Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has become the reference technique for removal of superficial colorectal neoplasia; however, the R0 resection rate for T1 cancers harboring focal invasive patterns is far from perfect on the vertical margin 1 . Recently, endoscopic intermuscular dissection (EID) has been described as a method of achieving free vertical margins by dissecting more deeply, between the two muscular layers 2 . This approach, which is feasible in the rectum where the two layers are thick, has two benefits: 1) maintaining the rectal longitudinal muscle without perforation and cell seeding, and 2) dissecting more deeply to achieve clear free vertical margins when the deep submucosa is invaded.
To facilitate intermuscular space exposure, as described in ESD, traction seems useful 3 . An adaptive traction device that is capable of being tightened to increase traction during the late stages of the procedure (A-TRACT-2 + 2; Hospices civils de Lyon, France) could be useful in these situations ( Fig. 1 , Video 1 ) 4 5 .
Fig. 1.
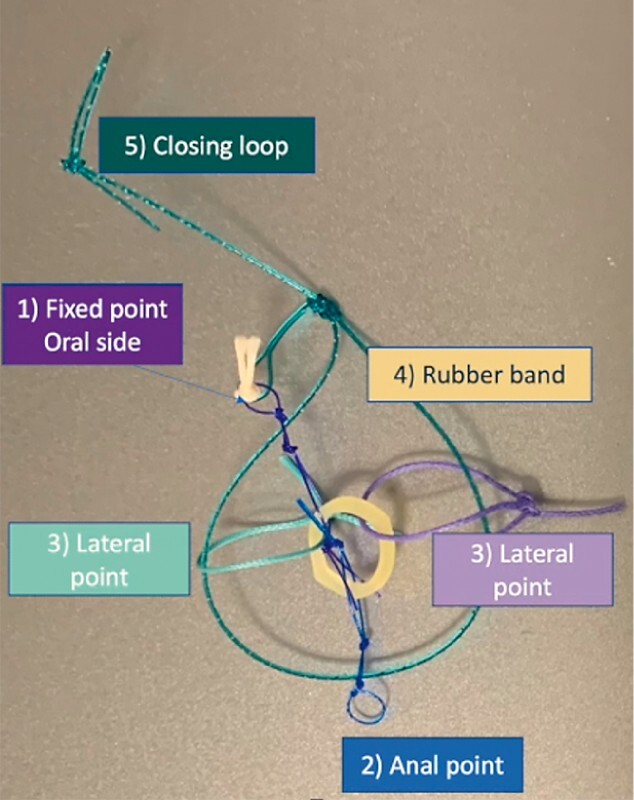
The different components of the A-TRACT device. 1 = fixed point attached to the oral side; 2 = second blue loop linked to the tightening band; 3 = lateral free loops to obtain traction at four cardinal points; 4 = rubber band attached to the opposite wall; 5 = closure loop with notched wire.
Video 1 Sequence of endoscopic intermuscular dissection using A-TRACT 2 + 2 (Hospices civils de Lyon, France).
We report the case of a 73-year-old patient with a 1.5 cm depressed tumor in the middle rectum with deep invasive patterns. After circumferential incision, the device was fixed with clips at points on the oral and anal edges. The rubber band was then caught and fixed to the opposite wall. The circular muscle layer was then cut to reach the intermuscular space and dissection progressed, injecting this space with the tip of the knife. During the procedure, more traction was needed on the muscle and the additional loop of the device was employed to apply traction directly to the circular layer. When traction began to decline, the device was tightened. The intermuscular exposure appeared more parallel to the scope and was ideal for the remaining procedure, leading to an R0 resection without adverse events. The final histology was a deep submucosal invasive adenocarcinoma (2400 microns) with significant budding. No adverse events occurred.
In conclusion, this device allowed adaptive traction that was useful during intermuscular dissection for T1 colorectal cancers.
Endoscopy_UCTN_Code_TTT_1AQ_2AD
Footnotes
Competing interests A patent for the device has been requested by our institution.
Endoscopy E-Videos : https://eref.thieme.de/e-videos .
Endoscopy E-Videos is an open access online section, reporting on interesting cases and new techniques in gastroenterological endoscopy. All papers include a high quality video and all contributions are freely accessible online. Processing charges apply (currently EUR 375), discounts and wavers acc. to HINARI are available. This section has its own submission website at https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/e-videos
References
- 1.Patenotte A, Yzet C, Wallenhorst T et al. Diagnostic endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal lesions with suspected deep invasion. Endoscopy. 2022 doi: 10.1055/a-1866-8080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moons L MG, Bastiaansen B AJ, Richir M C et al. Endoscopic intermuscular dissection for deep submucosal invasive cancer in the rectum: a new endoscopic approach. Endoscopy. 2022;54:993–998. doi: 10.1055/a-1748-8573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bordillon P, Pioche M, Wallenhorst T et al. Double-clip traction for colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection: a multicenter study of 599 consecutive cases (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;94:333–343. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Grimaldi J, Masgnaux L J, Rivory J et al. Multipolar traction with adjustable force increases procedure speed during endoscopic submucosal dissection: the A-TRACT-4 traction device. Endoscopy. 2022;54:E1013–E1014. doi: 10.1055/a-1904-7666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Masgnaux L J, Grimaldi J, Legros R et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in the colon using a novel adjustable traction device: A-TRACT-2. Endoscopy. 2022;54:E988–E989. doi: 10.1055/a-1888-3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


