Abstract
Labeled β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) analogues have been critical for uncovering new biochemical connections and quantitating enzymatic activity. They function as tracers for enzymology, flux analyses, and in situ measurements. Nevertheless, there is limited availability of specific types of analogues, especially radiolabeled NAD isotopologues. Here, we describe an improved enzymatic synthesis reaction for 32P- NAD+ with a yield of 98% ± 1%, using lowered concentrations of reactants and standard equipment. This represents the highest reported yield for the enzymatic synthesis of NAD+ to date. With the high yield we were able to directly use the reaction product to generate derivatives, such as 32P-NADP. The high-yield enzymatic synthesis is versatile for a broad variety of labels and NAD derivatives. Its advantages include lowered concentrations of reactants, providing sufficient amounts of product for downstream applications, and minimizing intermediate purification steps.
Keywords: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl transferase, inorganic pyrophosphatase, thin layer chromatography, oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide kinase, radiolabeled nucleotides
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides (NAD) are conserved coenzymes used by cells to facilitate reversible oxidoreductive reactions via transfer of hydride ions. In this scenario, the relative levels of oxidized dinucleotide (NAD+, NADP) compared to their reduced counterparts (NADH, NADPH) will influence the capacity for either oxidative or reductive reactions to occur. Distinctly, oxidized NAD+ and its derivatives (e.g., ADPR, cADPR, NAADP) have additional roles as signaling molecules and can regulate enzymatic activities as required cosubstrates or ligands. In this second scenario, the concentration of available nucleotide can limit signal transduction. These distinct usages sometimes converge, and this has been shown as a mechanism to coordinate regulation of intracellular pathways during adipogenesis.1,2 Given the complexity of processes that depend on NAD metabolites, the concentrations of these molecules are tightly regulated inside and outside of cells, and its levels are compartmentalized subcellularly.1,3
Molecular analogues of NAD have been instrumental in advancing our understanding of this complex biology. For example, isotopologues with multiple labels have been used to quantitate mass spectrometry measurements, to uncover regulation of flux, and to obtain enzymatic rates.4−8 By measuring specifically labeled NAD pools amid complex mixtures, researchers can quantitatively determine alterations in flux and concentrations. In the example of the mammalian mitochondrial NAD+ transporter,9−11 kinetic rate measurements of NAD+ uptake in intact and respiring mitochondria were made feasible with radiolabeled NAD+, and investigation into the roles of mitochondrial NAD+ in cells was feasible with heavy-atom labeled NAD+.9−12 Labeled NAD+ molecules were distinguishable from the unlabeled resident pool, allowing small additions to be measured over the course of the experiments; this resolution could not have been achieved by simply measuring final mitochondrial NAD+ amounts. Moreover, specific advantages of isotopologues include that they are structurally identical and recognized by endogenous enzymes as cognate substrates. Despite the broad utility of radiolabeled NAD isotopologues, the availability of these reagents is limited.
To address this, we sought to improve the yield of the enzymatic synthesis of NAD+ to facilitate the ability for individual laboratories to obtain specifically labeled NAD and NAD derivatives.13−16 We surmised that a higher yield reaction would be amenable for labeling experiments and for generating labeled NAD derivatives. Moreover, we sought a high-yield reaction that could be performed using standard equipment as a useful and versatile resource for many laboratories.
