Key Points
Question
Does β-blockade for up to 14 days with landiolol reduce organ failure as measured by the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score for critically ill patients with tachycardia and septic shock treated with high-dose norepinephrine for more than 24 hours?
Findings
In this randomized clinical trial enrolling 126 patients with tachycardia and established septic shock (treated with norepinephrine for >24 hours), the administration of landiolol intravenously to reduce heart rate to less than 95/min compared with standard care did not significantly decrease organ failure as measured by the mean SOFA score (8.8 vs 8.1, respectively) in the 14 days after randomization.
Meaning
These results do not support the use of landiolol for managing patients with tachycardia treated with norepinephrine for established septic shock.
Abstract
Importance
Patients with septic shock undergo adrenergic stress, which affects cardiac, immune, inflammatory, and metabolic pathways. β-Blockade may attenuate the adverse effects of catecholamine exposure and has been associated with reduced mortality.
Objectives
To assess the efficacy and safety of landiolol in patients with tachycardia and established septic shock requiring prolonged (>24 hours) vasopressor support.
Design, Setting, and Participants
An open-label, multicenter, randomized trial involving 126 adults (≥18 years) with tachycardia (heart rate ≥95/min) and established septic shock treated for at least 24 hours with continuous norepinephrine (≥0.1 μg/kg/min) in 40 UK National Health Service intensive care units. The trial ran from April 2018 to December 2021, with early termination in December 2021 due to a signal of possible harm.
Intervention
Sixty-three patients were randomized to receive standard care and 63 to receive landiolol infusion.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The primary outcome was the mean Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score from randomization through 14 days. Secondary outcomes included mortality at days 28 and 90 and the number of adverse events in each group.
Results
The trial was stopped prematurely on the advice of the independent data monitoring committee because it was unlikely to demonstrate benefit and because of possible harm. Of a planned 340 participants, 126 (37%) were enrolled (mean age, 55.6 years [95% CI, 52.7 to 58.5 years]; 58.7% male). The mean (SD) SOFA score in the landiolol group was 8.8 (3.9) compared with 8.1 (3.2) in the standard care group (mean difference [MD], 0.75 [95% CI, −0.49 to 2.0]; P = .24). Mortality at day 28 after randomization in the landiolol group was 37.1% (23 of 62) and 25.4% (16 of 63) in the standard care group (absolute difference, 11.7% [95% CI, −4.4% to 27.8%]; P = .16). Mortality at day 90 after randomization was 43.5% (27 of 62) in the landiolol group and 28.6% (18 of 63) in the standard care group (absolute difference, 15% [95% CI, −1.7% to 31.6%]; P = .08). There were no differences in the number of patients having at least one adverse event.
Conclusion and Relevance
Among patients with septic shock with tachycardia and treated with norepinephrine for more than 24 hours, an infusion of landiolol did not reduce organ failure measured by the SOFA score over 14 days from randomization. These results do not support the use of landiolol for managing tachycardia among patients treated with norepinephrine for established septic shock.
Trial Registration
EU Clinical Trials Register Eudra CT: 2017-001785-14; isrctn.org Identifier: ISRCTN12600919
This clinical trial assesses whether landiolol for patients with tachycardia and established septic shock requiring prolonged vasopressor support reduces the risk of organ failure.
Introduction
Autonomic dysfunction and tachycardia are associated with poor outcomes in septic shock1 with reported mortality of more than 70%2 in some studies. Norepinephrine is recommended for the maintenance of blood pressure in septic shock3 but has been associated with a variety of adverse effects including immunosuppression4 and myocardial damage.5 Bradycardia provides relative protection6 and interest has grown in the potential of β-adrenergic blockade to protect from the possible harmful effects of catecholamines.
The mechanisms by which β-blockade may produce benefits are unknown. Immunomodulation by reducing proinflammatory cytokines and prolonged survival times have been demonstrated in animals using β1-antagonism.7,8 Morelli et al9 reported the safety of a short-acting β-blocker, esmolol, in patients with septic shock and noted a markedly reduced adjusted hazard ratio (HR) mortality of 61% but as a nonprimary outcome and with a high mortality in the control group of more than 80%. A recent meta-analysis10 of 8 randomized studies using esmolol suggested that the 32% risk ratio decreased 28-day mortality, and a meta-analysis of 7 studies using either esmolol or landiolol in patients with sepsis and septic shock was associated with 32% lower 28-day mortality. Landiolol (Rapibloc, AOP Health) is a very short-acting β-blocker and is approximately 8 times more selective for the β1-receptor than esmolol.11 The study hypothesis was that the additional β1-receptor specificity would bring about myocardial protection and immunomodulation to confer benefits to a high-risk population. This pragmatic randomized trial was planned to recruit 340 patients with established septic shock treated with high-dose norepinephrine in 40 UK National Health Service (NHS ) intensive care units (ICUs).
Methods
The methods for this study were published.12 The trial was conducted in full conformance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki13 and to International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH)–Good Clinical Practice guidelines. The study procedures can be found in the study protocol (Supplement 1).12 Full details of the blinding, randomization, and sample size calculations can be found in the statistical analysis plan (Supplement 2).
Trial Design and Oversight
The Study into the Reversal of Septic Shock with Landiolol (STRESS-L) was an investigator-initiated, parallel-group, multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase 2b trial designed to assess the efficacy and safety of a continuous infusion of intravenous landiolol compared with standard care in adults with established septic shock and tachycardia.
It was conducted in 40 acute care National Health Service (NHS) hospitals in the UK. The trial protocol12 was approved by the East of England, Essex Research Ethics Committee (Reference, 17/EE/0368). Interim analyses were undertaken prior to each independent data monitoring committee (DMC) meeting, which occurred every 3 months. There were no formal stopping rules for futility or benefit.
Trial Participants
The study recruited adult patients (≥18 years) in an ICU diagnosed with septic shock, defined by consensus criteria (Sepsis-3),14 who having received adequate fluid resuscitation, were being treated with 0.1 μg/kg/min or more of norepinephrine (for >24 hours but <72 hours) at the time of randomization and were tachycardiac with a heart rate of 95/min or more. Sepsis-3 criteria were met if the patient had known or suspected infection, a Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score change of 2 or more from baseline, a blood lactate of 18 mg/dL (>2 mmol/L) at any point during shock resuscitation, and vasopressor therapy to maintain a mean arterial pressure either predefined by the clinician or at 65 mm Hg or higher. Patients were excluded if they had tachycardia because of pain or discomfort or had any noninfective form of vasodilatory shock (see trial protocol for extended inclusion and exclusion criteria Supplement 1).
