Abstract
Continuum elasticity is a powerful tool applicable in a broad range of physical systems and phenomena. Yet, understanding how and on what scales material disorder may lead to the breakdown of continuum elasticity is not fully understood. We show, based on recent theoretical developments and extensive numerical computations, that disordered elastic networks near a critical rigidity transition, such as strain-stiffened fibrous biopolymer networks that are abundant in living systems, reveal an anomalous long-range linear elastic response below a correlation length. This emergent anomalous elasticity, which is non-affine in nature, is shown to feature a qualitatively different multipole expansion structure compared to ordinary continuum elasticity, and a slower spatial decay of perturbations. The potential degree of universality of these results, their implications (e.g. for cell–cell communication through biological extracellular matrices) and open questions are briefly discussed.
Anomalous linear-elastic response calculated in a disordered spring network.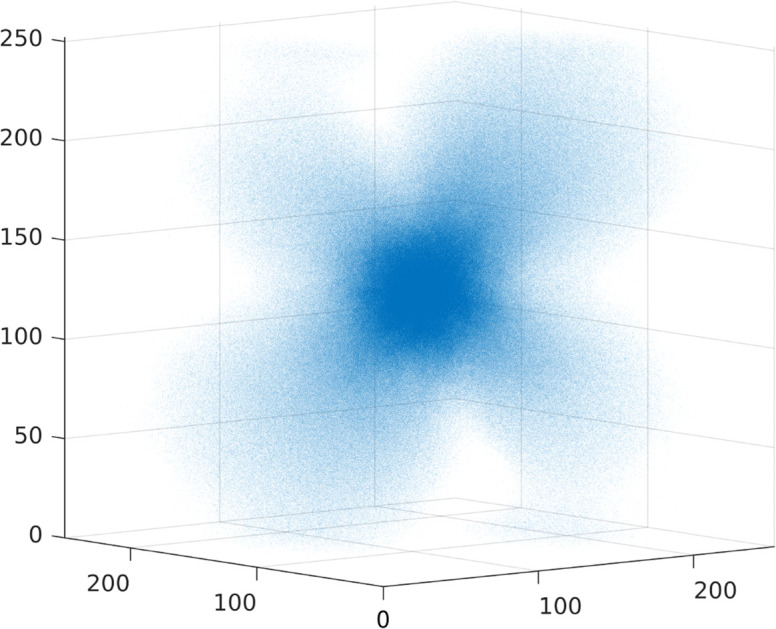
Continuum elasticity is a powerful tool that describes a huge range of phenomena in diverse physical systems, over sufficiently large lengthscales.1 On sufficiently small lengthscales, where the effect of material structure and disorder cannot be coarse-grained, continuum elasticity theory is expected to break down. The crossover between these two regimes is characterized by a correlation length ξ. Indeed, recent work has identified ξ for glassy systems, particle packings and elastic networks,2–8 and demonstrated the validity of continuum elasticity theory for lengthscales r that satisfy r ≫ ξ. In particular, the displacement response to a point force (monopole) perturbation decays as 1/r in three dimensions (3D) for r ≫ ξ, while the displacement response to a force dipole—which is proportional to the spatial gradient of the point force response1—decays as 1/r2. Yet, it remains unclear whether a generic elastic response exists for r ≪ ξ and if so, what form it takes.
For systems undergoing a glass transition upon cooling a melt, ξ has been shown to be of the order of 10 atomic distances and to vary mildly with glass formation history (e.g. the cooling rate).9 Consequently, it is difficult to imagine that a generic elastic response emerges on such a narrow range of scales and one expects that disorder and fluctuations dominate the elastic response for r < ξ in such systems. On the other hand, systems that undergo a critical rigidity transition—such as fibrous biopolymer networks that are abundant in living systems (e.g. collagen, fibrin and basement membrane) and that are known to undergo a dramatic stiffening transition when deformed to large enough strains10—feature a macroscopically large ξ close to the rigidity transition.5,11 In such cases, the regime r ≪ ξ spans many orders of magnitude and might possibly accommodate a generic elastic response. In this brief report, we consider such disordered networks near their rigidity transition and study their elastic response for r ≪ ξ.
