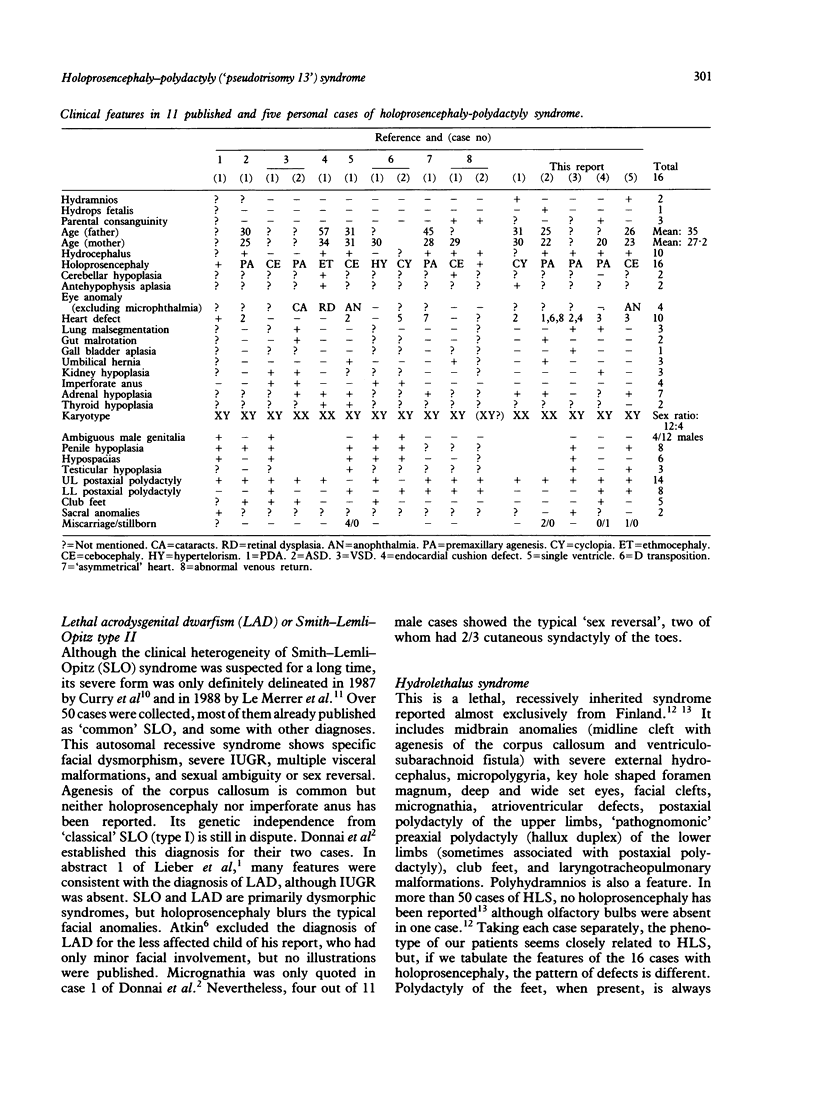
Abstract
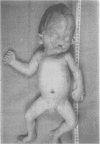
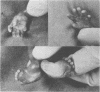
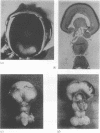
A syndrome of holoprosencephaly and postaxial polydactyly, associated with hydrocephalus, heart defect, adrenal hypoplasia, and other visceral malformations, has been observed in five unrelated children with normal chromosomes. Clinical overlap with lethal acrodysgenital dwarfism (Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome type II) and hydrolethalus syndrome is discussed. Recessive inheritance seems likely.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André S. A., Cordier M. P., Beaufrère A. M., Guillaud M., Robert J. M. Holoprosencéphalie, polydactylie, cardiopathie: nouveau syndrome ou un nouveau cas d'hydrolethalus? J Genet Hum. 1988 Dec;36(5):463–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anyane-Yeboa K., Collins M., Kupsky W., Maidman J., Malin J., Yeh M. Hydrolethalus (Salonen-Herva-Norio) syndrome: further clinicopathological delineation. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Apr;26(4):899–907. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aughton D. J., Cassidy S. B. Hydrolethalus syndrome: report of an apparent mild case, literature review, and differential diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Aug;27(4):935–942. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachman H., Clark R. D., Salahi W. Holoprosencephaly and polydactyly: a possible expression of the hydrolethalus syndrome. J Med Genet. 1990 Jan;27(1):50–52. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burck U. Genetic counselling in holoprosencephaly. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1982 Jun;37(3):231–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Jr Perspectives on holoprosencephaly: Part I. Epidemiology, genetics, and syndromology. Teratology. 1989 Sep;40(3):211–235. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420400304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Jr Perspectives on holoprosencephaly: Part III. Spectra, distinctions, continuities, and discontinuities. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Oct;34(2):271–288. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry C. J., Carey J. C., Holland J. S., Chopra D., Fineman R., Golabi M., Sherman S., Pagon R. A., Allanson J., Shulman S. Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome-type II: multiple congenital anomalies with male pseudohermaphroditism and frequent early lethality. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Jan;26(1):45–57. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnai D., Burn J., Hughes H. Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndromes: do they include the Pallister-Hall syndrome? Am J Med Genet. 1987 Nov;28(3):741–743. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grote W., Rehder H., Weisner D., Wiedemann H. R. Prenatal diagnosis of a probable hereditary syndrome with holoprosencephaly, hydrocephaly, octodactyly, and cardiac malformations. Eur J Pediatr. 1984 Dec;143(2):155–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00445808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Pallister P. D., Clarren S. K., Beckwith J. B., Wiglesworth F. W., Fraser F. C., Cho S., Benke P. J., Reed S. D. Congenital hypothalamic hamartoblastoma, hypopituitarism, imperforate anus and postaxial polydactyly--a new syndrome? Part I: clinical, causal, and pathogenetic considerations. Am J Med Genet. 1980;7(1):47–74. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320070110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt B. G., Seller M. J., Bennett C. P., Maxwell D. M. Holoprosencephaly, polydactyly and normal chromosomes: pseudo-trisomy 13? Clin Genet. 1989 Aug;36(2):141–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb03177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iafolla K., Fratkin J. D., Spiegel P. K., Cohen M. M., Jr, Graham J. M., Jr Case report and delineation of the congenital hypothalamic hamartoblastoma syndrome (Pallister-Hall syndrome). Am J Med Genet. 