Abstract
Objective
In acute pancreatitis (AP), bacterial translocation and subsequent infection of pancreatic necrosis are the main risk factors for severe disease and late death. Understanding how immunological host defence mechanisms fail to protect the intestinal barrier is of great importance in reducing the mortality risk of the disease. Here, we studied the role of the Treg/Th17 balance for maintaining the intestinal barrier function in a mouse model of severe AP.
Design
AP was induced by partial duct ligation in C57Bl/6 or DEREG mice, in which regulatory T-cells (Treg) were depleted by intraperitoneal injection of diphtheria toxin. By flow cytometry, functional suppression assays and transcriptional profiling we analysed Treg activation and characterised T-cells of the lamina propria as well as intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) regarding their activation and differentiation. Microbiota composition was examined in intestinal samples as well as in murine and human pancreatic necrosis by 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
Results
The prophylactic Treg-depletion enhanced the proinflammatory response in an experimental mouse model of AP but stabilised the intestinal immunological barrier function of Th17 cells and CD8+/γδTCR+ IELs. Treg depleted animals developed less bacterial translocation to the pancreas. Duodenal overgrowth of the facultative pathogenic taxa Escherichia/Shigella which associates with severe disease and infected necrosis was diminished in Treg depleted animals.
Conclusion
Tregs play a crucial role in the counterbalance against systemic inflammatory response syndrome. In AP, Treg-activation disturbs the duodenal barrier function and permits translocation of commensal bacteria into pancreatic necrosis. Targeting Tregs in AP may help to ameliorate the disease course.
Keywords: experimental pancreatitis, immune response, bacterial infection, acute pancreatitis
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
Infected necrosis is a severe complication during acute pancreatitis (AP) and is associated with a significant mortality.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
In an animal model, the experimental induction of AP associates with significant changes of the intestinal microbiota composition and a marked increase of facultative pathogenic bacteria. The same bacterial taxa are identified in necrotic tissue samples of pancreatitis patients.
During AP, activated regulatory T cells suppress the systemic immune response and impair the immunological intestinal barrier function.
The depletion of Tregs during AP reduced the bacterial translocation of facultative pathogenic strains into the inflamed pancreas.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
Regulatory T cells could represent a therapeutic target for the prevention of infected necrosis during severe AP which will improve the disease course and outcome.
Regulatory T cells could represent a therapeutic target for the prevention of infected necrosis during severe acute pancreatitis, which will improve the disease course and outcome.
Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is the most common non-malignant disease of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract leading to hospital admission with an increasing incidence over the past years in western countries.1 Eighty per cent of pancreatitis cases follow a self-limiting course of disease without complications or long-time hospitalisation. About 20% of patients develop severe AP (SAP), which is associated with systemic complications and increased morbidity and mortality.2 Infected pancreatic necrosis, which is believed to arise from translocation of commensal gut bacteria into the pancreas,3 is regarded to drive persistent organ failure and subsequent mortality.2 Initially bacteria need to overcome the intestinal barrier and evade the immune system to cause infected necrosis. Especially the Treg/Th17-balance is crucial for maintaining the intestinal barrier function and regulating tissue homoeostasis.4
Pancreatitis is a primarily sterile inflammation originating from premature intracellular protease activation. Activated zymogens trigger acinar cell death5 and activate the immune regulating transcription factor NFκB.6 This inflammatory process recruits macrophages and neutrophils to the site of inflammation which further increases the local damage.7–10 Macrophages represent the majority of resident pancreatic immune cells and their activation by damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) initiates a systemic immune-response,8 11–14 including the activation of the adaptive immune system through the release of cytokines.12 During an episode of AP resident lymphatic T-cells initiate a suppressive and anti-inflammatory response mediated by an increase in FOXP3+/CD25+ regulatory T-cells (Treg) and GATA3+ Th2-cells.12 15 This parallel initiation of a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and a compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome (CARS) is also known from sepsis or critical trauma.16 17
Systemic immunosuppression (CARS), in particular mediated by Tregs, can promote secondary infections18 and thus aggravate disease severity or cause non-pancreatic complications. To date, little is known about the relationship between the gut microbiome and the course of AP.19 Here, we investigated in an animal model of AP how Treg-mediated immunosuppression affects the gut microbiome composition and the translocation of bacteria into the inflamed pancreas.
Results
AP is associated with changes of the intestinal microbiota composition
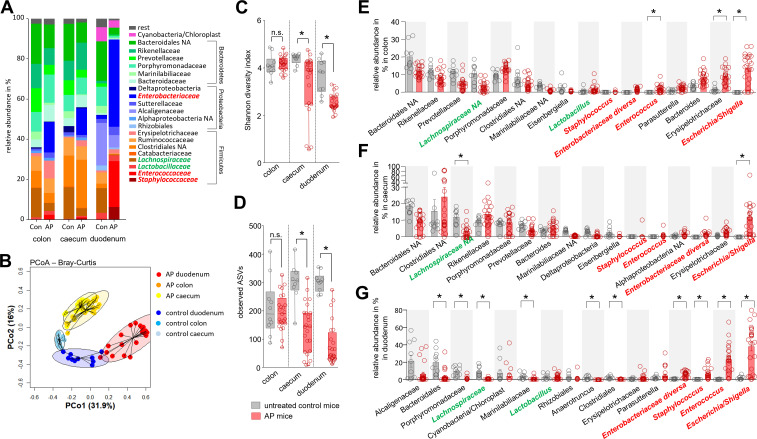
AP was induced by partial duct ligation in C57Bl/6-J mice. Duodenal aspirates and faecal samples from distal colon and caecum were collected from AP mice and untreated control animals. 16S rRNA gene sequencing revealed microbiota differences between control and AP mice (figure 1A). Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of all GI-tract samples confirmed microbiota changes, with the most prominent changes seen in duodenal aspirates (figure 1B, online supplemental figure S1A, B). A significantly reduced Shannon-diversity and amplicon sequence variant (ASV) richness was observed in the duodenal aspirates of AP animals. Smaller changes of the microbiota composition were observed in caecal but not in distal colonic samples (figure 1C, D). Analysis of the most abundant taxonomic units identified an increase of facultative pathogenic bacteria like Escherichia/Shigella, Enterobacteriaceae diversa, Enterococcus or Staphylococcus. Especially in duodenal samples all these taxa were significantly enriched during AP. In colon and caecum samples, we could also observe an increase of these facultative pathogenic bacteria, but only Escherichia/Shigella showed a significant increase in all parts of the GI-tract (figure 1E–G). Their high abundance in the duodenal section suggests bacterial overgrowth (online supplemental figure S1C). In contrast, the abundance of beneficial commensal bacteria such as Lachnospiraceae was decreased, and this effect was again most pronounced in the duodenum (figure 1E–G). To verify the results from the model of AP using partial pancreatic duct ligation we investigated the microbiome changes in duodenum and colon samples in a second pancreatitis model. To analyse comparable time points we induced pancreatitis via 8-hourly intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of Caerulein (50 µg/kg/bodyweight) over 3 days. Again, we saw significant changes in the intestinal microbiome composition with the strongest effects in the duodenum (online supplemental figure S2A–C). The disease severity in this model was significantly lower compared with the model induced by partial pancreatic duct ligation (online supplemental figure S2D, E) and we observed less pronounced changes of the intestinal microbiota composition (online supplemental figure S2A–C) and nearly no changes of the systemic immune response (online supplemental figure S2F–H).
Figure 1.
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is associated with changes of the intestinal microbiota composition. (A) Faecal samples from colon, caecum and duodenum were collected from C57Bl/6 mice with AP (n=24) and from untreated control animals Con (n=10). Isolated DNA was analysed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The microbiota composition and AP-associated changes of the taxonomic units with the highest abundance are illustrated by a stacked bar graph. (B) Principal coordinate analysis illustrates the changes of gut microbiome between untreated controls and AP mice. (C, D) Shannon-Diversity Index (C) and richness of observed species (D) demonstrate significant impact of AP on the duodenal microbiome composition. (E–G) The bar graph illustrates changes of the most abundant taxa in colonic (E), caecal (F) and duodenal samples (G) of AP (red) and control mice (grey). Facultative pathogenic were marked in red, beneficial commensal bacteria were marked in green. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student’s t-test and Kruskal-Wallis test followed by a Dunn’s multiple comparisons test to analyse differentially abundant taxa in colon, caecum and duodenum samples. Significance levels of p<0.05 are marked by an asterisk.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp001.pdf (736.8KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp002.pdf (2.5MB, pdf)
Intestinal microbiota changes correlate with the severity of AP and the systemic immune response
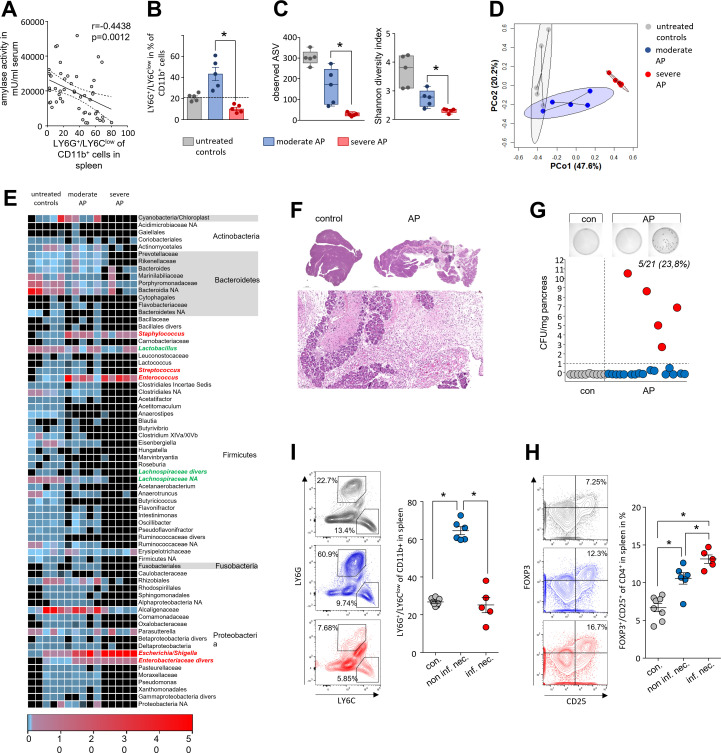
In the next step, we investigated how far the duodenal microbiome changes are influenced by disease severity and through the systemic immune response by analysing splenic lymphocytes. Unexpectedly LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells in spleen of AP mice increased significantly during AP but the concomitant decrease of serum amylase as marker of pancreatic damage suggested an inverse correlation to disease severity (figure 2A). Splenic LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells showed the same inverse correlation with serum lipase activity, histological damage and the serum cytokine level of IL-6 and TNFα (online supplemental figure S3A–C). Furthermore, we detected a positive correlation of splenic LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells with the spleen weight, and a negative correlation with the number of splenic CD25+/FOXP3+ Tregs which are significantly elevated during pancreatitis (online supplemental figure S3D, E). Elevated apoptosis in spleen could be responsible for the loss of LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells (online supplemental figure S3F). Based on these findings, we dichotomised the set of animals in a splenic LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+ high (moderate) or low cell (severe) cohort and investigated severity dependent changes of the duodenal microbiota composition (figure 2B). 16S rRNA gene sequencing analysis confirmed a severity-dependent loss of richness and diversity (figure 2C). PCoA of duodenal aspirates from moderate and SAP showed severity-dependent significant changes of the microbial composition (figure 2D). A detailed analysis of the most frequent duodenal microbiota taxa is illustrated in the heat map (figure 2E and online supplemental table 1). Facultative pathogenic bacterial clades like Escherichia/Shigella, Enterococcus or Staphylococcus were again detected with increased abundance (online supplemental figure S4A).