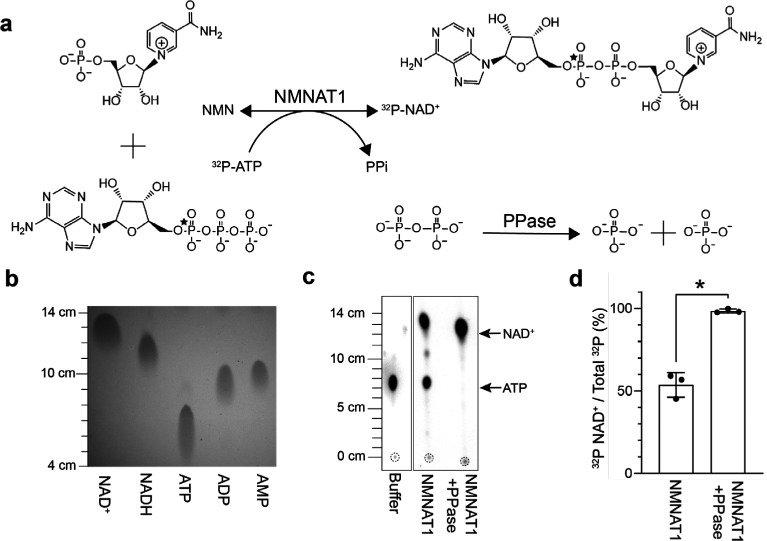
We considered an enzymatic strategy described by multiple groups, which relies on recombinant NMN adenylyl transferases (NMNAT enzymes) and ATP to generate β-NAD from either β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) or β-nicotinamide mononucleotide hydride (NMNH).13,14 This strategy had been adopted into a two-step synthesis to produce NAD+ derivatives such as nicotinamide 4′-thioribose NAD+ (S-NAD+) at 70% yield, starting from modified 4-thionicotinamide riboside.15 We reasoned that the synthesis of labeled NAD analogues could be simplified into a single-step process by including radiolabeled analogues directly at the adenylyl transferase step (Figure 1a). We also wanted to test the consequence of including inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPase) in the reaction to degrade the inorganic pyrophosphate (iPP) byproduct, with the idea that this could drive the forward reaction for a higher final yield (Figure 1a). This idea was supported by the addition of PPase in the combined reaction that improved the yield of NAD+ by ∼10%.16 However, whether PPase improved the adenylation step was never directly tested, and if Mg2+ is ever limiting, a formal possibility is that PPase could cleave ATP and limit the reaction by depleting ATP instead of promoting the forward reaction. Thus, we directly tested whether the addition of PPase improved the adenylation reaction of NMN in vitro and whether this could be used to incorporate a 32P label onto NAD+. An additional advantage is that the addition of PPase could eliminate the need for using initial reactants at high concentrations, which greatly facilitates the ability to use radiolabeled reactants. For comparison, the combined enzymatic synthesis reactions used millimolar concentrations of reactants.15,16 Notably, by simply adjusting the type of labeling on ATP or NMN, or using NMN derivatives (e.g., NMNH or nicotinic acid mononucleotide), this enzymatic synthesis could produce a variety of NAD-related nucleotides, highlighting the potential versatility of the approach. To monitor the reaction and to quantitate the yield, we used α-32P-ATP (3000 Ci/mmol, 10 mCi/mL) that had a single label at its α-phosphate, thus quantitation of 32P in the product would directly correlate with product formation.
Figure 1.
PPase improved the yield of the NMN adenylyl transferase reaction in vitro. (a) Proposed reaction for the enzymatic synthesis of 32P-NAD+ from 32P-ATP. Position of the 32P label is indicated by a star. (b) NAD+, NADH, ATP, ADP, and AMP standards (>95% purity, 5 μL of 50 μM stocks) were resolved with thin layer chromatography (TLC) using PEI cellulose F plates and imaged following excitation at 254 nm. (c) Representative images of 1 μL from the enzymatic reactions being resolved with TLC and quantitated following exposure with a phosphorimaging screen. Leading edges were measured from the origins (dashed circles). (d) Calculated yields of 32P-NAD+ (mean ± SD, n = 3, Student’s t test, *p < 0.01).
We used thin layer chromatography (TLC) to distinguish the synthesized products from its reactants.17 Briefly, cellulose plates were initially resolved to 5 cm above the origin using Milli-Q water in a lidded glass tank and air-dried. Plates were then resolved with 1.4 M LiCl to 15 cm above the origin.17 We quantitated the migration of known nucleotide standards and used this reference to identify 32P-labeled species in our reaction based on their migration patterns. To visualize the standards, we used PEI cellulose F plates with an incorporated fluorescent indicator for visualization of unlabeled molecules following 254 nm excitation (Figure 1b).
In parallel reactions, we combined 3 μM α-32P-ATP (≤120 μCi), 50 μM ATP, 50 μM NMN, and 5 μM NMNAT1 in a final buffer of 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 12 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM DTT. One unit of PPase was added to one of the reactions and omitted from the other. The reactions were incubated at 22 °C for 2 h, and 1 μL from each reaction was analyzed with TLC. To image the 32P-nucleotides, dried plates were wrapped in clear clingwrap and exposed to a phosphorimager screen for 3 min. Images were captured using a Typhoon scanner and individual spots were analyzed with ImageJ for distance of migration from origin and for their integrated intensities above background using the built-in gel analyzer feature. Integrated intensities for each spot were calculated as a percentage of the total intensity in the sample. The signal from 32P-NAD+ divided by the total 32P signal per lane was used to calculate the yield of the reaction.
