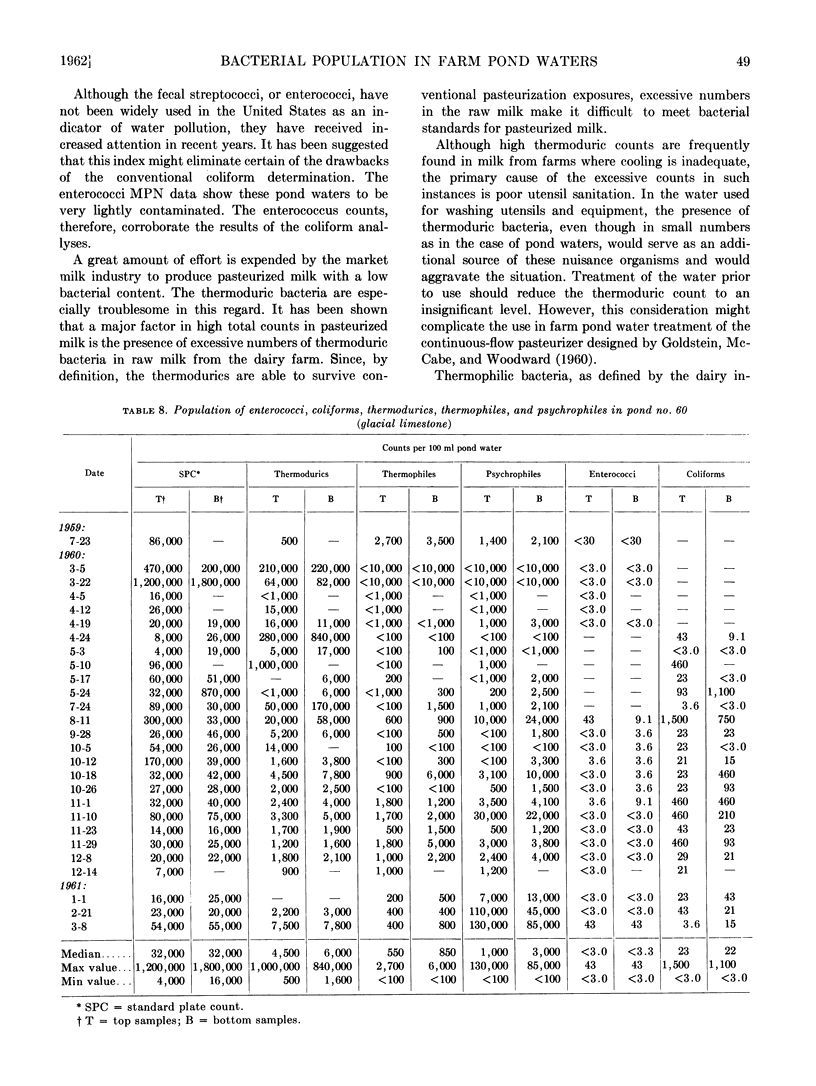
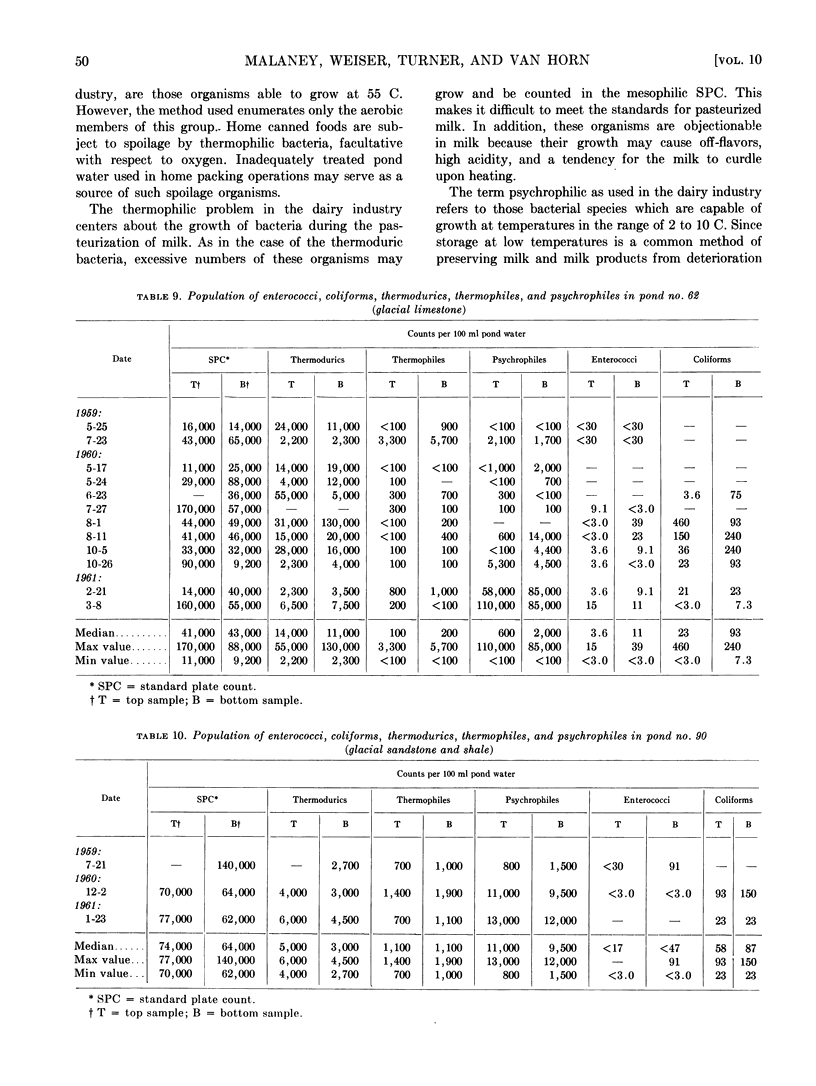
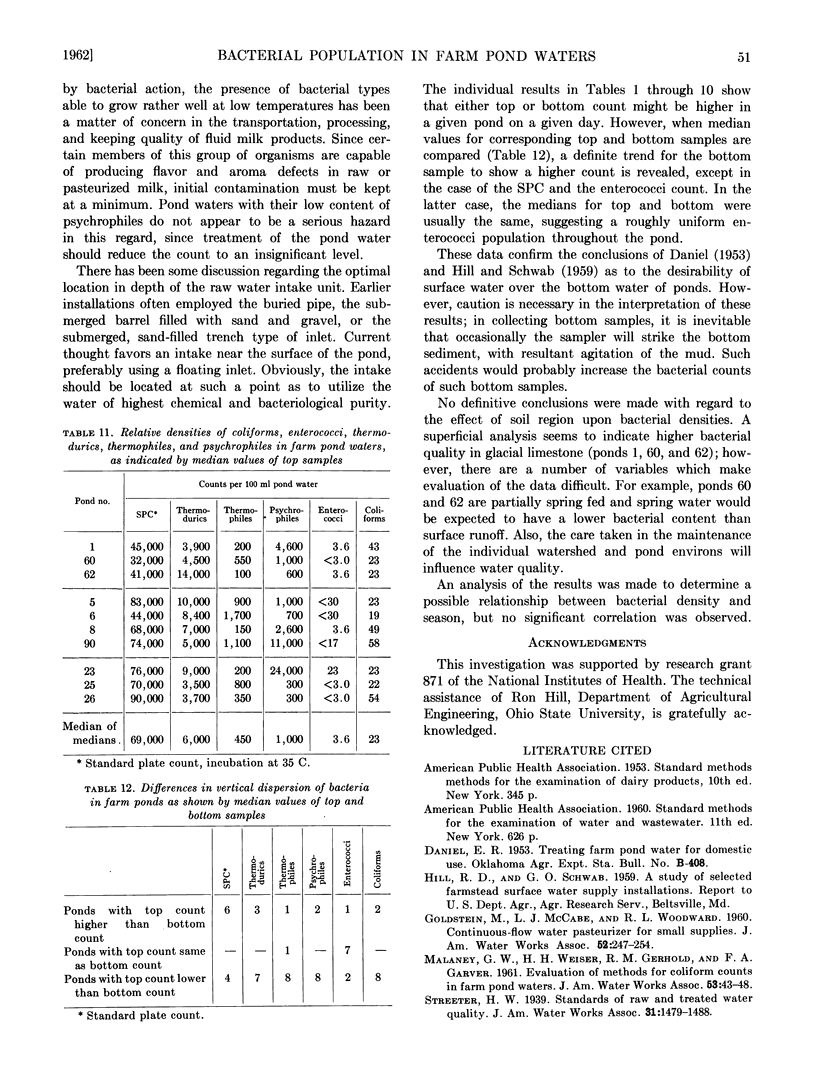
Abstract
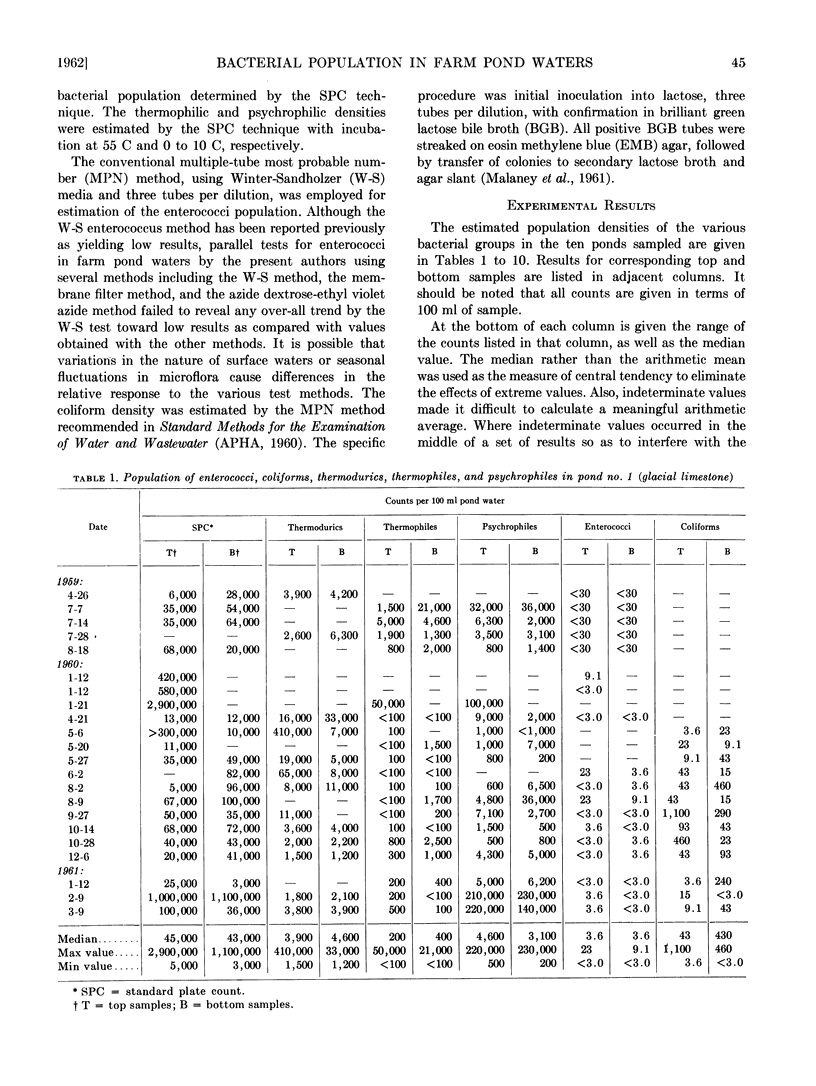