Figure 2.
Intestinal microbiota changes correlate with the severity of AP and the systemic immune response. (A) Dot plot illustrates negative correlation of LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells to the activity of serum amylase of mice with AP (n=50), significance of correlation was tested by Spearman’s rank correlation-coefficient. (B) Disease severity in animals was classified according to the percentage of LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells in spleen (n=5/group). (C) Box plots illustrate the duodenal microbiome species richness and Shannon-diversity according to moderate and severe pancreatitis. (D) Principal coordinate analysis illustrates significant differences of duodenal microbiome between these groups (permutational multivariate analysis of variance; control vs severe: p=0.007, R2=59.4%, control vs moderate: p=0.015, R2=24.5% and moderate vs severe: p=0.007, R2=48.4%). (E) Heat-map illustrates 16S rRNA gene sequencing results of the duodenal microbiome analysis, facultative pathogenic were marked in red, beneficial commensal bacteria were marked in green. (F) H&E-staining of pancreatic tissue of healthy and AP mice. (G) Colony forming units (CFU) were counted from necrotic tissue homogenates and exceeded the cut-off level of 1 CFU/mg tissue weight in 5 of 21 (23.8%) animals. (I) From infected (n=5) and non-infected (n=6) groups, we analysed in spleen the percentage of LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells and (H) the percentage of FOXP3+/CD25+/CD4+-cells. Statistical evaluation was done by unpaired Student’s t-test for independent samples and significance levels of p<0.05 are marked by an asterisk. AP, acute pancreatitis.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp003.pdf (1.9MB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp017.pdf (801.5KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp004.pdf (881.6KB, pdf)
Infected necrosis is a life-threatening complication of AP and regarded to originate from translocation of commensal gut bacteria. In our mouse model of AP we examined, bacterial infection of the ligated necrotic part of the pancreas by colony growth assays of the tissue homogenate on agar plates (figure 2F–G). In 5 of 21 animals, we detected a significant bacterial load in pancreatic necrosis with more than 1 colony-forming unit (CFU)/mg pancreas, which is comparable to infection rates seen in patients matched for severity.2 A negative correlation was detected for the rate of infection of pancreatic necrosis and number of splenic LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells (figure 2I and online supplemental figure S4B). To test a functional relationship between LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells and the infection of pancreatic necrosis we depleted LY6G+-cells by anti-LY6G antibody treatment before induction of pancreatitis. Treatment with anti-LY6G abolished LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells (online supplemental figure S4A–D) and did not affect bacterial translocation into the necrosis (S.4E). Our finding suggested that reduction of LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells in spleen can serve as marker to discriminate between moderate and SAP in mice, but apparently has no functional impact.
Since the depletion of LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells did not affect the adaptive immune cells (online supplemental figure S4F) we investigated in further experiments the cells of the adaptive immune response the spleen. Labelling of the IL-2 receptor-α-chain (CD25) on the surface of CD4+ T-cells (online supplemental figure S5A) revealed a significantly stronger increase in the number of activated CD25+ T-cells in those animals with an infected pancreatic necrosis, indicated by a bacterial load of more than 1 CFU/mg pancreatic tissue. CD69, a second activation marker of CD4+ T-cells, showed the same association (online supplemental figure S5B). We next investigated T-cell differentiation by labelling of the transcription factors TBET, GATA3 and FOXP3. Whereas Th1-cell differentiation transcription factor TBET was not affected by pancreatitis (online supplemental figure S5C), GATA3+ Th2-cell numbers were found elevated in the spleen, independent of bacterial infection (online supplemental figure S5D). Interestingly, the number of FOXP3+/CD25+ Tregs was significantly increased in animals suffering from pancreatitis and was highest in those with infected necrosis (figure 2H). Furthermore, we detected a direct correlation between Treg rates with the bacterial load (online supplemental figure S5E).
gutjnl-2022-327448supp005.pdf (637.4KB, pdf)
Imbalance of the Th17/Treg ratio in duodenal mucosa during AP
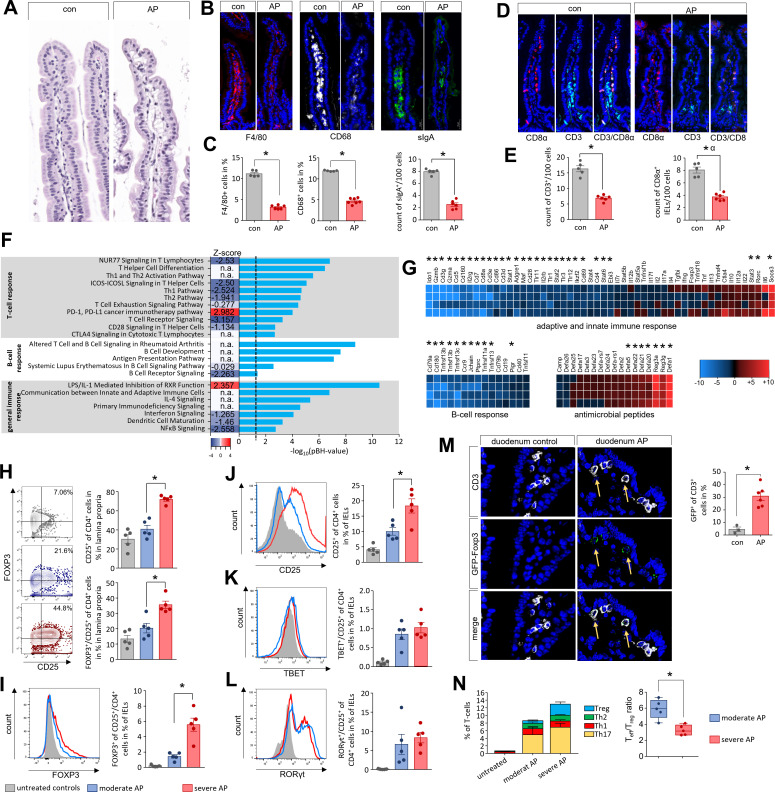
To colonise pancreatic necrosis commensal bacteria need to overcome the intestinal barrier. Duodenum histology of AP mice did not show obvious differences (figure 3A). Immunofluorescent labelling of F4/80 or CD68 demonstrated a significant reduction of macrophages within the lamina propria, also sIgA producing plasma cells were significantly reduced (figure 3B, C). The number of T-cells was also affected by AP, CD3+ T-cells within the lamina propria as well as CD8α+ intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) were significantly reduced (figure 3D, E). Additionally, we analysed global mRNA-profiles of mouse duodenal tissues (AP vs control) using Affymetrix GeneChip-arrays. Analysis of the generated transcriptome data by QIAGEN’s Ingenuity-Pathway-Analysis (IPA) software identified AP-specific differential gene expression in the T-cell-response, B-cell-response and other immune system-related pathways (figure 3F). Transcript levels of genes encoding T-cell surface markers CD3, CD8α, CD4 and CD28 were significantly reduced, while SOCS3 (suppressor of cytokine signalling 3) specific mRNA was significantly more abundant (figure 3G). B-cell-response markers like CD79A, TNFS13/proliferation-inducing ligand APRIL, TNFSF13B/B-cell activating factor BAFF, or JCHAIN (part of Immunglobulin A) exhibited significantly lower transcript levels in AP mice (figure 3G). In contrast to an apparently attenuated immune response, the mRNA abundance of anti-microbial defence peptides such as DEFA1, REG3A, REG3G, DEFA23, or DEFA21 was significantly higher in the duodenum of AP mice (figure 3G). The expression of genes encoding structural protein components of the intestinal barrier like tight junctions, desmosomes or adherence junctions were only in some cases affected by AP (online supplemental figure S6A). We could observe a significant downregulation of mRNAs encoding for Claudin15 (Cldn15), the Myosin light chain kinase (Mylk), cadherin related family member 2 (Cdhr2) or Pannexin 1 (Panx1), whereas other mRNAs showed a significant upregulation after onset of disease such as Dsp, encoding for Desmoplakin, Cdh5 encoding for the protein Cadherin 5 or the mRNAs encoding for mucins 2, 3 and 3a (Muc2, Muc3 and Muc3a). Crypt-cell proliferation, marked by KI67, was not affected by AP (online supplemental figure S6B). Most structural proteins were unaffected by AP like E-Cadherin (online supplemental figure S6C). On the other hand, AP exhibited significant effects also on several pathways of the immune homoeostasis (cytokines, transmembrane-receptors and transcriptional-regulators) in the duodenal system (online supplemental figure S6D–F).
Figure 3.