We show, based on recent theoretical developments and extensive numerical simulations, that the linear elastic response of disordered networks follows an anomalous power-law for r ≪ ξ, when ξ is sufficiently large, and that the decay is slower compared to the continuum elastic response for r ≫ ξ. Furthermore, we show that the anomalous linear elasticity for r ≪ ξ features a qualitatively different multipole expansion structure compared to continuum elasticity. These results may have significant implications for long-range mechanical interactions between distant cells through biological extracellular matrices,12 inspire the design of heterogeneous structures with unusual properties13 and pose new basic questions, which are briefly discussed.
Before reviewing our results, we emphasize that many previous efforts to explain anomalous elastic responses in various biophysical contexts invoke intrinsically nonlinear constitutive laws, see e.g.14–18 Contrary to those studies, in this work we consider model systems in which an anomalous linear response emerges, as also recently shown to occur in experiments on tensed fibrous hydrogels.19 We finally note that other approaches termed ‘anomalous elasticity’—describing different mechanical phenomena in amorphous materials—were recently put forward.20–22
Main result
We consider isotropic disordered networks whose nodes are connected by relaxed Hookean springs and whose proximity to a rigidity (jamming–unjamming) transition is controlled by the connectivity z (average springs per node), which is close to (yet larger than) the critical Maxwell threshold 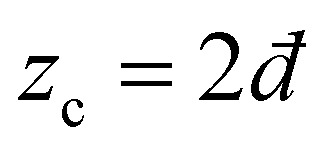 (where
(where 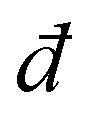 is the spatial dimension). Such disordered elastic networks feature a shear modulus that scales linearly with z − zc23 and
is the spatial dimension). Such disordered elastic networks feature a shear modulus that scales linearly with z − zc23 and
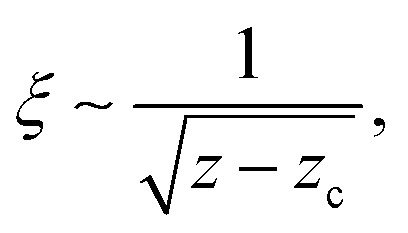 |
1 |
which diverges as z → zc.4,6,24,25 Several additional growing lengthscales were previously identified near the unjamming transition; a comprehensive review of those can be found in ref. 26. Our goal is to understand the elastic response of disordered elastic networks for r ≪ ξ.
The basic quantity we focus on is the displacement response u(r) to a force dipole applied at the origin. The reason we consider the dipole response (and not, for example, the monopole response) is three-fold. First, our results are relevant for fibrous biopolymer networks, which constitute extracellular matrices to which cells adhere in physiological contexts. Adherent cells apply to their surrounding extracellular matrices contractile forces that are predominantly dipolar.27 Second, contact formation between solid particles during dense suspension flows, where the overdamped response is analogous to elastic response, generates a force dipole.28 Finally, in many cases low-energy excitations in disordered systems are of dipolar nature, e.g. the universal nonphononic excitations in glasses.29
Consider then the response function C(r) ∼ 〈u(r)·u(r)〉, where 〈·〉 stands for an angular average, rendering C(r) a function of the distance r alone, and note that u(r) is normalized such that C(r) is dimensionless. Next, one can consider the integral 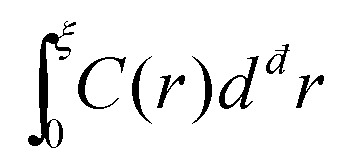 in đ spatial dimensions and ask about its scaling with ξ. If C(r) ∼ exp(−r/ξ) for r < ξ, then one obtains
in đ spatial dimensions and ask about its scaling with ξ. If C(r) ∼ exp(−r/ξ) for r < ξ, then one obtains 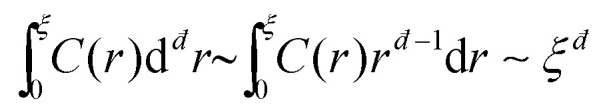 , i.e. the naive scaling with the correlation length ξ. However, recent work6,28,30,31 suggested that in fact
, i.e. the naive scaling with the correlation length ξ. However, recent work6,28,30,31 suggested that in fact
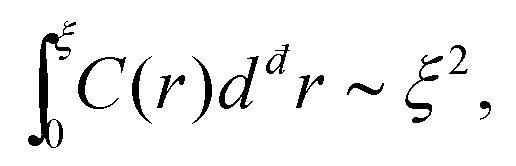 |
2 |
in any dimension đ.
