I, Prasad B V V. An atomic model of the outer layer of the bluetongue virus core derived from X-ray crystallography and electron cryomicroscopy. Structure. 1997;5:885–893. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Hagensee M E, Olson N H, Baker T S, Galloway D A. Three-dimensional structure of vaccinia virus-produced human papillomavirus type 1 capsids. J Virol. 1994;68:4503–4505. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4503-4505.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Halling C, Calandar R, Christie G E, Dale E C, Deho G, et al. DNA sequence of satellite bacteriophage P4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18:1649. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Harrison S C. Virus structure: high resolution perspectives. Adv Virus Res. 1983;28:175–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60724-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Harrison S C. Principles of virus structure. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Chanock R M, et al., editors. Fields virology. Vol. 2. New York, N.Y: Raven Press; 1990. pp. 37–61. [Google Scholar]
- 150.Harrison S C, Olson A J, Schutt C E, Winkler F K, Bricogne G. Tomato bushy stunt virus at 2.9Å resolution. Nature (London) 1978;276:368–373. doi: 10.1038/276368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Hax W M A, Lichtenegger S. A cryo-transfer system for EM400 electron microscopes. Electron Opt Rep. 1983;30:57–60. [Google Scholar]
- 152.Heide H G, Grund S. Eine tiefkuhlkette zum uberfuhren von wasserhaltigen biologischen objekten ins elektronenmikroskop. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974;48:259–268. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Henderson R. The potential and limitations of neutrons, electrons, and X-rays for atomic resolution microscopy of unstained biological molecules. Q Rev Biophys. 1995;28:171–193. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000305x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Henderson R, Baldwin J M, Ceska T A, Zemlin F, Beckmann E, Downing K H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990;213:899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Henderson R, Raeburn C, Vigers G. A side-entry cold holder for cryo-electron microscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 1991;35:45–53. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(91)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Hewat E A, Blaas D. Structure of a neutralizing antibody bound bivalently to human rhinovirus 2. EMBO J. 1996;15:1515–1523. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Hewat E A, Booth T F, Loudon P T, Roy P. Three-dimensional reconstruction of baculovirus expressed bluetongue virus core-like particles by cryo-electron microscopy. Virology. 1992;189:10–20. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90676-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Hewat E A, Booth T F, Roy P. Structure of bluetongue virus particles by cryoelectron microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1992;109:61–69. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90068-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Hewat E A, Booth T F, Roy P. Structure of correctly self-assembled bluetongue virus-like particles. J Struct Biol. 1994;112:183–191. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1994.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Hewat E A, Booth T F, Wade R W, Roy P. 3-D reconstruction of bluetongue virus tubules using cryoelectron microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1992;108:35–48. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90005-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Hewat E A, Marlovits T C, Blaas D. Structure of a neutralizing antibody bound monovalently to human rhinovirus 2. J Virol. 1998;72:4396–4402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.5.4396-4402.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Hewat E A, Verdaguer N, Fita I, Blakemore W, Brookes S, King A, Newman J, Domingo E, Mateu M G, Stuart D I. Structure of the complex of an Fab fragment of a neutralizing antibody with foot-and-mouth disease virus: positioning of a highly mobile antigenic group. EMBO J. 1997;16:1492–1500. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.7.1492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Hogle J M. The viral canyon. Curr Biol. 1993;3:278–281. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90178-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Homo J-C, Booy F, Labouesse P, Lepault J, Dubochet J. Improved anticontaminator for cryo-electron microscopy with a Philips EM 400. J Microsc. 1984;136:337–340. [Google Scholar]
- 165.Hong S S, Karayan L, Tournier J, Curiel D T, Boulanger P. Adenovirus type 5 fiber knob binds to MHC class I α2 domain at the surface of human epithelial and B lymphoblastoid cells. EMBO J. 1997;16:2294–2306. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.9.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Ilag L L, Olson N H, Dokland T, Music C L, Cheng R H, Bowen Z, McKenna R, Rossmann M G, Baker T S, Incardona N L. DNA packaging intermediates of bacteriophage φX174. Structure. 1995;3:353–363. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00167-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Imber R, Tsugita A, Wurtz M, Hohn T. Outer capsid protein of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1980;139:277–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Isaksen M, Rishovd S, Calendar R, Lindqvist B H. The polarity suppression factor of bacteriophage P4 is also a decoration protein of the P4 capsid. Virology. 1992;188:831–839. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90538-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Isaksen M I, Dokland T, Lindqvist B H. Characterization of the capsid associating activity of bacteriophage P4’s Psu protein. Virology. 1993;194:674–681. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Jack A, Harrison S C, Crowther R A. Structure of tomato bushy stunt virus. II. Comparison of results obtained by electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1975;97:163–172. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Jané-Valbuena J, Nibert M L, Spencer S M, Walker S B, Baker T S, Chen Y, Centonze V E, Schiff L A. Reovirus virion-like particles obtained by recoating infectious subvirion particles with baculovirus-expressed ς3 protein: an approach for analyzing ς3 functions during virus entry. J Virol. 1999;73:2963–2973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.4.2963-2973.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Janshoff A, Bong D, Steinem C, Johnson J, Ghadiri M. An animal virus-derived peptide switches membrane morphology: possible relevance to nodaviral transfection process. Biochemistry. 1999;38:5328–5336. doi: 10.1021/bi982976i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Jeng T-W, Chiu W. High resolution cryo system designed for JEM 100CX electron microscope. Ultramicroscopy. 1987;23:61–66. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(87)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Jeng T-W, Talmon Y, Chiu W. Containment system for the preparation of vitrified-hydrated virus specimens. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1988;8:343–348. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060080402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Johnson J E. Functional implications of protein-protein interactions in icosahedral viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:27–33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Johnson J E, Fisher A J. Principles of virus structure. In: Webster R G, Granoff A, editors. Encyclopedia of virology. Vol. 3. London, United Kingdom: Academic Press; 1994. pp. 1573–1586. [Google Scholar]
