Abstract
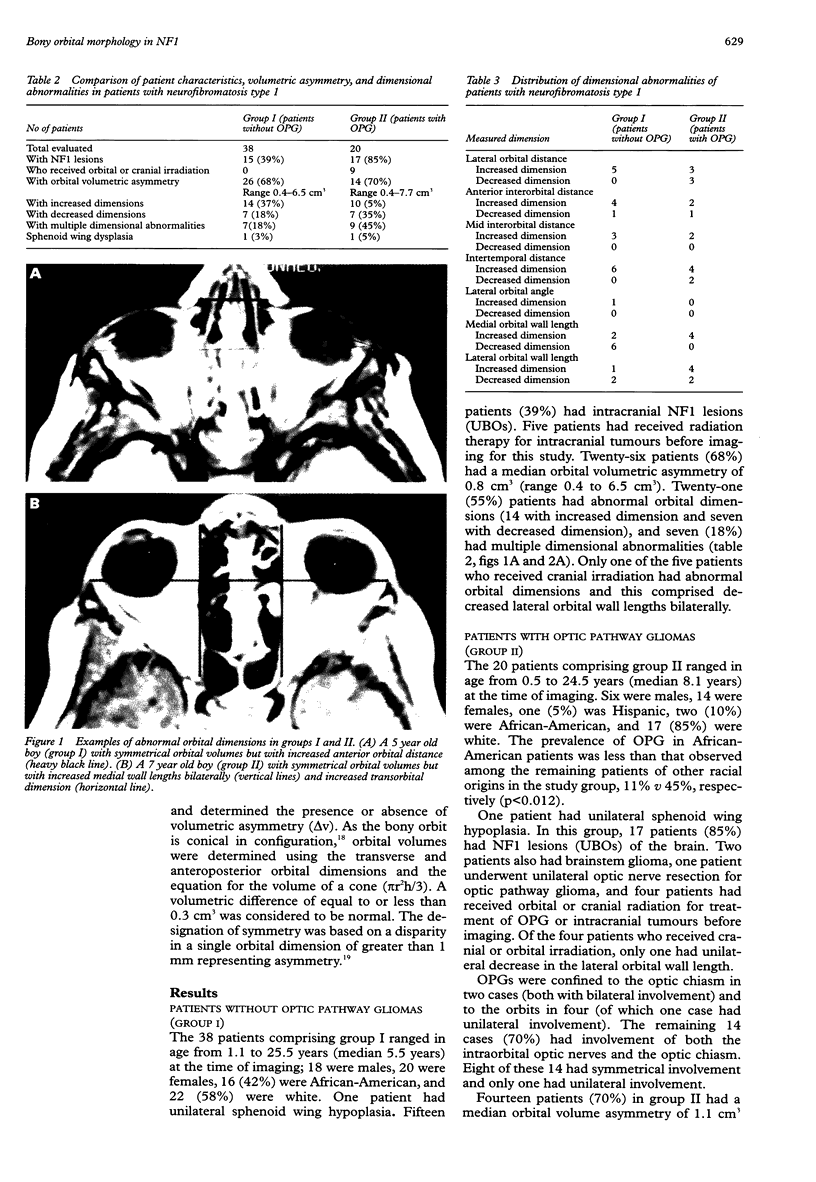
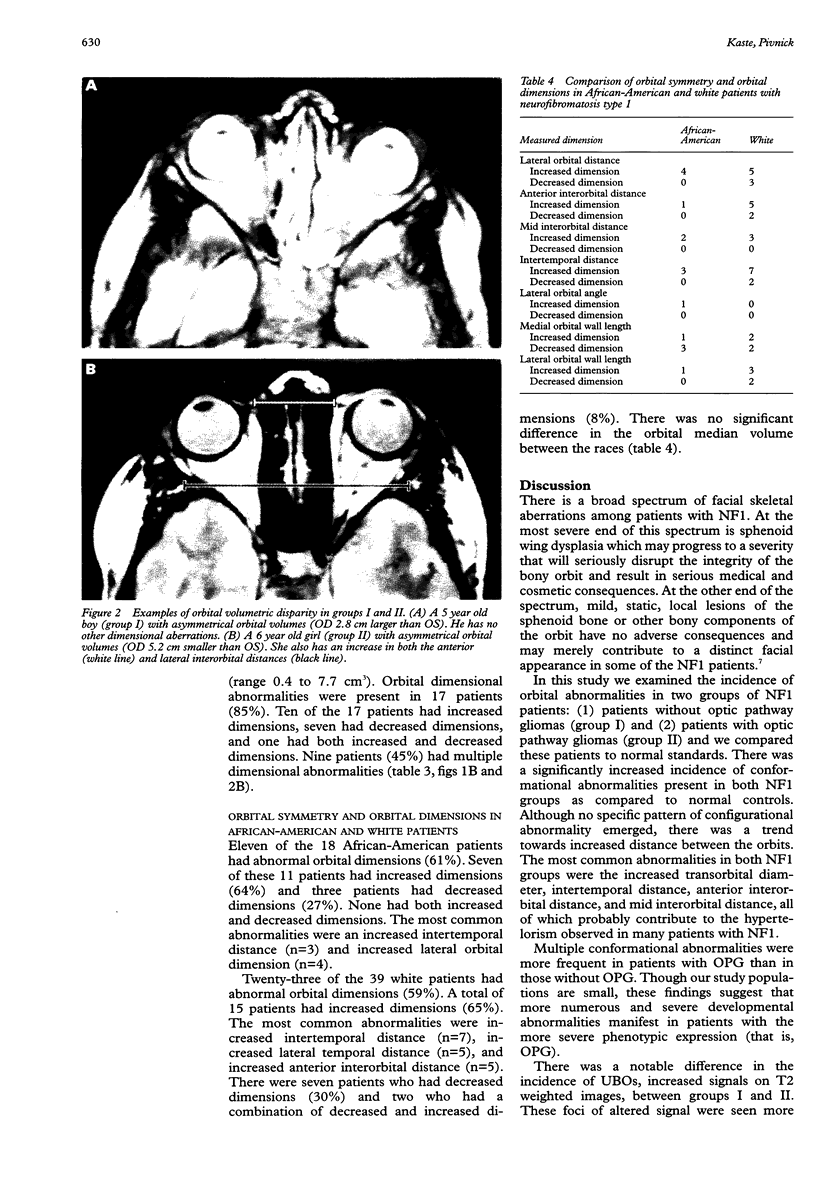
We retrospectively compared patients with NF1 with and without optic pathway gliomas (OPG) to determine the incidence and range of orbital developmental abnormalities and compared the incidence of OPG in African-Americans and whites. From cranial MR scans, we manually measured 14 orbital dimensions, compared them to published standards of Waitzman et al, calculated orbital volumes, and determined the presence or absence of volumetric symmetry (delta v) (delta v < or = 3 cm3 was considered to be symmetrical). We compared the results of orbital configurational assessment between patients with (group I) and those without OPG (group II). The study population comprised 58 patients, 24 boys, 18 African-American, and one Hispanic. Median age at imaging was 7 years (range 0.5-25.5 years). Fifty-eight percent had conformational abnormalities, 16 of whom had more than one abnormality (28%), the most frequent being increased intertemporal distance (n=10), increased lateral orbital distance (n=8), increased medial wall length (n=6), and decreased medial wall length (n=6). The increased intertemporal and lateral orbital distances may contribute to the appearance of hypertelorism. Only two patients had sphenoid wing hypoplasia. We found a high incidence of orbital dimensional abnormalities in the total population but more often saw multiple abnormalities in patients with OPG. However, no pattern of configurational abnormality emerged. OPG is less frequent in African-Americans. Orbital volumetric disparity seems to be independent of the presence of OPG.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURROWS E. H. BONE CHANGES IN ORBITAL NEUROFIBROMATOSIS. Br J Radiol. 1963 Aug;36:549–561. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-36-428-549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binet E. F., Kieffer S. A., Martin S. H., Peterson H. O. Orbital dysplasia in neurofibromatosis. Radiology. 1969 Oct;93(4):829–833. doi: 10.1148/93.