We observed that addition of PPase significantly improved the yield of the enzymatic adenylation reaction. Without PPase, we observed a mean yield of 54 ± 7% and substantial amounts of unconverted 32P-ATP, indicating that the reaction was at equilibrium (Figure 1c,d). This was consistent with previously reported yields of ∼70% in a combined reaction.15 In contrast, the addition of PPase appeared to prevent the main reaction from reaching equilibrium and resulted in a 98 ± 1% incorporation of the 32P signal into NAD+, corresponding to a yield of approximately 49 μM 32P-traced NAD+ (2.9 μM 32P-NAD+ and 46 μM unlabeled NAD+) (Figure 1c,d). Expected to be also remaining in the mixture would be ∼4 μM 32P-traced ATP (240 nM 32P-ATP and 3.8 μM unlabeled ATP), ∼1 μM NMN, as well as NMNAT1 and PPase enzymes. To stop the reaction, the tube was flash frozen with liquid nitrogen and stored at −20 °C.
In the reactions that did not include PPase, we observed 32P reaction contaminants that migrated ∼10.5 cm and that only appeared when coincubated with NMNAT1 (Figure 1c). Although this migration pattern corresponds to 32P-ADP/AMP, it is unclear how these contaminants originated. One possibility is that the NMNAT1 preparation resulted in a slower side-reaction with the residual 32P-ATP. With the addition of PPase, appearance of the 32P contaminants was lessened.
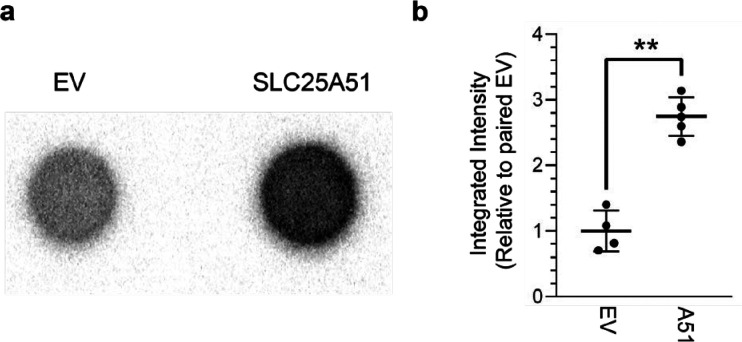
To further assess the synthesis of 32P-NAD+, we used a freshly thawed fraction of the reaction product to test whether it could be imported by human SLC25A51, a mitochondrial transporter that preferentially imports oxidized NAD+ over reduced NADH, nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), and nicotinamide (Nam) at physiological concentrations.9,10 In previous work, we showed that ectopic expression of human SLC25A51 complemented the selective import of NAD+ in isolated mitochondria from S. cerevisiae that were genetically ablated for their ability to import NAD+ (DKO mitochondria, Δndt1 Δndt2 BY4727).9 In vitro, we observed significantly increased uptake of the 32P-labeled product by human SLC25A51-expressing DKO mitochondria compared to mitochondria expressing the empty vector control (Figure 2 and Supporting Information). Together with the TLC results, the data indicated that 32P-NAD+ was the dominant labeled species in the reaction. NMR analyses of parallel unlabeled reactions supported the conclusion that NAD+ was the dominant product and that addition of PPase promoted increased yields of NAD+ (Figure S1).
Figure 2.
Selective uptake of radiolabeled reaction product by SLC25A51. (a) Representative 32P dot blots of in vitro NAD+ import assays from DKO mitochondria that either expressed empty vector (EV) or a human mitochondrial NAD+ transporter (SLC25A51). (b) Relative mean intensities following uptake of 32P product between paired EV and SLC25A51 conditions (mean ± SD, n = 4–5, Student’s t test, **p < 0.001).