Imbalance of the Th17/Treg ratio in duodenal mucosa during AP. (A–E) Histological examination of the duodenum illustrates changes of the intestinal mucosa in C57Bl/6 mice after induction of AP. (A–C) In contrast to only slight changes in H&E-staining we detected differences in immunofluorescent labelling of F4/80, CD68 as marker for macrophages and sIgA as marker for plasma cells (B), all cells were significantly decreased in AP mice (C). (D) CD3 as T-cell marker and CD8α as marker of IELs were labelled in small intestine. (E) Bar graphs illustrate significant changes of T-cells and IELs in duodenum. (F) The bar graph shows the -log10(pBH) values of overrepresented pathways from an IPA analysis which was based on differentially expressed transcriptome data of duodenal tissue from AP and control mice. Heatmap illustrates the z-score which indicates activation (positive z-score, red) or inhibition (negative z-score, blue) of this pathway. (G) Heat-map illustrates fold change differences of upregulated (red) and downregulated (blue) genes in duodenal tissue of AP mice compared with untreated controls. (H) Lymphocytes isolated from lamina propria as well as from the epithelial layer were analysed by flow cytometry. In CD4+ T-cells of the lamina propria the increased levels of CD25 and FOXP3 correlated with disease severity. (I–J) The numbers of CD4+/FOXP3+/CD25+-Tregs (I) and CD4+/CD25+-T-cells (J) from IELs were also increased in a severity-dependent manner. (K, L) Th17-cells marked by RORγt+/CD25+ (K) and Th1-cells marked by TBET+/CD25+ (L) did not show a severity dependent increase. (M) GFP-producing Tregs in the duodenum of DEREG-mice were detected by anti-GFP and anti-CD3 labelling and showed a significant increase after onset of AP. (N) AP induced a shift of the Teff/Treg ratio. Tregs showed a clear increase between moderate and severe AP in contrast to Teff cells (Th1, Th2 and Th17). Statistically significant differences were tested by unpaired Student’s t-test for independent samples and significance levels of p<0.05 are marked by an asterisk. AP, acute pancreatitis.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp006.pdf (2.2MB, pdf)
To evaluate the effect of disease severity on the intestinal immune response, we isolated and analysed lymphocytes of the lamina propria and duodenal IELs by flow cytometry with respect to disease severity (figure 3H–L). The purity of both cell types was confirmed detecting the CD8α/CD4 ratio (S.7A-B). We observed a severity-dependent decrease of CD4+ T cells in the lamina propria (online supplemental figure S7C). Within this population of CD4+ T-cells we measured an increase of CD25+/FOXP3+ Tregs during pancreatitis, with the highest numbers observed in SAP (figure 3H). The same result was obtained for the population of IELs, but at a significantly lower ratio (figure 3I). Within the duodenum we observed a severity-dependent increase in the number of CD25+/FOXP3+ Tregs (figure 3I, J). Furthermore, effector T-cell (Teff) numbers were significantly elevated during pancreatitis, the induction of CD25+/RORγt+ (Th17) IELs and CD25+/TBET+ (Th1) was not different between moderate or SAP. The ratio of CD25+/RORγt+ increased to nearly 10%, whereas CD25+/TBET+ did not rise above 1% of total IELs (figure 3K, L). Analysis of GFP-expressing Tregs in DEREG-mice (DEpletion of REGulatory T-cells)20 revealed after induction of AP a significant redistribution of GFP+/CD3+ T-cells within the lamina propria, confirming the cytometry analysis (figure 3M). Notably the Teff/Treg-ratio was significantly lower in animals suffering from SAP (figure 3N). In summary, these results suggest that AP causes general immunosuppression in the intestinal mucosa and pronounced changes of the intestinal microbiota composition.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp007.pdf (849KB, pdf)
Immune suppressive function of Tregs during AP
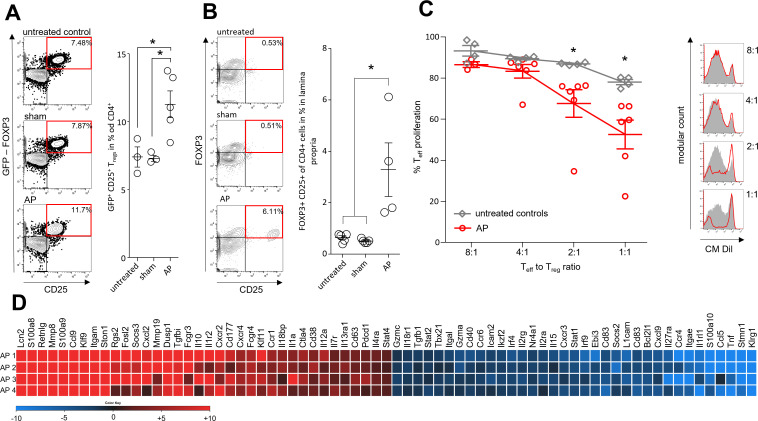
To illuminate the role of Tregs, we analysed their pancreatitis-associated suppressive capacity. AP was induced by partial duct ligation in DEREG-mice expressing a gene encoding a GFP-diphtheria toxin (DT) receptor fusion protein under the control of a Foxp3-promoter.20 GFP flow cytometric analysis confirmed increased Treg numbers after induction of AP (figure 4A). The same increase we could observe in T-cells isolated from the duodenum (figure 4B). Using a fluorescence-activated cell sorter, GFP-positive Tregs were isolated from the spleen of DEREG-mice after AP-induction and of control animals. We co-incubated the Tregs at ratios of 1:8, 1:4, 1:2 and 1:1 with naïve CM-Dil-labelled CD3/CD28 activated T-cells in the presence of IL-2. Dilution of CM-Dil fluorescence by cell division was used to measure the suppressive activities of Tregs on Teff-cell proliferation and showed a significantly stronger suppression by Tregs from AP animals (figure 4C). In addition, we analysed the transcriptome of the isolated Tregs using Affymetrix GeneChips. Expression of Il10 and Tgfbi were increased, whereas the mRNA levels of Tnf and Stat1 were decreased (figure 4D). Pathway analyses of the transcription data using IPA-software indicated AP-associated downregulation of cell cycle regulation and of the general immune response pathways in Tregs (online supplemental figure S8A). Upstream regulators included the cytokines IFNγ, IL-10, the transcription factors STAT3, FOXP3 and STAT6, and the transmembrane receptors IL10RA, CD28 and CTLA4 (online supplemental figure S8B–D).
Figure 4.
Immune suppressive function of Tregs during AP. AP was induced by partial duct ligation in DEREG- and C57Bl/6 mice. (A) The number of splenic GFP producing Tregs was increased in the AP group (n=5) but not in control or sham operated mice (n=3). (B) The same increase of FOXP3+/CD25+/CD4+ Tregs was observed in the small intestine. (n=5). (C) Suppression assays showed that Tregs from AP mice (red line) have an increased suppressive capacity on Teff cell proliferation. (D) Heat map illustrates fold changes of gene transcription in Tregs from AP mice (n=4) compared with untreated controls (n=4). Statistically significant differences were tested by unpaired Student’s t-test for independent samples and significance levels of p<0.05 are marked by an asterisk, corrected for multiple testing (bonferroni-correction). AP, acute pancreatitis.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp008.pdf (789.7KB, pdf)
We further analysed AP-induced alterations in the global mRNA profile of isolated Tregs from spleen and from duodenal samples. In both subsets the ‘PD-1, PD-L1 cancer immunotherapy pathway’ involved in Treg-mediated immunosuppression was significantly induced. Analysis of disease-related and biofunction-related pathways revealed negative activation scores for many immune pathways. Innate and adaptive immune cells seem equally affected and lymphocyte activation was significantly inhibited (online supplemental figure S9A–D).
gutjnl-2022-327448supp009.pdf (1MB, pdf)
Depletion of Tregs stabilises the homoeostasis of CD4+ T cells in the lamina propria as well as of CD8α+ IELs in the duodenum
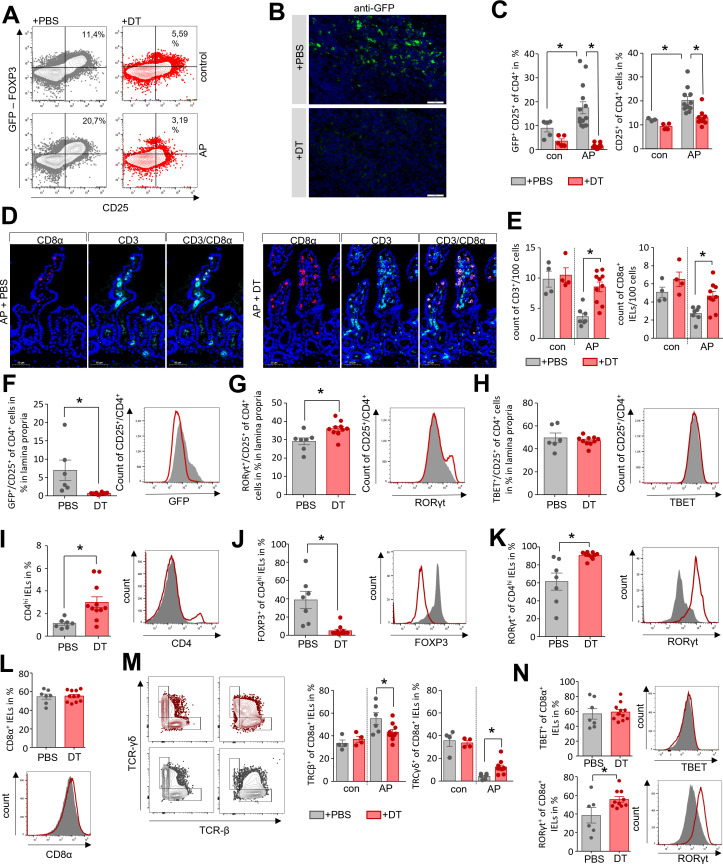
To verify the immunosuppressive effect of Tregs during AP we depleted Tregs in DEREG-mice by i.p. injection of DT before the induction of pancreatitis. The depletion of Tregs in adult mice does not result in autoimmune disease.21 By flow cytometry (figure 5A) and immunofluorescence detection of GFP+ cells in lymph nodes (figure 5B) we confirmed a significant reduction of GFP+/CD25+ Tregs in DT-treated animals, whereas phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-treated control mice showed the typical AP-induced increase of Tregs (figure 5C). The Teff populations in spleen, GATA3+/CD4+ Th2-cells and TBET+/CD4+ Th1-cells were significantly increased compared with control animals (online supplemental figure S10A). The population of splenic LY6G+/LY6Clow/CD11b+-cells, which inversely correlate with the disease severity were significantly elevated in DT-treated mice, whereas myeloperoxidase activity in lung tissue, a marker of lung injury, was comparable to PBS-treated controls (online supplemental figure S10B). We next investigated if the Treg depletion affects duodenal CD4+ T-cells and CD8α+ IELs populations. Immunofluorescence labelling of CD3+ T-cells and CD8α+ IELs showed, that following depletion of Tregs the numbers of CD3+ cells and CD8α+ IELs were significantly higher in DT-treated animals compared with PBS-treated mice (figure 5D, E). Subsequently, we isolated leucocytes from the duodenum of DT-treated DEREG-mice after induction of AP. PBS-treated animals were used as controls. In DT-treated animals GFP+/CD25+ CD4+ Tregs were absent from the lamina propria (figure 5F). Examination of CD4+Teff cells within the lamina propria showed an increase of RORγt+/CD25+ Th17-cells (figure 5G), whereas the number of TBET+/CD25+ Th1-cells was not changed after Treg depletion (figure 5H). Interestingly, we identified a population of CD4hi cells within the population of IELs which is increased in DT-treated animals (figure 5I). A detailed characterisation of this CD4hi population identified mainly GFP+/CD4hi Tregs and RORγt+/CD4hi Th17-cells. Whereas RORγt+/CD4hi Th17-cells persisted in DT-treated animals, Tregs were completely abolished (figure 5J, K). We further analysed the population of CD8α+ IELs, which account for the majority of IELs. While immunofluorescence labelling of CD8ɑ+ IELs and of CD3+ T-cells of the lamina propria showed a significant reduction in numbers (figure 5D, E), their ratio was not affected by DT-treatment (figure 5L). Surface markers allow to sort IELs into two different populations: (A) induced-IELs positive for CD4+/CD8α+ and TCRαβ+ (T-cell receptor), and (B) natural-IELs which are specific for CD8α+/TCRγδ+ or CD8αβ-/TCRαβ+.22 Analysis of TCRβ and TCRγδ on the surface of CD8α+ IELs in DEREG-mice revealed that the population of induced IELs (CD8α+/TCRβ+) was increased in AP, while the number of natural IELs (CD8α+/TCRγδ+) was significantly decreased. This TCRαβ+/TCRγδ+ shift was less pronounced in Treg-depleted mice (figure 5M). Finally, we investigated the presence of the transcription factors TBET and RORγt within the CD8α+ IELs. No differences in the number of TBET synthesising IELs were observed in the absence of Tregs, whereas RORγt producing IELs were significantly increased (figure 5N). In summary, the depletion of Tregs prevented the pancreatitis-induced reduction in T-cells in the lamina propria and of CD8α+ IELs. Flow cytometry data showed a significant increase of RORγt+ Th17-cells, as well as a sustained population of CD8α+/TCRγδ+ natural-IELs in DT-treated mice after the onset of AP.
Figure 5.