Interventions
The intervention was open-label because the landiolol dose was titrated to achieve a target heart rate. Investigators remained blinded to all group data during the trial.
Landiolol
The continuous intravenous infusion of landiolol was started at 1.0 µg/kg/min, increasing every 15 minutes by a step change of 1.0 µg/kg/min to reach the target heart rate of 80/min to 94/min with the expectation that this should be within 6 hours. While the patient was receiving vasopressor agents (norepinephrine and/or vasopressin), the landiolol infusion was adjusted by step changes of 1.0 µg/kg/min to maintain the target heart rate. The infusion was reduced by step change, and if necessary, ultimately stopped if the heart rate fell below 80/min; the infusion was deliberately weaned once all the vasopressor agents had been discontinued for 12 hours (which we defined as the end of norepinephrine treatment).
It was recommended that the landiolol infusion be stopped for at least 12 hours before the patient was discharged from the ICU (eFigure 1 and eTable 1 for cardiovascular management and infusion protocols, eFigure 2 for vasopressor infusion weaning protocol, and eFigure 3 for timing and weaning of the study drug are in Supplement 3).
Standard Care
The control group received standard care but did not receive any β-blockade for the duration of their ICU stay. Treatment management was based on the latest guidance from the Surviving Sepsis Campaign,15 which recommends that all patients receive timely source control, prompt, and appropriate empirical antibiotic treatment modified according to culture results, and appropriate fluid resuscitation to correct hypovolemia. The use of cardiac output monitoring was at the discretion of the local investigator. Three large international randomized trials16,17,18 and the subsequent patient-level meta-analysis19 had found that cardiac output monitoring did not improve outcomes, and the trial steering committee was of the opinion that to mandate it would pose a severe barrier to recruitment.
Adherence
Adherence with the drug infusion protocol was closely monitored and reviewed in monthly trial management meetings. A patient’s treatment protocol was said not to have been followed if (1) landiolol was not started, (2) landiolol was not started at the correct dose, (3) heart rate was reduced to less than 80/min and landiolol infusion had not been reduced, (4) heart rate was higher than 94/min and landiolol infusion was not increased, and (5) landiolol was not stopped after the end of norepinephrine treatment. The adherence criteria are stipulated in eTable 2 in Supplement 3 and the analysis criteria are stipulated in the statistical analysis plan (Supplement 2).
Procedure
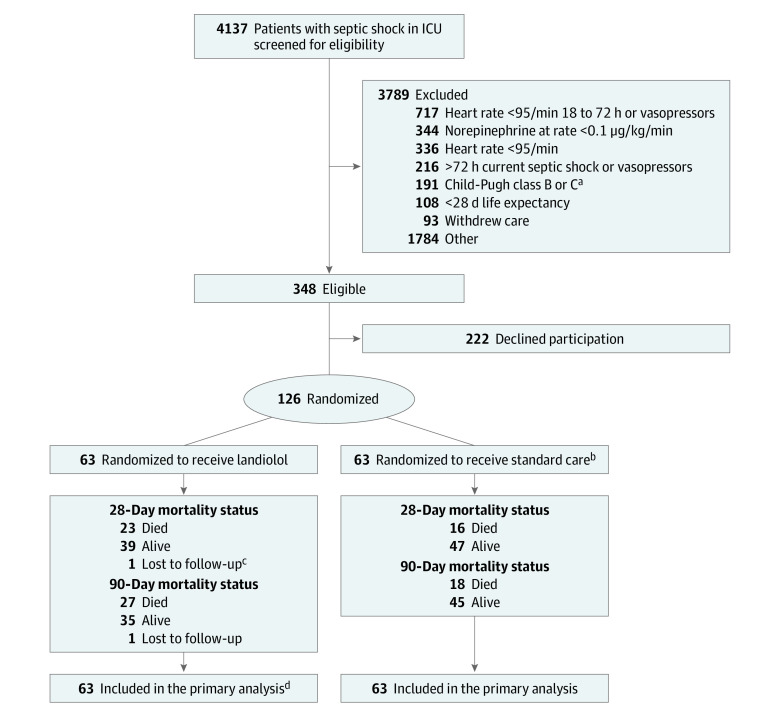
Detailed descriptions of the trial procedures are given in the published protocol12 and in Supplement 1 and Supplement 3. Patients in the ICU with septic shock were screened for eligibility upon initiation of norepinephrine so that there was a 24-hour window during which written consent was sought either from the patient or their legal representative. Ethical approval included approaching patients during this window even though our scoping data suggested that 90% would fall outside the inclusion criteria at the 24-hour time point and would not be randomized. This was usually because the heart rate or the norepinephrine dose had improved so that the heart rates were lower than what was needed for inclusion (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Flow of Patients in the STRESS-L Trial.
aA Child-Pugh score of 7 or more was excluded because of the risk of inappropriate inclusion in the study.
bOne patient was randomized in error because their heart rate was 84/min at the point of randomization. However, the patient remained in the trial on an intention-to-treat basis, and their routine data were collected.
cOnly 1 patient was recruited who had COVID-19.
dNine patients (7.1%) withdrew from treatment but remained in the follow-up. Of these, 8 were withdrawn by the clinician and 1 by their personal legal representative.
Outcomes
All outcomes were prespecified and outlined in the published protocol.12 We report no post hoc analyses.
Primary Outcome
The primary outcome was the mean SOFA score20 over the first 14 days after entry into the trial and while in the ICU. A modified version of the SOFA score was used (using respiratory, cardiovascular, liver, coagulation, and kidney measures, each scored 0-4), which excludes the neurological domain because therapeutic sedation markedly alters the Glasgow Coma Scale. The score ranged from 0 to 20. A higher score reflects a higher degree of organ dysfunction.