The latter indicates the existence of long-range correlations, i.e. that in fact C(r) ∼ r−2βexp(−r/ξ) for r < ξ, where the exponential exp(−r/ξ) represents the fact that continuum linear elasticity, which features a different power-law, dominates the response for r ≫ ξ. Consistency with eqn (2) requires that β = (đ − 2)/2.28 Consequently, in 3D (đ = 3) we have for the dipolar displacement response
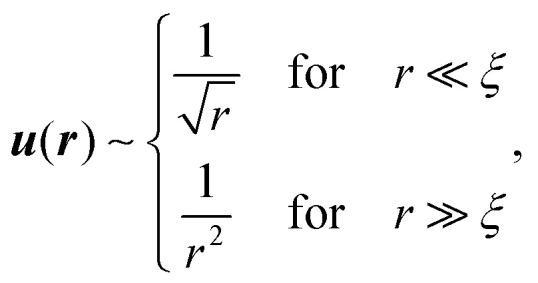 |
3 |
where for r ≫ ξ we just have the continuum elastic dipole response. Note that the dipolar response is predicted in eqn (3) to decay significantly slower for r ≪ ξ than for r ≫ ξ. The same argument leading to eqn (3) has been spelled out in the context of flowing dense suspensions28 (see the “Discussion and Conclusions” section therein, where the overdamped—not the elastic—response has been considered). A similar anomalous elastic response has been recently suggested using a Ginzburg–Landau description of the so-called overlap free-energy in a mean-field approach to glasses.31
To test the prediction in eqn (3), we set out to construct a response function that is slightly different than C(r) (yet, results for C(r) are presented in the ESI†). Our motivation for doing so is that we are not only interested in validating the form of u(r) for r ≪ ξ, but also in gaining insight into the structure of elasticity theory on these scales and the possible differences compared to continuum elasticity. The latter features a multipole expansion in which the nth multipole order involves a spatial gradient ∂ of the (n − 1)th one. Consequently, we construct a response function c(r) (see ESI† for details) that scales as |∂u(r)|2 for r ≫ ξ, and explore whether the corresponding structure persists also for r ≪ ξ. Moreover, |∂u(r)|2 is proportional to the elastic energy density of the dipolar response (to quadratic order), and hence is a directly relevant physical quantity.
The response for r ≪ ξ is expected to be strongly affected by disorder, and hence to be non-affine in nature32 and dominated by fluctuations.3 Consequently, we expect the angular average of spatial derivatives of the displacement vector u(r) to feature vectorial cancellations. As a result, one can hypothesize that c(r) for r ≪ ξ inherits its scaling from |u(r)|2, not from |∂u(r)|2. If true, then c(r) takes the form
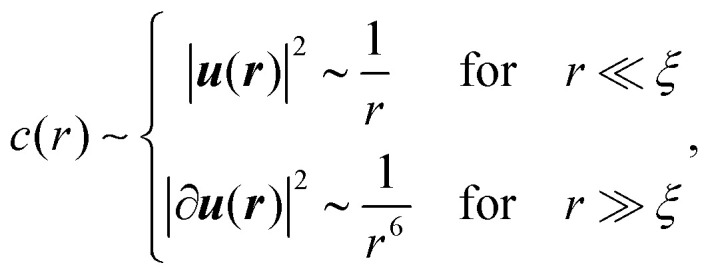 |
4 |
where c(r) ∼ |∂u(r)|2 ∼ r−6 for r ≫ ξ follows (by the construction of c(r)) from u(r) ∼ r−2 of eqn (3). Consequently, eqn (4) suggests that the elastic response for r ≪ ξ is anomalous not just in its power-law decay, as predicted in eqn (3), but also as it might not follow the multipole expansion structure of continuum elasticity.