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bognanno J. R., Edwards M. K., Lee T. A., Dunn D. W., Roos K. L., Klatte E. C. Cranial MR imaging in neurofibromatosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Aug;151(2):381–388. doi: 10.2214/ajr.151.2.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMario F. J., Jr, Bowers P., Jagjivan B., Burleson J., Langshur S., Greenstein R. M. Analysis of skull anthropometric measurements in patients with neurofibromatosis type-1. Invest Radiol. 1993 Feb;28(2):116–120. doi: 10.1097/00004424-199302000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egawa S., Tsukiyama I., Akine Y., Kajiura Y., Ogino T. Suppression of bony growth of the orbit after radiotherapy for retinoblastoma. Radiat Med. 1987 Nov-Dec;5(6):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardeur D., Palmieri A., Mashaly R. Cranial computed tomography in the phakomatoses. Neuroradiology. 1983;25(4):293–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00540239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyuron B., Dagys A. P., Munro I. R., Ross R. B. Effect of irradiation on facial growth: a 7- to 25-year follow-up. Ann Plast Surg. 1983 Nov;11(5):423–427. doi: 10.1097/00000637-198311000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT J. C., PUGH D. G. Skeletal lesions in neurofibromatosis. Radiology. 1961 Jan;76:1–20. doi: 10.1148/76.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huson S. M., Harper P. S., Compston D. A. Von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. A clinical and population study in south-east Wales. Brain. 1988 Dec;111(Pt 6):1355–1381. doi: 10.1093/brain/111.6.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JU D. M., MOSS M., CRIKELAIR G. F. EFFECT OF RADIATION ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF FACIAL STRUCTURES IN RETINOBLASTOMA CASES. Am J Surg. 1963 Nov;106:807–815. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(63)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby C. G., Go R. T., Beren R. A. Cranial CT of neurofibromatosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980 Sep;135(3):553–557. doi: 10.2214/ajr.135.3.