- 177.Johnson J E, Munshi S, Liljas L, Agrawal D, Olson N H, Reddy V, Fisher A, McKinney B, Schmidt T, Baker T S. Comparative studies of T=3 and T=4 icosahedral RNA insect viruses. Arch Virol. 1994;9:497–512. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9326-6_48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Johnson J E, Speir J A. Quasi-equivalent viruses: a paradigm for protein assemblies. J Mol Biol. 1997;269:665–675. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Joklik W K. Studies on the effect of chymotrypsin on reoviruses. Virology. 1972;49:700–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Jones T A, Zou J-Y, Cowan S W, Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991;47:110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Kaljot K T, Shaw R D, Rubin D H, Greenberg H B. Infectious rotavirus enters cells by direct cell membrane penetration, not by endocytosis. J Virol. 1988;62:1136–1144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1136-1144.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Katsura I, Kobayashi H. Structure and inherent properties of the bacteriophage lambda head shell. VII. Molecular design of the form determining major capsid protein. J Mol Biol. 1990;213:503–511. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Katsura I. Structure and inherent properties of the bacteriophage lambda head shell. I. Polyheads formed by two defective mutants in the major head protein. J Mol Biol. 1978;121:71–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Kenney J M, von Bonsdorf C-H, Nassal M, Fuller S D. Evolutionary conservation in the hepatitis B core structure: comparison of human and duck cores. Structure. 1995;3:1009–1019. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Kenney J M, Hantula J, Fuller S D, Mindich L, Ojala P M, Bamford D H. Bacteriophage φ-6 envelope elucidated by chemical crosslinking, immunodetection and cryo-electron microscopy. Virology. 1992;190:635–644. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90901-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Kenney J M, Sjöberg M, Garoff H, Fuller S D. Visualization of fusion activation of the Semliki Forest virus spike. Structure. 1994;2:823–832. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(94)00083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Kielian M. Membrane fusion and the alphavirus life cycle. Adv Virus Res. 1995;45:113–151. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Klug A, Finch J T. Structure of viruses of the papilloma-polyoma type. I. Human wart virus. J Mol Biol. 1965;11:403–423. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Klug A, Finch J T. Structure of viruses of the papilloma-polyoma type. IV. Analysis of tilting experiments in the electron microscope. J Mol Biol. 1968;31:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Kuhlbrandt W, Wang D N, Fujiyoshi Y. Atomic model of plant light-harvesting complex by electron crystallography. Nature (London) 1994;367:614–621. doi: 10.1038/367614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Kumar A, Reddy V S, Yusibov V, Chipman P R, Hata Y, Fita I, Fukuyama K, Rossmann M G, Loesch-Fries L S, Baker T S, Johnson J E. The structure of alfalfa mosaic virus capsid protein assembled as a T=1 icosahedral particle at 4.0-Å resolution. J Virol. 1997;71:7911–7916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.10.7911-7916.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Langmore J P, Smith M F. Quantitative energy-filtered electron microscopy of biological molecules in ice. Ultramicroscopy. 1992;46:349–373. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90024-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Lawton J A, Estes M K, Prasad B V V. Three-dimensional visualization of mRNA release from actively transcribing rotavirus particles. Nat Struct Biol. 1997;4:118–121. doi: 10.1038/nsb0297-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Lawton J A, Prasad B V V. Automated software package for icosahedral virus reconstruction. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:209–215. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Lawton J A, Zeng C Q-Y, Mukherjee S K, Cohen J, Estes M K, Prasad B V V. Three-dimensional structural analysis of recombinant rotavirus-like particles with intact and amino-terminal-deleted VP2: implications for the architecture of the VP2 capsid layer. J Virol. 1997;71:7353–7360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.10.7353-7360.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Lembcke G, Zemlin F. Proceedings of the XIIth International Congress on Electron Microscopy, Seattle, Wash. Vol. 1. San Francisco, Calif: San Francisco Press, Inc.; 1990. Projected structure of the surface protein of Sulfolobus spec B12 determined to a resolution of 1.0 nm by cryo-electron microscopy; pp. 102–103. [Google Scholar]