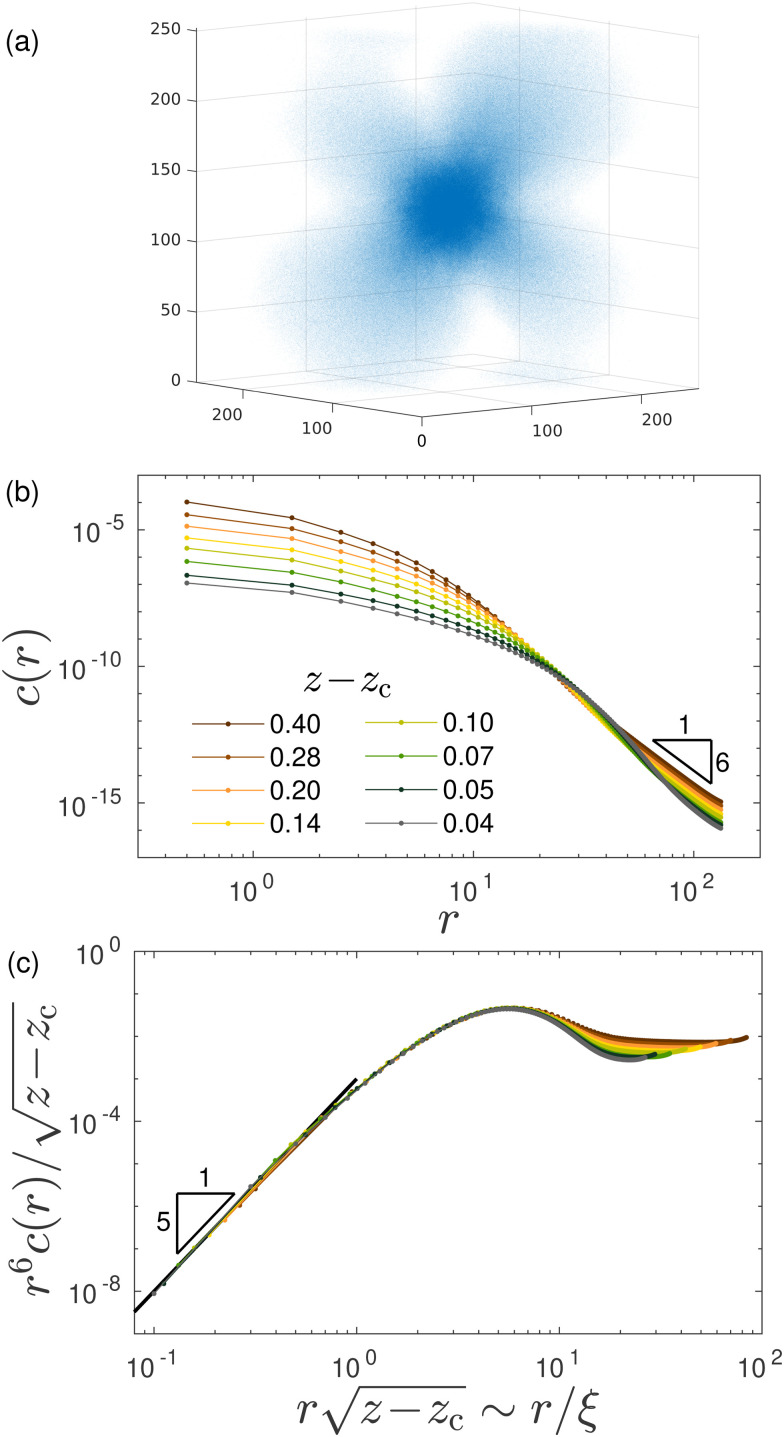
Quantitatively testing the prediction in eqn (4) requires very large networks that span a broad range of lengthscales and feature a sufficiently large correlation length ξ, which is controlled by z − zc. To that aim, we generated disordered elastic networks of 16 million nodes each for various z − zc values (see ESI†), and calculated their dipole response and subsequently c(r) following its network-level definition (see ESI,† where we also show C(r)). A single dipole response is shown in Fig. 1a. We first aim at verifying the continuum elastic response in eqn (4) for sufficiently large scales, i.e. for r ≫ ξ. In Fig. 1b, we plot c(r) for several small values of z − zc (as indicated in the legend). We find that indeed for sufficiently large r, all curves follow c(r) ∼ r−6 (and, as expected, more so the larger z − zc is, corresponding to smaller ξ).