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY R. E. THE EFFECT OF EARLY ENUCLEATION ON THE ORBIT; IN ANIMALS AND HUMANS. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965 Aug;60:277–306. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(65)90929-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaste S. C., Chen G., Fontanesi J., Crom D. B., Pratt C. B. Orbital development in long-term survivors of retinoblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 1997 Mar;15(3):1183–1189. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.3.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. F. DIFFUSE NEUROFIBROMATOSIS WITH PROPTOSIS. Br J Ophthalmol. 1931 May;15(5):272–279. doi: 10.1136/bjo.15.5.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtagh F. R., Boyd R. E., Okulski T. A. Internal auditory canal flaring in neurofibromatosis without acoustic neuroma. Arch Neurol. 1980 Dec;37(12):785–785. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500610065013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitzman A. A., Posnick J. C., Armstrong D. C., Pron G. E. Craniofacial skeletal measurements based on computed tomography: Part II. Normal values and growth trends. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1992 Mar;29(2):118–128. doi: 10.1597/1545-1569_1992_029_0118_csmboc_2.3.co_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerhof W., Delleman J. W., Wolters E., Dijkstra P. Neurofibromatosis and hypertelorism. Arch Dermatol. 1984 Dec;120(12):1579–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters E. C., Westerhof W., Delleman J. W., Dijkstra P. Hypertelorism in neurofibromatosis. Neuropediatrics. 1986 Nov;17(4):175–177. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. A., Bilaniuk L. T., Metzger R. A., Grossman R. I., Schut L., Bruce D. A. Computed tomography of orbitalfacial neurofibromatosis. Radiology. 1983 Jan;146(1):113–116. doi: 10.1148/radiology.146.1.6401362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]