Depletion of Tregs stabilises the homoeostasis of CD4+ T cells in the lamina propria as well as of CD8α+ IELs in the duodenum. AP pancreatitis was induced in DEREG mice by partial duct ligation, Tregs were depleted by diphtheria toxin (DT) (n=11), controls receive PBS (n=7). (A) The efficiency of Treg depletion with DT was verified by flow cytometry analysis of splenocytes. (B) Immunofluorescence detection of GFP-producing Tregs was performed in lymph nodes of DT-treated and PBS-treated mice. (C) Bar graphs show the ratios of CD25+ T-cells and GFP+/CD25+ Tregs analysed by flow cytometry of splenocytes. (D, E) Immunofluorescent labelling of CD3 and CD8α showed a significant persistence of the T-cell and IEL population in the absence of Tregs in DT-treated DEREG-mice compared with the PBS-treated group, (E). (F–N) Lymphocytes of the lamina propria and the epithelial layer were isolated from duodenum and analysed by flow cytometry. (F) Following Treg-depletion, no GFP+/CD25+ Tregs were detected within the lamina propria. (G, H) Bar graph show the numbers of RORγt+/CD25+ Th17-cells (G) and TBET+/CD25+ Th1-cells (H). (I) The bar graph shows a higher ratio of CD4hi expressing IELs in DT-treated mice. (J, K) In the CD4hi IELs we observed a shift from GFP+ Tregs (J) to RORγt+ Th17-cells (K). (L) The ratio of CD8α+ IELs was not affected by Treg-depletion. (M) Dot plot and bar graphs illustrate the ratio changes of TCRγδ+ IELs and TCRβ+ after DT-treatment. (N) Within the population of CD8α+ IELs we measured an increase in RORγt producing cells whereas TBET was not affected. Statistically significant differences were tested by unpaired student’s t-test for independent samples and significance levels of p<0.05 are marked by an asterisk. AP, acute pancreatitis; IELs, intraepithelial lymphocytes; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp010.pdf (1MB, pdf)
Depletion of Tregs attenuates microbial dysbiosis during pancreatitis and prevents bacterial translocation into pancreatic necrosis
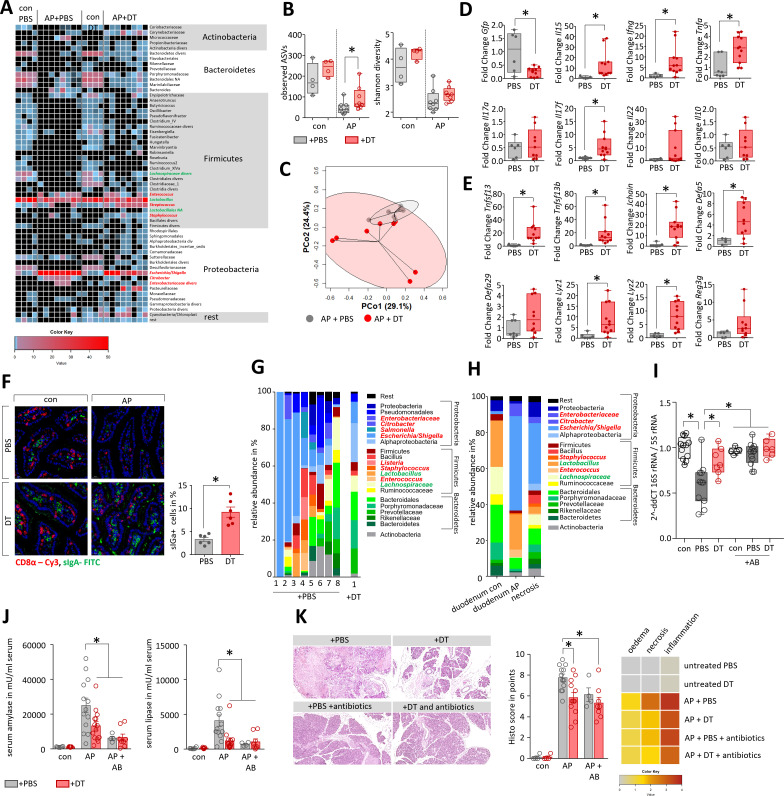
Treg-depletion resulted in increased Teff numbers thus we analysed whether this increase also affected microbial composition in AP. We performed 16S rRNA gene sequencing based on isolated DNA from duodenal aspirates of DEREG-mice. AP induced a pronounced reduction of bacterial taxa within the duodenal aspirates, comparable to what we observed in C57Bl/6 mice. In contrast to PBS-treated DEREG-controls, mice that had received DT before induction of AP retained a more varied microbial composition, indicated by a significantly higher ASV richness and different composition shown by PCoA (figure 6A–C, online supplemental table 2). Overgrowth of facultative bacterial pathogens like Escherichia/Shigella during AP was significantly reduced in the Treg depleted group (S.10C). Quantitative reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) confirmed the results from 16S RNA gene sequencing, the abundance of facultative pathogens like Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecium is significantly increased in mice with AP, but to a minor extend in the DT-treated mice. Beneficial strains like Lachnospiraceae or Lactobacillus remain unchanged (online supplemental figure S10D). We analysed duodenal tissue samples of these mice by RT-qPCR analysis and confirmed the loss of Tregs by a DT-treatment-dependent decrease in GFP transcript levels. During AP, we observed significantly higher transcript levels of the genes encoding IL-15, IFNγ, TNFα and IL-17F in DT-treated mice. Interestingly, transcripts for IL-17A, IL-22 or IL-10 did not differ between PBS-treated or DT-treated DEREG-mice (figure 6D). In Treg-depleted AP mice, the mRNA amounts of the bacterial defence genes Tnfsf13, Tnfsf13b, Jchain and Defa5 were significantly elevated. On the other hand, the transcript abundances of Defcr-rs1 and Reg3g encoding antimicrobial peptides were not significantly increased, while those of the genes encoding the bacteriolytic enzymes Lysozyme 1 and 2, which are normally secreted by Paneth cells, were significantly higher (figure 6E). The expression of genes encoding the physical barrier proteins Occludin and Claudin-1 was significantly increased in DT-treated mice whereas changes in other barrier proteins like E-Cadherin, Claudin-5, ZO-1 or Mucin-2 did not reach a significance level in DT-treated mice (online supplemental figure S10E). Importantly, immunofluorescent labelling of sIgA demonstrated that in Treg-depleted animals the population of sIgA producing cells within the lamina propria remained constant in pancreatitis (figure 6F).
Figure 6.
Depletion of Tregs attenuates microbial dysbiosis during pancreatitis and prevents bacterial translocation into pancreatic necroses. (A) Heat-map illustrates the major microbial taxa in the duodenum of DEREG treated with PBS (n=8) or DT (n=8) after induction of AP. Animals without AP referred as healthy controls (0d). Facultative pathogenic were marked in red, beneficial commensal bacteria were marked in green. (B) Box plots illustrate Shannon-Diversity Index and species richness in DT- or PBS-treated DEREG-mice. (C) A principal coordinate analysis illustrates significant differences of the duodenal microbiome between these groups (permutational multivariate analysis of variance; control vs severe: p<0.001, R2=18.2%). (D, E) Box plots show RT-qPCR analysis of duodenal transcriptional changes after depletion of Tregs. (F) Immunofluorescent labelling of sIgA producing cells in the duodenal mucosa from control and AP animals showed significantly decreased numbers of sIgA producing cells in AP mice which received PBS. (G) Staked-bar graphs illustrates bacterial taxa which could be identified in all samples with more than 5.000 clean reads from pancreatic necrosis in DEREG AP-mice (8 PBS treated vs 1 DT treated DEREG-mice). (H) The same bacterial taxa that appear or expand in the duodenum of AP-mice are found in murine pancreatic necrosis samples. The stacked bar graphs show the mean of all mice. (I) We analysed control (con) and duct-ligated DEREG mice with AP (PBS and DT) by 16S rRNA gene RT-qPCR analysis of isolated DNA from pancreatic tissue. Decreased Ct values indicate bacterial infection in the pancreas of mice with AP with a significant greater extent in the PBS-treated group compared with Treg depleted mice. Antibiotic treatment (+AB) significantly reduced the copy number of bacterial 16S rRNA gene in the pancreas and therefore prevented bacterial translocation during AP. (J, K) To evaluate how Tregs and microbiome composition affect the disease severity DEREG mice were treated after AP induction with antibiotics (AB), either in presence (+PBS) or absence (+DT) of Tregs. (J) Disease severity was evaluated by analysis of serum amylase and lipase. (K) Pancreatic histology was analysed by H&E-staining of tissue sections, histology score was evaluated by quantification of oedema, necrosis and leucocyte infiltration. The heatmap illustrates the mean result for all groups. Statistically significant differences were tested by unpaired Student’s t-test for independent samples. For more than two groups, statistical significance was determined by ANOVA one way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni correction for multiple testing, significance levels of p<0.05 are marked by an asterisk. ANOVA, analysis of variance; DT, diphtheria toxin; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp018.pdf (745.9KB, pdf)
Finally, we analysed whether Treg-depletion improves the stability of the intestinal barrier. We performed 16S rRNA gene sequencing in pancreatic tissue DNA of AP mice to detect any bacterial traces. A cut-off of 5000 clean reads was exceeded in 8/25 (32%) of PBS-treated mice, indicating infected pancreatic necrosis. In contrast, only 1/14 (7.14%) DT-treated mice reached the cut-off level (online supplemental figure S10F). Statistical analysis by Mann-Whitney test confirmed a significantly lower bacterial contamination of necrotic tissue in Treg-depleted mice. Facultative pathogens like Escherichia/Shigella, Enterobacteriaceae diversa, Staphylococcus or Enterococcus represented one of the 15th most abundant taxa within the necrotic areas (figure 6G, online supplemental figure S11A, B). A comparison between pancreatic samples and gut samples identified ASVs, which were observed with increased abundance both in duodenal samples (Escherichia/Shigella, Enterococcus and Citrobacter) as well as in necrotic areas of the pancreas (online supplemental figure S11C–E). In a comparative analysis we observed that the very same bacterial taxa that appear or multiply in the duodenal aspirates from AP-animals were isolated from murine pancreatic necrosis (figure 6H). Quantitative RT-qPCR revealed significantly higher numbers of 16S RNA gene copies (shown as lower dCt value) in the pancreas of PBS-treated mice compared with DT-treated mice with AP (figure 6I). Oral administration of an antibiotic cocktail containing 10 mg/mL ampicillin, 10 mg/mL neomycin, 5 mg/mL vancomycin and 10 mg/mL metronidazole, was performed every 12 hours over the experimental period23 and prevented bacterial translocation into the pancreas comparable to the depletion of Tregs by DT (figure 6I). 16S RNA gene sequencing of duodenal samples showed that antibiotic treatment prevented bacterial overgrowth in the duodenum of facultative pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia/Shigella, Enterococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterobacteriaceae or Klebsiella, whereas beneficial taxa like Lactobacillus remained (online supplemental figure S12A–C). We analysed in DT-treated animals whether the depletion of Tregs or an antibiotic therapy ameliorated the severity of pancreatitis. Enzymatic activities of common severity markers such as serum amylase and serum lipase were significantly lower in DT-treated and antibiotic-treated animals (figure 6J). In H&E-stained pancreatic sections less organ damage was seen in the Treg depleted mice as well as in antibiotic-treated mice. Histological scoring confirmed significantly less damage and reduced pancreatic necrosis in DT-treated and antibiotic-treated mice (figure 6K, online supplemental figure S12D). In conclusion, the results suggest that the ameliorating effect of Treg-depletion on disease severity is mainly due to the reduction of bacterial translocation. Depletion of Tregs in combination with antibiotic treatment showed no additional benefit.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp011.pdf (711.2KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp012.pdf (803.8KB, pdf)
Bacterial infection of human pancreatic necrosis
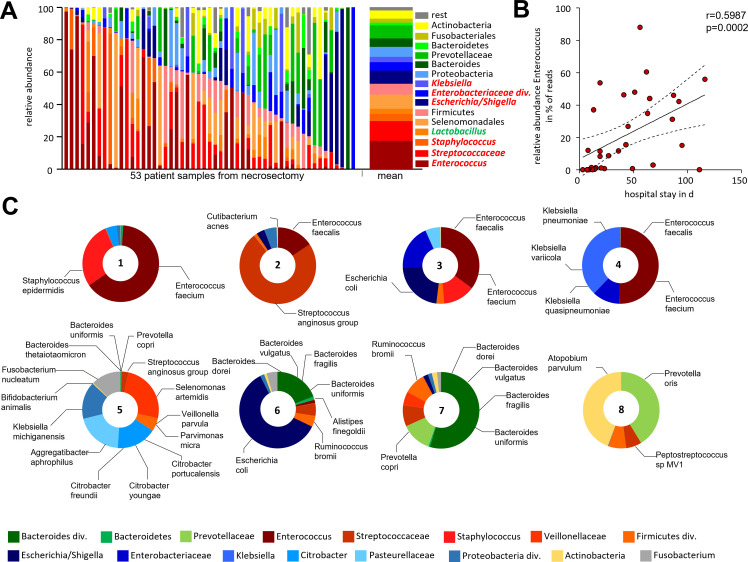
