Abstract
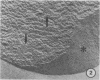
Comparison of several lipid reconstitution methods showed that they were not equally efficient at transferring the predominant thylakoid lipid, monogalactosyldiglyceride (MG), to the aqueous phase. We report a reverse phase evaporation method that employs Freon 11 as a lipid solvent and is capable of successfully hydrating MG in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) at room temperature within minutes. Using this method it is possible to force an equal weight mixture of MG and digalactosyldiglyceride into small bilayer vesicles without the formation of inverted micellar `lipidic particles' in the membranes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Stewart T. P., Boni L. T. The nature of lipidic particles and their roles in polymorphic transitions. Chem Phys Lipids. 1983 Aug;33(2):113–126. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(83)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Stewart T. P., Boni L. T., Yeagle P. L. Membrane fusion through point defects in bilayers. Science. 1981 May 22;212(4497):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.7233185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Reese T. S., Miller R. G. Phospholipid bilayer deformations associated with interbilayer contact and fusion. Nature. 1981 Sep 17;293(5829):237–238. doi: 10.1038/293237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Lemasters J. J., Höchli M., Hackenbrock C. R. Fusion of liposomes with mitochondrial inner membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Lemasters J. J., Höchli M., Hackenbrock C. R. Liposome-mitochondrial inner membrane fusion. Lateral diffusion of integral electron transfer components. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3748–3756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Brain A. P., Quinn P. J., Williams W. P. Formation of inverted lipid micelles in aqueous dispersions of mixed sn-3-galactosyldiacylglycerols induced by heat and ethylene glycol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 7;686(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Williams W. P., Brain A. P., Dickens M. J., Quinn P. J. Formation of inverted micelles in dispersions of mixed galactolipids. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):488–490. doi: 10.1038/293488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Williams W. P., Quinn P. J. The structure and thermotropic properties of pure 1,2-diacylgalactosylglycerols in aqueous systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 23;663(2):380–389. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. G., Green J. P., Nichols B. W. The phase behavior of monogalactosyl, digalactosyl, and sulphoquinovosyl diglycerides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 18;311(4):531–544. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel C. O., Jordan A. E., Miller K. R. Addition of lipid to the photosynthetic membrane: effects on membrane structure and energy transfer. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):113–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]