Abstract
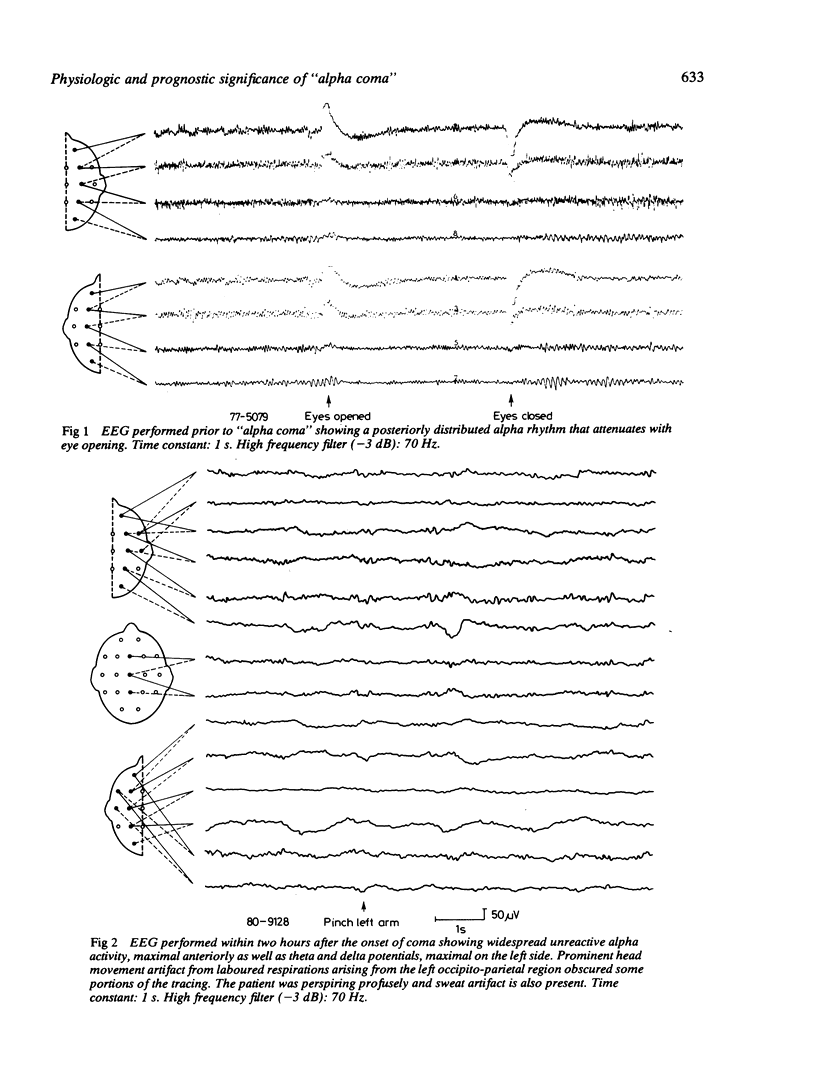
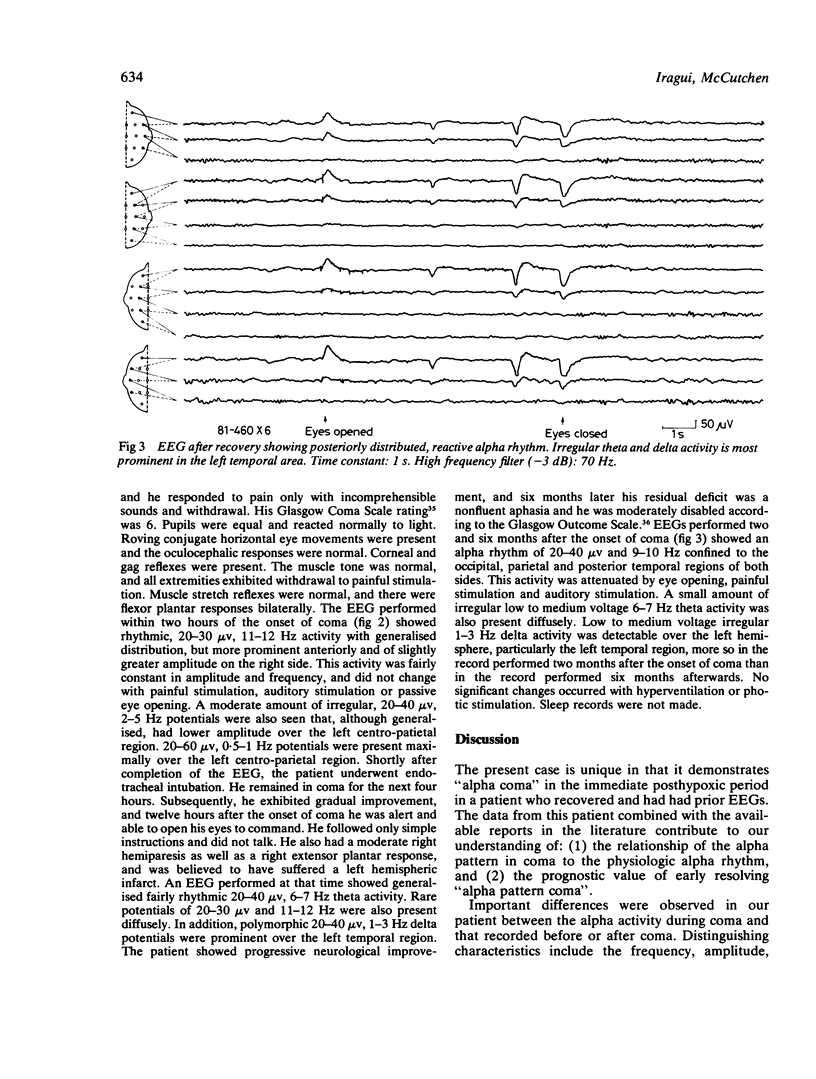
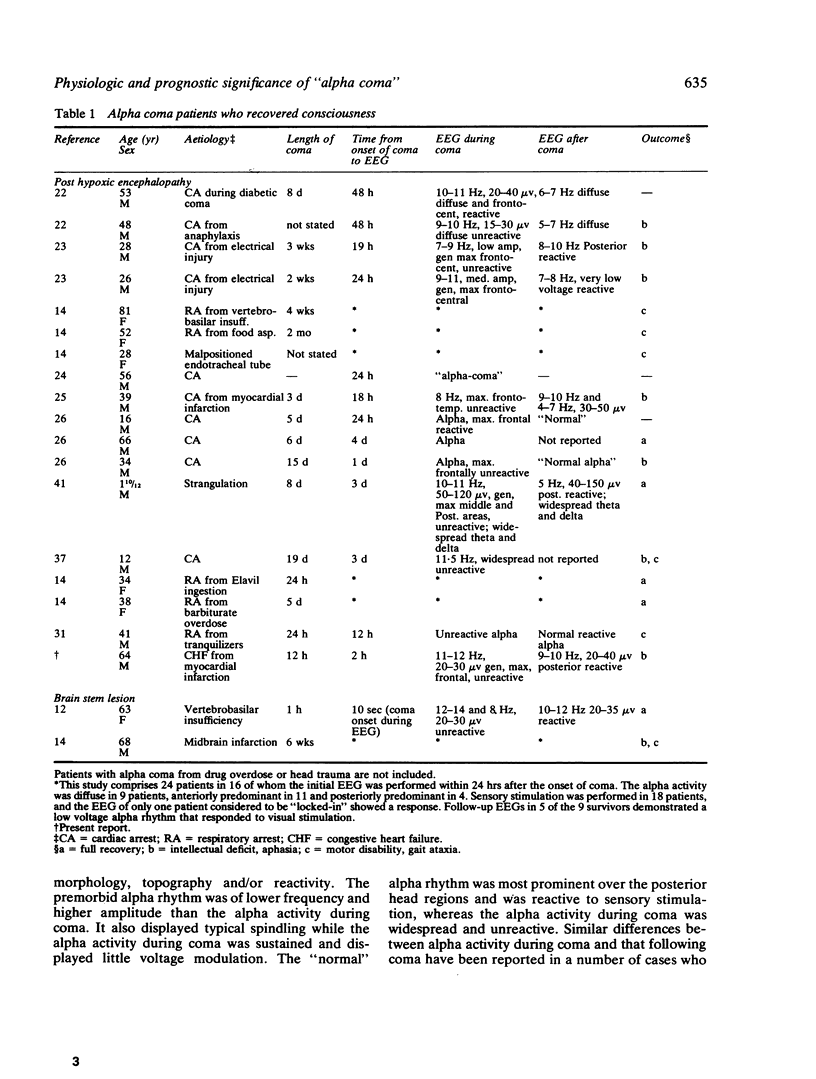
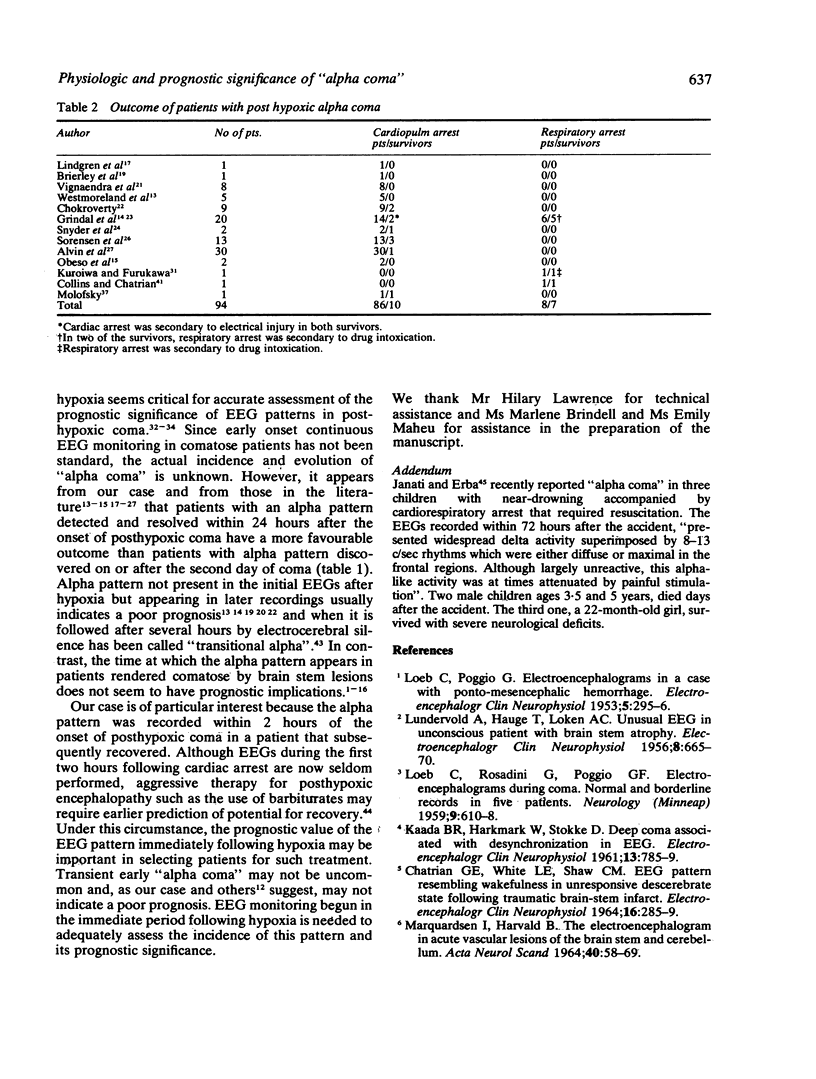
A patient with posthypoxic "alpha coma" is described whose EEGs were recorded before coma, within two hours following the onset of coma and after recovery. The differences observed between the alpha activity during coma and that seen before and after suggest that the alpha activity during coma and the physiologic alpha rhythm are different phenomena. This case, as well as others reported, also suggests that "alpha coma" resolving in the first 24 hours following hypoxia may have a better prognosis than "alpha coma" detected after the first day, and stresses the need for EEG monitoring begun in the immediate period following hypoxia in order to assess accurately the prognostic significance of this EEG pattern in the early stages of postanoxic encephalopathy. The aetiology of "alpha coma" also affects outcome. The survival rate appears higher in patients with respiratory arrest than in those with combined cardiopulmonary arrest.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen N. Life or death of the brain after cardiac arrest. Neurology. 1977 Sep;27(9):805–806. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.9.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alving J., Møller M., Sindrup E., Nielsen B. L. 'alpha pattern coma' following cerebral anoxia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1979 Jul;47(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(79)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnie C. D., Prior P. F., Lloyd D. S., Scott D. F., Margerison J. H. Electroencephalographic prediction of fatal anoxic brain damage after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Br Med J. 1970 Oct 31;4(5730):265–268. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5730.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley J. B., Graham D. I., Adams J. H., Simpsom J. A. Neocortical death after cardiac arrest. A clinical, neurophysiological, and neuropathological report of two cases. Lancet. 1971 Sep 11;2(7724):560–565. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATRIAN G. E., WHITE L. E., Jr, SHAW C. M. EEG PATTERN RESEMBLING WAKEFULNESS IN UNRESPONSIVE DECEREBRATE STATE FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN-STEM INFARCT. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1964 Mar;16:285–289. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(64)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll W. M., Mastaglia F. L. Alpha and beta coma in drug intoxication uncomplicated by cerebral hypoxia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1979 Jan;46(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(79)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T. N., Moretti L., Prensky A. L. Clinical and electroencephalographic manifestations of vascular lesions of the pons. Neurology. 1968 Apr;18(4):357–368. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.4.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chokroverty S. "Alpha-like" rhythms in electroencephalograms in coma after cariac arrest. Neurology. 1975 Jul;25(7):655–663. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.7.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. T., Chatrian G. E. EEG rhythm of alpha frequency in a 22-month-old child after strangulation. Neurology. 1980 Dec;30(12):1316–1319. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.12.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias A., Scott D. F. Alpha coma: a case report. Clin Electroencephalogr. 1981 Jul;12(3):130–132. doi: 10.1177/155005948101200305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Hirano M., Nakamura I., Kawai Y. The two survival cases of alpha-pattern coma caused by large amounts of hypnotica and neuroleptica. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1980;34(4):451–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1980.tb02450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindal A. B., Suter C. "Alpha-pattern coma" in high voltage electrical injury. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1975 May;38(5):521–526. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(75)90193-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindal A. B., Suter C., Martinez A. J. Alpha-pattern coma: 24 cases with 9 survivors. Ann Neurol. 1977 Apr;1(4):371–377. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guterman B., Sebastian P., Sodha N. Recovery from alpha coma after lorazepam overdose. Clin Electroencephalogr. 1981 Oct;12(4):205–208. doi: 10.1177/155005948101200407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUGE T., LOKEN A. C., LUNDERVOLD A. Unusual EEG in unconscious patient with brain stem atrophy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1956 Nov;8(4):665–670. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(56)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes C. H., Bryan-Smyth L. The electroencephalogram in the "locked-in" syndrome. Neurology. 1974 Nov;24(11):1015–1018. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.11.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homan R. W., Jones M. G. Alpha-pattern coma in a 2-month-old child. Ann Neurol. 