The bacterial colonisation of human pancreatic necrosis samples was analysed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. H&E-staining of these samples showed no remaining intact acinar tissue architecture (online supplemental figure S13A, B). For 58 individual patients (online supplemental figure S13C), samples ASVs were inferred from PCR-amplified 16S rRNA gene sequences. Samples with >5.000 clean reads (53/58) of representative ASV sequences were subsequently analysed (figure 7A). Firmicutes was found to be the most dominant phylum, representing more than 50% of the total relative abundance, mainly consisting of the genera Enterococcus, Streptococcus and Staphylococcus. The family of Enterobacteriaceae (phylum: Proteobacteria) also showed a high abundance with Escherichia/Shigella as the most frequent taxa (online supplemental figure S13D), the same taxa we observed in murine necrosis. Other phyla like Bacteroidetes, Fusobacteria or Actinobacteria were found with considerably lower abundance. Some patients underwent multiple subsequent necrosectomy procedures and the analysis of follow-up samples showed that the microbiome in these necrotic samples was rather stable over periods of several weeks (online supplemental figure S14A). Infection of pancreatic necrosis by Enterococcus showed a significant correlation with the length of hospitalisation (figure 7B). None of the other 15 frequent taxa (online supplemental figure S13D) of facultative pathogens or the commensal gut bacteria showed this kind of correlation (online supplemental figure S14B). Subgroup analyses regarding AP versus acute episode of CP showed differences, but the high variance in the microbiome composition of pancreatic necrosis and the relative low number of patients did not allow to draw firm conclusions (online supplemental figure S14C). Additional metagenomic sequencing of eight necrosis samples (figure 7C) identified the infecting bacterial species Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Escherichia coli, Bacteroides spp and Citrobacter spp, these taxa are frequently found in the gut.
Figure 7.
Bacterial infection of human pancreatic necrosis. (A) The bar chart represents the major bacterial taxonomic units that were identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing in 53 samples of human pancreatic necrosis. Facultative pathogenic were marked in red, beneficial commensal bacteria were marked in green. (B) Enterococcus was observed in necrosectomy samples of 33 patients and thus represented the most abundant taxon and showed a positive correlation with the duration of hospitalisation (Spearman correlation p=0.0002, Spearman r=0.599). (C) Bacterial species were analysed using metagenomic-shotgun sequencing of eight selected necrosis samples. Identified commensal gut bacteria include from the phylum Firmicutes Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium and Streptococcus anginosus. In addition, Escherichia coli (phylum of Proteobacteria) and Bacteroides dorei, Bacteroides vulgatus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides uniformis and Prevotella copri as representatives of the phylum Bacteroidetes were detected.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp013.pdf (1.6MB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp014.pdf (750.9KB, pdf)
In summary, our observations suggest that the infection of pancreatic necrosis is driven by commensal facultative pathogenic bacteria from the gut. In mice we demonstrated that CD25+/FOXP3+ Tregs are activated in AP, which contributes to a state of immunosuppression and affects the leakiness of intestinal mucosa (online supplemental figure S15). The suppression of lymphocytes in the lamina propria as well as of IELs in the duodenum allows overgrowth of facultative pathogenic bacteria and a breakdown of the intestinal barrier function which paves the way for bacterial translocation and infection of pancreatic necrosis.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp015.pdf (380.3KB, pdf)
Discussion
AP is a leading cause of hospital admission among GI disorders and infected pancreatic necrosis represents a major therapeutic challenge and a life-threatening event in the course of the disease.2 24 The effect of the immune response driving infected necrosis has not been studied in detail, but it is assumed that in the later phase of the disease CARS triggers commensal bacteria translocation from the intestine into pancreatic necrosis. While SIRS has been intensively studied in patients and animal models,7–9 25 the mechanisms leading to CARS or immunosuppression are not well understood. Recent data suggest that SIRS and CARS are competing processes and run in parallel in pancreatitis,12 26 similar to the situations in sepsis16 or severe trauma.17 Further evidence suggested a link between the intestinal mucosa immune response and commensal bacteria,27 where an imbalance is associated with changes in the intestinal microbial composition as observed in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).28
In the current study, we demonstrate a prominent role of Tregs that get activated in AP and contribute to a breakdown of the duodenal mucosa barrier function. Consequently, the compromised mucosal barrier facilitates translocation and colonisation of pancreatic necrosis by commensal facultative pathogenic bacteria. The development of AP is accompanied by a complex immune response, which involves innate immune cells such as macrophages7 8 and neutrophils,7 9 as well as cells of the adaptive immune system such as T-cells.12 15 AP represents a primarily sterile inflammation driven by necrotic acinar cell death where proinflammatory macrophages react to DAMPs and stimulate the systemic immune responses by the release of cytokines and chemokines.8 11–13 On the other side, counter regulating CD25+/FOXP3+ Tregs are activated in parallel.12 15 Increased numbers of activated Tregs 16 29 are considered to facilitate secondary infections.30 Whereas pancreatic necrosis triggers proinflammation and development of SIRS, systemic anti-inflammation arises to prevent the development of vasoplegic shock. In our study, we identified Tregs to play a central part in mediating immunosuppression. In mice suffering from AP, increased numbers of Tregs with high suppressive capacity exert a negative systemic influence on Teff proliferation and differentiation. This immunosuppression also affects the intestinal mucosa, where large numbers of T-cells build a defence line against the intestinal microbiome. Treg help preserve the barrier function and are essential for the maintenance of tolerance against commensal bacteria, which in turn also influence the Treg response via their metabolites.31 Apparently, in the course of pancreatitis, this quid pro quo situation sometimes gets out of hand. Following onset of AP two things happen: (1) reduced zymogen secretion causes microbial dysbiosis,32 33 (2) a Treg-mediated systemic immunosuppression weakens the intestinal immune defence against facultative pathogen overgrowth. In our mouse model of AP we observed a positive correlation between Tregs and infected necrosis. The prophylactic depletion of Tregs in DEREG-mice20 was shown to mitigate pancreatitis and to reduce the bacterial load of necrosis. The suppressive capacity of Teff by Tregs was confirmed in spleen and in the intestinal mucosa. Consequently, a significant reduction of duodenal lymphocytes could be demonstrated in histology, flow cytometry and transcriptome analyses of duodenal tissue. We identified upstream regulators such as TGFβ and IL-1β, which were transcriptionally induced in duodenum and in splenic Tregs, whereas the T-cell growth factor IL-2 was repressed. Recent studies indicated a central role of IL-1β for T-cell apoptosis after severe injuries,34 which is associated with an increased risk for secondary infections. During AP IL-1β is released at high rates by pancreatic macrophages.12 Tregs are known to induce Teff apoptosis,35 but are themselves resistant to apoptosis inducing ligands.36 Taken together these observations may explain the loss of duodenal Teff during AP. Furthermore, a comparative transcriptome analysis of Tregs showed increased signalling via STAT3, which is known to be essential for Treg-mediated suppression of a Th17 response.37 Furthermore, the cytokines IL-6 and TGFβ play crucial roles for the balance of FOXP3+/CD25+ Tregs and RORγt+ Th17-cells.38 In the duodenal tissue, we observed a pancreatitis-induced upregulation of IL-6 and TGFβ and we counted increased numbers of FOXP3+/CD25+ Tregs and RORγt+ Th17-cells.
Th17-cells are involved in maintaining intestinal integrity and barrier function.39 In addition to host factors or metabolites from the gut microbiome, microbial dysbiosis in itself like the one induced by AP is able to influence the Treg/Th17 balance.40 41 Species of Clostridia, a highly polyphyletic class of Firmicutes, have been reported to induce a Th17 or Treg response,40–42 commensal strains from the genus Bacteroides are also known inducers of Tregs.43 Microbial dysbiosis like the one observed in mouse models of AP and infection of human necrosis often results in increased abundance of Proteobacteria, 44 which are able to influence the T-cell response.45 This effect on the immune system is not restricted to single strains as it is well accepted that the microbiome as a whole interacts with the intestinal immune system and is a silent regulator of various disease-related pathomechanisms.44 Mice suffering from AP have a clearly reduced microbiota-diversity and richness in their duodenum and caecum, which correlates with an increased immunosuppression mediated via FOXP3+/CD25+ Tregs. In Treg -depleted animals, these pancreatitis-induced microbiota changes are less pronounced, which could be explained by a persistence of an intact Th17-sIgA-axis,46 even in the absence of Treg. The overgrowth of facultative pathogens Escherichia/Shigella, Enterococcus or Staphylococcus is attenuated and a higher Teff response in Treg-depleted mice seems sufficient to prevent bacteria from crossing the intestinal barrier. 16S rRNA gene sequencing of colonic, caecal and duodenal samples suggests that the bacterial colonisation of pancreatic necrosis originates from the duodenum. In our mouse model of partial duct ligation an invasion of bacteria via the pancreatic duct can be excluded, hence the microbes must have overcome the intestinal barrier. The fact that the same facultative pathogenic taxa from our mouse model were identified in human pancreatic necrosis suggests a general pathomechanism and indicates clinical relevance of our findings. Notably, the translocation of Enterococcus into human necrosis correlates with hospital admission, one reason being, that antibiotic-resistant enterococci in particular are becoming more common and more difficult to treat.47 However, our analysis of human samples lacks information on differences in the patient’s antibiotic regimen, including length of antibiotic treatment, the time point of sample retrieval within the course of the disease, enteral feeding, resistant strains and additional proton pump inhibitor and/or enzyme replacement therapy.