- 197.Lepault J, Booy F P, Dubochet J. Electron microscopy of frozen biological specimens. J Microsc. 1983;129:89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1983.tb04163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Lepault J, Dubochet J. Electron microscopy of frozen hydrated specimens: preparation and characteristics. Methods Enzymol. 1986;127:719–730. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)27056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Lepault J, Dubochet J, Baschong W, Kellenberger E. Organization of double-stranded DNA in bacteriophages: a study by cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified samples. EMBO J. 1987;6:1507–1512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Lepault J, Freeman R, Dubochet J. Electron beam induced ‘vitrified ice.’. J Microsc. 1983;132:RP3–RP4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1983.tb04225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Liddington R C, Yan Y, Moulai J, Sahli R, Benjamin T L, Harrison S C. Structure of simian virus 40 at 3.8-Å resolution. Nature (London) 1991;354:278–284. doi: 10.1038/354278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Liljas L. The structure of spherical viruses. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1986;48:1–36. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(86)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Liljas L, Unge T, Jones T A, Fridborg K, Lövgren S, Skoglund U, Strandberg B. The structure of satellite tobacco necrosis virus at 3.0Å resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982;159:93–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Liljestrom P, Lusa S, Huylebroeck D, Garoff H. In vitro mutagenesis of a full-length cDNA clone of Semliki Forest virus: the small 6,000-molecular-weight membrane protein modulates virus release. J Virol. 1991;65:4107–4113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4107-4113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Liu H, Smith T J, Lee W-M, Mosser A G, Rueckert R R, Olson N H, Cheng R H, Baker T S. Structure determination of an Fab fragment that neutralizes human rhinovirus 14 and analysis of the Fab-virus complex. J Mol Biol. 1994;240:127–137. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.López S, Arias C F, Méndez E, Espejo R T. Conservation in rotaviruses of the protein region containing the two sites associated with trypsin enhancement of infectivity. Virology. 1986;154:224–227. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90445-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Lu G, Zhou Z H, Baker M L, Jakana J, Cai D, Wei X, Chen S, Gu X, Chiu W. Structure of double-shelled rice dwarf virus. J Virol. 1998;72:8541–8549. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.11.8541-8549.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Luo C, Butcher S, Bamford D H. Isolation of a phospholipid-free protein shell of bacteriophage PRD1, an Escherichia coli virus with an internal membrane. Virology. 1993;194:564–569. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Luongo C L, Dryden K A, Farsetta D L, Margraf R L, Severson T F, Olson N H, Fields B N, Baker T S, Nibert M L. Localization of a C-terminal region of λ2 protein in reovirus cores. J Virol. 1997;71:8035–8040. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.10.8035-8040.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Mancini E J, de Haas F, Fuller S D. High resolution icosahedral reconstruction: fulfilling the promise of cryo-electron microscopy. Structure. 1997;5:741–750. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00229-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Mandelkow E-M, Mandelkow E. Unstained microtubules studied by cryo-electron microscopy: substructure, supertwist and disassembly. J Mol Biol. 1985;181:123–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90330-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Mandelkow E-M, Mandelkow E, Milligan R A. Microtubule dynamics and microtubule caps: a time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy study. J Cell Biol. 1991;114:977–991. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Marvik O J, Dokland T, Nokling R H, Jacobson E, Larsen T, Lindquist B H. The capsid size-determining protein sid forms an external scaffold on phage P4 procapsids. J Mol Biol. 1995;251:59–75. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.McKenna R, Olson N H, Chipman P R, Baker T S, Booth T F, Christensen J, Aasted B, Fox J M, Bloom M E, Wolfinbarger J B, Agbandje-McKenna M. Three-dimensional structure of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus: implications for disease pathogenicity. J Virol. 1999;73:6882–6891. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.8.6882-6891.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.McMath T A, Curzon A E, Frindt R F. A double Faraday cup attachment for relative intensity measurements on an electron microscope. J Phys E Sci Instrum. 1982;15:988–990. [Google Scholar]
- 216.Mellema J E, Amos L A. Three-dimensional image reconstruction of turnip yellow mosaic virus. J Mol Biol. 1972;72:819–822. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Metcalf P, Cyrklaff M, Adrian M. The three-dimensional structure of reovirus obtained by cryo-electron microscopy. EMBO J. 1991;10:3129–3136. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Milligan R A, Brisson A, Unwin P N T. Molecular structure determination of crystalline specimens in frozen aqueous solutions. Ultramicroscopy. 1984;13:1–10. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(84)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Mindich L, Bamford D H. Lipid containing bacteriophages. In: Calendar R, editor. The bacteriophages. Vol. 2. New York, N.Y: Plenum Press; 1988. pp. 475–520. [Google Scholar]
- 220.Murialdo H. Bacteriophage lambda DNA maturation and packaging. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:125–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Murialdo H, Ray P N. Model for arrangement of minor structural proteins in the head of bacteriophage λ. Nature (London) 1975;257:815–817. doi: 10.1038/257815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Murphy F A. Virus taxonomy. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, et al., editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed. Vol. 2. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven; 1996. pp. 15–57. [Google Scholar]
- 223.Newcomb W W, Brown J C, Booy F P, Steven A C. Nucleocapsid mass and capsomer protein stoichiometry in equine herpesvirus 1: scanning transmission electron microscopic study. J Virol. 1989;63:3777–3783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3777-3783.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Newcomb W W, Trus B L, Booy F P, Steven A C, Wall J S, Brown J C. Structure of the herpes simplex virus capsid. Molecular composition of the pentons and the triplexes. J Mol Biol. 1993;232:499–511. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Nibert M L, Schiff L A, Fields B N. Reoviruses and their replication. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, et al., editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed. Vol. 2. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven; 1996. pp. 1557–1596. [Google Scholar]
- 226.Nibert M L, Schiff L A, Fields B N. Mammalian reoviruses contain a myristoylated structural protein. J Virol. 1991;65:1960–1967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1960-1967.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Olkonnen V M, Gottlieb P, Strassman J, Qiao X, Bamford D H, Mindich L. In vitro assembly of infectious nucleocapsids of φ6: formation of a recombinant double stranded RNA virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:9173–9177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Olson N H, Baker T S. Magnification calibration and the determination of spherical virus diameters using cryo-microscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 1989;30:281–298. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(89)90057-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Olson N H, Baker T S, Bomu W, Johnson J E, Hendry D A. The three-dimensional structure of frozen-hydrated Nudaurelia capensis beta virus. Electron Microsc Soc Am Proc. 1987;45:650–651. [Google Scholar]