1981 Jun;9(6):611–613. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janati A., Erba G. Electroencephalographic correlates of near-drowning encephalopathy in children. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1982 Feb;53(2):182–191. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(82)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett B., Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. Lancet. 1975 Mar 1;1(7905):480–484. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92830-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. N., Binnie C. D., Fung D., Hamblin J. J. Reversible coma with an EEG pattern normally associated with wakefulness. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972 Jul;33(1):107–109. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(72)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa Y., Furukawa T. EEG prognostication in drug-related alpha coma. Arch Neurol. 1981 Mar;38(3):200–200. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510030094019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEB C., POGGIO G. Electroencephalograms in a case with ponto-mesencephalic haemorrhage. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1953 May;5(2):295–296. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(53)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEB C., ROSADINI G., POGGIO G. F. Electroencephalograms during coma; normal and borderline records in 5 patients. Neurology. 1959 Sep;9:610–618. doi: 10.1212/wnl.9.9.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmi H., Hubbert C. H., Faris A. A. The electroencephalogram after resuscitation of cardiocirculatory arrest. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):997–1002. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren S., Petersén I., Zwetnow N. Prediction of death in serious brain damage. Acta Chir Scand. 1968;134(6):405–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARQUARDSEN J., HARVALD B. THE ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM IN ACUTE VASCULAR LESIONS OF THE BRAIN STEM AND THE CEREBELLUM. Acta Neurol Scand. 1964;40:58–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1964.tb04266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molofsky W. J. Alpha coma in a child. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Jan;45(1):95–95. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller M. 'Alpha-pattern coma' and survival after cardiac arrest. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1978 Apr;44(4):518–522. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(78)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAMPIGLIONE G. Electroencephalographic studies after cardiorespiratory resuscitation. Proc R Soc Med. 1962 Aug;55:653–657. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pampiglione G., Harden A. Resuscitation after cardiocirculatory arrest. Prognostic evaluation of early electroencephalographic findings. Lancet. 1968 Jun 15;1(7555):1261–1265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radermecker J. Severe acute necrosis of the pons with long survival. Electro-clinical symptoms and absence of cerebral lesions. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;23(3):281–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder B. D., Ramirez-Lassepas M., Lippert D. M. Neurologic status and prognosis after cardiopulmonary arrest: I. A retrospective study. Neurology. 1977 Sep;27(9):807–811. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.9.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen K., Thomassen A., Wernberg M. Prognostic significance of alpha frequency EEG rhythm in coma after cardiac arrest. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Sep;41(9):840–842. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.9.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teasdale G., Jennett B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet. 1974 Jul 13;2(7872):81–84. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91639-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignaendra V., Wilkus R. J., Copass M. K., Chatrian G. E. Electroencephalographic rhythms of alpha frequency in comatose patients after cardiopulmonary arrest. Neurology. 1974 Jun;24(6):582–588. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.6.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmoreland B. F., Klass D. W., Sharbrough F. W., Reagan T. J. Alpha-coma. Electroencephalographic, clinical, pathologic, and etiologic correlations. Arch Neurol. 1975 Nov;32(11):713–718. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490530035001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkus R. J., Harvey F., Ojemann L. M., Lettich E. Electroencephalogram and sensory evoked potentials. Findings in an unresponsive patient with pontine infarct. Arch Neurol. 1971 Jun;24(6):538–544. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00480360072009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Stevland N., Kimura J. Alpha-pattern coma in a 2-year-old child. Arch Neurol. 1979 Apr;36(4):225–227. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500400079013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