The intestinal mucosal barrier prevents bacteria from invading the body but, at the same time, maintains tolerance to commensal intestinal bacteria. IELs are important regulatory cells of the gut barrier integrity22 and a dysregulation of IELs has previously been associated with IBD.48 In contrast to the chronic inflamed situation, we observed in AP a highly significant decrease of CD8α+/γδTCR+ IELs, which are known to play a crucial role in anti-microbial defence.49 γδTCR+ IELs represent natural IELs which develop independently from the thymus. Their proliferation is regulated by Tregs in order to maintain immune homoeostasis.50 After induction of AP we observed a general decrease of IELs, including a significant shift from γδTCR+ natural-IELs to αβTCR+ induced-IELs. The depletion of Tregs did not prevent this shift but attenuated the reduction of the CD8α+/γδTCR+ IELs which help to maintain the barrier function. Besides the CD8α+ IELs also CD4hi IELs were increased in the absence of Tregs. They were identified as Th17-cells by expression of the transcription factor RORγt. Interestingly, in PBS-treated mice, we identified a population of CD4hi/FOXP3+ Tregs, which were completely absent in DT-treated DEREG mice. It is known that Tregs from the lamina propria migrate into the epithelium and to change their differentiation through the loss of FOXP3 and ThPOK in a microbiota dependent manner. Presumably this occurs in an effort to control gut inflammation.51
In conclusion, our study demonstrates that in an SAP the bacterial infection of necrosis originates from a changed microbiota composition of the duodenum. The systemic immunosuppressive capacity of Tregs weakens the duodenal antibacterial mucosa defence by inhibiting Teffs in the lamina propria, as well as IELs, especially CD8α+/γδTCR+ IELs. We identified facultative pathogens Escherichia/Shigella, Enterococcus or Staphylococcus in mouse AP models as well as in pancreatic necrosis of AP patients. In both cases these pathogenic bacteria were able to overcome the intestinal barrier and to invade pancreatic necrosis. A depletion of FOXP3+/CD25+ Tregs in our mouse model of AP successfully attenuated bacterial infection of necrosis. Our data identified a critical role of Tregs affecting disease severity of AP and demonstrate the importance of an intact intestinal barrier in preventing complications caused by bacterial translocation.
Material and methods
Human sample collection
Samples of pancreatic necrosis were collected from patients undergoing endoscopic drainage therapy at the University Medicine Greifswald in the years 2016–2020.
Animal model
All animal experiments were performed based on the ARRIVE guideline, after the approval by the state Committee for animal experiments (LALLF-MV, Landesamt für Landwirtschaft, Lebensmittelsicherheit und Fischerei Mecklenburg-Vorpommern). C57Bl/6 mice were purchased from Charles River (Sulzfeld, Germany) and DEREG mice were available from our own animal facility (University Medicine Greifswald, Germany). A necrotic form of AP was induced by partial pancreatic duct ligation and one additional single i.p.-injection of caerulein (50 µg/kg/bodyweight) 2 days later8 (online supplemental figure S16A). GFP+regulatory T cells (Tregs) were depleted in DEREG mice20 21 by i.p. injection of 1 µg DT 3 days before and at the day of induction of pancreatitis. Control animals received PBS injections (online supplemental figure S16B). Depletion of Ly6g+ cells was achieved by i.p. injection of 200 µg of anti-Ly6g antibody (BP0075-1, BioCell) 24 hours before and 1 day after induction of pancreatitis.14 Control animals received rat IgG2a isotype antibody (BP0089, BioCell). Antibiotic treatment was achieved by oral administration of 200 µL of an antibiotic composition containing 10 mg/mL ampicillin (A9393, Sigma), 10 mg/mL neomycin (PHR1491, Sigma), 5 mg/mL vancomycin (V2002, Sigma) and 10 mg/mL metronidazole (M3761, Sigma).23 Antibiotic treatment was performed two times daily starting at the day of onset of AP (online supplemental figure S16C). Animals from one shipment (Charles River Germany) were used to ensure uniform microbial colonisation and animals were housed in numbers of 5–6 animals per cage. There was no mixed housing of animals with AP and controls. We deliberately did not mix these groups to avoid a possible horizontal microbiome transfer.
gutjnl-2022-327448supp016.pdf (528.6KB, pdf)
All animals were sacrificed 3 days after induction of SAP. The collected serum was stored at −80°C. Pancreas, lymph nodes, small intestine and lung were removed and either fixed in 4.5% formaldehyde, embedded in TissueTec for histological analysis or were shock frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C. Spleen and small intestine were removed and homogenised immediately for flow cytometry analysis.
Caerulein induced pancreatitis was started by eight-hourly i.p. injections of caerulein (50 µg/kg/bodyweight) for three consecutive days. One day after the last injections mice were sacrificed (online supplemental figure S16D).
16S rRNA gene Sequencing
DNA was isolated from murine duodenal, caecal and colonic samples using the PSP Spin Stool DNA kit from Stratec Molecular (Berlin, Germany), DNA of human and murine pancreatic necrosis was isolated by PureLink Quick Plasmid Miniprep Kit (Invitrogen) for amplification of the V1-V2 region of bacterial 16S rRNA genes) and sequenced on MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, USA) as previously described.32 52 Sequencing data were processed using the DADA2 package (V.1.14)53 for R (V.3.61). Briefly, forward and reverse reads were trimmed to 230 and 180 bp, respectively, or at the first base with a quality of 5. Reads-pairs with ambiguous basecalls or expected errors larger than 2 were discarded. Error profiles were inferred from 10⁹ bases from randomly selected clean forward and reverse reads separately, which were subsequently used for read correction and inference of ASV. Chimeric reads were identified and removed from the dataset using a de novo consensus-based approach to create the final ASV-by-sample count table. Taxonomic annotations of ASV sequences were inferred using the Bayesian classifier of the DADA2 package and the Ribosomal Database Project release 16 database.54 Only samples with more than 5.000 clean reads were included in our further analysis. 16S rRNA sequencing data have been deposited in a public repository (DOI 10.5281/zendodo.7111473).55 Due to the high abundance of the taxa Escherichia/Shigella, we presented the data separately, whereas the other taxa of the family Enterobacteriaceae were summarised into the taxon Enterobacteriaceae diversa. Bar graphs and staked bar graphs represent the 10 most abundant taxa identified in each group. Heat maps represent all taxa with a relative abundance of ≥0.1%.
Metagenome analysis
For metagenome analysis, quality as well as quantity of DNA samples were determined by using the Genomic DNA ScreenTape (Agilent, Illumina, Santa Clara, USA). Subsequently, metagenomic libraries were prepared by using Illumina DNA Flex Library Preparation Kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Sequencing was performed with 2×150 bp on a NovaSeq machine SP FlowCell (Illumina). Raw sequencing data were quality controlled using the bbduk.sh software from the BBTools software suite (V.38.79–0) to remove low quality sequence data as well as non-biological sequences from Illumina sequencing adaptors and PhiX spike-in control. Host DNA sequences were removed by mapping against the GRCh38.13 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assembly/GCF_000001405.39/) human genome reference sequence using bowtie2 (V.2.3.5.1).56 Metaphlan (V.3)57 was used for microbial community profiling using the clean metagenomic sequence data as input files.
Antibodies
The following antibodies and kits were used for immunofluorescence and flow-cytometry analysis: anti-CD4-PerCP/Cy5.5 (100434, BioLegend), anti-CD4-BV605 (100548, BioLegend), anti-CD4-PE (100408, BioLegend), anti-CD4-BV650 (100469, BioLegend), anti-CD25-Alexa647 (102020, BioLegend), anti-CD25-PE/Cy7 (102016, BioLegend), anti-CD25-FITC (101908, BioLegend), anti-CD69 BV510 (104532, BioLegend), anti-CD8a-PE (100708, BioLegend), anti-RORγt-Vio515 (130-124-078, MiltenyiBiotec), anti-GATA3-BV421 (653814, BioLegend), anti-GATA3-PE (653804, BioLegend) anti-TBET- PerCP/Cy5.5 (644806, BioLegend), anti-Tbet-BV421 (644816, BioLegend) anti-FOXP3-APC (130-093-013, MiltenyiBiotec), anti-CD11b- PerCP/Cy5.5 (101228, BioLegend), anti-LY6G-BV421 (127628, BioLegend), anti-LY6C-BV605 (128036, BioLegend), anti- TCRβ -BV421 (109229, BioLegend, anti-TCRγδ-PE (118108, BioLegend), anti CD3 (100202; BioLegend), anti-CD68 (ABIN181836, antibodies-online), anti GFP (ab6673, abcam), anti-IgA (NB7501, Novus), anti-E-cadherin (610182, BD Transduction Laboratories), anti-Ki-67 (IHC-00375, Bethyl), anti-F4/80-PE (123110, BioLegend) anti-FITC IgG (SAB4600050, sigma), anti-rat-Cy5 (112-175-143, Jackson ImmunoResearch), anti-goat-FITC (205-095-108, Jackson ImmunoResearch).
Bacteriological analysis of murine pancreatic tissue
The pancreas of mice was removed under sterile conditions. The ligated part of the pancreas, which was clearly identifiable by the surgical string as well as by the AP, was prepared, weighed and immediately homogenised in sterile phosphate-buffered saline. Homogenates were plated on 2% LB-Agar plates at a dilution of 1:10 and 1:100 (3 plates each dilution and sample) and incubated for 24 hours at 37°C. Colonies were counted and CFU/mg pancreatic tissue were calculated.
Isolation of lymphocytes from small intestine
We used the Lamina Propria Dissociation Kit (130-097-410, MiltenyiBiotec) for the preparation of single cell suspensions from samples of 3–5 cm mouse small intestine according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The tissue was cut longitudinally and laterally into small pieces. IELs were separated from the mucosa by shaking the tissue pieces in a predigestion solution (HBSS(w/o), 5 mM EDTA, 5% fetal calf serum (FCS), 1 mM DTT) for 20 min at 37°C and passing the tissue solution through a 100 µm cell strainer. This step was repeated three times. Finally, the lamina propria tissue was further treated with the manufactures enzyme mix and dissociated with the gentleMACS Dissociator (130-093-235, MiltenyiBiotec).
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry analysis was done on cells isolated from the spleen and small intestines. Splenocytes were separated through a 70 µm cell strainer. After washing and lysis of erythrocytes (10× Lysis Buffer: 1,5M NH4Cl, 100 mM KHCO3, 0,5M EDTA), 1×106 cells were preincubated with 1 µL FcR Blocking Reagent (130-092-575, MiltenyiBiotec) and stained for extracellular surface marker (CD4, CD8α and CD25; CD11b, Ly6g and Ly6c or CD4, CD8α, TCRβ and TCRγδ) at 4°C for 30 min. The Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set (130-122-981, MiltenyiBiotec) was used for fixation and permeabilisation. Afterwards, the cells were again treated with FcR Blocking Reagent and stained for transcription factors (RORγt, GATA3, TBET and FOXP3) at 4°C for 30 min. Data evaluation was done by flow cytometry (BD, LSRII) and FlowJo (BD).
