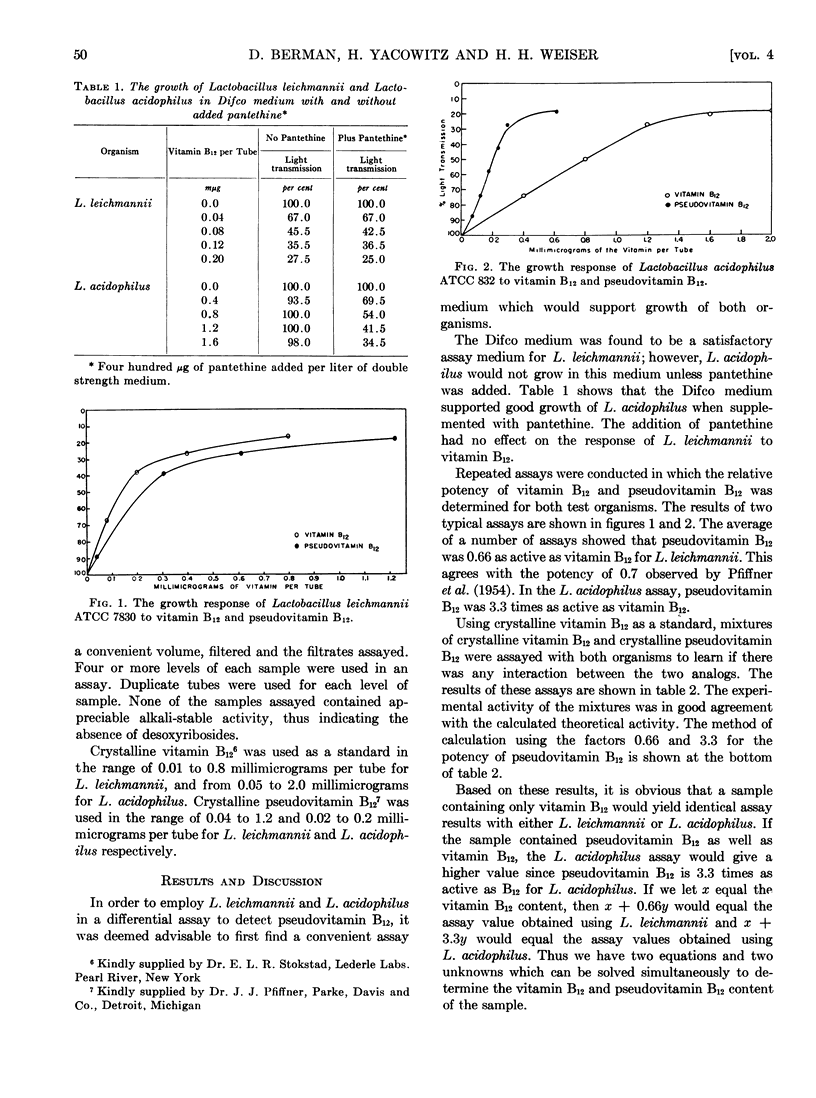
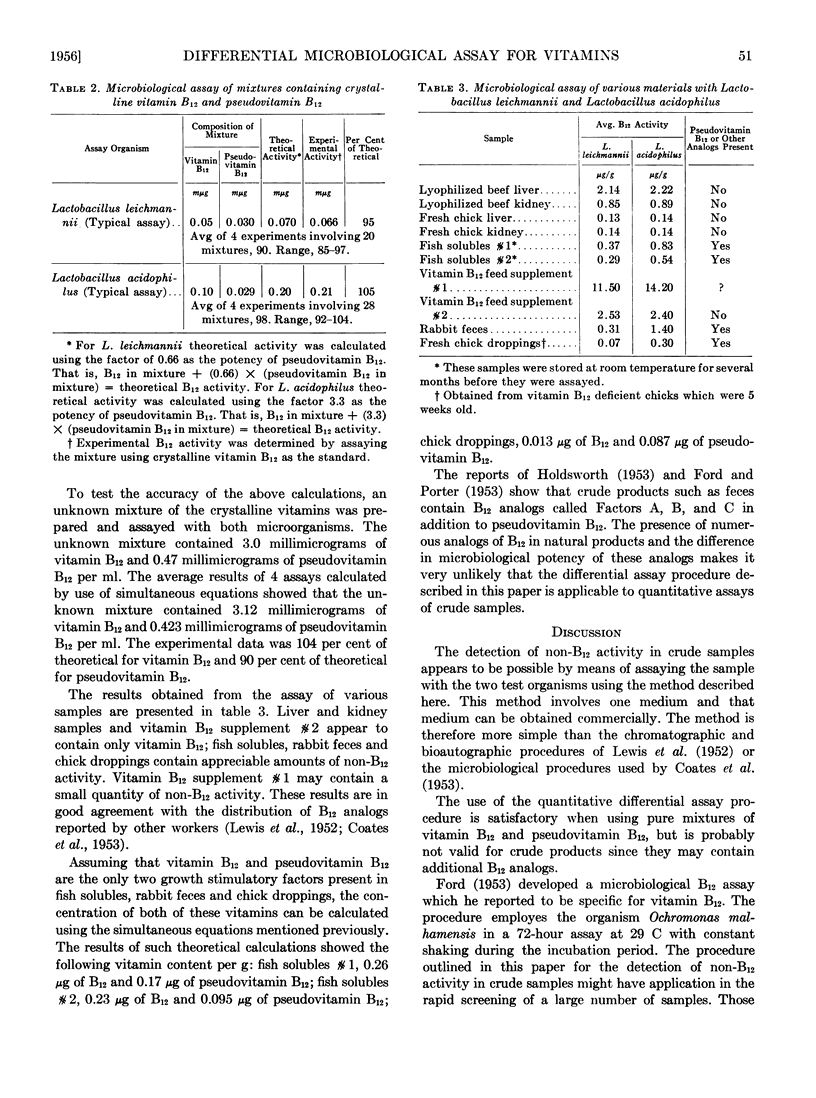
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COATES M. E., FORD J. E., HARRISON G. F., KON S. K., PORTER J. W. Vitamin B12-like compounds. I. Vitamin B12 activity for chicks and for different micro-organisms of gut contents and faeces. Br J Nutr. 1953;7(4):319–326. doi: 10.1079/bjn19530041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD J. E., PORTER J. W. Vitamin B12 like compounds. II. Some properties of compounds isolated from bovine gut contents and faeces. Br J Nutr. 1953;7(4):326–337. doi: 10.1079/bjn19530042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD J. E. The microbiological assay of vitamin B12; the specificity of the requirement of Ochromonas malhamensis for cyanocobalamin. Br J Nutr. 1953;7(4):299–306. doi: 10.1079/bjn19530039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSWORTH E. S. Differentiation of vitamin B12 active compounds by ionophoresis and microbiological assay; ionophoresis. Nature. 1953 Jan 24;171(4343):146–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS U. J., TAPPAN D. V., ELVEHJEM C. A. Properties and distribution of vitamin B12f. J Biol Chem. 1952 Dec;199(2):517–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