Fig. 1. (a) An example of the dipole displacement response u(r), calculated in a spring network of N = 16 M nodes and connectivity z = 6.04. The inner, denser region corresponds to the anomalous elastic response, while the outer region corresponds to the continuum elastic response (which also exhibits the well-known quadropular symmetry,29 to be contrasted with the much more isotropic anomalous response). (b) Response functions c(r) computed in networks of various connectivities z − zc, as indicated by the legend. For large r, c(r) approaches the r−6 scaling of continuum elasticity (cf.eqn (4)). (c) The same data as in panel (b), but here plotted as 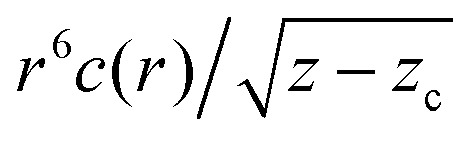 vs.
vs.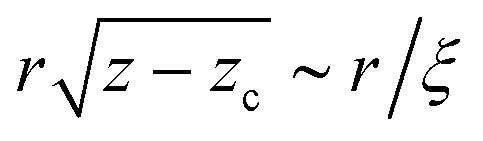 . The re-scaled representation reveals excellent collapse, which confirms that (i) the correlation length follows
. The re-scaled representation reveals excellent collapse, which confirms that (i) the correlation length follows 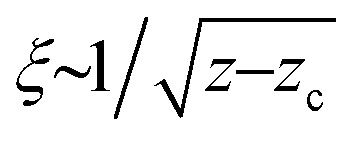 and that (ii) c(r) ∼ 1/r for r ≪ ξ, as hypothesized in eqn (4).
and that (ii) c(r) ∼ 1/r for r ≪ ξ, as hypothesized in eqn (4).
We then set out to test the prediction in eqn (4) for r ≪ ξ, which was our major goal. To that aim, we first note that assuming the spatial dependence of c(r) in this regime (cf.eqn (4)), one can also predict its z − zc dependence. The result reads c(r) ∼ (z − zc)3/r for r ≪ ξ (see ESI†). The latter implies that 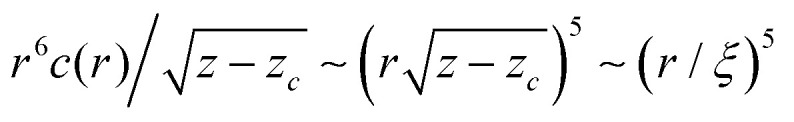 for r ≪ ξ. This prediction is tested in Fig. 1c and is shown to be in excellent quantitative agreement with the direct numerical calculations.
for r ≪ ξ. This prediction is tested in Fig. 1c and is shown to be in excellent quantitative agreement with the direct numerical calculations.
Discussion
The results presented above, based on recent theoretical developments and extensive numerical simulations, provide strong evidence for the existence of anomalous linear elasticity in disordered networks close to their rigidity transition, below a correlation length ξ that is expected to be macroscopically large. The elastic response for r ≪ ξ is anomalous, i.e. different from ordinary continuum elasticity that is valid for r ≫ ξ, in at least two major respects; first, the spatial decay of perturbations is slower (i.e. characterized by a smaller inverse power-law exponent) compared to continuum elasticity. Second, the elastic response for r ≪ ξ is highly non-affine and hence does not appear to follow the ordinary multipole expansion structure of continuum elasticity, where a higher order multipole response is obtained by spatial gradients of a lower order one.
Recent experiments on tensed fibrin hydrogels19 show that the linear response33 to a point force is anomalous, decaying as 1/rβ away from the perturbation—with β measurably smaller than 1—, instead of the 1/r decay expected from continuum linear elasticity. These results indicate that the mechanism generating anomalous elastic responses might not be the intrinsic nonlinearity of the constituent elements, as invoked in several previous works,14–18 but rather the physics discussed here. In this case, anomalous vibrational modes23—and not long wavelength (wave-like) modes—dominate the response at distances r < ξ.
The anomalous linear elasticity discussed here may have significant implications for various systems such as flowing dense suspensions5 (where the overdamped response is analogous to the elastic response) and strain-stiffened fibrous biopolymer networks that are abundant in living systems,10,11e.g. as extracellular matrices to which cells adhere and apply contractile forces.27 In the latter context, our results may imply that for r ≪ ξ distant cells can mechanically communicate over significantly longer distances12 (compared to continuum elasticity) using their active contractility, a capability that might be important in various physiological processes (e.g. tissue development).