Secondary Outcomes
The secondary outcomes included mortality at days 28 and 90 after randomization, length of hospital and ICU stay, mean infusion rate and duration of norepinephrine (over 14 days), dose and duration of inotropes (first 5 days), in-out and balance of total fluids (over 14 days), heart rate (over 14 days), blood glucose and blood lactate concentration (days 1, 2, 4, and 6 and at the end of norepinephrine treatment), and mean arterial pressure (over 5 days; eTable 3 in Supplement 3).
There were an additional 5 safety outcomes that were prespecified adverse events including bradycardia (heart rate, <50/min), bradycardia with hypotension requiring intervention (not including temporarily stopping the infusion), heart block, arrhythmia, and arrhythmia hypotension requiring intervention.
Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis plan21 is provided in Supplement 2. All analyses used an intention-to-treat principle.
As used in previous sepsis studies,22,23,24 the mean modified SOFA score during the ICU stay was calculated on each day from randomization while in the ICU (up to a maximum of 14 days) and dividing by the number of days from randomization and alive in the ICU. Patients who died or were discharged from the ICU before 14 days had only the days from randomization to death or discharge counted.
For continuous outcomes, linear mixed-effects regression models were fitted to estimate the treatment difference, 95% CI, and P value using bootstrapping (10 000 bootstrapped samples). Both unadjusted and adjusted (for age, sex, recruiting site [random effect], and baseline norepinephrine dose) estimates were obtained.
Categorical outcomes were assessed using mixed-effects logistic regression models, and a fixed-effect logistic regression model was used to report absolute difference (risk difference). For data collected over time, longitudinal models were used to estimate the treatment difference. For mortality outcomes at days 28 and 90, Kaplan-Meier plots give a visual representation of the time to death (univariate survival analysis). The proportional odds assumption was also checked in these survival models.
Prespecified subgroup analyses were undertaken for baseline shock severity (norepinephrine, 0.1 μg/kg/min-0.3 μg/kg/min vs >0.3 µg/kg/min) and use of β-blockers on ICU admission prior to randomization (yes/no) using formal statistical tests for interaction for the primary outcome using logistic regression models.
Missing data were imputed only for the primary outcome (statistical analysis plan Supplement 2). Three sensitivity analyses were carried out using different imputation techniques assessing the average SOFA score over 14 days and mortality as a composite outcome using the Pocock et al25 win-ratio method and an instrumental mean model26 to assess the effect of treatment protocol deviations.
The number and percentage of adverse events and serious adverse events from randomization to 90 days’ follow-up were summarized by treatment group and analyzed using the Fisher exact test.
Steroid doses were converted to hydrocortisone equivalents using the standard factors of 1 mg of dexamethasone equals 26.7 mg of hydrocortisone; 1 mg of methylprednisolone equals 5.0 mg of hydrocortisone; 1 mg of prednisolone equals 4.0 mg of hydrocortisone.
The diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) was based on the observation at randomization of infiltrates on chest radiography and the ratio of the arterial oxygen tension (Pao2) to the fraction of inspired oxygen (Fio2)—the Pao2:Fio2 ratio—according to the Berlin Consensus Criteria.27
Trial Termination
The study was terminated prematurely by the trial sponsor on December 15, 2021, based on the advice of the independent DMC that landiolol was unlikely to demonstrate benefit and because there was a signal for possible harm. The decision to stop was not based on a formal calculation of futility but based on the opinion of the DMC using all available information including outcome data from the interim analysis, analysis of lactate and norepinephrine, and feasibility of future recruitment.
Results
Patient Recruitment
Between April 19, 2018, and December 15, 2021, 126 patients were randomized in 40 centers in the UK. Recruitment was paused from March 18, 2020, to August 21, 2020, due to COVID-19. A total of 4137 patients were screened and 348 patients (8.4%) were potentially eligible (Figure 1). Of these, 126 (37%) gave informed written consent and were randomized: 63 to landiolol and 63 to standard care; no patients withdrew from the study. Patient characteristics were similar in the 2 treatment groups at baseline (Table 1 and eTable 4 in Supplement 3). The mean age was 55.6 years (95% CI, 52.7 to 58.5 years), and 58.7% were male.
Table 1. Baseline Patient Characteristics.
| No. (%) of patients | ||
|---|---|---|
| Landiolol (n = 63) | Standard care (n = 63) | |
| Age, mean (SD), y | 55.9 (16.2) | 55.3 (17.1) |
| Female | 26 (41.3) | 26 (41.3) |
| Male | 37 (58.7) | 37 (58.7) |
| Main site of the infection | ||
| Lungs | 28 (44.4) | 27 (42.9) |
| Abdomen | 21 (33.3) | 22 (34.9) |
| Other | 8 (12.7) | 13 (20.6) |
| Urine | 4 (6.3) | 1 (1.6) |
| Blood | 2 (3.2) | 0 |
| Location of infection acquisition | ||
| Community | 46 (73.0) | 45 (71.4) |
| Hospital | 17 (27.0) | 18 (28.6) |
| Patient met ARDS criteriaa | 20 (31.7) | 13 (20.6) |
| Concomitant illnesses | 57 (90.5) | 55 (87.3) |
| Received β-blockers | ||
| 2 wk Prior to ICU admission | 5 (14.3) | 6 (16.7) |
| During ICU admission prior to randomization | 3 (8.3) | 5 (13.9) |
| Steroid or hydrocortisone equivalent dose, mean (SD), mg | 170.6 (94.4) | 176.7 (100.8) |
| No. | 33 | 37 |
| Laboratory values at randomization | ||
| Arterial blood gases, median (IQR), mm Hg | ||
| Pao2 | 78.8 (67.5-91.5) | 74.3 (66.0-84.0) |
| No. | 62 | |
| Paco2 | 46.1 (41.3-57.0) | 44.3 (34.5-51.8) |
| No. | 62 | 62 |
| Glucose and lactate, mean (SD), mg/dL | ||
| Glucose | 138.1 (56.0) | 144.1 (51.4) |
| No. | 62 | |
| Lactate | 41.0 (25.6) | 40.9 (28.4) |
| No. | 62 | |
| MAP, mean (SD), mm Hg | 73.0 (9.1) | 72.3 (7.6) |
| No. | 62 | |
| Heart rate, mean (SD), beats/min | 110.6 (13.0) | 114.1 (16.8) |
| Atrial fibrillation at randomization | 7 (11.1) | 8 (12.7) |
| Norepinephrine dose, mean (SD), µg/kg/min | 0.37 (0.30) | 0.36 (0.22) |
| SOFA score, mean (SD)b | 10.1 (3.3) | 10.3 (2.4) |
Abbreviations: ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; ICU, intensive care unit; MAP, mean arterial pressure; Pao2, partial pressure of arterial oxygen; Paco2, partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
SI conversion factors: To convert glucose from mg/dL to mmol/L, multiply by 0.0555; lactate from mg/dL to mmol/L, multiply by 0.111.
