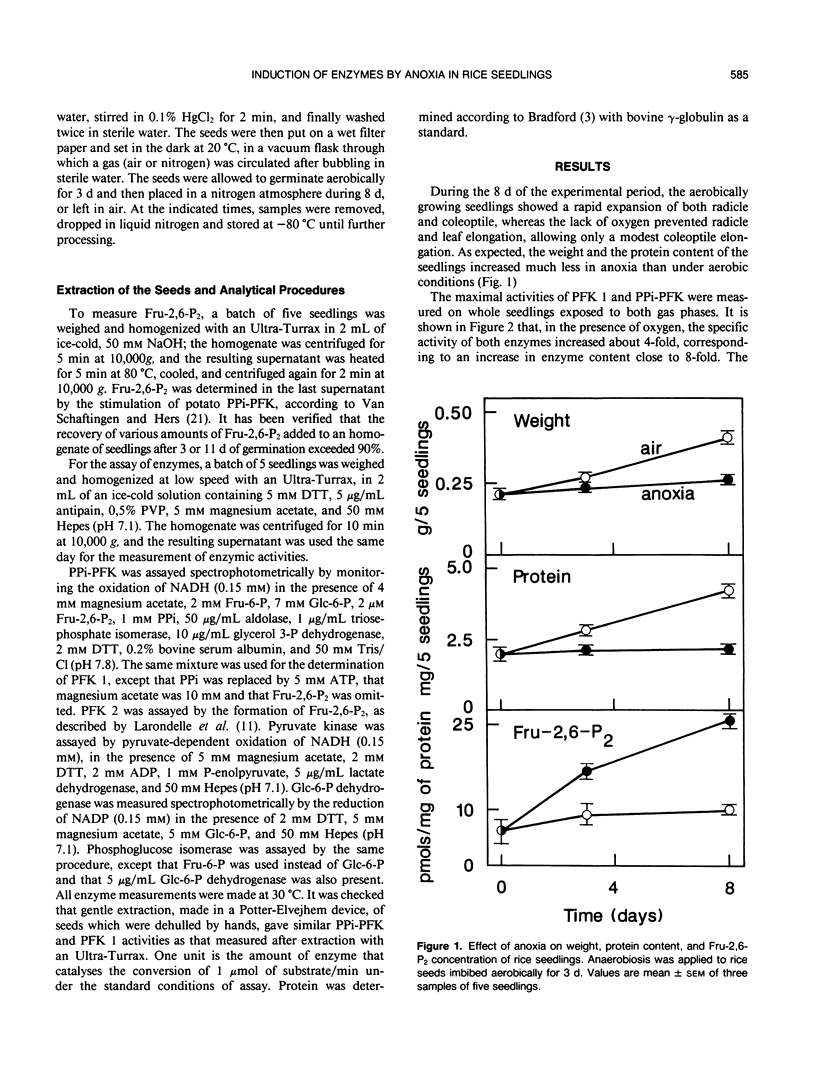
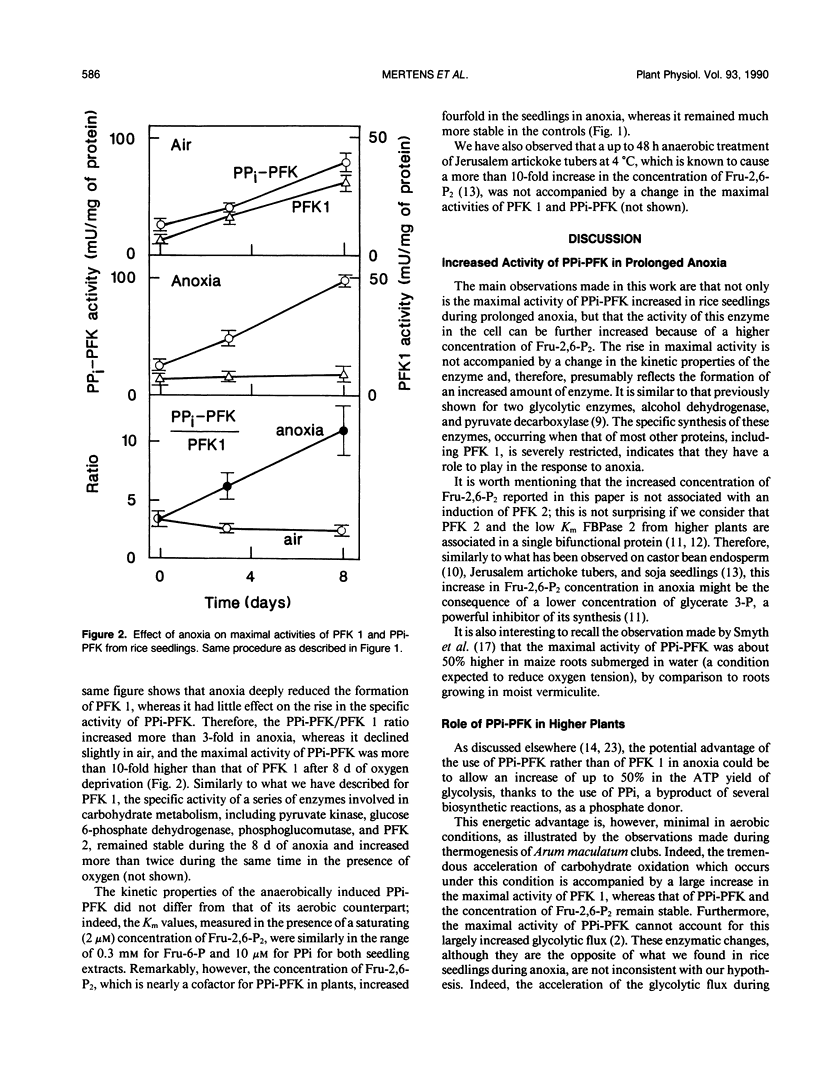
Abstract
Rice (Oryza sativa) seeds were imbibed for 3 days and the seedlings were further incubated for 8 days in the presence of either air or nitrogen. In aerobiosis, the specific activity of pyrophosphate:fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase and that of the ATP-dependent phosphofructokinase increased about fourfold. In anaerobiosis, the specific activity of ATP-dependent phosphofructokinase remained stable, whereas that of pyrophosphate:fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase increased as much as in the presence of oxygen and there was also a fourfold increase in the concentration of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, a potent stimulator of that enzyme. These data suggest a preferential involvement of pyrophosphate:fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase rather than of ATP-dependent phosphofructokinase in glycolysis during anaerobiosis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APP A. A., MEISS A. N. Effect of aeration on rice alcohol dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Sep;77(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnal N. W., Black C. C. Phosphofructokinase activities in photosynthetic organisms : the occurrence of pyrophosphate-dependent 6-phosphofructokinase in plants and algae. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):150–155. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnal N. W., Black C. C. Pyrophosphate-dependent 6-phosphofructokinase, a new glycolytic enzyme in pineapple leaves. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 15;86(1):20–26. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90376-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G., Hue L. Gluconeogenesis and related aspects of glycolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:617–653. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. C., Akazawa T. A novel sucrose synthase pathway for sucrose degradation in cultured sycamore cells. Plant Physiol. 1986 Aug;81(4):1008–1013. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.4.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger N. J., Beevers H. Synthesis and degradation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in endosperm of castor bean seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):358–364. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larondelle Y., Mertens E., Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate hydrolyzing enzymes in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jul;90(3):827–834. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.3.