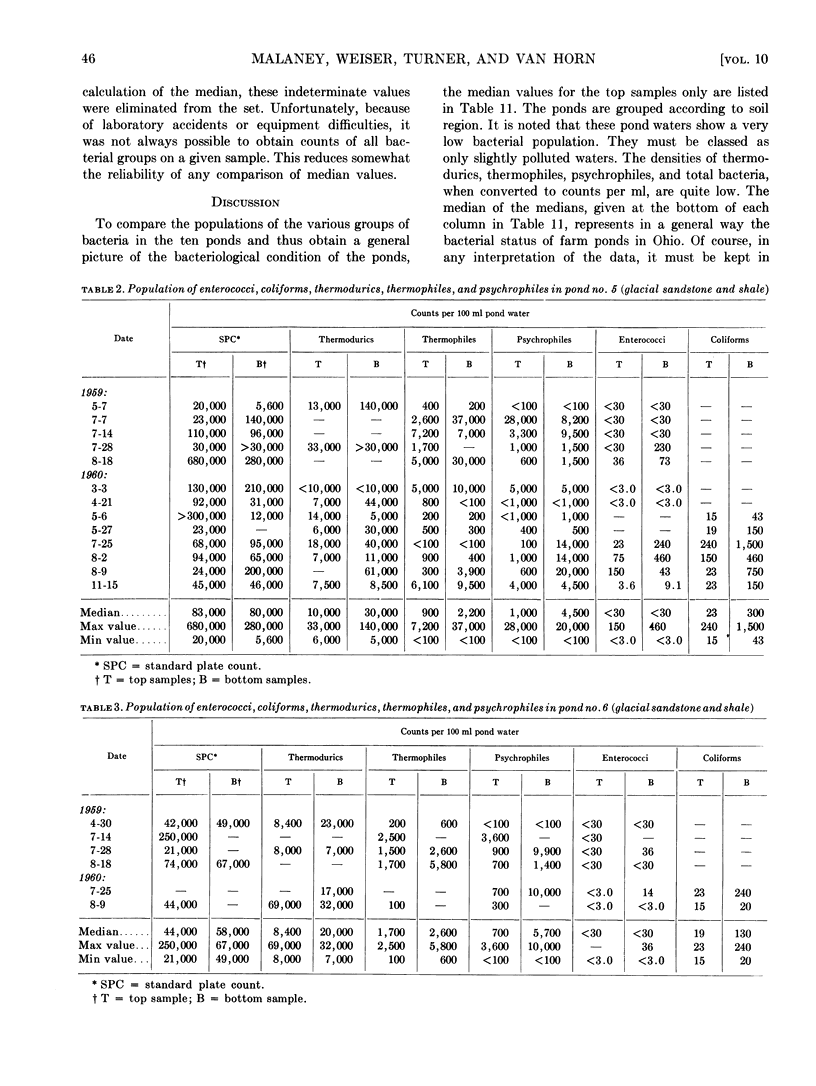
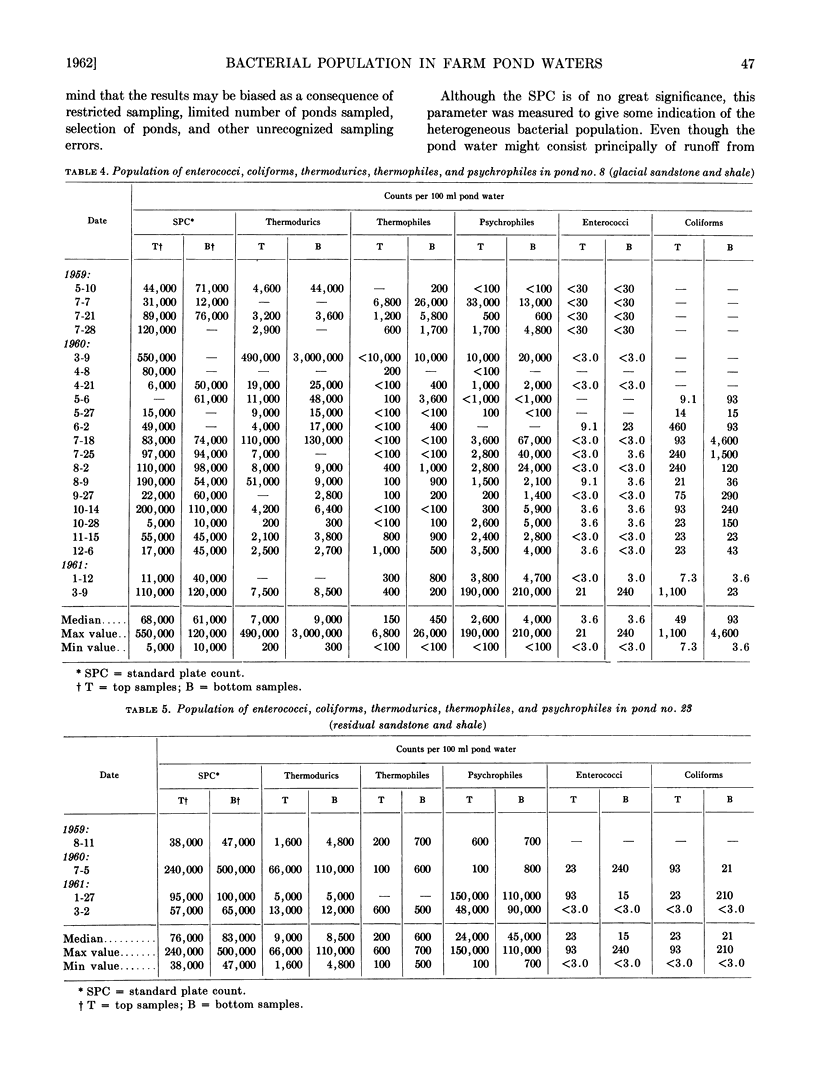
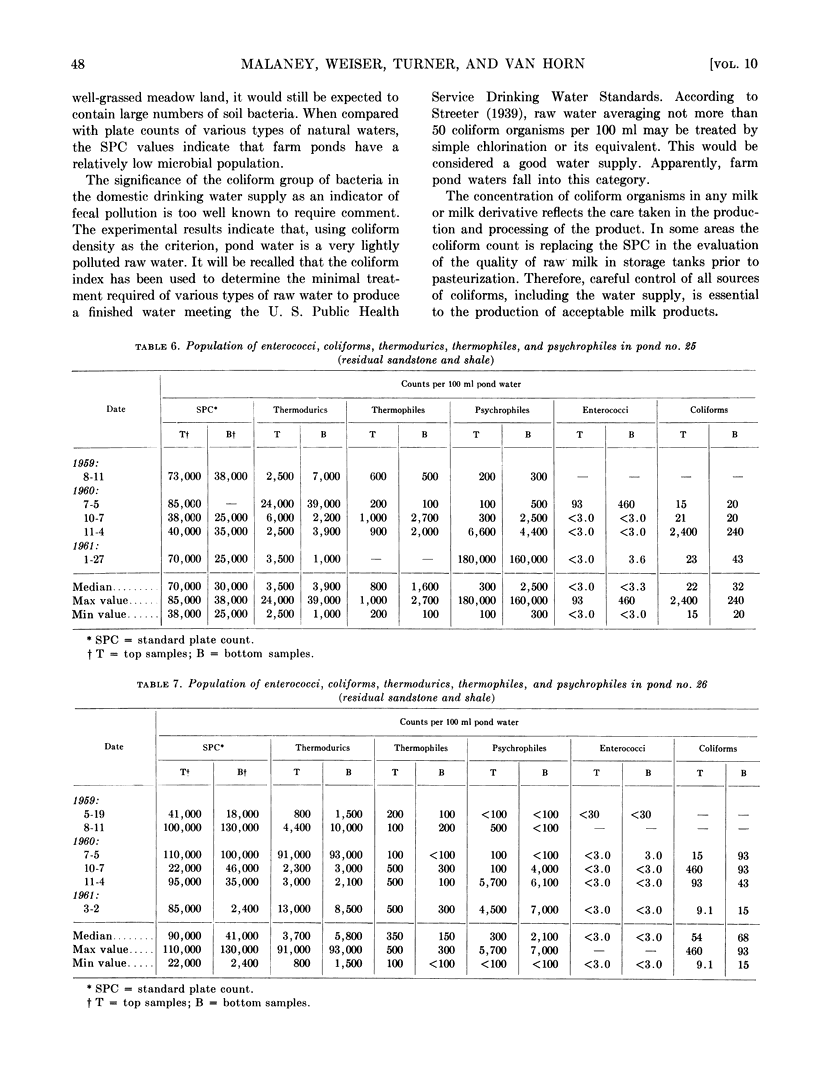
Untreated waters from ten farm ponds located in central, north central, southeastern, and southwestern Ohio were examined for numbers of coliforms, enterococci, thermodurics, thermophiles, and psychrophiles. The median population densities per 100 ml water for all ponds were: coliforms, 23; enterococci, 3.6; thermodurics, 6,000; thermophiles, 450; psychrophiles, 1,000. The results indicate that these farm pond waters were only lightly polluted and suggest that farm ponds, properly maintained, are a source of raw water of high bacteriological quality, requiring a minimum of treatment to be made suitable for domestic and livestock purposes.
Full text
PDF