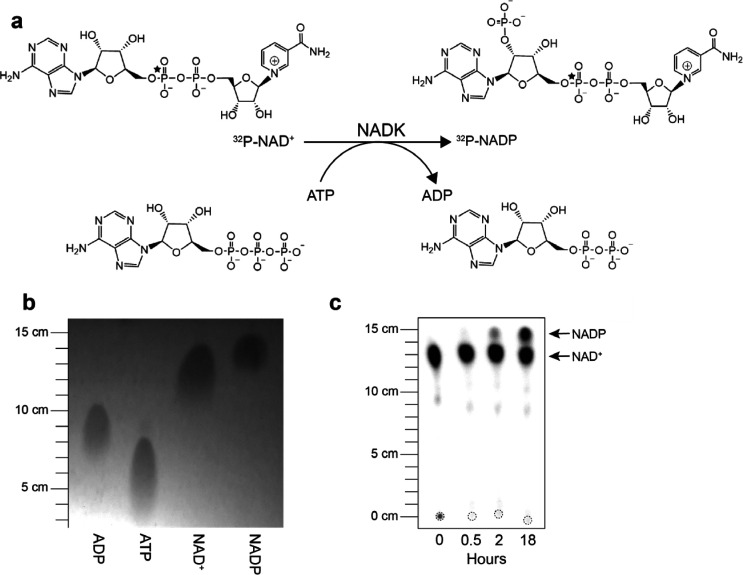
The high-yield adenylation reaction created an opportunity to directly use the product for generation of radiolabeled 32P-NAD derivatives. As proof-of-principle, we sought to generate 32P-NADP from 32P-NAD+ using recombinant human NAD kinase (hNADK) and ATP (Figure 3a).18,19 In a 20 μL reaction, we combined 3 μL of the reaction product (∼440 nM 32P-NAD+ final, ≤18 μCi), 50 μM NAD+, 100 μM ATP, 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 100 mM NaCl, and 5 mM MgCl2 with 5 μM hNADK. The reaction was incubated at 22 °C for 16 h, and 1 μL of the reaction was analyzed by TLC. The generated reference image (Figure 3b) indicated that NADP migrates farther than NAD+ under the described TLC conditions. We observed that approximately 22 and 55% of the 32P-NAD+ is converted to 32P-NADP within 2 and 18 h, respectively (Figure 3c). The data provided a proof-of-principle that the high-yield adenylation reaction generated by addition of PPase resulted in a sufficiently uniform α-32P product for the direct synthesis of labeled derivative α-32P-NADP with a minimization of side-reactions.
Figure 3.
Direct synthesis of labeled NADP from the 32P-NAD+ reaction product. (a) Proposed reaction for the synthesis of labeled NADP from 32P-NAD+. Position of the 32P label is indicated by a star. (b) ADP, ATP, NAD+, and NADP standards were resolved with TLC using PEI cellulose F plates and imaged following excitation at 254 nm. (c) Samples (1 μL) from the NADK enzymatic reaction were obtained at indicated time points, resolved with TLC, and radioactivity was detected with phosphorimaging. Leading edges were measured from respective origins (dashed circles).
In cases where a higher purity radiolabeled product is required, any resolvable 32P-traced nucleotide can be recovered following TLC. To demonstrate the feasibility of this technique, we performed an enzymatic synthesis without PPase and observed the expected product mixture including 32P-NAD+ and unreacted 32P-ATP (Figure S2a). We used a clean razor blade to isolate the cellulose from the TLC plate corresponding to 32P-traced NAD+ and extracted the nucleotide by filtration (Supporting Information). The recovered material was analyzed by TLC and predominantly contained the desired 32P-NAD+ (Figure S2a). This material could then be used in SLC25A51-dependent uptake assays, as described above (Figure S2b).
In conclusion, we have shown that addition of PPase in the NMN enzymatic adenylation reaction resulted in high-yield generation of NAD+, and this could be an effective method for generating labeled analogues. We expect that this approach could be expandable to work with other types of labels and placed in different positions. This high-yield reaction required lowered concentrations of reactants compared to previously published approaches.13−16 Thus, there is opportunity for a broad range of reactants and more diverse set of possible products. The NMNAT enzymes can utilize NAMN or NMNH as substrates, potentially producing labeled NAAD or NADH products.14,20 Additionally, the labeled NAD+ product can be directly used to generate labeled derivatives with an additional enzymatic reaction, such as NAADP, NADP(H), NADH or ADPR, without further processing. Methods for creating NADH by alcohol dehydrogenase and ADPR by porcine brain NAD+ nucleosidase are described in Feldmann et al.16 NAADP can be produced from NADP in vitro using CD38 at an acidic pH and high concentrations of NA.21 Notably the addition of PPase may not improve every adenylation reaction, highlighting the need to have empirically confirmed this approach. When attempting to test PPase with FAD synthetase (FADS) to recreate 32P-FAD from FMN and 32P-ATP, we observed that addition of PPase created an aberrant 32P product that migrated to ∼10.5 cm, and could represent AMP, ADP or cyclic-FMN (Figure S3).22 The appearance of a PPase-dependent aberrant product indicated that its utility may depend on the specific reaction.