Berlin Criteria27 of Pao2:Fio2 (fraction of inspired oxygen) ratio less than 300 and bilateral infiltrates on chest radiograph.
A 5-item SOFA score (respiratory, coagulation, cardiovascular, liver, and kidney). Each item scores from 0 (best, normal function) to 4 (worst, most abnormal function). The SOFA score is the mean of the 5 scores. Values in the table represent the results recorded at or closest prior to randomization.
Primary Outcome
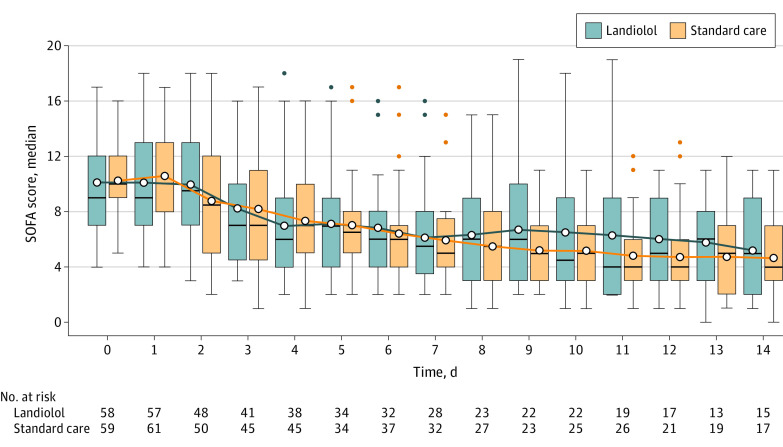
The mean (SD) SOFA score over the 14 days was 8.8 (3.9) for the landiolol group compared with 8.1 (3.2) for the standard care group. There was no evidence of a statistical difference between the interventions (mean difference [MD], 0.75 [95% CI, −0.49 to 2.0]; P = .24; Table 2 and Figure 2). The sensitivity analyses and the composite win-ratio test did not suggest evidence of a difference in the intervention group compared with the standard care (eTable 5 in Supplement 3).
Table 2. Primary and Secondary Outcomes, and Routinely Collected Data (Landiolol vs Standard Care).
| Landiolol (n = 63) | Standard care (n = 63) | Unadjusteda | Adjustedb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect estimate (95% CI) | P value | Effect estimate (95% CI) | P value | ||||
| Primary outcome | |||||||
| SOFA score, mean (SD) | 8.8 (3.9) | 8.1 (3.2) | MD, 0.75 (−0.49 to 2.0) | .24 | MD, 0.63 (−0.47 to 1.73) | .26 | |
| Secondary outcomes | |||||||
| 28-d mortality, total/No. (%) | 23/62 (37.1) | 16/63 (25.4) | |||||
| OR (95% CI) | 1.76 (0.77 to 4.03) | .18 | 1.75 (0.73 to 4.22) | .21 | |||
| RD (95% CI), % | 11.70 (−4.43 to 27.83) | .16 | 9.65 (−5.03 to 24.33) | .20 | |||
| 90-d mortality, No./total (%) | 27/62 (43.5) | 18/63 (28.6) | |||||
| OR (95% CI) | 2.04 (0.91 to 4.57) | .08 | 2.13 (0.88 to 5.16) | .09 | |||
| RD (95% CI), % | 14.98 (−1.66 to 31.6) | .08 | 12.77 (2.00 to 27.54) | .09 | |||
| Length of stay, mean (SD) | |||||||
| ICU survivors, d | 21.3 (31.7) | 19.6 (19.3) | MD, 1.72 (−8.94 to 12.39) | .75 | MD, 0.63 (−9.82 to 11.07) | .12 | |
| No. | 42 | 47 | |||||
| Hospital survivors, d | 49.1 (56.8) | 52.2 (42.6) | MD, −3.17 (−24.77 to 18.42) | .77 | MD, −3.88 (−24.66 to 16.88) | .71 | |
| No. | 38 | 42 | |||||
| Duration of norepinephrine, mean (SD), d | 5.3 (4.3) | 4.3 (1.9) | MD, 0.98 (−0.23 to 2.20) | .11 | MD, 1.05 (−0.16 to 2.27) | .09 | |
| No. | 61 | 59 | |||||
| Total cumulative dose of norepinephrine, µg/kg/min | MD, 0.10 (0.002 to 0.20) | .05 | MD, 0.07 (−0.003 to 0.15) | .06 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 0.34 (0.33) | 0.24 (0.23) | |||||
| Median (IQR) | 0.24 (0.16 to 0.37) | 0.17 (0.10 to 0.27) | |||||
| Duration of landiolol, mean (SD), d | 3.4 (4.0) | ||||||
| No. | 60 | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 2.0 (0.8 to 3.9) | ||||||
| Total cumulative dose of landiolol, mean (SD), µg/kg/min | 10.9 (10.2) | ||||||
| No. | 60 | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 6.7 (3.3 to 15.0) | ||||||
| Routinely collected data | |||||||
| Cardiovascular | |||||||
| MAP over 5 d, mean (SD), mm Hg | 73.2 (7.6) | 76.0 (6.5) | MD, −2.67 (−5.06 to −0.29) | .03 | MD, −2.64 (−4.94 to −0.33) | .002 | |
| Heart rate over 14 d, mean (SD), beats/min | 92.4 (10.4) | 98.6 (12.2) | MD, −6.46 (−10.46 to −2.46) | .002 | MD, −6.46 (−10.42 to −2.49) | .001 | |
| Glucose and lactate, mg/dL | |||||||
| Glucose | |||||||
| No. | 62 | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 136.5 (34.5) | 148.3 (38.0) | MD, −10.58 (−23.21 to 2.05) | .10 | MD, −10.70 (−23.37 to 1.97) | .10 | |
| Median (IQR) | 134.2 (112.3 to 152.1) | 140.1 (122.9 to 176.3) | |||||
| Lactate | |||||||
| No. | 62 | ||||||