- 230.Olson N H, Baker T S, Johnson J E, Hendry D A. The three-dimensional structure of frozen-hydrated Nudaurelia capensis β virus, a T=4 insect virus. J Struct Biol. 1990;105:111–122. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(90)90105-l. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Olson N H, Baker T S, Willingham P, Incardona N L. The three-dimensional structure of frozen-hydrated bacteriophage φX174. J Struct Biol. 1992;108:168–175. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90016-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Olson N H, Chipman P R, Bloom M E, McKenna R, Agbandje-McKenna M, Booth T F, Baker T S. Automated CCD data collection and 3D reconstruction of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. Proc Microsc Microanal. 1997;3:1117–1118. [Google Scholar]
- 233.Olson N H, Kolatkar P R, Oliveira M A, Cheng R H, Greve J M, McClelland A, Baker T S, Rossmann M G. Structure of a human rhinovirus complexed with its receptor molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:507–511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Olson N H, Lücken U, Walker S B, Otten M T, Baker T S. Cryoelectron microscopy and image reconstruction of spherical viruses with spot scan and FEG technologies. Proc Microsc Microanal. 1995;1:1086–1087. [Google Scholar]
- 235.Olson N H, Smith T J, Kolatkar P R, Oliveira M A, Rueckert R R, Greve J M, Rossmann M G, Baker T S. Proceedings of the Electron Microscopy Society of America. Vol. 50. San Francisco, Calif: San Francisco Press, Inc.; 1992. Cryoelectron microscopy of complexes of human rhinovirus with a monoclonal Fab and the viral cellular receptor; pp. 524–525. [Google Scholar]
- 236.Palmer K J, Tichelaar W, Myers N, Burns N R, Butcher S J, Kingsman A J, Fuller S D, Saibil H R. Cryo-electron microscopy structure of yeast Ty retrotransposon virus-like particles. J Virol. 1997;71:6863–6868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.9.6863-6868.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Paredes A M, Brown D T, Rothnagel R, Chiu W, Schoepp R J, Johnston R E, Prasad B V V. Three-dimensional structure of a membrane-containing virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:9095–9099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Paredes A M, Heidner H, Thuman-Commike P, Venkataram Prasad B V, Johnston R E, Chiu W. Structural localization of the E3 glycoprotein in attenuated Sindbis virus mutants. J Virol. 1998;72:1534–1541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.2.1534-1541.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Philipson L. Structure and assembly of adenoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;109:1–52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69460-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Porta C, Wang G, Cheng R H, Chen Z, Baker T S, Johnson J E. Direct imaging of interactions between an icosahedral virus conjugate Fab fragments by cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. Virology. 1994;204:777–788. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Prasad B V, Yamaguchi S, Roy S. Three-dimensional structure of single-shelled bluetongue virus. J Virol. 1992;66:2135–2142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2135-2142.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Prasad B V V, Burns J W, Marietta E, Estes M K, Chiu W. Localization of VP4 neutralization sites in rotavirus by three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy. Nature (London) 1990;343:476–479. doi: 10.1038/343476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Prasad B V V, Marietta E, Burns J W, Estes M K, Chiu W. Proc. XIIth Int. Cong. Electron Microscopy, Seattle, Wash. Vol. 1. San Francisco, Calif: San Francisco Press, Inc.; 1990. Three-dimensional structure of rotavirus-FAB complex; pp. 238–239. [Google Scholar]
- 244.Prasad B V V, Matson D O, Smith A W. Three-dimensional structure of calicivirus. J Mol Biol. 1994;240:256–264. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Prasad B V V, Prevelige P E, Marietta E, Chen R O, Thomas D, King J, Chiu W. Three-dimensional transformation of capsids associated with genome packaging in a bacterial virus. J Mol Biol. 1993;231:65–74. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Prasad B V V, Rothnagel R, Jiang X, Estes M K. Three-dimensional structure of baculovirus-expressed Norwalk virus capsids. J Virol. 1994;68:5117–5125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.5117-5125.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Prasad B V V, Rothnagel R, Zeng C Q-Y, Jakana J, Lawton J A, Chiu W, Estes M K. Visualization of ordered genomic RNA and localization of transcriptional complexes in rotavirus. Nature (London) 1996;382:471–473. doi: 10.1038/382471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Prasad B V V, Wang G J, Clerx J P M, Chiu W. Cryo-electron microscopy of spherical viruses: an application to rotaviruses. Micron. 1987;18:327–331. [Google Scholar]
- 249.Prasad B V V, Wang G J, Clerx J P M, Chiu W. Three-dimensional structure of rotavirus. J Mol Biol. 1988;199:269–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Prevelige P E, Jr, Thomas D, Aubrey K L, Towse S A, Thomas G J., Jr Subunit conformational changes accompanying bacteriophage P22 capsid maturation. Biochemistry. 1993;32:537–543. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Radermacher M, Wagenknecht T, Verschoor A, Frank J. Three-dimensional reconstruction from a single-exposure, random conical tilt series applied to the 50S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J Microsc. 1987;146:113–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1987.tb01333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Rayment I, Baker T S, Caspar D L D, Murakami W T. Polyoma virus capsid structure at 22.5Å resolution. Nature (London) 1982;295:110–115. doi: 10.1038/295110a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Renz D, Brown D T. Characteristics of Sindbis virus temperature-sensitive mutants in cultured BHK-21 and Aedes albopictus (mosquito) cells. J Virol. 1976;19:775–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.775-781.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Rey F, Harrison S. The structure of the envelope protein of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Nature (London) 1995;375:291–298. doi: 10.1038/375291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Roberts M M, White J L, Grütter M G, Burnett R M. Three-dimensional structure of the adenovirus major coat protein hexon. Science. 1986;232:1148–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.3704642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Robinson I K, Harrison S C. Structure of the expanded state of tomato bushy stunt virus. Nature (London) 1982;297:563–568. [Google Scholar]