Together, we have tested and described an approach that is versatile and easily adaptable for the improved enzymatic synthesis of labeled nicotinamide dinucleotides and derivatives. It has the potential to be expanded to include many other analogues and adenylated products with specific labels.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Marie Migaud at the University of South Alabama for guiding us to consider the NMNAT1 enzymatic reaction, advice, and discussion. We thank Prof. Adrian Keatinge-Clay and Dr. Takeshi Miyazawa at the University of Texas at Austin for guidance performing and analyzing the NMR experiments. Research in the laboratory was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health (DP2 GM126897), the PEW Charitable Trusts, and Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (RP210079).
Supporting Information Available
The Supporting Information is available free of charge at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.2c00065.
Figures S1–S3, corresponding figure captions, a detailed experimental methods section, and an extended reference section (PDF)
Accession Codes
Author Contributions
J.E., S.G., and X.A.C. conceptualized the project and contributed to experimental design. J.E. performed all experiments. The manuscript was written with contributions from all authors, and all authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. CRediT: Jared Eller conceptualization (equal), data curation (lead), writing-original draft (lead), writing-review & editing (equal); Shivansh Goyal conceptualization (equal), writing-review & editing (equal); Xiaolu Ang Cambronne conceptualization (equal), funding acquisition (lead), supervision (lead), writing-original draft (equal), writing-review & editing (equal).
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- Cambronne X. A.; Kraus W. L. Location, Location, Location: Compartmentalization of NAD+ Synthesis and Functions in Mammalian Cells. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45 (10), 858–873. 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.05.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu K. W.; Nandu T.; Kim J.; Challa S.; DeBerardinis R. J.; Kraus W. L. Metabolic regulation of transcription through compartmentalized NAD+ biosynthesis. Science 2018, 360 (6389), 5780. 10.1126/science.aan5780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strømland Ø.; Diab J.; Ferrario E.; Sverkeli L. J.; Ziegler M. The balance between NAD+ biosynthesis and consumption in ageing. Mech Ageing Dev. 2021, 199, 111569. 10.1016/j.mad.2021.111569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A.; Stojković V.; Kohen A. Synthesis of radiolabeled nicotinamide cofactors from labeled pyridines: versatile probes for enzyme kinetics. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 430 (2), 123–9. 10.1016/j.ab.2012.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubrich B. A.; Ramesha C.; Swinney D. C. Development of a Bioluminescent High-Throughput Screening Assay for Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Adenylyltransferase (NMNAT). SLAS Discovery 2020, 25 (1), 33–42. 10.1177/2472555219879644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trammell S. A.; Brenner C. Targeted, LCMS-based Metabolomics for Quantitative Measurement of NAD(+) Metabolites. Comput. Struct Biotechnol J. 2013, 4, e201301012. 10.5936/csbj.201301012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langelier M. F.; Zandarashvili L.; Aguiar P. M.; Black B. E.; Pascal J. M. NAD+ analog reveals PARP-1 substrate-blocking mechanism and allosteric communication from catalytic center to DNA-binding domains. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9 (1), 844. 10.1038/s41467-018-03234-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L.; Su X.; Quinn W. J. III; Hui S.; Krukenberg K.; Frederick D. W.; Redpath P.; Zhan L.; Chellappa K.; White E.; Migaud M.; Mitchison T. J.; Baur J. A.; Rabinowitz J. D. Quantitative Analysis of NAD Synthesis-Breakdown Fluxes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27 (5), 1067–1080.e5. 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.03.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luongo T. S.; Eller J. M.; Lu M. J.; Niere M.; Raith F.; Perry C.; Bornstein M. R.; Oliphint P.; Wang L.; McReynolds M. R.; Migaud M. E.; Rabinowitz J. D.; Johnson F. B.; Johnsson K.; Ziegler M.; Cambronne X. A.; Baur J. A. SLC25A51 is a mammalian mitochondrial NAD+ transporter. Nature. 