Our results also pose new questions and open the way for additional research directions. First, we focused here on the response to force dipoles, which is well motivated from the physical and biological perspectives, as discussed above. Yet, force monopoles (point forces) are of interest as well, both because they are of practical relevance and because of the unusual multipole structure of the anomalous elastic response we discussed. In particular, in view of our findings, one can speculate that the monopole response is identical to the dipole response scaling-wise, which should be tested in future work. Second, our analysis considered the amplitude squared of the response, i.e. |u(r)|2. It would be interesting to understand whether the same scaling remains valid for the average of the vectorial response itself, i.e.u(r), which is obviously subjected to vectorial cancellations due to the non-affine nature of the response, see for example the results of ref. 3.
Finally, the degree of universality of our results should be also tested in future work, e.g. in different disordered materials. In particular, we speculate that the same anomalous decay observed here below ξ also characterizes the universal spatial structure of soft quasilocalized excitations that generically emerge in structural glasses,29 and feature spatial structures that closely resemble responses to force dipoles.34
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Note added in proof
We became aware of ref. 36, where a continuum formalism predicts a non-affinity correlation function that features a spatial decay similar to that of C(r). Future work should clarify the possible relevance of the continuum formalism of ref. 36 to our findings.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Zylberg for developing and implementing the bond-dilution algorithm used in this work. E. L. acknowledges support from the NWO (Vidi grant no. 680-47-554/3259). E. B. acknowledges support from the Ben May Center for Chemical Theory and Computation and the Harold Perlman Family.
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2sm01253g
References
- Landau L. D. and Lifshitz E. M., Theory of elasticity, Butterworth-Heinemann, London, 1995 [Google Scholar]
- Head D. A. Levine A. J. MacKintosh F. C. Mechanical response of semiflexible networks to localized perturbations. Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys. 2005;72:061914. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.061914. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.061914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düring G. Lerner E. Wyart M. Phonon gap and localization lengths in floppy materials. Soft Matter. 2013;9:146–154. doi: 10.1039/C2SM25878A. doi: 10.1039/C2SM25878A. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. DeGiuli E. During G. Wyart M. Breakdown of continuum elasticity in amorphous solids. Soft Matter. 2014;10:5085–5092. doi: 10.1039/C4SM00311J. doi: 10.1039/C4SM00311J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düring G. Lerner E. Wyart M. Length scales and self-organization in dense suspension flows. Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys. 2014;89:022305. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.89.022305. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.89.022305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada M. Mizuno H. Wyart M. Ikeda A. Spatial structure of quasilocalized vibrations in nearly jammed amorphous solids. Phys. Rev. E. 2018;98:060901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.98.060901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.98.060901. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- González-López K. Shivam M. Zheng Y. Ciamarra M. P. Lerner E. Mechanical disorder of sticky-sphere glasses. I. Effect of attractive interactions. Phys. Rev. E. 2021;103:022605. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.103.022605. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.103.022605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainone C. Bouchbinder E. Lerner E. Pinching a glass reveals key properties of its soft spots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2020;117(10):5228–5234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1919958117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; . Available from: https://www.pnas.org/content/117/10/5228
- See refs 7, 8 for examples. We note that some glass-forming models—e.g. the model studied in ref. 35—, might feature a larger correlation length
- Sharma A. Licup A. J. Jansen K. A. Rens R. Sheinman M. Koenderink G. H. et al., Strain-controlled criticality governs the nonlinear mechanics of fibre networks. Nat. Phys. 2016;12(6):584–587. doi: 10.1038/nphys3628. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rens R. Villarroel C. Düring G. Lerner E. Micromechanical theory of strain stiffening of biopolymer networks. Phys. Rev. E. 2018;98:062411. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.98.062411. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.98.062411. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Alisafaei F. Chen X. Leahy T. Janmey P. A. Shenoy V. B. Long-range mechanical signaling in biological systems. Soft Matter. 2021;17:241–253. doi: 10.1039/D0SM01442G. doi: 10.1039/D0SM01442G. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acuna D. Gutiérrez F. Silva R. Palza H. Nunez A. S. Düring G. A three step recipe for designing auxetic materials on demand. Commun. Phys. 2022;5(1):113. doi: 10.1038/s42005-022-00876-5. doi: 10.1038/s42005-022-00876-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shokef Y. Safran S. A. Scaling Laws for the Response of Nonlinear Elastic Media with Implications for Cell Mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012;108:178103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.178103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.178103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. Abhilash A. S. Chen C. Wells R. Shenoy V. Long-Range Force Transmission in Fibrous Matrices Enabled by Tension-Driven Alignment of Fibers. Biophys. J. 2014;107(11):2592–2603. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.09.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; . Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006349514011096