Suppression assay
AP was induced in DEREG mice. After 3 days, the mice were sacrificed, the spleen was removed and splenocytes were separated through a 70 µm cell strainer. After washing with PBS, 10×106 cells/mL were sorted on a BD FACSAria III Cell Sorter for GFP+ Tregs. The cells were resuspended at a concentration of 5×105 cells/mL in TexMACS medium (130-097-196, MiltenyiBiotec).
T cells were isolated from the spleen of healthy wildtype mice (Naive CD4+T Cell Isolation Kit, Mouse, 130-104-453 Miltenyi Biotech) and were used as Teff cells. 1×106 Teff/ml were labelled with 1 mM CM-Dil (Vybrant CM-DiI Cell-Labeling Solution, V22885, Invitrogen) and stimulated with CD3/CD28 Beads (2 µL/Well, Dynabeads Mouse T-Activator CD3/CD28, 11 456D, GIBCO) and IL-2 (100 U/mL, 130-120-662 Miltenyi Biotech). The co-culture was incubated for 5d at Treg/Teff ratios of 1:1, 1:2, 1:4 and 1:8. After removal of the beads, the cells were stained for the surface marker CD4 and CD25 and analysed by flow cytometry (BD, LSRII). The Teff proliferation was calculated from the CM-Dil fluorescence.
Serum amylase and lipase activity determination
The enzyme activities of serum amylase and lipase were measured with the colorimetric kit Amyl (Ref 11876473316) and Lip (Ref. 11821792216) from Roche/Hitacho.
Determination of serum cytokines IL-6 and TNFα
Serum cytokine concentrations were determined by Cytometric Bead Array Mouse inflammation kit (BD 552364, BD Bioscience, San Jose, California, USA).
Determination of myeloperoxidase activity
The myeloperoxidase activity in tissue homogenates of the lung was determined by photometric measurement according to an established protocol as previously described.7
Apoptosis assay
TUNEL assay was performed from paraffin embedded murine spleen by FragEL DNA Fragmentation Detection Kit (QIA39-1EA, Millipore/Calbiochem Billerica, Massachusetts, USA).
Histology and immunofluorescence
H&E staining was done on 2 µm microtome sections from paraffin embedded tissue samples. Immunofluorescence staining was performed from 2 µm cryo slides fixed with acetone. After blocking with 20% FCS, primary antibodies were used at 1:200 dilution in blocking buffer and were incubated overnight at 4°C. Secondary antibodies were used in a dilution of 1:200 for 1 hour at room temperature. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI. Tissue sections were scanned with Pannoramic MIDI II (Sysmex) and analysed by QuantCenter-Software (Sysmex).
Microarray-based transcriptome analysis
Snap-frozen intestinal tissue samples were homogenised using the Retsch dismembrator in presence of 700 µL Trizol. Total RNA was isolated following the manufacturer’s instructions for total RNA isolation from Phenol/guanidinium thiocyanate-based RNA isolation methods (RNA_Clean-Up and Concentration Kit, Norgen, Thorold, Canada). After purification and quality assessment of the total RNA preparations, transcriptional profiling of intestinal tissue was performed using the WT Plus Kit and Clariom S mouse arrays (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Transcriptome analyses of isolated Tregs from spleen from 4 mice and four controls and duodenal mucosa from 4 mice with AP and four controls were performed accordingly. For probe set extraction and normalisation, expression raw data were transferred to the Transcriptome Analysis Console (TAC, 4.0.2.15, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). The generated gene expression data sets have been submitted to Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Statistical analysis of the case control study based on four biological replicates for each group was performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) with e-Bayesian correction. Statistically significant differential gene expression in terms of transcript levels was defined as a fold change of > |2| between the compared conditions and an FDR<0.05. Functional annotation and pathway analysis of differentially expressed genes were performed using the IPA software (Ingenuity Systems, version 68752261, Qiagen, Venlo, NL). Microarray data have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information GEO database and are accessible through the following GEO accession number: GSE196481.
Gene expression analysis by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
Mouse small intestine tissue was homogenised in TRIZOL for RNA extraction (TRIzol Reagenz, 15596026, Invitrogen). The isolated RNA was reversely transcribed in cDNA using the First strand cDNA synthesis kit using M-MLV Reverse transcriptase (28025013, Invitrogen). qPCR analysis was performed by using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (4309155, Applied Biosystems) on a QuantStudio 7 Flex Real-Time PCR System. Primer sequences are listed in the following table. Derived transcript level data were normalised to Rn5s and are shown as fold change relative to those of untreated control mice. The 2-ΔΔCt-method was used to determine relative changes in mRNA levels. Samples were analysed from 10 ng DNA for the determination of 16S rRNA gene in murine pancreas, 5S referred as control. The following primers were used; Gfp forward 5’-ACGTAAACGGCCACAAGTTC-3’, reverse 5’-AAGTCGTGCTGCTTCATGTG-3’, Tjp1 forward 5’-CCACCTCTGTCCAGCTCTTC-3’, reverse 5’-CACCGGAGTGATGGTTTTCT-3’, Cldn5 forward 5’-GCTCTCAGAGTCCGTTGACC-3’, reverse 5’-CTGCCCTTTCAGGTTAGCAG-3’, Ocln forward 5’-ACTCCTCCAATGGCAAAGTG-3’, reverse 5’-CCCCACCTGTCGTGTAGTCT-3’, Cldn1 forward 5’-TCCTTGCTGAATCTGAACA-3’, reverse 5’-AGCCATCCACATCTTCTG-3’, Muc2 forward 5’-CAAGTGATTGTGTTTCAGGCTC-3’, reverse 5’-TGGAGATGTTCTTGGTGCAG-3’, Defa5 forward 5’-AGGCTGATCCTATCCACAAAACAG-3’, reverse 5’-TGAAGAGCAGACCCTTCTTGGC-3’, Lyz2 forward 5’-ATGGAATGGCTGGCTACTATGG-3’, reverse 5’-ACCAGTATCGGCTATTGATCTGA-3’, Lyz1 forward 5’-GAGACCGAAGCACCGACTATG-3’, reverse 5’-CGGTTTTGACATTGTGTTCGC-3’, Reg3g forward 5’-TTCCTGTCCTCCATGATCAAAA-3’, reverse 5’-CATCCACCTCTGTTGGGTTCA-3’, Ifng forward 5’-TCTTCCTCATGGCTGTTTCTG-3’, reverse 5’-CACCATCCTTTTGCCAGTTC-3’, Il17a forward 5’-TCCAGAAGGCCCTCAGACTA-3’, reverse 5’-ACACCCACCAGCATCTTCTC-3’, Il10 forward 5’-TTGAATTCCCTGGGTGAGAAG-3’, reverse 5’-TCCACTGCCTTGCTCTTATTT-3’, Il22 forward 5’-TCAGCTCAGCTCCTGTCACAT-3’, reverse 5’-TCCCCAATCGCCTTGATCTCT-3’, Il15 forward 5’-CGTGCTCTACCTTGCAAACA-3’, reverse 5’-TCTCCTCCAGCTCCTCACAT-3’, Tnfa forward 5’-GCCTCCCTCTCATCAGTTCTAT-3’, reverse 5’-CACTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGA-3’, Il17f forward 5’-CGCCATTCAGCAAGAAATCC-3’, reverse 5’-CTCCAACCTGAAGGAATTAGAACAG-3’, Tnfsf13 forward 5’-CAGTCCTGCATCTTGTTCCA-3’, reverse 5’-GCAGATAAATTCCAGTGTCCC-3’, Tnfsf13b forward 5’-TGCCTTGGAGGAGAAAGAGA-3’, reverse 5’-GGCAGTGTTTTGGGCATATT-3’, Defa29 forward 5’-AGCAGCCATTGTGCGAAGAA-3’, reverse 5’-TGCTGTGTATTTGGAGCTTGG-3’, Cdh1 forward 5’-GGTTTTCTACAGCATCACCG-3’, reverse 5’-GCTTCCCCATTTGATGACAC-3’, Jchain forward 5’-CGTCCAAGAATTGGATGTGA-3’, reverse 5’-AGTGACAGGCTGGGATGG-3’, 16sRNA forward 5’-AAACTCAAATGAATTGACGG-3’, reverse 5’-TCACAACACGAGCTGACG-3’, 5sRNA forward 5’-GCCCGATCTCGTCTGATCTC-3’, reverse 5’-GCCTACAGCACCCGGT-3’, Lactoccocaceae forward 5’-AGCAGTAGGGAATCTTCCA-3’, reverse 5’-CACCGCTACACATGGAG-3’, Lachnospiraceae forward 5’-CGGTACCTGACTAAGAAGC-3’, reverse 5’-AGTTTCATTCTTGCGAACG-3’, E. coli forward 5’-GTTAATACCTTTGCTCATTGA-3’, reverse 5’-ACCAGGGTATCTAATCCTGT-3’, Enterococcus faecium forward 5’-CCCTTATTGTTAGTTGCCATCATT-3’, reverse 5’-ACTCGTTGTACTTCCCATTGT-3’,
Data analysis and statistics
All statistical analyses were performed using SigmaPlot or GraphPad Prism. All graphs were created by Sigma Plot, GraphPad Prism or ‘R’. Calculation of ‘Shannon diversity’ and ‘Richness’ as well as the PCoA (Bray-Curtis or Jaccard) were performed by using the R package ‘vegan’. Heat maps were created by R package ‘gplots’. The flow cytometry data were analysed and displayed using FlowJo software. Statistical analysis was performed using the two tailed Student’s t-test and the two tailed Mann-Whitney test, permutational multivariate ANOVA or ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction. Comparison of microbial taxa were analysed by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by a Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, or two tailed contrast analysis of taxa shown in heat maps.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jochen Huehn for providing the DEREG mice. Also many thanks to Kathrin Gladrow, Diana Krüger, Susanne Wiche and Jenny Radel for their technical support.
Footnotes
Twitter: @mruehlemann
Correction notice: This article has been corrected since it published Online First. The supplementary figures have been amended.
Contributors: Concept of the study: MS, F-UW and JG. Data acquisition and interpretation: JG, AW, AA, SA, GH, HM, MCR, CB, AF, TP, MS, BMB, FF and UV. Writing committee MS, F-UW and JG. Correction of manuscript and approval of final version: all. MS is responsible for the overall content as guarantor.
Funding: This work was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG SE 2702/2-1, SE 2702/2-3, GL 1096/1-1, GRK 1947, GRK 2719, SFB 1321: 329628492), the PePPP center of excellence MV (ESF/14-BM-A55-0045/16). Further support was received from the RESPONSE project (BMBF grant number 03ZZ0921E and 03ZZ0931F).
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient and public involvement: Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Data availability statement
Data are available in a public, open access repository. 16S rRNA sequencing data have been deposited in a public repository (DOI 10.5281/zendodo.7111473). Microarray data have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and are accessible through the following GEO accession number: GSE196481.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Consent obtained directly from patient(s).