2020, 588 (7836), 174–179. 10.1038/s41586-020-2741-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kory N.; Uit de Bos J.; van der Rijt S.; Jankovic N.; Güra M.; Arp N.; Pena I. A.; Prakash G.; Chan S. H.; Kunchok T.; Lewis C. A.; Sabatini D. M. MCART1/SLC25A51 is required for mitochondrial NAD transport. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6 (43), eabe5310. 10.1126/sciadv.abe5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardi E.; Agrimi G.; Goldmann U.; Fiume G.; Lindinger S.; Sedlyarov V.; Srndic I.; Gürtl B.; Agerer B.; Kartnig F.; Scarcia P.; Di Noia M. A.; Liñeiro E.; Rebsamen M.; Wiedmer T.; Bergthaler A.; Palmieri L.; Superti-Furga G. Epistasis-driven identification of SLC25A51 as a regulator of human mitochondrial NAD import. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11 (1), 6145. 10.1038/s41467-020-19871-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achreja A.; Yu T.; Mittal A.; Choppara S.; Animasahun O.; Nenwani M.; Wuchu F.; Meurs N.; Mohan A.; Jeon J. H.; Sarangi I.; Jayaraman A.; Owen S.; Kulkarni R.; Cusato M.; Weinberg F.; Kweon H. K.; Subramanian C.; Wicha M. S.; Merajver S. D.; Nagrath S.; Cho K. R.; DiFeo A.; Lu X.; Nagrath D. Metabolic collateral lethal target identification reveals MTHFD2 paralogue dependency in ovarian cancer. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4 (9), 1119–1137. 10.1038/s42255-022-00636-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger F.; Lau C.; Dahlmann M.; Ziegler M. Subcellular compartmentation and differential catalytic properties of the three human nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280 (43), 36334–41. 10.1074/jbc.M508660200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorci L.; Cimadamore F.; Scotti S.; Petrelli R.; Cappellacci L.; Franchetti P.; Orsomando G.; Magni G. Initial-rate kinetics of human NMN-adenylyltransferases: substrate and metal ion specificity, inhibition by products and multisubstrate analogues, and isozyme contributions to NAD+ biosynthesis. Biochemistry 2007, 46 (16), 4912–22. 10.1021/bi6023379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. N.; Dai Z.; Cheng Q.; Zhang Y. Chemoenzymatic Preparation of 4′-Thioribose NAD. Curr. Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2019, 77 (1), e83. 10.1002/cpnc.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann J.; Li Y.; Tor Y. Emissive Synthetic Cofactors: A Highly Responsive NAD+ Analogue Reveals Biomolecular Recognition Features. Chemistry 2019, 25 (17), 4379–4389. 10.1002/chem.201805520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett R. B.; Smith L. D. Modified procedures for the separation and fluorometric determination of adenine nucleotides. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 80 (2), 490–5. 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90671-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner F.; Niere M.; Ludwig A.; Ziegler M. Structural and functional characterization of human NAD kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288 (1), 69–74. 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi K.; Kawai S.; Murata K. Identification and characterization of a human mitochondrial NAD kinase. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1248. 10.1038/ncomms2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou T.; Kurnasov O.; Tomchick D. R.; Binns D. D.; Grishin N. V.; Marquez V. E.; Osterman A. L.; Zhang H. Structure of human nicotinamide/nicotinic acid mononucleotide adenylyltransferase. Basis for the dual substrate specificity and activation of the oncolytic agent tiazofurin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277 (15), 13148–54. 10.1074/jbc.M111469200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nam T. S.; Park D. R.; Rah S. Y.; Woo T. G.; Chung H. T.; Brenner C.; Kim U. H. Interleukin-8 drives CD38 to form NAADP from NADP+ and NAAD in the endolysosomes to mobilize Ca2+ and effect cell migration. FASEB J. 2020, 34 (9), 12565–12576. 10.1096/fj.202001249R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leone P.; Tolomeo M.; Barile M. Continuous and Discontinuous Approaches to Study FAD Synthesis and Degradation Catalyzed by Purified Recombinant FAD Synthase or Cellular Fractions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2280, 87–116. 10.1007/978-1-0716-1286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.