| Mean (SD), mg/dLa | 32.5 (31.2) | 24.5 (15.6) | MD, 6.48 (−1.12 to 14.08) | .10 | MD, 6.31 (−0.76 to 13.40) | .08 | |
| Median (IQR) | 21.3 (14.9 to 31.5) | 19.7 (15.7 to 25.7) | |||||
| Arterial blood gases, mean (SD), mm Hg | |||||||
| Pao2 | 79.8 (14.4) | 81.6 (21.1) | MD, −1.66 (−7.96 to 4.64) | .61 | MD, −1.55 (−7.83 to 4.72) | .63 | |
| Paco2 | 46.5 (10.2) | 44.8 (10.4) | MD, 1.38 (−1.95 to 4.72) | .42 | MD, 1.40 (−1.99 to 4.79) | .42 | |
| Steroid or hydrocortisone equivalent dose, mean (SD), mg | 167.9 (72.1) | 182.8 (112.8-166.7) | MD, −15.43 (−52.59 to 21.73) | .42 | MD, −21.0 (−56.32 to 14.31) | .24 | |
| No. | 43 | 44 | |||||
| Median (IQR) | 180.0 (133.3 to 200.0) | 166.7 (137.5 to 200.0) | |||||
Abbreviations: MAP, mean arterial pressure; MD, mean difference; OR, odds ratio; Pao2, partial pressure of arterial oxygen; Paco2, partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide; RD, risk difference, SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
SI conversion factors: To convert glucose from mg/dL to mmol/L, multiply by 0.0555; lactate from mg/dL to mmol/L, multiply by 0.111.
The value of the unadjusted MD may not be the same as the difference in means presented between the groups (landiolol vs standard care). This is because the model was fitted to the observed values for each time point, whereas the means are calculated by first calculating the mean for each patient over time and then the mean of the means over all patients in each group.
Adjusted for age, sex, and baseline norepinephrine value.
Figure 2. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Scores.
The median number of days from which the mean Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score was calculated from randomization was 11 days (IQR, 5-14) for the standard care group and 7 days (IQR, 3-14) for the landiolol group.
The horizontal black lines represent the median; box ends, IQR; the upper and lower whiskers, Q3+1.5 × IQR and Q1+1.5 × IQR, respectively; open circles, the mean of the SOFA score; and the filled circles, outliers.
Secondary Outcomes
The secondary outcomes are presented in Table 2 (eFigures 4 and 5A and B and eTable 6 in Supplement 3).
Mortality at day 28 was 37.1% (23 of 62) in the landiolol group and 25.4% (16 of 63) for standard care group (absolute difference, 11.7% [95% CI, −4.4% to 27.8%]; P = .16). The Cox proportional hazards model from day 0 to day 28 demonstrated no difference in survival between the treatment groups (unadjusted HR, 1.64 [95% CI, 0.87 to 3.10]; P = .13). Additional Cox proportional hazard modeling at day 90 was 43.5% (27 of 62) for the landiolol group and 28.6% (18 of 63) for the standard care group (absolute difference, 15%% [95% CI, −1.7% to 31.6%]; P = .08). eFigure 5b in Supplement 3 illustrates the Kaplan-Meier curve for mortality from day 0 to day 90 (Cox proportional unadjusted HR, 1.73 [95% CI, 0.95 to 3.15]; P = .07).
Over 14 days, the landiolol group had a lower mean heart rate (MD over time, −6.46/min [95% CI, −10.46 to −2.46]; P = .002; Table 2 and Figure 3B). There was a difference in the mean arterial pressure over 5 days with average values lower in the landiolol group (MD over time, −2.67 mm Hg [95% CI, −5.06 to −0.29]; P = .03: Table 2 and Figure 3A).
Figure 3. Mean Arterial Pressure and Heart Rate.
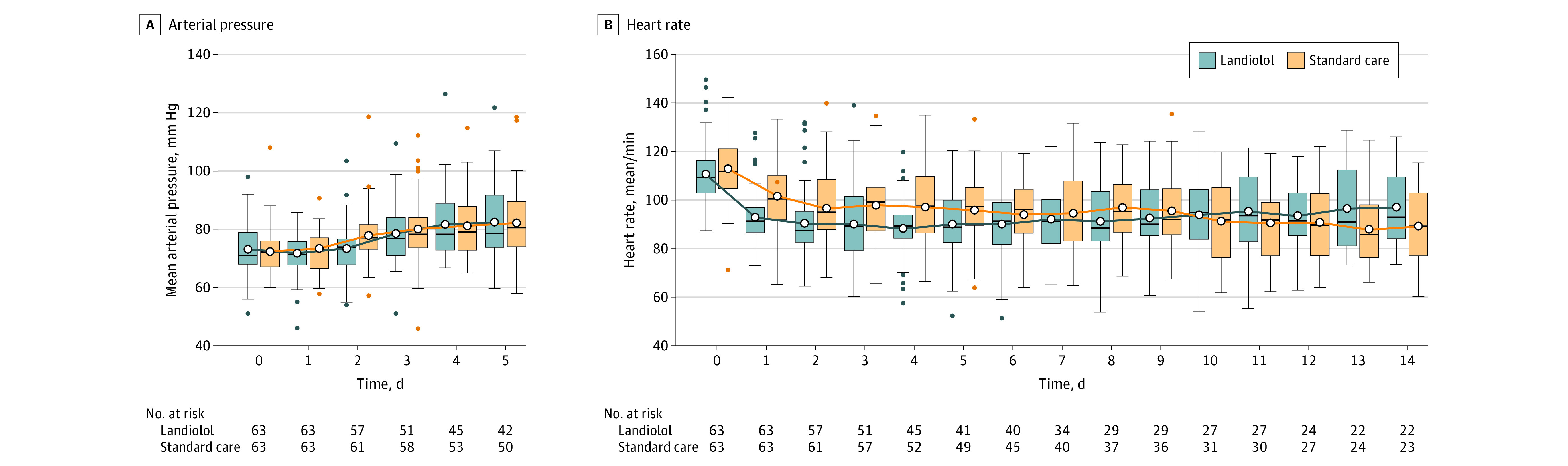
A statistically significant difference in the mean arterial pressure was noted between the interventions at day 2 (mean difference [MD], −4.53 [95% CI, −7.69 to −1.36]; P = .005). Statistically significant differences in the heart rate between the interventions was noted at day 1 (MD, −8.66 [95% CI, −13.20 to −4.12]; P < .001) and day 4 (MD, −8.68 [95% CI, −14.73 to 2.62]; P = .003).