- 257.Rossmann M G. Viral cell recognition and entry. Protein Sci. 1994;3:1712–1725. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Rossmann M G, Arnold E, Erickson J W, Frankenberger E A, Griffith J P, Hecht H J, Johnson J E, Kamer G, Luo M, Mosser A G, Rueckert R R, Sherry B, Vriend G. Structure of human cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature (London) 1985;317:145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Rossmann M G, Greve J M, Kolatkar P R, Olson N H, Smith T J, McKinlay M A, Rueckert R R. Rhinovirus attachment and cell entry. In: Chiu W, Burnett R M, Garcea R L, editors. Structural biology of viruses. New York, N.Y: Oxford University Press; 1997. pp. 105–133. [Google Scholar]
- 260.Rossmann M G, Johnson J E. Icosahedral RNA virus structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:533–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Rossmann M G, Olson N H, Kolatkar P R, Oliveira M A, Cheng R H, Greve J M, McClelland A, Baker T S. Crystallographic and cryo EM analysis of virion-receptor interactions. Arch Virol. 1994;9:531–541. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9326-6_51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Roy P. Orbiviruses and their replication. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, et al., editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed. Vol. 2. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven; 1996. pp. 1709–1734. [Google Scholar]
- 263.Ryu S E, Kwong P D, Truneh A, Porter T G, Arthos J, Rosenberg M, Dai X, Xuong N, Axel R, Sweet R W, Hendrickson W A. Crystal structure of an HIV-binding recombinant fragment of human CD4. Nature (London) 1990;348:419–426. doi: 10.1038/348419a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Salunke D M, Caspar D L D, Garcea R L. Self-assembly of purified polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. Cell. 1986;46:895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Sanger F, Coulson A R, Hong G F, Hill D F, Peterson G B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage λ DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982;162:729–772. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Schoehn G. Reconstructions tridimensionnelles de virus icosaédriques par cryomicroscopie èlectronique: application au virus Broadhaven et à l’adenovirus humain de sérotype 3. Physique. Grenoble, France: Université Joseph Fourier-Grenoble I; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 267.Schoehn G, Fender P, Chroboczek J, Hewat E A. Adenovirus 3 penton dodecahedron exhibits structural changes of the base on fibre binding. EMBO J. 1996;15:6841–6848. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Schoehn G, Moss S R, Nuttall P A, Hewat E A. Structure of Broadhaven virus by cryoelectron microscopy: correlation of structural and antigenic properties of Broadhaven virus and Bluetongue virus outer capsid proteins. Virology. 1997;235:191–200. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Schrag J D, Prasad B V V, Rixon F J, Chiu W. Three-dimensional structure of the HSV1 nucleocapsid. Cell. 1989;56:651–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90587-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Shannon C E. Communication in the presence of noise. Proc Inst Radio Eng. 1949;37:10–20. [Google Scholar]
- 271.Shaw A L, Rothnagel R, Chen D, Ramig R F, Chiu W, Prasad B V V. Three-dimensional visualization of the rotavirus hemagglutinin structure. Cell. 1993;74:693–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90516-S. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Shaw A L, Samal S K, Subramanian K, Prasad B V V. The structure of aquareovirus shows how the different geometries of the two layers of the capsid are reconciled to provide symmetrical interactions and stabilization. Structure. 1996;4:957–967. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Sheehan B, Fuller S D, Pique M E, Yeager M. AVS software for visualization in molecular microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:99–105. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Sherry B, Mosser A G, Colonno R J, Rueckert R R. Use of monoclonal antibodies on a common cold picornavirus, human rhinovirus 14. J Virol. 1986;57:246–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.246-257.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Shore D, Deho G, Tsipis J, Goldstein R. Determination of capsid size by satellite bacteriophage P4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1978;75:4165–4169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Simons K, Garoff H. The budding mechanisms of envelope animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1980;50:1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Simpson A A, Chipman P R, Baker T S, Tijssen P, Rossmann M G. The structure of an insect parvovirus (Galleria mellonella densovirus) at 3.7 Å resolution. Structure. 1998;6:1355–1367. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00136-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Sinclair J F, Tzagoloff A, Levine D, Mindich L. Proteins of the bacteriophage φ6. Virology. 1975;75:198–208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.685-695.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Singh S, Rothnagel R, Prasad B V V, Buckley B. Expression of tobacco ringspot virus capsid protein and satellite RNA in insect cells and three-dimensional structure of tobacco ringspot virus-like particles. Virology. 1995;213:472–481. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Six E W. The helper dependence of satellite bacteriophage P4: which gene functions of bacteriophage P2 are needed by P4? Virology. 1975;67:249–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90422-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Six E W, Klug C A C. Bacteriophage P4: a satellite virus depending on a helper such as prophage P2. Virology. 1973;51:327–347. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Skoglund U, Öfverstedt L-G, Burnett R M, Bricogne G. Maximum-entropy three-dimensional reconstruction with deconvolution of the contrast transfer function: a test application with adenovirus. J Struct Biol. 1996;117:173–188. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 283.Smith M F, Langmore J P. Quantitation of molecular densities by cryo-electron microscopy: determination of the radial density distribution of tobacco mosaic virus. J Mol Biol. 1992;226:763–774. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90631-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 284.Smith T J, Baker T S. Picornaviruses: epitopes, canyons, and pockets. Adv Virus Res. 1999;52:1–23. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60297-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 285.Smith T J, Chase E S, Schmidt T J, Olson N H, Baker T S. Neutralizing antibody to human rhinovirus 14 penetrates the receptor-binding canyon. Nature (London) 1996;383:350–354. doi: 10.1038/383350a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 286.Smith T J, Cheng R H, Olson N H, Peterson P, Chase E, Kuhn R J, Baker T S. Putative receptor binding sites on alphaviruses as visualized by cryoelectron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:10648–10652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 287.Smith T J, Mosser A G, Baker T S. Structural studies on the mechanisms of antibody-mediated neutralization of human rhinovirus. Semin Virol. 1995;6:233–242. [Google Scholar]