- Xu X. Safran S. A. Nonlinearities of biopolymer gels increase the range of force transmission. Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys. 2015;92:032728. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.92.032728. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.92.032728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirote C. Shokef Y. Mean-field interactions between living cells in linear and nonlinear elastic matrices. Phys. Rev. E. 2021;104:024411. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.104.024411. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.104.024411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist F., Saggiorato G. and Lenz M., Generic Stress Rectification in Nonlinear Elastic Media, arXiv, 2022, preprint, arXiv:220604444. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04444 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Goren S. Levin M. Brand G. Lesman A. Sorkin R. Probing Local Force Propagation in Tensed Fibrous Gels. Small. 2022:2202573. doi: 10.1002/smll.202202573. doi: 10.1002/smll.202202573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charan H. and Moshe M., Procaccia I. Anomalous Elasticity and Emergent Dipole Screening in Three-Dimensional Amorphous Solids, arXiv, 2022, preprint, arXiv:220905311. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.05311 [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kumar A. Moshe M. Procaccia I. Singh M. Anomalous elasticity in classical glass formers. Phys. Rev. E. 2022;106:015001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.106.015001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.106.015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lematre A. Mondal C. Moshe M. Procaccia I. Roy S. Screiber-Re’em K. Anomalous elasticity and plastic screening in amorphous solids. Phys. Rev. E. 2021;104:024904. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.104.024904. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.104.024904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyart M. On the rigidity of amorphous solids. Ann Phys Fr. 2005;30(3):1–96. doi: 10.1051/anphys:2006003. doi: 10.1051/anphys:2006003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Silbert L. E. Liu A. J. Nagel S. R. Vibrations and Diverging Length Scales Near the Unjamming Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005;95:098301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.098301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.098301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenholz S. S. Goodrich C. P. Kogan O. Liu A. J. Nagel S. R. Stability of jammed packings II: the transverse length scale. Soft Matter. 2013;9:11000–11006. doi: 10.1039/C3SM51096D. doi: 10.1039/C3SM51096D. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. Quasilocalized states of self stress in packing-derived networks. Eur. Phys. J. E. 2018;41(8):93. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2018-11705-9. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2018-11705-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz U. S. Safran S. A. Physics of adherent cells. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2013;85:1327–1381. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.85.1327. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.85.1327. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Düring G. Lerner E. Wyart M. Effect of particle collisions in dense suspension flows. Phys. Rev. E. 2016;94:022601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.94.022601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.94.022601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. Bouchbinder E. Low-energy quasilocalized excitations in structural glasses. J. Chem. Phys. 2021;155(20):200901. doi: 10.1063/5.0069477. doi: 10.1063/5.0069477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan L. DeGiuli E. Wyart M. On variational arguments for vibrational modes near jamming. Europhys. Lett. 2016;114(2):26003. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/114/26003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; . Available from: http://stacks.iop.org/0295-5075/114/i=2/a=26003
- Ji W. de Geus T. W. J. Agoritsas E. Wyart M. Mean-field description for the architecture of low-energy excitations in glasses. Phys. Rev. E. 2022;105:044601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.105.044601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.105.044601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenbroek W. G. Zeravcic Z. van Saarloos W. van Hecke M. Non-affine response: Jammed packings vs. spring networks. Europhys. Lett. 2009;87(3):34004. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/87/34004. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/87/34004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- The linearity of the response is highlighted in ref. 19 and is explicitly demonstrated in the Supporting Information therein, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/action/downloadSupplement?doi=10.1002%2Fsmll.202202573&file=smll202202573-sup-0001-SuppMat.pdf
- Lerner E. Bouchbinder E. A characteristic energy scale in glasses. J. Chem. Phys. 2018;148(21):214502. doi: 10.1063/1.5024776. doi: 10.1063/1.5024776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaître A. Stress hyperuniformity and transient oscillatory-exponential correlation decay as signatures of strength vs. fragility in glasses. J. Chem. Phys. 2021;155(19):194501. doi: 10.1063/5.0065613. doi: 10.1063/5.0065613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDonna B. A. Lubensky T. C. Nonaffine correlations in random elastic media. Phys. Rev. E. 2005;72:066619. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.066619. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.066619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.