The horizontal black lines represent the median; box, IQR; the upper and lower whiskers, Q3+1.5 × IQR and Q1+1.5 × IQR, respectively; open circles, the mean; and the filled circles, outliers.
The average norepinephrine infusion rate was greater in the landiolol group (µg/kg/min MD, 0.10 [95% CI, 0.002 to 0.20]; P = .05; Table 2). Having adjusted for predefined covariates, requirements in the landiolol group remained greater (MD, 0.07 [95% CI, −0.003 to 0.15]; P = .06; Table 2).
Patients in the landiolol group had a numerically higher mean (SD) lactate concentration over the course of the study (mean, 32.5 mg/dL [31.2]) than the standard care group (mean, 24.5 mg/dL [15.6]; MD over time, 6.48 mg/dL [95% CI, −1.12 to 14.08]; P = .10; Table 2).
All the other clinical outcomes and comparisons showed no evidence of a difference between the treatment groups.
Subgroup Analyses
Among 3 subgroups evaluated, evidence of statistical difference between treatment groups existed (eTable 7 in Supplement 3). For example, among the subgroup defined by baseline shock severity (norepinephrine 0.1 µg/kg/min-0.3 µg/kg/min vs >0.3 µg/kg/min), the treatment by subgroup effect was not statistically significant (P = .47).
Adverse Events
The proportion of patients with at least 1 adverse event did not differ significantly between the groups: 17.5% (10 of 63) of those receiving landiolol and 12.7% (8 of 63) of those receiving standard care (P = .80). However, 25.4% (16 of 63) of patients in the landiolol group experienced serious adverse events vs 6.4% (4 of 63) in the standard care group (P = .006, Fisher exact test; eTable 8 in Supplement 3).
Treatment protocol for 5 patients (7.9%) of 63 in the landiolol group was not followed. Details of those patients are outlined in eTable 13 in Supplement 3. Further information about protocol treatment deviations may be found in eTables 9 through 15 in Supplement 3. Further details of site screening and recruitment may be found in eFigure 6 and eTables 16 through 19 in Supplement 3.
Discussion
In a trial investigating landiolol administration to patients with tachycardia and septic shock treated with high-dose norepinephrine, there was no difference in mean SOFA score during the 14 days following randomization. The trial was stopped after recruiting 126 of its expected 340 patients because it was considered unlikely that landiolol would demonstrate benefit should recruitment have continued to the study’s full sample size and because there was a signal of possible harm in relation to mortality in the intervention group. Although landiolol use in critically ill patients has been reported in cases studies28 and in a previous randomized study,29 these reported only the drug’s safety and efficacy in heart rate reduction. To our knowledge, this is the first study to report a clinical outcome assessing the effect of landiolol on organ failure in critically ill patients with septic shock.
This study was designed to replicate a previous study by Morelli et al,9 which reported a dramatic reduction in 28-day mortality with the use of esmolol in a similar cohort: 80.5% mortality in the control group vs 49.4% in the esmolol group (adjusted HR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.26-0.59; P < .001). When designing this study, it was felt that there was not enough information to provide statistical power for a study based on 28-day mortality. The outcome SOFA score over 14 days was used because this has been demonstrated to have a good correlation with ICU mortality. Its predictive value is similar regardless of length of stay30 and was used in other trials assessing cardiovascular interventions in sepsis, most notably the Levosimendan for the Prevention of Acute Organ Dysfunction in Sepsis (LeoPARDs) study.22 In contrast to Morelli et al, this current study used landiolol rather than esmolol; personnel at the study sites were unfamiliar with β-blockade for this group of critically ill patients and the ultrashort-acting properties of landiolol provided additional safety in the event of cardiovascular instability.
Morelli et al also used the nonadrenergic calcium sensitizer levosimendan to improve systemic oxygen delivery when mixed venous saturation concentrations decreased or arterial lactate concentrations increased. This was not the case in this study. The patients receiving landiolol had higher mean lactate and norepinephrine requirements, which may indicate a reduction in cardiac output.
Morelli et al included a mixed-venous oxygen saturation higher than 65% as one of their inclusion criteria. The use of cardiac output monitoring and the decision to add a positive inotrope such as dobutamine (as suggested by the Surviving Sepsis Campaign3) or levosimendan (as used by Morelli) was left to the discretion of the clinical team, which was a pragmatic reflection of septic shock resuscitation in the UK but may present a limitation. Many patients with septic shock treated with norepinephrine experience some degree of septic cardiomyopathy5 and may be dependent on a tachycardia to maintain cardiac output. A recent post hoc analysis31 of 45 patients with septic shock with persistent tachycardia who were treated with esmolol showed that those with a less vigorous arterial trace (as measured by the change in pressure with time, dP/dtmax), were more likely to decrease their cardiac output during esmolol treatment.
The results of this study suggest that there is no benefit of landiolol used for short durations initiated during severe critical illness. There is an association with improved survival for patients already treated with longer-acting, nonspecific β-blockers prior to ICU admission32,33 and for ICU patients with septic shock.34 Kuo et al35 reported premorbid β-selective (but not nonselective) β-blockade reduced ICU mortality (adjusted HR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.18-0.92; P = .03). If there is a benefit to β-blockade in critical illness, it may be only seen with longer-term use. This should be tested in a prospective clinical trial.