- 288.Smith T J, Olson N H, Cheng R H, Chase E S, Baker T S. Structure of a human rhinovirus-bivalently bound antibody complex: implications for viral neutralization and antibody flexibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:7015–7018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 289.Smith T J, Olson N H, Cheng R H, Liu H, Chase E S, Lee W M, Leippe D M, Mosser A G, Rueckert R R, Baker T S. Structure of human rhinovirus complexed with Fab fragments from a neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1993;67:1148–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1148-1158.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 290.Speir J A, Munshi S, Wang G, Baker T S, Johnson J E. Structures of the native and swollen forms of cowpea chlorotic mottle virus determined by X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy. Structure. 1995;3:63–78. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00135-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 291.Spencer J V, Trus B L, Booy F P, Steven A C, Newcomb W W, Brown J C. Structure of the herpes simplex virus capsid: peptide A862-H880 of the major capsid protein is displayed on the rim of the capsomer protrusions. Virology. 1997;228:229–235. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.8392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 292.Spencer S M, Sgro J-Y, Dryden K A, Baker T S, Nibert M L. IRIS explorer software for radial-depth cueing reovirus particles and other macromolecular structures determined by cryoelectron microscopy and image reconstruction. J Struct Biol. 1997;120:11–21. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1997.3902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 293.Stehle T, Yan Y, Benjamin T L, Harrison S C. Structure of murine polyoma virus complexed with an oligosaccharide receptor fragment. Nature (London) 1994;369:160–163. doi: 10.1038/369160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 294.Steven A C, Trus B L, Booy F P, Cheng N, Zlotnick A, Caston J R, Conway J F. The making and breaking of symmetry in virus capsid assembly: glimpses of capsid biology from cryoelectron microscopy. FASEB J. 1997;11:733–742. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.11.10.9271358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 295.Stewart M. Electron microscopy of biological macromolecules: frozen hydrated methods and computer image processing. In: Duke P J, Michette A G, editors. Modern microscopies: techniques and applications. New York, N.Y: Plenum Press; 1990. pp. 9–39. [Google Scholar]
- 296.Stewart P L, Burnett R M, Cyrklaff M, Fuller S D. Image reconstruction reveals the complex molecular organization of adenovirus. Cell. 1991;67:145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90578-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 297.Stewart P L, Chiu C Y, Huang S, Muir T, Zhao Y, Chait B, Mathias P, Nemerow G R. Cryo-EM visualization of an exposed RGD epitope on adenovirus that escapes antibody neutralization. EMBO J. 1997;16:1189–1198. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.6.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 298.Stewart P L, Fuller S D, Burnett R M. Difference imaging of adenovirus: bridging the resolution gap between X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy. EMBO J. 1993;12:2589–2599. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05919.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 299.Stewart P L, Nemerow G R. Combining structures from cryo-electron microscopy and x-ray crystallography. JMSA Proc Microsc Microanal. 1995;53:44–45. [Google Scholar]
- 300.Tao Y, Olson N H, Xu W, Anderson D L, Rossmann M G, Baker T S. Assembly of a tailed bacterial virus and its genome release studied in three dimensions. Cell. 1998;95:431–437. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81773-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 301.Taylor K A. Electron microscopy of frozen, hydrated biological specimens. Electron Microsc Soc Am Proc. 1975;33:300–301. [Google Scholar]
- 302.Taylor K A, Glaeser R M. A method for maintaining specimen hydration by sandwiching between thin films. Electron Microsc Soc Am Proc. 1973;31:342–343. [Google Scholar]
- 303.Taylor K A, Glaeser R M. Electron microscopy of frozen hydrated biological specimens. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976;55:448–456. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 304.Thon F. Phase contrast electron microscopy. In: Valdre U, editor. Electron microscopy in material science. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1971. pp. 570–625. [Google Scholar]
- 305.Thouvenin E, Laurent S, Madelaine M-F, Rasschaert D, Vautherot J-F, Hewat E A. Bivalent binding of neutralising antibody to a calicivirus involves the torsional flexibility of the antibody hinge. J Mol Biol. 1997;270:238–246. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 306.Thuman-Commike P A, Chiu W. PTOOL: a software package for the selection of particles from electron cyromicroscopy spot-scan images. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:41–47. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 307.Thuman-Commike P A, Chiu W. Improved common line-based icosahedral particle image orientation estimation algorithms. Ultramicroscopy. 1997;68:231–255. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3991(97)00033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 308.Thuman-Commike P A, Greene B, Jakana J, Prasad B V V, King J, Prevelige P E, Jr, Chiu W. Three-dimensional structure of scaffolding containing phage P22 procapsids by electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1996;260:85–98. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 309.Thuman-Commike P A, Greene B, Malinski J A, King J, Chiu W. Role of the scaffolding protein in P22 procapsid size determination suggested by T=4 and T=7 procapsid structures. Biophys J. 1998;74:559–568. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77814-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 310.Trinick J, Cooper J. Concentration of solutes during preparation of aqueous suspensions for cryo-electron microscopy. J Microsc. 1990;159:215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1990.tb04778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 311.Trus B L, Booy F P, Newcomb W W, Brown J C, Homa F L, Thomsen D R, Steven A C. The herpes simplex virus procapsid: structure, conformational changes upon maturation, and roles of the triplex proteins VP19c and VP23 in assembly. J Mol Biol. 1996;263:447–462. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(96)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 312.Trus B L, Homa F L, Booy F P, Newcomb W W, Thompson D R, Cheng N, Brown J C, Steven A C. Herpes simplex virus capsids assembled in insect cells infected with recombinant baculoviruses: structural authenticity and localization of vp26. J Virol. 1995;69:7362–7366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.11.7362-7366.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 313.Trus B L, Newcomb W W, Booy F P, Brown J C, Steven A C. Distinct monoclonal antibodies separately label the hexons or the pentons of herpes simplex virus capsid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:11508–11512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 314.Trus B L, Roden R B S, Greenstone H L, Vrhel M, Schiller J T, Booy F P. Novel structural features of bovine papillomavirus capsid revealed by a three-dimensional reconstruction to 9 Å resolution. Nat Struct Biol. 1997;4:413–420. doi: 10.1038/nsb0597-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 315.Tsao J, Chapman M S, Agbandje M, Keller W, Smith K, Wu H, Luo M, Smith T J, Rossman M G, Compans R W, Parrish C R. The three-dimensional structure of canine parvovirus and its functional implications. Science. 1991;251:1456–1464. doi: 10.1126/science.2006420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 316.Turner J N, Hausner G G J, Parsons D F. An optimized Faraday cage design for electron beam current measurements. J Phys E Sci Instrum. 1975;8:954–957. [Google Scholar]
- 317.Unwin P N T, Henderson R. Molecular structure determination by electron microscopy of unstained crystalline specimens. J Mol Biol. 1975;94:425–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 318.Unwin P N T, Klug A. Electron microscopy of the stacked disc aggregate of tobacco mosaic virus protein. I. Three-dimensional image reconstruction. J Mol Biol. 1974;87:641–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 319.Van Etten J L, Lane L, Gonzales C, Partridge J, Vidaver A. Comparative properties of bacteriophage φ6 and φ6 nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1976;18:652–658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.652-658.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 320.Van Etten J L, Vidaver A K, Koski R K, Semancik J S. RNA polymerase activity associated with bacteriophage φ6. J Virol. 1973;12:464–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.464-471.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 321.van Heel M. Similarity measures between images. Ultramicroscopy. 1987;21:95–100. [Google Scholar]
- 322.van Heel M, Harauz G, Orlova E V. A new generation of the IMAGIC image processing system. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:17–24. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 323.van Oostrum J, Burnett R M. Molecular composition of the adenovirus type 2 virion. J Virol. 1985;56:439–448. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.439-448.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 324.Varghese J N, Laver W G, Colman P M. Structure of the influenza virus glycoprotein antigen neuraminidase at 2.9Å resolution. Nature (London) 1983;303:35–40. doi: 10.1038/303035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 325.Vénien-Bryan C, Fuller S D. The organization of the spike complex of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1994;236:572–583. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 326.Vogel R H, Provencher S W. Three-dimensional reconstruction from electron micrographs of disordered specimens. II. Implementation and results. Ultramicroscopy. 1988;25:223–240. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(88)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 327.Vogel R H, Provencher S W, Bonsdorff C-H, Adrian M, Dubochet J. Envelope structure of Semliki Forest virus reconstructed from cryo-electron micrographs. Nature (London) 1986;320:533–535. doi: 10.1038/320533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 328.Von Seggern D J, Chiu C Y, Fleck S K, Stewart P L, Nemerow G R. A helper-independent adenovirus vector with E1, E3, and fiber deleted: structure and infectivity of fiberless particles. J Virol. 1999;73:1601–1608. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.2.1601-1608.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 329.Wade R H. A brief look at imaging and contrast transfer. Ultramicroscopy. 1992;46:145–156. [Google Scholar]
- 330.Wade R H, Chrétien D. Cryo-electron microscopy of microtubules. J Struct Biol. 1993;110:1–27. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1993.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 331.Wade R H, Frank J. Electron microscope transfer functions for partially coherent axial illumination and chromatic defocus spread. Optik. 1977;49:81–92. [Google Scholar]
- 332.Wade R H, Hewat E A. Cryoelectron microscopy of macromolecular complexes. Biol Cell. 1994;80:211–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1994.tb00932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 333.Wahlberg J M, Bron R, Wilschut J, Garoff H. Membrane fusion of Semliki Forest virus involves homotrimers of the fusion protein. J Virol. 1992;66:7309–7318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7309-7318.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 334.Walker M, Zhang X-Z, Jiang W, Trinick J, White H D. Observation of transient disorder during myosin subfragment-1 binding to actin by stopped-flow fluorescence and millisecond time resolution electron cryomicroscopy: evidence that the start of the crossbridge power stroke in muscle has variable geometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:465–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 335.Wang G, Dryden K A, Coombs K M, Furlong D B, Baker T S. Proceedings of the XIIth International Congress on Electron Microscopy, Seattle, Wash. Vol. 1. San Francisco, Calif: San Francisco Press, Inc.; 1990. Cryo-electron microscopy of reovirus intermediate subviral 1 particles; pp. 276–277. [Google Scholar]
- 335a.Wang, G. J. Personal communication.