1989 Aug;33(4):489–499. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson V. P. Holoprosencephaly: a developmental field defect. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Oct;34(2):258–264. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrer M. L., Briard M. L., Girard S., Mulliez N., Moraine C., Imbert M. C. Lethal acrodysgenital dwarfism: a severe lethal condition resembling Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. J Med Genet. 1988 Feb;25(2):88–95. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.2.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerman P., Fryns J. P. Holoprosencephaly and postaxial polydactyly: another observation. J Med Genet. 1988 Jul;25(7):501–502. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.7.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerman P., Fryns J. P., van der Steen K., Kleczkowska A., Lauweryns J. The pathology of trisomy 13 syndrome. A study of 12 cases. Hum Genet. 1988 Dec;80(4):349–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00273650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münke M. Clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular approaches to the genetic heterogeneity of holoprosencephaly. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Oct;34(2):237–245. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallister P. D., Hecht F., Herrman J. Three additional cases of the congenital hypothalamic "hamartoblastoma" (Pallister-Hall) syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Aug;33(4):500–501. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip N., Apicella N., Lassman I., Ayme S., Mattei J. F., Giraud F. The acrocallosal syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Feb;147(2):206–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00442226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach E., Demyer W., Conneally P. M., Palmer C., Merritt A. D. Holoprosencephaly: birth data, benetic and demographic analyses of 30 families. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(2):294–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen R., Herva R. Hydrolethalus syndrome. J Med Genet. 1990 Dec;27(12):756–759. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.12.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen R., Herva R., Norio R. The hydrolethalus syndrome: delineation of a "new", lethal malformation syndrome based on 28 patients. Clin Genet. 1981 May;19(5):321–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb00718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinzel A., Kaufmann U. The acrocallosal syndrome in sisters. Clin Genet. 1986 Nov;30(5):399–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinzel A., Schmid W. Hallux duplication, postaxial polydactyly, absence of the corpus callosum, severe mental retardation, and additional anomalies in two unrelated patients: a new syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1980;6(3):241–249. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320060308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiota K., Tanimura T. Holoprosencephaly, ventricular septal defect, and postaxial polydactyly in a human embryo. J Med Genet. 1988 Jul;25(7):502–503. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.7.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váradi V., Szabó L., Papp Z. Syndrome of polydactyly, cleft lip/palate or lingual lump, and psychomotor retardation in endogamic gypsies. J Med Genet. 1980 Apr;17(2):119–122. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.2.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. D., Madders D. J. Unknown syndrome: holoprosencephaly, congenital heart defects, and polydactyly. J Med Genet. 1987 Nov;24(11):714–715. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.11.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]