The mortality in our control group was much lower than expected. Validation of the Sepsis-3 definition for septic shock36 analyzed 28 150 participants in the Surviving Sepsis Campaign database demonstrated that the patient group requiring vasopressors to maintain mean blood pressure at 65 mm Hg or greater and having a serum lactate level greater than 18 mg/dL after fluid resuscitation had a mortality of 42.3% (95% CI, 41.2%-43.3%). Mortality for septic shock was 38% in a recent Cochrane Systematic Review.37 Although it is satisfying that the mortality from such severe septic shock continues to fall, we cannot explain why the mortality in the standard care group in this study was 28.6% at day 90 among these otherwise high-risk patients.
Limitations
There were several limitations to our study. First, it is unknown whether outcomes would have been different if the landiolol administration had been started before or after the 24-hour treatment with norepinephrine time point or at a different dose of norepinephrine or whether patient subphenotypes exist. It is not possible to infer whether these findings are a class effect, applicable to all β-blocking drugs or due to the high specificity for the β1-receptor of landiolol. Second, although the primary outcome was selected because it had been previously used in other septic shock trials,22,23,24 it does not deal well with deaths and discharges from ICU. Third, decisions around withdrawal of life-sustaining measures leading to patient death or timing of discharge from ICU were not controlled for over the course of the study and may have impacted the primary outcome. Fourth, although this was a pragmatic study, data are lacking on cardiac function (either through cardiac output monitoring or echocardiography), and this hinders the ability to identify patient groups who may have benefitted from or have been harmed by the intervention. Fifth, by stopping prematurely, the trial may not have sufficient power to describe clinically important effects and further post hoc subgroup analysis may have too few patients to reveal clinically important differences.
Conclusions
This study was stopped after recruiting 126 of 340 patients because it was unlikely to demonstrate benefit should recruitment have continued and there was a signal of possible harm in the intervention group. In patients with septic shock with tachycardia and treated with norepinephrine for more than 24 hours, an infusion of landiolol did not improve organ function as measured by the SOFA score over 14 days from randomization. These results do not support the use of landiolol in the management of patients with tachycardia while receiving norepinephrine undergoing treatment for established septic shock.
Section Editor: Christopher Seymour, MD, Associate Editor, JAMA (christopher.seymour@jamanetwork.org).
Trial Protocol
Statistical Analysis Plan
eFigure 1. STRESS-L study drug infusion protocol
eFigure 2. STRESS-L vasopressor infusion protocol
eFigure 3. STRESS-L timing and weaning of the study drug
eTable 1. Landiolol infusion rate
eTable 2. Compliance on Landiolol infusion
eTable 3. Trial assessments
eTable 4. Other baseline characteristics for patients in the STRESS-L Study
eTable 5. Sensitivity analysis of primary outcome analysis (landiolol vs standard care)
eFigure 4. Mean SOFA score over 14 days using (a) complete case analysis, (b) METHOD 1 imputation (as described in the manuscript methods section). Figures on the lines inside the plots represent the number of observations used to calculate the mean SOFA score
eFigure 5a. Kaplan-Meier curve over 28 days period by treatment arms
eFigure 5b. Kaplan-Meier curve over 90 days period by treatment arms
eTable 6. Routinely collected in-fluid and out-fluid data (landiolol vs Standard care)
eTable 7. Subgroup analysis for mean SOFA score over 14 days in the landiolol arm vs standard arm
eTable 8. Adverse event and serious adverse events
eTable 9. Details of non-complier patients
eTable 10. Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) and Serious Adverse Reactions (SARs)
eTable 11. Detailed summary of all reported adverse events
eTable 12. Protocol deviations
eTable 13. Details of protocol deviations
eTable 14. Protocol violations
eTable 15. Details of Protocol Violations
eFigure 6. Cumulative site opening over the course of the study
eTable 16. Site recruitment
eTable 17. Sites closed to recruitment during the course of STRESS-L
eTable 18. Screening (pre-randomization)
eTable 19. Top 10 reasons for non-enrolment (by site) into STRESS-L
Nonauthor Collaborators. The STRESS-L Collaborators
Data Sharing Statement
References
- 1.Schwartz A, Brotfain E, Koyfman L, Klein M. Cardiac arrhythmias in a septic ICU population: a review. J Crit Care Med (Targu Mures). 2015;1(4):140-146. doi: 10.1515/jccm-2015-0027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schmidt H, Müller-Werdan U, Hoffmann T, et al. Autonomic dysfunction predicts mortality in patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome of different age groups. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(9):1994-2002. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000178181.91250.99 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med. 2021;49(11):e1063-e1143. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005337 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Singer M. Catecholamine treatment for shock—equally good or bad? Lancet. 2007;370(9588):636-637. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61317-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rudiger A, Singer M. Mechanisms of sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(6):1599-1608. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000266683.64081.02 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Beesley SJ, Wilson EL, Lanspa MJ, et al. Relative bradycardia in patients with septic shock requiring vasopressor therapy. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(2):225-233. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ackland GL, Yao ST, Rudiger A, et al. Cardioprotection, attenuated systemic inflammation, and survival benefit of β1-adrenoceptor blockade in severe sepsis in rats. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(2):388-394. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181c03dfa [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ibrahim-Zada I, Rhee P, Gomez CT, Weller J, Friese RS. Inhibition of sepsis-induced inflammatory response by β1-adrenergic antagonists. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014;76(2):320-327. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Morelli A, Ertmer C, Westphal M, et al. Effect of heart rate control with esmolol on hemodynamic and clinical outcomes in patients with septic shock: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;310(16):1683-1691. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.278477 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang J, Chen C, Liu Y, Yang Y, Yang X, Yang J. Benefits of esmolol in adults with sepsis and septic shock: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(27):e29820. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029820 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Iguchi S, Iwamura H, Nishizaki M, et al. Development of a highly cardioselective ultra short-acting beta-blocker, ONO-1101. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1992;40(6):1462-1469. doi: 10.1248/cpb.40.1462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lall R, Mistry D, Skilton E, et al. Study into the reversal of septic shock with landiolol (beta blockade): STRESS-L Study protocol for a randomised trial. BMJ Open. 2021;11(2):e043194. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-043194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.World Medical Association . World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. 2013;310(20):2191-2194. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.281053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):801-810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, et al. ; Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee including The Pediatric Subgroup . Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39(2):165-228. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2769-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yealy DM, Kellum JA, Huang DT, et al. ; ProCESS Investigators . A randomized trial of protocol-based care for early septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(18):1683-1693. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1401602 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.ARISE Investigators; ANZICS Clinical Trial Group . Goal-Directed Resuscitation for Patients with Early Septic Shock. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(16):1496-1506. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1404380 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mouncey PR, Osborn TM, Power GS, et al. ; ProMISe Trial Investigators . Trial of early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(14):1301-1311. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500896 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rowan KM, Angus DC, Bailey M, et al. ; PRISM Investigators . Early, goal-directed therapy for septic shock—a patient-level meta-analysis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(23):2223-2234. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1701380 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure, on behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(7):707-710. doi: 10.1007/BF01709751 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.STRESS-L information for the public. Warwick Clinical Trials Unit. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://warwick.ac.uk/fac/sci/med/research/ctu/trials/stressl/public/
- 22.Gordon AC, Perkins GD, Singer M, et al. Levosimendan for the prevention of acute organ dysfunction in sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(17):1638-1648. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1609409 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Briegel J, Forst H, Haller M, et al. Stress doses of hydrocortisone reverse hyperdynamic septic shock: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, single-center study. Crit Care Med. 1999;27(4):723-732. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199904000-00025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brunkhorst FM, Oppert M, Marx G, et al. ; German Study Group Competence Network Sepsis (SepNet) . Effect of empirical treatment with moxifloxacin and meropenem vs meropenem on sepsis-related organ dysfunction in patients with severe sepsis: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2012;307(22):2390-2399. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.5833 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pocock SJ, Ariti CA, Collier TJ, Wang D. The win ratio: a new approach to the analysis of composite endpoints in clinical trials based on clinical priorities. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(2):176-182. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr352 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Baiocchi M, Cheng J, Small DS. Instrumental variable methods for causal inference. Stat Med. 2014;33(13):2297-2340. doi: 10.1002/sim.6128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, et al. ; ARDS Definition Task Force . Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA. 2012;307(23):2526-2533. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.5669 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mizuno J, Yoshiya I, Yokoyama T, Yamada Y, Arita H, Hanaoka K. Age- and sex-related differences in dose-dependent hemodynamic response to landiolol hydrochloride during general anesthesia. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;63(3):243-252. doi: 10.1007/s00228-006-0249-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kakihana Y, Nishida O, Taniguchi T, et al. ; J-Land 3S Study Group . Efficacy and safety of landiolol, an ultra-short-acting β1-selective antagonist, for treatment of sepsis-related tachyarrhythmia (J-Land 3S): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(9):863-872. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30037-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ferreira FL, Bota DP, Bross A, Mélot C, Vincent JL. Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients. JAMA. 2001;286(14):1754-1758. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.14.1754 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Morelli A, Romano SM, Sanfilippo F, et al. Systolic-dicrotic notch pressure difference can identify tachycardic patients with septic shock at risk of cardiovascular decompensation following pharmacological heart rate reduction. Br J Anaesth. 2020;125(6):1018-1024. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2020.05.058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Macchia A, Romero M, Comignani PD, et al. Previous prescription of β-blockers is associated with reduced mortality among patients hospitalized in intensive care units for sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2012;40(10):2768-2772. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31825b9509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Christensen S, Johansen MB, Tønnesen E, et al. Preadmission beta-blocker use and 30-day mortality among patients in intensive care: a cohort study. Crit Care. 2011;15(2):R87. doi: 10.1186/cc10085 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fuchs C, Wauschkuhn S, Scheer C, et al. Continuing chronic beta-blockade in the acute phase of severe sepsis and septic shock is associated with decreased mortality rates up to 90 days. Br J Anaesth. 2017;119(4):616-625. doi: 10.1093/bja/aex231 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kuo M-J, Chou R-H, Lu Y-W, et al. Premorbid β1-selective (but not non-selective) β-blocker exposure reduces intensive care unit mortality among septic patients. J Intensive Care. 2021;9(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s40560-021-00553-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shankar-Hari M, Phillips GS, Levy ML, et al. ; Sepsis Definitions Task Force . Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: for the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):775-787. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gamper G, Havel C, Arrich J, et al. Vasopressors for hypotensive shock. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2(2):CD003709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Trial Protocol
Statistical Analysis Plan
eFigure 1. STRESS-L study drug infusion protocol
eFigure 2. STRESS-L vasopressor infusion protocol
eFigure 3. STRESS-L timing and weaning of the study drug
eTable 1. Landiolol infusion rate
eTable 2. Compliance on Landiolol infusion
eTable 3. Trial assessments
eTable 4. Other baseline characteristics for patients in the STRESS-L Study
eTable 5. Sensitivity analysis of primary outcome analysis (landiolol vs standard care)
eFigure 4. Mean SOFA score over 14 days using (a) complete case analysis, (b) METHOD 1 imputation (as described in the manuscript methods section). Figures on the lines inside the plots represent the number of observations used to calculate the mean SOFA score
eFigure 5a. Kaplan-Meier curve over 28 days period by treatment arms
eFigure 5b. Kaplan-Meier curve over 90 days period by treatment arms
eTable 6. Routinely collected in-fluid and out-fluid data (landiolol vs Standard care)
eTable 7. Subgroup analysis for mean SOFA score over 14 days in the landiolol arm vs standard arm
eTable 8. Adverse event and serious adverse events
eTable 9. Details of non-complier patients
eTable 10. Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) and Serious Adverse Reactions (SARs)
eTable 11. Detailed summary of all reported adverse events
eTable 12. Protocol deviations
eTable 13. Details of protocol deviations
eTable 14. Protocol violations
eTable 15. Details of Protocol Violations
eFigure 6. Cumulative site opening over the course of the study
eTable 16. Site recruitment
eTable 17. Sites closed to recruitment during the course of STRESS-L
eTable 18. Screening (pre-randomization)
eTable 19. Top 10 reasons for non-enrolment (by site) into STRESS-L
Nonauthor Collaborators. The STRESS-L Collaborators
Data Sharing Statement