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larondelle Y., Mertens E., Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Purification and properties of spinach leaf phosphofructokinase 2/fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 1;161(2):351–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens E., Van Schaftingen E., Müller M. Presence of a fructose-2,6-bisphosphate-insensitive pyrophosphate: fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase in the anaerobic protozoa Tritrichomonas foetus, Trichomonas vaginalis and Isotricha prostoma. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Dec;37(2):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocquot B., Prat C., Mouches C., Pradet A. Effect of anoxia on energy charge and protein synthesis in rice embryo. Plant Physiol. 1981 Sep;68(3):636–640. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.3.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabularse D. C., Anderson R. L. D-Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: a naturally occurring activator for inorganic pyrophosphate:D-fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase in plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 15;103(3):848–855. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90888-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1987;59:315–395. doi: 10.1002/9780470123058.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Formation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate from fructose 1,6-bisphosphate by intramolecular cyclisation followed by alkaline hydrolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):319–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Lederer B., Bartrons R., Hers H. G. A kinetic study of pyrophosphate: fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase from potato tubers. Application to a microassay of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):191–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H. G. Some reactions in which inorganic pyrophosphate replaces ATP and serves as a source of energy. Fed Proc. 1977 Aug;36(9):2197–2206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu D. P., Sung S. J., Loboda T., Kormanik P. P., Black C. C. Characterization of Sucrolysis via the Uridine Diphosphate and Pyrophosphate-Dependent Sucrose Synthase Pathway. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jun;90(2):635–642. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.2.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ap Rees T., Green J. H., Wilson P. M. Pyrophosphate:fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase and glycolysis in non-photosynthetic tissues of higher plants. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):299–304. doi: 10.1042/bj2270299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


