Abstract
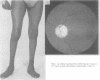
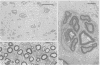
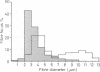
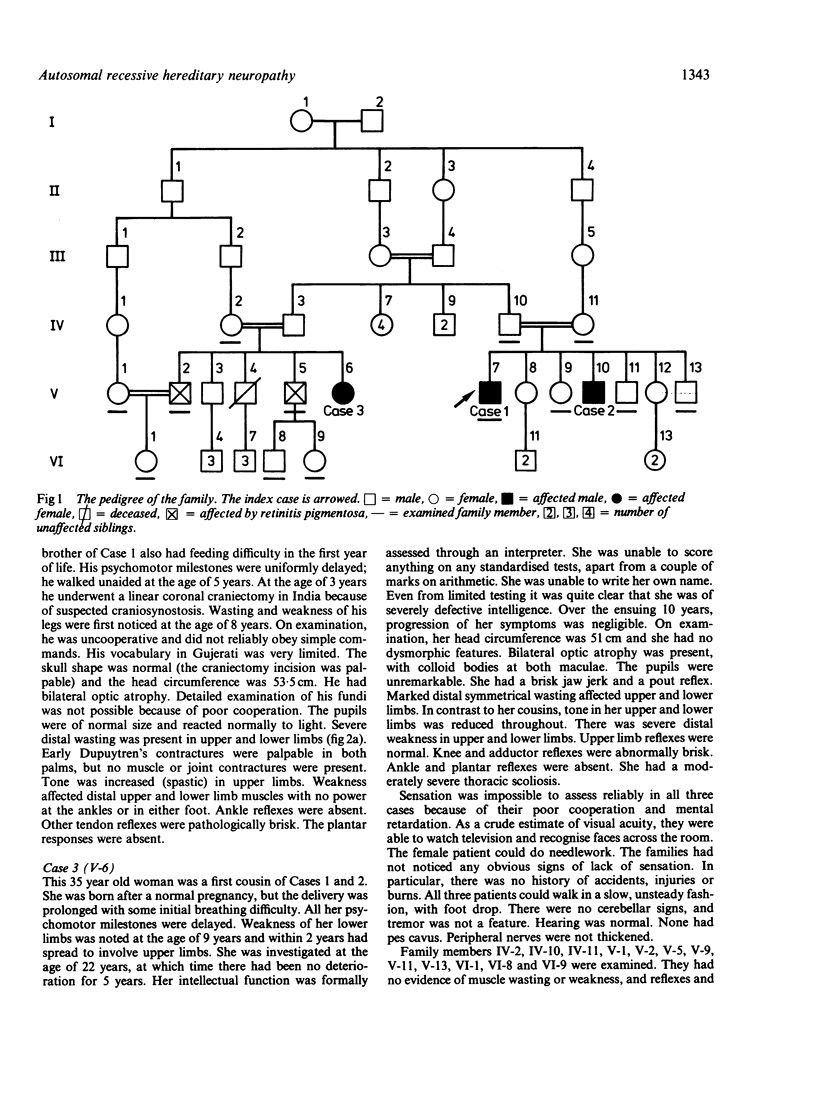
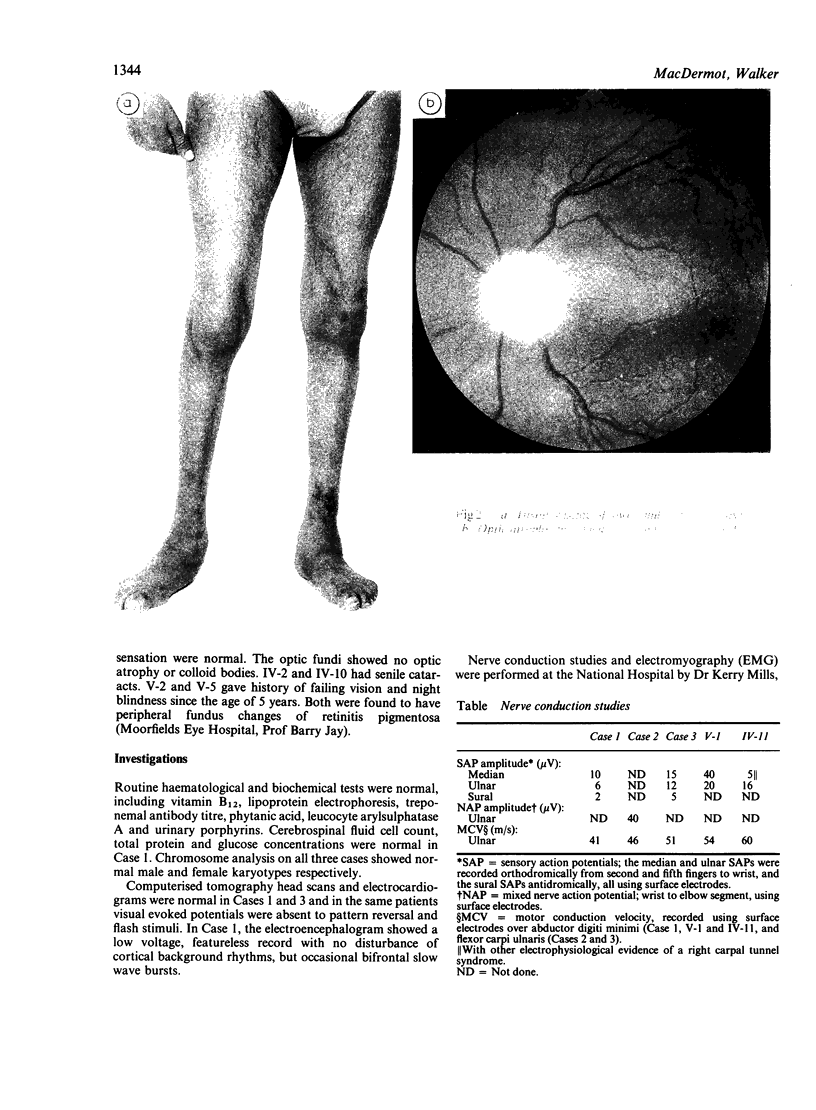
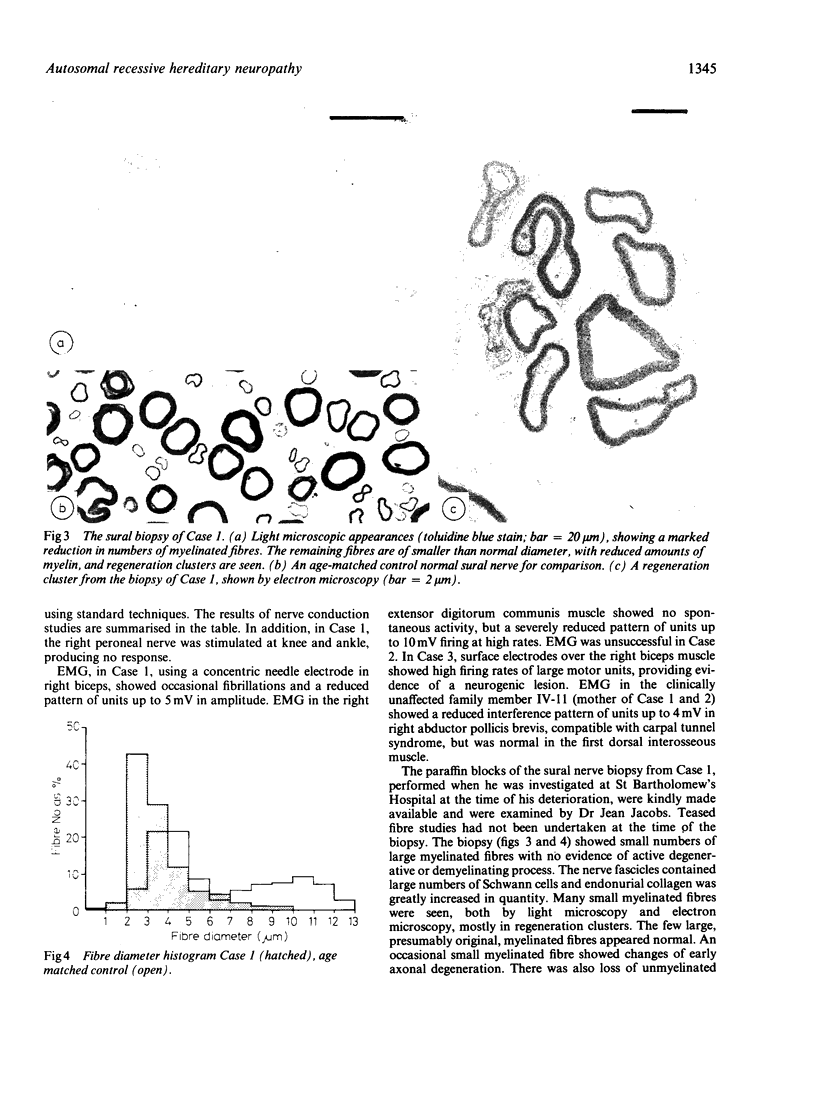
A syndrome is described, consisting of severe neurogenic distal wasting, generalised muscle weakness, absent ankle reflexes, pyramidal signs, mental retardation, optic atrophy and retinal colloid bodies. A sural nerve biopsy from one case showed loss of nerve fibres suggesting the diagnosis of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy. Progression of the disorder was very slow, all patients still being able to walk more than 20 years after the onset. The persons affected with this syndrome were two brothers and their female cousin from a large Gujerati pedigree where consanguinity was high. Autosomal recessive inheritance is therefore suggested.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cowchock F. S., Duckett S. W., Streletz L. J., Graziani L. J., Jackson L. G. X-linked motor-sensory neuropathy type-II with deafness and mental retardation: a new disorder. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Feb;20(2):307–315. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross H. E., McKusick V. A. The Troyer syndrome. A recessive form of spastic paraplegia with distal muscle wasting. Arch Neurol. 1967 May;16(5):473–485. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470230025003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. J., Bradley W. G., Madrid R. The peroneal muscular atrophy syndrome: clinical, genetic, electrophysiological and nerve biopsy studies. I. Clinical, genetic and electrophysiological findings and classification. J Genet Hum. 1978 Dec;26(4):311–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARIGA J., COLLE G., GUAZZI G. C. SUR L'EXTENSION SUPRASPINALE DES L'ESIONS DANS L'ATROPHIE DE CHARCOT-MARIE-TOOTH. Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg. 1964 Jun;64:617–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Thomas P. K. Peroneal muscular atrophy with pyramidal features. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Feb;47(2):168–172. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Thomas P. K. The clinical features of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy types I and II. Brain. 1980 Jun;103(2):259–280. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita H., Inoue N., Araki S., Kuroiwa Y. Optic atrophy, neural deafness, and distal neurogenic amyotrophy; report of a family with two affected siblings. Arch Neurol. 1970 Apr;22(4):357–364. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480220071010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg P. O. Hereditary polyneuropathy, oligophrenia, premature menopause and acromicria. A new syndrome. Eur Neurol. 1971;5(2):84–98. doi: 10.1159/000114062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Low P. A., Morgan J. A. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease with Leber optic atrophy. Neurology. 1978 Feb;28(2):179–184. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. N., Chutorian A. Familial opticoacoustic nerve degeneration and polyneuropathy. Neurology. 1967 Sep;17(9):827–832. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.9.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]