Ethics approval
This study involves human participants and was approved by University Medicine Greifswald (III UV91/03 and III UV91/03). Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
References
- 1. Peery AF, Crockett SD, Murphy CC, et al. Burden and cost of gastrointestinal, liver, and pancreatic diseases in the United States: update 2018. Gastroenterology 2019;156:254–72. 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. van Dijk SM, Hallensleben NDL, van Santvoort HC, et al. Acute pancreatitis: recent advances through randomised trials. Gut 2017;66:2024–32. 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313595 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Wolbrink DRJ, Kolwijck E, Ten Oever J, et al. Management of infected pancreatic necrosis in the intensive care unit: a narrative review. Clin Microbiol Infect 2020;26:18–25. 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.06.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Neumann C, Blume J, Roy U, et al. c-Maf-dependent Treg cell control of intestinal TH17 cells and IgA establishes host-microbiota homeostasis. Nat Immunol 2019;20:471–81. 10.1038/s41590-019-0316-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Sendler M, Maertin S, John D, et al. Cathepsin B activity initiates apoptosis via digestive protease activation in pancreatic acinar cells and experimental pancreatitis. J Biol Chem 2016;291:14717–31. 10.1074/jbc.M116.718999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Gukovsky I, Gukovskaya AS, Blinman TA, et al. Early NF-kappaB activation is associated with hormone-induced pancreatitis. Am J Physiol 1998;275:G1402–14. 10.1152/ajpgi.1998.275.6.G1402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Sendler M, Dummer A, Weiss FU, et al. Tumour necrosis factor α secretion induces protease activation and acinar cell necrosis in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice. Gut 2013;62:430–9. 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300771 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Sendler M, Weiss F-U, Golchert J, et al. Cathepsin B-mediated activation of trypsinogen in Endocytosing macrophages increases severity of pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2018;154:704–18. 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Gukovskaya AS, Vaquero E, Zaninovic V, et al. Neutrophils and NADPH oxidase mediate intrapancreatic trypsin activation in murine experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2002;122:974–84. 10.1053/gast.2002.32409 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. John DS, Aschenbach J, Krüger B, et al. Deficiency of cathepsin C ameliorates severity of acute pancreatitis by reduction of neutrophil elastase activation and cleavage of E-cadherin. J Biol Chem 2019;294:697–707. 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Wu J, Zhang L, Shi J, et al. Macrophage phenotypic switch orchestrates the inflammation and repair/regeneration following acute pancreatitis injury. EBioMedicine 2020;58:102920. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Sendler M, van den Brandt C, Glaubitz J, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome regulates development of systemic inflammatory response and compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndromes in mice with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2020;158:253–69. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Zhao Q, Wei Y, Pandol SJ, et al. STING Signaling Promotes Inflammation in Experimental Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2018;154:1822–35. 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Wilden A, Glaubitz J, Otto O, et al. Mobilization of CD11b+/Ly6c hi monocytes causes multi organ dysfunction syndrome in acute pancreatitis. Front Immunol 2022;13:991295. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.991295 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Glaubitz J, Wilden A, van den Brandt C, et al. Experimental pancreatitis is characterized by rapid T cell activation, Th2 differentiation that parallels disease severity, and improvement after CD4+ T cell depletion. Pancreatology 2020;20:1637–47. 10.1016/j.pan.2020.10.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G, Payen D. Sepsis-Induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 2013;13:862–74. 10.1038/nri3552 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Xiao W, Mindrinos MN, Seok J, et al. A genomic storm in critically injured humans. J Exp Med 2011;208:2581–90. 10.1084/jem.20111354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Gentile LF, Cuenca AG, Efron PA, et al. Persistent inflammation and immunosuppression: a common syndrome and new horizon for surgical intensive care. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2012;72:1491–501. 10.1097/TA.0b013e318256e000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Memba R, Duggan SN, Ni Chonchubhair HM, et al. The potential role of gut microbiota in pancreatic disease: a systematic review. Pancreatology 2017;17:867–74. 10.1016/j.pan.2017.09.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Lahl K, Loddenkemper C, Drouin C, et al. Selective depletion of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induces a scurfy-like disease. J Exp Med 2007;204:57–63. 10.1084/jem.20061852 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Glaubitz J, Wilden A, Golchert J, et al. In mouse chronic pancreatitis CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells control pancreatic fibrosis by suppression of the type 2 immune response. Nat Commun 2022;13:4502. 10.1038/s41467-022-32195-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Cheroutre H, Lambolez F, Mucida D. The light and dark sides of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Nat Rev Immunol 2011;11:445–56. 10.1038/nri3007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kennedy EA, King KY, Baldridge MT. Mouse microbiota models: comparing germ-free mice and antibiotics treatment as tools for modifying gut bacteria. Front Physiol 2018;9:1534. 10.3389/fphys.2018.01534 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Petrov MS, Shanbhag S, Chakraborty M, et al. Organ failure and infection of pancreatic necrosis as determinants of mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2010;139:813–20. 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Mofidi R, Duff MD, Wigmore SJ, et al. Association between early systemic inflammatory response, severity of multiorgan dysfunction and death in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg 2006;93:738–44. 10.1002/bjs.5290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Zhang R, Shi J, Zhang R, et al. Expanded CD14 hi CD16- Immunosuppressive Monocytes Predict Disease Severity in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. J Immunol 2019;202:2578–84. 10.4049/jimmunol.1801194 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Rooks MG, Garrett WS. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2016;16:341–52. 10.1038/nri.2016.42 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Honda K, Littman DR. The microbiome in infectious disease and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol 2012;30:759–95. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-074937 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Venet F, Chung C-S, Monneret G, et al. Regulatory T cell populations in sepsis and trauma. J Leukoc Biol 2008;83:523–35. 10.1189/jlb.0607371 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Conway Morris A, Anderson N, Brittan M, et al. Combined dysfunctions of immune cells predict nosocomial infection in critically ill patients. Br J Anaesth 2013;111:778–87. 10.1093/bja/aet205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Kamada N, Seo S-U, Chen GY, et al. Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2013;13:321–35. 10.1038/nri3430 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Frost F, Kacprowski T, Rühlemann M, et al. Impaired exocrine pancreatic function associates with changes in intestinal microbiota composition and diversity. Gastroenterology 2019;156:1010–5. 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Ahuja M, Schwartz DM, Tandon M, et al. Orai1-Mediated antimicrobial secretion from pancreatic acini shapes the gut microbiome and regulates gut innate immunity. Cell Metab 2017;25:635–46. 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.02.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Roth S, Cao J, Singh V, et al. Post-Injury immunosuppression and secondary infections are caused by an AIM2 inflammasome-driven signaling cascade. Immunity 2021;54:648–59. 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.02.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Pandiyan P, Zheng L, Ishihara S, et al. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce cytokine deprivation-mediated apoptosis of effector CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 2007;8:1353–62. 10.1038/ni1536 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Fritzsching B, Oberle N, Pauly E, et al. Naive regulatory T cells: a novel subpopulation defined by resistance toward CD95L-mediated cell death. Blood 2006;108:3371–8. 10.1182/blood-2006-02-005660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Chaudhry A, Rudra D, Treuting P, et al. CD4+ regulatory T cells control TH17 responses in a STAT3-dependent manner. Science 2009;326:986–91. 10.1126/science.1172702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 2006;441:235–8. 10.1038/nature04753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Lee JS, Tato CM, Joyce-Shaikh B, et al. Interleukin-23-Independent IL-17 production regulates intestinal epithelial permeability. Immunity 2015;43:727–38. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.09.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Omenetti S, Pizarro TT. The Treg/Th17 axis: a dynamic balance regulated by the gut microbiome. Front Immunol 2015;6:639. 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00639 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Ivanov II, Atarashi K, Manel N, et al. Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented filamentous bacteria. Cell 2009;139:485–98. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.09.033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Oshima K, et al. Treg induction by a rationally selected mixture of clostridia strains from the human microbiota. Nature 2013;500:232–6. 10.1038/nature12331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Round JL, Lee SM, Li J, et al. The Toll-like receptor 2 pathway establishes colonization by a commensal of the human microbiota. Science 2011;332:974–7. 10.1126/science.1206095 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Shin N-R, Whon TW, Bae J-W. Proteobacteria: microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol 2015;33:496–503. 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.06.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Garrett WS, Gallini CA, Yatsunenko T, et al. Enterobacteriaceae act in concert with the gut microbiota to induce spontaneous and maternally transmitted colitis. Cell Host Microbe 2010;8:292–300. 10.1016/j.chom.2010.08.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Cao AT, Yao S, Gong B, et al. Th17 cells upregulate polymeric Ig receptor and intestinal IgA and contribute to intestinal homeostasis. J Immunol 2012;189:4666–73. 10.4049/jimmunol.1200955 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Fisher K, Phillips C. The ecology, epidemiology and virulence of Enterococcus. Microbiology 2009;155:1749–57. 10.1099/mic.0.026385-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Vivinus-Nébot M, Frin-Mathy G, Bzioueche H, et al. Functional bowel symptoms in quiescent inflammatory bowel diseases: role of epithelial barrier disruption and low-grade inflammation. Gut 2014;63:744–52. 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Hoytema van Konijnenburg DP, Reis BS, Pedicord VA, et al. Intestinal epithelial and intraepithelial T cell crosstalk mediates a dynamic response to infection. Cell 2017;171:783–94. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.08.046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Park S-G, Mathur R, Long M, et al. T regulatory cells maintain intestinal homeostasis by suppressing γδ T cells. Immunity 2010;33:791–803. 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.10.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Sujino T, London M, Hoytema van Konijnenburg DP, et al. Tissue adaptation of regulatory and intraepithelial CD4⁺ T cells controls gut inflammation. Science 2016;352:1581–6. 10.1126/science.aaf3892 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Frost F, Kacprowski T, Rühlemann M, et al. Long-Term instability of the intestinal microbiome is associated with metabolic liver disease, low microbiota diversity, diabetes mellitus and impaired exocrine pancreatic function. Gut 2021;70:522–30. 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322753 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, et al. DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 2016;13:581–3. 10.1038/nmeth.3869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, et al. Ribosomal database project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2014;42:D633–42. 10.1093/nar/gkt1244 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Matthias S. Microbial analysis of mouse and human pancreatic necrosis 2022. 10.5281/ZENODO.7111473 [DOI]
- 56. Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 2012;9:357–9. 10.1038/nmeth.1923 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Beghini F, McIver LJ, Blanco-Míguez A, et al. Integrating taxonomic, functional, and strain-level profiling of diverse microbial communities with bioBakery 3. Elife 2021;10:e65088. 10.7554/eLife.65088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
gutjnl-2022-327448supp001.pdf (736.8KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp002.pdf (2.5MB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp003.pdf (1.9MB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp017.pdf (801.5KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp004.pdf (881.6KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp005.pdf (637.4KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp006.pdf (2.2MB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp007.pdf (849KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp008.pdf (789.7KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp009.pdf (1MB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp010.pdf (1MB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp018.pdf (745.9KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp011.pdf (711.2KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp012.pdf (803.8KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp013.pdf (1.6MB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp014.pdf (750.9KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp015.pdf (380.3KB, pdf)
gutjnl-2022-327448supp016.pdf (528.6KB, pdf)
Data Availability Statement
Data are available in a public, open access repository. 16S rRNA sequencing data have been deposited in a public repository (DOI 10.5281/zendodo.7111473). Microarray data have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and are accessible through the following GEO accession number: GSE196481.