- 336.Wang G-J, Porta C, Chen Z, Baker T S, Johnson J E. Identification of a Fab interaction footprint site on an icosahedral virus by cryoelectron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. Nature (London) 1992;355:275–278. doi: 10.1038/355275a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 337.Wang G-J, Porta C, Chen Z, Cheng R H, Baker T S, Johnson J E. The analysis of a spherical virus-Fab interaction by cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. In: Kuo K H, Zhai Z H, editors. Electron microscopy II. 5th Asian Pacific Electron Microscopy Conference. River Edge, N.J: World Scientific Publishing; 1992. pp. 158–159. [Google Scholar]
- 338.Wang J, Yan Y, Garrett T P J, Liu J, Rodgers D W, Garlick R L, Tarr G E, Husain Y, Reinherz E L, Harrison S C. Atomic structure of a fragment of human CD4 containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature (London) 1990;348:411–418. doi: 10.1038/348411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 339.Wery J-P, Reddy V S, Hosur M V, Johnson J E. The refined three-dimensional structure of an insect virus at 2.8 Å resolution. J Mol Biol. 1994;235:565–586. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 340.Wickham T J, Filardo E J, Cheresh D A, Nemerow G R. Integrin αvβ5 selectively promotes adenovirus mediated cell membrane permeabilization. J Cell Biol. 1994;127:257–264. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 341.Wickham T J, Mathias P, Cheresh D A, Nemerow G R. Integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 promote adenovirus internalization but not virus attachment. Cell. 1993;73:309–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90231-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 342.Wickner R B. Viruses of yeasts, fungi and parasitic microorganisms. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, et al., editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed. Vol. 1. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven; 1996. pp. 557–585. [Google Scholar]
- 343.Wikoff W R, Tsai C J, Wang G, Baker T S, Johnson J E. The structure of cucumber mosaic virus: cryoelectron microscopy, X-ray crystallography, and sequence analysis. Virology. 1997;232:91–97. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 344.Wikoff W R, Wang G, Parrish C R, Cheng R H, Strassheim M L, Baker T S, Rossmann M G. The structure of a neutralized virus: canine parvovirus complexed with neutralizing antibody fragment. Structure. 1994;2:595–607. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00062-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 345.Williams R C, Fisher H W. Electron microscopy of tobacco mosaic virus under conditions of minimal beam exposure. J Mol Biol. 1970;52:121–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 346.Williams R C, Richards K E. Capsid structure of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1974;88:547–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90501-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 347.Wilson I A, Skehel J J, Wiley D C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3Å resolution. Nature (London) 1981;289:366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 348.Wingfield P T, Stahl S J, Thomsen D R, Homa F L, Booy F P, Trus B L, Steven A C. Hexon-only binding of VP26 reflects differences between the hexon and penton conformations of VP5, the major capsid protein of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1997;71:8955–8961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.12.8955-8961.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 349.Winkelmann D A, Baker T S, Rayment I. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1 from electron microscopy of sectioned crystals. J Cell Biol. 1991;114:701–713. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 350.Winkler F K, Schutt C E, Harrison S C, Bricogne G. Tomato bushy stunt virus at 5.5 Å resolution. Nature (London) 1977;265:509–513. doi: 10.1038/265509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 351.Yan X, Olson N, Van Etten J, Baker T. Cryo-electron microscopy and image reconstruction of PBCV-1, an algal virus with T=169, icosahedral lattice symmetry. Proc Microsc Microanal. 1998;4:948–949. . Springer-Verlag, New York, N.Y. [Google Scholar]
- 352.Yeager M, Berrimann J A, Baker T S, Bellamy A R. Three-dimensional structure of the rotavirus hemagglutinin VP4 by cryo-electron microscopy and difference map analysis. EMBO J. 1994;13:1011–1018. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06349.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 353.Yeager M, Dryden K A, Olson N H, Greenberg H B, Baker T S. Three-dimensional structure of rhesus rotavirus by cryoelectron microscopy and image reconstruction. J Cell Biol. 1990;110:2133–2144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 354.Zemlin F. Desired features of cryoelectron microscope for the electron crystallography of biological material. Ultramicroscopy. 1992;46:25–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 355.Zemlin F, Beckmann E. Proceedings of the XIIth International Congress on Electron Microscopy, Seattle, Wash. Vol. 1. San Francisco, Calif: San Francisco Press; 1990. High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy of 2-D protein crystals; pp. 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- 356.Zhang H, Zhang J, Yu X, Lu X, Zhang Q, Jakana J, Chen D H, Zhang X, Zhou Z H. Visualization of protein-RNA interactions in cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1999;73:1624–1629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.2.1624-1629.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 357.Zhang W, Olson N, McKinney B, Kuhn R, Baker T. Cryo-electron microscopy of aura viruses. Proc Microsc Microanal. 1998;4:946–947. . Springer-Verlag, New York, N.Y. [Google Scholar]
- 358.Zhao X, Fox J M, Olson N H, Baker T S, Young M J. In vitro assembly of cowpea chlorotic mottle virus from coat protein expressed in Escherichia coli and in vitro-transcribed viral cDNA. Virology. 1995;207:486–494. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 359.Zhou Z H, Chen D H, Jakana J, Rixon F J, Chiu W. Visualization of tegument-capsid interactions and DNA in intact herpes simplex virus type 1 virions. J Virol. 1999;73:3210–3218. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.4.3210-3218.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 360.Zhou Z H, Chiu W. Prospects for using an IVEM with a FEG for imaging macromolecules towards atomic resolution. Ultramicroscopy. 1993;49:407–416. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(93)90246-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 361.Zhou Z H, Chiu W, Haskell K, Spears H J, Jakana J, Rixon F J, Scott L R. Refinement of herpesvirus B-capsid structure on parallel supercomputers. Biophys J. 1998;74:576–588. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77816-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 362.Zhou Z H, He J, Jakana J, Tatman J D, Rixon F J, Chiu W. Assembly of VP26 in herpes simplex virus-1 inferred from structures of wild-type and recombinant capsids. Nat Struct Biol. 1995;2:1026–1030. doi: 10.1038/nsb1195-1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 363.Zhou Z H, Prasad B V V, Jakana J, Rixon F J, Chiu W. Protein subunit structures in the herpes simplex virus A-capsid determined from 400kV spot-scan electron cryomicroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1994;242:456–469. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 364.Zlotnick A. Localization of the C terminus of the assembly domain of hepatitis B capsid protein: implications for morphogenesis and organization of encapsidated RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:9556–9561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.18.9556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 365.Zlotnick A, Cheng N, Conway J F, Booy F P, Steven A C, Stahl S J, Wingfield P T. Dimorphism of hepatitis B virus capsids is strongly influenced by the C-terminus of the capsid protein. Biochemistry. 1996;35:7412–7421. doi: 10.1021/bi9604800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]